NICTA Short Course. Network Analysis. Vijay Sivaraman. Day 1 Queueing Systems and Markov Chains. Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-1
|
|
|
- Gladys Ramsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NICTA Short Course Network Analysis Vijay Sivaraman Day 1 Queueing Systems and Markov Chains Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-1
2 Outline Why a short course on mathematical analysis? Limited current course offering (at UNSW EE/CSE) Students differ in exposure to analytical techniques Helps develop deeper insight into your problem / solution Often a must for major conferences / journals Greek in thesis always looks cooler! What this course is about: How to start building a model for your research problem Focus is on formulating the model What this course is not about: Not a rigorous theory of any particular topic(s) Not focus on how to solve a model Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-2
3 Analysis in Network Research Quantify: loss, delay, throughput/efficiency Wired network: Scheduling algorithms (priority, weighted fair, ) Congestion control algorithms Wireless (LAN, mesh, sensor) network: MAC protocol for time-varying channel Probabilistic routing algorithm Optical network: Evaluate architecture of new optical switch Map traffic to wavelengths (traffic grooming) Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-3
4 Some Analysis Techniques Queuing theory: loss/delay in packet networks Markov models: network traffic, protocols, Fluid models: Rate-control, congestion-control, traffic flow Graph theory: routing, resilience, network structure Combinatorial analysis: Randomized and approximation algorithms Optimization techniques: Network design, routing, power, efficiency Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-4
5 What is Your Research? What communication system are you studying? New architecture, algorithm, protocol? What metrics are you interested in? Loss, delay, efficiency, quality? What are the inputs to your system? Traffic pattern, channel conditions, error rates, Background in analysis: Familiar with some techniques? Tried any techniques for your research problem? Extent of success? Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-5
6 How to start Modeling? Building a Markov model: Define state of a system Chart out how the system changes state Solve to get probabilities of each state Compute metrics of interest (loss, delay, etc.) and we are done! If only life were so easy! Let s consider a very simple system Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-6
7 An M/M/1 Queueing System Single queue Single server (single transmission line) Customers (packets) arrive according to a Poisson process with rate λ per second The service time distribution is exponential with mean 1/μ seconds First-In-First-Out service Infinite buffer λ μ Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-7
8 What are Poisson and Exponential? f(x) Service time: Exponential pdf: cdf: μx f ( x) = μe, x 0 μx F( x) = 1 e pdf Has memory-less property P( x > s + t x > t) = P( x > s), s, t > 0 x Arrival process: Poisson It is a counting process for the number of randomly occurring pointevents observed in a given interval of time, e.g. Tasks arriving at a processor Messages arriving to a network Customers arriving at a supermarket checkout Radioactive particles from a source Inter-event time has an exponential distribution [homework: proof] Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-8
9 Poisson Process: definition Let the r.v. N(t,τ) denote number of events in (t,τ] Let o(h) denotes an expression f(h) such that lim 0 f ( h) / h = h 0 A Poisson process {N(0,t)}, t 0, with rate λ is such that: 1. P[N(t,t+h)=0] = 1 - λh + o(h) 2. P[N(t,t+h)=1] = λh + o(h) 3. P[N(t,t+h)=2] = o(h) 4. N(0,t) and N(t,t+h) are independent for all t, h > 0 Every small interval has equal likelihood of event occurrence Events are thus completely random in time Time-homogeneity property: for all τ: P[N(τ, τ+t)] = P[N(0,t)] = P[N(t)] Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-9
10 Poisson Process: properties Claim: The number of events N(t) in any interval of length t is a Poisson r.v. with parameter λt: λt k P[ N( t) = k] = e ( λt) k! Claim: Mean number of events in any interval of length t: E[ N( t)] = = k 0 kp[ N( t) = k] = λt Claim: Poisson is a limiting approximation of binomial (λt = np) : i n λ Claim: Inter-event time (i.e. time between successive events) is an exponential r.v. with parameter λ lim i n i p (1 p) = e i n Homework: prove that time to first arrival is exponential Homework: prove that time to next arrival is exponential λt ( t) i! Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-10
11 M/M/1 Markov Chain Representation Objective: system state should have Markov property P X j X = x ; u s) = P( X = j X = x ) History is summarized in the state State: number of customers N(t) in system at time t Should state include time customer has spent in server? Should state include time elapsed since last customer arrival? Markov chain representation of system state: ( s+ t = u u s+ t s s Arrows show possible state transitions and associated rate λ λ λ n n+1 μ μ μ Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-11
12 Solving the Markov Chain Balance principle: For any set of states A, the flux out of set A equals the flux into set A Balance applied to A = {n}: λ p0 = μ p1, n = 0 ( λ + μ) p = λ p + μ p n 1 Balance applied to A = {0,1,..n-1}: n n+ 1, n = 1,2,K Can solve to obtain: where λ p n 1 = μ pn, n = ρ = λ / μ p n 1, 2,K n = ( 1 ρ) ρ, n = 0,1,2,... Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-12
13 Mean Performance Measures System utilisation: ρ = λ / μ = 1 p 0 Mean number of customers in system: ρ E[ n] = np = n = 0 n 1 ρ How long on average does a customer spend in the system? τ = n 1 E[ ] p n = n= 0 μ μ λ Can also deduce this using Little s law : Probability of loss? E [ n] = λe[ τ ] Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-13
14 M/M/1 Variations M/M/c: multiple servers operating in parallel Load-balancing on multiple links M/M/1/K: queue limited to K customers Finite queue capacity Bulk arrivals / service: Simultaneous arrivals or service Multiple classes of customers Priority scheduling Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-14
15 Problem You are designing an all-optical packet switch which has very small storage memory (say 10 KB) and carries TCP and UDP traffic. We want to evaluate the performance of this switch if it were installed in the Internet. Metrics: TCP throughput and UDP loss What traffic model to use? What are the arrival rates? Can we build a Markov model? What if TCP packets are on average 5 times larger than UDP packets? What if TCP and UDP are in separate queues and UDP gets priority service? Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-15
