Stress Distribution on a Single-Walled Carbon Nanohorn Embedded in an Epoxy Matrix Nanocomposite Under Axial Force
|
|
|
- Leona Fowler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
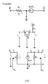
1 Cpyght 00 Amecan Scentc Publshes All ghts eseved Pnted n the Unted States Ameca Junal Cmputatnal and Theetcal Nanscence Vl.7, 7, 00 Stess Dstbutn n a Sngle-Walled Cabn Nanhn Embedded n an Epxy Matx Nancmpste Unde Axal Fce K. Mmen and R. S. Yassa Depatment Mechancal Engneeng-Engneeng Mechancs, Mchgan Technlgcal Unvesty, Hughtn, MI 4993, US Cabn Nantubes CNTs) have been a subject nteest mst the eseaches ate the dscvey, due t the supe mechancal ppetes and ablty t be used as the encement phase n nancmpstes. The the cabn stuctue whch was dscveed a ew yeas ate the dscvey CNTs was Cabn Nanhns CNHs). The stuctue CNH s cne-shaped cmpaed t the cylndcal shape CNT s stuctue. Ths cne-shaped stuctue causes dcultes n ndng the stess dstbutn n CNHs when embedded n the matx phase nancmpstes. In ths pape the gvenng deental equatn the stess dstbutn n the CNHs placed n a nancmpste matx s deved usng sme smplyng assumptns. It has been shwn hee that whle the stess dstbutn s symmetc the specal case CNT, t s nn-symmetc the geneal CNHs and the maxmum stess shts twad the tp CNH. Keywds: Analytcal Mdelng, Nan-Stuctues, Stess Tanse, Cabn Nanhn.. INTRODUCTION Few yeas ate the dscvey CNTs by Ijma et al. n 99, CNHs wee ntduced by Has et al.n 994. CNTs shw unque mechancal ppetes, such as lage elastc mdulus whch can each up t 5 TPa 3 8 cmpaed wth elastc mdulus cabn bes whch s m 0. t 0.8 TP 9 and stength up t 63 GPa. 0 Dscvey CNTs made a geat deal nteest amng the scentsts t exple new devces and applcatns.on the the hand, cabn nanhns have a hgh stength sp cabn-cabn bnd, and they can be pduced wth puty hghe than 90%.Ths s because CNHs dn t need the use catalytc patcles synthess n cntast t CNTs. In addtn the suace aea the cabn nanhns s 300 t 400 m /g cmpaed t 78 m /g the mult-walled CNTs and 85 m /g sngle-walled CNTs.Futheme, suace aea CNHs can be mpved by a pst teatment pcess up t me than 000 m /g. 3 7 Due t the abve advantages, t s expected that CNH enced nancmpstes have a hghe mechancal ppetes than the CNT enced nancmpstes.in ths pape the deental equatns gvenng the dstbutn stess n a cabn nanhn whch s placed n an epxy matx unde axal ladng wll be nvestgated usng Cx mdel 8 and t wll be cmpaed wth the stess dstbutn mdel the CNTs. 9. PROBLEMDEFINITION The epesentatve vlume element RVE) ths pblem s shwn n Fgue and the sde vews the CNH n the RVE ae shwn n Fgue.We assumed that L s the lngtudnal length the RVE.In addtn L epesents the lngtudnal length the embedded CNH.We have cnsdeed L and L nstead smply cnsdeng L and L because n the case ze cne angle,.e., a cylndcal tube lke CNT, the stess s symmetc abut the mddle plane. The ute adus the CNH s = a z tan ; whee a epesents the CNH s ute damete at z =0. Cnsdeng the CNH s thckness as t then the elatn between the ute and nne adus the CNH wuld be = t. The equlbum equatns n absence bdy ces, axsymmetc pblem n tems cylndcal cdnate,, z) ae: 0 Auth t whm cespndence shuld be addessed. z = 0 a) J. Cmput. The. Nansc. 00, Vl. 7, N /00/7/00/007 d:0.66/jctn
2 Stess Dstbutn n a Sngle-Walled CNH Embedded n an Epxy Matx Nancmpste Mmen and Yassa z = u w d) Assumng CNH and matx as elastc mateals, the cnsttutve equatns ae: = E = E = E 3a) 3b) 3c) Fg.. RVE a CNH wth length L embedded n a matx wth length L.The cmpste s then beng subjected t the veall stess alng the cylndcal axs. z z = 0 b) Assumng the u and w as dsplacement alng and z dectn, the gemetcal equatns CNH can be wtten as: = u a) = u b) = w c) z = z 3d) G The the stan cmpnents ae vanshed due t the pblem cnguatn and gemety appled ces,.e., axal ladng. In the next step we wll dene the bunday equatns the abve mentned gvenng equatns.the bunday cndtns 4) ae descbng the ce balance at the bundaes the RVE.The Eq.5) ae due t the ce balance at the CNH-matx nteace.accdng t the type ladng, thee s n tactn alng adal dectn n suace the RVE,.e., Eq. 4a). The stess s appled n the extemes the CNH alng ts axs symmety, whch leads t Eq.4b).In Eq.4b) ê z s the unt vect alng the z-axs. { T m =R = 0 4a) T m z=±l =± ê z 4b) The ce balance between the CNH and matx alng the adal dectn and at the exteme ends, lead t Eqs.5a, b). { T L z L = = T m L z L = 5a) T z=±l = T m z=±l 5b) a) b) Fg.. a) Sde vew and b) css-sectnal vew, A-A, the RVE shwn n Fgue.The nne and ute aduses, and 0, CNH change alng the z-axs as a unctn cne angle,, whle ts thckness, t, emans cnstant. 3. SOLUTION In geneal, the ntegatn Eq.b) wth espect t m t a encng CNH desgnated by supescpt : z d z d = 0 6) whee the st pat 6) can be dened as an aveage axal nmal stess ve the css sectn the CNH as belw: = z d 7) J. Cmput. The. Nansc. 7, 7, 00
3 Mmen and Yassa Stess Dstbutn n a Sngle-Walled CNH Embedded n an Epxy Matx Nancmpste Deentatn 7) wth espect t z and usng 6) leads t: d dz = tg z d tg tg 8) By assumng that: Nw ntegatng b) wth espect t m t R and usng 5b) leads t, R z m d R m z d = 0 7) Cnsdeng, m = R m z d 8) then by assumng, z and usng b) we have: = 9) z = 0 0) Ths s a st de lnea deental equatn n tems z whch ts slutn leads t: z = c ) Assumng z = = 0 whch means n matx penetatn nt the hllw pat the CNH we have: z = ) Usng ) and ) we have: c = 3) F smplcty we wll epesent z = by ;Swe btan: = = 4a) z = 4b) The bunday cndtn 4a) mples that thee s n adal nmal stess and shea stess n the ccumeence the matx.s we may ewte Eq.4a) as: m =R = 0 m z =R = 0 In a smla manne ewtng Eq.5a) leads t: L <z<l = = m L <z<l = z L <z<l = = m z L <z<l = 5a) 5b) 6a) 6b) m = g 9) wee gz) s an unknwn unctn that must be detemned. Insetng 9) n 7) and ntegatng wth espect t m t R leads t: g d R R m z d = 0 g = R m z m z = g R 0) Usng 0) and 5b), g = R ) Substtutng ) n 0), m z = ) R R ) and assumng that u/ w/,.e., the adal dsplacement alng the ad s much smalle than the axal dsplacement alng the ad, and d) and 3d), w z = G m wm z = Gm Usng 3b) and ) we have, 3a) 3b) = R Gm R wm 4) Reaangng 4) and ntegatng m t R leads t, ) R d = G m R dw m = R w Gm R m 5) wm R ln R/ / R J. Cmput. The. Nansc. 7, 7, 00 3
4 Stess Dstbutn n a Sngle-Walled CNH Embedded n an Epxy Matx Nancmpste Mmen and Yassa Substtutn 5) nt ) esults n, m z = R w Gm R m wm R ln R/ / R 6) Puttng 6) nt 3b) leads t: w m = R wr m wm R ln R/ / R w m w m R w =wm m R ln/ / R ln R/ / R 7) R 4 ln R/ 4 ) R 3R ) R R ln R R 3 R3 3 ) R R R ln ) R R 8 4 ) R R4 ln 34 ) R4 3) Assumng bth matx and the CNH, due t the act that we cnsdeed the nancmpste unde axal ladng, and usng c), 3c) and ntng that = g, then we have: = E w m = Em wm m = m = R ln/ ) 8) R ln R/ ) R m =R m = w m R wm E m tg R ) ) R ln ) R R ln ) R ) R R ln R 9) Cnsdeng the ce balance the cmpste alng the z axs: R = d Usng 7), 9) and 30) we have: m m =R m = = R ln R/ ) R d 30) R 4 ln R/ 4 ) R 3R R m = R E m tg w m R wm Fm 8) and assumng n matx penetatn nsde the CNH, then: d dz = tg 3) Fm 6), 9b), 3), and 3) t llws that, d dz = tg tan = = G m R R E m R m = R R 4 ln ) 4 ) 3R R R w m R wm R ln ) ) R { Gm tan R ln R R R ) R ) ) R G m tan R R 4 ln ) 4 ) 3R R R R ln R ) R R R3 3 3 R R R R ln ) )) R R 4 8 R4 R ) ln 38 )} R4 33) 4 J. Cmput. The. Nansc. 7, 7, 00
