The Self-Excite Vibrations of Multi-Scoop Digger Machine
|
|
|
- Susanna Edwards
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 12, No. 1 (2008) c Technical University of Lodz The Self-Excite Vibrations of Multi-Scoop Digger Machine Józef Giergiel Department of Applied Mechanics and Robotics, Rzeszow University of Technology Received (18 October 2007) Revised (25 November 2007) Accepted (30 January 2008) In his work energetic method Has been tested. The conditions connected with creation of the self-excite vibrations in mutli-tools digger machine. The safety conditions to avoid dangerous work conditions have been presented. This article is a continuation and extension of the work [3]. Keywords: kinematics, dynamics, vibrations, digger machine 1. Introduction The device able to produce undamping vibrations and characterize that have: source of energy, regulation valve (regulate the energy in the system) and feedback loop control. Is called the self-excite vibration system. For the self-excite vibration systems the most significant case is the mode of energy consumption. This mode enable to recognize autonomous self-excited system from nonautonomous systems, which energy flow is connected with outer forces (depending on time) acting. In the equation which describe self-excite system, the time is not presented in apparent way, the source of energy is constant (do not depends on time) and the energy flow is regulated by it-self by vibrating system. When we look at self-excite systems with 1 DOF we can enumerate the following elements Fig. 1. I permanent source of energy, II vibrating system, III regulators, IV feedback between vibrating system and regulator with the help of which the vibrating system controls the energy supply. The elements I and II are linear, elements III should be nonlinear. As a result of existing feedback there is mutual influence between the regulator and the vibrating system, which allows self-excite system to control its own energetic levels, which may result in (despite the losses in the system) undamping periodical vibrations. Technology know many self-excite systems which have been described in scientific works [1, 2, 3]. This system include also building machines (Fig. 2)
2 80 Giergiel, J Figure 1 The multi-scoop digger machine a type of machine characterized by the constant digging process, equipped witch many digging tools, called scoops, placed in equal distances on a chain or a wheel. Machines used in mining are used in multidimensional excavation and in the process of storing materials. There are one of the biggest machines designed for earth excavations, their dimensions exceed 200 m length and 100 m height, the mass is greater than tons and efficiency is greater than m 3 excavated materials per hour. The smaller machines of this type are used to dig holes and are called trench excavator. Figure 2 The multi-scoop digger machine 2. The power engineering of self-excite vibrations One of the most general points of view is the power engineering point of view. We take in to consideration the energy balance of desired phenomena. The idea of selfexcite vibration system can be described in the following way: Lets assume that vibration exist. The energy of those vibrations should decrease as a result of: loss or energy transfer as vibration to the user. The loss of energy is supplemented by source of energy from which some part of energy is directed by valve to the vibrating system in each period. Certainly the constant vibrations are possible just in one case where energy inflow from source of energy in period equals the loss of energy with in this time.
3 The Self-Excite Vibrations of Multi-Scoop This condition of the energy balance is a condition of growing vibrations. It is obvious that if the energy balance is not in equilibrium (it means the loss of energy in the system is not reduced) the vibration will be disappearing. In the opposite situation the vibrations will be growing. In this work the energetic method of measuring the self-excided vibrations has been presented. The vibrating system of bodies is a system where dissipation is positive, if we have disappearing vibrations. Those Conditions for 1 DOF are described by inequalities (1) where firs means that coefficient of elasticity is greater than 0 and second means that system have positive dissipation [4]. f (x) x f(x) elasticity characteristic, R(x) damping characteristic. 3. The multi-scoop wheel vibrations examination > 0, R (ẋ) 0 (1) The examination was leaded on the example of self-excided vibrations connected with multi-scoop wheel of digging machine. In this case scoop wheel with extension arm in horizontal surface has been taken in to consideration. In this surface vibration frequency of the extension arm is much lower than in vertical surface. In some conditions the rotational motion of the extension arm can be the source of not beneficial vibrations in the machine. This type of vibrations is classified as self-excided. Those vibrations are created in non preserved system where the loss of energy is compensated by the source of energy which is included in the vibrating system. Figure 3 The vibrating system with 1 DOF The diagram scheme for his self-excite system has been presented in Fig. 1. The source of energy is a rotational motion of the extension arm with constant speed. The energy regulator is moment from frictional force and the vibrating system is scoop wheel. In this complex system the frictional force is a feedback.
4 82 Giergiel, J The purpose of his analyze is to give the reasons of self-excided vibrations creation on scoop wheel and give also conditions where we can eliminate those vibrations. Because of that the vibrating system has been substituted by the model based on I DOF (Fig. 3) The following signs have been assumed on the Fig. 3: m reduced mass of digging tool, M the mass of rotary construction, k substitional elasticity coefficient for the extension arm, β the substitional coefficient of construction and inside friction. In his work there is assumption that the velocity of rotary construction v k and circular velocity v o of wheel is constant. In this case the resistance forces which are generated by ground we can describe as follow: value of circular force R r = R ri value of normal force R n = R ni value of side force R b = R bi Under influence of force R b the tool is moving according to rotary construction. The dynamic motion equations for the taken model hale been presented below: mẍ + kx + βẋ = R b (2) x The Wheel displacement with tool. The value of the side force acting on one scoop can be expressed in the form: R ri the value of tangent force on scoop, R ni the value of normal force on scoop, ϕ the angle of cutting tool setting on scoop. The values of R ri i R ni are equal: R bi = R ri v k v o R ni sin ϕ (3) R ri = k r ab sin α R ni = R i ctg (δ o + µ) R ni [ctg (δ o + µ) + ctg (δ 1 + µ)] sin ϕ k r coefficient of the digging resistance in N/cm 2, ab thickness and width of tool (Fig. 4), δ 0 the angle of slice, δ 1 the angle between cutting trajectory and frictional surface, µ the angle of friction between the ground and Edg of cutting, R ni The additional resistance from the cutting tool. The ab product on the base of work [2] equal: q ab = rk p (1 cos α n ) q r k p α n the capacity of one scoop, the scoop wheel radius, the ground coefficient, the full angle of cutting wheel. (4) (5)
5 The Self-Excite Vibrations of Multi-Scoop Figure 4 The cutting tool The v k and b because of vibrations are not constant and it is possible to express it in the form: ( vk = v k ẋ, b = b 1 ẋ ) (6) v o The value of the force R b acting on the wheel, on the bases of equations (3) - (6) and necessary mathematical operations can be expressed in the following form: R b = A [ ] 2vk ctg (δ o + µ) sin ϕ ẋ + A ẋ 2 + B (7) The quantity A and B in the equation (7) have the form presented below: A = zk F α n q rk [ p 2π ] vk B = A ctg (δ o + µ) sin ϕ + R ni [ctg (δ o + µ) + ctg (δ 1 + µ) sin ϕ] v o (8) n the quantity of the scoops working simultaneously. The equation (2) after the substitution (7) and transformation application x 1 = x + b we can describe in the following form: k { mẍ 1 + kx 1 + α o + A [ ]} 2vk ctg (δ o + µ) sin ϕ ẋ 1 A ẋ 2 1 = 0 (9) v k x o Equation (9) will be describing damping vibrations if the system will be dissipatic. It means where the formula (1) will be fulfilled. { f (x) = kx 1, R = β + A [ ]} 2vk ctg (δ o + µ) sin ϕ ẋ A ẋ 2 (10) v k x o
6 84 Giergiel, J After substitution (10) to (1) we received: {[ k > 0, α o + A ( ) ]} 2vk ctg (δ o + µ) sin ϕ ẋ 1 A ẋ (11) v k x o The first inequality In (11) is always fulfilled, the second inequality will be fulfilled for the small ẋ 1 and for: α o + A [ ] 2v ctg (δ o + µ) sin ϕ > 0 (12) If we assume condition connected with energy In the system it means where α o = 0, the vibration will be damping when: v k v o > 1 2 ctg (δ o + µ) sin ϕ (13) In Fig. 5 has been presented quantity v k /v o in dependence with angle of cutting tool setting on the scoop by the assumed angle δ o + µ.. The angle ϕ In the process of cutting is in range 30 0 ϕ From the Fig. 5 we see that vibration is damping when, for assumed α o = 0, the value v k /v o for assumed angle δ o + µ, should be on the appropriate curve or above it. From the analysis it results that the vibrations are damping if the inequality (12) is fulfilled also if the inequality (13) is fulfilled vibrations are damping. The self-excite vibrations are possible if the condition (12) is not fulfilled and also if the condition (13) is not fulfilled. The system in this case have negative dissipation for the arbitrary ẏ. Figure 5. Figure 6. If the condition (12) or (13) for the the arbitrary ẏis not meet the dissipation of the system (8) is also negative, it means that it can exist self-excided vibrations for the scoop wheel with extension arm. The equation (9) has been used in simulation for the input data presented belowe: m = 25T, k = 100kN/m, β = , ϕ = 90 o, δ o + µ = 450. The results of those calculations have been presented on the scope in Fig. 6 to Fig. 8 for the different values of v k /v o. m = 25T, k = 100kN/m, β = , ϕ = 90 o, δ o + µ = 450.
