Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems
|
|
|
- Audrey Lee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems Problem 1: Customers arrive at a grocery store s checkout counter according to a Poisson process with rate 1 per minute. Each customer carries a number of items that is uniformly distributed between 1 and. The store has 2 checkout counter, each capable of processing items at a rate of 15 per minute. To reduce the customer waiting time in the queue, the store manager considers dedicating one of the two counters to customers with x items or less and dedicating the other counter to customers with more than x items. Write a small computer program to find the value of x that minimizes the average customer waiting time. Solution: First note that one counter is not sufficient to serve all the customers. If we consider all the customers together, each customer carries on average 20.5 items, which requires 20.5 = 1.37 minutes to serve. Since the customer arrival rate is 1 per minute, the 15 utilization will be above 1 if only one counter is used. Assume that Counter 1 serves customers with x items or less and Counter 2 serves customers with more than x items, where 1 x 39. Let λ i denote the customer arrival rate to Counter i, i = 1, 2, and r be the rate of processing items at each counter. By definition, we have r = 15 items per minute. Let us consider Counter 1 first. Since only customers with x items or less go to Counter 1, λ 1 = x per minute. The customers arriving at Counter 1 bring with them 1, 2,..., x items uniformly distributed. Let S 1 denote the customer service time at Counter 1. We have x 1 E[S 1 ] = x i r = 1 + x E[S 2 1] = x ( ) 1 i 2 x = r x i 2 225x Let ρ 1 = λ 1 E[S 1 ]. For ρ 1 < 1, we must have x 34. By the P-K formula, the mean waiting time at Counter 1 is W 1 = λ 1E[S 2 1] 2(1 ρ 1 ) 1
2 Similarly, the customer arrival rate to Counter 2 is λ 2 customer service time at Counter 2. Then, = x. Let S 2 denote the E[S 2 2] = E[S 2 ] = 1 x i r = x + 41 ( ) 1 i 2 x = r i x Let ρ 2 = λ 2 E[S 2 ]. For ρ 2 < 1, we must have x 21. By the P-K formula, the mean waiting time at Counter 2 is W 2 = λ 2E[S 2 2] 2(1 ρ 2 ) The mean waiting time of the customers is given by W = x W 1 + x W 2 Note that W is a function of x for 21 x 34. We write a computer program (Matlab file week08 q1.m) to calculate how W varies with x. The figure below shows how W varies with x. It can be seen that the minimum value of W is achieved at x = Meaning waiting time x 2
3 Problem 2: A computer system receives requests from a Poisson process at a rate of 10 requests per second. Assume that % of the requests are of type a and the remaining are of type b. For request type a, its average service time is 0.1 seconds and the coefficient of variation of its service time is 1.5. For request type b, its average service time is 0.08 seconds and the coefficient of variation of its service time is 1.2. Compute the average response time for each type of requests under the following scenarios: 1. Requests of types a and b have equal priorities 2. Requests of type b have non-preemptive priority over requests of type a 3. Requests of type b have preemptive priority over requests of type a Solution: Let C a, σ a, E[S a ] and E[S 2 a] denote, respectively, the coefficient of variation, standard deviation, mean and second moment of the service time of requests of type a. Recall that the coefficient of variation of a random variable is its standard deviation divided by mean, i.e C a = σ a /E[S a ]. Using the relation we have σ 2 a = E[S 2 a] (E[S a ]) 2 E[S 2 a] = (E[S a ]) 2 (1 + C 2 a) Since we know E[S a ] = 0.1 and C a = 1.5, we can compute E[S 2 a] using the above equation. Similarly, let C b, σ b, E[S b ] and E[S 2 b ] denote, respectively, the coefficient of variation, standard deviation, mean and second moment of the service time of requests of type b. We have E[S 2 b ] = (E[S b ]) 2 (1 + C 2 b ) Since we know E[S b ] = 0.08 and C b = 1.2, we can compute E[S 2 b ] using the above equation. 1. Requests of types a and b have equal priorities: This is an M/G/1 queue without priority. The arrival rate is 10 requests per second (= λ). Since % of the request are type a and the remaining are type b, we have the mean service time E[S] and second moment E[S 2 ] of the aggregate are, respectively, E[S] = 0.3E[S a ] + 0.7E[S b ] 3
4 The mean response time is therefore where ρ = λe[s]. E[S 2 ] = 0.3E[S 2 a] + 0.7E[S 2 b ] T = E[S] + λe[s2 ] 2(1 ρ) 2. Requests of type b have non-preemptive priority over requests of type a: Let R = 1 2 (0.3λE[S2 a] + 0.7λE[S 2 b ]) The response time of type b requests is The response time of type a requests is T a = E[S a ] + ρ a = 0.3λE[S a ] ρ b = 0.7λE[S b ] T b = E[S b ] + R 1 ρ b R (1 ρ a ρ b )(1 ρ b ) 3. Requests of type b have preemptive priority over requests of type a: Let R a = 1 2 (0.3λE[S2 a] + 0.7λE[S 2 b ]) The response time of type b requests is The response time of type a requests is R b = 1 2 (0.7λE[S2 b ]) ρ a = 0.3λE[S a ] ρ b = 0.7λE[S b ] R b T b = E[S b ] + 1 ρ b T a = E[S a] R a + 1 ρ b (1 ρ a ρ b )(1 ρ b ) The response time results are summarized in the following table: 4
5 Type Part 1 Part 2 Part 3 a b Observe that the response time for type b requests have become better because it has a higher priority, this is of course at the expense of type a requests which have a lower priority. Problem 3: A communication line capable of transmitting at a rate of 50 kbits per second will be used to accommodate 10 sessions each generating Poisson traffic at a rate of 150 packets per minute. Packet lengths are distributed as follows: 10% of the packets are 100 bits long and the rest are 1500 bits long. Find the mean queue length and how long a packet has to wait before it starts its transmission on the communication line. You can assume that there is sufficient buffer space to store the queueing packets. Solution: The system behaves as an M/G/1 queueing system. Since there are 10 sessions each generating Poisson traffic at a rate of 150 packets per minute, the packet arrival rate λ to the communication line is 1500 packets per minute or 25 packets per second. With a transmission rate of 50 kbits per second, a 100-bit packet requires a transmission time (service time in queueing theory terminology) of seconds and a 1500-bit packet requires a transmission time of seconds. Given that 10% of the packets are 100 bits long and the rest are 1500 bits long, the mean service time is E[S] = = sec and the second moment of the service time is E[S 2 ] = = sec 2 The mean waiting time W, according to the P-K formula, which applies to an M/G/1 queueing system, is λe[s 2 ] W = = sec 2(1 λe[s]) By the Little s Law, the mean queue length in the buffer is given by N w = λ W = packets 5
Queueing Theory I Summary! Little s Law! Queueing System Notation! Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K "
 Queueing Theory I Summary Little s Law Queueing System Notation Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K " Little s Law a(t): the process that counts the number of arrivals
Queueing Theory I Summary Little s Law Queueing System Notation Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K " Little s Law a(t): the process that counts the number of arrivals
EE 368. Weeks 3 (Notes)
 EE 368 Weeks 3 (Notes) 1 State of a Queuing System State: Set of parameters that describe the condition of the system at a point in time. Why do we need it? Average size of Queue Average waiting time How
EE 368 Weeks 3 (Notes) 1 State of a Queuing System State: Set of parameters that describe the condition of the system at a point in time. Why do we need it? Average size of Queue Average waiting time How
COMP9334: Capacity Planning of Computer Systems and Networks
 COMP9334: Capacity Planning of Computer Systems and Networks Week 2: Operational analysis Lecturer: Prof. Sanjay Jha NETWORKS RESEARCH GROUP, CSE, UNSW Operational analysis Operational: Collect performance
COMP9334: Capacity Planning of Computer Systems and Networks Week 2: Operational analysis Lecturer: Prof. Sanjay Jha NETWORKS RESEARCH GROUP, CSE, UNSW Operational analysis Operational: Collect performance
Exercises Stochastic Performance Modelling. Hamilton Institute, Summer 2010
 Exercises Stochastic Performance Modelling Hamilton Institute, Summer Instruction Exercise Let X be a non-negative random variable with E[X ]
Exercises Stochastic Performance Modelling Hamilton Institute, Summer Instruction Exercise Let X be a non-negative random variable with E[X ]
Multiaccess Problem. How to let distributed users (efficiently) share a single broadcast channel? How to form a queue for distributed users?