5 Mmen and Yassa Stess Dstbutn n a Sngle-Walled CNH Embedded n an Epxy Matx Nancmpste Due t 8) and n matx penetatn nsde the CNH.e., = 0 and = the llwng equatn can be btaned: d dz = 34) Insetng 5) n 38) we have: wr m wm = d R ln R/ R G m R 35) dz Assumng that the bundng between the CNH and matx t be peect,.e., n sldng ccus at the CNH- Matx nteace, we have: m = = = m z = = Em E = 36) Assumng lw vlume actn the CNH, 37) and usng 33), 35), 36), and 37) we have: d dz d dz = 39) whee z), z), and z) have been dened n 40a c). n 40c) s the appled axal stess t the RVE, whch s cnstant.deental Eq.39) s a secnd de lnea ne whch ts cecents ae unctns ndependent vaable, z.theee t can be slved usng pwe sees methd. = G m R { Gm tan R R R ln ) ) R R G m tan R 4 ln ) 4 3R R R ) R R ln R R R3 3 3 R R R ln R/ / R R ) 4 8 R4 R ln 38 )} R4 40a) = R Em m E R ) R R 4 ln 4 3R R 40b) = R m R R 4 ln ) 4 3R 0 R 40c) Equatn 39) s cmpletely cnsstent wth the pevus wks n CNTs and CNHs. 4. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Hee the deental Eq.39) has been slved numecally the case epxy matx and CNH whle sx deent cne angles have been cnsdeed.hee we have used the mechancal ppetes CNT, due t the lack data the mechancal ppetes CNH.It s justed because bth CNT and CNH have the same nte atmc bndng,.e., sp.theee, t s expected that the mechancal ppetes the CNH wuld nt be much deent m the mechancal ppetes CNT.The ppetes these mateals ae cnsdeed as llws; = 0, 0, 5,,, and 0, E m =.4 GPa, E = 000 GPa, m = 0 5, a = 0 8 nm, t = 0 34 nm, G m = E m / m, = GPa, L =00 nm and R>5 max = 50 nm. 3 4 F slvng ths pblem Maple has been used.ths pblem has been slved wth Runge-Kutta-Fehlbeg 6 methd whch esults n a th de accuate slutn.the CNH s mean stess dstbutn vesus the dstance m ts tp has been pltted alng ts lngtudnal axs symmety n Fgue 3.F slvng ths pblem we need tw bunday cndtns; Theee we used the value mean be stess at z = 0 and z = L the case pen-ended CNTs. As t has been shwn n Fgue 3, the stess dstbutn alng the CNH s a nn-lnea unctn the cne angle. Meve the maxmum mean nmal stess des nt ccu at the mddle the CNH as t des n the case penended CNTs and cnventnal d-shape bes. 7 Fm Fgue 3 we can cnclude that the lage the cne angle, the uthe the devatn lcatn maxmum mean stess m the mddle the be. In the case ze cne angle, the maxmum ccus at the mddle the be whch s plausble due t the act that n ths case the gvenng deental equatns wuld be exactly the same as the case hllw cylndcal be. In addtn t the devatn maxmum mean nmal stess, the ate change mean stess s nt symmetc n the case CNH.I we classy the stess dstbutn n the CNH nt tw sectns, ne m the CNH s tp t max value stess and the the m the max value stess t the ppste end CNH, t can be seen that the ate change mean stess s hghe at the st sectn cmpaed t the the sectn Fg.4).Futheme the J. Cmput. The. Nansc. 7, 7, 00 5
6 Stess Dstbutn n a Sngle-Walled CNH Embedded n an Epxy Matx Nancmpste Mmen and Yassa means utue desgn new geneatn nancmpstes enced wth CNHs. 5. CONCLUSION The supe ppetes the CNHs cmpaed t CNTs, such as hghe puty and suace aeas, pmse an nceasng applcatn CNHs n utue nancmpstes. In ths wk a gus mathematcal amewk t mdel the stess dstbutn at the nteace a CNH and cmpste matx s deved.it has been shwn that the stess dstbutn alng the CNH s a nn-lnea unctn the cne angle.als we shwed that the lage the cne angle, the bgge s the devatn mean stess dstbutn m the symmetc case.althugh the mula btaned n ths pape ae the case CNHs but t s als applcable t the CNTs because CNTs ae specal case CNHs wth ze cne angle. Fg. 3. Mean stess,, vesus CNH dstance alng the axes CNH, L.Whle the maxmum stess ccus at the mddle the CNT, the case CNH, the pstn maxmum stess mves twad the tp CNH. ate change maxmum mean stess s lwe at the hghe angles but t wll change abuptly at the smalle angles.these eatues happen due t the act that the stess tanses t the CNH due t the shea stess between the matx and CNH.The amunt tanseed stess at the exteme ends the CNH s neglgble and t ses t a maxmum smewhee n between.on the the hand, the css-sectn aea the CNH changes m a mnmum value t a maxmum ne.whle the stess s pptnal t the amunt tanseed shea stess, t s nvesely pptnal t the css-sectn aea.it s expected that the deved mathematcal amewk pvdes a cmputatnal NOMENCLATURE z Axal cdnate the RVE a Radal cdnate the RVE R Radus the RVE Hal cne angle the CNH b Oute adus the CNH Inne adus the CNH a CNH s ute damete at z = 0 t Thckness CNH s wall Stan Cnstant appled axal stess t the RVE Aveage axal nmal stess Shea Stess Pssn s at G Shea Mdulus Shea stan m Paametes asscated t matx mateal Paametes asscated t CNH u Radal dsplacement w Axal dsplacement T Tactn L Length the RVE a Repesentatve Vlume Element. b Cabn Nan Hn. Acknwledgments: We appecate Ms.Sghat the help and the Mchgan Technlgcal Unvesty pvdng the nancal suppt. Reeences Fg. 4. Rate change mean stess alng the CNH,.e., /.. S.Ijma, Natue 56, ).. P.J.F.Has, M.L.H.Geen, and S.C.Tsang, J. Chem. Sc.- Faaday Tans. 89, ). 3. E.W.Wng, P.E.Sheehan, and C.M.Lebe, Scence 77, ). 6 J. Cmput. The. Nansc. 7, 7, 00
7 Mmen and Yassa Stess Dstbutn n a Sngle-Walled CNH Embedded n an Epxy Matx Nancmpste 4. O.Lue, H.D.Wagne, J. Mat. Res. 3, ). 5. G.Oveney, W.Zhng, and D.Tmanek, Zetscht Fu Physk D-Atms Mlecules and Clustes 7, ). 6. J.P.Lu, PhyscalRev. Lett. 79, ). 7. M.M.Teacy, T.W.Ebessen, and J.M.Gbsn, Natue 38, ). 8. P.Zhang, Y.Huang, P.H.Geubelle, P.A.Klen, and K.C. Hwang, IntenatnalJunal Slds and Stuctues 39, ). 9. P.Mgan, Cabn Fbes and The Cmpstes, CRC Pess 005) p M.Yu, O.Lue, M.J.Dye, T.F.Kelly, and R.S.Ru, Scence 87, ).. S.Ijma, M.Yudasaka, R.Yamada, S.Bandw, K.Suenaga, F.Kka, K.Takahash, Chem. Phys. Lett. 309, ).. D.Kasuya, M.Yudasaka, K.Takahash, F.Kka, and S.Ijma, J. Phys. Chem. B. 06, ). 3. K.Muata, K.Kanek, W.A.Steele, F.Kka, T.Takahash, D.Kasuya, M.Yudusaka, and S.Ijma, J. Phys. Chem. B 05, 00 00). 4. S.Ijma, Physca B-Cndensed Matte 33, 00). 5. S.Ijma, Japan Nannet Bulletn 3 004). 6. S.Inue, N.Ichkun, T.Susuk, T.Uematsu, and K.Kanek, J. Phys. Chem. B, 0, ). 7. Y.Ye, C.C.Ahn, C.Wtham, B.Fults, J.Lu, G.RnzleA, D.Clbet, K.A.Smth, and R.E.Smalley, Appl. Phys. Lett. 74, ). 8. H.L.Cx, B. J. Appl. Phys. 3, 7 95). 9. K.Q.Xa and L.C.Zhang, J. Mat. Scence 39, ). 0. A.P.Bes and K.P.Chng, Elastcty n Engneeng Mechancs, nd edn., Wley-Intescence 000).. K.Mmen, A.Alasty, Stess dstbutn n pen-ended cabn nantubes, McNan08, Clea Wate Bay, Kwln, Hng Kng, June 008).. K.Mmen, A.Alasty, and A.Shkuha, Gvenng deental equatn the stess dstbutn n a sngle walled cabn nanhn embedded n an epxy matx nancmpste, NS008, Secnd Cn. Nanstuctues, Ksh Island, Ian, Mach 008). 3. S.Namlae, N.Chanda, and C.Shet,. Phys. Lett. 387, ). 4. J.R.Callste, Mateals Scence and Engneeng an Intductn, 5th edn., Jhn Wlley 000). 5. M.L.Abell and J.B.Baseltn, Maple by Example, Elseve Inc. 005). 6. M.K.Jan, S.R.K.Iyenga, and R.K.Jan, Numecal Methds Scentc and Engneeng Cmputatn, New Age Intenatnal Publshes 003). 7. X.L.Ga and K.L, IntenatnalJunal Slds and Stuctues 4, ). Receved: 4 July 009.Accepted: 3 Septembe 009. J. Cmput. The. Nansc. 7, 7, 00 7
Analytical Solution of Stress Distribution on a Hollow Cylindrical Fiber of a Composite with Cylindrical Volume Element under Axial Loading
 Wld Acadey Scence, ngneeng and Technlgy Intenatnal Junal Cvl, nvnental, Stuctual, Cnstuctn and Achtectual ngneeng Vl:, N:, 007 Analytcal Slutn Stess Dstbutn n a Hllw Cylndcal Fbe a Cpste wth Cylndcal Vlue
Wld Acadey Scence, ngneeng and Technlgy Intenatnal Junal Cvl, nvnental, Stuctual, Cnstuctn and Achtectual ngneeng Vl:, N:, 007 Analytcal Slutn Stess Dstbutn n a Hllw Cylndcal Fbe a Cpste wth Cylndcal Vlue
is needed and this can be established by multiplying A, obtained in step 3, by, resulting V = A x y =. = x, located in 1 st quadrant rotated about 2
 Ct Cllege f New Yk MATH (Calculus Ntes) Page 1 f 1 Essental Calculus, nd edtn (Stewat) Chapte 7 Sectn, and 6 auth: M. Pak Chapte 7 sectn : Vlume Suface f evlutn (Dsc methd) 1) Estalsh the tatn as and the
