ACE Engineering Academy. Hyderabad Delhi Bhopal Pune Bhubaneswar Bengaluru Lucknow Patna Chennai Vijayawada Visakhapatnam Tirupati
|
|
|
- Moris Greene
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 : : GATE_06_Forenoon Session -5 carry one mark each GENERAL APTITUDE 0. If I were you, I that laptop, It s much too expensive. (A) won t buy (B) shan t buy (C) wouldn t buy (D) would buy Ans: (C) In if clause (type) were is in the past tense so the so main clause should be in the conditional clause (past tense). Therefore C is the best answer 0. He turned a deaf ear to my request. What does the underlined phrasal verb mean? (A) ignored (B) appreciated (C) twisted (D) returned Ans: (A) turned a deaf ear means ignored 03. Choose the most appropriate set of words from the options given below to complete the following sentence. is a will, is a way. (A) Wear, there, their (B) Were, their, there (C) Where, there, there (D) Where, their, their Ans: (C) Where there is a will there is a way. It is a quotation 04. (x% of y) + (y% of x) is equivalent to. (A) % of xy (B) % of (xy/00) (C) xy % of 00 (D) 00 % of xy Ans: (A)
3 (x% of y) + (y% of x) = x y y x xy xy 00 xy 00 = % of xy : 3 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session 05. The sum of the digits of a two digit number is. If the new number formed by reversing the digits is greater than the original number by 54, find the original number. (A) 39 (B) 57 (C) 66 (D) 93 Ans: (A) The new number formed by reversing the digits is greater than the original number is possible in options A and B only. Options A : Sum of two digits in the number = = After reversing the two digits number = 93 The difference between the new number formed and original number = = 54 option A is correct. Option B : original number = 57 After reversing, the number is formed = 75 The difference between these two numbers = = 8 It is not.
4 : 4 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session
5 : 5 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session 06-0 Carry two marks each 06. Two finance companies, P and Q, declared fixed annual rates of interest on the amounts invested with them. The rates of interest offered by these companies may differ from year to year. Yearwise annual rates of interest offered by these companies are shown by the line graph provided below P Q If the amounts invested in the companies, P and Q, in 006 are in the ratio 8:9, then the amounts received after one year as interests from companies P and Q would be in the ratio: (A) :3 (B) 3:4 (C) 6:7 (D) 4:3 Ans: (D) The amounts invested in the companies of, P and Q in 006 = 8 : 9 The rate of interest of company P in 006 = 6% The rate of interest of company Q in 006 = 4% The amounts received after one year by P and Q companies in 006 year P Q 6% of 8 : 4% of : : Today, we consider Ashoka as a great ruler because of the copious evidence he left behind in the form of stone carved edicts. Historians tend to correlate greatness of a king at his time with the availability of evidence today. Which of the following can be logically inferred from the above sentences?
6 : 6 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session Ans: (A) Emperors who do not leave significant sculpted evidence are completely forgotten. (B) Ashoka produced stone carved edicts to ensure that later historians will respect him. (C) Statues of kings are a reminder of their greatness. (D) A king s greatness, as we know him today, is interpreted by historians. (D) Today, historians correlate greatness of a king at his time with the availability of evidence. This statement leads to the best inference i.e. option D 08 Fact : Humans are mammals. Fact : Some humans are engineers. Fact 3: Engineers build houses. If the above statements are facts, which of the following can be logically inferred? I. All mammals build houses. II. Engineers are mammals. III. Some humans are not engineers. (A) II only. (B) III only. (C) I, II and III. (D) I only. Ans: (B) From given facts, the following venn diagram is possible. H = Humans M = Mammals E = Engineers BH = Build houses From above diagram, statement III is true. H M E BH 09. A square pyramid has a base perimeter x, and the slant height is half of the perimeter. What is the lateral surface area of the pyramid? (A) x (B) 0.75 x (C) 0.50 x (D) 0.5 x
7 : 7 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session Ans: (D) Base perimeter of square pyramid = x = p x Slant height l Lateral surface area of pyramid Base perimeter (p) slant height (l) x x 4 p l x = 0.5x x x/4 x/4 x/ 0. Ananth takes 6 hours and Bharath takes 4 hours to read a book. Both started reading copies of the book at the same time. After how many hours is the number of pages to be read by Ananth, twice that to be read by Bharath? Assume Ananth and Bharath read all the pages with constant pace. (A) (B) (C) 3 (D) 4 Ans: (C) Ananth takes 6 hours to read a book Bharath takes 4 hours to read a book L.C.M = The number of pages read by Ananth and Bharath must be (or) multiple of only. If Ananth read number of pages in 6 hrs hr = 6 = pages If Bharath read number of pages in 4 hrs
8 : 8 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session hr = 4 = 3 pages hrs Option A Ananth Bharath Read pages Not read 0 pages Read 3 pages Not read 9 pages 0 : 9 it is not hrs Option B Read 4 pages Ananth Not read 8 pages Read 6 pages Bharath Not read 6 pages 8 : 6 4 : 3 it is not Options C 3 hrs Ananth Bharath Read 6 pages Not read 6 pages Read 9 pages Not read 3 pages : After 3 hours is the number of pages to be read by Ananth, twice that to be read by Bharath.
9 : 9 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session
10 : 0 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session 0 Q. 5 carry one mark each The eigenvalues of the matrix are 0 (A) i and i (B) and (C) 0 and (D) 0 and Ans: (A) + = 0; = + = i = i 0. The number of solutions of the simultaneous algebraic equations y = 3x + 3 and y = 3x+5 is (A) zero (B) (C) (D) infinite Ans: (A) y = 3x+5 & y = 3x+3 are parallel to each other No solution is zero solution x 03. At x = 0, the function is f (x) sin ( < x <, L >0) L (A) continuous and differentiable. (B) not continuous and not differentiable. (C) not continuous but differentiable. (D) continuous but not differentiable. Ans: (D) f x x sin L at x = 0 is having graph -L -L 0 L L It is continuous at x = 0 but not differential at x = 0
11 For the two functions f x, y x 3xy and : : GATE_06_Forenoon Session g x, y 3x y y which one of the following options is correct? (A) f x g x (B) f x g y (C) f g y x (D) f g y x Ans: (C) f g 6xy; 6xy y x f g y x 05. The function Z z is singular at z 4 f (A) z = (B) z = (C) z = i (D) z = i Ans: (D) To get singular points let z +4 = 0 z = 4 z = i 06. A fair coin is tossed N times. The probability that head does not turn up in any of the tosses is (A) N (B) N (C) N (D) N Ans: (C) 07. A normal random variable X has the following probability density function f X x e 8 x 8 (A) 0 (B), x Then (C) f X x dx (D) e
12 : : GATE_06_Forenoon Session Ans: (B) e x x t dx dt dx = dt 0 e t dt t V t = V = e 0 V V dv t dt = dv dt dv V = e 0 V V 08. The elastic modulus of a rigid perfectly plastic solid is (A) 0 (B) (C)00 (D)infinity Ans: (A) Modulus is slope of curve (i.e zero) in elastic region Stress Strain 09. Consider the following statements: (P) Hardness is the resistance of a material to indentation. (Q) Elastic modulus is a measure of ductility. (R) Deflection depends on stiffness. (S) The total area under the stress-strain curve is a measure of resilience. Among the above statements, the correct ones are (A) P and Q only. (B) Q and S only. (C) P and R only. (D) R and S only.
