Exergy and the Dead State
|
|
|
- Giles Chase
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EXERGY
2 The energy content of the universe is constant, just as its mass content is. Yet at times of crisis we are bombarded with speeches and articles on how to conserve energy. As engineers, we know that energy is already conserved. What is not conserved is exergy, which is the useful work potential of the energy. Once the exergy is wasted, it can never be recovered. When we use energy (to heat our homes, for example), we are not destroying any energy; we are merely converting it to a less useful form, a form of less exergy. Exergy and the Dead State The useful work potential of a system is the amount of energy we extract as useful work. The useful work potential of a system at the specified state is called exergy. Exergy is a property and is associated with the state of the system and the environment. A system that is in equilibrium with its surroundings has zero exergy and is said to be at the dead state. The exergy of the thermal energy of thermal reservoirs is equivalent to the work output of a Carnot heat engine operating between the reservoir and the environment.
3 Exergy Forms Now let s determine the exergy of various forms of energy. Exergy of kinetic energy Kinetic energy is a form of mechanical energy and can be converted directly into work. Kinetic energy itself is the work potential or exergy of kinetic energy independent of the temperature and pressure of the environment. Exergy of kinetic energy: Exergy of potential energy x ke ke V (kj/kg) Potential energy is a form of mechanical energy and can be converted directly into work. Potential energy itself is the work potential or exergy of potential energy independent of the temperature and pressure of the environment. Potential energy itself is the work potential or exergy of potential energy independent of the temperature and pressure of the environment. Exergy of potential energy: x pe gz pe (kj/kg) 3
4 Useful Work The work done by work producing devices is not always entirely in a useable form. Consider the piston-cylinder device shown in the following figure. The work done by the gas expanding in the piston-cylinder device is the boundary work and can be written as W P dv ( P P ) dv P dv W P dv b, useful
5 The actual work done by the gas is W W P dv b, useful 0 Wb, useful P0 V V1 ( ) The word done on the surroundings is Wsurr P0 dv P0 ( V V1 ) Any useful work delivered by a piston-cylinder device is due to the pressure above the atmospheric level. Reversible Work W W W u Reversible work W rev is defined as the maximum amount of useful work that can be produced (or the minimum work that needs to be supplied) as a system undergoes a process between the specified initial and final states. This is the useful work output (or input) obtained when the process between the initial and final states is executed in a totally reversible manner. Irreversibility The difference between the reversible work W rev and the useful work Wu is due to the irreversibilities present during the process and is called the irreversibility I. It is 5 equivalent to the exergy destroyed and is expressed as surr
6 Reversible Work Reversible work W rev is defined as the maximum amount of useful work that can be produced (or the minimum work that needs to be supplied) as a system undergoes a process between the specified initial and final states. This is the useful work output (or input) obtained when the process between the initial and final states is executed in a totally reversible manner. Irreversibility The difference between the reversible work W rev and the useful work Wu is due to the irreversibilities present during the process and is called the irreversibility I. It is equivalent to the exergy destroyed and is expressed as I Xdestroyed T0 Sgen Wrev, out Wu, out Wu, in Wrev, in where S gen is the entropy generated during the process. For a totally reversible process, the useful and reversible work terms are identical and thus irreversibility is zero. 6
7 Irreversibility can be viewed as the wasted work potential or the lost opportunity to do work. It represents the energy that could have been converted to work but was not. Exergy destroyed represents the lost work potential and is also called the wasted work or lost work. Second-Law Efficiency The second-law efficiency is a measure of the performance of a device relative to the performance under reversible conditions for the same end states and is given by For heat engines and other workproducing devices and For refrigerators, heat pumps, and other work-consuming devices. II th W W u th, rev rev COP II COP rev W W rev u 7
8 In general, the second-law efficiency is expressed as II Exergy recovered Exergy supplied 1 Exergy destroyed Exergy supplied Exergy of change of a system Consider heat transferred to or from a closed system whenever there is a temperature difference across the system boundary. The exergy for a system may be determined by considering how much of this heat transfer is converted to work entirely. Let s take a second look at the following figure. 8
9 Taking the heat transfer to be from the system to its surroundings, the conservation of energy is E E de in out system 0 Q W du The work is the boundary work and can be written as W P dv ( P P ) dv P dv W P dv b, useful Any useful work delivered by a piston-cylinder device is due to the pressure above the atmospheric level. To assure the reversibility of the process, the heat transfer occurs through a reversible heat engine. T W Q (1 ) Q Q T T Qnet Q ds T T W Q T ds 0 HE th 0 HE 0 Q W T ds HE 0 Q T 9
10 HE 0 b, useful 0 W T ds W P dv du W W W total useful b, useful HE du P dv T ds 0 0 Integrating from the given state (no subscript) to the dead state (0 subscript), we have W ( U U) P ( V V ) T ( S S) total useful ( U U ) P ( V V ) T ( S S ) This is the total useful work due to a system undergoing a reversible process from a given state to the dead state, which is the definition of exergy. Including the kinetic energy and potential energy, the exergy of a closed system is V X ( U U0) P0 ( V V0 ) T0 ( S S0) m mgz on a unit mass basis, the closed system (or nonflow) exergy is V ( u u0) P0 ( v v0 ) T0 ( s s0) gz ( e e ) P ( v v ) T ( s s )
