Outline Network structure and objectives Routing Routing protocol protocol System analysis Results Conclusion Slide 2
|
|
|
- Martha Osborne
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2007 Radio and Wireless Symposium 9 11 January 2007, Long Beach, CA. Lifetime-Aware Hierarchical Wireless Sensor Network Architecture with Mobile Overlays Maryam Soltan, Morteza Maleki, and Massoud Pedram Department of Electrical Engineering University of Southern California Slide 1
2 Outline Network structure and objectives Routing protocol System analysis Results Conclusion Slide 2
3 Hierarchical Network Structure Sensor nodes Event Aggregation Relay ( (EAR EAR) )nodes Mobile Aerial Infrastructure overlay (MAIL)) nodes Base Station Flight Trajectory MAIL Node EAR Node Sensor Node M# of fmail nodes Base N # of EAR nodes Station Base Station Recurrent cycle Network Monitoring Lifetime (MoL) Flat architecture Slide 3
4 Objectives Analysis of concurrent controllable mobility and multi-hop routing in a multi-tier tier network Base Station Design and Analysis of Mobility-aware routing protocol Slide 4
5 Motivation Lower energy dissipation Longer lifetime. Energy consumption for wireless transmission: ε = ed β t d : Distance et : Energy dissipation for transmitting unit of data over unit of distance β : Path loss exponent Hierarchical network structure and multi-hop routing lowers energy dissipation. Mobility brings symmetry in battery depletion Slide 5
6 Bounded Hop Count Routing (BHR) Multi-hop routing between EAR nodes Less network delay and smaller storage size Shorter distance Less transmission power Dynamic Hop Count (DHC) vs. Initial Hop Count (IHC) mobility Routing delays transmission, propagation and queueing Bounded number of hops route if hop count <= H Storage, delay, and energy trade-off Slide 6
7 T 6 s 7 T 5 EAR Node Cluster and State Transitions in Each Cycle... Wait (S1) state Forward Chain γ S2 state μ 1... MAIL Coverage Area (Single Hop Routing) v... Backward Chain i j j+1 j+2 μ 2 k k+nc-1 k+nc k+nc+1 l... k + 1 k+nc-2 S3 state S4 state S5 S6 state S7 state (Nc -2) nodes T 7 s 1 T 1 Active States s7 s 6 s 2 s 5 s 3 T 2 s 5 3 T 4 s 4 T 3 Network of queues with vacation and variable service rate over time Slide 7
8 Queuing Analysis of Each EAR Node Wait (S1) state S2 state Forward Chain (Single Hop Routing) i j j+1 j+2 μ k 2... γ... v... Backward Chain k+nc-1 k+nc k+nc+1... μ 1 k + 1 k+nc-2 S3 state S4 state S6 state S7 state (a) Temporal variation of arrival rate for node i (b) Temporal variations of departure rate μ or μ 1 2 if Qi ( t ) > ( ) { t> T 0 1 Ui () t = For, Ai() t if Qi() t = 0 otherwise U ( t) = 0 i (c) () Temporal Variations of queue size l A i () t Ut i() Q i (t) + H ( H 1) (a) H 2 + μ 1 H.<μ 2 <μ 1 Δt B ( ) T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 μ H 1 2 μ ( H 1) 2 ( H 2 ) Δt B T1 T2 T3 T4 T 5 T6 7 L 1 μ 1 L 2 + μ μ L L 4 μ2 s 1 s 2 s 3 s 4 s 5 s 6 s 7 T 1 T2 T3 T 4 5 T T T T T Slide 8 (b) (c) M
9 Waiting Time in Queues EAR-to to-ear link delay: t link1 State durations: T i Avg. waiting in each EAR node: W t = W + ( 1/ μ ) link 1 1 t : link 1 Set as a variable T i Queueing analysis as a function of t link1 W as a function of t link1 System of two equations W Slide 9
10 Average Number of Hops for a Packet Transmission Hop count for packet delivery from an EAR node hi () t to a MAIL node Between 1 to H DHC seen by an EAR node during one cycle H 1 H Temporal average of DHC for a packet delivery 1 DHC t1 t2 t3 1 H 1 + h = H ( T1 + T2) + ( T4 + T5) + ( ) ( T3 + T6 ) T 2 M Δt s (H-1) Δt s (c+n ) Δ t tc c s (n ) Δt c s (H-1) Δts tn= Tcyc Slide 10
11 Network Delay Average delay for a packet to reach a MAIL node, D net D net ( h 1) 1 = h W + + μ μ 1 2 Waiting time in queues EAR-to-MAIL communication EAR-to-EAR communications Slide 11
12 Network Lifetime Average energy consumption for a packet delivery: E = ( h 1) ee + em e E : Avg. energy consumption for EAR-to-EAR communication e E M : Avg. energy consumption for EAR-to-MAIL communication Average # of packets generated during lifetime of the network: N T net 0 ( ) E N T N E T. 0 net E net = = E Slide 12
13 Max T vh,, Nc sys T = Min( T, c T ) sys net e Optimization Problem s.. t D D, B B, c C C net max p max M max Convex epigraph form: f 1 T f, f 1/ ct 1/ T sys e net Min f vhr,, c T e : MAIL endurance time T net : Network lifetime B p : Peak queue size C M M: : Recharge Cost c : # of charge occasions st.. ke f E 0, ρ v f c α E M 0 and D D, B B, c C C net max p max M max 3 ( T 3 1 ) e v Slide 13
14 Sample scenario: Simulation Results 1000 EAR nodes Q i (t) 1 Random distribution ib i Two MAIL nodes μ 2 e t for EAR-to-EAR: e t for EAR-to-MAIL: 10 (pjoul/bit/m 2 ) 1 T2 T3 : μ + μ1 μ2 s 1 s 2 s 3 s 4 s s 5 s 6 7 T T T T T Slide 14
15 Simulation Results Cont. Delay: Dnet 1 vm H 2 Lifetime: T net 1 H 2 Slide 15
16 Concluding Remarks Lifetime and delay aware deployment strategy A mobility-aware multi-hop routing protocol (Bounded hop count routing (BHR)) To control the trade off between delay, buffer size and lifetime Analysis of lifetime, delay, and buffer size Optimization problem formulation Packet level simulator Slide 16
Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems
 Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems Introduction to Queuing Systems System Performance Measures & Little s Law Equilibrium Solution of Birth-Death Processes Analysis of Single-Station Queuing Systems
Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems Introduction to Queuing Systems System Performance Measures & Little s Law Equilibrium Solution of Birth-Death Processes Analysis of Single-Station Queuing Systems
Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems
 Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems Problem 1: Customers arrive at a grocery store s checkout counter according to a Poisson process with rate 1 per minute. Each customer carries a number of items
Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems Problem 1: Customers arrive at a grocery store s checkout counter according to a Poisson process with rate 1 per minute. Each customer carries a number of items
Queuing Networks: Burke s Theorem, Kleinrock s Approximation, and Jackson s Theorem. Wade Trappe
 Queuing Networks: Burke s Theorem, Kleinrock s Approximation, and Jackson s Theorem Wade Trappe Lecture Overview Network of Queues Introduction Queues in Tandem roduct Form Solutions Burke s Theorem What
Queuing Networks: Burke s Theorem, Kleinrock s Approximation, and Jackson s Theorem Wade Trappe Lecture Overview Network of Queues Introduction Queues in Tandem roduct Form Solutions Burke s Theorem What
Energy Optimal Control for Time Varying Wireless Networks. Michael J. Neely University of Southern California
 Energy Optimal Control for Time Varying Wireless Networks Michael J. Neely University of Southern California http://www-rcf.usc.edu/~mjneely Part 1: A single wireless downlink (L links) L 2 1 S={Totally
Energy Optimal Control for Time Varying Wireless Networks Michael J. Neely University of Southern California http://www-rcf.usc.edu/~mjneely Part 1: A single wireless downlink (L links) L 2 1 S={Totally
WiFi MAC Models David Malone
 WiFi MAC Models David Malone November 26, MACSI Hamilton Institute, NUIM, Ireland Talk outline Introducing the 82.11 CSMA/CA MAC. Finite load 82.11 model and its predictions. Issues with standard 82.11,
WiFi MAC Models David Malone November 26, MACSI Hamilton Institute, NUIM, Ireland Talk outline Introducing the 82.11 CSMA/CA MAC. Finite load 82.11 model and its predictions. Issues with standard 82.11,
Mathematical Analysis of IEEE Energy Efficiency
 Information Engineering Department University of Padova Mathematical Analysis of IEEE 802.11 Energy Efficiency A. Zanella and F. De Pellegrini IEEE WPMC 2004 Padova, Sept. 12 15, 2004 A. Zanella and F.
