General Aptitude (GA) Set-2. Q.1 The dress her so well that they all immediately her on her appearance.
|
|
|
- Reynard Barber
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GATE 018 General Aptitude (GA) Set- Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The dress her so well that they all immediately her on her appearance. The words that best fill the blanks in the above sentence are (A) complemented, complemented (C) complimented, complimented (B) complimented, complemented (D) complemented, complimented Q. The judge s standing in the legal community, though shaken by false allegations of wrongdoing, remained. The word that best fills the blank in the above sentence is (A) undiminished (B) damaged (C) illegal (D) uncertain Q.3 Find the missing group of letters in the following series: BC, FGH, LMNO, (A) UVWXY (B) TUVWX (C) STUVW (D) RSTUV Q.4 The perimeters of a circle, a square and an equilateral triangle are equal. Which one of the following statements is true? (A) The circle has the largest area. (B) The square has the largest area. (C) The equilateral triangle has the largest area. (D) All the three shapes have the same area. Q.5 The value of the expression is. 1+log u vw 1+log v wu 1+log w uv (A) -1 (B) 0 (C) 1 (D) 3 Q. 6 Q. 10 carry two marks each. Q.6 Forty students watched films A, B and C over a week. Each student watched either only one film or all three. Thirteen students watched film A, sixteen students watched film B and nineteen students watched film C. How many students watched all three films? (A) 0 (B) (C) 4 (D) 8 GA 1/3
2 GATE 018 General Aptitude (GA) Set- Q.7 A wire would enclose an area of 1936 m, if it is bent into a square. The wire is cut into two pieces. The longer piece is thrice as long as the shorter piece. The long and the short pieces are bent into a square and a circle, respectively. Which of the following choices is closest to the sum of the areas enclosed by the two pieces in square meters? (A) 1096 (B) 1111 (C) 143 (D) 486 Q.8 A contract is to be completed in 5 days and 15 identical robots were employed, each operational for 7 hours a day. After 39 days, five-seventh of the work was completed. How many additional robots would be required to complete the work on time, if each robot is now operational for 8 hours a day? (A) 50 (B) 89 (C) 146 (D) 175 Q.9 A house has a number which needs to be identified. The following three statements are given that can help in identifying the house number. i. If the house number is a multiple of 3, then it is a number from 50 to 59. ii. If the house number is NOT a multiple of 4, then it is a number from 60 to 69. iii. If the house number is NOT a multiple of 6, then it is a number from 70 to 79. What is the house number? (A) 54 (B) 65 (C) 66 (D) 76 GA /3
3 GATE 018 General Aptitude (GA) Set- Q.10 An unbiased coin is tossed six times in a row and four different such trials are conducted. One trial implies six tosses of the coin. If H stands for head and T stands for tail, the following are the observations from the four trials: (1) HTHTHT () TTHHHT (3) HTTHHT (4) HHHT. Which statement describing the last two coin tosses of the fourth trial has the highest probability of being correct? (A) Two T will occur. (B) One H and one T will occur. (C) Two H will occur. (D) One H will be followed by one T. END OF THE QUESTION PAPER GA 3/3
4 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. f() x Q.1 The Fourier cosine series for an even function is given by f ( x) a0 an cos( nx). n 1 The value of the coefficient for the function f ( x) cos ( x) in [0, ] is a (A) 0.5 (B) 0.0 (C) 0.5 (D) 1.0 Q. x The divergence of the vector field u e cos yiˆ sin y ˆj (A) 0 x x (B) e cos y e sin y (C) e x cos y (D) e x sin y is Q.3 Consider a function equation is known as the u (A) Wave equation (B) Heat equation (C) Laplace s equation (D) Elasticity equation which depends on position x and time t. The partial differential u u t x Q.4 3 dy 3 If y is the solution of the differential equation x 0 dx is y, y 0 1, the value of y 1 (A) (B) 1 (C) 0 (D) 1 Q.5 The minimum axial compressive load, P, required to initiate buckling for a pinned-pinned slender column with bending stiffness EI and length L is (A) EI P (B) 4L EI P (C) L 3 EI P (D) 4L P 4 EI L ME 1/15
5 Q.6 A frictionless gear train is shown in the figure. The leftmost 1-teeth gear is given a torque of 100 N-m. The output torque from the 60-teeth gear on the right in N-m is 1 Teeth T =100 N-m 48 Teeth 1 Teeth 60 Teeth (A) 5 (B) 0 (C) 500 (D) 000 Q.7 In a single degree of freedom underdamped spring-mass-damper system as shown in the figure, an additional damper is added in parallel such that the system still remains underdamped. Which one of the following statements is ALWAYS true? M K C (A) Transmissibility will increase. (B) Transmissibility will decrease. (C) Time period of free oscillations will increase. (D) Time period of free oscillations will decrease. Q.8 Pre-tensioning of a bolted joint is used to (A) strain harden the bolt head (C) increase stiffness of the bolted joint (B) decrease stiffness of the bolted joint (D) prevent yielding of the thread root Q.9 The peak wavelength of radiation emitted by a black body at a temperature of 000 K is 1.45 µm. If the peak wavelength of emitted radiation changes to.90 µm, then the temperature (in K) of the black body is (A) 500 (B) 1000 (C) 4000 (D) 8000 ME /15
6 Q.10 For an ideal gas with constant properties undergoing a quasi-static process, which one of the following represents the change of entropy (s) from state 1 to? (A) (B) (C) (D) T P s C p ln Rln T1 P1 T V s C V ln C p ln T1 V1 T P s C P ln CV ln T1 P1 T V1 s C V ln R ln T1 V Q.11 Select the correct statement for 50% reaction stage in a steam turbine. (A) The rotor blade is symmetric. (B) The stator blade is symmetric. (C) The absolute inlet flow angle is equal to absolute exit flow angle. (D) The absolute exit flow angle is equal to inlet angle of rotor blade. Q.1 Denoting L as liquid and M as solid in a phase-diagram with the subscripts representing different phases, a eutectoid reaction is described by (A) M 1 M M 3 (B) L1 M 1 M (C) L1 M 1 M (D) M1M M 3 Q.13 During solidification of a pure molten metal, the grains in the casting near the mould wall are (A) coarse and randomly oriented (B) fine and randomly oriented (C) fine and ordered (D) coarse and ordered Q.14 Match the following products with the suitable manufacturing process Product Manufacturing Process P Toothpaste tube 1 Centrifugal casting Q Metallic pipes Blow moulding R Plastic bottles 3 Rolling S Threaded bolts 4 Impact extrusion (A) P-4, Q-3, R-1, S- (B) P-, Q-1, R-3, S-4 (C) P-4, Q-1, R-, S-3 (D) P-1, Q-3, R-4, S- ME 3/15
7 Q.15 Feed rate in slab milling operation is equal to (A) rotation per minute (rpm) (B) product of rpm and number of teeth in the cutter (C) product of rpm, feed per tooth and number of teeth in the cutter (D) product of rpm, feed per tooth and number of teeth in contact Q.16 Metal removal in electric discharge machining takes place through (A) ion displacement (B) melting and vaporization (C) corrosive reaction (D) plastic shear Q.17 The preferred option for holding an odd-shaped workpiece in a centre lathe is (A) live and dead centres (B) three jaw chuck (C) lathe dog (D) four jaw chuck Q.18 A local tyre distributor expects to sell approximately 9600 steel belted radial tyres next year. Annual carrying cost is Rs. 16 per tyre and ordering cost is Rs. 75. The economic order quantity of the tyres is (A) 64 (B) 1 (C) 300 (D) 100 Q.19 If A = then det(a -1 ) is (correct to two decimal places). Q.0 A hollow circular shaft of inner radius 10 mm, outer radius 0 mm and length 1 m is to be used as a torsional spring. If the shear modulus of the material of the shaft is 150 GPa, the torsional stiffness of the shaft (in kn-m/rad) is (correct to two decimal places). Q.1 Fatigue life of a material for a fully reversed loading condition is estimated from a N , where is the stress amplitude in MPa and N is the failure life in cycles. The maximum a 5 allowable stress amplitude (in MPa) for a life of 110 cycles under the same loading condition is (correct to two decimal places). ME 4/15
