Applications of Statics, Including Problem-Solving Strategies
|
|
|
- Alan Andrews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Applications of Statics, Including Problem-Solving Strategies Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Statics can be applied to a variety of situations, ranging from raising a drawbridge to bad posture and back strain. We begin with a discussion of problem-solving strategies specifically used for statics. Since statics is a special case of Newton s laws, both the general problem-solving strategies and the special strategies for Newton s laws, discussed in Problem-Solving Strategies, still apply. Problem-Solving Strategy: Static Equilibrium Situations 1. The first step is to determine whether or not the system is in static equilibrium. This condition is always the case when the acceleration of the system is zero and accelerated rotation does not occur. 2. It is particularly important to draw a free body diagram for the system of interest. Carefully label all forces, and note their relative magnitudes, directions, and points of application whenever these are known. 3. Solve the problem by applying either or both of the conditions for equilibrium (represented by the equations net F 0 and net τ 0, depending on the list of known and unknown factors. If the second condition is involved, choose the pivot point to simplify the solution. Any pivot point can be chosen, but the most useful ones cause torques by unknown forces to be zero. (Torque is zero if the force is applied at the pivot (then r 0), or along a line through the pivot point (then θ 0)). Always choose a convenient coordinate system for projecting forces. 4. Check the solution to see if it is reasonable by examining the magnitude, direction, and units of the answer. The importance of this last step never diminishes, although in unfamiliar applications, it is usually more difficult to judge reasonableness. These judgments become progressively easier with experience. 1/6
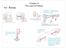
2 Now let us apply this problem-solving strategy for the pole vaulter shown in the three figures below. The pole is uniform and has a mass of 5.00 kg. In [link], the pole s cg lies halfway between the vaulter s hands. It seems reasonable that the force exerted by each hand is equal to half the weight of the pole, or 24.5 N. This obviously satisfies the first condition for equilibrium (net F 0). The second condition (net 1 children in msub 0) is also satisfied, as we can see by choosing the cg to be the pivot point. The weight exerts no torque about a pivot point located at the cg, since it is applied at that point and its lever arm is zero. The equal forces exerted by the hands are equidistant from the chosen pivot, and so they exert equal and opposite torques. Similar arguments hold for other systems where supporting forces are exerted symmetrically about the cg. For example, the four legs of a uniform table each support one-fourth of its weight. In [link], a pole vaulter holding a pole with its cg halfway between his hands is shown. Each hand exerts a force equal to half the weight of the pole, F R F L w / 2. (b) The pole vaulter moves the pole to his left, and the forces that the hands exert are no longer equal. See [link]. If the pole is held with its cg to the left of the person, then he must push down with his right hand and up with his left. The forces he exerts are larger here because they are in opposite directions and the cg is at a long distance from either hand. Similar observations can be made using a meter stick held at different locations along its length. A pole vaulter holds a pole horizontally with both hands. 2/6
3 A pole vaulter is holding a pole horizontally with both hands. The center of gravity is near his right hand. A pole vaulter is holding a pole horizontally with both hands. The center of gravity is to the left side of the vaulter. If the pole vaulter holds the pole as shown in [link], the situation is not as simple. The total force he exerts is still equal to the weight of the pole, but it is not evenly divided between his hands. (If F L F R, then the torques about the cg would not be equal since the lever arms are different.) Logically, the right hand should support more weight, since it is closer to the cg. In fact, if the right hand is moved directly under the cg, it will support all the weight. This situation is exactly analogous to two people carrying a load; the one closer to the cg carries more of its weight. Finding the forces F L and F R is straightforward, as the next example shows. If the pole vaulter holds the pole from near the end of the pole ([link]), the direction of the force applied by the right hand of the vaulter reverses its direction. What Force Is Needed to Support a Weight Held Near Its CG? For the situation shown in [link], calculate: (a) F R, the force exerted by the right hand, and (b) F L, the force exerted by the left hand. The hands are m apart, and the cg of the pole is m from the left hand. 3/6
4 Strategy [link] includes a free body diagram for the pole, the system of interest. There is not enough information to use the first condition for equilibrium (net F 0), since two of the three forces are unknown and the hand forces cannot be assumed to be equal in this case. There is enough information to use the second condition for equilibrium (net τ 0) if the pivot point is chosen to be at either hand, thereby making the torque from that hand zero. We choose to locate the pivot at the left hand in this part of the problem, to eliminate the torque from the left hand. Solution for (a) There are now only two nonzero torques, those from the gravitational force (τ w ) and from the push or pull of the right hand (τ R ). Stating the second condition in terms of clockwise and counterclockwise torques, net τ cw net τ ccw. or the algebraic sum of the torques is zero. Here this is τ R τ w since the weight of the pole creates a counterclockwise torque and the right hand counters with a clockwise toque. Using the definition of torque, τ rf sin θ, noting that θ 90º, and substituting known values, we obtain (0.900 m)(f R) (0.600 m)(mg). Thus, F R (0.667)(5.00 kg)(9.80 m/s 2 ) 32.7 N. Solution for (b) The first condition for equilibrium is based on the free body diagram in the figure. This implies that by Newton s second law: F L + F R mg 0 4/6
5 From this we can conclude: F L + F R w mg Solving for F L, we obtain F L mg F R mg 32.7 N (5.00 kg)(9.80 m/s 2 ) 32.7 N 16.3 N Discussion F L is seen to be exactly half of F R, as we might have guessed, since F L is applied twice as far from the cg as F R. If the pole vaulter holds the pole as he might at the start of a run, shown in [link], the forces change again. Both are considerably greater, and one force reverses direction. Take-Home Experiment This is an experiment to perform while standing in a bus or a train. Stand facing sideways. How do you move your body to readjust the distribution of your mass as the bus accelerates and decelerates? Now stand facing forward. How do you move your body to readjust the distribution of your mass as the bus accelerates and decelerates? Why is it easier and safer to stand facing sideways rather than forward? Note: For your safety (and those around you), make sure you are holding onto something while you carry out this activity! PhET Explorations: Balancing Act Play with objects on a teeter totter to learn about balance. Test what you've learned by trying the Balance Challenge game. Balancing Act 5/6
6 Summary Statics can be applied to a variety of situations, ranging from raising a drawbridge to bad posture and back strain. We have discussed the problemsolving strategies specifically useful for statics. Statics is a special case of Newton s laws, both the general problem-solving strategies and the special strategies for Newton s laws, discussed in Problem-Solving Strategies, still apply. Conceptual Questions When visiting some countries, you may see a person balancing a load on the head. Explain why the center of mass of the load needs to be directly above the person s neck vertebrae. Problems & Exercises To get up on the roof, a person (mass 70.0 kg) places a 6.00-m aluminum ladder (mass 10.0 kg) against the house on a concrete pad with the base of the ladder 2.00 m from the house. The ladder rests against a plastic rain gutter, which we can assume to be frictionless. The center of mass of the ladder is 2 m from the bottom. The person is standing 3 m from the bottom. What are the magnitudes of the forces on the ladder at the top and bottom? In [link], the cg of the pole held by the pole vaulter is 2.00 m from the left hand, and the hands are m apart. Calculate the force exerted by (a) his right hand and (b) his left hand. (c) If each hand supports half the weight of the pole in [link], show that the second condition for equilibrium (net 1 children in msub 0) is satisfied for a pivot other than the one located at the center of gravity of the pole. Explicitly show how you follow the steps in the Problem-Solving Strategy for static equilibrium described above. 6/6