Information Engineering Department University of Padova Mathematical Analysis of IEEE 802.11 Energy Efficiency A. Zanella and F. De Pellegrini IEEE WPMC 2004 Padova, Sept. 12 15, 2004 A. Zanella and F.
Call Completion Probability in Heterogeneous Networks with Energy Harvesting Base Stations
 Call Completion Probability in Heterogeneous Networks with Energy Harvesting Base Stations Craig Wang, Salman Durrani, Jing Guo and Xiangyun (Sean) Zhou Research School of Engineering, The Australian National
Call Completion Probability in Heterogeneous Networks with Energy Harvesting Base Stations Craig Wang, Salman Durrani, Jing Guo and Xiangyun (Sean) Zhou Research School of Engineering, The Australian National
Quiz 1 EE 549 Wednesday, Feb. 27, 2008
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA, SPRING 2008 1 Quiz 1 EE 549 Wednesday, Feb. 27, 2008 INSTRUCTIONS This quiz lasts for 85 minutes. This quiz is closed book and closed notes. No Calculators or laptops
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA, SPRING 2008 1 Quiz 1 EE 549 Wednesday, Feb. 27, 2008 INSTRUCTIONS This quiz lasts for 85 minutes. This quiz is closed book and closed notes. No Calculators or laptops
Delay QoS Provisioning and Optimal Resource Allocation for Wireless Networks
 Syracuse University SURFACE Dissertations - ALL SURFACE June 2017 Delay QoS Provisioning and Optimal Resource Allocation for Wireless Networks Yi Li Syracuse University Follow this and additional works
Syracuse University SURFACE Dissertations - ALL SURFACE June 2017 Delay QoS Provisioning and Optimal Resource Allocation for Wireless Networks Yi Li Syracuse University Follow this and additional works
NICTA Short Course. Network Analysis. Vijay Sivaraman. Day 1 Queueing Systems and Markov Chains. Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-1
 NICTA Short Course Network Analysis Vijay Sivaraman Day 1 Queueing Systems and Markov Chains Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-1 Outline Why a short course on mathematical analysis? Limited current course offering
NICTA Short Course Network Analysis Vijay Sivaraman Day 1 Queueing Systems and Markov Chains Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-1 Outline Why a short course on mathematical analysis? Limited current course offering
Stochastic Optimization for Undergraduate Computer Science Students
 Stochastic Optimization for Undergraduate Computer Science Students Professor Joongheon Kim School of Computer Science and Engineering, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Republic of Korea 1 Reference 2 Outline
Stochastic Optimization for Undergraduate Computer Science Students Professor Joongheon Kim School of Computer Science and Engineering, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Republic of Korea 1 Reference 2 Outline
Queueing Theory I Summary! Little s Law! Queueing System Notation! Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K "
 Queueing Theory I Summary Little s Law Queueing System Notation Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K " Little s Law a(t): the process that counts the number of arrivals
Queueing Theory I Summary Little s Law Queueing System Notation Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K " Little s Law a(t): the process that counts the number of arrivals
Channel Selection in Cognitive Radio Networks with Opportunistic RF Energy Harvesting
 1 Channel Selection in Cognitive Radio Networks with Opportunistic RF Energy Harvesting Dusit Niyato 1, Ping Wang 1, and Dong In Kim 2 1 School of Computer Engineering, Nanyang Technological University
1 Channel Selection in Cognitive Radio Networks with Opportunistic RF Energy Harvesting Dusit Niyato 1, Ping Wang 1, and Dong In Kim 2 1 School of Computer Engineering, Nanyang Technological University
Introduction to queuing theory
 Introduction to queuing theory Claude Rigault ENST claude.rigault@enst.fr Introduction to Queuing theory 1 Outline The problem The number of clients in a system The client process Delay processes Loss
Introduction to queuing theory Claude Rigault ENST claude.rigault@enst.fr Introduction to Queuing theory 1 Outline The problem The number of clients in a system The client process Delay processes Loss
Fraud within Asymmetric Multi-Hop Cellular Networks
 Financial Cryptography 2005 EPFL, Lausanne, Switzerland ÉCOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FÉDÉRALE DE LAUSANNE Wireless networks Single-hop cellular network Multi-hop network Multi-hop cellular network Asymmetric multi-hop
Financial Cryptography 2005 EPFL, Lausanne, Switzerland ÉCOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FÉDÉRALE DE LAUSANNE Wireless networks Single-hop cellular network Multi-hop network Multi-hop cellular network Asymmetric multi-hop
Power Allocation and Coverage for a Relay-Assisted Downlink with Voice Users
 Power Allocation and Coverage for a Relay-Assisted Downlink with Voice Users Junjik Bae, Randall Berry, and Michael L. Honig Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Northwestern University,
Power Allocation and Coverage for a Relay-Assisted Downlink with Voice Users Junjik Bae, Randall Berry, and Michael L. Honig Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Northwestern University,
Stability Analysis in a Cognitive Radio System with Cooperative Beamforming
 Stability Analysis in a Cognitive Radio System with Cooperative Beamforming Mohammed Karmoose 1 Ahmed Sultan 1 Moustafa Youseff 2 1 Electrical Engineering Dept, Alexandria University 2 E-JUST Agenda 1
Stability Analysis in a Cognitive Radio System with Cooperative Beamforming Mohammed Karmoose 1 Ahmed Sultan 1 Moustafa Youseff 2 1 Electrical Engineering Dept, Alexandria University 2 E-JUST Agenda 1
Networking = Plumbing. Queueing Analysis: I. Last Lecture. Lecture Outline. Jeremiah Deng. 29 July 2013
 Networking = Plumbing TELE302 Lecture 7 Queueing Analysis: I Jeremiah Deng University of Otago 29 July 2013 Jeremiah Deng (University of Otago) TELE302 Lecture 7 29 July 2013 1 / 33 Lecture Outline Jeremiah
Networking = Plumbing TELE302 Lecture 7 Queueing Analysis: I Jeremiah Deng University of Otago 29 July 2013 Jeremiah Deng (University of Otago) TELE302 Lecture 7 29 July 2013 1 / 33 Lecture Outline Jeremiah
A Simple Energy Model for the Harvesting and Leakage in a Supercapacitor
 International Workshop on Novel approaches to Energy Measurement and Evaluation in Wireless Networks A Simple Energy Model for the Harvesting and Leakage in a Supercapacitor Aravind Kailas Dept. of Electrical
International Workshop on Novel approaches to Energy Measurement and Evaluation in Wireless Networks A Simple Energy Model for the Harvesting and Leakage in a Supercapacitor Aravind Kailas Dept. of Electrical
Energy Harvesting Multiple Access Channel with Peak Temperature Constraints
 Energy Harvesting Multiple Access Channel with Peak Temperature Constraints Abdulrahman Baknina, Omur Ozel 2, and Sennur Ulukus Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Maryland,
