Lecture 6 mechanical system modeling equivalent mass gears
|
|
|
- Clementine Campbell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 M Mechanical System Analysis 기계시스템해석 lecture 6,7,8 Dongjun Lee ( 이동준 ) Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering Seoul National University Dongjun Lee Lecture 6 mechanical system modeling equivalent mass gears Dongjun Lee 1
2 Lecture 7 planar dynamics energy method mechanical drives spring elements Dongjun Lee natural frequency damper effect of damping Lecture 8 we are currently doing Chapter 4. Dongjun Lee 2
3 crash dummy Mechanical System Modeling suspension mass & inertia spring deformed under force; return to original shape when force removed potential energy storage 1 2 mass[kg] inertia[kgm 2 ] Dongjun Lee kinetic energy storage damper slow down motion; dissipate energy Mass Spring Damper Energetics system dynamics total energy damping dissipation energy input by Dongjun Lee 3
4 Mass/Inertia: 2D Case translation dynamics (w.r.t. CoM) rotation dynamics (w.r.t. CoM) : D Alembert often, more convenient to use or D Alembert =0 if P is fied for 2D rotation about a fied point,, Dongjun Lee rolling constraint (no sliding/bouncing) Eample α translation dynamics Dongjun Lee rotation dynamics w.r.t. G friction (unknown) sin sin to maintain rotation dynamics w.r.t. P no slip sin no need to compute! minimum friction coefficient for no slip tan producible by a P 4
5 Energy Methods energy conservation: a prelude to Lagrangian/Hamiltonian dynamics eample rolling constraints: system dynamics: 2 2 sin can think of multiple masses as one lumped mass * no need to compute friction force F: why? Dongjun Lee Mechanical Drives kinematic constraint: gear ratio speed reducer if N>1, ideal gear bo real gear bo torque amplification efficiency (friction, inertia, etc) 60 80% system dynamics / Dongjun Lee 1 5
6 E 2.3.5: Simple Robot Arm kinematic constraint 1 energies cos, motor feels lighter load system dynamics sin 1 DOF system Dongjun Lee Differential Drive Dongjun Lee 6
7 Differential Drive Dongjun Lee symbol eternal force force equation and potential energy Linear Spring Elements deflection free length >0: tension <0: compression if f=0, =0 1 2 quadratic spring constant (or stiffness) [N/m] eamples: : small deformation, linear elastic material, etc shear modulus potential Dongjun Lee * for more, see tables 4.1.1,
8 Free Length and Equilibrium, 1) w.r.t..., 2) w.r.t. (from equilibrium L) : free length : from free length : from zero 1) w.r.t. 2) w.r.t. (from equilibrium ),..,.., : static deflection = / : from equilibrium : deflection from free length w.r.t. equilibrium, we can write the system dynamics s.t. Dongjun Lee parallel connection Parallel and Serial Connections f1 f2 same deflection n spring connection serial connection f f o same force o f o n spring connection Dongjun Lee 8
9 Distributed Inertia and Equivalent Mass y : rod length : end position : initial coordinate (0, : rod coordinate (0),, 0, 0, 0 mass per unit length: infinitesimal mass moves with velocity, at linear velocity assumption, 3 Dongjun Lee equivalent mass of rod Natural Frequency and Rayleigh Method, 0, 0,0 simple harmonic oscillation Im + j j Re natural frequency (amplitude) and (phase) depend on the initial conditions if input is also sinusoid with, (resonance) Rayleigh Method: if 0, is conserved Dongjun Lee 9
10 Eample P : equilibrium 0: mass mass less rod 0?? Dongjun Lee Linear Damper symbol eternal force f linear damper equation relative velocity damping coefficient [N/(m/s)] energy is always dissipated via damper relative velocity Dongjun Lee 10
11 Eamples dashpot shock absorber hole length cylinder diameter door closer viscosity hole diameter viscous bearing pressure bearing length ale diameter viscosity lubrication layer Dongjun Lee Hydraulic Damper [Sec. 7.4] hole length cylinder diameter force equation viscosity hole diameter,, 0 continuity equation (incompressible) laminar flow resistance 1, 128, * if 2 2 (parallel) * if two holes: /2(series) 8 2 if Dongjun Lee 11
12 Door Closer? equation of motion series : deflection from door closing 1 2 orifice equation Δ 1 2 Dongjun Lee adjustable Damped Oscillations With non zero initial condition 0,0 w/ 0 Im + j j Re effect of damping 1) if 0 / keep oscillating (un damped) 2) if 2 damped oscillation (under damped) 3) if 2 sin, no oscillation (critically damped; optimal) 4) if 2 no oscillation, but slow (over damped) Dongjun Lee 12
13 Quad Car Model 1) quarter car body 2) wheel +tire +ale equation of motions are coupled: need to be simultaneously solved Dongjun Lee Net Lecture Lagrange Dynamics Dongjun Lee 13
Contents. Dynamics and control of mechanical systems. Focus on
 Dynamics and control of mechanical systems Date Day 1 (01/08) Day 2 (03/08) Day 3 (05/08) Day 4 (07/08) Day 5 (09/08) Day 6 (11/08) Content Review of the basics of mechanics. Kinematics of rigid bodies
Dynamics and control of mechanical systems Date Day 1 (01/08) Day 2 (03/08) Day 3 (05/08) Day 4 (07/08) Day 5 (09/08) Day 6 (11/08) Content Review of the basics of mechanics. Kinematics of rigid bodies
Dynamics and control of mechanical systems
 Dynamics and control of mechanical systems Date Day 1 (03/05) - 05/05 Day 2 (07/05) Day 3 (09/05) Day 4 (11/05) Day 5 (14/05) Day 6 (16/05) Content Review of the basics of mechanics. Kinematics of rigid
Dynamics and control of mechanical systems Date Day 1 (03/05) - 05/05 Day 2 (07/05) Day 3 (09/05) Day 4 (11/05) Day 5 (14/05) Day 6 (16/05) Content Review of the basics of mechanics. Kinematics of rigid
Dynamic Modelling of Mechanical Systems
 Dynamic Modelling of Mechanical Systems Dr. Bishakh Bhattacharya Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering g IIT Kanpur Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc - Funded by MHRD Hints of the Last Assignment
Dynamic Modelling of Mechanical Systems Dr. Bishakh Bhattacharya Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering g IIT Kanpur Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc - Funded by MHRD Hints of the Last Assignment
Mathematical Modeling and response analysis of mechanical systems are the subjects of this chapter.
