Heat & Temperature. Grade 7 Science - Unit 2 Pgs
|
|
|
- Claud Burns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Heat & Temperature Grade 7 Science - Unit 2 Pgs
2 4.1 Temperature PTemperature is the measure of how much heat is in a substance. PTemperature is measured in degrees Celcius ( C) PIt is difficult to judge how hot or cold something is by touching or looking at it. A better way is to measure the temperature of the object.
3 PTo measure temperature accurately we use a thermometer. P The Celcius scale is the most frequently used scale for measuring temperature.
4 4.2 Temperature Galileo P Hundreds of years ago, there was no way to measure temperatures exactly... only estimates. P In 1596, Galileo, an Italian scientist invented the thermoscope. P A thermoscope is a device that detects changes in temperature but does not have a temperature scale.
5 Thermometer P The word thermometer is made from two words: Thermo - meaning heat
6 P Normal human body temperature is 37 C. When you get a fever, that is the body fighting infection. Raising the body s temperature kills bacteria, but if it goes too high, it can cause damage, especially to the brain. It is also dangerous when the body temperature goes too low. This is called HYPOTHERMIA. (Hyperthermia - too high) P Accurate temperature measurement is important: When measuring body temperature for fever. We use a special type of thermometer with a constriction above the bulb. At a weather station For baking cakes and cookies
7 The Celcius Scale P Invented by Anders Celcius scientist, in the 1700's, a Swedish P He made his scale by marking the freezing point of pure water as 0 and the boiling point of pure water as 100. P He divided the distance between these two points by 100 degrees and used the symbol
8 PHe proposed a new temperature scale that started at absolute zero and had the units that were the same size as the Temperature The Kelvin Scale P In the 1800's, William Thompson (AKA Lord Kelvin), while studying different gases, developed the idea that there is a Coldest possible temperature - absolute zero
9 Bimetalic Strip This strip is made up of two different metals that expand by two different amounts when heated. - It is an experiment that demonstrates thermal expansion. Two metals with different thermal expansion coefficients are bonded together and when heated, one will expand more than the other, causing the strip to bend to one side. No matter which way you direct the flame, the metal which expands more will bend in the same direction. This is used as a thermometer because the more intense the heat, the bigger the curve in the metal.
10
11 Thermometer P When a thermometer is built or made, it must be calibrated. (P. 125) PMost temperature scales are based on TWO fixed points Freezing point of fresh water C( 0) Boiling point of fresh water ( 1C00)
12 Types of Thermometers P 1. Clinical Thermometer Measures body temperature Has a constriction above the bulb. As liquid is warmed by patient s body heat, it expands past the constriction and rises up the bore so the temperature can be read. After the temperature has been taken, the liquid cools and contracts, but the liquid does not move past the constriction. You must shake the thermometer to get the liquid to move down.
13 Types of Thermometers P 2. Thermostat Measures temperature in an appliance or room It switches the appliance on or off at a pre-set temperature. Set the thermostat at 20 Celcius... if the temperature goes above 20 C, the thermostat causes the heater to shut off. When the temperature goes below 20 C, the thermostat causes the heater to turn on.
14 Thermostats
15 Types of Thermometers P 3. Thermocouple A thermometer that uses electricity to measure temperature It contains two different metal wires that are joined at one end or COUPLED The other ends are joined to a meter that measures electricity The amount of electricity that passes through the wires varies depending on the temperature These types of thermometers are used for places where people cannot go (inside computers, smokestacks, volcanoes, etc.)
16 Thermocouple
17 Types of Thermometers P 4. Resistance Thermometers P Operates on electricity, just like a thermocouple, but it can be used in even higher temperatures than a thermocouple. In this kind of thermometer, a platinum wire is used.
18 Types of Thermometers P 5. Optical Thermometer P Heat is a form of light... infrared light.the amount of infrared light given off by an object can be detected using an optical thermometer. P Infrared Thermogram - special type of photograph that shows differences in temperature.
19 Thermometers Calibrating a Thermometer P 1. Place the bulb of the thermometer in a mixture of pure water and ice. P 2. Observe the colored liquid until it no longer moves P 3. Mark this point as 0 degrees Celcuis. P 4. Remove thermometer, and place bulb in boiling water. P 5. Observe the colored liquid unitl it no longer moves. P 6. Mark this point as 100 degrees Celcius. P 7. Equally divide into 100 spaces (each space is one degree.)
Heat & Temperature. Grade 7 Science - Unit 2 Pgs
 Heat & Temperature Grade 7 Science - Unit 2 Pgs 104-225 Temperature P Temperature is the measure of how much heat is in a substance. P Temperature is measured in degrees Celcius ( C) P It is difficult
Heat & Temperature Grade 7 Science - Unit 2 Pgs 104-225 Temperature P Temperature is the measure of how much heat is in a substance. P Temperature is measured in degrees Celcius ( C) P It is difficult
Unit 4 : Heat and Temperature. Topic 1 - Using Energy from Heat
 Topic 1 - Using Energy from Heat In what ways have humans made thermal energy work for them? Topic 2 - Mesuring Temperature A relative idea about temperature is that it tells. This can be done by using
Topic 1 - Using Energy from Heat In what ways have humans made thermal energy work for them? Topic 2 - Mesuring Temperature A relative idea about temperature is that it tells. This can be done by using
 Since ancient times, people have needed thermal energy (heat) to cook their food and to keep them warm. And since the beginning of time, uncontrolled heat has scorched and spoiled the taste of food and
Since ancient times, people have needed thermal energy (heat) to cook their food and to keep them warm. And since the beginning of time, uncontrolled heat has scorched and spoiled the taste of food and
Thermal energy. Thermal energy is the internal energy of a substance. I.e. Thermal energy is the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules.
