CONSIDERATIONS ON THE FRONT- END READOUT FOR CRYOGENIC PARTICLE DETECTORS
|
|
|
- Randall Poole
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ONSIERTIONS ON THE FRONT- EN REOUT FOR RYOGENI PRTILE ETETORS GINLUIGI PESSIN INFN Isttuto Nazonale d Fsca Nucleare and Unversta' degl Stud d Mlano-Bcocca, Va elora 6, 033 Mlano Italy PESSIN@MI.INFN.IT
2 OUTLINE OF THE TLK. SIGNL TO NOISE RTIO, S/N, FOR PRTILE ETETORS;. HOIE OF THE POSSIBLE PREMPLIFIER ONFIGURTIONS; 3. EFFETS OF NOISE SOURES OF NON INTRINSI ORIGIN; 4. POSSIBLE REUTION OF NON INTRINSI EFFETS; 5. OL ELETRONI VS ROOM TEMPERTURE ELETRONI; 6. ONFIGURTION FOR THE OL ELETRONI; 7. TIVE EVIES FOR LOW TEMPERTURE OPERTION; 8. TIVE EVIES FOR ROOM TEMPERTURE OPERTION; 9. REOUT FOR RRY OF ETETORS.
3 . SIGNL TO NOISE RTIO FOR RYOGENI ETETORS QS T T V = Q S T O V O V O = N T T THE SIGNL TO NOISE RTIO IS: S N π 0 N Q T T S T H S N N π = d Q S T e π V O d t m d π Q 0 S V O SHWRT INEQULITY T d WHTEVER IS THE SYSTEM TRNSFER FUNTION. THE SIGN = IS VLI WHEN V O IS SENT TO THE FILTER OPTIMUM F. HVING THE TRNSFER FUNTION: * * S T t H = K e m N PRTIL SES 3
4 4.a THE HRGE OR URRENT SENSITIVE ONFIGURTION.a THE HRGE OR URRENT SENSITIVE ONFIGURTION - QS e V O Q S V F O = T F = THEN: π 0 H. d e S Q N S THE S/N EPENS ON THE VLUE OF THE PREMPLIFIER INPUT IMPENE THROUGH. F T F = THEN: e V F F O VIRTUL GROUN V - 0. = e V F F O IN GENERL: F >> P LET'S PUT: P =
5 5.b THE VOLTGE SENSITIVE ONFIGURTION.b THE VOLTGE SENSITIVE ONFIGURTION - QS z F F e z O V Q S V O = T = THEN: O e V = T = THEN: π 0 VOL. d e S Q N S LTHOUGH THE INPUT IMPENE IS BOOTSTRPPE THE S/N EPENS STILL ON IT. THE PREMPLIFIER ONFIGURTION OES NOT HVE EFFET ON THE S/N. V V F F F = P LET S LL: P =
6 6.c OPTIMITION OF THE PREMPLIFIER INPUT TRNSISTOR.c OPTIMITION OF THE PREMPLIFIER INPUT TRNSISTOR P = π 0 d e S Q N S THE INPUT IMPENE OF THE PREMPLIFIER IS GENERLLY WELL PPROXIMTE BY PITNE: SMLL TRNSISTOR RE: LRGER NOISE N SMLL. LRGE TRNSISTOR RE: SMLLER NOISE BUT LRGE. π 0 O O d e S Q N S π 0 O O d e S Q N S IT IS VLI THT: O e e = O = ONE THE TEHNOLOGY HS BEEN SELETE ON THE BSIS OF THE SIGNL BNWITH, IT EXISTS N OPTIMUM RE FOR THE INPUT TRNSISTOR THT MXIMIES THE S/N.