7 The Self-Excite Vibrations of Multi-Scoop Figure 7. Figure 8. In the Fig. 6 the courses of phase trajectory Has been presented. In this case the coefficient connected with ẏ is positive. The vibrations have dual characteristic in accordance to initial conditions. In the range of point of balance the vibrations are disappearing and point (0, 0) is statically asymptotic. After some range of point of balance vibration can growing. In Fig. 7 the courses of phase trajectory for the condition y = 0 has been presented. The trajectories are divided by function described by equation x 1 = A,ẋ 1 = mv kv o. Inside of this function trajectories k 2A are closed and vibrations are periodic. The amplitude of those vibrations depends on initial conditions. Outside of this function trajectories are open and closed to this function, there are oscillations and the velocity and displacement are going in to infinity. The theoretical and practical results are the some. In the Fig. 8 the courses of phase trajectory for coefficient connected with ẏ is negative. The vibrations are growing and point of balance is not stable. 4. Conclusions The presented theoretical analysis of undamping vibrations of the digging machine results in the conclusion the when you design and exploit it it is necessary to apply the above mentioned dependencies in order to avoid dangerous undamped vibrations. An improper assumption of the construction parameters may cause failure and what fallows to significante financiale costs. References [1] Giergiel, J.: Drgania mechaniczne, Wyd. Nauk. Dyd. AGH, Kraków [2] Giergiel, J.: Metoda energetyczna badania drgań samowzbudnych, Z.N. Oficyna Wyd. PRz., Rzeszów, [3] Giergiel, J.: Drgania samowzbudne maszyn budowlanych, Z.N. Oficyna Wyd. PRz., Rzeszów, [4] Kokiewicz, W.: Jednostkowe si ly i opory kopania w procesach roboczych wielonaczyniowych koparek ko lowych, POLTEGOR, [5] Kononenienko, W.O.: Kolebatelnyje systemy s ograniczenem wozbużdenem, Moskwa This work is under the contract N /0750
8
Dynamics Modeling and Identification of the Amigobot Robot
 Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 14, No. 1 (2010) 65 79 c Technical University of Lodz Dynamics Modeling and Identification of the Amigobot Robot Tomasz Buratowski Department of Robotics and Mechatronics,
Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 14, No. 1 (2010) 65 79 c Technical University of Lodz Dynamics Modeling and Identification of the Amigobot Robot Tomasz Buratowski Department of Robotics and Mechatronics,
EQUIVALENT SINGLE-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEM AND FREE VIBRATION
 1 EQUIVALENT SINGLE-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEM AND FREE VIBRATION The course on Mechanical Vibration is an important part of the Mechanical Engineering undergraduate curriculum. It is necessary for the development
1 EQUIVALENT SINGLE-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEM AND FREE VIBRATION The course on Mechanical Vibration is an important part of the Mechanical Engineering undergraduate curriculum. It is necessary for the development
SIMULATION OF THE RESITIVE FORCES ACTING ON THE BUCKET OF WHEEL LOADER BY USE OF DEM
 SIMULATION OF THE RESITIVE FORCES ACTING ON THE BUCKET OF WHEEL LOADER BY USE OF DEM Hiroshi TAKAHASHI Department of Geoscience and Technology Graduate School of Engineering Tohoku University Sendai 980-8579,
SIMULATION OF THE RESITIVE FORCES ACTING ON THE BUCKET OF WHEEL LOADER BY USE OF DEM Hiroshi TAKAHASHI Department of Geoscience and Technology Graduate School of Engineering Tohoku University Sendai 980-8579,
Chapter a. Spring constant, k : The change in the force per unit length change of the spring. b. Coefficient of subgrade reaction, k:
 Principles of Soil Dynamics 3rd Edition Das SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/principles-soil-dynamics-3rd-editiondas-solutions-manual/ Chapter
Principles of Soil Dynamics 3rd Edition Das SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/principles-soil-dynamics-3rd-editiondas-solutions-manual/ Chapter
Identification of the Mathematical Model of an Underwater Robot Using Artificial Inteligence
 Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 18, No. 2 2014 135 149 c Lodz University of Technology Identification of the Mathematical Model of an Underwater Robot Using Artificial Inteligence Józef Giergiel
Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 18, No. 2 2014 135 149 c Lodz University of Technology Identification of the Mathematical Model of an Underwater Robot Using Artificial Inteligence Józef Giergiel
AP Physics C: Work, Energy, and Power Practice
 AP Physics C: Work, Energy, and Power Practice 1981M2. A swing seat of mass M is connected to a fixed point P by a massless cord of length L. A child also of mass M sits on the seat and begins to swing
AP Physics C: Work, Energy, and Power Practice 1981M2. A swing seat of mass M is connected to a fixed point P by a massless cord of length L. A child also of mass M sits on the seat and begins to swing
Perturbation Method in the Analysis of Manipulator Inertial Vibrations
 Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 15, No. 2 (2011) 149 160 c Technical University of Lodz Perturbation Method in the Analysis of Manipulator Inertial Vibrations Przemys law Szumiński Division of
Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 15, No. 2 (2011) 149 160 c Technical University of Lodz Perturbation Method in the Analysis of Manipulator Inertial Vibrations Przemys law Szumiński Division of
Nonlinear effects on the rotor driven by a motor with limited power
 Applied and Computational Mechanics 1 (007) 603-61 Nonlinear effects on the rotor driven by a motor with limited power L. Pst Institute of Thermomechanics, Academy of Sciences of CR, Dolejškova 5,18 00
Applied and Computational Mechanics 1 (007) 603-61 Nonlinear effects on the rotor driven by a motor with limited power L. Pst Institute of Thermomechanics, Academy of Sciences of CR, Dolejškova 5,18 00
Modeling and tracking control of wheeled mobile robots
 Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 1, No 1 (6) 7 81 c Technical University of Lodz Modeling and tracking control of wheeled mobile robots Józef Giergiel, Maciej T. Trojnacki Department of Applied
Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 1, No 1 (6) 7 81 c Technical University of Lodz Modeling and tracking control of wheeled mobile robots Józef Giergiel, Maciej T. Trojnacki Department of Applied
Lectures Chapter 10 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 7 th edition)
 PH 201-4A spring 2007 Simple Harmonic Motion Lectures 24-25 Chapter 10 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 7 th edition) 1 The Ideal Spring Springs are objects that exhibit elastic behavior. It will return back
PH 201-4A spring 2007 Simple Harmonic Motion Lectures 24-25 Chapter 10 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 7 th edition) 1 The Ideal Spring Springs are objects that exhibit elastic behavior. It will return back
Chapter 15. Oscillatory Motion
 Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion Part 2 Oscillations and Mechanical Waves Periodic motion is the repeating motion of an object in which it continues to return to a given position after a fixed time interval.
Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion Part 2 Oscillations and Mechanical Waves Periodic motion is the repeating motion of an object in which it continues to return to a given position after a fixed time interval.
7.6 Journal Bearings
 7.6 Journal Bearings 7.6 Journal Bearings Procedures and Strategies, page 1 of 2 Procedures and Strategies for Solving Problems Involving Frictional Forces on Journal Bearings For problems involving a
7.6 Journal Bearings 7.6 Journal Bearings Procedures and Strategies, page 1 of 2 Procedures and Strategies for Solving Problems Involving Frictional Forces on Journal Bearings For problems involving a
Passive control. Carles Batlle. II EURON/GEOPLEX Summer School on Modeling and Control of Complex Dynamical Systems Bertinoro, Italy, July
 Passive control theory II Carles Batlle II EURON/GEOPLEX Summer School on Modeling and Control of Complex Dynamical Systems Bertinoro, Italy, July 18-22 2005 Contents of this lecture Interconnection and
Passive control theory II Carles Batlle II EURON/GEOPLEX Summer School on Modeling and Control of Complex Dynamical Systems Bertinoro, Italy, July 18-22 2005 Contents of this lecture Interconnection and
Forced Oscillations in a Linear System Problems
 Forced Oscillations in a Linear System Problems Summary of the Principal Formulas The differential equation of forced oscillations for the kinematic excitation: ϕ + 2γ ϕ + ω 2 0ϕ = ω 2 0φ 0 sin ωt. Steady-state
Forced Oscillations in a Linear System Problems Summary of the Principal Formulas The differential equation of forced oscillations for the kinematic excitation: ϕ + 2γ ϕ + ω 2 0ϕ = ω 2 0φ 0 sin ωt. Steady-state
Structural Dynamics Lecture 4. Outline of Lecture 4. Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems. Formulation of Equations of Motions. Undamped Eigenvibrations.
 Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems Formulation of Equations of Motions. Newton s 2 nd Law Applied to Free Masses. D Alembert s Principle. Basic Equations of Motion for Forced Vibrations of Linear
Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems Formulation of Equations of Motions. Newton s 2 nd Law Applied to Free Masses. D Alembert s Principle. Basic Equations of Motion for Forced Vibrations of Linear
8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7)
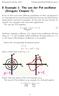 8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7) So far we have seen some different possibilities of what can happen in two-dimensional systems (local and global attractors and bifurcations)
8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7) So far we have seen some different possibilities of what can happen in two-dimensional systems (local and global attractors and bifurcations)
NYS STANDARD/KEY IDEA/PERFORMANCE INDICATOR 5.1 a-e. 5.1a Measured quantities can be classified as either vector or scalar.
 INDICATOR 5.1 a-e September Unit 1 Units and Scientific Notation SI System of Units Unit Conversion Scientific Notation Significant Figures Graphical Analysis Unit Kinematics Scalar vs. vector Displacement/dis
INDICATOR 5.1 a-e September Unit 1 Units and Scientific Notation SI System of Units Unit Conversion Scientific Notation Significant Figures Graphical Analysis Unit Kinematics Scalar vs. vector Displacement/dis
Stabilization and Passivity-Based Control
 DISC Systems and Control Theory of Nonlinear Systems, 2010 1 Stabilization and Passivity-Based Control Lecture 8 Nonlinear Dynamical Control Systems, Chapter 10, plus handout from R. Sepulchre, Constructive
DISC Systems and Control Theory of Nonlinear Systems, 2010 1 Stabilization and Passivity-Based Control Lecture 8 Nonlinear Dynamical Control Systems, Chapter 10, plus handout from R. Sepulchre, Constructive
Introduction to Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering
 Module 1 Introduction to Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering by Dr. Deepankar Choudhury Professor Department of Civil Engineering IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400 076, India. Email: dc@civil.iitb.ac.in URL:
Module 1 Introduction to Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering by Dr. Deepankar Choudhury Professor Department of Civil Engineering IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400 076, India. Email: dc@civil.iitb.ac.in URL:
TOPIC E: OSCILLATIONS EXAMPLES SPRING Q1. Find general solutions for the following differential equations:
 TOPIC E: OSCILLATIONS EXAMPLES SPRING 2019 Mathematics of Oscillating Systems Q1. Find general solutions for the following differential equations: Undamped Free Vibration Q2. A 4 g mass is suspended by
TOPIC E: OSCILLATIONS EXAMPLES SPRING 2019 Mathematics of Oscillating Systems Q1. Find general solutions for the following differential equations: Undamped Free Vibration Q2. A 4 g mass is suspended by
2007 Problem Topic Comment 1 Kinematics Position-time equation Kinematics 7 2 Kinematics Velocity-time graph Dynamics 6 3 Kinematics Average velocity
 2007 Problem Topic Comment 1 Kinematics Position-time equation Kinematics 7 2 Kinematics Velocity-time graph Dynamics 6 3 Kinematics Average velocity Energy 7 4 Kinematics Free fall Collisions 3 5 Dynamics
2007 Problem Topic Comment 1 Kinematics Position-time equation Kinematics 7 2 Kinematics Velocity-time graph Dynamics 6 3 Kinematics Average velocity Energy 7 4 Kinematics Free fall Collisions 3 5 Dynamics
Oscillatory Motion SHM
 Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion SHM Dr. Armen Kocharian Periodic Motion Periodic motion is motion of an object that regularly repeats The object returns to a given position after a fixed time interval A
Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion SHM Dr. Armen Kocharian Periodic Motion Periodic motion is motion of an object that regularly repeats The object returns to a given position after a fixed time interval A
ELEC4631 s Lecture 2: Dynamic Control Systems 7 March Overview of dynamic control systems
 ELEC4631 s Lecture 2: Dynamic Control Systems 7 March 2011 Overview of dynamic control systems Goals of Controller design Autonomous dynamic systems Linear Multi-input multi-output (MIMO) systems Bat flight
ELEC4631 s Lecture 2: Dynamic Control Systems 7 March 2011 Overview of dynamic control systems Goals of Controller design Autonomous dynamic systems Linear Multi-input multi-output (MIMO) systems Bat flight
Purpose of the experiment
 Work and Energy PES 1160 General Physics Lab I Purpose of the experiment What is Work and how is related to Force? To understand the work done by a constant force and a variable force. To see how gravitational
Work and Energy PES 1160 General Physics Lab I Purpose of the experiment What is Work and how is related to Force? To understand the work done by a constant force and a variable force. To see how gravitational
Lecture 6 mechanical system modeling equivalent mass gears
 M2794.25 Mechanical System Analysis 기계시스템해석 lecture 6,7,8 Dongjun Lee ( 이동준 ) Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering Seoul National University Dongjun Lee Lecture 6 mechanical system modeling
M2794.25 Mechanical System Analysis 기계시스템해석 lecture 6,7,8 Dongjun Lee ( 이동준 ) Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering Seoul National University Dongjun Lee Lecture 6 mechanical system modeling
Introduction to Mechanical Vibration
 2103433 Introduction to Mechanical Vibration Nopdanai Ajavakom (NAV) 1 Course Topics Introduction to Vibration What is vibration? Basic concepts of vibration Modeling Linearization Single-Degree-of-Freedom
2103433 Introduction to Mechanical Vibration Nopdanai Ajavakom (NAV) 1 Course Topics Introduction to Vibration What is vibration? Basic concepts of vibration Modeling Linearization Single-Degree-of-Freedom
