MAE 320 Thermodynamics HW 4 Assignment
|
|
|
- Janel Robertson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MAE 0 Thermodynamics HW 4 Assignment The homework is de Friday, October 7 th, 06. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the soltion from any sorce is not acceptable. (). Mltiple choice (0 points) (a). Which statement is inalid regarding a closed system? (A) Energy can transfer across the bondary of the closed system. (B) The mass of the closed system remains constant (C) The olme of the closed system always remains constant. (D) The pressre of the closed system may change with time (b). Which statement is alid regarding a polytropic process? (A) The pressre of the closed system always remains constant dring a polytropic process. (B) The olme of the closed system always remains constant dring a polytropic process. (C) The temperatre of the closed system always remains constant dring a polytropic process. (D) Heat may transfer across the bondary of the closed system dring a polytropic process. (c). Which statement is inalid regarding a specific heat: (A) c and c p are properties. They are intensie properties. (B) c and c p are applied to any sbstance ndergoing any process. (C) c is related to the changes in internal energy and c p to the changes in enthalpy. (D) c is always greater than c p (E) c and c p are temperatre-dependent for any sbstance. (d). An 8 L of piston-cylinder system contains air at 00 kpa and 00 K. Now air is compressed isothermally to a olme of L. The bondary work dring this compression process is closest to (A). kj (B).8 kj (C) -. kj (D) kj (E) 9. kj V W b PV ln 00kPa 8 0 m ln( ). kj V 8 (e) 0.0 kg of orange is cooled from 0 C to 5 C in a refrigerator. The amont of heat transferred from the orange to the refrigerator is closest to (Hint: aerage specific heat of oranges can be obtained from a Table in Appendix ) (A) 7.40 kj (B).5 kj (C) 4.85 kj
2 (D) kj (E).50 kj From Table A-c to find ot C. o o Q U mc ( T T ) 0.kg (.75kJ / kg C) (5 0) C. 5kJ (f) A closed system ndergoes the series of qasi-eqilibrim processes shown here. The bondary work done dring the whole process is closest to (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) 40 kj 40 kj 40 kj 40 kj 680 kj Recall that the bondary work integral is the area nder qasi-eqilibrim processes on a P-V state diagram. Hence, W 00 (0.7-0.) + 00 (0.5-0.) / + 00 ( ) 40 kj.
3 . A piston-cylinder deice contains. kg R-4a at 4 bar and 50 C. Now R-4a is cooled at constant pressre ntil its temperatre drops to 0 C ( points). (a) draw a T- diagram, label the satrated temperatre, the specific olmes and the temperatres of the initial and final states (b) determine the bondary work done dring this expansion process, in kj. (c) calclate the amont of heat that transferred into the piston, in kj (a) Sate : at P 400 kpa, T sat, 8.9 o C from Table A- Since T > T sat,, it is sperheated apor. From Table A-, m /kg, kj/kg Sate : From Table A-, m /kg, 5.97 kj/kg 50 o C 0 o C 8.9 o C T ( o C) (m /kg) (b) A closed system ndergoes a constant pressre process. Therefore, W b P( V V ) mp( ) W b.kg (400kPa)( ) m / kg.95kpa m. 95kJ (c). For a closed system, the energy balance eqation is: Q W U U m( ) b Q Wb + m( ).95kJ +.kg ( ) kj / kg 8. kj The heat transfered into the system is -8.kJ. The negatie sign indicates the direction of the heat transfer is opposite to the assmed heat transfer into system.
4 4. An ideal gas within a piston-cylinder assembly ndergoes a thermodynamic cycle consisting of the following three processes ( points): Process : Compression with PV constant; from P bar, V.6 m to V 0. m ; U U. Process : Constant pressre expansion process to V V. Process : Constant olme. U - U -549 kj. The changes in the kinetic energy and potential energy can be ignored. (a) Sketch the cycle on a P-V diagram (b) Calclate the bondary work and the net heat transfer dring Process, in kj (c) Calclate the bondary work and the net heat transfer for Process, in kj (d) Calclate the bondary work and the net heat transfer for Process, in kj (a) See P-V diagram on the right V 0. (b) W PV ln 00kPa.6m ln( ). 7kJ V.6 Since Q W U 0, Hence Q W. 7kJ (c) Based on the ideal gas eqation: P V PV C P P V / V ) 00kPa(.6 / 0.) 800kPa ( PVC For a constant process: W P ( V V ) P ( V V ) 800kPa (.6 0.) m 0kJ Since Q W U, Hence Q W + U ) ( U For a cycle, U 0, that is, ( U ) + ( U ) + ( U ) 0 Since U 0, Hence, ( U U ) ( U ) 549kJ Q 0kJ + 549kJ 4669kJ (d) For a constant olme process, W 0 Q W U 549kJ 4
5 5. As shown in the figre, a piston-cylinder assembly whose piston is resting on a stop contains 800 L of helim gas, initially at 00 kpa and 5 o C. The pressre of helim needed for the piston to start to moe is 50 kpa. (0 points). (a) Calclate the mass of helim in the cylinder (b) Assming a constant specific heat of helim dring this process, determine the heat gain or loss needed for this piston to start moing (State ), in kj. (a). R can be obtained from Table A- consider he is idea gas: P V (00 kpa)(0.8 m ) m RT (.0769 kpa m /kg K)(98 K) 0.9 kg Base on the state eqation of ideal gas: PVmRT T T P / P ) 98K(50 /00) 745K ( (b). For a closed system, the energy balance eqation is: Q Wb U m( ) The specific heat of helim can be obtained from Table A- The bondary work is zero. Q m o ) mc ( T T ) 0.9kg (.56kJ / kg C)(745 98) K kJ ( 5