Energy Harvesting Multiple Access Channel with Peak Temperature Constraints Abdulrahman Baknina, Omur Ozel 2, and Sennur Ulukus Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Maryland,
Open Loop Optimal Control of Base Station Activation for Green Networks
 Open Loop Optimal Control of Base Station Activation for Green etworks Sreenath Ramanath, Veeraruna Kavitha,2 and Eitan Altman IRIA, Sophia-Antipolis, France, 2 Universite d Avignon, Avignon, France Abstract
Open Loop Optimal Control of Base Station Activation for Green etworks Sreenath Ramanath, Veeraruna Kavitha,2 and Eitan Altman IRIA, Sophia-Antipolis, France, 2 Universite d Avignon, Avignon, France Abstract
SAMPLING AND INVERSION
 SAMPLING AND INVERSION Darryl Veitch dveitch@unimelb.edu.au CUBIN, Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering University of Melbourne Workshop on Sampling the Internet, Paris 2005 A TALK WITH TWO
SAMPLING AND INVERSION Darryl Veitch dveitch@unimelb.edu.au CUBIN, Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering University of Melbourne Workshop on Sampling the Internet, Paris 2005 A TALK WITH TWO
Time Reversibility and Burke s Theorem
 Queuing Analysis: Time Reversibility and Burke s Theorem Hongwei Zhang http://www.cs.wayne.edu/~hzhang Acknowledgement: this lecture is partially based on the slides of Dr. Yannis A. Korilis. Outline Time-Reversal
Queuing Analysis: Time Reversibility and Burke s Theorem Hongwei Zhang http://www.cs.wayne.edu/~hzhang Acknowledgement: this lecture is partially based on the slides of Dr. Yannis A. Korilis. Outline Time-Reversal
Computer Networks More general queuing systems
 Computer Networks More general queuing systems Saad Mneimneh Computer Science Hunter College of CUNY New York M/G/ Introduction We now consider a queuing system where the customer service times have a
Computer Networks More general queuing systems Saad Mneimneh Computer Science Hunter College of CUNY New York M/G/ Introduction We now consider a queuing system where the customer service times have a
Optimal Utility-Lifetime Trade-off in Self-regulating Wireless Sensor Networks: A Distributed Approach
 Optimal Utility-Lifetime Trade-off in Self-regulating Wireless Sensor Networks: A Distributed Approach Hithesh Nama, WINLAB, Rutgers University Dr. Narayan Mandayam, WINLAB, Rutgers University Joint work
Optimal Utility-Lifetime Trade-off in Self-regulating Wireless Sensor Networks: A Distributed Approach Hithesh Nama, WINLAB, Rutgers University Dr. Narayan Mandayam, WINLAB, Rutgers University Joint work
Microprocessor Power Analysis by Labeled Simulation
 Microprocessor Power Analysis by Labeled Simulation Cheng-Ta Hsieh, Kevin Chen and Massoud Pedram University of Southern California Dept. of EE-Systems Los Angeles CA 989 Outline! Introduction! Problem
Microprocessor Power Analysis by Labeled Simulation Cheng-Ta Hsieh, Kevin Chen and Massoud Pedram University of Southern California Dept. of EE-Systems Los Angeles CA 989 Outline! Introduction! Problem
Decodability Analysis of Finite Memory Random Linear Coding in Line Networks
 Decodability Analysis of Finite Memory Random Linear Coding in Line Networks Nima Torabkhani, Faramarz Fekri School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta GA 30332,
Decodability Analysis of Finite Memory Random Linear Coding in Line Networks Nima Torabkhani, Faramarz Fekri School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta GA 30332,
Location Determination Technologies for Sensor Networks
 Location Determination Technologies for Sensor Networks Moustafa Youssef University of Maryland at College Park UMBC Talk March, 2007 Motivation Location is important: Determining the location of an event
Location Determination Technologies for Sensor Networks Moustafa Youssef University of Maryland at College Park UMBC Talk March, 2007 Motivation Location is important: Determining the location of an event
Queueing Theory and Simulation. Introduction
 Queueing Theory and Simulation Based on the slides of Dr. Dharma P. Agrawal, University of Cincinnati and Dr. Hiroyuki Ohsaki Graduate School of Information Science & Technology, Osaka University, Japan
Queueing Theory and Simulation Based on the slides of Dr. Dharma P. Agrawal, University of Cincinnati and Dr. Hiroyuki Ohsaki Graduate School of Information Science & Technology, Osaka University, Japan
Homework 1 - SOLUTION
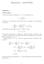 Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
Optimal Sleep Scheduling for a Wireless Sensor Network Node
 1 Optimal Sleep Scheduling for a Wireless Sensor Network Node David Shuman and Mingyan Liu Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Department University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI 4819-2122 dishuman,mingyan}@umich.edu
1 Optimal Sleep Scheduling for a Wireless Sensor Network Node David Shuman and Mingyan Liu Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Department University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI 4819-2122 dishuman,mingyan}@umich.edu
Course Outline Introduction to Transportation Highway Users and their Performance Geometric Design Pavement Design
 Course Outline Introduction to Transportation Highway Users and their Performance Geometric Design Pavement Design Speed Studies - Project Traffic Queuing Intersections Level of Service in Highways and
Course Outline Introduction to Transportation Highway Users and their Performance Geometric Design Pavement Design Speed Studies - Project Traffic Queuing Intersections Level of Service in Highways and
EP2200 Course Project 2017 Project II - Mobile Computation Offloading
 EP2200 Course Project 2017 Project II - Mobile Computation Offloading 1 Introduction Queuing theory provides us a very useful mathematic tool that can be used to analytically evaluate the performance of
EP2200 Course Project 2017 Project II - Mobile Computation Offloading 1 Introduction Queuing theory provides us a very useful mathematic tool that can be used to analytically evaluate the performance of
Intro to Queueing Theory
 1 Intro to Queueing Theory Little s Law M/G/1 queue Conservation Law 1/31/017 M/G/1 queue (Simon S. Lam) 1 Little s Law No assumptions applicable to any system whose arrivals and departures are observable
1 Intro to Queueing Theory Little s Law M/G/1 queue Conservation Law 1/31/017 M/G/1 queue (Simon S. Lam) 1 Little s Law No assumptions applicable to any system whose arrivals and departures are observable
Broadcasting with a Battery Limited Energy Harvesting Rechargeable Transmitter
 roadcasting with a attery Limited Energy Harvesting Rechargeable Transmitter Omur Ozel, Jing Yang 2, and Sennur Ulukus Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Maryland, College
roadcasting with a attery Limited Energy Harvesting Rechargeable Transmitter Omur Ozel, Jing Yang 2, and Sennur Ulukus Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Maryland, College
Approximate Queueing Model for Multi-rate Multi-user MIMO systems.
