SIMPLE RANKINE CYCLE. 3 expander. boiler. pump. condenser 1 W Q. cycle cycle. net. shaft
|
|
|
- Nigel Blair
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SIMPLE RANKINE CYCLE um boiler exander condener Steady Flow, Oen Sytem - region ace Steady Flow Energy Equation for Procee m (u Pum Proce,, Boiler Proce,, V ρg) 0, 0, Exanion Proce,, 0, Condener Proce,, 0, aft out out m m m ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) m Firt Law cycle cycle δ cycle cycle cycle δ net for Cycle cycle
2 ) ( ) ( ientroicroce VmR R IdealGaModel PROPERIES m m m u m u ysytem Unteadu gz V u m OenSytem E CloedSytem FIRSLA boundary o
3 CARNO CYCLE IH AER. C Carnot net H S L H L C net maximum at 0 C : net Carnot net.9 % 0. kj/kg maximum area H
4 SUPERHEA RANKINE CYCLE boiler um condener REHEA RANKINE CYCLE um boiler condener turbe
5 U Firt Law dq du dw dq d ubitiutg for dq and dw, d d ( du) ( d) ubitiutg for du, ( d d d) ( d) d d d for an adiabaticroce, d 0 d dw d u d du d d d d Second Law Boundary ork roerty defition, i an exact differential Examle: water umed from ia to 0 ia w ( ) ( 0ia ia) i/f w.lb/ft lbf 0 ft lbf w ft., (ft of fluid) lbm. lbm ft ft ft lbf BU w..0 BU/lb lb ft lb m Examle: water umed from 00 kpa to 00 kpa w ( ) w.000 m /kg w.0 m kg kpa, f m ( 00 kpa 00 kpa) kj/kg
6 A team ower lant run on a reeat cycle and roduce 0 M. e turbe let condition are 0 MPA, 00 C and MPA, 00 C. e condener oerate at 0 kpa. e efficiency of te turbe i 0%. e efficiency of te um i 9%. Determe: a) te turbe exit condition b) te cycle efficiency and c) te ma flow rate of te team. boiler 9% 0 MPa MPa 0 kpa 0% 9 0 condener turbe ex
7 A team ower lant run on a reeat cycle and roduce 0 M. e turbe let condition are 0 MPA, 00 C and MPA, 00 C. e condener oerate at 0 kpa. e efficiency of te turbe i 0%. e efficiency of te um i 9%. Determe: a) te turbe exit condition, b) te cycle efficiency and c) te ma flow rate of te team. Pt kpa 0 MPa 0 MPa 0 MPa 0 MPa MPa MPa MPa 0 kpa 0 kpa % 0 MPa MPa 0 kpa 0% ex
8 9-9 ex. J/kg MPa, 0. kj/kg.9 0) (0, kj/kg. 9.. kj/kg kj/kg MPa able A -, water, comreed liquid um um umactural actual um ideal um actual um ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) C) 90 9., (. kj/kg kj/kg x kpa, 90.0 kj/kg..... O at fg f 9
9 out d ( ) ( ) ( ) (. 0.9). kj/kg ( 0 ) (.9.) ( ) ( 0 ) um (. 90.0) ( 9..) d out net... net. cycle.0%. otal ork 0,000kJ/ec m Secific ork kj/kg kj/kg.. kg/ec 9-9 ex
10 EES Model
11
12 and deendent on at d FIRS LA LA δ δ Cycle CLOSED SYSEM quantity of ma E Proce δq du d Procee and for c, c, c, adiabatic, olytroic OPEN SYSEM V m (u Procee comreion, region ace gz) exanion, eat excanger, trottlg, diffuer, nozzle UNSEADY SYSEM unequal ma flow m u m u (m m ) Firt Law i an Energy Balance o boundary
13 PROPERIES Idealal Ga Model R room temerature cand c unieral ga contant R (.metric,.engli) molecular weigt R c c te ame unit Ientroic roce k k cln cln k k Rln Rln contant, 0, 0 Real Gae Steam, R a ABLES ma ga x ma mixture f x fg (alo u,,) - f x (alo u,,) ub cooled f Ideal Ga wit emerature deendent cand c ablea Pr Pr ablea roblem
14 SECOND LA PROCESS EFFICIENCY actual Heat Enge exanion roce benefit ork ientroic ideal ientroic effort ideal comreion roce out actual by Firt Law function ( ) CYCLE EFFICIENCY H, L H H CYCLE L L δ deendent of at roerty? FIRS ANDSECOND LAS COMBINED δ d du d 0 for reerible rocee > 0 for irreerible rocee S m > 0 iolated ytem, irreerible rocee out H L CARNO reerible H L COPrefrigerator out H L out H out COPeat um out H L
15 ermodynamic Problem Solg ecnique. Problem Statement Carbon dioxide i contaed a cylder wit a iton. e carbon dioxide i comreed wit eat remoal from, to,. e ga i ten eated from, to, at contant olume and ten exanded witout eat tranfer to te origal tate ot.. Scematic. Select ermodynamic Sytem oen - cloed - control olume a cloed termodynamic ytem comoed to te ma of carbon dioxide te cylder. Proerty Diagram tate ot - rocee - cycle,,,. Proerty Determation, u Concet Sytem Proertie State Pot Proce Cycle. Law of ermodynamic?? E? material flow? CO
1 = The rate at which the entropy of the high temperature reservoir changes, according to the definition of the entropy, is
 8-7 8-9 A reverible eat um wit eciied reervoir temerature i conidered. e entroy cange o two reervoir i to be calculated and it i to be determed i ti eat um atiie te creae entroy rcile. Aumtion e eat um
8-7 8-9 A reverible eat um wit eciied reervoir temerature i conidered. e entroy cange o two reervoir i to be calculated and it i to be determed i ti eat um atiie te creae entroy rcile. Aumtion e eat um
Kelvin Planck Statement of the Second Law. Clausius Statement of the Second Law
 Kelv Planck Statement of te Second aw It is imossible to construct an enge wic, oeratg a cycle, will roduce no oter effect tan te extraction of eat from a sgle reservoir and te erformance of an equivalent
Kelv Planck Statement of te Second aw It is imossible to construct an enge wic, oeratg a cycle, will roduce no oter effect tan te extraction of eat from a sgle reservoir and te erformance of an equivalent
NEWCOMEN ATMOSPHERIC ENGINE
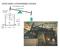 NECMEN AMSPERIC ENGINE atmoseric ressure Ford Museum, 760 strokes/m F 7 stroke 5 sia steam 8 50 F water NECMEN AMSPERIC ENGINE atmoseric ressure Ford Museum, 760 strokes/m 5 sia steam 8 F 50 F water 7
NECMEN AMSPERIC ENGINE atmoseric ressure Ford Museum, 760 strokes/m F 7 stroke 5 sia steam 8 50 F water NECMEN AMSPERIC ENGINE atmoseric ressure Ford Museum, 760 strokes/m 5 sia steam 8 F 50 F water 7
( )( ) 7 MPa q in = = 10 kpa q out. 1 h. = s. Thus, and = 38.9% (b) (c) The rate of heat rejection to the cooling water and its temperature rise are
 . A team poer plant operate on a imple ideal Ranke cycle beteen te peciied preure limit. e termal eiciency o te cycle, te ma lo rate o te team, and te temperature rie o te coolg ater are to be determed.