 Chapter 3 Mechanical Systems A. Bazoune 3.1 INRODUCION Mathematical Modeling and response analysis of mechanical systems are the subjects of this chapter. 3. MECHANICAL ELEMENS Any mechanical system consists
Chapter 3 Mechanical Systems A. Bazoune 3.1 INRODUCION Mathematical Modeling and response analysis of mechanical systems are the subjects of this chapter. 3. MECHANICAL ELEMENS Any mechanical system consists
T1 T e c h n i c a l S e c t i o n
 1.5 Principles of Noise Reduction A good vibration isolation system is reducing vibration transmission through structures and thus, radiation of these vibration into air, thereby reducing noise. There
1.5 Principles of Noise Reduction A good vibration isolation system is reducing vibration transmission through structures and thus, radiation of these vibration into air, thereby reducing noise. There
Modeling of a Mechanical System
 Chapter 3 Modeling of a Mechanical System 3.1 Units Currently, there are two systems of units: One is the international system (SI) metric system, the other is the British engineering system (BES) the
Chapter 3 Modeling of a Mechanical System 3.1 Units Currently, there are two systems of units: One is the international system (SI) metric system, the other is the British engineering system (BES) the
EQUIVALENT SINGLE-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEM AND FREE VIBRATION
 1 EQUIVALENT SINGLE-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEM AND FREE VIBRATION The course on Mechanical Vibration is an important part of the Mechanical Engineering undergraduate curriculum. It is necessary for the development
1 EQUIVALENT SINGLE-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEM AND FREE VIBRATION The course on Mechanical Vibration is an important part of the Mechanical Engineering undergraduate curriculum. It is necessary for the development
2007 Problem Topic Comment 1 Kinematics Position-time equation Kinematics 7 2 Kinematics Velocity-time graph Dynamics 6 3 Kinematics Average velocity
 2007 Problem Topic Comment 1 Kinematics Position-time equation Kinematics 7 2 Kinematics Velocity-time graph Dynamics 6 3 Kinematics Average velocity Energy 7 4 Kinematics Free fall Collisions 3 5 Dynamics
2007 Problem Topic Comment 1 Kinematics Position-time equation Kinematics 7 2 Kinematics Velocity-time graph Dynamics 6 3 Kinematics Average velocity Energy 7 4 Kinematics Free fall Collisions 3 5 Dynamics
In this lecture you will learn the following
 Module 9 : Forced Vibration with Harmonic Excitation; Undamped Systems and resonance; Viscously Damped Systems; Frequency Response Characteristics and Phase Lag; Systems with Base Excitation; Transmissibility
Module 9 : Forced Vibration with Harmonic Excitation; Undamped Systems and resonance; Viscously Damped Systems; Frequency Response Characteristics and Phase Lag; Systems with Base Excitation; Transmissibility
Figure XP3.1 (a) Mass in equilibrium, (b) Freebody diagram, (c) Kinematic constraint relation Example Problem 3.1 Figure XP3.1 illustrates a mass m
 LECTURE 7. MORE VIBRATIONS ` Figure XP3.1 (a) Mass in equilibrium, (b) Freebody diagram, (c) Kinematic constraint relation Example Problem 3.1 Figure XP3.1 illustrates a mass m that is in equilibrium and
LECTURE 7. MORE VIBRATIONS ` Figure XP3.1 (a) Mass in equilibrium, (b) Freebody diagram, (c) Kinematic constraint relation Example Problem 3.1 Figure XP3.1 illustrates a mass m that is in equilibrium and
Structural Dynamics. Spring mass system. The spring force is given by and F(t) is the driving force. Start by applying Newton s second law (F=ma).
 Structural Dynamics Spring mass system. The spring force is given by and F(t) is the driving force. Start by applying Newton s second law (F=ma). We will now look at free vibrations. Considering the free
Structural Dynamics Spring mass system. The spring force is given by and F(t) is the driving force. Start by applying Newton s second law (F=ma). We will now look at free vibrations. Considering the free
Modeling Mechanical Systems
 Modeling Mechanical Systems Mechanical systems can be either translational or rotational. Although the fundamental relationships for both types are derived from Newton s law, they are different enough
Modeling Mechanical Systems Mechanical systems can be either translational or rotational. Although the fundamental relationships for both types are derived from Newton s law, they are different enough
Mechatronics. MANE 4490 Fall 2002 Assignment # 1
 Mechatronics MANE 4490 Fall 2002 Assignment # 1 1. For each of the physical models shown in Figure 1, derive the mathematical model (equation of motion). All displacements are measured from the static
Mechatronics MANE 4490 Fall 2002 Assignment # 1 1. For each of the physical models shown in Figure 1, derive the mathematical model (equation of motion). All displacements are measured from the static
The... of a particle is defined as its change in position in some time interval.
 Distance is the. of a path followed by a particle. Distance is a quantity. The... of a particle is defined as its change in position in some time interval. Displacement is a.. quantity. The... of a particle
Distance is the. of a path followed by a particle. Distance is a quantity. The... of a particle is defined as its change in position in some time interval. Displacement is a.. quantity. The... of a particle
Rutgers University Department of Physics & Astronomy. 01:750:271 Honors Physics I Fall Lecture 19. Home Page. Title Page. Page 1 of 36.
 Rutgers University Department of Physics & Astronomy 01:750:271 Honors Physics I Fall 2015 Lecture 19 Page 1 of 36 12. Equilibrium and Elasticity How do objects behave under applied external forces? Under
Rutgers University Department of Physics & Astronomy 01:750:271 Honors Physics I Fall 2015 Lecture 19 Page 1 of 36 12. Equilibrium and Elasticity How do objects behave under applied external forces? Under
The Modeling of Single-dof Mechanical Systems
 The Modeling of Single-dof Mechanical Systems Lagrange equation for a single-dof system: where: q: is the generalized coordinate; T: is the total kinetic energy of the system; V: is the total potential
The Modeling of Single-dof Mechanical Systems Lagrange equation for a single-dof system: where: q: is the generalized coordinate; T: is the total kinetic energy of the system; V: is the total potential
Introduction to Mechanical Vibration
 2103433 Introduction to Mechanical Vibration Nopdanai Ajavakom (NAV) 1 Course Topics Introduction to Vibration What is vibration? Basic concepts of vibration Modeling Linearization Single-Degree-of-Freedom
2103433 Introduction to Mechanical Vibration Nopdanai Ajavakom (NAV) 1 Course Topics Introduction to Vibration What is vibration? Basic concepts of vibration Modeling Linearization Single-Degree-of-Freedom
Structural Dynamics Lecture 4. Outline of Lecture 4. Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems. Formulation of Equations of Motions. Undamped Eigenvibrations.
 Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems Formulation of Equations of Motions. Newton s 2 nd Law Applied to Free Masses. D Alembert s Principle. Basic Equations of Motion for Forced Vibrations of Linear
Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems Formulation of Equations of Motions. Newton s 2 nd Law Applied to Free Masses. D Alembert s Principle. Basic Equations of Motion for Forced Vibrations of Linear
1 2 Models, Theories, and Laws 1.5 Distinguish between models, theories, and laws 2.1 State the origin of significant figures in measurement
 Textbook Correlation Textbook Correlation Physics 1115/2015 Chapter 1 Introduction, Measurement, Estimating 1.1 Describe thoughts of Aristotle vs. Galileo in describing motion 1 1 Nature of Science 1.2
Textbook Correlation Textbook Correlation Physics 1115/2015 Chapter 1 Introduction, Measurement, Estimating 1.1 Describe thoughts of Aristotle vs. Galileo in describing motion 1 1 Nature of Science 1.2
Vibration Control Prof. Dr. S. P. Harsha Department of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee
 Vibration Control Prof. Dr. S. P. Harsha Department of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Module - 1 Review of Basics of Mechanical Vibrations Lecture - 2 Introduction
Vibration Control Prof. Dr. S. P. Harsha Department of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Module - 1 Review of Basics of Mechanical Vibrations Lecture - 2 Introduction
Step 1: Mathematical Modeling
 083 Mechanical Vibrations Lesson Vibration Analysis Procedure The analysis of a vibrating system usually involves four steps: mathematical modeling derivation of the governing uations solution of the uations
083 Mechanical Vibrations Lesson Vibration Analysis Procedure The analysis of a vibrating system usually involves four steps: mathematical modeling derivation of the governing uations solution of the uations
Dynamics of Machinery
 Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
Engineering Science OUTCOME 2 - TUTORIAL 3 FREE VIBRATIONS
 Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 5 Engineering Science L/60/404 OUTCOME 2 - TUTORIAL 3 FREE VIBRATIONS UNIT CONTENT OUTCOME 2 Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements
Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 5 Engineering Science L/60/404 OUTCOME 2 - TUTORIAL 3 FREE VIBRATIONS UNIT CONTENT OUTCOME 2 Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements
Introduction to Continuous Systems. Continuous Systems. Strings, Torsional Rods and Beams.
 Outline of Continuous Systems. Introduction to Continuous Systems. Continuous Systems. Strings, Torsional Rods and Beams. Vibrations of Flexible Strings. Torsional Vibration of Rods. Bernoulli-Euler Beams.
Outline of Continuous Systems. Introduction to Continuous Systems. Continuous Systems. Strings, Torsional Rods and Beams. Vibrations of Flexible Strings. Torsional Vibration of Rods. Bernoulli-Euler Beams.
A Guide to linear dynamic analysis with Damping
 A Guide to linear dynamic analysis with Damping This guide starts from the applications of linear dynamic response and its role in FEA simulation. Fundamental concepts and principles will be introduced
A Guide to linear dynamic analysis with Damping This guide starts from the applications of linear dynamic response and its role in FEA simulation. Fundamental concepts and principles will be introduced
Section 2.2 : Electromechanical. analogies PHILIPE HERZOG AND GUILLAUME PENELET
 Section 2.2 : Electromechanical analogies PHILIPE HERZOG AND GUILLAUME PENELET Paternité - Pas d'utilisation Commerciale - Partage des Conditions Initiales à l'identique : http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.0/fr/
Section 2.2 : Electromechanical analogies PHILIPE HERZOG AND GUILLAUME PENELET Paternité - Pas d'utilisation Commerciale - Partage des Conditions Initiales à l'identique : http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.0/fr/
CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 25: Ch.17, Sec.4-5
 1 / 36 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 25: Ch.17, Sec.4-5 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Date: 2 / 36 EQUATIONS OF MOTION: ROTATION
1 / 36 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 25: Ch.17, Sec.4-5 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Date: 2 / 36 EQUATIONS OF MOTION: ROTATION
Figure 5.28 (a) Spring-restrained cylinder, (b) Kinematic variables, (c) Free-body diagram
 Lecture 30. MORE GENERAL-MOTION/ROLLING- WITHOUT-SLIPPING EXAMPLES A Cylinder, Restrained by a Spring and Rolling on a Plane Figure 5.28 (a) Spring-restrained cylinder, (b) Kinematic variables, (c) Free-body
Lecture 30. MORE GENERAL-MOTION/ROLLING- WITHOUT-SLIPPING EXAMPLES A Cylinder, Restrained by a Spring and Rolling on a Plane Figure 5.28 (a) Spring-restrained cylinder, (b) Kinematic variables, (c) Free-body
The student will experimentally determine the parameters to represent the behavior of a damped oscillatory system of one degree of freedom.
 Practice 3 NAME STUDENT ID LAB GROUP PROFESSOR INSTRUCTOR Vibrations of systems of one degree of freedom with damping QUIZ 10% PARTICIPATION & PRESENTATION 5% INVESTIGATION 10% DESIGN PROBLEM 15% CALCULATIONS
Practice 3 NAME STUDENT ID LAB GROUP PROFESSOR INSTRUCTOR Vibrations of systems of one degree of freedom with damping QUIZ 10% PARTICIPATION & PRESENTATION 5% INVESTIGATION 10% DESIGN PROBLEM 15% CALCULATIONS
Exponential decay. The deviations in amplitude over 30 periods rise to more than ±20%. Fig 1 a rod and ball pendulum
 Exponential decay A counter example There is a common belief that the damping of the motion of a pendulum in air is exponential, or nearly so, in all situations. To explore the limits of that approximation
Exponential decay A counter example There is a common belief that the damping of the motion of a pendulum in air is exponential, or nearly so, in all situations. To explore the limits of that approximation
a) Find the equation of motion of the system and write it in matrix form.