 An Approximate Queueing Model for Multi-rate Multi-user MIMO systems Boris Bellalta,Vanesa Daza, Miquel Oliver Abstract A queueing model for Multi-rate Multi-user MIMO systems is presented. The model is
An Approximate Queueing Model for Multi-rate Multi-user MIMO systems Boris Bellalta,Vanesa Daza, Miquel Oliver Abstract A queueing model for Multi-rate Multi-user MIMO systems is presented. The model is
Chapter 2 Queueing Theory and Simulation
 Chapter 2 Queueing Theory and Simulation Based on the slides of Dr. Dharma P. Agrawal, University of Cincinnati and Dr. Hiroyuki Ohsaki Graduate School of Information Science & Technology, Osaka University,
Chapter 2 Queueing Theory and Simulation Based on the slides of Dr. Dharma P. Agrawal, University of Cincinnati and Dr. Hiroyuki Ohsaki Graduate School of Information Science & Technology, Osaka University,
requests/sec. The total channel load is requests/sec. Using slot as the time unit, the total channel load is 50 ( ) = 1
 Prof. X. Shen E&CE 70 : Examples #2 Problem Consider the following Aloha systems. (a) A group of N users share a 56 kbps pure Aloha channel. Each user generates at a Passion rate of one 000-bit packet
Prof. X. Shen E&CE 70 : Examples #2 Problem Consider the following Aloha systems. (a) A group of N users share a 56 kbps pure Aloha channel. Each user generates at a Passion rate of one 000-bit packet
Chapter 5. Elementary Performance Analysis
 Chapter 5 Elementary Performance Analysis 1 5.0 2 5.1 Ref: Mischa Schwartz Telecommunication Networks Addison-Wesley publishing company 1988 3 4 p t T m T P(k)= 5 6 5.2 : arrived rate : service rate 7
Chapter 5 Elementary Performance Analysis 1 5.0 2 5.1 Ref: Mischa Schwartz Telecommunication Networks Addison-Wesley publishing company 1988 3 4 p t T m T P(k)= 5 6 5.2 : arrived rate : service rate 7
ABSTRACT WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS. criterion. Therefore, it is imperative to design advanced transmission schemes to
 ABSTRACT Title of dissertation: DELAY MINIMIZATION IN ENERGY CONSTRAINED WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS Jing Yang, Doctor of Philosophy, 2010 Dissertation directed by: Professor Şennur Ulukuş Department of Electrical
ABSTRACT Title of dissertation: DELAY MINIMIZATION IN ENERGY CONSTRAINED WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS Jing Yang, Doctor of Philosophy, 2010 Dissertation directed by: Professor Şennur Ulukuş Department of Electrical
Detecting Wormhole Attacks in Wireless Networks Using Local Neighborhood Information
 Detecting Wormhole Attacks in Wireless Networks Using Local Neighborhood Information W. Znaidi M. Minier and JP. Babau Centre d'innovations en Télécommunication & Intégration de services wassim.znaidi@insa-lyon.fr
Detecting Wormhole Attacks in Wireless Networks Using Local Neighborhood Information W. Znaidi M. Minier and JP. Babau Centre d'innovations en Télécommunication & Intégration de services wassim.znaidi@insa-lyon.fr
Markov decision processes with threshold-based piecewise-linear optimal policies
 1/31 Markov decision processes with threshold-based piecewise-linear optimal policies T. Erseghe, A. Zanella, C. Codemo Dept. of Information Engineering, University of Padova, Italy Padova, June 2, 213
1/31 Markov decision processes with threshold-based piecewise-linear optimal policies T. Erseghe, A. Zanella, C. Codemo Dept. of Information Engineering, University of Padova, Italy Padova, June 2, 213
AN ENHANCED ENERGY SAVING STRATEGY FOR AN ACTIVE DRX IN LTE WIRELESS NETWORKS. Received December 2012; revised April 2013
 International Journal of Innovative Computing, Information and Control ICIC International c 2013 ISSN 1349-4198 Volume 9, Number 11, November 2013 pp. 4373 4387 AN ENHANCED ENERGY SAVING STRATEGY FOR AN
International Journal of Innovative Computing, Information and Control ICIC International c 2013 ISSN 1349-4198 Volume 9, Number 11, November 2013 pp. 4373 4387 AN ENHANCED ENERGY SAVING STRATEGY FOR AN
NODE ACTIVATION POLICIES FOR ENERGY-EFFICIENT COVERAGE IN RECHARGEABLE SENSOR SYSTEMS
 NODE ACTIVATION POLICIES FOR ENERGY-EFFICIENT COVERAGE IN RECHARGEABLE SENSOR SYSTEMS By Neeraj Jaggi A Thesis Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Partial Fulfillment
NODE ACTIVATION POLICIES FOR ENERGY-EFFICIENT COVERAGE IN RECHARGEABLE SENSOR SYSTEMS By Neeraj Jaggi A Thesis Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Partial Fulfillment
On the Performance of Two-Hop Relay Mobile Ad Hoc Networks under Buffer Constraint
 On the Performance of Two-Hop Relay Mobile Ad Hoc Networks under Buffer Constraint by Jia Liu A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
On the Performance of Two-Hop Relay Mobile Ad Hoc Networks under Buffer Constraint by Jia Liu A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
COMP9334: Capacity Planning of Computer Systems and Networks
 COMP9334: Capacity Planning of Computer Systems and Networks Week 2: Operational analysis Lecturer: Prof. Sanjay Jha NETWORKS RESEARCH GROUP, CSE, UNSW Operational analysis Operational: Collect performance
COMP9334: Capacity Planning of Computer Systems and Networks Week 2: Operational analysis Lecturer: Prof. Sanjay Jha NETWORKS RESEARCH GROUP, CSE, UNSW Operational analysis Operational: Collect performance
Analysis and Performance Evaluation of Dynamic Frame Slotted-ALOHA in Wireless Machine-to-Machine Networks with Energy Harvesting
 and Performance Evaluation of Dynamic Frame Slotted-ALOHA in Wireless Machine-to-Machine Networks with Energy Harvesting Shuang Wu, Yue Chen, Kok K Chai Queen Mary University of London London, U.K. Email:
and Performance Evaluation of Dynamic Frame Slotted-ALOHA in Wireless Machine-to-Machine Networks with Energy Harvesting Shuang Wu, Yue Chen, Kok K Chai Queen Mary University of London London, U.K. Email:
Link Models for Packet Switching
 Link Models for Packet Switching To begin our study of the performance of communications networks, we will study a model of a single link in a message switched network. The important feature of this model
Link Models for Packet Switching To begin our study of the performance of communications networks, we will study a model of a single link in a message switched network. The important feature of this model