. A team poer plant operate on a imple ideal Ranke cycle beteen te peciied preure limit. e termal eiciency o te cycle, te ma lo rate o te team, and te temperature rie o te coolg ater are to be determed.
300 kpa 77 C. (d) If we neglect kinetic energy in the calculation of energy transport by mass
 6-6- Air flows steadily a ie at a secified state. The diameter of the ie, the rate of flow energy, and the rate of energy transort by mass are to be determed. Also, the error oled the determation of energy
6-6- Air flows steadily a ie at a secified state. The diameter of the ie, the rate of flow energy, and the rate of energy transort by mass are to be determed. Also, the error oled the determation of energy
Lecture 38: Vapor-compression refrigeration systems
 ME 200 Termodynamics I Lecture 38: Vapor-compression refrigeration systems Yong Li Sangai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Cuan Road Sangai, 200240, P. R. Cina Email
ME 200 Termodynamics I Lecture 38: Vapor-compression refrigeration systems Yong Li Sangai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Cuan Road Sangai, 200240, P. R. Cina Email
T Turbine 8. Boiler fwh fwh I Condenser 4 3 P II P I P III. (a) From the steam tables (Tables A-4, A-5, and A-6), = = 10 MPa. = 0.
 - - A team poer plant operate on an ideal regenerative anke cycle it to open feedater eater. e poer put of te poer plant and te termal efficiency of te cycle are to be determed. Aumption Steady operatg
- - A team poer plant operate on an ideal regenerative anke cycle it to open feedater eater. e poer put of te poer plant and te termal efficiency of te cycle are to be determed. Aumption Steady operatg
The average velocity of water in the tube and the Reynolds number are Hot R-134a
 hater 0:, 8, 4, 47, 50, 5, 55, 7, 75, 77, 8 and 85. 0- Refrigerant-4a is cooled by water a double-ie heat exchanger. he overall heat transfer coefficient is to be determed. Assumtions he thermal resistance
hater 0:, 8, 4, 47, 50, 5, 55, 7, 75, 77, 8 and 85. 0- Refrigerant-4a is cooled by water a double-ie heat exchanger. he overall heat transfer coefficient is to be determed. Assumtions he thermal resistance
Thermodynamics Lecture Series
 Termodynamics Lecture Series Ideal Ranke Cycle Te Practical Cycle Applied Sciences Education Researc Group (ASERG) Faculty of Applied Sciences Universiti Teknologi MARA email: drjjlanita@otmail.com ttp://www5.uitm.edu.my/faculties/fsg/drjj1.tml
Termodynamics Lecture Series Ideal Ranke Cycle Te Practical Cycle Applied Sciences Education Researc Group (ASERG) Faculty of Applied Sciences Universiti Teknologi MARA email: drjjlanita@otmail.com ttp://www5.uitm.edu.my/faculties/fsg/drjj1.tml
å Q d = 0 T dq =0 ò T reversible processes 1
 δ reeribe ree d Caiu Inequaity fr an Irreeribe Cye eeribe Cye fr a CaiuInequaity fr a yemed f a reeribe andan irreeribe re irre re Entry Definitin and Cange DEFINE A POPEY S S re irre S S S ENOPY reeribe
δ reeribe ree d Caiu Inequaity fr an Irreeribe Cye eeribe Cye fr a CaiuInequaity fr a yemed f a reeribe andan irreeribe re irre re Entry Definitin and Cange DEFINE A POPEY S S re irre S S S ENOPY reeribe
v v = = Mixing chamber: = 30 or, = s6 Then, and = 52.4% Turbine Boiler process heater Condenser 7 MPa Q in 0.6 MPa Q proces 10 kpa Q out
 0-0- A cogeneration plant i to generate poer and proce eat. art o te team extracted rom te turbe at a relatively ig preure i ued or proce eatg. e poer produced and te utilization actor o te plant are to
0-0- A cogeneration plant i to generate poer and proce eat. art o te team extracted rom te turbe at a relatively ig preure i ued or proce eatg. e poer produced and te utilization actor o te plant are to
First Name Last Name CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 1 10:30 am Div. 2 2:30 pm Div. 3 4:30 pm Prof. Gore Prof. Udupa Prof. Chen
 CIRCLE YOUR LECURE BELOW: Div. 1 10:30 am Div. :30 m Div. 3 4:30 m Prof. Gore Prof. Udua Prof. Chen EXAM # 3 INSRUCIONS 1. his is a closed book examination. All needed roerty tables are rovided.. Do not
CIRCLE YOUR LECURE BELOW: Div. 1 10:30 am Div. :30 m Div. 3 4:30 m Prof. Gore Prof. Udua Prof. Chen EXAM # 3 INSRUCIONS 1. his is a closed book examination. All needed roerty tables are rovided.. Do not
The Second Law implies:
 e Send Law ilie: ) Heat Engine η W in H H L H L H, H H ) Ablute eerature H H L L Sale, L L W ) Fr a yle H H L L H 4) Fr an Ideal Ga Cyle H H L L L δ reerible ree d Claiu Inequality δ eerible Cyle fr a
e Send Law ilie: ) Heat Engine η W in H H L H L H, H H ) Ablute eerature H H L L Sale, L L W ) Fr a yle H H L L H 4) Fr an Ideal Ga Cyle H H L L L δ reerible ree d Claiu Inequality δ eerible Cyle fr a
8-4 P 2. = 12 kw. AIR T = const. Therefore, Q &
 8-4 8-4 Air i compreed teadily by a compreor. e air temperature i mataed contant by eat rejection to te urroundg. e rate o entropy cange o air i to be determed. Aumption i i a teady-low proce ce tere i
8-4 8-4 Air i compreed teadily by a compreor. e air temperature i mataed contant by eat rejection to te urroundg. e rate o entropy cange o air i to be determed. Aumption i i a teady-low proce ce tere i
Solutions to Homework #10
 Solution to Homeork #0 0-6 A teady-lo Carnot enge it ater a te orkg luid operate at peciied condition. e termal eiciency, te preure at te turbe let, and te ork put are to be determed. Aumption Steady operatg
Solution to Homeork #0 0-6 A teady-lo Carnot enge it ater a te orkg luid operate at peciied condition. e termal eiciency, te preure at te turbe let, and te ork put are to be determed. Aumption Steady operatg
Problem 1 The turbine is an open system. We identify the steam contained the turbine as the control volume. dt + + =
 ME Fall 8 HW olution Problem he turbe i an open ytem. We identiy the team contaed the turbe a the control volume. Ma conervation: t law o thermodynamic: Aumption: dm m m m dt + + de V V V m h + + gz +
ME Fall 8 HW olution Problem he turbe i an open ytem. We identiy the team contaed the turbe a the control volume. Ma conervation: t law o thermodynamic: Aumption: dm m m m dt + + de V V V m h + + gz +
Unit code: H/ QCF level: 5 Credit value: 15 OUTCOME 1 - THERMODYNAMIC SYSTEMS TUTORIAL 2
 Unit 43: Plant and Process Princiles Unit code: H/60 44 QCF level: 5 Credit value: 5 OUCOME - HERMODYNAMIC SYSEMS UORIAL Understand thermodynamic systems as alied to lant engineering rocesses hermodynamic
Unit 43: Plant and Process Princiles Unit code: H/60 44 QCF level: 5 Credit value: 5 OUCOME - HERMODYNAMIC SYSEMS UORIAL Understand thermodynamic systems as alied to lant engineering rocesses hermodynamic
Special Topic: Binary Vapor Cycles
 0- Special opic: Bary Vapor ycle 0- Bary poer cycle i a cycle ic i actually a combation o to cycle; one te ig temperature region, and te oter te lo temperature region. It purpoe i to creae termal eiciency.