Ct Cllege f New Yk MATH (Calculus Ntes) Page 1 f 1 Essental Calculus, nd edtn (Stewat) Chapte 7 Sectn, and 6 auth: M. Pak Chapte 7 sectn : Vlume Suface f evlutn (Dsc methd) 1) Estalsh the tatn as and the
Introduction of Two Port Network Negative Feedback (Uni lateral Case) Feedback Topology Analysis of feedback applications
 Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w Pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83h 3 Feedback w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w Pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83h 3 Feedback w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
Electric potential energy Electrostatic force does work on a particle : Potential energy (: i initial state f : final state):
 Electc ptental enegy Electstatc fce des wk n a patcle : v v v v W = F s = E s. Ptental enegy (: ntal state f : fnal state): Δ U = U U = W. f ΔU Electc ptental : Δ : ptental enegy pe unt chag e. J ( Jule)
Electc ptental enegy Electstatc fce des wk n a patcle : v v v v W = F s = E s. Ptental enegy (: ntal state f : fnal state): Δ U = U U = W. f ΔU Electc ptental : Δ : ptental enegy pe unt chag e. J ( Jule)
Module 9 Thin and thick cylinders
 Mdule 9 Thn and thck cylndes Vesn 2 ME, IIT Khaagu Lessn 3 Desgn ncles f thck cylndes Vesn 2 ME, IIT Khaagu Instuctnal Objectves: At the end f ths lessn, the students shuld have the knwledge f: Falue thees
Mdule 9 Thn and thck cylndes Vesn 2 ME, IIT Khaagu Lessn 3 Desgn ncles f thck cylndes Vesn 2 ME, IIT Khaagu Instuctnal Objectves: At the end f ths lessn, the students shuld have the knwledge f: Falue thees
element k Using FEM to Solve Truss Problems
 sng EM t Slve Truss Prblems A truss s an engneerng structure cmpsed straght members, a certan materal, that are tpcall pn-ned at ther ends. Such members are als called tw-rce members snce the can nl transmt
sng EM t Slve Truss Prblems A truss s an engneerng structure cmpsed straght members, a certan materal, that are tpcall pn-ned at ther ends. Such members are als called tw-rce members snce the can nl transmt
Lecture 2 Feedback Amplifier
 Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w-pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un-lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse-Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83hkn 3 Feedback mples w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w-pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un-lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse-Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83hkn 3 Feedback mples w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
COMPLEMENTARY ENERGY METHOD FOR CURVED COMPOSITE BEAMS
 ultscence - XXX. mcocd Intenatonal ultdscplnay Scentfc Confeence Unvesty of skolc Hungay - pl 06 ISBN 978-963-358-3- COPLEENTRY ENERGY ETHOD FOR CURVED COPOSITE BES Ákos József Lengyel István Ecsed ssstant
ultscence - XXX. mcocd Intenatonal ultdscplnay Scentfc Confeence Unvesty of skolc Hungay - pl 06 ISBN 978-963-358-3- COPLEENTRY ENERGY ETHOD FOR CURVED COPOSITE BES Ákos József Lengyel István Ecsed ssstant
ME311 Machine Design
 ME311 Machne Desgn Lectue 8: Cylnes W Dnfel Nv017 Fafel Unvesty Schl f Engneeng Thn-Walle Cylnes (Yu aleay cvee ths n Bee & Jhnstn.) A essuze cylne s cnsee t be Thn-Walle f ts wall thckness s less than.5%
ME311 Machne Desgn Lectue 8: Cylnes W Dnfel Nv017 Fafel Unvesty Schl f Engneeng Thn-Walle Cylnes (Yu aleay cvee ths n Bee & Jhnstn.) A essuze cylne s cnsee t be Thn-Walle f ts wall thckness s less than.5%
Example 11: The man shown in Figure (a) pulls on the cord with a force of 70
 Chapte Tw ce System 35.4 α α 100 Rx cs 0.354 R 69.3 35.4 β β 100 Ry cs 0.354 R 111 Example 11: The man shwn in igue (a) pulls n the cd with a fce f 70 lb. Repesent this fce actin n the suppt A as Catesian
Chapte Tw ce System 35.4 α α 100 Rx cs 0.354 R 69.3 35.4 β β 100 Ry cs 0.354 R 111 Example 11: The man shwn in igue (a) pulls n the cd with a fce f 70 lb. Repesent this fce actin n the suppt A as Catesian
A criterion of warpage about center-anchored deformable focusing micromirrors
 A cten f wapage abut cente-anched defmable fcusng mcms MENG-JU LIN Depatment f Mechancal and Cmpute Aded Engneeng Feng Cha Unvesty N., Wen-Hwa Rd., achung, awan 7, R. O. C. AIWAN, R.O.C. Abstact: - A cten
A cten f wapage abut cente-anched defmable fcusng mcms MENG-JU LIN Depatment f Mechancal and Cmpute Aded Engneeng Feng Cha Unvesty N., Wen-Hwa Rd., achung, awan 7, R. O. C. AIWAN, R.O.C. Abstact: - A cten
(5) Furthermore, the third constraint implies the following equation: (6)
 T-Element Refactng System f Gaussan and Annula-Gaussan Beams Tansfmatn Abdallah K. Che *, Nabl I. Khachab, Mahmud K. Habb Electcal Engneeng Depatment, Cllege f Engneeng and Petleum, Kuat Unvesty, P. O.
T-Element Refactng System f Gaussan and Annula-Gaussan Beams Tansfmatn Abdallah K. Che *, Nabl I. Khachab, Mahmud K. Habb Electcal Engneeng Depatment, Cllege f Engneeng and Petleum, Kuat Unvesty, P. O.
Chapter 3, Solution 1C.
 COSMOS: Cmplete Onlne Slutns Manual Organzatn System Chapter 3, Slutn C. (a If the lateral surfaces f the rd are nsulated, the heat transfer surface area f the cylndrcal rd s the bttm r the tp surface
COSMOS: Cmplete Onlne Slutns Manual Organzatn System Chapter 3, Slutn C. (a If the lateral surfaces f the rd are nsulated, the heat transfer surface area f the cylndrcal rd s the bttm r the tp surface
Shakedown Analysis of a Composite Cylinder with a Cross-hole
 hakedwn nalyss f a Cmpste Cylnde wth a Css-hle Hafeng Chen *, Wehang Chen, Tanba L, James Ue Depatment f Mechancal Engneeng, Unvesty f tathclyde, Glasgw, G XJ, UK bstact: In ths study, bth the lwe and
hakedwn nalyss f a Cmpste Cylnde wth a Css-hle Hafeng Chen *, Wehang Chen, Tanba L, James Ue Depatment f Mechancal Engneeng, Unvesty f tathclyde, Glasgw, G XJ, UK bstact: In ths study, bth the lwe and
T-model: - + v o. v i. i o. v e. R i
 T-mdel: e gm - V Rc e e e gme R R R 23 e e e gme R R The s/c tanscnductance: G m e m g gm e 0 The nput esstance: R e e e e The utput esstance: R R 0 /c unladed ltage gan, R a g R m e gmr e 0 m e g me e/e
T-mdel: e gm - V Rc e e e gme R R R 23 e e e gme R R The s/c tanscnductance: G m e m g gm e 0 The nput esstance: R e e e e The utput esstance: R R 0 /c unladed ltage gan, R a g R m e gmr e 0 m e g me e/e
Selective Convexity in Extended GDEA Model
 Appled Mathematcal Scences, Vl. 5, 20, n. 78, 386-3873 Selectve nvet n Etended GDEA Mdel Sevan Shaee a and Fahad Hssenadeh Ltf b a. Depatment f Mathematcs, ehan Nth Banch, Islamc Aad Unvest, ehan, Ian
Appled Mathematcal Scences, Vl. 5, 20, n. 78, 386-3873 Selectve nvet n Etended GDEA Mdel Sevan Shaee a and Fahad Hssenadeh Ltf b a. Depatment f Mathematcs, ehan Nth Banch, Islamc Aad Unvest, ehan, Ian
Parametric Examination including Brief Survey of Composite and Homogenous Closed Ended Cylindrical Pressure Vessels
 Jacb Nagle Paametc Examnatn ncludng Bef Suvey f Cmste and Hmgenus Clsed Ended Cylndcal Pessue Vessels JACOB NAGLER Faculty f Aesace Engneeng Technn Hafa 3000 ISRAEL syank@tx.technn.ac.l syanktx@gmal.cm
Jacb Nagle Paametc Examnatn ncludng Bef Suvey f Cmste and Hmgenus Clsed Ended Cylndcal Pessue Vessels JACOB NAGLER Faculty f Aesace Engneeng Technn Hafa 3000 ISRAEL syank@tx.technn.ac.l syanktx@gmal.cm
Mathematical Modeling & Analysis of Brake Pad for Wear Characteristics
 Intenatnal Cnfeence n Ideas, Impact and Innvatn n Mechancal Engneeng (ICIIIME 07 ISSN: -869 Vlume: 5 Issue: 6 048 056 Mathematcal Mdelng & Analyss f Bake Pad f Wea Chaactestcs S. R. Kakad, R.M. Me, D.
Intenatnal Cnfeence n Ideas, Impact and Innvatn n Mechancal Engneeng (ICIIIME 07 ISSN: -869 Vlume: 5 Issue: 6 048 056 Mathematcal Mdelng & Analyss f Bake Pad f Wea Chaactestcs S. R. Kakad, R.M. Me, D.