ABSTRACT ENERGY HARVESTING COMMUNICATION NETWORKS WITH SYSTEM COSTS. Title of dissertation: Ahmed Arafa, Doctor of Philosophy, 2017
 ABSTRACT Title of dissertation: ENERGY HARVESTING COMMUNICATION NETWORKS WITH SYSTEM COSTS Ahmed Arafa, Doctor of Philosophy, 2017 Dissertation directed by: Professor Şennur Ulukuş Department of Electrical
ABSTRACT Title of dissertation: ENERGY HARVESTING COMMUNICATION NETWORKS WITH SYSTEM COSTS Ahmed Arafa, Doctor of Philosophy, 2017 Dissertation directed by: Professor Şennur Ulukuş Department of Electrical
Fairness and Optimal Stochastic Control for Heterogeneous Networks
 λ 91 λ 93 Fairness and Optimal Stochastic Control for Heterogeneous Networks sensor network wired network wireless 9 8 7 6 5 λ 48 λ 42 4 3 0 1 2 λ n R n U n Michael J. Neely (USC) Eytan Modiano (MIT) Chih-Ping
λ 91 λ 93 Fairness and Optimal Stochastic Control for Heterogeneous Networks sensor network wired network wireless 9 8 7 6 5 λ 48 λ 42 4 3 0 1 2 λ n R n U n Michael J. Neely (USC) Eytan Modiano (MIT) Chih-Ping
Adaptive Contact Probing Mechanisms for Delay Tolerant Applications. Wang Wei, Vikram Srinivasan, Mehul Motani
 Adaptive Contact Probing Mechanisms for Delay Tolerant Applications Wang Wei, Vikram Srinivasan, Mehul Motani Outline Introduction Modeling contact processes Real world contact traces Designing energy
Adaptive Contact Probing Mechanisms for Delay Tolerant Applications Wang Wei, Vikram Srinivasan, Mehul Motani Outline Introduction Modeling contact processes Real world contact traces Designing energy
Dynamic Power Allocation and Routing for Time Varying Wireless Networks
 Dynamic Power Allocation and Routing for Time Varying Wireless Networks X 14 (t) X 12 (t) 1 3 4 k a P ak () t P a tot X 21 (t) 2 N X 2N (t) X N4 (t) µ ab () rate µ ab µ ab (p, S 3 ) µ ab µ ac () µ ab (p,
Dynamic Power Allocation and Routing for Time Varying Wireless Networks X 14 (t) X 12 (t) 1 3 4 k a P ak () t P a tot X 21 (t) 2 N X 2N (t) X N4 (t) µ ab () rate µ ab µ ab (p, S 3 ) µ ab µ ac () µ ab (p,
MAT SYS 5120 (Winter 2012) Assignment 5 (not to be submitted) There are 4 questions.
 MAT 4371 - SYS 5120 (Winter 2012) Assignment 5 (not to be submitted) There are 4 questions. Question 1: Consider the following generator for a continuous time Markov chain. 4 1 3 Q = 2 5 3 5 2 7 (a) Give
MAT 4371 - SYS 5120 (Winter 2012) Assignment 5 (not to be submitted) There are 4 questions. Question 1: Consider the following generator for a continuous time Markov chain. 4 1 3 Q = 2 5 3 5 2 7 (a) Give
Cooperative Energy Harvesting Communications with Relaying and Energy Sharing
 Cooperative Energy Harvesting Communications with Relaying and Energy Sharing Kaya Tutuncuoglu and Aylin Yener Department of Electrical Engineering The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA
Cooperative Energy Harvesting Communications with Relaying and Energy Sharing Kaya Tutuncuoglu and Aylin Yener Department of Electrical Engineering The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA
6 Solving Queueing Models
 6 Solving Queueing Models 6.1 Introduction In this note we look at the solution of systems of queues, starting with simple isolated queues. The benefits of using predefined, easily classified queues will
6 Solving Queueing Models 6.1 Introduction In this note we look at the solution of systems of queues, starting with simple isolated queues. The benefits of using predefined, easily classified queues will
Stochastic Models in Computer Science A Tutorial
 Stochastic Models in Computer Science A Tutorial Dr. Snehanshu Saha Department of Computer Science PESIT BSC, Bengaluru WCI 2015 - August 10 to August 13 1 Introduction 2 Random Variable 3 Introduction
Stochastic Models in Computer Science A Tutorial Dr. Snehanshu Saha Department of Computer Science PESIT BSC, Bengaluru WCI 2015 - August 10 to August 13 1 Introduction 2 Random Variable 3 Introduction
Modelling, Simulation & Computing Laboratory (msclab) Faculty of Engineering, Universiti Malaysia Sabah, Malaysia
 1.0 Introduction Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) Long term congestion solutions Advanced technologies Facilitate complex transportation systems Dynamic Modelling of transportation (on-road traffic):
1.0 Introduction Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) Long term congestion solutions Advanced technologies Facilitate complex transportation systems Dynamic Modelling of transportation (on-road traffic):
Energy Efficient Transmission Strategies for Body Sensor Networks with Energy Harvesting
 Energy Efficient Transmission Strategies for Body Sensor Networks with Energy Harvesting Alireza Seyedi Department of ECE, University of Rochester, Rochester, NY USA e-mail: alireza@ece.rochester.edu Biplab
Energy Efficient Transmission Strategies for Body Sensor Networks with Energy Harvesting Alireza Seyedi Department of ECE, University of Rochester, Rochester, NY USA e-mail: alireza@ece.rochester.edu Biplab
Discrete-event simulations
 Discrete-event simulations Lecturer: Dmitri A. Moltchanov E-mail: moltchan@cs.tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/kurssit/elt-53606/ OUTLINE: Why do we need simulations? Step-by-step simulations; Classifications;
Discrete-event simulations Lecturer: Dmitri A. Moltchanov E-mail: moltchan@cs.tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/kurssit/elt-53606/ OUTLINE: Why do we need simulations? Step-by-step simulations; Classifications;
Relaying Information Streams
 Relaying Information Streams Anant Sahai UC Berkeley EECS sahai@eecs.berkeley.edu Originally given: Oct 2, 2002 This was a talk only. I was never able to rigorously formalize the back-of-the-envelope reasoning
Relaying Information Streams Anant Sahai UC Berkeley EECS sahai@eecs.berkeley.edu Originally given: Oct 2, 2002 This was a talk only. I was never able to rigorously formalize the back-of-the-envelope reasoning
Exercises Solutions. Automation IEA, LTH. Chapter 2 Manufacturing and process systems. Chapter 5 Discrete manufacturing problems
 Exercises Solutions Note, that we have not formulated the answers for all the review questions. You will find the answers for many questions by reading and reflecting about the text in the book. Chapter
