Answers to the problems from problem solving classes
|
|
|
- Andrea Joseph
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Answers to the problems from problem solving classes Class, multiaccess communication 3. Solution : Let λ Q 5 customers per minute be the rate at which customers arrive to the queue for ordering, T Q 5 minutes be the average time each customer spends waiting in the queue. By Little s theorem we get N Q λ Q T Q 25 customers in the queue on average. Let λ E 0.5λ Q 2.5 customers per minute be the rate at which customers arrive from the ordering queue to sit down and eat in the restaurant, T E 20 minutes be the average time to eat the meal. Little s theorem gives us N E λ E T E customers on average eating in the restaurant. So, in total there are N N Q + N E customers in the restaurant on average. Solution 2: Let λ 5 customers per minute be the rate at which customers arrive to the restaurant. P(eat in) P(take out) /2, Tqueue 5 minutes, T eat 20 minutes, average time per customer Tavg TqueueP(take out)+ (Tqueue + T eat )P(eat in) 5 /2 + (5 + 20) /2 30 /2 5 minutes. By Little s theorem we get average number of customers in the restaurant as N λtavg (a). Let p n (k) be the probability to have n backlogged nodes during time slot k. The transition probability P i,j is the probability to have j backlogged nodes in next time slot given that we have i backlogged nodes in the current time slot. Now, computing p n (k + ) by decomposing into conditioning on all possible previous states give us p n (k + ) i n+ p i (k)p i,n p i (k)p i,n () since P i,n 0 if i > n + because it is impossible to successfully transmit more than one packet during a time slot. Assuming that the steady-state probabilities exists, p n lim k p n (k), taking the limit as k of () gives us p n n+ i0 p ip i,n. Furthermore we have to have total probability, so m i0 p i. (b). Separating last term of sum, p n n i0 p ip i,n +p n+ P n+,n and solving for p n+ yields p n+ n p n p i P i,n P n+,n i0 i0
2 (c). Using the results from (b) p p 2 (p 0 p 0 P 0,0 ) p 0 ( P 0,0 ) P,0 P,0 (p p P, p 0 P 0, ) P 2, (p ( P, ) p 0 P 0, ) P 2, p0 ( P 0,0 )( P, ) p 0 P 0, P 2, P,0 p 0 (( P 0,0 )( P, ) P,0 P 0, ) P 2, P,0 (d). From above we have the equations p p 0 ( P 0,0 ) P,0 p 0 p 2 (( P 0,0 )( P, ) P,0 P 0, ) P 2, P,0 inserting them into p 0 + p + p 2 yields ( p 0 + P 0,0 + ( P ) 0,0)( P, ) P,0 P 0, P,0 P 2, P,0 using common denominator and solving for p 0 gives us p 0 P 2, P,0 P 2, P,0 + P 2, ( P 0,0 ) + ( P 0,0 )( P, ) P,0 P 0, P 2, P,0 P,0 (P 2, P 0, ) + ( P 0,0 )( + P 2, P, ) P 2, P,0 P,0 P 2, + ( P 0,0 )( + P 2, P, ) since P 0, 0 because we can t go from no backlogged nodes to just backlogged node. We can go further than the problem stated in the book by expressing the transition probabilities in terms of retransmission probability q r and packet arrival probability q a, we have P 0,0 ( 2 ) ( q a )q a + ( 2 0 ) ( q a ) 2 2( q a )q a + ( q a ) 2 ( q a )(2q a + q a ) ( q a )( + q a ) qa 2 P,0 ( q a ) q r ( q a )q r 0 2
3 P, q a ( q r ) + ( q a )( q r ) 0 0 q a ( q r ) + ( q a )( q r ) q r 0 2 P 2, ( q r )q r 2( q r )q r 0 and inserting those into our expression for p 0 we obtain p 0 p p 2 2( q a )( q r )q r 2( q a )( q r )q r + q 2 a (3 2q r) 2( q r )q 2 a 2( q a )( q r )q r + q 2 a(3 2q r ) q 2 a 2( q a )( q r )q r + q 2 a(3 2q r ) 4.3 (a). The arrival rate, as a function of the attempt rate, is a straight line from (/e, /e) to (, 0). (b). The probability for a successful transmittion is Ps Q a (,n)q r (0,n)+ Q a (0,n)Q r (,n) and when n m we have Ps Q a (,m)q r (0,m) + Q a (0,m)Q r (,m) m 0 + ( q r ) m q r m( m )m m ( m )m and in case q r and q a are small we have Ps e (m) and (m) (m m)q a + mq r mq r, and the first expression we derived indeed e as m. (c). Any straight line from (,0) to (mq a,mq a ) will pass the departure curve only once. (d). We have (n) (m n)q a + nq r mq a + n(q r q a ) e + n( m me ) e + n m ( e ) so e n m ( e ) solving for n we get n m( e ), which is the number of backlogged nodes that corresponds e to any given attempt rate. Now we can compute the arrival rate (m n)q a nq r by inserting that expression for n and obtain ( e ) m m e e e e e which is our arrival rate expressed in terms of the attempt rate. In the equilibrium point this has to equal the departure rate e, so the equation we want to solve numerically 3
4 is e e which is (e )e or (e )e which we can iterate a few times from starting value to obtain the approximate solution (e). From (d) we have n m e e 4.5 e e so almost 9% of the arriving packets are not accepted into the system but discarded due to the node they are arriving to being backlogged. (a). iven that a specific packet has not been successfully transmitted before time slot i it will be transmitted successfully with probability pq r. Let T q be the the time a packet is queued up in the system, we then have P(T q 0) p P(T q ) P(T q T q > 0)P(T q > 0) pq r ( p) P(T q 2) P(T q 2 T q > )P(T q > ) pq r ( p)( pq r ) P(T q 3) P(T q 3 T q > 2)P(T q > 2) pq r ( p)( pq r ) 2. P(T q k) P(T q k T q > k )P(T q > k ) pq r ( p)( pq r ) k so we can compute the expected queueing time as E[T q ] kpq r ( pq r ) k ( p) p( p)q r k( pq r ) k k now consider k kxk d dx x p( p)q r (pq r) 2 k d dx xk d dx k k xk d dx x x ( x) 2. Inserting x pq r now yields E[T q ] ( p) pq r. After the queueing time it takes another time slot to transmit the packet so in total we have the expected delay T + T q + p pq r. (b). For a given backlogged packet, when we have n backlogged nodes, the probability for successful transmission is p ( q a ) m n ( q r ) n, since the m n not backlogged packet can t have any arrivals and the remaining n backlogged nodes should not retransmit. Thus p q r ( q a ) m n ( q r ) n e (qa(m n)+qrn) e (n). Similarly if we are given a newly arrived packet, the probability for successful transmission is p ( q a ) m n ( q r ) n q a ( q a ) m n ( q r ) n e (qa(m n)+qrn) e (n). 4