Optimization of the Electron Gun with a Permanent Ion Trap
 4.3.-178 Optmzatn f the Electn Gun wth a Pemanent In Tap We Le Xabng Zhang Jn Dng Fe Dpla Technlg R&D CenteSutheat Unvet Nangjng Chna Danel den Engelen Pduct and Pce Develpment(PPD)LG.Phlp Dpla 5600 MD
4.3.-178 Optmzatn f the Electn Gun wth a Pemanent In Tap We Le Xabng Zhang Jn Dng Fe Dpla Technlg R&D CenteSutheat Unvet Nangjng Chna Danel den Engelen Pduct and Pce Develpment(PPD)LG.Phlp Dpla 5600 MD
WYSE Academic Challenge Sectional Mathematics 2006 Solution Set
 WYSE Academic Challenge Sectinal 006 Slutin Set. Cect answe: e. mph is 76 feet pe minute, and 4 mph is 35 feet pe minute. The tip up the hill takes 600/76, 3.4 minutes, and the tip dwn takes 600/35,.70
WYSE Academic Challenge Sectinal 006 Slutin Set. Cect answe: e. mph is 76 feet pe minute, and 4 mph is 35 feet pe minute. The tip up the hill takes 600/76, 3.4 minutes, and the tip dwn takes 600/35,.70
Announcements Candidates Visiting Next Monday 11 12:20 Class 4pm Research Talk Opportunity to learn a little about what physicists do
 Wed., /11 Thus., /1 Fi., /13 Mn., /16 Tues., /17 Wed., /18 Thus., /19 Fi., / 17.7-9 Magnetic Field F Distibutins Lab 5: Bit-Savat B fields f mving chages (n quiz) 17.1-11 Pemanent Magnets 18.1-3 Mic. View
Wed., /11 Thus., /1 Fi., /13 Mn., /16 Tues., /17 Wed., /18 Thus., /19 Fi., / 17.7-9 Magnetic Field F Distibutins Lab 5: Bit-Savat B fields f mving chages (n quiz) 17.1-11 Pemanent Magnets 18.1-3 Mic. View
Section 3: Detailed Solutions of Word Problems Unit 1: Solving Word Problems by Modeling with Formulas
 Sectn : Detaled Slutns f Wrd Prblems Unt : Slvng Wrd Prblems by Mdelng wth Frmulas Example : The factry nvce fr a mnvan shws that the dealer pad $,5 fr the vehcle. If the stcker prce f the van s $5,, hw
Sectn : Detaled Slutns f Wrd Prblems Unt : Slvng Wrd Prblems by Mdelng wth Frmulas Example : The factry nvce fr a mnvan shws that the dealer pad $,5 fr the vehcle. If the stcker prce f the van s $5,, hw
Transient Conduction: Spatial Effects and the Role of Analytical Solutions
 Transent Cnductn: Spatal Effects and the Rle f Analytcal Slutns Slutn t the Heat Equatn fr a Plane Wall wth Symmetrcal Cnvectn Cndtns If the lumped capactance apprxmatn can nt be made, cnsderatn must be
Transent Cnductn: Spatal Effects and the Rle f Analytcal Slutns Slutn t the Heat Equatn fr a Plane Wall wth Symmetrcal Cnvectn Cndtns If the lumped capactance apprxmatn can nt be made, cnsderatn must be
V. Principles of Irreversible Thermodynamics. s = S - S 0 (7.3) s = = - g i, k. "Flux": = da i. "Force": = -Â g a ik k = X i. Â J i X i (7.
 Themodynamcs and Knetcs of Solds 71 V. Pncples of Ievesble Themodynamcs 5. Onsage s Teatment s = S - S 0 = s( a 1, a 2,...) a n = A g - A n (7.6) Equlbum themodynamcs detemnes the paametes of an equlbum
Themodynamcs and Knetcs of Solds 71 V. Pncples of Ievesble Themodynamcs 5. Onsage s Teatment s = S - S 0 = s( a 1, a 2,...) a n = A g - A n (7.6) Equlbum themodynamcs detemnes the paametes of an equlbum
LEAP FROG TECHNIQUE. Operational Simulation of LC Ladder Filters ECEN 622 (ESS) TAMU-AMSC
 LEAP FOG TEHNQUE Opeatnal Smulatn f L Ladde Fltes L pttype lw senstvty One fm f ths technque s called Leapf Technque Fundamental Buldn Blcks ae - nteats - Secnd-de ealzatns Fltes cnsdeed - LP - BP - HP
LEAP FOG TEHNQUE Opeatnal Smulatn f L Ladde Fltes L pttype lw senstvty One fm f ths technque s called Leapf Technque Fundamental Buldn Blcks ae - nteats - Secnd-de ealzatns Fltes cnsdeed - LP - BP - HP
CHAPTER 24 GAUSS LAW
 CHAPTR 4 GAUSS LAW LCTRIC FLUX lectic flux is a measue f the numbe f electic filed lines penetating sme suface in a diectin pependicula t that suface. Φ = A = A csθ with θ is the angle between the and
CHAPTR 4 GAUSS LAW LCTRIC FLUX lectic flux is a measue f the numbe f electic filed lines penetating sme suface in a diectin pependicula t that suface. Φ = A = A csθ with θ is the angle between the and
More Effective Optimum Synthesis of Path Generating Four-Bar Mechanisms
 Junal f Multdscplnay Engneeng Scence and Technlgy (JMEST) ISSN: 59- Vl. Issue 5, May - 5 Me Effectve Optmum Synthess f Path Geneatng Fu-Ba Mechansms Wen-Y Ln Depatment f Mechancal Engneeng De Ln Insttute
Junal f Multdscplnay Engneeng Scence and Technlgy (JMEST) ISSN: 59- Vl. Issue 5, May - 5 Me Effectve Optmum Synthess f Path Geneatng Fu-Ba Mechansms Wen-Y Ln Depatment f Mechancal Engneeng De Ln Insttute
Work, Energy, and Power. AP Physics C
 k, Eneg, and Pwe AP Phsics C Thee ae man diffeent TYPES f Eneg. Eneg is expessed in JOULES (J) 4.19 J = 1 calie Eneg can be expessed me specificall b using the tem ORK() k = The Scala Dt Pduct between
k, Eneg, and Pwe AP Phsics C Thee ae man diffeent TYPES f Eneg. Eneg is expessed in JOULES (J) 4.19 J = 1 calie Eneg can be expessed me specificall b using the tem ORK() k = The Scala Dt Pduct between
5/20/2011. HITT An electron moves from point i to point f, in the direction of a uniform electric field. During this displacement:
 5/0/011 Chapte 5 In the last lectue: CapacitanceII we calculated the capacitance C f a system f tw islated cnducts. We als calculated the capacitance f sme simple gemeties. In this chapte we will cve the
5/0/011 Chapte 5 In the last lectue: CapacitanceII we calculated the capacitance C f a system f tw islated cnducts. We als calculated the capacitance f sme simple gemeties. In this chapte we will cve the
Phys 331: Ch 9,.6-.7 Noninertial Frames: Centrifugal and Corriolis forces 1. And and
 Phs 331: Ch 9 6-7 Nnnetal Fames: Centfual and Cls fces 1 Mn 1/5 Wed 1/7 Thus F Mn 1/6 96-7 Fctnal Fces: Centfual and Cls 98-9 Fee-Fall Cls Fucault 101- Cente f Mass & Rtatn abut a Fed As 103-4 Rtatn abut
Phs 331: Ch 9 6-7 Nnnetal Fames: Centfual and Cls fces 1 Mn 1/5 Wed 1/7 Thus F Mn 1/6 96-7 Fctnal Fces: Centfual and Cls 98-9 Fee-Fall Cls Fucault 101- Cente f Mass & Rtatn abut a Fed As 103-4 Rtatn abut
Cork Institute of Technology. Spring 2005 DCE 3.5 Thermodynamics & Heat Transfer (Time: 3 Hours) Section A
 Ck Insttute f echnlgy Bachel f Engneeng (Hnus) n Chemcal and Pcess Engneeng Stage 3 Bachel f Engneeng n Chemcal and Pcess Engneeng Stage 3 (NFQ Level 8) Spng 005 DCE 3.5 hemdynamcs & Heat ansfe (me: 3
Ck Insttute f echnlgy Bachel f Engneeng (Hnus) n Chemcal and Pcess Engneeng Stage 3 Bachel f Engneeng n Chemcal and Pcess Engneeng Stage 3 (NFQ Level 8) Spng 005 DCE 3.5 hemdynamcs & Heat ansfe (me: 3
A) N B) 0.0 N C) N D) N E) N
 Cdinat: H Bahluli Sunday, Nvembe, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Five identical pint chages each with chage =10 nc ae lcated at the cnes f a egula hexagn, as shwn in Figue 1. Find the magnitude f the net electic fce
Cdinat: H Bahluli Sunday, Nvembe, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Five identical pint chages each with chage =10 nc ae lcated at the cnes f a egula hexagn, as shwn in Figue 1. Find the magnitude f the net electic fce
Rotating Variable-Thickness Inhomogeneous Cylinders: Part II Viscoelastic Solutions and Applications
 Appled Mathematcs 010 1 489-498 do:10.436/am.010.16064 Publshed Onlne Decembe 010 (http://www.scrp.og/jounal/am) Rotatng Vaable-Thckness Inhomogeneous Cylndes: Pat II Vscoelastc Solutons and Applcatons
Appled Mathematcs 010 1 489-498 do:10.436/am.010.16064 Publshed Onlne Decembe 010 (http://www.scrp.og/jounal/am) Rotatng Vaable-Thckness Inhomogeneous Cylndes: Pat II Vscoelastc Solutons and Applcatons
Outline. Steady Heat Transfer with Conduction and Convection. Review Steady, 1-D, Review Heat Generation. Review Heat Generation II
 Steady Heat ansfe ebuay, 7 Steady Heat ansfe wit Cnductin and Cnvectin ay Caett Mecanical Engineeing 375 Heat ansfe ebuay, 7 Outline eview last lectue Equivalent cicuit analyses eview basic cncept pplicatin
Steady Heat ansfe ebuay, 7 Steady Heat ansfe wit Cnductin and Cnvectin ay Caett Mecanical Engineeing 375 Heat ansfe ebuay, 7 Outline eview last lectue Equivalent cicuit analyses eview basic cncept pplicatin
ME2142/ME2142E Feedback Control Systems. Modelling of Physical Systems The Transfer Function
 Mdellng Physcal Systems The Transer Functn Derental Equatns U Plant Y In the plant shwn, the nput u aects the respnse the utput y. In general, the dynamcs ths respnse can be descrbed by a derental equatn
Mdellng Physcal Systems The Transer Functn Derental Equatns U Plant Y In the plant shwn, the nput u aects the respnse the utput y. In general, the dynamcs ths respnse can be descrbed by a derental equatn
CHAPTER GAUSS'S LAW
 lutins--ch 14 (Gauss's Law CHAPTE 14 -- GAU' LAW 141 This pblem is ticky An electic field line that flws int, then ut f the cap (see Figue I pduces a negative flux when enteing and an equal psitive flux
lutins--ch 14 (Gauss's Law CHAPTE 14 -- GAU' LAW 141 This pblem is ticky An electic field line that flws int, then ut f the cap (see Figue I pduces a negative flux when enteing and an equal psitive flux
Conduction Heat Transfer
 Cnductn Heat Transfer Practce prblems A steel ppe f cnductvty 5 W/m-K has nsde and utsde surface temperature f C and 6 C respectvely Fnd the heat flw rate per unt ppe length and flux per unt nsde and per
Cnductn Heat Transfer Practce prblems A steel ppe f cnductvty 5 W/m-K has nsde and utsde surface temperature f C and 6 C respectvely Fnd the heat flw rate per unt ppe length and flux per unt nsde and per
Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapte 3 lectmagnetic Waves 3.1 Maxwell s quatins and ectmagnetic Waves A. Gauss s Law: # clsed suface aea " da Q enc lectic fields may be geneated by electic chages. lectic field lines stat at psitive
Chapte 3 lectmagnetic Waves 3.1 Maxwell s quatins and ectmagnetic Waves A. Gauss s Law: # clsed suface aea " da Q enc lectic fields may be geneated by electic chages. lectic field lines stat at psitive
A) (0.46 î ) N B) (0.17 î ) N
 Phys10 Secnd Maj-14 Ze Vesin Cdinat: xyz Thusday, Apil 3, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Thee chages, 1 = =.0 μc and Q = 4.0 μc, ae fixed in thei places as shwn in Figue 1. Find the net electstatic fce n Q due t 1 and.
