Simple machines. ( Fxd) input. = (Fxd) output
|
|
|
- Shanon Bell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Announcements l LON-CAPA #5 and Mastering Physics Chapters 15 and 18 due Tuesday Feb. 18 l Average for exam 1 is 28/40 l The course will be graded on a curve with the average about 3.0, so if you received 28, you should be close to the 3.0 mark l I won t try to make a grading scale for each exam, but will let you know where you stand after the 2 nd exam l Note that the grading for problem 22 for the 3 rd version of the exam has to be re-done the correct answer is c, not e
2 Simple machines l A machine is a device for multiplying forces or simply changing the direction of forces l The principle underlying every machine is the conservation of energy l One simple machine is the lever l A force downwards on one side creates an upward force on the other side l But that s not the big deal l The big deal is that work input = work output l (ForceXdistance) input = (ForceXdistance) output It s a way of multiplying force, although the movement on the input side has to be larger ( Fxd) input = (Fxd) output fulcrum With the car jack, a 50N force acting over 25 cm becomes a 5000N force acting over 0.25 cm
3 Archimedes l Discovered the principle of the lever and once stated Give me a lever and a fulcrum and I can move the world l Also discovered the principle of bouyancy and is credited with shouting Eureka* as he ran naked from his bath, after discovering this principle * I have found it *Don t try this at home
4 Pulleys l A simple pulley can be used to change the direction of a force l With this arrangement, a load can be lifted with half of the input force (the tension in the rope provides the other half) l A block and tackle is a system of pulleys that multiplies force l Note that energy is not multiplied. It takes the same amount of work to raise the 500 N weight
5 Efficiency l Mostly we ve been talking about ideal machines, where 100% of input energy goes to output work l But in any real transformation of energy, some energy is dissipated to molecular kinetic energy, i.e. thermal energy l We define the efficiency by Efficiency = useful energy output total energy input
6 Sources of energy l Except for nuclear energy, essentially all of our energy sources derive the sun including coal, oil, wood, hydroelectric, wind (geothermal energy indirectly from nuclear) this answered a question that arose in the 1800 s; why is the interior of the Earth still hot? l Sunlight can be directly transformed into electricity by photovoltaic cells, like those in solar-power calculators about 1 kilowatt per square meter available in sunlight photovoltaic cells typically around 30% efficient l Oil is running out, so you hear a lot about running cars on hydrogen l But hydrogen is not a source of energy, but rather a way of storing it l You can produce hydrogen by the process of electrolysis on water H 2 0->H 2 + O l But it takes an energy input to bring about the electrolysis, and if you use coal, then that does nothing to solve the greenhouse gas problem
7 Temperature l The quantity that indicates how warm or cold an object is compared to some standard is called temperature l We use a device graduated in a scale to measure the temperature a thermometer works by means of expansion or contraction of a liquid, usually mercury or colored alcohol l The most common temperature scale in the world is the Celcius (also called Centrigrade) scale named after Anders Celcius 100 degrees between the freezing point of water and its boiling point l But in the United States, the Farenheit scale is more common, named after the German physicist Farenheit in this scale, water freezes at 32 degrees and boils at 212 degrees 0 o is the temperature of the coldest salt water solution in official use only in the US and in Belize The Quest for Absolute Zero
8 Conversions l Temperature (C) = 5/9 X ( temperature (F) -32 o ) l The two are equal at -40 o, cold no matter what scale you use to quote it l You should know how to convert from one to the other
9 Temperature and heat l Temperature is proportional to the average kinetic energy per particle in a substance how fast the atoms are moving in a gas or liquid or how fast the atoms are vibrating in a solid l Thermal energy refers to the sum of the kinetic energy of all particles in a substance l If I take a cup of hot water and pour out half of it, the temperature of the remaining half is still the same, but the thermal energy has been cut in half l When we measure the temperature of a object, thermal energy flows between the thermometer and the object l Eventually the thermometer and the object come to thermal equilibrium same average kinetic energy per particle
10 States of matter l As the temperature of an object increases, a solid object will melt and become a liquid; with more heat input the liquid will vaporize and become a gas l As the temperature is increased further, molecules dissociate into atoms and atoms lose some or all or their electrons, thereby forming a cloud of electrically charged particles, or a plasma l Plasmas exist in stars, where the temperatures can reach millions of degrees l There is no upper limit on temperature l Four states of matter solid liquid gas plasma hottest temperature ever generated on Earth is ~2 billion degrees C
11 Absolute zero l In the 19th century, physicists found something amazing l Suppose you start with a gas at 0 o C l The volume decreases by a fraction 1/273 for every degree decrease in temperature l This implied that if a gas were cooled to -273 o C, it would decrease to zero volume of course, by this point the gas would have turned into a liquid, but it brings up the idea that, while there is no upper limit to temperature, there is a lower limit l At o C, molecules have lost all available kinetic energy It s impossible to remove any more heat l This temperature is called absolute zero l The Kelvin temperature scale uses absolute zero as the zero of the temperature scale (but the degrees are the same size as for the Celcius scale) l The temperature scale is named after Lord Kelvin, another illustrious Scottish physicist originally William Thomson The Quest for Absolute Zero
12 iclicker question l Absolute zero corresponds to a temperature of A) 0 o K B) -273 o C C) D) both of these none of these
13 iclicker question l Absolute zero corresponds to a temperature of A) 0 o K B) -273 o C C) D) both of these none of these
14 Units for heat l Heat is measured in units of energy, or Joules l It takes 4.18 Joules to raise 1 gram of water by 1 degree C this is an experiment that either you have performed, or will perform, in ISP209L l The energy ratings of food are determined from the energy released when they are burned a person s metabolism is really burning, at a slow rate l The heat unit for food is the kilocalorie able to raise 1 kg of water by 1 degree C l To avoid confusion, the food unit is called a Calorie (=1000 calories)
15 Temperature and kinetic energy in a gas l Temperature is proportional to the average kinetic energy per particle in a substance how fast the atoms are moving in a gas or liquid or how fast the atoms are vibrating in a solid l Average kinetic energy of a gas molecule KE = 1 2 mv 2 KE average = 3 2 k B T k B =1.38X10-23 J/ o K Boltzmann s constant T is the temperature in degrees Kelvin l Suppose I have 22.4 liters of air at room temperature (300 o K) l What is its energy content? l To make it simple, assume that the air is all nitrogen (instead of 80%) l 22.4 liters is one mole or 6.02E23 atoms " KE molecule = 3 $ # 2% k T = " 3 $ B # 2% 1.38X10 23 J /K KE molecule = 6.2X10 21 J KE N 2 = 6.02X10 23 xke molecule = 3739J l What is the average speed of a N 2 molecule? KE molecule = 1 2 m N 2v 2 v 500m /s ( )( 300 o K) )
