µ Differential Equations MAΘ National Convention 2017 For all questions, answer choice E) NOTA means that none of the above answers is correct.
|
|
|
- Gyles Greene
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 µ Differential Equations MAΘ National Convention 07 For all questions, answer choice E) NOTA means that none of the above answers is correct.. C) Since f (, ) = +, (0) = and h =. Use Euler s method, we have 0 + ( ) ( h) = (0) + hf (0, (0)) = + =. C) Since + ( ) ( h) = ( h) + hf ( h, ( h)) = + = + ( ) 9 ( h) = ( h) + hf ( h, ( h)) = + = f (, ) = +, (0) = and h =. Use Euler s method, The end of this Euler strut is ( h, ( h)) = ( h, (0) + hf (0, (0))) = (, ) The first slope is the average of 5 f(0, ) + f(, ) + f (0, (0)) + f ( h, ( h)) 9 = = =. 8. C) It is eas to see implies c = 5 so the solution is t u. D) Let =, =, t h e n 5. E) u = sin t t cost + c which means, so the solution is ( ) ( ) = = = + c ( ) 5 = +. sin = can be rewritten as = sin cos +.. Condition ( ) = ( 5) = 0 = ( ) = 0,,. = sin cos + c. Condition ( ) 6 uu sin t =. The general solution is t u (0) = impliesc = =. The correct answer is D.
2 µ Differential Equations MAΘ National Convention A) The integrating factor of given equation is cos e. Multipl cos e and integrating the given cos cos equation, we have the general solution is e = c e. Condition ( ) = implies c = so cos cos the solution is ( + ) e =. It is eas to see ( + ) e = passes through point (,). The correct answer is A. d 7. D) The integrating factor is e = e. The correct answer is D 8. A) The integrating factor ise d implies c = so the solution is e d =. The general solution is = =. It is eas to see () 0 = c +. Condition (0, ) =. The correct answer is A sin 9. C) The integrating factor is. The general solution is 0 t = dt + c. Using 0 t sin t condition (,0) implies c = 0 dt = 0Si() so the solution is = 0(Si(0) Si()). The 0 t correct answer is C. 0. C) The general solution is sin = ( + ) + c. Using condition (0, ) implies c = so the solution is sin = ( + ). It is eas to see (0) =, ( ) =. 6. A) Since + = + = = ( ) = = + c Using condition (,) implies c = so the solution is ( ) =. The correct answer is A.. D) Rewrite the given equation in the standard form case is given b a + =. So the function f in this a + f (, ) =. The given equation is Euler homogeneous if and onl if c( a + ) f (, ) is scale invariant. It is eas to see f ( c, c) = = f (, ) for c( ) an real number a. The correct answer is D. ( + ). B) Rewrite the given equation in the form =.The general solution is ( + ) ( + ) = ln + c. Condition (, 0) implies c = so = ln +, () =. ( + ) ( + ) The correct answer is B.
3 µ Differential Equations MAΘ National Convention 07. B) It is eas to see N(, ) = +, M (, ) = a + bsin.the given equation is an eact if and M N onl if = a = =. Therefore, constant a =. B is correct answer. 5. B) It is eas to see (, ) N = e + cos, M (, ) = e sin.the equation is eact since M N = e sin =. e + cos = c is the general. B is correct answer. M N + 6. B) It is eas to see N(, ) = +, M (, ) = + and = = N ( + ) which is independent. The integrating factor is. B is correct answer. N M 7. C) Since = = which is M we multipl the given equation b independent. The integrating factor can be, the resulting equation is 5 d + ( + 0 ) d = 0. The general solution is answer. 6 0 c + =. C is correct 8. D) + = 0 can be rewritten in standard form + = 0. Use pd e = d, we have pd d e e = = =. D is correct answer. d d ln 9. E) The auiliar equation of given equation is r + r 5 = 0 has roots r = or r = 5. The 5 general solution is = Ae + Be. Initial conditions implies A=, B=, we have 5 = e + e. No correct answer was provided so the correct answer is E. 0. D) The auiliar equation of given equation is r + = 0 has roots r = i or r = i. The general solution is = Acos + Bsin. Initial condition onl implies B =, we have = Acos + sin (0) =. D is correct answer.. After. C) It is eas to see =satisfies equation and =, we have correct answer. sin c = +. Integrating + = 0 =. Integrating =, we have cos c = +. D is
4 µ Differential Equations MAΘ National Convention 07. C) The critical point is f (, ) = ( + )( )( ) = 0 =, =, =. C is correct answer.. D) From = +, (0) =, (0) =, we have (0) = and = + (0) = + ( ) =. D is correct answer.. A) From =, (0) =, () =, we have = + c b integrating. Substituting () = into general solution implies c =. That is = +. On the other hand, we have = =. Therefore, (0) = =. A is correct answer. (0) 5. D) From =, we have () = = ( ) = ( ) + = ( )( ) Therefore, () (0) = ( )( ) = 0. D is correct answer. 6. B) From given equation, we have = = Therefore, =, n = =, = 6 = 6, =!. B is correct answer. ( n) n + 7. B) The auiliar equation of given equation is form of particular solution is B is correct answer. p r r + = 0 has roots r r =. Substituting into given equation, we have A = =. We assume the p = e. 8. E) From the given equation = ( + ) +, we have 0 ( ) = + +, which implies = c ( + ) and + + = 0. The solution is = ( + ) c + c or = + A. Condition () = ( + ) implies A= 0, c=, The solution is = or =. = passes points (0,0) and ( + ) (, ) while = passes points (,0). E is correct answer.
