The Performance Impact of Delay Announcements
|
|
|
- Alisha Willis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Performance Impact of Delay Announcements Taking Account of Customer Response IEOR 4615, Service Engineering, Professor Whitt Supplement to Lecture 21, April 21, 2015
2 Review: The Purpose of Delay Announcements A service system manager may want to tell each customer an estimate of the delay that customer will experience in order to: Improve customer satisfaction. Uncertain Waits are longer than known finite waits. Improve performance for the customers who are served. By inducing some customers to balk or abandon earlier and then retry later when the system is more lightly loaded. But what will be the performance impact of the delay announcements?
3 A Model of Customer Response Make delay announcement (single-number w) to each new arrival, with number depending upon system state at that time. But we need to consider the customer response Assume: balk (leave immediately) with probability B(w) If join, abandon before time t with probability F(t w) Need to consider equilibrium: 1 Customer response depends on announcement. 2 Announcement depends upon system state or history (performance). 3 System performance depends upon customer response.
4 Example: The All-Exponential Response Model delay announcement w to each new arrival, with number w depending upon system state at that time. customer response balk (leave immediately) with probability B(w) = 1 e βw for constant β > 0. If join, abandon before time t with probability F(t w) = 1 e γt, 0 t w, = 1 e γw e δt, 0 < w t <, where γ and δ are positive constants.
5 Problem for Today What to announce? Delay of Last to Enter Service (LES) Fixed Deterministic (FD) Announcement, corresponding to equilibrium expected delay How to study performance impact? deterministic fluid model simulation iterative numerical algorithm (for FD) for M/M/s + GI using engineering solution (approximation) from WW (2005)
6 Review: The G/GI/s+GI Fluid Model Approximation for the G/GI/s + GI Stochastic Queueing Model service facility λ arrival process waiting room departures abandonment F(x) = P(T a x) (T a time to abandon) s servers G(x) = P(T s x) (T s service time)
7 Many-Server Heavy-Traffic (MSHT) Limit Increasing Scale Increasing Scale a sequence of G/GI/s + GI models indexed by n, arrival rate grows: λ n /n λ as n, number of servers grows: s n /n s as n, service-time cdf G and patience cdf F held fixed independent of n with mean service time 1: µ 1 0 x dg(x) 1.
8 The G/GI/s+GI Fluid Model Model data: (λ, s, G, F) and initial conditions. service facility λ input flow waiting room departure flow abandonment F(x) = proportion abandoning by time x capacity s G(x) = proportion served by time x
9 The Overloaded Fluid Model in Steady State fluid density arriving time t in the past in service sg c (u) in queue F c (t) s w + u w time t 0
10 Use Fluid Model to Study Performance Impact Direct Response to Delay Announcement in service in queue s w~ ) ( b sg c (u) w~ b u w ~ b w ~ a 0
11 Equilibrium Delay in service sg c (u) in queue F c (t) ( w~ ) s w ~ e ) ( 1 w~ u ~w w ~ e ~w 2 time t 0 1 1
12 Equilibrium Delay in Overloaded Fluid Model Recall that : λ > s and µ = 1. Without announcements: λf c (w) = s M/GI/s+M Model: λe θw = s and w = With announcements: λb c (w)f c (w w) = s all-exponential customer response model: log (ρ) θ, ρ = λ/s λe βweq e γweq = s and w eq = log (ρ) β + γ It is reasonable to expect that β + γ > θ, so that announcements reduce the delay of served customers.
13 Impact of Delay Announcement in Fluid Model Cycling Around the Equilibrium Delay in service in queue s ( w 1 ) ( w~ e ) ( w 2 ) s w ~ w ~ w time t 2 e w 1 0 n
14 Conclusions of Study, Armony et al Under general conditions, there exists a unique equilibrium delay in the fluid model. Direct iteration w n+1 = d(w n ) as shown above can lead to oscillations. Damped iterations produce convergence: w n+1 = pd(w n ) + (1 p)w n LES delay and fluid equilibrium delay both work well in simulations But LES (1) lower variance and (2) more robust, does not depend on the model.
15 Experiments: Numerical Comparisons Consider overloaded M/M/s+M queueing model. Consider all-exponential customer response model. Queueing Model Parameters: λ = 140, µ = 1.0, s = 100, θ = 1.0 Customer Response Parameters: β = 1.0, γ = 0.5, δ = 0.5 and 4.0 Performance with and without announcements Algorithms compared to simulation
16 Performance With and Without Announcements Fluid and algorithm for M/M/100 + M with fixed announcement: ρ = 1.4 perform. no announce with announce w eq = measure exact fluid δ = 0.5 δ = 4.0 fluid P(Balk) P(abandon) P(B A) E[Q] E[W S] SD[W S]
17 Simulation Results With Announcements Algorithm (INA) and simulation for M/M/100 + M with LES and fixed. perform. δ = 0.5 δ = 4.0 measure INA sim(fixed) LES INA sim(fixed) LES P(Balk) P(abandon) P(B A) E[Q] E[W S] SD[W S] E[ W W a S]
18 SUMMARY 1 We have studied the performance impact of delay announcements. 2 We introduced a model of customer response. 3 The long-run performance is an equilibrium. 4 Fluid, INA and simulation reveal performance of LES. 5 LES and fixed announcements have nearly the same mean. 6 LES is more accurate, i.e., E[ W W a S] is lower.
19 References M. Armony, N. Shimkin and WW. The Impact of Delay Announcements in Many-Server Queues with Abandonment. Operations Research 57 (2009) WW. Improving Service By Informing Customers About Anticipated Delays. Management Science 45 (1999) WW. Engineering Solution of a Basic Call-Center Model. Management Science 51 (2005) WW. Fluid Models for Multiserver Queues with Abandonments. Operations Research 54 (2006) (See lecture 10.)