11 Here, u 0, v 0, and s 0 are the properties of the system evaluated at the dead state. Note that the exergy of the internal energy of a system is zero at the dead state is zero since u = u 0, v = v 0, and s = s 0 at that state. The exergy change of a closed system during a process is simply the difference between the final and initial exergies of the system, X X X m( ) 1 1 ( E E ) P ( V V ) T ( S S ) V V1 ( U U0) P0 ( V V0 ) T0 ( S S0) m mg( z z1) On a unit mass basis the exergy change of a closed system is ( ) 1 ( e e ) P ( v v ) T ( s s ) V V1 ( u u0) P0 ( v v0 ) T0 ( s s0) g( z z1) 11
12 Exergy of flow The energy needed to force mass to flow into or out of a control volume is the flow work per unit mass given by: wflow Pv The exergy of flow work is the excess of flow work done against atmospheric air at P 0 to displace it by volume v. According to the above figure, the useful work potential due to flow work is w Pv P v flow, energy 0 1
13 Thus, the exergy of flow energy is Flow Exergy x Pv Pv ( P P ) v flow energy 0 0 Since flow energy is the sum of nonflow energy and the flow energy, the exergy of flow is the sum of the exergies of nonflow exergy and flow exergy. x x x flowing fluid nonflowing fluid flow exergy The flow (or stream) exergy is given by V ( u u0) P0 ( v v0 ) T0 ( s s0) gz ( P P0 ) v V ( u Pv) ( u0 P0 v0 ) T0 ( s s0) gz V ( h h0 ) T0 ( s s0) gz V ( h h0 ) T0 ( s s0) gz 13
14 The exergy of flow can be negative if the pressure is lower than atmospheric pressure. The exergy change of a fluid stream as it undergoes a process from state 1 to state is V V1 1 h h1 T0 s s1 g z z1 Exergy Transfer by Heat, Work, and Mass ( ) ( ) ( ) Exergy can be transferred by heat, work, and mass flow, and exergy transfer accompanied by heat, work, and mass transfer are given by the following. Exergy transfer by heat transfer By the second law we know that only a portion of heat transfer at a temperature above the environment temperature can be converted into work. The maximum useful work is produced from it by passing this heat transfer through a reversible heat engine. The exergy transfer by heat is Xheat 1 T T Exergy transfer by heat: 0 Q 14
15 Note in the above figure that entropy generation is always by exergy destruction and that heat transfer Q at a location at temperature T is always accompanied by entropy transfer in the amount of Q/T and exergy transfer in the amount of (1-T 0 /T)Q. Note that exergy transfer by heat is zero for adiabatic systems. 15
16 Exergy transfer by work Exergy is the useful work potential, and the exergy transfer by work can simply be expressed as Exergy transfer by work: X work W W W surr (for boundary work) (for other forms of work) where Wsurr P0 ( V V1 ), P 0 is atmospheric pressure, and V 1 and V are the initial and final volumes of the system. The exergy transfer for shaft work and electrical work is equal to the work W itself. Note that exergy transfer by work is zero for systems that have no work. Exergy transfer by mass Mass flow is a mechanism to transport exergy, entropy, and energy into or out of a system. As mass in the amount m enters or leaves a system the exergy transfer is given by Exergy transfer by mass: X mass m 16
17 Note that exergy transfer by mass is zero for systems that involve no flow. The Decrease of Exergy Principle and Exergy Destruction The exergy of an isolated system during a process always decreases or, in the limiting case of a reversible process, remains constant. This is known as the decrease of exergy principle and is expressed as Exergy Destruction X ( X X ) 0 isolated 1 isolated Irreversibilities such as friction, mixing, chemical reactions, heat transfer through finite temperature difference, unrestrained expansion, non-quasi-equilibrium compression, or expansion always generate entropy, and anything that generates entropy always destroys exergy. The exergy destroyed is proportional to the entropy generated as expressed as X T S destroyed 0 gen 17
18 The decrease of exergy principle does not imply that the exergy of a system cannot increase. The exergy change of a system can be positive or negative during a process, but exergy destroyed cannot be negative. The decrease of exergy principle can be summarized as follows: Exergy Balances X destroyed 0 Irreversible proces 0 Reversible process 0 Impossible process Exergy balance for any system undergoing any process can be expressed as General: Total Total Total Change in the exergy exergy exergy total exergy entering leaving destroyed of the system X X X X in out destroyed system General, rate form: Net exergy transfer Exergy Change by heat, work, and mass destruction in exergy X X X X in out destroyed system Rate of net exergy transfer Rate of exergy Rate of change by heat, work, and mass destruction of exergy 18
19 General, unit-mass basis: where ( x x ) x x in out destroyed system X X X heat work mass system T 1 T W useful m X dx / dt 0 system Q For a reversible process, the exergy destruction term, Xdestroyed, is zero. Considering the system to be a general control volume and taking the positive direction of heat transfer to be to the system and the positive direction of work transfer to be from the system, the general exergy balance relations can be expressed more explicitly as 1 T Q W P ( V V ) m m X X X i i ee Tk 0 k 0 1 destroyed 1 T dv dx 0 CV CV 1 Qk W P0 mii mee X destroyed Tk dt dt 19
20 where the subscripts are i = inlet, e = exit, 1 = initial state, and = final state of the system. For closed systems, no mass crosses the boundaries and we omit the terms containing the sum over the inlets and exits. Example 8-1 Oxygen gas is compressed in a piston-cylinder device from an initial state of 0.8 m 3 /kg and 5 o C to a final state of 0.1 m 3 /kg and 87 o C. Determine the reversible work input and the increase in the exergy of the oxygen during this process. Assume the surroundings to be at 5 o C and 100 kpa. We assume that oxygen is an ideal gas with constant specific heats. From Table A-, R = kj/kgk. The specific heat is determined at the average temperature T av T T (5 87) C 156 C (156 73)K 49K 1 Table A-(b) gives C v, ave = kj/kgk. 0
21 The entropy change of oxygen is T v s s1 Cv, ave ln R ln T v m 0.1 kj (87 73) K kj kg ln ln kg K (5 73) kg K m 0.8 kg kj kg K 3 K We calculate the reversible work input, which represents the minimum work input W rev,in in this case, from the exergy balance by setting the exergy destruction equal to zero. X X X X in out destroyed system Net exergy transfer Exergy Change by heat, work, and mass destruction in exergy W X X rev,in 1 1