 Thermal energy Thermal energy is the internal energy of a substance. I.e. Thermal energy is the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. Heat is the transfer of thermal energy between substances. Until the
Thermal energy Thermal energy is the internal energy of a substance. I.e. Thermal energy is the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. Heat is the transfer of thermal energy between substances. Until the
Heat and Temperature Practice Quiz Topic 2 - Measuring Temperature
 Heat and Temperature Practice Quiz Topic 2 - Measuring Temperature 1. Estimating temperature is something that we do automatically. Touching something to see how hot or cold it is is one technique that
Heat and Temperature Practice Quiz Topic 2 - Measuring Temperature 1. Estimating temperature is something that we do automatically. Touching something to see how hot or cold it is is one technique that
Recap: Bernoulli s Principle
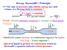 Recap: Bernoulli s Principle The sum of pressure plus kinetic energy per unit volume of a flowing fluid is constant. P + ½ρv 2 = constant pressure K.E. per unit volume (ρ = mass vol ) Result: Relates pressure
Recap: Bernoulli s Principle The sum of pressure plus kinetic energy per unit volume of a flowing fluid is constant. P + ½ρv 2 = constant pressure K.E. per unit volume (ρ = mass vol ) Result: Relates pressure
Unit 5 Thermodynamics
 Unit 5 Thermodynamics Unit 13: Heat and Temperature Unit 14: Thermal Expansion /Heat Exchange/ Change of Phase Test: Units 13-14 Thermal Energy The total kinetic and potential energy of all the molecules
Unit 5 Thermodynamics Unit 13: Heat and Temperature Unit 14: Thermal Expansion /Heat Exchange/ Change of Phase Test: Units 13-14 Thermal Energy The total kinetic and potential energy of all the molecules
Thermal energy 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE
 Thermal energy 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE Temperature There s more to temperature than the idea of hot and cold. Remember that all matter is made up of tiny particles that are constantly moving even in solid objects.
Thermal energy 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE Temperature There s more to temperature than the idea of hot and cold. Remember that all matter is made up of tiny particles that are constantly moving even in solid objects.
4. Thermometry. Temperature and Heat Flow Temperature Scales Thermometers
 4. Thermometry Measuring temperature by sensation is very imprecise. That is why we need a temperature scale and a thermometer to measure temperature more accurately. Temperature and Heat Flow Temperature
4. Thermometry Measuring temperature by sensation is very imprecise. That is why we need a temperature scale and a thermometer to measure temperature more accurately. Temperature and Heat Flow Temperature
Heat and Temperature
 Heat and Temperature Temperature What does temperature have to do with energy? What three temperature scales are commonly used? What makes things feel hot or cold? Intro: Discussion A person from Seattle
Heat and Temperature Temperature What does temperature have to do with energy? What three temperature scales are commonly used? What makes things feel hot or cold? Intro: Discussion A person from Seattle
Science In Action 7 Heat and Temperature Section Quiz
 Section 2 Heat affects Matter in different ways 2.1 States of Matter and The Particle Model 1. Water has a distinct characteristic that sets it apart from other liquids on Earth. Water expands when it
Section 2 Heat affects Matter in different ways 2.1 States of Matter and The Particle Model 1. Water has a distinct characteristic that sets it apart from other liquids on Earth. Water expands when it
Heat and temperature are different. Heat is a type of energy. Heat is the total energy of all the particles in an object.
 Heat & Temperature Heat vs. Temperature Heat and temperature are different. Heat is a type of energy. Heat is the total energy of all the particles in an object. Temperature is the average energy of each
Heat & Temperature Heat vs. Temperature Heat and temperature are different. Heat is a type of energy. Heat is the total energy of all the particles in an object. Temperature is the average energy of each
Unit 6: Thermal Physics
 Unit 6: Thermal Physics 6.1 Thermal Expansion Objectives Describe qualitatively the thermal expansion of solids, liquids, and gases at constant pressure Identify and explain some of the everyday applications
Unit 6: Thermal Physics 6.1 Thermal Expansion Objectives Describe qualitatively the thermal expansion of solids, liquids, and gases at constant pressure Identify and explain some of the everyday applications
Physics 111. Lecture 35 (Walker: ) Thermal Physics I: Temperature Thermal Expansion. April 29, Temperature (T)
 Physics 111 Lecture 35 (Walker: 16.1-3) Thermal Physics I: Temperature Thermal Expansion April 29, 2009 Lecture 35 1/26 Temperature (T) Temperature (T) is a measure of how hot or cold something is Temperature
Physics 111 Lecture 35 (Walker: 16.1-3) Thermal Physics I: Temperature Thermal Expansion April 29, 2009 Lecture 35 1/26 Temperature (T) Temperature (T) is a measure of how hot or cold something is Temperature
Al-Saudia Virtual Academy Online tuiton Pakistan Online Tutor Pakistan. Heat
 Al-Saudia Virtual Academy Online tuiton Pakistan Online Tutor Pakistan Heat Nature of Heat: Heat is the transfer of energy (every in transit) from one body to another due to the temperature difference
Al-Saudia Virtual Academy Online tuiton Pakistan Online Tutor Pakistan Heat Nature of Heat: Heat is the transfer of energy (every in transit) from one body to another due to the temperature difference
the energy of motion!
 What are the molecules of matter doing all the time?! Heat and Temperature! Notes! All matter is composed of continually jiggling atoms or molecules! The jiggling is! If something is vibrating, what kind
What are the molecules of matter doing all the time?! Heat and Temperature! Notes! All matter is composed of continually jiggling atoms or molecules! The jiggling is! If something is vibrating, what kind
3. EFFECTS OF HEAT. Thus, heat can be defined as a form of energy that gives the sensation of hotness or coldness
 3. EFFECTS OF HEAT In the previous class you have learnt that heat is a form of energy. Heat can be obtained from various sources like the sun, fire, etc. When we read the weather forecast we observe that
3. EFFECTS OF HEAT In the previous class you have learnt that heat is a form of energy. Heat can be obtained from various sources like the sun, fire, etc. When we read the weather forecast we observe that
PROGRAM OF PHYSICS. Lecturer: Dr. DO Xuan Hoi Room A
 PROGRAM OF PHYSICS Lecturer: Dr. DO Xuan Hoi Room A1. 503 E-mail : dxhoi@hcmiu.edu.vn PHYSICS 2 (FLUID MECHANICS AND THERMAL PHYSICS) 02 credits (30 periods) Chapter 1 Fluid Mechanics Chapter 2 Heat, Temperature
PROGRAM OF PHYSICS Lecturer: Dr. DO Xuan Hoi Room A1. 503 E-mail : dxhoi@hcmiu.edu.vn PHYSICS 2 (FLUID MECHANICS AND THERMAL PHYSICS) 02 credits (30 periods) Chapter 1 Fluid Mechanics Chapter 2 Heat, Temperature
Temperature and Heat. Chapter 10. Table of Contents. Chapter 10. Chapter 10. Bellringer. Objectives. Chapter 10. Chapter 10
 Heat and Heat Technology Table of Contents Temperature and Heat Section 3 Matter and Heat Bellringer Objectives The temperature of boiling water is 100 on the Celsius scale and 212 on the Fahrenheit scale.