DOUBOCHINSKI S REVERSE-PARAMETRICAL PENDULUM AND MOTOR
 DOUBOCHINSKI S REVERSE-PARAMETRICAL PENDULUM AND MOTOR Summary Danil DOUBOCHINSKI E-Mail: doubochinski.danil@gmail.com The type of systems in which the excitation of motion periodic due to high-frequency
DOUBOCHINSKI S REVERSE-PARAMETRICAL PENDULUM AND MOTOR Summary Danil DOUBOCHINSKI E-Mail: doubochinski.danil@gmail.com The type of systems in which the excitation of motion periodic due to high-frequency
Nonlinear Autonomous Systems of Differential
 Chapter 4 Nonlinear Autonomous Systems of Differential Equations 4.0 The Phase Plane: Linear Systems 4.0.1 Introduction Consider a system of the form x = A(x), (4.0.1) where A is independent of t. Such
Chapter 4 Nonlinear Autonomous Systems of Differential Equations 4.0 The Phase Plane: Linear Systems 4.0.1 Introduction Consider a system of the form x = A(x), (4.0.1) where A is independent of t. Such
DYNAMIC STABILITY OF MACHINES WITH ARTICULATED FRAME STEERING IN AUTOMATIC WARNING SYSTEM ASPECT
 Automation and Robotics in Construction XII E. Budny, A. McCrea, K.Szymanski (Editors) 1995 IMBiGS. All Rights reserved. 299 DYNAMIC STABILITY OF MACHINES WITH ARTICULATED FRAME STEERING IN AUTOMATIC WARNING
Automation and Robotics in Construction XII E. Budny, A. McCrea, K.Szymanski (Editors) 1995 IMBiGS. All Rights reserved. 299 DYNAMIC STABILITY OF MACHINES WITH ARTICULATED FRAME STEERING IN AUTOMATIC WARNING
1-DOF Vibration Characteristics. MCE371: Vibrations. Prof. Richter. Department of Mechanical Engineering. Handout 7 Fall 2017
 MCE371: Vibrations Prof. Richter Department of Mechanical Engineering Handout 7 Fall 2017 Free Undamped Vibration Follow Palm, Sect. 3.2, 3.3 (pp 120-138), 3.5 (pp 144-151), 3.8 (pp. 167-169) The equation
MCE371: Vibrations Prof. Richter Department of Mechanical Engineering Handout 7 Fall 2017 Free Undamped Vibration Follow Palm, Sect. 3.2, 3.3 (pp 120-138), 3.5 (pp 144-151), 3.8 (pp. 167-169) The equation
FOUR-POINT CONTACT SLEWING RINGS - without gear [ O ]
![FOUR-POINT CONTACT SLEWING RINGS - without gear [ O ] FOUR-POINT CONTACT SLEWING RINGS - without gear [ O ]](/thumbs/96/126795264.jpg) FOUR-POINT CONTACT SLEWING RINGS - without gear [ O ] Number of the Loading Boundary Dimensions Static Ax.Basic Load Rating Designation Weight Abutment Dimensions Curve d D T C oa G J 1 J 2 N 1 N 2 n 1
FOUR-POINT CONTACT SLEWING RINGS - without gear [ O ] Number of the Loading Boundary Dimensions Static Ax.Basic Load Rating Designation Weight Abutment Dimensions Curve d D T C oa G J 1 J 2 N 1 N 2 n 1
The... of a particle is defined as its change in position in some time interval.
 Distance is the. of a path followed by a particle. Distance is a quantity. The... of a particle is defined as its change in position in some time interval. Displacement is a.. quantity. The... of a particle
Distance is the. of a path followed by a particle. Distance is a quantity. The... of a particle is defined as its change in position in some time interval. Displacement is a.. quantity. The... of a particle
Figure 5.16 Compound pendulum: (a) At rest in equilibrium, (b) General position with coordinate θ, Freebody
 Lecture 27. THE COMPOUND PENDULUM Figure 5.16 Compound pendulum: (a) At rest in equilibrium, (b) General position with coordinate θ, Freebody diagram The term compound is used to distinguish the present
Lecture 27. THE COMPOUND PENDULUM Figure 5.16 Compound pendulum: (a) At rest in equilibrium, (b) General position with coordinate θ, Freebody diagram The term compound is used to distinguish the present
ME8230 Nonlinear Dynamics
 ME8230 Nonlinear Dynamics Lecture 1, part 1 Introduction, some basic math background, and some random examples Prof. Manoj Srinivasan Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering srinivasan.88@osu.edu Spring mass
ME8230 Nonlinear Dynamics Lecture 1, part 1 Introduction, some basic math background, and some random examples Prof. Manoj Srinivasan Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering srinivasan.88@osu.edu Spring mass
Automatic Control 2. Nonlinear systems. Prof. Alberto Bemporad. University of Trento. Academic year
 Automatic Control 2 Nonlinear systems Prof. Alberto Bemporad University of Trento Academic year 2010-2011 Prof. Alberto Bemporad (University of Trento) Automatic Control 2 Academic year 2010-2011 1 / 18
Automatic Control 2 Nonlinear systems Prof. Alberto Bemporad University of Trento Academic year 2010-2011 Prof. Alberto Bemporad (University of Trento) Automatic Control 2 Academic year 2010-2011 1 / 18
D(s) G(s) A control system design definition
 R E Compensation D(s) U Plant G(s) Y Figure 7. A control system design definition x x x 2 x 2 U 2 s s 7 2 Y Figure 7.2 A block diagram representing Eq. (7.) in control form z U 2 s z Y 4 z 2 s z 2 3 Figure
R E Compensation D(s) U Plant G(s) Y Figure 7. A control system design definition x x x 2 x 2 U 2 s s 7 2 Y Figure 7.2 A block diagram representing Eq. (7.) in control form z U 2 s z Y 4 z 2 s z 2 3 Figure
Chapter 14. Oscillations. Oscillations Introductory Terminology Simple Harmonic Motion:
 Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations Introductory Terminology Simple Harmonic Motion: Kinematics Energy Examples of Simple Harmonic Oscillators Damped and Forced Oscillations. Resonance. Periodic Motion
Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations Introductory Terminology Simple Harmonic Motion: Kinematics Energy Examples of Simple Harmonic Oscillators Damped and Forced Oscillations. Resonance. Periodic Motion
Dynamics of Machinery
 Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
VTU-NPTEL-NMEICT Project
 MODULE-II --- SINGLE DOF FREE S VTU-NPTEL-NMEICT Project Progress Report The Project on Development of Remaining Three Quadrants to NPTEL Phase-I under grant in aid NMEICT, MHRD, New Delhi SME Name : Course
MODULE-II --- SINGLE DOF FREE S VTU-NPTEL-NMEICT Project Progress Report The Project on Development of Remaining Three Quadrants to NPTEL Phase-I under grant in aid NMEICT, MHRD, New Delhi SME Name : Course
Measurement Techniques for Engineers. Motion and Vibration Measurement
 Measurement Techniques for Engineers Motion and Vibration Measurement Introduction Quantities that may need to be measured are velocity, acceleration and vibration amplitude Quantities useful in predicting
Measurement Techniques for Engineers Motion and Vibration Measurement Introduction Quantities that may need to be measured are velocity, acceleration and vibration amplitude Quantities useful in predicting
A Guide to linear dynamic analysis with Damping
 A Guide to linear dynamic analysis with Damping This guide starts from the applications of linear dynamic response and its role in FEA simulation. Fundamental concepts and principles will be introduced
A Guide to linear dynamic analysis with Damping This guide starts from the applications of linear dynamic response and its role in FEA simulation. Fundamental concepts and principles will be introduced
Theory and Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Dr. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
 Theory and Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Dr. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 2 Simpul Rotors Lecture - 2 Jeffcott Rotor Model In the
Theory and Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Dr. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 2 Simpul Rotors Lecture - 2 Jeffcott Rotor Model In the
Some Aspects of Structural Dynamics
 Appendix B Some Aspects of Structural Dynamics This Appendix deals with some aspects of the dynamic behavior of SDOF and MDOF. It starts with the formulation of the equation of motion of SDOF systems.