20 More References on Fluid Models Y. Liu and WW. The G t /GI/s t + GI Many-Server Fluid Queue. Queueing Systems 71 (2012) Y. Liu and WW. A Network of Time-Varying Many-Server Fluid Queues with Customer Abandonment. Oper. Res. 59 (2011) Y. Liu and WW. Algorithms for Time-Varying Networks of Many-Server Fluid Queues. Informs J. on Computing 26 (2014) Y. Liu and WW. A Many-Server Fluid Limit for the G t /GI/s t + GI Queueing Model Experiencing Periods of Overloading. Operations Research Letters 40 (2012)
Making Delay Announcements
 Making Delay Announcements Performance Impact and Predicting Queueing Delays Ward Whitt With Mor Armony, Rouba Ibrahim and Nahum Shimkin March 7, 2012 Last Class 1 The Overloaded G/GI/s + GI Fluid Queue
Making Delay Announcements Performance Impact and Predicting Queueing Delays Ward Whitt With Mor Armony, Rouba Ibrahim and Nahum Shimkin March 7, 2012 Last Class 1 The Overloaded G/GI/s + GI Fluid Queue
Delay Announcements. Predicting Queueing Delays for Delay Announcements. IEOR 4615, Service Engineering, Professor Whitt. Lecture 21, April 21, 2015
 Delay Announcements Predicting Queueing Delays for Delay Announcements IEOR 4615, Service Engineering, Professor Whitt Lecture 21, April 21, 2015 OUTLINE Delay Announcements: Why, What and When? [Slide
Delay Announcements Predicting Queueing Delays for Delay Announcements IEOR 4615, Service Engineering, Professor Whitt Lecture 21, April 21, 2015 OUTLINE Delay Announcements: Why, What and When? [Slide
Lecture 9: Deterministic Fluid Models and Many-Server Heavy-Traffic Limits. IEOR 4615: Service Engineering Professor Whitt February 19, 2015
 Lecture 9: Deterministic Fluid Models and Many-Server Heavy-Traffic Limits IEOR 4615: Service Engineering Professor Whitt February 19, 2015 Outline Deterministic Fluid Models Directly From Data: Cumulative
Lecture 9: Deterministic Fluid Models and Many-Server Heavy-Traffic Limits IEOR 4615: Service Engineering Professor Whitt February 19, 2015 Outline Deterministic Fluid Models Directly From Data: Cumulative
SENSITIVITY OF PERFORMANCE IN THE ERLANG-A QUEUEING MODEL TO CHANGES IN THE MODEL PARAMETERS
 SENSITIVITY OF PERFORMANCE IN THE ERLANG-A QUEUEING MODEL TO CHANGES IN THE MODEL PARAMETERS by Ward Whitt Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research Columbia University, New York, NY
SENSITIVITY OF PERFORMANCE IN THE ERLANG-A QUEUEING MODEL TO CHANGES IN THE MODEL PARAMETERS by Ward Whitt Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research Columbia University, New York, NY
Economy of Scale in Multiserver Service Systems: A Retrospective. Ward Whitt. IEOR Department. Columbia University
 Economy of Scale in Multiserver Service Systems: A Retrospective Ward Whitt IEOR Department Columbia University Ancient Relics A. K. Erlang (1924) On the rational determination of the number of circuits.
Economy of Scale in Multiserver Service Systems: A Retrospective Ward Whitt IEOR Department Columbia University Ancient Relics A. K. Erlang (1924) On the rational determination of the number of circuits.
REAL-TIME DELAY ESTIMATION BASED ON DELAY HISTORY IN MANY-SERVER SERVICE SYSTEMS WITH TIME-VARYING ARRIVALS
 REAL-TIME DELAY ESTIMATION BASED ON DELAY HISTORY IN MANY-SERVER SERVICE SYSTEMS WITH TIME-VARYING ARRIVALS by Rouba Ibrahim and Ward Whitt IEOR Department Columbia University 500 West 120th Street 313
REAL-TIME DELAY ESTIMATION BASED ON DELAY HISTORY IN MANY-SERVER SERVICE SYSTEMS WITH TIME-VARYING ARRIVALS by Rouba Ibrahim and Ward Whitt IEOR Department Columbia University 500 West 120th Street 313
Q = (c) Assuming that Ricoh has been working continuously for 7 days, what is the probability that it will remain working at least 8 more days?
 IEOR 4106: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Spring 2005, Professor Whitt, Second Midterm Exam Chapters 5-6 in Ross, Thursday, March 31, 11:00am-1:00pm Open Book: but only the Ross
IEOR 4106: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Spring 2005, Professor Whitt, Second Midterm Exam Chapters 5-6 in Ross, Thursday, March 31, 11:00am-1:00pm Open Book: but only the Ross
ENGINEERING SOLUTION OF A BASIC CALL-CENTER MODEL
 ENGINEERING SOLUTION OF A BASIC CALL-CENTER MODEL by Ward Whitt Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research Columbia University, New York, NY 10027 Abstract An algorithm is developed to
ENGINEERING SOLUTION OF A BASIC CALL-CENTER MODEL by Ward Whitt Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research Columbia University, New York, NY 10027 Abstract An algorithm is developed to
DELAY PREDICTORS FOR CUSTOMER SERVICE SYSTEMS WITH TIME-VARYING PARAMETERS. Rouba Ibrahim Ward Whitt
 Proceedings of the 21 Winter Simulation Conference B. Johansson, S. Jain, J. Montoya-Torres, J. Hugan, and E. Yücesan, eds. DELAY PREDICTORS FOR CUSTOMER SERVICE SYSTEMS WITH TIME-VARYING PARAMETERS Rouba
Proceedings of the 21 Winter Simulation Conference B. Johansson, S. Jain, J. Montoya-Torres, J. Hugan, and E. Yücesan, eds. DELAY PREDICTORS FOR CUSTOMER SERVICE SYSTEMS WITH TIME-VARYING PARAMETERS Rouba
ec1 e-companion to Liu and Whitt: Stabilizing Performance
 ec1 This page is intentionally blank. Proper e-companion title page, with INFORMS branding and exact metadata of the main paper, will be produced by the INFORMS office when the issue is being assembled.
ec1 This page is intentionally blank. Proper e-companion title page, with INFORMS branding and exact metadata of the main paper, will be produced by the INFORMS office when the issue is being assembled.
Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems
 Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems Introduction to Queuing Systems System Performance Measures & Little s Law Equilibrium Solution of Birth-Death Processes Analysis of Single-Station Queuing Systems
Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems Introduction to Queuing Systems System Performance Measures & Little s Law Equilibrium Solution of Birth-Death Processes Analysis of Single-Station Queuing Systems
Dynamic Control of Parallel-Server Systems
 Dynamic Control of Parallel-Server Systems Jim Dai Georgia Institute of Technology Tolga Tezcan University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign May 13, 2009 Jim Dai (Georgia Tech) Many-Server Asymptotic Optimality
Dynamic Control of Parallel-Server Systems Jim Dai Georgia Institute of Technology Tolga Tezcan University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign May 13, 2009 Jim Dai (Georgia Tech) Many-Server Asymptotic Optimality
Online Supplement to Delay-Based Service Differentiation with Many Servers and Time-Varying Arrival Rates
 Online Supplement to Delay-Based Service Differentiation with Many Servers and Time-Varying Arrival Rates Xu Sun and Ward Whitt Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research, Columbia University
Online Supplement to Delay-Based Service Differentiation with Many Servers and Time-Varying Arrival Rates Xu Sun and Ward Whitt Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research, Columbia University