16 iclicker question l Whether one object is warmer than another has most to do with A) molecular kinetic energy B) molecular potential energy C) heat flow D) masses of internal particles
17 iclicker question l Whether one object is warmer than another has most to do with A) molecular kinetic energy B) molecular potential energy C) heat flow D) masses of internal particles
Gravitational potential energy
 Announcements l CAPA homework 4 due on Thursday Sept 27 at 10 AM l Please register your iclicker through LON-CAPA if you want to receive credit only a few of you have not l Help room hours (1248 BPS) Ian
Announcements l CAPA homework 4 due on Thursday Sept 27 at 10 AM l Please register your iclicker through LON-CAPA if you want to receive credit only a few of you have not l Help room hours (1248 BPS) Ian
Temperature. coldest salt water solution in official use only in the US and in Belize. The Quest for Absolute Zero ( )
 Announcements l Help room hours (1248 BPS) Ian La Valley(TA) Mon 4-6 PM (except not Monday Sept 17) Tues 12-3 PM Wed 6-9 PM Fri 10 AM-noon l First exam Tuesday Oct. 2 10:20 AM this room you may bring 1
Announcements l Help room hours (1248 BPS) Ian La Valley(TA) Mon 4-6 PM (except not Monday Sept 17) Tues 12-3 PM Wed 6-9 PM Fri 10 AM-noon l First exam Tuesday Oct. 2 10:20 AM this room you may bring 1
* Defining Temperature * Temperature is proportional to the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. * Temperature * Internal energy
 * Defining Temperature * We associate temperature with how hot or cold an object feels. * Our sense of touch serves as a qualitative indicator of temperature. * Energy must be either added or removed from
* Defining Temperature * We associate temperature with how hot or cold an object feels. * Our sense of touch serves as a qualitative indicator of temperature. * Energy must be either added or removed from
Chapter 7 Notes. Matter is made of tiny particles in constant motion
 Chapter 7 Notes Section 7.1 Matter is made of tiny particles in constant motion Atomic Theory Greek philosophers (430 BC ) Democritus and Leucippus proposed that matter is made of tiny particles called
Chapter 7 Notes Section 7.1 Matter is made of tiny particles in constant motion Atomic Theory Greek philosophers (430 BC ) Democritus and Leucippus proposed that matter is made of tiny particles called
the energy of motion!
 What are the molecules of matter doing all the time?! Heat and Temperature! Notes! All matter is composed of continually jiggling atoms or molecules! The jiggling is! If something is vibrating, what kind
What are the molecules of matter doing all the time?! Heat and Temperature! Notes! All matter is composed of continually jiggling atoms or molecules! The jiggling is! If something is vibrating, what kind
SI Measurements. (also known as metric system ) SI stands for System International or International System of Measurement
 SI Measurements (also known as metric system ) SI stands for System International or International System of Measurement SI Measurements (also known as metric system ) What about it? Common Language for
SI Measurements (also known as metric system ) SI stands for System International or International System of Measurement SI Measurements (also known as metric system ) What about it? Common Language for
Lecture Outline. Chapter 7: Energy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 7: Energy This lecture will help you understand: Energy Work Power Mechanical Energy: Potential and Kinetic Work-Energy Theorem Conservation of Energy Machines Efficiency Recycled
Lecture Outline Chapter 7: Energy This lecture will help you understand: Energy Work Power Mechanical Energy: Potential and Kinetic Work-Energy Theorem Conservation of Energy Machines Efficiency Recycled
Lecture Outline. Chapter 7: Energy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 7: Energy This lecture will help you understand: Energy Work Power Mechanical Energy: Potential and Kinetic Work-Energy Theorem Conservation of Energy Machines Efficiency Recycled
Lecture Outline Chapter 7: Energy This lecture will help you understand: Energy Work Power Mechanical Energy: Potential and Kinetic Work-Energy Theorem Conservation of Energy Machines Efficiency Recycled
Energy, Temperature, & Heat. Energy, Temperature, & Heat. Temperature Scales 1/17/11
 Energy, Temperature, & Heat Energy is the ability to do work (push, pull, lift) on some form of matter. Chapter 2 Potential energy is the potential for work (mass x gravity x height) Kinetic energy is
Energy, Temperature, & Heat Energy is the ability to do work (push, pull, lift) on some form of matter. Chapter 2 Potential energy is the potential for work (mass x gravity x height) Kinetic energy is
Temp vs. Heat. Absolute Temperature Scales. Common Temperature Scales. Thermal Energy. Heat and Temperature are not the same!!
 Thermal Energy Heat and Temperature are not the same!! Cold is the absence of heat, not an energy Same concept as light/dark Cold can t come in, heat flows out Heat flows from High Temp Low Temp Temp vs.
Thermal Energy Heat and Temperature are not the same!! Cold is the absence of heat, not an energy Same concept as light/dark Cold can t come in, heat flows out Heat flows from High Temp Low Temp Temp vs.
Exercises. 9.1 Work (pages ) 9.2 Power (pages ) 9.3 Mechanical Energy (page 147)
 Exercises 9.1 Work (pages 145 146) 1. Circle the letter next to the correct mathematical equation for work. work = force distance work = distance force c. work = force distance d. work = force distance
Exercises 9.1 Work (pages 145 146) 1. Circle the letter next to the correct mathematical equation for work. work = force distance work = distance force c. work = force distance d. work = force distance
Chapter 14: Temperature and Heat
 Chapter 14 Lecture Chapter 14: Temperature and Heat Goals for Chapter 14 To study temperature and temperature scales. To describe thermal expansion and its applications. To explore and solve problems involving
Chapter 14 Lecture Chapter 14: Temperature and Heat Goals for Chapter 14 To study temperature and temperature scales. To describe thermal expansion and its applications. To explore and solve problems involving
Today. Finish Ch. 6 on Momentum Start Ch. 7 on Energy
 Today Finish Ch. 6 on Momentum Start Ch. 7 on Energy Next three lectures (Sep 16, 20, 23) : Energy (Ch7) and Rotation (Ch.8) will be taught by Dr. Yonatan Abranyos, as I will be away at a research conference
Today Finish Ch. 6 on Momentum Start Ch. 7 on Energy Next three lectures (Sep 16, 20, 23) : Energy (Ch7) and Rotation (Ch.8) will be taught by Dr. Yonatan Abranyos, as I will be away at a research conference
Page 1 SPH3U. Heat. What is Heat? Thermal Physics. Waterloo Collegiate Institute. Some Definitions. Still More Heat
 SPH3U Thermal Physics electrons and holes in semiconductors An Introductory ourse in Thermodynamics converting energy into work magnetism thin films and surface chemistry thermal radiation (global warming)
SPH3U Thermal Physics electrons and holes in semiconductors An Introductory ourse in Thermodynamics converting energy into work magnetism thin films and surface chemistry thermal radiation (global warming)
Thermal energy 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE
 Thermal energy 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE Temperature There s more to temperature than the idea of hot and cold. Remember that all matter is made up of tiny particles that are constantly moving even in solid objects.