8 Q. The viscous laminar flow of air over a flat plate results in the formation of a boundary layer. The boundary layer thickness at the end of the plate of length L isl. When the plate length is increased to twice its original length, the percentage change in laminar boundary layer thickness at the end of the plate (with respect to L) is (correct to two decimal places). Q.3 An engine operates on the reversible cycle as shown in the figure. The work output from the engine (in kj/cycle) is (correct to two decimal places). Q.4 The arrival of customers over fixed time intervals in a bank follow a Poisson distribution with an average of 30 customers/hour. The probability that the time between successive customer arrival is between 1 and 3 minutes is (correct to two decimal places). ME 5/15
9 Q.5 A ball is dropped from rest from a height of 1 m in a frictionless tube as shown in the figure. If the tube profile is approximated by two straight lines (ignoring the curved portion), the total distance travelled (in m) by the ball is (correct to two decimal places). ME 6/15
10 Q. 6 Q. 55 carry two marks each. Q.6 Let z be a complex variable. For a counter-clockwise integration around a unit circle C, centred at origin, C 1 5z 4 dz = Aπi, the value of A is (A) /5 (B) 1/ (C) (D) 4/5 Q.7 Let X1 and X be two independent exponentially distributed random variables with means 0.5 and 0.5, respectively. Then Y = min (X1, X) is (A) exponentially distributed with mean 1 6 (B) exponentially distributed with mean (C) normally distributed with mean 3 4 (D) normally distributed with mean 1 6 Q.8 For a position vector r x i y j z k the norm of the vector can be defined as r x y z. Given a function ln r, its gradient is (A) r (B) r r (C) r r r (D) r r 3 Q.9 In a rigid body in plane motion, the point R is accelerating with respect to point P at m/s. If the instantaneous acceleration of point Q is zero, the acceleration (in m/s ) of point R is (A) 8 33 (B) 10 5 (C) (D) 8 17 ME 7/15
11 Q.30 A rigid rod of length 1 m is resting at an angle dragged with a velocity of the velocity V (in m/s) of point Q as it moves along the wall without losing contact is 45 o as shown in the figure. The end P is U 5 m/s to the right. At the instant shown, the magnitude of (A) 5 (B) 6 (C) 8 (D) 10 Q.31 A bar of circular cross section is clamped at ends P and Q as shown in the figure. A torsional moment T = 150 Nm is applied at a distance of 100 mm from end P. The torsional reactions (T P, T Q ) in Nm at the ends P and Q respectively are (All dimensions are in mm) (A) (50, 100) (B) (75, 75) (C) (100, 50) (D) (10, 30) ME 8/15
12 Q.3 In a cam-follower, the follower rises by h as the cam rotates by (radians) at constant angular velocity (radians/s). The follower is uniformly accelerating during the first half of the rise period and it is uniformly decelerating in the latter half of the rise period. Assuming that the magnitudes of the acceleration and deceleration are same, the maximum velocity of the follower is (A) 4h (B) hω (C) h (D) h Q.33 A bimetallic cylindrical bar of cross sectional area 1 m is made by bonding Steel (Young s modulus = 10 GPa) and Aluminium (Young s modulus = 70 GPa) as shown in 6 the figure. To maintain tensile axial strain of magnitude 10 in Steel bar and compressive 6 axial strain of magnitude 10 in Aluminum bar, the magnitude of the required force P (in kn) along the indicated direction is (A) 70 (B) 140 (C) 10 (D) 80 Q.34 Air flows at the rate of 1.5 m 3 /s through a horizontal pipe with a gradually reducing crosssection as shown in the figure. The two cross-sections of the pipe have diameters of 400 mm and 00 mm. Take the air density as 1. kg/m 3 and assume inviscid incompressible flow. The change in pressure p p (in kpa) between sections 1 and is 1 00 mm Air Flow 1.5 m 3 /s mm (A) 1.8 (B).56 (C).13 (D) 1.8 ME 9/15
13 Q.35 The problem of maximizing and x 5 has (A) no solution (B) one solution (C) two solutions (D) more than two solutions z x x 1 subject to constraints x1 x 10, x1 0, x 0 Q.36 Given the ordinary differential equation with places). y(0) 0 and dy (0) 1 dx d y dy 6y 0 dx dx, the value of y(1) is (correct to two decimal R 100 Q.37 A thin-walled cylindrical can with rigid end caps has a mean radius mm and a wall thickness of mm. The can is pressurized and an additional tensile stress of 50 MPa is imposed along the axial direction as shown in the figure. Assume that the state of stress in the wall is uniform along its length. If the magnitudes of axial and circumferential components of stress in the can are equal, the pressure (in MPa) inside the can is (correct to two decimal places). t 5 Q.38 A bar is subjected to a combination of a steady load of 60 kn and a load fluctuating between10 kn and 90 kn. The corrected endurance limit of the bar is 150 MPa, the yield strength of the material is 480 MPa and the ultimate strength of the material is 600 MPa. The bar cross-section is square with side a. If the factor of safety is, the value of a (in mm), according to the modified Goodman s criterion, is (correct to two decimal places). ME 10/15
14 Q.39 A force of 100 N is applied to the centre of a circular disc, of mass 10 kg and radius 1 m, resting on a floor as shown in the figure. If the disc rolls without slipping on the floor, the linear acceleration (in m/s ) of the centre of the disc is (correct to two decimal places). 100N Q A frictionless circular piston of area m and mass 100 kg sinks into a cylindrical container of the same area filled with water of density 1000 kg/m 3 as shown in the figure The container has a hole of area m at the bottom that is open to the atmosphere. Assuming there is no leakage from the edges of the piston and considering water to be incompressible, the magnitude of the piston velocity (in m/s) at the instant shown is (correct to three decimal places). p atm g = 10 m/s 100 kg 0.5 m ME 11/15
15 Q.41 A 0. m thick infinite black plate having a thermal conductivity of 3.96 W/m-K is exposed to two infinite black surfaces at 300 K and 400 K as shown in the figure. At steady state, the surface temperature of the plate facing the cold side is 350 K. The value of Stefan- Boltzmann constant,, is W/m K 4. Assuming 1-D heat conduction, the magnitude of heat flux through the plate (in W/m ) is (correct to two decimal places). 0. m 300 K vacuum vacuum 400 K Q.4 Air is held inside a non-insulated cylinder using a piston (mass M=5 kg and area A=100 cm ) and stoppers (of negligible area), as shown in the figure. The initial pressure and temperature T i of air inside the cylinder are 00 kpa and 400C, respectively. The ambient P and temperature T pressure are 100 kpa and 7C, respectively. The temperature of the air inside the cylinder (C) at which the piston will begin to move is (correct to two decimal places). P i ME 1/15