Applications of Statics, Including Problem-Solving Strategies
 OpenStax-CNX module: m42173 1 Applications of Statics, Including Problem-Solving Strategies OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
OpenStax-CNX module: m42173 1 Applications of Statics, Including Problem-Solving Strategies OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
Static Equilibrium; Torque
 Static Equilibrium; Torque The Conditions for Equilibrium An object with forces acting on it, but that is not moving, is said to be in equilibrium. The first condition for equilibrium is that the net force
Static Equilibrium; Torque The Conditions for Equilibrium An object with forces acting on it, but that is not moving, is said to be in equilibrium. The first condition for equilibrium is that the net force
9 STATICS AND TORQUE. Learning Objectives. Introduction to Statics and Torque
 CHAPTER 9 STATICS AND TORQUE 291 9 STATICS AND TORQUE Figure 9.1 On a short time scale, rocks like these in Australia s Kings Canyon are static, or motionless relative to the Earth. (credit: freeaussiestock.com)
CHAPTER 9 STATICS AND TORQUE 291 9 STATICS AND TORQUE Figure 9.1 On a short time scale, rocks like these in Australia s Kings Canyon are static, or motionless relative to the Earth. (credit: freeaussiestock.com)
Section 2: Static Equilibrium II- Balancing Torques
 Section 2: Static Equilibrium II- Balancing Torques Last Section: If (ie. Forces up = Forces down and Forces left = Forces right), then the object will have no translatory motion. In other words, the object
Section 2: Static Equilibrium II- Balancing Torques Last Section: If (ie. Forces up = Forces down and Forces left = Forces right), then the object will have no translatory motion. In other words, the object
Section 2: Static Equilibrium II- Balancing Torques
 Section 2: Static Equilibrium II- Balancing Torques Last Section: If (ie. Forces up = Forces down and Forces left = Forces right), then the object will have no translatory motion. In other words, the object
Section 2: Static Equilibrium II- Balancing Torques Last Section: If (ie. Forces up = Forces down and Forces left = Forces right), then the object will have no translatory motion. In other words, the object
Consider two students pushing with equal force on opposite sides of a desk. Looking top-down on the desk:
 1 Bodies in Equilibrium Recall Newton's First Law: if there is no unbalanced force on a body (i.e. if F Net = 0), the body is in equilibrium. That is, if a body is in equilibrium, then all the forces on
1 Bodies in Equilibrium Recall Newton's First Law: if there is no unbalanced force on a body (i.e. if F Net = 0), the body is in equilibrium. That is, if a body is in equilibrium, then all the forces on
P12 Torque Notes.notebook. March 26, Torques
 Torques The size of a torque depends on two things: 1. The size of the force being applied (a larger force will have a greater effect) 2. The distance away from the pivot point (the further away from this
Torques The size of a torque depends on two things: 1. The size of the force being applied (a larger force will have a greater effect) 2. The distance away from the pivot point (the further away from this
Torque and Static Equilibrium
 Torque and Static Equilibrium Rigid Bodies Rigid body: An extended object in which the distance between any two points in the object is constant in time. Examples: sphere, disk Effect of external forces
Torque and Static Equilibrium Rigid Bodies Rigid body: An extended object in which the distance between any two points in the object is constant in time. Examples: sphere, disk Effect of external forces
Lab 17 Torques/Moments
 Lab 17 Torques/Moments Name Partner s Name I. Introduction/Theory Terminology: The word 'torque' does not typically appear in the index to statics books such as Bedford and Fowler. For these authors, the
Lab 17 Torques/Moments Name Partner s Name I. Introduction/Theory Terminology: The word 'torque' does not typically appear in the index to statics books such as Bedford and Fowler. For these authors, the
LECTURE 15 TORQUE AND CENTER OF GRAVITY
 LECTURE 15 TORQUE AND CENTER OF GRAVITY 7.3 Torque Net torque 7.4 Gravitational torque and the center of gravity Calculating the position of the center of gravity What is unusual about this door? Learning
LECTURE 15 TORQUE AND CENTER OF GRAVITY 7.3 Torque Net torque 7.4 Gravitational torque and the center of gravity Calculating the position of the center of gravity What is unusual about this door? Learning
Rotational Equilibrium
 Rotational Equilibrium 6-1 Rotational Equilibrium INTRODUCTION Have you ever tried to pull a stubborn nail out of a board or develop your forearm muscles by lifting weights? Both these activities involve
Rotational Equilibrium 6-1 Rotational Equilibrium INTRODUCTION Have you ever tried to pull a stubborn nail out of a board or develop your forearm muscles by lifting weights? Both these activities involve
Unit 1: Equilibrium and Center of Mass
 Unit 1: Equilibrium and Center of Mass FORCES What is a force? Forces are a result of the interaction between two objects. They push things, pull things, keep things together, pull things apart. It s really
Unit 1: Equilibrium and Center of Mass FORCES What is a force? Forces are a result of the interaction between two objects. They push things, pull things, keep things together, pull things apart. It s really
Recap I. Angular position: Angular displacement: s. Angular velocity: Angular Acceleration:
 Recap I Angular position: Angular displacement: s Angular velocity: Angular Acceleration: Every point on a rotating rigid object has the same angular, but not the same linear motion! Recap II Circular
Recap I Angular position: Angular displacement: s Angular velocity: Angular Acceleration: Every point on a rotating rigid object has the same angular, but not the same linear motion! Recap II Circular
Chapter 8. Centripetal Force and The Law of Gravity
 Chapter 8 Centripetal Force and The Law of Gravity Centripetal Acceleration An object traveling in a circle, even though it moves with a constant speed, will have an acceleration The centripetal acceleration
Chapter 8 Centripetal Force and The Law of Gravity Centripetal Acceleration An object traveling in a circle, even though it moves with a constant speed, will have an acceleration The centripetal acceleration
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion and Equilibrium. 1. Give explanation of torque in own words after doing balance-the-torques lab as an inquiry introduction
 Chapter 8 Rotational Motion and Equilibrium Name 1. Give explanation of torque in own words after doing balance-the-torques lab as an inquiry introduction 1. The distance between a turning axis and the
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion and Equilibrium Name 1. Give explanation of torque in own words after doing balance-the-torques lab as an inquiry introduction 1. The distance between a turning axis and the
Equilibrium. For an object to remain in equilibrium, two conditions must be met. The object must have no net force: and no net torque:
 Equilibrium For an object to remain in equilibrium, two conditions must be met. The object must have no net force: F v = 0 and no net torque: v τ = 0 Worksheet A uniform rod with a length L and a mass
Equilibrium For an object to remain in equilibrium, two conditions must be met. The object must have no net force: F v = 0 and no net torque: v τ = 0 Worksheet A uniform rod with a length L and a mass
Center of Mass. A baseball thrown into the air follows a smooth parabolic path. A baseball bat thrown into the air does not follow a smooth path.
