7.6 Journal Bearings
|
|
|
- Theodora Fisher
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 7.6 Journal Bearings
2 7.6 Journal Bearings Procedures and Strategies, page 1 of 2 Procedures and Strategies for Solving Problems Involving Frictional Forces on Journal Bearings For problems involving a loosely fitting pulley (or wheel or collar or similar device) on a fixed shaft, follow these steps. Fixed shaft F Pulley Belt forces acting on pulley are equal. 1. Calculate the angle of friction and radius r f of the circle of friction from the equations tan -1 where is the coefficient of friction r f = r sin where r is the radius of the shaft (which, because the pulley fits "loosely", is approximately equal to the inner radius of the pulley) Contact point P 1 F For clarity, the difference in size between the radius of the shaft and the inner radius of the pulley has been exaggerated in the diagram. 2. Draw circles showing the positions and contact point of the shaft and the central hole in the pulley, when no rotation has occurred. 3. Draw circles showing the positions and contact point of the shaft and the pulley hole, after rotation has occurred. F Fixed shaft Pulley Belt forces acting on pulley are not equal. Unbalanced forces cause pulley to rotate to new contact point. P 2 F + F
3 7.6 Journal Bearings Procedures and Strategies, page 2 of 2 4. Draw a sketch of the pulley, with the circle of friction inside. On this sketch, show the friction force from the shaft opposing the rotation. Furthermore, show the line of action of the resultant of the normal and friction force, say R, passing through the contact point and lying tangent to a circle of radius rf (the circle of friction). 5. Draw a free-body diagram of the pulley, expressing R in terms of x and y components, Rx and R y. 6. Write equilibrium equations: Sum forces in the x and y directions and sum moments about the center of the pulley. Note that the moment of R is R r f, because R is tangent to the circle of friction, which has radius r f. Also, R = Rx 2 + R y 2 7. Solve the equations. Note: The above discussion applies when the pulley fits loosely on a fixed shaft. If instead the pulley is rigidly fixed to the shaft, but the shaft fits loosely on a supporting bearing, then the steps above can be followed, except that a) the shaft rotates to a new contact point relative to the fixed bearing, and b) a free-body diagram of the shaft rather than the pulley is used. Circle of friction (not the shaft) Frictional force opposes rotation F Sense of rotation of pulley Rx f R Pulley r f N Pulley P 2 r f Line of action of resultant, R, is tangent to circle of friction. P 2 R = Rx 2 + R y 2 R y F + F
4 7.6 Journal Bearings Problem Statement for Example 1 1. The pulley has a radius of 80 mm and has negligible weight. If the pulley fits loosely on a 12-mm-diameter fixed shaft, and the coefficient of static friction is s = 0.2, determine the minimum force F required to start the pulley rotating clockwise. F 80 mm 140 N
5 7.6 Journal Bearings Problem Statement for Example 2 2. The pulley has a radius of 80 mm and has negligible weight. If the pulley fits loosely on a 12-mm-diameter fixed shaft, and the pulley rotates with constant angular velocity counterclockwise, determine the coefficient of kinetic friction, µ k. 135 N 80 mm 140 N
6 7.6 Journal Bearings Problem Statement for Example 3 3. The force from the belt causes the 130-mm-radius pulley to rotate counterclockwise with constant angular velocity. The pulley fits loosely on a fixed shaft of 24-mm diameter. Determine the value of the belt force F if the coefficient of kinetic friction is µ k = 0.3. Assume that no slipping occurs between the belt and pulley. 100 N 130 mm F
7 7.6 Journal Bearings Problem Statement for Example 4 4. The stepped pulley has radii of 4 in. and 8 in. and fits loosely on a 0.5-in.-diameter fixed shaft. If the given loads cause the pulley to rotate clockwise with a constant angular velocity, determine the normal and frictional forces from the shaft acting on the pulley. Also find the coefficient of kinetic friction, µ k. 8 in. 4 in. 20 lb 40.5 lb
8 7.6 Journal Bearings Problem Statement for Example 5 5. The couple forces P are intended to rotate the shaft and wind the cable around the drum, thus raising the 5-kg mass. The shaft has a diameter of 30 mm and fits loosely in the journal bearing B. If the combined mass of the shaft handle A and drum C is 15 kg, and the coefficient of static friction is µs = 0.2, determine the minimum value of P required to initiate upward motion of the 5-kg mass. Assume the drum C is attached rigidly to the shaft. Diameter of drum = 200 mm C 5 kg P A B 150 mm 150 mm P
9 7.6 Journal Bearings Problem Statement for Example 6 6. Pulleys A and B are identical. Each has a radius of 10 in., weighs 10 lb and fits loosely on a 0.5-in.-diameter fixed shaft. Determine the maximum value of the weight W that may be supported without causing the pulleys to rotate. Also calculate the value of the tension in the cord between the pulleys. The coefficient of static friction is µs = in. 10 in. A B 100 lb W
10 7.6 Journal Bearings Problem Statement for Example 7 7. The 100-kg cart has four 200-mm-diameter wheels, 25-mm-diameter axles, and center of mass G. Each wheel has a mass of 10 kg. The coefficient of kinetic friction is Determine the horizontal force P required to move the cart at constant speed. Assume that the axles do not rotate, the wheels fit loosely on the axles, and rolling resistance between the wheels and the plane is negligible. 100 kg G P 100 mm 400 mm 400 mm
11 7.6 Journal Bearings Problem Statement for Example 8 8. The 100-kg cart has four 300-mm-diameter wheels, 30-mm-diameter axles, and center of mass G. Determine the angle for which the cart will roll down the incline at constant speed. Also determine the reactions from the incline acting on each wheel. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.2. Assume that rolling resistance and the weight of the wheels are negligible, the wheels fit loosely on the axles, and the axles do not rotate. 200 mm G 500 mm 500 mm
12
Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Forces and Accelerations
 Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Forces and Accelerations Reference: Beer, Ferdinand P. et al, Vector Mechanics for Engineers : Dynamics, 8 th Edition, Mc GrawHill Hibbeler R.C., Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics,
Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Forces and Accelerations Reference: Beer, Ferdinand P. et al, Vector Mechanics for Engineers : Dynamics, 8 th Edition, Mc GrawHill Hibbeler R.C., Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics,
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
 Engineering Mechanics: Statics Chapter 6B: Applications of Friction in Machines Wedges Used to produce small position adjustments of a body or to apply large forces When sliding is impending, the resultant
Engineering Mechanics: Statics Chapter 6B: Applications of Friction in Machines Wedges Used to produce small position adjustments of a body or to apply large forces When sliding is impending, the resultant
STATICS. Friction VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: Eighth Edition CHAPTER. Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr.