16 Q.43 A standard vapor compression refrigeration cycle operating with a condensing temperature o o of 35 C and an evaporating temperature of 10 C develops 15 kw of cooling. The p-h diagram shows the enthalpies at various states. If the isentropic efficiency of the compressor is 0.75, the magnitude of compressor power (in kw) is (correct to two decimal places). Q.44 o Ambient air is at a pressure of 100 kpa, dry bulb temperature of 30 C and 60% relative o humidity. The saturation pressure of water at 30 C is 4.4 kpa. The specific humidity of air (in g/kg of dry air) is (correct to two decimal places). Q.45 A test is conducted on a one-fifth scale model of a Francis turbine under a head of m and volumetric flow rate of 1 m 3 /s at 450 rpm. Take the water density and the acceleration due to gravity as 10 3 kg/m 3 and 10 m/s, respectively. Assume no losses both in model and prototype turbines. The power (in MW) of a full sized turbine while working under a head of 30 m is (correct to two decimal places). ME 13/15
17 Q.46 The true stress (in MPa) versus true strain relationship for a metal is given by The cross-sectional area at the start of a test (when the stress and strain values are equal to zero) is 100 mm. The cross-sectional area at the time of necking (in mm ) is (correct to two decimal places) Q.47 A steel wire is drawn from an initial diameter (d i ) of 10 mm to a final diameter (d f ) of 7.5 mm. The half cone angle () of the die is 5 and the coefficient of friction () between the die and the wire is 0.1. The average of the initial and final yield stress [( Y ) avg ] is 350 MPa. The equation for drawing stress f, (in MPa) is given as: f = (σ Y ) avg {1 + 1 μ cotα μ cot α } [1 (d f ) ] d i The drawing stress (in MPa) required to carry out this operation is (correct to two decimal places). Q.48 Following data correspond to an orthogonal turning of a 100 mm diameter rod on a lathe. Rake angle: ; Uncut chip thickness: 0.5 mm; nominal chip thickness after the cut: 1.5 mm. The shear angle (in degrees) for this process is (correct to two decimal places). 15 o Q.49 Taylor s tool life equation is used to estimate the life of a batch of identical HSS twist drills by drilling through holes at constant feed in 0 mm thick mild steel plates. In test 1, a drill lasted 300 holes at 150 rpm while in test, another drill lasted 00 holes at 300 rpm. The maximum number of holes that can be made by another drill from the above batch at 00 rpm is (correct to two decimal places). Q.50 For sand-casting a steel rectangular plate with dimensions 80 mm 10 mm 0 mm, a cylindrical riser has to be designed. The height of the riser is equal to its diameter. The total solidification time for the casting is minutes. In Chvorinov s law for the estimation of the total solidification time, exponent is to be taken as. For a solidification time of 3 minutes in the riser, the diameter (in mm) of the riser is (correct to two decimal places). ME 14/15
18 Q.51 The arc lengths of a directed graph of a project are as shown in the figure. The shortest path length from node 1 to node 6 is. Q.5 A circular hole of 5 mm diameter and depth of 0 mm is machined by EDM process. The material removal rate (in mm 3 /min) is expressed as IT, where A and the melting point of the material, T 1600 C. The time (in minutes) for machining this hole is (correct to two decimal places) I 300 Q.53 A welding operation is being performed with voltage = 30 V and current = 100 A. The cross-sectional area of the weld bead is 0 mm. The work-piece and filler are of titanium for which the specific energy of melting is 14 J/mm 3. Assuming a thermal efficiency of the welding process 70%, the welding speed (in mm/s) is (correct to two decimal places). Q.54 Steam in the condenser of a thermal power plant is to be condensed at a temperature of 30C with cooling water which enters the tubes of the condenser at 14C and exits at C. The total surface area of the tubes is 50 m, and the overall heat transfer coefficient is 000 W/m K. The heat transfer (in MW) to the condenser is (correct to two decimal places). Q.55 A vehicle powered by a spark ignition engine follows air standard Otto cycle (=1.4). The engine generates 70 kw while consuming 10.3 kg/hr of fuel. The calorific value of fuel is 44,000 kj/kg. The compression ratio is (correct to two decimal places). END OF THE QUESTION PAPER ME 15/15
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
General Aptitude (GA) Set-2. Q.1 The dress her so well that they all immediately her on her appearance.
 General Aptitude (GA) Set-2 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The dress her so well that they all immediately her on her appearance. The words that best fill the blanks in the above sentence are (A) complemented,
General Aptitude (GA) Set-2 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The dress her so well that they all immediately her on her appearance. The words that best fill the blanks in the above sentence are (A) complemented,
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 At least one eigenvalue of a singular matrix is (A) positive (B) zero (C) negative (D) imaginary Q. At x = 0, the function f( x) = x has (A) a minimum (C) a point of
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 At least one eigenvalue of a singular matrix is (A) positive (B) zero (C) negative (D) imaginary Q. At x = 0, the function f( x) = x has (A) a minimum (C) a point of
SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Paper II. Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.
 We RoU No. 700095 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper II Time ; 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 0 Instructions
We RoU No. 700095 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper II Time ; 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 0 Instructions
PES Institute of Technology
 PES Institute of Technology Bangalore south campus, Bangalore-5460100 Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty name : Madhu M Date: 29/06/2012 SEM : 3 rd A SEC Subject : MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Subject
PES Institute of Technology Bangalore south campus, Bangalore-5460100 Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty name : Madhu M Date: 29/06/2012 SEM : 3 rd A SEC Subject : MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Subject
Set 1. a. 100 kj/kg b. 110 kj/kg c. 140 kj/kg d. 150 kj/kg
 Set 1 1. Two blocks which are at different states are brought into contact with each other and allowed to reach a final state of thermal equilibrium. The final temperature attained is specified by the
Set 1 1. Two blocks which are at different states are brought into contact with each other and allowed to reach a final state of thermal equilibrium. The final temperature attained is specified by the
SILVER OAK COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ADITYA SILVER OAK INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 SUBJECT: ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (2131905) (ME) DATE: 11-08-2017 TIME: 10:00 am to 11:30 am TOTAL MARKS: 40 Q.1 (a) Answer following questions in short/brief: 1. Energy of an isolated system is always
SUBJECT: ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (2131905) (ME) DATE: 11-08-2017 TIME: 10:00 am to 11:30 am TOTAL MARKS: 40 Q.1 (a) Answer following questions in short/brief: 1. Energy of an isolated system is always
R13. II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, AE, MTE) PART-A
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, AE, MTE) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, AE, MTE) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
General Aptitude (GA) Set-1. The words that best fill the blanks in the above sentence are.