7 . HOIE OF THE POSSIBLE PREMPLIFIER ONFIGURTION QS VOLTGE SEN. PREM. IFFERENTIL SEN. PREM. QS - HIGH INPUT IMPENE; INPUT FLOTING; OUPLING OR ; LRGE ROSS-TLK; THE OUTPUT SIGNL EPENS ON THE ETETOR IMPENE. THE SME S BOVE BUT WITH NO ROSS-TLK HRGE OR URRENT SEN. PREM. QS F LOW INPUT IMPENE; INPUT VOLTGE FIXE BY THE PREMPLIFIER INPUT EVIE; OUPLING S NTURL SOLUTION; NO ROSS-TLK; THE OUTPUT SIGNL OES NOT EPEN ON THE ETETOR IMPENE. 7
8 3.a EFFETS OF NOISE SOURES OF NON INTRINSI ORIGIN: MIROPHONISM MIROPHONISM IS GIVEN BY EFFETS: ETETOR FRITION; MOVEMENT OF THE ONNETING WIRES. P PO P cos O t WITH R THE ETETOR IMPENE N O THE MONOHROMTI OSILLTING FREQUENY: R V o P V P BIS sn ot P R o P MEHNIL VIBRTIONS OF WIRES N ETETOR. N, IF THE ETETOR IMPENE IS LRGE ENOUGH, R P > O : V V BIS P P sn o t P V F THE ETETOR IS OUPLE TROUGH N R > O : Q P P VBIS sn F P IN SE OF OUPLING: Q P F P P V sn o o t t >> Q 8
9 9 3.b EFFETS OF NOISE SOURES OF NON INTRINSI ORIGIN: ROSS-TLK H P R IF THE ETETOR IMPENE IS LRGE ENOUGH: V R V R P H P F V R V R PRE 0 H P V I PRE 0, LREY R F SINE THE YNMI INPUT PITNE PRE OF THE PREMPLIFIER IS VERY LRGE. H P HENE THE HRGE OR URRENT SENSITIVE PREMPLIFIER IS FREE FROM ROSS-TLK.
10 0 4.a POSSIBLE REUTION OF NON INTRINSI EFFETS: MIROPHONISM IFFERENTIL VOLTGE ONFIGURTION c P c P - THE WIRES MUST BE TIE TOGETHER FIRMLY SO NY FLUTUTION BEOMES EQUL N NELS T THE IFFERENTIL PREMPLIFIER INPUT. IFFERENTIL HRGE ONFIGURTION P F F - THE IFFERENTIL ONFIGURTION HS LRGER PREMPLIFIER INPUT NOISE, FTOR OR, EPENING ON IRUIT ONFIGURTION. P
11 4.b POSSIBLE REUTION OF NON INTRINSI EFFETS: ROSS-TLK IFFERENTIL VOLTGE ONFIGURTION H H c P c P c P - R c P - THE IFFERENTIL ONFIGURTION LLOWS LSO TO TO RELIE SUPPRESSION OF THE ROSS-TLK. NOW THE THE INUING SIGNL IS GENERTE BY PIR OF OUPLE WIRES N TERMINTES ON PIR OR OUPLE WIRES: IT BEOMES OMMON MOE SIGNL.
12 5. OL ELETRONI VS ROOM TEMPERTURE ELETRONI THE USE OF OL ELETRONI IS OF OURSE THE OPTIMUM HOIE. NEVERTHELESS THE ROOM TEMPERTURE OPTION IS BY FR MORE PRTIL N OFTEN LLOWS TO OBTIN SIMILR RESULTS. REFRIGERTOR L T B 0mK P T E 00K SELETION RULES FOR HIGH SPEE N LRGE IMPENE P MUST BE MINIMIE. FOR THIS SITUTION IT IS MUST TO LOTE THE FRONT-EN LOSE TO THE ETETOR, T LOW TEMPERTURE. OL ELETRONI PRSITI PITNE = P REFRIGERTOR T B 0mK L P P - IF THE SPEE OF RESPONSE IS SLOW ENOUGH, P N BE TOLERTE N THE ROOM TEMPERTURE ELETRONI N LLOW EQUTE RESULTS. IT IS REOMMENE TO USE IFFERENTIL ONFIGURTION. THE VOLTGE SENSITIVE ONE BEING BETTER HOIE.
13 3 6.a ONFIGURTION FOR THE OL ELETRONI: OL STGE THE TYPIL SOLUTION IS THE SIMPLER ONE: SOURE FOLLOWER, THT LLOWS TO HVE THE MINIML POWER ISSIPTION INSIE THE REFRIGERTOR. REFRIGERTOR R L V S IIS ET. BIS LOW NOISE II STGE VOL. GIN JFET BIS OPTIMITION GIN = Room Tem. x V R V OUT THE OPTIMITION OF THE GIN IS ME T ROOM TEMPERTURE BY BOOTSTRPPING TION ON BOTH THE SOURE N THE RIN OF THE OL JFET. old V EE R S x R S G.PESSIN, et all, TO BE PUBLISHE ON IEEE TR. ON NU.IENE
14 4 6.b ONFIGURTION FOR THE OL ELETRONI: II STGE T ROOM THE II STGE IS OMPOSE OF THE PRLLELING ONNETION OF 4 LOW SERIES NOISE OPERTIONL MPLIFIER, LT08 THE SERIES NOISE OF THIS PREMPLIFIER IS EXTREMELY LOW, BELOW nv/ Hz. F.GTTI ET LL, NIM 444, p.9, 000 OUPLING. THE OFFSET UE TO THE JFET V GS MUST BE IVIE BY THE FULL GIN. PRLLEL NOISE MY BE PROBLEM T LOW FREQUENY: T 0 Hz, IT N ONTRIBUTE WITH BOUT nv/ Hz.
