Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
|
|
|
- Lorraine Small
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 C1 Order and Degree of a Differential Equation : Order : Order is the highest differential appearing in a differential equation. MDE 1 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION Degree : It is determined b the degree of the highest order derivative present in it after the differential equation is cleared of radicals and fractions so far as the derivatives are concerned. m d f (, ) m d n m d f(, ) d 1 1 n 1 nk d...fk (, ) d 1 m The above differential equation has the order m and degree n 1. Practice Problems : 1. The order of the differential equation whose general solution is given b = (c 1 + c )e 4 + c is 4 1. The degree of the differential equation, of which = 4a( + a) is a solution, is 1 of these. The order of the differential equation whose general solution is given b : c = c 1 cos( + c ) (c + c 4 ) a 5 c6 sin( c 7 ) is 4 5 [Answers : (1) d () b () c] 0 c e C Formation of Differential Equation : The differential equation corresponding to a famil of curve can be obtained b using the following steps : Identif the number of essential arbitrar constant in equation of curve. If arbitrar constants appear in addition, subtraction, multiplication or division, then we can club them to reduce into one new arbitrar constant. Differentiate the equation of curve till the required order. Eliminate the arbitrar constant from the equation of curve and additional equation obtained in step above. 1. The differential equation of the famil of curves = e (A cos + B sin ), where A and B are arbitrar constants, is d d d d 0 0 d d d d d d 0 of these d d [Answers : (1) c] C Solution of a Differentible Equation : The solution or the integral of a differential equation is, therefore, a relation between dependent and independent variables (free from derivatives) such that it satisfies the given differential equation. Einstein Classes, Unit No. 10, 10, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Etn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
2 MDE Practice Problems : 1. The solution of the differential equation, d d + d = 0 is constant constant constant. The solution of the differential equation; d ( e + e / ) = d (e / e ) is / = ln(e / + ) = ln(e / + ) + = ln(e / + ) = ln(e / + ) [Answers : (1) a () b] C4 Solution of elementar tpes of first order and first degree differential equations : d Equations Reducible to the Variables Separable form : Its general form is = f(a + b + c) d a, b 0. To solve this, put a + b + c = t. Homogeneous Differential Equation : C5 d f(, ) A differential equation of the form where f and g are homogeneous function of and, and d g(, ) of the same degree, is called homogeneous differential equation and can be solved easil b putting = v. Equations Reduciable to the Homogeneous form Equations of the form d d a b c A B C can be made homogeneous (in new variables X and Y) be substituting = X + h and = Y + k, where h and k are constants. Now, h and k are chosen such that ah + bk + c = 0, and Ah + Bk + C = 0; the differential equation can now be solved b putting Y = vx. C6 Linear differential equations of first order : The differential equation d P Q, is linear in, where P and Q are functions of. d Integrating Factor (I.F.) : It is an epression which when multiplied to a differential equation converts it into an eact form. I.F. for linear differential equation = Pd e (constant of integration will not be considered) d After multipling above equation b I.F. both side, it becomes (.e Pd ) = d.e Pd Q.e Pd d + c. Pd Qe Some times differential equation becomes linear if is taken as the dependent variable and as independent variable. The differential equation has then the following form : Einstein Classes, Unit No. 10, 10, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Etn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
3 MDE d P d 1 Q 1 Practice Problems :. where P 1 and Q 1 are functions of. pthe I.F. now is d 1. Solution of the differential equation ( ) is d P 1 d e = (c + ) = (c ) = (c ) = (c + ). The equation of the curve whose tangent at an point (, ) makes an angle tan 1 ( + ) with -ais and which passes through (1, ) is = 6e ( 1) ( 1) = 6e = 6e ( 1) None of these [Answers : (1) d () a] C7 Time saving tips : 1. The equation of the form d n P Q where P and Q are functions of onl and n is constant d n d 1n {n 0, 1} can be reduced to linear form b. P. Q and put 1 n = v. d. Some important integers factors (I.F.) for the quick solutions 1 d d (i) d tan (ii) d d dlog (iii) d( m n ) = m 1. n 1.(md + nd) (iv) 1 d d d log Einstein Classes, Unit No. 10, 10, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Etn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
4 MDE 4 SINGLE CORRECT CHOICE TYPE 1. The solution of the differential equation, d d + d = 0 is constant constant constant. The solution of the differential equation; d ( e + e / ) = d (e / e ) is / = ln(e / + ) = ln(e / + ) + = ln(e / + ) = ln(e / + ). The differential equation of all the conics whose aes coincide with the coordinate aes is given b d d d.. 0 d d d d d d.. 0 d d d d d d. 0 d d d d d d.. 0 d d d 4. For an differential function = f(); the value of d d d. d is d d The curve is satisfing the following differential equation d d ( ) 1 and d d = 0 for = 1, then the value of at = is 1 6. Tangent is drawn at an point P of a curve which passes through (1, 1) cutting -ais and -ais at A and B respectivel. If AP : BP = : 1, then the curve is passing through the point 1, 8 1, , 8, A curve is satisfing the following differential d d equation 0. The curve is d d passing through the point (, 1) (1, ) ( 1, 1) (, ) 8. Let f : R R and g : R R be twice differentiable functions satisfing f () g(),f (1) g(1) 4 and f() = g() = 9. The value of f(4) g(4) is equal to The order of the differential equation whose c e general solution is given b = (c 1 + c )e + c 4 is The solution of the differential equation d 1 cos is d 1 sin c 1 cos c 1 tan c Einstein Classes, Unit No. 10, 10, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Etn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
5 MDE 5 EXCERCISE BASED ON NEW PATTERN COMPREHENSION TYPE Comprehension-1 Consider the curve cos 1 1 sin t dt cos t sin dt (0 /) 1/ 8 1/ 8 and the curve satisfing the differential equation ( + )d = ( )d passing through (4, ) 1. The curve is parallel to -ais parallel to -ais is a straight line passing through the origin. The solution of the differential equation is + = 0 + = 0 + = 0. The area bounded b the curve and satisfing the differential equation is Comprension For a certain curve = f() satisfing d 6 4 ; f() has a local minimum value 5 d when = The equation of the curve is = = = The global maimum of f() is The global minimum of f() is MATRIX-MATCH TYPE Matching-1 Column - A Column - B (A) The order of the differe- (P) 1 ntial equation d d 1 is d d (B) The degree of the (Q) two differential equation d 1 is d (C) The degree of the (R) differential equation of the famil of all parabolas whose ais is the -ais, are respectivel (D) The order of the differen- (S) tial equation of the famil of the circles touching the -ais at the origin MULTIPLE CORRECT CHOICE TYPE d 1. The solution of ( + ) = 1 is d 1/ = + Ce / the solution of an equation which is reducible to linear equation. / = 1 + e / 1 / Ce. The differential equation of the curve for which the initial ordinate ( intercept) of an tangent is equal to the corresponding subnormal is linear is homogeneous has separable variables of these Einstein Classes, Unit No. 10, 10, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Etn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
