Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium; Elasticity and Fracture
|
|
|
- Gertrude McDonald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients of this work are expected to abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended pedagogical purposes and the needs of other instructors who rely on these materials. Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 12 Physics for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium; Elasticity and racture 1
2 Units of Chapter 12 The Conditions for Equilibrium Solving Statics Problems Stability and Balance Elasticity; Stress and Strain racture 12-1 The Conditions for Equilibrium An object with forces acting on it, but with zero net force, is said to be in equilibrium. The first condition for equilibrium: 2
3 12-1 The Conditions for Equilibrium Example 12-1: Chandelier cord tension. Calculate the tensions A and B in the two cords that are connected to the vertical cord supporting the 200 kg chandelier shown. Ignore the mass of the cords The Conditions for Equilibrium Example 12-1: Chandelier cord tension. y direction : sin A 2260 N sin 60 x direction : - cos60 0 B A A B A cos cos N 3
4 12-1 The Conditions for Equilibrium The second condition of equilibrium is that there be no torque around any axis; the choice of axis is arbitrary. Although the net force on it is zero, the ruler will move (rotate). A pair of equal forces acting in opposite directions but at different points on an object (as shown here) is referred to as a couple The Conditions for Equilibrium Conceptual Example 12-2: A lever. This bar is being used as a lever to pry up a large rock. The small rock acts as a fulcrum (pivot point). The force required at the long end of the bar can be quite a bit smaller than the rock s weight mg, since it is the torques that balance in the rotation about the fulcrum. If, however, the leverage isn t sufficient, and the large rock isn t budged, what are two ways to increase the leverage? One way is to lengthen the lever, perhaps with a pipe slid over the end as shown. Another way is to move the small rock closer to the big rock; this increases the ratio of the two lever arms considerably. 4
5 1. Choose one object at a time, and make a freebody diagram by showing all the forces on it and where they act. 2. Choose a coordinate system and resolve forces into components. 3. Write equilibrium equations for the forces. 4. Choose any axis perpendicular to the plane of the forces and write the torque equilibrium equation. A clever choice here can simplify the problem enormously. 5. Solve Solving Statics Problems 12-2 Solving Statics Problems Example 12-3: Balancing a seesaw. A board of mass M = 2.0 kg serves as a seesaw for two children. Child A has a mass of 30 kg and sits 2.5 m from the pivot point, P (his center of gravity is 2.5 m from the pivot). At what distance x from the pivot must child B, of mass 25 kg, place herself to balance the seesaw? Assume the board is uniform and centered over the pivot. 5
6 12-2 Solving Statics Problems Example 12-3: Balancing a seesaw. Take ccw as ve or equilibrium τ 0 ( l ccw - cw g x(25g) x 3.0 m 25 Note that and Mg do not produce a torque as l N In this case we do not need the force equations. ) Solving Statics Problems If a force in your solution comes out negative (as A will here), it just means that it s in the opposite direction from the one you chose. This is trivial to fix, so don t worry about getting all the signs of the forces right before you start solving. 6
7 12-2 Solving Statics Problems Example 12-4: orce exerted by biceps muscle. How much force must the biceps muscle exert when a 5.0 kg ball is held in the hand (a) with the arm horizontal, and (b) when the arm is at a 45 angle? The biceps muscle is connected to the forearm by a tendon attached 5.0 cm from the elbow joint. Assume that the mass of forearm and hand together is 2.0 kg and their CG is as shown Solving Statics Problems Example 12-4: orce exerted by biceps muscle. How much force must the biceps muscle exert when a 5.0 kg ball is held in the hand (a) with the arm horizontal. J is the force on the joint Calculate τ about the joint so that will not appear in equation as 5.0 M M (30 175) g (15 2.0g 355.0g) N 5.0 l J 7
8 12-2 Solving Statics Problems Example 12-4: orce exerted by biceps muscle. How much force must the biceps muscle exert when a 5.0 kg ball is held in the hand (b) when the arm is at a 45 angle? All forces are the same and all distances are reduced by the same factor of cos45 O which leads to the same torque equation, so M = 400 N as in part (a). If J was required use = 0 M J W arm W ball = Solving Statics Problems Example 12-5: Hinged beam and cable. A uniform beam, 2.20 m long with mass m = 25.0 kg, is mounted by a small hinge on a wall. The beam is held in a horizontal position by a cable that makes an angle θ = The beam supports a sign of mass M = 28.0 kg suspended from its end. Determine the components of the force H that the (smooth) hinge exerts on the beam, and the tension T in the supporting cable. 8