Heat and Heat Technology Table of Contents Temperature and Heat Section 3 Matter and Heat Bellringer Objectives The temperature of boiling water is 100 on the Celsius scale and 212 on the Fahrenheit scale.
Chapter 10. Thermal Physics
 Chapter 10 Thermal Physics Thermal Physics Thermal physics is the study of Temperature Heat How these affect matter Thermal Physics, cont Descriptions require definitions of temperature, heat and internal
Chapter 10 Thermal Physics Thermal Physics Thermal physics is the study of Temperature Heat How these affect matter Thermal Physics, cont Descriptions require definitions of temperature, heat and internal
Period 5: Thermal Energy, the Microscopic Picture
 Name Section Period 5: Thermal Energy, the Microscopic Picture 5.1 How Is Temperature Related to Molecular Motion? 1) Temperature Your instructor will discuss molecular motion and temperature. a) At a
Name Section Period 5: Thermal Energy, the Microscopic Picture 5.1 How Is Temperature Related to Molecular Motion? 1) Temperature Your instructor will discuss molecular motion and temperature. a) At a
Problem: Convert 25kg to ug. Problem: Convert 482mL to cl. Problem: How many micrograms are in a kilogram? Problem: How many ml are in 1 ounce?
 Problem: Convert 25kg to ug. Problem: Convert 482mL to cl. Problem: How many micrograms are in a kilogram? Problem: How many ml are in 1 ounce? Problem: How many ml are in 1 tsp? Problem: A nerve impulse
Problem: Convert 25kg to ug. Problem: Convert 482mL to cl. Problem: How many micrograms are in a kilogram? Problem: How many ml are in 1 ounce? Problem: How many ml are in 1 tsp? Problem: A nerve impulse
WELCOME TO PERIOD 5: THERMAL ENERGY, THE MICROSCOPIC PICTURE. Homework #4 is due today at the beginning of class.
 WELCOME TO PERIOD 5: THERMAL ENERGY, THE MICROSCOPIC PICTURE Homework #4 is due today at the beginning of class. PHYSICS 1104 PERIOD 5 How are temperatures measured? How do atoms and molecules act at different
WELCOME TO PERIOD 5: THERMAL ENERGY, THE MICROSCOPIC PICTURE Homework #4 is due today at the beginning of class. PHYSICS 1104 PERIOD 5 How are temperatures measured? How do atoms and molecules act at different
What does temperature have to do with energy? What three temperature scales are commonly used? What makes things feel hot or cold?
 Heat and Temperature Section 1: Temperature What does temperature have to do with energy? What three temperature scales are commonly used? What makes things feel hot or cold? 1 Intro: Discussion A person
Heat and Temperature Section 1: Temperature What does temperature have to do with energy? What three temperature scales are commonly used? What makes things feel hot or cold? 1 Intro: Discussion A person
BUTTERFLY LAB METAMORPHOSIS & THE ENVIRONMENT. Handouts 6th & 7th Grade Science Unit EarthsBirthday.org
 METAMORPHOSIS & THE ENVIRONMENT Handouts 6th & 7th Grade Science Unit 1 800 698 4438 EarthsBirthday.org BUTTERFLY LAB CONTENTS Note: Answer Keys are in the Teacher Guide. Handout: Controlled Experiment
METAMORPHOSIS & THE ENVIRONMENT Handouts 6th & 7th Grade Science Unit 1 800 698 4438 EarthsBirthday.org BUTTERFLY LAB CONTENTS Note: Answer Keys are in the Teacher Guide. Handout: Controlled Experiment
Chapter 14 Heat and Temperature Notes
 Chapter 14 Heat and Temperature Notes Section 1: Temperature The degree of or of an object. Related to the of an object s atoms or molecules What makes something hot? o Particles that make up o They have
Chapter 14 Heat and Temperature Notes Section 1: Temperature The degree of or of an object. Related to the of an object s atoms or molecules What makes something hot? o Particles that make up o They have
1. How much heat was needed to raise the bullet to its final temperature?
 Name: Date: Use the following to answer question 1: A 0.0500-kg lead bullet of volume 5.00 10 6 m 3 at 20.0 C hits a block that is made of an ideal thermal insulator and comes to rest at its center. At
Name: Date: Use the following to answer question 1: A 0.0500-kg lead bullet of volume 5.00 10 6 m 3 at 20.0 C hits a block that is made of an ideal thermal insulator and comes to rest at its center. At
Lecture 2: Zero law of thermodynamics
 Lecture 2: Zero law of thermodynamics 1. Thermometers and temperature scales 2. Thermal contact and thermal equilibrium 3. Zeroth law of thermodynamics 1. Thermometers and Temperature scales We often associate
Lecture 2: Zero law of thermodynamics 1. Thermometers and temperature scales 2. Thermal contact and thermal equilibrium 3. Zeroth law of thermodynamics 1. Thermometers and Temperature scales We often associate
CIE Physics IGCSE. Topic 2: Thermal Physics
 CIE Physics IGCSE Topic 2: Thermal Physics Summary Notes Simple kinetic molecular model of matter Molecular model Solids Molecules close together in regular pattern Strong intermolecular forces of attraction
CIE Physics IGCSE Topic 2: Thermal Physics Summary Notes Simple kinetic molecular model of matter Molecular model Solids Molecules close together in regular pattern Strong intermolecular forces of attraction
PURE PHYSICS THERMAL PHYSICS (PART I)
 PURE PHYSICS THERMAL PHYSICS (PART I) 1 The kinetic theory of matter states that all matters are made up of or, which are in and motion. forces hold the atoms or molecules together. The nature of these
PURE PHYSICS THERMAL PHYSICS (PART I) 1 The kinetic theory of matter states that all matters are made up of or, which are in and motion. forces hold the atoms or molecules together. The nature of these
Heat and temperature are related and often confused, but they are not the same.