0- Special opic: Bary Vapor ycle 0- Bary poer cycle i a cycle ic i actually a combation o to cycle; one te ig temperature region, and te oter te lo temperature region. It purpoe i to creae termal eiciency.
Chapter 1 Fundamentals
 Chater Fundamentals. Overview of Thermodynamics Industrial Revolution brought in large scale automation of many tedious tasks which were earlier being erformed through manual or animal labour. Inventors
Chater Fundamentals. Overview of Thermodynamics Industrial Revolution brought in large scale automation of many tedious tasks which were earlier being erformed through manual or animal labour. Inventors
KNOWN: Air undergoes a polytropic process in a piston-cylinder assembly. The work is known.
 PROBLEM.7 A hown in Fig. P.7, 0 ft of air at T = 00 o R, 00 lbf/in. undergoe a polytropic expanion to a final preure of 5.4 lbf/in. The proce follow pv. = contant. The work i W = 94.4 Btu. Auming ideal
PROBLEM.7 A hown in Fig. P.7, 0 ft of air at T = 00 o R, 00 lbf/in. undergoe a polytropic expanion to a final preure of 5.4 lbf/in. The proce follow pv. = contant. The work i W = 94.4 Btu. Auming ideal
2b m 1b: Sat liq C, h = kj/kg tot 3a: 1 MPa, s = s 3 -> h 3a = kj/kg, T 3b
 .6 A upercritical team power plant ha a high preure of 0 Ma and an exit condener temperature of 50 C. he maximum temperature in the boiler i 000 C and the turbine exhaut i aturated vapor here i one open
.6 A upercritical team power plant ha a high preure of 0 Ma and an exit condener temperature of 50 C. he maximum temperature in the boiler i 000 C and the turbine exhaut i aturated vapor here i one open
CHEE 221: Chemical Processes and Systems
 CH 221: Chemical Processes and Systems Module 4. nergy Balances without Reaction Part a: Introduction to nergy Balances (Felder & Rousseau Ch 7.0 7.4 nergy and nergy Balances: very chemical rocess volves
CH 221: Chemical Processes and Systems Module 4. nergy Balances without Reaction Part a: Introduction to nergy Balances (Felder & Rousseau Ch 7.0 7.4 nergy and nergy Balances: very chemical rocess volves
Lecture 13 Heat Engines
 Lecture 3 Heat Engines hermodynamic rocesses and entroy hermodynamic cycles Extracting work from heat - How do we define engine efficiency? - Carnot cycle: the best ossible efficiency Reading for this
Lecture 3 Heat Engines hermodynamic rocesses and entroy hermodynamic cycles Extracting work from heat - How do we define engine efficiency? - Carnot cycle: the best ossible efficiency Reading for this
Chapter 9 Practical cycles
 Prof.. undararajan Chater 9 Practical cycles 9. Introduction In Chaters 7 and 8, it was shown that a reversible engine based on the Carnot cycle (two reversible isothermal heat transfers and two reversible
Prof.. undararajan Chater 9 Practical cycles 9. Introduction In Chaters 7 and 8, it was shown that a reversible engine based on the Carnot cycle (two reversible isothermal heat transfers and two reversible
( ) Given: In a constant pressure combustor. C4H10 and theoretical air burns at P1 = 0.2 MPa, T1 = 600K. Products exit at P2 = 0.
 (SP 9) N-butane (C4H1) i burned with 85 percent theoretical air, and the product of combution, an equilibrium mixture containing only O, CO, CO, H, HO, N, and NO, exit from a combution chamber at K,. MPa.
(SP 9) N-butane (C4H1) i burned with 85 percent theoretical air, and the product of combution, an equilibrium mixture containing only O, CO, CO, H, HO, N, and NO, exit from a combution chamber at K,. MPa.