5 (c). Substituting p e into E[T q ] from (b) gives us E[T q ] e q re. In equilibrium we have e (m n )q a, i.e. e (m n )q a. Using that we now obtain E[T q ] (m n )q a q r (m n )q a (m n )q a (m n )q a q r (m n )q a + n q r (m n )q a (m n )q a q r n (m n )q a Thus, since T + T q we have the claimed result. (d). Attempt rate (n) (m n)q a +nq r mq a +n(q r q a ) n m, at equilibrium we have e (m n)q a, so we get ( n m )e ( n m ) 0.3( n m ) solving numerically for n m we get the stable equilibrium state n as n m 0.243, which is n n m/8, and we get T + 0.3( n m ) m + (8 ) m 2. m 2. 5
Multiaccess Communication
 Information Networks p. 1 Multiaccess Communication Satellite systems, radio networks (WLAN), Ethernet segment The received signal is the sum of attenuated transmitted signals from a set of other nodes,
Information Networks p. 1 Multiaccess Communication Satellite systems, radio networks (WLAN), Ethernet segment The received signal is the sum of attenuated transmitted signals from a set of other nodes,
Markov Chain Model for ALOHA protocol
 Markov Chain Model for ALOHA protocol Laila Daniel and Krishnan Narayanan April 22, 2012 Outline of the talk A Markov chain (MC) model for Slotted ALOHA Basic properties of Discrete-time Markov Chain Stability
Markov Chain Model for ALOHA protocol Laila Daniel and Krishnan Narayanan April 22, 2012 Outline of the talk A Markov chain (MC) model for Slotted ALOHA Basic properties of Discrete-time Markov Chain Stability
Power Laws in ALOHA Systems
 Power Laws in ALOHA Systems E6083: lecture 8 Prof. Predrag R. Jelenković Dept. of Electrical Engineering Columbia University, NY 10027, USA predrag@ee.columbia.edu March 6, 2007 Jelenković (Columbia University)
Power Laws in ALOHA Systems E6083: lecture 8 Prof. Predrag R. Jelenković Dept. of Electrical Engineering Columbia University, NY 10027, USA predrag@ee.columbia.edu March 6, 2007 Jelenković (Columbia University)
16:330:543 Communication Networks I Midterm Exam November 7, 2005
 l l l l l l l l 1 3 np n = ρ 1 ρ = λ µ λ. n= T = E[N] = 1 λ µ λ = 1 µ 1. 16:33:543 Communication Networks I Midterm Exam November 7, 5 You have 16 minutes to complete this four problem exam. If you know
l l l l l l l l 1 3 np n = ρ 1 ρ = λ µ λ. n= T = E[N] = 1 λ µ λ = 1 µ 1. 16:33:543 Communication Networks I Midterm Exam November 7, 5 You have 16 minutes to complete this four problem exam. If you know
Computer Networks More general queuing systems
 Computer Networks More general queuing systems Saad Mneimneh Computer Science Hunter College of CUNY New York M/G/ Introduction We now consider a queuing system where the customer service times have a
Computer Networks More general queuing systems Saad Mneimneh Computer Science Hunter College of CUNY New York M/G/ Introduction We now consider a queuing system where the customer service times have a
Multimedia Communication Services Traffic Modeling and Streaming
 Multimedia Communication Services Medium Access Control algorithms Aloha Slotted: performance analysis with finite nodes Università degli Studi di Brescia A.A. 2014/2015 Francesco Gringoli Master of Science
Multimedia Communication Services Medium Access Control algorithms Aloha Slotted: performance analysis with finite nodes Università degli Studi di Brescia A.A. 2014/2015 Francesco Gringoli Master of Science
requests/sec. The total channel load is requests/sec. Using slot as the time unit, the total channel load is 50 ( ) = 1
 Prof. X. Shen E&CE 70 : Examples #2 Problem Consider the following Aloha systems. (a) A group of N users share a 56 kbps pure Aloha channel. Each user generates at a Passion rate of one 000-bit packet
Prof. X. Shen E&CE 70 : Examples #2 Problem Consider the following Aloha systems. (a) A group of N users share a 56 kbps pure Aloha channel. Each user generates at a Passion rate of one 000-bit packet
ECE 3511: Communications Networks Theory and Analysis. Fall Quarter Instructor: Prof. A. Bruce McDonald. Lecture Topic
 ECE 3511: Communications Networks Theory and Analysis Fall Quarter 2002 Instructor: Prof. A. Bruce McDonald Lecture Topic Introductory Analysis of M/G/1 Queueing Systems Module Number One Steady-State
ECE 3511: Communications Networks Theory and Analysis Fall Quarter 2002 Instructor: Prof. A. Bruce McDonald Lecture Topic Introductory Analysis of M/G/1 Queueing Systems Module Number One Steady-State
Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems
 Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems Introduction to Queuing Systems System Performance Measures & Little s Law Equilibrium Solution of Birth-Death Processes Analysis of Single-Station Queuing Systems
Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems Introduction to Queuing Systems System Performance Measures & Little s Law Equilibrium Solution of Birth-Death Processes Analysis of Single-Station Queuing Systems
Link Models for Packet Switching
 Link Models for Packet Switching To begin our study of the performance of communications networks, we will study a model of a single link in a message switched network. The important feature of this model
Link Models for Packet Switching To begin our study of the performance of communications networks, we will study a model of a single link in a message switched network. The important feature of this model
Queueing Theory and Simulation. Introduction
 Queueing Theory and Simulation Based on the slides of Dr. Dharma P. Agrawal, University of Cincinnati and Dr. Hiroyuki Ohsaki Graduate School of Information Science & Technology, Osaka University, Japan
Queueing Theory and Simulation Based on the slides of Dr. Dharma P. Agrawal, University of Cincinnati and Dr. Hiroyuki Ohsaki Graduate School of Information Science & Technology, Osaka University, Japan
Chapter 5. Elementary Performance Analysis
 Chapter 5 Elementary Performance Analysis 1 5.0 2 5.1 Ref: Mischa Schwartz Telecommunication Networks Addison-Wesley publishing company 1988 3 4 p t T m T P(k)= 5 6 5.2 : arrived rate : service rate 7
Chapter 5 Elementary Performance Analysis 1 5.0 2 5.1 Ref: Mischa Schwartz Telecommunication Networks Addison-Wesley publishing company 1988 3 4 p t T m T P(k)= 5 6 5.2 : arrived rate : service rate 7
UNIVERSITY OF YORK. MSc Examinations 2004 MATHEMATICS Networks. Time Allowed: 3 hours.