Phys10 Secnd Maj-14 Ze Vesin Cdinat: xyz Thusday, Apil 3, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Thee chages, 1 = =.0 μc and Q = 4.0 μc, ae fixed in thei places as shwn in Figue 1. Find the net electstatic fce n Q due t 1 and.
CTN 2/23/16. EE 247B/ME 218: Introduction to MEMS Design Lecture 11m2: Mechanics of Materials. Copyright 2016 Regents of the University of California
 Vlume Change fr a Unaxal Stress Istrpc lastcty n 3D Istrpc = same n all drectns The cmplete stress-stran relatns fr an strpc elastc Stresses actng n a dfferental vlume element sld n 3D: (.e., a generalzed
Vlume Change fr a Unaxal Stress Istrpc lastcty n 3D Istrpc = same n all drectns The cmplete stress-stran relatns fr an strpc elastc Stresses actng n a dfferental vlume element sld n 3D: (.e., a generalzed
( ) α is determined to be a solution of the one-dimensional minimization problem: = 2. min = 2
 Homewo (Patal Solton) Posted on Mach, 999 MEAM 5 Deental Eqaton Methods n Mechancs. Sole the ollowng mat eqaton A b by () Steepest Descent Method and/o Pecondtoned SD Method Snce the coecent mat A s symmetc,
Homewo (Patal Solton) Posted on Mach, 999 MEAM 5 Deental Eqaton Methods n Mechancs. Sole the ollowng mat eqaton A b by () Steepest Descent Method and/o Pecondtoned SD Method Snce the coecent mat A s symmetc,
CSJM University Class: B.Sc.-II Sub:Physics Paper-II Title: Electromagnetics Unit-1: Electrostatics Lecture: 1 to 4
 CSJM Unvesty Class: B.Sc.-II Sub:Physcs Pape-II Ttle: Electomagnetcs Unt-: Electostatcs Lectue: to 4 Electostatcs: It deals the study of behavo of statc o statonay Chages. Electc Chage: It s popety by
CSJM Unvesty Class: B.Sc.-II Sub:Physcs Pape-II Ttle: Electomagnetcs Unt-: Electostatcs Lectue: to 4 Electostatcs: It deals the study of behavo of statc o statonay Chages. Electc Chage: It s popety by
SHAKEDOWN BEHAVIOUR OF COMPOSITE CYLINDERS WITH CROSS HOLE
 HKEDOWN BEHIOU OF COMPOITE CYLINDE WITH CO HOLE Hafeng Chen Deatment f Mechancal Engneeng Unvesty f tathclyde Glasgw, ctland, UK Wehang Chen Deatment f Mechancal Engneeng Unvesty f tathclyde Glasgw, ctland,
HKEDOWN BEHIOU OF COMPOITE CYLINDE WITH CO HOLE Hafeng Chen Deatment f Mechancal Engneeng Unvesty f tathclyde Glasgw, ctland, UK Wehang Chen Deatment f Mechancal Engneeng Unvesty f tathclyde Glasgw, ctland,
Hotelling s Rule. Therefore arbitrage forces P(t) = P o e rt.
 Htelling s Rule In what fllws I will use the tem pice t dente unit pfit. hat is, the nminal mney pice minus the aveage cst f pductin. We begin with cmpetitin. Suppse that a fim wns a small pa, a, f the
Htelling s Rule In what fllws I will use the tem pice t dente unit pfit. hat is, the nminal mney pice minus the aveage cst f pductin. We begin with cmpetitin. Suppse that a fim wns a small pa, a, f the
CIRCLE YOUR DIVISION: Div. 1 (9:30 am) Div. 2 (11:30 am) Div. 3 (2:30 pm) Prof. Ruan Prof. Naik Mr. Singh
 Frst CIRCLE YOUR DIVISION: Dv. 1 (9:30 am) Dv. (11:30 am) Dv. 3 (:30 m) Prf. Ruan Prf. Na Mr. Sngh Schl f Mechancal Engneerng Purdue Unversty ME315 Heat and Mass ransfer Eam #3 Wednesday Nvember 17 010
Frst CIRCLE YOUR DIVISION: Dv. 1 (9:30 am) Dv. (11:30 am) Dv. 3 (:30 m) Prf. Ruan Prf. Na Mr. Sngh Schl f Mechancal Engneerng Purdue Unversty ME315 Heat and Mass ransfer Eam #3 Wednesday Nvember 17 010
Remember: When an object falls due to gravity its potential energy decreases.
 Chapte 5: lectc Potental As mentoned seveal tmes dung the uate Newton s law o gavty and Coulomb s law ae dentcal n the mathematcal om. So, most thngs that ae tue o gavty ae also tue o electostatcs! Hee
Chapte 5: lectc Potental As mentoned seveal tmes dung the uate Newton s law o gavty and Coulomb s law ae dentcal n the mathematcal om. So, most thngs that ae tue o gavty ae also tue o electostatcs! Hee
Molecular Dynamic Simulations of Nickel Nanowires at Various Temperatures
 Intenatonal Jounal of Scentfc and Innovatve Mathematcal Reseach (IJSIMR Volume 2, Issue 3, Mach 204, PP 30-305 ISS 2347-307X (Pnt & ISS 2347-342 (Onlne www.acounals.og Molecula Dynamc Smulatons of ckel
Intenatonal Jounal of Scentfc and Innovatve Mathematcal Reseach (IJSIMR Volume 2, Issue 3, Mach 204, PP 30-305 ISS 2347-307X (Pnt & ISS 2347-342 (Onlne www.acounals.og Molecula Dynamc Smulatons of ckel
March 15. Induction and Inductance Chapter 31
 Mach 15 Inductin and Inductance Chapte 31 > Fces due t B fields Lentz fce τ On a mving chage F B On a cuent F il B Cuent caying cil feels a tque = µ B Review > Cuents geneate B field Bit-Savat law = qv
Mach 15 Inductin and Inductance Chapte 31 > Fces due t B fields Lentz fce τ On a mving chage F B On a cuent F il B Cuent caying cil feels a tque = µ B Review > Cuents geneate B field Bit-Savat law = qv
Example
 hapte Exaple.6-3. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5 A single hllw fibe is placed within a vey lage glass tube. he hllw fibe is 0 c in length and has a
hapte Exaple.6-3. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5 A single hllw fibe is placed within a vey lage glass tube. he hllw fibe is 0 c in length and has a
Drawing of Hollow Multilayered All-Polymer Fibers
 Mate. Res. Sc. Symp. Pc. Vl. 90 006 Mateals Reseach Scety 090-S01-05 Dawng f Hllw Multlayeed All-Plyme Fbes El Pne, Chales Dubs, Nng Gu, Yan Ga, Alexande Dupus, Suanne Lacx, and Maksm Skbgaty Écle Plytechnque
Mate. Res. Sc. Symp. Pc. Vl. 90 006 Mateals Reseach Scety 090-S01-05 Dawng f Hllw Multlayeed All-Plyme Fbes El Pne, Chales Dubs, Nng Gu, Yan Ga, Alexande Dupus, Suanne Lacx, and Maksm Skbgaty Écle Plytechnque
Wp/Lmin. Wn/Lmin 2.5V
 UNIVERITY OF CALIFORNIA Cllege f Engneerng Department f Electrcal Engneerng and Cmputer cences Andre Vladmrescu Hmewrk #7 EEC Due Frday, Aprl 8 th, pm @ 0 Cry Prblem #.5V Wp/Lmn 0.0V Wp/Lmn n ut Wn/Lmn.5V
UNIVERITY OF CALIFORNIA Cllege f Engneerng Department f Electrcal Engneerng and Cmputer cences Andre Vladmrescu Hmewrk #7 EEC Due Frday, Aprl 8 th, pm @ 0 Cry Prblem #.5V Wp/Lmn 0.0V Wp/Lmn n ut Wn/Lmn.5V
ME 3600 Control Systems Frequency Domain Analysis
 ME 3600 Cntl Systems Fequency Dmain Analysis The fequency espnse f a system is defined as the steady-state espnse f the system t a sinusidal (hamnic) input. F linea systems, the esulting utput is itself
ME 3600 Cntl Systems Fequency Dmain Analysis The fequency espnse f a system is defined as the steady-state espnse f the system t a sinusidal (hamnic) input. F linea systems, the esulting utput is itself