6 6. Steam at 75 kpa and 8 percent qality is contained in a spring-loaded piston-cylinder deice with an initial olme of m. Steam is now heated ntil the pressre and olme rise to 5 kpa and 5 m. Dring this process, the pressre increases linearly with change in the olme (6 points) (a) Calclate the mass of steam contained in the cylinder (b) Determine the internal energy at the initial and final states. (c) Calclate the work done dring the process, in kj (d) Determine the heat transfer dring the process, in kj Assmptions The cylinder is stationary and ths the kinetic and potential energy changes are zero. There are no work interactions inoled other than the bondary work. The thermal energy stored in the cylinder itself is negligible. 4 The compression or expansion process is qasieqilibrim. Analysis We take the contents of the cylinder as the system. This is closed system since no mass enters or leaes. The energy balance for this stationary closed system can be expressed as (a). The initial state is satrated mixtre at 75 kpa. The specific olme and internal energy at this state are (Table A-5), f + x (0.08)( ) fg The mass of water is V m m. kg 0.78 m /kg 0.78 m /kg (b). the initial internal energy: f + x fg (0.08)(.8) 55.0 kj/kg The final specific olme is V m m m. kg The final state is now fixed. Since f << g, its is a mixtre of two phases. x g f f /kg The internal energy at this specific olme and 5 kpa pressre is + x 50.47kJ / kg kJ kg f g / kj/kg (c). Since this is a linear process, the work done is eqal to the area nder the process line -: P + P (75 + 5)kPa kj W b,ot Area ( V V) (5 )m 450 kj kpa m 6
7 (d) For a closed system: Q in W b,ot Q in U m( W b,ot + m( ) Sbstitting into energy balance eqation gies Qin b,ot ) (since KE PE 0) W + m( ) 450 kj + (. kg)( ) kj/kg,750 kj P 5 kpa 75 kpa 7. Describe the operating principle and the major components between any two ot of the following types of refrigerators inclding Compressor refrigerators, Peltier refrigerators, Solar refrigerators, Thermal mass refrigerators, Magnetic refrigerators and Acostic refrigerators. Yo mst inclde one that ses a refrigerant, and another that does not se any refrigerant. Please describe the history of the deelopment of refrigerants sed for gas-compressor refrigerators, and the state-of-the-art refrigerant. The essay shold cite at least three references, mst be typed in single-space, times new roman font, point, no shorter than one page (5 points). 7
Chapter 4 ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
 4- Chapter 4 ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS Mog Bondary ork 4-C It represents the bondary work for qasi-eqilibrim processes. 4-C Yes. 4-C The area nder the process cre, and ths the bondary work done,
4- Chapter 4 ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS Mog Bondary ork 4-C It represents the bondary work for qasi-eqilibrim processes. 4-C Yes. 4-C The area nder the process cre, and ths the bondary work done,
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES. The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial.
 THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 2 THERMODYNAMIC PRINCIPLES SAE
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 2 THERMODYNAMIC PRINCIPLES SAE
KNOWN: Data are provided for a closed system undergoing a process involving work, heat transfer, change in elevation, and change in velocity.
 Problem 44 A closed system of mass of 10 kg undergoes a process during which there is energy transfer by work from the system of 0147 kj per kg, an elevation decrease of 50 m, and an increase in velocity
Problem 44 A closed system of mass of 10 kg undergoes a process during which there is energy transfer by work from the system of 0147 kj per kg, an elevation decrease of 50 m, and an increase in velocity
Outline. Example. Solution. Property evaluation examples Specific heat Internal energy, enthalpy, and specific heats of solids and liquids Examples
 Outline Property ealuation examples Specific heat Internal energy, enthalpy, and specific heats of solids and liquids s A piston-cylinder deice initially contains 0.5m of saturated water apor at 00kPa.
Outline Property ealuation examples Specific heat Internal energy, enthalpy, and specific heats of solids and liquids s A piston-cylinder deice initially contains 0.5m of saturated water apor at 00kPa.
MAE 110A. Homework 3: Solutions 10/20/2017
 MAE 110A Homework 3: Solutions 10/20/2017 3.10: For H 2O, determine the specified property at the indicated state. Locate the state on a sketch of the T-v diagram. Given a) T 140 C, v 0.5 m 3 kg b) p 30MPa,
MAE 110A Homework 3: Solutions 10/20/2017 3.10: For H 2O, determine the specified property at the indicated state. Locate the state on a sketch of the T-v diagram. Given a) T 140 C, v 0.5 m 3 kg b) p 30MPa,
PROBLEM 6.3. Using the appropriate table, determine the indicated property. In each case, locate the state on sketches of the T-v and T-s diagrams.
 PROBLEM 63 Using the appropriate table, determine the indicated property In each case, locate the state on sketches of the -v and -s diagrams (a) water at p = 040 bar, h = 147714 kj/kg K Find s, in kj/kg
PROBLEM 63 Using the appropriate table, determine the indicated property In each case, locate the state on sketches of the -v and -s diagrams (a) water at p = 040 bar, h = 147714 kj/kg K Find s, in kj/kg
Introduction to Thermodynamic Cycles Part 1 1 st Law of Thermodynamics and Gas Power Cycles
 Introduction to Thermodynamic Cycles Part 1 1 st Law of Thermodynamics and Gas Power Cycles by James Doane, PhD, PE Contents 1.0 Course Oeriew... 4.0 Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics... 4.1 Temperature
Introduction to Thermodynamic Cycles Part 1 1 st Law of Thermodynamics and Gas Power Cycles by James Doane, PhD, PE Contents 1.0 Course Oeriew... 4.0 Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics... 4.1 Temperature
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit.
 I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
+ m B1 = 1. u A1. u B1. - m B1 = V A. /v A = , u B1 + V B. = 5.5 kg => = V tot. Table B.1.