Thermal energy 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE Temperature There s more to temperature than the idea of hot and cold. Remember that all matter is made up of tiny particles that are constantly moving even in solid objects.
Atoms and molecules are in motion and have energy
 Atoms and molecules are in motion and have energy By now you know that substances are made of atoms and molecules. These atoms and molecules are always in motion and have attractions to each other. When
Atoms and molecules are in motion and have energy By now you know that substances are made of atoms and molecules. These atoms and molecules are always in motion and have attractions to each other. When
ENERGY. Unit 12: IPC
 ENERGY Unit 12: IPC WHAT IS ENERGY? Energy- is the ability to do work. Energy is the ability to cause a change. Energy can change an object s: motion shape temperature color THERMAL internal motion of
ENERGY Unit 12: IPC WHAT IS ENERGY? Energy- is the ability to do work. Energy is the ability to cause a change. Energy can change an object s: motion shape temperature color THERMAL internal motion of
Conceptual Physics Fundamentals
 Conceptual Physics Fundamentals Chapter 8: TEMPERATURE, HEAT, AND THERMODYNAMICS This lecture will help you understand: Temperature Absolute Zero Internal Energy Heat Quantity of Heat The Laws of Thermodynamics
Conceptual Physics Fundamentals Chapter 8: TEMPERATURE, HEAT, AND THERMODYNAMICS This lecture will help you understand: Temperature Absolute Zero Internal Energy Heat Quantity of Heat The Laws of Thermodynamics
Chapter Notes: Temperature, Energy and Thermal Properties of Materials Mr. Kiledjian
 Chapter 10-11 Notes: Temperature, Energy and Thermal Properties of Materials Mr. Kiledjian 1) Temperature 2) Expansion of Matter 3) Ideal Gas Law 4) Kinetic Theory of Gases 5) Energy, Heat transfer and
Chapter 10-11 Notes: Temperature, Energy and Thermal Properties of Materials Mr. Kiledjian 1) Temperature 2) Expansion of Matter 3) Ideal Gas Law 4) Kinetic Theory of Gases 5) Energy, Heat transfer and
Archimedes Principle
 Archimedes Principle applies in air the more air an object displaces, the greater the buoyant force on it if an object displaces its weight, it hovers at a constant altitude if an object displaces less
Archimedes Principle applies in air the more air an object displaces, the greater the buoyant force on it if an object displaces its weight, it hovers at a constant altitude if an object displaces less
Chapter 21: Temperature, Heat and Expansion
 Chapter 21: Temperature, Heat and Expansion All matter solid, liquid and gas is made of atoms or molecules, which are continually jiggling. As this jiggling is a movement, all these particles must have
Chapter 21: Temperature, Heat and Expansion All matter solid, liquid and gas is made of atoms or molecules, which are continually jiggling. As this jiggling is a movement, all these particles must have
Temperature Energy and Heat
 CHAPTER 3 Temperature Energy and Heat 3.1 Temperature What is temperature? Why is temperature important in chemistry? How is energy related to temperature? 2 3.1 Temperature Milk fat particles are being
CHAPTER 3 Temperature Energy and Heat 3.1 Temperature What is temperature? Why is temperature important in chemistry? How is energy related to temperature? 2 3.1 Temperature Milk fat particles are being
October 5 A. Bell Work B. Have 4.2 Notes I Out for a stamp C. Today we will work on 4.2 Notes II D. Homework: 4.2 Notes II (due tomorrow end of
 October 5 A. Bell Work B. Have 4.2 Notes I Out for a stamp C. Today we will work on 4.2 Notes II D. Homework: 4.2 Notes II (due tomorrow end of class) Read 4.3 and take notes (due Monday) 4.2 Key Concept:
October 5 A. Bell Work B. Have 4.2 Notes I Out for a stamp C. Today we will work on 4.2 Notes II D. Homework: 4.2 Notes II (due tomorrow end of class) Read 4.3 and take notes (due Monday) 4.2 Key Concept:
PROGRAM OF PHYSICS. Lecturer: Dr. DO Xuan Hoi Room A
 PROGRAM OF PHYSICS Lecturer: Dr. DO Xuan Hoi Room A1. 503 E-mail : dxhoi@hcmiu.edu.vn PHYSICS 2 (FLUID MECHANICS AND THERMAL PHYSICS) 02 credits (30 periods) Chapter 1 Fluid Mechanics Chapter 2 Heat, Temperature
PROGRAM OF PHYSICS Lecturer: Dr. DO Xuan Hoi Room A1. 503 E-mail : dxhoi@hcmiu.edu.vn PHYSICS 2 (FLUID MECHANICS AND THERMAL PHYSICS) 02 credits (30 periods) Chapter 1 Fluid Mechanics Chapter 2 Heat, Temperature
matter/index.html
 http://www.colorado.edu/physics/2000/index.pl http://www.harcourtschool.com/activity/states_of_ matter/index.html Thermal Energy Ch 6-1 Temperature and Heat Objectives Explain the kinetic theory of matter
http://www.colorado.edu/physics/2000/index.pl http://www.harcourtschool.com/activity/states_of_ matter/index.html Thermal Energy Ch 6-1 Temperature and Heat Objectives Explain the kinetic theory of matter
Chapter 14 Heat. Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 14 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 14 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 14 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Bernoulli s Principle. Application: Lift. Bernoulli s Principle. Main Points 3/13/15. Demo: Blowing on a sheet of paper
 Bernoulli s Principle Demo: Blowing on a sheet of paper Where the speed of a fluid increases, internal pressure in the fluid decreases. Due to continuous flow of a fluid: what goes in must come out! Fluid
Bernoulli s Principle Demo: Blowing on a sheet of paper Where the speed of a fluid increases, internal pressure in the fluid decreases. Due to continuous flow of a fluid: what goes in must come out! Fluid
Unit 2: Energy THERMAL ENERGY HEAT TRANSFER POTENTIAL VS. KINETIC ENERGY WORK POWER SIMPLE MACHINES
 Unit 2: Energy THERMAL ENERGY HEAT TRANSFER POTENTIAL VS. KINETIC ENERGY WORK POWER SIMPLE MACHINES Bellringer Day 01 1. What is energy? 2. There are different forms of energy. Name two. What is Energy?