9 Example 12-5: Hinged beam and cable. T x T cos τ 0 (, Calculate about hinge ccw is ve ccw 0 l lt y mg lmg 0 2 m T sin g M 2 m g M ( / 2) T 794 N sin sin 30 Now use 0 Hx Hy Hy Hy cw Tx Ty Tx Hx 0 & Hx Mg mg 0 Mg mg Ty Ty Hy Tx sin have no torque about hinge) ( M m) g cos 794cos N sin ( ) sin N T T T l = 2.20 m m = 25.0 kg M = 28.0 kg = Solving Statics Problems Example 12-6: Ladder. A 5.0 m long ladder leans against a smooth wall at a point 4.0 m above a cement floor. The ladder is uniform and has mass m = 12.0 kg. Assuming the wall is frictionless (but the floor is not), determine the forces exerted on the ladder by the floor and by the wall. 9
10 12-2 Solving Statics Problems Example 12-6: Ladder. l L 5.0 m x l l 0 W x /2 1.5 m m 3.0 m Example 12-6: Ladder. l L 5.0 m x l l 0 W x /2 1.5 m 4.0 m m 10
11 12-2 Solving Statics Problems Example 12-6: Ladder. Since there are 3 unknowns we need all 3 conditions for equilibrium. As there is no friction at wall 0 τ ccw W Cx y x 0 0 [calculate about floor (O)] cw lmg l W W Cy Cx 0 l N N mg 0 W W 0 W l Cy Cx W mg 0 is normal to the wall. mg N W Answer : W C C 2 Cx Cy -1 Cy 1118 tan tan 70 to x axis Cx N in - ve x direction 126 N at 70above x axis N 11
12 12-3 Stability and Balance If the forces on an object are such that they tend to return it to its equilibrium position, it is said to be in stable equilibrium Stability and Balance If, however, the forces tend to move it away from its equilibrium point, it is said to be in unstable equilibrium. 12
13 12-3 Stability and Balance An object in stable equilibrium may become unstable if it is tipped so that its center of gravity is outside the pivot point. Of course, it will be stable again once it lands! 12-3 Stability and Balance People carrying heavy loads automatically adjust their posture so their center of mass is over their feet. This can lead to injury if the contortion is too great. 13
14 12-4 Elasticity; Stress and Strain Hooke s law: the change in length is proportional to the applied force Elasticity; Stress and Strain This proportionality holds until the force reaches the proportional limit. Beyond that, the object will still return to its original shape up to the elastic limit. Beyond the elastic limit, the material is permanently deformed, and it breaks at the breaking point. 14
15 12-4 Elasticity; Stress and Strain The change in length of a stretched object depends not only on the applied force, but also on its length, cross-sectional area and the material from which it is made. The material factor, E, is called the elastic modulus or Young s modulus, and it has been measured for many materials Elasticity; Stress and Strain 15
16 12-4 Elasticity; Stress and Strain Example 12-7: Tension in piano wire. A 1.60 m long steel piano wire has a diameter of 0.20 cm. How great is the tension in the wire if it stretches 0.25 cm when tightened? 1 l l l 0 = 1.60 m 0 E A l =0.25 cm = m EAl d = 0.20 cm = m r = m l0 A = r 2 = m E = N/m N 12-4 Elasticity; Stress and Strain Stress is defined as the force per unit area. Strain is defined as the ratio of the change in length to the original length. Therefore, the elastic modulus is equal to the stress divided by the strain: 16
17 12-4 Elasticity; Stress and Strain In tensile stress, forces tend to stretch the object Elasticity; Stress and Strain Compressional stress is exactly the opposite of tensional stress. These columns are under compression. 17
18 12-4 Elasticity; Stress and Strain The three types of stress for rigid objects: 12-4 Elasticity; Stress and Strain The shear strain, where G is the shear modulus: 18
19 12-4 Elasticity; Stress and Strain If an object is subjected to inward forces on all sides, its volume changes depending on its bulk modulus. This is the only deformation that applies to fluids. or 12-5 racture If the stress on an object is too great, the object will fracture. The ultimate strengths of materials under tensile stress, compressional stress, and shear stress have been measured. When designing a structure, it is a good idea to keep anticipated stresses less than 1/3 to 1/10 of the ultimate strength. 19
20 12-5 racture 12-5 racture Example 12-8: Breaking the piano wire. A steel piano wire is 1.60 m long with a diameter of 0.20 cm. Approximately what tension force would break it? d = 0.20 cm = m r = m A = r 2 = m 2 Maximul Tensile Stress A N/m Tensile Strength = N/m 2 Tensile Strength N 20
21 12-5 racture A horizontal beam will be under both tensile and compressive stress due to its own weight. Therefore, it must be made of a material that is strong under both compression and tension. Summary of Chapter 12 An object at rest is in equilibrium; the study of such objects is called statics. In order for an object to be in equilibrium, there must be no net force on it along any coordinate, and there must be no net torque around any axis. An object in static equilibrium can be in stable, unstable, or neutral equilibrium. 21
22 Summary of Chapter 12 Materials can be under compression, tension, or shear stress. If the force is too great, the material will exceed its elastic limit; if the force continues to increase, the material will fracture. 22
Statics. Phys101 Lectures 19,20. Key points: The Conditions for static equilibrium Solving statics problems Stress and strain. Ref: 9-1,2,3,4,5.