6 MDE 6. Consider the following famil of curves = e (Acos + Bsin) where A, B are constant. Chooose the correct statments its differential equation has second order the differential equation of the curve is given b d d. d d its differential equation has third order of these 4. The equation of the curve passing through (1, ) whose differential equation is ( + )d = ( )d, is given b a + b + c = 0, then a = 1 b = c = 5 all the above 5. A student studing a foreign language has 50 verbs to memorize. The rate at which the student can memorize these verbs is proportional to the number of verbs remaining to be momorized; that is, if the student memorizes verbs in t minutes. d k(50 ) dt Assume that initiall no verbs are momorized, and suppose that 0 verbs are memorized in the first 0 minutes. Then The number of verbs memorized b the students in one hour is The number of verbs memorized b the students in one hour is 4.5 The number of hours after which the student have onl one verb left to memorize is.8 (Answers) EXCERCISE BASED ON NEW PATTERN COMPREHENSION TYPE 1. a. b. a 4. a 5. c 6. b MATRIX-MATCH TYPE 1. [A-Q; B-Q; C-P; D-P] MULTIPLE CORRECT CHOICE TYPE 1. a, b, d. a, b. a, b 4. a, b, c, d 5. a, b, c Einstein Classes, Unit No. 10, 10, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Etn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
7 MDE 7 INITIAL STEP EXERCISE (SUBJECTIVE) 1. Solve d d ( ) ( )( ). d. Solve. d 1 d d. Solve ( ) 0. d d 4. Determine all curve for which the ratios of the length of the segment intercept b an tangent on the - ais to the length of the radius vector is a constant. 5. Solve the equation (t)dt ( 1) t(t)dt, Given two curves : = f() passing through (0, 1) and f (t)dt passing through (0, 1/n). The tangent drawn to both the curves at the points with equal abscissas intersect on the -ais find the curve = f(). 7. A normal is drawn at a point P(, ) of a curve. It meets the -ais and the -ais in point A and B, 1 1 respectivel, such that 1, where O is OA OB the origin, find the equation of such a curve passing through (5, 4). 8. Solve the differential equation 9. Solve 10. Solve : ( )d = ( )d. d d d d Solve : cos (d d) sin (d d) 0 1. Reduce the equation d + ( + )d = 0 to a homogeneous equation and then solve it. d 14. If () (sin + log ), find (). d 15. Solve the following differential equation. 16. Solve : 17. Solve : (1 )d + ( 5 )d = 0. d (1 ) ( 1) a d f d d. f 18. The tangent at a point P of a curve meets the ais of in N; the line through P parallel to the ais of meets the ais of at M; O is the origin. If the area of MON is constant. Show that the curve is a hperbola. 19. Prove the orthogonal of curves 1, a b where is a parameter, is self orthogonal. 0. A and B are two separate reservoirs of water. The capacit of A is double that of B. Both the reservoirs are filled completel with water. Water is released simultaneousl from both the reservoirs. For each of the reservoirs, the rate of flow out at an instant is proportional to the quantit of water left in the reservoir. After one hour, the quantit of water in A is 1.5 times the quantit of water in B. After how man hours from the time of release of water, do both A and B have the same quantit of water? d e d 11. Solve : 1 e d e 1 d 0 Einstein Classes, Unit No. 10, 10, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Etn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
8 MDE 8 FINAL STEP EXERCISE (SUBJECTIVE) 1. Let u() and v() satisf the differential equations du dv p()u f () and p()v g(), d d where p(), f() and g() are continuous functions. If u( 1 ) > v ( 1 ) for some 1 and f() > g(), for all > 1, prove that an point (, ), where > 1, does not satisf the equation = u() and = v().. Find the pair of curves such that : the tangents drawn at points with equal abscissas intersect on the -ais. the normal drawn at points with equal abscissas intersect on -ais. one curve passes through (1, 1) and other passes through (, ). Determine the equation of the curve passing through the points (a, a) (a > 0) in the form = f() which satisf the differential equation; a d. d 4. Find the famil of curves, the subtangent at an point of which is the arithmetic mean of the co-ordinates of the point of tangenc. 5. There are 100 million litres of fluoridated water in the reservoir containing a cit s water suppl, and the water contains 700 kg of fluoride. To decrease the fluoride content, fresh water runs into the reservoir at the rate of million litres per da, and the miture of water and fluoride, kept uniform, runs out of the reservoir at the same rate. How man kilograms of fluoride are in the reservoir 60 das after the pure water started to flow into the reservoir? 6. Find the time required for a clindrical tank of radius r and height H to empt through a round of area a at the bottom. The flow through a hole is according to the law v(t) = u gh(t) and v(t) and h(t) are respectivel the velocit of flow through the hole and the height of the water level above the hole at time t and g is the acceleration due to gravit (u is a constant quantit). 7. Let f(, ) = 0 be a curve passing through the point (0, ) such that all the ras coming from a fied point source when reflected from it are parallel. Determine all such possible curves. 8. If the area of a triangle formed b tangent at an point on the curve and co-ordinates aes is constant, then form the differential equations of all such curves and hence prove that the curve is either a straight line or a hperbola. 9. A curve is such that the length of perpendicular from origin on the tangent at an point P of the curve is equal to the absciassa of P. Prove that the differen- d tial equation of the curve is 0 d and hence find the curve. 10. A curve passing through (1, ) has its slope at an point (, ) equal to. Find the area of the region bounded b the curve and the line 4 = The normal at an point P(, ) of a curve meets the -ais at G. If the distance of G from the origin be twice the abscissa of P, prove that the curve is a rectangular hperbola. ANSWERS (SINGLE CORRECT CHOICE TYPE) 1. a. b. d 4. a 5. d 6. a 7. b 8. c 9. d 10. a Einstein Classes, Unit No. 10, 10, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Etn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
9 MDE 9 ANSWERS SUBJECTIVE (INITIAL STEP EXERCISE) 1. X Y X 4 v 1 Ke Here, X = +, Y = and v = Y/X. = (1 ) + c (1 ) 1/4. ( + c 1 ) ( + ln c ) = 0 4. c k ln 5. c e 1/ 6. f() = e n 7. ( 1) + ( 1) = 5 8. log log c 1 9. k 10. log c e 11. c e 1. sin = c tan log[ ( ) ] c 14. cos sin cos log 9 c 15. c c 1 a 17. cf 0. log 4/ ANSWERS SUBJECTIVE (FINAL STEP EXERCISE).,. 1 e a 1 e k k 4. ( ) = c kg [approimatel] 6. r ua H g 7. = 4( + 1), = 4( 1) 9. + = c Einstein Classes, Unit No. 10, 10, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Etn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION
 MDE DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION NCERT Solved eamples upto the section 9. (Introduction) and 9. (Basic Concepts) : Eample : Find the order and degree, if defined, of each of the following differential equations
MDE DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION NCERT Solved eamples upto the section 9. (Introduction) and 9. (Basic Concepts) : Eample : Find the order and degree, if defined, of each of the following differential equations
Get Solution of These Packages & Learn by Video Tutorials on SHORT REVISION
 FREE Download Stu Pacage from website: www.teoclasses.com & www.mathsbsuhag.com Get Solution of These Pacages & Learn b Video Tutorials on www.mathsbsuhag.com SHORT REVISION DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF FIRST
FREE Download Stu Pacage from website: www.teoclasses.com & www.mathsbsuhag.com Get Solution of These Pacages & Learn b Video Tutorials on www.mathsbsuhag.com SHORT REVISION DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF FIRST
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION. Contents. Theory Exercise Exercise Exercise Exercise
 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION Contents Topic Page No. Theor 0-0 Eercise - 04-0 Eercise - - Eercise - - 7 Eercise - 4 8-9 Answer Ke 0 - Sllabus Formation of ordinar differential equations, solution of homogeneous
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION Contents Topic Page No. Theor 0-0 Eercise - 04-0 Eercise - - Eercise - - 7 Eercise - 4 8-9 Answer Ke 0 - Sllabus Formation of ordinar differential equations, solution of homogeneous