Appendix B Some Aspects of Structural Dynamics This Appendix deals with some aspects of the dynamic behavior of SDOF and MDOF. It starts with the formulation of the equation of motion of SDOF systems.
APPLIED MATHEMATICS ADVANCED LEVEL
 APPLIED MATHEMATICS ADVANCED LEVEL INTRODUCTION This syllabus serves to examine candidates knowledge and skills in introductory mathematical and statistical methods, and their applications. For applications
APPLIED MATHEMATICS ADVANCED LEVEL INTRODUCTION This syllabus serves to examine candidates knowledge and skills in introductory mathematical and statistical methods, and their applications. For applications
Structural Dynamics. Spring mass system. The spring force is given by and F(t) is the driving force. Start by applying Newton s second law (F=ma).
 Structural Dynamics Spring mass system. The spring force is given by and F(t) is the driving force. Start by applying Newton s second law (F=ma). We will now look at free vibrations. Considering the free
Structural Dynamics Spring mass system. The spring force is given by and F(t) is the driving force. Start by applying Newton s second law (F=ma). We will now look at free vibrations. Considering the free
Jamil Sami Haddad 1, Waleed Momani 2
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 78-1684,p-ISSN: 30-334X, Volume 11, Issue 4 Ver. VIII (Jul- Aug. 014), PP 46-5 A comparison of two theoretical methods of the materials
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 78-1684,p-ISSN: 30-334X, Volume 11, Issue 4 Ver. VIII (Jul- Aug. 014), PP 46-5 A comparison of two theoretical methods of the materials
16.30/31, Fall 2010 Recitation # 13
 16.30/31, Fall 2010 Recitation # 13 Brandon Luders December 6, 2010 In this recitation, we tie the ideas of Lyapunov stability analysis (LSA) back to previous ways we have demonstrated stability - but
16.30/31, Fall 2010 Recitation # 13 Brandon Luders December 6, 2010 In this recitation, we tie the ideas of Lyapunov stability analysis (LSA) back to previous ways we have demonstrated stability - but
Advanced Dynamics. - Lecture 4 Lagrange Equations. Paolo Tiso Spring Semester 2017 ETH Zürich
 Advanced Dynamics - Lecture 4 Lagrange Equations Paolo Tiso Spring Semester 2017 ETH Zürich LECTURE OBJECTIVES 1. Derive the Lagrange equations of a system of particles; 2. Show that the equation of motion
Advanced Dynamics - Lecture 4 Lagrange Equations Paolo Tiso Spring Semester 2017 ETH Zürich LECTURE OBJECTIVES 1. Derive the Lagrange equations of a system of particles; 2. Show that the equation of motion
Solution of Additional Exercises for Chapter 4
 1 1. (1) Try V (x) = 1 (x 1 + x ). Solution of Additional Exercises for Chapter 4 V (x) = x 1 ( x 1 + x ) x = x 1 x + x 1 x In the neighborhood of the origin, the term (x 1 + x ) dominates. Hence, the
1 1. (1) Try V (x) = 1 (x 1 + x ). Solution of Additional Exercises for Chapter 4 V (x) = x 1 ( x 1 + x ) x = x 1 x + x 1 x In the neighborhood of the origin, the term (x 1 + x ) dominates. Hence, the
Dynamic Loads CE 543. Examples. Harmonic Loads
 CE 543 Structural Dynamics Introduction Dynamic Loads Dynamic loads are time-varying loads. (But time-varying loads may not require dynamic analysis.) Dynamics loads can be grouped in one of the following
CE 543 Structural Dynamics Introduction Dynamic Loads Dynamic loads are time-varying loads. (But time-varying loads may not require dynamic analysis.) Dynamics loads can be grouped in one of the following
Differential Equations
 Differential Equations A differential equation (DE) is an equation which involves an unknown function f (x) as well as some of its derivatives. To solve a differential equation means to find the unknown
Differential Equations A differential equation (DE) is an equation which involves an unknown function f (x) as well as some of its derivatives. To solve a differential equation means to find the unknown
Energy balance in self-powered MR damper-based vibration reduction system
 BULLETIN OF THE POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES TECHNICAL SCIENCES, Vol. 59, No. 1, 2011 DOI: 10.2478/v10175-011-0011-4 Varia Energy balance in self-powered MR damper-based vibration reduction system J. SNAMINA
BULLETIN OF THE POLISH ACADEMY OF SCIENCES TECHNICAL SCIENCES, Vol. 59, No. 1, 2011 DOI: 10.2478/v10175-011-0011-4 Varia Energy balance in self-powered MR damper-based vibration reduction system J. SNAMINA
WEEK 1 Dynamics of Machinery
 WEEK 1 Dynamics of Machinery References Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, J.J. Uicker, G.R.Pennock ve J.E. Shigley, 2003 Makine Dinamiği, Prof. Dr. Eres SÖYLEMEZ, 2013 Uygulamalı Makine Dinamiği, Jeremy
WEEK 1 Dynamics of Machinery References Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, J.J. Uicker, G.R.Pennock ve J.E. Shigley, 2003 Makine Dinamiği, Prof. Dr. Eres SÖYLEMEZ, 2013 Uygulamalı Makine Dinamiği, Jeremy
The content contained in all sections of chapter 6 of the textbook is included on the AP Physics B exam.
 WORK AND ENERGY PREVIEW Work is the scalar product of the force acting on an object and the displacement through which it acts. When work is done on or by a system, the energy of that system is always
WORK AND ENERGY PREVIEW Work is the scalar product of the force acting on an object and the displacement through which it acts. When work is done on or by a system, the energy of that system is always
Structural Dynamics Lecture 2. Outline of Lecture 2. Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.)