 Phys101 Lectures 19,20 Statics Key points: The Conditions for static equilibrium Solving statics problems Stress and strain Ref: 9-1,2,3,4,5. Page 1 The Conditions for Static Equilibrium An object in static
Phys101 Lectures 19,20 Statics Key points: The Conditions for static equilibrium Solving statics problems Stress and strain Ref: 9-1,2,3,4,5. Page 1 The Conditions for Static Equilibrium An object in static
Static Equilibrium; Elasticity & Fracture
 Static Equilibrium; Elasticity & Fracture The Conditions for Equilibrium Statics is concerned with the calculation of the forces acting on and within structures that are in equilibrium. An object with
Static Equilibrium; Elasticity & Fracture The Conditions for Equilibrium Statics is concerned with the calculation of the forces acting on and within structures that are in equilibrium. An object with
Static Equilibrium; Torque
 Static Equilibrium; Torque The Conditions for Equilibrium An object with forces acting on it, but that is not moving, is said to be in equilibrium. The first condition for equilibrium is that the net force
Static Equilibrium; Torque The Conditions for Equilibrium An object with forces acting on it, but that is not moving, is said to be in equilibrium. The first condition for equilibrium is that the net force
CHAPTER 12 STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY. Conditions for static equilibrium Center of gravity (weight) Examples of static equilibrium
 CHAPTER 12 STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY As previously defined, an object is in equilibrium when it is at rest or moving with constant velocity, i.e., with no net force acting on it. The following
CHAPTER 12 STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY As previously defined, an object is in equilibrium when it is at rest or moving with constant velocity, i.e., with no net force acting on it. The following
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 7 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th Edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 7 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th Edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 7 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th Edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 4 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 4 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 4 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 4 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 4 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 4 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the
Chapter 7 Work and Energy
 8/04/0 Lecture PowerPoints 009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student
8/04/0 Lecture PowerPoints 009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student
Static Equilibrium and Elasticity. Luis Anchordoqui
 Static Equilibrium and Elasticity The Conditions for Equilibrium An object with forces acting on it, but that is not moving, is said to be in equilibrium. The Conditions for Equilibrium (cont d) The first
Static Equilibrium and Elasticity The Conditions for Equilibrium An object with forces acting on it, but that is not moving, is said to be in equilibrium. The Conditions for Equilibrium (cont d) The first
Chapter 9- Static Equilibrium
 Chapter 9- Static Equilibrium Changes in Office-hours The following changes will take place until the end of the semester Office-hours: - Monday, 12:00-13:00h - Wednesday, 14:00-15:00h - Friday, 13:00-14:00h
Chapter 9- Static Equilibrium Changes in Office-hours The following changes will take place until the end of the semester Office-hours: - Monday, 12:00-13:00h - Wednesday, 14:00-15:00h - Friday, 13:00-14:00h
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 5 Physics for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition. Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 5 Physics for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 5 Physics for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely
Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium
 Chapter Static Equilibrium. Analysis Model: Rigid Body in Equilibrium. More on the Center of Gravity. Examples of Rigid Objects in Static Equilibrium CHAPTER : STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY.) The Conditions
Chapter Static Equilibrium. Analysis Model: Rigid Body in Equilibrium. More on the Center of Gravity. Examples of Rigid Objects in Static Equilibrium CHAPTER : STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY.) The Conditions
Chapter 12. Static Equilibrium and Elasticity
 Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium and Elasticity Static Equilibrium Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial
Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium and Elasticity Static Equilibrium Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial
PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #23
 PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #23 Monday, April 29, 2013 Conditions for Equilibrium Elastic Properties of Solids Young s Modulus Bulk Modulus Density and Specific Gravity luid and Pressure Today s homework
PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #23 Monday, April 29, 2013 Conditions for Equilibrium Elastic Properties of Solids Young s Modulus Bulk Modulus Density and Specific Gravity luid and Pressure Today s homework
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 4 Physics: for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 4 Physics: for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 4 Physics: for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided
LECTURE 22 EQUILIBRIUM. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 22 EQUILIBRIUM Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 22 2 Reading chapter 11-3 to 11-4 Static equilibrium Center of mass and balance Static equilibrium 3 If a rigid object is in equilibrium (constant
LECTURE 22 EQUILIBRIUM Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 22 2 Reading chapter 11-3 to 11-4 Static equilibrium Center of mass and balance Static equilibrium 3 If a rigid object is in equilibrium (constant
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 10 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 10 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 10 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 8 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 8 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 8 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the