 Eighth E 8 Friction CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University Contents Introduction Laws of Dry Friction.
Eighth E 8 Friction CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University Contents Introduction Laws of Dry Friction.
5.2 Rigid Bodies and Two-Dimensional Force Systems
 5.2 Rigid odies and Two-Dimensional Force Systems 5.2 Rigid odies and Two-Dimensional Force Systems Procedures and Strategies, page 1 of 1 Procedures and Strategies for Solving Problems Involving Equilibrium
5.2 Rigid odies and Two-Dimensional Force Systems 5.2 Rigid odies and Two-Dimensional Force Systems Procedures and Strategies, page 1 of 1 Procedures and Strategies for Solving Problems Involving Equilibrium
Definition. is a measure of how much a force acting on an object causes that object to rotate, symbol is, (Greek letter tau)
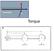 Torque Definition is a measure of how much a force acting on an object causes that object to rotate, symbol is, (Greek letter tau) = r F = rfsin, r = distance from pivot to force, F is the applied force
Torque Definition is a measure of how much a force acting on an object causes that object to rotate, symbol is, (Greek letter tau) = r F = rfsin, r = distance from pivot to force, F is the applied force
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
 Engineering Mechanics: Statics Chapter 6B: Applications of Friction in Machines Wedges Used to produce small position adjustments of a body or to apply large forces When sliding is impending, the resultant
Engineering Mechanics: Statics Chapter 6B: Applications of Friction in Machines Wedges Used to produce small position adjustments of a body or to apply large forces When sliding is impending, the resultant
Overview. Dry Friction Wedges Flatbelts Screws Bearings Rolling Resistance
 Friction Chapter 8 Overview Dry Friction Wedges Flatbelts Screws Bearings Rolling Resistance Dry Friction Friction is defined as a force of resistance acting on a body which prevents slipping of the body
Friction Chapter 8 Overview Dry Friction Wedges Flatbelts Screws Bearings Rolling Resistance Dry Friction Friction is defined as a force of resistance acting on a body which prevents slipping of the body
EQUATIONS OF MOTION: GENERAL PLANE MOTION (Section 17.5) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to analyze the planar kinetics of a rigid body
 EQUATIONS OF MOTION: GENERAL PLANE MOTION (Section 17.5) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to analyze the planar kinetics of a rigid body undergoing general plane motion. APPLICATIONS As the soil
EQUATIONS OF MOTION: GENERAL PLANE MOTION (Section 17.5) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to analyze the planar kinetics of a rigid body undergoing general plane motion. APPLICATIONS As the soil
M D P L sin x FN L sin C W L sin C fl cos D 0.
 789 roblem 9.26 he masses of the ladder and person are 18 kg and 90 kg, respectively. he center of mass of the 4-m ladder is at its midpoint. If D 30, what is the minimum coefficient of static friction
789 roblem 9.26 he masses of the ladder and person are 18 kg and 90 kg, respectively. he center of mass of the 4-m ladder is at its midpoint. If D 30, what is the minimum coefficient of static friction
Engineering Mechanics. Friction in Action
 Engineering Mechanics Friction in Action What is friction? Friction is a retarding force that opposes motion. Friction types: Static friction Kinetic friction Fluid friction Sources of dry friction Dry
Engineering Mechanics Friction in Action What is friction? Friction is a retarding force that opposes motion. Friction types: Static friction Kinetic friction Fluid friction Sources of dry friction Dry
PLANAR KINETIC EQUATIONS OF MOTION: TRANSLATION
 PLANAR KINETIC EQUATIONS OF MOTION: TRANSLATION Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Apply the three equations of motion for a rigid body in planar motion. 2. Analyze problems involving translational
PLANAR KINETIC EQUATIONS OF MOTION: TRANSLATION Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Apply the three equations of motion for a rigid body in planar motion. 2. Analyze problems involving translational
General Physics 1. School of Science, University of Tehran Fall Exercises (set 07)
 General Physics 1 School of Science, University of Tehran Fall 1396-97 Exercises (set 07) 1. In Fig., wheel A of radius r A 10cm is coupled by belt B to wheel C of radius r C 25 cm. The angular speed of
General Physics 1 School of Science, University of Tehran Fall 1396-97 Exercises (set 07) 1. In Fig., wheel A of radius r A 10cm is coupled by belt B to wheel C of radius r C 25 cm. The angular speed of
Rotation review packet. Name:
 Rotation review packet. Name:. A pulley of mass m 1 =M and radius R is mounted on frictionless bearings about a fixed axis through O. A block of equal mass m =M, suspended by a cord wrapped around the
Rotation review packet. Name:. A pulley of mass m 1 =M and radius R is mounted on frictionless bearings about a fixed axis through O. A block of equal mass m =M, suspended by a cord wrapped around the
CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 25: Ch.17, Sec.4-5
 1 / 36 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 25: Ch.17, Sec.4-5 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Date: 2 / 36 EQUATIONS OF MOTION: ROTATION
1 / 36 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 25: Ch.17, Sec.4-5 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Date: 2 / 36 EQUATIONS OF MOTION: ROTATION
(a) On the dots below that represent the students, draw and label free-body diagrams showing the forces on Student A and on Student B.
 2003 B1. (15 points) A rope of negligible mass passes over a pulley of negligible mass attached to the ceiling, as shown above. One end of the rope is held by Student A of mass 70 kg, who is at rest on
2003 B1. (15 points) A rope of negligible mass passes over a pulley of negligible mass attached to the ceiling, as shown above. One end of the rope is held by Student A of mass 70 kg, who is at rest on
Final Exam April 30, 2013
 Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a calculator during the exam. Usage of mobile phones and other electronic
Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a calculator during the exam. Usage of mobile phones and other electronic
7.7 Rolling Resistance
 7.7 Rolling Resistance 7.7 Rolling Resistance Example 1, page 1 of 4 1. The fertilizer spreader and the fertilizer it contains have a combined mass of 40 kg and a center of gravity located at point G.