Unit 2: Energy THERMAL ENERGY HEAT TRANSFER POTENTIAL VS. KINETIC ENERGY WORK POWER SIMPLE MACHINES Bellringer Day 01 1. What is energy? 2. There are different forms of energy. Name two. What is Energy?
Chapter 14 Temperature and Heat
 Chapter 14 Temperature and Heat To understand temperature and temperature scales. To describe thermal expansion and its applications. To explore and solve problems involving heat, phase changes and calorimetry.
Chapter 14 Temperature and Heat To understand temperature and temperature scales. To describe thermal expansion and its applications. To explore and solve problems involving heat, phase changes and calorimetry.
Physics Mechanics
 1 Physics 170 - Mechanics Lecture 35 Heat 2 Definition and Units of Heat Heat is a form of energy, and therefore is measured in joules. There are other units of heat, the most common one is the kilocalorie:
1 Physics 170 - Mechanics Lecture 35 Heat 2 Definition and Units of Heat Heat is a form of energy, and therefore is measured in joules. There are other units of heat, the most common one is the kilocalorie:
High temperature He is hot
 Lecture 9 What is Temperature and Heat? High temperature He is hot Some important definitions * Two objects are in Thermal contact with each other if energy can be exchanged between them. Thermal equilibrium
Lecture 9 What is Temperature and Heat? High temperature He is hot Some important definitions * Two objects are in Thermal contact with each other if energy can be exchanged between them. Thermal equilibrium
Chapter 11. Energy in Thermal Processes
 Chapter 11 Energy in Thermal Processes Energy Transfer When two objects of different temperatures are placed in thermal contact, the temperature of the warmer decreases and the temperature of the cooler
Chapter 11 Energy in Thermal Processes Energy Transfer When two objects of different temperatures are placed in thermal contact, the temperature of the warmer decreases and the temperature of the cooler
Kinetic Theory of Matter
 1 Temperature and Thermal Energy Kinetic Theory of Matter The motion of the particles in matter is described by kinetic theory of matter. Matter is composed of particles that are atoms, molecules, or ions
1 Temperature and Thermal Energy Kinetic Theory of Matter The motion of the particles in matter is described by kinetic theory of matter. Matter is composed of particles that are atoms, molecules, or ions
The Kinetic Theory of Matter. Temperature. Temperature. Temperature. Temperature. Chapter 6 HEAT
 The Kinetic Theory of Matter Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Chapter 6 HEAT Kinetic Theory of Matter: Matter is made up of tiny particles (atoms or molecules) that are always in
The Kinetic Theory of Matter Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Chapter 6 HEAT Kinetic Theory of Matter: Matter is made up of tiny particles (atoms or molecules) that are always in
Chapter 4. Properties of Matter
 Chapter 4 Properties of Matter A burning log undergoes chemical change resulting in the release of energy in the form of heat and light. The physical properties of the log change during the Introduction
Chapter 4 Properties of Matter A burning log undergoes chemical change resulting in the release of energy in the form of heat and light. The physical properties of the log change during the Introduction
Agenda. Chapter 10, Problem 26. All matter is made of atoms. Atomic Structure 4/8/14. What is the structure of matter? Atomic Terminology
 Agenda Today: HW Quiz, Thermal physics (i.e., heat) Thursday: Finish thermal physics, atomic structure (lots of review from chemistry!) Chapter 10, Problem 26 A boy reaches out of a window and tosses a
Agenda Today: HW Quiz, Thermal physics (i.e., heat) Thursday: Finish thermal physics, atomic structure (lots of review from chemistry!) Chapter 10, Problem 26 A boy reaches out of a window and tosses a
STATES OF MATTER NOTES..
 STATES OF MATTER NOTES.. While you are reading, answer the following which will help you with the States of Matter Project. What is matter (definition): What are the states of matter and what are the characteristics/properties
STATES OF MATTER NOTES.. While you are reading, answer the following which will help you with the States of Matter Project. What is matter (definition): What are the states of matter and what are the characteristics/properties
Thermal energy. Thermal energy is the internal energy of a substance. I.e. Thermal energy is the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules.
 Thermal energy Thermal energy is the internal energy of a substance. I.e. Thermal energy is the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. Heat is the transfer of thermal energy between substances. Until the
Thermal energy Thermal energy is the internal energy of a substance. I.e. Thermal energy is the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. Heat is the transfer of thermal energy between substances. Until the
Recap. There are 3 different temperature scales: Celsius, Kelvin, and Fahrenheit
 Recap Temperature, T, is related to the average kinetic energy of each atom/molecule the given material consists of: The ideal gas law relates pressure to density and temperature: There are 3 different
Recap Temperature, T, is related to the average kinetic energy of each atom/molecule the given material consists of: The ideal gas law relates pressure to density and temperature: There are 3 different
Thermodynamics Test Wednesday 12/20
 Thermodynamics Test Wednesday 12/20 HEAT AND TEMPERATURE 1 Temperature Temperature: A measure of how hot (or cold) something is Specifically, a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in
Thermodynamics Test Wednesday 12/20 HEAT AND TEMPERATURE 1 Temperature Temperature: A measure of how hot (or cold) something is Specifically, a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in