Static Equilibrium. Lecture 22. Chapter 12. Physics I Department of Physics and Applied Physics
 Lecture 22 Chapter 12 Physics I 12.02.2013 Static Equilibrium Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov2013/physics1fall.html
Lecture 22 Chapter 12 Physics I 12.02.2013 Static Equilibrium Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov2013/physics1fall.html
Lecture Presentation Chapter 8 Equilibrium and Elasticity
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 8 Equilibrium and Elasticity Suggested Videos for Chapter 8 Prelecture Videos Static Equilibrium Elasticity Video Tutor Solutions Equilibrium and Elasticity Class Videos Center
Lecture Presentation Chapter 8 Equilibrium and Elasticity Suggested Videos for Chapter 8 Prelecture Videos Static Equilibrium Elasticity Video Tutor Solutions Equilibrium and Elasticity Class Videos Center
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 6 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 6 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 6 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
ConcepTest Clicker Questions. Chapter 27 Physics: for Scientists & Engineers with Modern Physics, 4th edition Giancoli
 ConcepTest Clicker Questions Chapter 27 Physics: for Scientists & Engineers with Modern Physics, 4th edition Giancoli 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws
ConcepTest Clicker Questions Chapter 27 Physics: for Scientists & Engineers with Modern Physics, 4th edition Giancoli 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 7 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 7 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 7 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Equilibrium & Elasticity
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 12 Equilibrium & Elasticity Static equilibrium Elasticity 1. A uniform steel bar of length 3.0 m and weight 20 N rests on two supports (A and B) at its ends. A block
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 12 Equilibrium & Elasticity Static equilibrium Elasticity 1. A uniform steel bar of length 3.0 m and weight 20 N rests on two supports (A and B) at its ends. A block
2007 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 5 Physics, 3 rd Edition James S. Walker 2007 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture Outlines Chapter 5 Physics, 3 rd Edition James S. Walker 2007 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
2/28/2006 Statics ( F.Robilliard) 1
 2/28/2006 Statics (.Robilliard) 1 Extended Bodies: In our discussion so far, we have considered essentially only point masses, under the action of forces. We now broaden our considerations to extended
2/28/2006 Statics (.Robilliard) 1 Extended Bodies: In our discussion so far, we have considered essentially only point masses, under the action of forces. We now broaden our considerations to extended
Equilibrium. the linear momentum,, of the center of mass is constant
 Equilibrium is the state of an object where: Equilibrium the linear momentum,, of the center of mass is constant Feb. 19, 2018 the angular momentum,, about the its center of mass, or any other point, is
Equilibrium is the state of an object where: Equilibrium the linear momentum,, of the center of mass is constant Feb. 19, 2018 the angular momentum,, about the its center of mass, or any other point, is
Torque and Static Equilibrium
 Torque and Static Equilibrium Rigid Bodies Rigid body: An extended object in which the distance between any two points in the object is constant in time. Examples: sphere, disk Effect of external forces
Torque and Static Equilibrium Rigid Bodies Rigid body: An extended object in which the distance between any two points in the object is constant in time. Examples: sphere, disk Effect of external forces
9/29/2014. Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors. 3-1 Vectors and Scalars. Contents of Chapter Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 3 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 3 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
UNIVERSITY PHYSICS I. Professor Meade Brooks, Collin College. Chapter 12: STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY
 UNIVERSITY PHYSICS I Professor Meade Brooks, Collin College Chapter 12: STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY Two stilt walkers in standing position. All forces acting on each stilt walker balance out; neither
UNIVERSITY PHYSICS I Professor Meade Brooks, Collin College Chapter 12: STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY Two stilt walkers in standing position. All forces acting on each stilt walker balance out; neither
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 16 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 16 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 16 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Chapter 9 TORQUE & Rotational Kinematics
 Chapter 9 TORQUE & Rotational Kinematics This motionless person is in static equilibrium. The forces acting on him add up to zero. Both forces are vertical in this case. This car is in dynamic equilibrium
Chapter 9 TORQUE & Rotational Kinematics This motionless person is in static equilibrium. The forces acting on him add up to zero. Both forces are vertical in this case. This car is in dynamic equilibrium
EQUILIBRIUM and ELASTICITY
 PH 221-1D Spring 2013 EQUILIBRIUM and ELASTICITY Lectures 30-32 Chapter 12 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 9 th edition) 1 Chapter 12 Equilibrium and Elasticity In this chapter we will
PH 221-1D Spring 2013 EQUILIBRIUM and ELASTICITY Lectures 30-32 Chapter 12 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 9 th edition) 1 Chapter 12 Equilibrium and Elasticity In this chapter we will
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 16 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 16 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 16 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Static Equilibrium and Torque
 10.3 Static Equilibrium and Torque SECTION OUTCOMES Use vector analysis in two dimensions for systems involving static equilibrium and torques. Apply static torques to structures such as seesaws and bridges.
10.3 Static Equilibrium and Torque SECTION OUTCOMES Use vector analysis in two dimensions for systems involving static equilibrium and torques. Apply static torques to structures such as seesaws and bridges.
Rutgers University Department of Physics & Astronomy. 01:750:271 Honors Physics I Fall Lecture 19. Home Page. Title Page. Page 1 of 36.