5 µ Differential Equations MAΘ National Convention A) The auiliar equation is r + r = 0 has roots r = r = 0, r =. We assume the given equation has a particular solution in the form = ( Asin + Bcos ) e. Substituting into the given equation, we have p = ( sin + cos ) e. A is correct answer D) From given equation cot cos, ( c cos + = ) = 5, we have sin =. Condition ( 9 cos ) = 5 implies sin =, ( 5 cos ) = implies T sin =. ( ( ) ( )) =. The correct answer is D. T = 6 p
Basics Concepts and Ideas First Order Differential Equations. Dr. Omar R. Daoud
 Basics Concepts and Ideas First Order Differential Equations Dr. Omar R. Daoud Differential Equations Man Phsical laws and relations appear mathematicall in the form of Differentia Equations The are one
Basics Concepts and Ideas First Order Differential Equations Dr. Omar R. Daoud Differential Equations Man Phsical laws and relations appear mathematicall in the form of Differentia Equations The are one
2 nd ORDER O.D.E.s SUBSTITUTIONS
 nd ORDER O.D.E.s SUBSTITUTIONS Question 1 (***+) d y y 8y + 16y = d d d, y 0, Find the general solution of the above differential equation by using the transformation equation t = y. Give the answer in
nd ORDER O.D.E.s SUBSTITUTIONS Question 1 (***+) d y y 8y + 16y = d d d, y 0, Find the general solution of the above differential equation by using the transformation equation t = y. Give the answer in
MAE 82 Engineering Mathematics
 Class otes : First Order Differential Equation on Linear AE 8 Engineering athematics Universe on Linear umerical Linearization on Linear Special Cases Analtical o General Solution Linear Analtical General
Class otes : First Order Differential Equation on Linear AE 8 Engineering athematics Universe on Linear umerical Linearization on Linear Special Cases Analtical o General Solution Linear Analtical General
Edexcel Further Pure 2
 Edecel Further Pure Second order differential equations Section : Non-homogeneous second order differential equations Notes and Eamples These notes contain subsections on Finding particular integrals Finding
Edecel Further Pure Second order differential equations Section : Non-homogeneous second order differential equations Notes and Eamples These notes contain subsections on Finding particular integrals Finding
ME 391 Mechanical Engineering Analysis
 Solve the following differential equations. ME 9 Mechanical Engineering Analysis Eam # Practice Problems Solutions. e u 5sin() with u(=)= We may rearrange this equation to e u 5sin() and note that it is
Solve the following differential equations. ME 9 Mechanical Engineering Analysis Eam # Practice Problems Solutions. e u 5sin() with u(=)= We may rearrange this equation to e u 5sin() and note that it is
Brief Notes on Differential Equations
 Brief Notes on Differential Equations (A) Searable First-Order Differential Equations Solve the following differential equations b searation of variables: (a) (b) Solution ( 1 ) (a) The ODE becomes d and
Brief Notes on Differential Equations (A) Searable First-Order Differential Equations Solve the following differential equations b searation of variables: (a) (b) Solution ( 1 ) (a) The ODE becomes d and
Simple Harmonic Motion Concept Questions
 Simple Harmonic Motion Concept Questions Question 1 Which of the following functions x(t) has a second derivative which is proportional to the negative of the function d x! " x? dt 1 1. x( t ) = at. x(
Simple Harmonic Motion Concept Questions Question 1 Which of the following functions x(t) has a second derivative which is proportional to the negative of the function d x! " x? dt 1 1. x( t ) = at. x(
Name Class. 5. Find the particular solution to given the general solution y C cos x and the. x 2 y
 10 Differential Equations Test Form A 1. Find the general solution to the first order differential equation: y 1 yy 0. 1 (a) (b) ln y 1 y ln y 1 C y y C y 1 C y 1 y C. Find the general solution to the
10 Differential Equations Test Form A 1. Find the general solution to the first order differential equation: y 1 yy 0. 1 (a) (b) ln y 1 y ln y 1 C y y C y 1 C y 1 y C. Find the general solution to the
INSTRUCTOR S SOLUTIONS MANUAL SECTION 17.1 (PAGE 902)
 INSTRUCTOR S SOLUTIONS MANUAL SECTION 7 PAGE 90 CHAPTER 7 ORDINARY DIFFEREN- TIAL EQUATIONS Section 7 Classifing Differential Equations page 90 = 5: st order, linear, homogeneous d d + = : nd order, linear,
INSTRUCTOR S SOLUTIONS MANUAL SECTION 7 PAGE 90 CHAPTER 7 ORDINARY DIFFEREN- TIAL EQUATIONS Section 7 Classifing Differential Equations page 90 = 5: st order, linear, homogeneous d d + = : nd order, linear,
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) MATHEMATICS Precalculus Martin Huard Fall 2007 Semester Review. 1. Simplify each expression. 4a b c. x y. 18x. x 2x.
 MATHEMATICS 0-009-0 Precalculus Martin Huard Fall 007. Simplif each epression. a) 8 8 g) ( ) ( j) m) a b c a b 8 8 8 n f) t t ) h) + + + + k) + + + n) + + + + + ( ) i) + n 8 + 9 z + l) 8 o) ( + ) ( + )
MATHEMATICS 0-009-0 Precalculus Martin Huard Fall 007. Simplif each epression. a) 8 8 g) ( ) ( j) m) a b c a b 8 8 8 n f) t t ) h) + + + + k) + + + n) + + + + + ( ) i) + n 8 + 9 z + l) 8 o) ( + ) ( + )
SPS Mathematical Methods
 SPS 2281 - Mathematical Methods Assignment No. 2 Deadline: 11th March 2015, before 4:45 p.m. INSTRUCTIONS: Answer the following questions. Check our answer for odd number questions at the back of the tetbook.
SPS 2281 - Mathematical Methods Assignment No. 2 Deadline: 11th March 2015, before 4:45 p.m. INSTRUCTIONS: Answer the following questions. Check our answer for odd number questions at the back of the tetbook.
(a) Show that there is a root α of f (x) = 0 in the interval [1.2, 1.3]. (2)
![(a) Show that there is a root α of f (x) = 0 in the interval [1.2, 1.3]. (2) (a) Show that there is a root α of f (x) = 0 in the interval [1.2, 1.3]. (2)](/thumbs/85/92620692.jpg) . f() = 4 cosec 4 +, where is in radians. (a) Show that there is a root α of f () = 0 in the interval [.,.3]. Show that the equation f() = 0 can be written in the form = + sin 4 Use the iterative formula
. f() = 4 cosec 4 +, where is in radians. (a) Show that there is a root α of f () = 0 in the interval [.,.3]. Show that the equation f() = 0 can be written in the form = + sin 4 Use the iterative formula
Methods in differential equations mixed exercise 7
 Methos in ifferential equations mie eercise 7 tan lnsec The integrating factor is e = e = sec Multiplying the equation by this factor gives: sec + ysectan= sec ( sec sec y = y sec= sec = tan+ c y= sin+
Methos in ifferential equations mie eercise 7 tan lnsec The integrating factor is e = e = sec Multiplying the equation by this factor gives: sec + ysectan= sec ( sec sec y = y sec= sec = tan+ c y= sin+
MATH Non-Euclidean Geometry Exercise Set #9 Solutions
 MATH 6118-090 Non-Euclidean Geometry Exercise Set #9 Solutions 1. Consider the doubly asymptotic triangle AMN in H where What is the image of AMN under the isometry γ 1? Use this to find the hyperbolic
MATH 6118-090 Non-Euclidean Geometry Exercise Set #9 Solutions 1. Consider the doubly asymptotic triangle AMN in H where What is the image of AMN under the isometry γ 1? Use this to find the hyperbolic
Assignment # 8, Math 370, Fall 2018 SOLUTIONS:
 Assignment # 8, Math 370, Fall 018 SOLUTIONS: Problem 1: Solve the equations (a) y y = 3x + x 4, (i) y(0) = 1, y (0) = 1, y (0) = 1. Characteristic equation: α 3 α = 0 so α 1, = 0 and α 3 =. y c = C 1
Assignment # 8, Math 370, Fall 018 SOLUTIONS: Problem 1: Solve the equations (a) y y = 3x + x 4, (i) y(0) = 1, y (0) = 1, y (0) = 1. Characteristic equation: α 3 α = 0 so α 1, = 0 and α 3 =. y c = C 1
Review for Ma 221 Final Exam
 Review for Ma 22 Final Exam The Ma 22 Final Exam from December 995.a) Solve the initial value problem 2xcosy 3x2 y dx x 3 x 2 sin y y dy 0 y 0 2 The equation is first order, for which we have techniques
Review for Ma 22 Final Exam The Ma 22 Final Exam from December 995.a) Solve the initial value problem 2xcosy 3x2 y dx x 3 x 2 sin y y dy 0 y 0 2 The equation is first order, for which we have techniques
Sec 4 Maths SET D PAPER 2
 S4MA Set D Paper Sec 4 Maths Exam papers with worked solutions SET D PAPER Compiled by THE MATHS CAFE P a g e Answer all questions. Write your answers and working on the separate Answer Paper provided.