Lesson 9.1 Using the Distance Formula
 Lesson. Using the Distance Formula. Find the eact distance between each pair of points. a. (0, 0) and (, ) b. (0, 0) and (7, ) c. (, 8) and (, ) d. (, ) and (, 7) e. (, 7) and (8, ) f. (8, ) and (, 0)
Lesson. Using the Distance Formula. Find the eact distance between each pair of points. a. (0, 0) and (, ) b. (0, 0) and (7, ) c. (, 8) and (, ) d. (, ) and (, 7) e. (, 7) and (8, ) f. (8, ) and (, 0)
1 is equal to. 1 (B) a. (C) a (B) (D) 4. (C) P lies inside both C & E (D) P lies inside C but outside E. (B) 1 (D) 1
 Single Correct Q. Two mutuall perpendicular tangents of the parabola = a meet the ais in P and P. If S is the focus of the parabola then l a (SP ) is equal to (SP ) l (B) a (C) a Q. ABCD and EFGC are squares
Single Correct Q. Two mutuall perpendicular tangents of the parabola = a meet the ais in P and P. If S is the focus of the parabola then l a (SP ) is equal to (SP ) l (B) a (C) a Q. ABCD and EFGC are squares
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION
 MD DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION Sllabus : Ordinar diffrntial quations, thir ordr and dgr. Formation of diffrntial quations. Solution of diffrntial quations b th mthod of sparation of variabls, solution of homognous
MD DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION Sllabus : Ordinar diffrntial quations, thir ordr and dgr. Formation of diffrntial quations. Solution of diffrntial quations b th mthod of sparation of variabls, solution of homognous
Q.2 A, B and C are points in the xy plane such that A(1, 2) ; B (5, 6) and AC = 3BC. Then. (C) 1 1 or
 STRAIGHT LINE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. A variable rectangle PQRS has its sides parallel to fied directions. Q and S lie respectivel on the lines = a, = a and P lies on the ais. Then the locus of R
STRAIGHT LINE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. A variable rectangle PQRS has its sides parallel to fied directions. Q and S lie respectivel on the lines = a, = a and P lies on the ais. Then the locus of R
Circles MODULE - II Coordinate Geometry CIRCLES. Notice the path in which the tip of the hand of a watch moves. (see Fig. 11.1)
 CIRCLES Notice the path in which the tip of the hand of a watch moves. (see Fig..) 0 9 3 8 4 7 6 5 Fig.. Fig.. Again, notice the curve traced out when a nail is fied at a point and a thread of certain
CIRCLES Notice the path in which the tip of the hand of a watch moves. (see Fig..) 0 9 3 8 4 7 6 5 Fig.. Fig.. Again, notice the curve traced out when a nail is fied at a point and a thread of certain
Mathematics Extension 1
 013 HIGHER SCHL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATIN Mathematics Etension 1 General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time hours Write using black or blue pen Black pen is preferred Board-approved calculators
013 HIGHER SCHL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATIN Mathematics Etension 1 General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time hours Write using black or blue pen Black pen is preferred Board-approved calculators
1 (C) 1 e. Q.3 The angle between the tangent lines to the graph of the function f (x) = ( 2t 5)dt at the points where (C) (A) 0 (B) 1/2 (C) 1 (D) 3
 [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. Point 'A' lies on the curve y e and has the coordinate (, ) where > 0. Point B has the coordinates (, 0). If 'O' is the origin then the maimum area of the triangle AOB is (A)
[STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. Point 'A' lies on the curve y e and has the coordinate (, ) where > 0. Point B has the coordinates (, 0). If 'O' is the origin then the maimum area of the triangle AOB is (A)
EINSTEIN CLASSES. C B S E XIIth Board PRACTICE ASSIGNMENT
 EINSTEIN CLASSES P R E S E N T S C B S E XIIth Board PRACTICE ASSIGNMENT MATHEMATICS NOTE THE FOLLOWING POINTS : Einstein Classes is primarily concerned with the preparation of JEE-ADVANCE /JEE-MAIN/BITS/PMT/AIIMS
EINSTEIN CLASSES P R E S E N T S C B S E XIIth Board PRACTICE ASSIGNMENT MATHEMATICS NOTE THE FOLLOWING POINTS : Einstein Classes is primarily concerned with the preparation of JEE-ADVANCE /JEE-MAIN/BITS/PMT/AIIMS
1 k. cos tan? Higher Maths Non Calculator Practice Practice Paper A. 1. A sequence is defined by the recurrence relation u 2u 1, u 3.
 Higher Maths Non Calculator Practice Practice Paper A. A sequence is defined b the recurrence relation u u, u. n n What is the value of u?. The line with equation k 9 is parallel to the line with gradient
Higher Maths Non Calculator Practice Practice Paper A. A sequence is defined b the recurrence relation u u, u. n n What is the value of u?. The line with equation k 9 is parallel to the line with gradient
Partial Differential Equations
 ++++++++++ Partial Differential Equations Previous ear Questions from 016 to 199 Ramanasri 017 S H O P NO- 4, 1 S T F L O O R, N E A R R A P I D F L O U R M I L L S, O L D R A J E N D E R N A G A R, N
++++++++++ Partial Differential Equations Previous ear Questions from 016 to 199 Ramanasri 017 S H O P NO- 4, 1 S T F L O O R, N E A R R A P I D F L O U R M I L L S, O L D R A J E N D E R N A G A R, N
Answers for NSSH exam paper 2 type of questions, based on the syllabus part 2 (includes 16)
 Answers for NSSH eam paper type of questions, based on the syllabus part (includes 6) Section Integration dy 6 6. (a) Integrate with respect to : d y c ( )d or d The curve passes through P(,) so = 6/ +
Answers for NSSH eam paper type of questions, based on the syllabus part (includes 6) Section Integration dy 6 6. (a) Integrate with respect to : d y c ( )d or d The curve passes through P(,) so = 6/ +
Objective Mathematics
 . A tangent to the ellipse is intersected by a b the tangents at the etremities of the major ais at 'P' and 'Q' circle on PQ as diameter always passes through : (a) one fied point two fied points (c) four
. A tangent to the ellipse is intersected by a b the tangents at the etremities of the major ais at 'P' and 'Q' circle on PQ as diameter always passes through : (a) one fied point two fied points (c) four
CHAPTER 72 AREAS UNDER AND BETWEEN CURVES
 CHAPTER 7 AREAS UNDER AND BETWEEN CURVES EXERCISE 8 Page 77. Show by integration that the area of the triangle formed by the line y, the ordinates and and the -ais is 6 square units. A sketch of y is shown
CHAPTER 7 AREAS UNDER AND BETWEEN CURVES EXERCISE 8 Page 77. Show by integration that the area of the triangle formed by the line y, the ordinates and and the -ais is 6 square units. A sketch of y is shown
Mathematics Extension 2
 Student Number ABBOTSLEIGH AUGUST 007 YEAR ASSESSMENT 4 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE TRIAL EXAMINATION Mathematics Etension General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes. Working time 3 hours. Write using blue
Student Number ABBOTSLEIGH AUGUST 007 YEAR ASSESSMENT 4 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE TRIAL EXAMINATION Mathematics Etension General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes. Working time 3 hours. Write using blue
l (D) 36 (C) 9 x + a sin at which the tangent is parallel to x-axis lie on
 Dpp- to MATHEMATICS Dail Practice Problems Target IIT JEE 00 CLASS : XIII (VXYZ) DPP. NO.- to DPP- Q. If on a given base, a triangle be described such that the sum of the tangents of the base angles is
Dpp- to MATHEMATICS Dail Practice Problems Target IIT JEE 00 CLASS : XIII (VXYZ) DPP. NO.- to DPP- Q. If on a given base, a triangle be described such that the sum of the tangents of the base angles is
SPS Mathematical Methods
 SPS 2281 - Mathematical Methods Assignment No. 2 Deadline: 11th March 2015, before 4:45 p.m. INSTRUCTIONS: Answer the following questions. Check our answer for odd number questions at the back of the tetbook.
SPS 2281 - Mathematical Methods Assignment No. 2 Deadline: 11th March 2015, before 4:45 p.m. INSTRUCTIONS: Answer the following questions. Check our answer for odd number questions at the back of the tetbook.