 Rutgers University Department of Physics & Astronomy 01:750:271 Honors Physics I Fall 2015 Lecture 19 Page 1 of 36 12. Equilibrium and Elasticity How do objects behave under applied external forces? Under
Rutgers University Department of Physics & Astronomy 01:750:271 Honors Physics I Fall 2015 Lecture 19 Page 1 of 36 12. Equilibrium and Elasticity How do objects behave under applied external forces? Under
PHY 1150 Doug Davis Chapter 8; Static Equilibrium 8.3, 10, 22, 29, 52, 55, 56, 74
 PHY 1150 Doug Davis Chapter 8; Static Equilibrium 8.3, 10, 22, 29, 52, 55, 56, 74 8.3 A 2-kg ball is held in position by a horizontal string and a string that makes an angle of 30 with the vertical, as
PHY 1150 Doug Davis Chapter 8; Static Equilibrium 8.3, 10, 22, 29, 52, 55, 56, 74 8.3 A 2-kg ball is held in position by a horizontal string and a string that makes an angle of 30 with the vertical, as
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 13: ROTATIONAL EQUILIBRIUM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com EXAMPLE: POSITION OF SECOND KID ON SEESAW EXAMPLE: A 4 m-long seesaw 50 kg in mass and of uniform mass distribution is pivoted on a fulcrum at its middle, as shown. Two kids sit on
!! www.clutchprep.com EXAMPLE: POSITION OF SECOND KID ON SEESAW EXAMPLE: A 4 m-long seesaw 50 kg in mass and of uniform mass distribution is pivoted on a fulcrum at its middle, as shown. Two kids sit on
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 2 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 2 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 2 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Physics 8 Wednesday, October 28, 2015
 Physics 8 Wednesday, October 8, 015 HW7 (due this Friday will be quite easy in comparison with HW6, to make up for your having a lot to read this week. For today, you read Chapter 3 (analyzes cables, trusses,
Physics 8 Wednesday, October 8, 015 HW7 (due this Friday will be quite easy in comparison with HW6, to make up for your having a lot to read this week. For today, you read Chapter 3 (analyzes cables, trusses,
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 11. Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 11 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 11 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
TEST REPORT. Question file: P Copyright:
 Date: February-12-16 Time: 2:00:28 PM TEST REPORT Question file: P12-2006 Copyright: Test Date: 21/10/2010 Test Name: EquilibriumPractice Test Form: 0 Test Version: 0 Test Points: 138.00 Test File: EquilibriumPractice
Date: February-12-16 Time: 2:00:28 PM TEST REPORT Question file: P12-2006 Copyright: Test Date: 21/10/2010 Test Name: EquilibriumPractice Test Form: 0 Test Version: 0 Test Points: 138.00 Test File: EquilibriumPractice
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 2 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 2 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 2 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the
Lecture Outlines Chapter 22. Physics, 3 rd Edition James S. Walker
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 22 Physics, 3 rd Edition James S. Walker 2007 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in
Lecture Outlines Chapter 22 Physics, 3 rd Edition James S. Walker 2007 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in
is the study of and. We study objects. is the study of and. We study objects.
 Static Equilibrium Translational Forces Torque Unit 4 Statics Dynamics vs Statics is the study of and. We study objects. is the study of and. We study objects. Recall Newton s First Law All objects remain
Static Equilibrium Translational Forces Torque Unit 4 Statics Dynamics vs Statics is the study of and. We study objects. is the study of and. We study objects. Recall Newton s First Law All objects remain
HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL
 HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT STATIC EQUILIBRIUM MULTIPLE CHOICE / 33 OPEN ENDED / 80 TOTAL / 113 NAME: 1. State the condition for translational equilibrium. A. ΣF = 0 B. ΣF
HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT STATIC EQUILIBRIUM MULTIPLE CHOICE / 33 OPEN ENDED / 80 TOTAL / 113 NAME: 1. State the condition for translational equilibrium. A. ΣF = 0 B. ΣF
Unit 4 Statics. Static Equilibrium Translational Forces Torque
 Unit 4 Statics Static Equilibrium Translational Forces Torque 1 Dynamics vs Statics Dynamics: is the study of forces and motion. We study why objects move. Statics: is the study of forces and NO motion.
Unit 4 Statics Static Equilibrium Translational Forces Torque 1 Dynamics vs Statics Dynamics: is the study of forces and motion. We study why objects move. Statics: is the study of forces and NO motion.
Consider two students pushing with equal force on opposite sides of a desk. Looking top-down on the desk:
 1 Bodies in Equilibrium Recall Newton's First Law: if there is no unbalanced force on a body (i.e. if F Net = 0), the body is in equilibrium. That is, if a body is in equilibrium, then all the forces on
1 Bodies in Equilibrium Recall Newton's First Law: if there is no unbalanced force on a body (i.e. if F Net = 0), the body is in equilibrium. That is, if a body is in equilibrium, then all the forces on
ConcepTest PowerPoints
 ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 4 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 4 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Lecture Outlines Chapter 9. Physics, 3 rd Edition James S. Walker
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 9 Physics, 3 rd Edition James S. Walker 2007 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture Outlines Chapter 9 Physics, 3 rd Edition James S. Walker 2007 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Torque and Static Equilibrium
 Torque and Static Equilibrium Ch. 7.3, 8.1 (KJF 3 rd ed.) Phys 114 Eyres Torque 1 Causing rotation: Torque Three factors affect the how a force can affect the rotation: The magnitude of the force The distance,
Torque and Static Equilibrium Ch. 7.3, 8.1 (KJF 3 rd ed.) Phys 114 Eyres Torque 1 Causing rotation: Torque Three factors affect the how a force can affect the rotation: The magnitude of the force The distance,
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 20 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 20 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 20 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 16 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 16 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 16 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Physics 211 Week 10. Statics: Walking the Plank (Solution)
 Statics: Walking the Plank (Solution) A uniform horizontal beam 8 m long is attached by a frictionless pivot to a wall. A cable making an angle of 37 o, attached to the beam 5 m from the pivot point, supports
Statics: Walking the Plank (Solution) A uniform horizontal beam 8 m long is attached by a frictionless pivot to a wall. A cable making an angle of 37 o, attached to the beam 5 m from the pivot point, supports
Lecture Outlines Chapter 3. Physics, 3 rd Edition James S. Walker
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 3 Physics, 3 rd Edition James S. Walker 2007 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture Outlines Chapter 3 Physics, 3 rd Edition James S. Walker 2007 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 1 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 1 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 20 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 20 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 20 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Section 2: Static Equilibrium II- Balancing Torques
 Section 2: Static Equilibrium II- Balancing Torques Last Section: If (ie. Forces up = Forces down and Forces left = Forces right), then the object will have no translatory motion. In other words, the object
Section 2: Static Equilibrium II- Balancing Torques Last Section: If (ie. Forces up = Forces down and Forces left = Forces right), then the object will have no translatory motion. In other words, the object
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 16 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 16 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 16 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Center of Mass. A baseball thrown into the air follows a smooth parabolic path. A baseball bat thrown into the air does not follow a smooth path.