S4MA Set D Paper Sec 4 Maths Exam papers with worked solutions SET D PAPER Compiled by THE MATHS CAFE P a g e Answer all questions. Write your answers and working on the separate Answer Paper provided.
Mathematics. Section B. CBSE XII Mathematics 2012 Solution (SET 2) General Instructions:
 CBSE XII Mathematics 0 Solution (SET ) General Instructions: Mathematics (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) All questions are compulsor. The question paper consists of 9 questions divided into three Sections A, B
CBSE XII Mathematics 0 Solution (SET ) General Instructions: Mathematics (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) All questions are compulsor. The question paper consists of 9 questions divided into three Sections A, B
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
 C1 Order and Degree of a Differential Equation : Order : Order is the highest differential appearing in a differential equation. MDE 1 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION Degree : It is determined b the degree of the
C1 Order and Degree of a Differential Equation : Order : Order is the highest differential appearing in a differential equation. MDE 1 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION Degree : It is determined b the degree of the
INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS. Mathematics, in general, is fundamentally the science of self-evident things. FELIX KLEIN
 . Introduction Mathematics, in general, is fundamentally the science of self-evident things. FELIX KLEIN In Chapter, we have studied that the inverse of a function f, denoted by f, eists if f is one-one
. Introduction Mathematics, in general, is fundamentally the science of self-evident things. FELIX KLEIN In Chapter, we have studied that the inverse of a function f, denoted by f, eists if f is one-one
ENGI 3424 Mid Term Test Solutions Page 1 of 9
 ENGI 344 Mid Term Test 07 0 Solutions Page of 9. The displacement st of the free end of a mass spring sstem beond the equilibrium position is governed b the ordinar differential equation d s ds 3t 6 5s
ENGI 344 Mid Term Test 07 0 Solutions Page of 9. The displacement st of the free end of a mass spring sstem beond the equilibrium position is governed b the ordinar differential equation d s ds 3t 6 5s
Math 217 Practice Exam 1. Page Which of the following differential equations is exact?
 Page 1 1. Which of the following differential equations is exact? (a) (3x x 3 )dx + (3x 3x 2 ) d = 0 (b) sin(x) dx + cos(x) d = 0 (c) x 2 x 2 = 0 (d) (1 + e x ) + (2 + xe x ) d = 0 CORRECT dx (e) e x dx
Page 1 1. Which of the following differential equations is exact? (a) (3x x 3 )dx + (3x 3x 2 ) d = 0 (b) sin(x) dx + cos(x) d = 0 (c) x 2 x 2 = 0 (d) (1 + e x ) + (2 + xe x ) d = 0 CORRECT dx (e) e x dx
 Q.1. Which one of the following is scalar quantity? Displacement Option Electric field Acceleration Work Correct Answer 4 w = F.ds; it does not have any direction, it s a scalar quantity. Q.. Which one
Q.1. Which one of the following is scalar quantity? Displacement Option Electric field Acceleration Work Correct Answer 4 w = F.ds; it does not have any direction, it s a scalar quantity. Q.. Which one
Mechanical Energy and Simple Harmonic Oscillator
 Mechanical Energy and Simple Harmonic Oscillator Simple Harmonic Motion Hooke s Law Define system, choose coordinate system. Draw free-body diagram. Hooke s Law! F spring =!kx ˆi! kx = d x m dt Checkpoint
Mechanical Energy and Simple Harmonic Oscillator Simple Harmonic Motion Hooke s Law Define system, choose coordinate system. Draw free-body diagram. Hooke s Law! F spring =!kx ˆi! kx = d x m dt Checkpoint
Paper Reference. Core Mathematics C3 Advanced. Thursday 11 June 2009 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes. Mathematical Formulae (Orange or Green)
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 6665/01 Edecel GCE Core Mathematics C3 Advanced Thursday 11 June 009 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for eamination Mathematical Formulae
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 6665/01 Edecel GCE Core Mathematics C3 Advanced Thursday 11 June 009 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for eamination Mathematical Formulae
Additional Topics in Differential Equations
 0537_cop6.qd 0/8/08 :6 PM Page 3 6 Additional Topics in Differential Equations In Chapter 6, ou studied differential equations. In this chapter, ou will learn additional techniques for solving differential
0537_cop6.qd 0/8/08 :6 PM Page 3 6 Additional Topics in Differential Equations In Chapter 6, ou studied differential equations. In this chapter, ou will learn additional techniques for solving differential
Math120R: Precalculus Final Exam Review, Fall 2017
 Math0R: Precalculus Final Eam Review, Fall 07 This study aid is intended to help you review for the final eam. Do not epect this review to be identical to the actual final eam. Refer to your course notes,
Math0R: Precalculus Final Eam Review, Fall 07 This study aid is intended to help you review for the final eam. Do not epect this review to be identical to the actual final eam. Refer to your course notes,
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION. Contents. Theory Exercise Exercise Exercise Exercise
 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION Contents Topic Page No. Theor 0-0 Eercise - 04-0 Eercise - - Eercise - - 7 Eercise - 4 8-9 Answer Ke 0 - Sllabus Formation of ordinar differential equations, solution of homogeneous
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION Contents Topic Page No. Theor 0-0 Eercise - 04-0 Eercise - - Eercise - - 7 Eercise - 4 8-9 Answer Ke 0 - Sllabus Formation of ordinar differential equations, solution of homogeneous
NST1A: Mathematics II (Course A) End of Course Summary, Lent 2011
 General notes Proofs NT1A: Mathematics II (Course A) End of Course ummar, Lent 011 tuart Dalziel (011) s.dalziel@damtp.cam.ac.uk This course is not about proofs, but rather about using different techniques.
General notes Proofs NT1A: Mathematics II (Course A) End of Course ummar, Lent 011 tuart Dalziel (011) s.dalziel@damtp.cam.ac.uk This course is not about proofs, but rather about using different techniques.