CALCULUS BASIC SUMMER REVIEW
 NAME CALCULUS BASIC SUMMER REVIEW Slope of a non vertical line: rise y y y m run Point Slope Equation: y y m( ) The slope is m and a point on your line is, ). ( y Slope-Intercept Equation: y m b slope=
NAME CALCULUS BASIC SUMMER REVIEW Slope of a non vertical line: rise y y y m run Point Slope Equation: y y m( ) The slope is m and a point on your line is, ). ( y Slope-Intercept Equation: y m b slope=
MA123, Chapter 1: Equations, functions and graphs (pp. 1-15)
 MA123, Chapter 1: Equations, functions and graphs (pp. 1-15) Date: Chapter Goals: Identif solutions to an equation. Solve an equation for one variable in terms of another. What is a function? Understand
MA123, Chapter 1: Equations, functions and graphs (pp. 1-15) Date: Chapter Goals: Identif solutions to an equation. Solve an equation for one variable in terms of another. What is a function? Understand
CHAPTER 6 Differential Equations
 CHAPTER 6 Differential Equations Section 6. Slope Fields and Euler s Method.............. 55 Section 6. Differential Equations: Growth and Deca........ 557 Section 6. Separation of Variables and the Logistic
CHAPTER 6 Differential Equations Section 6. Slope Fields and Euler s Method.............. 55 Section 6. Differential Equations: Growth and Deca........ 557 Section 6. Separation of Variables and the Logistic
The region enclosed by the curve of f and the x-axis is rotated 360 about the x-axis. Find the volume of the solid formed.
 Section A ln. Let g() =, for > 0. ln Use the quotient rule to show that g ( ). 3 (b) The graph of g has a maimum point at A. Find the -coordinate of A. (Total 7 marks) 6. Let h() =. Find h (0). cos 3.
Section A ln. Let g() =, for > 0. ln Use the quotient rule to show that g ( ). 3 (b) The graph of g has a maimum point at A. Find the -coordinate of A. (Total 7 marks) 6. Let h() =. Find h (0). cos 3.
Drill Exercise Differential equations by abhijit kumar jha DRILL EXERCISE - 1 DRILL EXERCISE - 2. e x, where c 1
 DRILL EXERCISE -. Find the order and degree (if defined) of the differential equation 5 4 3 d y d y. Find the order and degree (if defined) of the differential equation n. 3. Find the order and degree
DRILL EXERCISE -. Find the order and degree (if defined) of the differential equation 5 4 3 d y d y. Find the order and degree (if defined) of the differential equation n. 3. Find the order and degree
(6, 4, 0) = (3, 2, 0). Find the equation of the sphere that has the line segment from P to Q as a diameter.
 Solutions Review for Eam #1 Math 1260 1. Consider the points P = (2, 5, 1) and Q = (4, 1, 1). (a) Find the distance from P to Q. Solution. dist(p, Q) = (4 2) 2 + (1 + 5) 2 + (1 + 1) 2 = 4 + 36 + 4 = 44
Solutions Review for Eam #1 Math 1260 1. Consider the points P = (2, 5, 1) and Q = (4, 1, 1). (a) Find the distance from P to Q. Solution. dist(p, Q) = (4 2) 2 + (1 + 5) 2 + (1 + 1) 2 = 4 + 36 + 4 = 44
e x for x 0. Find the coordinates of the point of inflexion and justify that it is a point of inflexion. (Total 7 marks)
 Chapter 0 Application of differential calculus 014 GDC required 1. Consider the curve with equation f () = e for 0. Find the coordinates of the point of infleion and justify that it is a point of infleion.
Chapter 0 Application of differential calculus 014 GDC required 1. Consider the curve with equation f () = e for 0. Find the coordinates of the point of infleion and justify that it is a point of infleion.
π (sinπ ) + cos π + C = C = 0 C = 1
 National Mu Alpha Theta Diff EQ page Mississippi, 00 Differential Equations Topic Test: Complete Solutions Note: For each problem, where there is no choice (e), assume (e) none of the above.. State the
National Mu Alpha Theta Diff EQ page Mississippi, 00 Differential Equations Topic Test: Complete Solutions Note: For each problem, where there is no choice (e), assume (e) none of the above.. State the
Add Math (4047) Paper 2
 1. Solve the simultaneous equations 5 and 1. [5]. (i) Sketch the graph of, showing the coordinates of the points where our graph meets the coordinate aes. [] Solve the equation 10, giving our answer correct
1. Solve the simultaneous equations 5 and 1. [5]. (i) Sketch the graph of, showing the coordinates of the points where our graph meets the coordinate aes. [] Solve the equation 10, giving our answer correct
MATHEMATICS 4 UNIT (ADDITIONAL) HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION. Time allowed Three hours (Plus 5 minutes reading time)
 N E W S O U T H W A L E S HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION 997 MATHEMATICS UNIT (ADDITIONAL) Time allowed Three hours (Plus 5 minutes reading time) DIRECTIONS TO CANDIDATES Attempt ALL questions.
N E W S O U T H W A L E S HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION 997 MATHEMATICS UNIT (ADDITIONAL) Time allowed Three hours (Plus 5 minutes reading time) DIRECTIONS TO CANDIDATES Attempt ALL questions.
UNCORRECTED. To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relations: y = x 1 y 2 = x
 5A galler of graphs Objectives To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relations: = = = (rectangular hperbola) + = (circle). To be able to sketch the graphs of these relations. To be able
5A galler of graphs Objectives To recognise the rules of a number of common algebraic relations: = = = (rectangular hperbola) + = (circle). To be able to sketch the graphs of these relations. To be able
1. First-order ODE s
 18.03 EXERCISES 1. First-order ODE s 1A. Introduction; Separation of Variables 1A-1. Verif that each of the following ODE s has the indicated solutions (c i,a are constants): a) 2 + = 0, = c 1 e x +c 2
18.03 EXERCISES 1. First-order ODE s 1A. Introduction; Separation of Variables 1A-1. Verif that each of the following ODE s has the indicated solutions (c i,a are constants): a) 2 + = 0, = c 1 e x +c 2
1985 AP Calculus AB: Section I
 985 AP Calculus AB: Section I 9 Minutes No Calculator Notes: () In this eamination, ln denotes the natural logarithm of (that is, logarithm to the base e). () Unless otherwise specified, the domain of
985 AP Calculus AB: Section I 9 Minutes No Calculator Notes: () In this eamination, ln denotes the natural logarithm of (that is, logarithm to the base e). () Unless otherwise specified, the domain of
(a) Use washer cross sections: a washer has
 Section 8 V / (sec tan ) / / / / [ tan sec tan ] / / (sec sec tan + tan ) + tan sec / + A( ) s w (sec tan ), and / V (sec tan ), which b / same method as in part (a) equals A cross section has width w
Section 8 V / (sec tan ) / / / / [ tan sec tan ] / / (sec sec tan + tan ) + tan sec / + A( ) s w (sec tan ), and / V (sec tan ), which b / same method as in part (a) equals A cross section has width w
Math 323 Exam 2 - Practice Problem Solutions. 2. Given the vectors a = 1,2,0, b = 1,0,2, and c = 0,1,1, compute the following:
 Math 323 Eam 2 - Practice Problem Solutions 1. Given the vectors a = 2,, 1, b = 3, 2,4, and c = 1, 4,, compute the following: (a) A unit vector in the direction of c. u = c c = 1, 4, 1 4 =,, 1+16+ 17 17
Math 323 Eam 2 - Practice Problem Solutions 1. Given the vectors a = 2,, 1, b = 3, 2,4, and c = 1, 4,, compute the following: (a) A unit vector in the direction of c. u = c c = 1, 4, 1 4 =,, 1+16+ 17 17
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
 MCN COMPLEX NUMBER C The complex number Complex number is denoted by ie = a + ib, where a is called as real part of (denoted by Re and b is called as imaginary part of (denoted by Im Here i =, also i =,
MCN COMPLEX NUMBER C The complex number Complex number is denoted by ie = a + ib, where a is called as real part of (denoted by Re and b is called as imaginary part of (denoted by Im Here i =, also i =,
Math 101 chapter six practice exam MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Math 1 chapter si practice eam MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Which equation matches the given calculator-generated graph and description?
Math 1 chapter si practice eam MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Which equation matches the given calculator-generated graph and description?