 Center of Mass A baseball thrown into the air follows a smooth parabolic path. A baseball bat thrown into the air does not follow a smooth path. The bat wobbles about a special point. This point stays
Center of Mass A baseball thrown into the air follows a smooth parabolic path. A baseball bat thrown into the air does not follow a smooth path. The bat wobbles about a special point. This point stays
Today we applied our knowledge of vectors to different kinds of problems.
 DAY 18 Summary of Primary Topics Covered Center of Mass and More Vector Examples Today we applied our knowledge of vectors to different kinds of problems. Working these problems is a matter of taking concepts
DAY 18 Summary of Primary Topics Covered Center of Mass and More Vector Examples Today we applied our knowledge of vectors to different kinds of problems. Working these problems is a matter of taking concepts
Torque rotational force which causes a change in rotational motion. This force is defined by linear force multiplied by a radius.
 Warm up A remote-controlled car's wheel accelerates at 22.4 rad/s 2. If the wheel begins with an angular speed of 10.8 rad/s, what is the wheel's angular speed after exactly three full turns? AP Physics
Warm up A remote-controlled car's wheel accelerates at 22.4 rad/s 2. If the wheel begins with an angular speed of 10.8 rad/s, what is the wheel's angular speed after exactly three full turns? AP Physics
Simple Machines. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 F Simple Machines Simple Machines Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Simple machines are devices that can be used to multiply or augment a force that we apply often at the expense of a distance through which we apply
F Simple Machines Simple Machines Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Simple machines are devices that can be used to multiply or augment a force that we apply often at the expense of a distance through which we apply
Equilibrium Notes 1 Translational Equilibrium
 Equilibrium Notes 1 Translational Equilibrium Ex. A 20.0 kg object is suspended by a rope as shown. What is the net force acting on it? Ex. Ok that was easy, now that same 20.0 kg object is lifted at a
Equilibrium Notes 1 Translational Equilibrium Ex. A 20.0 kg object is suspended by a rope as shown. What is the net force acting on it? Ex. Ok that was easy, now that same 20.0 kg object is lifted at a
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 21
 PHYSICS 149: Lecture 21 Chapter 8: Torque and Angular Momentum 8.2 Torque 8.4 Equilibrium Revisited 8.8 Angular Momentum Lecture 21 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 Midterm Exam 2 Wednesday, April 6, 6:30
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 21 Chapter 8: Torque and Angular Momentum 8.2 Torque 8.4 Equilibrium Revisited 8.8 Angular Momentum Lecture 21 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 Midterm Exam 2 Wednesday, April 6, 6:30
Physics 101: Lecture 15 Torque, F=ma for rotation, and Equilibrium
 Physics 101: Lecture 15 Torque, F=ma for rotation, and Equilibrium Strike (Day 10) Prelectures, checkpoints, lectures continue with no change. Take-home quizzes this week. See Elaine Schulte s email. HW
Physics 101: Lecture 15 Torque, F=ma for rotation, and Equilibrium Strike (Day 10) Prelectures, checkpoints, lectures continue with no change. Take-home quizzes this week. See Elaine Schulte s email. HW
Physics 1A Lecture 10B
 Physics 1A Lecture 10B "Sometimes the world puts a spin on life. When our equilibrium returns to us, we understand more because we've seen the whole picture. --Davis Barton Cross Products Another way to
Physics 1A Lecture 10B "Sometimes the world puts a spin on life. When our equilibrium returns to us, we understand more because we've seen the whole picture. --Davis Barton Cross Products Another way to
LECTURE 22 EQUILIBRIUM. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 22 EQUILIBRIUM Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 22 2 Reading chapter 11-3 to 11-4 Static equilibrium Center of mass and balance Static equilibrium 3 If a rigid object is in equilibrium (constant
LECTURE 22 EQUILIBRIUM Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 22 2 Reading chapter 11-3 to 11-4 Static equilibrium Center of mass and balance Static equilibrium 3 If a rigid object is in equilibrium (constant
Static Equilibrium and Torque
 10.3 Static Equilibrium and Torque SECTION OUTCOMES Use vector analysis in two dimensions for systems involving static equilibrium and torques. Apply static torques to structures such as seesaws and bridges.
10.3 Static Equilibrium and Torque SECTION OUTCOMES Use vector analysis in two dimensions for systems involving static equilibrium and torques. Apply static torques to structures such as seesaws and bridges.