2017 FAMAT State Convention. Alpha Trigonometry
 017 FAMAT State Convention Alpha Trigonometry 1 On this test, select the best answer choice for each question. If you believe that the correct answer is not among the choices, or that the question is flawed,
017 FAMAT State Convention Alpha Trigonometry 1 On this test, select the best answer choice for each question. If you believe that the correct answer is not among the choices, or that the question is flawed,
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 SUMMER 8 EXAMINATION Important Instructions to eaminers: ) The answers should be eamined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. ) The model answer and the answer written
SUMMER 8 EXAMINATION Important Instructions to eaminers: ) The answers should be eamined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. ) The model answer and the answer written
2014 HSC Mathematics Extension 2 Marking Guidelines
 04 HSC Mathematics Extension Marking Guidelines Section I Multiple-choice Answer Key Question Answer D A 3 B 4 C 5 C 6 D 7 B 8 B 9 A 0 D BOSTES 04 HSC Mathematics Extension Marking Guidelines Section II
04 HSC Mathematics Extension Marking Guidelines Section I Multiple-choice Answer Key Question Answer D A 3 B 4 C 5 C 6 D 7 B 8 B 9 A 0 D BOSTES 04 HSC Mathematics Extension Marking Guidelines Section II
Section 7.2 Addition and Subtraction Identities. In this section, we begin expanding our repertoire of trigonometric identities.
 Section 7. Addition and Subtraction Identities 47 Section 7. Addition and Subtraction Identities In this section, we begin expanding our repertoire of trigonometric identities. Identities The sum and difference
Section 7. Addition and Subtraction Identities 47 Section 7. Addition and Subtraction Identities In this section, we begin expanding our repertoire of trigonometric identities. Identities The sum and difference
Mathematics 104 Fall Term 2006 Solutions to Final Exam. sin(ln t) dt = e x sin(x) dx.
 Mathematics 14 Fall Term 26 Solutions to Final Exam 1. Evaluate sin(ln t) dt. Solution. We first make the substitution t = e x, for which dt = e x. This gives sin(ln t) dt = e x sin(x). To evaluate the
Mathematics 14 Fall Term 26 Solutions to Final Exam 1. Evaluate sin(ln t) dt. Solution. We first make the substitution t = e x, for which dt = e x. This gives sin(ln t) dt = e x sin(x). To evaluate the
Substituting this into the differential equation and solving for u, we have. + u2. du = 3x + c. ( )
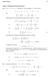 Worked Solutions 27 Chapter 6: Simplifying Through Substitution 6 a Let u = 3 + 3y + 2 Solving for y computing y we then see that 3y = u 3 2 y = u 3 2 3 = d [ u 3 2 3 = 3 Substituting this into the differential
Worked Solutions 27 Chapter 6: Simplifying Through Substitution 6 a Let u = 3 + 3y + 2 Solving for y computing y we then see that 3y = u 3 2 y = u 3 2 3 = d [ u 3 2 3 = 3 Substituting this into the differential
First Order Differential Equations f ( x,
 Chapter d dx First Order Differential Equations f ( x, ).1 Linear Equations; Method of Integrating Factors Usuall the general first order linear equations has the form p( t ) g ( t ) (1) where pt () and
Chapter d dx First Order Differential Equations f ( x, ).1 Linear Equations; Method of Integrating Factors Usuall the general first order linear equations has the form p( t ) g ( t ) (1) where pt () and
Slender Structures Load carrying principles
 Slender Structures Load carrying principles Continuously Elastic Supported (basic) Cases: Etension, shear Euler-Bernoulli beam (Winkler 1867) v2017-2 Hans Welleman 1 Content (preliminary schedule) Basic
Slender Structures Load carrying principles Continuously Elastic Supported (basic) Cases: Etension, shear Euler-Bernoulli beam (Winkler 1867) v2017-2 Hans Welleman 1 Content (preliminary schedule) Basic
Systems of Linear ODEs
 P a g e 1 Systems of Linear ODEs Systems of ordinary differential equations can be solved in much the same way as discrete dynamical systems if the differential equations are linear. We will focus here
P a g e 1 Systems of Linear ODEs Systems of ordinary differential equations can be solved in much the same way as discrete dynamical systems if the differential equations are linear. We will focus here
Important Instructions to the Examiners:
 (ISO/IEC - 7 - Certified) Winter Eamination Subject & Code: Applied Maths (7) Model Answer Page No: /6 Important Instructions to the Eaminers: ) The answers should be eamined by key words and not as word-to-word
(ISO/IEC - 7 - Certified) Winter Eamination Subject & Code: Applied Maths (7) Model Answer Page No: /6 Important Instructions to the Eaminers: ) The answers should be eamined by key words and not as word-to-word
SCATTERING. V 0 x a. V V x a. d Asin kx 2m dx. 2mE k. Acos x or Asin. A cosh x or Asinh
 SCATTERING Consider a particle of mass m moving along the x axis with energy E. It encounters a potential given by V0 x a VV x a 0 In the region x > a we have with d E Asinkx m dx In the region x < a we
SCATTERING Consider a particle of mass m moving along the x axis with energy E. It encounters a potential given by V0 x a VV x a 0 In the region x > a we have with d E Asinkx m dx In the region x < a we
Particular Solutions
 Particular Solutions Our eamples so far in this section have involved some constant of integration, K. We now move on to see particular solutions, where we know some boundar conditions and we substitute
Particular Solutions Our eamples so far in this section have involved some constant of integration, K. We now move on to see particular solutions, where we know some boundar conditions and we substitute
2.8 Implicit Differentiation
 .8 Implicit Differentiation Section.8 Notes Page 1 Before I tell ou what implicit differentiation is, let s start with an example: EXAMPLE: Find if x. This question is asking us to find the derivative
.8 Implicit Differentiation Section.8 Notes Page 1 Before I tell ou what implicit differentiation is, let s start with an example: EXAMPLE: Find if x. This question is asking us to find the derivative
Part: Frequency and Time Domain
 Numerical Methods Fourier Transform Pair Part: Frequency and Time Domain For more details on this topic Go to Clic on eyword Clic on Fourier Transform Pair You are free to Share to copy, distribute, display
Numerical Methods Fourier Transform Pair Part: Frequency and Time Domain For more details on this topic Go to Clic on eyword Clic on Fourier Transform Pair You are free to Share to copy, distribute, display
METHODS OF DIFFERENTIATION. Contents. Theory Objective Question Subjective Question 10. NCERT Board Questions
 METHODS OF DIFFERENTIATION Contents Topic Page No. Theor 0 0 Objective Question 0 09 Subjective Question 0 NCERT Board Questions Answer Ke 4 Sllabus Derivative of a function, derivative of the sum, difference,
METHODS OF DIFFERENTIATION Contents Topic Page No. Theor 0 0 Objective Question 0 09 Subjective Question 0 NCERT Board Questions Answer Ke 4 Sllabus Derivative of a function, derivative of the sum, difference,
TRIGONOMETRY ANSWERS FOR HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS ; 9) 2; 10) 0; 23) (, ); 24) 28) (, 4] ; 29) [7, )
![TRIGONOMETRY ANSWERS FOR HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS ; 9) 2; 10) 0; 23) (, ); 24) 28) (, 4] ; 29) [7, ) TRIGONOMETRY ANSWERS FOR HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS ; 9) 2; 10) 0; 23) (, ); 24) 28) (, 4] ; 29) [7, )](/thumbs/75/72244542.jpg) Homework Assignment # ) (,6) ) (, ) ) ( 8, ) ) (,0) ) (0, ) 6) (,0) 7) 8) 9) 0) 0 ) undefined ) ) ) ) 6 or 6) or Homework Assignment # ) ( 6) ) ( ) ) ( ) ) ) 6) ( ) or ( ) 7) ( ) or ( ) 8) 9) 0) or ( )
Homework Assignment # ) (,6) ) (, ) ) ( 8, ) ) (,0) ) (0, ) 6) (,0) 7) 8) 9) 0) 0 ) undefined ) ) ) ) 6 or 6) or Homework Assignment # ) ( 6) ) ( ) ) ( ) ) ) 6) ( ) or ( ) 7) ( ) or ( ) 8) 9) 0) or ( )