 UNIVERSITY OF YORK MSc Examinations 2004 MATHEMATICS Networks Time Allowed: 3 hours. Answer 4 questions. Standard calculators will be provided but should be unnecessary. 1 Turn over 2 continued on next
UNIVERSITY OF YORK MSc Examinations 2004 MATHEMATICS Networks Time Allowed: 3 hours. Answer 4 questions. Standard calculators will be provided but should be unnecessary. 1 Turn over 2 continued on next
Analysis of random-access MAC schemes
 Analysis of random-access MA schemes M. Veeraraghavan and Tao i ast updated: Sept. 203. Slotted Aloha [4] First-order analysis: if we assume there are infinite number of nodes, the number of new arrivals
Analysis of random-access MA schemes M. Veeraraghavan and Tao i ast updated: Sept. 203. Slotted Aloha [4] First-order analysis: if we assume there are infinite number of nodes, the number of new arrivals
Queueing Theory I Summary! Little s Law! Queueing System Notation! Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K "
 Queueing Theory I Summary Little s Law Queueing System Notation Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K " Little s Law a(t): the process that counts the number of arrivals
Queueing Theory I Summary Little s Law Queueing System Notation Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K " Little s Law a(t): the process that counts the number of arrivals
Chapter 2 Queueing Theory and Simulation
 Chapter 2 Queueing Theory and Simulation Based on the slides of Dr. Dharma P. Agrawal, University of Cincinnati and Dr. Hiroyuki Ohsaki Graduate School of Information Science & Technology, Osaka University,
Chapter 2 Queueing Theory and Simulation Based on the slides of Dr. Dharma P. Agrawal, University of Cincinnati and Dr. Hiroyuki Ohsaki Graduate School of Information Science & Technology, Osaka University,
Lecture 7: Simulation of Markov Processes. Pasi Lassila Department of Communications and Networking
 Lecture 7: Simulation of Markov Processes Pasi Lassila Department of Communications and Networking Contents Markov processes theory recap Elementary queuing models for data networks Simulation of Markov
Lecture 7: Simulation of Markov Processes Pasi Lassila Department of Communications and Networking Contents Markov processes theory recap Elementary queuing models for data networks Simulation of Markov
Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems
 Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems Problem 1: Customers arrive at a grocery store s checkout counter according to a Poisson process with rate 1 per minute. Each customer carries a number of items
Solutions to COMP9334 Week 8 Sample Problems Problem 1: Customers arrive at a grocery store s checkout counter according to a Poisson process with rate 1 per minute. Each customer carries a number of items
QUEUING MODELS AND MARKOV PROCESSES
 QUEUING MODELS AND MARKOV ROCESSES Queues form when customer demand for a service cannot be met immediately. They occur because of fluctuations in demand levels so that models of queuing are intrinsically
QUEUING MODELS AND MARKOV ROCESSES Queues form when customer demand for a service cannot be met immediately. They occur because of fluctuations in demand levels so that models of queuing are intrinsically
EE 368. Weeks 3 (Notes)
 EE 368 Weeks 3 (Notes) 1 State of a Queuing System State: Set of parameters that describe the condition of the system at a point in time. Why do we need it? Average size of Queue Average waiting time How
EE 368 Weeks 3 (Notes) 1 State of a Queuing System State: Set of parameters that describe the condition of the system at a point in time. Why do we need it? Average size of Queue Average waiting time How
Modeling and Simulation NETW 707
 Modeling and Simulation NETW 707 Lecture 6 ARQ Modeling: Modeling Error/Flow Control Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Data Link Layer Data Link Layer provides
Modeling and Simulation NETW 707 Lecture 6 ARQ Modeling: Modeling Error/Flow Control Course Instructor: Dr.-Ing. Maggie Mashaly maggie.ezzat@guc.edu.eg C3.220 1 Data Link Layer Data Link Layer provides
Introduction to queuing theory
 Introduction to queuing theory Claude Rigault ENST claude.rigault@enst.fr Introduction to Queuing theory 1 Outline The problem The number of clients in a system The client process Delay processes Loss
Introduction to queuing theory Claude Rigault ENST claude.rigault@enst.fr Introduction to Queuing theory 1 Outline The problem The number of clients in a system The client process Delay processes Loss
Networking = Plumbing. Queueing Analysis: I. Last Lecture. Lecture Outline. Jeremiah Deng. 29 July 2013
 Networking = Plumbing TELE302 Lecture 7 Queueing Analysis: I Jeremiah Deng University of Otago 29 July 2013 Jeremiah Deng (University of Otago) TELE302 Lecture 7 29 July 2013 1 / 33 Lecture Outline Jeremiah
Networking = Plumbing TELE302 Lecture 7 Queueing Analysis: I Jeremiah Deng University of Otago 29 July 2013 Jeremiah Deng (University of Otago) TELE302 Lecture 7 29 July 2013 1 / 33 Lecture Outline Jeremiah
On the Throughput-Optimality of CSMA Policies in Multihop Wireless Networks
 Technical Report Computer Networks Research Lab Department of Computer Science University of Toronto CNRL-08-002 August 29th, 2008 On the Throughput-Optimality of CSMA Policies in Multihop Wireless Networks
Technical Report Computer Networks Research Lab Department of Computer Science University of Toronto CNRL-08-002 August 29th, 2008 On the Throughput-Optimality of CSMA Policies in Multihop Wireless Networks
reversed chain is ergodic and has the same equilibrium probabilities (check that π j =
 Lecture 10 Networks of queues In this lecture we shall finally get around to consider what happens when queues are part of networks (which, after all, is the topic of the course). Firstly we shall need
Lecture 10 Networks of queues In this lecture we shall finally get around to consider what happens when queues are part of networks (which, after all, is the topic of the course). Firstly we shall need
Queue length analysis for multicast: Limits of performance and achievable queue length with random linear coding
 Queue length analysis for multicast: Limits of performance and achievable queue length with random linear coding The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available Please share how this access benefits
Queue length analysis for multicast: Limits of performance and achievable queue length with random linear coding The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available Please share how this access benefits