13 : 3 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session Ans: (C) Hardness of a material will be measured by indentation technique. If a material undergo more strain (deflection) in elastic region means stiffness is low. 0. A beam is subjected to an inclined concentrated load as shown in the figure below. Neglect the weight of the beam. The correct Free Body Diagram of the beam is (A) (B) (C) (D) Ans: (B)
14 : 4 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session. Consider a circular cam with a flat face follower as shown in the figure below. The cam is rotated in the plane of the paper about point P lying 5 mm away from its center. The radius of the cam is 0 mm. The distance (in mm) between the highest and the lowest positions of the flat face follower is 5 mm P (A) 5 (B) 0 (C) 40 (D) 45 Ans: (B) For the highest position the distance between the cam center and follower = (r+5) mm For the lowest position it is (r 5) mm So the distance between the two positions = (r+5) (r 5) = 0 mm. A vertical cylindrical tank of m diameter is filled with water up to a height of 5 m from its bottom. Top surface of water is exposed to atmosphere. A hole of 5 mm area forms at the bottom of the tank. Considering the coefficient of discharge of the hole to be unity and the acceleration due to gravity to be 0 m/s, the rate of leakage of water (in litre/min) through the hole from the tank to the atmosphere, under the given conditions, is Ans: (3) V g h 0 5 0m / s Q = AV = = 50 5 m 3 /sec = 0.05 liter/sec = = 3 lit/min
15 : 5 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session
16 : 6 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session 3. The figure below shows an air standard Diesel cycle in p-v diagram. The cut-off ratio is given by: 3 P 4 V (A) v v 3 (B) v v (C) v v 3 (D) v v 3 Ans: (C)
17 : 7 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session 4. The ratio of press force required to punch a square hole of 30 mm side in a mm thick aluminium sheet to that needed to punch a square hole of 60 mm side in a mm thick aluminium sheet is Ans: (0.5) F Ratio of force F max max 4x 4x t t u u x t x t Which one of the following is a natural polymer? (A) Cellulose (B) Nylon (C) Polyester (D) Polyvinyl chloride Ans: (A) cellulose is made by C, H,O atoms can be extracted from trees. 6. In powder metallurgy, sintering of the component (A) increases density and reduces ductility (B) increases porosity and reduces density (C) increases density and reduces porosity (D) increases porosity and reduces brittleness Ans: (B) During sintering the solvent added at mixing stage will evaporate and produce porosity which comes the reduction in density of the component. 7. A single point right handed turning tool is used for straight turning. The feed is 0.5 mm/rev and the uncut chip thickness is found to be 0.5 mm. The inclination angle of the main cutting edge is 0 o. The back rake angle (in degrees) is Ans: (0 0 ) Turning operation, i = inclination angle = 0,
18 : 8 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session f = 0.5 mm/rev, t = 0.5 = f cos C s cos Cs C s = 0 f 0.5 = 90 C s = 90 0 = 90 tan b = sin tan i + cos tan = sin90 tan0 + cos 90 tan = = 0.76 b = tan (0.76) = 0 8. Consider the following statements. (P) Electrolyte is used in Electro-chemical machining. (Q) Electrolyte is used in Electrical discharge machining. (R) Abrasive-slurry is used in Ultrasonic machining. (S) Abrasive-slurry is used in Abrasive jet machining. Among the above statements, the correct ones are (A) P and R only (B) Q and S only (C) Q, R and S only (D) P and Q only Ans: (A) In EDM, dielectric fluid is used. Hence Q is wrong. 9. Consider the following statements. (P) Computer aided process planning (CAPP) takes input from material requirement plan (MRP). (Q) Production flow analysis helps in work cell formation. (R) Group technology takes input from choice of machining or cutting parameters. Among the above statements, the correct one(s) is (are) (A) P only (B) Q and R only (C) P and R only (D) Q only Ans: (B) CAPP will takes inputs from design but not from MRP. Hence P is wrong.
19 : 9 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session 0. The limits of a shaft designated as 00h5 are mm and mm. Similarly, the limits of a shaft designated as 00h8 are mm and mm. If a shaft is designated as 00h6, the fundamental deviation (in m) for the same is (A) (B) zero (C) (D) 4 Ans: (B) Fundamental deviation for shaft h is always zero irrespective of grade of tolerance.. The roughness profile of a surface is depicted below. Profile height centre-line of the profile m m X 5 mm The surface roughness parameter R a (in m) is. Ans: (0) R a h n The facility layout technique that uses relationship (REL) chart is (A) CRAFT. (B) Travel chart. (C) Partial Set Covering. (D) ALDEP.
20 Ans: (D) ALDEP BASED ON REL REQUIREMENTS : 0 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session 3. For a random variable, X, let X be the sample average. The sample size is n. The mean and the standard deviation of X are µ and σ, respectively. The standard deviation of X is (A) n (B) (C ) (D) n n Ans: (D) Standard deviation, s n 4. ST and NT denote the standard time and the normal time, respectively, to complete a job. Allowance = LL ST, where 0 < LL<. Which one of the following relationships is correct? NT NT (A) ST (B) ST=NT(+LL) (C ) ST (D) ST=NT( LL) LL LL Ans: (A) RA = Relaxation allowance = LL ST ST = NT + RA ST = NT + LL ST ST ( LL) = NT NT ST LL 5. The throughput rate of a production system is 0 units per hour. The average flow time is 30 Ans: (C) minutes and the cycle time is 3 minutes. The average inventory (in units) in the system is (A).5 (B) 9 (C) 0 (D).33 Average max.production min.production units
21 : : GATE_06_Forenoon Session Q. 6 Q. 55 carry two marks each The range of values of k for which the function f (x) k 4 x 6x 8x has a local maxima at point x = 0 is (A) k < or k > (B) k or k (C) < k < (D) k Ans: (A) f(x) = 3x 3 +8x +(k 4)x f(x) = 96 x + 36x + (k 4) f(0) = (k 4) < 0 k 4 < 0 k < (or) k > 7. lim 5x e x x 0 is equal to. Ans: (5) 5x 5x e e = Lt 5 5 x0 5x 5x 5x 5x e e = Lt 5 Lt 5 x0 5x x0 5x = 5 5 = 5 8. To solve the equation sinx = x by Newton-Raphson method, the initial guess was chosen to be x =.0. Consider x in radian only. The value of x (in radian) obtained after one iteration will be closest to (A) 8.0 (B).90 (C).099 (D).0
22 : : GATE_06_Forenoon Session Ans: (B) f(x) = sin x x f(x)(sin x x) h f(x) cos x = x = +h = = In linear gas tungsten arc welding of two plates of the same material, the peak temperature T (in K) is given as c q T, where q is the heat input per unit length (in J/m) of weld, is the thermal diffusivity (in m /s) of the plate materials and C is a constant independent of process parameters and material types. Two welding cases are given below. Case I: V = 5 V, I = 00 A, v = 5 mm/s, k = 50 W/mK, = 3000 kg/m 3, C = 900 J/kg-K Case II: V = 5 V, I = 300 A, v = 0 mm/s, k = 50 W/mK, = 8000 kg/m 3, C = 450 J/kg-K Ans: (A) where, V is welding voltage, I is welding current, v is welding speed, and k, and C refer to the thermal conductivity, the density and the specific heat of the plate materials, respectively. Consider that electrical energy is completely converted to thermal energy. All other conditions remain same. The ratio of the peak temperature in Case I to that in Case II is (A) 3 k C (B) (C) (D)
23 : 3 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session VI 5 00 q 60 3 r q T T q q A bar of rectangular cross-sectional area of 50 mm is pulled from both the sides by equal forces of 00 N as shown in the figure below. The shear stress (in MPa) alo ng the plane making an angle 45 0 with the axis, shown as a dashed line in the figure, is. 00 N 00 N 45 o Ans: () 00 / 50 max MPa 3. A m 0 mm 0 mm cantilever beam is subjected to a uniformly distributed load per unit length of 00 N/m as shown in the figure below. The normal stress (in MPa) due to bending at point P is.
24 : 4 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session Point P 00 N/m m Ans: (300) M 00 50N m 3 M MPa(Tension) Z A thin-walled cylindrical pressure vessel of internal diameter m is designed to withstand an Ans: (5) internal pressure of 500 kpa (gauge). If the allowable normal s tress at any point within the cylindrical portion of the vessel is 00 MPa, the minimum thickness of the plate of the vessel (in mm) is. P = 500 kpa = 0.5 MPa h = 00 MPa,D = m h PD t t thickness, t = 5mm 33. An engine, connected with a flywheel, is designed to operate at an average angular speed of 800 rpm. During operation of the engine, the maximum change in kinetic energy in a cycle is found to be 640 J. In order to keep the fluctuation of the angular speed within ±% of its average value, the moment of inertia (in kg-m ) of the flywheel should be.