 5.6 A rigid tank is divided into two rooms by a membrane, both containing water, shown in Fig. P5.6. Room A is at 200 kpa, v = 0.5 m3/kg, VA = m3, and room B contains 3.5 kg at 0.5 MPa, 400 C. The membrane
5.6 A rigid tank is divided into two rooms by a membrane, both containing water, shown in Fig. P5.6. Room A is at 200 kpa, v = 0.5 m3/kg, VA = m3, and room B contains 3.5 kg at 0.5 MPa, 400 C. The membrane
First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems
 First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems Content The First Law of Thermodynamics Energy Balance Energy Change of a System Mechanisms of Energy Transfer First Law of Thermodynamics in Closed Systems Moving
First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems Content The First Law of Thermodynamics Energy Balance Energy Change of a System Mechanisms of Energy Transfer First Law of Thermodynamics in Closed Systems Moving
MAE 320 HW 7B. 1e. For an isolated system, please circle the parameter which will change with time. (a) Total energy;
 MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems
 Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
Chapter 4. Energy Analysis of Closed Systems
 Chapter 4 Energy Analysis of Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics is an expression of the conservation of energy principle. Energy can cross the boundaries of a closed system in the form of heat
Chapter 4 Energy Analysis of Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics is an expression of the conservation of energy principle. Energy can cross the boundaries of a closed system in the form of heat
ME 200 Final Exam December 12, :00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m.
 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 1:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. Mongia Abraham Sojka Bae Naik ME 200 Final Exam December 12, 2011 8:00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m. INSTRUCTIONS
CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 1:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. Mongia Abraham Sojka Bae Naik ME 200 Final Exam December 12, 2011 8:00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m. INSTRUCTIONS
PROBLEMS
 PROBLEMS------------------------------------------------ - 7- Thermodynamic Variables and the Eqation of State 1. Compter (a) the nmber of moles and (b) the nmber of molecles in 1.00 cm of an ideal gas
PROBLEMS------------------------------------------------ - 7- Thermodynamic Variables and the Eqation of State 1. Compter (a) the nmber of moles and (b) the nmber of molecles in 1.00 cm of an ideal gas
ME Thermodynamics I = = = 98.3% 1
 HW-08 (25 points) i) : a) 1 Since ν f < ν < ν g we conclude the state is a Saturated Liquid-Vapor Mixture (SLVM) 1, from the saturation tables we obtain p 3.6154 bar. 1 Calculating the quality, x: x ν
HW-08 (25 points) i) : a) 1 Since ν f < ν < ν g we conclude the state is a Saturated Liquid-Vapor Mixture (SLVM) 1, from the saturation tables we obtain p 3.6154 bar. 1 Calculating the quality, x: x ν
- Apply closed system energy balances, observe sign convention for work and heat transfer.
 CHAPTER : ENERGY AND THE FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Objectives: - In this chapter we discuss energy and develop equations for applying the principle of conservation of energy. Learning Outcomes: - Demonstrate
CHAPTER : ENERGY AND THE FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Objectives: - In this chapter we discuss energy and develop equations for applying the principle of conservation of energy. Learning Outcomes: - Demonstrate
First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems
 utorial # First Law of hermodynamics: Closed Systems Problem -7 A 0.-m tank contains oxygen initially at 00kPa and 7 C. A paddle wheel within the tank is rotated until the pressure inside rise to 50kPa.
utorial # First Law of hermodynamics: Closed Systems Problem -7 A 0.-m tank contains oxygen initially at 00kPa and 7 C. A paddle wheel within the tank is rotated until the pressure inside rise to 50kPa.
Dr Ali Jawarneh. Hashemite University
 Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University Examine the moving boundary work or P d work commonly encountered in reciprocating devices such as automotive engines and compressors.
Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University Examine the moving boundary work or P d work commonly encountered in reciprocating devices such as automotive engines and compressors.
Thermodynamics I Spring 1432/1433H (2011/2012H) Saturday, Wednesday 8:00am - 10:00am & Monday 8:00am - 9:00am MEP 261 Class ZA
 Thermodynamics I Spring 1432/1433H (2011/2012H) Saturday, Wednesday 8:00am - 10:00am & Monday 8:00am - 9:00am MEP 261 Class ZA Dr. Walid A. Aissa Associate Professor, Mech. Engg. Dept. Faculty of Engineering
Thermodynamics I Spring 1432/1433H (2011/2012H) Saturday, Wednesday 8:00am - 10:00am & Monday 8:00am - 9:00am MEP 261 Class ZA Dr. Walid A. Aissa Associate Professor, Mech. Engg. Dept. Faculty of Engineering
ME Thermodynamics I
 Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
Find: a) Mass of the air, in kg, b) final temperature of the air, in K, and c) amount of entropy produced, in kj/k.
 PROBLEM 6.25 Three m 3 of air in a rigid, insulated container fitted with a paddle wheel is initially at 295 K, 200 kpa. The air receives 1546 kj of work from the paddle wheel. Assuming the ideal gas model,
PROBLEM 6.25 Three m 3 of air in a rigid, insulated container fitted with a paddle wheel is initially at 295 K, 200 kpa. The air receives 1546 kj of work from the paddle wheel. Assuming the ideal gas model,
Analysis of Enthalpy Approximation for Compressed Liquid Water
 Analysis of Entalpy Approximation for Compressed Liqid Water Milioje M. Kostic e-mail: kostic@ni.ed Nortern Illinois Uniersity, DeKalb, IL 60115-2854 It is cstom to approximate solid and liqid termodynamic
Analysis of Entalpy Approximation for Compressed Liqid Water Milioje M. Kostic e-mail: kostic@ni.ed Nortern Illinois Uniersity, DeKalb, IL 60115-2854 It is cstom to approximate solid and liqid termodynamic
ME 200 Final Exam December 14, :00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m.