7.7 Rolling Resistance 7.7 Rolling Resistance Example 1, page 1 of 4 1. The fertilizer spreader and the fertilizer it contains have a combined mass of 40 kg and a center of gravity located at point G.
E 490 FE Exam Prep. Engineering Mechanics
 E 490 FE Exam Prep Engineering Mechanics 2008 E 490 Course Topics Statics Newton s Laws of Motion Resultant Force Systems Moment of Forces and Couples Equilibrium Pulley Systems Trusses Centroid of an
E 490 FE Exam Prep Engineering Mechanics 2008 E 490 Course Topics Statics Newton s Laws of Motion Resultant Force Systems Moment of Forces and Couples Equilibrium Pulley Systems Trusses Centroid of an
General Definition of Torque, final. Lever Arm. General Definition of Torque 7/29/2010. Units of Chapter 10
 Units of Chapter 10 Determining Moments of Inertia Rotational Kinetic Energy Rotational Plus Translational Motion; Rolling Why Does a Rolling Sphere Slow Down? General Definition of Torque, final Taking
Units of Chapter 10 Determining Moments of Inertia Rotational Kinetic Energy Rotational Plus Translational Motion; Rolling Why Does a Rolling Sphere Slow Down? General Definition of Torque, final Taking
SOLUTION 8 7. To hold lever: a+ M O = 0; F B (0.15) - 5 = 0; F B = N. Require = N N B = N 0.3. Lever,
 8 3. If the coefficient of static friction at is m s = 0.4 and the collar at is smooth so it only exerts a horizontal force on the pipe, determine the minimum distance x so that the bracket can support
8 3. If the coefficient of static friction at is m s = 0.4 and the collar at is smooth so it only exerts a horizontal force on the pipe, determine the minimum distance x so that the bracket can support
6. Find the net torque on the wheel in Figure about the axle through O if a = 10.0 cm and b = 25.0 cm.
 1. During a certain period of time, the angular position of a swinging door is described by θ = 5.00 + 10.0t + 2.00t 2, where θ is in radians and t is in seconds. Determine the angular position, angular
1. During a certain period of time, the angular position of a swinging door is described by θ = 5.00 + 10.0t + 2.00t 2, where θ is in radians and t is in seconds. Determine the angular position, angular
Name Student ID Score Last First. I = 2mR 2 /5 around the sphere s center of mass?
 NOTE: ignore air resistance in all Questions. In all Questions choose the answer that is the closest!! Question I. (15 pts) Rotation 1. (5 pts) A bowling ball that has an 11 cm radius and a 7.2 kg mass
NOTE: ignore air resistance in all Questions. In all Questions choose the answer that is the closest!! Question I. (15 pts) Rotation 1. (5 pts) A bowling ball that has an 11 cm radius and a 7.2 kg mass
ME 230 Kinematics and Dynamics
 ME 230 Kinematics and Dynamics Wei-Chih Wang Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Washington Lecture 6: Particle Kinetics Kinetics of a particle (Chapter 13) - 13.4-13.6 Chapter 13: Objectives
ME 230 Kinematics and Dynamics Wei-Chih Wang Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Washington Lecture 6: Particle Kinetics Kinetics of a particle (Chapter 13) - 13.4-13.6 Chapter 13: Objectives
1 MR SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 2013
 SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
However, the friction forces are limited in magnitude and will not prevent motion if sufficiently large forces are applied.
 FRICTION 1 Introduction In preceding chapters, it was assumed that surfaces in contact were either frictionless (surfaces could move freely with respect to each other) or rough (tangential forces prevent
FRICTION 1 Introduction In preceding chapters, it was assumed that surfaces in contact were either frictionless (surfaces could move freely with respect to each other) or rough (tangential forces prevent
Chapter 10 Practice Test
 Chapter 10 Practice Test 1. At t = 0, a wheel rotating about a fixed axis at a constant angular acceleration of 0.40 rad/s 2 has an angular velocity of 1.5 rad/s and an angular position of 2.3 rad. What
Chapter 10 Practice Test 1. At t = 0, a wheel rotating about a fixed axis at a constant angular acceleration of 0.40 rad/s 2 has an angular velocity of 1.5 rad/s and an angular position of 2.3 rad. What
DYNAMICS MOMENT OF INERTIA
 DYNAMICS MOMENT OF INERTIA S TO SELF ASSESSMENT EXERCISE No.1 1. A cylinder has a mass of 1 kg, outer radius of 0.05 m and radius of gyration 0.03 m. It is allowed to roll down an inclined plane until
DYNAMICS MOMENT OF INERTIA S TO SELF ASSESSMENT EXERCISE No.1 1. A cylinder has a mass of 1 kg, outer radius of 0.05 m and radius of gyration 0.03 m. It is allowed to roll down an inclined plane until
Chapter 8 - Rotational Dynamics and Equilibrium REVIEW
 Pagpalain ka! (Good luck, in Filipino) Date Chapter 8 - Rotational Dynamics and Equilibrium REVIEW TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) When a rigid body
Pagpalain ka! (Good luck, in Filipino) Date Chapter 8 - Rotational Dynamics and Equilibrium REVIEW TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) When a rigid body
Exam 3 April 16, 2014
 Exam 3 Instructions: You have 60 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a calculator during the exam. Usage of mobile phones and other electronic
Exam 3 Instructions: You have 60 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a calculator during the exam. Usage of mobile phones and other electronic
b) Fluid friction: occurs when adjacent layers in a fluid are moving at different velocities.
 Ch.6 Friction Types of friction a) Dry friction: occurs when non smooth (non ideal) surfaces of two solids are in contact under a condition of sliding or a tendency to slide. (also called Coulomb friction)
Ch.6 Friction Types of friction a) Dry friction: occurs when non smooth (non ideal) surfaces of two solids are in contact under a condition of sliding or a tendency to slide. (also called Coulomb friction)
Webreview Torque and Rotation Practice Test
 Please do not write on test. ID A Webreview - 8.2 Torque and Rotation Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A 0.30-m-radius automobile
Please do not write on test. ID A Webreview - 8.2 Torque and Rotation Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A 0.30-m-radius automobile
Faculty of Engineering and Department of Physics Engineering Physics 131 Final Examination Saturday April 21, 2018; 14:00 pm 16:30 pm
 Faculty of Engineering and Department of Physics Engineering Physics 131 Final Examination Saturday April 21, 2018; 14:00 pm 16:30 pm 1. Closed book exam. No notes or textbooks allowed. 2. Formula sheets
Faculty of Engineering and Department of Physics Engineering Physics 131 Final Examination Saturday April 21, 2018; 14:00 pm 16:30 pm 1. Closed book exam. No notes or textbooks allowed. 2. Formula sheets
Name. ME 270 Fall 2005 Final Exam PROBLEM NO. 1. Given: A distributed load is applied to the top link which is, in turn, supported by link AC.