16 Non-Markovian Systems What if service times are not exponential? Several approaches can be used [see Kleinrock]: Semi-Markov model (studied next) Method of stages Lindley s equations Method of supplementary variables Embed Markov chain at customer departure instances: Why does that make the system Markovian? What is the state? What are the transition probabilities? How do you solve the Markov chain? Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-16
17 M/G/1 Queuing System Consider the problem again: You are designing an all-optical packet switch which has very small storage memory (say 10 KB) and carries TCP and UDP traffic. We want to evaluate the performance of this switch if it were installed in the Internet. Suppose TCP packet are fixed-size 1000 bytes and UDP packets are fixed-size 200 bytes? States? Transition probabilities? How to solve balance equations? Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-17
Queueing Theory I Summary! Little s Law! Queueing System Notation! Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K "
 Queueing Theory I Summary Little s Law Queueing System Notation Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K " Little s Law a(t): the process that counts the number of arrivals
Queueing Theory I Summary Little s Law Queueing System Notation Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K " Little s Law a(t): the process that counts the number of arrivals
Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems
 Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems Introduction to Queuing Systems System Performance Measures & Little s Law Equilibrium Solution of Birth-Death Processes Analysis of Single-Station Queuing Systems
Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems Introduction to Queuing Systems System Performance Measures & Little s Law Equilibrium Solution of Birth-Death Processes Analysis of Single-Station Queuing Systems
Link Models for Packet Switching
 Link Models for Packet Switching To begin our study of the performance of communications networks, we will study a model of a single link in a message switched network. The important feature of this model
Link Models for Packet Switching To begin our study of the performance of communications networks, we will study a model of a single link in a message switched network. The important feature of this model
GI/M/1 and GI/M/m queuing systems
 GI/M/1 and GI/M/m queuing systems Dmitri A. Moltchanov moltchan@cs.tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/kurssit/tlt-2716/ OUTLINE: GI/M/1 queuing system; Methods of analysis; Imbedded Markov chain approach; Waiting
GI/M/1 and GI/M/m queuing systems Dmitri A. Moltchanov moltchan@cs.tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/kurssit/tlt-2716/ OUTLINE: GI/M/1 queuing system; Methods of analysis; Imbedded Markov chain approach; Waiting
Introduction to Markov Chains, Queuing Theory, and Network Performance
 Introduction to Markov Chains, Queuing Theory, and Network Performance Marceau Coupechoux Telecom ParisTech, departement Informatique et Réseaux marceau.coupechoux@telecom-paristech.fr IT.2403 Modélisation
Introduction to Markov Chains, Queuing Theory, and Network Performance Marceau Coupechoux Telecom ParisTech, departement Informatique et Réseaux marceau.coupechoux@telecom-paristech.fr IT.2403 Modélisation
Continuous Time Processes
 page 102 Chapter 7 Continuous Time Processes 7.1 Introduction In a continuous time stochastic process (with discrete state space), a change of state can occur at any time instant. The associated point
page 102 Chapter 7 Continuous Time Processes 7.1 Introduction In a continuous time stochastic process (with discrete state space), a change of state can occur at any time instant. The associated point
Birth-Death Processes
 Birth-Death Processes Birth-Death Processes: Transient Solution Poisson Process: State Distribution Poisson Process: Inter-arrival Times Dr Conor McArdle EE414 - Birth-Death Processes 1/17 Birth-Death
Birth-Death Processes Birth-Death Processes: Transient Solution Poisson Process: State Distribution Poisson Process: Inter-arrival Times Dr Conor McArdle EE414 - Birth-Death Processes 1/17 Birth-Death
Intro to Queueing Theory
 1 Intro to Queueing Theory Little s Law M/G/1 queue Conservation Law 1/31/017 M/G/1 queue (Simon S. Lam) 1 Little s Law No assumptions applicable to any system whose arrivals and departures are observable
1 Intro to Queueing Theory Little s Law M/G/1 queue Conservation Law 1/31/017 M/G/1 queue (Simon S. Lam) 1 Little s Law No assumptions applicable to any system whose arrivals and departures are observable
Networking = Plumbing. Queueing Analysis: I. Last Lecture. Lecture Outline. Jeremiah Deng. 29 July 2013
 Networking = Plumbing TELE302 Lecture 7 Queueing Analysis: I Jeremiah Deng University of Otago 29 July 2013 Jeremiah Deng (University of Otago) TELE302 Lecture 7 29 July 2013 1 / 33 Lecture Outline Jeremiah
Networking = Plumbing TELE302 Lecture 7 Queueing Analysis: I Jeremiah Deng University of Otago 29 July 2013 Jeremiah Deng (University of Otago) TELE302 Lecture 7 29 July 2013 1 / 33 Lecture Outline Jeremiah
Introduction to queuing theory
 Introduction to queuing theory Claude Rigault ENST claude.rigault@enst.fr Introduction to Queuing theory 1 Outline The problem The number of clients in a system The client process Delay processes Loss
Introduction to queuing theory Claude Rigault ENST claude.rigault@enst.fr Introduction to Queuing theory 1 Outline The problem The number of clients in a system The client process Delay processes Loss
Computer Systems Modelling
 Computer Systems Modelling Computer Laboratory Computer Science Tripos, Part II Michaelmas Term 2003 R. J. Gibbens Problem sheet William Gates Building JJ Thomson Avenue Cambridge CB3 0FD http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/
Computer Systems Modelling Computer Laboratory Computer Science Tripos, Part II Michaelmas Term 2003 R. J. Gibbens Problem sheet William Gates Building JJ Thomson Avenue Cambridge CB3 0FD http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/
Queueing Theory and Simulation. Introduction
 Queueing Theory and Simulation Based on the slides of Dr. Dharma P. Agrawal, University of Cincinnati and Dr. Hiroyuki Ohsaki Graduate School of Information Science & Technology, Osaka University, Japan
Queueing Theory and Simulation Based on the slides of Dr. Dharma P. Agrawal, University of Cincinnati and Dr. Hiroyuki Ohsaki Graduate School of Information Science & Technology, Osaka University, Japan
M/G/1 and M/G/1/K systems
 M/G/1 and M/G/1/K systems Dmitri A. Moltchanov dmitri.moltchanov@tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/kurssit/elt-53606/ OUTLINE: Description of M/G/1 system; Methods of analysis; Residual life approach; Imbedded