 Outline of Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.) Linear Viscous Damped Eigenvibrations. Logarithmic decrement. Response to Harmonic and Periodic Loads. 1 Single-Degreee-of-Freedom Systems (cont.). Linear
Outline of Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.) Linear Viscous Damped Eigenvibrations. Logarithmic decrement. Response to Harmonic and Periodic Loads. 1 Single-Degreee-of-Freedom Systems (cont.). Linear
AA242B: MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS
 AA242B: MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS 1 / 50 AA242B: MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS Undamped Vibrations of n-dof Systems These slides are based on the recommended textbook: M. Géradin and D. Rixen, Mechanical Vibrations:
AA242B: MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS 1 / 50 AA242B: MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS Undamped Vibrations of n-dof Systems These slides are based on the recommended textbook: M. Géradin and D. Rixen, Mechanical Vibrations:
Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition, 2017
 A Correlation of Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition, 2017 To the AP Physics C: Mechanics Course Descriptions AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which was not
A Correlation of Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition, 2017 To the AP Physics C: Mechanics Course Descriptions AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which was not
Classification of Phase Portraits at Equilibria for u (t) = f( u(t))
 Classification of Phase Portraits at Equilibria for u t = f ut Transfer of Local Linearized Phase Portrait Transfer of Local Linearized Stability How to Classify Linear Equilibria Justification of the
Classification of Phase Portraits at Equilibria for u t = f ut Transfer of Local Linearized Phase Portrait Transfer of Local Linearized Stability How to Classify Linear Equilibria Justification of the
D.A.V. PUBLIC SCHOOL, UPPAL S SOUTHEND, SECTOR 49, GURUGRAM CLASS XI (PHYSICS) Academic plan for
 D.A.V. PUBLIC SCHOOL, UPPAL S SOUTHEND, SECTOR 49, GURUGRAM CLASS XI (PHYSICS) Academic plan for 2017-2018 UNIT NAME OF UNIT WEIGHTAGE 1. 2. 3. Physical World and Measurement Kinemetics Laws of Motion
D.A.V. PUBLIC SCHOOL, UPPAL S SOUTHEND, SECTOR 49, GURUGRAM CLASS XI (PHYSICS) Academic plan for 2017-2018 UNIT NAME OF UNIT WEIGHTAGE 1. 2. 3. Physical World and Measurement Kinemetics Laws of Motion
USE OF MECHANICAL RESONANCE IN MACHINES DRIVE SYSTEMS
 USE OF MECHANICAL RESONANCE IN MACHINES DRIVE SYSTEMS Wieslaw Fiebig, Jakub Wrobel Wroclaw University of Science and Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Lukasiewicza 7/9, 51-370 Wroclaw, Poland
USE OF MECHANICAL RESONANCE IN MACHINES DRIVE SYSTEMS Wieslaw Fiebig, Jakub Wrobel Wroclaw University of Science and Technology, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Lukasiewicza 7/9, 51-370 Wroclaw, Poland
Chapter 4. Motion in Two Dimensions
 Chapter 4 Motion in Two Dimensions Kinematics in Two Dimensions Will study the vector nature of position, velocity and acceleration in greater detail Will treat projectile motion and uniform circular motion
Chapter 4 Motion in Two Dimensions Kinematics in Two Dimensions Will study the vector nature of position, velocity and acceleration in greater detail Will treat projectile motion and uniform circular motion
Chapter 12 Vibrations and Waves Simple Harmonic Motion page
 Chapter 2 Vibrations and Waves 2- Simple Harmonic Motion page 438-45 Hooke s Law Periodic motion the object has a repeated motion that follows the same path, the object swings to and fro. Examples: a pendulum
Chapter 2 Vibrations and Waves 2- Simple Harmonic Motion page 438-45 Hooke s Law Periodic motion the object has a repeated motion that follows the same path, the object swings to and fro. Examples: a pendulum
Chapter 14 Periodic Motion
 Chapter 14 Periodic Motion 1 Describing Oscillation First, we want to describe the kinematical and dynamical quantities associated with Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM), for example, x, v x, a x, and F x.
Chapter 14 Periodic Motion 1 Describing Oscillation First, we want to describe the kinematical and dynamical quantities associated with Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM), for example, x, v x, a x, and F x.
Giacomo Boffi. Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile Ambientale e Territoriale Politecnico di Milano
 http://intranet.dica.polimi.it/people/boffi-giacomo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile Ambientale e Territoriale Politecnico di Milano April 21, 2017 Outline of Structural Members Elastic-plastic Idealization
http://intranet.dica.polimi.it/people/boffi-giacomo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile Ambientale e Territoriale Politecnico di Milano April 21, 2017 Outline of Structural Members Elastic-plastic Idealization
Nonlinear Systems and Control Lecture # 12 Converse Lyapunov Functions & Time Varying Systems. p. 1/1
 Nonlinear Systems and Control Lecture # 12 Converse Lyapunov Functions & Time Varying Systems p. 1/1 p. 2/1 Converse Lyapunov Theorem Exponential Stability Let x = 0 be an exponentially stable equilibrium
Nonlinear Systems and Control Lecture # 12 Converse Lyapunov Functions & Time Varying Systems p. 1/1 p. 2/1 Converse Lyapunov Theorem Exponential Stability Let x = 0 be an exponentially stable equilibrium
Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Dynamics and Control
 Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Dynamics and Control 151-0851-00 V lecture: CAB G11 Tuesday 10:15 12:00, every week exercise: HG E1.2 Wednesday 8:15 10:00, according to schedule (about every 2nd week) Marco
Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Dynamics and Control 151-0851-00 V lecture: CAB G11 Tuesday 10:15 12:00, every week exercise: HG E1.2 Wednesday 8:15 10:00, according to schedule (about every 2nd week) Marco
Periodic Motion. Periodic motion is motion of an object that. regularly repeats
 Periodic Motion Periodic motion is motion of an object that regularly repeats The object returns to a given position after a fixed time interval A special kind of periodic motion occurs in mechanical systems
Periodic Motion Periodic motion is motion of an object that regularly repeats The object returns to a given position after a fixed time interval A special kind of periodic motion occurs in mechanical systems
Name: Fall 2014 CLOSED BOOK
 Name: Fall 2014 1. Rod AB with weight W = 40 lb is pinned at A to a vertical axle which rotates with constant angular velocity ω =15 rad/s. The rod position is maintained by a horizontal wire BC. Determine
Name: Fall 2014 1. Rod AB with weight W = 40 lb is pinned at A to a vertical axle which rotates with constant angular velocity ω =15 rad/s. The rod position is maintained by a horizontal wire BC. Determine
ET-105(A) : PHYSICS. Show that only an infinitesimal rotation can be regarded as a vector.