Random Access Protocols ALOHA
 Random Access Protocols ALOHA 1 ALOHA Invented by N. Abramson in 1970-Pure ALOHA Uncontrolled users (no coordination among users) Same packet (frame) size Instant feedback Large (~ infinite) population
Random Access Protocols ALOHA 1 ALOHA Invented by N. Abramson in 1970-Pure ALOHA Uncontrolled users (no coordination among users) Same packet (frame) size Instant feedback Large (~ infinite) population
Introduction to Markov Chains, Queuing Theory, and Network Performance
 Introduction to Markov Chains, Queuing Theory, and Network Performance Marceau Coupechoux Telecom ParisTech, departement Informatique et Réseaux marceau.coupechoux@telecom-paristech.fr IT.2403 Modélisation
Introduction to Markov Chains, Queuing Theory, and Network Performance Marceau Coupechoux Telecom ParisTech, departement Informatique et Réseaux marceau.coupechoux@telecom-paristech.fr IT.2403 Modélisation
1.225 Transportation Flow Systems Quiz (December 17, 2001; Duration: 3 hours)
 1.225 Transportation Flow Systems Quiz (December 17, 2001; Duration: 3 hours) Student Name: Alias: Instructions: 1. This exam is open-book 2. No cooperation is permitted 3. Please write down your name
1.225 Transportation Flow Systems Quiz (December 17, 2001; Duration: 3 hours) Student Name: Alias: Instructions: 1. This exam is open-book 2. No cooperation is permitted 3. Please write down your name
Stochastic Optimization for Undergraduate Computer Science Students
 Stochastic Optimization for Undergraduate Computer Science Students Professor Joongheon Kim School of Computer Science and Engineering, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Republic of Korea 1 Reference 2 Outline
Stochastic Optimization for Undergraduate Computer Science Students Professor Joongheon Kim School of Computer Science and Engineering, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Republic of Korea 1 Reference 2 Outline
Quiz 1 EE 549 Wednesday, Feb. 27, 2008
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA, SPRING 2008 1 Quiz 1 EE 549 Wednesday, Feb. 27, 2008 INSTRUCTIONS This quiz lasts for 85 minutes. This quiz is closed book and closed notes. No Calculators or laptops
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA, SPRING 2008 1 Quiz 1 EE 549 Wednesday, Feb. 27, 2008 INSTRUCTIONS This quiz lasts for 85 minutes. This quiz is closed book and closed notes. No Calculators or laptops
Ways to study a system System
 Simulation What is simulation? Simple synonym: imitation We are interested in studying a system Instead of experimenting with the system itself we experiment with a model of the system Ways to study a
Simulation What is simulation? Simple synonym: imitation We are interested in studying a system Instead of experimenting with the system itself we experiment with a model of the system Ways to study a
Introduction to Queuing Networks Solutions to Problem Sheet 3
 Introduction to Queuing Networks Solutions to Problem Sheet 3 1. (a) The state space is the whole numbers {, 1, 2,...}. The transition rates are q i,i+1 λ for all i and q i, for all i 1 since, when a bus
Introduction to Queuing Networks Solutions to Problem Sheet 3 1. (a) The state space is the whole numbers {, 1, 2,...}. The transition rates are q i,i+1 λ for all i and q i, for all i 1 since, when a bus
Lan Performance LAB Ethernet : CSMA/CD TOKEN RING: TOKEN
 Lan Performance LAB Ethernet : CSMA/CD TOKEN RING: TOKEN Ethernet Frame Format 7 b y te s 1 b y te 2 o r 6 b y te s 2 o r 6 b y te s 2 b y te s 4-1 5 0 0 b y te s 4 b y te s P r e a m b le S ta r t F r
Lan Performance LAB Ethernet : CSMA/CD TOKEN RING: TOKEN Ethernet Frame Format 7 b y te s 1 b y te 2 o r 6 b y te s 2 o r 6 b y te s 2 b y te s 4-1 5 0 0 b y te s 4 b y te s P r e a m b le S ta r t F r
Queuing Networks: Burke s Theorem, Kleinrock s Approximation, and Jackson s Theorem. Wade Trappe
 Queuing Networks: Burke s Theorem, Kleinrock s Approximation, and Jackson s Theorem Wade Trappe Lecture Overview Network of Queues Introduction Queues in Tandem roduct Form Solutions Burke s Theorem What
Queuing Networks: Burke s Theorem, Kleinrock s Approximation, and Jackson s Theorem Wade Trappe Lecture Overview Network of Queues Introduction Queues in Tandem roduct Form Solutions Burke s Theorem What
Lecture Notes of Communication Network I y: part 5. Lijun Qian. Rutgers The State University of New Jersey. 94 Brett Road. Piscataway, NJ
 Lecture Notes of Communication Network I y: part 5 Lijun Qian Department of Electrical Engineering Rutgers The State University of New Jersey 94 Brett Road Piscataway, NJ 08854-8058 October 6, 1998 Abstract
Lecture Notes of Communication Network I y: part 5 Lijun Qian Department of Electrical Engineering Rutgers The State University of New Jersey 94 Brett Road Piscataway, NJ 08854-8058 October 6, 1998 Abstract
Link Models for Circuit Switching
 Link Models for Circuit Switching The basis of traffic engineering for telecommunication networks is the Erlang loss function. It basically allows us to determine the amount of telephone traffic that can
Link Models for Circuit Switching The basis of traffic engineering for telecommunication networks is the Erlang loss function. It basically allows us to determine the amount of telephone traffic that can
Homework 1 - SOLUTION
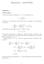 Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
EFFICIENT COMPUTATION OF PROBABILITIES OF EVENTS DESCRIBED BY ORDER STATISTICS AND APPLICATION TO A PROBLEM OFQUEUES
 EFFICIENT COMPUTATION OF PROBABILITIES OF EVENTS DESCRIBED BY ORDER STATISTICS AND APPLICATION TO A PROBLEM OFQUEUES Lee K. Jones and Richard C. Larson OR 249-91 May 1991 Efficient Computation of Probabilities
EFFICIENT COMPUTATION OF PROBABILITIES OF EVENTS DESCRIBED BY ORDER STATISTICS AND APPLICATION TO A PROBLEM OFQUEUES Lee K. Jones and Richard C. Larson OR 249-91 May 1991 Efficient Computation of Probabilities
MAT SYS 5120 (Winter 2012) Assignment 5 (not to be submitted) There are 4 questions.
 MAT 4371 - SYS 5120 (Winter 2012) Assignment 5 (not to be submitted) There are 4 questions. Question 1: Consider the following generator for a continuous time Markov chain. 4 1 3 Q = 2 5 3 5 2 7 (a) Give
MAT 4371 - SYS 5120 (Winter 2012) Assignment 5 (not to be submitted) There are 4 questions. Question 1: Consider the following generator for a continuous time Markov chain. 4 1 3 Q = 2 5 3 5 2 7 (a) Give
IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I, Fall 2003, Professor Whitt. Solutions to Final Exam: Thursday, December 18.
 IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I, Fall 23, Professor Whitt Solutions to Final Exam: Thursday, December 18. Below are six questions with several parts. Do as much as you can. Show your work. 1. Two-Pump Gas
IEOR 6711: Stochastic Models I, Fall 23, Professor Whitt Solutions to Final Exam: Thursday, December 18. Below are six questions with several parts. Do as much as you can. Show your work. 1. Two-Pump Gas
Input-queued switches: Scheduling algorithms for a crossbar switch. EE 384X Packet Switch Architectures 1
 Input-queued switches: Scheduling algorithms for a crossbar switch EE 84X Packet Switch Architectures Overview Today s lecture - the input-buffered switch architecture - the head-of-line blocking phenomenon
Input-queued switches: Scheduling algorithms for a crossbar switch EE 84X Packet Switch Architectures Overview Today s lecture - the input-buffered switch architecture - the head-of-line blocking phenomenon
Recap. Probability, stochastic processes, Markov chains. ELEC-C7210 Modeling and analysis of communication networks
 Recap Probability, stochastic processes, Markov chains ELEC-C7210 Modeling and analysis of communication networks 1 Recap: Probability theory important distributions Discrete distributions Geometric distribution
Recap Probability, stochastic processes, Markov chains ELEC-C7210 Modeling and analysis of communication networks 1 Recap: Probability theory important distributions Discrete distributions Geometric distribution
ENERGY harvesting (EH), a technology to collect energy. Optimal Relaying in Energy Harvesting Wireless Networks with Wireless-Powered Relays
 Optimal elaying in Energy Harvesting Wireless Networks with Wireless-Powered elays Masoumeh Moradian, tudent Member, IEEE, Farid Ashtiani, Member, IEEE, and Ying Jun (Angela) Zhang, enior Member, IEEE
Optimal elaying in Energy Harvesting Wireless Networks with Wireless-Powered elays Masoumeh Moradian, tudent Member, IEEE, Farid Ashtiani, Member, IEEE, and Ying Jun (Angela) Zhang, enior Member, IEEE
λ λ λ In-class problems
 In-class problems 1. Customers arrive at a single-service facility at a Poisson rate of 40 per hour. When two or fewer customers are present, a single attendant operates the facility, and the service time
In-class problems 1. Customers arrive at a single-service facility at a Poisson rate of 40 per hour. When two or fewer customers are present, a single attendant operates the facility, and the service time
MARKOV PROCESSES. Valerio Di Valerio
 MARKOV PROCESSES Valerio Di Valerio Stochastic Process Definition: a stochastic process is a collection of random variables {X(t)} indexed by time t T Each X(t) X is a random variable that satisfy some
MARKOV PROCESSES Valerio Di Valerio Stochastic Process Definition: a stochastic process is a collection of random variables {X(t)} indexed by time t T Each X(t) X is a random variable that satisfy some
2905 Queueing Theory and Simulation PART IV: SIMULATION
 2905 Queueing Theory and Simulation PART IV: SIMULATION 22 Random Numbers A fundamental step in a simulation study is the generation of random numbers, where a random number represents the value of a random
2905 Queueing Theory and Simulation PART IV: SIMULATION 22 Random Numbers A fundamental step in a simulation study is the generation of random numbers, where a random number represents the value of a random
P (L d k = n). P (L(t) = n),
 4 M/G/1 queue In the M/G/1 queue customers arrive according to a Poisson process with rate λ and they are treated in order of arrival The service times are independent and identically distributed with
4 M/G/1 queue In the M/G/1 queue customers arrive according to a Poisson process with rate λ and they are treated in order of arrival The service times are independent and identically distributed with
Introduction to queuing theory
 Introduction to queuing theory Queu(e)ing theory Queu(e)ing theory is the branch of mathematics devoted to how objects (packets in a network, people in a bank, processes in a CPU etc etc) join and leave
Introduction to queuing theory Queu(e)ing theory Queu(e)ing theory is the branch of mathematics devoted to how objects (packets in a network, people in a bank, processes in a CPU etc etc) join and leave
YORK UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ARTS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS MATH , YEAR APPLIED OPTIMIZATION (TEST #4 ) (SOLUTIONS)
 YORK UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ARTS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS Instructor : Dr. Igor Poliakov MATH 4570 6.0, YEAR 2006-07 APPLIED OPTIMIZATION (TEST #4 ) (SOLUTIONS) March 29, 2007 Name (print)
YORK UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ARTS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS Instructor : Dr. Igor Poliakov MATH 4570 6.0, YEAR 2006-07 APPLIED OPTIMIZATION (TEST #4 ) (SOLUTIONS) March 29, 2007 Name (print)
A preemptive repeat priority queue with resampling: Performance analysis
 Ann Oper Res (2006) 46:89 202 DOI 0.007/s0479-006-0053-4 A preemptive repeat priority queue with resampling: Performance analysis Joris Walraevens Bart Steyaert Herwig Bruneel Published online: 6 July
Ann Oper Res (2006) 46:89 202 DOI 0.007/s0479-006-0053-4 A preemptive repeat priority queue with resampling: Performance analysis Joris Walraevens Bart Steyaert Herwig Bruneel Published online: 6 July
Solution: The process is a compound Poisson Process with E[N (t)] = λt/p by Wald's equation.
![Solution: The process is a compound Poisson Process with E[N (t)] = λt/p by Wald's equation. Solution: The process is a compound Poisson Process with E[N (t)] = λt/p by Wald's equation.](/thumbs/90/103037502.jpg) Solutions Stochastic Processes and Simulation II, May 18, 217 Problem 1: Poisson Processes Let {N(t), t } be a homogeneous Poisson Process on (, ) with rate λ. Let {S i, i = 1, 2, } be the points of the
Solutions Stochastic Processes and Simulation II, May 18, 217 Problem 1: Poisson Processes Let {N(t), t } be a homogeneous Poisson Process on (, ) with rate λ. Let {S i, i = 1, 2, } be the points of the
LECTURE 3. Last time:
 LECTURE 3 Last time: Mutual Information. Convexity and concavity Jensen s inequality Information Inequality Data processing theorem Fano s Inequality Lecture outline Stochastic processes, Entropy rate
LECTURE 3 Last time: Mutual Information. Convexity and concavity Jensen s inequality Information Inequality Data processing theorem Fano s Inequality Lecture outline Stochastic processes, Entropy rate
Stochastic Models in Computer Science A Tutorial
 Stochastic Models in Computer Science A Tutorial Dr. Snehanshu Saha Department of Computer Science PESIT BSC, Bengaluru WCI 2015 - August 10 to August 13 1 Introduction 2 Random Variable 3 Introduction
Stochastic Models in Computer Science A Tutorial Dr. Snehanshu Saha Department of Computer Science PESIT BSC, Bengaluru WCI 2015 - August 10 to August 13 1 Introduction 2 Random Variable 3 Introduction
Dynamic Power Allocation and Routing for Time Varying Wireless Networks
 Dynamic Power Allocation and Routing for Time Varying Wireless Networks X 14 (t) X 12 (t) 1 3 4 k a P ak () t P a tot X 21 (t) 2 N X 2N (t) X N4 (t) µ ab () rate µ ab µ ab (p, S 3 ) µ ab µ ac () µ ab (p,
Dynamic Power Allocation and Routing for Time Varying Wireless Networks X 14 (t) X 12 (t) 1 3 4 k a P ak () t P a tot X 21 (t) 2 N X 2N (t) X N4 (t) µ ab () rate µ ab µ ab (p, S 3 ) µ ab µ ac () µ ab (p,
Wireless Internet Exercises
 Wireless Internet Exercises Prof. Alessandro Redondi 2018-05-28 1 WLAN 1.1 Exercise 1 A Wi-Fi network has the following features: Physical layer transmission rate: 54 Mbps MAC layer header: 28 bytes MAC
Wireless Internet Exercises Prof. Alessandro Redondi 2018-05-28 1 WLAN 1.1 Exercise 1 A Wi-Fi network has the following features: Physical layer transmission rate: 54 Mbps MAC layer header: 28 bytes MAC
Chapter 3 Balance equations, birth-death processes, continuous Markov Chains
 Chapter 3 Balance equations, birth-death processes, continuous Markov Chains Ioannis Glaropoulos November 4, 2012 1 Exercise 3.2 Consider a birth-death process with 3 states, where the transition rate
Chapter 3 Balance equations, birth-death processes, continuous Markov Chains Ioannis Glaropoulos November 4, 2012 1 Exercise 3.2 Consider a birth-death process with 3 states, where the transition rate
GI/M/1 and GI/M/m queuing systems
 GI/M/1 and GI/M/m queuing systems Dmitri A. Moltchanov moltchan@cs.tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/kurssit/tlt-2716/ OUTLINE: GI/M/1 queuing system; Methods of analysis; Imbedded Markov chain approach; Waiting
GI/M/1 and GI/M/m queuing systems Dmitri A. Moltchanov moltchan@cs.tut.fi http://www.cs.tut.fi/kurssit/tlt-2716/ OUTLINE: GI/M/1 queuing system; Methods of analysis; Imbedded Markov chain approach; Waiting
Systems Simulation Chapter 6: Queuing Models
 Systems Simulation Chapter 6: Queuing Models Fatih Cavdur fatihcavdur@uludag.edu.tr April 2, 2014 Introduction Introduction Simulation is often used in the analysis of queuing models. A simple but typical
Systems Simulation Chapter 6: Queuing Models Fatih Cavdur fatihcavdur@uludag.edu.tr April 2, 2014 Introduction Introduction Simulation is often used in the analysis of queuing models. A simple but typical
NICTA Short Course. Network Analysis. Vijay Sivaraman. Day 1 Queueing Systems and Markov Chains. Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-1
 NICTA Short Course Network Analysis Vijay Sivaraman Day 1 Queueing Systems and Markov Chains Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-1 Outline Why a short course on mathematical analysis? Limited current course offering
NICTA Short Course Network Analysis Vijay Sivaraman Day 1 Queueing Systems and Markov Chains Network Analysis, 2008s2 1-1 Outline Why a short course on mathematical analysis? Limited current course offering
Chapter 8 Queuing Theory Roanna Gee. W = average number of time a customer spends in the system.