MATHEMATICS 200 December 2011 Final Exam Solutions
 MATHEMATICS December 11 Final Eam Solutions 1. Consider the function f(, ) e +4. (a) Draw a contour map of f, showing all tpes of level curves that occur. (b) Find the equation of the tangent plane to
MATHEMATICS December 11 Final Eam Solutions 1. Consider the function f(, ) e +4. (a) Draw a contour map of f, showing all tpes of level curves that occur. (b) Find the equation of the tangent plane to
Methods of Integration
 U96-b)! Use the substitution u = - to evaluate U95-b)! 4 Methods of Integration d. Evaluate 9 d using the substitution u = + 9. UNIT MATHEMATICS (HSC) METHODS OF INTEGRATION CSSA «8» U94-b)! Use the substitution
U96-b)! Use the substitution u = - to evaluate U95-b)! 4 Methods of Integration d. Evaluate 9 d using the substitution u = + 9. UNIT MATHEMATICS (HSC) METHODS OF INTEGRATION CSSA «8» U94-b)! Use the substitution
PREPARED BY: ER. VINEET LOOMBA (B.TECH. IIT ROORKEE) 60 Best JEE Main and Advanced Level Problems (IIT-JEE). Prepared by IITians.
 www. Class XI TARGET : JEE Main/Adv PREPARED BY: ER. VINEET LOOMBA (B.TECH. IIT ROORKEE) ALP ADVANCED LEVEL PROBLEMS Straight Lines 60 Best JEE Main and Advanced Level Problems (IIT-JEE). Prepared b IITians.
www. Class XI TARGET : JEE Main/Adv PREPARED BY: ER. VINEET LOOMBA (B.TECH. IIT ROORKEE) ALP ADVANCED LEVEL PROBLEMS Straight Lines 60 Best JEE Main and Advanced Level Problems (IIT-JEE). Prepared b IITians.
Review for Test 2 Calculus I
 Review for Test Calculus I Find the absolute etreme values of the function on the interval. ) f() = -, - ) g() = - + 8-6, ) F() = -,.5 ) F() =, - 6 5) g() = 7-8, - Find the absolute etreme values of the
Review for Test Calculus I Find the absolute etreme values of the function on the interval. ) f() = -, - ) g() = - + 8-6, ) F() = -,.5 ) F() =, - 6 5) g() = 7-8, - Find the absolute etreme values of the
Coordinate geometry. + bx + c. Vertical asymptote. Sketch graphs of hyperbolas (including asymptotic behaviour) from the general
 A Sketch graphs of = a m b n c where m = or and n = or B Reciprocal graphs C Graphs of circles and ellipses D Graphs of hperbolas E Partial fractions F Sketch graphs using partial fractions Coordinate
A Sketch graphs of = a m b n c where m = or and n = or B Reciprocal graphs C Graphs of circles and ellipses D Graphs of hperbolas E Partial fractions F Sketch graphs using partial fractions Coordinate
CHAPTER 2: Partial Derivatives. 2.2 Increments and Differential
 CHAPTER : Partial Derivatives.1 Definition of a Partial Derivative. Increments and Differential.3 Chain Rules.4 Local Etrema.5 Absolute Etrema 1 Chapter : Partial Derivatives.1 Definition of a Partial
CHAPTER : Partial Derivatives.1 Definition of a Partial Derivative. Increments and Differential.3 Chain Rules.4 Local Etrema.5 Absolute Etrema 1 Chapter : Partial Derivatives.1 Definition of a Partial
1998 AP Calculus AB: Section I, Part A
 55 Minutes No Calculator Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers for which f () is a real number.. What is the -coordinate of the point
55 Minutes No Calculator Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers for which f () is a real number.. What is the -coordinate of the point
 4 TANGENTS AND NORMALS OBJECTIVE PROBLEMS. For a curve = f(x) if = x then the angle made b the tangent at (,) with OX is ) π / 4 ) π / tan tan / ) 4). The angle made b the tangent line at (,) on the curve
4 TANGENTS AND NORMALS OBJECTIVE PROBLEMS. For a curve = f(x) if = x then the angle made b the tangent at (,) with OX is ) π / 4 ) π / tan tan / ) 4). The angle made b the tangent line at (,) on the curve
HEAT-3 APPLICATION OF DERIVATIVES BY ABHIJIT KUMAR JHA MAX-MARKS-(112(3)+20(5)=436)
 HEAT- APPLICATION OF DERIVATIVES BY ABHIJIT KUMAR JHA TIME-(HRS) Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) MAX-MARKS-(()+0(5)=6) Q. Suppose & are the point of maimum and the point of minimum
HEAT- APPLICATION OF DERIVATIVES BY ABHIJIT KUMAR JHA TIME-(HRS) Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) MAX-MARKS-(()+0(5)=6) Q. Suppose & are the point of maimum and the point of minimum
TO THE STUDENT: To best prepare for Test 4, do all the problems on separate paper. The answers are given at the end of the review sheet.
 MATH TEST 4 REVIEW TO THE STUDENT: To best prepare for Test 4, do all the problems on separate paper. The answers are given at the end of the review sheet. PART NON-CALCULATOR DIRECTIONS: The problems
MATH TEST 4 REVIEW TO THE STUDENT: To best prepare for Test 4, do all the problems on separate paper. The answers are given at the end of the review sheet. PART NON-CALCULATOR DIRECTIONS: The problems
2. Find the value of y for which the line through A and B has the given slope m: A(-2, 3), B(4, y), 2 3
 . Find an equation for the line that contains the points (, -) and (6, 9).. Find the value of y for which the line through A and B has the given slope m: A(-, ), B(4, y), m.. Find an equation for the line
. Find an equation for the line that contains the points (, -) and (6, 9).. Find the value of y for which the line through A and B has the given slope m: A(-, ), B(4, y), m.. Find an equation for the line
Integration Past Papers Unit 2 Outcome 2
 Integration Past Papers Unit 2 utcome 2 Multiple Choice Questions Each correct answer in this section is worth two marks.. Evaluate A. 2 B. 7 6 C. 2 D. 2 4 /2 d. 2. The diagram shows the area bounded b
Integration Past Papers Unit 2 utcome 2 Multiple Choice Questions Each correct answer in this section is worth two marks.. Evaluate A. 2 B. 7 6 C. 2 D. 2 4 /2 d. 2. The diagram shows the area bounded b
MATH 115: Final Exam Review. Can you find the distance between two points and the midpoint of a line segment? (1.1)
 MATH : Final Eam Review Can ou find the distance between two points and the midpoint of a line segment? (.) () Consider the points A (,) and ( 6, ) B. (a) Find the distance between A and B. (b) Find the
MATH : Final Eam Review Can ou find the distance between two points and the midpoint of a line segment? (.) () Consider the points A (,) and ( 6, ) B. (a) Find the distance between A and B. (b) Find the
Review Exercises for Chapter 2
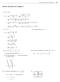 Review Eercises for Chapter 367 Review Eercises for Chapter. f 1 1 f f f lim lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 lim lim 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4. 8. f f f f lim lim lim lim lim f 4, 1 4, if < if (a) Nonremovable
Review Eercises for Chapter 367 Review Eercises for Chapter. f 1 1 f f f lim lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 lim lim 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4. 8. f f f f lim lim lim lim lim f 4, 1 4, if < if (a) Nonremovable
Answer Key 1973 BC 1969 BC 24. A 14. A 24. C 25. A 26. C 27. C 28. D 29. C 30. D 31. C 13. C 12. D 12. E 3. A 32. B 27. E 34. C 14. D 25. B 26.
 Answer Key 969 BC 97 BC. C. E. B. D 5. E 6. B 7. D 8. C 9. D. A. B. E. C. D 5. B 6. B 7. B 8. E 9. C. A. B. E. D. C 5. A 6. C 7. C 8. D 9. C. D. C. B. A. D 5. A 6. B 7. D 8. A 9. D. E. D. B. E. E 5. E.
Answer Key 969 BC 97 BC. C. E. B. D 5. E 6. B 7. D 8. C 9. D. A. B. E. C. D 5. B 6. B 7. B 8. E 9. C. A. B. E. D. C 5. A 6. C 7. C 8. D 9. C. D. C. B. A. D 5. A 6. B 7. D 8. A 9. D. E. D. B. E. E 5. E.