Chapter 9 TORQUE & Rotational Kinematics
 Chapter 9 TORQUE & Rotational Kinematics This motionless person is in static equilibrium. The forces acting on him add up to zero. Both forces are vertical in this case. This car is in dynamic equilibrium
Chapter 9 TORQUE & Rotational Kinematics This motionless person is in static equilibrium. The forces acting on him add up to zero. Both forces are vertical in this case. This car is in dynamic equilibrium
= o + t = ot + ½ t 2 = o + 2
 Chapters 8-9 Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics Rotational motion Rotational motion refers to the motion of an object or system that spins about an axis. The axis of rotation is the line about which the
Chapters 8-9 Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics Rotational motion Rotational motion refers to the motion of an object or system that spins about an axis. The axis of rotation is the line about which the
Problem-Solving Strategies
 Connexions module: m42076 1 Problem-Solving Strategies OpenStax College This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License Abstract Understand and
Connexions module: m42076 1 Problem-Solving Strategies OpenStax College This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License Abstract Understand and
Static Equilibrium and Elasticity. Luis Anchordoqui
 Static Equilibrium and Elasticity The Conditions for Equilibrium An object with forces acting on it, but that is not moving, is said to be in equilibrium. The Conditions for Equilibrium (cont d) The first
Static Equilibrium and Elasticity The Conditions for Equilibrium An object with forces acting on it, but that is not moving, is said to be in equilibrium. The Conditions for Equilibrium (cont d) The first
use one of the methods to compute the magnitude of the torque, given the magnitudes of the force and position vector
 PH2213 : Examples from Chapter 12 : Static Equilibrium Equilibrium represents the condition where an object is not accelerating (either linearly or angularly). It can still be moving (and rotating), it
PH2213 : Examples from Chapter 12 : Static Equilibrium Equilibrium represents the condition where an object is not accelerating (either linearly or angularly). It can still be moving (and rotating), it
SPH 4C Unit 2 Mechanical Systems
 SPH 4C Unit 2 Mechanical Systems Forces and Free Body Diagrams Learning Goal: I can consistently identify and draw Free Body Diagrams for given real world situations. There are 4 fundamental forces Gravity
SPH 4C Unit 2 Mechanical Systems Forces and Free Body Diagrams Learning Goal: I can consistently identify and draw Free Body Diagrams for given real world situations. There are 4 fundamental forces Gravity
Chapter 5: Forces in Equilibrium
 Chapter 5: Forces in Equilibrium I don't know what I may seem to the world, but, as to myself, I seem to have been only like a boy playing on the sea shore, and diverting myself in now and then finding
Chapter 5: Forces in Equilibrium I don't know what I may seem to the world, but, as to myself, I seem to have been only like a boy playing on the sea shore, and diverting myself in now and then finding
Torque. Objectives. Assessment. Assessment. Equations. Physics terms 6/2/14
 Objectives Calculate torque given the lever arm (perpendicular distance) and the force. Calculate torque in newton meters and in pound feet. Interpret positive and negative signs in the context of torque.
Objectives Calculate torque given the lever arm (perpendicular distance) and the force. Calculate torque in newton meters and in pound feet. Interpret positive and negative signs in the context of torque.
Equilibrium Notes 1 Translational Equilibrium
 Equilibrium Notes 1 Translational Equilibrium A 20.0 kg object is suspended by a rope as shown. What is the net force acting on it? Ok that was easy, now that same 20.0 kg object is lifted at a velocity
Equilibrium Notes 1 Translational Equilibrium A 20.0 kg object is suspended by a rope as shown. What is the net force acting on it? Ok that was easy, now that same 20.0 kg object is lifted at a velocity
UNIT 6 STATICS AND TORQUE. Objectives. to be able to solve problems involving static equilibrium
 to understand the concept of torque to be able to calculate torques UNIT 6 STATICS AND TORQUE Objectives to understand the concept of static equilibrium to be able to solve problems involving static equilibrium
to understand the concept of torque to be able to calculate torques UNIT 6 STATICS AND TORQUE Objectives to understand the concept of static equilibrium to be able to solve problems involving static equilibrium
Torque and Static Equilibrium
 Torque and Static Equilibrium Ch. 7.3, 8.1 (KJF 3 rd ed.) Phys 114 Eyres Torque 1 Causing rotation: Torque Three factors affect the how a force can affect the rotation: The magnitude of the force The distance,
Torque and Static Equilibrium Ch. 7.3, 8.1 (KJF 3 rd ed.) Phys 114 Eyres Torque 1 Causing rotation: Torque Three factors affect the how a force can affect the rotation: The magnitude of the force The distance,
Rotational Equilibrium
 Rotational Equilibrium In this laboratory, we study the conditions for static equilibrium. Axis Through the Center of Gravity Suspend the meter stick at its center of gravity, with its numbers increasing
Rotational Equilibrium In this laboratory, we study the conditions for static equilibrium. Axis Through the Center of Gravity Suspend the meter stick at its center of gravity, with its numbers increasing
Chapter 9- Static Equilibrium
 Chapter 9- Static Equilibrium Changes in Office-hours The following changes will take place until the end of the semester Office-hours: - Monday, 12:00-13:00h - Wednesday, 14:00-15:00h - Friday, 13:00-14:00h
Chapter 9- Static Equilibrium Changes in Office-hours The following changes will take place until the end of the semester Office-hours: - Monday, 12:00-13:00h - Wednesday, 14:00-15:00h - Friday, 13:00-14:00h
CHAPTER 12 STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY. Conditions for static equilibrium Center of gravity (weight) Examples of static equilibrium
 CHAPTER 12 STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY As previously defined, an object is in equilibrium when it is at rest or moving with constant velocity, i.e., with no net force acting on it. The following
CHAPTER 12 STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY As previously defined, an object is in equilibrium when it is at rest or moving with constant velocity, i.e., with no net force acting on it. The following
Science Olympiad. Machines. Roger Demos
 Science Olympiad Machines. Roger Demos Some Basic Physics Concepts What do Machines do? Do they allow one to do more work? Not really, at best they make completing a task easier. So then what do Machines
Science Olympiad Machines. Roger Demos Some Basic Physics Concepts What do Machines do? Do they allow one to do more work? Not really, at best they make completing a task easier. So then what do Machines
Chapter 9. Rotational Dynamics
 Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics In pure translational motion, all points on an object travel on parallel paths. The most general motion is a combination of translation and rotation. 1) Torque Produces angular
Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics In pure translational motion, all points on an object travel on parallel paths. The most general motion is a combination of translation and rotation. 1) Torque Produces angular