 GATE 2018 General Aptitude (GA) Set-1 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 Going by the that many hands make light work, the school involved all the students in the task. The words that best fill the blanks
GATE 2018 General Aptitude (GA) Set-1 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 Going by the that many hands make light work, the school involved all the students in the task. The words that best fill the blanks
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown.
 D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
Set 2 (d) 150 C (a) 0.45 (d) can be positive, negative or zero (C) 8.5 J/K (a) 0.1
 Set 2 1. In a new temperature scale say o p, the boiling and freezing points of water at one atmosphere are 100 p and 300 p respectively. Correlate this scale with the Centigrade scale. The reading of
Set 2 1. In a new temperature scale say o p, the boiling and freezing points of water at one atmosphere are 100 p and 300 p respectively. Correlate this scale with the Centigrade scale. The reading of
General Aptitude - GA Set-3. Q.1 Based on the given statements, select the appropriate option with respect to grammar and usage.
 GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-3 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 Based on the given statements, select the appropriate option with respect to grammar and usage. Statements (i) (ii) The height of
GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-3 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 Based on the given statements, select the appropriate option with respect to grammar and usage. Statements (i) (ii) The height of
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
Mechanical Engineering Excerise 1
 Mechanical Engineering Excerise 1 1. Given that the determinant of the matrix 2 6 0 the matrix 4 12 8 is 2 0 4 1 3 0 2 6 4 1 0 2 is 12, the determinant of (A) 96 (B) 24 (C) 24 (D) 96 2. x sin x Lt 1 cosx
Mechanical Engineering Excerise 1 1. Given that the determinant of the matrix 2 6 0 the matrix 4 12 8 is 2 0 4 1 3 0 2 6 4 1 0 2 is 12, the determinant of (A) 96 (B) 24 (C) 24 (D) 96 2. x sin x Lt 1 cosx
: APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE
 COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 200 INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. Candidates should attempt
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 200 INSTRUCTIONS Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions. Candidates should attempt
PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM - 613 403 - THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub : Strength of Materials Year / Sem: II / III Sub Code : MEB 310
PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM - 613 403 - THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub : Strength of Materials Year / Sem: II / III Sub Code : MEB 310
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5
 COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPICS PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPICS PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy
 Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
Tuesday, February 11, Chapter 3. Load and Stress Analysis. Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE
 1 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Chapter Outline Equilibrium & Free-Body Diagrams Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Singularity Functions Stress Cartesian Stress Components Mohr s Circle for
1 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Chapter Outline Equilibrium & Free-Body Diagrams Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Singularity Functions Stress Cartesian Stress Components Mohr s Circle for
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 GATE 2016 General Aptitude GA Set-7 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 If I were you, I that laptop. It s much too expensive. (A) won t buy (C) wouldn t buy (B) shan t buy (D) would buy Q.2 He turned a
GATE 2016 General Aptitude GA Set-7 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 If I were you, I that laptop. It s much too expensive. (A) won t buy (C) wouldn t buy (B) shan t buy (D) would buy Q.2 He turned a
The University of Melbourne Engineering Mechanics
 The University of Melbourne 436-291 Engineering Mechanics Tutorial Four Poisson s Ratio and Axial Loading Part A (Introductory) 1. (Problem 9-22 from Hibbeler - Statics and Mechanics of Materials) A short
The University of Melbourne 436-291 Engineering Mechanics Tutorial Four Poisson s Ratio and Axial Loading Part A (Introductory) 1. (Problem 9-22 from Hibbeler - Statics and Mechanics of Materials) A short
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each.
 GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
Answers to questions in each section should be tied together and handed in separately.
 EGT0 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IA Wednesday 4 June 014 9 to 1 Paper 1 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Answer all questions. The approximate number of marks allocated to each part of a question is indicated in the
EGT0 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IA Wednesday 4 June 014 9 to 1 Paper 1 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Answer all questions. The approximate number of marks allocated to each part of a question is indicated in the
Samantha Ramirez, MSE. Stress. The intensity of the internal force acting on a specific plane (area) passing through a point. F 2
 Samantha Ramirez, MSE Stress The intensity of the internal force acting on a specific plane (area) passing through a point. Δ ΔA Δ z Δ 1 2 ΔA Δ x Δ y ΔA is an infinitesimal size area with a uniform force
Samantha Ramirez, MSE Stress The intensity of the internal force acting on a specific plane (area) passing through a point. Δ ΔA Δ z Δ 1 2 ΔA Δ x Δ y ΔA is an infinitesimal size area with a uniform force
Downloaded from Downloaded from / 1
 PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY III SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2002 LEVEL : B. E. (Civil) SUBJECT: BEG256CI, Strength of Material Full Marks: 80 TIME: 03:00 hrs Pass marks: 32 Candidates are required to give their
PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY III SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2002 LEVEL : B. E. (Civil) SUBJECT: BEG256CI, Strength of Material Full Marks: 80 TIME: 03:00 hrs Pass marks: 32 Candidates are required to give their
QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SEMESTER: III SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A
 DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
[5] Stress and Strain
![[5] Stress and Strain [5] Stress and Strain](/thumbs/95/123344550.jpg) [5] Stress and Strain Page 1 of 34 [5] Stress and Strain [5.1] Internal Stress of Solids [5.2] Design of Simple Connections (will not be covered in class) [5.3] Deformation and Strain [5.4] Hooke s Law
[5] Stress and Strain Page 1 of 34 [5] Stress and Strain [5.1] Internal Stress of Solids [5.2] Design of Simple Connections (will not be covered in class) [5.3] Deformation and Strain [5.4] Hooke s Law
PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [ ] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics
![PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [ ] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [ ] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics](/thumbs/92/109382806.jpg) Page1 PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [2910601] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics 1. Differentiate between Scalar and Vector quantity. Write S.I.
Page1 PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [2910601] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics 1. Differentiate between Scalar and Vector quantity. Write S.I.
NORMAL STRESS. The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts.