 Multiaccess Problem How to let distributed users (efficiently) share a single broadcast channel? How to form a queue for distributed users? z The protocols we used to solve this multiaccess problem are
Multiaccess Problem How to let distributed users (efficiently) share a single broadcast channel? How to form a queue for distributed users? z The protocols we used to solve this multiaccess problem are
Lecture 7: Simulation of Markov Processes. Pasi Lassila Department of Communications and Networking
 Lecture 7: Simulation of Markov Processes Pasi Lassila Department of Communications and Networking Contents Markov processes theory recap Elementary queuing models for data networks Simulation of Markov
Lecture 7: Simulation of Markov Processes Pasi Lassila Department of Communications and Networking Contents Markov processes theory recap Elementary queuing models for data networks Simulation of Markov
Chapter 5: Special Types of Queuing Models
 Chapter 5: Special Types of Queuing Models Some General Queueing Models Discouraged Arrivals Impatient Arrivals Bulk Service and Bulk Arrivals OR37-Dr.Khalid Al-Nowibet 1 5.1 General Queueing Models 1.
Chapter 5: Special Types of Queuing Models Some General Queueing Models Discouraged Arrivals Impatient Arrivals Bulk Service and Bulk Arrivals OR37-Dr.Khalid Al-Nowibet 1 5.1 General Queueing Models 1.
requests/sec. The total channel load is requests/sec. Using slot as the time unit, the total channel load is 50 ( ) = 1
 Prof. X. Shen E&CE 70 : Examples #2 Problem Consider the following Aloha systems. (a) A group of N users share a 56 kbps pure Aloha channel. Each user generates at a Passion rate of one 000-bit packet
Prof. X. Shen E&CE 70 : Examples #2 Problem Consider the following Aloha systems. (a) A group of N users share a 56 kbps pure Aloha channel. Each user generates at a Passion rate of one 000-bit packet
Queueing Systems: Lecture 3. Amedeo R. Odoni October 18, Announcements
 Queueing Systems: Lecture 3 Amedeo R. Odoni October 18, 006 Announcements PS #3 due tomorrow by 3 PM Office hours Odoni: Wed, 10/18, :30-4:30; next week: Tue, 10/4 Quiz #1: October 5, open book, in class;
Queueing Systems: Lecture 3 Amedeo R. Odoni October 18, 006 Announcements PS #3 due tomorrow by 3 PM Office hours Odoni: Wed, 10/18, :30-4:30; next week: Tue, 10/4 Quiz #1: October 5, open book, in class;
CS 798: Homework Assignment 3 (Queueing Theory)
 1.0 Little s law Assigned: October 6, 009 Patients arriving to the emergency room at the Grand River Hospital have a mean waiting time of three hours. It has been found that, averaged over the period of
1.0 Little s law Assigned: October 6, 009 Patients arriving to the emergency room at the Grand River Hospital have a mean waiting time of three hours. It has been found that, averaged over the period of
6 Solving Queueing Models
 6 Solving Queueing Models 6.1 Introduction In this note we look at the solution of systems of queues, starting with simple isolated queues. The benefits of using predefined, easily classified queues will
6 Solving Queueing Models 6.1 Introduction In this note we look at the solution of systems of queues, starting with simple isolated queues. The benefits of using predefined, easily classified queues will
Link Models for Circuit Switching
 Link Models for Circuit Switching The basis of traffic engineering for telecommunication networks is the Erlang loss function. It basically allows us to determine the amount of telephone traffic that can
Link Models for Circuit Switching The basis of traffic engineering for telecommunication networks is the Erlang loss function. It basically allows us to determine the amount of telephone traffic that can
Intro to Queueing Theory
 1 Intro to Queueing Theory Little s Law M/G/1 queue Conservation Law 1/31/017 M/G/1 queue (Simon S. Lam) 1 Little s Law No assumptions applicable to any system whose arrivals and departures are observable
1 Intro to Queueing Theory Little s Law M/G/1 queue Conservation Law 1/31/017 M/G/1 queue (Simon S. Lam) 1 Little s Law No assumptions applicable to any system whose arrivals and departures are observable
Chapter 3 Balance equations, birth-death processes, continuous Markov Chains
 Chapter 3 Balance equations, birth-death processes, continuous Markov Chains Ioannis Glaropoulos November 4, 2012 1 Exercise 3.2 Consider a birth-death process with 3 states, where the transition rate
Chapter 3 Balance equations, birth-death processes, continuous Markov Chains Ioannis Glaropoulos November 4, 2012 1 Exercise 3.2 Consider a birth-death process with 3 states, where the transition rate
Computer Networks More general queuing systems
 Computer Networks More general queuing systems Saad Mneimneh Computer Science Hunter College of CUNY New York M/G/ Introduction We now consider a queuing system where the customer service times have a
Computer Networks More general queuing systems Saad Mneimneh Computer Science Hunter College of CUNY New York M/G/ Introduction We now consider a queuing system where the customer service times have a
CDA5530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks. Chapter 4: Elementary Queuing Theory
 CDA5530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks Chapter 4: Elementary Queuing Theory Definition Queuing system: a buffer (waiting room), service facility (one or more servers) a scheduling policy
CDA5530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks Chapter 4: Elementary Queuing Theory Definition Queuing system: a buffer (waiting room), service facility (one or more servers) a scheduling policy
NATCOR: Stochastic Modelling
 NATCOR: Stochastic Modelling Queueing Theory II Chris Kirkbride Management Science 2017 Overview of Today s Sessions I Introduction to Queueing Modelling II Multiclass Queueing Models III Queueing Control
NATCOR: Stochastic Modelling Queueing Theory II Chris Kirkbride Management Science 2017 Overview of Today s Sessions I Introduction to Queueing Modelling II Multiclass Queueing Models III Queueing Control
Queueing Theory and Simulation. Introduction
 Queueing Theory and Simulation Based on the slides of Dr. Dharma P. Agrawal, University of Cincinnati and Dr. Hiroyuki Ohsaki Graduate School of Information Science & Technology, Osaka University, Japan
Queueing Theory and Simulation Based on the slides of Dr. Dharma P. Agrawal, University of Cincinnati and Dr. Hiroyuki Ohsaki Graduate School of Information Science & Technology, Osaka University, Japan
11 The M/G/1 system with priorities