Torques and Static Equilibrium
 Torques and Static Equilibrium INTRODUCTION Archimedes, Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, inventor and astronomer, was widely regarded as the leading scientist of the ancient world. He made a study
Torques and Static Equilibrium INTRODUCTION Archimedes, Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, inventor and astronomer, was widely regarded as the leading scientist of the ancient world. He made a study
Application of Forces. Chapter Eight. Torque. Force vs. Torque. Torque, cont. Direction of Torque 4/7/2015
 Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille Chapter Eight Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics Application of Forces The point of application of a force is important This was ignored in treating objects as
Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille Chapter Eight Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics Application of Forces The point of application of a force is important This was ignored in treating objects as
Models and Anthropometry
 Learning Objectives Models and Anthropometry Readings: some of Chapter 8 [in text] some of Chapter 11 [in text] By the end of this lecture, you should be able to: Describe common anthropometric measurements
Learning Objectives Models and Anthropometry Readings: some of Chapter 8 [in text] some of Chapter 11 [in text] By the end of this lecture, you should be able to: Describe common anthropometric measurements
Solution Derivations for Capa #12
 Solution Derivations for Capa #12 1) A hoop of radius 0.200 m and mass 0.460 kg, is suspended by a point on it s perimeter as shown in the figure. If the hoop is allowed to oscillate side to side as a
Solution Derivations for Capa #12 1) A hoop of radius 0.200 m and mass 0.460 kg, is suspended by a point on it s perimeter as shown in the figure. If the hoop is allowed to oscillate side to side as a
TEST REPORT. Question file: P Copyright:
 Date: February-12-16 Time: 2:00:28 PM TEST REPORT Question file: P12-2006 Copyright: Test Date: 21/10/2010 Test Name: EquilibriumPractice Test Form: 0 Test Version: 0 Test Points: 138.00 Test File: EquilibriumPractice
Date: February-12-16 Time: 2:00:28 PM TEST REPORT Question file: P12-2006 Copyright: Test Date: 21/10/2010 Test Name: EquilibriumPractice Test Form: 0 Test Version: 0 Test Points: 138.00 Test File: EquilibriumPractice
Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics
 Chapter 9 ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS PREVIEW A force acting at a perpendicular distance from a rotation point, such as pushing a doorknob and causing the door to rotate on its hinges, produces a torque. If the
Chapter 9 ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS PREVIEW A force acting at a perpendicular distance from a rotation point, such as pushing a doorknob and causing the door to rotate on its hinges, produces a torque. If the
Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium
 Chapter Static Equilibrium. Analysis Model: Rigid Body in Equilibrium. More on the Center of Gravity. Examples of Rigid Objects in Static Equilibrium CHAPTER : STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY.) The Conditions
Chapter Static Equilibrium. Analysis Model: Rigid Body in Equilibrium. More on the Center of Gravity. Examples of Rigid Objects in Static Equilibrium CHAPTER : STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY.) The Conditions
Torque. Physics 6A. Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB
 Physics 6A Torque is what causes angular acceleration (just like a force causes linear acceleration) Torque is what causes angular acceleration (just like a force causes linear acceleration) For a torque
Physics 6A Torque is what causes angular acceleration (just like a force causes linear acceleration) Torque is what causes angular acceleration (just like a force causes linear acceleration) For a torque
Lecture Presentation Chapter 8 Equilibrium and Elasticity
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 8 Equilibrium and Elasticity Suggested Videos for Chapter 8 Prelecture Videos Static Equilibrium Elasticity Video Tutor Solutions Equilibrium and Elasticity Class Videos Center
Lecture Presentation Chapter 8 Equilibrium and Elasticity Suggested Videos for Chapter 8 Prelecture Videos Static Equilibrium Elasticity Video Tutor Solutions Equilibrium and Elasticity Class Videos Center
Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium; Elasticity and Fracture
 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination
2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination
PHYSICS 12 NAME: Electrostatics Review
 NAME: Electrostatics Review 1. The diagram below shows two positive charges of magnitude Q and 2Q. Which vector best represents the direction of the electric field at point P, which is equidistant from
NAME: Electrostatics Review 1. The diagram below shows two positive charges of magnitude Q and 2Q. Which vector best represents the direction of the electric field at point P, which is equidistant from
Name Section Number Team Number
 Physics 218 LAB: TORQUES and STATIC EQUILIBRIUM Name Section Number Team Number Introduction One purpose of this lab is to introduce you to quantity called torque or, as engineers cail it, moment of a
Physics 218 LAB: TORQUES and STATIC EQUILIBRIUM Name Section Number Team Number Introduction One purpose of this lab is to introduce you to quantity called torque or, as engineers cail it, moment of a
Physics 2210 Fall smartphysics Rotational Statics 11/18/2015
 Physics 2210 Fall 2015 smartphysics 17-18 Rotational Statics 11/18/2015 τ TT = L T 1 sin 150 = 1 T 2 1L Poll 11-18-01 τ TT = L 2 T 2 sin 150 = 1 4 T 2L 150 150 τ gg = L 2 MM sin +90 = 1 2 MMM +90 MM τ
Physics 2210 Fall 2015 smartphysics 17-18 Rotational Statics 11/18/2015 τ TT = L T 1 sin 150 = 1 T 2 1L Poll 11-18-01 τ TT = L 2 T 2 sin 150 = 1 4 T 2L 150 150 τ gg = L 2 MM sin +90 = 1 2 MMM +90 MM τ
Chapter 12. Static Equilibrium and Elasticity
 Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium and Elasticity Static Equilibrium Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial
Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium and Elasticity Static Equilibrium Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial
PHY 1150 Doug Davis Chapter 8; Static Equilibrium 8.3, 10, 22, 29, 52, 55, 56, 74
 PHY 1150 Doug Davis Chapter 8; Static Equilibrium 8.3, 10, 22, 29, 52, 55, 56, 74 8.3 A 2-kg ball is held in position by a horizontal string and a string that makes an angle of 30 with the vertical, as
PHY 1150 Doug Davis Chapter 8; Static Equilibrium 8.3, 10, 22, 29, 52, 55, 56, 74 8.3 A 2-kg ball is held in position by a horizontal string and a string that makes an angle of 30 with the vertical, as
Physics 111. Lecture 22 (Walker: ) Torque Rotational Dynamics Static Equilibrium Oct. 28, 2009
 Physics 111 Lecture 22 (Walker: 11.1-3) Torque Rotational Dynamics Static Equilibrium Oct. 28, 2009 Lecture 22 1/26 Torque (τ) We define a quantity called torque which is a measure of twisting effort.
Physics 111 Lecture 22 (Walker: 11.1-3) Torque Rotational Dynamics Static Equilibrium Oct. 28, 2009 Lecture 22 1/26 Torque (τ) We define a quantity called torque which is a measure of twisting effort.
Lab 2: Equilibrium. Note: the Vector Review from the beginning of this book should be read and understood prior to coming to class!