 No. of Printed Pages : 7 ET-105(A) B.Tech. Civil (Construction Management) / B.Tech. Civil (Water Resources Engineering) / BTCLEVI / BTMEVI / BTELVI / BTECVI / BTCSVI Term-End Examination June, 2017 ET-105(A)
No. of Printed Pages : 7 ET-105(A) B.Tech. Civil (Construction Management) / B.Tech. Civil (Water Resources Engineering) / BTCLEVI / BTMEVI / BTELVI / BTECVI / BTCSVI Term-End Examination June, 2017 ET-105(A)
Week Topics of study Home/Independent Learning Assessment (If in addition to homework) 7 th September 2015
 Week Topics of study Home/Independent Learning Assessment (If in addition to homework) 7 th September Teacher feedback to prompt action FP1: No lessons Student to write feedback in here when necessary
Week Topics of study Home/Independent Learning Assessment (If in addition to homework) 7 th September Teacher feedback to prompt action FP1: No lessons Student to write feedback in here when necessary
Nonlinear Control Lecture 1: Introduction
 Nonlinear Control Lecture 1: Introduction Farzaneh Abdollahi Department of Electrical Engineering Amirkabir University of Technology Fall 2011 Farzaneh Abdollahi Nonlinear Control Lecture 1 1/15 Motivation
Nonlinear Control Lecture 1: Introduction Farzaneh Abdollahi Department of Electrical Engineering Amirkabir University of Technology Fall 2011 Farzaneh Abdollahi Nonlinear Control Lecture 1 1/15 Motivation
AP Physics C Summer Homework. Questions labeled in [brackets] are required only for students who have completed AP Calculus AB
![AP Physics C Summer Homework. Questions labeled in [brackets] are required only for students who have completed AP Calculus AB AP Physics C Summer Homework. Questions labeled in [brackets] are required only for students who have completed AP Calculus AB](/thumbs/96/128301637.jpg) 1. AP Physics C Summer Homework NAME: Questions labeled in [brackets] are required only for students who have completed AP Calculus AB 2. Fill in the radian conversion of each angle and the trigonometric
1. AP Physics C Summer Homework NAME: Questions labeled in [brackets] are required only for students who have completed AP Calculus AB 2. Fill in the radian conversion of each angle and the trigonometric
System Control Engineering 0
 System Control Engineering 0 Koichi Hashimoto Graduate School of Information Sciences Text: Nonlinear Control Systems Analysis and Design, Wiley Author: Horacio J. Marquez Web: http://www.ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp/~koichi/system_control/
System Control Engineering 0 Koichi Hashimoto Graduate School of Information Sciences Text: Nonlinear Control Systems Analysis and Design, Wiley Author: Horacio J. Marquez Web: http://www.ic.is.tohoku.ac.jp/~koichi/system_control/
3 Mathematical modeling of the torsional dynamics of a drill string
 3 Mathematical modeling of the torsional dynamics of a drill string 3.1 Introduction Many works about torsional vibrations on drilling systems [1, 12, 18, 24, 41] have been published using different numerical
3 Mathematical modeling of the torsional dynamics of a drill string 3.1 Introduction Many works about torsional vibrations on drilling systems [1, 12, 18, 24, 41] have been published using different numerical
A plane autonomous system is a pair of simultaneous first-order differential equations,
 Chapter 11 Phase-Plane Techniques 11.1 Plane Autonomous Systems A plane autonomous system is a pair of simultaneous first-order differential equations, ẋ = f(x, y), ẏ = g(x, y). This system has an equilibrium
Chapter 11 Phase-Plane Techniques 11.1 Plane Autonomous Systems A plane autonomous system is a pair of simultaneous first-order differential equations, ẋ = f(x, y), ẏ = g(x, y). This system has an equilibrium
Video 8.1 Vijay Kumar. Property of University of Pennsylvania, Vijay Kumar
 Video 8.1 Vijay Kumar 1 Definitions State State equations Equilibrium 2 Stability Stable Unstable Neutrally (Critically) Stable 3 Stability Translate the origin to x e x(t) =0 is stable (Lyapunov stable)
Video 8.1 Vijay Kumar 1 Definitions State State equations Equilibrium 2 Stability Stable Unstable Neutrally (Critically) Stable 3 Stability Translate the origin to x e x(t) =0 is stable (Lyapunov stable)
Chapter 12. Recall that when a spring is stretched a distance x, it will pull back with a force given by: F = -kx
 Chapter 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Oscillatory Motion Recall that when a spring is stretched a distance x, it will pull back with a force given by: F = -kx When the mass is released, the spring will pull
Chapter 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Oscillatory Motion Recall that when a spring is stretched a distance x, it will pull back with a force given by: F = -kx When the mass is released, the spring will pull
E209A: Analysis and Control of Nonlinear Systems Problem Set 6 Solutions
 E9A: Analysis and Control of Nonlinear Systems Problem Set 6 Solutions Michael Vitus Gabe Hoffmann Stanford University Winter 7 Problem 1 The governing equations are: ẋ 1 = x 1 + x 1 x ẋ = x + x 3 Using
E9A: Analysis and Control of Nonlinear Systems Problem Set 6 Solutions Michael Vitus Gabe Hoffmann Stanford University Winter 7 Problem 1 The governing equations are: ẋ 1 = x 1 + x 1 x ẋ = x + x 3 Using
Introduction to structural dynamics
 Introduction to structural dynamics p n m n u n p n-1 p 3... m n-1 m 3... u n-1 u 3 k 1 c 1 u 1 u 2 k 2 m p 1 1 c 2 m2 p 2 k n c n m n u n p n m 2 p 2 u 2 m 1 p 1 u 1 Static vs dynamic analysis Static
Introduction to structural dynamics p n m n u n p n-1 p 3... m n-1 m 3... u n-1 u 3 k 1 c 1 u 1 u 2 k 2 m p 1 1 c 2 m2 p 2 k n c n m n u n p n m 2 p 2 u 2 m 1 p 1 u 1 Static vs dynamic analysis Static
Active Integral Vibration Control of Elastic Bodies
 Applied and Computational Mechanics 2 (2008) 379 388 Active Integral Vibration Control of Elastic Bodies M. Smrž a,m.valášek a, a Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, CTU in Prague, Karlovo nam. 13, 121
Applied and Computational Mechanics 2 (2008) 379 388 Active Integral Vibration Control of Elastic Bodies M. Smrž a,m.valášek a, a Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, CTU in Prague, Karlovo nam. 13, 121
2.21 Rectilinear Motion: Uniform Acceleration Under a Constant Force. Motion of a Particle
 60 CHAPTER 2 Newtonian Mechanics: Rectilinear Motion of a Particle Motion of a Particle F=ma is the fundamental equation of motion for a particle subject to the influ ence of a net force, F. We emphasize
60 CHAPTER 2 Newtonian Mechanics: Rectilinear Motion of a Particle Motion of a Particle F=ma is the fundamental equation of motion for a particle subject to the influ ence of a net force, F. We emphasize
Math 266: Phase Plane Portrait
 Math 266: Phase Plane Portrait Long Jin Purdue, Spring 2018 Review: Phase line for an autonomous equation For a single autonomous equation y = f (y) we used a phase line to illustrate the equilibrium solutions
Math 266: Phase Plane Portrait Long Jin Purdue, Spring 2018 Review: Phase line for an autonomous equation For a single autonomous equation y = f (y) we used a phase line to illustrate the equilibrium solutions
Chapter 23: Principles of Passive Vibration Control: Design of absorber
 Chapter 23: Principles of Passive Vibration Control: Design of absorber INTRODUCTION The term 'vibration absorber' is used for passive devices attached to the vibrating structure. Such devices are made
Chapter 23: Principles of Passive Vibration Control: Design of absorber INTRODUCTION The term 'vibration absorber' is used for passive devices attached to the vibrating structure. Such devices are made
Dynamics and Control of the GyroPTO Wave Energy Point Absorber under Sea Waves
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 99 (7) 88 8 X International Conference on Structural Dynamics, EURODYN 7 Dynamics and Control of the GyroPTO Wave Energy Point