 Name ME 270 Fall 2005 Final Exam PROBLEM NO. 1 Given: A distributed load is applied to the top link which is, in turn, supported by link AC. Find: a) Draw a free body diagram of link BCDE and one of link
Name ME 270 Fall 2005 Final Exam PROBLEM NO. 1 Given: A distributed load is applied to the top link which is, in turn, supported by link AC. Find: a) Draw a free body diagram of link BCDE and one of link
Problem Solving Circular Motion Dynamics Challenge Problems
 Problem 1: Double Star System Problem Solving Circular Motion Dynamics Challenge Problems Consider a double star system under the influence of gravitational force between the stars. Star 1 has mass m 1
Problem 1: Double Star System Problem Solving Circular Motion Dynamics Challenge Problems Consider a double star system under the influence of gravitational force between the stars. Star 1 has mass m 1
The University of Melbourne Engineering Mechanics
 The University of Melbourne 436-291 Engineering Mechanics Tutorial Eleven Instantaneous Centre and General Motion Part A (Introductory) 1. (Problem 5/93 from Meriam and Kraige - Dynamics) For the instant
The University of Melbourne 436-291 Engineering Mechanics Tutorial Eleven Instantaneous Centre and General Motion Part A (Introductory) 1. (Problem 5/93 from Meriam and Kraige - Dynamics) For the instant
Question Bank Chapter -4- Part -2-
 Ishik University / Sulaimani Civil Engineering Department Question Bank Chapter -4- Part -2-1 Problem -1- Determine the magnitude of F so that the resultant couple moment acting on the beam is 1.5 kn m
Ishik University / Sulaimani Civil Engineering Department Question Bank Chapter -4- Part -2-1 Problem -1- Determine the magnitude of F so that the resultant couple moment acting on the beam is 1.5 kn m
DYNAMICS ME HOMEWORK PROBLEM SETS
 DYNAMICS ME 34010 HOMEWORK PROBLEM SETS Mahmoud M. Safadi 1, M.B. Rubin 2 1 safadi@technion.ac.il, 2 mbrubin@technion.ac.il Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Technion Israel Institute of Technology Spring
DYNAMICS ME 34010 HOMEWORK PROBLEM SETS Mahmoud M. Safadi 1, M.B. Rubin 2 1 safadi@technion.ac.il, 2 mbrubin@technion.ac.il Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Technion Israel Institute of Technology Spring
It will be most difficult for the ant to adhere to the wheel as it revolves past which of the four points? A) I B) II C) III D) IV
 AP Physics 1 Lesson 16 Homework Newton s First and Second Law of Rotational Motion Outcomes Define rotational inertia, torque, and center of gravity. State and explain Newton s first Law of Motion as it
AP Physics 1 Lesson 16 Homework Newton s First and Second Law of Rotational Motion Outcomes Define rotational inertia, torque, and center of gravity. State and explain Newton s first Law of Motion as it
Free-Body Diagrams. Introduction
 Free-Body Diagrams Introduction A Free-Body Diagram is a basic two or three-dimensional representation of an object used to show all present forces and moments. The purpose of the diagram is to deconstruct
Free-Body Diagrams Introduction A Free-Body Diagram is a basic two or three-dimensional representation of an object used to show all present forces and moments. The purpose of the diagram is to deconstruct
Statics Chapter II Fall 2018 Exercises Corresponding to Sections 2.1, 2.2, and 2.3
 Statics Chapter II Fall 2018 Exercises Corresponding to Sections 2.1, 2.2, and 2.3 2 3 Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR = F1 + F2 and its direction, measured counterclockwise from the
Statics Chapter II Fall 2018 Exercises Corresponding to Sections 2.1, 2.2, and 2.3 2 3 Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR = F1 + F2 and its direction, measured counterclockwise from the
Q2. A machine carries a 4.0 kg package from an initial position of d ˆ. = (2.0 m)j at t = 0 to a final position of d ˆ ˆ
 Coordinator: Dr. S. Kunwar Monday, March 25, 2019 Page: 1 Q1. An object moves in a horizontal circle at constant speed. The work done by the centripetal force is zero because: A) the centripetal force
Coordinator: Dr. S. Kunwar Monday, March 25, 2019 Page: 1 Q1. An object moves in a horizontal circle at constant speed. The work done by the centripetal force is zero because: A) the centripetal force
Physics 101 Lecture 5 Newton`s Laws
 Physics 101 Lecture 5 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department The Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law qfrictional forces q Examples
Physics 101 Lecture 5 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department The Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law qfrictional forces q Examples
Sample 5. Determine the tension in the cable and the horizontal and vertical components of reaction at the pin A. Neglect the size of the pulley.