25 : 5 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session Ans: (44.45) Given mean speed N = 800 rpm N rad / sec 60 Fluctuation of energy E = 640 J Fluctuation of speed = % Moment of inertia I =? We know E = I C s E 640 I = kg-m Cs N A m m square opening in a vertical wall is covered with a metallic plate of the same dimensions as shown in the figure below. Consider the acceleration due to gravity to be 0.0 m/s. The force (in kn) exerted by water on the plate is P atm water m m P atm vertical wall m m square plate vertical wall Ans: (0) F gah 0000 ( ) = 0 kn
26 : 6 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session 35. An ideal gas of mass m is contained in a rigid tank of volume V at a pressure P. During a reversible process its pressure reduces to P. Following statements are made regarding the process. (P) Heat is transferred from the gas. (Q) Work done by the gas is zero. (R) Entropy of the gas remains constant. (S) Entropy of the gas decreases. Among the above statements, the correct ones are (A) P and R only (B) P, Q and R only (C) Q and R only (D) P, Q and S only Ans: (D) At constant volume to decrease pressure, temperature has to be decreased. So heat has to be transferred from the gas. As the change in volume is zero, work done by the gas is zero. Entropy of the gas decrease as system is losing heat. 36. A long slender metallic rod of length L is used as a fin. As shown in the figure below, the left end of the fin is kept at a constant temperature t b. The fin loses heat by convection to the atmosphere which is at a temperature t a (t a < t b ). Four options of temperature profiles are shown. Identify the correct option. convection t b x atmosphere at t a x=l (A) (B) temperature t b t a 0 x L temperature t b t a 0 x L
27 : 7 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session (C) (D) Ans: (B) temperature t b t a 0 x L temperature t b t a 0 x L cosh m(l c x) cosh m L 0 c d 0, so angle of inclination of tangents for curve should increase with x dx 37. In a fully developed turbulent flow through a circular pipe, a head loss of h is observed. The diameter of the pipe is increased by 0% for the same flow rate and a head loss of h is noted. Assume friction factor for both the cases of pipe flow is the same. The ratio of (A) 0.34 (B) 0.6 (C) 0.87 (D).00 Ans: (B) flq For turbulent flow h.d h d 5 h d h.d 5 h h is closest to 38. Two cast iron blocks P and Q, each of 500 mm length, have the same cross-sectional area. Block P has rectangular cross-section of 00 mm 00 mm. Block Q is of square cross-section. Both P and Q were cast under the same conditions with all their surfaces enclosed within the mould. The solidification time of a casting is proportional to the square of the ratio of its volume to its surface area. The ratio of solidification time of the block P to that of the block Q is.
28 : 8 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session Ans: (0.906) L P = L Q = 500, Block P is rectangular = 0000 Block Q is square (Ac) P = (Ac) Q = x x M P mm V A s M Q V A s P Q M M P Q A 300 mm long copper wire of uniform cross-section is pulled in tension so that a maximum tensile stress of 70 MPa is developed within the wire. The entire deformation of the wire remains linearly elastic. The elastic modulus of copper is 00 GPa. The resultant elongation (in mm) is. Ans: (0.8 mm) Given l = 300 mm
29 : 9 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session max = 70 MPa E = 00 GPa max E l =800 3 m = 0.8mm 40. In a single-pass rolling operation, a 00 mm wide metallic strip is rolled from a thickness 0 mm to a thickness 6 mm. The roll radius is 00 mm and it rotates at 00 rpm. The roll-strip contact length is a function of roll radius and, initial and final thickness of the strip. If the average flow stress in plane strain of the strip material in the roll gap is 500 MPa, the roll separating force (in kn) is Ans: (598) b = 00 mm, H 0 = 0mm, H = 6mm, R = 00 mm, N = 00 rpm y = 500 MPa, Roll separating force 3 y L b L 4H L RH by assuming maximum reduction H R H 8 R.S.F = N kN
30 : 30 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session 4. Two solid cylinders of equal diameter have different heights. They are compressed plastically by a pair of rigid dies to create the same percentage reduction in their respective heights. Consider that the die-workpiece interface friction is negligible. The ratio of the final diameter of the shorter cylinder to that of the longer cylinder is Let d = d = d h = height of first cylinder h = height of second cylinder assume h < h let % reduction in height = 0% I st cylinder h h f h h 0 h f = 0. h 0 h f = h 0 0. h 0 = 0.9 h 0 A 0 h 0 = A f h f d 0 h 0 = d f h f d d f 0 h h 0 f d 0 h h 0 =.054 d 0 =.054 (d 0 ) II nd cylinder A 0 h 0 = A f h f d 0 h 0 = d f h f d d f 0 h h 0 f h 0 d0 =.054 (d 0 ) 0.9h 0
31 : 3 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session Ratio d 0 d 0 d 0 d 0 4. Two flat steel sheets, each of.5 mm thickness, are being resistance spot welded using a current of 6000 A and weld time of 0. s. The contact resistance at the interface between the two sheets is 00 and the specific energy to melt steel is J/m 3. A spherical melt pool of diameter 4 mm is formed at the interface due to the current flow. Consider that electrical energy is completely converted to thermal energy. The ratio of the heat used for melting to the total resistive heat generated is Ans: (0.37) t =.5 mm, I = 6000A, = 0.sec R = 00 Heat required, (H.R/m 3 )= 00 9 J/m 3 nugget diameter = d = 4mm (sphere ) Heat generated = I R = = 440 J Heat required = volume heat required/m 3 4 R = J H.R / m Heat required H.I Heat generated
32 : 3 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session 43. A cylindrical bar of 00 mm diameter is orthogonally straight turned with cutting velocity, feed and depth of cut of 0 m/min, 0.5 mm/rev and 4 mm, respectively. The specific cutting energy of the work material is 0 9 J/m 3. Neglect the contribution of feed force towards cutting power. The main or tangential cutting force (in N) is Ans: (000) Orthogonal cutting D = 00 mm, V c = 0 m/min, f = 0.5 mm/rev d = 4mm, Specific cutting energy (Sp.C.E) = 0 9 J/m 3 power Specific cutting energy F V f d V 0 C C C 6 J / m F C = Sp.C.E f d or Work done MRR 44. A 60 mm wide block of low carbon steel is face milled at a cutting speed of 0 m/min, feed of 0. mm/tooth and axial depth of cut of 4 mm. A schematic representation of the face milling process is shown below. The diameter of the cutter is 0 mm and it has cutting edges. The material removal rate (in mm 3 /s) is 0 mm 60 mm feed work piece + cutter schematic representation (top view)
33 : 33 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session Ans: (57.887) b = 60 mm, V = 0 m/min t = 0. mmtooth, d = 4 mm End mill cutter, D = 0 mm z = f m = f t z N = 0. 0 = rpm MRR = bdf m = = mm 3 /min = mm 3 /sec 45. In abrasive water jet machining, the velocity of water at the exit of the orifice, before mixing Ans: (680) with abrasives, is 800 m/s. The mass flow rate of water is 3.4 kg/min. The abrasives are added to the water jet at a rate of 0.6 kg/min with negligible velocity. Assume that at the end of the focusing tube, abrasive particles and water come out with equal velocity. Consider that there is no air in the abrasive water jet. Assuming conservation of momentum, the velocity (in m/s) of the abrasive water jet at the end of the focusing tube is V w = 800 m/s m w = 3.4 kg/min m a = 0.6 kg/min m a v a m w v w m a m w V V = V 5 V = = = 680 m/sec
34 : 34 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session 46. A single axis CNC table is driven by a DC servo motor that is directly coupled to a lead screw of 5 mm pitch. The circular encoder attached to the lead screw generates 000 voltage pulses per revolution of the lead screw. The table moves at a constant speed of 6 m/min. The corresponding frequency (in khz) of the voltage pulses generated by the circular encoder is p = 5 mm 000 pulses rev of motor rev of lead screw Velocity of table = 6 m/min = 6000 mm/min = 00 mm/sec 000 pulses rev of lead screw 5 mm 5 pulse mm 000 BLU = mm Table speed = BLU Rate of Pulses Rate of pulses = = 0000 pulses/sec = 0000 Hz = 0 khz A helical gear with involute tooth profile has been machined with a disc-type form gear milling Ans: (69.8) cutter. The helical gear has 30 teeth and a helix angle of 30 o. The module of the gear milling cutter is. The pitch circle diameter (in mm) of the helical gear is m n = normal module = mm Pitch circle diameter, Z mn 30 d cos cos 30 = 69.8mm
35 : 35 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session 48. A quality control engineer has collected 5 samples, each of size 30. The numbers of defective items in the samples are given in the table below. Sample Number I II III IV V Number of defective items The upper three-sigma (3σ) control limit for the proportion of defective items in any sample is Ans: UCL = sumof defectives p samplesize number of samples Standard error of proportion p p p n Central line = p = 0. Upper control limit = p 3 p = = Lower control limit = p 3 p = = 0
36 : 36 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session 49. A job consists of two work elements, P and Q. Completion time (in minutes) of each work element was measured. A pilot study involved collecting a sample of 40 observations. The results of this pilot study are summarized in the table below. Work element Mean completion time (in minutes) Standard deviation (in minutes) P 0.50 Q 0.05 Ans: (96) For the main study, the minimum sample size for the sample mean time of any work element to be within 0. minutes of its true mean time with 95% confidence (corresponding standard normal value, Z 0.05 =.96 is Standard deviation = s = 0.5 minutes Error of study = h = 0. minutes Z 0.05 =.96 h Zs h = observations 0. Standard deviation = s = 0.05 minutes Error of study = h = 0. minutes Z 0.05 =.96 h Zs h = observations 0. Larger of the two values is 96. Hence study should be continued upto 96 observations.