M/G/1 and M/G/1/K systems Dmitri A. Moltchanov dmitri.moltchanov@tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/kurssit/elt-53606/ OUTLINE: Description of M/G/1 system; Methods of analysis; Residual life approach; Imbedded
Chapter 2 Queueing Theory and Simulation
 Chapter 2 Queueing Theory and Simulation Based on the slides of Dr. Dharma P. Agrawal, University of Cincinnati and Dr. Hiroyuki Ohsaki Graduate School of Information Science & Technology, Osaka University,
Chapter 2 Queueing Theory and Simulation Based on the slides of Dr. Dharma P. Agrawal, University of Cincinnati and Dr. Hiroyuki Ohsaki Graduate School of Information Science & Technology, Osaka University,
The exponential distribution and the Poisson process
 The exponential distribution and the Poisson process 1-1 Exponential Distribution: Basic Facts PDF f(t) = { λe λt, t 0 0, t < 0 CDF Pr{T t) = 0 t λe λu du = 1 e λt (t 0) Mean E[T] = 1 λ Variance Var[T]
The exponential distribution and the Poisson process 1-1 Exponential Distribution: Basic Facts PDF f(t) = { λe λt, t 0 0, t < 0 CDF Pr{T t) = 0 t λe λu du = 1 e λt (t 0) Mean E[T] = 1 λ Variance Var[T]
CDA5530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks. Chapter 4: Elementary Queuing Theory
 CDA5530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks Chapter 4: Elementary Queuing Theory Definition Queuing system: a buffer (waiting room), service facility (one or more servers) a scheduling policy
CDA5530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks Chapter 4: Elementary Queuing Theory Definition Queuing system: a buffer (waiting room), service facility (one or more servers) a scheduling policy
CPSC 531: System Modeling and Simulation. Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Fall 2017
 CPSC 531: System Modeling and Simulation Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Fall 2017 Motivating Quote for Queueing Models Good things come to those who wait - poet/writer
CPSC 531: System Modeling and Simulation Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Fall 2017 Motivating Quote for Queueing Models Good things come to those who wait - poet/writer
16:330:543 Communication Networks I Midterm Exam November 7, 2005
 l l l l l l l l 1 3 np n = ρ 1 ρ = λ µ λ. n= T = E[N] = 1 λ µ λ = 1 µ 1. 16:33:543 Communication Networks I Midterm Exam November 7, 5 You have 16 minutes to complete this four problem exam. If you know
l l l l l l l l 1 3 np n = ρ 1 ρ = λ µ λ. n= T = E[N] = 1 λ µ λ = 1 µ 1. 16:33:543 Communication Networks I Midterm Exam November 7, 5 You have 16 minutes to complete this four problem exam. If you know
Chapter 3 Balance equations, birth-death processes, continuous Markov Chains
 Chapter 3 Balance equations, birth-death processes, continuous Markov Chains Ioannis Glaropoulos November 4, 2012 1 Exercise 3.2 Consider a birth-death process with 3 states, where the transition rate
Chapter 3 Balance equations, birth-death processes, continuous Markov Chains Ioannis Glaropoulos November 4, 2012 1 Exercise 3.2 Consider a birth-death process with 3 states, where the transition rate
Figure 10.1: Recording when the event E occurs
 10 Poisson Processes Let T R be an interval. A family of random variables {X(t) ; t T} is called a continuous time stochastic process. We often consider T = [0, 1] and T = [0, ). As X(t) is a random variable
10 Poisson Processes Let T R be an interval. A family of random variables {X(t) ; t T} is called a continuous time stochastic process. We often consider T = [0, 1] and T = [0, ). As X(t) is a random variable
Part I Stochastic variables and Markov chains
 Part I Stochastic variables and Markov chains Random variables describe the behaviour of a phenomenon independent of any specific sample space Distribution function (cdf, cumulative distribution function)
Part I Stochastic variables and Markov chains Random variables describe the behaviour of a phenomenon independent of any specific sample space Distribution function (cdf, cumulative distribution function)
Part II: continuous time Markov chain (CTMC)
 Part II: continuous time Markov chain (CTMC) Continuous time discrete state Markov process Definition (Markovian property) X(t) is a CTMC, if for any n and any sequence t 1
Part II: continuous time Markov chain (CTMC) Continuous time discrete state Markov process Definition (Markovian property) X(t) is a CTMC, if for any n and any sequence t 1
CS418 Operating Systems
 CS418 Operating Systems Lecture 14 Queuing Analysis Textbook: Operating Systems by William Stallings 1 1. Why Queuing Analysis? If the system environment changes (like the number of users is doubled),
CS418 Operating Systems Lecture 14 Queuing Analysis Textbook: Operating Systems by William Stallings 1 1. Why Queuing Analysis? If the system environment changes (like the number of users is doubled),
Homework 1 - SOLUTION
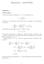 Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
Chapter 2. Poisson Processes. Prof. Shun-Ren Yang Department of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan
 Chapter 2. Poisson Processes Prof. Shun-Ren Yang Department of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan Outline Introduction to Poisson Processes Definition of arrival process Definition
Chapter 2. Poisson Processes Prof. Shun-Ren Yang Department of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan Outline Introduction to Poisson Processes Definition of arrival process Definition
Name of the Student:
 SUBJECT NAME : Probability & Queueing Theory SUBJECT CODE : MA 6453 MATERIAL NAME : Part A questions REGULATION : R2013 UPDATED ON : November 2017 (Upto N/D 2017 QP) (Scan the above QR code for the direct
SUBJECT NAME : Probability & Queueing Theory SUBJECT CODE : MA 6453 MATERIAL NAME : Part A questions REGULATION : R2013 UPDATED ON : November 2017 (Upto N/D 2017 QP) (Scan the above QR code for the direct
Queuing Theory. Using the Math. Management Science
 Queuing Theory Using the Math 1 Markov Processes (Chains) A process consisting of a countable sequence of stages, that can be judged at each stage to fall into future states independent of how the process
Queuing Theory Using the Math 1 Markov Processes (Chains) A process consisting of a countable sequence of stages, that can be judged at each stage to fall into future states independent of how the process
6 Solving Queueing Models
 6 Solving Queueing Models 6.1 Introduction In this note we look at the solution of systems of queues, starting with simple isolated queues. The benefits of using predefined, easily classified queues will
6 Solving Queueing Models 6.1 Introduction In this note we look at the solution of systems of queues, starting with simple isolated queues. The benefits of using predefined, easily classified queues will