 NORMAL STRESS The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts. σ = force/area = P/A where σ = the normal stress P = the centric
NORMAL STRESS The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts. σ = force/area = P/A where σ = the normal stress P = the centric
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 009 Mechanical
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 009 Mechanical
Topic wise Tests. Complex Variables, Numerical Methods and Probability and Statistics.
 ME-01 ME-02 ME-03 ME-04 GEM-1 GEM-2 GMC 1 Mechanics) GHT 1 Topic wise Tests Each test carries 25 marks and 45 minutes duration Test consists of 5 one mark questions and 10 two marks questions Tests will
ME-01 ME-02 ME-03 ME-04 GEM-1 GEM-2 GMC 1 Mechanics) GHT 1 Topic wise Tests Each test carries 25 marks and 45 minutes duration Test consists of 5 one mark questions and 10 two marks questions Tests will
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 For the given fluctuating fatigue load, the values of stress amplitude and stress ratio are respectively MPa 250 200 150 100 50 0 Time (A) 100 MPa and 5 (B) 250 MPa
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 For the given fluctuating fatigue load, the values of stress amplitude and stress ratio are respectively MPa 250 200 150 100 50 0 Time (A) 100 MPa and 5 (B) 250 MPa
CIVL222 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS. Chapter 6. Torsion
 CIVL222 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Chapter 6 Torsion Definition Torque is a moment that tends to twist a member about its longitudinal axis. Slender members subjected to a twisting load are said to be in torsion.
CIVL222 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Chapter 6 Torsion Definition Torque is a moment that tends to twist a member about its longitudinal axis. Slender members subjected to a twisting load are said to be in torsion.
CHAPTER 3 THE EFFECTS OF FORCES ON MATERIALS
 CHAPTER THE EFFECTS OF FORCES ON MATERIALS EXERCISE 1, Page 50 1. A rectangular bar having a cross-sectional area of 80 mm has a tensile force of 0 kn applied to it. Determine the stress in the bar. Stress
CHAPTER THE EFFECTS OF FORCES ON MATERIALS EXERCISE 1, Page 50 1. A rectangular bar having a cross-sectional area of 80 mm has a tensile force of 0 kn applied to it. Determine the stress in the bar. Stress
ROTATING RING. Volume of small element = Rdθbt if weight density of ring = ρ weight of small element = ρrbtdθ. Figure 1 Rotating ring
 ROTATIONAL STRESSES INTRODUCTION High centrifugal forces are developed in machine components rotating at a high angular speed of the order of 100 to 500 revolutions per second (rps). High centrifugal force
ROTATIONAL STRESSES INTRODUCTION High centrifugal forces are developed in machine components rotating at a high angular speed of the order of 100 to 500 revolutions per second (rps). High centrifugal force
1. A pure shear deformation is shown. The volume is unchanged. What is the strain tensor.
 Elasticity Homework Problems 2014 Section 1. The Strain Tensor. 1. A pure shear deformation is shown. The volume is unchanged. What is the strain tensor. 2. Given a steel bar compressed with a deformation
Elasticity Homework Problems 2014 Section 1. The Strain Tensor. 1. A pure shear deformation is shown. The volume is unchanged. What is the strain tensor. 2. Given a steel bar compressed with a deformation
If there is convective heat transfer from outer surface to fluid maintained at T W.
 Heat Transfer 1. What are the different modes of heat transfer? Explain with examples. 2. State Fourier s Law of heat conduction? Write some of their applications. 3. State the effect of variation of temperature
Heat Transfer 1. What are the different modes of heat transfer? Explain with examples. 2. State Fourier s Law of heat conduction? Write some of their applications. 3. State the effect of variation of temperature
Shared on QualifyGate.com
 1 Section - I (General Aptitude) Q.1 Choose the correct verb to fill in the blank below: Let us. (a) introvert (b) alternate (c) atheist (d) altruist Q. Choose the most appropriate word from the options
1 Section - I (General Aptitude) Q.1 Choose the correct verb to fill in the blank below: Let us. (a) introvert (b) alternate (c) atheist (d) altruist Q. Choose the most appropriate word from the options
2012 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
 R10 SET - 1 II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, MM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
R10 SET - 1 II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, MM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
(48) CHAPTER 3: TORSION
 (48) CHAPTER 3: TORSION Introduction: In this chapter structural members and machine parts that are in torsion will be considered. More specifically, you will analyze the stresses and strains in members
(48) CHAPTER 3: TORSION Introduction: In this chapter structural members and machine parts that are in torsion will be considered. More specifically, you will analyze the stresses and strains in members
Civil Services Examination-1989
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PAPER I Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum marks: 300 INSTRUCTIONS Each question is printed both in Hindi and in English. Answers must be written in the, medium specified in the Admission.
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PAPER I Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum marks: 300 INSTRUCTIONS Each question is printed both in Hindi and in English. Answers must be written in the, medium specified in the Admission.
9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
 9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Deforming force Deforming force is the force which changes the shape or size of a body. Restoring force Restoring force is the internal force developed inside the body
9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Deforming force Deforming force is the force which changes the shape or size of a body. Restoring force Restoring force is the internal force developed inside the body
Shared on QualifyGate.com
 GTE 014 Brief nalysis (Based on student test experiences in the stream of ME on 16th February, 014 - Second Session) Section wise analysis of the paper 1 Mark Marks Total No of Questions Engineering Mathematics
GTE 014 Brief nalysis (Based on student test experiences in the stream of ME on 16th February, 014 - Second Session) Section wise analysis of the paper 1 Mark Marks Total No of Questions Engineering Mathematics
NAME: Given Formulae: Law of Cosines: Law of Sines:
 NME: Given Formulae: Law of Cosines: EXM 3 PST PROBLEMS (LESSONS 21 TO 28) 100 points Thursday, November 16, 2017, 7pm to 9:30, Room 200 You are allowed to use a calculator and drawing equipment, only.
NME: Given Formulae: Law of Cosines: EXM 3 PST PROBLEMS (LESSONS 21 TO 28) 100 points Thursday, November 16, 2017, 7pm to 9:30, Room 200 You are allowed to use a calculator and drawing equipment, only.
Torsion Stresses in Tubes and Rods
 Torsion Stresses in Tubes and Rods This initial analysis is valid only for a restricted range of problem for which the assumptions are: Rod is initially straight. Rod twists without bending. Material is
Torsion Stresses in Tubes and Rods This initial analysis is valid only for a restricted range of problem for which the assumptions are: Rod is initially straight. Rod twists without bending. Material is
Engineering Science OUTCOME 1 - TUTORIAL 4 COLUMNS
 Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: Credit value: 15 Engineering Science L/601/10 OUTCOME 1 - TUTORIAL COLUMNS 1. Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements of static engineering systems
Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: Credit value: 15 Engineering Science L/601/10 OUTCOME 1 - TUTORIAL COLUMNS 1. Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements of static engineering systems
Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW SVCET
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW 1. What do you understand by pure substance? A pure substance is defined as one that is homogeneous and invariable in chemical composition
Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW 1. What do you understand by pure substance? A pure substance is defined as one that is homogeneous and invariable in chemical composition
GATE 2009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper
 GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper. For a matrix [M]= x [M]. The value of x is given by GATE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING 009 (ME) GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper Q. No. 0 Carry One
GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper. For a matrix [M]= x [M]. The value of x is given by GATE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING 009 (ME) GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper Q. No. 0 Carry One
SEM-2016(03)-II MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Paper -11. Please read each of the following instructions carefully before. attempting questions.
 Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(03)-II MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper -11 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 300 Instructions
Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(03)-II MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper -11 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 300 Instructions
UNIT-I STRESS, STRAIN. 1. A Member A B C D is subjected to loading as shown in fig determine the total elongation. Take E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2
 UNIT-I STRESS, STRAIN 1. A Member A B C D is subjected to loading as shown in fig determine the total elongation. Take E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2 Young s modulus E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2 Area1=900mm 2 Area2=400mm 2 Area3=625mm
UNIT-I STRESS, STRAIN 1. A Member A B C D is subjected to loading as shown in fig determine the total elongation. Take E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2 Young s modulus E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2 Area1=900mm 2 Area2=400mm 2 Area3=625mm
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK. Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV UNIT I STRESS, STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART A (2 MARKS)
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV UNIT I STRESS, STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART A (2 MARKS)
MAAE 2202 A. Come to the PASS workshop with your mock exam complete. During the workshop you can work with other students to review your work.
 It is most beneficial to you to write this mock final exam UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the exam in 3 hours. Work on your own. Keep your textbook closed. Attempt every question. After the
It is most beneficial to you to write this mock final exam UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the exam in 3 hours. Work on your own. Keep your textbook closed. Attempt every question. After the
 GATE question papers: Mechanical Engineering, 20 (ME) Q. - Q. 25 carry one mark.. A streamline and an equipotential line in a flow field (A) are parallel to each other (B) are perpendicular to each other
GATE question papers: Mechanical Engineering, 20 (ME) Q. - Q. 25 carry one mark.. A streamline and an equipotential line in a flow field (A) are parallel to each other (B) are perpendicular to each other
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1 Question Paper Analysis 2 Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom ANALYSIS OF GATE 2012 Mechanical
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1 Question Paper Analysis 2 Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom ANALYSIS OF GATE 2012 Mechanical
Mechanics of Solids. Mechanics Of Solids. Suraj kr. Ray Department of Civil Engineering
 Mechanics Of Solids Suraj kr. Ray (surajjj2445@gmail.com) Department of Civil Engineering 1 Mechanics of Solids is a branch of applied mechanics that deals with the behaviour of solid bodies subjected
Mechanics Of Solids Suraj kr. Ray (surajjj2445@gmail.com) Department of Civil Engineering 1 Mechanics of Solids is a branch of applied mechanics that deals with the behaviour of solid bodies subjected
AE302,ME302,DAE14,DME14
 AE302,ME302,DAE14,DME14 III SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION, JANUARY-2013 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY-I Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 75 GROUP A : Answer any three questions. (Question No. 1 is compulsory) Q.1 What
AE302,ME302,DAE14,DME14 III SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION, JANUARY-2013 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY-I Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 75 GROUP A : Answer any three questions. (Question No. 1 is compulsory) Q.1 What
GATE 2012 Mechanical Engineering Set - C
 GATE 2012 Mechanical Engineering Set - C Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. 1. Consider the function in the interval. At the point is (A) Continuous and differentiable. (B) Non-continuous and differentiable
GATE 2012 Mechanical Engineering Set - C Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. 1. Consider the function in the interval. At the point is (A) Continuous and differentiable. (B) Non-continuous and differentiable
Torsion of Shafts Learning objectives
 Torsion of Shafts Shafts are structural members with length significantly greater than the largest cross-sectional dimension used in transmitting torque from one plane to another. Learning objectives Understand
Torsion of Shafts Shafts are structural members with length significantly greater than the largest cross-sectional dimension used in transmitting torque from one plane to another. Learning objectives Understand
ME : MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 013 Question Booklet Code C ME : MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Read the following instructions carefully. 1. Do not open the seal of the Question Booklet until you are
013 Question Booklet Code C ME : MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Read the following instructions carefully. 1. Do not open the seal of the Question Booklet until you are
Chapter 3. Load and Stress Analysis. Lecture Slides
 Lecture Slides Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2015 by McGraw Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner.
Lecture Slides Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2015 by McGraw Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner.
OUTCOME 1 - TUTORIAL 3 BENDING MOMENTS. You should judge your progress by completing the self assessment exercises. CONTENTS
 Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 15 Engineering Science L/601/1404 OUTCOME 1 - TUTORIAL 3 BENDING MOMENTS 1. Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements of static engineering
Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 15 Engineering Science L/601/1404 OUTCOME 1 - TUTORIAL 3 BENDING MOMENTS 1. Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements of static engineering
Answer Key. Mechanical Engineering GATE Afternoon Session 1st Feb, Write us at Phone: ,
 Answer Key of Shared on QualifyGate.com Mechanical Engineering GATE-2015 Afternoon Session 1st Feb, 2015 Write us at info@madeeasy.in Phone: 011-45124612, 9958995830 www.madeeasy.in 1 Section - I (General
Answer Key of Shared on QualifyGate.com Mechanical Engineering GATE-2015 Afternoon Session 1st Feb, 2015 Write us at info@madeeasy.in Phone: 011-45124612, 9958995830 www.madeeasy.in 1 Section - I (General
2 Navier-Stokes Equations
 1 Integral analysis 1. Water enters a pipe bend horizontally with a uniform velocity, u 1 = 5 m/s. The pipe is bended at 90 so that the water leaves it vertically downwards. The input diameter d 1 = 0.1
1 Integral analysis 1. Water enters a pipe bend horizontally with a uniform velocity, u 1 = 5 m/s. The pipe is bended at 90 so that the water leaves it vertically downwards. The input diameter d 1 = 0.1
COURSE TITLE : THEORY OF STRUCTURES -I COURSE CODE : 3013 COURSE CATEGORY : B PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/SEMESTER: 90 CREDITS : 6
 COURSE TITLE : THEORY OF STRUCTURES -I COURSE CODE : 0 COURSE CATEGORY : B PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/SEMESTER: 90 CREDITS : 6 TIME SCHEDULE Module Topics Period Moment of forces Support reactions Centre
COURSE TITLE : THEORY OF STRUCTURES -I COURSE CODE : 0 COURSE CATEGORY : B PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/SEMESTER: 90 CREDITS : 6 TIME SCHEDULE Module Topics Period Moment of forces Support reactions Centre
Sample Question Paper
 Scheme I Sample Question Paper Program Name : Mechanical Engineering Program Group Program Code : AE/ME/PG/PT/FG Semester : Third Course Title : Strength of Materials Marks : 70 Time: 3 Hrs. Instructions:
Scheme I Sample Question Paper Program Name : Mechanical Engineering Program Group Program Code : AE/ME/PG/PT/FG Semester : Third Course Title : Strength of Materials Marks : 70 Time: 3 Hrs. Instructions:
The problem of transmitting a torque or rotary motion from one plane to another is frequently encountered in machine design.