 Lab 2: Equilibrium Note: This lab will be conducted over 2 weeks, with half the class working with forces while the other half works with torques the first week, and then switching the second week. Description
Lab 2: Equilibrium Note: This lab will be conducted over 2 weeks, with half the class working with forces while the other half works with torques the first week, and then switching the second week. Description
III. Angular Momentum Conservation (Chap. 10) Rotation. We repeat Chap. 2-8 with rotatiing objects. Eqs. of motion. Energy.
 Chap. 10: Rotational Motion I. Rotational Kinematics II. Rotational Dynamics - Newton s Law for Rotation III. Angular Momentum Conservation (Chap. 10) 1 Toward Exam 3 Eqs. of motion o To study angular
Chap. 10: Rotational Motion I. Rotational Kinematics II. Rotational Dynamics - Newton s Law for Rotation III. Angular Momentum Conservation (Chap. 10) 1 Toward Exam 3 Eqs. of motion o To study angular
Rotational N.2 nd Law
 Lecture 19 Chapter 12 Rotational N.2 nd Law Torque Newton 2 nd Law again!? That s it. He crossed the line! Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi IN THIS CHAPTER, you will
Lecture 19 Chapter 12 Rotational N.2 nd Law Torque Newton 2 nd Law again!? That s it. He crossed the line! Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi IN THIS CHAPTER, you will
Lecture 8. Torque. and Equilibrium. Pre-reading: KJF 8.1 and 8.2
 Lecture 8 Torque and Equilibrium Pre-reading: KJF 8.1 and 8.2 Archimedes Lever Rule At equilibrium (and with forces 90 to lever): r 1 F 1 = r 2 F 2 2 General Lever Rule For general angles r 1 F 1 sin θ
Lecture 8 Torque and Equilibrium Pre-reading: KJF 8.1 and 8.2 Archimedes Lever Rule At equilibrium (and with forces 90 to lever): r 1 F 1 = r 2 F 2 2 General Lever Rule For general angles r 1 F 1 sin θ
The student will be able to: 1 Determine the torque of an applied force and solve related problems.
 Honors Physics Assignment Rotational Mechanics Reading Chapters 10 and 11 Objectives/HW The student will be able to: HW: 1 Determine the torque of an applied force and solve related problems. (t = rx r
Honors Physics Assignment Rotational Mechanics Reading Chapters 10 and 11 Objectives/HW The student will be able to: HW: 1 Determine the torque of an applied force and solve related problems. (t = rx r
Rotation. I. Kinematics - Angular analogs
 Rotation I. Kinematics - Angular analogs II. III. IV. Dynamics - Torque and Rotational Inertia Work and Energy Angular Momentum - Bodies and particles V. Elliptical Orbits The student will be able to:
Rotation I. Kinematics - Angular analogs II. III. IV. Dynamics - Torque and Rotational Inertia Work and Energy Angular Momentum - Bodies and particles V. Elliptical Orbits The student will be able to:
Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton s Laws of Motion
 Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton s Laws of Motion Units of Chapter 4 Force Newton s First Law of Motion Mass Newton s Second Law of Motion Newton s Third Law of Motion Weight the Force of Gravity; and the Normal
Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton s Laws of Motion Units of Chapter 4 Force Newton s First Law of Motion Mass Newton s Second Law of Motion Newton s Third Law of Motion Weight the Force of Gravity; and the Normal
Rotational N.2 nd Law
 Lecture 0 Chapter 1 Physics I Rotational N. nd Law Torque Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi IN THIS CHAPTER, you will continue discussing rotational dynamics Today
Lecture 0 Chapter 1 Physics I Rotational N. nd Law Torque Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi IN THIS CHAPTER, you will continue discussing rotational dynamics Today
Physics 6A Lab Experiment 6
 Biceps Muscle Model Physics 6A Lab Experiment 6 APPARATUS Biceps model Large mass hanger with four 1-kg masses Small mass hanger for hand end of forearm bar with five 100-g masses Meter stick Centimeter
Biceps Muscle Model Physics 6A Lab Experiment 6 APPARATUS Biceps model Large mass hanger with four 1-kg masses Small mass hanger for hand end of forearm bar with five 100-g masses Meter stick Centimeter
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 4 Physics: for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 4 Physics: for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 4 Physics: for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided
( )( ) ( )( ) Fall 2017 PHYS 131 Week 9 Recitation: Chapter 9: 5, 10, 12, 13, 31, 34
 Fall 07 PHYS 3 Chapter 9: 5, 0,, 3, 3, 34 5. ssm The drawing shows a jet engine suspended beneath the wing of an airplane. The weight W of the engine is 0 00 N and acts as shown in the drawing. In flight
Fall 07 PHYS 3 Chapter 9: 5, 0,, 3, 3, 34 5. ssm The drawing shows a jet engine suspended beneath the wing of an airplane. The weight W of the engine is 0 00 N and acts as shown in the drawing. In flight
Physics A - PHY 2048C
 Physics A - PHY 2048C and 11/15/2017 My Office Hours: Thursday 2:00-3:00 PM 212 Keen Building Warm-up Questions 1 Did you read Chapter 12 in the textbook on? 2 Must an object be rotating to have a moment
Physics A - PHY 2048C and 11/15/2017 My Office Hours: Thursday 2:00-3:00 PM 212 Keen Building Warm-up Questions 1 Did you read Chapter 12 in the textbook on? 2 Must an object be rotating to have a moment
HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL
 HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT STATIC EQUILIBRIUM MULTIPLE CHOICE / 33 OPEN ENDED / 80 TOTAL / 113 NAME: 1. State the condition for translational equilibrium. A. ΣF = 0 B. ΣF
HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT STATIC EQUILIBRIUM MULTIPLE CHOICE / 33 OPEN ENDED / 80 TOTAL / 113 NAME: 1. State the condition for translational equilibrium. A. ΣF = 0 B. ΣF
Physics 201 Lab 9: Torque and the Center of Mass Dr. Timothy C. Black
 Theoretical Discussion Physics 201 Lab 9: Torque and the Center of Mass Dr. Timothy C. Black For each of the linear kinematic variables; displacement r, velocity v and acceleration a; there is a corresponding
Theoretical Discussion Physics 201 Lab 9: Torque and the Center of Mass Dr. Timothy C. Black For each of the linear kinematic variables; displacement r, velocity v and acceleration a; there is a corresponding
Unit 4 Statics. Static Equilibrium Translational Forces Torque
 Unit 4 Statics Static Equilibrium Translational Forces Torque 1 Dynamics vs Statics Dynamics: is the study of forces and motion. We study why objects move. Statics: is the study of forces and NO motion.
