Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive
|
|
|
- Doreen Bradford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization Intensive : viscosity, specific volume, pressure, Temperature, velocity, density, specific entropy, mole fraction, surface tension, elevation, Thermal conductivity, specific heat, refractive index, electrical conductivity, Type A Question 1. Which of the following is correct? A. Gauge pressure = Absolute pressure- Atmospheric pressure B. Gauge pressure = Absolute pressure + Atmospheric pressure C. Atmospheric pressure = Gauge pressure + Absolute pressure D. Absolute pressure = Gauge pressure - Atmospheric pressure 2. The Work done in a free expansion (Unrestrained expansion) or Throttling process is? A. Zero B. Maximum C. Positive D. Minimum 3. A system does not work even when heat is added to it. Which of the following may happen to the system? A. The system expands B. The internal energy of the system increases C. Both A and B D. Neither A nor B 4. Which of the following is a pure substance? A. Iron B. Gasoline C. Cow s milk D. Sea water 5. Which one of the following expresses the reversible work done by the system (steady flow)? A. pdv B. - vdp C. - pdv D. vdp 6. Consider the following statements: 1. Zeroth law of thermodynamics is related to measurement of temperature 2. Entropy is related to first law of thermodynamics 3. Internal energy of an ideal gas is a function of temperature and pressure Which of the above statements is/are correct? A. 1 only B. 2 and 3 1
2 C. 1 and 3 D. 2 only 7. Match List-I (Parameter) with List-II (Property) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists: List-I List-II A. Volume 1. Path function B. Density 2. Intensive property C. Pressure 3. Extensive property D. Work 4. Point function A B C D A B C D Carnot cycle refrigerator operate between 250K and 300K, the COP is? A. 6 B. 5 C. 1.2 D What is the efficiency of a heat engine that operates between reservoirs oftemperatures as 1400 K and 1000K? A. 4% B % C % D. 40% 10. A Refrigerator & Heat pump operate between the same Temperature limits. If COP of the refrigerator is 4, the COP of heat pump would be: A. 3 B. 5 C. 4 D The higher temp limit of a Carnot engine is 773K while its lower temp limit is 400K less than this temperature, the efficiency of the Carnot engine is: A % B % C % D % 12. Consider a refrigerator and a heat pump working on the reversed Carnot cycle between the same temperature limits. which of the following is correct A. COP refrigerator = COP of heat pump B. COP refrigerator = COP of heat pump - 1 C. COP refrigerator = COP of heat pump + 1 2
3 D. COP refrigerator = inverse of COP of heat pump 13. A heat engine operating the source temperature at infinite C and rejecting heat at a ambient condition the efficiency of ideal hypothetical cycle (Carnot cycle ) can be A. less than 50% B. infinite % C. 100% D. must be less than 100% 12. If the thermal efficiency of Carnot engine is 0.20 The COP of a Carnot refrigerator working on same temperature limit A. 5 B. 4 C. 6 D Work done is zero for the following process A. constant volume B. free expansion C. throttling D. all of the above 14. The unit of energy in SI units is. A. Joulemeter B. Joule(Nm) C. Joulemeter D. Watt 15. The first law of thermodynamics for steady flow: A. Accounts for all energy entering and leaving a control volume B. Is an energy balance for a specified mass of fluid C. Is an expression of the conservation of linear momentum D. Is primarily concerned with heat transfer. 16. The absolute zero temperature is taken as? A C B K C. 0 F D K 17. Absolute zero pressure will occur A. at sea level B. when molecular momentum of the system becomes zero C. under vacuum conditions D. at a temperature of K 18. The following are examples of some intensive and extensive properties: 1. Pressure 2. Temperature 3. Volume 4. Velocity 5. Electric charge 6. Magnetisation 7. Viscosity 8. Potential energy. Which one of the following sets gives the correct combination of intensive and extensive properties? 3
4 Intensive Extensive A. 1,2,3,4 5,6,7,8 B. 1,3,5,7 2,4,6,8 C. 1,2,4,7 3,5,6,8 D. 2,3,6,8 1,4,5,7 19. It is the characteristic feature of Quasi-static process system? A. Infinite slowness B. Rapidity C. Stability D. Stationary existence 20. Which of the following are intensive properties? 1. Kinetic Energy 2. Specific Enthalpy 3. Pressure 4. Entropy Select the correct answer using the code given below: A. 1 and 3 B. 2 and 3 C. 1, 3 and 4 D. 2 and Air is compressed adiabatically in a steady flow process with negligible change in potential and kinetic energy. The Work done in the process is given by: A. Pdv B. + Pdv C. vdp D. + vdp 22. Consider the following properties: 1. Temperature 2. Viscosity 3. Specific entropy 4. Thermal conductivity, Which of the above properties of a system is/are intensive? A. 1 only B. 2 and 3 only C. 2, 3 and 4 only D. 1, 2, 3 and Which one of the following is the extensive property of a thermodynamic system? A. Volume B. Pressure C. Temperature D. Density 24. Consider the following properties: 1. Entropy 2. Viscosity 3. Temperature 4. Specific heat at constant volume 4
5 Which of the above properties of a system is/are extensive? A. 1 only B. 1 and 2 only C. 2, 3 and 4 D. 1, 2 and A closed thermodynamic system is one in which A. There is no energy or mass transfer across the boundary B. There is no mass transfer, but energy transfer exists C. There is no energy transfer, but mass transfer exists D. Both energy and mass transfer take place across the boundary, but the mass transfer is controlled by valves 26. Ice kept in a well-insulated thermo flask is an example of which system? A. Closed system B. Isolated systems C. Open system ` D. Non-flow adiabatic system 27. Measurement of temperature is based on... law of thermodynamics? A. Zeroth law of thermodynamics B. First law of thermodynamics C. Second law of thermodynamics D. Third law of thermodynamics 28. Consider the following statements: 1. Zeroth law of thermodynamics is related to temperature 2. Entropy is related to first law of thermodynamics 3. Internal energy of an ideal gas is a function of temperature and pressure Which of the above statements is/are correct? A. 1 only B. 2 and 3 C. 1 and 3 D. 2 only 29. Zeroth Law of thermodynamics states that A. Two thermodynamic systems are always in thermal equilibrium with each other. B. If two systems are in thermal equilibrium, then the third system will also be in thermal equilibrium with each other. C. Two systems not in thermal equilibrium with a third system are also not in thermal equilibrium with each other. D. When two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, they are in thermal equilibrium with each other. 30. Assertion (A): The change in heat and work cannot be expressed as difference between the end states. 5
6 Reason (R): Heat and work are both exact differentials. A. Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A B. Both A and R are individually true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A C. A is true but R is false D. A is false but R is true 31. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists: List-I List-II A. Reversible cycle 1. Measurement of temperature B. Mechanical work 2. Clapeyron equation C. Zeroth Law 3.Clausius Theorem D. Heat 4. High grade energy 5. 3rd law of thermodynamics 6. Inexact differential Codes: A B C D A B C D Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer: List-I List-II A. The entropy of a pure crystalline is zero at absolute zero temperature 1. 1 st law of thermodynamics B. Spontaneous processes occur in a certain direction 2. 2 nd law of thermodynamics C. If two bodies are in thermal equilibrium with a third body, 3. 3 rd law of thermodynamics then they are also in thermal equilibrium with each other D. The law of conservation of energy 4. 0 th law of thermodynamics. Codes: A B C D A B C D In free expansion of a gas between two equilibrium states, the work transfer involved A. Can be calculated by joining the two states on p-v coordinates by any path and estimating the area below B. Can be calculated by joining the two states by a quasi-static path and then finding the area below 6