 11 The M/G/1 system with priorities In this chapter we analyse queueing models with different types of customers, where one or more types of customers have priority over other types. More precisely we
11 The M/G/1 system with priorities In this chapter we analyse queueing models with different types of customers, where one or more types of customers have priority over other types. More precisely we
Queuing Analysis. Chapter Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
 Queuing Analysis Chapter 13 13-1 Chapter Topics Elements of Waiting Line Analysis The Single-Server Waiting Line System Undefined and Constant Service Times Finite Queue Length Finite Calling Problem The
Queuing Analysis Chapter 13 13-1 Chapter Topics Elements of Waiting Line Analysis The Single-Server Waiting Line System Undefined and Constant Service Times Finite Queue Length Finite Calling Problem The
Chapter 2 Queueing Theory and Simulation
 Chapter 2 Queueing Theory and Simulation Based on the slides of Dr. Dharma P. Agrawal, University of Cincinnati and Dr. Hiroyuki Ohsaki Graduate School of Information Science & Technology, Osaka University,
Chapter 2 Queueing Theory and Simulation Based on the slides of Dr. Dharma P. Agrawal, University of Cincinnati and Dr. Hiroyuki Ohsaki Graduate School of Information Science & Technology, Osaka University,
ISyE 2030 Practice Test 2
 1 NAME ISyE 2030 Practice Test 2 Summer 2005 This test is open notes, open books. You have exactly 75 minutes. 1. Short-Answer Questions (a) TRUE or FALSE? If arrivals occur according to a Poisson process
1 NAME ISyE 2030 Practice Test 2 Summer 2005 This test is open notes, open books. You have exactly 75 minutes. 1. Short-Answer Questions (a) TRUE or FALSE? If arrivals occur according to a Poisson process
16:330:543 Communication Networks I Midterm Exam November 7, 2005
 l l l l l l l l 1 3 np n = ρ 1 ρ = λ µ λ. n= T = E[N] = 1 λ µ λ = 1 µ 1. 16:33:543 Communication Networks I Midterm Exam November 7, 5 You have 16 minutes to complete this four problem exam. If you know
l l l l l l l l 1 3 np n = ρ 1 ρ = λ µ λ. n= T = E[N] = 1 λ µ λ = 1 µ 1. 16:33:543 Communication Networks I Midterm Exam November 7, 5 You have 16 minutes to complete this four problem exam. If you know
Little s result. T = average sojourn time (time spent) in the system N = average number of customers in the system. Little s result says that
 J. Virtamo 38.143 Queueing Theory / Little s result 1 Little s result The result Little s result or Little s theorem is a very simple (but fundamental) relation between the arrival rate of customers, average
J. Virtamo 38.143 Queueing Theory / Little s result 1 Little s result The result Little s result or Little s theorem is a very simple (but fundamental) relation between the arrival rate of customers, average
Chapter 5. Elementary Performance Analysis
 Chapter 5 Elementary Performance Analysis 1 5.0 2 5.1 Ref: Mischa Schwartz Telecommunication Networks Addison-Wesley publishing company 1988 3 4 p t T m T P(k)= 5 6 5.2 : arrived rate : service rate 7
Chapter 5 Elementary Performance Analysis 1 5.0 2 5.1 Ref: Mischa Schwartz Telecommunication Networks Addison-Wesley publishing company 1988 3 4 p t T m T P(k)= 5 6 5.2 : arrived rate : service rate 7
5/15/18. Operations Research: An Introduction Hamdy A. Taha. Copyright 2011, 2007 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 The objective of queuing analysis is to offer a reasonably satisfactory service to waiting customers. Unlike the other tools of OR, queuing theory is not an optimization technique. Rather, it determines
The objective of queuing analysis is to offer a reasonably satisfactory service to waiting customers. Unlike the other tools of OR, queuing theory is not an optimization technique. Rather, it determines
Course Outline Introduction to Transportation Highway Users and their Performance Geometric Design Pavement Design
 Course Outline Introduction to Transportation Highway Users and their Performance Geometric Design Pavement Design Speed Studies - Project Traffic Queuing Intersections Level of Service in Highways and
Course Outline Introduction to Transportation Highway Users and their Performance Geometric Design Pavement Design Speed Studies - Project Traffic Queuing Intersections Level of Service in Highways and
Sandwich shop : a queuing net work with finite disposable resources queue and infinite resources queue
 Sandwich shop : a queuing net work with finite disposable resources queue and infinite resources queue Final project for ISYE 680: Queuing systems and Applications Hongtan Sun May 5, 05 Introduction As
Sandwich shop : a queuing net work with finite disposable resources queue and infinite resources queue Final project for ISYE 680: Queuing systems and Applications Hongtan Sun May 5, 05 Introduction As
M/G/1 and Priority Queueing
 M/G/1 and Priority Queueing Richard T. B. Ma School of Computing National University of Singapore CS 5229: Advanced Compute Networks Outline PASTA M/G/1 Workload and FIFO Delay Pollaczek Khinchine Formula
M/G/1 and Priority Queueing Richard T. B. Ma School of Computing National University of Singapore CS 5229: Advanced Compute Networks Outline PASTA M/G/1 Workload and FIFO Delay Pollaczek Khinchine Formula
NICTA Short Course. Network Analysis. Vijay Sivaraman. Day 1 Queueing Systems and Markov Chains. Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-1
 NICTA Short Course Network Analysis Vijay Sivaraman Day 1 Queueing Systems and Markov Chains Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-1 Outline Why a short course on mathematical analysis? Limited current course offering
NICTA Short Course Network Analysis Vijay Sivaraman Day 1 Queueing Systems and Markov Chains Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-1 Outline Why a short course on mathematical analysis? Limited current course offering
Homework 1 - SOLUTION
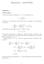 Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
Queueing Theory II. Summary. ! M/M/1 Output process. ! Networks of Queue! Method of Stages. ! General Distributions
 Queueing Theory II Summary! M/M/1 Output process! Networks of Queue! Method of Stages " Erlang Distribution " Hyperexponential Distribution! General Distributions " Embedded Markov Chains M/M/1 Output
Queueing Theory II Summary! M/M/1 Output process! Networks of Queue! Method of Stages " Erlang Distribution " Hyperexponential Distribution! General Distributions " Embedded Markov Chains M/M/1 Output
Class 11 Non-Parametric Models of a Service System; GI/GI/1, GI/GI/n: Exact & Approximate Analysis.