 Center of Mass A baseball thrown into the air follows a smooth parabolic path. A baseball bat thrown into the air does not follow a smooth path. The bat wobbles about a special point. This point stays
Center of Mass A baseball thrown into the air follows a smooth parabolic path. A baseball bat thrown into the air does not follow a smooth path. The bat wobbles about a special point. This point stays
P12 Torque Notes.notebook. March 26, Torques
 Torques The size of a torque depends on two things: 1. The size of the force being applied (a larger force will have a greater effect) 2. The distance away from the pivot point (the further away from this
Torques The size of a torque depends on two things: 1. The size of the force being applied (a larger force will have a greater effect) 2. The distance away from the pivot point (the further away from this
ConcepTest PowerPoints
 ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 6 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 6 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 10 Lecture Outline Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations Elastic Deformations Hooke s Law Stress and
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations Elastic Deformations Hooke s Law Stress and
12/1/2014. Chapter 5 Circular Motion; Gravitation. Contents of Chapter 5. Contents of Chapter Kinematics of Uniform Circular Motion
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 5 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli Chapter 5 Circular Motion; Gravitation This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 5 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli Chapter 5 Circular Motion; Gravitation This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided
ConcepTest Clicker Questions. Chapter 26 Physics: for Scientists & Engineers with Modern Physics, 4th edition Giancoli
 ConcepTest Clicker Questions Chapter 26 Physics: for Scientists & Engineers with Modern Physics, 4th edition Giancoli 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws
ConcepTest Clicker Questions Chapter 26 Physics: for Scientists & Engineers with Modern Physics, 4th edition Giancoli 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 3 Physics for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 3 Physics for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 3 Physics for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided
9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
 9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Deforming force Deforming force is the force which changes the shape or size of a body. Restoring force Restoring force is the internal force developed inside the body
9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Deforming force Deforming force is the force which changes the shape or size of a body. Restoring force Restoring force is the internal force developed inside the body
ConcepTest PowerPoints
 ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 16 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 16 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
2008 FXA THREE FORCES IN EQUILIBRIUM 1. Candidates should be able to : TRIANGLE OF FORCES RULE
 THREE ORCES IN EQUILIBRIUM 1 Candidates should be able to : TRIANGLE O ORCES RULE Draw and use a triangle of forces to represent the equilibrium of three forces acting at a point in an object. State that
THREE ORCES IN EQUILIBRIUM 1 Candidates should be able to : TRIANGLE O ORCES RULE Draw and use a triangle of forces to represent the equilibrium of three forces acting at a point in an object. State that
Be on time Switch off mobile phones. Put away laptops. Being present = Participating actively
 A couple of house rules Be on time Switch off mobile phones Put away laptops Being present = Participating actively Het basisvak Toegepaste Natuurwetenschappen http://www.phys.tue.nl/nfcmr/natuur/collegenatuur.html
A couple of house rules Be on time Switch off mobile phones Put away laptops Being present = Participating actively Het basisvak Toegepaste Natuurwetenschappen http://www.phys.tue.nl/nfcmr/natuur/collegenatuur.html
ConcepTest PowerPoints. Chapter 2 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 3 rd edition Fishbane Gasiorowicz Thornton Pearson Prentice Hall
 ConcepTest PowerPoints 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall Chapter 2 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 3 rd edition Fishbane Gasiorowicz Thornton This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
ConcepTest PowerPoints 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall Chapter 2 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 3 rd edition Fishbane Gasiorowicz Thornton This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
4/14/11. Chapter 12 Static equilibrium and Elasticity Lecture 2. Condition for static equilibrium. Stability An object is in equilibrium:
 About Midterm Exam 3 When and where Thurs April 21 th, 5:45-7:00 pm Rooms: Same as Exam I and II, See course webpage. Your TA will give a brief review during the discussion session. Coverage: Chapts 9
About Midterm Exam 3 When and where Thurs April 21 th, 5:45-7:00 pm Rooms: Same as Exam I and II, See course webpage. Your TA will give a brief review during the discussion session. Coverage: Chapts 9