37 : 37 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session 50. Consider a system with 0 identical components connected in series. The time to failure of each Ans: component is exponentially distributed with a failure rate of 0.0 per 500 days. The reliability of the system after 400 days of operation is R s = e -nt Failure rate, t = 400 days n = 0 in series R S e For a process, the quality loss coefficient is 5. The target value on the dimension to be attained through the process is 50 mm. If the maximum loss permissible (in monetary terms) is INR 80, the maximum allowable deviation (in mm) from the target is (A) 4 (B) 0 (C) 4 (D) 0 Ans: (C) R A 0 0 R = Quality loss coefficient A 0 = Economic consequence 0 = Functional limit or customer tolerance R = 5, A 0 = 80, A R 5
38 : 38 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session 5. Consider a network with nodes,, 3, 4, 5 and 6. The nodes are connected with directed arcs as shown in the table below. The respective costs (in INR) incurred while traversing the directed arcs are also mentioned. Directed arcs Cost (in INR) The second shortest path from node to node 6 (i.e. the path that has the second least total cost and does not use any part of the shortest path) has a total cost (in INR) of (A) 7 (B) 8 (C) 5 (D) 9 Ans: (C) Path Duration = = = = = = = = 5
39 : 39 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session 53. Five jobs need to be processed on a single machine. All the jobs are available for processing at time t = 0. Their respective processing times are given below. Jobs I II III IV V Processing times (in minutes) The average completion time (in minutes) of jobs as per the Shortest Processing Time rule is (A) 9.8 (B) 4. (C) 49.0 (D).0 Ans: (B) SPT RULE Job Time Completion time (c i ) II 4 4 III 7 V I 3 35 IV 4 49 C i = Mean completion Time C n 5 i 4. min 54. Transportation costs (in INR/unit) from factories to respective markets are given in the table below. The market requirements and factory capacities are also given. Using the North-West Corner method, the quantity (in units) to be transported from factory R to market II is Factory Requirements (in units) P Q R S I Market II III 4 30 Factory capacity(in units) (A) 30 (B) 0 (C) 0 (D) 0
40 : 40 : GATE_06_Forenoon Session Ans: (C) Supply = = 00 units Demand = = 00 units FACTORY P Q R S REQ I X X 50 II 4 X X 0 III X X Factory R to market II is 0 units. 55. In a given year, a restaurant earned INR 38,500 in revenues. In that year, total expenses incurred Ans: 8300 were INR 30,000 and the depreciation amount was INR 3,00. At 40% tax rate, the net cash flow (in INR) for that year was Amount (INR) Yearly revenue Total expenses Earning before taxes 8500 Tax 40% 3400 Earnings after taxes (EAT) 500 Depreciation 300 Net Cash flow = (EAT + Depreciation) 8300
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 GATE 2016 General Aptitude GA Set-7 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 If I were you, I that laptop. It s much too expensive. (A) won t buy (C) wouldn t buy (B) shan t buy (D) would buy Q.2 He turned a
GATE 2016 General Aptitude GA Set-7 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 If I were you, I that laptop. It s much too expensive. (A) won t buy (C) wouldn t buy (B) shan t buy (D) would buy Q.2 He turned a
PES Institute of Technology
 PES Institute of Technology Bangalore south campus, Bangalore-5460100 Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty name : Madhu M Date: 29/06/2012 SEM : 3 rd A SEC Subject : MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Subject
PES Institute of Technology Bangalore south campus, Bangalore-5460100 Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty name : Madhu M Date: 29/06/2012 SEM : 3 rd A SEC Subject : MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Subject
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SEMESTER: III SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A
 DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown.
 D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
Tuesday, February 11, Chapter 3. Load and Stress Analysis. Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE
 1 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Chapter Outline Equilibrium & Free-Body Diagrams Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Singularity Functions Stress Cartesian Stress Components Mohr s Circle for
1 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Chapter Outline Equilibrium & Free-Body Diagrams Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Singularity Functions Stress Cartesian Stress Components Mohr s Circle for
UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL 4.1 INTRODUCTION 4.2 DYNAMICALLY EQUIVALENT SYSTEM. Structure. Objectives. 4.1 Introduction
 UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4. Dynamically Equivalent System 4.3 Turning Moment Diagram 4.3.1 Turning Moment Diagram of a Single Cylinder 4-storke IC Engine 4.3. Turning Moment
UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4. Dynamically Equivalent System 4.3 Turning Moment Diagram 4.3.1 Turning Moment Diagram of a Single Cylinder 4-storke IC Engine 4.3. Turning Moment
9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
 9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Deforming force Deforming force is the force which changes the shape or size of a body. Restoring force Restoring force is the internal force developed inside the body
9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Deforming force Deforming force is the force which changes the shape or size of a body. Restoring force Restoring force is the internal force developed inside the body
Members Subjected to Torsional Loads
 Members Subjected to Torsional Loads Torsion of circular shafts Definition of Torsion: Consider a shaft rigidly clamped at one end and twisted at the other end by a torque T = F.d applied in a plane perpendicular
Members Subjected to Torsional Loads Torsion of circular shafts Definition of Torsion: Consider a shaft rigidly clamped at one end and twisted at the other end by a torque T = F.d applied in a plane perpendicular
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 At least one eigenvalue of a singular matrix is (A) positive (B) zero (C) negative (D) imaginary Q. At x = 0, the function f( x) = x has (A) a minimum (C) a point of
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 At least one eigenvalue of a singular matrix is (A) positive (B) zero (C) negative (D) imaginary Q. At x = 0, the function f( x) = x has (A) a minimum (C) a point of
Mechanical Engineering Excerise 1
 Mechanical Engineering Excerise 1 1. Given that the determinant of the matrix 2 6 0 the matrix 4 12 8 is 2 0 4 1 3 0 2 6 4 1 0 2 is 12, the determinant of (A) 96 (B) 24 (C) 24 (D) 96 2. x sin x Lt 1 cosx
Mechanical Engineering Excerise 1 1. Given that the determinant of the matrix 2 6 0 the matrix 4 12 8 is 2 0 4 1 3 0 2 6 4 1 0 2 is 12, the determinant of (A) 96 (B) 24 (C) 24 (D) 96 2. x sin x Lt 1 cosx
Chapter 3. Load and Stress Analysis. Lecture Slides
 Lecture Slides Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2015 by McGraw Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner.
Lecture Slides Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2015 by McGraw Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner.
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each.
 GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
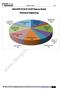
 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
Sub. Code:
 Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. ) The model answer and the answer written by candidate may
Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. ) The model answer and the answer written by candidate may
2012 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
 R10 SET - 1 II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, MM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
R10 SET - 1 II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, MM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM - 613 403 - THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub : Strength of Materials Year / Sem: II / III Sub Code : MEB 310
PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM - 613 403 - THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub : Strength of Materials Year / Sem: II / III Sub Code : MEB 310
Shared on QualifyGate.com
 GTE 014 Brief nalysis (Based on student test experiences in the stream of ME on 16th February, 014 - Second Session) Section wise analysis of the paper 1 Mark Marks Total No of Questions Engineering Mathematics
GTE 014 Brief nalysis (Based on student test experiences in the stream of ME on 16th February, 014 - Second Session) Section wise analysis of the paper 1 Mark Marks Total No of Questions Engineering Mathematics
SRI CHANDRASEKHARENDRA SARASWATHI VISWA MAHAVIDHYALAYA
 SRI CHANDRASEKHARENDRA SARASWATHI VISWA MAHAVIDHYALAYA (Declared as Deemed-to-be University under Section 3 of the UGC Act, 1956, Vide notification No.F.9.9/92-U-3 dated 26 th May 1993 of the Govt. of
SRI CHANDRASEKHARENDRA SARASWATHI VISWA MAHAVIDHYALAYA (Declared as Deemed-to-be University under Section 3 of the UGC Act, 1956, Vide notification No.F.9.9/92-U-3 dated 26 th May 1993 of the Govt. of
ISHIK UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF MECHATRONICS ENGINEERING
 ISHIK UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF MECHATRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK FOR THE MECHANICS OF MATERIALS-I 1. A rod 150 cm long and of diameter 2.0 cm is subjected to an axial pull of 20 kn. If the modulus
ISHIK UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF MECHATRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK FOR THE MECHANICS OF MATERIALS-I 1. A rod 150 cm long and of diameter 2.0 cm is subjected to an axial pull of 20 kn. If the modulus
Sample Question Paper
 Scheme I Sample Question Paper Program Name : Mechanical Engineering Program Group Program Code : AE/ME/PG/PT/FG Semester : Third Course Title : Strength of Materials Marks : 70 Time: 3 Hrs. Instructions:
Scheme I Sample Question Paper Program Name : Mechanical Engineering Program Group Program Code : AE/ME/PG/PT/FG Semester : Third Course Title : Strength of Materials Marks : 70 Time: 3 Hrs. Instructions:
PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [ ] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics
![PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [ ] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [ ] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics](/thumbs/92/109382806.jpg) Page1 PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [2910601] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics 1. Differentiate between Scalar and Vector quantity. Write S.I.
Page1 PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [2910601] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics 1. Differentiate between Scalar and Vector quantity. Write S.I.
Downloaded from Downloaded from / 1
 PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY III SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2002 LEVEL : B. E. (Civil) SUBJECT: BEG256CI, Strength of Material Full Marks: 80 TIME: 03:00 hrs Pass marks: 32 Candidates are required to give their
PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY III SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2002 LEVEL : B. E. (Civil) SUBJECT: BEG256CI, Strength of Material Full Marks: 80 TIME: 03:00 hrs Pass marks: 32 Candidates are required to give their
UNIT-I STRESS, STRAIN. 1. A Member A B C D is subjected to loading as shown in fig determine the total elongation. Take E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2
 UNIT-I STRESS, STRAIN 1. A Member A B C D is subjected to loading as shown in fig determine the total elongation. Take E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2 Young s modulus E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2 Area1=900mm 2 Area2=400mm 2 Area3=625mm
UNIT-I STRESS, STRAIN 1. A Member A B C D is subjected to loading as shown in fig determine the total elongation. Take E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2 Young s modulus E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2 Area1=900mm 2 Area2=400mm 2 Area3=625mm
R13. II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, AE, MTE) PART-A
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, AE, MTE) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, AE, MTE) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK. Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV UNIT I STRESS, STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART A (2 MARKS)
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV UNIT I STRESS, STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART A (2 MARKS)
CE6306 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS TWO MARK QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS ACADEMIC YEAR
 CE6306 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS TWO MARK QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS ACADEMIC YEAR 2014-2015 UNIT - 1 STRESS, STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART- A 1. Define tensile stress and tensile strain. The stress induced
CE6306 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS TWO MARK QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS ACADEMIC YEAR 2014-2015 UNIT - 1 STRESS, STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART- A 1. Define tensile stress and tensile strain. The stress induced
NORMAL STRESS. The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts.
 NORMAL STRESS The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts. σ = force/area = P/A where σ = the normal stress P = the centric
NORMAL STRESS The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts. σ = force/area = P/A where σ = the normal stress P = the centric
Set 1. a. 100 kj/kg b. 110 kj/kg c. 140 kj/kg d. 150 kj/kg
 Set 1 1. Two blocks which are at different states are brought into contact with each other and allowed to reach a final state of thermal equilibrium. The final temperature attained is specified by the
Set 1 1. Two blocks which are at different states are brought into contact with each other and allowed to reach a final state of thermal equilibrium. The final temperature attained is specified by the
Physics 201 Midterm Exam 3
 Name: Date: _ Physics 201 Midterm Exam 3 Information and Instructions Student ID Number: Section Number: TA Name: Please fill in all the information above Please write and bubble your Name and Student
Name: Date: _ Physics 201 Midterm Exam 3 Information and Instructions Student ID Number: Section Number: TA Name: Please fill in all the information above Please write and bubble your Name and Student
CIVL222 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS. Chapter 6. Torsion
 CIVL222 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Chapter 6 Torsion Definition Torque is a moment that tends to twist a member about its longitudinal axis. Slender members subjected to a twisting load are said to be in torsion.
CIVL222 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Chapter 6 Torsion Definition Torque is a moment that tends to twist a member about its longitudinal axis. Slender members subjected to a twisting load are said to be in torsion.
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 General ptitude G Set-8 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The chairman requested the aggrieved shareholders to him. () bare with () bore with (C) bear with (D) bare Q.2 Identify the correct spelling out
General ptitude G Set-8 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The chairman requested the aggrieved shareholders to him. () bare with () bore with (C) bear with (D) bare Q.2 Identify the correct spelling out
PORTMORE COMMUNITY COLLEGE ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY
 PORTMORE COMMUNITY COLLEGE ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 JUNE 2011 COURSE NAME: Mechanical Engineering Science CODE: GROUP: ADET 1 DATE: JUNE 28 TIME: DURATION:
PORTMORE COMMUNITY COLLEGE ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 JUNE 2011 COURSE NAME: Mechanical Engineering Science CODE: GROUP: ADET 1 DATE: JUNE 28 TIME: DURATION:
Mechanics of Materials II. Chapter III. A review of the fundamental formulation of stress, strain, and deflection
 Mechanics of Materials II Chapter III A review of the fundamental formulation of stress, strain, and deflection Outline Introduction Assumtions and limitations Axial loading Torsion of circular shafts
Mechanics of Materials II Chapter III A review of the fundamental formulation of stress, strain, and deflection Outline Introduction Assumtions and limitations Axial loading Torsion of circular shafts
Set 2 (d) 150 C (a) 0.45 (d) can be positive, negative or zero (C) 8.5 J/K (a) 0.1
 Set 2 1. In a new temperature scale say o p, the boiling and freezing points of water at one atmosphere are 100 p and 300 p respectively. Correlate this scale with the Centigrade scale. The reading of
Set 2 1. In a new temperature scale say o p, the boiling and freezing points of water at one atmosphere are 100 p and 300 p respectively. Correlate this scale with the Centigrade scale. The reading of
Physics 201 Midterm Exam 3
 Physics 201 Midterm Exam 3 Information and Instructions Student ID Number: Section Number: TA Name: Please fill in all the information above. Please write and bubble your Name and Student Id number on
Physics 201 Midterm Exam 3 Information and Instructions Student ID Number: Section Number: TA Name: Please fill in all the information above. Please write and bubble your Name and Student Id number on
IIT-JEE 2012 PAPER - 1 PART - I : PHYSICS. Section I : Single Correct Answer Type
 IIT-JEE PAPER - PART - I : PHYSICS Section I : Single Correct Answer Type This section contains multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of which ONLY ONE is
IIT-JEE PAPER - PART - I : PHYSICS Section I : Single Correct Answer Type This section contains multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of which ONLY ONE is
General Aptitude (GA) Set-2. Q.1 The dress her so well that they all immediately her on her appearance.
 General Aptitude (GA) Set-2 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The dress her so well that they all immediately her on her appearance. The words that best fill the blanks in the above sentence are (A) complemented,
General Aptitude (GA) Set-2 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The dress her so well that they all immediately her on her appearance. The words that best fill the blanks in the above sentence are (A) complemented,
STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS
 1 UNIT I STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define: Stress When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The
1 UNIT I STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define: Stress When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The
UNIT 1 STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define stress. When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation.