Lecture 38: Equations of Rigid-Body Motion
 Lecture 38: Equations of Rigid-Body Motion It s going to be easiest to find the equations of motion for the object in the body frame i.e., the frame where the axes are principal axes In general, we can
Lecture 38: Equations of Rigid-Body Motion It s going to be easiest to find the equations of motion for the object in the body frame i.e., the frame where the axes are principal axes In general, we can
C10.4 Notes and Formulas. (a) (b) (c) Figure 2 (a) A graph is symmetric with respect to the line θ =
 C10.4 Notes and Formulas symmetry tests A polar equation describes a curve on the polar grid. The graph of a polar equation can be evaluated for three types of symmetry, as shown in Figure. Figure A graph
C10.4 Notes and Formulas symmetry tests A polar equation describes a curve on the polar grid. The graph of a polar equation can be evaluated for three types of symmetry, as shown in Figure. Figure A graph
Integration Techniques for the AB exam
 For the AB eam, students need to: determine antiderivatives of the basic functions calculate antiderivatives of functions using u-substitution use algebraic manipulation to rewrite the integrand prior
For the AB eam, students need to: determine antiderivatives of the basic functions calculate antiderivatives of functions using u-substitution use algebraic manipulation to rewrite the integrand prior
APPM 2360: Midterm exam 1 February 15, 2017
 APPM 36: Midterm exam 1 February 15, 17 On the front of your Bluebook write: (1) your name, () your instructor s name, (3) your recitation section number and () a grading table. Text books, class notes,
APPM 36: Midterm exam 1 February 15, 17 On the front of your Bluebook write: (1) your name, () your instructor s name, (3) your recitation section number and () a grading table. Text books, class notes,
C3 papers June 2007 to 2008
 physicsandmathstutor.com June 007 C3 papers June 007 to 008 1. Find the exact solutions to the equations (a) ln x + ln 3 = ln 6, (b) e x + 3e x = 4. *N6109A04* physicsandmathstutor.com June 007 x + 3 9+
physicsandmathstutor.com June 007 C3 papers June 007 to 008 1. Find the exact solutions to the equations (a) ln x + ln 3 = ln 6, (b) e x + 3e x = 4. *N6109A04* physicsandmathstutor.com June 007 x + 3 9+
REFERENCE: CROFT & DAVISON CHAPTER 20 BLOCKS 1-3
 IV ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS REFERENCE: CROFT & DAVISON CHAPTER 0 BLOCKS 1-3 INTRODUCTION AND TERMINOLOGY INTRODUCTION A differential equation (d.e.) e) is an equation involving an unknown function
IV ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS REFERENCE: CROFT & DAVISON CHAPTER 0 BLOCKS 1-3 INTRODUCTION AND TERMINOLOGY INTRODUCTION A differential equation (d.e.) e) is an equation involving an unknown function
y »x 2» x 1. Find x if a = be 2x, lna = 7, and ln b = 3 HAL ln 7 HBL 2 HCL 7 HDL 4 HEL e 3
 . Find if a = be, lna =, and ln b = HAL ln HBL HCL HDL HEL e a = be and taing the natural log of both sides, we have ln a = ln b + ln e ln a = ln b + = + = B. lim b b b = HAL b HBL b HCL b HDL b HEL b
. Find if a = be, lna =, and ln b = HAL ln HBL HCL HDL HEL e a = be and taing the natural log of both sides, we have ln a = ln b + ln e ln a = ln b + = + = B. lim b b b = HAL b HBL b HCL b HDL b HEL b
Pure Further Mathematics 2. Revision Notes
 Pure Further Mathematics Revision Notes October 016 FP OCT 016 SDB Further Pure 1 Inequalities... 3 Algebraic solutions... 3 Graphical solutions... 4 Series Method of Differences... 5 3 Comple Numbers...
Pure Further Mathematics Revision Notes October 016 FP OCT 016 SDB Further Pure 1 Inequalities... 3 Algebraic solutions... 3 Graphical solutions... 4 Series Method of Differences... 5 3 Comple Numbers...
π (sinπ ) + cos π + C = C = 0 C = 1
 National Mu Alpha Theta Diff EQ page Mississippi, 00 Differential Equations Topic Test: Complete Solutions Note: For each problem, where there is no choice (e), assume (e) none of the above.. State the
National Mu Alpha Theta Diff EQ page Mississippi, 00 Differential Equations Topic Test: Complete Solutions Note: For each problem, where there is no choice (e), assume (e) none of the above.. State the
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. D) D: (-, 0) (0, )
 Midterm Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the domain and graph the function. ) G(t) = t - 3 ) 3 - -3 - - 3 - - -3
Midterm Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the domain and graph the function. ) G(t) = t - 3 ) 3 - -3 - - 3 - - -3
Problems with an # after the number are the only ones that a calculator is required for in the solving process.
 Instructions: Make sure all problems are numbered in order. (Level : If the problem had an *please skip that number) All work is in pencil, and is shown completely. Graphs are drawn out by hand. If you
Instructions: Make sure all problems are numbered in order. (Level : If the problem had an *please skip that number) All work is in pencil, and is shown completely. Graphs are drawn out by hand. If you
dy dx 1. If y 2 3xy = 18, then at the point H1, 3L is HAL 1 HBL 0 HCL 1 HDL 4 HEL 8 kx + 8 k + x The value of k is
 . If = 8, then d d at the point H, L is 0 HCL HDL HEL 8. The equation of the line tangent to the curve = k + 8 k + The value of k is at = is = +. HCL HDL HEL. If f HL = and f H L =, then find f HL d 0
. If = 8, then d d at the point H, L is 0 HCL HDL HEL 8. The equation of the line tangent to the curve = k + 8 k + The value of k is at = is = +. HCL HDL HEL. If f HL = and f H L =, then find f HL d 0
Lecture 38: Equations of Rigid-Body Motion
 Lecture 38: Equations of Rigid-Body Motion It s going to be easiest to find the equations of motion for the object in the body frame i.e., the frame where the axes are principal axes In general, we can
Lecture 38: Equations of Rigid-Body Motion It s going to be easiest to find the equations of motion for the object in the body frame i.e., the frame where the axes are principal axes In general, we can
2. Find the value of y for which the line through A and B has the given slope m: A(-2, 3), B(4, y), 2 3
 . Find an equation for the line that contains the points (, -) and (6, 9).. Find the value of y for which the line through A and B has the given slope m: A(-, ), B(4, y), m.. Find an equation for the line
. Find an equation for the line that contains the points (, -) and (6, 9).. Find the value of y for which the line through A and B has the given slope m: A(-, ), B(4, y), m.. Find an equation for the line
S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III. Applied Mathematics. Q.1 Attempt any TEN of the following : [20] Q.1(a)
![S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III. Applied Mathematics. Q.1 Attempt any TEN of the following : [20] Q.1(a) S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III. Applied Mathematics. Q.1 Attempt any TEN of the following : [20] Q.1(a)](/thumbs/82/85468378.jpg) S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III Applied Mathematics Time : Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : Q. Attempt any TEN of the following : [] Q.(a) Find the gradient of the tangent of the curve y at 4. []
S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III Applied Mathematics Time : Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : Q. Attempt any TEN of the following : [] Q.(a) Find the gradient of the tangent of the curve y at 4. []
Math 1B Final Exam, Solution. Prof. Mina Aganagic Lecture 2, Spring (6 points) Use substitution and integration by parts to find:
 Math B Final Eam, Solution Prof. Mina Aganagic Lecture 2, Spring 20 The eam is closed book, apart from a sheet of notes 8. Calculators are not allowed. It is your responsibility to write your answers clearly..