 Heat and temperature are related and often confused, but they are not the same. Heat Definition: Heat is energy that is transferred from one body to another as a result of a difference in temperature Symbol:
Heat and temperature are related and often confused, but they are not the same. Heat Definition: Heat is energy that is transferred from one body to another as a result of a difference in temperature Symbol:
TEMPERATURE AND THERMAL EXPANSION
 TEMPERATURE AND THERMAL EXPANSION After boiling water, you will feel that the water is hotter than before, or you can say that the water temperature is higher than before. Otherwise, when you pick an ice,
TEMPERATURE AND THERMAL EXPANSION After boiling water, you will feel that the water is hotter than before, or you can say that the water temperature is higher than before. Otherwise, when you pick an ice,
Chapters 16 Temperature and Heat
 Chapters 16 Temperature and Heat 1 Overview of Chapter 16 Temperature and the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Temperature Scales Thermal Expansion Heat and Mechanical Work Specific Heat Conduction, Convection,
Chapters 16 Temperature and Heat 1 Overview of Chapter 16 Temperature and the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Temperature Scales Thermal Expansion Heat and Mechanical Work Specific Heat Conduction, Convection,
Simple machines. ( Fxd) input. = (Fxd) output
 Announcements l LON-CAPA #5 and Mastering Physics Chapters 15 and 18 due Tuesday Feb. 18 l Average for exam 1 is 28/40 l The course will be graded on a curve with the average about 3.0, so if you received
Announcements l LON-CAPA #5 and Mastering Physics Chapters 15 and 18 due Tuesday Feb. 18 l Average for exam 1 is 28/40 l The course will be graded on a curve with the average about 3.0, so if you received
Lecture 6. Temperature and Heat 27 September 2018
 Lecture 6. Temperature and Heat 27 September 2018 Wannapong Triampo, Ph.D. Korey Stringer 7-31-01 27 Yrs Old 6 3 335 lbs Eraste Autin 7-25-01 18 Yrs Old 6 2 250 lbs Preston Birdsong 8-13-00 18 Yrs Old
Lecture 6. Temperature and Heat 27 September 2018 Wannapong Triampo, Ph.D. Korey Stringer 7-31-01 27 Yrs Old 6 3 335 lbs Eraste Autin 7-25-01 18 Yrs Old 6 2 250 lbs Preston Birdsong 8-13-00 18 Yrs Old
THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
 CHP # 8 HERMA PROPERIES OF MAER Q.1 Differentiate between heat and temperature? (Ans) Heat It can be defined as "the sum of kinetic energy of the molecules present in a substance is called heat". Heat
CHP # 8 HERMA PROPERIES OF MAER Q.1 Differentiate between heat and temperature? (Ans) Heat It can be defined as "the sum of kinetic energy of the molecules present in a substance is called heat". Heat
Chapter 21: Temperature, Heat and Expansion
 Chapter 21: Temperature, Heat and Expansion All matter solid, liquid and gas is made of atoms or molecules, which are continually jiggling. As this jiggling is a movement, all these particles must have
Chapter 21: Temperature, Heat and Expansion All matter solid, liquid and gas is made of atoms or molecules, which are continually jiggling. As this jiggling is a movement, all these particles must have
Introduction. Measurement of temperature is generally considered to be one of the simplest and most accurate measurements performed in engineering.
 Slide Nr. 0 of 15 Slides Introduction Measurement of temperature is generally considered to be one of the simplest and most accurate measurements performed in engineering. Some important considerations
Slide Nr. 0 of 15 Slides Introduction Measurement of temperature is generally considered to be one of the simplest and most accurate measurements performed in engineering. Some important considerations
Chapter 16. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 16 Temperature and Heat Units of Chapter 16 Temperature and the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Temperature Scales Thermal Expansion Heat and Mechanical Work Specific Heats Conduction, Convection,
Chapter 16 Temperature and Heat Units of Chapter 16 Temperature and the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Temperature Scales Thermal Expansion Heat and Mechanical Work Specific Heats Conduction, Convection,
Physical Science Chapter 5 Cont2. Temperature & Heat
 Physical Science Chapter 5 Cont2 Temperature & Heat What are we going to study? Temperature Heat Specific Heat and Latent Heat Heat Transfer Phases of Matter The Kinetic Theory of Gases Thermodynamics
Physical Science Chapter 5 Cont2 Temperature & Heat What are we going to study? Temperature Heat Specific Heat and Latent Heat Heat Transfer Phases of Matter The Kinetic Theory of Gases Thermodynamics
Thermometry. History. History 1/21/18. The art or science of temperature observation
 Thermometry The art or science of temperature observation History No one person credited with the invention of the thermometer; developed over time Avicenna used this principal to show that hotness and
Thermometry The art or science of temperature observation History No one person credited with the invention of the thermometer; developed over time Avicenna used this principal to show that hotness and
HEAT AND TEMPERATURE Vikasana-Bridge Course 2012
 HEAT AND TEMPERATURE TOPICS Introduction Effects of heat Specific heat Basics of thermodynamics Introduction Heat may be defined as energy in transit from a high temperature region to a lower temperature
HEAT AND TEMPERATURE TOPICS Introduction Effects of heat Specific heat Basics of thermodynamics Introduction Heat may be defined as energy in transit from a high temperature region to a lower temperature
HEAT HISTORY. D. Whitehall
 1 HEAT HISTORY 18 th Century In the 18 th century it was assumed that there was an invisible substance called caloric. When objects got it was assumed that they gained caloric, therefore hot objects should
1 HEAT HISTORY 18 th Century In the 18 th century it was assumed that there was an invisible substance called caloric. When objects got it was assumed that they gained caloric, therefore hot objects should
Dr.Salwa Alsaleh fac.ksu.edu.sa/salwams
 Dr.Salwa Alsaleh Salwams@ksu.edu.sa fac.ksu.edu.sa/salwams What is Temperature? It is the measurement of the AVERAGE kinetic energy of the particles of matter. Temperature We associate the concept of temperature
Dr.Salwa Alsaleh Salwams@ksu.edu.sa fac.ksu.edu.sa/salwams What is Temperature? It is the measurement of the AVERAGE kinetic energy of the particles of matter. Temperature We associate the concept of temperature