QUESTION BANK ON. CONIC SECTION (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola)
 QUESTION BANK ON CONIC SECTION (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola) Question bank on Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. Two mutually perpendicular tangents
QUESTION BANK ON CONIC SECTION (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola) Question bank on Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. Two mutually perpendicular tangents
Vector-Valued Functions
 Vector-Valued Functions 1 Parametric curves 8 ' 1 6 1 4 8 1 6 4 1 ' 4 6 8 Figure 1: Which curve is a graph of a function? 1 4 6 8 1 8 1 6 4 1 ' 4 6 8 Figure : A graph of a function: = f() 8 ' 1 6 4 1 1
Vector-Valued Functions 1 Parametric curves 8 ' 1 6 1 4 8 1 6 4 1 ' 4 6 8 Figure 1: Which curve is a graph of a function? 1 4 6 8 1 8 1 6 4 1 ' 4 6 8 Figure : A graph of a function: = f() 8 ' 1 6 4 1 1
Solutions to O Level Add Math paper
 Solutions to O Level Add Math paper 4. Bab food is heated in a microwave to a temperature of C. It subsequentl cools in such a wa that its temperature, T C, t minutes after removal from the microwave,
Solutions to O Level Add Math paper 4. Bab food is heated in a microwave to a temperature of C. It subsequentl cools in such a wa that its temperature, T C, t minutes after removal from the microwave,
Grade 12 Mathematics. unimaths.co.za. Revision Questions. (Including Solutions)
 Grade 12 Mathematics Revision Questions (Including Solutions) unimaths.co.za Get read for universit mathematics b downloading free lessons taken from Unimaths Intro Workbook. Visit unimaths.co.za for more
Grade 12 Mathematics Revision Questions (Including Solutions) unimaths.co.za Get read for universit mathematics b downloading free lessons taken from Unimaths Intro Workbook. Visit unimaths.co.za for more
Integration Techniques for the AB exam
 For the AB eam, students need to: determine antiderivatives of the basic functions calculate antiderivatives of functions using u-substitution use algebraic manipulation to rewrite the integrand prior
For the AB eam, students need to: determine antiderivatives of the basic functions calculate antiderivatives of functions using u-substitution use algebraic manipulation to rewrite the integrand prior
MATH 150/GRACEY PRACTICE FINAL. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MATH 0/GRACEY PRACTICE FINAL Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Choose the graph that represents the given function without using
MATH 0/GRACEY PRACTICE FINAL Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Choose the graph that represents the given function without using
Identifying second degree equations
 Chapter 7 Identifing second degree equations 71 The eigenvalue method In this section we appl eigenvalue methods to determine the geometrical nature of the second degree equation a 2 + 2h + b 2 + 2g +
Chapter 7 Identifing second degree equations 71 The eigenvalue method In this section we appl eigenvalue methods to determine the geometrical nature of the second degree equation a 2 + 2h + b 2 + 2g +
Learning Goals. College of Charleston Department of Mathematics Math 101: College Algebra Final Exam Review Problems 1
 College of Charleston Department of Mathematics Math 0: College Algebra Final Eam Review Problems Learning Goals (AL-) Arithmetic of Real and Comple Numbers: I can classif numbers as natural, integer,
College of Charleston Department of Mathematics Math 0: College Algebra Final Eam Review Problems Learning Goals (AL-) Arithmetic of Real and Comple Numbers: I can classif numbers as natural, integer,
2. (i) Find the equation of the circle which passes through ( 7, 1) and has centre ( 4, 3).
 Circle 1. (i) Find the equation of the circle with centre ( 7, 3) and of radius 10. (ii) Find the centre of the circle 2x 2 + 2y 2 + 6x + 8y 1 = 0 (iii) What is the radius of the circle 3x 2 + 3y 2 + 5x
Circle 1. (i) Find the equation of the circle with centre ( 7, 3) and of radius 10. (ii) Find the centre of the circle 2x 2 + 2y 2 + 6x + 8y 1 = 0 (iii) What is the radius of the circle 3x 2 + 3y 2 + 5x
ZETA MATHS. Higher Mathematics Revision Checklist
 ZETA MATHS Higher Mathematics Revision Checklist Contents: Epressions & Functions Page Logarithmic & Eponential Functions Addition Formulae. 3 Wave Function.... 4 Graphs of Functions. 5 Sets of Functions
ZETA MATHS Higher Mathematics Revision Checklist Contents: Epressions & Functions Page Logarithmic & Eponential Functions Addition Formulae. 3 Wave Function.... 4 Graphs of Functions. 5 Sets of Functions
Functions of Several Variables
 Chapter 1 Functions of Several Variables 1.1 Introduction A real valued function of n variables is a function f : R, where the domain is a subset of R n. So: for each ( 1,,..., n ) in, the value of f is
Chapter 1 Functions of Several Variables 1.1 Introduction A real valued function of n variables is a function f : R, where the domain is a subset of R n. So: for each ( 1,,..., n ) in, the value of f is
Name Please print your name as it appears on the class roster.
 Berkele Cit College Practice Problems Math 1 Precalculus - Final Eam Preparation Name Please print our name as it appears on the class roster. SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes
Berkele Cit College Practice Problems Math 1 Precalculus - Final Eam Preparation Name Please print our name as it appears on the class roster. SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes
COORDINATE GEOMETRY BASIC CONCEPTS AND FORMULAE. To find the length of a line segment joining two points A(x 1, y 1 ) and B(x 2, y 2 ), use
 COORDINATE GEOMETRY BASIC CONCEPTS AND FORMULAE I. Length of a Line Segment: The distance between two points A ( x1, 1 ) B ( x, ) is given b A B = ( x x1) ( 1) To find the length of a line segment joining
COORDINATE GEOMETRY BASIC CONCEPTS AND FORMULAE I. Length of a Line Segment: The distance between two points A ( x1, 1 ) B ( x, ) is given b A B = ( x x1) ( 1) To find the length of a line segment joining
PART A: Answer in the space provided. Each correct answer is worth one mark each.