 Sample 1 The tongs are designed to handle hot steel tubes which are being heat-treated in an oil bath. For a 20 jaw opening, what is the minimum coefficient of static friction between the jaws and the
Sample 1 The tongs are designed to handle hot steel tubes which are being heat-treated in an oil bath. For a 20 jaw opening, what is the minimum coefficient of static friction between the jaws and the
PROBLEM 16.4 SOLUTION
 PROBLEM 16.4 The motion of the.5-kg rod AB is guided b two small wheels which roll freel in horizontal slots. If a force P of magnitude 8 N is applied at B, determine (a) the acceleration of the rod, (b)
PROBLEM 16.4 The motion of the.5-kg rod AB is guided b two small wheels which roll freel in horizontal slots. If a force P of magnitude 8 N is applied at B, determine (a) the acceleration of the rod, (b)
PY205N Spring The vectors a, b, and c. are related by c = a b. The diagram below that best illustrates this relationship is (a) I
 PY205N Spring 2013 Final exam, practice version MODIFIED This practice exam is to help students prepare for the final exam to be given at the end of the semester. Please note that while problems on this
PY205N Spring 2013 Final exam, practice version MODIFIED This practice exam is to help students prepare for the final exam to be given at the end of the semester. Please note that while problems on this
Chapter 10: Friction A gem cannot be polished without friction, nor an individual perfected without
 Chapter 10: Friction 10-1 Chapter 10 Friction A gem cannot be polished without friction, nor an individual perfected without trials. Lucius Annaeus Seneca (4 BC - 65 AD) 10.1 Overview When two bodies are
Chapter 10: Friction 10-1 Chapter 10 Friction A gem cannot be polished without friction, nor an individual perfected without trials. Lucius Annaeus Seneca (4 BC - 65 AD) 10.1 Overview When two bodies are
AP Physics C: Rotation II. (Torque and Rotational Dynamics, Rolling Motion) Problems
 AP Physics C: Rotation II (Torque and Rotational Dynamics, Rolling Motion) Problems 1980M3. A billiard ball has mass M, radius R, and moment of inertia about the center of mass I c = 2 MR²/5 The ball is
AP Physics C: Rotation II (Torque and Rotational Dynamics, Rolling Motion) Problems 1980M3. A billiard ball has mass M, radius R, and moment of inertia about the center of mass I c = 2 MR²/5 The ball is
Chapter 9-10 Test Review
 Chapter 9-10 Test Review Chapter Summary 9.2. The Second Condition for Equilibrium Explain torque and the factors on which it depends. Describe the role of torque in rotational mechanics. 10.1. Angular
Chapter 9-10 Test Review Chapter Summary 9.2. The Second Condition for Equilibrium Explain torque and the factors on which it depends. Describe the role of torque in rotational mechanics. 10.1. Angular
The Laws of Motion. Newton s first law Force Mass Newton s second law Gravitational Force Newton s third law Examples
 The Laws of Motion Newton s first law Force Mass Newton s second law Gravitational Force Newton s third law Examples Gravitational Force Gravitational force is a vector Expressed by Newton s Law of Universal
The Laws of Motion Newton s first law Force Mass Newton s second law Gravitational Force Newton s third law Examples Gravitational Force Gravitational force is a vector Expressed by Newton s Law of Universal
Dynamics Plane kinematics of rigid bodies Section 4: TJW Rotation: Example 1
 Section 4: TJW Rotation: Example 1 The pinion A of the hoist motor drives gear B, which is attached to the hoisting drum. The load L is lifted from its rest position and acquires an upward velocity of
Section 4: TJW Rotation: Example 1 The pinion A of the hoist motor drives gear B, which is attached to the hoisting drum. The load L is lifted from its rest position and acquires an upward velocity of
Name (please print): UW ID# score last first
 Name (please print): UW ID# score last first Question I. (20 pts) Projectile motion A ball of mass 0.3 kg is thrown at an angle of 30 o above the horizontal. Ignore air resistance. It hits the ground 100
Name (please print): UW ID# score last first Question I. (20 pts) Projectile motion A ball of mass 0.3 kg is thrown at an angle of 30 o above the horizontal. Ignore air resistance. It hits the ground 100
Physics for Scientist and Engineers third edition Rotational Motion About a Fixed Axis Problems
 A particular bird s eye can just distinguish objects that subtend an angle no smaller than about 3 E -4 rad, A) How many degrees is this B) How small an object can the bird just distinguish when flying
A particular bird s eye can just distinguish objects that subtend an angle no smaller than about 3 E -4 rad, A) How many degrees is this B) How small an object can the bird just distinguish when flying
PH201 Chapter 5 Solutions
 PH201 Chapter 5 Solutions 5.4. Set Up: For each object use coordinates where +y is upward. Each object has Call the objects 1 and 2, with and Solve: (a) The free-body diagrams for each object are shown
PH201 Chapter 5 Solutions 5.4. Set Up: For each object use coordinates where +y is upward. Each object has Call the objects 1 and 2, with and Solve: (a) The free-body diagrams for each object are shown
STATICS. Bodies. Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: Design of a support
 4 Equilibrium CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University of Rigid Bodies 2010 The McGraw-Hill Companies,
4 Equilibrium CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University of Rigid Bodies 2010 The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Simple Machines. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 F Simple Machines Simple Machines Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Simple machines are devices that can be used to multiply or augment a force that we apply often at the expense of a distance through which we apply
F Simple Machines Simple Machines Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Simple machines are devices that can be used to multiply or augment a force that we apply often at the expense of a distance through which we apply
CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 28: Ch.17, Sec.2 3
 1 / 20 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 28: Ch.17, Sec.2 3 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Monday, November 1, 2011 2 / 20 PLANAR KINETIC
1 / 20 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 28: Ch.17, Sec.2 3 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Monday, November 1, 2011 2 / 20 PLANAR KINETIC
Equilibrium: Forces and Torques
 Practice 15B Answers are available in the classroom and on the website. Scan this QR code for a direct link. Equilibrium: Forces and Torques 16. Lynn walks across a 9.0 m long plank bridge. The mass of