15 6.c ONFIGURTION FOR THE OL ELETRONI: II STGE T ROOM REFRIGERTOR V S nv/ Hz 0. Hz:.6 nv/ Hz WHITE NOISE, FEEBK INLUE: nv/ Hz Hz V EE INPUT BIS URRENT < 00 p. Parallel NOISE < 6 f/ Hz. VOLTGE GIN = 000 OWN TO 0.5 Hz. VOLTGE GIN = G.PESSIN, et all, TO BE PUBLISHE ON IEEE TR. ON NU.IENE THE MONITORING OF THE BSELINE N BE ME URTELY N THE OFFSET IS ESILY TO BE JUSTE. 5
16 6.c ONFIGURTION FOR THE OL ELETRONI: EXMPLES STJ SQUI ROOM VSP STJ SQUI RTFE: FEEBK ETIL M.J.van UUREN, et all, LT7, p.98..e.mrtin, et all, WOLTW4, p.87, 000 TES SQUI ROOM VSP P.ollng, et all, NIM 354, p.408, 995. SQUI RRY ROOM SP SQUI RRY SQUI ROOM VSP..E.MRTIN, et all, REW. SIE.INSTR., 7, p.3543, 000 6
17 7 7.a TIVE EVIES FOR LOW TEMPERTURE OPERTION MNY EVIES RE BLE TO WORK T RYOGENI TEMPERTURE. THE ONLY ONE THT IS NOT EQUTE FOR THIS PPLITION IS THE S BIPOLR TRNSISTOR. HERE THERE IS THE LIST OF THE POSSIBLE HOIE: EVIE SI MOS S JFET Ge JFET Gas MESFET l X Ga -X s HEMT SGe HBJT MINIMUM TEMPERTURE OF OPERTION LHe LN N BELOW LHe LHe LHe LHe OPTIMUM TEMPERTURE OF OPERTION K K LHe LHe NO T EH EVIE HS ITS OWN TEMPERTURE OF OPERTION N NOISE PERFORMNE.
18 7.a TIVE EVIES FOR LOW TEMPERTURE OPERTION: PHYSIS ONUTION BN FREE ELETRON ELETRONS RE FREE IN THE ONUTION BN. VLENE BN E d ONORS THERML ENERGY NEES TO ELETRONS TO JUMP FROM THE ONOR LEVEL TO THE ONUTION BN. IF THE ONOR LEVEL IS NON-EGENERTE, I.E. << THN THE VILBLE STTES IN THE ONUTION BN, THE POPULTION OF ELETRON IN THE ONUTION BN T LOW TEMPERTURE IS PROPORTIONL TO: TTENUTION Ed K BT e SEMI. E d mev TTENUTION 70 K 0 K Gas Ge S SILION TENS TO OMPLETE FREEE-OUT T LOW TEMPERTURE, LTHOUGH THE PPLIE ELETRI FIEL HELPS IN EXTRTING ELETRONS FROM ONORS ENTERS. 8
19 9 7.b TIVE EVIES FOR LOW TEMPERTURE OPERTION MOS TRNSISTORS RE THE MORE STUIE T LOW TEMPERTURE. T THE SME TIME THEY RE LSO THE LESS USE S LOW NOISE FRONT-EN, EXEPT FOR FEW MONOLITHI PPLITIONS FOR HIGH FREQUENY EVIES. MOS EVIES O NOT SUFFER FREEE-OUT LTHOUGH ME OF SILION. S oxde n p-sub G n THE ELETRI FIEL IS HIGH N IS BLE TO EXTRT ELETRON FROM THE SUBSTRTE, LTHOUGH THE PRESENE OF FREEE-OUT. UE TO THE ELETRI FIEL EFFET THEY RE BLE TO WORK OWN TO 4. K; THEY SHOW LRGE /f FREQUENY NOISE; p-mos RE GENERLLY LESS NOISY THN n-mos UE TO OXIE TRPPING ETRPPING MEHNISM;