Queueing Theory I Summary! Little s Law! Queueing System Notation! Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K "
 Queueing Theory I Summary Little s Law Queueing System Notation Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K " Little s Law a(t): the process that counts the number of arrivals
Queueing Theory I Summary Little s Law Queueing System Notation Stationary Analysis of Elementary Queueing Systems " M/M/1 " M/M/m " M/M/1/K " Little s Law a(t): the process that counts the number of arrivals
Erlang-C = M/M/N. agents. queue ACD. arrivals. busy ACD. queue. abandonment BACK FRONT. lost calls. arrivals. lost calls
 Erlang-C = M/M/N agents arrivals ACD queue Erlang-A lost calls FRONT BACK arrivals busy ACD queue abandonment lost calls Erlang-C = M/M/N agents arrivals ACD queue Rough Performance Analysis
Erlang-C = M/M/N agents arrivals ACD queue Erlang-A lost calls FRONT BACK arrivals busy ACD queue abandonment lost calls Erlang-C = M/M/N agents arrivals ACD queue Rough Performance Analysis
Stabilizing Customer Abandonment in Many-Server Queues with Time-Varying Arrivals
 Submitted to Operations Research manuscript OPRE-29-6-259; OPRE-211-12-597.R1 Stabilizing Customer Abandonment in Many-Server Queues with -Varying Arrivals Yunan Liu Department of Industrial Engineering,
Submitted to Operations Research manuscript OPRE-29-6-259; OPRE-211-12-597.R1 Stabilizing Customer Abandonment in Many-Server Queues with -Varying Arrivals Yunan Liu Department of Industrial Engineering,
A multi-class fluid model for a contact center with skill-based routing
 Int. J. Electron. Commun. (AEÜ) ( ) www.elsevier.de/aeue A multi-class fluid model for a contact center with skill-based routing Ward Whitt Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research,
Int. J. Electron. Commun. (AEÜ) ( ) www.elsevier.de/aeue A multi-class fluid model for a contact center with skill-based routing Ward Whitt Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research,
Managing Call Centers with Many Strategic Agents
 Managing Call Centers with Many Strategic Agents Rouba Ibrahim, Kenan Arifoglu Management Science and Innovation, UCL YEQT Workshop - Eindhoven November 2014 Work Schedule Flexibility 86SwofwthewqBestwCompanieswtowWorkwForqwofferw
Managing Call Centers with Many Strategic Agents Rouba Ibrahim, Kenan Arifoglu Management Science and Innovation, UCL YEQT Workshop - Eindhoven November 2014 Work Schedule Flexibility 86SwofwthewqBestwCompanieswtowWorkwForqwofferw
Wait-Time Predictors for Customer Service Systems with Time-Varying Demand and Capacity
 OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 59, No. 5, September October 211, pp. 116 1118 issn 3-364X eissn 1526-5463 11 595 116 http://dx.doi.org/1.1287/opre.111.974 211 INFORMS Wait-Time Predictors for Customer Service
OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 59, No. 5, September October 211, pp. 116 1118 issn 3-364X eissn 1526-5463 11 595 116 http://dx.doi.org/1.1287/opre.111.974 211 INFORMS Wait-Time Predictors for Customer Service
REAL-TIME DELAY ESTIMATION BASED ON DELAY HISTORY IN MANY-SERVER SERVICE SYSTEMS WITH TIME-VARYING ARRIVALS
 REAL-TIME DELAY ESTIMATION BASED ON DELAY HISTORY IN MANY-SERVER SERVICE SYSTEMS WITH TIME-VARYING ARRIVALS Abstract Motivated by interest in making delay announcements in service systems, we study real-time
REAL-TIME DELAY ESTIMATION BASED ON DELAY HISTORY IN MANY-SERVER SERVICE SYSTEMS WITH TIME-VARYING ARRIVALS Abstract Motivated by interest in making delay announcements in service systems, we study real-time
SOLUTIONS IEOR 3106: Second Midterm Exam, Chapters 5-6, November 8, 2012
 SOLUTIONS IEOR 3106: Second Midterm Exam, Chapters 5-6, November 8, 2012 This exam is closed book. YOU NEED TO SHOW YOUR WORK. Honor Code: Students are expected to behave honorably, following the accepted
SOLUTIONS IEOR 3106: Second Midterm Exam, Chapters 5-6, November 8, 2012 This exam is closed book. YOU NEED TO SHOW YOUR WORK. Honor Code: Students are expected to behave honorably, following the accepted
STABILIZING PERFORMANCE IN NETWORKS OF QUEUES WITH TIME-VARYING ARRIVAL RATES
 Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences, 28, 24, 49 449. doi:.7/s2699648484 STABILIZING PERFORMANCE IN NETWORKS OF QUEUES WITH TIME-VARYING ARRIVAL RATES YUNAN LIU AND WARD WHITT Department
Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences, 28, 24, 49 449. doi:.7/s2699648484 STABILIZING PERFORMANCE IN NETWORKS OF QUEUES WITH TIME-VARYING ARRIVAL RATES YUNAN LIU AND WARD WHITT Department
REAL-TIME DELAY ESTIMATION BASED ON DELAY HISTORY SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 REAL-TIME DELAY ESTIMATION BASED ON DELAY HISTORY SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL by Rouba Ibrahim and Ward Whitt IEOR Department Columbia University {rei2101, ww2040}@columbia.edu Abstract Motivated by interest
REAL-TIME DELAY ESTIMATION BASED ON DELAY HISTORY SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL by Rouba Ibrahim and Ward Whitt IEOR Department Columbia University {rei2101, ww2040}@columbia.edu Abstract Motivated by interest
Modeling Service Networks with Time-Varying Demand
 Modeling Service with Time-Varying Demand - Performance Approximations and Staffing Controls (with Beixiang He, Liam Huang, Korhan Aras, Ward Whitt) Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering NC
Modeling Service with Time-Varying Demand - Performance Approximations and Staffing Controls (with Beixiang He, Liam Huang, Korhan Aras, Ward Whitt) Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering NC
Analysis of a Two-Phase Queueing System with Impatient Customers and Multiple Vacations
 The Tenth International Symposium on Operations Research and Its Applications (ISORA 211) Dunhuang, China, August 28 31, 211 Copyright 211 ORSC & APORC, pp. 292 298 Analysis of a Two-Phase Queueing System
The Tenth International Symposium on Operations Research and Its Applications (ISORA 211) Dunhuang, China, August 28 31, 211 Copyright 211 ORSC & APORC, pp. 292 298 Analysis of a Two-Phase Queueing System
BIRTH DEATH PROCESSES AND QUEUEING SYSTEMS
 BIRTH DEATH PROCESSES AND QUEUEING SYSTEMS Andrea Bobbio Anno Accademico 999-2000 Queueing Systems 2 Notation for Queueing Systems /λ mean time between arrivals S = /µ ρ = λ/µ N mean service time traffic
BIRTH DEATH PROCESSES AND QUEUEING SYSTEMS Andrea Bobbio Anno Accademico 999-2000 Queueing Systems 2 Notation for Queueing Systems /λ mean time between arrivals S = /µ ρ = λ/µ N mean service time traffic
Stabilizing Customer Abandonment in Many-Server Queues with Time-Varying Arrivals
 OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 6, No. 6, November December 212, pp. 1551 1564 ISSN 3-364X (print) ISSN 1526-5463 (online) http://dx.doi.org/1.1287/opre.112.114 212 INFORMS Stabilizing Customer Abandonment in
OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 6, No. 6, November December 212, pp. 1551 1564 ISSN 3-364X (print) ISSN 1526-5463 (online) http://dx.doi.org/1.1287/opre.112.114 212 INFORMS Stabilizing Customer Abandonment in
Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0.
![Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0. Since D has an exponential distribution, E[D] = 0.09 years. Since {A(t) : t 0} is a Poisson process with rate λ = 10, 000, A(0.](/thumbs/95/124116804.jpg) IEOR 46: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Chapters 5-6 in Ross, Thursday, April, 4:5-5:35pm SOLUTIONS to Second Midterm Exam, Spring 9, Open Book: but only the Ross textbook, the
IEOR 46: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Chapters 5-6 in Ross, Thursday, April, 4:5-5:35pm SOLUTIONS to Second Midterm Exam, Spring 9, Open Book: but only the Ross textbook, the
Non Markovian Queues (contd.)
 MODULE 7: RENEWAL PROCESSES 29 Lecture 5 Non Markovian Queues (contd) For the case where the service time is constant, V ar(b) = 0, then the P-K formula for M/D/ queue reduces to L s = ρ + ρ 2 2( ρ) where
MODULE 7: RENEWAL PROCESSES 29 Lecture 5 Non Markovian Queues (contd) For the case where the service time is constant, V ar(b) = 0, then the P-K formula for M/D/ queue reduces to L s = ρ + ρ 2 2( ρ) where
Service Engineering January Laws of Congestion
 Service Engineering January 2004 http://ie.technion.ac.il/serveng2004 Laws of Congestion The Law for (The) Causes of Operational Queues Scarce Resources Synchronization Gaps (in DS PERT Networks) Linear
Service Engineering January 2004 http://ie.technion.ac.il/serveng2004 Laws of Congestion The Law for (The) Causes of Operational Queues Scarce Resources Synchronization Gaps (in DS PERT Networks) Linear
Electronic Companion Fluid Models for Overloaded Multi-Class Many-Server Queueing Systems with FCFS Routing
 Submitted to Management Science manuscript MS-251-27 Electronic Companion Fluid Models for Overloaded Multi-Class Many-Server Queueing Systems with FCFS Routing Rishi Talreja, Ward Whitt Department of
Submitted to Management Science manuscript MS-251-27 Electronic Companion Fluid Models for Overloaded Multi-Class Many-Server Queueing Systems with FCFS Routing Rishi Talreja, Ward Whitt Department of
APPENDIX to Stabilizing Performance in Many-Server Queues with Time-Varying Arrivals and Customer Feedback
 APPENDIX to Stabilizing Performance in Many-Server Queues with -Varying Arrivals and Customer Feedback Yunan Liu and Ward Whitt Department of Industrial Engineering North Carolina State University Raleigh,
APPENDIX to Stabilizing Performance in Many-Server Queues with -Varying Arrivals and Customer Feedback Yunan Liu and Ward Whitt Department of Industrial Engineering North Carolina State University Raleigh,
Chapter 6 Queueing Models. Banks, Carson, Nelson & Nicol Discrete-Event System Simulation
 Chapter 6 Queueing Models Banks, Carson, Nelson & Nicol Discrete-Event System Simulation Purpose Simulation is often used in the analysis of queueing models. A simple but typical queueing model: Queueing
Chapter 6 Queueing Models Banks, Carson, Nelson & Nicol Discrete-Event System Simulation Purpose Simulation is often used in the analysis of queueing models. A simple but typical queueing model: Queueing
ESTIMATING WAITING TIMES WITH THE TIME-VARYING LITTLE S LAW
 ESTIMATING WAITING TIMES WITH THE TIME-VARYING LITTLE S LAW Song-Hee Kim and Ward Whitt Industrial Engineering and Operations Research Columbia University New York, NY, 10027 {sk3116, ww2040}@columbia.edu
ESTIMATING WAITING TIMES WITH THE TIME-VARYING LITTLE S LAW Song-Hee Kim and Ward Whitt Industrial Engineering and Operations Research Columbia University New York, NY, 10027 {sk3116, ww2040}@columbia.edu
Wait-Time Predictors for Customer Service Systems With Time-Varying Demand and Capacity
 Submitted to Operations Research manuscript (Please, provide the mansucript number!) Wait-Time Predictors for Customer Service Systems With Time-Varying Demand and Capacity Rouba Ibrahim, Ward Whitt Department
Submitted to Operations Research manuscript (Please, provide the mansucript number!) Wait-Time Predictors for Customer Service Systems With Time-Varying Demand and Capacity Rouba Ibrahim, Ward Whitt Department
A Study on M x /G/1 Queuing System with Essential, Optional Service, Modified Vacation and Setup time
 A Study on M x /G/1 Queuing System with Essential, Optional Service, Modified Vacation and Setup time E. Ramesh Kumar 1, L. Poornima 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Mathematics, CMS College of Science
A Study on M x /G/1 Queuing System with Essential, Optional Service, Modified Vacation and Setup time E. Ramesh Kumar 1, L. Poornima 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Mathematics, CMS College of Science
Stochastic-Process Limits
 Ward Whitt Stochastic-Process Limits An Introduction to Stochastic-Process Limits and Their Application to Queues With 68 Illustrations Springer Contents Preface vii 1 Experiencing Statistical Regularity
Ward Whitt Stochastic-Process Limits An Introduction to Stochastic-Process Limits and Their Application to Queues With 68 Illustrations Springer Contents Preface vii 1 Experiencing Statistical Regularity
Figure 10.1: Recording when the event E occurs
 10 Poisson Processes Let T R be an interval. A family of random variables {X(t) ; t T} is called a continuous time stochastic process. We often consider T = [0, 1] and T = [0, ). As X(t) is a random variable
10 Poisson Processes Let T R be an interval. A family of random variables {X(t) ; t T} is called a continuous time stochastic process. We often consider T = [0, 1] and T = [0, ). As X(t) is a random variable
Introduction to Queueing Theory with Applications to Air Transportation Systems
 Introduction to Queueing Theory with Applications to Air Transportation Systems John Shortle George Mason University February 28, 2018 Outline Why stochastic models matter M/M/1 queue Little s law Priority
Introduction to Queueing Theory with Applications to Air Transportation Systems John Shortle George Mason University February 28, 2018 Outline Why stochastic models matter M/M/1 queue Little s law Priority
Queueing Theory. VK Room: M Last updated: October 17, 2013.
 Queueing Theory VK Room: M1.30 knightva@cf.ac.uk www.vincent-knight.com Last updated: October 17, 2013. 1 / 63 Overview Description of Queueing Processes The Single Server Markovian Queue Multi Server
Queueing Theory VK Room: M1.30 knightva@cf.ac.uk www.vincent-knight.com Last updated: October 17, 2013. 1 / 63 Overview Description of Queueing Processes The Single Server Markovian Queue Multi Server
CDA5530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks. Chapter 4: Elementary Queuing Theory
 CDA5530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks Chapter 4: Elementary Queuing Theory Definition Queuing system: a buffer (waiting room), service facility (one or more servers) a scheduling policy
CDA5530: Performance Models of Computers and Networks Chapter 4: Elementary Queuing Theory Definition Queuing system: a buffer (waiting room), service facility (one or more servers) a scheduling policy
The G t /GI/s t + GI Many-Server Fluid Queue: Longer Online Version with Appendix
 Queueing Systems manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) January 4, 22 The G t /GI/s t + GI Many-Server Fluid Queue: Longer Online Version with Appendix Yunan Liu Ward Whitt Received: date / Accepted:
Queueing Systems manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) January 4, 22 The G t /GI/s t + GI Many-Server Fluid Queue: Longer Online Version with Appendix Yunan Liu Ward Whitt Received: date / Accepted:
STAFFING A CALL CENTER WITH UNCERTAIN ARRIVAL RATE AND ABSENTEEISM
 STAFFING A CALL CENTER WITH UNCERTAIN ARRIVAL RATE AND ABSENTEEISM by Ward Whitt Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research Columbia University, New York, NY 10027 6699 Abstract This
STAFFING A CALL CENTER WITH UNCERTAIN ARRIVAL RATE AND ABSENTEEISM by Ward Whitt Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research Columbia University, New York, NY 10027 6699 Abstract This
An M/M/1/N Queuing system with Encouraged Arrivals
 Global Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics. ISS 0973-1768 Volume 13, umber 7 (2017), pp. 3443-3453 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com An M/M/1/ Queuing system with Encouraged
Global Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics. ISS 0973-1768 Volume 13, umber 7 (2017), pp. 3443-3453 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com An M/M/1/ Queuing system with Encouraged
Classical Queueing Models.