 .003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set Problem : Torsional Oscillator Two disks of radius r and r and mass m and m are mounted in series with steel shafts. The shaft between the base and m has length L
.003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set Problem : Torsional Oscillator Two disks of radius r and r and mass m and m are mounted in series with steel shafts. The shaft between the base and m has length L
TOPIC E: OSCILLATIONS EXAMPLES SPRING Q1. Find general solutions for the following differential equations:
 TOPIC E: OSCILLATIONS EXAMPLES SPRING 2019 Mathematics of Oscillating Systems Q1. Find general solutions for the following differential equations: Undamped Free Vibration Q2. A 4 g mass is suspended by
TOPIC E: OSCILLATIONS EXAMPLES SPRING 2019 Mathematics of Oscillating Systems Q1. Find general solutions for the following differential equations: Undamped Free Vibration Q2. A 4 g mass is suspended by
Impact. m k. Natural Period of Vibration τ. Static load Gray area Impact load t > 3 τ. Absorbing energy. Carrying loads
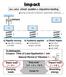 Impact also called shock, sudden or impulsive loading driving a nail with a hammer, automobile collisions. dashpot a) Rapidly moving vehicles crossing a bridge To distinguish: b) Suddenly applied c) Direct
Impact also called shock, sudden or impulsive loading driving a nail with a hammer, automobile collisions. dashpot a) Rapidly moving vehicles crossing a bridge To distinguish: b) Suddenly applied c) Direct
Chapter 14 Oscillations. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations of a Spring Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator Simple Harmonic Motion Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum The Physical
Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations of a Spring Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator Simple Harmonic Motion Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum The Physical
Translational Mechanical Systems
 Translational Mechanical Systems Basic (Idealized) Modeling Elements Interconnection Relationships -Physical Laws Derive Equation of Motion (EOM) - SDOF Energy Transfer Series and Parallel Connections
Translational Mechanical Systems Basic (Idealized) Modeling Elements Interconnection Relationships -Physical Laws Derive Equation of Motion (EOM) - SDOF Energy Transfer Series and Parallel Connections
Structural Dynamics Lecture 2. Outline of Lecture 2. Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.)
 Outline of Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.) Linear Viscous Damped Eigenvibrations. Logarithmic decrement. Response to Harmonic and Periodic Loads. 1 Single-Degreee-of-Freedom Systems (cont.). Linear
Outline of Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.) Linear Viscous Damped Eigenvibrations. Logarithmic decrement. Response to Harmonic and Periodic Loads. 1 Single-Degreee-of-Freedom Systems (cont.). Linear
Forced Oscillations in a Linear System Problems
 Forced Oscillations in a Linear System Problems Summary of the Principal Formulas The differential equation of forced oscillations for the kinematic excitation: ϕ + 2γ ϕ + ω 2 0ϕ = ω 2 0φ 0 sin ωt. Steady-state
Forced Oscillations in a Linear System Problems Summary of the Principal Formulas The differential equation of forced oscillations for the kinematic excitation: ϕ + 2γ ϕ + ω 2 0ϕ = ω 2 0φ 0 sin ωt. Steady-state
UNIT-I (FORCE ANALYSIS)
 DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEACH AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK ME2302 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY III YEAR/ V SEMESTER UNIT-I (FORCE ANALYSIS) PART-A (2 marks)
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEACH AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK ME2302 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY III YEAR/ V SEMESTER UNIT-I (FORCE ANALYSIS) PART-A (2 marks)
LANMARK UNIVERSITY OMU-ARAN, KWARA STATE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MECHANICS OF MACHINE (MCE 322). LECTURER: ENGR.
 LANMARK UNIVERSITY OMU-ARAN, KWARA STATE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MECHANICS OF MACHINE (MCE 322). LECTURER: ENGR. IBIKUNLE ROTIMI ADEDAYO SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION. Introduction Consider
LANMARK UNIVERSITY OMU-ARAN, KWARA STATE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MECHANICS OF MACHINE (MCE 322). LECTURER: ENGR. IBIKUNLE ROTIMI ADEDAYO SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION. Introduction Consider
Dynamic Mechanical Analysis of Solid Polymers and Polymer Melts
 Polymer Physics 2015 Matilda Larsson Dynamic Mechanical Analysis of Solid Polymers and Polymer Melts Polymer & Materials Chemistry Introduction Two common instruments for dynamic mechanical thermal analysis
Polymer Physics 2015 Matilda Larsson Dynamic Mechanical Analysis of Solid Polymers and Polymer Melts Polymer & Materials Chemistry Introduction Two common instruments for dynamic mechanical thermal analysis
Introduction to structural dynamics
 Introduction to structural dynamics p n m n u n p n-1 p 3... m n-1 m 3... u n-1 u 3 k 1 c 1 u 1 u 2 k 2 m p 1 1 c 2 m2 p 2 k n c n m n u n p n m 2 p 2 u 2 m 1 p 1 u 1 Static vs dynamic analysis Static
Introduction to structural dynamics p n m n u n p n-1 p 3... m n-1 m 3... u n-1 u 3 k 1 c 1 u 1 u 2 k 2 m p 1 1 c 2 m2 p 2 k n c n m n u n p n m 2 p 2 u 2 m 1 p 1 u 1 Static vs dynamic analysis Static
DSC HW 3: Assigned 6/25/11, Due 7/2/12 Page 1
 DSC HW 3: Assigned 6/25/11, Due 7/2/12 Page 1 Problem 1 (Motor-Fan): A motor and fan are to be connected as shown in Figure 1. The torque-speed characteristics of the motor and fan are plotted on the same
DSC HW 3: Assigned 6/25/11, Due 7/2/12 Page 1 Problem 1 (Motor-Fan): A motor and fan are to be connected as shown in Figure 1. The torque-speed characteristics of the motor and fan are plotted on the same
ME2302 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY
 ME2302 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY TWO MARKS QUESTION AND ANSWERS 1. What are the conditions for a body to be in static and dynamic equilibrium? Necessary and sufficient conditions for static and dynamic equilibrium
ME2302 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY TWO MARKS QUESTION AND ANSWERS 1. What are the conditions for a body to be in static and dynamic equilibrium? Necessary and sufficient conditions for static and dynamic equilibrium
General Physics I. Lecture 12: Applications of Oscillatory Motion. Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 )
 General Physics I Lecture 1: Applications of Oscillatory Motion Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 ) inwan@zju.edu.cn http://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~inwan/ Outline The pendulum Comparing simple harmonic motion and uniform circular
General Physics I Lecture 1: Applications of Oscillatory Motion Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 ) inwan@zju.edu.cn http://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~inwan/ Outline The pendulum Comparing simple harmonic motion and uniform circular
Problem 1: Find the Equation of Motion from the static equilibrium position for the following systems: 1) Assumptions
 Problem 1: Find the Equation of Motion from the static equilibrium position for the following systems: 1) Assumptions k 2 Wheels roll without friction k 1 Motion will not cause block to hit the supports
Problem 1: Find the Equation of Motion from the static equilibrium position for the following systems: 1) Assumptions k 2 Wheels roll without friction k 1 Motion will not cause block to hit the supports
Index. Index. More information. in this web service Cambridge University Press
 A-type elements, 4 7, 18, 31, 168, 198, 202, 219, 220, 222, 225 A-type variables. See Across variable ac current, 172, 251 ac induction motor, 251 Acceleration rotational, 30 translational, 16 Accumulator,
A-type elements, 4 7, 18, 31, 168, 198, 202, 219, 220, 222, 225 A-type variables. See Across variable ac current, 172, 251 ac induction motor, 251 Acceleration rotational, 30 translational, 16 Accumulator,
PHYSICS. Chapter 15 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 15 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 15 Oscillations IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about systems that oscillate in simple harmonic
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 15 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 15 Oscillations IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about systems that oscillate in simple harmonic
7. Vibrations DE2-EA 2.1: M4DE. Dr Connor Myant
 DE2-EA 2.1: M4DE Dr Connor Myant 7. Vibrations Comments and corrections to connor.myant@imperial.ac.uk Lecture resources may be found on Blackboard and at http://connormyant.com Contents Introduction...
