Probabilistic modeling. The slides are closely adapted from Subhransu Maji s slides
|
|
|
- Oliver Brendan Kennedy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Probabilistic modeling The slides are closely adapted from Subhransu Maji s slides
2 Overview So far the models and algorithms you have learned about are relatively disconnected Probabilistic modeling framework unites the two Learning can be viewed as statistical inference Two kinds of data models Generative Conditional Two kinds of probability models Parametric Non-parametric 2
3 Classification by density estimation The data is generated according to a distribution D Suppose you had access to D, then classification becomes simple: This is the Bayes optimal classifier which achieves the smallest expected loss among all classifiers : expected loss of a predictor Unfortunately, we don t have access to the distribution 3
4 Classification by density estimation This suggests that one way to learn a classifier is to estimate D Training data parametric distribution Estimation We will assume that each point is independently generated from D A new point doesn t depend on previous points Estimate the parameters of the distribution Commonly referred to as the i.i.d assumption or independently and identically distributed assumption 4
5 Statistical estimation Coin toss: observed sequence {H, T, H, H} Probability of H: What is the value of that best explains the observed data? Maximum likelihood principle (MLE): pick parameters of the distribution that maximize the likelihood of the observed data Likelihood of data: i.i.d data Maximize likelihood: 5
6 Log-likelihood It is convenient to maximize the logarithm of the likelihood instead Log-likelihood of the observed data: Maximizing the log-likelihood is equivalent to maximizing likelihood Log is a concave monotonic function Products become sums Numerically stable 6
7 Log-likelihood Log-likelihood of observing H-many heads and T-many tails: Maximizing the log-likelihood: 7
8 Rolling a die Suppose you are rolling a k-sided die with parameters: You observe: Log-likelihood of the data: Maximizing the log-likelihood by setting the derivative to zero: We need additional constraints: 8
9 Lagrangian multipliers Constrained optimization: subject to: Unconstrained optimization: At optimality: 9
10 Naive Bayes Consider the binary prediction problem Let the data be distributed according to a probability distribution: We can simplify this using the chain rule of probability: Naive Bayes assumption: E.g., The words free and money are independent given spam 10
11 Naive Bayes Naive Bayes assumption: We can simplify the joint probability distribution as: // simpler distribution At this point we can start parametrizing the distribution 11
12 Naive Bayes: a simple case Case: binary labels and binary features Probability of the data: }1+2D parameters // label +1 // label -1 12
13 Naive Bayes: parameter estimation Given data we can estimate the parameters by maximizing data likelihood Similar to the coin toss example the maximum likelihood estimates are: // fraction of the data with label as +1 // fraction of the instances with 1 among +1 // fraction of the instances with 1 among -1 Other cases: Nominal features: Multinomial distribution (like rolling a die) Continuous features: Gaussian distribution inductive bias 13
14 Naive Bayes: prediction To make predictions compute: // Bayes optimal prediction // Bayes rule For binary labels we can also compute the likelihood ratio: Or the log likelihood ratio: 14
15 Naive Bayes: decision boundary Naive bayes classifier has a linear decision boundary! 15
16 Generative and conditional models Generative models: Model the joint distribution p(x,y) Use Bayes rule to compute the label posterior Need to make simplifying assumptions (e.g. Naive bayes) In most cases we are given x and are only interested in the labels y Conditional models: Model the distribution p(y x) Saves some modeling effort Can assume a simpler parametrization of the distribution p(y x) Most of ML we did so far directly aimed at predicting y from x 16
17 Conditional models: regression Assume that y has a linear relationship with x Generative story of the dataset: For i = 1 to N, Compute: Compute: Compute: This can be written as:, and The log-likelihood of the dataset is: Maximizing log-likelihood is equivalent to minimizing squared error 17
18 Conditional models: classification The sigmoid function: Maps - 0, 1 σ(-z) = 1-σ(z), dσ/dz = σ(z)(1-σ(z)) Generative story of the data: For i = 1 to N, Compute: Compute: Compute: 18
19 Conditional models: classification The log-likelihood of the dataset is: // ignoring constants Maximizing log-likelihood is equivalent to minimizing logistic loss This is also called as logistic regression 19
20 Regularization with priors Coin toss: {H,H,H,H} β = 1 Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE): likelihood Maximum a-posteriori estimation (MAP): prior likelihood data probability MAP estimation in log space: log-prior log-likelihood 20
21 Regularization with priors: coin toss Beta distribution as a prior on β Posterior over β given the prior and H-many heads and T-many tails: 21
22 Conjugate priors If the prior and posterior are in the same family, then the prior is conjugate to the likelihood posterior prior likelihood Beta is conjugate to Bernoulli Prior: Beta(a, b) Data: {H, T} Posterior: Beta(a+H, b+t) Interpretation of the prior: pseudo count of a-1 heads and b-1 tails Dirichlet is conjugate to Multinomial Prior: Data: {k1, k2,, kn} occurrence of each side Posterior: Interpretation of the prior: pseudo count of ai -1 for the i th side 22
23 Regularization with priors: regression Assume that y has a linear relationship with x Generative story of the dataset: For i = 1 to N, Compute: Compute: Compute: Assume a Gaussian prior on the weights: MAP estimate of w: Laplace prior for l1 MAP is same as l2 regularized least-squares regression 23
24 Non-parametric density models So far we assumed that the probability distribution was parametric Gaussian distribution, Binomial distribution, etc This allowed us to estimate the data distribution by estimating the parameters of the probability distribution However, the data distribution can be complicated For example there might be multiple modes Non-parametricdensity models offer a flexible alternative 24
25 Density estimation using histograms This is the simplest example of a non-parametricdensity model The bin size is a hyperparameter of the model too large too small 25
26 Kernel density estimation Histograms are sums of delta functions centered at each point The hyperparameter b controls the width of the delta function The function K is called the kernel function These density estimators are also called as Parzen window estimators Set hyperparameters by cross-validation MLE estimate is b=0. This is clearly wrong (overfitting) 26