7 C. Is zero D. Is equal to heat generated by friction during expansion 34. Thermodynamic work is the product of A. Two intensive properties B. Two extensive properties C. An intensive property and change in an extensive property D. An extensive property and change in an intensive property 35. For the expression pdv to represent the work, which of the following conditions should apply? A. The system is closed one and process takes place in non-flow system B. The process is non-quasi static C. The boundary of the system should not move in order that work may be transferred D. If the system is open one, it should be non-reversible 36. Match items in List-I (Process) with those in List-II (Characteristic) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists: List-I List-II A. Throttling process 1. No work done B. Isentropic process 2. No change in entropy C. Free expansion 3. Constant internal energy D. Isothermal process 4. Constant enthalpy Codes: A B C D A B C D The cyclic integral of this is zero A. Work Transfer B. Heat Transfer C. Temperature D. Latent Heat 38. Which of the following statement is true A. Specific volume is extensive property B. Intensive properties are independent on size of system and may vary from place to place within the system at any moment C. Work is extensive property D. Heat is intensive property 7
8 39. The processes occurring in open system which permit the transfer of mass to and from the system, are known as A. Flow processes B. Non-flow processes C. Adiabatic processes D. None of these 40. If Gauge pressure measured inside compressor is 12 bar what is absolute pressure in co compressor kn/m 2? A. 1200kN/m 2 B kN/m 2 C. 1300kN/m 2 D kN/m An adiabatic process is one in which A. No heat enters or leaves the gas B. The temperature of the gas changes C. The change in internal energy is equal to the mechanical work done D. All of these 42. Sum of internal energy (U) and the product of pressure and volume (p.v) is known as by? A. Work done B. Entropy C. Enthalpy D. Exergy 43. The value of 1 mm of Hg is equal to? A N/m 2 B N/m 2 C kn/m 2 D kn/m According to Kelvin-Planck's statement of second law of thermodynamics A. It is impossible to construct an engine working on a cyclic process, whose sole purpose is to convert heat energy into work B. It is possible to construct an engine working on a cyclic process, whose sole purpose is to convert heat energy into work C. It is impossible to construct a device which operates in a cyclic process and produces no effect other than the transfer of heat from a cold body to a hot body D. None of the above 45. Kelvin Planck's law deals with A. conservation of heat B. conservation of work C. conversion of heat into work 8
9 D. conversion from work into heat E. conservation of mass 46. A Fan is running in insulated room (Heat generation in a room is zero) the temperature of the room A. Will decrease with time B. Will increase with time C. Will constant D. May increase or Decrease 47. A process, in which the temperature of the working substance remains constant, is called A. Isobaric process B. Isothermal Process C. Adiabatic process D. Isenthalpic Process 48. PMM II violates the A. Clausius statement (It is also statement of second law) B. Kelvin- Plank statement C. First law D. Third law 49. Entropy of the universe is A. continuously increasing B. continuously decreasing C. zero D. constant 50. The efficiency of thermodynamic cycle cannot be infinite since it A. Violates the first law of thermodynamics B. Violates the second law of thermodynamics C. Violates the third law of thermodynamics D. Reject no heat 51. Which of the following gives the generalized equation for the First law of thermodynamics A. Q- W = ΔE B. Q- W = KE C. Q- W = Δh D. Q-W = ΔU 52. Which of the following is related to Zeroth law of thermodynamics... A. Introduces the concept of Internal Energy B. Provide basis for measurement of temperature C. Introduces the concept of Entropy, Exergy and Kelvin temperature scale D. Absolute zero pressure 9
10 53. Which of the following is related to First law of thermodynamics... A. Introduces the concept of Internal Energy B. Provide measurement of temperature C. Introduces the concept of Entropy, Exergy and Kelvin temperature scale D. Absolute zero pressure 54. Which of the following is related to Second law of thermodynamics... A. Introduces the concept of Internal Energy B. Provide measurement of temperature C. Introduces the concept of Entropy, Exergy D. Absolute zero temperature 55. Which of the following is related to Third law of thermodynamics... A. Introduces the concept of Internal Energy B. Provide basis for measurement of temperature C. Introduces the concept of Entropy, Exergy and Kelvin temperature scale D. Absolute zero temperature 56. Which of the following is the PMM of First kind (I) and It violates the...law of Thermodynamics A. A heat engine which produces energy from nothing and violates the first law B. A heat engine which produces energy from coal and violates the first law C. A heat engine which 100% convert the heat to 100% work and violates the Second law D. A heat engine which 100% heat to 100% work and violates the Third law 57. Which of the following is the PMM of Second kind (II) and It violates the...law of Thermodynamics A. A heat engine which produces energy from nothing and violates the first law B. A heat engine which produces energy from coal and violates the first law C. A heat engine which convert 100% heat to 100% work and violates the Second law D. A heat engine which 100% heat to 100% work and violates the first law 58. According to Clausis statement of second law of thermodynamics A. heat can't be transferred from low temperature source to high temperature source B. heat can be transferred for low temperature to high temperature source by using refrigeration cycle. C. heat can be transferred from low temperature to high temperature source if COP of process is more than unity D. heat can't be transferred from low temperature to high temperature source without the aid of external energy 59. Heat and work are A. point functions B. system properties C. path functions 10