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 99 (7) 88 8 X International Conference on Structural Dynamics, EURODYN 7 Dynamics and Control of the GyroPTO Wave Energy Point
Theory of Vibrations in Stewart Platforms
 Theory of Vibrations in Stewart Platforms J.M. Selig and X. Ding School of Computing, Info. Sys. & Maths. South Bank University London SE1 0AA, U.K. (seligjm@sbu.ac.uk) Abstract This article develops a
Theory of Vibrations in Stewart Platforms J.M. Selig and X. Ding School of Computing, Info. Sys. & Maths. South Bank University London SE1 0AA, U.K. (seligjm@sbu.ac.uk) Abstract This article develops a
Section 3.7: Mechanical and Electrical Vibrations
 Section 3.7: Mechanical and Electrical Vibrations Second order linear equations with constant coefficients serve as mathematical models for mechanical and electrical oscillations. For example, the motion
Section 3.7: Mechanical and Electrical Vibrations Second order linear equations with constant coefficients serve as mathematical models for mechanical and electrical oscillations. For example, the motion
AP PHYSICS 1 BIG IDEAS AND LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 AP PHYSICS 1 BIG IDEAS AND LEARNING OBJECTIVES KINEMATICS 3.A.1.1: The student is able to express the motion of an object using narrative, mathematical, and graphical representations. [SP 1.5, 2.1, 2.2]
AP PHYSICS 1 BIG IDEAS AND LEARNING OBJECTIVES KINEMATICS 3.A.1.1: The student is able to express the motion of an object using narrative, mathematical, and graphical representations. [SP 1.5, 2.1, 2.2]
sc Control Systems Design Q.1, Sem.1, Ac. Yr. 2010/11
 sc46 - Control Systems Design Q Sem Ac Yr / Mock Exam originally given November 5 9 Notes: Please be reminded that only an A4 paper with formulas may be used during the exam no other material is to be
sc46 - Control Systems Design Q Sem Ac Yr / Mock Exam originally given November 5 9 Notes: Please be reminded that only an A4 paper with formulas may be used during the exam no other material is to be
Physics 351, Spring 2017, Homework #3. Due at start of class, Friday, February 3, 2017
 Physics 351, Spring 2017, Homework #3. Due at start of class, Friday, February 3, 2017 Course info is at positron.hep.upenn.edu/p351 When you finish this homework, remember to visit the feedback page at
Physics 351, Spring 2017, Homework #3. Due at start of class, Friday, February 3, 2017 Course info is at positron.hep.upenn.edu/p351 When you finish this homework, remember to visit the feedback page at
The Liapunov Method for Determining Stability (DRAFT)
 44 The Liapunov Method for Determining Stability (DRAFT) 44.1 The Liapunov Method, Naively Developed In the last chapter, we discussed describing trajectories of a 2 2 autonomous system x = F(x) as level
44 The Liapunov Method for Determining Stability (DRAFT) 44.1 The Liapunov Method, Naively Developed In the last chapter, we discussed describing trajectories of a 2 2 autonomous system x = F(x) as level
Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille. Chapter Thirteen. Vibrations and Waves
 Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille Chapter Thirteen Vibrations and Waves Periodic Motion and Waves Periodic motion is one of the most important kinds of physical behavior Will include a closer look at Hooke
Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille Chapter Thirteen Vibrations and Waves Periodic Motion and Waves Periodic motion is one of the most important kinds of physical behavior Will include a closer look at Hooke
Oscillations. Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Position, Velocity, Acceleration SHM Forces SHM Energy Period of oscillation Damping and Resonance
 Oscillations Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Position, Velocity, Acceleration SHM Forces SHM Energy Period of oscillation Damping and Resonance 1 Revision problem Please try problem #31 on page 480 A pendulum
Oscillations Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Position, Velocity, Acceleration SHM Forces SHM Energy Period of oscillation Damping and Resonance 1 Revision problem Please try problem #31 on page 480 A pendulum
LAST TIME: Simple Pendulum:
 LAST TIME: Simple Pendulum: The displacement from equilibrium, x is the arclength s = L. s / L x / L Accelerating & Restoring Force in the tangential direction, taking cw as positive initial displacement
LAST TIME: Simple Pendulum: The displacement from equilibrium, x is the arclength s = L. s / L x / L Accelerating & Restoring Force in the tangential direction, taking cw as positive initial displacement
CS491/691: Introduction to Aerial Robotics
 CS491/691: Introduction to Aerial Robotics Topic: Midterm Preparation Dr. Kostas Alexis (CSE) Areas of Focus Coordinate system transformations (CST) MAV Dynamics (MAVD) Navigation Sensors (NS) State Estimation
CS491/691: Introduction to Aerial Robotics Topic: Midterm Preparation Dr. Kostas Alexis (CSE) Areas of Focus Coordinate system transformations (CST) MAV Dynamics (MAVD) Navigation Sensors (NS) State Estimation
Chapter 4. Motion in Two Dimensions. Professor Wa el Salah
 Chapter 4 Motion in Two Dimensions Kinematics in Two Dimensions Will study the vector nature of position, velocity and acceleration in greater detail. Will treat projectile motion and uniform circular
Chapter 4 Motion in Two Dimensions Kinematics in Two Dimensions Will study the vector nature of position, velocity and acceleration in greater detail. Will treat projectile motion and uniform circular
Laboratory notes. Torsional Vibration Absorber
 Titurus, Marsico & Wagg Torsional Vibration Absorber UoB/1-11, v1. Laboratory notes Torsional Vibration Absorber Contents 1 Objectives... Apparatus... 3 Theory... 3 3.1 Background information... 3 3. Undamped
Titurus, Marsico & Wagg Torsional Vibration Absorber UoB/1-11, v1. Laboratory notes Torsional Vibration Absorber Contents 1 Objectives... Apparatus... 3 Theory... 3 3.1 Background information... 3 3. Undamped
The maximum kinetic energy is directly proportional to the frequency. The time for one oscillation is directly proportional to the frequency.
 Q1.For a body performing simple harmonic motion, which one of the following statements is correct? The maximum kinetic energy is directly proportional to the frequency. The time for one oscillation is
Q1.For a body performing simple harmonic motion, which one of the following statements is correct? The maximum kinetic energy is directly proportional to the frequency. The time for one oscillation is
AP Physics C Mechanics Objectives
 AP Physics C Mechanics Objectives I. KINEMATICS A. Motion in One Dimension 1. The relationships among position, velocity and acceleration a. Given a graph of position vs. time, identify or sketch a graph
AP Physics C Mechanics Objectives I. KINEMATICS A. Motion in One Dimension 1. The relationships among position, velocity and acceleration a. Given a graph of position vs. time, identify or sketch a graph
September. Text: Physics: Principles & Problems, Merrill-Glencoe NYS STANDARD/KEY IDEA/PERFORMANCE INDICATOR
 September Unit Units and Scientific Notation SI System of Units Unit Conversion Scientific Notation Significant Figures Graphical Analysis Unit Kinematics Scalar vs. vector Displacement/distance Velocity/speed
September Unit Units and Scientific Notation SI System of Units Unit Conversion Scientific Notation Significant Figures Graphical Analysis Unit Kinematics Scalar vs. vector Displacement/distance Velocity/speed
PHYSICS 311: Classical Mechanics Final Exam Solution Key (2017)
 PHYSICS 311: Classical Mechanics Final Exam Solution Key (017) 1. [5 points] Short Answers (5 points each) (a) In a sentence or two, explain why bicycle wheels are large, with all of the mass at the edge,
PHYSICS 311: Classical Mechanics Final Exam Solution Key (017) 1. [5 points] Short Answers (5 points each) (a) In a sentence or two, explain why bicycle wheels are large, with all of the mass at the edge,