 Service Engineering Class 11 Non-Parametric Models of a Service System; GI/GI/1, GI/GI/n: Exact & Approximate Analysis. G/G/1 Queue: Virtual Waiting Time (Unfinished Work). GI/GI/1: Lindley s Equations
Service Engineering Class 11 Non-Parametric Models of a Service System; GI/GI/1, GI/GI/n: Exact & Approximate Analysis. G/G/1 Queue: Virtual Waiting Time (Unfinished Work). GI/GI/1: Lindley s Equations
CS418 Operating Systems
 CS418 Operating Systems Lecture 14 Queuing Analysis Textbook: Operating Systems by William Stallings 1 1. Why Queuing Analysis? If the system environment changes (like the number of users is doubled),
CS418 Operating Systems Lecture 14 Queuing Analysis Textbook: Operating Systems by William Stallings 1 1. Why Queuing Analysis? If the system environment changes (like the number of users is doubled),
Verification and Validation. CS1538: Introduction to Simulations
 Verification and Validation CS1538: Introduction to Simulations Steps in a Simulation Study Problem & Objective Formulation Model Conceptualization Data Collection Model translation, Verification, Validation
Verification and Validation CS1538: Introduction to Simulations Steps in a Simulation Study Problem & Objective Formulation Model Conceptualization Data Collection Model translation, Verification, Validation
Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems
 Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems Introduction to Queuing Systems System Performance Measures & Little s Law Equilibrium Solution of Birth-Death Processes Analysis of Single-Station Queuing Systems
Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems Introduction to Queuing Systems System Performance Measures & Little s Law Equilibrium Solution of Birth-Death Processes Analysis of Single-Station Queuing Systems
Chapter 8 Queuing Theory Roanna Gee. W = average number of time a customer spends in the system.
 8. Preliminaries L, L Q, W, W Q L = average number of customers in the system. L Q = average number of customers waiting in queue. W = average number of time a customer spends in the system. W Q = average
8. Preliminaries L, L Q, W, W Q L = average number of customers in the system. L Q = average number of customers waiting in queue. W = average number of time a customer spends in the system. W Q = average
Networking = Plumbing. Queueing Analysis: I. Last Lecture. Lecture Outline. Jeremiah Deng. 29 July 2013
 Networking = Plumbing TELE302 Lecture 7 Queueing Analysis: I Jeremiah Deng University of Otago 29 July 2013 Jeremiah Deng (University of Otago) TELE302 Lecture 7 29 July 2013 1 / 33 Lecture Outline Jeremiah
Networking = Plumbing TELE302 Lecture 7 Queueing Analysis: I Jeremiah Deng University of Otago 29 July 2013 Jeremiah Deng (University of Otago) TELE302 Lecture 7 29 July 2013 1 / 33 Lecture Outline Jeremiah
Systems Simulation Chapter 6: Queuing Models
 Systems Simulation Chapter 6: Queuing Models Fatih Cavdur fatihcavdur@uludag.edu.tr April 2, 2014 Introduction Introduction Simulation is often used in the analysis of queuing models. A simple but typical
Systems Simulation Chapter 6: Queuing Models Fatih Cavdur fatihcavdur@uludag.edu.tr April 2, 2014 Introduction Introduction Simulation is often used in the analysis of queuing models. A simple but typical
CPSC 531: System Modeling and Simulation. Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Fall 2017
 CPSC 531: System Modeling and Simulation Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Fall 2017 Motivating Quote for Queueing Models Good things come to those who wait - poet/writer
CPSC 531: System Modeling and Simulation Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Fall 2017 Motivating Quote for Queueing Models Good things come to those who wait - poet/writer
Control of Fork-Join Networks in Heavy-Traffic
 in Heavy-Traffic Asaf Zviran Based on MSc work under the guidance of Rami Atar (Technion) and Avishai Mandelbaum (Technion) Industrial Engineering and Management Technion June 2010 Introduction Network
in Heavy-Traffic Asaf Zviran Based on MSc work under the guidance of Rami Atar (Technion) and Avishai Mandelbaum (Technion) Industrial Engineering and Management Technion June 2010 Introduction Network
Approximate Queueing Model for Multi-rate Multi-user MIMO systems.
 An Approximate Queueing Model for Multi-rate Multi-user MIMO systems Boris Bellalta,Vanesa Daza, Miquel Oliver Abstract A queueing model for Multi-rate Multi-user MIMO systems is presented. The model is
An Approximate Queueing Model for Multi-rate Multi-user MIMO systems Boris Bellalta,Vanesa Daza, Miquel Oliver Abstract A queueing model for Multi-rate Multi-user MIMO systems is presented. The model is
Capacity management for packet-switched networks with heterogeneous sources. Linda de Jonge. Master Thesis July 29, 2009.
 Capacity management for packet-switched networks with heterogeneous sources Linda de Jonge Master Thesis July 29, 2009 Supervisors Dr. Frank Roijers Prof. dr. ir. Sem Borst Dr. Andreas Löpker Industrial
Capacity management for packet-switched networks with heterogeneous sources Linda de Jonge Master Thesis July 29, 2009 Supervisors Dr. Frank Roijers Prof. dr. ir. Sem Borst Dr. Andreas Löpker Industrial
MSA 640 Homework #2 Due September 17, points total / 20 points per question Show all work leading to your answers
 Name MSA 640 Homework #2 Due September 17, 2010 100 points total / 20 points per question Show all work leading to your answers 1. The annual demand for a particular type of valve is 3,500 units. The cost
Name MSA 640 Homework #2 Due September 17, 2010 100 points total / 20 points per question Show all work leading to your answers 1. The annual demand for a particular type of valve is 3,500 units. The cost
The Timing Capacity of Single-Server Queues with Multiple Flows
 The Timing Capacity of Single-Server Queues with Multiple Flows Xin Liu and R. Srikant Coordinated Science Laboratory University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign March 14, 2003 Timing Channel Information
The Timing Capacity of Single-Server Queues with Multiple Flows Xin Liu and R. Srikant Coordinated Science Laboratory University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign March 14, 2003 Timing Channel Information
Queueing Theory. VK Room: M Last updated: October 17, 2013.