Exercises Solutions Note, that we have not formulated the answers for all the review questions. You will find the answers for many questions by reading and reflecting about the text in the book. Chapter
Answers to the problems from problem solving classes
 Answers to the problems from problem solving classes Class, multiaccess communication 3. Solution : Let λ Q 5 customers per minute be the rate at which customers arrive to the queue for ordering, T Q 5
Answers to the problems from problem solving classes Class, multiaccess communication 3. Solution : Let λ Q 5 customers per minute be the rate at which customers arrive to the queue for ordering, T Q 5
HYPOTHESIS TESTING OVER A RANDOM ACCESS CHANNEL IN WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS
 HYPOTHESIS TESTING OVER A RANDOM ACCESS CHANNEL IN WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS Elvis Bottega,, Petar Popovski, Michele Zorzi, Hiroyuki Yomo, and Ramjee Prasad Center for TeleInFrastructure (CTIF), Aalborg
HYPOTHESIS TESTING OVER A RANDOM ACCESS CHANNEL IN WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS Elvis Bottega,, Petar Popovski, Michele Zorzi, Hiroyuki Yomo, and Ramjee Prasad Center for TeleInFrastructure (CTIF), Aalborg
Introduction to Markov Chains, Queuing Theory, and Network Performance
 Introduction to Markov Chains, Queuing Theory, and Network Performance Marceau Coupechoux Telecom ParisTech, departement Informatique et Réseaux marceau.coupechoux@telecom-paristech.fr IT.2403 Modélisation
Introduction to Markov Chains, Queuing Theory, and Network Performance Marceau Coupechoux Telecom ParisTech, departement Informatique et Réseaux marceau.coupechoux@telecom-paristech.fr IT.2403 Modélisation
A Quantitative View: Delay, Throughput, Loss
 A Quantitative View: Delay, Throughput, Loss Antonio Carzaniga Faculty of Informatics University of Lugano September 27, 2017 Outline Quantitative analysis of data transfer concepts for network applications
A Quantitative View: Delay, Throughput, Loss Antonio Carzaniga Faculty of Informatics University of Lugano September 27, 2017 Outline Quantitative analysis of data transfer concepts for network applications
Delay, feedback, and the price of ignorance
 Delay, feedback, and the price of ignorance Anant Sahai based in part on joint work with students: Tunc Simsek Cheng Chang Wireless Foundations Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
Delay, feedback, and the price of ignorance Anant Sahai based in part on joint work with students: Tunc Simsek Cheng Chang Wireless Foundations Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
Cooperative HARQ with Poisson Interference and Opportunistic Routing
 Cooperative HARQ with Poisson Interference and Opportunistic Routing Amogh Rajanna & Mostafa Kaveh Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN USA. Outline
Cooperative HARQ with Poisson Interference and Opportunistic Routing Amogh Rajanna & Mostafa Kaveh Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN USA. Outline
Quality of Real-Time Streaming in Wireless Cellular Networks : Stochastic Modeling and Analysis
 Quality of Real-Time Streaming in Wireless Cellular Networs : Stochastic Modeling and Analysis B. Blaszczyszyn, M. Jovanovic and M. K. Karray Based on paper [1] WiOpt/WiVid Mai 16th, 2014 Outline Introduction
Quality of Real-Time Streaming in Wireless Cellular Networs : Stochastic Modeling and Analysis B. Blaszczyszyn, M. Jovanovic and M. K. Karray Based on paper [1] WiOpt/WiVid Mai 16th, 2014 Outline Introduction
Modeling the Residual Energy and Lifetime of Energy Harvesting Sensor Nodes
 Globecom 212 - Symposium on Selected Areas in Communications Modeling the Residual Energy and Lifetime of Energy Harvesting Sensor Nodes M. Yousof Naderi, Stefano Basagni and Kaushik R. Chowdhury Department
Globecom 212 - Symposium on Selected Areas in Communications Modeling the Residual Energy and Lifetime of Energy Harvesting Sensor Nodes M. Yousof Naderi, Stefano Basagni and Kaushik R. Chowdhury Department
Performance Evaluation of Large Scale Communication Networks
 POLITECNICO DI TORINO SCUOLA DI DOTTORATO Dottorato in Ingegneria Elettronica e delle Telecomunicazioni XXIII ciclo Tesi di Dottorato Performance Evaluation of Large Scale Communication Networks Valentina
POLITECNICO DI TORINO SCUOLA DI DOTTORATO Dottorato in Ingegneria Elettronica e delle Telecomunicazioni XXIII ciclo Tesi di Dottorato Performance Evaluation of Large Scale Communication Networks Valentina
How do Wireless Chains Behave? The Impact of MAC Interactions
 The Impact of MAC Interactions S. Razak 1 Vinay Kolar 2 N. Abu-Ghazaleh 1 K. Harras 1 1 Department of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University, Qatar 2 Department of Wireless Networks RWTH Aachen University,
The Impact of MAC Interactions S. Razak 1 Vinay Kolar 2 N. Abu-Ghazaleh 1 K. Harras 1 1 Department of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University, Qatar 2 Department of Wireless Networks RWTH Aachen University,
Modeling and Simulation NETW 707
 Modeling and Simulation NETW 707 Lecture 6 ARQ Modeling: Modeling Error/Flow Control Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Data Link Layer Data Link Layer provides
Modeling and Simulation NETW 707 Lecture 6 ARQ Modeling: Modeling Error/Flow Control Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Data Link Layer Data Link Layer provides
Power Controlled FCFS Splitting Algorithm for Wireless Networks
 Power Controlled FCFS Splitting Algorithm for Wireless Networks Ashutosh Deepak Gore Abhay Karandikar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology - Bombay COMNET Workshop, July
Power Controlled FCFS Splitting Algorithm for Wireless Networks Ashutosh Deepak Gore Abhay Karandikar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology - Bombay COMNET Workshop, July
Data Gathering and Personalized Broadcasting in Radio Grids with Interferences
 Data Gathering and Personalized Broadcasting in Radio Grids with Interferences Jean-Claude Bermond a,, Bi Li a,b, Nicolas Nisse a, Hervé Rivano c, Min-Li Yu d a Coati Project, INRIA I3S(CNRS/UNSA), Sophia
Data Gathering and Personalized Broadcasting in Radio Grids with Interferences Jean-Claude Bermond a,, Bi Li a,b, Nicolas Nisse a, Hervé Rivano c, Min-Li Yu d a Coati Project, INRIA I3S(CNRS/UNSA), Sophia