 UNIT 1 STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define stress. When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The magnitude
UNIT 1 STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define stress. When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The magnitude
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
 Chapter Nine MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS MCQ I 9.1 Modulus of rigidity of ideal liquids is (a) infinity. (b) zero. (c) unity. (d) some finite small non-zero constant value. 9. The maximum load a wire
Chapter Nine MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS MCQ I 9.1 Modulus of rigidity of ideal liquids is (a) infinity. (b) zero. (c) unity. (d) some finite small non-zero constant value. 9. The maximum load a wire
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5
 COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPICS PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPICS PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING EXAMINATIONS. SEMESTER 2 May 2013
 ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 May 2013 COURSE NAME: CODE: Mechanical Engineering Science [8 CHARACTER COURSE CODE] GROUP: AD-ENG 1 DATE: TIME: DURATION: "[EXAM DATE]" "[TIME OF
ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 2 May 2013 COURSE NAME: CODE: Mechanical Engineering Science [8 CHARACTER COURSE CODE] GROUP: AD-ENG 1 DATE: TIME: DURATION: "[EXAM DATE]" "[TIME OF
Practice Test 3. Name: Date: ID: A. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Date: _ Practice Test 3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A wheel rotates about a fixed axis with an initial angular velocity of 20
Name: Date: _ Practice Test 3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A wheel rotates about a fixed axis with an initial angular velocity of 20
Grade XI. Physics Exam Preparation Booklet. Chapter-wise Important Questions. #GrowWithGreen
 Grade XI Physics Exam Preparation Booklet Chapter-wise Important Questions #GrowWithGreen Units and Measurements Q1. After reading the physics book, Anamika recalled and noted down the expression for the
Grade XI Physics Exam Preparation Booklet Chapter-wise Important Questions #GrowWithGreen Units and Measurements Q1. After reading the physics book, Anamika recalled and noted down the expression for the
: APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE
 COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
(48) CHAPTER 3: TORSION
 (48) CHAPTER 3: TORSION Introduction: In this chapter structural members and machine parts that are in torsion will be considered. More specifically, you will analyze the stresses and strains in members
(48) CHAPTER 3: TORSION Introduction: In this chapter structural members and machine parts that are in torsion will be considered. More specifically, you will analyze the stresses and strains in members
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
STRESS, STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS
 VELAMMAL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, MADURAI 625009 DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING CE8301 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS I -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
VELAMMAL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, MADURAI 625009 DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING CE8301 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS I -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Name :. Roll No. :... Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B.TECH (CE-NEW)/SEM-3/CE-301/ SOLID MECHANICS
 Name :. Roll No. :..... Invigilator s Signature :.. 2011 SOLID MECHANICS Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates are required to give their answers
Name :. Roll No. :..... Invigilator s Signature :.. 2011 SOLID MECHANICS Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates are required to give their answers
18.Define the term modulus of resilience. May/June Define Principal Stress. 20. Define Hydrostatic Pressure.
 CE6306 STREGNTH OF MATERIALS Question Bank Unit-I STRESS, STRAIN, DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART-A 1. Define Poison s Ratio May/June 2009 2. What is thermal stress? May/June 2009 3. Estimate the load carried
CE6306 STREGNTH OF MATERIALS Question Bank Unit-I STRESS, STRAIN, DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART-A 1. Define Poison s Ratio May/June 2009 2. What is thermal stress? May/June 2009 3. Estimate the load carried
COURSE TITLE : THEORY OF STRUCTURES -I COURSE CODE : 3013 COURSE CATEGORY : B PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/SEMESTER: 90 CREDITS : 6
 COURSE TITLE : THEORY OF STRUCTURES -I COURSE CODE : 0 COURSE CATEGORY : B PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/SEMESTER: 90 CREDITS : 6 TIME SCHEDULE Module Topics Period Moment of forces Support reactions Centre
COURSE TITLE : THEORY OF STRUCTURES -I COURSE CODE : 0 COURSE CATEGORY : B PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/SEMESTER: 90 CREDITS : 6 TIME SCHEDULE Module Topics Period Moment of forces Support reactions Centre
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA SCIENCE FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 1 - STATIC AND DYNAMIC FORCES TUTORIAL 3 STRESS AND STRAIN
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA SCIENCE FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 1 - STATIC AND DYNAMIC FORCES TUTORIAL 3 STRESS AND STRAIN 1 Static and dynamic forces Forces: definitions of: matter, mass, weight,
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA SCIENCE FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 1 - STATIC AND DYNAMIC FORCES TUTORIAL 3 STRESS AND STRAIN 1 Static and dynamic forces Forces: definitions of: matter, mass, weight,
NAME: Given Formulae: Law of Cosines: Law of Sines:
 NME: Given Formulae: Law of Cosines: EXM 3 PST PROBLEMS (LESSONS 21 TO 28) 100 points Thursday, November 16, 2017, 7pm to 9:30, Room 200 You are allowed to use a calculator and drawing equipment, only.
NME: Given Formulae: Law of Cosines: EXM 3 PST PROBLEMS (LESSONS 21 TO 28) 100 points Thursday, November 16, 2017, 7pm to 9:30, Room 200 You are allowed to use a calculator and drawing equipment, only.
2014 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 R10 SET - 1 II. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, March 2014 MEHNIS OF MTERILS (ivil Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 nswer any FIVE Questions ll Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
R10 SET - 1 II. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, March 2014 MEHNIS OF MTERILS (ivil Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 nswer any FIVE Questions ll Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
GATE SOLUTIONS E N G I N E E R I N G
 GATE SOLUTIONS C I V I L E N G I N E E R I N G From (1987-018) Office : F-16, (Lower Basement), Katwaria Sarai, New Delhi-110016 Phone : 011-65064 Mobile : 81309090, 9711853908 E-mail: info@iesmasterpublications.com,
GATE SOLUTIONS C I V I L E N G I N E E R I N G From (1987-018) Office : F-16, (Lower Basement), Katwaria Sarai, New Delhi-110016 Phone : 011-65064 Mobile : 81309090, 9711853908 E-mail: info@iesmasterpublications.com,
LANMARK UNIVERSITY OMU-ARAN, KWARA STATE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MECHANICS OF MACHINE (MCE 322). LECTURER: ENGR.
 LANMARK UNIVERSITY OMU-ARAN, KWARA STATE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MECHANICS OF MACHINE (MCE 322). LECTURER: ENGR. IBIKUNLE ROTIMI ADEDAYO SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION. Introduction Consider
LANMARK UNIVERSITY OMU-ARAN, KWARA STATE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MECHANICS OF MACHINE (MCE 322). LECTURER: ENGR. IBIKUNLE ROTIMI ADEDAYO SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION. Introduction Consider
Engineering Science OUTCOME 1 - TUTORIAL 4 COLUMNS
 Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: Credit value: 15 Engineering Science L/601/10 OUTCOME 1 - TUTORIAL COLUMNS 1. Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements of static engineering systems
Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: Credit value: 15 Engineering Science L/601/10 OUTCOME 1 - TUTORIAL COLUMNS 1. Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements of static engineering systems
MAAE 2202 A. Come to the PASS workshop with your mock exam complete. During the workshop you can work with other students to review your work.
 It is most beneficial to you to write this mock final exam UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the exam in 3 hours. Work on your own. Keep your textbook closed. Attempt every question. After the
It is most beneficial to you to write this mock final exam UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the exam in 3 hours. Work on your own. Keep your textbook closed. Attempt every question. After the
[7] Torsion. [7.1] Torsion. [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion. [7] Torsion Page 1 of 21
![[7] Torsion. [7.1] Torsion. [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion. [7] Torsion Page 1 of 21 [7] Torsion. [7.1] Torsion. [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion. [7] Torsion Page 1 of 21](/thumbs/88/115835122.jpg) [7] Torsion Page 1 of 21 [7] Torsion [7.1] Torsion [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion [7] Torsion Page 2 of 21 [7.1] Torsion SHEAR STRAIN DUE TO TORSION 1) A shaft with a circular cross section is
[7] Torsion Page 1 of 21 [7] Torsion [7.1] Torsion [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion [7] Torsion Page 2 of 21 [7.1] Torsion SHEAR STRAIN DUE TO TORSION 1) A shaft with a circular cross section is
3 Hours/100 Marks Seat No.
 *17304* 17304 14115 3 Hours/100 Marks Seat No. Instructions : (1) All questions are compulsory. (2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (3) Figures to the right indicate full
*17304* 17304 14115 3 Hours/100 Marks Seat No. Instructions : (1) All questions are compulsory. (2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (3) Figures to the right indicate full
1. A pure shear deformation is shown. The volume is unchanged. What is the strain tensor.
 Elasticity Homework Problems 2014 Section 1. The Strain Tensor. 1. A pure shear deformation is shown. The volume is unchanged. What is the strain tensor. 2. Given a steel bar compressed with a deformation
Elasticity Homework Problems 2014 Section 1. The Strain Tensor. 1. A pure shear deformation is shown. The volume is unchanged. What is the strain tensor. 2. Given a steel bar compressed with a deformation
General Aptitude (GA) Set-1. The words that best fill the blanks in the above sentence are.