 Queueing Theory VK Room: M1.30 knightva@cf.ac.uk www.vincent-knight.com Last updated: October 17, 2013. 1 / 63 Overview Description of Queueing Processes The Single Server Markovian Queue Multi Server
Queueing Theory VK Room: M1.30 knightva@cf.ac.uk www.vincent-knight.com Last updated: October 17, 2013. 1 / 63 Overview Description of Queueing Processes The Single Server Markovian Queue Multi Server
Answers to selected exercises
 Answers to selected exercises A First Course in Stochastic Models, Henk C. Tijms 1.1 ( ) 1.2 (a) Let waiting time if passengers already arrived,. Then,, (b) { (c) Long-run fraction for is (d) Let waiting
Answers to selected exercises A First Course in Stochastic Models, Henk C. Tijms 1.1 ( ) 1.2 (a) Let waiting time if passengers already arrived,. Then,, (b) { (c) Long-run fraction for is (d) Let waiting
Introduction to Queueing Theory
 Introduction to Queueing Theory Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Jain@eecs.berkeley.edu or Jain@wustl.edu A Mini-Course offered at UC Berkeley, Sept-Oct 2012 These slides and audio/video recordings
Introduction to Queueing Theory Raj Jain Washington University in Saint Louis Jain@eecs.berkeley.edu or Jain@wustl.edu A Mini-Course offered at UC Berkeley, Sept-Oct 2012 These slides and audio/video recordings
2905 Queueing Theory and Simulation PART IV: SIMULATION
 2905 Queueing Theory and Simulation PART IV: SIMULATION 22 Random Numbers A fundamental step in a simulation study is the generation of random numbers, where a random number represents the value of a random
2905 Queueing Theory and Simulation PART IV: SIMULATION 22 Random Numbers A fundamental step in a simulation study is the generation of random numbers, where a random number represents the value of a random
Introduction to Queueing Theory with Applications to Air Transportation Systems
 Introduction to Queueing Theory with Applications to Air Transportation Systems John Shortle George Mason University February 28, 2018 Outline Why stochastic models matter M/M/1 queue Little s law Priority
Introduction to Queueing Theory with Applications to Air Transportation Systems John Shortle George Mason University February 28, 2018 Outline Why stochastic models matter M/M/1 queue Little s law Priority
ECE 3511: Communications Networks Theory and Analysis. Fall Quarter Instructor: Prof. A. Bruce McDonald. Lecture Topic
 ECE 3511: Communications Networks Theory and Analysis Fall Quarter 2002 Instructor: Prof. A. Bruce McDonald Lecture Topic Introductory Analysis of M/G/1 Queueing Systems Module Number One Steady-State
ECE 3511: Communications Networks Theory and Analysis Fall Quarter 2002 Instructor: Prof. A. Bruce McDonald Lecture Topic Introductory Analysis of M/G/1 Queueing Systems Module Number One Steady-State
BIRTH DEATH PROCESSES AND QUEUEING SYSTEMS
 BIRTH DEATH PROCESSES AND QUEUEING SYSTEMS Andrea Bobbio Anno Accademico 999-2000 Queueing Systems 2 Notation for Queueing Systems /λ mean time between arrivals S = /µ ρ = λ/µ N mean service time traffic
BIRTH DEATH PROCESSES AND QUEUEING SYSTEMS Andrea Bobbio Anno Accademico 999-2000 Queueing Systems 2 Notation for Queueing Systems /λ mean time between arrivals S = /µ ρ = λ/µ N mean service time traffic
Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 3. Models of Queuing
 Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 3. Models of Queuing Husheng Li Min Kao Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville Spring, 2016 1/13 Terminology of
Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 3. Models of Queuing Husheng Li Min Kao Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville Spring, 2016 1/13 Terminology of
QUEUING SYSTEM. Yetunde Folajimi, PhD
 QUEUING SYSTEM Yetunde Folajimi, PhD Part 2 Queuing Models Queueing models are constructed so that queue lengths and waiting times can be predicted They help us to understand and quantify the effect of
QUEUING SYSTEM Yetunde Folajimi, PhD Part 2 Queuing Models Queueing models are constructed so that queue lengths and waiting times can be predicted They help us to understand and quantify the effect of
NANYANG TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SEMESTER I EXAMINATION MH4702/MAS446/MTH437 Probabilistic Methods in OR
 NANYANG TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SEMESTER I EXAMINATION 2013-201 MH702/MAS6/MTH37 Probabilistic Methods in OR December 2013 TIME ALLOWED: 2 HOURS INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES 1. This examination paper contains
NANYANG TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SEMESTER I EXAMINATION 2013-201 MH702/MAS6/MTH37 Probabilistic Methods in OR December 2013 TIME ALLOWED: 2 HOURS INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES 1. This examination paper contains
On the Partitioning of Servers in Queueing Systems during Rush Hour
 On the Partitioning of Servers in Queueing Systems during Rush Hour Bin Hu Saif Benjaafar Department of Operations and Management Science, Ross School of Business, University of Michigan at Ann Arbor,
On the Partitioning of Servers in Queueing Systems during Rush Hour Bin Hu Saif Benjaafar Department of Operations and Management Science, Ross School of Business, University of Michigan at Ann Arbor,
A Queueing System with Queue Length Dependent Service Times, with Applications to Cell Discarding in ATM Networks
 A Queueing System with Queue Length Dependent Service Times, with Applications to Cell Discarding in ATM Networks by Doo Il Choi, Charles Knessl and Charles Tier University of Illinois at Chicago 85 South
A Queueing System with Queue Length Dependent Service Times, with Applications to Cell Discarding in ATM Networks by Doo Il Choi, Charles Knessl and Charles Tier University of Illinois at Chicago 85 South
CDA6530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks. Chapter 8: Discrete Event Simulation (DES)
 CDA6530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks Chapter 8: Discrete Event Simulation (DES) Simulation Studies Models with analytical formulas Calculate the numerical solutions Differential equations
CDA6530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks Chapter 8: Discrete Event Simulation (DES) Simulation Studies Models with analytical formulas Calculate the numerical solutions Differential equations
Computer Systems Modelling
 Computer Systems Modelling Computer Laboratory Computer Science Tripos, Part II Michaelmas Term 2003 R. J. Gibbens Problem sheet William Gates Building JJ Thomson Avenue Cambridge CB3 0FD http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/
Computer Systems Modelling Computer Laboratory Computer Science Tripos, Part II Michaelmas Term 2003 R. J. Gibbens Problem sheet William Gates Building JJ Thomson Avenue Cambridge CB3 0FD http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/
IOE 202: lectures 11 and 12 outline
 IOE 202: lectures 11 and 12 outline Announcements Last time... Queueing models intro Performance characteristics of a queueing system Steady state analysis of an M/M/1 queueing system Other queueing systems,
IOE 202: lectures 11 and 12 outline Announcements Last time... Queueing models intro Performance characteristics of a queueing system Steady state analysis of an M/M/1 queueing system Other queueing systems,
Course Documents Authorized Duration: 120 minutes. Questions are generally independent. You can respond to any question before the other.