Chapters 17 &19 Temperature, Thermal Expansion and The Ideal Gas Law
 Chapters 17 &19 Temperature, Thermal Expansion and The Ideal Gas Law Units of Chapter 17 & 19 Temperature and the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Temperature Scales Thermal Expansion Heat and Mechanical Work
Chapters 17 &19 Temperature, Thermal Expansion and The Ideal Gas Law Units of Chapter 17 & 19 Temperature and the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Temperature Scales Thermal Expansion Heat and Mechanical Work
Conceptual Physics Fundamentals
 Conceptual Physics Fundamentals Chapter 8: TEMPERATURE, HEAT, AND THERMODYNAMICS This lecture will help you understand: Temperature Absolute Zero Internal Energy Heat Quantity of Heat The Laws of Thermodynamics
Conceptual Physics Fundamentals Chapter 8: TEMPERATURE, HEAT, AND THERMODYNAMICS This lecture will help you understand: Temperature Absolute Zero Internal Energy Heat Quantity of Heat The Laws of Thermodynamics
Lecture 21. Temperature. Thermal Expansion. Heat and Internal Energy. Cutnell+Johnson: , Temperature
 Lecture 21 Temperature Thermal Expansion Heat and Internal Energy Cutnell+Johnson: 12.1-12.7, 14.3 Temperature So far in this class we ve usually talked about large objects, and we ve treated the object
Lecture 21 Temperature Thermal Expansion Heat and Internal Energy Cutnell+Johnson: 12.1-12.7, 14.3 Temperature So far in this class we ve usually talked about large objects, and we ve treated the object
Chapter: Heat and States
 Table of Contents Chapter: Heat and States of Matter Section 1: Temperature and Thermal Energy Section 2: States of Matter Section 3: Transferring Thermal Energy Section 4: Using Thermal Energy 1 Temperature
Table of Contents Chapter: Heat and States of Matter Section 1: Temperature and Thermal Energy Section 2: States of Matter Section 3: Transferring Thermal Energy Section 4: Using Thermal Energy 1 Temperature
Chapter 11. Energy in Thermal Processes
 Chapter 11 Energy in Thermal Processes Energy Transfer When two objects of different temperatures are placed in thermal contact, the temperature of the warmer decreases and the temperature of the cooler
Chapter 11 Energy in Thermal Processes Energy Transfer When two objects of different temperatures are placed in thermal contact, the temperature of the warmer decreases and the temperature of the cooler
Chapter 14 Heat and Temperature Notes
 Chapter 14 Heat and Temperature Notes Section 1: Temperature The degree of or of an object. Related to the of an object s atoms or molecules What makes something hot? o Particles that make up o They have
Chapter 14 Heat and Temperature Notes Section 1: Temperature The degree of or of an object. Related to the of an object s atoms or molecules What makes something hot? o Particles that make up o They have
Chapter 10 Temperature and Heat
 Chapter 10 Temperature and Heat Thermodynamics deals with 1. Temperature. 2. The transfer and transformation of energy. 3. The relationship between macroscopic properties and microscopic dynamics. Temperature
Chapter 10 Temperature and Heat Thermodynamics deals with 1. Temperature. 2. The transfer and transformation of energy. 3. The relationship between macroscopic properties and microscopic dynamics. Temperature
UNIT 5: WORK and ENERGY RECORD ALL ANSWERS ON ANSWER SHEET.
 PHYSICAL SCIENCE UNIT 5: WORK and ENERGY RECORD ALL ANSWERS ON ANSWER SHEET. name 1. Which of the following processes requires the most work? a. A 10 kg weight rests on a table. b. A person holds a 1 kg
PHYSICAL SCIENCE UNIT 5: WORK and ENERGY RECORD ALL ANSWERS ON ANSWER SHEET. name 1. Which of the following processes requires the most work? a. A 10 kg weight rests on a table. b. A person holds a 1 kg
3.2 Units of Measurement > Chapter 3 Scientific Measurement. 3.2 Units of Measurement. 3.1 Using and Expressing Measurements
 Chapter 3 Scientific Measurement 3.1 Using and Expressing Measurements 3.2 Units of Measurement 3.3 Solving Conversion Problems 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
Chapter 3 Scientific Measurement 3.1 Using and Expressing Measurements 3.2 Units of Measurement 3.3 Solving Conversion Problems 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved.
EDULABZ INTERNATIONAL. Heat ASSIGNMENT
 Heat ASSIGNMENT 1. Fill in the blank spaces by choosing the correct words from the list given below : List : substance, thermal capacity, mass, latent, heat, cold, constant, water, J C 1, fusion, hot.
Heat ASSIGNMENT 1. Fill in the blank spaces by choosing the correct words from the list given below : List : substance, thermal capacity, mass, latent, heat, cold, constant, water, J C 1, fusion, hot.
SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY AND HEAT OF FUSION
 SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY AND HEAT OF FUSION Apparatus on each table: Thermometer, metal cube, complete calorimeter, outer calorimeter can (aluminum only), balance, 4 styrofoam cups, graduated container,
SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY AND HEAT OF FUSION Apparatus on each table: Thermometer, metal cube, complete calorimeter, outer calorimeter can (aluminum only), balance, 4 styrofoam cups, graduated container,
Solids, Liquids, and Gases. Chapter 14
 Solids, Liquids, and Gases Chapter 14 Matter & Thermal Energy Matter can exist as a solid, a liquid, a gas or a plasma. The Molecular Kinetic Theory of Matter explains their differences and how they can
Solids, Liquids, and Gases Chapter 14 Matter & Thermal Energy Matter can exist as a solid, a liquid, a gas or a plasma. The Molecular Kinetic Theory of Matter explains their differences and how they can
A). Yes. B). No. Q15 Is it possible for a solid metal ball to float in mercury?