 Sergey Zeltyn January 2005 STAT 99. Service Engineering. The Wharton School. University of Pennsylvania. Based on: Classical Queueing Models. Mandelbaum A. Service Engineering course, Technion. http://iew3.technion.ac.il/serveng2005w
Sergey Zeltyn January 2005 STAT 99. Service Engineering. The Wharton School. University of Pennsylvania. Based on: Classical Queueing Models. Mandelbaum A. Service Engineering course, Technion. http://iew3.technion.ac.il/serveng2005w
A Fluid Approximation for Service Systems Responding to Unexpected Overloads
 OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 59, No. 5, September October 2011, pp. 1159 1170 issn 0030-364X eissn 1526-5463 11 5905 1159 http://dx.doi.org/10.1287/opre.1110.0985 2011 INFORMS A Fluid Approximation for Service
OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 59, No. 5, September October 2011, pp. 1159 1170 issn 0030-364X eissn 1526-5463 11 5905 1159 http://dx.doi.org/10.1287/opre.1110.0985 2011 INFORMS A Fluid Approximation for Service
A Diffusion Approximation for the G/GI/n/m Queue
 OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 52, No. 6, November December 2004, pp. 922 941 issn 0030-364X eissn 1526-5463 04 5206 0922 informs doi 10.1287/opre.1040.0136 2004 INFORMS A Diffusion Approximation for the G/GI/n/m
OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 52, No. 6, November December 2004, pp. 922 941 issn 0030-364X eissn 1526-5463 04 5206 0922 informs doi 10.1287/opre.1040.0136 2004 INFORMS A Diffusion Approximation for the G/GI/n/m
Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 3. Models of Queuing
 Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 3. Models of Queuing Husheng Li Min Kao Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville Spring, 2016 1/13 Terminology of
Advanced Computer Networks Lecture 3. Models of Queuing Husheng Li Min Kao Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville Spring, 2016 1/13 Terminology of
λ λ λ In-class problems
 In-class problems 1. Customers arrive at a single-service facility at a Poisson rate of 40 per hour. When two or fewer customers are present, a single attendant operates the facility, and the service time
In-class problems 1. Customers arrive at a single-service facility at a Poisson rate of 40 per hour. When two or fewer customers are present, a single attendant operates the facility, and the service time
IMPROVING SERVICE BY INFORMING CUSTOMERS ABOUT ANTICIPATED DELAYS. Ward Whitt 1 AT&T Labs Research. April 14, 1998
 IMPROVING SERVICE BY INFORMING CUSTOMERS ABOUT ANTICIPATED DELAYS by Ward Whitt 1 AT&T Labs Research April 14, 1998 Management Science 45 (1999) 192 207 1 Room A117, AT&T Labs, 180 Park Avenue, Florham
IMPROVING SERVICE BY INFORMING CUSTOMERS ABOUT ANTICIPATED DELAYS by Ward Whitt 1 AT&T Labs Research April 14, 1998 Management Science 45 (1999) 192 207 1 Room A117, AT&T Labs, 180 Park Avenue, Florham
(b) What is the variance of the time until the second customer arrives, starting empty, assuming that we measure time in minutes?
 IEOR 3106: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Fall 2006, Professor Whitt SOLUTIONS to Final Exam Chapters 4-7 and 10 in Ross, Tuesday, December 19, 4:10pm-7:00pm Open Book: but only
IEOR 3106: Introduction to Operations Research: Stochastic Models Fall 2006, Professor Whitt SOLUTIONS to Final Exam Chapters 4-7 and 10 in Ross, Tuesday, December 19, 4:10pm-7:00pm Open Book: but only
Dynamic Call Center Routing Policies Using Call Waiting and Agent Idle Times Online Supplement
 Submitted to imanufacturing & Service Operations Management manuscript MSOM-11-370.R3 Dynamic Call Center Routing Policies Using Call Waiting and Agent Idle Times Online Supplement (Authors names blinded
Submitted to imanufacturing & Service Operations Management manuscript MSOM-11-370.R3 Dynamic Call Center Routing Policies Using Call Waiting and Agent Idle Times Online Supplement (Authors names blinded
1.225 Transportation Flow Systems Quiz (December 17, 2001; Duration: 3 hours)
 1.225 Transportation Flow Systems Quiz (December 17, 2001; Duration: 3 hours) Student Name: Alias: Instructions: 1. This exam is open-book 2. No cooperation is permitted 3. Please write down your name
1.225 Transportation Flow Systems Quiz (December 17, 2001; Duration: 3 hours) Student Name: Alias: Instructions: 1. This exam is open-book 2. No cooperation is permitted 3. Please write down your name
Queues and Queueing Networks
 Queues and Queueing Networks Sanjay K. Bose Dept. of EEE, IITG Copyright 2015, Sanjay K. Bose 1 Introduction to Queueing Models and Queueing Analysis Copyright 2015, Sanjay K. Bose 2 Model of a Queue Arrivals
Queues and Queueing Networks Sanjay K. Bose Dept. of EEE, IITG Copyright 2015, Sanjay K. Bose 1 Introduction to Queueing Models and Queueing Analysis Copyright 2015, Sanjay K. Bose 2 Model of a Queue Arrivals
Stabilizing Performance in a Service System with Time-Varying Arrivals and Customer Feedback
 Stabilizing Performance in a Service System with Time-Varying Arrivals and Customer Feedback Yunan Liu a, Ward Whitt b, a Department of Industrial Engineering, North Carolina State University, Raleigh,
Stabilizing Performance in a Service System with Time-Varying Arrivals and Customer Feedback Yunan Liu a, Ward Whitt b, a Department of Industrial Engineering, North Carolina State University, Raleigh,
Class 11 Non-Parametric Models of a Service System; GI/GI/1, GI/GI/n: Exact & Approximate Analysis.