Lecture 7: Simulation of Markov Processes. Pasi Lassila Department of Communications and Networking
 Lecture 7: Simulation of Markov Processes Pasi Lassila Department of Communications and Networking Contents Markov processes theory recap Elementary queuing models for data networks Simulation of Markov
Lecture 7: Simulation of Markov Processes Pasi Lassila Department of Communications and Networking Contents Markov processes theory recap Elementary queuing models for data networks Simulation of Markov
CS 798: Homework Assignment 3 (Queueing Theory)
 1.0 Little s law Assigned: October 6, 009 Patients arriving to the emergency room at the Grand River Hospital have a mean waiting time of three hours. It has been found that, averaged over the period of
1.0 Little s law Assigned: October 6, 009 Patients arriving to the emergency room at the Grand River Hospital have a mean waiting time of three hours. It has been found that, averaged over the period of
Data analysis and stochastic modeling
 Data analysis and stochastic modeling Lecture 7 An introduction to queueing theory Guillaume Gravier guillaume.gravier@irisa.fr with a lot of help from Paul Jensen s course http://www.me.utexas.edu/ jensen/ormm/instruction/powerpoint/or_models_09/14_queuing.ppt
Data analysis and stochastic modeling Lecture 7 An introduction to queueing theory Guillaume Gravier guillaume.gravier@irisa.fr with a lot of help from Paul Jensen s course http://www.me.utexas.edu/ jensen/ormm/instruction/powerpoint/or_models_09/14_queuing.ppt
Stochastic Models in Computer Science A Tutorial
 Stochastic Models in Computer Science A Tutorial Dr. Snehanshu Saha Department of Computer Science PESIT BSC, Bengaluru WCI 2015 - August 10 to August 13 1 Introduction 2 Random Variable 3 Introduction
Stochastic Models in Computer Science A Tutorial Dr. Snehanshu Saha Department of Computer Science PESIT BSC, Bengaluru WCI 2015 - August 10 to August 13 1 Introduction 2 Random Variable 3 Introduction
Queueing Systems: Lecture 3. Amedeo R. Odoni October 18, Announcements
 Queueing Systems: Lecture 3 Amedeo R. Odoni October 18, 006 Announcements PS #3 due tomorrow by 3 PM Office hours Odoni: Wed, 10/18, :30-4:30; next week: Tue, 10/4 Quiz #1: October 5, open book, in class;
Queueing Systems: Lecture 3 Amedeo R. Odoni October 18, 006 Announcements PS #3 due tomorrow by 3 PM Office hours Odoni: Wed, 10/18, :30-4:30; next week: Tue, 10/4 Quiz #1: October 5, open book, in class;
LECTURE #6 BIRTH-DEATH PROCESS
 LECTURE #6 BIRTH-DEATH PROCESS 204528 Queueing Theory and Applications in Networks Assoc. Prof., Ph.D. (รศ.ดร. อน นต ผลเพ ม) Computer Engineering Department, Kasetsart University Outline 2 Birth-Death
LECTURE #6 BIRTH-DEATH PROCESS 204528 Queueing Theory and Applications in Networks Assoc. Prof., Ph.D. (รศ.ดร. อน นต ผลเพ ม) Computer Engineering Department, Kasetsart University Outline 2 Birth-Death
EE 368. Weeks 3 (Notes)
 EE 368 Weeks 3 (Notes) 1 State of a Queuing System State: Set of parameters that describe the condition of the system at a point in time. Why do we need it? Average size of Queue Average waiting time How
EE 368 Weeks 3 (Notes) 1 State of a Queuing System State: Set of parameters that describe the condition of the system at a point in time. Why do we need it? Average size of Queue Average waiting time How
Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems
 Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems Problem 1: Customers arrive at a grocery store s checkout counter according to a Poisson process with rate 1 per minute. Each customer carries a number of items
Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems Problem 1: Customers arrive at a grocery store s checkout counter according to a Poisson process with rate 1 per minute. Each customer carries a number of items
Introduction to Queuing Theory. Mathematical Modelling
 Queuing Theory, COMPSCI 742 S2C, 2014 p. 1/23 Introduction to Queuing Theory and Mathematical Modelling Computer Science 742 S2C, 2014 Nevil Brownlee, with acknowledgements to Peter Fenwick, Ulrich Speidel
Queuing Theory, COMPSCI 742 S2C, 2014 p. 1/23 Introduction to Queuing Theory and Mathematical Modelling Computer Science 742 S2C, 2014 Nevil Brownlee, with acknowledgements to Peter Fenwick, Ulrich Speidel
Discrete-event simulations
 Discrete-event simulations Lecturer: Dmitri A. Moltchanov E-mail: moltchan@cs.tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/kurssit/elt-53606/ OUTLINE: Why do we need simulations? Step-by-step simulations; Classifications;
Discrete-event simulations Lecturer: Dmitri A. Moltchanov E-mail: moltchan@cs.tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/kurssit/elt-53606/ OUTLINE: Why do we need simulations? Step-by-step simulations; Classifications;
PBW 654 Applied Statistics - I Urban Operations Research
 PBW 654 Applied Statistics - I Urban Operations Research Lecture 2.I Queuing Systems An Introduction Operations Research Models Deterministic Models Linear Programming Integer Programming Network Optimization
PBW 654 Applied Statistics - I Urban Operations Research Lecture 2.I Queuing Systems An Introduction Operations Research Models Deterministic Models Linear Programming Integer Programming Network Optimization
Queueing Theory. VK Room: M Last updated: October 17, 2013.
 Queueing Theory VK Room: M1.30 knightva@cf.ac.uk www.vincent-knight.com Last updated: October 17, 2013. 1 / 63 Overview Description of Queueing Processes The Single Server Markovian Queue Multi Server
Queueing Theory VK Room: M1.30 knightva@cf.ac.uk www.vincent-knight.com Last updated: October 17, 2013. 1 / 63 Overview Description of Queueing Processes The Single Server Markovian Queue Multi Server
Optimization and Simulation
 Optimization and Simulation Simulating events: the Michel Bierlaire Transport and Mobility Laboratory School of Architecture, Civil and Environmental Engineering Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne
Optimization and Simulation Simulating events: the Michel Bierlaire Transport and Mobility Laboratory School of Architecture, Civil and Environmental Engineering Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne
Introduction to Queueing Theory
 Introduction to Queueing Theory Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Jain@eecs.berkeley.edu or Jain@wustl.edu A Mini-Course offered at UC Berkeley, Sept-Oct 2012 These slides and audio/video recordings
Introduction to Queueing Theory Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Jain@eecs.berkeley.edu or Jain@wustl.edu A Mini-Course offered at UC Berkeley, Sept-Oct 2012 These slides and audio/video recordings
Dynamic resource sharing