20 7.c TIVE EVIES FOR LOW TEMPERTURE OPERTION: MOS EXMPLE OF NOISE FOR n-mos N p-mos TRNSISTOR FROM 5 K TO 300 K. n-mos p-mos UNKNOWN RE 0 K 5 K E..HENRIKS, et all, PHYSI V.47B, P.9 E.SIMOEN, et all, PRO. OF NOIS IN PHYSIL SYSTEM, P.57, 997 T = 4. K = 0. pf ESTIMTE FROM THE PPER. Hz: 630 nv/ Hz. 50 K 300 K g m = 00 µ/v THE PRMETER H f, THE PROUT OF THE /f NOISE OEFFIIENT N THE INPUT PITNE OF THE TRNSISTOR RESULTS IN: 4.5 nv/ Hz WHITE H f = f = 8 X 0-6 J. MOS HVING 5 pf HS: H f / = 6 nv/ Hz. 0
21 7.d TIVE EVIES FOR LOW TEMPERTURE OPERTION: O MOS ONE ESILY WY TO USE MOS TRNSISTORS IS WITH MOS OPERTIONL MPLIFIER. T LEST ONE, IS BLE TO WORK: TL 0. NOISE IMPROVES T 77 K, NO T WERE PRESENTE BELOW. ROOM G.LOMBRI, et all, WOLTE3, p.85, 998. ROOM 00 Hz 77 K 00 Hz 8.9 nv/ Hz 5. nv/ Hz ROOM 0K Hz 77 K 0 KHz 8 nv/ Hz 3.3 nv/ Hz
22 7.e TIVE EVIES FOR LOW TEMPERTURE OPERTION: Ge JFET TWO GROUPS RE EVELOPING Ge JFET FOR LOW TEMPERTURE PPLITION. THE TRNSISTORS WORK WELL OWN TO LOW TEMPERTURE, BUT /f NOISE SEEMS NOT YET THE WISHE FOR. 4. K ROOM 77 K THE INPUT PITNE IS BETWEEN 0 pf N 40 pf. THE Hz IS 000 nv/ Hz T 4. K. THIS ORRESPON TO N H f = X 0-3 J. H f = X K. N..S, et all, SOL. ST. ELE., 44, p.937, 000. OPTIMUM TEMPERTURE ROUN 60 K. 60 pf < < 00 pf H f =.5 X 0-5 J. WHITE NOISE LOSE TO nv/ Hz. R.R.WR, et all, WOLTE4, p.05, 000.
23 3 7.f TIVE EVIES FOR LOW TEMPERTURE OPERTION: Gas MESFET ET THE Gas MESFET PRESENTS LRGE /f NOISE, WHIH LOWERS T RYOGENI TEMPERTURES. = 7 pf THE NOISE T Hz FOR THIS EVIE IS BOUT 80 nv/ Hz. THIS ORRESPONS TO PRMETER H f OF: H f =.6 X 0-5 J G.PESSIN, et all, IEEE TR. NU. SI., 4, p. 60, 994. HRTERISTI OF Gaa MESFET IS THE STRONG VRIBILITY OF /f NOISE FROM WFER TO WFER. SMPLES PURHSE T IFFERENT TIMES N SHOW VER IFFERENT NOISE. G.PESSIN, et all, JPN. J. PPL. PHYS., 37, p. 5, 998.