 Service Engineering Class 11 Non-Parametric Models of a Service System; GI/GI/1, GI/GI/n: Exact & Approximate Analysis. G/G/1 Queue: Virtual Waiting Time (Unfinished Work). GI/GI/1: Lindley s Equations
Service Engineering Class 11 Non-Parametric Models of a Service System; GI/GI/1, GI/GI/n: Exact & Approximate Analysis. G/G/1 Queue: Virtual Waiting Time (Unfinished Work). GI/GI/1: Lindley s Equations
Queueing Theory II. Summary. ! M/M/1 Output process. ! Networks of Queue! Method of Stages. ! General Distributions
 Queueing Theory II Summary! M/M/1 Output process! Networks of Queue! Method of Stages " Erlang Distribution " Hyperexponential Distribution! General Distributions " Embedded Markov Chains M/M/1 Output
Queueing Theory II Summary! M/M/1 Output process! Networks of Queue! Method of Stages " Erlang Distribution " Hyperexponential Distribution! General Distributions " Embedded Markov Chains M/M/1 Output
The M/M/n+G Queue: Summary of Performance Measures
 The M/M/n+G Queue: Summary of Performance Measures Avishai Mandelbaum and Sergey Zeltyn Faculty of Industrial Engineering & Management Technion Haifa 32 ISRAEL emails: avim@tx.technion.ac.il zeltyn@ie.technion.ac.il
The M/M/n+G Queue: Summary of Performance Measures Avishai Mandelbaum and Sergey Zeltyn Faculty of Industrial Engineering & Management Technion Haifa 32 ISRAEL emails: avim@tx.technion.ac.il zeltyn@ie.technion.ac.il
CPSC 531: System Modeling and Simulation. Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Fall 2017
 CPSC 531: System Modeling and Simulation Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Fall 2017 Motivating Quote for Queueing Models Good things come to those who wait - poet/writer
CPSC 531: System Modeling and Simulation Carey Williamson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Fall 2017 Motivating Quote for Queueing Models Good things come to those who wait - poet/writer
A STAFFING ALGORITHM FOR CALL CENTERS WITH SKILL-BASED ROUTING: SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 A STAFFING ALGORITHM FOR CALL CENTERS WITH SKILL-BASED ROUTING: SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL by Rodney B. Wallace IBM and The George Washington University rodney.wallace@us.ibm.com Ward Whitt Columbia University
A STAFFING ALGORITHM FOR CALL CENTERS WITH SKILL-BASED ROUTING: SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL by Rodney B. Wallace IBM and The George Washington University rodney.wallace@us.ibm.com Ward Whitt Columbia University
A Fluid Approximation for Service Systems Responding to Unexpected Overloads
 Submitted to Operations Research manuscript 28-9-55.R2, Longer Online Version 6/28/1 A Fluid Approximation for Service Systems Responding to Unexpected Overloads Ohad Perry Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica
Submitted to Operations Research manuscript 28-9-55.R2, Longer Online Version 6/28/1 A Fluid Approximation for Service Systems Responding to Unexpected Overloads Ohad Perry Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica
Exercises Stochastic Performance Modelling. Hamilton Institute, Summer 2010
 Exercises Stochastic Performance Modelling Hamilton Institute, Summer Instruction Exercise Let X be a non-negative random variable with E[X ]
Exercises Stochastic Performance Modelling Hamilton Institute, Summer Instruction Exercise Let X be a non-negative random variable with E[X ]
Designing a Telephone Call Center with Impatient Customers
 Designing a Telephone Call Center with Impatient Customers with Ofer Garnett Marty Reiman Sergey Zeltyn Appendix: Strong Approximations of M/M/ + Source: ErlangA QEDandSTROG FIAL.tex M/M/ + M System Poisson
Designing a Telephone Call Center with Impatient Customers with Ofer Garnett Marty Reiman Sergey Zeltyn Appendix: Strong Approximations of M/M/ + Source: ErlangA QEDandSTROG FIAL.tex M/M/ + M System Poisson
Stationary Analysis of a Multiserver queue with multiple working vacation and impatient customers
 Available at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 932-9466 Vol. 2, Issue 2 (December 207), pp. 658 670 Applications and Applied Mathematics: An International Journal (AAM) Stationary Analysis of
Available at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 932-9466 Vol. 2, Issue 2 (December 207), pp. 658 670 Applications and Applied Mathematics: An International Journal (AAM) Stationary Analysis of
Probability and Statistics Concepts
 University of Central Florida Computer Science Division COT 5611 - Operating Systems. Spring 014 - dcm Probability and Statistics Concepts Random Variable: a rule that assigns a numerical value to each
University of Central Florida Computer Science Division COT 5611 - Operating Systems. Spring 014 - dcm Probability and Statistics Concepts Random Variable: a rule that assigns a numerical value to each
Slides 9: Queuing Models
 Slides 9: Queuing Models Purpose Simulation is often used in the analysis of queuing models. A simple but typical queuing model is: Queuing models provide the analyst with a powerful tool for designing
Slides 9: Queuing Models Purpose Simulation is often used in the analysis of queuing models. A simple but typical queuing model is: Queuing models provide the analyst with a powerful tool for designing
Real-Time Delay Prediction in Customer Service Systems
 Real-Time Delay Prediction in Customer Service Systems Rouba Ibrahim Submitted in partial fulfillment of the Requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
Real-Time Delay Prediction in Customer Service Systems Rouba Ibrahim Submitted in partial fulfillment of the Requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
Queuing Networks: Burke s Theorem, Kleinrock s Approximation, and Jackson s Theorem. Wade Trappe
 Queuing Networks: Burke s Theorem, Kleinrock s Approximation, and Jackson s Theorem Wade Trappe Lecture Overview Network of Queues Introduction Queues in Tandem roduct Form Solutions Burke s Theorem What
Queuing Networks: Burke s Theorem, Kleinrock s Approximation, and Jackson s Theorem Wade Trappe Lecture Overview Network of Queues Introduction Queues in Tandem roduct Form Solutions Burke s Theorem What
QUEUING MODELS AND MARKOV PROCESSES
 QUEUING MODELS AND MARKOV ROCESSES Queues form when customer demand for a service cannot be met immediately. They occur because of fluctuations in demand levels so that models of queuing are intrinsically
QUEUING MODELS AND MARKOV ROCESSES Queues form when customer demand for a service cannot be met immediately. They occur because of fluctuations in demand levels so that models of queuing are intrinsically
Routing and Staffing in Large-Scale Service Systems: The Case of Homogeneous Impatient Customers and Heterogeneous Servers 1
 Routing and Staffing in Large-Scale Service Systems: The Case of Homogeneous Impatient Customers and Heterogeneous Servers 1 Mor Armony 2 Avishai Mandelbaum 3 June 25, 2008 Abstract Motivated by call centers,
Routing and Staffing in Large-Scale Service Systems: The Case of Homogeneous Impatient Customers and Heterogeneous Servers 1 Mor Armony 2 Avishai Mandelbaum 3 June 25, 2008 Abstract Motivated by call centers,
Data-Based Resource-View of Service Networks: Performance Analysis, Delay Prediction and Asymptotics. PhD Proposal. Nitzan Carmeli.