Practice 15B Answers are available in the classroom and on the website. Scan this QR code for a direct link. Equilibrium: Forces and Torques 16. Lynn walks across a 9.0 m long plank bridge. The mass of
Force and Moment. Figure 1 Figure 2
 Force and Moment 1 Determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant of the two forces shown, using (a) the parallelogram law (b) the sine law. [1391 N, 47.8 ] Figure 1 Figure 2 2 The force F of magnitude
Force and Moment 1 Determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant of the two forces shown, using (a) the parallelogram law (b) the sine law. [1391 N, 47.8 ] Figure 1 Figure 2 2 The force F of magnitude
Problems. B 60 mm. 80 mm. 80 mm. 120 mm
 roblems roblem 4.1 When the power to an electric motor is turned on, the motor reaches its rated speed of 3300 rpm in 6 s, and when the power is turned off, the motor coasts to rest in 80 s. ssume uniformly
roblems roblem 4.1 When the power to an electric motor is turned on, the motor reaches its rated speed of 3300 rpm in 6 s, and when the power is turned off, the motor coasts to rest in 80 s. ssume uniformly
Final Exam December 15, 2014
 Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use the ME approved calculator only during the exam. Usage of mobile phones
Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use the ME approved calculator only during the exam. Usage of mobile phones
Physics 2211 ABC Quiz #3 Solutions Spring 2017
 Physics 2211 ABC Quiz #3 Solutions Spring 2017 I. (16 points) A block of mass m b is suspended vertically on a ideal cord that then passes through a frictionless hole and is attached to a sphere of mass
Physics 2211 ABC Quiz #3 Solutions Spring 2017 I. (16 points) A block of mass m b is suspended vertically on a ideal cord that then passes through a frictionless hole and is attached to a sphere of mass
Core Mathematics M1. Dynamics (Planes)
 Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics M1 Dynamics (Planes) Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Green) Items included with question papers Nil Advice to Candidates You must ensure that your
Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics M1 Dynamics (Planes) Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae (Green) Items included with question papers Nil Advice to Candidates You must ensure that your
Mechatronics. MANE 4490 Fall 2002 Assignment # 1
 Mechatronics MANE 4490 Fall 2002 Assignment # 1 1. For each of the physical models shown in Figure 1, derive the mathematical model (equation of motion). All displacements are measured from the static
Mechatronics MANE 4490 Fall 2002 Assignment # 1 1. For each of the physical models shown in Figure 1, derive the mathematical model (equation of motion). All displacements are measured from the static
CHARACTERISTICS OF DRY FRICTION & PROBLEMS INVOLVING DRY FRICTION
 CHARACTERISTICS OF DRY FRICTION & PROBLEMS INVOLVING DRY FRICTION Today s Objective: Students will be able to: a) Understand the characteristics of dry friction. b) Draw a FBD including friction. c) Solve
CHARACTERISTICS OF DRY FRICTION & PROBLEMS INVOLVING DRY FRICTION Today s Objective: Students will be able to: a) Understand the characteristics of dry friction. b) Draw a FBD including friction. c) Solve
+ ] B A BA / t BA / n. B G BG / t BG / n. a = (5)(4) = 80 in./s. A G AG / t AG / n. ] + [48 in./s ]
![+ ] B A BA / t BA / n. B G BG / t BG / n. a = (5)(4) = 80 in./s. A G AG / t AG / n. ] + [48 in./s ] + ] B A BA / t BA / n. B G BG / t BG / n. a = (5)(4) = 80 in./s. A G AG / t AG / n. ] + [48 in./s ]](/thumbs/78/77322745.jpg) PROLEM 15.113 3-in.-radius drum is rigidly attached to a 5-in.-radius drum as shown. One of the drums rolls without sliding on the surface shown, and a cord is wound around the other drum. Knowing that
PROLEM 15.113 3-in.-radius drum is rigidly attached to a 5-in.-radius drum as shown. One of the drums rolls without sliding on the surface shown, and a cord is wound around the other drum. Knowing that
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 11. Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 11 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 11 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
Suggested Problems. Chapter 1
 Suggested Problems Ch1: 49, 51, 86, 89, 93, 95, 96, 102. Ch2: 9, 18, 20, 44, 51, 74, 75, 93. Ch3: 4, 14, 46, 54, 56, 75, 91, 80, 82, 83. Ch4: 15, 59, 60, 62. Ch5: 14, 52, 54, 65, 67, 83, 87, 88, 91, 93,
Suggested Problems Ch1: 49, 51, 86, 89, 93, 95, 96, 102. Ch2: 9, 18, 20, 44, 51, 74, 75, 93. Ch3: 4, 14, 46, 54, 56, 75, 91, 80, 82, 83. Ch4: 15, 59, 60, 62. Ch5: 14, 52, 54, 65, 67, 83, 87, 88, 91, 93,
AP Physics 1: Rotational Motion & Dynamics: Problem Set
 AP Physics 1: Rotational Motion & Dynamics: Problem Set I. Axis of Rotation and Angular Properties 1. How many radians are subtended by a 0.10 m arc of a circle of radius 0.40 m? 2. How many degrees are
AP Physics 1: Rotational Motion & Dynamics: Problem Set I. Axis of Rotation and Angular Properties 1. How many radians are subtended by a 0.10 m arc of a circle of radius 0.40 m? 2. How many degrees are
Unit 21 Couples and Resultants with Couples
 Unit 21 Couples and Resultants with Couples Page 21-1 Couples A couple is defined as (21-5) Moment of Couple The coplanar forces F 1 and F 2 make up a couple and the coordinate axes are chosen so that
Unit 21 Couples and Resultants with Couples Page 21-1 Couples A couple is defined as (21-5) Moment of Couple The coplanar forces F 1 and F 2 make up a couple and the coordinate axes are chosen so that
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Torque
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Torque 1. A uniform meterstick of mass 0.20 kg is pivoted at the 40 cm mark. Where should one hang a mass of 0.50 kg to balance the stick? (A) 16 cm (B) 36 cm (C) 44
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Torque 1. A uniform meterstick of mass 0.20 kg is pivoted at the 40 cm mark. Where should one hang a mass of 0.50 kg to balance the stick? (A) 16 cm (B) 36 cm (C) 44
11.1 Virtual Work Procedures and Strategies, page 1 of 2
 11.1 Virtual Work 11.1 Virtual Work rocedures and Strategies, page 1 of 2 rocedures and Strategies for Solving roblems Involving Virtual Work 1. Identify a single coordinate, q, that will completely define
11.1 Virtual Work 11.1 Virtual Work rocedures and Strategies, page 1 of 2 rocedures and Strategies for Solving roblems Involving Virtual Work 1. Identify a single coordinate, q, that will completely define
SKAA 1213 Engineering Mechanics