 CHAPER ORSION ORSION orsion refers to the twisting of a structural member when it is loaded by moments/torques that produce rotation about the longitudinal axis of the member he problem of transmitting
CHAPER ORSION ORSION orsion refers to the twisting of a structural member when it is loaded by moments/torques that produce rotation about the longitudinal axis of the member he problem of transmitting
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 General ptitude G Set-8 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The chairman requested the aggrieved shareholders to him. () bare with () bore with (C) bear with (D) bare Q.2 Identify the correct spelling out
General ptitude G Set-8 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The chairman requested the aggrieved shareholders to him. () bare with () bore with (C) bear with (D) bare Q.2 Identify the correct spelling out
and F NAME: ME rd Sample Final Exam PROBLEM 1 (25 points) Prob. 1 questions are all or nothing. PROBLEM 1A. (5 points)
 ME 270 3 rd Sample inal Exam PROBLEM 1 (25 points) Prob. 1 questions are all or nothing. PROBLEM 1A. (5 points) IND: In your own words, please state Newton s Laws: 1 st Law = 2 nd Law = 3 rd Law = PROBLEM
ME 270 3 rd Sample inal Exam PROBLEM 1 (25 points) Prob. 1 questions are all or nothing. PROBLEM 1A. (5 points) IND: In your own words, please state Newton s Laws: 1 st Law = 2 nd Law = 3 rd Law = PROBLEM
GATE SOLUTIONS E N G I N E E R I N G
 GATE SOLUTIONS C I V I L E N G I N E E R I N G From (1987-018) Office : F-16, (Lower Basement), Katwaria Sarai, New Delhi-110016 Phone : 011-65064 Mobile : 81309090, 9711853908 E-mail: info@iesmasterpublications.com,
GATE SOLUTIONS C I V I L E N G I N E E R I N G From (1987-018) Office : F-16, (Lower Basement), Katwaria Sarai, New Delhi-110016 Phone : 011-65064 Mobile : 81309090, 9711853908 E-mail: info@iesmasterpublications.com,
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS
 SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS LIST OF TOPICS Static s Friction Kinematics Dynamics Machines Strength of Materials Hydrostatics Hydrodynamics A STATICS 1 Solves problems involving forces
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS LIST OF TOPICS Static s Friction Kinematics Dynamics Machines Strength of Materials Hydrostatics Hydrodynamics A STATICS 1 Solves problems involving forces
GATE: 2006 ME: Mechanical Engineering
 GATE: 2006 ME: Mechanical Engineering Q. 1 Q. 20 Carry One Mark Each. 1. Match the items in columns I and II. Column I (P) Gauss-Seidel method (Q) Forward Newton-Gauss method (R) Runge-Kutta method (S)
GATE: 2006 ME: Mechanical Engineering Q. 1 Q. 20 Carry One Mark Each. 1. Match the items in columns I and II. Column I (P) Gauss-Seidel method (Q) Forward Newton-Gauss method (R) Runge-Kutta method (S)
Sub. Code:
 Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. ) The model answer and the answer written by candidate may
Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. ) The model answer and the answer written by candidate may
EMA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 3 Torsion
 EMA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 3 Torsion Introduction Stress and strain in components subjected to torque T Circular Cross-section shape Material Shaft design Non-circular
EMA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 3 Torsion Introduction Stress and strain in components subjected to torque T Circular Cross-section shape Material Shaft design Non-circular
SRI CHANDRASEKHARENDRA SARASWATHI VISWA MAHAVIDHYALAYA
 SRI CHANDRASEKHARENDRA SARASWATHI VISWA MAHAVIDHYALAYA (Declared as Deemed-to-be University under Section 3 of the UGC Act, 1956, Vide notification No.F.9.9/92-U-3 dated 26 th May 1993 of the Govt. of
SRI CHANDRASEKHARENDRA SARASWATHI VISWA MAHAVIDHYALAYA (Declared as Deemed-to-be University under Section 3 of the UGC Act, 1956, Vide notification No.F.9.9/92-U-3 dated 26 th May 1993 of the Govt. of
18.Define the term modulus of resilience. May/June Define Principal Stress. 20. Define Hydrostatic Pressure.
 CE6306 STREGNTH OF MATERIALS Question Bank Unit-I STRESS, STRAIN, DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART-A 1. Define Poison s Ratio May/June 2009 2. What is thermal stress? May/June 2009 3. Estimate the load carried
CE6306 STREGNTH OF MATERIALS Question Bank Unit-I STRESS, STRAIN, DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART-A 1. Define Poison s Ratio May/June 2009 2. What is thermal stress? May/June 2009 3. Estimate the load carried
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
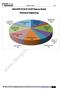 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
Name :. Roll No. :... Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B.TECH (CE-NEW)/SEM-3/CE-301/ SOLID MECHANICS
 Name :. Roll No. :..... Invigilator s Signature :.. 2011 SOLID MECHANICS Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates are required to give their answers
Name :. Roll No. :..... Invigilator s Signature :.. 2011 SOLID MECHANICS Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates are required to give their answers
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-67 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2007
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-67 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2007
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
 Chapter Nine MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS MCQ I 9.1 Modulus of rigidity of ideal liquids is (a) infinity. (b) zero. (c) unity. (d) some finite small non-zero constant value. 9. The maximum load a wire
Chapter Nine MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS MCQ I 9.1 Modulus of rigidity of ideal liquids is (a) infinity. (b) zero. (c) unity. (d) some finite small non-zero constant value. 9. The maximum load a wire
TOPIC D: ROTATION EXAMPLES SPRING 2018
 TOPIC D: ROTATION EXAMPLES SPRING 018 Q1. A car accelerates uniformly from rest to 80 km hr 1 in 6 s. The wheels have a radius of 30 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the wheels? Q. The University
TOPIC D: ROTATION EXAMPLES SPRING 018 Q1. A car accelerates uniformly from rest to 80 km hr 1 in 6 s. The wheels have a radius of 30 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the wheels? Q. The University
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
 BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
R13 SET - 1 '' ''' '' ' '''' Code No RT21033
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
Mechanics of Materials II. Chapter III. A review of the fundamental formulation of stress, strain, and deflection
 Mechanics of Materials II Chapter III A review of the fundamental formulation of stress, strain, and deflection Outline Introduction Assumtions and limitations Axial loading Torsion of circular shafts
Mechanics of Materials II Chapter III A review of the fundamental formulation of stress, strain, and deflection Outline Introduction Assumtions and limitations Axial loading Torsion of circular shafts
SESSION - 1. Auhippo.com
 SESSION - 1 Auhippo.com 013 Question Booklet Code A ME : MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Read the following instructions carefully. 1. Do not open the seal of the Question