Chapter 17. Temperature. Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 17 Temperature Dr. Armen Kocharian Temperature We associate the concept of temperature with how hot or cold an objects feels Our senses provide us with a qualitative indication of temperature Our
Chapter 17 Temperature Dr. Armen Kocharian Temperature We associate the concept of temperature with how hot or cold an objects feels Our senses provide us with a qualitative indication of temperature Our
Thermometry And Thermal Expansion
 Thermometry And Thermal Expansion 1. Define heat (a) on conventional basis (b) on the basis of kinetic model. Ans. (a) On the conventional basis heat is the from of energy which causes in us sensation
Thermometry And Thermal Expansion 1. Define heat (a) on conventional basis (b) on the basis of kinetic model. Ans. (a) On the conventional basis heat is the from of energy which causes in us sensation
Chapter 16 Temperature and Heat
 Chapter 16 Temperature and Heat 16-1 Temperature and the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Definition of heat: Heat is the energy transferred between objects because of a temperature difference. Objects are
Chapter 16 Temperature and Heat 16-1 Temperature and the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Definition of heat: Heat is the energy transferred between objects because of a temperature difference. Objects are
Conceptual Physics Fundamentals
 Conceptual Physics Fundamentals Chapter 8: TEMPERATURE, HEAT, AND THERMODYNAMICS This lecture will help you understand: Temperature Absolute Zero Internal Energy Heat Quantity of Heat The Laws of Thermodynamics
Conceptual Physics Fundamentals Chapter 8: TEMPERATURE, HEAT, AND THERMODYNAMICS This lecture will help you understand: Temperature Absolute Zero Internal Energy Heat Quantity of Heat The Laws of Thermodynamics
P5 Heat and Particles Revision Kinetic Model of Matter: States of matter
 P5 Heat and Particles Revision Kinetic Model of Matter: States of matter State Size Shape Solid occupies a fixed volume has a fixed shape Liquid occupies a fixed volume takes the shape of its container
P5 Heat and Particles Revision Kinetic Model of Matter: States of matter State Size Shape Solid occupies a fixed volume has a fixed shape Liquid occupies a fixed volume takes the shape of its container
Demonstrate understanding of aspects of heat
 Demonstrate understanding of aspects of heat Heat Transfer Temperature - temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles making up an object (measured in C or K) 0 K = -273 o C
Demonstrate understanding of aspects of heat Heat Transfer Temperature - temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles making up an object (measured in C or K) 0 K = -273 o C
Very Dynamic! Energy in the Earth s Atmosphere. How Does it Get Here? All Objects Radiate Energy!
 Energy in the Earth s Atmosphere Unit Essential Question: What are the different features of the atmosphere that characterize our weather. How does the atmosphere influence life and how does life influence
Energy in the Earth s Atmosphere Unit Essential Question: What are the different features of the atmosphere that characterize our weather. How does the atmosphere influence life and how does life influence
Chapter 4: Heat Capacity and Heat Transfer
 Chapter 4: Heat Capacity and Heat Transfer Chapter 4: Heat Capacity and Heat Transfer Chapter 4: Heat Capacity and Heat Transfer 4.1 Material Structure 4.2 Temperature and Material Properties 4.3 Heating
Chapter 4: Heat Capacity and Heat Transfer Chapter 4: Heat Capacity and Heat Transfer Chapter 4: Heat Capacity and Heat Transfer 4.1 Material Structure 4.2 Temperature and Material Properties 4.3 Heating
Temperature * OpenStax
 OpenStax-CNX module: m42214 1 Temperature * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Dene temperature. Convert temperatures
OpenStax-CNX module: m42214 1 Temperature * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Dene temperature. Convert temperatures
Thermodynamics. Atoms are in constant motion, which increases with temperature.
 Thermodynamics SOME DEFINITIONS: THERMO related to heat DYNAMICS the study of motion SYSTEM an object or set of objects ENVIRONMENT the rest of the universe MICROSCOPIC at an atomic or molecular level
Thermodynamics SOME DEFINITIONS: THERMO related to heat DYNAMICS the study of motion SYSTEM an object or set of objects ENVIRONMENT the rest of the universe MICROSCOPIC at an atomic or molecular level
Exercises Temperature (pages ) 1. Define temperature. 2. Explain how a common liquid thermometer works.
 Exercises 21.1 Temperature (pages 407 408) 1. Define temperature. 2. Explain how a common liquid thermometer works. Match each number with the corresponding description. Temperature Description 3. 273
Exercises 21.1 Temperature (pages 407 408) 1. Define temperature. 2. Explain how a common liquid thermometer works. Match each number with the corresponding description. Temperature Description 3. 273
NIT 6 MATTER AND HEAT
 NIT 6 MATTER AND HEAT Radiation Convection Thermostat Spread as Spread as Conduction Used in technology as Spread as Bi-Metal Strips HEAT Solid state In Solids Liquid Gas state state State Changes causes
NIT 6 MATTER AND HEAT Radiation Convection Thermostat Spread as Spread as Conduction Used in technology as Spread as Bi-Metal Strips HEAT Solid state In Solids Liquid Gas state state State Changes causes
ASEN 2002 Experimental Laboratory 1: Temperature Measurement and an Blow Dryer Test
 ASEN 2002 Experimental Laboratory 1: Temperature Measurement and an Blow Dryer Test Assigned 6 September 2000 Individual Lab Reports due 3 October 2000 OBJECTIVES Learn the basic concepts and definitions
ASEN 2002 Experimental Laboratory 1: Temperature Measurement and an Blow Dryer Test Assigned 6 September 2000 Individual Lab Reports due 3 October 2000 OBJECTIVES Learn the basic concepts and definitions
Thermodynamics Thermal Equilibrium Temperature
 Thermodynamics Thermal Equilibrium Temperature Lana Sheridan De Anza College April 18, 2017 Last time Torricelli s Law applications of Bernoulli s equation Overview heat, thermal equilibrium, and the 0th
Thermodynamics Thermal Equilibrium Temperature Lana Sheridan De Anza College April 18, 2017 Last time Torricelli s Law applications of Bernoulli s equation Overview heat, thermal equilibrium, and the 0th
Thermal Energy. Thermal Energy is the TRANSFER of kinetic energy between two objects that are at different temperatures.