27 Kernel density estimation: example Rectangle kernel 27
28 Kernel density estimation: example Gaussian kernel 28
29 Kernel density classifier Estimate p(x +1) and p(x -1) separately Compute likelihood ratio: p(+1)p(x +1) / p(-1)p(x -1) Predict class +1 if LR > 1 small width large width knn classifier is a Kernel density classifier with kernel width = distance to the k th nearest neighbor Figure from Duda et al. 29
30 Summary Probabilistic modeling views learning as statistical inference Two ways to estimate parameters of the distribution Maximum likelihood: maximize p(d θ) Maximum a-posteriori: maximize p(θ D) Two kinds of data models Generative: p(y, x) Example: Naive bayes, Kernel density Conditional: p(y x) Example: Linear and logistic regression Two kinds of probability models Parametric: Gaussian, Bernoulli, etc Learning by MLE and MAP Non-parametric: kernel density estimators Learning by cross validation 30
31 Slides credit Slides are highly adapted from Subhransu Maji s course. Figure of the logistic and linear regression are from Wikipedia Figure of the beta distribution is from Wikipedia Figures for kernel density estimation are from (the page has an interactive demo) Parzen window figure: Pattern Classification, Duda, Hart & Stork Some slides are based on the CIML book by Hal Daume III 31
Bayesian Methods: Naïve Bayes
 Bayesian Methods: aïve Bayes icholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas based on the slides of Vibhav Gogate Last Time Parameter learning Learning the parameter of a simple coin flipping model Prior
Bayesian Methods: aïve Bayes icholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas based on the slides of Vibhav Gogate Last Time Parameter learning Learning the parameter of a simple coin flipping model Prior
PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHAPTER 2: PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS
 PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHAPTER 2: PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Parametric Distributions Basic building blocks: Need to determine given Representation: or? Recall Curve Fitting Binary Variables
PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHAPTER 2: PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Parametric Distributions Basic building blocks: Need to determine given Representation: or? Recall Curve Fitting Binary Variables
Parametric Models. Dr. Shuang LIANG. School of Software Engineering TongJi University Fall, 2012
 Parametric Models Dr. Shuang LIANG School of Software Engineering TongJi University Fall, 2012 Today s Topics Maximum Likelihood Estimation Bayesian Density Estimation Today s Topics Maximum Likelihood
Parametric Models Dr. Shuang LIANG School of Software Engineering TongJi University Fall, 2012 Today s Topics Maximum Likelihood Estimation Bayesian Density Estimation Today s Topics Maximum Likelihood
Bayesian Learning. HT2015: SC4 Statistical Data Mining and Machine Learning. Maximum Likelihood Principle. The Bayesian Learning Framework
 HT5: SC4 Statistical Data Mining and Machine Learning Dino Sejdinovic Department of Statistics Oxford http://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/~sejdinov/sdmml.html Maximum Likelihood Principle A generative model for
HT5: SC4 Statistical Data Mining and Machine Learning Dino Sejdinovic Department of Statistics Oxford http://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/~sejdinov/sdmml.html Maximum Likelihood Principle A generative model for
Naïve Bayes Introduction to Machine Learning. Matt Gormley Lecture 18 Oct. 31, 2018
 10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Naïve Bayes Matt Gormley Lecture 18 Oct. 31, 2018 1 Reminders Homework 6: PAC Learning
10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Naïve Bayes Matt Gormley Lecture 18 Oct. 31, 2018 1 Reminders Homework 6: PAC Learning
MLE/MAP + Naïve Bayes
 10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University MLE/MAP + Naïve Bayes MLE / MAP Readings: Estimating Probabilities (Mitchell, 2016)
10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University MLE/MAP + Naïve Bayes MLE / MAP Readings: Estimating Probabilities (Mitchell, 2016)
MLE/MAP + Naïve Bayes
 10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University MLE/MAP + Naïve Bayes Matt Gormley Lecture 19 March 20, 2018 1 Midterm Exam Reminders
10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University MLE/MAP + Naïve Bayes Matt Gormley Lecture 19 March 20, 2018 1 Midterm Exam Reminders
Naïve Bayes classification
 Naïve Bayes classification 1 Probability theory Random variable: a variable whose possible values are numerical outcomes of a random phenomenon. Examples: A person s height, the outcome of a coin toss
Naïve Bayes classification 1 Probability theory Random variable: a variable whose possible values are numerical outcomes of a random phenomenon. Examples: A person s height, the outcome of a coin toss
Naïve Bayes classification. p ij 11/15/16. Probability theory. Probability theory. Probability theory. X P (X = x i )=1 i. Marginal Probability
 Probability theory Naïve Bayes classification Random variable: a variable whose possible values are numerical outcomes of a random phenomenon. s: A person s height, the outcome of a coin toss Distinguish
Probability theory Naïve Bayes classification Random variable: a variable whose possible values are numerical outcomes of a random phenomenon. s: A person s height, the outcome of a coin toss Distinguish
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining. MLE and MAP Fall 2017
 CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining MLE and MAP Fall 2017 Assignment 3: Admin 1 late day to hand in tonight, 2 late days for Wednesday. Assignment 4: Due Friday of next week. Last Time: Multi-Class
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining MLE and MAP Fall 2017 Assignment 3: Admin 1 late day to hand in tonight, 2 late days for Wednesday. Assignment 4: Due Friday of next week. Last Time: Multi-Class
Expectation maximization
 Expectation maximization Subhransu Maji CMSCI 689: Machine Learning 14 April 2015 Motivation Suppose you are building a naive Bayes spam classifier. After your are done your boss tells you that there is
Expectation maximization Subhransu Maji CMSCI 689: Machine Learning 14 April 2015 Motivation Suppose you are building a naive Bayes spam classifier. After your are done your boss tells you that there is
Bayesian Models in Machine Learning
 Bayesian Models in Machine Learning Lukáš Burget Escuela de Ciencias Informáticas 2017 Buenos Aires, July 24-29 2017 Frequentist vs. Bayesian Frequentist point of view: Probability is the frequency of
Bayesian Models in Machine Learning Lukáš Burget Escuela de Ciencias Informáticas 2017 Buenos Aires, July 24-29 2017 Frequentist vs. Bayesian Frequentist point of view: Probability is the frequency of