DE2-EA 2.1: M4DE Dr Connor Myant 7. Vibrations Comments and corrections to connor.myant@imperial.ac.uk Lecture resources may be found on Blackboard and at http://connormyant.com Contents Introduction...
Sample Physics Placement Exam
 Sample Physics 130-1 Placement Exam A. Multiple Choice Questions: 1. A cable is used to take construction equipment from the ground to the top of a tall building. During the trip up, when (if ever) is
Sample Physics 130-1 Placement Exam A. Multiple Choice Questions: 1. A cable is used to take construction equipment from the ground to the top of a tall building. During the trip up, when (if ever) is
Rotational Motion. Rotational Motion. Rotational Motion
 I. Rotational Kinematics II. Rotational Dynamics (Netwton s Law for Rotation) III. Angular Momentum Conservation 1. Remember how Newton s Laws for translational motion were studied: 1. Kinematics (x =
I. Rotational Kinematics II. Rotational Dynamics (Netwton s Law for Rotation) III. Angular Momentum Conservation 1. Remember how Newton s Laws for translational motion were studied: 1. Kinematics (x =
Q1. Which of the following is the correct combination of dimensions for energy?
 Tuesday, June 15, 2010 Page: 1 Q1. Which of the following is the correct combination of dimensions for energy? A) ML 2 /T 2 B) LT 2 /M C) MLT D) M 2 L 3 T E) ML/T 2 Q2. Two cars are initially 150 kilometers
Tuesday, June 15, 2010 Page: 1 Q1. Which of the following is the correct combination of dimensions for energy? A) ML 2 /T 2 B) LT 2 /M C) MLT D) M 2 L 3 T E) ML/T 2 Q2. Two cars are initially 150 kilometers
Chapter 14 Oscillations. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 Oscillations 14-1 Oscillations of a Spring If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The
Chapter 14 Oscillations 14-1 Oscillations of a Spring If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The
e jωt = cos(ωt) + jsin(ωt),
 This chapter introduces you to the most useful mechanical oscillator model, a mass-spring system with a single degree of freedom. Basic understanding of this system is the gateway to the understanding
This chapter introduces you to the most useful mechanical oscillator model, a mass-spring system with a single degree of freedom. Basic understanding of this system is the gateway to the understanding
Chapter 14. Oscillations. Oscillations Introductory Terminology Simple Harmonic Motion:
 Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations Introductory Terminology Simple Harmonic Motion: Kinematics Energy Examples of Simple Harmonic Oscillators Damped and Forced Oscillations. Resonance. Periodic Motion
Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations Introductory Terminology Simple Harmonic Motion: Kinematics Energy Examples of Simple Harmonic Oscillators Damped and Forced Oscillations. Resonance. Periodic Motion
Terramechanics MARYLAND. Overview of wheel-soil interactions Sources of rolling resistance on soil Rover propulsion analysis U N I V E R S I T Y O F
 Overview of wheel-soil interactions Sources of rolling resistance on soil Rover propulsion analysis 2007 David L. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu Soil Mechanics Wheel rolling over
Overview of wheel-soil interactions Sources of rolling resistance on soil Rover propulsion analysis 2007 David L. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu Soil Mechanics Wheel rolling over
Physics Mechanics. Lecture 32 Oscillations II
 Physics 170 - Mechanics Lecture 32 Oscillations II Gravitational Potential Energy A plot of the gravitational potential energy U g looks like this: Energy Conservation Total mechanical energy of an object
Physics 170 - Mechanics Lecture 32 Oscillations II Gravitational Potential Energy A plot of the gravitational potential energy U g looks like this: Energy Conservation Total mechanical energy of an object
1.053J/2.003J Dynamics and Control I Fall Final Exam 18 th December, 2007
 1.053J/2.003J Dynamics and Control I Fall 2007 Final Exam 18 th December, 2007 Important Notes: 1. You are allowed to use three letter-size sheets (two-sides each) of notes. 2. There are five (5) problems
1.053J/2.003J Dynamics and Control I Fall 2007 Final Exam 18 th December, 2007 Important Notes: 1. You are allowed to use three letter-size sheets (two-sides each) of notes. 2. There are five (5) problems
This equation of motion may be solved either by differential equation method or by graphical method as discussed below:
 2.15. Frequency of Under Damped Forced Vibrations Consider a system consisting of spring, mass and damper as shown in Fig. 22. Let the system is acted upon by an external periodic (i.e. simple harmonic)
2.15. Frequency of Under Damped Forced Vibrations Consider a system consisting of spring, mass and damper as shown in Fig. 22. Let the system is acted upon by an external periodic (i.e. simple harmonic)
Chapter 14 Oscillations
 Chapter 14 Oscillations If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The mass and spring system is a
Chapter 14 Oscillations If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic. The mass and spring system is a
Contents. I Introduction 1. Preface. xiii
 Contents Preface xiii I Introduction 1 1 Continuous matter 3 1.1 Molecules................................ 4 1.2 The continuum approximation.................... 6 1.3 Newtonian mechanics.........................