 SKAA 1213 Engineering Mechanics TOPIC 6 FRICTION Lecturers: Rosli Anang Dr. Mohd Yunus Ishak Dr. Tan Cher Siang Lesson 7 Outline Introduction Equilibrium on a horizontal plane Equilibrium i on an inclined
SKAA 1213 Engineering Mechanics TOPIC 6 FRICTION Lecturers: Rosli Anang Dr. Mohd Yunus Ishak Dr. Tan Cher Siang Lesson 7 Outline Introduction Equilibrium on a horizontal plane Equilibrium i on an inclined
Uniform Circular Motion AP
 Uniform Circular Motion AP Uniform circular motion is motion in a circle at the same speed Speed is constant, velocity direction changes the speed of an object moving in a circle is given by v circumference
Uniform Circular Motion AP Uniform circular motion is motion in a circle at the same speed Speed is constant, velocity direction changes the speed of an object moving in a circle is given by v circumference
PHY218 SPRING 2016 Review for Exam#3: Week 12 Review: Linear Momentum, Collisions, Rotational Motion, and Equilibrium
 PHY218 SPRING 2016 Review for Exam#3: Week 12 Review: Linear Momentum, Collisions, Rotational Motion, and Equilibrium These are selected problems that you are to solve independently or in a team of 2-3
PHY218 SPRING 2016 Review for Exam#3: Week 12 Review: Linear Momentum, Collisions, Rotational Motion, and Equilibrium These are selected problems that you are to solve independently or in a team of 2-3
5. Plane Kinetics of Rigid Bodies
 5. Plane Kinetics of Rigid Bodies 5.1 Mass moments of inertia 5.2 General equations of motion 5.3 Translation 5.4 Fixed axis rotation 5.5 General plane motion 5.6 Work and energy relations 5.7 Impulse
5. Plane Kinetics of Rigid Bodies 5.1 Mass moments of inertia 5.2 General equations of motion 5.3 Translation 5.4 Fixed axis rotation 5.5 General plane motion 5.6 Work and energy relations 5.7 Impulse
3. Kinetics of Particles
 3. Kinetics of Particles 3.1 Force, Mass and Acceleration 3.3 Impulse and Momentum 3.4 Impact 1 3.1 Force, Mass and Acceleration We draw two important conclusions from the results of the experiments. First,
3. Kinetics of Particles 3.1 Force, Mass and Acceleration 3.3 Impulse and Momentum 3.4 Impact 1 3.1 Force, Mass and Acceleration We draw two important conclusions from the results of the experiments. First,
Addis Ababa University Addis Ababa Institute of Technology School Of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Extension Division Assignment 2
 Addis Ababa University Addis Ababa Institute of Technology School Of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Extension Division Assignment 2 1. The 50-kg crate is projected along the floor with an initial
Addis Ababa University Addis Ababa Institute of Technology School Of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Extension Division Assignment 2 1. The 50-kg crate is projected along the floor with an initial
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING ENGINEERING MECHANICS QUESTION BANK UNIT I - PART-A
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING ENGINEERING MECHANICS QUESTION BANK Sub. Code: CE1151 Sub. Name: Engg. Mechanics UNIT I - PART-A Sem / Year II / I 1.Distinguish the following system of forces with a suitable
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING ENGINEERING MECHANICS QUESTION BANK Sub. Code: CE1151 Sub. Name: Engg. Mechanics UNIT I - PART-A Sem / Year II / I 1.Distinguish the following system of forces with a suitable
Name: Date: Period: AP Physics C Rotational Motion HO19
 1.) A wheel turns with constant acceleration 0.450 rad/s 2. (9-9) Rotational Motion H19 How much time does it take to reach an angular velocity of 8.00 rad/s, starting from rest? Through how many revolutions
1.) A wheel turns with constant acceleration 0.450 rad/s 2. (9-9) Rotational Motion H19 How much time does it take to reach an angular velocity of 8.00 rad/s, starting from rest? Through how many revolutions
Lecture 4 February 13, Mechanization
 Lecture 4 February 13, 2006 Mechanization US Energy Consumption from all forms of energy from 1850-2000 1 The Lever Archimedes (Greek mathematician, 287 to 212 B.C.) who is believed to have said, Give
Lecture 4 February 13, 2006 Mechanization US Energy Consumption from all forms of energy from 1850-2000 1 The Lever Archimedes (Greek mathematician, 287 to 212 B.C.) who is believed to have said, Give
Total 0/15. 0/1 points POE MC.17. [ ]
![Total 0/15. 0/1 points POE MC.17. [ ] Total 0/15. 0/1 points POE MC.17. [ ]](/thumbs/90/103711827.jpg) Sample Problems to KSEA (2383954) Current Score: 0/15 Question Points 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 Total 0/15 1. 0/1 points POE1 2000.MC.17.
Sample Problems to KSEA (2383954) Current Score: 0/15 Question Points 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 0/1 Total 0/15 1. 0/1 points POE1 2000.MC.17.
SECOND MIDTERM -- REVIEW PROBLEMS
 Physics 10 Spring 009 George A. WIllaims SECOND MIDTERM -- REVIEW PROBLEMS A solution set is available on the course web page in pdf format. A data sheet is provided. No solutions for the following problems:
Physics 10 Spring 009 George A. WIllaims SECOND MIDTERM -- REVIEW PROBLEMS A solution set is available on the course web page in pdf format. A data sheet is provided. No solutions for the following problems:
TUTORIAL SHEET 1. magnitude of P and the values of ø and θ. Ans: ø =74 0 and θ= 53 0
 TUTORIAL SHEET 1 1. The rectangular platform is hinged at A and B and supported by a cable which passes over a frictionless hook at E. Knowing that the tension in the cable is 1349N, determine the moment
TUTORIAL SHEET 1 1. The rectangular platform is hinged at A and B and supported by a cable which passes over a frictionless hook at E. Knowing that the tension in the cable is 1349N, determine the moment
Chapter 9: Rotational Dynamics Tuesday, September 17, 2013
 Chapter 9: Rotational Dynamics Tuesday, September 17, 2013 10:00 PM The fundamental idea of Newtonian dynamics is that "things happen for a reason;" to be more specific, there is no need to explain rest
Chapter 9: Rotational Dynamics Tuesday, September 17, 2013 10:00 PM The fundamental idea of Newtonian dynamics is that "things happen for a reason;" to be more specific, there is no need to explain rest
CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 9: Ch.13, Sec.4-5
 1 / 40 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 9: Ch.13, Sec.4-5 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa 2 / 40 EQUATIONS OF MOTION:RECTANGULAR COORDINATES
1 / 40 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 9: Ch.13, Sec.4-5 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa 2 / 40 EQUATIONS OF MOTION:RECTANGULAR COORDINATES
Unit 1 Lesson 1.1 Mechanisms. Simple Machines. The Six Simple Machines. The Six Simple Machines. Project Lead The Way, Inc.