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining
 CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining MLE and MAP Original version of these slides by Mark Schmidt, with modifications by Mike Gelbart. 1 Admin Assignment 4: Due tonight. Assignment 5: Will be released
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining MLE and MAP Original version of these slides by Mark Schmidt, with modifications by Mike Gelbart. 1 Admin Assignment 4: Due tonight. Assignment 5: Will be released
Machine Learning
 Machine Learning 10-601 Tom M. Mitchell Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University September 22, 2011 Today: MLE and MAP Bayes Classifiers Naïve Bayes Readings: Mitchell: Naïve Bayes and Logistic
Machine Learning 10-601 Tom M. Mitchell Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University September 22, 2011 Today: MLE and MAP Bayes Classifiers Naïve Bayes Readings: Mitchell: Naïve Bayes and Logistic
Bayesian Learning (II)
 Universität Potsdam Institut für Informatik Lehrstuhl Maschinelles Lernen Bayesian Learning (II) Niels Landwehr Overview Probabilities, expected values, variance Basic concepts of Bayesian learning MAP
Universität Potsdam Institut für Informatik Lehrstuhl Maschinelles Lernen Bayesian Learning (II) Niels Landwehr Overview Probabilities, expected values, variance Basic concepts of Bayesian learning MAP
Machine Learning CMPT 726 Simon Fraser University. Binomial Parameter Estimation
 Machine Learning CMPT 726 Simon Fraser University Binomial Parameter Estimation Outline Maximum Likelihood Estimation Smoothed Frequencies, Laplace Correction. Bayesian Approach. Conjugate Prior. Uniform
Machine Learning CMPT 726 Simon Fraser University Binomial Parameter Estimation Outline Maximum Likelihood Estimation Smoothed Frequencies, Laplace Correction. Bayesian Approach. Conjugate Prior. Uniform
Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Bishop Chapter 2: Probability Distributions
 Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning Chapter 2: Probability Distributions Cécile Amblard Alex Kläser Jakob Verbeek October 11, 27 Probability Distributions: General Density Estimation: given a finite
Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning Chapter 2: Probability Distributions Cécile Amblard Alex Kläser Jakob Verbeek October 11, 27 Probability Distributions: General Density Estimation: given a finite
Midterm Review CS 7301: Advanced Machine Learning. Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas
 Midterm Review CS 7301: Advanced Machine Learning Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Supervised Learning Issues in supervised learning What makes learning hard Point Estimation: MLE vs Bayesian
Midterm Review CS 7301: Advanced Machine Learning Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Supervised Learning Issues in supervised learning What makes learning hard Point Estimation: MLE vs Bayesian
Introduction to Probabilistic Machine Learning
 Introduction to Probabilistic Machine Learning Piyush Rai Dept. of CSE, IIT Kanpur (Mini-course 1) Nov 03, 2015 Piyush Rai (IIT Kanpur) Introduction to Probabilistic Machine Learning 1 Machine Learning
Introduction to Probabilistic Machine Learning Piyush Rai Dept. of CSE, IIT Kanpur (Mini-course 1) Nov 03, 2015 Piyush Rai (IIT Kanpur) Introduction to Probabilistic Machine Learning 1 Machine Learning
Probability and Estimation. Alan Moses
 Probability and Estimation Alan Moses Random variables and probability A random variable is like a variable in algebra (e.g., y=e x ), but where at least part of the variability is taken to be stochastic.
Probability and Estimation Alan Moses Random variables and probability A random variable is like a variable in algebra (e.g., y=e x ), but where at least part of the variability is taken to be stochastic.
Classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology. M. Soleymani Fall 2012
 Classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2012 Topics Discriminant functions Logistic regression Perceptron Generative models Generative vs. discriminative
Classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2012 Topics Discriminant functions Logistic regression Perceptron Generative models Generative vs. discriminative
Learning Bayesian network : Given structure and completely observed data
 Learning Bayesian network : Given structure and completely observed data Probabilistic Graphical Models Sharif University of Technology Spring 2017 Soleymani Learning problem Target: true distribution
Learning Bayesian network : Given structure and completely observed data Probabilistic Graphical Models Sharif University of Technology Spring 2017 Soleymani Learning problem Target: true distribution
Naïve Bayes. Jia-Bin Huang. Virginia Tech Spring 2019 ECE-5424G / CS-5824
 Naïve Bayes Jia-Bin Huang ECE-5424G / CS-5824 Virginia Tech Spring 2019 Administrative HW 1 out today. Please start early! Office hours Chen: Wed 4pm-5pm Shih-Yang: Fri 3pm-4pm Location: Whittemore 266
Naïve Bayes Jia-Bin Huang ECE-5424G / CS-5824 Virginia Tech Spring 2019 Administrative HW 1 out today. Please start early! Office hours Chen: Wed 4pm-5pm Shih-Yang: Fri 3pm-4pm Location: Whittemore 266
Midterm Review CS 6375: Machine Learning. Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas
 Midterm Review CS 6375: Machine Learning Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Machine Learning Supervised Learning Unsupervised Learning Reinforcement Learning Parametric Y Continuous Non-parametric
Midterm Review CS 6375: Machine Learning Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Machine Learning Supervised Learning Unsupervised Learning Reinforcement Learning Parametric Y Continuous Non-parametric
Machine Learning
 Machine Learning 10-601 Tom M. Mitchell Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University January 26, 2015 Today: Bayes Classifiers Conditional Independence Naïve Bayes Readings: Mitchell: Naïve Bayes
Machine Learning 10-601 Tom M. Mitchell Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University January 26, 2015 Today: Bayes Classifiers Conditional Independence Naïve Bayes Readings: Mitchell: Naïve Bayes
Lecture : Probabilistic Machine Learning
 Lecture : Probabilistic Machine Learning Riashat Islam Reasoning and Learning Lab McGill University September 11, 2018 ML : Many Methods with Many Links Modelling Views of Machine Learning Machine Learning
Lecture : Probabilistic Machine Learning Riashat Islam Reasoning and Learning Lab McGill University September 11, 2018 ML : Many Methods with Many Links Modelling Views of Machine Learning Machine Learning
Naïve Bayes Introduction to Machine Learning. Matt Gormley Lecture 3 September 14, Readings: Mitchell Ch Murphy Ch.