 8. Preliminaries L, L Q, W, W Q L = average number of customers in the system. L Q = average number of customers waiting in queue. W = average number of time a customer spends in the system. W Q = average
8. Preliminaries L, L Q, W, W Q L = average number of customers in the system. L Q = average number of customers waiting in queue. W = average number of time a customer spends in the system. W Q = average
Performance analysis of queueing systems with resequencing
 UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI SALERNO Dipartimento di Matematica Dottorato di Ricerca in Matematica XIV ciclo - Nuova serie Performance analysis of queueing systems with resequencing Candidato: Caraccio Ilaria
UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI SALERNO Dipartimento di Matematica Dottorato di Ricerca in Matematica XIV ciclo - Nuova serie Performance analysis of queueing systems with resequencing Candidato: Caraccio Ilaria
An Evolutionary Game Perspective to ALOHA with power control
 An Evolutionary Game Perspective to ALOHA with power control E. Altman a, N. Bonneau a, M. Debbah b and G. Caire b a MAESTRO, INRIA Sophia-Antipolis, 004 Route des Lucioles, B.P.93, 0690 Sophia-Antipolis,
An Evolutionary Game Perspective to ALOHA with power control E. Altman a, N. Bonneau a, M. Debbah b and G. Caire b a MAESTRO, INRIA Sophia-Antipolis, 004 Route des Lucioles, B.P.93, 0690 Sophia-Antipolis,
Digital Networks. Dr. Vladimir Sidorenko Prof. Dr. -Ing. Martin Bossert
 Digital Networks Dr. Vladimir Sidorenko Prof. Dr. -Ing. Martin Bossert University of Ulm Institute of Telecommunications and Applied Information Theory February 22, 2008 Contents Introduction to probability
Digital Networks Dr. Vladimir Sidorenko Prof. Dr. -Ing. Martin Bossert University of Ulm Institute of Telecommunications and Applied Information Theory February 22, 2008 Contents Introduction to probability
Energy minimization based Resource Scheduling for Strict Delay Constrained Wireless Communications
 Energy minimization based Resource Scheduling for Strict Delay Constrained Wireless Communications Ibrahim Fawaz 1,2, Philippe Ciblat 2, and Mireille Sarkiss 1 1 LIST, CEA, Communicating Systems Laboratory,
Energy minimization based Resource Scheduling for Strict Delay Constrained Wireless Communications Ibrahim Fawaz 1,2, Philippe Ciblat 2, and Mireille Sarkiss 1 1 LIST, CEA, Communicating Systems Laboratory,
One billion+ terminals in voice network alone
 Traffic Engineering Traffic Engineering One billion+ terminals in voice networ alone Plus data, video, fax, finance, etc. Imagine all users want service simultaneously its not even nearly possible (despite
Traffic Engineering Traffic Engineering One billion+ terminals in voice networ alone Plus data, video, fax, finance, etc. Imagine all users want service simultaneously its not even nearly possible (despite
Part I Stochastic variables and Markov chains
 Part I Stochastic variables and Markov chains Random variables describe the behaviour of a phenomenon independent of any specific sample space Distribution function (cdf, cumulative distribution function)
Part I Stochastic variables and Markov chains Random variables describe the behaviour of a phenomenon independent of any specific sample space Distribution function (cdf, cumulative distribution function)
COMP9334: Capacity Planning of Computer Systems and Networks
 COMP9334: Capacity Planning of Computer Systems and Networks Week 2: Operational analysis Lecturer: Prof. Sanjay Jha NETWORKS RESEARCH GROUP, CSE, UNSW Operational analysis Operational: Collect performance
COMP9334: Capacity Planning of Computer Systems and Networks Week 2: Operational analysis Lecturer: Prof. Sanjay Jha NETWORKS RESEARCH GROUP, CSE, UNSW Operational analysis Operational: Collect performance
Stability Analysis in a Cognitive Radio System with Cooperative Beamforming
 Stability Analysis in a Cognitive Radio System with Cooperative Beamforming Mohammed Karmoose 1 Ahmed Sultan 1 Moustafa Youseff 2 1 Electrical Engineering Dept, Alexandria University 2 E-JUST Agenda 1
Stability Analysis in a Cognitive Radio System with Cooperative Beamforming Mohammed Karmoose 1 Ahmed Sultan 1 Moustafa Youseff 2 1 Electrical Engineering Dept, Alexandria University 2 E-JUST Agenda 1
Performance Analysis of a System with Bursty Traffic and Adjustable Transmission Times
 Performance Analysis of a System with Bursty Traffic and Adjustable Transmission Times Nikolaos Pappas Department of Science and Technology, Linköping University, Sweden E-mail: nikolaospappas@liuse arxiv:1809085v1
Performance Analysis of a System with Bursty Traffic and Adjustable Transmission Times Nikolaos Pappas Department of Science and Technology, Linköping University, Sweden E-mail: nikolaospappas@liuse arxiv:1809085v1
BIRTH DEATH PROCESSES AND QUEUEING SYSTEMS
 BIRTH DEATH PROCESSES AND QUEUEING SYSTEMS Andrea Bobbio Anno Accademico 999-2000 Queueing Systems 2 Notation for Queueing Systems /λ mean time between arrivals S = /µ ρ = λ/µ N mean service time traffic
BIRTH DEATH PROCESSES AND QUEUEING SYSTEMS Andrea Bobbio Anno Accademico 999-2000 Queueing Systems 2 Notation for Queueing Systems /λ mean time between arrivals S = /µ ρ = λ/µ N mean service time traffic
On ARQ for Packet Erasure Channels with Bernoulli Arrivals
 On ARQ for Packet Erasure Channels with Bernoulli Arrivals Dinkar Vasudevan, Vijay G. Subramanian and Douglas J. Leith Hamilton Institute, National University of Ireland, Maynooth Abstract We study packet
On ARQ for Packet Erasure Channels with Bernoulli Arrivals Dinkar Vasudevan, Vijay G. Subramanian and Douglas J. Leith Hamilton Institute, National University of Ireland, Maynooth Abstract We study packet
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.262 Discrete Stochastic Processes Midterm Quiz April 6, 2010 There are 5 questions, each with several parts.