Delft University of Technology DEPARTMENT OF AEROSPACE ENGINEERING
 Delft University of Technology DEPRTMENT OF EROSPCE ENGINEERING Course: Physics I (E-04) Course year: Date: 7-0-0 Time: 4:00-7:00 Student name and itials (capital letters): Student number:. You have attended
Delft University of Technology DEPRTMENT OF EROSPCE ENGINEERING Course: Physics I (E-04) Course year: Date: 7-0-0 Time: 4:00-7:00 Student name and itials (capital letters): Student number:. You have attended
Lecture 13. Heat Engines. Thermodynamic processes and entropy Thermodynamic cycles Extracting work from heat
 Lecture 3 Heat Engines hermodynamic rocesses and entroy hermodynamic cycles Extracting work from heat - How do we define engine efficiency? - Carnot cycle: the best ossible efficiency Reading for this
Lecture 3 Heat Engines hermodynamic rocesses and entroy hermodynamic cycles Extracting work from heat - How do we define engine efficiency? - Carnot cycle: the best ossible efficiency Reading for this
C H A P T E R ,1752'8&7,21
 CHAPTER The first law of thermodynamics is a secial case of the fundamental and general law of conseration of energy, which is alied to thermal henomena in thermodynamic system. The basic law of energy
CHAPTER The first law of thermodynamics is a secial case of the fundamental and general law of conseration of energy, which is alied to thermal henomena in thermodynamic system. The basic law of energy
MAE 11. Homework 8: Solutions 11/30/2018
 MAE 11 Homework 8: Solutions 11/30/2018 MAE 11 Fall 2018 HW #8 Due: Friday, November 30 (beginning of class at 12:00p) Requirements:: Include T s diagram for all cycles. Also include p v diagrams for Ch
MAE 11 Homework 8: Solutions 11/30/2018 MAE 11 Fall 2018 HW #8 Due: Friday, November 30 (beginning of class at 12:00p) Requirements:: Include T s diagram for all cycles. Also include p v diagrams for Ch
Thermodynamic Properties are Measurements p,t,v, u,h,s - measure directly -measure by change
 Thermodynamic Proerties are Measurements,T,, u,h,s - measure directly -measure by change s Tables T T Proerty Data Cure its Tables Correlation's, Boyles Law Tables c@tc limited hand calculations Equations
Thermodynamic Proerties are Measurements,T,, u,h,s - measure directly -measure by change s Tables T T Proerty Data Cure its Tables Correlation's, Boyles Law Tables c@tc limited hand calculations Equations
Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 322 Mechanical Engineering Thermodynamics. Calculation of Entropy Changes. Lecture 19
 Department of Mecanical Engineering ME Mecanical Engineering ermodynamics Calculation of Entropy Canges Lecture 9 e Gibbs Equations How are entropy alues calculated? Clausius found tat, dq dq m re re ds
Department of Mecanical Engineering ME Mecanical Engineering ermodynamics Calculation of Entropy Canges Lecture 9 e Gibbs Equations How are entropy alues calculated? Clausius found tat, dq dq m re re ds
(b) The heat transfer can be determined from an energy balance on the system
 8-5 Heat is transferred to a iston-cylinder device wit a set of stos. e work done, te eat transfer, te exergy destroyed, and te second-law efficiency are to be deterined. Assutions e device is stationary
8-5 Heat is transferred to a iston-cylinder device wit a set of stos. e work done, te eat transfer, te exergy destroyed, and te second-law efficiency are to be deterined. Assutions e device is stationary
Engineering Thermodynamics. Chapter 4. The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chater 4 The First Law of Thermodynamics It is the law that relates the arious forms of energies for system of different tyes. It is simly the exression of the conseration of energy rcile The first law
Chater 4 The First Law of Thermodynamics It is the law that relates the arious forms of energies for system of different tyes. It is simly the exression of the conseration of energy rcile The first law
NODIA AND COMPANY. GATE SOLVED PAPER Mechanical Engineering Thermodynamics. Copyright By NODIA & COMPANY
 No art of this ublication may be reroduced or distributed in any form or any means, electronic, mechanical, hotocoying, or otherwise without the rior ermission of the author. GAE SOLVED PAPER Mechanical
No art of this ublication may be reroduced or distributed in any form or any means, electronic, mechanical, hotocoying, or otherwise without the rior ermission of the author. GAE SOLVED PAPER Mechanical
Availability and Irreversibility
 Availability and Irreversibility 1.0 Overview A critical application of thermodynamics is finding the maximum amount of work that can be extracted from a given energy resource. This calculation forms the
Availability and Irreversibility 1.0 Overview A critical application of thermodynamics is finding the maximum amount of work that can be extracted from a given energy resource. This calculation forms the
Unit Workbook 2 - Level 5 ENG U64 Thermofluids 2018 UniCourse Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Sample
 Pearson BTEC Level 5 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 64: Thermofluids Unit Workbook 2 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 2 Vapour Power Cycles Page 1 of 26 2.1 Power Cycles Unit
Pearson BTEC Level 5 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 64: Thermofluids Unit Workbook 2 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 2 Vapour Power Cycles Page 1 of 26 2.1 Power Cycles Unit
Chapter 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES
 5- Chapter 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL OLUMES Conseration of Mass 5-C Mass, energy, momentum, and electric charge are consered, and olume and entropy are not consered durg a process. 5-C Mass
5- Chapter 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL OLUMES Conseration of Mass 5-C Mass, energy, momentum, and electric charge are consered, and olume and entropy are not consered durg a process. 5-C Mass
HEAT, WORK, AND THE FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
 HET, ORK, ND THE FIRST L OF THERMODYNMIS 8 EXERISES Section 8. The First Law of Thermodynamics 5. INTERPRET e identify the system as the water in the insulated container. The roblem involves calculating
HET, ORK, ND THE FIRST L OF THERMODYNMIS 8 EXERISES Section 8. The First Law of Thermodynamics 5. INTERPRET e identify the system as the water in the insulated container. The roblem involves calculating
m = P 1V 1 RT 1 P 2 = P 1. P 2 V 2 T 2 = P 1V 1 T 1 V 1 2 V 1 T 2 = T 1. {z} T 2 = T 1 1W 2 = PdV = P 1 (V 2 V 1 ). Z T2 (c vo + αt)dt.
 NAME: SOLUTION AME 0 Thermodynamic Examination Prof J M Power March 00 Happy 56th birthday, Sir Dugald Clerk, inventor of the two-troke engine, b March 85 (5) A calorically imperfect ideal ga, with ga
NAME: SOLUTION AME 0 Thermodynamic Examination Prof J M Power March 00 Happy 56th birthday, Sir Dugald Clerk, inventor of the two-troke engine, b March 85 (5) A calorically imperfect ideal ga, with ga
MAE320-HW7A. 1b). The entropy of an isolated system increases during a process. A). sometimes B). always C). never D).
 MAE0-W7A The homework i due Monday, November 4, 06. Each problem i worth the point indicated. Copying o the olution rom another i not acceptable. (). Multiple choice (0 point) a). Which tatement i invalid
MAE0-W7A The homework i due Monday, November 4, 06. Each problem i worth the point indicated. Copying o the olution rom another i not acceptable. (). Multiple choice (0 point) a). Which tatement i invalid
c Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq (BUET) Thermodynamic Processes & Efficiency ME 6101 (2017) 2 / 25 T145 = Q + W cv + i h 2 = h (V2 1 V 2 2)
 Thermodynamic Processes & Isentropic Efficiency Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Thermodynamic Processes & Isentropic Efficiency Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
FINAL EXAM. ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW:
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
SPC 407 Sheet 6 - Solution Compressible Flow Fanno Flow
 SPC 407 Sheet 6 - Solution Comressible Flow Fanno Flow 1. What is the effect of friction on flow velocity in subsonic and suersonic Fanno flow? Friction increases the flow velocity in subsonic Fanno flow,
SPC 407 Sheet 6 - Solution Comressible Flow Fanno Flow 1. What is the effect of friction on flow velocity in subsonic and suersonic Fanno flow? Friction increases the flow velocity in subsonic Fanno flow,
Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle
 ME 00 Thermodynamics I Spring 015 Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R.