 Thermal Energy Thermal Energy is the TRANSFER of kinetic energy between two objects that are at different temperatures. And remember: heat will always transfer from a warm object to a cold object. HEAT
Thermal Energy Thermal Energy is the TRANSFER of kinetic energy between two objects that are at different temperatures. And remember: heat will always transfer from a warm object to a cold object. HEAT
Simpo PDF Merge and Split Unregistered Version -
 Simpo PDF Merge and Split Unregistered Version - http://wwwsimpopdfcom 6 If the zeroth law of thermodynamics were not valid, which of the following could not be considered a property of an object? A Pressure
Simpo PDF Merge and Split Unregistered Version - http://wwwsimpopdfcom 6 If the zeroth law of thermodynamics were not valid, which of the following could not be considered a property of an object? A Pressure
3.2 Units of Measurement > Chapter 3 Scientific Measurement. 3.2 Units of Measurement. 3.1 Using and Expressing Measurements
 Chapter 3 Scientific Measurement 3.1 Using and Expressing Measurements 3.2 Units of Measurement 3.3 Solving Conversion Problems 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
Chapter 3 Scientific Measurement 3.1 Using and Expressing Measurements 3.2 Units of Measurement 3.3 Solving Conversion Problems 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
* Defining Temperature * Temperature is proportional to the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. * Temperature * Internal energy
 * Defining Temperature * We associate temperature with how hot or cold an object feels. * Our sense of touch serves as a qualitative indicator of temperature. * Energy must be either added or removed from
* Defining Temperature * We associate temperature with how hot or cold an object feels. * Our sense of touch serves as a qualitative indicator of temperature. * Energy must be either added or removed from
Handout 10: Heat and heat transfer. Heat capacity
 1 Handout 10: Heat and heat transfer Heat capacity Consider an experiment in Figure 1. Heater is inserted into a solid substance of mass m and the temperature rise T degrees Celsius is measured by a thermometer.
1 Handout 10: Heat and heat transfer Heat capacity Consider an experiment in Figure 1. Heater is inserted into a solid substance of mass m and the temperature rise T degrees Celsius is measured by a thermometer.
Tick the box next to those resources for which the Sun is also the source of energy.
 1 (a) The source of solar energy is the Sun. Tick the box next to those resources for which the Sun is also the source of energy. coal geothermal hydroelectric nuclear wind [2] (b) Fig. 4.1 shows a solar
1 (a) The source of solar energy is the Sun. Tick the box next to those resources for which the Sun is also the source of energy. coal geothermal hydroelectric nuclear wind [2] (b) Fig. 4.1 shows a solar
THERMODYNAMICS WRITTEN TEST PORTION GOPHER INVITATIONAL JANUARY 6TH 2018 NAMES TEAM NAME AND NUMBER SCHOOL
 THERMODYNAMICS WRITTEN TEST PORTION GOPHER INVITATIONAL JANUARY 6TH 2018 NAMES TEAM NAME AND NUMBER SCHOOL TIME ALLOWED: 30 MINUTES DO NOT TURN THE PAGE UNTIL YOU ARE INSTRUCTED TO DO SO. Multiple Choice:
THERMODYNAMICS WRITTEN TEST PORTION GOPHER INVITATIONAL JANUARY 6TH 2018 NAMES TEAM NAME AND NUMBER SCHOOL TIME ALLOWED: 30 MINUTES DO NOT TURN THE PAGE UNTIL YOU ARE INSTRUCTED TO DO SO. Multiple Choice:
Weather Unit. Welcome Back! Begin Semester 2 1/20/2010. Seating Changes Final Exam Averages S1 Routine Changes for S2 Review Expectations.
 Welcome Back! Begin Semester 2 Weather Unit I-2 to I-6 Seating Changes Final Exam Averages S1 Routine Changes for S2 Review Expectations Beginning of Class (ChemCatalyst) Chemistry Binders and note-taking
Welcome Back! Begin Semester 2 Weather Unit I-2 to I-6 Seating Changes Final Exam Averages S1 Routine Changes for S2 Review Expectations Beginning of Class (ChemCatalyst) Chemistry Binders and note-taking
3.2 The International System of Units HR/Name. temperature: Celsius scale: Kelvin scale: Vocabulary. absolute zero:
 temperature: Celsius scale: Kelvin scale: Reading Assignment: pages 73-79 Vocabulary International System of s (SI): absolute zero: meter (m): energy: liter (L): joule (J): kilogram: gram (g): calorie
temperature: Celsius scale: Kelvin scale: Reading Assignment: pages 73-79 Vocabulary International System of s (SI): absolute zero: meter (m): energy: liter (L): joule (J): kilogram: gram (g): calorie
Chapter 14: Temperature and Heat
 Chapter 14 Lecture Chapter 14: Temperature and Heat Goals for Chapter 14 To study temperature and temperature scales. To describe thermal expansion and its applications. To explore and solve problems involving
Chapter 14 Lecture Chapter 14: Temperature and Heat Goals for Chapter 14 To study temperature and temperature scales. To describe thermal expansion and its applications. To explore and solve problems involving
Figure 1.1. Relation between Celsius and Fahrenheit scales. From Figure 1.1. (1.1)
 CHAPTER I ELEMENTS OF APPLIED THERMODYNAMICS 1.1. INTRODUCTION. The Air Conditioning systems extract heat from some closed location and deliver it to other places. To better understanding the principles
CHAPTER I ELEMENTS OF APPLIED THERMODYNAMICS 1.1. INTRODUCTION. The Air Conditioning systems extract heat from some closed location and deliver it to other places. To better understanding the principles
PAPER 2 THEORY QUESTIONS
 PAPER 2 THEORY QUESTIONS 1 Fig. 1.1 shows the arrangement of atoms in a solid block. Fig. 1.1 (a) End X of the block is heated. Energy is conducted to end Y, which becomes warm. (i) Explain how heat is
PAPER 2 THEORY QUESTIONS 1 Fig. 1.1 shows the arrangement of atoms in a solid block. Fig. 1.1 (a) End X of the block is heated. Energy is conducted to end Y, which becomes warm. (i) Explain how heat is
Name Date. Physical and Chemical Changes
 Name Date Physical and Chemical Changes Physical Changes Physical Change: A change in which no new substances form Do not change the type of matter an object is made of You change the shape, size or more
Name Date Physical and Chemical Changes Physical Changes Physical Change: A change in which no new substances form Do not change the type of matter an object is made of You change the shape, size or more
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore THERMO METER For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore THERMO METER For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Temperature Scales. Temperature, and Temperature Dependent on Physical Properties. Temperature. Temperature Scale
 Temperature Scales The Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin Temperature Scales: Temperature, and Temperature Dependent on Physical Properties Physics Enhancement Programme Dr. M.H. CHAN, HKBU 9 T F T 5 T T
Temperature Scales The Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin Temperature Scales: Temperature, and Temperature Dependent on Physical Properties Physics Enhancement Programme Dr. M.H. CHAN, HKBU 9 T F T 5 T T
Observing Climate. How do we measure climate parameters? Surface Measurements. - Temperature > Wind Chill Temperature Index > Heat Index.