 Mechanisms Simple Machines Lever, Wheel and Axle, and Pulley 2012 Simple Machines Mechanisms that manipulate magnitude of force and distance. The Six Simple Machines Lever Wheel and Axle Pulley The Six
Mechanisms Simple Machines Lever, Wheel and Axle, and Pulley 2012 Simple Machines Mechanisms that manipulate magnitude of force and distance. The Six Simple Machines Lever Wheel and Axle Pulley The Six
if the initial displacement and velocities are zero each. [ ] PART-B
![if the initial displacement and velocities are zero each. [ ] PART-B if the initial displacement and velocities are zero each. [ ] PART-B](/thumbs/86/94772448.jpg) Set No - 1 I. Tech II Semester Regular Examinations ugust - 2014 ENGINEERING MECHNICS (Common to ECE, EEE, EIE, io-tech, E Com.E, gri. E) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Question Paper Consists of Part- and
Set No - 1 I. Tech II Semester Regular Examinations ugust - 2014 ENGINEERING MECHNICS (Common to ECE, EEE, EIE, io-tech, E Com.E, gri. E) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Question Paper Consists of Part- and
ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER /13
 ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 2012/13 COURSE NAME: ENGINEERING MECHANICS - STATICS CODE: ENG 2008 GROUP: AD ENG II DATE: May 2013 TIME: DURATION: 2 HOURS INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This
ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 2012/13 COURSE NAME: ENGINEERING MECHANICS - STATICS CODE: ENG 2008 GROUP: AD ENG II DATE: May 2013 TIME: DURATION: 2 HOURS INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN GE MECHANICS III FINAL EXAM APRIL 18, 2011 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN GE 226.3 MECHANICS III FINAL EXAM APRIL 18, 2011 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS LAST NAME (printed): FIRST NAME (printed): STUDENT NUMBER: EXAMINATION
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN GE 226.3 MECHANICS III FINAL EXAM APRIL 18, 2011 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS LAST NAME (printed): FIRST NAME (printed): STUDENT NUMBER: EXAMINATION
AP Physics C: Mechanics Sample Multiple-Choice Questions
 AP Physics C: Mechanics Sample Multiple-Choice Questions The materials included in these files are intended for noncommercial use by AP teachers for course and exam preparation; permission for any other
AP Physics C: Mechanics Sample Multiple-Choice Questions The materials included in these files are intended for noncommercial use by AP teachers for course and exam preparation; permission for any other
Chapter 4. Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion. continued
 Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion continued 4.9 Static and Kinetic Frictional Forces When an object is in contact with a surface forces can act on the objects. The component of this force acting
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion continued 4.9 Static and Kinetic Frictional Forces When an object is in contact with a surface forces can act on the objects. The component of this force acting
1. Replace the given system of forces acting on a body as shown in figure 1 by a single force and couple acting at the point A.
 Code No: Z0321 / R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech - Regular Examinations, June 2009 CLASSICAL MECHANICS ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering and Automobile
Code No: Z0321 / R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech - Regular Examinations, June 2009 CLASSICAL MECHANICS ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering and Automobile
Review PHYS114 Chapters 4-7
 Review PHYS114 Chapters 4-7 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A 27 kg object is accelerated at a rate of 1.7 m/s 2. What force does
Review PHYS114 Chapters 4-7 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A 27 kg object is accelerated at a rate of 1.7 m/s 2. What force does
 第 1 頁, 共 7 頁 Chap10 1. Test Bank, Question 3 One revolution per minute is about: 0.0524 rad/s 0.105 rad/s 0.95 rad/s 1.57 rad/s 6.28 rad/s 2. *Chapter 10, Problem 8 The angular acceleration of a wheel
第 1 頁, 共 7 頁 Chap10 1. Test Bank, Question 3 One revolution per minute is about: 0.0524 rad/s 0.105 rad/s 0.95 rad/s 1.57 rad/s 6.28 rad/s 2. *Chapter 10, Problem 8 The angular acceleration of a wheel
FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Thursday, 11 December 2014, 6 PM to 9 PM, Field House Gym
 FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Thursday, 11 December 2014, 6 PM to 9 PM, Field House Gym NAME: STUDENT ID: INSTRUCTION 1. This exam booklet has 13 pages. Make sure none are missing 2.
FALL TERM EXAM, PHYS 1211, INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Thursday, 11 December 2014, 6 PM to 9 PM, Field House Gym NAME: STUDENT ID: INSTRUCTION 1. This exam booklet has 13 pages. Make sure none are missing 2.
16.07 Dynamics. Problem Set 10
 NAME :..................... Massachusetts Institute of Technology 16.07 Dynamics Problem Set 10 Out date: Nov. 7, 2007 Due date: Nov. 14, 2007 Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Study Time Time Spent
NAME :..................... Massachusetts Institute of Technology 16.07 Dynamics Problem Set 10 Out date: Nov. 7, 2007 Due date: Nov. 14, 2007 Problem 1 Problem 2 Problem 3 Problem 4 Study Time Time Spent
Rolling, Torque, Angular Momentum
 Chapter 11 Rolling, Torque, Angular Momentum Copyright 11.2 Rolling as Translational and Rotation Combined Motion of Translation : i.e.motion along a straight line Motion of Rotation : rotation about a
Chapter 11 Rolling, Torque, Angular Momentum Copyright 11.2 Rolling as Translational and Rotation Combined Motion of Translation : i.e.motion along a straight line Motion of Rotation : rotation about a
Problem Set x Classical Mechanics, Fall 2016 Massachusetts Institute of Technology. 1. Moment of Inertia: Disc and Washer
 8.01x Classical Mechanics, Fall 2016 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Problem Set 10 1. Moment of Inertia: Disc and Washer (a) A thin uniform disc of mass M and radius R is mounted on an axis passing
8.01x Classical Mechanics, Fall 2016 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Problem Set 10 1. Moment of Inertia: Disc and Washer (a) A thin uniform disc of mass M and radius R is mounted on an axis passing
Introduction to Statics
 Introduction to Statics.PDF Edition Version 0.95 Unit 26 Friction of Machine Elements Helen Margaret Lester Plants Late Professor Emerita Wallace Starr Venable Emeritus Associate Professor West Virginia
Introduction to Statics.PDF Edition Version 0.95 Unit 26 Friction of Machine Elements Helen Margaret Lester Plants Late Professor Emerita Wallace Starr Venable Emeritus Associate Professor West Virginia
NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION, EQUATIONS OF MOTION, & EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SYSTEM OF PARTICLES
 NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION, EQUATIONS OF MOTION, & EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SYSTEM OF PARTICLES Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Write the equation of motion for an accelerating body. 2. Draw the
NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION, EQUATIONS OF MOTION, & EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR A SYSTEM OF PARTICLES Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Write the equation of motion for an accelerating body. 2. Draw the