Contents Preface xiii I Introduction 1 1 Continuous matter 3 1.1 Molecules................................ 4 1.2 The continuum approximation.................... 6 1.3 Newtonian mechanics.........................
CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 27: Ch.18, Sec.1 5
 1 / 42 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 27: Ch.18, Sec.1 5 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Tuesday, November 27, 2012 2 / 42 KINETIC
1 / 42 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 27: Ch.18, Sec.1 5 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Tuesday, November 27, 2012 2 / 42 KINETIC
Mechanics II. Which of the following relations among the forces W, k, N, and F must be true?
 Mechanics II 1. By applying a force F on a block, a person pulls a block along a rough surface at constant velocity v (see Figure below; directions, but not necessarily magnitudes, are indicated). Which
Mechanics II 1. By applying a force F on a block, a person pulls a block along a rough surface at constant velocity v (see Figure below; directions, but not necessarily magnitudes, are indicated). Which
PY205N Spring The vectors a, b, and c. are related by c = a b. The diagram below that best illustrates this relationship is (a) I
 PY205N Spring 2013 Final exam, practice version MODIFIED This practice exam is to help students prepare for the final exam to be given at the end of the semester. Please note that while problems on this
PY205N Spring 2013 Final exam, practice version MODIFIED This practice exam is to help students prepare for the final exam to be given at the end of the semester. Please note that while problems on this
PLANAR KINETICS OF A RIGID BODY: WORK AND ENERGY Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Define the various ways a force and couple do work.
 PLANAR KINETICS OF A RIGID BODY: WORK AND ENERGY Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Define the various ways a force and couple do work. In-Class Activities: 2. Apply the principle of work
PLANAR KINETICS OF A RIGID BODY: WORK AND ENERGY Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Define the various ways a force and couple do work. In-Class Activities: 2. Apply the principle of work
Final Exam Solution Dynamics :45 12:15. Problem 1 Bateau
 Final Exam Solution Dynamics 2 191157140 31-01-2013 8:45 12:15 Problem 1 Bateau Bateau is a trapeze act by Cirque du Soleil in which artists perform aerial maneuvers on a boat shaped structure. The boat
Final Exam Solution Dynamics 2 191157140 31-01-2013 8:45 12:15 Problem 1 Bateau Bateau is a trapeze act by Cirque du Soleil in which artists perform aerial maneuvers on a boat shaped structure. The boat
18.12 FORCED-DAMPED VIBRATIONS
 8. ORCED-DAMPED VIBRATIONS Vibrations A mass m is attached to a helical spring and is suspended from a fixed support as before. Damping is also provided in the system ith a dashpot (ig. 8.). Before the
8. ORCED-DAMPED VIBRATIONS Vibrations A mass m is attached to a helical spring and is suspended from a fixed support as before. Damping is also provided in the system ith a dashpot (ig. 8.). Before the
Midterm 3 Review (Ch 9-14)
 Midterm 3 Review (Ch 9-14) PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun Copyright 2008 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson
Midterm 3 Review (Ch 9-14) PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun Copyright 2008 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson
CE 6701 Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering Dr. P. Venkateswara Rao
 CE 6701 Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering Dr. P. Venkateswara Rao Associate Professor Dept. of Civil Engineering SVCE, Sriperumbudur Difference between static loading and dynamic loading Degree
CE 6701 Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering Dr. P. Venkateswara Rao Associate Professor Dept. of Civil Engineering SVCE, Sriperumbudur Difference between static loading and dynamic loading Degree
Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition, 2017
 A Correlation of Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition, 2017 To the AP Physics C: Mechanics Course Descriptions AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which was not
A Correlation of Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition, 2017 To the AP Physics C: Mechanics Course Descriptions AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which was not
Energy Considerations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 4 French, Chapter 3 Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Energy Considerations The force in Hooke s law is = Potential energy can be used to describe conservative
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 4 French, Chapter 3 Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Energy Considerations The force in Hooke s law is = Potential energy can be used to describe conservative
of the four-bar linkage shown in Figure 1 is T 12
 ME 5 - Machine Design I Fall Semester 0 Name of Student Lab Section Number FINL EM. OPEN BOOK ND CLOSED NOTES Wednesday, December th, 0 Use the blank paper provided for your solutions write on one side
ME 5 - Machine Design I Fall Semester 0 Name of Student Lab Section Number FINL EM. OPEN BOOK ND CLOSED NOTES Wednesday, December th, 0 Use the blank paper provided for your solutions write on one side
E 490 FE Exam Prep. Engineering Mechanics
 E 490 FE Exam Prep Engineering Mechanics 2008 E 490 Course Topics Statics Newton s Laws of Motion Resultant Force Systems Moment of Forces and Couples Equilibrium Pulley Systems Trusses Centroid of an
E 490 FE Exam Prep Engineering Mechanics 2008 E 490 Course Topics Statics Newton s Laws of Motion Resultant Force Systems Moment of Forces and Couples Equilibrium Pulley Systems Trusses Centroid of an
VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF E-GLASS FIBRE RESIN MONO LEAF SPRING USED IN LMV
 VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF E-GLASS FIBRE RESIN MONO LEAF SPRING USED IN LMV Mohansing R. Pardeshi 1, Dr. (Prof.) P. K. Sharma 2, Prof. Amit Singh 1 M.tech Research Scholar, 2 Guide & Head, 3 Co-guide & Assistant
VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF E-GLASS FIBRE RESIN MONO LEAF SPRING USED IN LMV Mohansing R. Pardeshi 1, Dr. (Prof.) P. K. Sharma 2, Prof. Amit Singh 1 M.tech Research Scholar, 2 Guide & Head, 3 Co-guide & Assistant
Lecture 15 Strain and stress in beams
 Spring, 2019 ME 323 Mechanics of Materials Lecture 15 Strain and stress in beams Reading assignment: 6.1 6.2 News: Instructor: Prof. Marcial Gonzalez Last modified: 1/6/19 9:42:38 PM Beam theory (@ ME
Spring, 2019 ME 323 Mechanics of Materials Lecture 15 Strain and stress in beams Reading assignment: 6.1 6.2 News: Instructor: Prof. Marcial Gonzalez Last modified: 1/6/19 9:42:38 PM Beam theory (@ ME
Chapter 14 Oscillations
 Chapter 14 Oscillations Chapter Goal: To understand systems that oscillate with simple harmonic motion. Slide 14-2 Chapter 14 Preview Slide 14-3 Chapter 14 Preview Slide 14-4 Chapter 14 Preview Slide 14-5
Chapter 14 Oscillations Chapter Goal: To understand systems that oscillate with simple harmonic motion. Slide 14-2 Chapter 14 Preview Slide 14-3 Chapter 14 Preview Slide 14-4 Chapter 14 Preview Slide 14-5
PHYSICS. Course Structure. Unit Topics Marks. Physical World and Measurement. 1 Physical World. 2 Units and Measurements.