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 6 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 6 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 6 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
Equilibrium Notes 1 Translational Equilibrium
 Equilibrium Notes 1 Translational Equilibrium Ex. A 20.0 kg object is suspended by a rope as shown. What is the net force acting on it? Ex. Ok that was easy, now that same 20.0 kg object is lifted at a
Equilibrium Notes 1 Translational Equilibrium Ex. A 20.0 kg object is suspended by a rope as shown. What is the net force acting on it? Ex. Ok that was easy, now that same 20.0 kg object is lifted at a
Equilibrium. Today: Center of Gravity Static Equilibrium. Sign convention for torques: (-) CW torque (+) CCW torque
 Tue Sept 29 Assign 5 Friday Exam Mon Oct 5 Morton 235 7:15-9:15 PM Email by Wednesday afternoon at the latest if conflict Q/A Sunday 1-3,4-6,7-9 Today: Center of Gravity Static Equilibrium Sign convention
Tue Sept 29 Assign 5 Friday Exam Mon Oct 5 Morton 235 7:15-9:15 PM Email by Wednesday afternoon at the latest if conflict Q/A Sunday 1-3,4-6,7-9 Today: Center of Gravity Static Equilibrium Sign convention
Physics 101 Lecture 12 Equilibrium
 Physics 101 Lecture 12 Equilibrium Assist. Prof. Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com Static Equilibrium q Equilibrium and static equilibrium q Static equilibrium conditions n Net eternal
Physics 101 Lecture 12 Equilibrium Assist. Prof. Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com Static Equilibrium q Equilibrium and static equilibrium q Static equilibrium conditions n Net eternal
Announcements. Suppose your scores are 12, 16, 15. (16/20)*20 + (15/20)*15 + (12/20)*15 = out of a possible
 nnouncements Exam grades will be posted on Sakai soon. Probably riday. Exam 3 will be riday, ugust 3. Today is July 19. Only weeks to the next exam. How do the test grades work? Highest exam 0% Next exam
nnouncements Exam grades will be posted on Sakai soon. Probably riday. Exam 3 will be riday, ugust 3. Today is July 19. Only weeks to the next exam. How do the test grades work? Highest exam 0% Next exam
Physics 2210 Homework 18 Spring 2015
 Physics 2210 Homework 18 Spring 2015 Charles Jui April 12, 2015 IE Sphere Incline Wording A solid sphere of uniform density starts from rest and rolls without slipping down an inclined plane with angle
Physics 2210 Homework 18 Spring 2015 Charles Jui April 12, 2015 IE Sphere Incline Wording A solid sphere of uniform density starts from rest and rolls without slipping down an inclined plane with angle
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Torque
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Torque 1. A uniform meterstick of mass 0.20 kg is pivoted at the 40 cm mark. Where should one hang a mass of 0.50 kg to balance the stick? (A) 16 cm (B) 36 cm (C) 44
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Torque 1. A uniform meterstick of mass 0.20 kg is pivoted at the 40 cm mark. Where should one hang a mass of 0.50 kg to balance the stick? (A) 16 cm (B) 36 cm (C) 44
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 2 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th Edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 2 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th Edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 2 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th Edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is
Exam 3 PREP Chapters 6, 7, 8
 PHY241 - General Physics I Dr. Carlson, Fall 2013 Prep Exam 3 PREP Chapters 6, 7, 8 Name TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) Astronauts in orbiting satellites
PHY241 - General Physics I Dr. Carlson, Fall 2013 Prep Exam 3 PREP Chapters 6, 7, 8 Name TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) Astronauts in orbiting satellites
Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics
 Chapter 9 ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS PREVIEW A force acting at a perpendicular distance from a rotation point, such as pushing a doorknob and causing the door to rotate on its hinges, produces a torque. If the
Chapter 9 ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS PREVIEW A force acting at a perpendicular distance from a rotation point, such as pushing a doorknob and causing the door to rotate on its hinges, produces a torque. If the
LECTURE 15 TORQUE AND CENTER OF GRAVITY
 LECTURE 15 TORQUE AND CENTER OF GRAVITY 7.3 Torque Net torque 7.4 Gravitational torque and the center of gravity Calculating the position of the center of gravity What is unusual about this door? Learning
LECTURE 15 TORQUE AND CENTER OF GRAVITY 7.3 Torque Net torque 7.4 Gravitational torque and the center of gravity Calculating the position of the center of gravity What is unusual about this door? Learning
Practice. Newton s 3 Laws of Motion. Recall. Forces a push or pull acting on an object; a vector quantity measured in Newtons (kg m/s²)
 Practice A car starts from rest and travels upwards along a straight road inclined at an angle of 5 from the horizontal. The length of the road is 450 m and the mass of the car is 800 kg. The speed of
Practice A car starts from rest and travels upwards along a straight road inclined at an angle of 5 from the horizontal. The length of the road is 450 m and the mass of the car is 800 kg. The speed of
4.0 m s 2. 2 A submarine descends vertically at constant velocity. The three forces acting on the submarine are viscous drag, upthrust and weight.