 J. Virtamo 38.34 Teletraffic Theory / Dynamic resource sharing and balanced fairness Dynamic resource sharing In previous lectures we have studied different notions of fair resource sharing. Our focus
J. Virtamo 38.34 Teletraffic Theory / Dynamic resource sharing and balanced fairness Dynamic resource sharing In previous lectures we have studied different notions of fair resource sharing. Our focus
Wireless Internet Exercises
 Wireless Internet Exercises Prof. Alessandro Redondi 2018-05-28 1 WLAN 1.1 Exercise 1 A Wi-Fi network has the following features: Physical layer transmission rate: 54 Mbps MAC layer header: 28 bytes MAC
Wireless Internet Exercises Prof. Alessandro Redondi 2018-05-28 1 WLAN 1.1 Exercise 1 A Wi-Fi network has the following features: Physical layer transmission rate: 54 Mbps MAC layer header: 28 bytes MAC
Intro Refresher Reversibility Open networks Closed networks Multiclass networks Other networks. Queuing Networks. Florence Perronnin
 Queuing Networks Florence Perronnin Polytech Grenoble - UGA March 23, 27 F. Perronnin (UGA) Queuing Networks March 23, 27 / 46 Outline Introduction to Queuing Networks 2 Refresher: M/M/ queue 3 Reversibility
Queuing Networks Florence Perronnin Polytech Grenoble - UGA March 23, 27 F. Perronnin (UGA) Queuing Networks March 23, 27 / 46 Outline Introduction to Queuing Networks 2 Refresher: M/M/ queue 3 Reversibility
BIRTH DEATH PROCESSES AND QUEUEING SYSTEMS
 BIRTH DEATH PROCESSES AND QUEUEING SYSTEMS Andrea Bobbio Anno Accademico 999-2000 Queueing Systems 2 Notation for Queueing Systems /λ mean time between arrivals S = /µ ρ = λ/µ N mean service time traffic
BIRTH DEATH PROCESSES AND QUEUEING SYSTEMS Andrea Bobbio Anno Accademico 999-2000 Queueing Systems 2 Notation for Queueing Systems /λ mean time between arrivals S = /µ ρ = λ/µ N mean service time traffic
Introduction to Queueing Theory
 Introduction to Queueing Theory Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: 30-1 Overview Queueing Notation
Introduction to Queueing Theory Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Saint Louis, MO 63130 Jain@cse.wustl.edu Audio/Video recordings of this lecture are available at: 30-1 Overview Queueing Notation
Review of Queuing Models
 Review of Queuing Models Recitation, Apr. 1st Guillaume Roels 15.763J Manufacturing System and Supply Chain Design http://michael.toren.net/slides/ipqueue/slide001.html 2005 Guillaume Roels Outline Overview,
Review of Queuing Models Recitation, Apr. 1st Guillaume Roels 15.763J Manufacturing System and Supply Chain Design http://michael.toren.net/slides/ipqueue/slide001.html 2005 Guillaume Roels Outline Overview,
Introduction to queuing theory
 Introduction to queuing theory Queu(e)ing theory Queu(e)ing theory is the branch of mathematics devoted to how objects (packets in a network, people in a bank, processes in a CPU etc etc) join and leave
Introduction to queuing theory Queu(e)ing theory Queu(e)ing theory is the branch of mathematics devoted to how objects (packets in a network, people in a bank, processes in a CPU etc etc) join and leave
Probability and Statistics Concepts
 University of Central Florida Computer Science Division COT 5611 - Operating Systems. Spring 014 - dcm Probability and Statistics Concepts Random Variable: a rule that assigns a numerical value to each
University of Central Florida Computer Science Division COT 5611 - Operating Systems. Spring 014 - dcm Probability and Statistics Concepts Random Variable: a rule that assigns a numerical value to each
λ λ λ In-class problems
 In-class problems 1. Customers arrive at a single-service facility at a Poisson rate of 40 per hour. When two or fewer customers are present, a single attendant operates the facility, and the service time
In-class problems 1. Customers arrive at a single-service facility at a Poisson rate of 40 per hour. When two or fewer customers are present, a single attendant operates the facility, and the service time
COMP9334 Capacity Planning for Computer Systems and Networks
 COMP9334 Capacity Planning for Computer Systems and Networks Week 2: Operational Analysis and Workload Characterisation COMP9334 1 Last lecture Modelling of computer systems using Queueing Networks Open
COMP9334 Capacity Planning for Computer Systems and Networks Week 2: Operational Analysis and Workload Characterisation COMP9334 1 Last lecture Modelling of computer systems using Queueing Networks Open
Queuing Theory and Stochas St t ochas ic Service Syste y ms Li Xia
 Queuing Theory and Stochastic Service Systems Li Xia Syllabus Instructor Li Xia 夏俐, FIT 3 618, 62793029, xial@tsinghua.edu.cn Text book D. Gross, J.F. Shortle, J.M. Thompson, and C.M. Harris, Fundamentals
Queuing Theory and Stochastic Service Systems Li Xia Syllabus Instructor Li Xia 夏俐, FIT 3 618, 62793029, xial@tsinghua.edu.cn Text book D. Gross, J.F. Shortle, J.M. Thompson, and C.M. Harris, Fundamentals
Queueing Theory II. Summary. ! M/M/1 Output process. ! Networks of Queue! Method of Stages. ! General Distributions
 Queueing Theory II Summary! M/M/1 Output process! Networks of Queue! Method of Stages " Erlang Distribution " Hyperexponential Distribution! General Distributions " Embedded Markov Chains M/M/1 Output
Queueing Theory II Summary! M/M/1 Output process! Networks of Queue! Method of Stages " Erlang Distribution " Hyperexponential Distribution! General Distributions " Embedded Markov Chains M/M/1 Output
QUEUING SYSTEM. Yetunde Folajimi, PhD
 QUEUING SYSTEM Yetunde Folajimi, PhD Part 2 Queuing Models Queueing models are constructed so that queue lengths and waiting times can be predicted They help us to understand and quantify the effect of
QUEUING SYSTEM Yetunde Folajimi, PhD Part 2 Queuing Models Queueing models are constructed so that queue lengths and waiting times can be predicted They help us to understand and quantify the effect of
Elementary queueing system
 Elementary queueing system Kendall notation Little s Law PASTA theorem Basics of M/M/1 queue M/M/1 with preemptive-resume priority M/M/1 with non-preemptive priority 1 History of queueing theory An old
Elementary queueing system Kendall notation Little s Law PASTA theorem Basics of M/M/1 queue M/M/1 with preemptive-resume priority M/M/1 with non-preemptive priority 1 History of queueing theory An old
Introduction to Queueing Theory with Applications to Air Transportation Systems
 Introduction to Queueing Theory with Applications to Air Transportation Systems John Shortle George Mason University February 28, 2018 Outline Why stochastic models matter M/M/1 queue Little s law Priority
Introduction to Queueing Theory with Applications to Air Transportation Systems John Shortle George Mason University February 28, 2018 Outline Why stochastic models matter M/M/1 queue Little s law Priority
IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I, Fall 2003, Professor Whitt. Solutions to Final Exam: Thursday, December 18.
 IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I, Fall 23, Professor Whitt Solutions to Final Exam: Thursday, December 18. Below are six questions with several parts. Do as much as you can. Show your work. 1. Two-Pump Gas
IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I, Fall 23, Professor Whitt Solutions to Final Exam: Thursday, December 18. Below are six questions with several parts. Do as much as you can. Show your work. 1. Two-Pump Gas
Performance Modelling of Computer Systems
 Performance Modelling of Computer Systems Mirco Tribastone Institut für Informatik Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Fundamentals of Queueing Theory Tribastone (IFI LMU) Performance Modelling of Computer
Performance Modelling of Computer Systems Mirco Tribastone Institut für Informatik Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Fundamentals of Queueing Theory Tribastone (IFI LMU) Performance Modelling of Computer
Performance Analysis of Priority Queueing Schemes in Internet Routers
 Conference on Information Sciences and Systems, The Johns Hopkins University, March 8, Performance Analysis of Priority Queueing Schemes in Internet Routers Ashvin Lakshmikantha Coordinated Science Lab
Conference on Information Sciences and Systems, The Johns Hopkins University, March 8, Performance Analysis of Priority Queueing Schemes in Internet Routers Ashvin Lakshmikantha Coordinated Science Lab
Multiaccess Problem. How to let distributed users (efficiently) share a single broadcast channel? How to form a queue for distributed users?
 Multiaccess Problem How to let distributed users (efficiently) share a single broadcast channel? How to form a queue for distributed users? z The protocols we used to solve this multiaccess problem are
Multiaccess Problem How to let distributed users (efficiently) share a single broadcast channel? How to form a queue for distributed users? z The protocols we used to solve this multiaccess problem are
Non Markovian Queues (contd.)
 MODULE 7: RENEWAL PROCESSES 29 Lecture 5 Non Markovian Queues (contd) For the case where the service time is constant, V ar(b) = 0, then the P-K formula for M/D/ queue reduces to L s = ρ + ρ 2 2( ρ) where
MODULE 7: RENEWAL PROCESSES 29 Lecture 5 Non Markovian Queues (contd) For the case where the service time is constant, V ar(b) = 0, then the P-K formula for M/D/ queue reduces to L s = ρ + ρ 2 2( ρ) where
EE126: Probability and Random Processes
 EE126: Probability and Random Processes Lecture 18: Poisson Process Abhay Parekh UC Berkeley March 17, 2011 1 1 Review 2 Poisson Process 2 Bernoulli Process An arrival process comprised of a sequence of
EE126: Probability and Random Processes Lecture 18: Poisson Process Abhay Parekh UC Berkeley March 17, 2011 1 1 Review 2 Poisson Process 2 Bernoulli Process An arrival process comprised of a sequence of
Efficient Nonlinear Optimizations of Queuing Systems
 Efficient Nonlinear Optimizations of Queuing Systems Mung Chiang, Arak Sutivong, and Stephen Boyd Electrical Engineering Department, Stanford University, CA 9435 Abstract We present a systematic treatment
Efficient Nonlinear Optimizations of Queuing Systems Mung Chiang, Arak Sutivong, and Stephen Boyd Electrical Engineering Department, Stanford University, CA 9435 Abstract We present a systematic treatment
Queueing Networks G. Rubino INRIA / IRISA, Rennes, France
 Queueing Networks G. Rubino INRIA / IRISA, Rennes, France February 2006 Index 1. Open nets: Basic Jackson result 2 2. Open nets: Internet performance evaluation 18 3. Closed nets: Basic Gordon-Newell result
Queueing Networks G. Rubino INRIA / IRISA, Rennes, France February 2006 Index 1. Open nets: Basic Jackson result 2 2. Open nets: Internet performance evaluation 18 3. Closed nets: Basic Gordon-Newell result
WiFi MAC Models David Malone
 WiFi MAC Models David Malone November 26, MACSI Hamilton Institute, NUIM, Ireland Talk outline Introducing the 82.11 CSMA/CA MAC. Finite load 82.11 model and its predictions. Issues with standard 82.11,
WiFi MAC Models David Malone November 26, MACSI Hamilton Institute, NUIM, Ireland Talk outline Introducing the 82.11 CSMA/CA MAC. Finite load 82.11 model and its predictions. Issues with standard 82.11,
Link Models for Circuit Switching
 Link Models for Circuit Switching The basis of traffic engineering for telecommunication networks is the Erlang loss function. It basically allows us to determine the amount of telephone traffic that can
Link Models for Circuit Switching The basis of traffic engineering for telecommunication networks is the Erlang loss function. It basically allows us to determine the amount of telephone traffic that can
A Study on Performance Analysis of Queuing System with Multiple Heterogeneous Servers
 UNIVERSITY OF OKLAHOMA GENERAL EXAM REPORT A Study on Performance Analysis of Queuing System with Multiple Heterogeneous Servers Prepared by HUSNU SANER NARMAN husnu@ou.edu based on the papers 1) F. S.
UNIVERSITY OF OKLAHOMA GENERAL EXAM REPORT A Study on Performance Analysis of Queuing System with Multiple Heterogeneous Servers Prepared by HUSNU SANER NARMAN husnu@ou.edu based on the papers 1) F. S.
Readings: Finish Section 5.2
 LECTURE 19 Readings: Finish Section 5.2 Lecture outline Markov Processes I Checkout counter example. Markov process: definition. -step transition probabilities. Classification of states. Example: Checkout
LECTURE 19 Readings: Finish Section 5.2 Lecture outline Markov Processes I Checkout counter example. Markov process: definition. -step transition probabilities. Classification of states. Example: Checkout
Measurements made for web data, media (IP Radio and TV, BBC Iplayer: Port 80 TCP) and VoIP (Skype: Port UDP) traffic.
 Real time statistical measurements of IPT(Inter-Packet time) of network traffic were done by designing and coding of efficient measurement tools based on the Libpcap package. Traditional Approach of measuring
Real time statistical measurements of IPT(Inter-Packet time) of network traffic were done by designing and coding of efficient measurement tools based on the Libpcap package. Traditional Approach of measuring
Exponential Distribution and Poisson Process
 Exponential Distribution and Poisson Process Stochastic Processes - Lecture Notes Fatih Cavdur to accompany Introduction to Probability Models by Sheldon M. Ross Fall 215 Outline Introduction Exponential
Exponential Distribution and Poisson Process Stochastic Processes - Lecture Notes Fatih Cavdur to accompany Introduction to Probability Models by Sheldon M. Ross Fall 215 Outline Introduction Exponential
Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0.
![Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0. Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0.](/thumbs/95/124116804.jpg) IEOR 46: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Chapters 5-6 in Ross, Thursday, April, 4:5-5:35pm SOLUTIONS to Second Midterm Exam, Spring 9, Open Book: but only the Ross textbook, the
IEOR 46: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Chapters 5-6 in Ross, Thursday, April, 4:5-5:35pm SOLUTIONS to Second Midterm Exam, Spring 9, Open Book: but only the Ross textbook, the
Capacity management for packet-switched networks with heterogeneous sources. Linda de Jonge. Master Thesis July 29, 2009.