Markov Chain Model for ALOHA protocol
 Markov Chain Model for ALOHA protocol Laila Daniel and Krishnan Narayanan April 22, 2012 Outline of the talk A Markov chain (MC) model for Slotted ALOHA Basic properties of Discrete-time Markov Chain Stability
Markov Chain Model for ALOHA protocol Laila Daniel and Krishnan Narayanan April 22, 2012 Outline of the talk A Markov chain (MC) model for Slotted ALOHA Basic properties of Discrete-time Markov Chain Stability
An Algebraic Approach to Network Coding
 An Algebraic Approach to July 30 31, 2009 Outline 1 2 a 3 Linear 4 Digital Communication Digital communication networks are integral parts of our lives these days; so, we want to know how to most effectively
An Algebraic Approach to July 30 31, 2009 Outline 1 2 a 3 Linear 4 Digital Communication Digital communication networks are integral parts of our lives these days; so, we want to know how to most effectively
Generating Random Variates II and Examples
 Generating Random Variates II and Examples Holger Füßler Holger Füßler Universität Mannheim Summer 2004 Side note: TexPoint» TexPoint is a Powerpoint add-in that enables the easy use of Latex symbols and
Generating Random Variates II and Examples Holger Füßler Holger Füßler Universität Mannheim Summer 2004 Side note: TexPoint» TexPoint is a Powerpoint add-in that enables the easy use of Latex symbols and
STABILITY OF FINITE-USER SLOTTED ALOHA UNDER PARTIAL INTERFERENCE IN WIRELESS MESH NETWORKS
 The 8th Annual IEEE International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC 7) STABILITY OF FINITE-USER SLOTTED ALOHA UNDER PARTIAL INTERFERENCE IN WIRELESS MESH NETWORKS Ka-Hung
The 8th Annual IEEE International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC 7) STABILITY OF FINITE-USER SLOTTED ALOHA UNDER PARTIAL INTERFERENCE IN WIRELESS MESH NETWORKS Ka-Hung
CE351 Transportation Systems: Planning and Design
 CE351 Transportation Systems: Planning and Design TOPIC: Level of Service (LOS) at Traffic Signals 1 Course Outline Introduction to Transportation Highway Users and their Performance Geometric Design Pavement
CE351 Transportation Systems: Planning and Design TOPIC: Level of Service (LOS) at Traffic Signals 1 Course Outline Introduction to Transportation Highway Users and their Performance Geometric Design Pavement
Wireless Internet Exercises
 Wireless Internet Exercises Prof. Alessandro Redondi 2018-05-28 1 WLAN 1.1 Exercise 1 A Wi-Fi network has the following features: Physical layer transmission rate: 54 Mbps MAC layer header: 28 bytes MAC
Wireless Internet Exercises Prof. Alessandro Redondi 2018-05-28 1 WLAN 1.1 Exercise 1 A Wi-Fi network has the following features: Physical layer transmission rate: 54 Mbps MAC layer header: 28 bytes MAC
Design of discrete-event simulations
 Design of discrete-event simulations Lecturer: Dmitri A. Moltchanov E-mail: moltchan@cs.tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/kurssit/tlt-2707/ OUTLINE: Discrete event simulation; Event advance design; Unit-time
Design of discrete-event simulations Lecturer: Dmitri A. Moltchanov E-mail: moltchan@cs.tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/kurssit/tlt-2707/ OUTLINE: Discrete event simulation; Event advance design; Unit-time
ENERGY harvesting (EH), a technology to collect energy. Optimal Relaying in Energy Harvesting Wireless Networks with Wireless-Powered Relays
 Optimal elaying in Energy Harvesting Wireless Networks with Wireless-Powered elays Masoumeh Moradian, tudent Member, IEEE, Farid Ashtiani, Member, IEEE, and Ying Jun (Angela) Zhang, enior Member, IEEE
Optimal elaying in Energy Harvesting Wireless Networks with Wireless-Powered elays Masoumeh Moradian, tudent Member, IEEE, Farid Ashtiani, Member, IEEE, and Ying Jun (Angela) Zhang, enior Member, IEEE
An engineering approximation for the mean waiting time in the M/H 2 b /s queue
 An engineering approximation for the mean waiting time in the M/H b /s queue Francisco Barceló Universidad Politécnica de Catalunya c/ Jordi Girona, -3, Barcelona 08034 Email : barcelo@entel.upc.es Abstract
An engineering approximation for the mean waiting time in the M/H b /s queue Francisco Barceló Universidad Politécnica de Catalunya c/ Jordi Girona, -3, Barcelona 08034 Email : barcelo@entel.upc.es Abstract
Temporal Reachability Graphs
 Temporal Reachability Graphs John Whitbeck, Marcelo Dias de Amorim, Vania Conan and Jean-Loup Guillaume August 25th, 212 Intro : Contact Traces 2/16 Intro : Contact Traces 2/16 Intro : Contact Traces Time
Temporal Reachability Graphs John Whitbeck, Marcelo Dias de Amorim, Vania Conan and Jean-Loup Guillaume August 25th, 212 Intro : Contact Traces 2/16 Intro : Contact Traces 2/16 Intro : Contact Traces Time
Extracting mobility behavior from cell phone data DATA SIM Summer School 2013
 Extracting mobility behavior from cell phone data DATA SIM Summer School 2013 PETER WIDHALM Mobility Department Dynamic Transportation Systems T +43(0) 50550-6655 F +43(0) 50550-6439 peter.widhalm@ait.ac.at
Extracting mobility behavior from cell phone data DATA SIM Summer School 2013 PETER WIDHALM Mobility Department Dynamic Transportation Systems T +43(0) 50550-6655 F +43(0) 50550-6439 peter.widhalm@ait.ac.at
EE 550: Notes on Markov chains, Travel Times, and Opportunistic Routing
 EE 550: Notes on Markov chains, Travel Times, and Opportunistic Routing Michael J. Neely University of Southern California http://www-bcf.usc.edu/ mjneely 1 Abstract This collection of notes provides a
EE 550: Notes on Markov chains, Travel Times, and Opportunistic Routing Michael J. Neely University of Southern California http://www-bcf.usc.edu/ mjneely 1 Abstract This collection of notes provides a
Multi-Dimensional Online Tracking
 Multi-Dimensional Online Tracking Ke Yi and Qin Zhang Hong Kong University of Science & Technology SODA 2009 January 4-6, 2009 1-1 A natural problem Bob: tracker f(t) g(t) Alice: observer (t, g(t)) t 2-1
Multi-Dimensional Online Tracking Ke Yi and Qin Zhang Hong Kong University of Science & Technology SODA 2009 January 4-6, 2009 1-1 A natural problem Bob: tracker f(t) g(t) Alice: observer (t, g(t)) t 2-1