 Q15 Is it possible for a solid metal ball to float in mercury? A). Yes. B). No. The upward force is the weight of liquid displaced and the downward force is the weight of the ball. If the density of the
Q15 Is it possible for a solid metal ball to float in mercury? A). Yes. B). No. The upward force is the weight of liquid displaced and the downward force is the weight of the ball. If the density of the
Chapter 11. Important to distinguish between them. They are not interchangeable. They mean very different things when used in physics Internal Energy
 Chapter 11 Energy in Thermal Processes Energy Transfer When two objects of different temperatures are placed in thermal contact, the temperature of the warmer decreases and the temperature of the cooler
Chapter 11 Energy in Thermal Processes Energy Transfer When two objects of different temperatures are placed in thermal contact, the temperature of the warmer decreases and the temperature of the cooler
Physical Science Chapter 5 Cont2. Temperature & Heat
 Physical Science Chapter 5 Cont2 Temperature & Heat What are we going to study? Temperature Heat Specific Heat and Latent Heat Heat Transfer Phases of Matter The Kinetic Theory of Gases Thermodynamics
Physical Science Chapter 5 Cont2 Temperature & Heat What are we going to study? Temperature Heat Specific Heat and Latent Heat Heat Transfer Phases of Matter The Kinetic Theory of Gases Thermodynamics
 Since ancient times, people have needed thermal energy (heat) to cook their food and to keep them warm. And since the beginning of time, uncontrolled heat has scorched and spoiled the taste of food and
Since ancient times, people have needed thermal energy (heat) to cook their food and to keep them warm. And since the beginning of time, uncontrolled heat has scorched and spoiled the taste of food and
Ch 100: Fundamentals for Chemistry
 Ch 100: Fundamentals for Chemistry Chapter 4: Properties of Matter Lecture Notes Physical & Chemical Properties Physical Properties are the characteristics of matter that can be changed without changing
Ch 100: Fundamentals for Chemistry Chapter 4: Properties of Matter Lecture Notes Physical & Chemical Properties Physical Properties are the characteristics of matter that can be changed without changing
Recap: Bernoulli s Principle
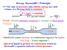 Recap: Bernoulli s Principle The sum of pressure plus kinetic energy per unit volume of a flowing fluid is constant. P + ½ρv 2 = constant pressure K.E. per unit volume (ρ = mass vol ) Result: Relates pressure
Recap: Bernoulli s Principle The sum of pressure plus kinetic energy per unit volume of a flowing fluid is constant. P + ½ρv 2 = constant pressure K.E. per unit volume (ρ = mass vol ) Result: Relates pressure
Lecture Presentation. Chapter 6. Thermochemistry. Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 6 Thermochemistry Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University Chemical Hand Warmers Most hand warmers work by using the heat released from the slow oxidation of iron 4 Fe(s)
Lecture Presentation Chapter 6 Thermochemistry Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University Chemical Hand Warmers Most hand warmers work by using the heat released from the slow oxidation of iron 4 Fe(s)
Physics 111. Lecture 39 (Walker: 17.6, 18.2) Latent Heat Internal Energy First Law of Thermodynamics May 8, Latent Heats
 Physics 111 Lecture 39 (Walker: 17.6, 18.2) Latent Heat Internal Energy First Law of Thermodynamics May 8, 2009 Lecture 39 1/26 Latent Heats The heat required to convert from one phase to another is called
Physics 111 Lecture 39 (Walker: 17.6, 18.2) Latent Heat Internal Energy First Law of Thermodynamics May 8, 2009 Lecture 39 1/26 Latent Heats The heat required to convert from one phase to another is called
PE = mgh. Potential energy. What is g here? Let s pick up where we left off last time..the topic was gravitational potential energy
 Let s pick up where we left off last time..the topic was gravitational potential energy Now, let s talk about a second form of energy Potential energy Imagine you are standing on top of half dome in Yosemite
Let s pick up where we left off last time..the topic was gravitational potential energy Now, let s talk about a second form of energy Potential energy Imagine you are standing on top of half dome in Yosemite
Temperature, Heat, and Expansion
 Thermodynamics (Based on Chapters 21-24) Temperature, Heat, and Expansion (Ch 21) Warmth is the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. Temperature (21.1) The measure of how hot and cold things are is temperature.
Thermodynamics (Based on Chapters 21-24) Temperature, Heat, and Expansion (Ch 21) Warmth is the kinetic energy of atoms and molecules. Temperature (21.1) The measure of how hot and cold things are is temperature.
Unit 5 Thermodynamics
 Unit 5 Thermodynamics Unit 13: Heat and Temperature Unit 14: Thermal Expansion /Heat Exchange/ Change of Phase Test: Units 13-14 Thermal Energy The total kinetic and potential energy of all the molecules
Unit 5 Thermodynamics Unit 13: Heat and Temperature Unit 14: Thermal Expansion /Heat Exchange/ Change of Phase Test: Units 13-14 Thermal Energy The total kinetic and potential energy of all the molecules
Today: Chapter 7 -- Energy
 Today: Chapter 7 -- Energy Energy is a central concept in all of science. We will discuss how energy appears in different forms, but cannot be created or destroyed. Some forms are more useful than others
Today: Chapter 7 -- Energy Energy is a central concept in all of science. We will discuss how energy appears in different forms, but cannot be created or destroyed. Some forms are more useful than others
Physics 207 Lecture 23
 Thermodynamics A practical science initially concerned with economics, industry, real life problems. DYNAMICS -- Concerned with the concepts of energy transfers between a system and its environment and
Thermodynamics A practical science initially concerned with economics, industry, real life problems. DYNAMICS -- Concerned with the concepts of energy transfers between a system and its environment and
CHEMISTRY: Chapter 10 Prep-Test
 CHEMISTRY: Chapter 10 Prep-Test Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. calorimeter d. temperature b. calorie e. specific heat c. joule f. heat 1. quantity of heat needed to raise
CHEMISTRY: Chapter 10 Prep-Test Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. calorimeter d. temperature b. calorie e. specific heat c. joule f. heat 1. quantity of heat needed to raise
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 14 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 14 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 14 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Thermodynamics Problem Set. The amount of heat necessary to raise a body one degree of temperature (K or o C) is called:
 Thermodynamics Problem Set 1. 100 o C converted to both the Fahrenheit scale and the kelvin scale is which of the following? a. 238 o F, 373.15 K b. 88 o F, 273.15 K c. 238 o F, 273.15 K d. 212 o F, 373.15
Thermodynamics Problem Set 1. 100 o C converted to both the Fahrenheit scale and the kelvin scale is which of the following? a. 238 o F, 373.15 K b. 88 o F, 273.15 K c. 238 o F, 273.15 K d. 212 o F, 373.15
THERMODYNAMICS. Thermodynamics is the study of energy relationships that involve heat, mechanical work, and other aspects of energy and heat transfer.
 THERMODYNAMICS Thermodynamics is the study of energy relationships that involve heat, mechanical work, and other aspects of energy and heat transfer. Central Heating Objectives: After finishing this unit,
THERMODYNAMICS Thermodynamics is the study of energy relationships that involve heat, mechanical work, and other aspects of energy and heat transfer. Central Heating Objectives: After finishing this unit,
First Law of Thermodynamics: energy cannot be created or destroyed.
 1 CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS ANSWERS energy = anything that has the capacity to do work work = force acting over a distance Energy (E) = Work = Force x Distance First Law of Thermodynamics: energy cannot
1 CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS ANSWERS energy = anything that has the capacity to do work work = force acting over a distance Energy (E) = Work = Force x Distance First Law of Thermodynamics: energy cannot
Physics 100 Lecture 5. Laws of Thermodynamics February 5, 2018
 3 Physics 100 Lecture 5 Laws of Thermodynamics February 5, 2018 4 Class Quiz 2-3: A block of wood loses 100 J of gravitational potential energy as it slides down a ramp. If it has 90 J of kinetic energy
3 Physics 100 Lecture 5 Laws of Thermodynamics February 5, 2018 4 Class Quiz 2-3: A block of wood loses 100 J of gravitational potential energy as it slides down a ramp. If it has 90 J of kinetic energy
Preview. Heat Section 1. Section 1 Temperature and Thermal Equilibrium. Section 2 Defining Heat. Section 3 Changes in Temperature and Phase
 Heat Section 1 Preview Section 1 Temperature and Thermal Equilibrium Section 2 Defining Heat Section 3 Changes in Temperature and Phase Heat Section 1 TEKS The student is expected to: 6E describe how the
Heat Section 1 Preview Section 1 Temperature and Thermal Equilibrium Section 2 Defining Heat Section 3 Changes in Temperature and Phase Heat Section 1 TEKS The student is expected to: 6E describe how the
What kinds of energy do you see?