 School of Computer Science 10-701 Introduction to Machine Learning aïve Bayes Readings: Mitchell Ch. 6.1 6.10 Murphy Ch. 3 Matt Gormley Lecture 3 September 14, 2016 1 Homewor 1: due 9/26/16 Project Proposal:
School of Computer Science 10-701 Introduction to Machine Learning aïve Bayes Readings: Mitchell Ch. 6.1 6.10 Murphy Ch. 3 Matt Gormley Lecture 3 September 14, 2016 1 Homewor 1: due 9/26/16 Project Proposal:
Last Time. Today. Bayesian Learning. The Distributions We Love. CSE 446 Gaussian Naïve Bayes & Logistic Regression
 CSE 446 Gaussian Naïve Bayes & Logistic Regression Winter 22 Dan Weld Learning Gaussians Naïve Bayes Last Time Gaussians Naïve Bayes Logistic Regression Today Some slides from Carlos Guestrin, Luke Zettlemoyer
CSE 446 Gaussian Naïve Bayes & Logistic Regression Winter 22 Dan Weld Learning Gaussians Naïve Bayes Last Time Gaussians Naïve Bayes Logistic Regression Today Some slides from Carlos Guestrin, Luke Zettlemoyer
ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017
 ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017 Outline Probabilistic interpretation of linear regression - Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) - Maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation Bias-variance trade-off Linear
ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017 Outline Probabilistic interpretation of linear regression - Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) - Maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation Bias-variance trade-off Linear
Machine Learning. Lecture 4: Regularization and Bayesian Statistics. Feng Li. https://funglee.github.io
 Machine Learning Lecture 4: Regularization and Bayesian Statistics Feng Li fli@sdu.edu.cn https://funglee.github.io School of Computer Science and Technology Shandong University Fall 207 Overfitting Problem
Machine Learning Lecture 4: Regularization and Bayesian Statistics Feng Li fli@sdu.edu.cn https://funglee.github.io School of Computer Science and Technology Shandong University Fall 207 Overfitting Problem
Introduc)on to Bayesian methods (con)nued) - Lecture 16
 Introduc)on to Bayesian methods (con)nued) - Lecture 16 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Carlos Guestrin, Dan Klein, and Vibhav Gogate Outline of lectures Review of
Introduc)on to Bayesian methods (con)nued) - Lecture 16 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Carlos Guestrin, Dan Klein, and Vibhav Gogate Outline of lectures Review of
CSCI-567: Machine Learning (Spring 2019)
 CSCI-567: Machine Learning (Spring 2019) Prof. Victor Adamchik U of Southern California Mar. 19, 2019 March 19, 2019 1 / 43 Administration March 19, 2019 2 / 43 Administration TA3 is due this week March
CSCI-567: Machine Learning (Spring 2019) Prof. Victor Adamchik U of Southern California Mar. 19, 2019 March 19, 2019 1 / 43 Administration March 19, 2019 2 / 43 Administration TA3 is due this week March
Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5
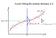 Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5 Maximum Likelihood Bishop 1.2.5 Model Likelihood differentiation p(t x, w, β) = Maximum Likelihood N N ( t n y(x n, w), β 1). (1.61) n=1 As we did in the case of the
Curve Fitting Re-visited, Bishop1.2.5 Maximum Likelihood Bishop 1.2.5 Model Likelihood differentiation p(t x, w, β) = Maximum Likelihood N N ( t n y(x n, w), β 1). (1.61) n=1 As we did in the case of the
Probability Theory for Machine Learning. Chris Cremer September 2015
 Probability Theory for Machine Learning Chris Cremer September 2015 Outline Motivation Probability Definitions and Rules Probability Distributions MLE for Gaussian Parameter Estimation MLE and Least Squares
Probability Theory for Machine Learning Chris Cremer September 2015 Outline Motivation Probability Definitions and Rules Probability Distributions MLE for Gaussian Parameter Estimation MLE and Least Squares
Parametric Techniques Lecture 3
 Parametric Techniques Lecture 3 Jason Corso SUNY at Buffalo 22 January 2009 J. Corso (SUNY at Buffalo) Parametric Techniques Lecture 3 22 January 2009 1 / 39 Introduction In Lecture 2, we learned how to
Parametric Techniques Lecture 3 Jason Corso SUNY at Buffalo 22 January 2009 J. Corso (SUNY at Buffalo) Parametric Techniques Lecture 3 22 January 2009 1 / 39 Introduction In Lecture 2, we learned how to
CMU-Q Lecture 24:
 CMU-Q 15-381 Lecture 24: Supervised Learning 2 Teacher: Gianni A. Di Caro SUPERVISED LEARNING Hypotheses space Hypothesis function Labeled Given Errors Performance criteria Given a collection of input
CMU-Q 15-381 Lecture 24: Supervised Learning 2 Teacher: Gianni A. Di Caro SUPERVISED LEARNING Hypotheses space Hypothesis function Labeled Given Errors Performance criteria Given a collection of input
Non-parametric Methods
 Non-parametric Methods Machine Learning Alireza Ghane Non-Parametric Methods Alireza Ghane / Torsten Möller 1 Outline Machine Learning: What, Why, and How? Curve Fitting: (e.g.) Regression and Model Selection
Non-parametric Methods Machine Learning Alireza Ghane Non-Parametric Methods Alireza Ghane / Torsten Möller 1 Outline Machine Learning: What, Why, and How? Curve Fitting: (e.g.) Regression and Model Selection
The Bayes classifier
 The Bayes classifier Consider where is a random vector in is a random variable (depending on ) Let be a classifier with probability of error/risk given by The Bayes classifier (denoted ) is the optimal
The Bayes classifier Consider where is a random vector in is a random variable (depending on ) Let be a classifier with probability of error/risk given by The Bayes classifier (denoted ) is the optimal
Logistic Regression Review Fall 2012 Recitation. September 25, 2012 TA: Selen Uguroglu
 Logistic Regression Review 10-601 Fall 2012 Recitation September 25, 2012 TA: Selen Uguroglu!1 Outline Decision Theory Logistic regression Goal Loss function Inference Gradient Descent!2 Training Data
Logistic Regression Review 10-601 Fall 2012 Recitation September 25, 2012 TA: Selen Uguroglu!1 Outline Decision Theory Logistic regression Goal Loss function Inference Gradient Descent!2 Training Data
Generative Models for Discrete Data
 Generative Models for Discrete Data ddebarr@uw.edu 2016-04-21 Agenda Bayesian Concept Learning Beta-Binomial Model Dirichlet-Multinomial Model Naïve Bayes Classifiers Bayesian Concept Learning Numbers
Generative Models for Discrete Data ddebarr@uw.edu 2016-04-21 Agenda Bayesian Concept Learning Beta-Binomial Model Dirichlet-Multinomial Model Naïve Bayes Classifiers Bayesian Concept Learning Numbers
COMP 551 Applied Machine Learning Lecture 19: Bayesian Inference
 COMP 551 Applied Machine Learning Lecture 19: Bayesian Inference Associate Instructor: (herke.vanhoof@mcgill.ca) Class web page: www.cs.mcgill.ca/~jpineau/comp551 Unless otherwise noted, all material posted
COMP 551 Applied Machine Learning Lecture 19: Bayesian Inference Associate Instructor: (herke.vanhoof@mcgill.ca) Class web page: www.cs.mcgill.ca/~jpineau/comp551 Unless otherwise noted, all material posted
Representation. Stefano Ermon, Aditya Grover. Stanford University. Lecture 2
 Representation Stefano Ermon, Aditya Grover Stanford University Lecture 2 Stefano Ermon, Aditya Grover (AI Lab) Deep Generative Models Lecture 2 1 / 32 Learning a generative model We are given a training
Representation Stefano Ermon, Aditya Grover Stanford University Lecture 2 Stefano Ermon, Aditya Grover (AI Lab) Deep Generative Models Lecture 2 1 / 32 Learning a generative model We are given a training
Parametric Techniques
 Parametric Techniques Jason J. Corso SUNY at Buffalo J. Corso (SUNY at Buffalo) Parametric Techniques 1 / 39 Introduction When covering Bayesian Decision Theory, we assumed the full probabilistic structure
Parametric Techniques Jason J. Corso SUNY at Buffalo J. Corso (SUNY at Buffalo) Parametric Techniques 1 / 39 Introduction When covering Bayesian Decision Theory, we assumed the full probabilistic structure
Introduction: MLE, MAP, Bayesian reasoning (28/8/13)
 STA561: Probabilistic machine learning Introduction: MLE, MAP, Bayesian reasoning (28/8/13) Lecturer: Barbara Engelhardt Scribes: K. Ulrich, J. Subramanian, N. Raval, J. O Hollaren 1 Classifiers In this
STA561: Probabilistic machine learning Introduction: MLE, MAP, Bayesian reasoning (28/8/13) Lecturer: Barbara Engelhardt Scribes: K. Ulrich, J. Subramanian, N. Raval, J. O Hollaren 1 Classifiers In this
Announcements. Proposals graded
 Announcements Proposals graded Kevin Jamieson 2018 1 Bayesian Methods Machine Learning CSE546 Kevin Jamieson University of Washington November 1, 2018 2018 Kevin Jamieson 2 MLE Recap - coin flips Data:
Announcements Proposals graded Kevin Jamieson 2018 1 Bayesian Methods Machine Learning CSE546 Kevin Jamieson University of Washington November 1, 2018 2018 Kevin Jamieson 2 MLE Recap - coin flips Data:
6.867 Machine Learning
 6.867 Machine Learning Problem set 1 Solutions Thursday, September 19 What and how to turn in? Turn in short written answers to the questions explicitly stated, and when requested to explain or prove.