22 Therefore, the change in exergy and the reversible work are identical in this case. Substituting the closed system exergy relation, the reversible work input during this process is determined to be w rev,in 1 ( u u ) P ( v v ) T ( s s ) C ( T T ) P ( v v ) T ( s s ) v,ave kj m kj 3 kg m kpa (87 5)K 100 kpa( ) kg K kj (5 73)K( ) kg K kj 14.1 kg The increase in exergy of the oxygen is kj x x1 1 wrev, in 14.1 kg
23 Example 8- Steam enters an adiabatic turbine at 6 MPa, 600C, and 80 m/s and leaves at 50 kpa, 100C, and 140 m/s. The surroundings to the turbine are at 5C. If the power output of the turbine is 5MW, determine (a)the power potential of the steam at its inlet conditions, in MW. (b) the reversible power, in MW. (c)the second law efficiency. We assume steady-flow and neglect changes in potential energy. 3
24 The mass flow rate of the steam is determined from the steady-flow energy equation applied to the actual process, Conservation of mass for the steady flow gives The work done by the turbine and the mass flow rate are E E E 0 (steady) in out systems Rate of net energy transfer Rate of change by heat, work, and mass of energy V1 V m1 ( h1 ) m ( h ) Wout 0 m m m in out system Rate of net mass transfer m m 1 m out ( h 1 h ) ke 1 Rate of change of mass 0 m m m V V Wout m ( h1 h ) W 1 4
25 where From the steam tables: V V ke 1 (140 m/s) (80 m/s) 1kJ/kg 1000m /s kj 6.6 kg kj h P1 6 MPa kg kj kg K kj h 68.4 P 50 kpa kg o T kj 100 C s kg K kj h0 h o f@5 C P0 100 kpa kg o T kj 0 5 C s0 s o f@5 C kg K o T1 600 C s 1 5
26 W m out ( h 1 h ) ke 5 MW 1000 kj/s kj ( ) MW kg kg 5.16 s The power potential of the steam at the inlet conditions is equivalent to its exergy at the inlet state. Recall that we neglect the potential energy of the flow. 0 V1 1 m 1 m ( h1 h0 ) T0 ( s1 s0) gz1 kj kj ( ) (98 K)( ) kg kg kg K s (80m/s) kj/kg 1000m /s kg kj MW s kg 1000 kj/s 7.91MW 6
27 The power output of the turbine if there are no irreversibilities is the reversible power and is determined from the rate form of the exergy balance applied on the turbine and setting the exergy destruction term equal to zero. W X X X X in out destroyed system Rate of net exergy transfer Rate of exergy Rate of change by heat, work, and mass destruction of exergy m( ) rev, out 1 X 0 0 (steady) in X out m W m 1 rev, out 0 m ( h h ) T ( s s ) ke pe W rev, out kj ( ) (98 K)( ) kg kg 5.16 s kj 6.6 kg kg kj MW s kg 1000 kj/s 5.81MW kj kg K 7
28 The second-law efficiency is determined from W 5MW II 86.1% W 5.81MW rev 8
Today lecture. 1. Entropy change in an isolated system 2. Exergy
 Today lecture 1. Entropy change in an isolated system. Exergy - What is exergy? - Reversible Work & Irreversibility - Second-Law Efficiency - Exergy change of a system For a fixed mass For a flow stream
Today lecture 1. Entropy change in an isolated system. Exergy - What is exergy? - Reversible Work & Irreversibility - Second-Law Efficiency - Exergy change of a system For a fixed mass For a flow stream
Chapter 7. Entropy. by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
Previous lecture. Today lecture
 Previous lecture ds relations (derive from steady energy balance) Gibb s equations Entropy change in liquid and solid Equations of & v, & P, and P & for steady isentropic process of ideal gas Isentropic
Previous lecture ds relations (derive from steady energy balance) Gibb s equations Entropy change in liquid and solid Equations of & v, & P, and P & for steady isentropic process of ideal gas Isentropic
5/6/ :41 PM. Chapter 6. Using Entropy. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY. Copyright Hany A. Al-Ansary and S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1
 CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
Chapter 8. The increased awareness that the world s energy EXERGY: A MEASURE OF WORK POTENTIAL. Objectives
 Chapter 8 EXERGY: A MEASURE OF WORK POTENTIAL The increased awareness that the world s energy resources are limited has caused many countries to reexamine their energy policies and take drastic measures
Chapter 8 EXERGY: A MEASURE OF WORK POTENTIAL The increased awareness that the world s energy resources are limited has caused many countries to reexamine their energy policies and take drastic measures
Chapter 7. Entropy: A Measure of Disorder
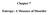 Chapter 7 Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Entropy and the Clausius Inequality The second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of microscopic
Chapter 7 Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Entropy and the Clausius Inequality The second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of microscopic
first law of ThermodyNamics
 first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
Where F1 is the force and dl1 is the infinitesimal displacement, but F1 = p1a1
 In order to force the fluid to flow across the boundary of the system against a pressure p1, work is done on the boundary of the system. The amount of work done is dw = - F1.dl1, Where F1 is the force
In order to force the fluid to flow across the boundary of the system against a pressure p1, work is done on the boundary of the system. The amount of work done is dw = - F1.dl1, Where F1 is the force
The First Law of Thermodynamics. By: Yidnekachew Messele
 The First Law of Thermodynamics By: Yidnekachew Messele It is the law that relates the various forms of energies for system of different types. It is simply the expression of the conservation of energy
The First Law of Thermodynamics By: Yidnekachew Messele It is the law that relates the various forms of energies for system of different types. It is simply the expression of the conservation of energy
First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems
 First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems Content The First Law of Thermodynamics Energy Balance Energy Change of a System Mechanisms of Energy Transfer First Law of Thermodynamics in Closed Systems Moving
First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems Content The First Law of Thermodynamics Energy Balance Energy Change of a System Mechanisms of Energy Transfer First Law of Thermodynamics in Closed Systems Moving
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit.
 I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Çengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2015 CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES Lecture slides by Dr. Fawzi Elfghi
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Çengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2015 CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES Lecture slides by Dr. Fawzi Elfghi
In the next lecture...