SESSION - 1 Auhippo.com 013 Question Booklet Code A ME : MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Read the following instructions carefully. 1. Do not open the seal of the Question
March 24, Chapter 4. Deflection and Stiffness. Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 4 Deflection and Stiffness 1 2 Chapter Outline Spring Rates Tension, Compression, and Torsion Deflection Due to Bending Beam Deflection Methods Beam Deflections by Superposition Strain Energy Castigliano
Chapter 4 Deflection and Stiffness 1 2 Chapter Outline Spring Rates Tension, Compression, and Torsion Deflection Due to Bending Beam Deflection Methods Beam Deflections by Superposition Strain Energy Castigliano
2. Polar moment of inertia As stated above, the polar second moment of area, J is defined as. Sample copy
 GATE PATHSHALA - 91. Polar moment of inertia As stated above, the polar second moment of area, is defined as z π r dr 0 R r π R π D For a solid shaft π (6) QP 0 π d Solid shaft π d Hollow shaft, " ( do
GATE PATHSHALA - 91. Polar moment of inertia As stated above, the polar second moment of area, is defined as z π r dr 0 R r π R π D For a solid shaft π (6) QP 0 π d Solid shaft π d Hollow shaft, " ( do
The example of shafts; a) Rotating Machinery; Propeller shaft, Drive shaft b) Structural Systems; Landing gear strut, Flap drive mechanism
 TORSION OBJECTIVES: This chapter starts with torsion theory in the circular cross section followed by the behaviour of torsion member. The calculation of the stress stress and the angle of twist will be
TORSION OBJECTIVES: This chapter starts with torsion theory in the circular cross section followed by the behaviour of torsion member. The calculation of the stress stress and the angle of twist will be
Strength of Materials (15CV 32)
 Strength of Materials (15CV 32) Module 1 : Simple Stresses and Strains Dr. H. Ananthan, Professor, VVIET,MYSURU 8/21/2017 Introduction, Definition and concept and of stress and strain. Hooke s law, Stress-Strain
Strength of Materials (15CV 32) Module 1 : Simple Stresses and Strains Dr. H. Ananthan, Professor, VVIET,MYSURU 8/21/2017 Introduction, Definition and concept and of stress and strain. Hooke s law, Stress-Strain
High Tech High Top Hat Technicians. An Introduction to Solid Mechanics. Is that supposed to bend there?
 High Tech High Top Hat Technicians An Introduction to Solid Mechanics Or Is that supposed to bend there? Why don't we fall through the floor? The power of any Spring is in the same proportion with the
High Tech High Top Hat Technicians An Introduction to Solid Mechanics Or Is that supposed to bend there? Why don't we fall through the floor? The power of any Spring is in the same proportion with the
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -00 04 CIVIL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Course Name : STRENGTH OF MATERIALS II Course Code : A404 Class : II B. Tech II Semester Section
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -00 04 CIVIL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Course Name : STRENGTH OF MATERIALS II Course Code : A404 Class : II B. Tech II Semester Section
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 GATE 2019 General Aptitude (GA) Set-2 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 John Thomas, an writer, passed away in 2018. (A) imminent (C) eminent (B) prominent (D) dominant Q.2 I permitted him to leave, I
GATE 2019 General Aptitude (GA) Set-2 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 John Thomas, an writer, passed away in 2018. (A) imminent (C) eminent (B) prominent (D) dominant Q.2 I permitted him to leave, I
Members Subjected to Torsional Loads
 Members Subjected to Torsional Loads Torsion of circular shafts Definition of Torsion: Consider a shaft rigidly clamped at one end and twisted at the other end by a torque T = F.d applied in a plane perpendicular
Members Subjected to Torsional Loads Torsion of circular shafts Definition of Torsion: Consider a shaft rigidly clamped at one end and twisted at the other end by a torque T = F.d applied in a plane perpendicular
D e s i g n o f R i v e t e d J o i n t s, C o t t e r & K n u c k l e J o i n t s
 D e s i g n o f R i v e t e d J o i n t s, C o t t e r & K n u c k l e J o i n t s 1. Design of various types of riveted joints under different static loading conditions, eccentrically loaded riveted joints.
D e s i g n o f R i v e t e d J o i n t s, C o t t e r & K n u c k l e J o i n t s 1. Design of various types of riveted joints under different static loading conditions, eccentrically loaded riveted joints.
BE Semester- I ( ) Question Bank (MECHANICS OF SOLIDS)
 BE Semester- I ( ) Question Bank (MECHANICS OF SOLIDS) All questions carry equal marks(10 marks) Q.1 (a) Write the SI units of following quantities and also mention whether it is scalar or vector: (i)
BE Semester- I ( ) Question Bank (MECHANICS OF SOLIDS) All questions carry equal marks(10 marks) Q.1 (a) Write the SI units of following quantities and also mention whether it is scalar or vector: (i)
[7] Torsion. [7.1] Torsion. [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion. [7] Torsion Page 1 of 21
![[7] Torsion. [7.1] Torsion. [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion. [7] Torsion Page 1 of 21 [7] Torsion. [7.1] Torsion. [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion. [7] Torsion Page 1 of 21](/thumbs/88/115835122.jpg) [7] Torsion Page 1 of 21 [7] Torsion [7.1] Torsion [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion [7] Torsion Page 2 of 21 [7.1] Torsion SHEAR STRAIN DUE TO TORSION 1) A shaft with a circular cross section is
[7] Torsion Page 1 of 21 [7] Torsion [7.1] Torsion [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion [7] Torsion Page 2 of 21 [7.1] Torsion SHEAR STRAIN DUE TO TORSION 1) A shaft with a circular cross section is
This equation of motion may be solved either by differential equation method or by graphical method as discussed below:
 2.15. Frequency of Under Damped Forced Vibrations Consider a system consisting of spring, mass and damper as shown in Fig. 22. Let the system is acted upon by an external periodic (i.e. simple harmonic)
2.15. Frequency of Under Damped Forced Vibrations Consider a system consisting of spring, mass and damper as shown in Fig. 22. Let the system is acted upon by an external periodic (i.e. simple harmonic)
GATE: 2003 ME: Mechanical Engineering
 GATE: 2003 ME: Mechanical Engineering 1. is equal to 0 1 1 2. The accuracy of Simpson s rule quadrature for a step size h is O(h 2 ) O(h 4 ) O(h 3 ) O(h 5 ) 3. For the matrix the Eigen values are 3 and
GATE: 2003 ME: Mechanical Engineering 1. is equal to 0 1 1 2. The accuracy of Simpson s rule quadrature for a step size h is O(h 2 ) O(h 4 ) O(h 3 ) O(h 5 ) 3. For the matrix the Eigen values are 3 and
 Question 9.1: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 10 5 m 2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 10 5 m 2 under a given load.
Question 9.1: A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 10 5 m 2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 10 5 m 2 under a given load.