 PART A: Answer in the space provided. Each correct answer is worth one mark each. 1. Find the slope of the tangent to the curve at the point (,6). =. If the tangent line to the curve k( ) = is horizontal,
PART A: Answer in the space provided. Each correct answer is worth one mark each. 1. Find the slope of the tangent to the curve at the point (,6). =. If the tangent line to the curve k( ) = is horizontal,
MATHEMATICS HSC Course Assessment Task 3 (Trial Examination) June 21, QUESTION Total MARKS
 MATHEMATICS 0 HSC Course Assessment Task (Trial Eamination) June, 0 General instructions Working time hours. (plus 5 minutes reading time) Write using blue or black pen. Where diagrams are to be sketched,
MATHEMATICS 0 HSC Course Assessment Task (Trial Eamination) June, 0 General instructions Working time hours. (plus 5 minutes reading time) Write using blue or black pen. Where diagrams are to be sketched,
C H A P T E R 9 Topics in Analytic Geometry
 C H A P T E R Topics in Analtic Geometr Section. Circles and Parabolas.................... 77 Section. Ellipses........................... 7 Section. Hperbolas......................... 7 Section. Rotation
C H A P T E R Topics in Analtic Geometr Section. Circles and Parabolas.................... 77 Section. Ellipses........................... 7 Section. Hperbolas......................... 7 Section. Rotation
Instructor: Imelda Valencia Course: A3 Honors Pre Calculus
 Student: Date: Instructor: Imelda Valencia Course: A3 Honors Pre Calculus 01 017 Assignment: Summer Homework for those who will be taking FOCA 017 01 onl available until Sept. 15 1. Write the epression
Student: Date: Instructor: Imelda Valencia Course: A3 Honors Pre Calculus 01 017 Assignment: Summer Homework for those who will be taking FOCA 017 01 onl available until Sept. 15 1. Write the epression
FILL THE ANSWER HERE
 HOM ASSIGNMNT # 0 STRAIGHT OBJCTIV TYP. If A, B & C are matrices of order such that A =, B = 9, C =, then (AC) is equal to - (A) 8 6. The length of the sub-tangent to the curve y = (A) 8 0 0 8 ( ) 5 5
HOM ASSIGNMNT # 0 STRAIGHT OBJCTIV TYP. If A, B & C are matrices of order such that A =, B = 9, C =, then (AC) is equal to - (A) 8 6. The length of the sub-tangent to the curve y = (A) 8 0 0 8 ( ) 5 5
1998 AP Calculus AB: Section I, Part A
 998 AP Calculus AB: 55 Minutes No Calculator Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers for which f () is a real number.. What is the -coordinate
998 AP Calculus AB: 55 Minutes No Calculator Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers for which f () is a real number.. What is the -coordinate
Ordinary Differential Equations (ODE)
 ++++++++++ Ordinary Differential Equations (ODE) Previous year Questions from 07 to 99 Ramanasri Institute W E B S I T E : M A T H E M A T I C S O P T I O N A L. C O M C O N T A C T : 8 7 5 0 7 0 6 6 /
++++++++++ Ordinary Differential Equations (ODE) Previous year Questions from 07 to 99 Ramanasri Institute W E B S I T E : M A T H E M A T I C S O P T I O N A L. C O M C O N T A C T : 8 7 5 0 7 0 6 6 /
Lines, Conics, Tangents, Limits and the Derivative
 Lines, Conics, Tangents, Limits and te Derivative Te Straigt Line An two points on te (,) plane wen joined form a line segment. If te line segment is etended beond te two points ten it is called a straigt
Lines, Conics, Tangents, Limits and te Derivative Te Straigt Line An two points on te (,) plane wen joined form a line segment. If te line segment is etended beond te two points ten it is called a straigt
ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 3 Solutions [Multiple Integration; Lines of Force]
![ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 3 Solutions [Multiple Integration; Lines of Force] ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 3 Solutions [Multiple Integration; Lines of Force]](/thumbs/84/89723886.jpg) ENGI 44 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Facult of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set Solutions [Multiple Integration; Lines of Force]. Evaluate D da over the triangular region D that is bounded
ENGI 44 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Facult of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set Solutions [Multiple Integration; Lines of Force]. Evaluate D da over the triangular region D that is bounded
POINT. Preface. The concept of Point is very important for the study of coordinate
 POINT Preface The concept of Point is ver important for the stud of coordinate geometr. This chapter deals with various forms of representing a Point and several associated properties. The concept of coordinates
POINT Preface The concept of Point is ver important for the stud of coordinate geometr. This chapter deals with various forms of representing a Point and several associated properties. The concept of coordinates
The details of the derivation of the equations of conics are com-
 Part 6 Conic sections Introduction Consider the double cone shown in the diagram, joined at the verte. These cones are right circular cones in the sense that slicing the double cones with planes at right-angles
Part 6 Conic sections Introduction Consider the double cone shown in the diagram, joined at the verte. These cones are right circular cones in the sense that slicing the double cones with planes at right-angles
y = f(x + 4) a) Example: A repeating X by using two linear equations y = ±x. b) Example: y = f(x - 3). The translation is
 Answers Chapter Function Transformations. Horizontal and Vertical Translations, pages to. a h, k h, k - c h -, k d h 7, k - e h -, k. a A (-,, B (-,, C (-,, D (,, E (, A (-, -, B (-,, C (,, D (, -, E (,
Answers Chapter Function Transformations. Horizontal and Vertical Translations, pages to. a h, k h, k - c h -, k d h 7, k - e h -, k. a A (-,, B (-,, C (-,, D (,, E (, A (-, -, B (-,, C (,, D (, -, E (,
MATHEMATICS PAPER IB COORDINATE GEOMETRY(2D &3D) AND CALCULUS. Note: This question paper consists of three sections A,B and C.
 MATHEMATICS PAPER IB COORDINATE GEOMETRY(D &3D) AND CALCULUS. TIME : 3hrs Ma. Marks.75 Note: This question paper consists of three sections A,B and C. SECTION A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS. 0X =0.
MATHEMATICS PAPER IB COORDINATE GEOMETRY(D &3D) AND CALCULUS. TIME : 3hrs Ma. Marks.75 Note: This question paper consists of three sections A,B and C. SECTION A VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS. 0X =0.
10.4 Nonlinear Inequalities and Systems of Inequalities. OBJECTIVES 1 Graph a Nonlinear Inequality. 2 Graph a System of Nonlinear Inequalities.
 Section 0. Nonlinear Inequalities and Sstems of Inequalities 6 CONCEPT EXTENSIONS For the eercises below, see the Concept Check in this section.. Without graphing, how can ou tell that the graph of + =
Section 0. Nonlinear Inequalities and Sstems of Inequalities 6 CONCEPT EXTENSIONS For the eercises below, see the Concept Check in this section.. Without graphing, how can ou tell that the graph of + =
2.2 SEPARABLE VARIABLES
 44 CHAPTER FIRST-ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 6 Consider the autonomous DE 6 Use our ideas from Problem 5 to find intervals on the -ais for which solution curves are concave up and intervals for which
44 CHAPTER FIRST-ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 6 Consider the autonomous DE 6 Use our ideas from Problem 5 to find intervals on the -ais for which solution curves are concave up and intervals for which
NO CALCULATORS: 1. Find A) 1 B) 0 C) D) 2. Find the points of discontinuity of the function y of discontinuity.
 AP CALCULUS BC NO CALCULATORS: MIDTERM REVIEW. Find lim 7 7 9. B) C) D). Find the points of discontinuit of the function of discontinuit. 9. For each discontinuit identif the tpe A. Removable discontinuit
AP CALCULUS BC NO CALCULATORS: MIDTERM REVIEW. Find lim 7 7 9. B) C) D). Find the points of discontinuit of the function of discontinuit. 9. For each discontinuit identif the tpe A. Removable discontinuit
SYSTEM OF CIRCLES OBJECTIVES (a) Touch each other internally (b) Touch each other externally
 SYSTEM OF CIRCLES OBJECTIVES. A circle passes through (0, 0) and (, 0) and touches the circle x + y = 9, then the centre of circle is (a) (c) 3,, (b) (d) 3,, ±. The equation of the circle having its centre
SYSTEM OF CIRCLES OBJECTIVES. A circle passes through (0, 0) and (, 0) and touches the circle x + y = 9, then the centre of circle is (a) (c) 3,, (b) (d) 3,, ±. The equation of the circle having its centre
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS
 005-CE A MATH HONG KONG CERTIFICATE OF EDUCATION EXAMINATION 005 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS :00 pm 5:0 pm (½ hours) This paper must be answered in English 1. Answer ALL questions in Section A and any FOUR
005-CE A MATH HONG KONG CERTIFICATE OF EDUCATION EXAMINATION 005 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS :00 pm 5:0 pm (½ hours) This paper must be answered in English 1. Answer ALL questions in Section A and any FOUR
CHAPTER 11 Vector-Valued Functions
 CHAPTER Vector-Valued Functions Section. Vector-Valued Functions...................... 9 Section. Differentiation and Integration of Vector-Valued Functions.... Section. Velocit and Acceleration.....................
CHAPTER Vector-Valued Functions Section. Vector-Valued Functions...................... 9 Section. Differentiation and Integration of Vector-Valued Functions.... Section. Velocit and Acceleration.....................