 GATE 2018 General Aptitude (GA) Set-1 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 Going by the that many hands make light work, the school involved all the students in the task. The words that best fill the blanks
GATE 2018 General Aptitude (GA) Set-1 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 Going by the that many hands make light work, the school involved all the students in the task. The words that best fill the blanks
PI : PRODUCTION AND INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING
 013 Question Booklet Code PI : PRODUCTION AND INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING A Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Read the following instructions carefully. 1. Do not open the seal of the Question Booklet
013 Question Booklet Code PI : PRODUCTION AND INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING A Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Read the following instructions carefully. 1. Do not open the seal of the Question Booklet
SESSION - 1. Auhippo.com
 SESSION - 1 013 Question Booklet Code PI : PRODUCTION AND INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING A Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Read the following instructions carefully. 1. Do not open the seal of the Question
SESSION - 1 013 Question Booklet Code PI : PRODUCTION AND INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING A Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Read the following instructions carefully. 1. Do not open the seal of the Question
SN QUESTION YEAR MARK 1. State and prove the relationship between shearing stress and rate of change of bending moment at a section in a loaded beam.
 ALPHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (21000) ASSIGNMENT 1 SIMPLE STRESSES AND STRAINS SN QUESTION YEAR MARK 1 State and prove the relationship
ALPHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (21000) ASSIGNMENT 1 SIMPLE STRESSES AND STRAINS SN QUESTION YEAR MARK 1 State and prove the relationship
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -00 04 CIVIL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Course Name : STRENGTH OF MATERIALS II Course Code : A404 Class : II B. Tech II Semester Section
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -00 04 CIVIL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Course Name : STRENGTH OF MATERIALS II Course Code : A404 Class : II B. Tech II Semester Section
TOPIC D: ROTATION EXAMPLES SPRING 2018
 TOPIC D: ROTATION EXAMPLES SPRING 018 Q1. A car accelerates uniformly from rest to 80 km hr 1 in 6 s. The wheels have a radius of 30 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the wheels? Q. The University
TOPIC D: ROTATION EXAMPLES SPRING 018 Q1. A car accelerates uniformly from rest to 80 km hr 1 in 6 s. The wheels have a radius of 30 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the wheels? Q. The University
Mechanics of Materials Primer
 Mechanics of Materials rimer Notation: A = area (net = with holes, bearing = in contact, etc...) b = total width of material at a horizontal section d = diameter of a hole D = symbol for diameter E = modulus
Mechanics of Materials rimer Notation: A = area (net = with holes, bearing = in contact, etc...) b = total width of material at a horizontal section d = diameter of a hole D = symbol for diameter E = modulus
2. Polar moment of inertia As stated above, the polar second moment of area, J is defined as. Sample copy
 GATE PATHSHALA - 91. Polar moment of inertia As stated above, the polar second moment of area, is defined as z π r dr 0 R r π R π D For a solid shaft π (6) QP 0 π d Solid shaft π d Hollow shaft, " ( do
GATE PATHSHALA - 91. Polar moment of inertia As stated above, the polar second moment of area, is defined as z π r dr 0 R r π R π D For a solid shaft π (6) QP 0 π d Solid shaft π d Hollow shaft, " ( do
Topic wise Tests. Complex Variables, Numerical Methods and Probability and Statistics.
 ME-01 ME-02 ME-03 ME-04 GEM-1 GEM-2 GMC 1 Mechanics) GHT 1 Topic wise Tests Each test carries 25 marks and 45 minutes duration Test consists of 5 one mark questions and 10 two marks questions Tests will
ME-01 ME-02 ME-03 ME-04 GEM-1 GEM-2 GMC 1 Mechanics) GHT 1 Topic wise Tests Each test carries 25 marks and 45 minutes duration Test consists of 5 one mark questions and 10 two marks questions Tests will
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy
 Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
ENGI Multiple Integration Page 8-01
 ENGI 345 8. Multiple Integration Page 8-01 8. Multiple Integration This chapter provides only a very brief introduction to the major topic of multiple integration. Uses of multiple integration include
ENGI 345 8. Multiple Integration Page 8-01 8. Multiple Integration This chapter provides only a very brief introduction to the major topic of multiple integration. Uses of multiple integration include
CHAPTER 3 THE EFFECTS OF FORCES ON MATERIALS
 CHAPTER THE EFFECTS OF FORCES ON MATERIALS EXERCISE 1, Page 50 1. A rectangular bar having a cross-sectional area of 80 mm has a tensile force of 0 kn applied to it. Determine the stress in the bar. Stress
CHAPTER THE EFFECTS OF FORCES ON MATERIALS EXERCISE 1, Page 50 1. A rectangular bar having a cross-sectional area of 80 mm has a tensile force of 0 kn applied to it. Determine the stress in the bar. Stress
EMA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 3 Torsion
 EMA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 3 Torsion Introduction Stress and strain in components subjected to torque T Circular Cross-section shape Material Shaft design Non-circular
EMA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 3 Torsion Introduction Stress and strain in components subjected to torque T Circular Cross-section shape Material Shaft design Non-circular
BE Semester- I ( ) Question Bank (MECHANICS OF SOLIDS)
 BE Semester- I ( ) Question Bank (MECHANICS OF SOLIDS) All questions carry equal marks(10 marks) Q.1 (a) Write the SI units of following quantities and also mention whether it is scalar or vector: (i)
BE Semester- I ( ) Question Bank (MECHANICS OF SOLIDS) All questions carry equal marks(10 marks) Q.1 (a) Write the SI units of following quantities and also mention whether it is scalar or vector: (i)
Mechanics of Solids. Mechanics Of Solids. Suraj kr. Ray Department of Civil Engineering
 Mechanics Of Solids Suraj kr. Ray (surajjj2445@gmail.com) Department of Civil Engineering 1 Mechanics of Solids is a branch of applied mechanics that deals with the behaviour of solid bodies subjected
Mechanics Of Solids Suraj kr. Ray (surajjj2445@gmail.com) Department of Civil Engineering 1 Mechanics of Solids is a branch of applied mechanics that deals with the behaviour of solid bodies subjected
March 24, Chapter 4. Deflection and Stiffness. Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 4 Deflection and Stiffness 1 2 Chapter Outline Spring Rates Tension, Compression, and Torsion Deflection Due to Bending Beam Deflection Methods Beam Deflections by Superposition Strain Energy Castigliano
Chapter 4 Deflection and Stiffness 1 2 Chapter Outline Spring Rates Tension, Compression, and Torsion Deflection Due to Bending Beam Deflection Methods Beam Deflections by Superposition Strain Energy Castigliano
[5] Stress and Strain
![[5] Stress and Strain [5] Stress and Strain](/thumbs/95/123344550.jpg) [5] Stress and Strain Page 1 of 34 [5] Stress and Strain [5.1] Internal Stress of Solids [5.2] Design of Simple Connections (will not be covered in class) [5.3] Deformation and Strain [5.4] Hooke s Law
[5] Stress and Strain Page 1 of 34 [5] Stress and Strain [5.1] Internal Stress of Solids [5.2] Design of Simple Connections (will not be covered in class) [5.3] Deformation and Strain [5.4] Hooke s Law
Samantha Ramirez, MSE. Stress. The intensity of the internal force acting on a specific plane (area) passing through a point. F 2
 Samantha Ramirez, MSE Stress The intensity of the internal force acting on a specific plane (area) passing through a point. Δ ΔA Δ z Δ 1 2 ΔA Δ x Δ y ΔA is an infinitesimal size area with a uniform force
Samantha Ramirez, MSE Stress The intensity of the internal force acting on a specific plane (area) passing through a point. Δ ΔA Δ z Δ 1 2 ΔA Δ x Δ y ΔA is an infinitesimal size area with a uniform force
High Tech High Top Hat Technicians. An Introduction to Solid Mechanics. Is that supposed to bend there?