Queueing Theory II. Summary. ! M/M/1 Output process. ! Networks of Queue! Method of Stages. ! General Distributions
 Queueing Theory II Summary! M/M/1 Output process! Networks of Queue! Method of Stages " Erlang Distribution " Hyperexponential Distribution! General Distributions " Embedded Markov Chains M/M/1 Output
Queueing Theory II Summary! M/M/1 Output process! Networks of Queue! Method of Stages " Erlang Distribution " Hyperexponential Distribution! General Distributions " Embedded Markov Chains M/M/1 Output
Reducing The Data Transmission in Wireless Sensor Networks Using The Principal Component Analysis
 Reducing The Data Transmission in Wireless Sensor Networks Using The Principal Component Analysis A Rooshenas, H R Rabiee, A Movaghar, M Y Naderi The Sixth International Conference on Intelligent Sensors,
Reducing The Data Transmission in Wireless Sensor Networks Using The Principal Component Analysis A Rooshenas, H R Rabiee, A Movaghar, M Y Naderi The Sixth International Conference on Intelligent Sensors,
Chapter 3 Balance equations, birth-death processes, continuous Markov Chains
 Chapter 3 Balance equations, birth-death processes, continuous Markov Chains Ioannis Glaropoulos November 4, 2012 1 Exercise 3.2 Consider a birth-death process with 3 states, where the transition rate
Chapter 3 Balance equations, birth-death processes, continuous Markov Chains Ioannis Glaropoulos November 4, 2012 1 Exercise 3.2 Consider a birth-death process with 3 states, where the transition rate
Energy Balanced Data Propagation in Wireless Sensor Networks
 Energy Balanced Data Propagation in Wireless Sensor Networks Charilaos Efthymiou Computer Technology Institute University of Patras, Greece euthimio@ceid.upatras.gr Sotiris Nikoletseas Computer Technology
Energy Balanced Data Propagation in Wireless Sensor Networks Charilaos Efthymiou Computer Technology Institute University of Patras, Greece euthimio@ceid.upatras.gr Sotiris Nikoletseas Computer Technology
ATM VP-Based Ring Network Exclusive Video or Data Traffics
 ATM VP-Based Ring Network Exclusive Video or Data Traffics In this chapter, the performance characteristic of the proposed ATM VP-Based Ring Network exclusive video or data traffic is studied. The maximum
ATM VP-Based Ring Network Exclusive Video or Data Traffics In this chapter, the performance characteristic of the proposed ATM VP-Based Ring Network exclusive video or data traffic is studied. The maximum
Signalling Analysis for Adaptive TCD Routing in ISL Networks *
 COST 272 Packet-Oriented Service delivery via Satellite Signalling Analysis for Adaptive TCD Routing in ISL Networks * Ales Svigelj, Mihael Mohorcic, Gorazd Kandus Jozef Stefan Institute, Ljubljana, Slovenia
COST 272 Packet-Oriented Service delivery via Satellite Signalling Analysis for Adaptive TCD Routing in ISL Networks * Ales Svigelj, Mihael Mohorcic, Gorazd Kandus Jozef Stefan Institute, Ljubljana, Slovenia
CS 798: Homework Assignment 3 (Queueing Theory)
 1.0 Little s law Assigned: October 6, 009 Patients arriving to the emergency room at the Grand River Hospital have a mean waiting time of three hours. It has been found that, averaged over the period of
1.0 Little s law Assigned: October 6, 009 Patients arriving to the emergency room at the Grand River Hospital have a mean waiting time of three hours. It has been found that, averaged over the period of
Data analysis and stochastic modeling
 Data analysis and stochastic modeling Lecture 7 An introduction to queueing theory Guillaume Gravier guillaume.gravier@irisa.fr with a lot of help from Paul Jensen s course http://www.me.utexas.edu/ jensen/ormm/instruction/powerpoint/or_models_09/14_queuing.ppt
Data analysis and stochastic modeling Lecture 7 An introduction to queueing theory Guillaume Gravier guillaume.gravier@irisa.fr with a lot of help from Paul Jensen s course http://www.me.utexas.edu/ jensen/ormm/instruction/powerpoint/or_models_09/14_queuing.ppt
Energy Cooperation and Traffic Management in Cellular Networks with Renewable Energy
 Energy Cooperation and Traffic Management in Cellular Networks with Renewable Energy Hyun-Suk Lee Dept. of Electrical and Electronic Eng., Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea Jang-Won Lee Dept. of Electrical
Energy Cooperation and Traffic Management in Cellular Networks with Renewable Energy Hyun-Suk Lee Dept. of Electrical and Electronic Eng., Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea Jang-Won Lee Dept. of Electrical
DATA ROUTING WITH WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS
 DATA ROUTING WITH WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS By Thomas J. Reale III A Project Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree
DATA ROUTING WITH WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS By Thomas J. Reale III A Project Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree
Dynamic Power Management under Uncertain Information. University of Southern California Los Angeles CA
 Dynamic Power Management under Uncertain Information Hwisung Jung and Massoud Pedram University of Southern California Los Angeles CA Agenda Introduction Background Stochastic Decision-Making Framework
Dynamic Power Management under Uncertain Information Hwisung Jung and Massoud Pedram University of Southern California Los Angeles CA Agenda Introduction Background Stochastic Decision-Making Framework
LECTURE 3. Last time:
 LECTURE 3 Last time: Mutual Information. Convexity and concavity Jensen s inequality Information Inequality Data processing theorem Fano s Inequality Lecture outline Stochastic processes, Entropy rate
LECTURE 3 Last time: Mutual Information. Convexity and concavity Jensen s inequality Information Inequality Data processing theorem Fano s Inequality Lecture outline Stochastic processes, Entropy rate
The Factor: Inferring Protocol Performance Using Inter-link Reception Correlation
 The Factor: Inferring Protocol Performance Using Inter-link Reception Correlation Kannan Srinivasan, Mayank Jain, Jung Il Choi, Tahir Azim, Edward S Kim, Philip Levis and Bhaskar Krishnamachari MobiCom
The Factor: Inferring Protocol Performance Using Inter-link Reception Correlation Kannan Srinivasan, Mayank Jain, Jung Il Choi, Tahir Azim, Edward S Kim, Philip Levis and Bhaskar Krishnamachari MobiCom