Math B Final Eam, Solution Prof. Mina Aganagic Lecture 2, Spring 20 The eam is closed book, apart from a sheet of notes 8. Calculators are not allowed. It is your responsibility to write your answers clearly..
90 Chapter 5 Logarithmic, Exponential, and Other Transcendental Functions. Name Class. (a) (b) ln x (c) (a) (b) (c) 1 x. y e (a) 0 (b) y.
 90 Chapter 5 Logarithmic, Eponential, and Other Transcendental Functions Test Form A Chapter 5 Name Class Date Section. Find the derivative: f ln. 6. Differentiate: y. ln y y y y. Find dy d if ey y. y
90 Chapter 5 Logarithmic, Eponential, and Other Transcendental Functions Test Form A Chapter 5 Name Class Date Section. Find the derivative: f ln. 6. Differentiate: y. ln y y y y. Find dy d if ey y. y
Math 21a Homework 07 Solutions Spring, 2014
 Math a Homework 7 Solutions Spring, 4. valuate the iterated integral. a) Stewart.7 # 6 ) e d d d We perform the iterated integral: e d d d e d d e d [ e [ ] 4 e + 4e. Note that we ve twice done an integral
Math a Homework 7 Solutions Spring, 4. valuate the iterated integral. a) Stewart.7 # 6 ) e d d d We perform the iterated integral: e d d d e d d e d [ e [ ] 4 e + 4e. Note that we ve twice done an integral
2016 SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS
 2016 SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS External Examination 2016 FOR OFFICE USE ONLY SUPERVISOR CHECK ATTACH SACE REGISTRATION NUMBER LABEL TO THIS BOX Graphics calculator Brand Model Computer software RE-MARKED
2016 SPECIALIST MATHEMATICS External Examination 2016 FOR OFFICE USE ONLY SUPERVISOR CHECK ATTACH SACE REGISTRATION NUMBER LABEL TO THIS BOX Graphics calculator Brand Model Computer software RE-MARKED
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chapter Practice Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the general solution to the eact differential equation. ) dy dt =
Chapter Practice Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the general solution to the eact differential equation. ) dy dt =
Logarithmic Functions
 Metropolitan Community College The Natural Logarithmic Function The natural logarithmic function is defined on (0, ) as ln x = x 1 1 t dt. Example 1. Evaluate ln 1. Example 1. Evaluate ln 1. Solution.
Metropolitan Community College The Natural Logarithmic Function The natural logarithmic function is defined on (0, ) as ln x = x 1 1 t dt. Example 1. Evaluate ln 1. Example 1. Evaluate ln 1. Solution.
Question No: 24 ( Marks: 10 ) parallel, perpendicular or none of these?
 ALL IN ONE Mega File MTH0 Midterm PAPERS, MCQz & subjective Created BY Farhan & Ali BS (cs) rd sem Hackers Group Mandi Bahauddin Remember us in your prayers Mindhacker4@gmail.com Hearthacker4@gmail.com
ALL IN ONE Mega File MTH0 Midterm PAPERS, MCQz & subjective Created BY Farhan & Ali BS (cs) rd sem Hackers Group Mandi Bahauddin Remember us in your prayers Mindhacker4@gmail.com Hearthacker4@gmail.com
EXACT EQUATIONS AND INTEGRATING FACTORS
 MAP- EXACT EQUATIONS AND INTEGRATING FACTORS First-order Differential Equations for Which We Can Find Eact Solutions Stu the patterns carefully. The first step of any solution is correct identification
MAP- EXACT EQUATIONS AND INTEGRATING FACTORS First-order Differential Equations for Which We Can Find Eact Solutions Stu the patterns carefully. The first step of any solution is correct identification
Objective Mathematics
 Chapter No - ( Area Bounded by Curves ). Normal at (, ) is given by : y y. f ( ) or f ( ). Area d ()() 7 Square units. Area (8)() 6 dy. ( ) d y c or f ( ) c f () c f ( ) As shown in figure, point P is
Chapter No - ( Area Bounded by Curves ). Normal at (, ) is given by : y y. f ( ) or f ( ). Area d ()() 7 Square units. Area (8)() 6 dy. ( ) d y c or f ( ) c f () c f ( ) As shown in figure, point P is
6.1: Reciprocal, Quotient & Pythagorean Identities
 Math Pre-Calculus 6.: Reciprocal, Quotient & Pythagorean Identities A trigonometric identity is an equation that is valid for all values of the variable(s) for which the equation is defined. In this chapter
Math Pre-Calculus 6.: Reciprocal, Quotient & Pythagorean Identities A trigonometric identity is an equation that is valid for all values of the variable(s) for which the equation is defined. In this chapter
Pre-Cal Review 13.2 Parent Functions and Their Domain
 Pre-Cal Review. Parent Functions and Their Domain Name: Date: Per: Parent functions are used to identif available domain and ranges. If ou can quickl think of what the function looks like, ou can quickl
Pre-Cal Review. Parent Functions and Their Domain Name: Date: Per: Parent functions are used to identif available domain and ranges. If ou can quickl think of what the function looks like, ou can quickl
7.5 Elastic Buckling Columns and Buckling
 7.5 Elastic Buckling The initial theory of the buckling of columns was worked out by Euler in 1757, a nice example of a theory preceding the application, the application mainly being for the later invented
7.5 Elastic Buckling The initial theory of the buckling of columns was worked out by Euler in 1757, a nice example of a theory preceding the application, the application mainly being for the later invented
PreCalculus First Semester Exam Review
 PreCalculus First Semester Eam Review Name You may turn in this eam review for % bonus on your eam if all work is shown (correctly) and answers are correct. Please show work NEATLY and bo in or circle
PreCalculus First Semester Eam Review Name You may turn in this eam review for % bonus on your eam if all work is shown (correctly) and answers are correct. Please show work NEATLY and bo in or circle
I. Degrees and Radians minutes equal 1 degree seconds equal 1 minute. 3. Also, 3600 seconds equal 1 degree. 3.
 0//0 I. Degrees and Radians A. A degree is a unit of angular measure equal to /80 th of a straight angle. B. A degree is broken up into minutes and seconds (in the DMS degree minute second sstem) as follows:.