24 4 7.g TIVE EVIES FOR LOW TEMPERTURE OPERTION: Gas MESFET Seres nput nose of the Voltage fferental Preamplfer nv/ Hz 0 T=4k Vcc=3V Vee=-V f Hz V OUT OUT- V Q 7 Q 4 Q 6 Q 3 R R Q Q 5 R Q 8 IN Q Q I B R B S R B Q IN- R R O R V S R G O B V EE
25 5 B4 400/3 B 400/ 00 VO R IN 500 B5 400/ R BW B 4000/3 BM4 R F B99 BM5 RM B B9 V R6 B6 400/ OUT B9 B8 R3 Seres Nose ensty [nv/hz] Whte Nose T = 87 K = 50 pf LPM NM B70 B7 NL 40Kž VSS 0, Frequency [Hz]
26 7.d TIVE EVIES FOR LOW TEMPERTURE OPERTION: O MOS ONE ESILY WY TO USE MOS TRNSISTORS IS WITH MOS OPERTIONL MPLIFIER. T LEST ONE, IS BLE TO WORK: TL 0. NOISE IMPROVES T 77 K, NO T WERE PRESENTE BELOW. ROOM G.LOMBRI, et all, WOLTE3, p.85, 998. ROOM 00 Hz 77 K 00 Hz 8.9 nv/ Hz 5. nv/ Hz ROOM 0K Hz 77 K 0 KHz 8 nv/ Hz 3.3 nv/ Hz
27 7.e TIVE EVIES FOR LOW TEMPERTURE OPERTION: Ge JFET TWO GROUPS RE EVELOPING Ge JFET FOR LOW TEMPERTURE PPLITION. THE TRNSISTORS WORK WELL OWN TO LOW TEMPERTURE, BUT /f NOISE SEEMS NOT YET THE WISHE FOR. 4. K ROOM 77 K THE INPUT PITNE IS BETWEEN 0 pf N 40 pf. THE Hz IS 000 nv/ Hz T 4. K. THIS ORRESPON TO N H f = X 0-3 J. H f = X K. N..S, et all, SOL. ST. ELE., 44, p.937, 000. OPTIMUM TEMPERTURE ROUN 60 K. 60 pf < < 00 pf H f =.5 X 0-5 J. WHITE NOISE LOSE TO nv/ Hz. R.R.WR, et all, WOLTE4, p.05, 000.
28 3 7.f TIVE EVIES FOR LOW TEMPERTURE OPERTION: Gas MESFET ET THE Gas MESFET PRESENTS LRGE /f NOISE, WHIH LOWERS T RYOGENI TEMPERTURES. = 7 pf THE NOISE T Hz FOR THIS EVIE IS BOUT 80 nv/ Hz. THIS ORRESPONS TO PRMETER H f OF: H f =.6 X 0-5 J G.PESSIN, et all, IEEE TR. NU. SI., 4, p. 60, 994. HRTERISTI OF Gaa MESFET IS THE STRONG VRIBILITY OF /f NOISE FROM WFER TO WFER. SMPLES PURHSE T IFFERENT TIMES N SHOW VER IFFERENT NOISE. G.PESSIN, et all, JPN. J. PPL. PHYS., 37, p. 5, 998.
29 4 7.g TIVE EVIES FOR LOW TEMPERTURE OPERTION: Gas MESFET Seres nput nose of the Voltage fferental Preamplfer nv/ Hz 0 T=4k Vcc=3V Vee=-V f Hz V OUT OUT- V Q 7 Q 4 Q 6 Q 3 R R Q Q 5 R Q 8 IN Q Q I B R B S R B Q IN- R R O R V S R G O B V EE
30 5 B4 400/3 B 400/ 00 VO R IN 500 B5 400/ R BW B 4000/3 BM4 R F B99 BM5 RM B B9 V R6 B6 400/ OUT B9 B8 R3 Seres Nose ensty [nv/hz] Whte Nose T = 87 K = 50 pf LPM NM B70 B7 NL 40Kž VSS 0, Frequency [Hz]
Electronic Circuits I Revision after midterm
 Eletroni Ciruits I Revision fter miterm Dr. Ahme ElShfee, ACU : Fll 2018, Eletroni Ciruits I -1 / 14 - MCQ1 # Question If the frequeny of the input voltge in Figure 2 36 is inrese, the output voltge will
Eletroni Ciruits I Revision fter miterm Dr. Ahme ElShfee, ACU : Fll 2018, Eletroni Ciruits I -1 / 14 - MCQ1 # Question If the frequeny of the input voltge in Figure 2 36 is inrese, the output voltge will
18.06 Problem Set 4 Due Wednesday, Oct. 11, 2006 at 4:00 p.m. in 2-106
 8. Problem Set Due Wenesy, Ot., t : p.m. in - Problem Mony / Consier the eight vetors 5, 5, 5,..., () List ll of the one-element, linerly epenent sets forme from these. (b) Wht re the two-element, linerly
8. Problem Set Due Wenesy, Ot., t : p.m. in - Problem Mony / Consier the eight vetors 5, 5, 5,..., () List ll of the one-element, linerly epenent sets forme from these. (b) Wht re the two-element, linerly
AC/DC/AC Converters: Two-Level and Multilevel VSI