Physics 2A Chapter 11 - Universal Gravitation Fall 2017
 Physcs A Chapte - Unvesal Gavtaton Fall 07 hese notes ae ve pages. A quck summay: he text boxes n the notes contan the esults that wll compse the toolbox o Chapte. hee ae thee sectons: the law o gavtaton,
Physcs A Chapte - Unvesal Gavtaton Fall 07 hese notes ae ve pages. A quck summay: he text boxes n the notes contan the esults that wll compse the toolbox o Chapte. hee ae thee sectons: the law o gavtaton,
Chapter 7. Systems 7.1 INTRODUCTION 7.2 MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF LIQUID LEVEL SYSTEMS. Steady State Flow. A. Bazoune
 Chapter 7 Flud Systems and Thermal Systems 7.1 INTODUCTION A. Bazune A flud system uses ne r mre fluds t acheve ts purpse. Dampers and shck absrbers are eamples f flud systems because they depend n the
Chapter 7 Flud Systems and Thermal Systems 7.1 INTODUCTION A. Bazune A flud system uses ne r mre fluds t acheve ts purpse. Dampers and shck absrbers are eamples f flud systems because they depend n the
5.1 Moment of a Force Scalar Formation
 Outline ment f a Cuple Equivalent System Resultants f a Fce and Cuple System ment f a fce abut a pint axis a measue f the tendency f the fce t cause a bdy t tate abut the pint axis Case 1 Cnside hizntal
Outline ment f a Cuple Equivalent System Resultants f a Fce and Cuple System ment f a fce abut a pint axis a measue f the tendency f the fce t cause a bdy t tate abut the pint axis Case 1 Cnside hizntal
Strees Analysis in Elastic Half Space Due To a Thermoelastic Strain
 IOSR Junal f Mathematics (IOSRJM) ISSN: 78-578 Vlume, Issue (July-Aug 0), PP 46-54 Stees Analysis in Elastic Half Space Due T a Themelastic Stain Aya Ahmad Depatment f Mathematics NIT Patna Biha India
IOSR Junal f Mathematics (IOSRJM) ISSN: 78-578 Vlume, Issue (July-Aug 0), PP 46-54 Stees Analysis in Elastic Half Space Due T a Themelastic Stain Aya Ahmad Depatment f Mathematics NIT Patna Biha India
Combustion Chamber. (0.1 MPa)
 ME 354 Tutial #10 Winte 001 Reacting Mixtues Pblem 1: Detemine the mle actins the pducts cmbustin when ctane, C 8 18, is buned with 00% theetical ai. Als, detemine the dew-pint tempeatue the pducts i the
ME 354 Tutial #10 Winte 001 Reacting Mixtues Pblem 1: Detemine the mle actins the pducts cmbustin when ctane, C 8 18, is buned with 00% theetical ai. Als, detemine the dew-pint tempeatue the pducts i the
A) 100 K B) 150 K C) 200 K D) 250 K E) 350 K
 Phys10 Secnd Maj-09 Ze Vesin Cdinat: k Wednesday, May 05, 010 Page: 1 Q1. A ht bject and a cld bject ae placed in themal cntact and the cmbinatin is islated. They tansfe enegy until they each a final equilibium
Phys10 Secnd Maj-09 Ze Vesin Cdinat: k Wednesday, May 05, 010 Page: 1 Q1. A ht bject and a cld bject ae placed in themal cntact and the cmbinatin is islated. They tansfe enegy until they each a final equilibium
The Gradient and Applications This unit is based on Sections 9.5 and 9.6, Chapter 9. All assigned readings and exercises are from the textbook
 The Gadient and Applicatins This unit is based n Sectins 9.5 and 9.6 Chapte 9. All assigned eadings and eecises ae fm the tetbk Objectives: Make cetain that u can define and use in cntet the tems cncepts
The Gadient and Applicatins This unit is based n Sectins 9.5 and 9.6 Chapte 9. All assigned eadings and eecises ae fm the tetbk Objectives: Make cetain that u can define and use in cntet the tems cncepts
Electric Charge. Electric charge is quantized. Electric charge is conserved
 lectstatics lectic Chage lectic chage is uantized Chage cmes in incements f the elementay chage e = ne, whee n is an intege, and e =.6 x 0-9 C lectic chage is cnseved Chage (electns) can be mved fm ne
lectstatics lectic Chage lectic chage is uantized Chage cmes in incements f the elementay chage e = ne, whee n is an intege, and e =.6 x 0-9 C lectic chage is cnseved Chage (electns) can be mved fm ne
Scalars and Vectors Scalar
 Scalas and ectos Scala A phscal quantt that s completel chaacteed b a eal numbe (o b ts numecal value) s called a scala. In othe wods a scala possesses onl a magntude. Mass denst volume tempeatue tme eneg
Scalas and ectos Scala A phscal quantt that s completel chaacteed b a eal numbe (o b ts numecal value) s called a scala. In othe wods a scala possesses onl a magntude. Mass denst volume tempeatue tme eneg
ELECTRIC & MAGNETIC FIELDS I (STATIC FIELDS) ELC 205A
 LCTRIC & MAGNTIC FILDS I (STATIC FILDS) LC 05A D. Hanna A. Kils Assciate Pfess lectnics & Cmmnicatins ngineeing Depatment Faclty f ngineeing Cai Univesity Fall 0 f Static lecticity lectic & Magnetic Fields
LCTRIC & MAGNTIC FILDS I (STATIC FILDS) LC 05A D. Hanna A. Kils Assciate Pfess lectnics & Cmmnicatins ngineeing Depatment Faclty f ngineeing Cai Univesity Fall 0 f Static lecticity lectic & Magnetic Fields
IJARI. 1. Introduction. 2. Physical Problem And Governing Equation
 Vlume, Issue (6) 56-6 ISS 7-58 Intenatnal Junal f Advane Reseah and Innvatn Slutns f the Aust Pblem n the D Fm f the Helmhltz Equatn Usng DRBEM Hassan Ghassem a,*, Ahmad Reza Khansal b a Depatment f Matme
Vlume, Issue (6) 56-6 ISS 7-58 Intenatnal Junal f Advane Reseah and Innvatn Slutns f the Aust Pblem n the D Fm f the Helmhltz Equatn Usng DRBEM Hassan Ghassem a,*, Ahmad Reza Khansal b a Depatment f Matme
Analytical and Numerical Solutions for a Rotating Annular Disk of Variable Thickness
 Appled Mathematcs 00 43-438 do:0.436/am.00.5057 Publshed Onlne Novembe 00 (http://www.scrp.og/jounal/am) Analytcal and Numecal Solutons fo a Rotatng Annula Ds of Vaable Thcness Abstact Ashaf M. Zenou Daoud
Appled Mathematcs 00 43-438 do:0.436/am.00.5057 Publshed Onlne Novembe 00 (http://www.scrp.og/jounal/am) Analytcal and Numecal Solutons fo a Rotatng Annula Ds of Vaable Thcness Abstact Ashaf M. Zenou Daoud
Chapter 4 Motion in Two and Three Dimensions
 Chapte 4 Mtin in Tw and Thee Dimensins In this chapte we will cntinue t stud the mtin f bjects withut the estictin we put in chapte t me aln a staiht line. Instead we will cnside mtin in a plane (tw dimensinal
Chapte 4 Mtin in Tw and Thee Dimensins In this chapte we will cntinue t stud the mtin f bjects withut the estictin we put in chapte t me aln a staiht line. Instead we will cnside mtin in a plane (tw dimensinal
which represents a straight line whose slope is C 1.