 16 1 In the next lecture... Solve problems from Entropy Carnot cycle Exergy Second law efficiency 2 Problem 1 A heat engine receives reversibly 420 kj/cycle of heat from a source at 327 o C and rejects
16 1 In the next lecture... Solve problems from Entropy Carnot cycle Exergy Second law efficiency 2 Problem 1 A heat engine receives reversibly 420 kj/cycle of heat from a source at 327 o C and rejects
UNIT I Basic concepts and Work & Heat Transfer
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
Dishwasher. Heater. Homework Solutions ME Thermodynamics I Spring HW-1 (25 points)
 HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
Chapter 6. Using Entropy
 Chapter 6 Using Entropy Learning Outcomes Demonstrate understanding of key concepts related to entropy and the second law... including entropy transfer, entropy production, and the increase in entropy
Chapter 6 Using Entropy Learning Outcomes Demonstrate understanding of key concepts related to entropy and the second law... including entropy transfer, entropy production, and the increase in entropy
First Law of Thermodynamics
 First Law of Thermodynamics During an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy gained by the system must be exactly equal to the amount of energy lost by the surroundings.
First Law of Thermodynamics During an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy gained by the system must be exactly equal to the amount of energy lost by the surroundings.
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems
 Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
 BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes. by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes Conservation Principles for Control volumes The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for open systems (or control volumes)
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes Conservation Principles for Control volumes The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for open systems (or control volumes)
Thermodynamics II. Week 9
 hermodynamics II Week 9 Example Oxygen gas in a piston cylinder at 300K, 00 kpa with volume o. m 3 is compressed in a reversible adiabatic process to a final temperature of 700K. Find the final pressure
hermodynamics II Week 9 Example Oxygen gas in a piston cylinder at 300K, 00 kpa with volume o. m 3 is compressed in a reversible adiabatic process to a final temperature of 700K. Find the final pressure
CHAPTER 8 ENTROPY. Blank
 CHAPER 8 ENROPY Blank SONNAG/BORGNAKKE SUDY PROBLEM 8-8. A heat engine efficiency from the inequality of Clausius Consider an actual heat engine with efficiency of η working between reservoirs at and L.
CHAPER 8 ENROPY Blank SONNAG/BORGNAKKE SUDY PROBLEM 8-8. A heat engine efficiency from the inequality of Clausius Consider an actual heat engine with efficiency of η working between reservoirs at and L.
The exergy of asystemis the maximum useful work possible during a process that brings the system into equilibrium with aheat reservoir. (4.
 Energy Equation Entropy equation in Chapter 4: control mass approach The second law of thermodynamics Availability (exergy) The exergy of asystemis the maximum useful work possible during a process that
Energy Equation Entropy equation in Chapter 4: control mass approach The second law of thermodynamics Availability (exergy) The exergy of asystemis the maximum useful work possible during a process that
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES. The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial.
 THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 2 THERMODYNAMIC PRINCIPLES SAE
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 2 THERMODYNAMIC PRINCIPLES SAE
ME Thermodynamics I. Lecture Notes and Example Problems
 ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
a) The minimum work with which this process could be accomplished b) The entropy generated during the process
 ENSC 46 Tutorial, Week#6 Exergy: Control Mass Analysis An insulated piston-cylinder device contains L of saturated liquid water at a pressure of 50 kpa which is constant throughout the process. An electric
ENSC 46 Tutorial, Week#6 Exergy: Control Mass Analysis An insulated piston-cylinder device contains L of saturated liquid water at a pressure of 50 kpa which is constant throughout the process. An electric
ME 2322 Thermodynamics I PRE-LECTURE Lesson 23 Complete the items below Name:
 Lesson 23 1. (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent Carnot
Lesson 23 1. (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent Carnot
Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy
 Definition of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy - Some definitions. - The zeroth law. - Properties of pure substances. - Ideal gas law. - Entropy and the second law. Some
Definition of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy - Some definitions. - The zeroth law. - Properties of pure substances. - Ideal gas law. - Entropy and the second law. Some
ME 2322 Thermodynamics I PRE-LECTURE Lesson 23 Complete the items below Name:
 Lesson 23 1. (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: T η = T 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent
Lesson 23 1. (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: T η = T 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent
Thermodynamics ENGR360-MEP112 LECTURE 7
 Thermodynamics ENGR360-MEP11 LECTURE 7 Thermodynamics ENGR360/MEP11 Objectives: 1. Conservation of mass principle.. Conservation of energy principle applied to control volumes (first law of thermodynamics).
Thermodynamics ENGR360-MEP11 LECTURE 7 Thermodynamics ENGR360/MEP11 Objectives: 1. Conservation of mass principle.. Conservation of energy principle applied to control volumes (first law of thermodynamics).
Lecture 29-30: Closed system entropy balance
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I Spring 2016 Lecture 29-30: Closed system entropy balance Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 200240, P.
ME 200 Thermodynamics I Spring 2016 Lecture 29-30: Closed system entropy balance Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 200240, P.
Consequences of Second Law of Thermodynamics. Entropy. Clausius Inequity
 onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Reading Problems 7-1 7-3 7-88, 7-131, 7-135 7-6 7-10 8-24, 8-44, 8-46, 8-60, 8-73, 8-99, 8-128, 8-132, 8-1 8-10, 8-13 8-135, 8-148, 8-152, 8-166, 8-168, 8-189
Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Reading Problems 7-1 7-3 7-88, 7-131, 7-135 7-6 7-10 8-24, 8-44, 8-46, 8-60, 8-73, 8-99, 8-128, 8-132, 8-1 8-10, 8-13 8-135, 8-148, 8-152, 8-166, 8-168, 8-189
(1)5. Which of the following equations is always valid for a fixed mass system undergoing an irreversible or reversible process:
 Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
Find: a) Mass of the air, in kg, b) final temperature of the air, in K, and c) amount of entropy produced, in kj/k.