ME 00 Thermodynamics I Spring 015 Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R.
Actual exergy intake to perform the same task
 CHAPER : PRINCIPLES OF ENERGY CONSERVAION INRODUCION Energy conservation rinciles are based on thermodynamics If we look into the simle and most direct statement of the first law of thermodynamics, we
CHAPER : PRINCIPLES OF ENERGY CONSERVAION INRODUCION Energy conservation rinciles are based on thermodynamics If we look into the simle and most direct statement of the first law of thermodynamics, we
since (Q H /T H ) = (Q L /T L ) for reversible cycles. Also, since Q diff is a positive quantity. Thus,
 7-5 7-84 he alidity o the Clai eqality i to be demontrated g a reerible and an irreerible heat enge operatg between the ame temperatre limit. Analyi Conider two heat enge, one reerible and one irreerible,
7-5 7-84 he alidity o the Clai eqality i to be demontrated g a reerible and an irreerible heat enge operatg between the ame temperatre limit. Analyi Conider two heat enge, one reerible and one irreerible,
KNOWN: Pressure, temperature, and velocity of steam entering a 1.6-cm-diameter pipe.
 4.3 Steam enters a.6-cm-diameter pipe at 80 bar and 600 o C with a velocity of 50 m/s. Determine the mass flow rate, in kg/s. KNOWN: Pressure, temperature, and velocity of steam entering a.6-cm-diameter
4.3 Steam enters a.6-cm-diameter pipe at 80 bar and 600 o C with a velocity of 50 m/s. Determine the mass flow rate, in kg/s. KNOWN: Pressure, temperature, and velocity of steam entering a.6-cm-diameter
Readings for this homework assignment and upcoming lectures
 Homework #3 (group) Tuesday, February 13 by 4:00 pm 5290 exercises (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm extra credit (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm Readings for this homework assignment
Homework #3 (group) Tuesday, February 13 by 4:00 pm 5290 exercises (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm extra credit (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm Readings for this homework assignment
SOLUTION MANUAL CHAPTER 12
 SOLUION MANUAL CHAPER CONEN SUBSECION PROB NO. In-ext Concept Quetion a-g Concept problem - Brayton cycle, ga turbine - Regenerator, Intercooler, nonideal cycle 5-9 Ericon cycle 0- Jet engine cycle -5
SOLUION MANUAL CHAPER CONEN SUBSECION PROB NO. In-ext Concept Quetion a-g Concept problem - Brayton cycle, ga turbine - Regenerator, Intercooler, nonideal cycle 5-9 Ericon cycle 0- Jet engine cycle -5
SOLUTION MANUAL ENGLISH UNIT PROBLEMS CHAPTER 11 SONNTAG BORGNAKKE VAN WYLEN. FUNDAMENTALS of. Thermodynamics. Sixth Edition
 SOLUION MANUAL ENGLISH UNI PROBLEMS CHAPER SONNAG BORGNAKKE VAN WYLEN FUNDAMENALS of hermodynamic Sixth Edition CHAPER SUBSECION PROB NO. Rankine Cycle 67-8 Brayton Cycle 8-87 Otto, Dieel, Stirling and
SOLUION MANUAL ENGLISH UNI PROBLEMS CHAPER SONNAG BORGNAKKE VAN WYLEN FUNDAMENALS of hermodynamic Sixth Edition CHAPER SUBSECION PROB NO. Rankine Cycle 67-8 Brayton Cycle 8-87 Otto, Dieel, Stirling and
Thermodynamics II. Week 9
 hermodynamics II Week 9 Example Oxygen gas in a piston cylinder at 300K, 00 kpa with volume o. m 3 is compressed in a reversible adiabatic process to a final temperature of 700K. Find the final pressure
hermodynamics II Week 9 Example Oxygen gas in a piston cylinder at 300K, 00 kpa with volume o. m 3 is compressed in a reversible adiabatic process to a final temperature of 700K. Find the final pressure
02. Equilibrium Thermodynamics II: Engines
 University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Equilibrium Statistical Physics Physics Course Materials 205 02. Equilibrium Thermodynamics II: Engines Gerhard Müller University of Rhode Island, gmuller@uri.edu
University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Equilibrium Statistical Physics Physics Course Materials 205 02. Equilibrium Thermodynamics II: Engines Gerhard Müller University of Rhode Island, gmuller@uri.edu
+ m B1 = 1. u A1. u B1. - m B1 = V A. /v A = , u B1 + V B. = 5.5 kg => = V tot. Table B.1.
 5.6 A rigid tank is divided into two rooms by a membrane, both containing water, shown in Fig. P5.6. Room A is at 200 kpa, v = 0.5 m3/kg, VA = m3, and room B contains 3.5 kg at 0.5 MPa, 400 C. The membrane
5.6 A rigid tank is divided into two rooms by a membrane, both containing water, shown in Fig. P5.6. Room A is at 200 kpa, v = 0.5 m3/kg, VA = m3, and room B contains 3.5 kg at 0.5 MPa, 400 C. The membrane
Chapter 7. Entropy: A Measure of Disorder
 Chapter 7 Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Entropy and the Clausius Inequality The second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of microscopic
Chapter 7 Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Entropy and the Clausius Inequality The second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of microscopic