6.867 Machine Learning Problem set 1 Solutions Thursday, September 19 What and how to turn in? Turn in short written answers to the questions explicitly stated, and when requested to explain or prove.
Introduction to Machine Learning
 Introduction to Machine Learning Bayesian Classification Varun Chandola Computer Science & Engineering State University of New York at Buffalo Buffalo, NY, USA chandola@buffalo.edu Chandola@UB CSE 474/574
Introduction to Machine Learning Bayesian Classification Varun Chandola Computer Science & Engineering State University of New York at Buffalo Buffalo, NY, USA chandola@buffalo.edu Chandola@UB CSE 474/574
Some slides from Carlos Guestrin, Luke Zettlemoyer & K Gajos 2
 Logistics CSE 446: Point Estimation Winter 2012 PS2 out shortly Dan Weld Some slides from Carlos Guestrin, Luke Zettlemoyer & K Gajos 2 Last Time Random variables, distributions Marginal, joint & conditional
Logistics CSE 446: Point Estimation Winter 2012 PS2 out shortly Dan Weld Some slides from Carlos Guestrin, Luke Zettlemoyer & K Gajos 2 Last Time Random variables, distributions Marginal, joint & conditional
Computational Cognitive Science
 Computational Cognitive Science Lecture 8: Frank Keller School of Informatics University of Edinburgh keller@inf.ed.ac.uk Based on slides by Sharon Goldwater October 14, 2016 Frank Keller Computational
Computational Cognitive Science Lecture 8: Frank Keller School of Informatics University of Edinburgh keller@inf.ed.ac.uk Based on slides by Sharon Goldwater October 14, 2016 Frank Keller Computational
Lecture 4. Generative Models for Discrete Data - Part 3. Luigi Freda. ALCOR Lab DIAG University of Rome La Sapienza.
 Lecture 4 Generative Models for Discrete Data - Part 3 Luigi Freda ALCOR Lab DIAG University of Rome La Sapienza October 6, 2017 Luigi Freda ( La Sapienza University) Lecture 4 October 6, 2017 1 / 46 Outline
Lecture 4 Generative Models for Discrete Data - Part 3 Luigi Freda ALCOR Lab DIAG University of Rome La Sapienza October 6, 2017 Luigi Freda ( La Sapienza University) Lecture 4 October 6, 2017 1 / 46 Outline
Density Estimation. Seungjin Choi
 Density Estimation Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr http://mlg.postech.ac.kr/
Density Estimation Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr http://mlg.postech.ac.kr/
Logistic Regression. Machine Learning Fall 2018
 Logistic Regression Machine Learning Fall 2018 1 Where are e? We have seen the folloing ideas Linear models Learning as loss minimization Bayesian learning criteria (MAP and MLE estimation) The Naïve Bayes
Logistic Regression Machine Learning Fall 2018 1 Where are e? We have seen the folloing ideas Linear models Learning as loss minimization Bayesian learning criteria (MAP and MLE estimation) The Naïve Bayes
Midterm: CS 6375 Spring 2018
 Midterm: CS 6375 Spring 2018 The exam is closed book (1 cheat sheet allowed). Answer the questions in the spaces provided on the question sheets. If you run out of room for an answer, use an additional
Midterm: CS 6375 Spring 2018 The exam is closed book (1 cheat sheet allowed). Answer the questions in the spaces provided on the question sheets. If you run out of room for an answer, use an additional
Estimating Parameters
 Machine Learning 10-601 Tom M. Mitchell Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University September 13, 2012 Today: Bayes Classifiers Naïve Bayes Gaussian Naïve Bayes Readings: Mitchell: Naïve Bayes
Machine Learning 10-601 Tom M. Mitchell Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University September 13, 2012 Today: Bayes Classifiers Naïve Bayes Gaussian Naïve Bayes Readings: Mitchell: Naïve Bayes
Computational Cognitive Science
 Computational Cognitive Science Lecture 9: Bayesian Estimation Chris Lucas (Slides adapted from Frank Keller s) School of Informatics University of Edinburgh clucas2@inf.ed.ac.uk 17 October, 2017 1 / 28
Computational Cognitive Science Lecture 9: Bayesian Estimation Chris Lucas (Slides adapted from Frank Keller s) School of Informatics University of Edinburgh clucas2@inf.ed.ac.uk 17 October, 2017 1 / 28
Day 5: Generative models, structured classification
 Day 5: Generative models, structured classification Introduction to Machine Learning Summer School June 18, 2018 - June 29, 2018, Chicago Instructor: Suriya Gunasekar, TTI Chicago 22 June 2018 Linear regression
Day 5: Generative models, structured classification Introduction to Machine Learning Summer School June 18, 2018 - June 29, 2018, Chicago Instructor: Suriya Gunasekar, TTI Chicago 22 June 2018 Linear regression
Chapter 3: Maximum-Likelihood & Bayesian Parameter Estimation (part 1)
 HW 1 due today Parameter Estimation Biometrics CSE 190 Lecture 7 Today s lecture was on the blackboard. These slides are an alternative presentation of the material. CSE190, Winter10 CSE190, Winter10 Chapter
HW 1 due today Parameter Estimation Biometrics CSE 190 Lecture 7 Today s lecture was on the blackboard. These slides are an alternative presentation of the material. CSE190, Winter10 CSE190, Winter10 Chapter
Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington. September 30, 2013
 Bayesian Methods Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington September 30, 2013 1 What about prior n Billionaire says: Wait, I know that the thumbtack is close to 50-50. What can you
Bayesian Methods Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington September 30, 2013 1 What about prior n Billionaire says: Wait, I know that the thumbtack is close to 50-50. What can you
Bayesian Analysis for Natural Language Processing Lecture 2
 Bayesian Analysis for Natural Language Processing Lecture 2 Shay Cohen February 4, 2013 Administrativia The class has a mailing list: coms-e6998-11@cs.columbia.edu Need two volunteers for leading a discussion
Bayesian Analysis for Natural Language Processing Lecture 2 Shay Cohen February 4, 2013 Administrativia The class has a mailing list: coms-e6998-11@cs.columbia.edu Need two volunteers for leading a discussion