 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 11:30 a.m. Boregowda Boregowda Braun Bae 2:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Meyer Naik Hess ME 200 Final Exam December 14, 2015
CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 11:30 a.m. Boregowda Boregowda Braun Bae 2:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Meyer Naik Hess ME 200 Final Exam December 14, 2015
ME Thermodynamics I
 HW-03 (25 points) i) Given: for writing Given, Find, Basic equations Rigid tank containing nitrogen gas in two sections initially separated by a membrane. Find: Initial density (kg/m3) of nitrogen gas
HW-03 (25 points) i) Given: for writing Given, Find, Basic equations Rigid tank containing nitrogen gas in two sections initially separated by a membrane. Find: Initial density (kg/m3) of nitrogen gas
FINAL EXAM. ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW:
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
Dishwasher. Heater. Homework Solutions ME Thermodynamics I Spring HW-1 (25 points)
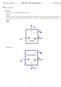 HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
12/21/2014 7:39 PM. Chapter 2. Energy and the 1st Law of Thermodynamics. Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 2 Energy and the 1st Law of Thermodynamics 1 2 Homework Assignment # 2 Problems: 1, 7, 14, 20, 30, 36, 42, 49, 56 Design and open end problem: 2.1D Due Monday 22/12/2014 3 Work and Kinetic Energy
Chapter 2 Energy and the 1st Law of Thermodynamics 1 2 Homework Assignment # 2 Problems: 1, 7, 14, 20, 30, 36, 42, 49, 56 Design and open end problem: 2.1D Due Monday 22/12/2014 3 Work and Kinetic Energy
Chapter 7: The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 7: he Second Law of hermodynamics he second law of thermodynamics asserts that processes occur in a certain direction and that the energy has quality as well as quantity he first law places no
Chapter 7: he Second Law of hermodynamics he second law of thermodynamics asserts that processes occur in a certain direction and that the energy has quality as well as quantity he first law places no
MAE 11. Homework 8: Solutions 11/30/2018
 MAE 11 Homework 8: Solutions 11/30/2018 MAE 11 Fall 2018 HW #8 Due: Friday, November 30 (beginning of class at 12:00p) Requirements:: Include T s diagram for all cycles. Also include p v diagrams for Ch
MAE 11 Homework 8: Solutions 11/30/2018 MAE 11 Fall 2018 HW #8 Due: Friday, November 30 (beginning of class at 12:00p) Requirements:: Include T s diagram for all cycles. Also include p v diagrams for Ch
To receive full credit all work must be clearly provided. Please use units in all answers.
 Exam is Open Textbook, Open Class Notes, Computers can be used (Computer limited to class notes, lectures, homework, book material, calculator, conversion utilities, etc. No searching for similar problems
Exam is Open Textbook, Open Class Notes, Computers can be used (Computer limited to class notes, lectures, homework, book material, calculator, conversion utilities, etc. No searching for similar problems
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes. by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
ME Thermodynamics I. Lecture Notes and Example Problems
 ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
 CHAPTER INTRODUCTION AND BASIC PRINCIPLES. (Tutorial). Determine if the following properties of the system are intensive or extensive properties: Property Intensive Extensive Volume Density Conductivity
CHAPTER INTRODUCTION AND BASIC PRINCIPLES. (Tutorial). Determine if the following properties of the system are intensive or extensive properties: Property Intensive Extensive Volume Density Conductivity
Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle
 ME 00 Thermodynamics I Spring 015 Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R.
ME 00 Thermodynamics I Spring 015 Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R.
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes Conservation Principles for Control volumes The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for open systems (or control volumes)
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes Conservation Principles for Control volumes The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for open systems (or control volumes)
ME 200 Exam 2 October 16, :30 p.m. to 7:30 p.m.
 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Solution Last Name 7:30 am 8:30 am 10:30 am 11:30 am Joglekar Bae Gore Abraham 1:30 pm 3:30 pm 4:30 pm Naik Naik Cheung ME 200 Exam 2 October 16, 2013 6:30 p.m. to
CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Solution Last Name 7:30 am 8:30 am 10:30 am 11:30 am Joglekar Bae Gore Abraham 1:30 pm 3:30 pm 4:30 pm Naik Naik Cheung ME 200 Exam 2 October 16, 2013 6:30 p.m. to
ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2015, Exam 3, 8 p.m. to 9 p.m. on April 14, 2015
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2015, Exam 3, 8 p.m. to 9 p.m. on April 14, 2015 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: 7:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 12:30 p.m. 2:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Joglekar Chen Chen Kittel Naik INSTRUCTIONS
ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2015, Exam 3, 8 p.m. to 9 p.m. on April 14, 2015 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: 7:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 12:30 p.m. 2:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Joglekar Chen Chen Kittel Naik INSTRUCTIONS
first law of ThermodyNamics
 first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
Where F1 is the force and dl1 is the infinitesimal displacement, but F1 = p1a1
 In order to force the fluid to flow across the boundary of the system against a pressure p1, work is done on the boundary of the system. The amount of work done is dw = - F1.dl1, Where F1 is the force
In order to force the fluid to flow across the boundary of the system against a pressure p1, work is done on the boundary of the system. The amount of work done is dw = - F1.dl1, Where F1 is the force
Chapter 3 First Law of Thermodynamics and Energy Equation
 Fundamentals of Thermodynamics Chapter 3 First Law of Thermodynamics and Energy Equation Prof. Siyoung Jeong Thermodynamics I MEE0-0 Spring 04 Thermal Engineering Lab. 3. The energy equation Thermal Engineering
Fundamentals of Thermodynamics Chapter 3 First Law of Thermodynamics and Energy Equation Prof. Siyoung Jeong Thermodynamics I MEE0-0 Spring 04 Thermal Engineering Lab. 3. The energy equation Thermal Engineering
(1)5. Which of the following equations is always valid for a fixed mass system undergoing an irreversible or reversible process:
 Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
First Law of Thermodynamics
 CH2303 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics I Unit II First Law of Thermodynamics Dr. M. Subramanian 07-July-2011 Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College
CH2303 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics I Unit II First Law of Thermodynamics Dr. M. Subramanian 07-July-2011 Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College
EVALUATING PROPERTIES FOR A PURE SUBSTANCES. By Ertanto Vetra
 EVALUATING PROPERTIES FOR A PURE SUBSTANCES 1 By Ertanto Vetra Outlines - TV, PV, PT, PVT Diagram - Property Tables - Introduction to Enthalpy - Reference State & Reference Values - Ideal Gas Equation
EVALUATING PROPERTIES FOR A PURE SUBSTANCES 1 By Ertanto Vetra Outlines - TV, PV, PT, PVT Diagram - Property Tables - Introduction to Enthalpy - Reference State & Reference Values - Ideal Gas Equation
SHRI RAMSWAROOP MEMORIAL COLLEGE OF ENGG. & MANAGEMENT
 B.Tech. [SEM III (ME-31, 32, 33,34,35 & 36)] QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour THERMODYNAMICS Max. Marks: 30 (EME-303) Note: Attempt All Questions. Q1) 2 kg of an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically from pressure
B.Tech. [SEM III (ME-31, 32, 33,34,35 & 36)] QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour THERMODYNAMICS Max. Marks: 30 (EME-303) Note: Attempt All Questions. Q1) 2 kg of an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically from pressure
Chapter 7. Entropy. by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
The First Law of Thermodynamics. By: Yidnekachew Messele
 The First Law of Thermodynamics By: Yidnekachew Messele It is the law that relates the various forms of energies for system of different types. It is simply the expression of the conservation of energy
The First Law of Thermodynamics By: Yidnekachew Messele It is the law that relates the various forms of energies for system of different types. It is simply the expression of the conservation of energy
1. (10) Calorically perfect ideal air at 300 K, 100 kpa, 1000 m/s, is brought to rest isentropically. Determine its final temperature.