 KINGDOM OF SAUDI ARABIA Ministry of Higher Education Al-Imam Muhammad Ibn Saud Islamic University Faculty of Computer Science and Information المملكة العربية السعودية وزارة التعليم العالي جامعة اإلمام
KINGDOM OF SAUDI ARABIA Ministry of Higher Education Al-Imam Muhammad Ibn Saud Islamic University Faculty of Computer Science and Information المملكة العربية السعودية وزارة التعليم العالي جامعة اإلمام
Non Markovian Queues (contd.)
 MODULE 7: RENEWAL PROCESSES 29 Lecture 5 Non Markovian Queues (contd) For the case where the service time is constant, V ar(b) = 0, then the P-K formula for M/D/ queue reduces to L s = ρ + ρ 2 2( ρ) where
MODULE 7: RENEWAL PROCESSES 29 Lecture 5 Non Markovian Queues (contd) For the case where the service time is constant, V ar(b) = 0, then the P-K formula for M/D/ queue reduces to L s = ρ + ρ 2 2( ρ) where
Queues and Queueing Networks
 Queues and Queueing Networks Sanjay K. Bose Dept. of EEE, IITG Copyright 2015, Sanjay K. Bose 1 Introduction to Queueing Models and Queueing Analysis Copyright 2015, Sanjay K. Bose 2 Model of a Queue Arrivals
Queues and Queueing Networks Sanjay K. Bose Dept. of EEE, IITG Copyright 2015, Sanjay K. Bose 1 Introduction to Queueing Models and Queueing Analysis Copyright 2015, Sanjay K. Bose 2 Model of a Queue Arrivals
UNIVERSITY OF YORK. MSc Examinations 2004 MATHEMATICS Networks. Time Allowed: 3 hours.
 UNIVERSITY OF YORK MSc Examinations 2004 MATHEMATICS Networks Time Allowed: 3 hours. Answer 4 questions. Standard calculators will be provided but should be unnecessary. 1 Turn over 2 continued on next
UNIVERSITY OF YORK MSc Examinations 2004 MATHEMATICS Networks Time Allowed: 3 hours. Answer 4 questions. Standard calculators will be provided but should be unnecessary. 1 Turn over 2 continued on next
An Admission Control Mechanism for Providing Service Differentiation in Optical Burst-Switching Networks
 An Admission Control Mechanism for Providing Service Differentiation in Optical Burst-Switching Networks Igor M. Moraes, Daniel de O. Cunha, Marco D. D. Bicudo, Rafael P. Laufer, and Otto Carlos M. B.
An Admission Control Mechanism for Providing Service Differentiation in Optical Burst-Switching Networks Igor M. Moraes, Daniel de O. Cunha, Marco D. D. Bicudo, Rafael P. Laufer, and Otto Carlos M. B.
A discrete-time priority queue with train arrivals
 A discrete-time priority queue with train arrivals Joris Walraevens, Sabine Wittevrongel and Herwig Bruneel SMACS Research Group Department of Telecommunications and Information Processing (IR07) Ghent
A discrete-time priority queue with train arrivals Joris Walraevens, Sabine Wittevrongel and Herwig Bruneel SMACS Research Group Department of Telecommunications and Information Processing (IR07) Ghent
EP2200 Course Project 2017 Project II - Mobile Computation Offloading
 EP2200 Course Project 2017 Project II - Mobile Computation Offloading 1 Introduction Queuing theory provides us a very useful mathematic tool that can be used to analytically evaluate the performance of
EP2200 Course Project 2017 Project II - Mobile Computation Offloading 1 Introduction Queuing theory provides us a very useful mathematic tool that can be used to analytically evaluate the performance of
Queuing Networks: Burke s Theorem, Kleinrock s Approximation, and Jackson s Theorem. Wade Trappe
 Queuing Networks: Burke s Theorem, Kleinrock s Approximation, and Jackson s Theorem Wade Trappe Lecture Overview Network of Queues Introduction Queues in Tandem roduct Form Solutions Burke s Theorem What
Queuing Networks: Burke s Theorem, Kleinrock s Approximation, and Jackson s Theorem Wade Trappe Lecture Overview Network of Queues Introduction Queues in Tandem roduct Form Solutions Burke s Theorem What
Chapter 6 Queueing Models. Banks, Carson, Nelson & Nicol Discrete-Event System Simulation
 Chapter 6 Queueing Models Banks, Carson, Nelson & Nicol Discrete-Event System Simulation Purpose Simulation is often used in the analysis of queueing models. A simple but typical queueing model: Queueing
Chapter 6 Queueing Models Banks, Carson, Nelson & Nicol Discrete-Event System Simulation Purpose Simulation is often used in the analysis of queueing models. A simple but typical queueing model: Queueing
Birth-Death Processes
 Birth-Death Processes Birth-Death Processes: Transient Solution Poisson Process: State Distribution Poisson Process: Inter-arrival Times Dr Conor McArdle EE414 - Birth-Death Processes 1/17 Birth-Death
Birth-Death Processes Birth-Death Processes: Transient Solution Poisson Process: State Distribution Poisson Process: Inter-arrival Times Dr Conor McArdle EE414 - Birth-Death Processes 1/17 Birth-Death
Outline Network structure and objectives Routing Routing protocol protocol System analysis Results Conclusion Slide 2
 2007 Radio and Wireless Symposium 9 11 January 2007, Long Beach, CA. Lifetime-Aware Hierarchical Wireless Sensor Network Architecture with Mobile Overlays Maryam Soltan, Morteza Maleki, and Massoud Pedram
2007 Radio and Wireless Symposium 9 11 January 2007, Long Beach, CA. Lifetime-Aware Hierarchical Wireless Sensor Network Architecture with Mobile Overlays Maryam Soltan, Morteza Maleki, and Massoud Pedram
An Analysis of the Preemptive Repeat Queueing Discipline
 An Analysis of the Preemptive Repeat Queueing Discipline Tony Field August 3, 26 Abstract An analysis of two variants of preemptive repeat or preemptive repeat queueing discipline is presented: one in
An Analysis of the Preemptive Repeat Queueing Discipline Tony Field August 3, 26 Abstract An analysis of two variants of preemptive repeat or preemptive repeat queueing discipline is presented: one in
An engineering approximation for the mean waiting time in the M/H 2 b /s queue
 An engineering approximation for the mean waiting time in the M/H b /s queue Francisco Barceló Universidad Politécnica de Catalunya c/ Jordi Girona, -3, Barcelona 08034 Email : barcelo@entel.upc.es Abstract
An engineering approximation for the mean waiting time in the M/H b /s queue Francisco Barceló Universidad Politécnica de Catalunya c/ Jordi Girona, -3, Barcelona 08034 Email : barcelo@entel.upc.es Abstract
Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0.
![Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0. Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0.](/thumbs/95/124116804.jpg) IEOR 46: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Chapters 5-6 in Ross, Thursday, April, 4:5-5:35pm SOLUTIONS to Second Midterm Exam, Spring 9, Open Book: but only the Ross textbook, the
IEOR 46: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Chapters 5-6 in Ross, Thursday, April, 4:5-5:35pm SOLUTIONS to Second Midterm Exam, Spring 9, Open Book: but only the Ross textbook, the
Contents Preface The Exponential Distribution and the Poisson Process Introduction to Renewal Theory
 Contents Preface... v 1 The Exponential Distribution and the Poisson Process... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 The Density, the Distribution, the Tail, and the Hazard Functions... 2 1.2.1 The Hazard Function
Contents Preface... v 1 The Exponential Distribution and the Poisson Process... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 The Density, the Distribution, the Tail, and the Hazard Functions... 2 1.2.1 The Hazard Function
[Chapter 6. Functions of Random Variables]
![[Chapter 6. Functions of Random Variables] [Chapter 6. Functions of Random Variables]](/thumbs/92/109648703.jpg) [Chapter 6. Functions of Random Variables] 6.1 Introduction 6.2 Finding the probability distribution of a function of random variables 6.3 The method of distribution functions 6.5 The method of Moment-generating
[Chapter 6. Functions of Random Variables] 6.1 Introduction 6.2 Finding the probability distribution of a function of random variables 6.3 The method of distribution functions 6.5 The method of Moment-generating
A Study on Performance Analysis of Queuing System with Multiple Heterogeneous Servers
 UNIVERSITY OF OKLAHOMA GENERAL EXAM REPORT A Study on Performance Analysis of Queuing System with Multiple Heterogeneous Servers Prepared by HUSNU SANER NARMAN husnu@ou.edu based on the papers 1) F. S.
UNIVERSITY OF OKLAHOMA GENERAL EXAM REPORT A Study on Performance Analysis of Queuing System with Multiple Heterogeneous Servers Prepared by HUSNU SANER NARMAN husnu@ou.edu based on the papers 1) F. S.
WiFi MAC Models David Malone
 WiFi MAC Models David Malone November 26, MACSI Hamilton Institute, NUIM, Ireland Talk outline Introducing the 82.11 CSMA/CA MAC. Finite load 82.11 model and its predictions. Issues with standard 82.11,
WiFi MAC Models David Malone November 26, MACSI Hamilton Institute, NUIM, Ireland Talk outline Introducing the 82.11 CSMA/CA MAC. Finite load 82.11 model and its predictions. Issues with standard 82.11,
page 1 This question-paper you hand in, together with your solutions. ================================================================
 age EXAMINATION Jan 9 Time :5-7:5 QUEUEING THEORY EP9, HF ( 6H78), Lecturer: Armin Halilovic Instructions:. You ARE allowed to use a calculator.. You are NOT allowed to use your own tables of mathematical
age EXAMINATION Jan 9 Time :5-7:5 QUEUEING THEORY EP9, HF ( 6H78), Lecturer: Armin Halilovic Instructions:. You ARE allowed to use a calculator.. You are NOT allowed to use your own tables of mathematical
On the Partitioning of Servers in Queueing Systems during Rush Hour
 On the Partitioning of Servers in Queueing Systems during Rush Hour This paper is motivated by two phenomena observed in many queueing systems in practice. The first is the partitioning of server capacity
On the Partitioning of Servers in Queueing Systems during Rush Hour This paper is motivated by two phenomena observed in many queueing systems in practice. The first is the partitioning of server capacity
Erlang-C = M/M/N. agents. queue ACD. arrivals. busy ACD. queue. abandonment BACK FRONT. lost calls. arrivals. lost calls
 Erlang-C = M/M/N agents arrivals ACD queue Erlang-A lost calls FRONT BACK arrivals busy ACD queue abandonment lost calls Erlang-C = M/M/N agents arrivals ACD queue Rough Performance Analysis
Erlang-C = M/M/N agents arrivals ACD queue Erlang-A lost calls FRONT BACK arrivals busy ACD queue abandonment lost calls Erlang-C = M/M/N agents arrivals ACD queue Rough Performance Analysis
Slides 9: Queuing Models
 Slides 9: Queuing Models Purpose Simulation is often used in the analysis of queuing models. A simple but typical queuing model is: Queuing models provide the analyst with a powerful tool for designing
Slides 9: Queuing Models Purpose Simulation is often used in the analysis of queuing models. A simple but typical queuing model is: Queuing models provide the analyst with a powerful tool for designing
PBW 654 Applied Statistics - I Urban Operations Research
 PBW 654 Applied Statistics - I Urban Operations Research Lecture 2.I Queuing Systems An Introduction Operations Research Models Deterministic Models Linear Programming Integer Programming Network Optimization
PBW 654 Applied Statistics - I Urban Operations Research Lecture 2.I Queuing Systems An Introduction Operations Research Models Deterministic Models Linear Programming Integer Programming Network Optimization
Bernoulli Counting Process with p=0.1
 Stat 28 October 29, 21 Today: More Ch 7 (Sections 7.4 and part of 7.) Midterm will cover Ch 7 to section 7.4 Review session will be Nov. Exercises to try (answers in book): 7.1-, 7.2-3, 7.3-3, 7.4-7 Where
Stat 28 October 29, 21 Today: More Ch 7 (Sections 7.4 and part of 7.) Midterm will cover Ch 7 to section 7.4 Review session will be Nov. Exercises to try (answers in book): 7.1-, 7.2-3, 7.3-3, 7.4-7 Where
COMP9334 Capacity Planning for Computer Systems and Networks
 COMP9334 Capacity Planning for Computer Systems and Networks Week 2: Operational Analysis and Workload Characterisation COMP9334 1 Last lecture Modelling of computer systems using Queueing Networks Open
COMP9334 Capacity Planning for Computer Systems and Networks Week 2: Operational Analysis and Workload Characterisation COMP9334 1 Last lecture Modelling of computer systems using Queueing Networks Open
EECS 126 Probability and Random Processes University of California, Berkeley: Fall 2014 Kannan Ramchandran November 13, 2014.