11 D. intensive properties E. extensive properties. 60. Which of the following are path function A. Work and Heat B. Work and Pressure C. Volume and pressure D. Volume and temperature 61. Which of the following are not boundary phenomenon A. Heat Transfer B. Work Transfer C. Mass Transfer D. Change of temperature 62. A system consisting single phase is called A. Closed system B. Heterogeneous system C. Isolated system D. homogenous system 63. An open system is one in which A. mass does not cross boundaries of the system, though energy may do so B. neither mass nor energy crosses the boundaries of the system C. both energy and mass cross the boundaries of the system D. mass crosses the boundary but not the energy 64. An control volume (Open system) in which A. A fixed region in space B. A specified mass C. isolated system D. mass crosses the boundary but not the energy 65. Properties of substances like pressure, temperature and density, in thermodynamic coordinates are A. path functions B. point functions C. cyclic functions D. real functions 66. The door of a running refrigerator inside a room was left open. Which of the following statements is correct? A. The room will be cooled to the temperature inside the refrigerator. B. The room will be cooled very slightly. C. The room will be gradually warmed up. D. The temperature of the air in room will remain unaffected. E. any one of above is possible depending on the capacity. 11
12 67. During throttling process A. heat exchange does not take place B. no work is done by expanding steam C. there is no change of internal energy of steam D. all of the above 68. Barometric pressure is equal to A. 760 mm Hg B. zero mm Hg C mm Hg D. 100mm Hg. 69. An adiabatic wall is one which A. prevents thermal interaction B. permits thermal interaction C. encourages thermal interaction D. discourages thermal interaction 70. If a system after undergoing a series of processes, returns to the initial state then A. process is thermodynamically in equilibrium B. process is executed in closed system cycle C. its entropy will change due to irreversibility D. sum of heat and work transfer will be zero 71 Isochoric (Isometric) process is one in which A. no mechanical work is done by the system B. mass and energy transfer do not take placein a system C. Temperature of system remains constant D. very little mechanical work is done by the system 72 A closed system is one in which A. mass does not cross boundaries of the system, though energy may do so B. mass crosses the boundary but not the energy C. neither mass nor energy crosses the boundaries of the system D. both energy and mass cross the boundaries of the system 73. An isolated system is one in which A. mass does not cross boundaries of the system, though energy may do so B. neither mass nor energy crosses the boundaries of the system C. both energy and mass cross the boundaries of the system D. mass crosses the boundary but not the energy E. thermodynamic reactions do not occur. 74. Which law states that the internal energy of a gas is a function of temperature A. Charles' law B. Joule's law 12
13 C. Regnault's law D. Boyle's law 75.The amount of Heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water through 1degree C A. Specific heat at constant volume B. Specific heat at constant pressure C. Kilo calorie D. none of above 76. Keeping the limitations imposed by the second-law of thermodynamics in mind, choose the wrong statement below: A. A heat engine cannot have a thermal efficiency of 100%. B. For all reversible processes, the second-law efficiency is 100%. C. The second-law efficiency of a heat engine cannot be greater than its thermal efficiency. D. The second-law efficiency of a process is 100% if no entropy is generated during that process. E. The coefficient of performance of a refrigerator can be greater than Two insulated tanks containing ideal gases at different pressure and temperature are connected to each other and gases are allowed to mix. The process that occurs can be called A. Free expansion B. Constant enthalpy C. Constant internal energy D. Reversible adiabatic 78. A balloon containing an ideal gas is initially kept in an evacuated and insulated room. The balloon ruptures and the gas fills up the entire room. Which one of the following statements is TRUE at the end of above process? A. The internal energy of the gas decreases from its initial value, but the enthalpy remains constant B. The internal energy of the gas increases from its initial value, but the enthalpy remains constant C. Both internal energy and enthalpy of the gas remain constant 79. Some MCQ based on Temperature conversion and Identify the correct equation for conversion, COP of Heat pump, refrigerator and efficiency and application of SFEE Type B Question 1. A heat pump is absorbing heat from the cold outdoors at 5 C and supplying heat to a house at 22 C at a rate of 18,000 kj/h. If the power consumed by the heat pump is 2.5 kw, the coefficient of performance of the heat pump is A
14 B. 1.0 C. 2.0 D. 5.0 Hint: T L =5 ºC T H =22 ºC Q H =18000/3600 kj/s W in =2.5 "kw" COP=Q H /W in if Q H and work given then don't use Temp formula 2. The heat transfer, Q, the work done W and the change in internal energy U are all zero in the case of A. A rigid vessel containing steam at 150 C left in the atmosphere which is at 25 C. B. 1 kg of gas contained in an insulated cylinder expanding as the piston moves slowly outwards. C. A rigid vessel containing ammonia gas connected through a valve to an evacuated rigid vessel, the vessel, the valve and the connecting pipes being well insulated and the valve being opened and after a time, conditions through the two vessels becoming uniform. D. 1 kg of air flowing adiabatically from the atmosphere into a previously evacuated bottle. 3. A 2-kW electric resistance heater in a room is turned on and kept on for 30 min. The amount of energy transferred to the room by the heater is A. 1 kj B. 60 kj C kj D kj E kj Hint:We= 2 kj/s time=30*60 sec Wnet=We*time ΔE=0 Q - W = ΔE Type C Question 1. Following figure indicates an 14
15 A. Open system. B. Closed system C. Isolated system D. Adiabatic system 2. Following figure indicates an A. Open system. B. Closed system C. Isolated system D. Adiabatic system 2. Following figure indicates an A. Open system. B. Closed system C. Isolated system D. Adiabatic system 3. Following figure indicates an A. Open system. B. Closed system C. Control volume D. Adiabatic system 2. Following figure indicates an A. Open system. B. Closed system C. Isolated system D. Adiabatic system 4. A Fan is running in insulated room as shown in fig. the temperature of the room A. Will decrease with time B. Will increase with time C. Will constant D. May increase or Decrease Type D Question 1. A gas expands in a frictionless piston-cylinder arrangement. The expansion process is very slow, and is resisted by an ambient pressure of 100 kpa. During the expansion process, the pressure of the system (gas) remains constant at 300 kpa. The change in 15
16 volume of the gas is 0.01 m3. The maximum amount of work that could be utilized from the above process is: A. 0kJ B. 1kJ C. 2kJ D. 3kJ Hint W =p*(change in V) Pressure will be ambient 2. A carnot heat engine receives 500 kj per cycle from a high temperature source of 625 Cand rejects heat to a low temperature sink at 30 C. Determine a. thermal efficiency of this carnot engine b. Amount of heat rejected to the sink per cycle A % and 169 kj B % and 16.4 kj C % and 146 kj D % and 14.6 kj 3. A closed system undergoes a process 1-2 for which the value of W 1-2 &Q 1-2 are 50kJ +20kJ resp. If the system is returned to state 1& the Q 2-1 is -10kJ, the work is: A. -80kJ B. +40kJ C. -20kJ D. -40kJ i.e 20-10=50+W 2 therefore W 2 = An apple with an average mass of 0.18 kg and average specific heat of 3.65 kj/kg. C is cooled from 22 C to 5 C. The amount of heat transferred from the apple is A kj B kj C. -20kJ D kj C=3.65 kj/kg.k m=0.18 kg T1=22 C T2=5 C Q - W = Change in energy (du) du=m*c*(t2-t1) kj 5. Two Carnot heat engines are operating in series such that the heat sink of the first engine serves as the heat source of the second one. If the source temperature of the first engine is 1600 K and the sink temperature of the second engine is 300 K and the thermal efficiencies of both engines are the same, the temperature of the intermediate reservoir is A. 950 K 16