 AME 5053 Intermediate Thermodynamics Examination Prof J M Powers 30 September 0 0 Calorically perfect ideal air at 300 K, 00 kpa, 000 m/s, is brought to rest isentropically Determine its final temperature
AME 5053 Intermediate Thermodynamics Examination Prof J M Powers 30 September 0 0 Calorically perfect ideal air at 300 K, 00 kpa, 000 m/s, is brought to rest isentropically Determine its final temperature
ME Thermodynamics I
 HW-6 (5 points) Given: Carbon dioxide goes through an adiabatic process in a piston-cylinder assembly. provided. Find: Calculate the entropy change for each case: State data is a) Constant specific heats
HW-6 (5 points) Given: Carbon dioxide goes through an adiabatic process in a piston-cylinder assembly. provided. Find: Calculate the entropy change for each case: State data is a) Constant specific heats
KNOWN: Pressure, temperature, and velocity of steam entering a 1.6-cm-diameter pipe.
 4.3 Steam enters a.6-cm-diameter pipe at 80 bar and 600 o C with a velocity of 50 m/s. Determine the mass flow rate, in kg/s. KNOWN: Pressure, temperature, and velocity of steam entering a.6-cm-diameter
4.3 Steam enters a.6-cm-diameter pipe at 80 bar and 600 o C with a velocity of 50 m/s. Determine the mass flow rate, in kg/s. KNOWN: Pressure, temperature, and velocity of steam entering a.6-cm-diameter
5/6/ :41 PM. Chapter 6. Using Entropy. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
PTT 277/3 APPLIED THERMODYNAMICS SEM 1 (2013/2014)
 PTT 77/3 APPLIED THERMODYNAMICS SEM 1 (013/014) 1 Energy can exist in numerous forms: Thermal Mechanical Kinetic Potential Electric Magnetic Chemical Nuclear The total energy of a system on a unit mass:
PTT 77/3 APPLIED THERMODYNAMICS SEM 1 (013/014) 1 Energy can exist in numerous forms: Thermal Mechanical Kinetic Potential Electric Magnetic Chemical Nuclear The total energy of a system on a unit mass:
ME 200 Exam 2 October 22, :30 p.m. to 7:30 p.m.
 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Solution Last Name 7:0 a.m. 8:0 a.m. 10:0 a.m. 11:0 a.m. Boregowda Boregowda Braun Bae :0 p.m. :0 p.m. 4:0 p.m. Meyer Naik Hess ME 00 Exam October, 015 6:0 p.m. to
CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Solution Last Name 7:0 a.m. 8:0 a.m. 10:0 a.m. 11:0 a.m. Boregowda Boregowda Braun Bae :0 p.m. :0 p.m. 4:0 p.m. Meyer Naik Hess ME 00 Exam October, 015 6:0 p.m. to
Week 5. Energy Analysis of Closed Systems. GENESYS Laboratory
 Week 5. Energy Analysis of Closed Systems Objectives 1. Examine the moving boundary work or PdV work commonly encountered in reciprocating devices such as automotive engines and compressors 2. Identify
Week 5. Energy Analysis of Closed Systems Objectives 1. Examine the moving boundary work or PdV work commonly encountered in reciprocating devices such as automotive engines and compressors 2. Identify
ME 201 Thermodynamics
 Spring 01 ME 01 Thermodynamics Property Evaluation Practice Problems II Solutions 1. Air at 100 K and 1 MPa goes to MPa isenthapically. Determine the entropy change. Substance Type: Ideal Gas (air) Process:
Spring 01 ME 01 Thermodynamics Property Evaluation Practice Problems II Solutions 1. Air at 100 K and 1 MPa goes to MPa isenthapically. Determine the entropy change. Substance Type: Ideal Gas (air) Process:
L = 2 λ 2 = λ (1) In other words, the wavelength of the wave in question equals to the string length,
 PHY 309 L. Soltions for Problem set # 6. Textbook problem Q.20 at the end of chapter 5: For any standing wave on a string, the distance between neighboring nodes is λ/2, one half of the wavelength. The
PHY 309 L. Soltions for Problem set # 6. Textbook problem Q.20 at the end of chapter 5: For any standing wave on a string, the distance between neighboring nodes is λ/2, one half of the wavelength. The
0.5 kpa (1000 Pa/kPa) *A. A = 70*9.81 N/500 N/m 2 = 1.37 m 2
 AREN 2110 Spring 2010 Homework #2: Due Friday, Jan 29, 6 PM Solutions 1. Consider a 70-kg woman who has a total footprint area of 400 cm2. She wishes to walk on the snow, but the snow cannot withstand
AREN 2110 Spring 2010 Homework #2: Due Friday, Jan 29, 6 PM Solutions 1. Consider a 70-kg woman who has a total footprint area of 400 cm2. She wishes to walk on the snow, but the snow cannot withstand
CHAPTER 2: THE NATURE OF ENERGY
 Principles of Engineering Thermodynamics st Edition Reisel Solutions Manual Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/principles-of-engineering-thermodynamics-st-edition-reisel-solutions-manual/
Principles of Engineering Thermodynamics st Edition Reisel Solutions Manual Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/principles-of-engineering-thermodynamics-st-edition-reisel-solutions-manual/
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA. PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS of THERMODYNAMICS NQF LEVEL 3 OUTCOME 2 -ENERGY TRANSFER
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS of THERMODYNAMICS NQF LEEL OUTCOME -ENERGY TRANSFER TUTORIAL - CLOSED THERMODYNAMIC SYSTEMS CONTENT Be able to quantify energy transfer
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS of THERMODYNAMICS NQF LEEL OUTCOME -ENERGY TRANSFER TUTORIAL - CLOSED THERMODYNAMIC SYSTEMS CONTENT Be able to quantify energy transfer