 EECS 126 Probability and Random Processes University of California, Berkeley: Fall 2014 Kannan Ramchandran November 13, 2014 Midterm Exam 2 Last name First name SID Rules. DO NOT open the exam until instructed
EECS 126 Probability and Random Processes University of California, Berkeley: Fall 2014 Kannan Ramchandran November 13, 2014 Midterm Exam 2 Last name First name SID Rules. DO NOT open the exam until instructed
Multi-class, multi-server queues with non-preemptive priorities
 Multi-class, multi-server queues with non-preemptive priorities Andrei Sleptcheno. EURANDOM, Eindhoven University of Technology, P.O. Box 53, 5600MB Eindhoven, The Netherlands. e-mail:sleptcheno@eurandom.tue.nl
Multi-class, multi-server queues with non-preemptive priorities Andrei Sleptcheno. EURANDOM, Eindhoven University of Technology, P.O. Box 53, 5600MB Eindhoven, The Netherlands. e-mail:sleptcheno@eurandom.tue.nl
M/G/FQ: STOCHASTIC ANALYSIS OF FAIR QUEUEING SYSTEMS
 M/G/FQ: STOCHASTIC ANALYSIS OF FAIR QUEUEING SYSTEMS MOHAMMED HAWA AND DAVID W. PETR Information and Telecommunications Technology Center University of Kansas, Lawrence, Kansas, 66045 email: {hawa, dwp}@ittc.ku.edu
M/G/FQ: STOCHASTIC ANALYSIS OF FAIR QUEUEING SYSTEMS MOHAMMED HAWA AND DAVID W. PETR Information and Telecommunications Technology Center University of Kansas, Lawrence, Kansas, 66045 email: {hawa, dwp}@ittc.ku.edu
2DI90 Probability & Statistics. 2DI90 Chapter 4 of MR
 2DI90 Probability & Statistics 2DI90 Chapter 4 of MR Recap - Random Variables ( 2.8 MR)! Example: X is the random variable corresponding to the temperature of the room at time t. x is the measured temperature
2DI90 Probability & Statistics 2DI90 Chapter 4 of MR Recap - Random Variables ( 2.8 MR)! Example: X is the random variable corresponding to the temperature of the room at time t. x is the measured temperature
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
 .203J/6.28J/3.665J/5.073J/6.76J/ESD.26J Quiz Solutions (a)(i) Without loss of generality we can pin down X at any fixed point. X 2 is still uniformly distributed over the square. Assuming that the police
.203J/6.28J/3.665J/5.073J/6.76J/ESD.26J Quiz Solutions (a)(i) Without loss of generality we can pin down X at any fixed point. X 2 is still uniformly distributed over the square. Assuming that the police
Section 1.2: A Single Server Queue
 Section 12: A Single Server Queue Discrete-Event Simulation: A First Course c 2006 Pearson Ed, Inc 0-13-142917-5 Discrete-Event Simulation: A First Course Section 12: A Single Server Queue 1/ 30 Section
Section 12: A Single Server Queue Discrete-Event Simulation: A First Course c 2006 Pearson Ed, Inc 0-13-142917-5 Discrete-Event Simulation: A First Course Section 12: A Single Server Queue 1/ 30 Section
Single-Server Service-Station (G/G/1)
 Service Engineering July 997 Last Revised January, 006 Single-Server Service-Station (G/G/) arrivals queue 000000000000 000000000000 departures Arrivals A = {A(t), t 0}, counting process, e.g., completely
Service Engineering July 997 Last Revised January, 006 Single-Server Service-Station (G/G/) arrivals queue 000000000000 000000000000 departures Arrivals A = {A(t), t 0}, counting process, e.g., completely
Queueing Review. Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman 10/6/16. (mostly from BCNN) Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA
 1 / 24 Queueing Review (mostly from BCNN) Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA 10/6/16 2 / 24 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Queueing Notation 3 Transient
1 / 24 Queueing Review (mostly from BCNN) Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA 10/6/16 2 / 24 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Queueing Notation 3 Transient
Queuing Theory and Stochas St t ochas ic Service Syste y ms Li Xia
 Queuing Theory and Stochastic Service Systems Li Xia Syllabus Instructor Li Xia 夏俐, FIT 3 618, 62793029, xial@tsinghua.edu.cn Text book D. Gross, J.F. Shortle, J.M. Thompson, and C.M. Harris, Fundamentals
Queuing Theory and Stochastic Service Systems Li Xia Syllabus Instructor Li Xia 夏俐, FIT 3 618, 62793029, xial@tsinghua.edu.cn Text book D. Gross, J.F. Shortle, J.M. Thompson, and C.M. Harris, Fundamentals
Chapter 1. Introduction. 1.1 Stochastic process
 Chapter 1 Introduction Process is a phenomenon that takes place in time. In many practical situations, the result of a process at any time may not be certain. Such a process is called a stochastic process.
Chapter 1 Introduction Process is a phenomenon that takes place in time. In many practical situations, the result of a process at any time may not be certain. Such a process is called a stochastic process.
Analysis of random-access MAC schemes
 Analysis of random-access MA schemes M. Veeraraghavan and Tao i ast updated: Sept. 203. Slotted Aloha [4] First-order analysis: if we assume there are infinite number of nodes, the number of new arrivals
Analysis of random-access MA schemes M. Veeraraghavan and Tao i ast updated: Sept. 203. Slotted Aloha [4] First-order analysis: if we assume there are infinite number of nodes, the number of new arrivals
Dynamic Control of Parallel-Server Systems
 Dynamic Control of Parallel-Server Systems Jim Dai Georgia Institute of Technology Tolga Tezcan University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign May 13, 2009 Jim Dai (Georgia Tech) Many-Server Asymptotic Optimality
Dynamic Control of Parallel-Server Systems Jim Dai Georgia Institute of Technology Tolga Tezcan University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign May 13, 2009 Jim Dai (Georgia Tech) Many-Server Asymptotic Optimality
Classical Queueing Models.
 Sergey Zeltyn January 2005 STAT 99. Service Engineering. The Wharton School. University of Pennsylvania. Based on: Classical Queueing Models. Mandelbaum A. Service Engineering course, Technion. http://iew3.technion.ac.il/serveng2005w
Sergey Zeltyn January 2005 STAT 99. Service Engineering. The Wharton School. University of Pennsylvania. Based on: Classical Queueing Models. Mandelbaum A. Service Engineering course, Technion. http://iew3.technion.ac.il/serveng2005w
Performance Analysis of Priority Queueing Schemes in Internet Routers
 Conference on Information Sciences and Systems, The Johns Hopkins University, March 8, Performance Analysis of Priority Queueing Schemes in Internet Routers Ashvin Lakshmikantha Coordinated Science Lab
Conference on Information Sciences and Systems, The Johns Hopkins University, March 8, Performance Analysis of Priority Queueing Schemes in Internet Routers Ashvin Lakshmikantha Coordinated Science Lab
Fuzzy Queues with Priority Discipline
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 4,, no., 575-58 Fuzzy Queues with Priority Discipline W. Ritha* and Lilly Robert Department of Mathematics Holy Cross College (Autonomous) Trichirapalli, Tamilnadu,
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 4,, no., 575-58 Fuzzy Queues with Priority Discipline W. Ritha* and Lilly Robert Department of Mathematics Holy Cross College (Autonomous) Trichirapalli, Tamilnadu,