Chapter 7. Entropy. by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
4. Energy balances Partly based on Chapter 4 of the De Nevers textbook.
 Lecture Notes CHE 31 Fluid Mechanics (Fall 010) 4 Energy balances Partly based on Chater 4 of the De Nevers textbook Energy fluid mechanics As for any quantity, we can set u an energy balance for a secific
Lecture Notes CHE 31 Fluid Mechanics (Fall 010) 4 Energy balances Partly based on Chater 4 of the De Nevers textbook Energy fluid mechanics As for any quantity, we can set u an energy balance for a secific
(British) (SI) British Metric L T [V] = L T. [a] = 2 [F] = F = 2 T
![(British) (SI) British Metric L T [V] = L T. [a] = 2 [F] = F = 2 T (British) (SI) British Metric L T [V] = L T. [a] = 2 [F] = F = 2 T](/thumbs/77/76088169.jpg) Hydraulics ecture # CWR 40 age () ecture # Outline: Review of terminology in fluid mechanics: Energy or work Hydraulic head Bernoulli s aw, Conductivity (examle) ransient & turbulent Friction head loss
Hydraulics ecture # CWR 40 age () ecture # Outline: Review of terminology in fluid mechanics: Energy or work Hydraulic head Bernoulli s aw, Conductivity (examle) ransient & turbulent Friction head loss
Chapter 7 Energy Principle
 Chater 7: Energy Princile By Dr Ali Jawarneh Hashemite University Outline In this chater we will: Derive and analyse the Energy equation. Analyse the flow and shaft work. Derive the equation for steady
Chater 7: Energy Princile By Dr Ali Jawarneh Hashemite University Outline In this chater we will: Derive and analyse the Energy equation. Analyse the flow and shaft work. Derive the equation for steady
first law of ThermodyNamics
 first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
Developing Transfer Functions from Heat & Material Balances
 Colorado Sool of Mine CHEN43 Stirred ank Heater Develoing ranfer untion from Heat & Material Balane Examle ranfer untion Stirred ank Heater,,, A,,,,, We will develo te tranfer funtion for a tirred tank
Colorado Sool of Mine CHEN43 Stirred ank Heater Develoing ranfer untion from Heat & Material Balane Examle ranfer untion Stirred ank Heater,,, A,,,,, We will develo te tranfer funtion for a tirred tank
Chapters 19 & 20 Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics
 Capters 19 & 20 Heat and te First Law of Termodynamics Te Zerot Law of Termodynamics Te First Law of Termodynamics Termal Processes Te Second Law of Termodynamics Heat Engines and te Carnot Cycle Refrigerators,
Capters 19 & 20 Heat and te First Law of Termodynamics Te Zerot Law of Termodynamics Te First Law of Termodynamics Termal Processes Te Second Law of Termodynamics Heat Engines and te Carnot Cycle Refrigerators,
F = U TS G = H TS. Availability, Irreversibility S K Mondal s Chapter 5. max. actual. univ. Ns =
 Availability, Irreversibility S K Mondal s Chater 5 I = W W 0 max ( S) = Δ univ actual 7. Irreversibility rate = I = rate of energy degradation = rate of energy loss (Wlost) = 0 S gen for all rocesses
Availability, Irreversibility S K Mondal s Chater 5 I = W W 0 max ( S) = Δ univ actual 7. Irreversibility rate = I = rate of energy degradation = rate of energy loss (Wlost) = 0 S gen for all rocesses
Theory of turbomachinery. Chapter 1
 Theory of turbomachinery Chater Introduction: Basic Princiles Take your choice of those that can best aid your action. (Shakeseare, Coriolanus) Introduction Definition Turbomachinery describes machines
Theory of turbomachinery Chater Introduction: Basic Princiles Take your choice of those that can best aid your action. (Shakeseare, Coriolanus) Introduction Definition Turbomachinery describes machines
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY. Copyright Hany A. Al-Ansary and S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1
 CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
COMPENDIUM OF EQUATIONS Unified Engineering Thermodynamics
 COMPENDIUM OF EQUAIONS Unified Engineering hermodynamics Note: It is with some reseration that I suly this comendium of equations. One of the common itfalls for engineering students is that they sole roblems
COMPENDIUM OF EQUAIONS Unified Engineering hermodynamics Note: It is with some reseration that I suly this comendium of equations. One of the common itfalls for engineering students is that they sole roblems
Notes on the function gsw_enthalpy_first_derivatives_ct_exact(sa,ct,p)
 Notes on gsw_entaly_first_derivatives_c_exact 1 Notes on te function gsw_entaly_first_derivatives_c_exact(c) is function gsw_entaly_first_derivatives_c_exact(c) evaluates two of te first order artial derivatives
Notes on gsw_entaly_first_derivatives_c_exact 1 Notes on te function gsw_entaly_first_derivatives_c_exact(c) is function gsw_entaly_first_derivatives_c_exact(c) evaluates two of te first order artial derivatives
ME 2322 Thermodynamics I PRE-LECTURE Lesson 10 Complete the items below Name:
 Lesson 10 1. (5 pt) If P > P sat (T), the phase is a subcooled liquid. 2. (5 pt) if P < P sat (T), the phase is superheated vapor. 3. (5 pt) if T > T sat (P), the phase is superheated vapor. 4. (5 pt)
Lesson 10 1. (5 pt) If P > P sat (T), the phase is a subcooled liquid. 2. (5 pt) if P < P sat (T), the phase is superheated vapor. 3. (5 pt) if T > T sat (P), the phase is superheated vapor. 4. (5 pt)
P=1 atm. vapor. liquid
 P1 atm ar liqid Q Gien and P Ser Heat Regin i, P < P sat > sat Cmressed Liqid Regin i, P > P sat < sat SEAM PRESUE AND EMPERAURE ABLES Satrated Liqid Line Satrated Var Line s s g g g g ree ables emeratre
P1 atm ar liqid Q Gien and P Ser Heat Regin i, P < P sat > sat Cmressed Liqid Regin i, P > P sat < sat SEAM PRESUE AND EMPERAURE ABLES Satrated Liqid Line Satrated Var Line s s g g g g ree ables emeratre
The exergy of asystemis the maximum useful work possible during a process that brings the system into equilibrium with aheat reservoir. (4.
 Energy Equation Entropy equation in Chapter 4: control mass approach The second law of thermodynamics Availability (exergy) The exergy of asystemis the maximum useful work possible during a process that
Energy Equation Entropy equation in Chapter 4: control mass approach The second law of thermodynamics Availability (exergy) The exergy of asystemis the maximum useful work possible during a process that
Thermodynamics Lecture Series
 Thermodynamics Lecture Series Second Law uality of Energy Applied Sciences Education Research Group (ASERG) Faculty of Applied Sciences Universiti Teknologi MARA email: drjjlanita@hotmail.com http://www.uitm.edu.my/faculties/fsg/drjj.html
Thermodynamics Lecture Series Second Law uality of Energy Applied Sciences Education Research Group (ASERG) Faculty of Applied Sciences Universiti Teknologi MARA email: drjjlanita@hotmail.com http://www.uitm.edu.my/faculties/fsg/drjj.html
Outline. Example. Solution. Property evaluation examples Specific heat Internal energy, enthalpy, and specific heats of solids and liquids Examples
 Outline Property ealuation examples Specific heat Internal energy, enthalpy, and specific heats of solids and liquids s A piston-cylinder deice initially contains 0.5m of saturated water apor at 00kPa.
Outline Property ealuation examples Specific heat Internal energy, enthalpy, and specific heats of solids and liquids s A piston-cylinder deice initially contains 0.5m of saturated water apor at 00kPa.