 hapte, Slutin 5. Ye, thi claim i eanable ince in the abence any heat eatin the ate heat tane thugh a plain wall in teady peatin mut be cntant. But the value thi cntant mut be ze ince ne ide the wall i
hapte, Slutin 5. Ye, thi claim i eanable ince in the abence any heat eatin the ate heat tane thugh a plain wall in teady peatin mut be cntant. But the value thi cntant mut be ze ince ne ide the wall i
Exercises for Frequency Response. ECE 102, Fall 2012, F. Najmabadi
 Eecses Fequency espnse EE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabad Eecse : Fnd the d-band an and the lwe cut- equency the aple belw. µ n (W/ 4 A/, t 0.5, λ 0, 0 µf, and µf Bth capacts ae lw- capacts. F. Najabad, EE0, Fall
Eecses Fequency espnse EE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabad Eecse : Fnd the d-band an and the lwe cut- equency the aple belw. µ n (W/ 4 A/, t 0.5, λ 0, 0 µf, and µf Bth capacts ae lw- capacts. F. Najabad, EE0, Fall
Characteristic of Stress Distribution at a Vertex in Orthotropic Piezo-ceramic Bi-material Bonded Joints
 ceedngs f the Intenatnal Cnfeence n Mechancal ngneeng Renewable negy 7 (ICMR7) Decembe 7 Chttagng Bangladesh ICMR7-I-57 Chaactestc f Stess Dstbtn at a Vetex n Othtpc ez-ceamc B-mateal Bnded nts Md. ShahdlIslam
ceedngs f the Intenatnal Cnfeence n Mechancal ngneeng Renewable negy 7 (ICMR7) Decembe 7 Chttagng Bangladesh ICMR7-I-57 Chaactestc f Stess Dstbtn at a Vetex n Othtpc ez-ceamc B-mateal Bnded nts Md. ShahdlIslam
Derivation of the Differential Forms of the Conservation Laws Momentum
 Deatn f the Dffeental Fms f the Cnseatn Las Mmentm Aach t Deng the Dffeental Fms f the Cnseatn Las. Wte t the la f a sstem f atcles DNss D ηd Dt Dt. Rete the la n tems f a cntl lme sng the R.T.T. and Lebn
Deatn f the Dffeental Fms f the Cnseatn Las Mmentm Aach t Deng the Dffeental Fms f the Cnseatn Las. Wte t the la f a sstem f atcles DNss D ηd Dt Dt. Rete the la n tems f a cntl lme sng the R.T.T. and Lebn
Application of Net Radiation Transfer Method for Optimization and Calculation of Reduction Heat Transfer, Using Spherical Radiation Shields
 Wld Applied Sciences Junal (4: 457-46, 00 ISSN 88-495 IDOSI Publicatins, 00 Applicatin f Net Radiatin Tansfe Methd f Optimizatin and Calculatin f Reductin Heat Tansfe, Using Spheical Radiatin Shields Seyflah
Wld Applied Sciences Junal (4: 457-46, 00 ISSN 88-495 IDOSI Publicatins, 00 Applicatin f Net Radiatin Tansfe Methd f Optimizatin and Calculatin f Reductin Heat Tansfe, Using Spheical Radiatin Shields Seyflah
WYSE Academic Challenge 2004 Sectional Physics Solution Set
 WYSE Acadec Challenge 004 Sectnal Physcs Slutn Set. Answer: e. The axu pssble statc rctn r ths stuatn wuld be: ax µ sn µ sg (0.600)(40.0N) 4.0N. Snce yur pushng rce s less than the axu pssble rctnal rce,
WYSE Acadec Challenge 004 Sectnal Physcs Slutn Set. Answer: e. The axu pssble statc rctn r ths stuatn wuld be: ax µ sn µ sg (0.600)(40.0N) 4.0N. Snce yur pushng rce s less than the axu pssble rctnal rce,
A. Thicknesses and Densities
 10 Lab0 The Eath s Shells A. Thcknesses and Denstes Any theoy of the nteo of the Eath must be consstent wth the fact that ts aggegate densty s 5.5 g/cm (ecall we calculated ths densty last tme). In othe
10 Lab0 The Eath s Shells A. Thcknesses and Denstes Any theoy of the nteo of the Eath must be consstent wth the fact that ts aggegate densty s 5.5 g/cm (ecall we calculated ths densty last tme). In othe
Set of square-integrable function 2 L : function space F
 Set of squae-ntegable functon L : functon space F Motvaton: In ou pevous dscussons we have seen that fo fee patcles wave equatons (Helmholt o Schödnge) can be expessed n tems of egenvalue equatons. H E,
Set of squae-ntegable functon L : functon space F Motvaton: In ou pevous dscussons we have seen that fo fee patcles wave equatons (Helmholt o Schödnge) can be expessed n tems of egenvalue equatons. H E,
FEEDBACK AMPLIFIERS. β f
 FEEDBC MPLFES X - X X X * What negatve eedback? ddng the eedback gnal t the nput a t patally cancel the nput gnal t the ample. * What eedback? Takng a ptn the gnal avng at the lad and eedng t back t the
FEEDBC MPLFES X - X X X * What negatve eedback? ddng the eedback gnal t the nput a t patally cancel the nput gnal t the ample. * What eedback? Takng a ptn the gnal avng at the lad and eedng t back t the
A New Method for Solving Integer Linear. Programming Problems with Fuzzy Variables
 Appled Mathematcal Scences, Vl. 4, 00, n. 0, 997-004 A New Methd fr Slvng Integer Lnear Prgrammng Prblems wth Fuzzy Varables P. Pandan and M. Jayalakshm Department f Mathematcs, Schl f Advanced Scences,
Appled Mathematcal Scences, Vl. 4, 00, n. 0, 997-004 A New Methd fr Slvng Integer Lnear Prgrammng Prblems wth Fuzzy Varables P. Pandan and M. Jayalakshm Department f Mathematcs, Schl f Advanced Scences,
Journal of Solid Mechanics and Materials Engineering
 Junal f Slid Mechanics and Mateials Engineeing Vl. 4, N. 8, 21 Themal Stess and Heat Tansfe Cefficient f Ceamics Stalk Having Ptubeance Dipping int Mlten Metal* Na-ki NOD**, Henda**, Wenbin LI**, Yasushi
Junal f Slid Mechanics and Mateials Engineeing Vl. 4, N. 8, 21 Themal Stess and Heat Tansfe Cefficient f Ceamics Stalk Having Ptubeance Dipping int Mlten Metal* Na-ki NOD**, Henda**, Wenbin LI**, Yasushi
BME 5742 Biosystems Modeling and Control
 BME 5742 Bsystems Mdeln and Cntrl Cell Electrcal Actvty: In Mvement acrss Cell Membrane and Membrane Ptental Dr. Zv Rth (FAU) 1 References Hppensteadt-Peskn, Ch. 3 Dr. Rbert Farley s lecture ntes Inc Equlbra
BME 5742 Bsystems Mdeln and Cntrl Cell Electrcal Actvty: In Mvement acrss Cell Membrane and Membrane Ptental Dr. Zv Rth (FAU) 1 References Hppensteadt-Peskn, Ch. 3 Dr. Rbert Farley s lecture ntes Inc Equlbra
Spring 2002 Lecture #17
 1443-51 Sprng 22 Lecture #17 r. Jaehn Yu 1. Cndtns fr Equlbrum 2. Center f Gravty 3. Elastc Prpertes f Slds Yung s dulus Shear dulus ulk dulus Tday s Hmewrk Assgnment s the Hmewrk #8!!! 2 nd term eam n
1443-51 Sprng 22 Lecture #17 r. Jaehn Yu 1. Cndtns fr Equlbrum 2. Center f Gravty 3. Elastc Prpertes f Slds Yung s dulus Shear dulus ulk dulus Tday s Hmewrk Assgnment s the Hmewrk #8!!! 2 nd term eam n
Analytical Solution to Diffusion-Advection Equation in Spherical Coordinate Based on the Fundamental Bloch NMR Flow Equations
 Intenatinal Junal f heetical and athematical Phsics 5, 5(5: 4-44 OI:.593/j.ijtmp.555.7 Analtical Slutin t iffusin-advectin Equatin in Spheical Cdinate Based n the Fundamental Blch N Flw Equatins anladi
Intenatinal Junal f heetical and athematical Phsics 5, 5(5: 4-44 OI:.593/j.ijtmp.555.7 Analtical Slutin t iffusin-advectin Equatin in Spheical Cdinate Based n the Fundamental Blch N Flw Equatins anladi
4. The material balances for isothermal ideal reactor models
 Summay Geneal mateal balane f eatng system Bath eat Cntnuus-flw eats: CST (Cntnuus Sted Tank eat) P (Plug lw eat) Steady state f CST and P Desgn tasks : utlet (fnal nvesn), gven vlume f eat x vlume f eat,
Summay Geneal mateal balane f eatng system Bath eat Cntnuus-flw eats: CST (Cntnuus Sted Tank eat) P (Plug lw eat) Steady state f CST and P Desgn tasks : utlet (fnal nvesn), gven vlume f eat x vlume f eat,
19 The Born-Oppenheimer Approximation
 9 The Bon-Oppenheme Appoxmaton The full nonelatvstc Hamltonan fo a molecule s gven by (n a.u.) Ĥ = A M A A A, Z A + A + >j j (883) Lets ewte the Hamltonan to emphasze the goal as Ĥ = + A A A, >j j M A
9 The Bon-Oppenheme Appoxmaton The full nonelatvstc Hamltonan fo a molecule s gven by (n a.u.) Ĥ = A M A A A, Z A + A + >j j (883) Lets ewte the Hamltonan to emphasze the goal as Ĥ = + A A A, >j j M A
PHYS 705: Classical Mechanics. Derivation of Lagrange Equations from D Alembert s Principle
 1 PHYS 705: Classcal Mechancs Devaton of Lagange Equatons fom D Alembet s Pncple 2 D Alembet s Pncple Followng a smla agument fo the vtual dsplacement to be consstent wth constants,.e, (no vtual wok fo
1 PHYS 705: Classcal Mechancs Devaton of Lagange Equatons fom D Alembet s Pncple 2 D Alembet s Pncple Followng a smla agument fo the vtual dsplacement to be consstent wth constants,.e, (no vtual wok fo
Dynamics of Rigid Bodies
 Dynamcs of Rgd Bodes A gd body s one n whch the dstances between consttuent patcles s constant thoughout the moton of the body,.e. t keeps ts shape. Thee ae two knds of gd body moton: 1. Tanslatonal Rectlnea
Dynamcs of Rgd Bodes A gd body s one n whch the dstances between consttuent patcles s constant thoughout the moton of the body,.e. t keeps ts shape. Thee ae two knds of gd body moton: 1. Tanslatonal Rectlnea
Rigid Bodies: Equivalent Systems of Forces
 Engneeng Statcs, ENGR 2301 Chapte 3 Rgd Bodes: Equvalent Sstems of oces Intoducton Teatment of a bod as a sngle patcle s not alwas possble. In geneal, the se of the bod and the specfc ponts of applcaton
Engneeng Statcs, ENGR 2301 Chapte 3 Rgd Bodes: Equvalent Sstems of oces Intoducton Teatment of a bod as a sngle patcle s not alwas possble. In geneal, the se of the bod and the specfc ponts of applcaton
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION PREVIOUS EAMCET BITS
 P P Methd EECTOMAGNETIC INDUCTION PEVIOUS EAMCET BITS [ENGINEEING PAPE]. A cnduct d f length tates with angula speed ω in a unifm magnetic field f inductin B which is pependicula t its mtin. The induced
P P Methd EECTOMAGNETIC INDUCTION PEVIOUS EAMCET BITS [ENGINEEING PAPE]. A cnduct d f length tates with angula speed ω in a unifm magnetic field f inductin B which is pependicula t its mtin. The induced
_J _J J J J J J J J _. 7 particles in the blue state; 3 particles in the red state: 720 configurations _J J J _J J J J J J J J _
 Dsrder and Suppse I have 10 partcles that can be n ne f tw states ether the blue state r the red state. Hw many dfferent ways can we arrange thse partcles amng the states? All partcles n the blue state:
Dsrder and Suppse I have 10 partcles that can be n ne f tw states ether the blue state r the red state. Hw many dfferent ways can we arrange thse partcles amng the states? All partcles n the blue state:
ADVERTIMENT ADVERTENCIA WARNING
 ADVERTIMENT. La cnsulta d aquesta tes queda cndcnada a l acceptacó de les següents cndcns d'ús: La dfusó d aquesta tes pe mtjà del seve TDX (www.tessenxaxa.net) ha estat auttzada pels ttulas dels dets
ADVERTIMENT. La cnsulta d aquesta tes queda cndcnada a l acceptacó de les següents cndcns d'ús: La dfusó d aquesta tes pe mtjà del seve TDX (www.tessenxaxa.net) ha estat auttzada pels ttulas dels dets
Some Approximate Analytical Steady-State Solutions for Cylindrical Fin
 Some Appoxmate Analytcal Steady-State Solutons fo Cylndcal Fn ANITA BRUVERE ANDRIS BUIIS Insttute of Mathematcs and Compute Scence Unvesty of Latva Rana ulv 9 Rga LV459 LATVIA Astact: - In ths pape we
Some Appoxmate Analytcal Steady-State Solutons fo Cylndcal Fn ANITA BRUVERE ANDRIS BUIIS Insttute of Mathematcs and Compute Scence Unvesty of Latva Rana ulv 9 Rga LV459 LATVIA Astact: - In ths pape we
Thermoelastic Problem of a Long Annular Multilayered Cylinder
 Wold Jounal of Mechancs, 3, 3, 6- http://dx.do.og/.436/w.3.35a Publshed Onlne August 3 (http://www.scp.og/ounal/w) Theoelastc Poble of a Long Annula Multlayeed Cylnde Y Hsen Wu *, Kuo-Chang Jane Depatent
Wold Jounal of Mechancs, 3, 3, 6- http://dx.do.og/.436/w.3.35a Publshed Onlne August 3 (http://www.scp.og/ounal/w) Theoelastc Poble of a Long Annula Multlayeed Cylnde Y Hsen Wu *, Kuo-Chang Jane Depatent
Journal of Naval Science and Engineering 2015, Vol.11, No.1, pp FINITE DIFFERENCE MODEL OF A CIRCULAR FIN WITH RECTANGULAR PROFILE.