 PROBLEM 6.25 Three m 3 of air in a rigid, insulated container fitted with a paddle wheel is initially at 295 K, 200 kpa. The air receives 1546 kj of work from the paddle wheel. Assuming the ideal gas model,
PROBLEM 6.25 Three m 3 of air in a rigid, insulated container fitted with a paddle wheel is initially at 295 K, 200 kpa. The air receives 1546 kj of work from the paddle wheel. Assuming the ideal gas model,
ME Thermodynamics I
 Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
Chapter 4. Energy Analysis of Closed Systems
 Chapter 4 Energy Analysis of Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics is an expression of the conservation of energy principle. Energy can cross the boundaries of a closed system in the form of heat
Chapter 4 Energy Analysis of Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics is an expression of the conservation of energy principle. Energy can cross the boundaries of a closed system in the form of heat
Spring_#8. Thermodynamics. Youngsuk Nam
 Spring_#8 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.krac kr Ch.7: Entropy Apply the second law of thermodynamics to processes. Define a new property called entropy to quantify the secondlaw effects. Establish
Spring_#8 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.krac kr Ch.7: Entropy Apply the second law of thermodynamics to processes. Define a new property called entropy to quantify the secondlaw effects. Establish
Availability and Irreversibility
 Availability and Irreversibility 1.0 Overview A critical application of thermodynamics is finding the maximum amount of work that can be extracted from a given energy resource. This calculation forms the
Availability and Irreversibility 1.0 Overview A critical application of thermodynamics is finding the maximum amount of work that can be extracted from a given energy resource. This calculation forms the
Isentropic Efficiency in Engineering Thermodynamics
 June 21, 2010 Isentropic Efficiency in Engineering Thermodynamics Introduction This article is a summary of selected parts of chapters 4, 5 and 6 in the textbook by Moran and Shapiro (2008. The intent
June 21, 2010 Isentropic Efficiency in Engineering Thermodynamics Introduction This article is a summary of selected parts of chapters 4, 5 and 6 in the textbook by Moran and Shapiro (2008. The intent
ME 300 Thermodynamics II Exam 1 September 27, :00 p.m. 9:00 p.m.
 ME 00 Thermodynamics II Exam 1 September 7, 01 8:00 p.m. 9:00 p.m. Name: Solution Section (Circle One): Sojka Naik 11:0 a.m. 1:0 p.m. Instructions: This is a closed book/notes exam. You may use a calculator.
ME 00 Thermodynamics II Exam 1 September 7, 01 8:00 p.m. 9:00 p.m. Name: Solution Section (Circle One): Sojka Naik 11:0 a.m. 1:0 p.m. Instructions: This is a closed book/notes exam. You may use a calculator.
Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I
 ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
Name: I have observed the honor code and have neither given nor received aid on this exam.
 ME 235 FINAL EXAM, ecember 16, 2011 K. Kurabayashi and. Siegel, ME ept. Exam Rules: Open Book and one page of notes allowed. There are 4 problems. Solve each problem on a separate page. Name: I have observed
ME 235 FINAL EXAM, ecember 16, 2011 K. Kurabayashi and. Siegel, ME ept. Exam Rules: Open Book and one page of notes allowed. There are 4 problems. Solve each problem on a separate page. Name: I have observed
Chapter 7. Dr Ali Jawarneh. Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University
 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University Objectives Apply the second law of thermodynamics to processes. Define a new property called entropy to quantify
Chapter 7 ENTROPY Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University Objectives Apply the second law of thermodynamics to processes. Define a new property called entropy to quantify
Consequences of Second Law of Thermodynamics. Entropy. Clausius Inequity
 onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive
 Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
ENT 254: Applied Thermodynamics
 ENT 54: Applied Thermodynamics Mr. Azizul bin Mohamad Mechanical Engineering Program School of Mechatronic Engineering Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) azizul@unimap.edu.my 019-4747351 04-9798679 Chapter
ENT 54: Applied Thermodynamics Mr. Azizul bin Mohamad Mechanical Engineering Program School of Mechatronic Engineering Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) azizul@unimap.edu.my 019-4747351 04-9798679 Chapter
Teaching schedule *15 18
 Teaching schedule Session *15 18 19 21 22 24 Topics 5. Gas power cycles Basic considerations in the analysis of power cycle; Carnot cycle; Air standard cycle; Reciprocating engines; Otto cycle; Diesel
Teaching schedule Session *15 18 19 21 22 24 Topics 5. Gas power cycles Basic considerations in the analysis of power cycle; Carnot cycle; Air standard cycle; Reciprocating engines; Otto cycle; Diesel
- Apply closed system energy balances, observe sign convention for work and heat transfer.
 CHAPTER : ENERGY AND THE FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Objectives: - In this chapter we discuss energy and develop equations for applying the principle of conservation of energy. Learning Outcomes: - Demonstrate
CHAPTER : ENERGY AND THE FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Objectives: - In this chapter we discuss energy and develop equations for applying the principle of conservation of energy. Learning Outcomes: - Demonstrate
c Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq (BUET) Entropy ME 203 (2017) 2 / 27 T037
 onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Fundamentals of Thermodynamics. Chapter 8. Exergy
 Fundamentals of Thermodynamics Chapter 8 Exergy Exergy Availability, available energy Anergy Unavailable energy Irreversible energy, reversible work, and irreversibility Exergy analysis : Pure Thermodynamics
Fundamentals of Thermodynamics Chapter 8 Exergy Exergy Availability, available energy Anergy Unavailable energy Irreversible energy, reversible work, and irreversibility Exergy analysis : Pure Thermodynamics
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals
 King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Mechanical Engineering Thermodynamics ME 04 BY Dr. Haitham Bahaidarah My Office Office Hours: :00 0:00 am SMW 03:00 04:00 pm UT Location: Building Room # 5.4
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Mechanical Engineering Thermodynamics ME 04 BY Dr. Haitham Bahaidarah My Office Office Hours: :00 0:00 am SMW 03:00 04:00 pm UT Location: Building Room # 5.4
Spring_#7. Thermodynamics. Youngsuk Nam.