17 B. 693 K C. 860 K D. 473 K Hint: (1600 -T intermediate )/1600 = (T intermediate -300)/ T intermediate 6. In a closed system, volume changes from 1.5m3 to 4.5 m3 and heat addition is 2000 kj. Calculate the Work done, given the pressure volume relation as p ={V 2 }Where p is in kpa and V is in m 3 A kj B J C kj D J Integration of Pdv 17
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
Where F1 is the force and dl1 is the infinitesimal displacement, but F1 = p1a1
 In order to force the fluid to flow across the boundary of the system against a pressure p1, work is done on the boundary of the system. The amount of work done is dw = - F1.dl1, Where F1 is the force
In order to force the fluid to flow across the boundary of the system against a pressure p1, work is done on the boundary of the system. The amount of work done is dw = - F1.dl1, Where F1 is the force
UNIT I Basic concepts and Work & Heat Transfer
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
CHAPTER - 12 THERMODYNAMICS
 CHAPER - HERMODYNAMICS ONE MARK QUESIONS. What is hermodynamics?. Mention the Macroscopic variables to specify the thermodynamics. 3. How does thermodynamics differ from Mechanics? 4. What is thermodynamic
CHAPER - HERMODYNAMICS ONE MARK QUESIONS. What is hermodynamics?. Mention the Macroscopic variables to specify the thermodynamics. 3. How does thermodynamics differ from Mechanics? 4. What is thermodynamic
1. INTRODUCTION TO REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITION
 CHAPTER ONE 1. INTRODUCTION TO REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITION Refrigeration may be defined as the process of reducing and maintaining a temperature of a space or material below that of the surroundings.
CHAPTER ONE 1. INTRODUCTION TO REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITION Refrigeration may be defined as the process of reducing and maintaining a temperature of a space or material below that of the surroundings.
MAE 320 HW 7B. 1e. For an isolated system, please circle the parameter which will change with time. (a) Total energy;
 MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES
 Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES Thermodynamics is that branch of science which deals with energy transfer A system may be closed, open or isolated system
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES Thermodynamics is that branch of science which deals with energy transfer A system may be closed, open or isolated system
T H E R M O D Y N A M I C S M E
 T H E R M O D Y N A M I C S M E THERMODYNAMICS CONTENTS 1 BASIC CONCEPTS IN THERMODYNAMICS 2 TEMPERATURE 3 WORK AND HEAT TRANSFER Thermodynamic system, surroundings, universe, system boundary Types of
T H E R M O D Y N A M I C S M E THERMODYNAMICS CONTENTS 1 BASIC CONCEPTS IN THERMODYNAMICS 2 TEMPERATURE 3 WORK AND HEAT TRANSFER Thermodynamic system, surroundings, universe, system boundary Types of
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS. B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A
 UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
 BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
Chapter 7. Entropy. by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
R13 SET - 1 '' ''' '' ' '''' Code No RT21033
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
THERMODYNAMICS SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION MECHANICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL THERMODYNAMICS THERMODYNAMICS THERMODYNAMICS
 1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION MECHANICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL 2 Syllabus: Thermal Engineering (Thermodynamics) Properties of Pure Substances : p-v & P-T diagrams of pure substance like H 2
1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION MECHANICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL 2 Syllabus: Thermal Engineering (Thermodynamics) Properties of Pure Substances : p-v & P-T diagrams of pure substance like H 2
Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 20 Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy gases Entropy solids & liquids Heat engines Refrigerators Second law of thermodynamics 1. The efficiency of
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 20 Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy gases Entropy solids & liquids Heat engines Refrigerators Second law of thermodynamics 1. The efficiency of
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A
 ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A 1. What is meant by thermodynamics system? (A/M 2006) Thermodynamics system is defined as any space or matter or group of matter
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A 1. What is meant by thermodynamics system? (A/M 2006) Thermodynamics system is defined as any space or matter or group of matter
THERMODYNAMICS b) If the temperatures of two bodies are equal then they are said to be in thermal equilibrium.
 THERMODYNAMICS Important Points:. Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics: a) This law gives the concept of temperature. b) If the temperatures of two bodies are equal then they are said to be in thermal equilibrium.
THERMODYNAMICS Important Points:. Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics: a) This law gives the concept of temperature. b) If the temperatures of two bodies are equal then they are said to be in thermal equilibrium.
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES
 Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES Thermodynamics is that branch of science which deals with energy transfer A system may be closed, open or isolated system
Chapter 1: FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS AND VARIOUS THERMODYMIC PROCESSES Thermodynamics is that branch of science which deals with energy transfer A system may be closed, open or isolated system
Spring_#7. Thermodynamics. Youngsuk Nam.
 Spring_#7 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.kr You can t connect the dots looking forward; you can only connect them looking backwards. So you have to trust that the dots will somehow connect in
Spring_#7 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.kr You can t connect the dots looking forward; you can only connect them looking backwards. So you have to trust that the dots will somehow connect in
THERMODYNAMICS. Zeroth law of thermodynamics. Isotherm
 12 THERMODYNAMICS Zeroth law of thermodynamics Two systems separately in thermal equilibrium with a third system are in thermal equilibrium with each other. Isotherm It is the graph connecting pressure
12 THERMODYNAMICS Zeroth law of thermodynamics Two systems separately in thermal equilibrium with a third system are in thermal equilibrium with each other. Isotherm It is the graph connecting pressure
Downloaded from
 Chapter 12 (Thermodynamics) Multiple Choice Questions Single Correct Answer Type Q1. An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial state (figure). Four processes are adiabatic,
Chapter 12 (Thermodynamics) Multiple Choice Questions Single Correct Answer Type Q1. An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial state (figure). Four processes are adiabatic,
QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 INTRODUCTION. 2. State zeroth law of thermodynamics? Write its importance in thermodynamics.
 QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 INTRODUCTION 1. What do you mean by thermodynamic equilibrium? How does it differ from thermal equilibrium? [05 Marks, June-2015] 2. State zeroth law of thermodynamics? Write its importance
QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 INTRODUCTION 1. What do you mean by thermodynamic equilibrium? How does it differ from thermal equilibrium? [05 Marks, June-2015] 2. State zeroth law of thermodynamics? Write its importance
Reversibility, Irreversibility and Carnot cycle. Irreversible Processes. Reversible Processes. Carnot Cycle
 Reversibility, Irreversibility and Carnot cycle The second law of thermodynamics distinguishes between reversible and irreversible processes. If a process can proceed in either direction without violating
Reversibility, Irreversibility and Carnot cycle The second law of thermodynamics distinguishes between reversible and irreversible processes. If a process can proceed in either direction without violating
Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW SVCET
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW 1. What do you understand by pure substance? A pure substance is defined as one that is homogeneous and invariable in chemical composition
Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW 1. What do you understand by pure substance? A pure substance is defined as one that is homogeneous and invariable in chemical composition
Equivalence of Kelvin-Planck and Clausius statements
 Equivalence of Kelvin-Planck and Clausius statements Violation of Clausius statement Violation of Kelvin-Planck statement Violation of Kelvin-Planck statement Violation of Clausius statement Violation
Equivalence of Kelvin-Planck and Clausius statements Violation of Clausius statement Violation of Kelvin-Planck statement Violation of Kelvin-Planck statement Violation of Clausius statement Violation
First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems
 First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems Content The First Law of Thermodynamics Energy Balance Energy Change of a System Mechanisms of Energy Transfer First Law of Thermodynamics in Closed Systems Moving
First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems Content The First Law of Thermodynamics Energy Balance Energy Change of a System Mechanisms of Energy Transfer First Law of Thermodynamics in Closed Systems Moving
(1)5. Which of the following equations is always valid for a fixed mass system undergoing an irreversible or reversible process:
 Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
5/6/ :41 PM. Chapter 6. Using Entropy. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 621 213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS UNIT-I Basic Concept and First Law 1. What do you understand
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 621 213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS UNIT-I Basic Concept and First Law 1. What do you understand
Engineering Thermodynamics. Chapter 5. The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 5.1 Introduction Chapter 5 The Second aw of Thermodynamics The second law of thermodynamics states that processes occur in a certain direction, not in just any direction. Physical processes in nature can
5.1 Introduction Chapter 5 The Second aw of Thermodynamics The second law of thermodynamics states that processes occur in a certain direction, not in just any direction. Physical processes in nature can
S.E. (Chemical Engineering) (Second Semester)EXAMINATION, 2012 THERMODYNAMICS-I (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100
 Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4162]-189 S.E. (Chemical Engineering) (Second Semester)EXAMINATION, 2012 THERMODYNAMICS-I (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks
Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4162]-189 S.E. (Chemical Engineering) (Second Semester)EXAMINATION, 2012 THERMODYNAMICS-I (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks
SHRI RAMSWAROOP MEMORIAL COLLEGE OF ENGG. & MANAGEMENT
 B.Tech. [SEM III (ME-31, 32, 33,34,35 & 36)] QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour THERMODYNAMICS Max. Marks: 30 (EME-303) Note: Attempt All Questions. Q1) 2 kg of an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically from pressure
B.Tech. [SEM III (ME-31, 32, 33,34,35 & 36)] QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour THERMODYNAMICS Max. Marks: 30 (EME-303) Note: Attempt All Questions. Q1) 2 kg of an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically from pressure
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ESE TOPIC WISE OBJECTIVE SOLVED PAPER-I FROM (1995-2017) UPSC Engineering Services Examination State Engineering Service Examination & Public Sector Examination. IES MASTER PUBLICATION
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ESE TOPIC WISE OBJECTIVE SOLVED PAPER-I FROM (1995-2017) UPSC Engineering Services Examination State Engineering Service Examination & Public Sector Examination. IES MASTER PUBLICATION
Chapter 12. The Laws of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy of a system can be increased by Adding energy to the system Doing work
Chapter 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy of a system can be increased by Adding energy to the system Doing work
Niraj Sir THERMODYNAMICS
 THERMODYNAMICS Thermal Equilibrium:- Two systems are said to be in thermal equilibrium with each other if they have the same temperature. Thermo dynamical system:- An assembly of large numbers of particles
THERMODYNAMICS Thermal Equilibrium:- Two systems are said to be in thermal equilibrium with each other if they have the same temperature. Thermo dynamical system:- An assembly of large numbers of particles
ME Thermodynamics I. Lecture Notes and Example Problems
 ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics Heat Engines Heat engines use a temperature difference involving a high temperature (T H ) and a low temperature (T C ) to do mechanical work.
Chapter 11 Heat Engines and The Second Law of Thermodynamics Heat Engines Heat engines use a temperature difference involving a high temperature (T H ) and a low temperature (T C ) to do mechanical work.
MARIA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 MARIA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY ATTOOR ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (TWO MARK QUESTION BANK) UNIT 1 (BASIC COMCEPTS AND FIRST LAW) 1. Define the term thermal engineering. Thermal engineering
MARIA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY ATTOOR ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (TWO MARK QUESTION BANK) UNIT 1 (BASIC COMCEPTS AND FIRST LAW) 1. Define the term thermal engineering. Thermal engineering
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ESE TOPICWISE OBJECTIVE SOLVED PAPER-I FROM (1995-2018) UPSC Engineering Services Examination State Engineering Service Examination & Public Sector Examination. IES MASTER PUBLICATION
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ESE TOPICWISE OBJECTIVE SOLVED PAPER-I FROM (1995-2018) UPSC Engineering Services Examination State Engineering Service Examination & Public Sector Examination. IES MASTER PUBLICATION
Basic thermodynamics. heat to the high temperature reservoir.