Chem 4501 Introduction to Thermodynamics, 3 Credits Kinetics, and Statistical Mechanics. Fall Semester Homework Problem Set Number 10 Solutions
 Chem 4501 Introdction to Thermodynamics, 3 Credits Kinetics, and Statistical Mechanics Fall Semester 2017 Homework Problem Set Nmber 10 Soltions 1. McQarrie and Simon, 10-4. Paraphrase: Apply Eler s theorem
Chem 4501 Introdction to Thermodynamics, 3 Credits Kinetics, and Statistical Mechanics Fall Semester 2017 Homework Problem Set Nmber 10 Soltions 1. McQarrie and Simon, 10-4. Paraphrase: Apply Eler s theorem
Chapter 7. Entropy: A Measure of Disorder
 Chapter 7 Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Entropy and the Clausius Inequality The second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of microscopic
Chapter 7 Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Entropy and the Clausius Inequality The second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of microscopic
Engineering Thermodynamics. Chapter 3. Energy Transport by Heat, Work and Mass
 Chapter 3 Energy Transport y Heat, ork and Mass 3. Energy of a System Energy can e viewed as the aility to cause change. Energy can exist in numerous forms such as thermal, mechanical, kinetic, potential,
Chapter 3 Energy Transport y Heat, ork and Mass 3. Energy of a System Energy can e viewed as the aility to cause change. Energy can exist in numerous forms such as thermal, mechanical, kinetic, potential,
Teaching schedule *15 18
 Teaching schedule Session *15 18 19 21 22 24 Topics 5. Gas power cycles Basic considerations in the analysis of power cycle; Carnot cycle; Air standard cycle; Reciprocating engines; Otto cycle; Diesel
Teaching schedule Session *15 18 19 21 22 24 Topics 5. Gas power cycles Basic considerations in the analysis of power cycle; Carnot cycle; Air standard cycle; Reciprocating engines; Otto cycle; Diesel
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Spring 2002
 10.213 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Spring 2002 Test 2 Solution Problem 1 (35 points) High pressure steam (stream 1) at a rate of 1000 kg/h initially at 3.5 MPa and 350 ºC is expanded in a turbine
10.213 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Spring 2002 Test 2 Solution Problem 1 (35 points) High pressure steam (stream 1) at a rate of 1000 kg/h initially at 3.5 MPa and 350 ºC is expanded in a turbine
Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore (21301jtsizemore) 1
 Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore 21301jtsizemore 1 This print-out should have 38 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering.
Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore 21301jtsizemore 1 This print-out should have 38 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering.
The first law of thermodynamics continued
 Lecture 7 The first law of thermodynamics continued Pre-reading: 19.5 Where we are The pressure p, volume V, and temperature T are related by an equation of state. For an ideal gas, pv = nrt = NkT For
Lecture 7 The first law of thermodynamics continued Pre-reading: 19.5 Where we are The pressure p, volume V, and temperature T are related by an equation of state. For an ideal gas, pv = nrt = NkT For
SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATIONS 2014/2015 ME258. Thermodynamics
 s SCHOOL OF COMPUING, ENGINEERING AND MAHEMAICS SEMESER EXAMINAIONS 04/05 ME58 hermodynamics ime allowed: WO hours Answer: Any FOUR Questions Items permitted: Any approved calculator Items supplied: Steam
s SCHOOL OF COMPUING, ENGINEERING AND MAHEMAICS SEMESER EXAMINAIONS 04/05 ME58 hermodynamics ime allowed: WO hours Answer: Any FOUR Questions Items permitted: Any approved calculator Items supplied: Steam
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS. B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A
 UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
Exergy and the Dead State
 EXERGY The energy content of the universe is constant, just as its mass content is. Yet at times of crisis we are bombarded with speeches and articles on how to conserve energy. As engineers, we know that
EXERGY The energy content of the universe is constant, just as its mass content is. Yet at times of crisis we are bombarded with speeches and articles on how to conserve energy. As engineers, we know that
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
Physics 111. Lecture 39 (Walker: 17.6, 18.2) Latent Heat Internal Energy First Law of Thermodynamics May 8, Latent Heats
 Physics 111 Lecture 39 (Walker: 17.6, 18.2) Latent Heat Internal Energy First Law of Thermodynamics May 8, 2009 Lecture 39 1/26 Latent Heats The heat required to convert from one phase to another is called
Physics 111 Lecture 39 (Walker: 17.6, 18.2) Latent Heat Internal Energy First Law of Thermodynamics May 8, 2009 Lecture 39 1/26 Latent Heats The heat required to convert from one phase to another is called
CHAPTER. The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems
 CHAPTER 3 The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems Closed system Energy can cross the boundary of a closed system in two forms: Heat and work FIGURE 3-1 Specifying the directions of heat and work.