 Data-Based Resource-View of Service Networks: Performance Analysis, Delay Prediction and Asymptotics PhD Proposal Nitzan Carmeli Advisers: Prof. Avishai Mandelbaum Dr. Galit Yom-Tov Technion - Israel Institute
Data-Based Resource-View of Service Networks: Performance Analysis, Delay Prediction and Asymptotics PhD Proposal Nitzan Carmeli Advisers: Prof. Avishai Mandelbaum Dr. Galit Yom-Tov Technion - Israel Institute
IEOR 8100: Topics in OR: Asymptotic Methods in Queueing Theory. Fall 2009, Professor Whitt. Class Lecture Notes: Wednesday, September 9.
 IEOR 8100: Topics in OR: Asymptotic Methods in Queueing Theory Fall 2009, Professor Whitt Class Lecture Notes: Wednesday, September 9. Heavy-Traffic Limits for the GI/G/1 Queue 1. The GI/G/1 Queue We will
IEOR 8100: Topics in OR: Asymptotic Methods in Queueing Theory Fall 2009, Professor Whitt Class Lecture Notes: Wednesday, September 9. Heavy-Traffic Limits for the GI/G/1 Queue 1. The GI/G/1 Queue We will
PBW 654 Applied Statistics - I Urban Operations Research
 PBW 654 Applied Statistics - I Urban Operations Research Lecture 2.I Queuing Systems An Introduction Operations Research Models Deterministic Models Linear Programming Integer Programming Network Optimization
PBW 654 Applied Statistics - I Urban Operations Research Lecture 2.I Queuing Systems An Introduction Operations Research Models Deterministic Models Linear Programming Integer Programming Network Optimization
Contact Centers with a Call-Back Option and Real-Time Delay Information
 OPERATIOS RESEARCH Vol. 52, o. 4, July August 2004, pp. 527 545 issn 0030-364X eissn 526-5463 04 5204 0527 informs doi 0.287/opre.040.023 2004 IFORMS Contact Centers with a Call-Back Option and Real-Time
OPERATIOS RESEARCH Vol. 52, o. 4, July August 2004, pp. 527 545 issn 0030-364X eissn 526-5463 04 5204 0527 informs doi 0.287/opre.040.023 2004 IFORMS Contact Centers with a Call-Back Option and Real-Time
We consider how two networked large-scale service systems that normally operate separately, such as call
 MANAGEMENT SCIENCE Vol. 55, No. 8, August 2009, pp. 1353 1367 issn 0025-1909 eissn 1526-5501 09 5508 1353 informs doi 10.1287/mnsc.1090.1025 2009 INFORMS Responding to Unexpected Overloads in Large-Scale
MANAGEMENT SCIENCE Vol. 55, No. 8, August 2009, pp. 1353 1367 issn 0025-1909 eissn 1526-5501 09 5508 1353 informs doi 10.1287/mnsc.1090.1025 2009 INFORMS Responding to Unexpected Overloads in Large-Scale
Queueing Systems: Lecture 3. Amedeo R. Odoni October 18, Announcements
 Queueing Systems: Lecture 3 Amedeo R. Odoni October 18, 006 Announcements PS #3 due tomorrow by 3 PM Office hours Odoni: Wed, 10/18, :30-4:30; next week: Tue, 10/4 Quiz #1: October 5, open book, in class;
Queueing Systems: Lecture 3 Amedeo R. Odoni October 18, 006 Announcements PS #3 due tomorrow by 3 PM Office hours Odoni: Wed, 10/18, :30-4:30; next week: Tue, 10/4 Quiz #1: October 5, open book, in class;
Simple queueing models
 Simple queueing models c University of Bristol, 2012 1 M/M/1 queue This model describes a queue with a single server which serves customers in the order in which they arrive. Customer arrivals constitute
Simple queueing models c University of Bristol, 2012 1 M/M/1 queue This model describes a queue with a single server which serves customers in the order in which they arrive. Customer arrivals constitute
Dynamic Call Center Routing Policies Using Call Waiting and Agent Idle Times Online Supplement
 Dynamic Call Center Routing Policies Using Call Waiting and Agent Idle Times Online Supplement Wyean Chan DIRO, Université de Montréal, C.P. 6128, Succ. Centre-Ville, Montréal (Québec), H3C 3J7, CANADA,
Dynamic Call Center Routing Policies Using Call Waiting and Agent Idle Times Online Supplement Wyean Chan DIRO, Université de Montréal, C.P. 6128, Succ. Centre-Ville, Montréal (Québec), H3C 3J7, CANADA,
Introduction to queuing theory
 Introduction to queuing theory Claude Rigault ENST claude.rigault@enst.fr Introduction to Queuing theory 1 Outline The problem The number of clients in a system The client process Delay processes Loss
Introduction to queuing theory Claude Rigault ENST claude.rigault@enst.fr Introduction to Queuing theory 1 Outline The problem The number of clients in a system The client process Delay processes Loss
1.225J J (ESD 205) Transportation Flow Systems
 1.225J J (ESD 25) Transportation Flow Systems Lecture 9 Simulation Models Prof. Ismail Chabini and Prof. Amedeo R. Odoni Lecture 9 Outline About this lecture: It is based on R16. Only material covered
1.225J J (ESD 25) Transportation Flow Systems Lecture 9 Simulation Models Prof. Ismail Chabini and Prof. Amedeo R. Odoni Lecture 9 Outline About this lecture: It is based on R16. Only material covered
Queueing Review. Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman 10/6/16. (mostly from BCNN) Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA
 1 / 24 Queueing Review (mostly from BCNN) Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA 10/6/16 2 / 24 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Queueing Notation 3 Transient
1 / 24 Queueing Review (mostly from BCNN) Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA 10/6/16 2 / 24 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Queueing Notation 3 Transient
Many-Server Loss Models with Non-Poisson Time-Varying Arrivals
 Many-Server Loss Models with Non-Poisson Time-Varying Arrivals Ward Whitt, Jingtong Zhao Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research, Columbia University, New York, New York 10027 Received
Many-Server Loss Models with Non-Poisson Time-Varying Arrivals Ward Whitt, Jingtong Zhao Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research, Columbia University, New York, New York 10027 Received
Introduction to Queuing Networks Solutions to Problem Sheet 3
 Introduction to Queuing Networks Solutions to Problem Sheet 3 1. (a) The state space is the whole numbers {, 1, 2,...}. The transition rates are q i,i+1 λ for all i and q i, for all i 1 since, when a bus
Introduction to Queuing Networks Solutions to Problem Sheet 3 1. (a) The state space is the whole numbers {, 1, 2,...}. The transition rates are q i,i+1 λ for all i and q i, for all i 1 since, when a bus
Continuous Time Processes
 page 102 Chapter 7 Continuous Time Processes 7.1 Introduction In a continuous time stochastic process (with discrete state space), a change of state can occur at any time instant. The associated point
page 102 Chapter 7 Continuous Time Processes 7.1 Introduction In a continuous time stochastic process (with discrete state space), a change of state can occur at any time instant. The associated point
6 Solving Queueing Models
 6 Solving Queueing Models 6.1 Introduction In this note we look at the solution of systems of queues, starting with simple isolated queues. The benefits of using predefined, easily classified queues will
6 Solving Queueing Models 6.1 Introduction In this note we look at the solution of systems of queues, starting with simple isolated queues. The benefits of using predefined, easily classified queues will
2905 Queueing Theory and Simulation PART IV: SIMULATION
 2905 Queueing Theory and Simulation PART IV: SIMULATION 22 Random Numbers A fundamental step in a simulation study is the generation of random numbers, where a random number represents the value of a random
2905 Queueing Theory and Simulation PART IV: SIMULATION 22 Random Numbers A fundamental step in a simulation study is the generation of random numbers, where a random number represents the value of a random
Routing and Staffing in Large-Scale Service Systems: The Case of Homogeneous Impatient Customers and Heterogeneous Servers
 OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 59, No. 1, January February 2011, pp. 50 65 issn 0030-364X eissn 1526-5463 11 5901 0050 informs doi 10.1287/opre.1100.0878 2011 INFORMS Routing and Staffing in Large-Scale Service
OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 59, No. 1, January February 2011, pp. 50 65 issn 0030-364X eissn 1526-5463 11 5901 0050 informs doi 10.1287/opre.1100.0878 2011 INFORMS Routing and Staffing in Large-Scale Service
2905 Queueing Theory and Simulation PART III: HIGHER DIMENSIONAL AND NON-MARKOVIAN QUEUES
 295 Queueing Theory and Simulation PART III: HIGHER DIMENSIONAL AND NON-MARKOVIAN QUEUES 16 Queueing Systems with Two Types of Customers In this section, we discuss queueing systems with two types of customers.