 Observing Climate 3-1 How do we measure climate parameters? Surface Measurements - Temperature > Wind Chill Temperature Index > Heat Index - Pressure Observing - To see a world in a grain of sand, And
Observing Climate 3-1 How do we measure climate parameters? Surface Measurements - Temperature > Wind Chill Temperature Index > Heat Index - Pressure Observing - To see a world in a grain of sand, And
Section 7. Temperature Measurement
 Section 7 Temperature Measurement 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 1 Working Definition Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules that make of a substance. After time,
Section 7 Temperature Measurement 7/25/2017 Engineering Measurements 7 1 Working Definition Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules that make of a substance. After time,
Lecture 2. Professor Hicks General Chemistry (CHE131) Spring Units. units are like apples and oranges. any number of
 Lecture 2 Professor Hicks General Chemistry (CHE131) Spring 2009 1 Units units are like apples and oranges any number of 1 inch any number! kilograms things with different types of units cannot be equated
Lecture 2 Professor Hicks General Chemistry (CHE131) Spring 2009 1 Units units are like apples and oranges any number of 1 inch any number! kilograms things with different types of units cannot be equated
Temperature and Heat. Two systems of temperature. Temperature conversions. PHY heat - J. Hedberg
 Temperature and Heat 1. Two systems of temperature 1. Temperature conversions 2. Real science (one scale to rule them all) 3. Temperature scales 2. Effects of temperature on materials 1. Linear Thermal
Temperature and Heat 1. Two systems of temperature 1. Temperature conversions 2. Real science (one scale to rule them all) 3. Temperature scales 2. Effects of temperature on materials 1. Linear Thermal
Archimedes Principle
 Archimedes Principle applies in air the more air an object displaces, the greater the buoyant force on it if an object displaces its weight, it hovers at a constant altitude if an object displaces less
Archimedes Principle applies in air the more air an object displaces, the greater the buoyant force on it if an object displaces its weight, it hovers at a constant altitude if an object displaces less
Physics 121, April 10, Temperature/Heat. Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester
 Physics 121, April 10, 2008. Temperature/Heat. Physics 121. April 10, 2008. Course Information Topics to be discussed today: Temperature Physics 121. April 10, 2008. Homework set # 8 is due on Saturday
Physics 121, April 10, 2008. Temperature/Heat. Physics 121. April 10, 2008. Course Information Topics to be discussed today: Temperature Physics 121. April 10, 2008. Homework set # 8 is due on Saturday
TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT. GROUP 3 Noah Beauchamp Kyle Camacho Jack Connolly Curtis Yu
 TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT GROUP 3 Noah Beauchamp Kyle Camacho Jack Connolly Curtis Yu Thermodynamics I Section 15 22 January 2018 Group 3 Page: 2 Abstract The Temperature Measurement lab involved using a
TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT GROUP 3 Noah Beauchamp Kyle Camacho Jack Connolly Curtis Yu Thermodynamics I Section 15 22 January 2018 Group 3 Page: 2 Abstract The Temperature Measurement lab involved using a
21) PHASE CHANGE: a change from one state (solid or liquid or gas) to another without a change in chemical composition.
 21) PHASE CHANGE: a change from one state (solid or liquid or gas) to another without a change in chemical composition. 22) Show that you understand how phase changes occur by writing an explanation for
21) PHASE CHANGE: a change from one state (solid or liquid or gas) to another without a change in chemical composition. 22) Show that you understand how phase changes occur by writing an explanation for
Temperature. Temperature Scales. Temperature (cont d) CHAPTER 14 Heat and Temperature
 Temperature CHAPTER 14 Heat and Temperature The temperature of a substance is proportional to the average kinetic energy of the substance s particles. As the average kinetic energy of the particles in
Temperature CHAPTER 14 Heat and Temperature The temperature of a substance is proportional to the average kinetic energy of the substance s particles. As the average kinetic energy of the particles in
Thermometer Calibration
 Thermometer Calibration Jane Doe: Introduction and references John Smith: Procedure Leo Patel: Results Mike Jones: Discussion/Conclusion Introduction: Thermometers measure the amount of thermal energy
Thermometer Calibration Jane Doe: Introduction and references John Smith: Procedure Leo Patel: Results Mike Jones: Discussion/Conclusion Introduction: Thermometers measure the amount of thermal energy
Heat and Temperature
 Chapter 4 Heat Heat and Temperature Heat is a form of energy Heat is the energy of random motion of molecules constituting the body. It flows from a hot body to a cold body. Unit of heat is joule (J) and
Chapter 4 Heat Heat and Temperature Heat is a form of energy Heat is the energy of random motion of molecules constituting the body. It flows from a hot body to a cold body. Unit of heat is joule (J) and
Level A Unit 4 Phases of Matter: Solid, Liquid, Gas
 P H Y S I C A L S C I E N C E Level A Unit 4 Phases of Matter: Solid, Liquid, Gas National Institute for Direct Instruction (NIFDI) Academic Core Level A Lesson 1 a. (Display 3 Phases of Matter chart:)
P H Y S I C A L S C I E N C E Level A Unit 4 Phases of Matter: Solid, Liquid, Gas National Institute for Direct Instruction (NIFDI) Academic Core Level A Lesson 1 a. (Display 3 Phases of Matter chart:)
Physics 207 Lecture 23
 Thermodynamics A practical science initially concerned with economics, industry, real life problems. DYNAMICS -- Concerned with the concepts of energy transfers between a system and its environment and
Thermodynamics A practical science initially concerned with economics, industry, real life problems. DYNAMICS -- Concerned with the concepts of energy transfers between a system and its environment and
Designing a Thermostat Worksheet
 Designing a Thermostat Worksheet Most of us have a thermostat in our homes to control heating and cooling systems of our home. These important devices help us save energy by automatically turning off energy
Designing a Thermostat Worksheet Most of us have a thermostat in our homes to control heating and cooling systems of our home. These important devices help us save energy by automatically turning off energy
Thermal Process Control Lap 4 Thermal Energy. Notes:
 Thermal Process Control Lap 4 Thermal Energy Notes: 1) Temperature Measurement a) Define temperature i) A measure of the amount of heat contained in a solid, liquid, or gas ii) Result of molecular motion
Thermal Process Control Lap 4 Thermal Energy Notes: 1) Temperature Measurement a) Define temperature i) A measure of the amount of heat contained in a solid, liquid, or gas ii) Result of molecular motion
What Is Air Temperature?