 Consider a heat engine that is operating in a cyclic process takes heat (QH) from a high temperature reservoir & converts completely into work (W), violating the Kelvin Planck statement. Let the work W,
Consider a heat engine that is operating in a cyclic process takes heat (QH) from a high temperature reservoir & converts completely into work (W), violating the Kelvin Planck statement. Let the work W,
Chapter 20. Heat Engines, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics. Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 20 Heat Engines, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Dr. Armen Kocharian First Law of Thermodynamics Review Review: The first law states that a change in internal energy in a system can
Chapter 20 Heat Engines, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Dr. Armen Kocharian First Law of Thermodynamics Review Review: The first law states that a change in internal energy in a system can
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems
 Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy
 Definition of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy - Some definitions. - The zeroth law. - Properties of pure substances. - Ideal gas law. - Entropy and the second law. Some
Definition of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy - Some definitions. - The zeroth law. - Properties of pure substances. - Ideal gas law. - Entropy and the second law. Some
THERMODYNAMICS CONCEPTUAL PROBLEMS
 THERMODYNAMICS CONCEPTUAL PROBLEMS Q-01 Is the heat supplied to a system always equal to the increases in its internal energy? Ans Acc. to first law of thermo- dynamics If heat is supplied in such a manner
THERMODYNAMICS CONCEPTUAL PROBLEMS Q-01 Is the heat supplied to a system always equal to the increases in its internal energy? Ans Acc. to first law of thermo- dynamics If heat is supplied in such a manner
Chapter 7. Dr Ali Jawarneh. Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University
 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University Objectives Apply the second law of thermodynamics to processes. Define a new property called entropy to quantify
Chapter 7 ENTROPY Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University Objectives Apply the second law of thermodynamics to processes. Define a new property called entropy to quantify
CHAPTER 2 ENERGY INTERACTION (HEAT AND WORK)
 CHATER ENERGY INTERACTION (HEAT AND WORK) Energy can cross the boundary of a closed system in two ways: Heat and Work. WORK The work is done by a force as it acts upon a body moving in direction of force.
CHATER ENERGY INTERACTION (HEAT AND WORK) Energy can cross the boundary of a closed system in two ways: Heat and Work. WORK The work is done by a force as it acts upon a body moving in direction of force.
Lecture Outline Chapter 18. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 18 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 18 The Laws of Thermodynamics Units of Chapter 18 The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermal Processes
Lecture Outline Chapter 18 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 18 The Laws of Thermodynamics Units of Chapter 18 The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermal Processes
Content. Entropy and principle of increasing entropy. Change of entropy in an ideal gas.
 Entropy Content Entropy and principle of increasing entropy. Change of entropy in an ideal gas. Entropy Entropy can be viewed as a measure of molecular disorder, or molecular randomness. As a system becomes
Entropy Content Entropy and principle of increasing entropy. Change of entropy in an ideal gas. Entropy Entropy can be viewed as a measure of molecular disorder, or molecular randomness. As a system becomes
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I
 ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
Thermodynamic system is classified into the following three systems. (ii) Closed System It exchanges only energy (not matter) with surroundings.
 1 P a g e The branch of physics which deals with the study of transformation of heat energy into other forms of energy and vice-versa. A thermodynamical system is said to be in thermal equilibrium when
1 P a g e The branch of physics which deals with the study of transformation of heat energy into other forms of energy and vice-versa. A thermodynamical system is said to be in thermal equilibrium when
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes. by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
R13. II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) PART- A
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B) 2. Answer
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B) 2. Answer
A thermodynamic system is taken from an initial state X along the path XYZX as shown in the PV-diagram.
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Thermodynamics 1. The maximum efficiency of a heat engine that operates between temperatures of 1500 K in the firing chamber and 600 K in the exhaust chamber is most
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Thermodynamics 1. The maximum efficiency of a heat engine that operates between temperatures of 1500 K in the firing chamber and 600 K in the exhaust chamber is most
Chapter 12. The Laws of Thermodynamics. First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy of a system can be increased by Adding energy to the system Doing work
Chapter 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy of a system can be increased by Adding energy to the system Doing work
SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
 SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS 2 ND Law of Thermodynamics Puts a limitation on the conversion of some forms of energy Determines the scope of an energy conversion and if an energy conversion is possible
SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS 2 ND Law of Thermodynamics Puts a limitation on the conversion of some forms of energy Determines the scope of an energy conversion and if an energy conversion is possible
Unit D-2: List of Subjects
 ES312 Energy Transfer Fundamentals Unit D: The Second Law of Thermodynamics ROAD MAP... D-1: From First to Second Law D-2: Second Law of Thermodynamics Unit D-2: List of Subjects Second Law of Thermodynamics
ES312 Energy Transfer Fundamentals Unit D: The Second Law of Thermodynamics ROAD MAP... D-1: From First to Second Law D-2: Second Law of Thermodynamics Unit D-2: List of Subjects Second Law of Thermodynamics
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY. Copyright Hany A. Al-Ansary and S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1
 CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
7. Development of the 2nd Law
 7-1 7. Development of the 2nd Law 7.1 1st Law Limitations The 1 st Law describes energy accounting. Once we have a process (or string of processes) we can calculate the relevant energy interactions. The
7-1 7. Development of the 2nd Law 7.1 1st Law Limitations The 1 st Law describes energy accounting. Once we have a process (or string of processes) we can calculate the relevant energy interactions. The
Introduction to Aerospace Propulsion. Prof. Bhaskar Roy. Prof. A. M. Pradeep. Department of Aerospace Engineering
 Introduction to Aerospace Propulsion Prof. Bhaskar Roy Prof. A. M. Pradeep Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module No. # 01 Lecture No. # 11 Reversible and irreversible
Introduction to Aerospace Propulsion Prof. Bhaskar Roy Prof. A. M. Pradeep Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Module No. # 01 Lecture No. # 11 Reversible and irreversible
Physics 5D PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Fall 2013
 Print your name: Physics 5D PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Fall 2013 Real Exam is Wednesday December 11 Thimann Lecture 3 4:00-7:00 pm Closed book exam two 8.5x11 sheets of notes ok Note: Avogadro s number N A =
Print your name: Physics 5D PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Fall 2013 Real Exam is Wednesday December 11 Thimann Lecture 3 4:00-7:00 pm Closed book exam two 8.5x11 sheets of notes ok Note: Avogadro s number N A =
열과유체, 에너지와친해지기 KAIST 기계공학과정상권
 열과유체, 에너지와친해지기 KAIST 기계공학과정상권 이번시간에는! 열역학 - 세상을움직이는스마트한법칙 물과공기로움직이는기계 사라지지않는에너지 / 증가하는엔트로피 열역학 - 세상을움직이는스마트한법칙 KAIST 기계공학과정상권 [ 학습목차 ] Thermofluids Energy conservation principle Energy Work (boundary work)
열과유체, 에너지와친해지기 KAIST 기계공학과정상권 이번시간에는! 열역학 - 세상을움직이는스마트한법칙 물과공기로움직이는기계 사라지지않는에너지 / 증가하는엔트로피 열역학 - 세상을움직이는스마트한법칙 KAIST 기계공학과정상권 [ 학습목차 ] Thermofluids Energy conservation principle Energy Work (boundary work)
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems. Temperature, Heat & The First Law of Thermodynamics
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 18 Temperature, Heat & The First Law of Thermodynamics Equilibrium & temperature scales Thermal expansion Exchange of heat First law of thermodynamics Heat conduction
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 18 Temperature, Heat & The First Law of Thermodynamics Equilibrium & temperature scales Thermal expansion Exchange of heat First law of thermodynamics Heat conduction
T H E R M O D Y N A M I C S M T
 T H E R M O D Y N A M I C S M T THERMODYNAMICS AND RATE PROCESSES CONTENTS CHAPTER DESCRIPTION PAGE NO 1 Thermodynamics NOTES 1.1. Definitions 1 1.2. Laws of Thermodynamics 3 1.2.1. Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
T H E R M O D Y N A M I C S M T THERMODYNAMICS AND RATE PROCESSES CONTENTS CHAPTER DESCRIPTION PAGE NO 1 Thermodynamics NOTES 1.1. Definitions 1 1.2. Laws of Thermodynamics 3 1.2.1. Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
IS A PARTICULAR PROCESS / REACTION FEASIBLE? TO WHAT EXTENT DOES THE PROCESS / REACTION PROCEED?