 PHYSICS Course Structure Unit Topics Marks I Physical World and Measurement 1 Physical World 2 Units and Measurements II Kinematics 3 Motion in a Straight Line 23 4 Motion in a Plane III Laws of Motion
PHYSICS Course Structure Unit Topics Marks I Physical World and Measurement 1 Physical World 2 Units and Measurements II Kinematics 3 Motion in a Straight Line 23 4 Motion in a Plane III Laws of Motion
Fundamentals Physics. Chapter 15 Oscillations
 Fundamentals Physics Tenth Edition Halliday Chapter 15 Oscillations 15-1 Simple Harmonic Motion (1 of 20) Learning Objectives 15.01 Distinguish simple harmonic motion from other types of periodic motion.
Fundamentals Physics Tenth Edition Halliday Chapter 15 Oscillations 15-1 Simple Harmonic Motion (1 of 20) Learning Objectives 15.01 Distinguish simple harmonic motion from other types of periodic motion.
Section 3.7: Mechanical and Electrical Vibrations
 Section 3.7: Mechanical and Electrical Vibrations Second order linear equations with constant coefficients serve as mathematical models for mechanical and electrical oscillations. For example, the motion
Section 3.7: Mechanical and Electrical Vibrations Second order linear equations with constant coefficients serve as mathematical models for mechanical and electrical oscillations. For example, the motion
Mechanical System Elements
 Mechanical System Elements Three basic mechanical elements: Spring (elastic) element Damper (frictional) element Mass (inertia) element Translational and rotational versions These are passive (non-energy
Mechanical System Elements Three basic mechanical elements: Spring (elastic) element Damper (frictional) element Mass (inertia) element Translational and rotational versions These are passive (non-energy
WORK SHEET FOR MEP311
 EXPERIMENT II-1A STUDY OF PRESSURE DISTRIBUTIONS IN LUBRICATING OIL FILMS USING MICHELL TILTING PAD APPARATUS OBJECTIVE To study generation of pressure profile along and across the thick fluid film (converging,
EXPERIMENT II-1A STUDY OF PRESSURE DISTRIBUTIONS IN LUBRICATING OIL FILMS USING MICHELL TILTING PAD APPARATUS OBJECTIVE To study generation of pressure profile along and across the thick fluid film (converging,
Agricultural Science 1B Principles & Processes in Agriculture. Mike Wheatland
 Agricultural Science 1B Principles & Processes in Agriculture Mike Wheatland (m.wheatland@physics.usyd.edu.au) Outline - Lectures weeks 9-12 Chapter 6: Balance in nature - description of energy balance
Agricultural Science 1B Principles & Processes in Agriculture Mike Wheatland (m.wheatland@physics.usyd.edu.au) Outline - Lectures weeks 9-12 Chapter 6: Balance in nature - description of energy balance
The basic principle to be used in mechanical systems to derive a mathematical model is Newton s law,
 Chapter. DYNAMIC MODELING Understanding the nature of the process to be controlled is a central issue for a control engineer. Thus the engineer must construct a model of the process with whatever information
Chapter. DYNAMIC MODELING Understanding the nature of the process to be controlled is a central issue for a control engineer. Thus the engineer must construct a model of the process with whatever information
Oscillations and Waves
 Oscillations and Waves Oscillation: Wave: Examples of oscillations: 1. mass on spring (eg. bungee jumping) 2. pendulum (eg. swing) 3. object bobbing in water (eg. buoy, boat) 4. vibrating cantilever (eg.
Oscillations and Waves Oscillation: Wave: Examples of oscillations: 1. mass on spring (eg. bungee jumping) 2. pendulum (eg. swing) 3. object bobbing in water (eg. buoy, boat) 4. vibrating cantilever (eg.