 2.2 Read What Is Air Temperature? In Learning Set 1, you used a thermometer to measure air temperature. But what exactly was the thermometer measuring? What is different about cold air and warm air that
2.2 Read What Is Air Temperature? In Learning Set 1, you used a thermometer to measure air temperature. But what exactly was the thermometer measuring? What is different about cold air and warm air that
Lecture Outlines Chapter 16. Physics, 3 rd Edition James S. Walker
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 16 Physics, 3 rd Edition James S. Walker 2007 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in
Lecture Outlines Chapter 16 Physics, 3 rd Edition James S. Walker 2007 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in
The Kinetic Theory of Matter. Temperature. Temperature. Temperature. Temperature. Chapter 6 HEAT
 The Kinetic Theory of Matter Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Chapter 6 HEAT Kinetic Theory of Matter: Matter is made up of tiny particles (atoms or molecules) that are always in
The Kinetic Theory of Matter Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Chapter 6 HEAT Kinetic Theory of Matter: Matter is made up of tiny particles (atoms or molecules) that are always in
What Is This Module About? What Will You Learn From This Module?
 What Is This Module About? Do you know what temperature is? Temperature is part of your everyday life? For example how hot do you like your coffee or milk to be? Do you like drinking ice-cold water? What
What Is This Module About? Do you know what temperature is? Temperature is part of your everyday life? For example how hot do you like your coffee or milk to be? Do you like drinking ice-cold water? What
Lesson 1: What are chemical changes?
 Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: What are chemical changes? Vocabulary Use with pp. 375 377 physical change a change in which the material keeps its identify chemical change a change in which one substance or
Lesson 1 Summary Lesson 1: What are chemical changes? Vocabulary Use with pp. 375 377 physical change a change in which the material keeps its identify chemical change a change in which one substance or
Temperature and Heat. Prof. Yury Kolomensky Apr 20, 2007
 Temperature and Heat Prof. Yury Kolomensky Apr 20, 2007 From Mechanics to Applications Mechanics: behavior of systems of few bodies Kinematics: motion vs time Translational and rotational Dynamics: Newton
Temperature and Heat Prof. Yury Kolomensky Apr 20, 2007 From Mechanics to Applications Mechanics: behavior of systems of few bodies Kinematics: motion vs time Translational and rotational Dynamics: Newton
Physics 1501 Lecture 35
 Physics 1501: Lecture 35 Todays Agenda Announcements Homework #11 (Dec. 2) and #12 (Dec. 9): 2 lowest dropped Honors students: see me after the class! Todays topics Chap.16: Temperature and Heat» Latent
Physics 1501: Lecture 35 Todays Agenda Announcements Homework #11 (Dec. 2) and #12 (Dec. 9): 2 lowest dropped Honors students: see me after the class! Todays topics Chap.16: Temperature and Heat» Latent
4.1. Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 4 - Heat GCKL UNDERSTANDING THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM. What is thermal equilibrium?
 4.1 4 UNDERSTANDING THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM What is thermal equilibrium? 1. ( Heat, Temperature ) is a form of energy that flows from a hot body to a cold body. 2. The SI unit for ( heat, temperature) is Joule,
4.1 4 UNDERSTANDING THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM What is thermal equilibrium? 1. ( Heat, Temperature ) is a form of energy that flows from a hot body to a cold body. 2. The SI unit for ( heat, temperature) is Joule,
Applied Natural Sciences
 Het basisvak Toegepaste Natuurwetenschappen http://www.phys.tue.nl/nfcmr/natuur/collegenatuur.html Applied Natural Sciences Leo Pel e mail: phys3nab@tue.nl http://tiny.cc/3nab0 Chapter 17 Temperature and
Het basisvak Toegepaste Natuurwetenschappen http://www.phys.tue.nl/nfcmr/natuur/collegenatuur.html Applied Natural Sciences Leo Pel e mail: phys3nab@tue.nl http://tiny.cc/3nab0 Chapter 17 Temperature and
InterActions Unit 4 Chapter 2 Sample Quiz KEY
 InterActions Unit 4 Chapter 2 Sample Quiz KEY REMEMBER exams are given for the last chapter in a unit. They are comprehensive. So practice taking the Unit 4 Chapter 1 quiz again along with this practice
InterActions Unit 4 Chapter 2 Sample Quiz KEY REMEMBER exams are given for the last chapter in a unit. They are comprehensive. So practice taking the Unit 4 Chapter 1 quiz again along with this practice
We call the characteristic of a system that determines how much its temperature will change heat capacity.
 3/3 Measuring Heat If all we do is add heat to a system its temperature will rise. How much the temperature rises depends on the system. We call the characteristic of a system that determines how much
3/3 Measuring Heat If all we do is add heat to a system its temperature will rise. How much the temperature rises depends on the system. We call the characteristic of a system that determines how much
Temperature, Heat, and Expansion
 Thermodynamics (Based on Chapters 21-24) Temperature, Heat, and Expansion (Ch 21) Warmth is the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. Temperature (21.1) The measure of how hot and cold things are is temperature.
Thermodynamics (Based on Chapters 21-24) Temperature, Heat, and Expansion (Ch 21) Warmth is the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. Temperature (21.1) The measure of how hot and cold things are is temperature.