Outline. Supervised Learning. Hong Chang. Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Machine Learning Methods (Fall 2012)
 Outline Hong Chang Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences Machine Learning Methods (Fall 2012) Outline Outline I 1 Linear Models for Regression Linear Regression Probabilistic Interpretation
Outline Hong Chang Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences Machine Learning Methods (Fall 2012) Outline Outline I 1 Linear Models for Regression Linear Regression Probabilistic Interpretation
COMP90051 Statistical Machine Learning
 COMP90051 Statistical Machine Learning Semester 2, 2017 Lecturer: Trevor Cohn 2. Statistical Schools Adapted from slides by Ben Rubinstein Statistical Schools of Thought Remainder of lecture is to provide
COMP90051 Statistical Machine Learning Semester 2, 2017 Lecturer: Trevor Cohn 2. Statistical Schools Adapted from slides by Ben Rubinstein Statistical Schools of Thought Remainder of lecture is to provide
Bias-Variance Tradeoff
 What s learning, revisited Overfitting Generative versus Discriminative Logistic Regression Machine Learning 10701/15781 Carlos Guestrin Carnegie Mellon University September 19 th, 2007 Bias-Variance Tradeoff
What s learning, revisited Overfitting Generative versus Discriminative Logistic Regression Machine Learning 10701/15781 Carlos Guestrin Carnegie Mellon University September 19 th, 2007 Bias-Variance Tradeoff
Instance-based Learning CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology. M. Soleymani Fall 2016
 Instance-based Learning CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2016 Outline Non-parametric approach Unsupervised: Non-parametric density estimation Parzen Windows Kn-Nearest
Instance-based Learning CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2016 Outline Non-parametric approach Unsupervised: Non-parametric density estimation Parzen Windows Kn-Nearest
CSC321 Lecture 18: Learning Probabilistic Models
 CSC321 Lecture 18: Learning Probabilistic Models Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 18: Learning Probabilistic Models 1 / 25 Overview So far in this course: mainly supervised learning Language modeling
CSC321 Lecture 18: Learning Probabilistic Models Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 18: Learning Probabilistic Models 1 / 25 Overview So far in this course: mainly supervised learning Language modeling
Generative Learning. INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder. November 29, 2018 Prof. Michael Paul
 Generative Learning INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder November 29, 2018 Prof. Michael Paul Generative vs Discriminative The classification algorithms we have seen so far
Generative Learning INFO-4604, Applied Machine Learning University of Colorado Boulder November 29, 2018 Prof. Michael Paul Generative vs Discriminative The classification algorithms we have seen so far
Machine Learning for Signal Processing Bayes Classification
 Machine Learning for Signal Processing Bayes Classification Class 16. 24 Oct 2017 Instructor: Bhiksha Raj - Abelino Jimenez 11755/18797 1 Recap: KNN A very effective and simple way of performing classification
Machine Learning for Signal Processing Bayes Classification Class 16. 24 Oct 2017 Instructor: Bhiksha Raj - Abelino Jimenez 11755/18797 1 Recap: KNN A very effective and simple way of performing classification
CS 361: Probability & Statistics
 October 17, 2017 CS 361: Probability & Statistics Inference Maximum likelihood: drawbacks A couple of things might trip up max likelihood estimation: 1) Finding the maximum of some functions can be quite
October 17, 2017 CS 361: Probability & Statistics Inference Maximum likelihood: drawbacks A couple of things might trip up max likelihood estimation: 1) Finding the maximum of some functions can be quite
Generative v. Discriminative classifiers Intuition
 Logistic Regression Machine Learning 10701/15781 Carlos Guestrin Carnegie Mellon University September 24 th, 2007 1 Generative v. Discriminative classifiers Intuition Want to Learn: h:x a Y X features
Logistic Regression Machine Learning 10701/15781 Carlos Guestrin Carnegie Mellon University September 24 th, 2007 1 Generative v. Discriminative classifiers Intuition Want to Learn: h:x a Y X features
Machine Learning for Signal Processing Bayes Classification and Regression
 Machine Learning for Signal Processing Bayes Classification and Regression Instructor: Bhiksha Raj 11755/18797 1 Recap: KNN A very effective and simple way of performing classification Simple model: For
Machine Learning for Signal Processing Bayes Classification and Regression Instructor: Bhiksha Raj 11755/18797 1 Recap: KNN A very effective and simple way of performing classification Simple model: For
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE Autumn Semester MACHINE LEARNING AND ADAPTIVE INTELLIGENCE
 Data Provided: None DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE Autumn Semester 203 204 MACHINE LEARNING AND ADAPTIVE INTELLIGENCE 2 hours Answer THREE of the four questions. All questions carry equal weight. Figures
Data Provided: None DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE Autumn Semester 203 204 MACHINE LEARNING AND ADAPTIVE INTELLIGENCE 2 hours Answer THREE of the four questions. All questions carry equal weight. Figures
PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS. J. Elder CSE 6390/PSYC 6225 Computational Modeling of Visual Perception
 PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Credits 2 These slides were sourced and/or modified from: Christopher Bishop, Microsoft UK Parametric Distributions 3 Basic building blocks: Need to determine given Representation:
PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS Credits 2 These slides were sourced and/or modified from: Christopher Bishop, Microsoft UK Parametric Distributions 3 Basic building blocks: Need to determine given Representation:
CPSC 540: Machine Learning
 CPSC 540: Machine Learning Empirical Bayes, Hierarchical Bayes Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia Winter 2017 Admin Assignment 5: Due April 10. Project description on Piazza. Final details coming
CPSC 540: Machine Learning Empirical Bayes, Hierarchical Bayes Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia Winter 2017 Admin Assignment 5: Due April 10. Project description on Piazza. Final details coming
Statistical and Learning Techniques in Computer Vision Lecture 2: Maximum Likelihood and Bayesian Estimation Jens Rittscher and Chuck Stewart
 Statistical and Learning Techniques in Computer Vision Lecture 2: Maximum Likelihood and Bayesian Estimation Jens Rittscher and Chuck Stewart 1 Motivation and Problem In Lecture 1 we briefly saw how histograms
Statistical and Learning Techniques in Computer Vision Lecture 2: Maximum Likelihood and Bayesian Estimation Jens Rittscher and Chuck Stewart 1 Motivation and Problem In Lecture 1 we briefly saw how histograms
STA414/2104 Statistical Methods for Machine Learning II
 STA414/2104 Statistical Methods for Machine Learning II Murat A. Erdogdu & David Duvenaud Department of Computer Science Department of Statistical Sciences Lecture 3 Slide credits: Russ Salakhutdinov Announcements
STA414/2104 Statistical Methods for Machine Learning II Murat A. Erdogdu & David Duvenaud Department of Computer Science Department of Statistical Sciences Lecture 3 Slide credits: Russ Salakhutdinov Announcements
COS513 LECTURE 8 STATISTICAL CONCEPTS
 COS513 LECTURE 8 STATISTICAL CONCEPTS NIKOLAI SLAVOV AND ANKUR PARIKH 1. MAKING MEANINGFUL STATEMENTS FROM JOINT PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS. A graphical model (GM) represents a family of probability distributions
COS513 LECTURE 8 STATISTICAL CONCEPTS NIKOLAI SLAVOV AND ANKUR PARIKH 1. MAKING MEANINGFUL STATEMENTS FROM JOINT PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS. A graphical model (GM) represents a family of probability distributions
The Naïve Bayes Classifier. Machine Learning Fall 2017
 The Naïve Bayes Classifier Machine Learning Fall 2017 1 Today s lecture The naïve Bayes Classifier Learning the naïve Bayes Classifier Practical concerns 2 Today s lecture The naïve Bayes Classifier Learning
The Naïve Bayes Classifier Machine Learning Fall 2017 1 Today s lecture The naïve Bayes Classifier Learning the naïve Bayes Classifier Practical concerns 2 Today s lecture The naïve Bayes Classifier Learning
Introduction to Bayesian Learning. Machine Learning Fall 2018
 Introduction to Bayesian Learning Machine Learning Fall 2018 1 What we have seen so far What does it mean to learn? Mistake-driven learning Learning by counting (and bounding) number of mistakes PAC learnability
Introduction to Bayesian Learning Machine Learning Fall 2018 1 What we have seen so far What does it mean to learn? Mistake-driven learning Learning by counting (and bounding) number of mistakes PAC learnability
6.867 Machine Learning
 6.867 Machine Learning Problem set 1 Due Thursday, September 19, in class What and how to turn in? Turn in short written answers to the questions explicitly stated, and when requested to explain or prove.
6.867 Machine Learning Problem set 1 Due Thursday, September 19, in class What and how to turn in? Turn in short written answers to the questions explicitly stated, and when requested to explain or prove.
Logistic Regression. Jia-Bin Huang. Virginia Tech Spring 2019 ECE-5424G / CS-5824
 Logistic Regression Jia-Bin Huang ECE-5424G / CS-5824 Virginia Tech Spring 2019 Administrative Please start HW 1 early! Questions are welcome! Two principles for estimating parameters Maximum Likelihood
Logistic Regression Jia-Bin Huang ECE-5424G / CS-5824 Virginia Tech Spring 2019 Administrative Please start HW 1 early! Questions are welcome! Two principles for estimating parameters Maximum Likelihood
Generative v. Discriminative classifiers Intuition
 Logistic Regression Machine Learning 070/578 Carlos Guestrin Carnegie Mellon University September 24 th, 2007 Generative v. Discriminative classifiers Intuition Want to Learn: h:x a Y X features Y target
Logistic Regression Machine Learning 070/578 Carlos Guestrin Carnegie Mellon University September 24 th, 2007 Generative v. Discriminative classifiers Intuition Want to Learn: h:x a Y X features Y target
Naive Bayes and Gaussian Bayes Classifier
 Naive Bayes and Gaussian Bayes Classifier Ladislav Rampasek slides by Mengye Ren and others February 22, 2016 Naive Bayes and Gaussian Bayes Classifier February 22, 2016 1 / 21 Naive Bayes Bayes Rule:
Naive Bayes and Gaussian Bayes Classifier Ladislav Rampasek slides by Mengye Ren and others February 22, 2016 Naive Bayes and Gaussian Bayes Classifier February 22, 2016 1 / 21 Naive Bayes Bayes Rule:
MIDTERM SOLUTIONS: FALL 2012 CS 6375 INSTRUCTOR: VIBHAV GOGATE
 MIDTERM SOLUTIONS: FALL 2012 CS 6375 INSTRUCTOR: VIBHAV GOGATE March 28, 2012 The exam is closed book. You are allowed a double sided one page cheat sheet. Answer the questions in the spaces provided on
MIDTERM SOLUTIONS: FALL 2012 CS 6375 INSTRUCTOR: VIBHAV GOGATE March 28, 2012 The exam is closed book. You are allowed a double sided one page cheat sheet. Answer the questions in the spaces provided on
Probabilistic Graphical Models
 Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture 11 CRFs, Exponential Family CS/CNS/EE 155 Andreas Krause Announcements Homework 2 due today Project milestones due next Monday (Nov 9) About half the work should
Probabilistic Graphical Models Lecture 11 CRFs, Exponential Family CS/CNS/EE 155 Andreas Krause Announcements Homework 2 due today Project milestones due next Monday (Nov 9) About half the work should
Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington. September 30, What about continuous variables?