 Limitations of First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics is a law of conservation of energy. It does not specify the direction of the process. All spontaneous processes processed in one
Limitations of First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics is a law of conservation of energy. It does not specify the direction of the process. All spontaneous processes processed in one
International Academy Invitational Tournament Keep the Heat Test Team Name. Team Number. Predicted Water Temp C
 International Academy Invitational Tournament Keep the Heat Test 2-4-2012 Team Name Team Number Predicted Water Temp C Circle the all of the correct answer to the below questions. One or more of the answers
International Academy Invitational Tournament Keep the Heat Test 2-4-2012 Team Name Team Number Predicted Water Temp C Circle the all of the correct answer to the below questions. One or more of the answers
Topics to be covered. Fundamental Concepts & Definitions: Thermodynamics; definition and scope. Microscopic
 time Class No Text/ Reference page Topics to be covered Fundamental Concepts & Definitions: Thermodynamics; definition and scope. Microscopic 1 and Macroscopic approaches. Engineering Thermodynamics Definition,,
time Class No Text/ Reference page Topics to be covered Fundamental Concepts & Definitions: Thermodynamics; definition and scope. Microscopic 1 and Macroscopic approaches. Engineering Thermodynamics Definition,,
Hence. The second law describes the direction of energy transfer in spontaneous processes
 * Heat and Work The first law of thermodynamics states that: Although energy has many forms, the total quantity of energy is constant. When energy disappears in one form, it appears simultaneously in other
* Heat and Work The first law of thermodynamics states that: Although energy has many forms, the total quantity of energy is constant. When energy disappears in one form, it appears simultaneously in other
Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas (2)
 1. This question is about thermodynamic processes. (a) Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas.......... An ideal gas is held in a container by a moveable
1. This question is about thermodynamic processes. (a) Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas.......... An ideal gas is held in a container by a moveable
First Law of Thermodynamics Basic Concepts
 236 7 PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 7 CHAPTER First Law of Thermodynamics Basic Concepts CONTENTS THERMODYNAMIC TERMS SYSTEM, BOUNDARY, SURROUNDINGS HOMOGENEOUS AND HETEROGENEOUS SYSTEMS TYPES OF THERMODYNAMIC SYSTEMS
236 7 PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY 7 CHAPTER First Law of Thermodynamics Basic Concepts CONTENTS THERMODYNAMIC TERMS SYSTEM, BOUNDARY, SURROUNDINGS HOMOGENEOUS AND HETEROGENEOUS SYSTEMS TYPES OF THERMODYNAMIC SYSTEMS
University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_21 Monday, November 26, 2007 Page 1
 University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_21 Monday, November 26, 2007 Page 1 Name: Date: 1. Let k be the Boltzmann constant. If the configuration of the molecules in a gas changes so that the multiplicity
University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_21 Monday, November 26, 2007 Page 1 Name: Date: 1. Let k be the Boltzmann constant. If the configuration of the molecules in a gas changes so that the multiplicity
Handout 12: Thermodynamics. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
 1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
CHAPTER 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
 CHAPTER 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 CHAPTER 6 -- The Second Law of Thermodynamics OUTCOME: Identify Valid (possible) Processes as those that satisfy both the first and
CHAPTER 6 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 CHAPTER 6 -- The Second Law of Thermodynamics OUTCOME: Identify Valid (possible) Processes as those that satisfy both the first and
Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore (21301jtsizemore) 1
 Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore 21301jtsizemore 1 This print-out should have 38 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering.
Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore 21301jtsizemore 1 This print-out should have 38 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering.
THERMODYNAMICS. Chapter Twelve MCQ I
 Chapter welve HERMODYNAMICS MCQ I. An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial state (Fig..). Four processes are adiabatic, isothermal, isobaric and isochoric. Out of,, and 4
Chapter welve HERMODYNAMICS MCQ I. An ideal gas undergoes four different processes from the same initial state (Fig..). Four processes are adiabatic, isothermal, isobaric and isochoric. Out of,, and 4
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6301-ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS
 SYED AMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE (Approved by the AICTE, New Delhi, Govt. of Tamilnadu and Affiliated to Anna University, chennai) Established in 1998 - An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution Dr. E.M.Abdullah
SYED AMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE (Approved by the AICTE, New Delhi, Govt. of Tamilnadu and Affiliated to Anna University, chennai) Established in 1998 - An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution Dr. E.M.Abdullah
Week 5. Energy Analysis of Closed Systems. GENESYS Laboratory
 Week 5. Energy Analysis of Closed Systems Objectives 1. Examine the moving boundary work or PdV work commonly encountered in reciprocating devices such as automotive engines and compressors 2. Identify
Week 5. Energy Analysis of Closed Systems Objectives 1. Examine the moving boundary work or PdV work commonly encountered in reciprocating devices such as automotive engines and compressors 2. Identify
first law of ThermodyNamics
 first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
Chapter 12 Thermodynamics
 Chapter 12 Thermodynamics 12.1 Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes System: definite quantity of matter with real or imaginary boundaries If heat transfer is impossible, the system is thermally
Chapter 12 Thermodynamics 12.1 Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes System: definite quantity of matter with real or imaginary boundaries If heat transfer is impossible, the system is thermally
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Name : THERMODYNAMICS Code : A30306 Class : II B. Tech I Semester Branch :
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Name : THERMODYNAMICS Code : A30306 Class : II B. Tech I Semester Branch :
ME 2322 Thermodynamics I PRE-LECTURE Lesson 23 Complete the items below Name:
 Lesson 23 1. (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: T η = T 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent
Lesson 23 1. (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: T η = T 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent
CONCEPTS AND DEFINITIONS. Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola
 CONCEPTS AND DEFINITIONS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS Science that involves design and analysis of devices and systems for energy conversion Deals with heat and work and
CONCEPTS AND DEFINITIONS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS Science that involves design and analysis of devices and systems for energy conversion Deals with heat and work and
Lecture 29-30: Closed system entropy balance
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I Spring 2016 Lecture 29-30: Closed system entropy balance Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 200240, P.