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.262 Discrete Stochastic Processes Midterm Quiz April 6, 2010 There are 5 questions, each with several parts.
Computer Systems Modelling
 Computer Systems Modelling Computer Laboratory Computer Science Tripos, Part II Michaelmas Term 2003 R. J. Gibbens Problem sheet William Gates Building JJ Thomson Avenue Cambridge CB3 0FD http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/
Computer Systems Modelling Computer Laboratory Computer Science Tripos, Part II Michaelmas Term 2003 R. J. Gibbens Problem sheet William Gates Building JJ Thomson Avenue Cambridge CB3 0FD http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/
On the Stability and Optimal Decentralized Throughput of CSMA with Multipacket Reception Capability
 On the Stability and Optimal Decentralized Throughput of CSMA with Multipacket Reception Capability Douglas S. Chan Toby Berger Lang Tong School of Electrical & Computer Engineering Cornell University,
On the Stability and Optimal Decentralized Throughput of CSMA with Multipacket Reception Capability Douglas S. Chan Toby Berger Lang Tong School of Electrical & Computer Engineering Cornell University,
Queueing Systems: Lecture 3. Amedeo R. Odoni October 18, Announcements
 Queueing Systems: Lecture 3 Amedeo R. Odoni October 18, 006 Announcements PS #3 due tomorrow by 3 PM Office hours Odoni: Wed, 10/18, :30-4:30; next week: Tue, 10/4 Quiz #1: October 5, open book, in class;
Queueing Systems: Lecture 3 Amedeo R. Odoni October 18, 006 Announcements PS #3 due tomorrow by 3 PM Office hours Odoni: Wed, 10/18, :30-4:30; next week: Tue, 10/4 Quiz #1: October 5, open book, in class;
Multiaccess Problem. How to let distributed users (efficiently) share a single broadcast channel? How to form a queue for distributed users?
 Multiaccess Problem How to let distributed users (efficiently) share a single broadcast channel? How to form a queue for distributed users? z The protocols we used to solve this multiaccess problem are
Multiaccess Problem How to let distributed users (efficiently) share a single broadcast channel? How to form a queue for distributed users? z The protocols we used to solve this multiaccess problem are
CPSC 531: System Modeling and Simulation. Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Fall 2017
 CPSC 531: System Modeling and Simulation Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Fall 2017 Motivating Quote for Queueing Models Good things come to those who wait - poet/writer
CPSC 531: System Modeling and Simulation Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Fall 2017 Motivating Quote for Queueing Models Good things come to those who wait - poet/writer
Probability Models in Electrical and Computer Engineering Mathematical models as tools in analysis and design Deterministic models Probability models
 Probability Models in Electrical and Computer Engineering Mathematical models as tools in analysis and design Deterministic models Probability models Statistical regularity Properties of relative frequency
Probability Models in Electrical and Computer Engineering Mathematical models as tools in analysis and design Deterministic models Probability models Statistical regularity Properties of relative frequency
Slides 9: Queuing Models
 Slides 9: Queuing Models Purpose Simulation is often used in the analysis of queuing models. A simple but typical queuing model is: Queuing models provide the analyst with a powerful tool for designing
Slides 9: Queuing Models Purpose Simulation is often used in the analysis of queuing models. A simple but typical queuing model is: Queuing models provide the analyst with a powerful tool for designing
Maximum Sum Rate of Slotted Aloha with Capture
 Maximum Sum Rate of Slotted Aloha with Capture Yitong Li and Lin Dai, Senior Member, IEEE arxiv:50.03380v3 [cs.it] 7 Dec 205 Abstract The sum rate performance of random-access networks crucially depends
Maximum Sum Rate of Slotted Aloha with Capture Yitong Li and Lin Dai, Senior Member, IEEE arxiv:50.03380v3 [cs.it] 7 Dec 205 Abstract The sum rate performance of random-access networks crucially depends
TCP over Cognitive Radio Channels
 1/43 TCP over Cognitive Radio Channels Sudheer Poojary Department of ECE, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore IEEE-IISc I-YES seminar 19 May 2016 2/43 Acknowledgments The work presented here was done
1/43 TCP over Cognitive Radio Channels Sudheer Poojary Department of ECE, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore IEEE-IISc I-YES seminar 19 May 2016 2/43 Acknowledgments The work presented here was done
Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0.
![Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0. Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0.](/thumbs/95/124116804.jpg) IEOR 46: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Chapters 5-6 in Ross, Thursday, April, 4:5-5:35pm SOLUTIONS to Second Midterm Exam, Spring 9, Open Book: but only the Ross textbook, the
IEOR 46: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Chapters 5-6 in Ross, Thursday, April, 4:5-5:35pm SOLUTIONS to Second Midterm Exam, Spring 9, Open Book: but only the Ross textbook, the
A Retrial Queueing model with FDL at OBS core node
 A Retrial Queueing model with FDL at OBS core node Chuong Dang Thanh a, Duc Pham Trung a, Thang Doan Van b a Faculty of Information Technology, College of Sciences, Hue University, Hue, Viet Nam. E-mail:
A Retrial Queueing model with FDL at OBS core node Chuong Dang Thanh a, Duc Pham Trung a, Thang Doan Van b a Faculty of Information Technology, College of Sciences, Hue University, Hue, Viet Nam. E-mail:
Second main application of Chernoff: analysis of load balancing. Already saw balls in bins example. oblivious algorithms only consider self packet.
 Routing Second main application of Chernoff: analysis of load balancing. Already saw balls in bins example synchronous message passing bidirectional links, one message per step queues on links permutation
Routing Second main application of Chernoff: analysis of load balancing. Already saw balls in bins example synchronous message passing bidirectional links, one message per step queues on links permutation
Statistics 253/317 Introduction to Probability Models. Winter Midterm Exam Friday, Feb 8, 2013
 Statistics 253/317 Introduction to Probability Models Winter 2014 - Midterm Exam Friday, Feb 8, 2013 Student Name (print): (a) Do not sit directly next to another student. (b) This is a closed-book, closed-note
Statistics 253/317 Introduction to Probability Models Winter 2014 - Midterm Exam Friday, Feb 8, 2013 Student Name (print): (a) Do not sit directly next to another student. (b) This is a closed-book, closed-note
Non Markovian Queues (contd.)