Efficiencies. Damian Vogt Course MJ2429. Nomenclature. Symbol Denotation Unit c Flow speed m/s c p. pressure c v. Specific heat at constant J/kgK
 Turbomachinery Lecture Notes 1 7-9-1 Efficiencies Damian Vogt Course MJ49 Nomenclature Subscrits Symbol Denotation Unit c Flow seed m/s c Secific heat at constant J/kgK ressure c v Secific heat at constant
Turbomachinery Lecture Notes 1 7-9-1 Efficiencies Damian Vogt Course MJ49 Nomenclature Subscrits Symbol Denotation Unit c Flow seed m/s c Secific heat at constant J/kgK ressure c v Secific heat at constant
ME Thermodynamics I. Lecture Notes and Example Problems
 ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
Teaching schedule *15 18
 Teaching schedule Session *15 18 19 21 22 24 Topics 5. Gas power cycles Basic considerations in the analysis of power cycle; Carnot cycle; Air standard cycle; Reciprocating engines; Otto cycle; Diesel
Teaching schedule Session *15 18 19 21 22 24 Topics 5. Gas power cycles Basic considerations in the analysis of power cycle; Carnot cycle; Air standard cycle; Reciprocating engines; Otto cycle; Diesel
Thermodynamic Relations
 7 hermodynamic elation 7.1. General aect. 7.. undamental of artial differentiation. 7.3. Some general thermodynamic relation. 7.4. Entroy equation (d equation). 7.5. Equation f internal energy and enthaly.
7 hermodynamic elation 7.1. General aect. 7.. undamental of artial differentiation. 7.3. Some general thermodynamic relation. 7.4. Entroy equation (d equation). 7.5. Equation f internal energy and enthaly.
ENERGY TRANSFER BY WORK: Electrical Work: When N Coulombs of electrical charge move through a potential difference V
 Weight, W = mg Where m=mass, g=gravitational acceleration ENERGY TRANSFER BY WOR: Sign convention: Work done on a system = (+) Work done by a system = (-) Density, ρ = m V kg m 3 Where m=mass, V =Volume
Weight, W = mg Where m=mass, g=gravitational acceleration ENERGY TRANSFER BY WOR: Sign convention: Work done on a system = (+) Work done by a system = (-) Density, ρ = m V kg m 3 Where m=mass, V =Volume
Number of extra papers used if any
 Last Name: First Name: Thermo no. ME 200 Thermodynamics 1 Fall 2018 Exam Circle your structor s last name Division 1 (7:0): Naik Division (1:0): Wassgren Division 6 (11:0): Sojka Division 2 (9:0): Choi
Last Name: First Name: Thermo no. ME 200 Thermodynamics 1 Fall 2018 Exam Circle your structor s last name Division 1 (7:0): Naik Division (1:0): Wassgren Division 6 (11:0): Sojka Division 2 (9:0): Choi
ME 2322 Thermodynamics I PRE-LECTURE Lesson 23 Complete the items below Name:
 Lesson 23 1. (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent Carnot
Lesson 23 1. (10 pt) Write the equation for the thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine below: 1 L H 2. (10 pt) Can the thermal efficiency of an actual engine ever exceed that of an equivalent Carnot
Course: MECH-341 Thermodynamics II Semester: Fall 2006
 FINAL EXAM Date: Thursday, December 21, 2006, 9 am 12 am Examiner: Prof. E. Timofeev Associate Examiner: Prof. D. Frost READ CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU PROCEED: Course: MECH-341 Thermodynamics II Semester: Fall
FINAL EXAM Date: Thursday, December 21, 2006, 9 am 12 am Examiner: Prof. E. Timofeev Associate Examiner: Prof. D. Frost READ CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU PROCEED: Course: MECH-341 Thermodynamics II Semester: Fall
Exergy and the Dead State
 EXERGY The energy content of the universe is constant, just as its mass content is. Yet at times of crisis we are bombarded with speeches and articles on how to conserve energy. As engineers, we know that
EXERGY The energy content of the universe is constant, just as its mass content is. Yet at times of crisis we are bombarded with speeches and articles on how to conserve energy. As engineers, we know that
Chapter 20: Exercises: 3, 7, 11, 22, 28, 34 EOC: 40, 43, 46, 58
 Chater 0: Exercises:, 7,,, 8, 4 EOC: 40, 4, 46, 8 E: A gasoline engine takes in.80 0 4 and delivers 800 of work er cycle. The heat is obtained by burning gasoline with a heat of combustion of 4.60 0 4.
Chater 0: Exercises:, 7,,, 8, 4 EOC: 40, 4, 46, 8 E: A gasoline engine takes in.80 0 4 and delivers 800 of work er cycle. The heat is obtained by burning gasoline with a heat of combustion of 4.60 0 4.
Systems Analysis. Prof. Cesar de Prada ISA-UVA
 Sytem Analyi Prof. Cear de Prada ISAUVA rada@autom.uva.e Aim Learn how to infer the dynamic behaviour of a cloed loo ytem from it model. Learn how to infer the change in the dynamic of a cloed loo ytem
Sytem Analyi Prof. Cear de Prada ISAUVA rada@autom.uva.e Aim Learn how to infer the dynamic behaviour of a cloed loo ytem from it model. Learn how to infer the change in the dynamic of a cloed loo ytem
Given: Hot fluid oil, Cold fluid - water (T 1, T 2 ) (t 1, t 2 ) Water
 . In a counter flow double pipe eat excanger, oil is cooled fro 85 to 55 by water entering at 5. Te ass flow rate of oil is 9,800 kg/ and specific eat f oil is 000 J/kg K. Te ass flow rate of water is
. In a counter flow double pipe eat excanger, oil is cooled fro 85 to 55 by water entering at 5. Te ass flow rate of oil is 9,800 kg/ and specific eat f oil is 000 J/kg K. Te ass flow rate of water is
Chapter 7: The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 7: he Second Law of hermodynamics he second law of thermodynamics asserts that processes occur in a certain direction and that the energy has quality as well as quantity he first law places no
Chapter 7: he Second Law of hermodynamics he second law of thermodynamics asserts that processes occur in a certain direction and that the energy has quality as well as quantity he first law places no
Chapter 7 ENTROPY. 7-3C The entropy change will be the same for both cases since entropy is a property and it has a fixed value at a fixed state.