0//0 I. Degrees and Radians A. A degree is a unit of angular measure equal to /80 th of a straight angle. B. A degree is broken up into minutes and seconds (in the DMS degree minute second sstem) as follows:.
Ordinary Differential Equations
 Ordinary Differential Equations (MA102 Mathematics II) Shyamashree Upadhyay IIT Guwahati Shyamashree Upadhyay ( IIT Guwahati ) Ordinary Differential Equations 1 / 15 Method of Undetermined Coefficients
Ordinary Differential Equations (MA102 Mathematics II) Shyamashree Upadhyay IIT Guwahati Shyamashree Upadhyay ( IIT Guwahati ) Ordinary Differential Equations 1 / 15 Method of Undetermined Coefficients
Board Answer Paper: MARCH 2014
 Board Answer Paper: MARCH 04 and Statistics SECTION I Q.. (A) Select and write the correct answer from the given alternatives in each of the following: i. (C) Let l 0, m 3, n be the direction cosines of
Board Answer Paper: MARCH 04 and Statistics SECTION I Q.. (A) Select and write the correct answer from the given alternatives in each of the following: i. (C) Let l 0, m 3, n be the direction cosines of
Sample Paper-05 Mathematics Class XII. Time allowed: 3 hours Answers Maximum Marks: 100. Section A. Section B
 Sample Paper-05 Mathematics Class XII Time allowed: hours Answers Maimum Marks: 00. No. (, ) R but (, ) R r. a () + ( ) + ( 5) 8 5 l, m, n 8 8 8. [0, ]. A A ( 8) 8 ( 6) A 8 Hence Prove tan cos sin sin
Sample Paper-05 Mathematics Class XII Time allowed: hours Answers Maimum Marks: 00. No. (, ) R but (, ) R r. a () + ( ) + ( 5) 8 5 l, m, n 8 8 8. [0, ]. A A ( 8) 8 ( 6) A 8 Hence Prove tan cos sin sin
MATH 120-Vectors, Law of Sinesw, Law of Cosines (20 )
 MATH 120-Vectors, Law of Sinesw, Law of Cosines (20 ) *Before we get into solving for oblique triangles, let's have a quick refresher on solving for right triangles' problems: Solving a Right Triangle
MATH 120-Vectors, Law of Sinesw, Law of Cosines (20 ) *Before we get into solving for oblique triangles, let's have a quick refresher on solving for right triangles' problems: Solving a Right Triangle
Ordinary Differential Equations
 ++++++++++ Ordinary Differential Equations Previous year Questions from 016 to 199 Ramanasri 016 S H O P NO- 4, 1 S T F L O O R, N E A R R A P I D F L O U R M I L L S, O L D R A J E N D E R N A G A R,
++++++++++ Ordinary Differential Equations Previous year Questions from 016 to 199 Ramanasri 016 S H O P NO- 4, 1 S T F L O O R, N E A R R A P I D F L O U R M I L L S, O L D R A J E N D E R N A G A R,
Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers x for which f (x) is a real number.
 997 AP Calculus BC: Section I, Part A 5 Minutes No Calculator Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers for which f () is a real number..
997 AP Calculus BC: Section I, Part A 5 Minutes No Calculator Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers for which f () is a real number..
ln 2 1 ln y x c y C x
 Lecure 14 Appendi B: Some sample problems from Boas Here are some soluions o he sample problems assigned for Chaper 8 8: 6 Soluion: We wan o find he soluion o he following firs order equaion using separaion
Lecure 14 Appendi B: Some sample problems from Boas Here are some soluions o he sample problems assigned for Chaper 8 8: 6 Soluion: We wan o find he soluion o he following firs order equaion using separaion
FP2 Mark Schemes from old P4, P5, P6 and FP1, FP2, FP3 papers (back to June 2002)
 FP Mark Schemes from old P, P5, P6 and FP, FP, FP papers (back to June 00) Please note that the following pages contain mark schemes for questions from past papers. The standard of the mark schemes is
FP Mark Schemes from old P, P5, P6 and FP, FP, FP papers (back to June 00) Please note that the following pages contain mark schemes for questions from past papers. The standard of the mark schemes is
Maximum and Minimum Values - 3.3
 Maimum and Minimum Values - 3.3. Critical Numbers Definition A point c in the domain of f is called a critical number offiff c or f c is not defined. Eample a. The graph of f is given below. Find all possible
Maimum and Minimum Values - 3.3. Critical Numbers Definition A point c in the domain of f is called a critical number offiff c or f c is not defined. Eample a. The graph of f is given below. Find all possible
Exact Equations. M(x,y) + N(x,y) y = 0, M(x,y) dx + N(x,y) dy = 0. M(x,y) + N(x,y) y = 0
 Eact Equations An eact equation is a first order differential equation that can be written in the form M(, + N(,, provided that there eists a function ψ(, such that = M (, and N(, = Note : Often the equation
Eact Equations An eact equation is a first order differential equation that can be written in the form M(, + N(,, provided that there eists a function ψ(, such that = M (, and N(, = Note : Often the equation
Exam 2 Solutions, Math March 17, ) = 1 2
 Eam Solutions, Math 56 March 7, 6. Use the trapezoidal rule with n = 3 to approimate (Note: The eact value of the integral is ln 5 +. (you do not need to verify this or use it in any way to complete this
Eam Solutions, Math 56 March 7, 6. Use the trapezoidal rule with n = 3 to approimate (Note: The eact value of the integral is ln 5 +. (you do not need to verify this or use it in any way to complete this
Unit #3 Rules of Differentiation Homework Packet
 Unit #3 Rules of Differentiation Homework Packet In the table below, a function is given. Show the algebraic analysis that leads to the derivative of the function. Find the derivative by the specified
Unit #3 Rules of Differentiation Homework Packet In the table below, a function is given. Show the algebraic analysis that leads to the derivative of the function. Find the derivative by the specified
Slope Fields and Differential Equations
 Slope Fields and Differential Equations Students should be able to: Draw a slope field at a specified number of points b hand. Sketch a solution that passes through a given point on a slope field. Match
Slope Fields and Differential Equations Students should be able to: Draw a slope field at a specified number of points b hand. Sketch a solution that passes through a given point on a slope field. Match
Torque and Simple Harmonic Motion
 Torque and Simple Harmonic Motion Recall: Fixed Axis Rotation Angle variable Angular velocity Angular acceleration Mass element Radius of orbit Kinematics!! " d# / dt! " d 2 # / dt 2!m i Moment of inertia
Torque and Simple Harmonic Motion Recall: Fixed Axis Rotation Angle variable Angular velocity Angular acceleration Mass element Radius of orbit Kinematics!! " d# / dt! " d 2 # / dt 2!m i Moment of inertia
THE COMPOUND ANGLE IDENTITIES
 TRIGONOMETRY THE COMPOUND ANGLE IDENTITIES Question 1 Prove the validity of each of the following trigonometric identities. a) sin x + cos x 4 4 b) cos x + + 3 sin x + 2cos x 3 3 c) cos 2x + + cos 2x cos
TRIGONOMETRY THE COMPOUND ANGLE IDENTITIES Question 1 Prove the validity of each of the following trigonometric identities. a) sin x + cos x 4 4 b) cos x + + 3 sin x + 2cos x 3 3 c) cos 2x + + cos 2x cos
(c) cos Arctan ( 3) ( ) PRECALCULUS ADVANCED REVIEW FOR FINAL FIRST SEMESTER
 PRECALCULUS ADVANCED REVIEW FOR FINAL FIRST SEMESTER Work the following on notebook paper ecept for the graphs. Do not use our calculator unless the problem tells ou to use it. Give three decimal places
PRECALCULUS ADVANCED REVIEW FOR FINAL FIRST SEMESTER Work the following on notebook paper ecept for the graphs. Do not use our calculator unless the problem tells ou to use it. Give three decimal places
( ) ( ) numerically using the DFT. The DTFT is defined. [ ]e. [ ] = x n. [ ]e j 2π Fn and the DFT is defined by X k. [ ]e j 2π kn/n with N = 5.