 Spring_#7 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.kr You can t connect the dots looking forward; you can only connect them looking backwards. So you have to trust that the dots will somehow connect in
Spring_#7 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.kr You can t connect the dots looking forward; you can only connect them looking backwards. So you have to trust that the dots will somehow connect in
Lecture 7, 8 and 9 : Thermodynamic process by: Asst. lect. Karrar Al-Mansoori CONTENTS. 7) Thermodynamic process, path and cycle 2
 CONTENTS Topics pages 7) Thermodynamic process, path and cycle 8) Reversibility and irreversibility 4 9) Thermodynamic processes and calculation of work 5 9.: Constant pressure process or isobaric process
CONTENTS Topics pages 7) Thermodynamic process, path and cycle 8) Reversibility and irreversibility 4 9) Thermodynamic processes and calculation of work 5 9.: Constant pressure process or isobaric process
ME 300 Thermodynamics II
 ME 300 Thermodynamics II Prof. S. H. Frankel Fall 2006 ME 300 Thermodynamics II 1 Week 1 Introduction/Motivation Review Unsteady analysis NEW! ME 300 Thermodynamics II 2 Today s Outline Introductions/motivations
ME 300 Thermodynamics II Prof. S. H. Frankel Fall 2006 ME 300 Thermodynamics II 1 Week 1 Introduction/Motivation Review Unsteady analysis NEW! ME 300 Thermodynamics II 2 Today s Outline Introductions/motivations
MAE 320 HW 7B. 1e. For an isolated system, please circle the parameter which will change with time. (a) Total energy;
 MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER. 20 June 2005
 ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER 20 June 2005 Midterm Examination R. Culham & M. Bahrami This is a 90 minute, closed-book examination. You are permitted to use one 8.5 in. 11 in. crib
ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER 20 June 2005 Midterm Examination R. Culham & M. Bahrami This is a 90 minute, closed-book examination. You are permitted to use one 8.5 in. 11 in. crib
ME Thermodynamics I
 HW-03 (25 points) i) Given: for writing Given, Find, Basic equations Rigid tank containing nitrogen gas in two sections initially separated by a membrane. Find: Initial density (kg/m3) of nitrogen gas
HW-03 (25 points) i) Given: for writing Given, Find, Basic equations Rigid tank containing nitrogen gas in two sections initially separated by a membrane. Find: Initial density (kg/m3) of nitrogen gas
SHRI RAMSWAROOP MEMORIAL COLLEGE OF ENGG. & MANAGEMENT
 B.Tech. [SEM III (ME-31, 32, 33,34,35 & 36)] QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour THERMODYNAMICS Max. Marks: 30 (EME-303) Note: Attempt All Questions. Q1) 2 kg of an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically from pressure
B.Tech. [SEM III (ME-31, 32, 33,34,35 & 36)] QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour THERMODYNAMICS Max. Marks: 30 (EME-303) Note: Attempt All Questions. Q1) 2 kg of an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically from pressure
Introduction CHAPTER Prime Movers. 1.2 Sources of Energy
 Introduction CHAPTER 1 1.1 Prime Movers Prime mover is a device which converts natural source of energy into mechanical work to drive machines for various applications. In olden days, man had to depend
Introduction CHAPTER 1 1.1 Prime Movers Prime mover is a device which converts natural source of energy into mechanical work to drive machines for various applications. In olden days, man had to depend
IS A PARTICULAR PROCESS / REACTION FEASIBLE? TO WHAT EXTENT DOES THE PROCESS / REACTION PROCEED?
 Limitations of First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics is a law of conservation of energy. It does not specify the direction of the process. All spontaneous processes processed in one
Limitations of First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics is a law of conservation of energy. It does not specify the direction of the process. All spontaneous processes processed in one
Lecture 34: Exergy Analysis- Concept
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I Lecture 34: Exergy Analysis- Concept Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 200240, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
ME 200 Thermodynamics I Lecture 34: Exergy Analysis- Concept Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 200240, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
Lecture 38: Vapor-compression refrigeration systems
 ME 200 Termodynamics I Lecture 38: Vapor-compression refrigeration systems Yong Li Sangai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Cuan Road Sangai, 200240, P. R. Cina Email
ME 200 Termodynamics I Lecture 38: Vapor-compression refrigeration systems Yong Li Sangai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Cuan Road Sangai, 200240, P. R. Cina Email
This follows from the Clausius inequality as a consequence of the second law of thermodynamics. Therefore. (for reversible process only) (22.
 Entropy Clausius inequality can be used to analyze the cyclic process in a quantitative manner. The second law became a law of wider applicability when Clausius introduced the property called entropy.
Entropy Clausius inequality can be used to analyze the cyclic process in a quantitative manner. The second law became a law of wider applicability when Clausius introduced the property called entropy.
Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW SVCET
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW 1. What do you understand by pure substance? A pure substance is defined as one that is homogeneous and invariable in chemical composition
Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW 1. What do you understand by pure substance? A pure substance is defined as one that is homogeneous and invariable in chemical composition
= for reversible < for irreversible
 CHAPER 6 Entropy Copyright he McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. he Clausius Inequality: δ 0 Cyclic integral his inequality is valid for all cycles, reversible
CHAPER 6 Entropy Copyright he McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. he Clausius Inequality: δ 0 Cyclic integral his inequality is valid for all cycles, reversible
First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems
 utorial # First Law of hermodynamics: Closed Systems Problem -7 A 0.-m tank contains oxygen initially at 00kPa and 7 C. A paddle wheel within the tank is rotated until the pressure inside rise to 50kPa.
utorial # First Law of hermodynamics: Closed Systems Problem -7 A 0.-m tank contains oxygen initially at 00kPa and 7 C. A paddle wheel within the tank is rotated until the pressure inside rise to 50kPa.