Unit 4 Statics Static Equilibrium Translational Forces Torque 1 Dynamics vs Statics Dynamics: is the study of forces and motion. We study why objects move. Statics: is the study of forces and NO motion.
Chapter 8. Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics
 Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics Force vs. Torque Forces cause accelerations Torques cause angular accelerations Force and torque are related Torque The door is free to rotate about
Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics Force vs. Torque Forces cause accelerations Torques cause angular accelerations Force and torque are related Torque The door is free to rotate about
Chapter 4. Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion. continued
 Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion continued Quiz 3 4.7 The Gravitational Force Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Every particle in the universe exerts an attractive force on every other
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion continued Quiz 3 4.7 The Gravitational Force Newton s Law of Universal Gravitation Every particle in the universe exerts an attractive force on every other
Review for 3 rd Midterm
 Review for 3 rd Midterm Midterm is on 4/19 at 7:30pm in the same rooms as before You are allowed one double sided sheet of paper with any handwritten notes you like. The moment-of-inertia about the center-of-mass
Review for 3 rd Midterm Midterm is on 4/19 at 7:30pm in the same rooms as before You are allowed one double sided sheet of paper with any handwritten notes you like. The moment-of-inertia about the center-of-mass
SPH3U Practice Test. True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false.
 True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. The reason your head feels like it jerks backward when pulling away from a stop sign is best explained by Newton's First Law. 2. An airplane
True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. The reason your head feels like it jerks backward when pulling away from a stop sign is best explained by Newton's First Law. 2. An airplane
 AP Physics 1- Torque, Rotational Inertia, and Angular Momentum Practice Problems FACT: The center of mass of a system of objects obeys Newton s second law- F = Ma cm. Usually the location of the center
AP Physics 1- Torque, Rotational Inertia, and Angular Momentum Practice Problems FACT: The center of mass of a system of objects obeys Newton s second law- F = Ma cm. Usually the location of the center
The student will be able to: the torque of an applied force and solve related problems.
 Honors Physics Assignment Rotational Mechanics Reading Chapters 10 and 11 Objectives/HW: Assignment #1 M: Assignment #2 M: Assignment #3 M: Assignment #4 M: 1 2 3 #1-5 #6-10 #14, 15, 17, 18, 20-23 #24,
Honors Physics Assignment Rotational Mechanics Reading Chapters 10 and 11 Objectives/HW: Assignment #1 M: Assignment #2 M: Assignment #3 M: Assignment #4 M: 1 2 3 #1-5 #6-10 #14, 15, 17, 18, 20-23 #24,
Rotational Dynamics continued
 Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics continued 9.1 The Action of Forces and Torques on Rigid Objects Chapter 8 developed the concepts of angular motion. θ : angles and radian measure for angular variables ω :
Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics continued 9.1 The Action of Forces and Torques on Rigid Objects Chapter 8 developed the concepts of angular motion. θ : angles and radian measure for angular variables ω :
Solutions to Physics: Principles with Applications, 5/E, Giancoli Chapter 9
 Solutions to Phsics: Principles with pplications, 5/E, Giancoli Chapter 9 CHPTER 9 6. We choose the coordinate sstem shown, with positive torques clockwise. We write τ = Iα about the point from the force
Solutions to Phsics: Principles with pplications, 5/E, Giancoli Chapter 9 CHPTER 9 6. We choose the coordinate sstem shown, with positive torques clockwise. We write τ = Iα about the point from the force
Chapter Test A. Teacher Notes and Answers Forces and the Laws of Motion. Assessment
 Assessment Chapter Test A Teacher Notes and Answers Forces and the Laws of Motion CHAPTER TEST A (GENERAL) 1. c 2. d 3. d 4. c 5. c 6. c 7. c 8. b 9. d 10. d 11. c 12. a 13. d 14. d 15. b 16. d 17. c 18.
Assessment Chapter Test A Teacher Notes and Answers Forces and the Laws of Motion CHAPTER TEST A (GENERAL) 1. c 2. d 3. d 4. c 5. c 6. c 7. c 8. b 9. d 10. d 11. c 12. a 13. d 14. d 15. b 16. d 17. c 18.
Study Guide. Physics 3104A. Science. Force, Motion and Energy. Adult Basic Education. Prerequisite: Physics 2104B or Physics 2204.
 Adult Basic Education Science Force, Motion and Energy Prerequisite: Physics 2104B or Physics 2204 Credit Value: 1 Text: Physics: Concepts and Connections. Irwin, 2002 Physics Concentration Physics 1104
Adult Basic Education Science Force, Motion and Energy Prerequisite: Physics 2104B or Physics 2204 Credit Value: 1 Text: Physics: Concepts and Connections. Irwin, 2002 Physics Concentration Physics 1104
Equilibrium. Today: Center of Gravity Static Equilibrium. Sign convention for torques: (-) CW torque (+) CCW torque
 Tue Sept 29 Assign 5 Friday Exam Mon Oct 5 Morton 235 7:15-9:15 PM Email by Wednesday afternoon at the latest if conflict Q/A Sunday 1-3,4-6,7-9 Today: Center of Gravity Static Equilibrium Sign convention
Tue Sept 29 Assign 5 Friday Exam Mon Oct 5 Morton 235 7:15-9:15 PM Email by Wednesday afternoon at the latest if conflict Q/A Sunday 1-3,4-6,7-9 Today: Center of Gravity Static Equilibrium Sign convention
Chapter 5 The Force Vector
 Conceptual Physics/ PEP Name: Date: Chapter 5 The Force Vector Section Review 5.1 1. Indicate whether each of the following units of measurement are scalar or vector units: Speed _scalar time scalar mass
Conceptual Physics/ PEP Name: Date: Chapter 5 The Force Vector Section Review 5.1 1. Indicate whether each of the following units of measurement are scalar or vector units: Speed _scalar time scalar mass
Physics 1A Lecture 4B. "Fig Newton: The force required to accelerate a fig inches per second. --J. Hart
 Physics 1A Lecture 4B "Fig Newton: The force required to accelerate a fig 39.37 inches per second. --J. Hart Types of Forces There are many types of forces that we will apply in this class, let s discuss
Physics 1A Lecture 4B "Fig Newton: The force required to accelerate a fig 39.37 inches per second. --J. Hart Types of Forces There are many types of forces that we will apply in this class, let s discuss
Semester 1 Revision. Last modified: 05/06/2018