(a) Show that there is a root α of f (x) = 0 in the interval [1.2, 1.3]. (2)
![(a) Show that there is a root α of f (x) = 0 in the interval [1.2, 1.3]. (2) (a) Show that there is a root α of f (x) = 0 in the interval [1.2, 1.3]. (2)](/thumbs/85/92620692.jpg) . f() = 4 cosec 4 +, where is in radians. (a) Show that there is a root α of f () = 0 in the interval [.,.3]. Show that the equation f() = 0 can be written in the form = + sin 4 Use the iterative formula
. f() = 4 cosec 4 +, where is in radians. (a) Show that there is a root α of f () = 0 in the interval [.,.3]. Show that the equation f() = 0 can be written in the form = + sin 4 Use the iterative formula
2014 HSC Mathematics Extension 1 Marking Guidelines
 04 HSC Mathematics Etension Marking Guidelines Section I Multiple-choice Answer Key Question Answer D A 3 C 4 D 5 B 6 B 7 A 8 D 9 C 0 C BOSTES 04 HSC Mathematics Etension Marking Guidelines Section II
04 HSC Mathematics Etension Marking Guidelines Section I Multiple-choice Answer Key Question Answer D A 3 C 4 D 5 B 6 B 7 A 8 D 9 C 0 C BOSTES 04 HSC Mathematics Etension Marking Guidelines Section II
Exact Differential Equations. The general solution of the equation is f x, y C. If f has continuous second partials, then M y 2 f
 APPENDIX C Additional Topics in Differential Equations APPENDIX C. Eact First-Order Equations Eact Differential Equations Integrating Factors Eact Differential Equations In Chapter 6, ou studied applications
APPENDIX C Additional Topics in Differential Equations APPENDIX C. Eact First-Order Equations Eact Differential Equations Integrating Factors Eact Differential Equations In Chapter 6, ou studied applications
PROBLEMS 13 - APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES Page 1
 PROBLEMS - APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES Page ( ) Water seeps out of a conical filter at the constant rate of 5 cc / sec. When the height of water level in the cone is 5 cm, find the rate at which the height
PROBLEMS - APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES Page ( ) Water seeps out of a conical filter at the constant rate of 5 cc / sec. When the height of water level in the cone is 5 cm, find the rate at which the height
17.3. Parametric Curves. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Parametric Curves 17.3 Introduction In this section we eamine et another wa of defining curves - the parametric description. We shall see that this is, in some was, far more useful than either the Cartesian
Parametric Curves 17.3 Introduction In this section we eamine et another wa of defining curves - the parametric description. We shall see that this is, in some was, far more useful than either the Cartesian
Secondary School Mathematics & Science Competition. Mathematics. Date: 1 st May, 2013
 Secondary School Mathematics & Science Competition Mathematics Date: 1 st May, 01 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes 1. Write your Name (both in English and Chinese), Name of School, Form, Date, Se, Language,
Secondary School Mathematics & Science Competition Mathematics Date: 1 st May, 01 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes 1. Write your Name (both in English and Chinese), Name of School, Form, Date, Se, Language,
IB Practice - Calculus - Differentiation Applications (V2 Legacy)
 IB Math High Level Year - Calc Practice: Differentiation Applications IB Practice - Calculus - Differentiation Applications (V Legacy). A particle moves along a straight line. When it is a distance s from
IB Math High Level Year - Calc Practice: Differentiation Applications IB Practice - Calculus - Differentiation Applications (V Legacy). A particle moves along a straight line. When it is a distance s from
*X100/301* X100/301 MATHEMATICS HIGHER. Units 1, 2 and 3 Paper 1 (Non-calculator) Read Carefully
 X00/0 NATINAL QUALIFICATINS 007 TUESDAY, 5 MAY 9.00 AM 0.0 AM MATHEMATICS HIGHER Units, and Paper (Non-calculator) Read Carefull Calculators ma NT be used in this paper. Full credit will be given onl where
X00/0 NATINAL QUALIFICATINS 007 TUESDAY, 5 MAY 9.00 AM 0.0 AM MATHEMATICS HIGHER Units, and Paper (Non-calculator) Read Carefull Calculators ma NT be used in this paper. Full credit will be given onl where
y=5 y=1+x 2 AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions
 AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions. Which of the following integrals correctly corresponds to the area of the shaded region in the figure to the right? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)
AP Calculus Chapter 5 Testbank Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions. Which of the following integrals correctly corresponds to the area of the shaded region in the figure to the right? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)
Graphs and polynomials
 1 1A The inomial theorem 1B Polnomials 1C Division of polnomials 1D Linear graphs 1E Quadratic graphs 1F Cuic graphs 1G Quartic graphs Graphs and polnomials AreAS of STud Graphs of polnomial functions
1 1A The inomial theorem 1B Polnomials 1C Division of polnomials 1D Linear graphs 1E Quadratic graphs 1F Cuic graphs 1G Quartic graphs Graphs and polnomials AreAS of STud Graphs of polnomial functions
Edexcel GCE A Level Maths. Further Maths 3 Coordinate Systems
 Edecel GCE A Level Maths Further Maths 3 Coordinate Sstems Edited b: K V Kumaran kumarmaths.weebl.com 1 kumarmaths.weebl.com kumarmaths.weebl.com 3 kumarmaths.weebl.com 4 kumarmaths.weebl.com 5 1. An ellipse
Edecel GCE A Level Maths Further Maths 3 Coordinate Sstems Edited b: K V Kumaran kumarmaths.weebl.com 1 kumarmaths.weebl.com kumarmaths.weebl.com 3 kumarmaths.weebl.com 4 kumarmaths.weebl.com 5 1. An ellipse
Review of Essential Skills and Knowledge
 Review of Essential Skills and Knowledge R Eponent Laws...50 R Epanding and Simplifing Polnomial Epressions...5 R 3 Factoring Polnomial Epressions...5 R Working with Rational Epressions...55 R 5 Slope
Review of Essential Skills and Knowledge R Eponent Laws...50 R Epanding and Simplifing Polnomial Epressions...5 R 3 Factoring Polnomial Epressions...5 R Working with Rational Epressions...55 R 5 Slope
Math 121. Practice Questions Chapters 2 and 3 Fall Find the other endpoint of the line segment that has the given endpoint and midpoint.
 Math 11. Practice Questions Chapters and 3 Fall 01 1. Find the other endpoint of the line segment that has the given endpoint and midpoint. Endpoint ( 7, ), Midpoint (, ). Solution: Let (, ) denote the
Math 11. Practice Questions Chapters and 3 Fall 01 1. Find the other endpoint of the line segment that has the given endpoint and midpoint. Endpoint ( 7, ), Midpoint (, ). Solution: Let (, ) denote the
STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE. Functions & Graphs
 STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Functions & Graphs Contents Functions and Relations... 1 Interval Notation... 3 Graphs: Linear Functions... 5 Lines and Gradients... 7 Graphs: Quadratic
STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Functions & Graphs Contents Functions and Relations... 1 Interval Notation... 3 Graphs: Linear Functions... 5 Lines and Gradients... 7 Graphs: Quadratic
2016 SEC 4 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS CW & HW
 FEB EXAM 06 SEC 4 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS CW & HW Find the values of k for which the line y 6 is a tangent to the curve k 7 y. Find also the coordinates of the point at which this tangent touches the curve.
FEB EXAM 06 SEC 4 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS CW & HW Find the values of k for which the line y 6 is a tangent to the curve k 7 y. Find also the coordinates of the point at which this tangent touches the curve.
MARIS STELLA HIGH SCHOOL PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION 2
 Class Inde Number Name MRIS STELL HIGH SCHOOL PRELIMINRY EXMINTION DDITIONL MTHEMTICS 406/0 8 September 008 Paper hours 0minutes dditional Materials: nswer Paper (6 Sheets RED THESE INSTRUCTIONS FIRST
Class Inde Number Name MRIS STELL HIGH SCHOOL PRELIMINRY EXMINTION DDITIONL MTHEMTICS 406/0 8 September 008 Paper hours 0minutes dditional Materials: nswer Paper (6 Sheets RED THESE INSTRUCTIONS FIRST
Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers x for which f (x) is a real number.
 997 AP Calculus BC: Section I, Part A 5 Minutes No Calculator Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers for which f () is a real number..
997 AP Calculus BC: Section I, Part A 5 Minutes No Calculator Note: Unless otherwise specified, the domain of a function f is assumed to be the set of all real numbers for which f () is a real number..