 Energy Transfer ICP FTF Day 2 April 16, 2012 HW: none Topic: Light (last day) Questions: 1. When light passes through a prism, which colors of light are bent the most? 2. Which two colors of paint could
Energy Transfer ICP FTF Day 2 April 16, 2012 HW: none Topic: Light (last day) Questions: 1. When light passes through a prism, which colors of light are bent the most? 2. Which two colors of paint could
2,000-gram mass of water compared to a 1,000-gram mass.
 11.2 Heat To change the temperature, you usually need to add or subtract energy. For example, when it s cold outside, you turn up the heat in your house or apartment and the temperature goes up. You know
11.2 Heat To change the temperature, you usually need to add or subtract energy. For example, when it s cold outside, you turn up the heat in your house or apartment and the temperature goes up. You know
Practice Packet: Energy. Regents Chemistry: Dr. Shanzer. Practice Packet. Chapter 4: Energy.
 Regents Chemistry: Dr. Shanzer Practice Packet Chapter 4: Energy http:/drshanzerchemistry.weebly.com Energy Objectives Define energy. Demonstrate the difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions
Regents Chemistry: Dr. Shanzer Practice Packet Chapter 4: Energy http:/drshanzerchemistry.weebly.com Energy Objectives Define energy. Demonstrate the difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions
Unit 4 - Energy & Heat SOL PS.6,7
 Unit 4 - Energy & Heat SOL PS.6,7 Bill Nye - Energy I. PS.6a - Potential & Kinetic Energy A. Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. B. Energy is either Potential or Kinetic. a. Potential Energy
Unit 4 - Energy & Heat SOL PS.6,7 Bill Nye - Energy I. PS.6a - Potential & Kinetic Energy A. Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. B. Energy is either Potential or Kinetic. a. Potential Energy
What does temperature have to do with energy? What three temperature scales are commonly used? What makes things feel hot or cold?
 Heat and Temperature Section 1: Temperature What does temperature have to do with energy? What three temperature scales are commonly used? What makes things feel hot or cold? 1 Intro: Discussion A person
Heat and Temperature Section 1: Temperature What does temperature have to do with energy? What three temperature scales are commonly used? What makes things feel hot or cold? 1 Intro: Discussion A person
Chapter 2. States of Matter
 Chapter 2 States of Matter 2-1 Matter Matter Matter Anything that takes up space and has mass. Is air matter? Yes. It takes up space and has mass. It has atoms. All matter is made up of atoms. ( Dalton
Chapter 2 States of Matter 2-1 Matter Matter Matter Anything that takes up space and has mass. Is air matter? Yes. It takes up space and has mass. It has atoms. All matter is made up of atoms. ( Dalton
Scientific Reasoning, logic and the nature of science
 Review Packet for Science SOL Scientific Reasoning, logic and the nature of science 1. What is the SI (metric) measurement for: a. Length b. Mass c. Volume d. Density e. Temperature f. Weight g. Force
Review Packet for Science SOL Scientific Reasoning, logic and the nature of science 1. What is the SI (metric) measurement for: a. Length b. Mass c. Volume d. Density e. Temperature f. Weight g. Force
There are three phases of matter: Solid, liquid and gas
 FLUIDS: Gases and Liquids Chapter 4 of text There are three phases of matter: Solid, liquid and gas Solids: Have form, constituents ( atoms and molecules) are in fixed positions (though they can vibrate
FLUIDS: Gases and Liquids Chapter 4 of text There are three phases of matter: Solid, liquid and gas Solids: Have form, constituents ( atoms and molecules) are in fixed positions (though they can vibrate
PHYSICS 220. Lecture 22. Textbook Sections Lecture 22 Purdue University, Physics 220 1
 PHYSICS 220 Lecture 22 Temperature and Ideal Gas Textbook Sections 14.1 14.3 Lecture 22 Purdue University, Physics 220 1 Overview Last Lecture Speed of sound v = sqrt(b/ρ) Intensity level β = (10 db) log
PHYSICS 220 Lecture 22 Temperature and Ideal Gas Textbook Sections 14.1 14.3 Lecture 22 Purdue University, Physics 220 1 Overview Last Lecture Speed of sound v = sqrt(b/ρ) Intensity level β = (10 db) log
Physics 1501 Lecture 35
 Physics 1501: Lecture 35 Todays Agenda Announcements Homework #11 (Dec. 2) and #12 (Dec. 9): 2 lowest dropped Honors students: see me after the class! Todays topics Chap.16: Temperature and Heat» Latent
Physics 1501: Lecture 35 Todays Agenda Announcements Homework #11 (Dec. 2) and #12 (Dec. 9): 2 lowest dropped Honors students: see me after the class! Todays topics Chap.16: Temperature and Heat» Latent
Mr Chiasson Advanced Chemistry 12 / Chemistry 12 1 Unit B: Thermochemical Changes
 Mr Chiasson Advanced Chemistry 12 / Chemistry 12 1 Unit B: Thermochemical Changes Students will be expected to: Compare the molar enthalpies of several combustion reactions involving organic compounds.
Mr Chiasson Advanced Chemistry 12 / Chemistry 12 1 Unit B: Thermochemical Changes Students will be expected to: Compare the molar enthalpies of several combustion reactions involving organic compounds.