 MODULE 7: RENEWAL PROCESSES 29 Lecture 5 Non Markovian Queues (contd) For the case where the service time is constant, V ar(b) = 0, then the P-K formula for M/D/ queue reduces to L s = ρ + ρ 2 2( ρ) where
MODULE 7: RENEWAL PROCESSES 29 Lecture 5 Non Markovian Queues (contd) For the case where the service time is constant, V ar(b) = 0, then the P-K formula for M/D/ queue reduces to L s = ρ + ρ 2 2( ρ) where
Figure 10.1: Recording when the event E occurs
 10 Poisson Processes Let T R be an interval. A family of random variables {X(t) ; t T} is called a continuous time stochastic process. We often consider T = [0, 1] and T = [0, ). As X(t) is a random variable
10 Poisson Processes Let T R be an interval. A family of random variables {X(t) ; t T} is called a continuous time stochastic process. We often consider T = [0, 1] and T = [0, ). As X(t) is a random variable
Data analysis and stochastic modeling
 Data analysis and stochastic modeling Lecture 7 An introduction to queueing theory Guillaume Gravier guillaume.gravier@irisa.fr with a lot of help from Paul Jensen s course http://www.me.utexas.edu/ jensen/ormm/instruction/powerpoint/or_models_09/14_queuing.ppt
Data analysis and stochastic modeling Lecture 7 An introduction to queueing theory Guillaume Gravier guillaume.gravier@irisa.fr with a lot of help from Paul Jensen s course http://www.me.utexas.edu/ jensen/ormm/instruction/powerpoint/or_models_09/14_queuing.ppt
NATCOR: Stochastic Modelling
 NATCOR: Stochastic Modelling Queueing Theory II Chris Kirkbride Management Science 2017 Overview of Today s Sessions I Introduction to Queueing Modelling II Multiclass Queueing Models III Queueing Control
NATCOR: Stochastic Modelling Queueing Theory II Chris Kirkbride Management Science 2017 Overview of Today s Sessions I Introduction to Queueing Modelling II Multiclass Queueing Models III Queueing Control
ABSTRACT WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS. criterion. Therefore, it is imperative to design advanced transmission schemes to
 ABSTRACT Title of dissertation: DELAY MINIMIZATION IN ENERGY CONSTRAINED WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS Jing Yang, Doctor of Philosophy, 2010 Dissertation directed by: Professor Şennur Ulukuş Department of Electrical
ABSTRACT Title of dissertation: DELAY MINIMIZATION IN ENERGY CONSTRAINED WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS Jing Yang, Doctor of Philosophy, 2010 Dissertation directed by: Professor Şennur Ulukuş Department of Electrical
Buzen s algorithm. Cyclic network Extension of Jackson networks
 Outline Buzen s algorithm Mean value analysis for Jackson networks Cyclic network Extension of Jackson networks BCMP network 1 Marginal Distributions based on Buzen s algorithm With Buzen s algorithm,
Outline Buzen s algorithm Mean value analysis for Jackson networks Cyclic network Extension of Jackson networks BCMP network 1 Marginal Distributions based on Buzen s algorithm With Buzen s algorithm,
TCOM 501: Networking Theory & Fundamentals. Lecture 6 February 19, 2003 Prof. Yannis A. Korilis
 TCOM 50: Networking Theory & Fundamentals Lecture 6 February 9, 003 Prof. Yannis A. Korilis 6- Topics Time-Reversal of Markov Chains Reversibility Truncating a Reversible Markov Chain Burke s Theorem Queues
TCOM 50: Networking Theory & Fundamentals Lecture 6 February 9, 003 Prof. Yannis A. Korilis 6- Topics Time-Reversal of Markov Chains Reversibility Truncating a Reversible Markov Chain Burke s Theorem Queues
CHAPTER 4. Networks of queues. 1. Open networks Suppose that we have a network of queues as given in Figure 4.1. Arrivals
 CHAPTER 4 Networks of queues. Open networks Suppose that we have a network of queues as given in Figure 4.. Arrivals Figure 4.. An open network can occur from outside of the network to any subset of nodes.
CHAPTER 4 Networks of queues. Open networks Suppose that we have a network of queues as given in Figure 4.. Arrivals Figure 4.. An open network can occur from outside of the network to any subset of nodes.
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Computer Engineering Dept
 King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Computer Engineering Dept COE 543 Mobile and Wireless Networks Term 032 Dr. Ashraf S. Hasan Mahmoud Rm 22-148-3 Ext. 1724 Email: ashraf@se.kfupm.edu.sa 3/15/2004
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Computer Engineering Dept COE 543 Mobile and Wireless Networks Term 032 Dr. Ashraf S. Hasan Mahmoud Rm 22-148-3 Ext. 1724 Email: ashraf@se.kfupm.edu.sa 3/15/2004
Solutions to Homework Discrete Stochastic Processes MIT, Spring 2011
 Exercise 6.5: Solutions to Homework 0 6.262 Discrete Stochastic Processes MIT, Spring 20 Consider the Markov process illustrated below. The transitions are labelled by the rate q ij at which those transitions
Exercise 6.5: Solutions to Homework 0 6.262 Discrete Stochastic Processes MIT, Spring 20 Consider the Markov process illustrated below. The transitions are labelled by the rate q ij at which those transitions
The Performance Impact of Delay Announcements
 The Performance Impact of Delay Announcements Taking Account of Customer Response IEOR 4615, Service Engineering, Professor Whitt Supplement to Lecture 21, April 21, 2015 Review: The Purpose of Delay Announcements
The Performance Impact of Delay Announcements Taking Account of Customer Response IEOR 4615, Service Engineering, Professor Whitt Supplement to Lecture 21, April 21, 2015 Review: The Purpose of Delay Announcements
Outline Network structure and objectives Routing Routing protocol protocol System analysis Results Conclusion Slide 2
 2007 Radio and Wireless Symposium 9 11 January 2007, Long Beach, CA. Lifetime-Aware Hierarchical Wireless Sensor Network Architecture with Mobile Overlays Maryam Soltan, Morteza Maleki, and Massoud Pedram
2007 Radio and Wireless Symposium 9 11 January 2007, Long Beach, CA. Lifetime-Aware Hierarchical Wireless Sensor Network Architecture with Mobile Overlays Maryam Soltan, Morteza Maleki, and Massoud Pedram
Discrete Event and Process Oriented Simulation (2)
 B. Maddah ENMG 622 Simulation 11/04/08 Discrete Event and Process Oriented Simulation (2) Discrete event hand simulation of an (s, S) periodic review inventory system Consider a retailer who sells a commodity
B. Maddah ENMG 622 Simulation 11/04/08 Discrete Event and Process Oriented Simulation (2) Discrete event hand simulation of an (s, S) periodic review inventory system Consider a retailer who sells a commodity
Average Age of Information with Hybrid ARQ under a Resource Constraint
 1 Average Age of Information with Hybrid ARQ under a Resource Constraint arxiv:1710.04971v3 [cs.it] 5 Dec 2018 Elif Tuğçe Ceran, Deniz Gündüz, and András György Department of Electrical and Electronic
1 Average Age of Information with Hybrid ARQ under a Resource Constraint arxiv:1710.04971v3 [cs.it] 5 Dec 2018 Elif Tuğçe Ceran, Deniz Gündüz, and András György Department of Electrical and Electronic