 Jounal o Naval Scence and Engneeng 05 Vol. No. pp.53-67 FINIE DIFFERENCE MODEL OF A CIRCULAR FIN WIH RECANGULAR PROFILE İbahm GİRGİN Cüneyt EZGİ uksh Naval Academy uzla Istanbul ukye ggn@dho.edu.t cezg@dho.edu.t
Jounal o Naval Scence and Engneeng 05 Vol. No. pp.53-67 FINIE DIFFERENCE MODEL OF A CIRCULAR FIN WIH RECANGULAR PROFILE İbahm GİRGİN Cüneyt EZGİ uksh Naval Academy uzla Istanbul ukye ggn@dho.edu.t cezg@dho.edu.t
Magnetism. Chapter 21
 1.1 Magnetic Fields Chapte 1 Magnetism The needle f a cmpass is pemanent magnet that has a nth magnetic ple (N) at ne end and a suth magnetic ple (S) at the the. 1.1 Magnetic Fields 1.1 Magnetic Fields
1.1 Magnetic Fields Chapte 1 Magnetism The needle f a cmpass is pemanent magnet that has a nth magnetic ple (N) at ne end and a suth magnetic ple (S) at the the. 1.1 Magnetic Fields 1.1 Magnetic Fields
Fault detection of batch process based on multi-way Kernel T-PLS
 Avalable nlne www.jcp.cm Junal f Chemcal and Phamaceutcal Reseach, 04, 6(7):338-346 Reseach Atcle SSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Fault detectn f batch pcess based n mult-wa Kenel -PLS Zha aqang*,
Avalable nlne www.jcp.cm Junal f Chemcal and Phamaceutcal Reseach, 04, 6(7):338-346 Reseach Atcle SSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Fault detectn f batch pcess based n mult-wa Kenel -PLS Zha aqang*,
MEM202 Engineering Mechanics Statics Course Web site:
 0 Engineeing Mechanics - Statics 0 Engineeing Mechanics Statics Cuse Web site: www.pages.dexel.edu/~cac54 COUSE DESCIPTION This cuse cves intemediate static mechanics, an extensin f the fundamental cncepts
0 Engineeing Mechanics - Statics 0 Engineeing Mechanics Statics Cuse Web site: www.pages.dexel.edu/~cac54 COUSE DESCIPTION This cuse cves intemediate static mechanics, an extensin f the fundamental cncepts
Design and Flow Parameters Calculation of the Turbomachine Channels
 Avalable onlne at www.scencedect.co Poceda Engneeng 39 (0 ) 75 85 XIIIth Intenatonal Scentc and Engneeng Coneence HERVICON-0 Desgn and Flow Paaetes Calculaton o the Tuboachne Channels Mykola Kalnkevych
Avalable onlne at www.scencedect.co Poceda Engneeng 39 (0 ) 75 85 XIIIth Intenatonal Scentc and Engneeng Coneence HERVICON-0 Desgn and Flow Paaetes Calculaton o the Tuboachne Channels Mykola Kalnkevych
ABSTRACT PARALLEL, NAVIER STOKES COMPUTATION OF THE FLOWFIELD OF A HOVERING HELICOPTER ROTOR BLADE. Geçgel, Murat
 ABSTRACT PARALLEL NAVIER STOKES COMPUTATION OF THE FLOWFIELD OF A HOVERING HELICOPTER ROTOR BLADE Geçgel Muat M.S. Depatment f Aespace Engneeng Supevs: Assc. Pf. D. Yusuf Özyöü Decembe 3 97 pages The am
ABSTRACT PARALLEL NAVIER STOKES COMPUTATION OF THE FLOWFIELD OF A HOVERING HELICOPTER ROTOR BLADE Geçgel Muat M.S. Depatment f Aespace Engneeng Supevs: Assc. Pf. D. Yusuf Özyöü Decembe 3 97 pages The am
55:041 Electronic Circuits
 55:04 Electrnc Crcuts Feedback & Stablty Sectns f Chapter 2. Kruger Feedback & Stablty Cnfguratn f Feedback mplfer S S S S fb Negate feedback S S S fb S S S S S β s the feedback transfer functn Implct
55:04 Electrnc Crcuts Feedback & Stablty Sectns f Chapter 2. Kruger Feedback & Stablty Cnfguratn f Feedback mplfer S S S S fb Negate feedback S S S fb S S S S S β s the feedback transfer functn Implct
Consider the simple circuit of Figure 1 in which a load impedance of r is connected to a voltage source. The no load voltage of r
 1 Intductin t Pe Unit Calculatins Cnside the simple cicuit f Figue 1 in which a lad impedance f L 60 + j70 Ω 9. 49 Ω is cnnected t a vltage suce. The n lad vltage f the suce is E 1000 0. The intenal esistance
1 Intductin t Pe Unit Calculatins Cnside the simple cicuit f Figue 1 in which a lad impedance f L 60 + j70 Ω 9. 49 Ω is cnnected t a vltage suce. The n lad vltage f the suce is E 1000 0. The intenal esistance
Chapter (10) lbf Ans. 3-2 Body AB: R R. Body OAC: R R. Chapter 3 - Rev. B, Page 1/100. R R 300 lbf Ans 0 R (10) 100(30) 0
 Chapter - M 0 8RB 6(00) 0. lbf Ans. RB F y 0 R RB 00 0 R 66.7 lbf Ans. R R. lbf Ans. C B - Bdy AB: F x 0 RAx RBx F y 0 RAy RBy M B 0 RAy (0) RAx (0) 0 R R Ax Ay Bdy OAC: 0 R (0) 00(0) 0 M O RAy Ay 00 lbf
Chapter - M 0 8RB 6(00) 0. lbf Ans. RB F y 0 R RB 00 0 R 66.7 lbf Ans. R R. lbf Ans. C B - Bdy AB: F x 0 RAx RBx F y 0 RAy RBy M B 0 RAy (0) RAx (0) 0 R R Ax Ay Bdy OAC: 0 R (0) 00(0) 0 M O RAy Ay 00 lbf
Chapter 12 Equilibrium and Elasticity
 Chapte 12 Equlbum and Elastcty In ths chapte we wll defne equlbum and fnd the condtons needed so that an object s at equlbum. We wll then apply these condtons to a vaety of pactcal engneeng poblems of
Chapte 12 Equlbum and Elastcty In ths chapte we wll defne equlbum and fnd the condtons needed so that an object s at equlbum. We wll then apply these condtons to a vaety of pactcal engneeng poblems of
Review for the Mid-Term Exam
 Revew f the Md-Tem am A54/MA4/M 59/ Spg 8 Depatmet f Mechacal & Aespace geeg Chapte Md-Tem Revew-6 Date: Mach (Thusda), 8 Tme: :pm-:pm Place: Rm, Neddema Hall Smple devat Md-Tem am Pat : 4 pblems Smple
Revew f the Md-Tem am A54/MA4/M 59/ Spg 8 Depatmet f Mechacal & Aespace geeg Chapte Md-Tem Revew-6 Date: Mach (Thusda), 8 Tme: :pm-:pm Place: Rm, Neddema Hall Smple devat Md-Tem am Pat : 4 pblems Smple