 Semester 1 Revision Last modified: 05/06/2018 Contents Links Motion with Uniform Acceleration Equations Method Example Forces Equations Method Example Static Equilibrium Equations Method Example Energy
Semester 1 Revision Last modified: 05/06/2018 Contents Links Motion with Uniform Acceleration Equations Method Example Forces Equations Method Example Static Equilibrium Equations Method Example Energy
Lecture 7: More on Newton s Laws
 Lecture 7: More on Newton s Laws Other Important Aspects of the Second Law: Note that = ma is a vector equation, i.e., it is equivalent to saying: = ma x y z = ma = ma An object accelerates in the same
Lecture 7: More on Newton s Laws Other Important Aspects of the Second Law: Note that = ma is a vector equation, i.e., it is equivalent to saying: = ma x y z = ma = ma An object accelerates in the same
Chapter 9. Rotational Dynamics
 Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics In pure translational motion, all points on an object travel on parallel paths. The most general motion is a combination of translation and rotation. 1) Torque Produces angular
Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics In pure translational motion, all points on an object travel on parallel paths. The most general motion is a combination of translation and rotation. 1) Torque Produces angular
Torque. 1. Torque - To make an object rotate, we must apply a force at a certain distance away from the axis => ex) opening a door
 Torque Level : Conceptual Physics Teacher : Kim 1. Torque - To make an object rotate, we must apply a force at a certain distance away from the axis => ex) opening a door Torque is defined as τ = r F where
Torque Level : Conceptual Physics Teacher : Kim 1. Torque - To make an object rotate, we must apply a force at a certain distance away from the axis => ex) opening a door Torque is defined as τ = r F where
Concept of Force Challenge Problem Solutions
 Concept of Force Challenge Problem Solutions Problem 1: Force Applied to Two Blocks Two blocks sitting on a frictionless table are pushed from the left by a horizontal force F, as shown below. a) Draw
Concept of Force Challenge Problem Solutions Problem 1: Force Applied to Two Blocks Two blocks sitting on a frictionless table are pushed from the left by a horizontal force F, as shown below. a) Draw
τ net l = r p L = Iω = d L dt = I α ΔL Angular momentum (one) Angular momentum (system, fixed axis) Newton s second law (system)
 l = r p L = Iω = d L dt = I α ΔL = 0 Angular momentum (one) Angular momentum (system, fixed axis) Newton s second law (system) Conserva
l = r p L = Iω = d L dt = I α ΔL = 0 Angular momentum (one) Angular momentum (system, fixed axis) Newton s second law (system) Conserva
4.0 m s 2. 2 A submarine descends vertically at constant velocity. The three forces acting on the submarine are viscous drag, upthrust and weight.
 1 1 wooden block of mass 0.60 kg is on a rough horizontal surface. force of 12 N is applied to the block and it accelerates at 4.0 m s 2. wooden block 4.0 m s 2 12 N hat is the magnitude of the frictional
1 1 wooden block of mass 0.60 kg is on a rough horizontal surface. force of 12 N is applied to the block and it accelerates at 4.0 m s 2. wooden block 4.0 m s 2 12 N hat is the magnitude of the frictional
Newton s First Law and IRFs
 Goals: Physics 207, Lecture 6, Sept. 22 Recognize different types of forces and know how they act on an object in a particle representation Identify forces and draw a Free Body Diagram Solve 1D and 2D
Goals: Physics 207, Lecture 6, Sept. 22 Recognize different types of forces and know how they act on an object in a particle representation Identify forces and draw a Free Body Diagram Solve 1D and 2D
Statics. Phys101 Lectures 19,20. Key points: The Conditions for static equilibrium Solving statics problems Stress and strain. Ref: 9-1,2,3,4,5.
 Phys101 Lectures 19,20 Statics Key points: The Conditions for static equilibrium Solving statics problems Stress and strain Ref: 9-1,2,3,4,5. Page 1 The Conditions for Static Equilibrium An object in static
Phys101 Lectures 19,20 Statics Key points: The Conditions for static equilibrium Solving statics problems Stress and strain Ref: 9-1,2,3,4,5. Page 1 The Conditions for Static Equilibrium An object in static
4.1 Forces. Chapter 4 The Laws of Motion
 4.1 Forces Chapter 4 he Laws of Motion 4.2 Newton s First Law it s not the nature of an object to stop, once set in motion, but rather to continue in its original state of motion. An object moves with
4.1 Forces Chapter 4 he Laws of Motion 4.2 Newton s First Law it s not the nature of an object to stop, once set in motion, but rather to continue in its original state of motion. An object moves with
Phys 1401: General Physics I
 1. (0 Points) What course is this? a. PHYS 1401 b. PHYS 1402 c. PHYS 2425 d. PHYS 2426 2. (0 Points) Which exam is this? a. Exam 1 b. Exam 2 c. Final Exam 3. (0 Points) What version of the exam is this?
1. (0 Points) What course is this? a. PHYS 1401 b. PHYS 1402 c. PHYS 2425 d. PHYS 2426 2. (0 Points) Which exam is this? a. Exam 1 b. Exam 2 c. Final Exam 3. (0 Points) What version of the exam is this?
θ Beam Pivot F r Figure 1. Figure 2. STATICS (Force Vectors, Tension & Torque) MBL-32 (Ver. 3/20/2006) Name: Lab Partner: Lab Partner:
 Please Circle Your Lab day: M T W T F Name: Lab Partner: Lab Partner: Project #1: Kinesthetic experiences with force vectors and torque. Project #2: How does torque depend on the lever arm? Project #1:
Please Circle Your Lab day: M T W T F Name: Lab Partner: Lab Partner: Project #1: Kinesthetic experiences with force vectors and torque. Project #2: How does torque depend on the lever arm? Project #1:
Physics 2210 Homework 18 Spring 2015
 Physics 2210 Homework 18 Spring 2015 Charles Jui April 12, 2015 IE Sphere Incline Wording A solid sphere of uniform density starts from rest and rolls without slipping down an inclined plane with angle
Physics 2210 Homework 18 Spring 2015 Charles Jui April 12, 2015 IE Sphere Incline Wording A solid sphere of uniform density starts from rest and rolls without slipping down an inclined plane with angle
The net force on a moving object is suddenly reduced to zero. As a consequence, the object
 The net force on a moving object is suddenly reduced to zero. As a consequence, the object (A) stops abruptly (B) stops during a short time interval (C) changes direction (D) continues at a constant velocity
The net force on a moving object is suddenly reduced to zero. As a consequence, the object (A) stops abruptly (B) stops during a short time interval (C) changes direction (D) continues at a constant velocity