CHAPTER 3 The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems Closed system Energy can cross the boundary of a closed system in two forms: Heat and work FIGURE 3-1 Specifying the directions of heat and work.
ME Thermodynamics I
 HW-22 (25 points) Given: 1 A gas power cycle with initial properties as listed on the EFD. The compressor pressure ratio is 25:1 Find: 1 Sketch all the processes on a p-h diagram and calculate the enthalpy,
HW-22 (25 points) Given: 1 A gas power cycle with initial properties as listed on the EFD. The compressor pressure ratio is 25:1 Find: 1 Sketch all the processes on a p-h diagram and calculate the enthalpy,
CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Çengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2015 CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES Lecture slides by Dr. Fawzi Elfghi
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Çengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2015 CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES Lecture slides by Dr. Fawzi Elfghi
Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas (2)
 1. This question is about thermodynamic processes. (a) Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas.......... An ideal gas is held in a container by a moveable
1. This question is about thermodynamic processes. (a) Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas.......... An ideal gas is held in a container by a moveable
GAS. Outline. Experiments. Device for in-class thought experiments to prove 1 st law. First law of thermodynamics Closed systems (no mass flow)
 Outline First law of thermodynamics Closed systems (no mass flow) Device for in-class thought experiments to prove 1 st law Rubber stops GAS Features: Quasi-equlibrium expansion/compression Constant volume
Outline First law of thermodynamics Closed systems (no mass flow) Device for in-class thought experiments to prove 1 st law Rubber stops GAS Features: Quasi-equlibrium expansion/compression Constant volume
Quasi Steady State Modelling of an Evaporator
 Qasi Steady State Modelling o an Evaporator Ed. Eitelberg NOY Bsiness 58 Baines Road, Drban 400, RSA controle@pixie.dw.ac.za Ed. Boje Electrical, Electronic & Compter Eng. University o Natal, Drban 404,
Qasi Steady State Modelling o an Evaporator Ed. Eitelberg NOY Bsiness 58 Baines Road, Drban 400, RSA controle@pixie.dw.ac.za Ed. Boje Electrical, Electronic & Compter Eng. University o Natal, Drban 404,
Lecture 40: Air standard cycle, internal combustion engines, Otto cycle
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I Spring 206 Lecture 40: Air standard cycle, internal combustion engines, Otto cycle Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan
ME 200 Thermodynamics I Spring 206 Lecture 40: Air standard cycle, internal combustion engines, Otto cycle Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan
LECTURE NOTE THERMODYNAMICS (GEC 221)
 LETURE NOTE ON THERMODYNAMIS (GE ) Thermodynamics is the branch of science that treats the arious phenomena of energy and related properties of matter especially the relationship between heat, work and
LETURE NOTE ON THERMODYNAMIS (GE ) Thermodynamics is the branch of science that treats the arious phenomena of energy and related properties of matter especially the relationship between heat, work and
III. Evaluating Properties. III. Evaluating Properties
 F. Property Tables 1. What s in the tables and why specific volumes, v (m /kg) (as v, v i, v f, v g ) pressure, P (kpa) temperature, T (C) internal energy, u (kj/kg) (as u, u i, u f, u g, u ig, u fg )
F. Property Tables 1. What s in the tables and why specific volumes, v (m /kg) (as v, v i, v f, v g ) pressure, P (kpa) temperature, T (C) internal energy, u (kj/kg) (as u, u i, u f, u g, u ig, u fg )
Thermodynamics I Chapter 2 Properties of Pure Substances
 Thermodynamics I Chapter 2 Properties of Pure Substances Mohsin Mohd Sies Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Properties of Pure Substances (Motivation) To quantify the changes
Thermodynamics I Chapter 2 Properties of Pure Substances Mohsin Mohd Sies Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Properties of Pure Substances (Motivation) To quantify the changes
CHAPTER 8 ENTROPY. Blank
 CHAPER 8 ENROPY Blank SONNAG/BORGNAKKE SUDY PROBLEM 8-8. A heat engine efficiency from the inequality of Clausius Consider an actual heat engine with efficiency of η working between reservoirs at and L.
CHAPER 8 ENROPY Blank SONNAG/BORGNAKKE SUDY PROBLEM 8-8. A heat engine efficiency from the inequality of Clausius Consider an actual heat engine with efficiency of η working between reservoirs at and L.
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES. The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial.
 THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 1 LIQUIDS VAPOURS - GASES SAE
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 1 LIQUIDS VAPOURS - GASES SAE
ECE309 THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER MIDTERM EXAMINATION. Instructor: R. Culham. Name: Student ID Number:
 ECE309 THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER MIDTERM EXAMINATION June 19, 2015 2:30 pm - 4:30 pm Instructor: R. Culham Name: Student ID Number: Instructions 1. This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. 2. Permitted
ECE309 THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER MIDTERM EXAMINATION June 19, 2015 2:30 pm - 4:30 pm Instructor: R. Culham Name: Student ID Number: Instructions 1. This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. 2. Permitted
ME 200 Thermodynamics 1 Spring Exam 2
 Last Name: First Name: Thermo no. ME 200 Thermodynamics 1 Sprg 2017 - Exam 2 Circle your structor s last name Ardekani Fisher Hess Naik Sojka (onle and on campus) INSTRUCTIONS This is a closed book and
Last Name: First Name: Thermo no. ME 200 Thermodynamics 1 Sprg 2017 - Exam 2 Circle your structor s last name Ardekani Fisher Hess Naik Sojka (onle and on campus) INSTRUCTIONS This is a closed book and
Energy Transport by. By: Yidnekachew Messele. Their sum constitutes the total energy E of a system.