 Capacity management for packet-switched networks with heterogeneous sources Linda de Jonge Master Thesis July 29, 2009 Supervisors Dr. Frank Roijers Prof. dr. ir. Sem Borst Dr. Andreas Löpker Industrial
Capacity management for packet-switched networks with heterogeneous sources Linda de Jonge Master Thesis July 29, 2009 Supervisors Dr. Frank Roijers Prof. dr. ir. Sem Borst Dr. Andreas Löpker Industrial
Chapter 10. Queuing Systems. D (Queuing Theory) Queuing theory is the branch of operations research concerned with waiting lines.
 Chapter 10 Queuing Systems D. 10. 1. (Queuing Theory) Queuing theory is the branch of operations research concerned with waiting lines. D. 10.. (Queuing System) A ueuing system consists of 1. a user source.
Chapter 10 Queuing Systems D. 10. 1. (Queuing Theory) Queuing theory is the branch of operations research concerned with waiting lines. D. 10.. (Queuing System) A ueuing system consists of 1. a user source.
Slides 9: Queuing Models
 Slides 9: Queuing Models Purpose Simulation is often used in the analysis of queuing models. A simple but typical queuing model is: Queuing models provide the analyst with a powerful tool for designing
Slides 9: Queuing Models Purpose Simulation is often used in the analysis of queuing models. A simple but typical queuing model is: Queuing models provide the analyst with a powerful tool for designing
Kendall notation. PASTA theorem Basics of M/M/1 queue
 Elementary queueing system Kendall notation Little s Law PASTA theorem Basics of M/M/1 queue 1 History of queueing theory An old research area Started in 1909, by Agner Erlang (to model the Copenhagen
Elementary queueing system Kendall notation Little s Law PASTA theorem Basics of M/M/1 queue 1 History of queueing theory An old research area Started in 1909, by Agner Erlang (to model the Copenhagen
Probability Models in Electrical and Computer Engineering Mathematical models as tools in analysis and design Deterministic models Probability models
 Probability Models in Electrical and Computer Engineering Mathematical models as tools in analysis and design Deterministic models Probability models Statistical regularity Properties of relative frequency
Probability Models in Electrical and Computer Engineering Mathematical models as tools in analysis and design Deterministic models Probability models Statistical regularity Properties of relative frequency
UNIVERSITY OF YORK. MSc Examinations 2004 MATHEMATICS Networks. Time Allowed: 3 hours.
 UNIVERSITY OF YORK MSc Examinations 2004 MATHEMATICS Networks Time Allowed: 3 hours. Answer 4 questions. Standard calculators will be provided but should be unnecessary. 1 Turn over 2 continued on next
UNIVERSITY OF YORK MSc Examinations 2004 MATHEMATICS Networks Time Allowed: 3 hours. Answer 4 questions. Standard calculators will be provided but should be unnecessary. 1 Turn over 2 continued on next
requests/sec. The total channel load is requests/sec. Using slot as the time unit, the total channel load is 50 ( ) = 1
 Prof. X. Shen E&CE 70 : Examples #2 Problem Consider the following Aloha systems. (a) A group of N users share a 56 kbps pure Aloha channel. Each user generates at a Passion rate of one 000-bit packet
Prof. X. Shen E&CE 70 : Examples #2 Problem Consider the following Aloha systems. (a) A group of N users share a 56 kbps pure Aloha channel. Each user generates at a Passion rate of one 000-bit packet
Queues and Queueing Networks
 Queues and Queueing Networks Sanjay K. Bose Dept. of EEE, IITG Copyright 2015, Sanjay K. Bose 1 Introduction to Queueing Models and Queueing Analysis Copyright 2015, Sanjay K. Bose 2 Model of a Queue Arrivals
Queues and Queueing Networks Sanjay K. Bose Dept. of EEE, IITG Copyright 2015, Sanjay K. Bose 1 Introduction to Queueing Models and Queueing Analysis Copyright 2015, Sanjay K. Bose 2 Model of a Queue Arrivals
Queueing systems. Renato Lo Cigno. Simulation and Performance Evaluation Queueing systems - Renato Lo Cigno 1
 Queueing systems Renato Lo Cigno Simulation and Performance Evaluation 2014-15 Queueing systems - Renato Lo Cigno 1 Queues A Birth-Death process is well modeled by a queue Indeed queues can be used to
Queueing systems Renato Lo Cigno Simulation and Performance Evaluation 2014-15 Queueing systems - Renato Lo Cigno 1 Queues A Birth-Death process is well modeled by a queue Indeed queues can be used to
Solutions to Homework Discrete Stochastic Processes MIT, Spring 2011
 Exercise 6.5: Solutions to Homework 0 6.262 Discrete Stochastic Processes MIT, Spring 20 Consider the Markov process illustrated below. The transitions are labelled by the rate q ij at which those transitions
Exercise 6.5: Solutions to Homework 0 6.262 Discrete Stochastic Processes MIT, Spring 20 Consider the Markov process illustrated below. The transitions are labelled by the rate q ij at which those transitions
Queuing Networks: Burke s Theorem, Kleinrock s Approximation, and Jackson s Theorem. Wade Trappe
 Queuing Networks: Burke s Theorem, Kleinrock s Approximation, and Jackson s Theorem Wade Trappe Lecture Overview Network of Queues Introduction Queues in Tandem roduct Form Solutions Burke s Theorem What
Queuing Networks: Burke s Theorem, Kleinrock s Approximation, and Jackson s Theorem Wade Trappe Lecture Overview Network of Queues Introduction Queues in Tandem roduct Form Solutions Burke s Theorem What
2905 Queueing Theory and Simulation PART IV: SIMULATION
 2905 Queueing Theory and Simulation PART IV: SIMULATION 22 Random Numbers A fundamental step in a simulation study is the generation of random numbers, where a random number represents the value of a random
2905 Queueing Theory and Simulation PART IV: SIMULATION 22 Random Numbers A fundamental step in a simulation study is the generation of random numbers, where a random number represents the value of a random
An Admission Control Mechanism for Providing Service Differentiation in Optical Burst-Switching Networks
 An Admission Control Mechanism for Providing Service Differentiation in Optical Burst-Switching Networks Igor M. Moraes, Daniel de O. Cunha, Marco D. D. Bicudo, Rafael P. Laufer, and Otto Carlos M. B.
An Admission Control Mechanism for Providing Service Differentiation in Optical Burst-Switching Networks Igor M. Moraes, Daniel de O. Cunha, Marco D. D. Bicudo, Rafael P. Laufer, and Otto Carlos M. B.