 Linear Regression Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington September 30, 2014 1 What about continuous variables? n Billionaire says: If I am measuring a continuous variable, what
Linear Regression Machine Learning CSE546 Carlos Guestrin University of Washington September 30, 2014 1 What about continuous variables? n Billionaire says: If I am measuring a continuous variable, what
Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10701
 Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10701 2. MLE, MAP, Bayes classification Barnabás Póczos & Aarti Singh 2014 Spring Administration http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~aarti/class/10701_spring14/index.html Blackboard
Introduction to Machine Learning CMU-10701 2. MLE, MAP, Bayes classification Barnabás Póczos & Aarti Singh 2014 Spring Administration http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~aarti/class/10701_spring14/index.html Blackboard
Introduction to Machine Learning
 Outline Introduction to Machine Learning Bayesian Classification Varun Chandola March 8, 017 1. {circular,large,light,smooth,thick}, malignant. {circular,large,light,irregular,thick}, malignant 3. {oval,large,dark,smooth,thin},
Outline Introduction to Machine Learning Bayesian Classification Varun Chandola March 8, 017 1. {circular,large,light,smooth,thick}, malignant. {circular,large,light,irregular,thick}, malignant 3. {oval,large,dark,smooth,thin},
Machine Learning
 Machine Learning 10-601 Tom M. Mitchell Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University August 30, 2017 Today: Decision trees Overfitting The Big Picture Coming soon Probabilistic learning MLE,
Machine Learning 10-601 Tom M. Mitchell Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University August 30, 2017 Today: Decision trees Overfitting The Big Picture Coming soon Probabilistic learning MLE,
Introduction to Machine Learning
 Introduction to Machine Learning Logistic Regression Varun Chandola Computer Science & Engineering State University of New York at Buffalo Buffalo, NY, USA chandola@buffalo.edu Chandola@UB CSE 474/574
Introduction to Machine Learning Logistic Regression Varun Chandola Computer Science & Engineering State University of New York at Buffalo Buffalo, NY, USA chandola@buffalo.edu Chandola@UB CSE 474/574
Discrete Binary Distributions
 Discrete Binary Distributions Carl Edward Rasmussen November th, 26 Carl Edward Rasmussen Discrete Binary Distributions November th, 26 / 5 Key concepts Bernoulli: probabilities over binary variables Binomial:
Discrete Binary Distributions Carl Edward Rasmussen November th, 26 Carl Edward Rasmussen Discrete Binary Distributions November th, 26 / 5 Key concepts Bernoulli: probabilities over binary variables Binomial:
Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning
 Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning CS 584: Big Data Analytics Material adapted from Radford Neal s tutorial (http://ftp.cs.utoronto.ca/pub/radford/bayes-tut.pdf), Zoubin Ghahramni (http://hunch.net/~coms-4771/zoubin_ghahramani_bayesian_learning.pdf),
Bayesian Methods for Machine Learning CS 584: Big Data Analytics Material adapted from Radford Neal s tutorial (http://ftp.cs.utoronto.ca/pub/radford/bayes-tut.pdf), Zoubin Ghahramni (http://hunch.net/~coms-4771/zoubin_ghahramani_bayesian_learning.pdf),
Bayesian Classifiers, Conditional Independence and Naïve Bayes. Required reading: Naïve Bayes and Logistic Regression (available on class website)
 Bayesian Classifiers, Conditional Independence and Naïve Bayes Required reading: Naïve Bayes and Logistic Regression (available on class website) Machine Learning 10-701 Tom M. Mitchell Machine Learning
Bayesian Classifiers, Conditional Independence and Naïve Bayes Required reading: Naïve Bayes and Logistic Regression (available on class website) Machine Learning 10-701 Tom M. Mitchell Machine Learning
Computational Perception. Bayesian Inference
 Computational Perception 15-485/785 January 24, 2008 Bayesian Inference The process of probabilistic inference 1. define model of problem 2. derive posterior distributions and estimators 3. estimate parameters
Computational Perception 15-485/785 January 24, 2008 Bayesian Inference The process of probabilistic inference 1. define model of problem 2. derive posterior distributions and estimators 3. estimate parameters
Machine Learning, Fall 2012 Homework 2
 0-60 Machine Learning, Fall 202 Homework 2 Instructors: Tom Mitchell, Ziv Bar-Joseph TA in charge: Selen Uguroglu email: sugurogl@cs.cmu.edu SOLUTIONS Naive Bayes, 20 points Problem. Basic concepts, 0
0-60 Machine Learning, Fall 202 Homework 2 Instructors: Tom Mitchell, Ziv Bar-Joseph TA in charge: Selen Uguroglu email: sugurogl@cs.cmu.edu SOLUTIONS Naive Bayes, 20 points Problem. Basic concepts, 0
Nonparametric Bayesian Methods (Gaussian Processes)
 [70240413 Statistical Machine Learning, Spring, 2015] Nonparametric Bayesian Methods (Gaussian Processes) Jun Zhu dcszj@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn http://bigml.cs.tsinghua.edu.cn/~jun State Key Lab of Intelligent
[70240413 Statistical Machine Learning, Spring, 2015] Nonparametric Bayesian Methods (Gaussian Processes) Jun Zhu dcszj@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn http://bigml.cs.tsinghua.edu.cn/~jun State Key Lab of Intelligent
Machine Learning Linear Classification. Prof. Matteo Matteucci
 Machine Learning Linear Classification Prof. Matteo Matteucci Recall from the first lecture 2 X R p Regression Y R Continuous Output X R p Y {Ω 0, Ω 1,, Ω K } Classification Discrete Output X R p Y (X)
Machine Learning Linear Classification Prof. Matteo Matteucci Recall from the first lecture 2 X R p Regression Y R Continuous Output X R p Y {Ω 0, Ω 1,, Ω K } Classification Discrete Output X R p Y (X)
Naïve Bayes. Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas
 Naïve Bayes Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Supervised Learning of Classifiers Find f Given: Training set {(x i, y i ) i = 1 n} Find: A good approximation to f : X Y Examples: what are
Naïve Bayes Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Supervised Learning of Classifiers Find f Given: Training set {(x i, y i ) i = 1 n} Find: A good approximation to f : X Y Examples: what are
Logistic Regression Introduction to Machine Learning. Matt Gormley Lecture 9 Sep. 26, 2018
 10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Logistic Regression Matt Gormley Lecture 9 Sep. 26, 2018 1 Reminders Homework 3:
10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Logistic Regression Matt Gormley Lecture 9 Sep. 26, 2018 1 Reminders Homework 3:
Perceptron. Subhransu Maji. CMPSCI 689: Machine Learning. 3 February February 2015
 Perceptron Subhransu Maji CMPSCI 689: Machine Learning 3 February 2015 5 February 2015 So far in the class Decision trees Inductive bias: use a combination of small number of features Nearest neighbor
Perceptron Subhransu Maji CMPSCI 689: Machine Learning 3 February 2015 5 February 2015 So far in the class Decision trees Inductive bias: use a combination of small number of features Nearest neighbor
CS 361: Probability & Statistics
 March 14, 2018 CS 361: Probability & Statistics Inference The prior From Bayes rule, we know that we can express our function of interest as Likelihood Prior Posterior The right hand side contains the
March 14, 2018 CS 361: Probability & Statistics Inference The prior From Bayes rule, we know that we can express our function of interest as Likelihood Prior Posterior The right hand side contains the
Probabilistic classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology. M. Soleymani Fall 2016
 Probabilistic classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2016 Topics Probabilistic approach Bayes decision theory Generative models Gaussian Bayes classifier
Probabilistic classification CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2016 Topics Probabilistic approach Bayes decision theory Generative models Gaussian Bayes classifier