CLAUSIUS INEQUALITY. PROOF: In Classroom
 Chapter 7 ENTROPY CLAUSIUS INEQUALITY PROOF: In Classroom 2 RESULTS OF CLAUSIUS INEQUALITY For internally reversible cycles δq = 0 T int rev For irreversible cycles δq < 0 T irr A quantity whose cyclic
Chapter 7 ENTROPY CLAUSIUS INEQUALITY PROOF: In Classroom 2 RESULTS OF CLAUSIUS INEQUALITY For internally reversible cycles δq = 0 T int rev For irreversible cycles δq < 0 T irr A quantity whose cyclic
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics. Chapter 7. KFUPM Housam Binous CHE 303
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Chapter 7 1 Thermodynamics of flow is based on mass, energy and entropy balances Fluid mechanics encompasses the above balances and conservation of momentum
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Chapter 7 1 Thermodynamics of flow is based on mass, energy and entropy balances Fluid mechanics encompasses the above balances and conservation of momentum
Week 2. Energy, Energy Transfer, And General Energy Analysis
 Week 2. Energy, Energy Transfer, And General Energy Analysis Objectives 1. Introduce the concept of energy and define its various forms 2. Discuss the nature of internal energy 3. Define the concept of
Week 2. Energy, Energy Transfer, And General Energy Analysis Objectives 1. Introduce the concept of energy and define its various forms 2. Discuss the nature of internal energy 3. Define the concept of
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, Chapter 7 ENTROPY
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Engineering Thermodynamics. Chapter 6. Entropy: a measure of Disorder 6.1 Introduction
 Engineering hermodynamics AAi Chapter 6 Entropy: a measure of Disorder 6. Introduction he second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of
Engineering hermodynamics AAi Chapter 6 Entropy: a measure of Disorder 6. Introduction he second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of
Chapter 5: Mass, Bernoulli, and Energy Equations
 Chapter 5: Mass, Bernoulli, and Energy Equations Introduction This chapter deals with 3 equations commonly used in fluid mechanics The mass equation is an expression of the conservation of mass principle.
Chapter 5: Mass, Bernoulli, and Energy Equations Introduction This chapter deals with 3 equations commonly used in fluid mechanics The mass equation is an expression of the conservation of mass principle.
Engineering Thermodynamics
 Engineering Thermodynamics Michael J. Moran Department of Mechanical Engineering The Ohio State University 2.1 Fundamentals...2-2 Basic Concepts and Definitions The First Law of Thermodynamics, Energy
Engineering Thermodynamics Michael J. Moran Department of Mechanical Engineering The Ohio State University 2.1 Fundamentals...2-2 Basic Concepts and Definitions The First Law of Thermodynamics, Energy
Content. Entropy and principle of increasing entropy. Change of entropy in an ideal gas.
 Entropy Content Entropy and principle of increasing entropy. Change of entropy in an ideal gas. Entropy Entropy can be viewed as a measure of molecular disorder, or molecular randomness. As a system becomes
Entropy Content Entropy and principle of increasing entropy. Change of entropy in an ideal gas. Entropy Entropy can be viewed as a measure of molecular disorder, or molecular randomness. As a system becomes
ME 354 THERMODYNAMICS 2 MIDTERM EXAMINATION. Instructor: R. Culham. Name: Student ID Number: Instructions
 ME 354 THERMODYNAMICS 2 MIDTERM EXAMINATION February 14, 2011 5:30 pm - 7:30 pm Instructor: R. Culham Name: Student ID Number: Instructions 1. This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. 2. Answer all questions
ME 354 THERMODYNAMICS 2 MIDTERM EXAMINATION February 14, 2011 5:30 pm - 7:30 pm Instructor: R. Culham Name: Student ID Number: Instructions 1. This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. 2. Answer all questions
 CHAPTER INTRODUCTION AND BASIC PRINCIPLES. (Tutorial). Determine if the following properties of the system are intensive or extensive properties: Property Intensive Extensive Volume Density Conductivity
CHAPTER INTRODUCTION AND BASIC PRINCIPLES. (Tutorial). Determine if the following properties of the system are intensive or extensive properties: Property Intensive Extensive Volume Density Conductivity
ENERGY TRANSFER BY WORK: Electrical Work: When N Coulombs of electrical charge move through a potential difference V
 Weight, W = mg Where m=mass, g=gravitational acceleration ENERGY TRANSFER BY WOR: Sign convention: Work done on a system = (+) Work done by a system = (-) Density, ρ = m V kg m 3 Where m=mass, V =Volume
Weight, W = mg Where m=mass, g=gravitational acceleration ENERGY TRANSFER BY WOR: Sign convention: Work done on a system = (+) Work done by a system = (-) Density, ρ = m V kg m 3 Where m=mass, V =Volume
ENTROPY. Chapter 7. Mehmet Kanoglu. Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition. Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles.
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Mehmet Kanoglu Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Mehmet Kanoglu Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required
Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle
 ME 00 Thermodynamics I Spring 015 Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R.
ME 00 Thermodynamics I Spring 015 Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R.
Engineering Thermodynamics. Chapter 5. The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 5.1 Introduction Chapter 5 The Second aw of Thermodynamics The second law of thermodynamics states that processes occur in a certain direction, not in just any direction. Physical processes in nature can
5.1 Introduction Chapter 5 The Second aw of Thermodynamics The second law of thermodynamics states that processes occur in a certain direction, not in just any direction. Physical processes in nature can
Review of First and Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Review of First and Second Law of Thermodynamics Reading Problems 4-1 4-4 4-32, 4-36, 4-87, 4-246 5-2 5-4, 5.7 6-1 6-13 6-122, 6-127, 6-130 Definitions SYSTEM: any specified collection of matter under
Review of First and Second Law of Thermodynamics Reading Problems 4-1 4-4 4-32, 4-36, 4-87, 4-246 5-2 5-4, 5.7 6-1 6-13 6-122, 6-127, 6-130 Definitions SYSTEM: any specified collection of matter under
Chapter One Reviews of Thermodynamics Update on 2013/9/13
 Chapter One Reviews of Thermodynamics Update on 2013/9/13 (1.1). Thermodynamic system An isolated system is a system that exchanges neither mass nor energy with its environment. An insulated rigid tank
Chapter One Reviews of Thermodynamics Update on 2013/9/13 (1.1). Thermodynamic system An isolated system is a system that exchanges neither mass nor energy with its environment. An insulated rigid tank
T098. c Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq (BUET) First Law of Thermodynamics ME 201 (2012) 2 / 26
 Conservation of Energy for a Closed System Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET Dhaka-, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Conservation of Energy for a Closed System Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET Dhaka-, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
+ m B1 = 1. u A1. u B1. - m B1 = V A. /v A = , u B1 + V B. = 5.5 kg => = V tot. Table B.1.