295 Queueing Theory and Simulation PART III: HIGHER DIMENSIONAL AND NON-MARKOVIAN QUEUES 16 Queueing Systems with Two Types of Customers In this section, we discuss queueing systems with two types of customers.
One billion+ terminals in voice network alone
 Traffic Engineering Traffic Engineering One billion+ terminals in voice networ alone Plus data, video, fax, finance, etc. Imagine all users want service simultaneously its not even nearly possible (despite
Traffic Engineering Traffic Engineering One billion+ terminals in voice networ alone Plus data, video, fax, finance, etc. Imagine all users want service simultaneously its not even nearly possible (despite
Proactive Care with Degrading Class Types
 Proactive Care with Degrading Class Types Yue Hu (DRO, Columbia Business School) Joint work with Prof. Carri Chan (DRO, Columbia Business School) and Prof. Jing Dong (DRO, Columbia Business School) Motivation
Proactive Care with Degrading Class Types Yue Hu (DRO, Columbia Business School) Joint work with Prof. Carri Chan (DRO, Columbia Business School) and Prof. Jing Dong (DRO, Columbia Business School) Motivation
Homework 1 - SOLUTION
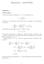 Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
Design, staffing and control of large service systems: The case of a single customer class and multiple server types. April 2, 2004 DRAFT.
 Design, staffing and control of large service systems: The case of a single customer class and multiple server types. Mor Armony 1 Avishai Mandelbaum 2 April 2, 2004 DRAFT Abstract Motivated by modern
Design, staffing and control of large service systems: The case of a single customer class and multiple server types. Mor Armony 1 Avishai Mandelbaum 2 April 2, 2004 DRAFT Abstract Motivated by modern
Periodic Load Balancing
 Queueing Systems 0 (2000)?? 1 Periodic Load Balancing Gisli Hjálmtýsson a Ward Whitt a a AT&T Labs, 180 Park Avenue, Building 103, Florham Park, NJ 07932-0971 E-mail: {gisli,wow}@research.att.com Queueing
Queueing Systems 0 (2000)?? 1 Periodic Load Balancing Gisli Hjálmtýsson a Ward Whitt a a AT&T Labs, 180 Park Avenue, Building 103, Florham Park, NJ 07932-0971 E-mail: {gisli,wow}@research.att.com Queueing
A DIFFUSION APPROXIMATION FOR THE G/GI/n/m QUEUE
 A DIFFUSION APPROXIMATION FOR THE G/GI/n/m QUEUE by Ward Whitt Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research Columbia University, New York, NY 10027 July 5, 2002 Revision: June 27, 2003
A DIFFUSION APPROXIMATION FOR THE G/GI/n/m QUEUE by Ward Whitt Department of Industrial Engineering and Operations Research Columbia University, New York, NY 10027 July 5, 2002 Revision: June 27, 2003
57:022 Principles of Design II Final Exam Solutions - Spring 1997
 57:022 Principles of Design II Final Exam Solutions - Spring 1997 Part: I II III IV V VI Total Possible Pts: 52 10 12 16 13 12 115 PART ONE Indicate "+" if True and "o" if False: + a. If a component's
57:022 Principles of Design II Final Exam Solutions - Spring 1997 Part: I II III IV V VI Total Possible Pts: 52 10 12 16 13 12 115 PART ONE Indicate "+" if True and "o" if False: + a. If a component's
Stochastic grey-box modeling of queueing systems: fitting birth-and-death processes to data
 Queueing Syst (2015) 79:391 426 DOI 10.1007/s11134-014-9429-3 Stochastic grey-box modeling of queueing systems: fitting birth-and-death processes to data James Dong Ward Whitt Received: 8 January 2014
Queueing Syst (2015) 79:391 426 DOI 10.1007/s11134-014-9429-3 Stochastic grey-box modeling of queueing systems: fitting birth-and-death processes to data James Dong Ward Whitt Received: 8 January 2014
Elementary queueing system
 Elementary queueing system Kendall notation Little s Law PASTA theorem Basics of M/M/1 queue M/M/1 with preemptive-resume priority M/M/1 with non-preemptive priority 1 History of queueing theory An old
Elementary queueing system Kendall notation Little s Law PASTA theorem Basics of M/M/1 queue M/M/1 with preemptive-resume priority M/M/1 with non-preemptive priority 1 History of queueing theory An old
Fluid Limit of A Many-Server Queueing Network with Abandonment
 Fluid Limit of A Many-Server Queueing Networ with Abandonment Weining Kang Guodong Pang October 22, 213 Abstract This paper studies a non-marovian many-server queueing networ with abandonment, where externally
Fluid Limit of A Many-Server Queueing Networ with Abandonment Weining Kang Guodong Pang October 22, 213 Abstract This paper studies a non-marovian many-server queueing networ with abandonment, where externally
Lecture Notes of Communication Network I y: part 5. Lijun Qian. Rutgers The State University of New Jersey. 94 Brett Road. Piscataway, NJ
 Lecture Notes of Communication Network I y: part 5 Lijun Qian Department of Electrical Engineering Rutgers The State University of New Jersey 94 Brett Road Piscataway, NJ 08854-8058 October 6, 1998 Abstract
Lecture Notes of Communication Network I y: part 5 Lijun Qian Department of Electrical Engineering Rutgers The State University of New Jersey 94 Brett Road Piscataway, NJ 08854-8058 October 6, 1998 Abstract
Queueing Review. Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman 10/25/17. (mostly from BCNN) Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA
 1 / 26 Queueing Review (mostly from BCNN) Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA 10/25/17 2 / 26 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Queueing Notation 3 Transient
1 / 26 Queueing Review (mostly from BCNN) Christos Alexopoulos and Dave Goldsman Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA 10/25/17 2 / 26 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Queueing Notation 3 Transient