 High Tech High Top Hat Technicians An Introduction to Solid Mechanics Or Is that supposed to bend there? Why don't we fall through the floor? The power of any Spring is in the same proportion with the
High Tech High Top Hat Technicians An Introduction to Solid Mechanics Or Is that supposed to bend there? Why don't we fall through the floor? The power of any Spring is in the same proportion with the
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS
 SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS LIST OF TOPICS Static s Friction Kinematics Dynamics Machines Strength of Materials Hydrostatics Hydrodynamics A STATICS 1 Solves problems involving forces
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS LIST OF TOPICS Static s Friction Kinematics Dynamics Machines Strength of Materials Hydrostatics Hydrodynamics A STATICS 1 Solves problems involving forces
N = Shear stress / Shear strain
 UNIT - I 1. What is meant by factor of safety? [A/M-15] It is the ratio between ultimate stress to the working stress. Factor of safety = Ultimate stress Permissible stress 2. Define Resilience. [A/M-15]
UNIT - I 1. What is meant by factor of safety? [A/M-15] It is the ratio between ultimate stress to the working stress. Factor of safety = Ultimate stress Permissible stress 2. Define Resilience. [A/M-15]
cos(θ)sin(θ) Alternative Exercise Correct Correct θ = 0 skiladæmi 10 Part A Part B Part C Due: 11:59pm on Wednesday, November 11, 2015
 skiladæmi 10 Due: 11:59pm on Wednesday, November 11, 015 You will receive no credit for items you complete after the assignment is due Grading Policy Alternative Exercise 1115 A bar with cross sectional
skiladæmi 10 Due: 11:59pm on Wednesday, November 11, 015 You will receive no credit for items you complete after the assignment is due Grading Policy Alternative Exercise 1115 A bar with cross sectional
SSC-JE MAINS ONLINE TEST SERIES / CIVIL ENGINEERING SOM + TOS
 SSC-JE MAINS ONLINE TEST SERIES / CIVIL ENGINEERING SOM + TOS Time Allowed:2 Hours Maximum Marks: 300 Attention: 1. Paper consists of Part A (Civil & Structural) Part B (Electrical) and Part C (Mechanical)
SSC-JE MAINS ONLINE TEST SERIES / CIVIL ENGINEERING SOM + TOS Time Allowed:2 Hours Maximum Marks: 300 Attention: 1. Paper consists of Part A (Civil & Structural) Part B (Electrical) and Part C (Mechanical)
General Aptitude (GA) Set-2. Q.1 The dress her so well that they all immediately her on her appearance.
 GATE 018 General Aptitude (GA) Set- Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The dress her so well that they all immediately her on her appearance. The words that best fill the blanks in the above sentence are
GATE 018 General Aptitude (GA) Set- Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The dress her so well that they all immediately her on her appearance. The words that best fill the blanks in the above sentence are
Mechanical Engineering Ph.D. Preliminary Qualifying Examination Solid Mechanics February 25, 2002
 student personal identification (ID) number on each sheet. Do not write your name on any sheet. #1. A homogeneous, isotropic, linear elastic bar has rectangular cross sectional area A, modulus of elasticity
student personal identification (ID) number on each sheet. Do not write your name on any sheet. #1. A homogeneous, isotropic, linear elastic bar has rectangular cross sectional area A, modulus of elasticity
PHYSICS 221 SPRING 2015
 PHYSICS 221 SPRING 2015 EXAM 2: April 2, 2015 8:15-10:15pm Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section # INSTRUCTIONS: This exam contains 25 multiple-choice questions plus 2 extra credit questions,
PHYSICS 221 SPRING 2015 EXAM 2: April 2, 2015 8:15-10:15pm Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section # INSTRUCTIONS: This exam contains 25 multiple-choice questions plus 2 extra credit questions,
Class XI Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of Solids Physics
 Book Name: NCERT Solutions Question : A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 5 3.0 0 m stretches by the same 5 amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 0 m
Book Name: NCERT Solutions Question : A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 5 3.0 0 m stretches by the same 5 amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 0 m
Laboratory 4 Bending Test of Materials
 Department of Materials and Metallurgical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering Technology, Dhaka MME 222 Materials Testing Sessional.50 Credits Laboratory 4 Bending Test of Materials. Objective
Department of Materials and Metallurgical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering Technology, Dhaka MME 222 Materials Testing Sessional.50 Credits Laboratory 4 Bending Test of Materials. Objective
Strength of Materials (15CV 32)
 Strength of Materials (15CV 32) Module 1 : Simple Stresses and Strains Dr. H. Ananthan, Professor, VVIET,MYSURU 8/21/2017 Introduction, Definition and concept and of stress and strain. Hooke s law, Stress-Strain
Strength of Materials (15CV 32) Module 1 : Simple Stresses and Strains Dr. H. Ananthan, Professor, VVIET,MYSURU 8/21/2017 Introduction, Definition and concept and of stress and strain. Hooke s law, Stress-Strain
Torsion of shafts with circular symmetry
 orsion of shafts with circular symmetry Introduction Consider a uniform bar which is subject to a torque, eg through the action of two forces F separated by distance d, hence Fd orsion is the resultant
orsion of shafts with circular symmetry Introduction Consider a uniform bar which is subject to a torque, eg through the action of two forces F separated by distance d, hence Fd orsion is the resultant
ME 243. Mechanics of Solids
 ME 243 Mechanics of Solids Lecture 2: Stress and Strain Ahmad Shahedi Shakil Lecturer, Dept. of Mechanical Engg, BUET E-mail: sshakil@me.buet.ac.bd, shakil6791@gmail.com Website: teacher.buet.ac.bd/sshakil
ME 243 Mechanics of Solids Lecture 2: Stress and Strain Ahmad Shahedi Shakil Lecturer, Dept. of Mechanical Engg, BUET E-mail: sshakil@me.buet.ac.bd, shakil6791@gmail.com Website: teacher.buet.ac.bd/sshakil
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK : AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING.
 Course Name Course Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 0 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING : Mechanics of Fluids : A00 : II-I- B. Tech Year : 0 0 Course Coordinator
Course Name Course Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 0 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING : Mechanics of Fluids : A00 : II-I- B. Tech Year : 0 0 Course Coordinator
Strength of Materials Prof S. K. Bhattacharya Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 18 Torsion - I
 Strength of Materials Prof S. K. Bhattacharya Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 18 Torsion - I Welcome to the first lesson of Module 4 which is on Torsion
Strength of Materials Prof S. K. Bhattacharya Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 18 Torsion - I Welcome to the first lesson of Module 4 which is on Torsion
ME : MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 013 Question Booklet Code C ME : MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Read the following instructions carefully. 1. Do not open the seal of the Question Booklet until you are
013 Question Booklet Code C ME : MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Read the following instructions carefully. 1. Do not open the seal of the Question Booklet until you are
Figure 1 Answer: = m
 Q1. Figure 1 shows a solid cylindrical steel rod of length =.0 m and diameter D =.0 cm. What will be increase in its length when m = 80 kg block is attached to its bottom end? (Young's modulus of steel
Q1. Figure 1 shows a solid cylindrical steel rod of length =.0 m and diameter D =.0 cm. What will be increase in its length when m = 80 kg block is attached to its bottom end? (Young's modulus of steel
On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
 Instructor(s): N. Sullivan PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2004 Final Exam December 13, 2011 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
Instructor(s): N. Sullivan PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2004 Final Exam December 13, 2011 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 200 INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. Candidates should attempt
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 200 INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. Candidates should attempt
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS. Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola
 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola Mechanics of materials branch of mechanics that studies the internal effects of stress and strain in a solid body. stress is associated with the
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola Mechanics of materials branch of mechanics that studies the internal effects of stress and strain in a solid body. stress is associated with the