![( ) ( ) numerically using the DFT. The DTFT is defined. [ ]e. [ ] = x n. [ ]e j 2π Fn and the DFT is defined by X k. [ ]e j 2π kn/n with N = 5. ( ) ( ) numerically using the DFT. The DTFT is defined. [ ]e. [ ] = x n. [ ]e j 2π Fn and the DFT is defined by X k. [ ]e j 2π kn/n with N = 5.](/thumbs/88/116792961.jpg) ( /13) in the Ω form. ind the DTT of 8rect 3 n 2 8rect ( 3( n 2) /13) 40drcl(,5)e j 4π Let = Ω / 2π. Then 8rect 3 n 2 40 drcl( Ω / 2π,5)e j 2Ω ( /13) ind the DTT of 8rect 3( n 2) /13 by X = x n numerically
( /13) in the Ω form. ind the DTT of 8rect 3 n 2 8rect ( 3( n 2) /13) 40drcl(,5)e j 4π Let = Ω / 2π. Then 8rect 3 n 2 40 drcl( Ω / 2π,5)e j 2Ω ( /13) ind the DTT of 8rect 3( n 2) /13 by X = x n numerically
Ordinary Differential Equations (ODE)
 ++++++++++ Ordinary Differential Equations (ODE) Previous year Questions from 07 to 99 Ramanasri Institute W E B S I T E : M A T H E M A T I C S O P T I O N A L. C O M C O N T A C T : 8 7 5 0 7 0 6 6 /
++++++++++ Ordinary Differential Equations (ODE) Previous year Questions from 07 to 99 Ramanasri Institute W E B S I T E : M A T H E M A T I C S O P T I O N A L. C O M C O N T A C T : 8 7 5 0 7 0 6 6 /
Integration Techniques for the AB exam
 For the AB eam, students need to: determine antiderivatives of the basic functions calculate antiderivatives of functions using u-substitution use algebraic manipulation to rewrite the integrand prior
For the AB eam, students need to: determine antiderivatives of the basic functions calculate antiderivatives of functions using u-substitution use algebraic manipulation to rewrite the integrand prior
Math 170 Calculus I Final Exam Review Solutions
 Math 70 Calculus I Final Eam Review Solutions. Find the following its: (a (b (c (d 3 = + = 6 + 5 = 3 + 0 3 4 = sin( (e 0 cos( = (f 0 ln(sin( ln(tan( = ln( (g (h 0 + cot( ln( = sin(π/ = π. Find any values
Math 70 Calculus I Final Eam Review Solutions. Find the following its: (a (b (c (d 3 = + = 6 + 5 = 3 + 0 3 4 = sin( (e 0 cos( = (f 0 ln(sin( ln(tan( = ln( (g (h 0 + cot( ln( = sin(π/ = π. Find any values
APPENDIX D Rotation and the General Second-Degree Equation
 APPENDIX D Rotation and the General Second-Degree Equation Rotation of Aes Invariants Under Rotation After rotation of the - and -aes counterclockwise through an angle, the rotated aes are denoted as the
APPENDIX D Rotation and the General Second-Degree Equation Rotation of Aes Invariants Under Rotation After rotation of the - and -aes counterclockwise through an angle, the rotated aes are denoted as the
Candidates sitting FP2 may also require those formulae listed under Further Pure Mathematics FP1 and Core Mathematics C1 C4. e π.
 F Further IAL Pure PAPERS: Mathematics FP 04-6 AND SPECIMEN Candidates sitting FP may also require those formulae listed under Further Pure Mathematics FP and Core Mathematics C C4. Area of a sector A
F Further IAL Pure PAPERS: Mathematics FP 04-6 AND SPECIMEN Candidates sitting FP may also require those formulae listed under Further Pure Mathematics FP and Core Mathematics C C4. Area of a sector A
Calculus w/applications Prerequisite Packet Paint Branch High School Math Department
 Updated 6/014 The problems in this packet are designed to help you review topics from previous math courses that are important to your success in Calculus with Applications. It is important that you take
Updated 6/014 The problems in this packet are designed to help you review topics from previous math courses that are important to your success in Calculus with Applications. It is important that you take
Partial differentiation. Background mathematics review
 Partial differentiation Background mathematics review David Miller Partial differentiation Partial derivatives Background mathematics review David Miller Partial derivative Suppose we have a function f(,)
Partial differentiation Background mathematics review David Miller Partial differentiation Partial derivatives Background mathematics review David Miller Partial derivative Suppose we have a function f(,)
Dr. Abdulla Eid. Section 3.8 Derivative of the inverse function and logarithms 3 Lecture. Dr. Abdulla Eid. MATHS 101: Calculus I. College of Science
 Section 3.8 Derivative of the inverse function and logarithms 3 Lecture College of Science MATHS 101: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Logarithmic Differentiation 1 / 19 Topics 1 Inverse Functions (1
Section 3.8 Derivative of the inverse function and logarithms 3 Lecture College of Science MATHS 101: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Logarithmic Differentiation 1 / 19 Topics 1 Inverse Functions (1
Additional Topics in Differential Equations
 6 Additional Topics in Differential Equations 6. Eact First-Order Equations 6. Second-Order Homogeneous Linear Equations 6.3 Second-Order Nonhomogeneous Linear Equations 6.4 Series Solutions of Differential
6 Additional Topics in Differential Equations 6. Eact First-Order Equations 6. Second-Order Homogeneous Linear Equations 6.3 Second-Order Nonhomogeneous Linear Equations 6.4 Series Solutions of Differential