Temperature and Heat. Two systems of temperature. Temperature conversions. PHY heat - J. Hedberg
 Temperature and Heat 1. Two systems of temperature 1. Temperature conversions 2. Real science (one scale to rule them all) 3. Temperature scales 2. Effects of temperature on materials 1. Linear Thermal
Temperature and Heat 1. Two systems of temperature 1. Temperature conversions 2. Real science (one scale to rule them all) 3. Temperature scales 2. Effects of temperature on materials 1. Linear Thermal
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 26
 PHYSICS 149: Lecture 26 Chapter 14: Heat 14.1 Internal Energy 14.2 Heat 14.3 Heat Capacity and Specific Heat 14.5 Phase Transitions 14.6 Thermal Conduction 14.7 Thermal Convection 14.8 Thermal Radiation
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 26 Chapter 14: Heat 14.1 Internal Energy 14.2 Heat 14.3 Heat Capacity and Specific Heat 14.5 Phase Transitions 14.6 Thermal Conduction 14.7 Thermal Convection 14.8 Thermal Radiation
Level A Unit 4 Phases of Matter: Solid, Liquid, Gas
 P H Y S I C A L S C I E N C E Level A Unit 4 Phases of Matter: Solid, Liquid, Gas National Institute for Direct Instruction (NIFDI) Academic Core Level A Lesson 1 a. (Display 3 Phases of Matter chart:)
P H Y S I C A L S C I E N C E Level A Unit 4 Phases of Matter: Solid, Liquid, Gas National Institute for Direct Instruction (NIFDI) Academic Core Level A Lesson 1 a. (Display 3 Phases of Matter chart:)
Temperature and Its Measurement
 Temperature and Its Measurement When the physical properties are no longer changing, the objects are said to be in thermal equilibrium. Two or more objects in thermal equilibrium have the same temperature.
Temperature and Its Measurement When the physical properties are no longer changing, the objects are said to be in thermal equilibrium. Two or more objects in thermal equilibrium have the same temperature.
14-Feb-18 INSIDE STARS. Matter and Energy. Matter and Energy. Matter and Energy. What is matter?
 What is matter? What is matter? It's what everything that occupies space and has mass is made of And everything like that is made out of chemical elements There are 92 naturally occurring chemical elements,
What is matter? What is matter? It's what everything that occupies space and has mass is made of And everything like that is made out of chemical elements There are 92 naturally occurring chemical elements,
Year 7 Recall Booklet. Name: Class:
 Year 7 Recall Booklet Name: Class: Energy Kinetic energy Moving things have kinetic energy. The heavier a thing is and the faster it moves the more kinetic energy it has. All moving things have kinetic
Year 7 Recall Booklet Name: Class: Energy Kinetic energy Moving things have kinetic energy. The heavier a thing is and the faster it moves the more kinetic energy it has. All moving things have kinetic
Temperature and Heat. Chapter 17. PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman
 Chapter 17 Temperature and Heat PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun Goals for Chapter 17 To delineate the three different
Chapter 17 Temperature and Heat PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun Goals for Chapter 17 To delineate the three different
Chapter 14 Temperature and Heat
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 14 Temperature and Heat Thermodynamics Starting a different area of physics called thermodynamics Thermodynamics focuses on energy rather than
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 14 Temperature and Heat Thermodynamics Starting a different area of physics called thermodynamics Thermodynamics focuses on energy rather than
Today. Work, Energy, Power loose ends Temperature Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Today Announcements: HW#5 is due by 8:00 am Wed. Feb. 5th. Extra Credit Exam due by Tomorrow 8am. Work, Energy, Power loose ends Temperature Second Law of Thermodynamics ISP09s9 Lecture 11-1- Energy and
Today Announcements: HW#5 is due by 8:00 am Wed. Feb. 5th. Extra Credit Exam due by Tomorrow 8am. Work, Energy, Power loose ends Temperature Second Law of Thermodynamics ISP09s9 Lecture 11-1- Energy and
Thermochemistry. The study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions and changes in state.
 Energy Thermochemistry The study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions and changes in state. The Nature of Energy Energy - the ability to do work or produce heat Energy is stored in the
Energy Thermochemistry The study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions and changes in state. The Nature of Energy Energy - the ability to do work or produce heat Energy is stored in the
Keep the Heat Test School Name. Team Number
 Keep the Heat Test 1-28-2012 School Name Team Number Circle the all of the correct answer to the below questions. One or more of the answers can be correct, if more than on one answer is correct, circle
Keep the Heat Test 1-28-2012 School Name Team Number Circle the all of the correct answer to the below questions. One or more of the answers can be correct, if more than on one answer is correct, circle
Most hand warmers work by using the heat released from the slow oxidation of iron: The amount your hand temperature rises depends on several factors:
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 6 Thermochemistry Chemical Hand Warmers Most hand warmers work by using the heat released from the slow oxidation of iron: Exothermic reaction 4 Fe(s) + 3 O 2 (g) 2 Fe 2 O
Lecture Presentation Chapter 6 Thermochemistry Chemical Hand Warmers Most hand warmers work by using the heat released from the slow oxidation of iron: Exothermic reaction 4 Fe(s) + 3 O 2 (g) 2 Fe 2 O
Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics Heat Engines Heat engines use a temperature difference involving a high temperature (T H ) and a low temperature (T C ) to do mechanical work.
Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics Heat Engines Heat engines use a temperature difference involving a high temperature (T H ) and a low temperature (T C ) to do mechanical work.
Unit 11: Temperature and heat
 Unit 11: Temperature and heat 1. Thermal energy 2. Temperature 3. Heat and thermal equlibrium 4. Effects of heat 5. Transference of heat 6. Conductors and insulators Think and answer a. Is it the same
Unit 11: Temperature and heat 1. Thermal energy 2. Temperature 3. Heat and thermal equlibrium 4. Effects of heat 5. Transference of heat 6. Conductors and insulators Think and answer a. Is it the same
Student Exploration: Temperature and Particle Motion
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Temperature and Particle Motion Vocabulary: absolute zero, Kelvin scale, kinetic energy, molecule, temperature, Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.)
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Temperature and Particle Motion Vocabulary: absolute zero, Kelvin scale, kinetic energy, molecule, temperature, Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.)
Thermochemistry, Reaction Rates, & Equillibrium
 Thermochemistry, Reaction Rates, & Equillibrium Reaction Rates The rate at which chemical reactions occur Reaction Rates RXN rate = rate at which reactants change into products over time. This tells you
Thermochemistry, Reaction Rates, & Equillibrium Reaction Rates The rate at which chemical reactions occur Reaction Rates RXN rate = rate at which reactants change into products over time. This tells you
Weather Unit. Welcome Back! Begin Semester 2 1/20/2010. Seating Changes Final Exam Averages S1 Routine Changes for S2 Review Expectations.
 Welcome Back! Begin Semester 2 Weather Unit I-2 to I-6 Seating Changes Final Exam Averages S1 Routine Changes for S2 Review Expectations Beginning of Class (ChemCatalyst) Chemistry Binders and note-taking
Welcome Back! Begin Semester 2 Weather Unit I-2 to I-6 Seating Changes Final Exam Averages S1 Routine Changes for S2 Review Expectations Beginning of Class (ChemCatalyst) Chemistry Binders and note-taking