 7- Chapter 7 ENROY Entropy and the Increae of Entropy rciple 7-C No. he δ Q repreent the net heat tranfer durg a cycle, which could be poitive. 7-C No. A ytem may produce more (or le) work than it receive
7- Chapter 7 ENROY Entropy and the Increae of Entropy rciple 7-C No. he δ Q repreent the net heat tranfer durg a cycle, which could be poitive. 7-C No. A ytem may produce more (or le) work than it receive
EVAPORATION. Robert evaporator. Balance equations Material balance (total) Component balance. Heat balance
 EAPORATION Roert eorator Balance equation Material alance (total) S S=Solution =aor =Steam K=Steam condenate S Comonent alance S S Heat alance S S v Merkel lot can e ued for otaining entaly data Heat ower
EAPORATION Roert eorator Balance equation Material alance (total) S S=Solution =aor =Steam K=Steam condenate S Comonent alance S S Heat alance S S v Merkel lot can e ued for otaining entaly data Heat ower
Chapter 2 Solutions. 2.1 (D) Pressure and temperature are dependent during phase change and independent when in a single phase.
 Chater Solutions.1 (D) Pressure and temerature are deendent during hase change and indeendent when in a single hase.. (B) Sublimation is the direct conversion of a solid to a gas. To observe this rocess,
Chater Solutions.1 (D) Pressure and temerature are deendent during hase change and indeendent when in a single hase.. (B) Sublimation is the direct conversion of a solid to a gas. To observe this rocess,
Then the amount of water that flows through the pipe during a differential time interval dt is (1) 4
 5-98 Review Problems 5-45 A tank oen to te atmosere is itially filled wit. e tank discarges to te atmosere troug a long ie connected to a valve. e itial discarge velocity from te tank and te time required
5-98 Review Problems 5-45 A tank oen to te atmosere is itially filled wit. e tank discarges to te atmosere troug a long ie connected to a valve. e itial discarge velocity from te tank and te time required
Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Reading Problems 7-1 7-3 7-88, 7-131, 7-135 7-6 7-10 8-24, 8-44, 8-46, 8-60, 8-73, 8-99, 8-128, 8-132, 8-1 8-10, 8-13 8-135, 8-148, 8-152, 8-166, 8-168, 8-189
Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Reading Problems 7-1 7-3 7-88, 7-131, 7-135 7-6 7-10 8-24, 8-44, 8-46, 8-60, 8-73, 8-99, 8-128, 8-132, 8-1 8-10, 8-13 8-135, 8-148, 8-152, 8-166, 8-168, 8-189
Chapter 4 Practice Problems
 Chater 4 ractice roblems (4.) (a) the number of microstates is N (b) 3 articles total 3! {, } 3 number microstates of secific arrangement (macrostate)!*! robability = (# microstates of secific arrangement)/(total
Chater 4 ractice roblems (4.) (a) the number of microstates is N (b) 3 articles total 3! {, } 3 number microstates of secific arrangement (macrostate)!*! robability = (# microstates of secific arrangement)/(total
ENT 254: Applied Thermodynamics
 ENT 54: Applied Thermodynamics Mr. Azizul bin Mohamad Mechanical Engineering Program School of Mechatronic Engineering Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) azizul@unimap.edu.my 019-4747351 04-9798679 Chapter
ENT 54: Applied Thermodynamics Mr. Azizul bin Mohamad Mechanical Engineering Program School of Mechatronic Engineering Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) azizul@unimap.edu.my 019-4747351 04-9798679 Chapter
Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 322 Mechanical Engineering Thermodynamics. Lecture 26. Use of Regeneration in Vapor Power Cycles
 Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 322 Mechanical Engineering Thermodynamics Lecture 2 Use of Regeneration in Vapor Power Cycles What is Regeneration? Goal of regeneration Reduce the fuel input requirements
Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 322 Mechanical Engineering Thermodynamics Lecture 2 Use of Regeneration in Vapor Power Cycles What is Regeneration? Goal of regeneration Reduce the fuel input requirements
ME Thermodynamics I
 Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
Consequences of Second Law of Thermodynamics. Entropy. Clausius Inequity
 onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES. The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial.
 THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 2 THERMODYNAMIC PRINCIPLES SAE
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 2 THERMODYNAMIC PRINCIPLES SAE
AE301 Aerodynamics I UNIT A: Fundamental Concepts
 AE301 Aerodynamics I UNIT A: Fundamental Concets ROAD MAP... A-1: Engineering Fundamentals Reiew A-: Standard Atmoshere A-3: Goerning Equations of Aerodynamics A-4: Airseed Measurements A-5: Aerodynamic
AE301 Aerodynamics I UNIT A: Fundamental Concets ROAD MAP... A-1: Engineering Fundamentals Reiew A-: Standard Atmoshere A-3: Goerning Equations of Aerodynamics A-4: Airseed Measurements A-5: Aerodynamic
Figure 1 Siemens PSSE Web Site
 Stability Analyi of Dynamic Sytem. In the lat few lecture we have een how mall ignal Lalace domain model may be contructed of the dynamic erformance of ower ytem. The tability of uch ytem i a matter of
Stability Analyi of Dynamic Sytem. In the lat few lecture we have een how mall ignal Lalace domain model may be contructed of the dynamic erformance of ower ytem. The tability of uch ytem i a matter of
Carnot Factor of a Vapour Power Cycle with Regenerative Extraction
 Journal of Modern Pysics, 2017, 8, 1795-1808 ttp://www.scirp.org/journal/jmp ISSN Online: 2153-120X ISSN Print: 2153-1196 arnot Factor of a Vapour Power ycle wit Regenerative Extraction Duparquet Alain
Journal of Modern Pysics, 2017, 8, 1795-1808 ttp://www.scirp.org/journal/jmp ISSN Online: 2153-120X ISSN Print: 2153-1196 arnot Factor of a Vapour Power ycle wit Regenerative Extraction Duparquet Alain
A short note on Reitlinger thermodynamic cycles
 short note on Reitlinger thermodynamic cycles melia arolina Saravigna eartment of lied Science and echnology, Politecnico di orino, orino, Italy bstract: It is well known that arnot cycle is the thermodynamic
short note on Reitlinger thermodynamic cycles melia arolina Saravigna eartment of lied Science and echnology, Politecnico di orino, orino, Italy bstract: It is well known that arnot cycle is the thermodynamic
ME 200 Thermodynamics 1 Fall 2017 Exam 3
 ME 200 hermodynamics 1 Fall 2017 Exam Circle your structor s last name Division 1: Naik Division : Wassgren Division 6: Braun Division 2: Sojka Division 4: Goldenste Division 7: Buckius Division 8: Meyer
ME 200 hermodynamics 1 Fall 2017 Exam Circle your structor s last name Division 1: Naik Division : Wassgren Division 6: Braun Division 2: Sojka Division 4: Goldenste Division 7: Buckius Division 8: Meyer