Systems Simulation Chapter 6: Queuing Models
 Systems Simulation Chapter 6: Queuing Models Fatih Cavdur fatihcavdur@uludag.edu.tr April 2, 2014 Introduction Introduction Simulation is often used in the analysis of queuing models. A simple but typical
Systems Simulation Chapter 6: Queuing Models Fatih Cavdur fatihcavdur@uludag.edu.tr April 2, 2014 Introduction Introduction Simulation is often used in the analysis of queuing models. A simple but typical
ECE 313 Probability with Engineering Applications Fall 2000
 Exponential random variables Exponential random variables arise in studies of waiting times, service times, etc X is called an exponential random variable with parameter λ if its pdf is given by f(u) =
Exponential random variables Exponential random variables arise in studies of waiting times, service times, etc X is called an exponential random variable with parameter λ if its pdf is given by f(u) =
EP2200 Course Project 2017 Project II - Mobile Computation Offloading
 EP2200 Course Project 2017 Project II - Mobile Computation Offloading 1 Introduction Queuing theory provides us a very useful mathematic tool that can be used to analytically evaluate the performance of
EP2200 Course Project 2017 Project II - Mobile Computation Offloading 1 Introduction Queuing theory provides us a very useful mathematic tool that can be used to analytically evaluate the performance of
Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 3. Models of Queuing
 Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 3. Models of Queuing Husheng Li Min Kao Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville Spring, 2016 1/13 Terminology of
Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 3. Models of Queuing Husheng Li Min Kao Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville Spring, 2016 1/13 Terminology of
Computer Systems Modelling
 Computer Systems Modelling Computer Laboratory Computer Science Tripos, Part II Lent Term 2010/11 R. J. Gibbens Problem sheet William Gates Building 15 JJ Thomson Avenue Cambridge CB3 0FD http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/
Computer Systems Modelling Computer Laboratory Computer Science Tripos, Part II Lent Term 2010/11 R. J. Gibbens Problem sheet William Gates Building 15 JJ Thomson Avenue Cambridge CB3 0FD http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/
Lecture Notes of Communication Network I y: part 5. Lijun Qian. Rutgers The State University of New Jersey. 94 Brett Road. Piscataway, NJ
 Lecture Notes of Communication Network I y: part 5 Lijun Qian Department of Electrical Engineering Rutgers The State University of New Jersey 94 Brett Road Piscataway, NJ 08854-8058 October 6, 1998 Abstract
Lecture Notes of Communication Network I y: part 5 Lijun Qian Department of Electrical Engineering Rutgers The State University of New Jersey 94 Brett Road Piscataway, NJ 08854-8058 October 6, 1998 Abstract
Control of Fork-Join Networks in Heavy-Traffic
 in Heavy-Traffic Asaf Zviran Based on MSc work under the guidance of Rami Atar (Technion) and Avishai Mandelbaum (Technion) Industrial Engineering and Management Technion June 2010 Introduction Network
in Heavy-Traffic Asaf Zviran Based on MSc work under the guidance of Rami Atar (Technion) and Avishai Mandelbaum (Technion) Industrial Engineering and Management Technion June 2010 Introduction Network
Class 11 Non-Parametric Models of a Service System; GI/GI/1, GI/GI/n: Exact & Approximate Analysis.
 Service Engineering Class 11 Non-Parametric Models of a Service System; GI/GI/1, GI/GI/n: Exact & Approximate Analysis. G/G/1 Queue: Virtual Waiting Time (Unfinished Work). GI/GI/1: Lindley s Equations
Service Engineering Class 11 Non-Parametric Models of a Service System; GI/GI/1, GI/GI/n: Exact & Approximate Analysis. G/G/1 Queue: Virtual Waiting Time (Unfinished Work). GI/GI/1: Lindley s Equations
Lecture 20: Reversible Processes and Queues
 Lecture 20: Reversible Processes and Queues 1 Examples of reversible processes 11 Birth-death processes We define two non-negative sequences birth and death rates denoted by {λ n : n N 0 } and {µ n : n
Lecture 20: Reversible Processes and Queues 1 Examples of reversible processes 11 Birth-death processes We define two non-negative sequences birth and death rates denoted by {λ n : n N 0 } and {µ n : n
Bernoulli Counting Process with p=0.1
 Stat 28 October 29, 21 Today: More Ch 7 (Sections 7.4 and part of 7.) Midterm will cover Ch 7 to section 7.4 Review session will be Nov. Exercises to try (answers in book): 7.1-, 7.2-3, 7.3-3, 7.4-7 Where
Stat 28 October 29, 21 Today: More Ch 7 (Sections 7.4 and part of 7.) Midterm will cover Ch 7 to section 7.4 Review session will be Nov. Exercises to try (answers in book): 7.1-, 7.2-3, 7.3-3, 7.4-7 Where
Chapter 1. Introduction. 1.1 Stochastic process
 Chapter 1 Introduction Process is a phenomenon that takes place in time. In many practical situations, the result of a process at any time may not be certain. Such a process is called a stochastic process.
Chapter 1 Introduction Process is a phenomenon that takes place in time. In many practical situations, the result of a process at any time may not be certain. Such a process is called a stochastic process.
5/15/18. Operations Research: An Introduction Hamdy A. Taha. Copyright 2011, 2007 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 The objective of queuing analysis is to offer a reasonably satisfactory service to waiting customers. Unlike the other tools of OR, queuing theory is not an optimization technique. Rather, it determines
The objective of queuing analysis is to offer a reasonably satisfactory service to waiting customers. Unlike the other tools of OR, queuing theory is not an optimization technique. Rather, it determines
MARKOV PROCESSES. Valerio Di Valerio
 MARKOV PROCESSES Valerio Di Valerio Stochastic Process Definition: a stochastic process is a collection of random variables {X(t)} indexed by time t T Each X(t) X is a random variable that satisfy some
MARKOV PROCESSES Valerio Di Valerio Stochastic Process Definition: a stochastic process is a collection of random variables {X(t)} indexed by time t T Each X(t) X is a random variable that satisfy some
Buzen s algorithm. Cyclic network Extension of Jackson networks
 Outline Buzen s algorithm Mean value analysis for Jackson networks Cyclic network Extension of Jackson networks BCMP network 1 Marginal Distributions based on Buzen s algorithm With Buzen s algorithm,
Outline Buzen s algorithm Mean value analysis for Jackson networks Cyclic network Extension of Jackson networks BCMP network 1 Marginal Distributions based on Buzen s algorithm With Buzen s algorithm,
Course Outline Introduction to Transportation Highway Users and their Performance Geometric Design Pavement Design
 Course Outline Introduction to Transportation Highway Users and their Performance Geometric Design Pavement Design Speed Studies - Project Traffic Queuing Intersections Level of Service in Highways and
Course Outline Introduction to Transportation Highway Users and their Performance Geometric Design Pavement Design Speed Studies - Project Traffic Queuing Intersections Level of Service in Highways and