ME 200 Thermodynamics I Spring 2016 Lecture 29-30: Closed system entropy balance Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 200240, P.
Speed Distribution at CONSTANT Temperature is given by the Maxwell Boltzmann Speed Distribution
 Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
Dishwasher. Heater. Homework Solutions ME Thermodynamics I Spring HW-1 (25 points)
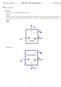 HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
ME 200 Final Exam December 12, :00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m.
 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 1:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. Mongia Abraham Sojka Bae Naik ME 200 Final Exam December 12, 2011 8:00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m. INSTRUCTIONS
CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 1:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. Mongia Abraham Sojka Bae Naik ME 200 Final Exam December 12, 2011 8:00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m. INSTRUCTIONS
Survey of Thermodynamic Processes and First and Second Laws
 Survey of Thermodynamic Processes and First and Second Laws Please select only one of the five choices, (a)-(e) for each of the 33 questions. All temperatures T are absolute temperatures. All experiments
Survey of Thermodynamic Processes and First and Second Laws Please select only one of the five choices, (a)-(e) for each of the 33 questions. All temperatures T are absolute temperatures. All experiments
Introduction CHAPTER Prime Movers. 1.2 Sources of Energy
 Introduction CHAPTER 1 1.1 Prime Movers Prime mover is a device which converts natural source of energy into mechanical work to drive machines for various applications. In olden days, man had to depend
Introduction CHAPTER 1 1.1 Prime Movers Prime mover is a device which converts natural source of energy into mechanical work to drive machines for various applications. In olden days, man had to depend
Chapter 4. Energy Analysis of Closed Systems
 Chapter 4 Energy Analysis of Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics is an expression of the conservation of energy principle. Energy can cross the boundaries of a closed system in the form of heat
Chapter 4 Energy Analysis of Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics is an expression of the conservation of energy principle. Energy can cross the boundaries of a closed system in the form of heat
Handout 12: Thermodynamics. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
 1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
11/22/11. If you add some heat to a substance, is it possible for the temperature of the substance to remain unchanged?
 Physics 101 Tuesday 11/22/11 Class 26" Chapter 17.2, 17.5, 17.6, 18.1, 18.2" Kinetic Theory" Latent Heat" Phase changes" 1 st law of thermodynamics" " Which one is not the assumption in kinetic theory
Physics 101 Tuesday 11/22/11 Class 26" Chapter 17.2, 17.5, 17.6, 18.1, 18.2" Kinetic Theory" Latent Heat" Phase changes" 1 st law of thermodynamics" " Which one is not the assumption in kinetic theory
Module - 1: Thermodynamics
 Thermodynamics: Module - : Thermodynamics Thermodynamics (Greek: thermos = heat and dynamic = change) is the study of the conversion of energy between heat and other forms, mechanical in particular. All
Thermodynamics: Module - : Thermodynamics Thermodynamics (Greek: thermos = heat and dynamic = change) is the study of the conversion of energy between heat and other forms, mechanical in particular. All
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes Conservation Principles for Control volumes The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for open systems (or control volumes)
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes Conservation Principles for Control volumes The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for open systems (or control volumes)
THERMODYNAMICS NOTES. These notes give a brief overview of engineering thermodynamics. They are based on the thermodynamics text by Black & Hartley.
 THERMODYNAMICS NOTES These notes give a brief overview of engineering thermodynamics. They are based on the thermodynamics text by Black & Hartley. Topics covered include: concepts; properties; conservation
THERMODYNAMICS NOTES These notes give a brief overview of engineering thermodynamics. They are based on the thermodynamics text by Black & Hartley. Topics covered include: concepts; properties; conservation
Basic Concepts S K Mondal s Chapter 1. Theory at a Glance (For GATE, IES & PSUs)
 Basic Concepts S K Mondal s Chapter. Basic Concepts heory at a Glance (For GAE, IES & PSUs) Intensive and Extensive Properties Intensive property: Whose value is independent of the size or extent i.e.
Basic Concepts S K Mondal s Chapter. Basic Concepts heory at a Glance (For GAE, IES & PSUs) Intensive and Extensive Properties Intensive property: Whose value is independent of the size or extent i.e.
Basic Thermodynamics Module 1
 Basic Thermodynamics Module 1 Lecture 9: Thermodynamic Properties of Fluids Thermodynamic Properties of fluids Most useful properties: Properties like pressure, volume and temperature which can be measured
Basic Thermodynamics Module 1 Lecture 9: Thermodynamic Properties of Fluids Thermodynamic Properties of fluids Most useful properties: Properties like pressure, volume and temperature which can be measured
Basic Thermodynamics. Prof. S. K. Som. Department of Mechanical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur.
 Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 06 Second Law and its Corollaries I Good afternoon, I welcome you all to this
Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S. K. Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 06 Second Law and its Corollaries I Good afternoon, I welcome you all to this
This follows from the Clausius inequality as a consequence of the second law of thermodynamics. Therefore. (for reversible process only) (22.
 Entropy Clausius inequality can be used to analyze the cyclic process in a quantitative manner. The second law became a law of wider applicability when Clausius introduced the property called entropy.
Entropy Clausius inequality can be used to analyze the cyclic process in a quantitative manner. The second law became a law of wider applicability when Clausius introduced the property called entropy.
Chapter 7. Entropy: A Measure of Disorder
 Chapter 7 Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Entropy and the Clausius Inequality The second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of microscopic
Chapter 7 Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Entropy and the Clausius Inequality The second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of microscopic
The first law of thermodynamics. U = internal energy. Q = amount of heat energy transfer
 Thermodynamics Investigation of the energy transfer by heat and work and how natural systems behave (Q) Heat transfer of energy due to temp differences. (W) Work transfer of energy through mechanical means.
Thermodynamics Investigation of the energy transfer by heat and work and how natural systems behave (Q) Heat transfer of energy due to temp differences. (W) Work transfer of energy through mechanical means.
The First Law of Thermodynamics. By: Yidnekachew Messele
 The First Law of Thermodynamics By: Yidnekachew Messele It is the law that relates the various forms of energies for system of different types. It is simply the expression of the conservation of energy
The First Law of Thermodynamics By: Yidnekachew Messele It is the law that relates the various forms of energies for system of different types. It is simply the expression of the conservation of energy