 5.6 A rigid tank is divided into two rooms by a membrane, both containing water, shown in Fig. P5.6. Room A is at 200 kpa, v = 0.5 m3/kg, VA = m3, and room B contains 3.5 kg at 0.5 MPa, 400 C. The membrane
5.6 A rigid tank is divided into two rooms by a membrane, both containing water, shown in Fig. P5.6. Room A is at 200 kpa, v = 0.5 m3/kg, VA = m3, and room B contains 3.5 kg at 0.5 MPa, 400 C. The membrane
THE FIRST LAW APPLIED TO STEADY FLOW PROCESSES
 Chapter 10 THE FIRST LAW APPLIED TO STEADY FLOW PROCESSES It is not the sun to overtake the moon, nor doth the night outstrip theday.theyfloateachinanorbit. The Holy Qur-ān In many engineering applications,
Chapter 10 THE FIRST LAW APPLIED TO STEADY FLOW PROCESSES It is not the sun to overtake the moon, nor doth the night outstrip theday.theyfloateachinanorbit. The Holy Qur-ān In many engineering applications,
1. (10) Calorically perfect ideal air at 300 K, 100 kpa, 1000 m/s, is brought to rest isentropically. Determine its final temperature.
 AME 5053 Intermediate Thermodynamics Examination Prof J M Powers 30 September 0 0 Calorically perfect ideal air at 300 K, 00 kpa, 000 m/s, is brought to rest isentropically Determine its final temperature
AME 5053 Intermediate Thermodynamics Examination Prof J M Powers 30 September 0 0 Calorically perfect ideal air at 300 K, 00 kpa, 000 m/s, is brought to rest isentropically Determine its final temperature
Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Entropy and the Second Law of hermodynamics Reading Problems 6-, 6-2, 6-7, 6-8, 6-6-8, 6-87, 7-7-0, 7-2, 7-3 7-39, 7-46, 7-6, 7-89, 7-, 7-22, 7-24, 7-30, 7-55, 7-58 Why do we need another law in thermodynamics?
Entropy and the Second Law of hermodynamics Reading Problems 6-, 6-2, 6-7, 6-8, 6-6-8, 6-87, 7-7-0, 7-2, 7-3 7-39, 7-46, 7-6, 7-89, 7-, 7-22, 7-24, 7-30, 7-55, 7-58 Why do we need another law in thermodynamics?
R13 SET - 1 '' ''' '' ' '''' Code No RT21033
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
7. Development of the 2nd Law
 7-1 7. Development of the 2nd Law 7.1 1st Law Limitations The 1 st Law describes energy accounting. Once we have a process (or string of processes) we can calculate the relevant energy interactions. The
7-1 7. Development of the 2nd Law 7.1 1st Law Limitations The 1 st Law describes energy accounting. Once we have a process (or string of processes) we can calculate the relevant energy interactions. The
Lecture Outline Chapter 18. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 18 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 18 The Laws of Thermodynamics Units of Chapter 18 The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermal Processes
Lecture Outline Chapter 18 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 18 The Laws of Thermodynamics Units of Chapter 18 The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermal Processes
FINAL EXAM. ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW:
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
KNOWN: Data are provided for a closed system undergoing a process involving work, heat transfer, change in elevation, and change in velocity.
 Problem 44 A closed system of mass of 10 kg undergoes a process during which there is energy transfer by work from the system of 0147 kj per kg, an elevation decrease of 50 m, and an increase in velocity
Problem 44 A closed system of mass of 10 kg undergoes a process during which there is energy transfer by work from the system of 0147 kj per kg, an elevation decrease of 50 m, and an increase in velocity
Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S.K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S.K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 12 Second Law and Available Energy III Good morning. I welcome you to this session.
Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S.K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 12 Second Law and Available Energy III Good morning. I welcome you to this session.
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011.
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Mehmet Kanoglu University of Gaziantep Copyright The McGraw-Hill
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Mehmet Kanoglu University of Gaziantep Copyright The McGraw-Hill
Answer Key THERMODYNAMICS TEST (a) 33. (d) 17. (c) 1. (a) 25. (a) 2. (b) 10. (d) 34. (b) 26. (c) 18. (d) 11. (c) 3. (d) 35. (c) 4. (d) 19.
 HERMODYNAMICS ES Answer Key. (a) 9. (a) 7. (c) 5. (a). (d). (b) 0. (d) 8. (d) 6. (c) 4. (b). (d). (c) 9. (b) 7. (c) 5. (c) 4. (d). (a) 0. (b) 8. (b) 6. (b) 5. (b). (d). (a) 9. (a) 7. (b) 6. (a) 4. (d).
HERMODYNAMICS ES Answer Key. (a) 9. (a) 7. (c) 5. (a). (d). (b) 0. (d) 8. (d) 6. (c) 4. (b). (d). (c) 9. (b) 7. (c) 5. (c) 4. (d). (a) 0. (b) 8. (b) 6. (b) 5. (b). (d). (a) 9. (a) 7. (b) 6. (a) 4. (d).
PROBLEM 6.3. Using the appropriate table, determine the indicated property. In each case, locate the state on sketches of the T-v and T-s diagrams.
 PROBLEM 63 Using the appropriate table, determine the indicated property In each case, locate the state on sketches of the -v and -s diagrams (a) water at p = 040 bar, h = 147714 kj/kg K Find s, in kj/kg
PROBLEM 63 Using the appropriate table, determine the indicated property In each case, locate the state on sketches of the -v and -s diagrams (a) water at p = 040 bar, h = 147714 kj/kg K Find s, in kj/kg