EQUATIONS OF MOTION: GENERAL PLANE MOTION (Section 17.5) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to analyze the planar kinetics of a rigid body
 EQUATIONS OF MOTION: GENERAL PLANE MOTION (Section 17.5) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to analyze the planar kinetics of a rigid body undergoing general plane motion. APPLICATIONS As the soil
EQUATIONS OF MOTION: GENERAL PLANE MOTION (Section 17.5) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to analyze the planar kinetics of a rigid body undergoing general plane motion. APPLICATIONS As the soil
11/17/10. Chapter 14. Oscillations. Chapter 14. Oscillations Topics: Simple Harmonic Motion. Simple Harmonic Motion
 11/17/10 Chapter 14. Oscillations This striking computergenerated image demonstrates an important type of motion: oscillatory motion. Examples of oscillatory motion include a car bouncing up and down,
11/17/10 Chapter 14. Oscillations This striking computergenerated image demonstrates an important type of motion: oscillatory motion. Examples of oscillatory motion include a car bouncing up and down,
Lectures Chapter 10 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 7 th edition)
 PH 201-4A spring 2007 Simple Harmonic Motion Lectures 24-25 Chapter 10 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 7 th edition) 1 The Ideal Spring Springs are objects that exhibit elastic behavior. It will return back
PH 201-4A spring 2007 Simple Harmonic Motion Lectures 24-25 Chapter 10 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 7 th edition) 1 The Ideal Spring Springs are objects that exhibit elastic behavior. It will return back
Advanced Vibrations. Elements of Analytical Dynamics. By: H. Ahmadian Lecture One
 Advanced Vibrations Lecture One Elements of Analytical Dynamics By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Elements of Analytical Dynamics Newton's laws were formulated for a single particle Can be extended to
Advanced Vibrations Lecture One Elements of Analytical Dynamics By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Elements of Analytical Dynamics Newton's laws were formulated for a single particle Can be extended to
Lecture 6 Physics 106 Spring 2006
 Lecture 6 Physics 106 Spring 2006 Angular Momentum Rolling Angular Momentum: Definition: Angular Momentum for rotation System of particles: Torque: l = r m v sinφ l = I ω [kg m 2 /s] http://web.njit.edu/~sirenko/
Lecture 6 Physics 106 Spring 2006 Angular Momentum Rolling Angular Momentum: Definition: Angular Momentum for rotation System of particles: Torque: l = r m v sinφ l = I ω [kg m 2 /s] http://web.njit.edu/~sirenko/
Road Vehicle Dynamics
 Road Vehicle Dynamics Table of Contents: Foreword Preface Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 General 1.2 Vehicle System Classification 1.3 Dynamic System 1.4 Classification of Dynamic System Models 1.5 Constraints,
Road Vehicle Dynamics Table of Contents: Foreword Preface Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 General 1.2 Vehicle System Classification 1.3 Dynamic System 1.4 Classification of Dynamic System Models 1.5 Constraints,
WEEK 1 Dynamics of Machinery
 WEEK 1 Dynamics of Machinery References Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, J.J. Uicker, G.R.Pennock ve J.E. Shigley, 2003 Makine Dinamiği, Prof. Dr. Eres SÖYLEMEZ, 2013 Uygulamalı Makine Dinamiği, Jeremy
WEEK 1 Dynamics of Machinery References Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, J.J. Uicker, G.R.Pennock ve J.E. Shigley, 2003 Makine Dinamiği, Prof. Dr. Eres SÖYLEMEZ, 2013 Uygulamalı Makine Dinamiği, Jeremy
1 MR SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 2013
 SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
Class XI Physics Syllabus One Paper Three Hours Max Marks: 70
 Class XI Physics Syllabus 2013 One Paper Three Hours Max Marks: 70 Class XI Weightage Unit I Physical World & Measurement 03 Unit II Kinematics 10 Unit III Laws of Motion 10 Unit IV Work, Energy & Power
Class XI Physics Syllabus 2013 One Paper Three Hours Max Marks: 70 Class XI Weightage Unit I Physical World & Measurement 03 Unit II Kinematics 10 Unit III Laws of Motion 10 Unit IV Work, Energy & Power
Name Date Period PROBLEM SET: ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS
 Accelerated Physics Rotational Dynamics Problem Set Page 1 of 5 Name Date Period PROBLEM SET: ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS Directions: Show all work on a separate piece of paper. Box your final answer. Don t forget
Accelerated Physics Rotational Dynamics Problem Set Page 1 of 5 Name Date Period PROBLEM SET: ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS Directions: Show all work on a separate piece of paper. Box your final answer. Don t forget
In the presence of viscous damping, a more generalized form of the Lagrange s equation of motion can be written as
 2 MODELING Once the control target is identified, which includes the state variable to be controlled (ex. speed, position, temperature, flow rate, etc), and once the system drives are identified (ex. force,
2 MODELING Once the control target is identified, which includes the state variable to be controlled (ex. speed, position, temperature, flow rate, etc), and once the system drives are identified (ex. force,
SOLUTION 8 7. To hold lever: a+ M O = 0; F B (0.15) - 5 = 0; F B = N. Require = N N B = N 0.3. Lever,
 8 3. If the coefficient of static friction at is m s = 0.4 and the collar at is smooth so it only exerts a horizontal force on the pipe, determine the minimum distance x so that the bracket can support
8 3. If the coefficient of static friction at is m s = 0.4 and the collar at is smooth so it only exerts a horizontal force on the pipe, determine the minimum distance x so that the bracket can support
STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS BASICS:
 BASICS: STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS Real-life structures are subjected to loads which vary with time Except self weight of the structure, all other loads vary with time In many cases, this variation of the load
BASICS: STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS Real-life structures are subjected to loads which vary with time Except self weight of the structure, all other loads vary with time In many cases, this variation of the load
III. Angular Momentum Conservation (Chap. 10) Rotation. We repeat Chap. 2-8 with rotatiing objects. Eqs. of motion. Energy.
 Chap. 10: Rotational Motion I. Rotational Kinematics II. Rotational Dynamics - Newton s Law for Rotation III. Angular Momentum Conservation (Chap. 10) 1 Toward Exam 3 Eqs. of motion o To study angular
Chap. 10: Rotational Motion I. Rotational Kinematics II. Rotational Dynamics - Newton s Law for Rotation III. Angular Momentum Conservation (Chap. 10) 1 Toward Exam 3 Eqs. of motion o To study angular
Back Matter Index The McGraw Hill Companies, 2004
 INDEX A Absolute viscosity, 294 Active zone, 468 Adjoint, 452 Admissible functions, 132 Air, 294 ALGOR, 12 Amplitude, 389, 391 Amplitude ratio, 396 ANSYS, 12 Applications fluid mechanics, 293 326. See
INDEX A Absolute viscosity, 294 Active zone, 468 Adjoint, 452 Admissible functions, 132 Air, 294 ALGOR, 12 Amplitude, 389, 391 Amplitude ratio, 396 ANSYS, 12 Applications fluid mechanics, 293 326. See
DIVIDED SYLLABUS ( ) - CLASS XI PHYSICS (CODE 042) COURSE STRUCTURE APRIL
 DIVIDED SYLLABUS (2015-16 ) - CLASS XI PHYSICS (CODE 042) COURSE STRUCTURE APRIL Unit I: Physical World and Measurement Physics Need for measurement: Units of measurement; systems of units; SI units, fundamental
DIVIDED SYLLABUS (2015-16 ) - CLASS XI PHYSICS (CODE 042) COURSE STRUCTURE APRIL Unit I: Physical World and Measurement Physics Need for measurement: Units of measurement; systems of units; SI units, fundamental
Kinematics, Dynamics, and Vibrations FE Review Session. Dr. David Herrin March 27, 2012
 Kinematics, Dynamics, and Vibrations FE Review Session Dr. David Herrin March 7, 0 Example A 0 g ball is released vertically from a height of 0 m. The ball strikes a horizontal surface and bounces back.
Kinematics, Dynamics, and Vibrations FE Review Session Dr. David Herrin March 7, 0 Example A 0 g ball is released vertically from a height of 0 m. The ball strikes a horizontal surface and bounces back.