 1 1 wooden block of mass 0.60 kg is on a rough horizontal surface. force of 12 N is applied to the block and it accelerates at 4.0 m s 2. wooden block 4.0 m s 2 12 N hat is the magnitude of the frictional
1 1 wooden block of mass 0.60 kg is on a rough horizontal surface. force of 12 N is applied to the block and it accelerates at 4.0 m s 2. wooden block 4.0 m s 2 12 N hat is the magnitude of the frictional
Physics 111. Lecture 22 (Walker: ) Torque Rotational Dynamics Static Equilibrium Oct. 28, 2009
 Physics 111 Lecture 22 (Walker: 11.1-3) Torque Rotational Dynamics Static Equilibrium Oct. 28, 2009 Lecture 22 1/26 Torque (τ) We define a quantity called torque which is a measure of twisting effort.
Physics 111 Lecture 22 (Walker: 11.1-3) Torque Rotational Dynamics Static Equilibrium Oct. 28, 2009 Lecture 22 1/26 Torque (τ) We define a quantity called torque which is a measure of twisting effort.
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 17 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 17 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 17 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 1 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 1 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 1 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Chapter Objectives. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
 Chapter Objectives To develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid body. To introduce the concept of the free-body diagram for a rigid body. To show how to solve rigid-body equilibrium problems using
Chapter Objectives To develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid body. To introduce the concept of the free-body diagram for a rigid body. To show how to solve rigid-body equilibrium problems using
Mechanics of Solids. Mechanics Of Solids. Suraj kr. Ray Department of Civil Engineering
 Mechanics Of Solids Suraj kr. Ray (surajjj2445@gmail.com) Department of Civil Engineering 1 Mechanics of Solids is a branch of applied mechanics that deals with the behaviour of solid bodies subjected
Mechanics Of Solids Suraj kr. Ray (surajjj2445@gmail.com) Department of Civil Engineering 1 Mechanics of Solids is a branch of applied mechanics that deals with the behaviour of solid bodies subjected
ΣF = 0 and Στ = 0 In 2-d: ΣF X = 0 and ΣF Y = 0 Goal: Write expression for Στ and ΣF
 Thur Sept 24 Assign 5 Friday Exam Mon Oct 5 Morton 235 7:15-9:15 PM Email if conflict Today: Rotation and Torques Static Equilibrium Sign convention for torques: (-) CW torque (+) CCW torque Equilibrium
Thur Sept 24 Assign 5 Friday Exam Mon Oct 5 Morton 235 7:15-9:15 PM Email if conflict Today: Rotation and Torques Static Equilibrium Sign convention for torques: (-) CW torque (+) CCW torque Equilibrium
Objectives: After completion of this module, you should be able to:
 Chapter 12 Objectives: After completion of this module, you should be able to: Demonstrate your understanding of elasticity, elastic limit, stress, strain, and ultimate strength. Write and apply formulas
Chapter 12 Objectives: After completion of this module, you should be able to: Demonstrate your understanding of elasticity, elastic limit, stress, strain, and ultimate strength. Write and apply formulas
ConcepTest PowerPoints
 ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 8 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 8 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Simple Machines. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 F Simple Machines Simple Machines Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Simple machines are devices that can be used to multiply or augment a force that we apply often at the expense of a distance through which we apply
F Simple Machines Simple Machines Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Simple machines are devices that can be used to multiply or augment a force that we apply often at the expense of a distance through which we apply
Definition. is a measure of how much a force acting on an object causes that object to rotate, symbol is, (Greek letter tau)
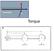 Torque Definition is a measure of how much a force acting on an object causes that object to rotate, symbol is, (Greek letter tau) = r F = rfsin, r = distance from pivot to force, F is the applied force
Torque Definition is a measure of how much a force acting on an object causes that object to rotate, symbol is, (Greek letter tau) = r F = rfsin, r = distance from pivot to force, F is the applied force
Chapter 9. Rotational Dynamics
 Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics In pure translational motion, all points on an object travel on parallel paths. The most general motion is a combination of translation and rotation. 1) Torque Produces angular
Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics In pure translational motion, all points on an object travel on parallel paths. The most general motion is a combination of translation and rotation. 1) Torque Produces angular
ConcepTest PowerPoints
 ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 19 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 19 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Physics 2210 Fall Review for Midterm Exam 2 10/07/2015
 Physics 2210 Fall 2015 Review for Midterm Exam 2 10/07/2015 Problem 1 (1/3) A spring of force constant k = 800 N/m and a relaxed length L 0 = 1.10 m has its upper end fixed/attached to a pivot in the ceiling.
Physics 2210 Fall 2015 Review for Midterm Exam 2 10/07/2015 Problem 1 (1/3) A spring of force constant k = 800 N/m and a relaxed length L 0 = 1.10 m has its upper end fixed/attached to a pivot in the ceiling.
Lecture Power Points. Chapter 16 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture Power Points Chapter 16 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Lecture Power Points Chapter 16 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 14 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 14 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 14 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