 Energy Transport y Heat, ork and Mass By: Yidnekachew Messele Energy of a System Energy can e viewed as the aility to cause change. Energy can exist in numerous forms such as thermal, mechanical, kinetic,
Energy Transport y Heat, ork and Mass By: Yidnekachew Messele Energy of a System Energy can e viewed as the aility to cause change. Energy can exist in numerous forms such as thermal, mechanical, kinetic,
Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW SVCET
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW 1. What do you understand by pure substance? A pure substance is defined as one that is homogeneous and invariable in chemical composition
Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW 1. What do you understand by pure substance? A pure substance is defined as one that is homogeneous and invariable in chemical composition
ME 201 Thermodynamics
 Fall 204 ME 20 Thermodynamics Homework #8 Solutions. A rigid wall, insulated container is divided into two regions by a removable wall. One region contains 0. lb m of CO at 00 F, while the other region
Fall 204 ME 20 Thermodynamics Homework #8 Solutions. A rigid wall, insulated container is divided into two regions by a removable wall. One region contains 0. lb m of CO at 00 F, while the other region
Content. Entropy and principle of increasing entropy. Change of entropy in an ideal gas.
 Entropy Content Entropy and principle of increasing entropy. Change of entropy in an ideal gas. Entropy Entropy can be viewed as a measure of molecular disorder, or molecular randomness. As a system becomes
Entropy Content Entropy and principle of increasing entropy. Change of entropy in an ideal gas. Entropy Entropy can be viewed as a measure of molecular disorder, or molecular randomness. As a system becomes
ME 201 Thermodynamics
 ME 0 Thermodynamics Solutions First Law Practice Problems. Consider a balloon that has been blown up inside a building and has been allowed to come to equilibrium with the inside temperature of 5 C and
ME 0 Thermodynamics Solutions First Law Practice Problems. Consider a balloon that has been blown up inside a building and has been allowed to come to equilibrium with the inside temperature of 5 C and
Modeling Effort on Chamber Clearing for IFE Liquid Chambers at UCLA
 Modeling Effort on Chamber Clearing for IFE Liqid Chambers at UCLA Presented by: P. Calderoni own Meeting on IFE Liqid Wall Chamber Dynamics Livermore CA May 5-6 3 Otline his presentation will address
Modeling Effort on Chamber Clearing for IFE Liqid Chambers at UCLA Presented by: P. Calderoni own Meeting on IFE Liqid Wall Chamber Dynamics Livermore CA May 5-6 3 Otline his presentation will address
Consequences of Second Law of Thermodynamics. Entropy. Clausius Inequity
 onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
R13 SET - 1 '' ''' '' ' '''' Code No RT21033
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
Momentum Equation. Necessary because body is not made up of a fixed assembly of particles Its volume is the same however Imaginary
 Momentm Eqation Interest in the momentm eqation: Qantification of proplsion rates esign strctres for power generation esign of pipeline systems to withstand forces at bends and other places where the flow
Momentm Eqation Interest in the momentm eqation: Qantification of proplsion rates esign strctres for power generation esign of pipeline systems to withstand forces at bends and other places where the flow
Numerical Model for Studying Cloud Formation Processes in the Tropics
 Astralian Jornal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(2): 189-193, 211 ISSN 1991-8178 Nmerical Model for Stdying Clod Formation Processes in the Tropics Chantawan Noisri, Dsadee Skawat Department of Mathematics
Astralian Jornal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(2): 189-193, 211 ISSN 1991-8178 Nmerical Model for Stdying Clod Formation Processes in the Tropics Chantawan Noisri, Dsadee Skawat Department of Mathematics
UNIFIED ENGINEERING Fall 2003 Ian A. Waitz
 Ian A. Waitz Problem T6. (Thermodynamics) Consider the following thermodynamic cycle. Assume all processes are quasi-static and involve an ideal gas. 3 p Const. volume heat addition 2 adiabatic expansion
Ian A. Waitz Problem T6. (Thermodynamics) Consider the following thermodynamic cycle. Assume all processes are quasi-static and involve an ideal gas. 3 p Const. volume heat addition 2 adiabatic expansion
Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive
 Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
ENERGY ANALYSIS: CLOSED SYSTEM
 ENERGY ANALYSIS: CLOSED SYSTEM A closed system can exchange energy with its surroundings through heat and work transer. In other words, work and heat are the orms that energy can be transerred across the
ENERGY ANALYSIS: CLOSED SYSTEM A closed system can exchange energy with its surroundings through heat and work transer. In other words, work and heat are the orms that energy can be transerred across the
ME 2322 Thermodynamics I PRE-LECTURE Lesson 10 Complete the items below Name:
 Lesson 10 1. (5 pt) If P > P sat (T), the phase is a subcooled liquid. 2. (5 pt) if P < P sat (T), the phase is superheated vapor. 3. (5 pt) if T > T sat (P), the phase is superheated vapor. 4. (5 pt)
Lesson 10 1. (5 pt) If P > P sat (T), the phase is a subcooled liquid. 2. (5 pt) if P < P sat (T), the phase is superheated vapor. 3. (5 pt) if T > T sat (P), the phase is superheated vapor. 4. (5 pt)
Course: MECH-341 Thermodynamics II Semester: Fall 2006
 FINAL EXAM Date: Thursday, December 21, 2006, 9 am 12 am Examiner: Prof. E. Timofeev Associate Examiner: Prof. D. Frost READ CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU PROCEED: Course: MECH-341 Thermodynamics II Semester: Fall
FINAL EXAM Date: Thursday, December 21, 2006, 9 am 12 am Examiner: Prof. E. Timofeev Associate Examiner: Prof. D. Frost READ CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU PROCEED: Course: MECH-341 Thermodynamics II Semester: Fall