 Sortes Ersmus Visit A/D/A onerters: Two-Leel nd Multileel VSI Josep Pou Antoni Aris Pge 1 Sortes Ersmus Visit Outline 1. Two-Leel Inerter 2. Multileel Inerters - sde H-Bridge Inerter - Flying-pitor Inerter
Sortes Ersmus Visit A/D/A onerters: Two-Leel nd Multileel VSI Josep Pou Antoni Aris Pge 1 Sortes Ersmus Visit Outline 1. Two-Leel Inerter 2. Multileel Inerters - sde H-Bridge Inerter - Flying-pitor Inerter
Electromagnetism Notes, NYU Spring 2018
 Eletromgnetism Notes, NYU Spring 208 April 2, 208 Ation formultion of EM. Free field desription Let us first onsider the free EM field, i.e. in the bsene of ny hrges or urrents. To tret this s mehnil system
Eletromgnetism Notes, NYU Spring 208 April 2, 208 Ation formultion of EM. Free field desription Let us first onsider the free EM field, i.e. in the bsene of ny hrges or urrents. To tret this s mehnil system
Magnetically Coupled Coil
 Mgnetilly Coupled Ciruits Overview Mutul Indutne Energy in Coupled Coils Liner Trnsformers Idel Trnsformers Portlnd Stte University ECE 22 Mgnetilly Coupled Ciruits Ver..3 Mgnetilly Coupled Coil i v L
Mgnetilly Coupled Ciruits Overview Mutul Indutne Energy in Coupled Coils Liner Trnsformers Idel Trnsformers Portlnd Stte University ECE 22 Mgnetilly Coupled Ciruits Ver..3 Mgnetilly Coupled Coil i v L
Dorf, R.C., Wan, Z. T- Equivalent Networks The Electrical Engineering Handbook Ed. Richard C. Dorf Boca Raton: CRC Press LLC, 2000
 orf, R.C., Wn,. T- Equivlent Networks The Eletril Engineering Hndook Ed. Rihrd C. orf Bo Rton: CRC Press LLC, 000 9 T P Equivlent Networks hen Wn University of Cliforni, vis Rihrd C. orf University of
orf, R.C., Wn,. T- Equivlent Networks The Eletril Engineering Hndook Ed. Rihrd C. orf Bo Rton: CRC Press LLC, 000 9 T P Equivlent Networks hen Wn University of Cliforni, vis Rihrd C. orf University of
Numbers and indices. 1.1 Fractions. GCSE C Example 1. Handy hint. Key point
 GCSE C Emple 7 Work out 9 Give your nswer in its simplest form Numers n inies Reiprote mens invert or turn upsie own The reiprol of is 9 9 Mke sure you only invert the frtion you re iviing y 7 You multiply
GCSE C Emple 7 Work out 9 Give your nswer in its simplest form Numers n inies Reiprote mens invert or turn upsie own The reiprol of is 9 9 Mke sure you only invert the frtion you re iviing y 7 You multiply
Proportions: A ratio is the quotient of two numbers. For example, 2 3
 Proportions: rtio is the quotient of two numers. For exmple, 2 3 is rtio of 2 n 3. n equlity of two rtios is proportion. For exmple, 3 7 = 15 is proportion. 45 If two sets of numers (none of whih is 0)
Proportions: rtio is the quotient of two numers. For exmple, 2 3 is rtio of 2 n 3. n equlity of two rtios is proportion. For exmple, 3 7 = 15 is proportion. 45 If two sets of numers (none of whih is 0)
8 THREE PHASE A.C. CIRCUITS
 8 THREE PHSE.. IRUITS The signls in hpter 7 were sinusoidl lternting voltges nd urrents of the so-lled single se type. n emf of suh type n e esily generted y rotting single loop of ondutor (or single winding),
8 THREE PHSE.. IRUITS The signls in hpter 7 were sinusoidl lternting voltges nd urrents of the so-lled single se type. n emf of suh type n e esily generted y rotting single loop of ondutor (or single winding),
CH 17: Flexible Mechanical Elements
 CH 17: lexible Mehnil Elements lexible mehnil elements (belts, hins, ropes re use in onveying systems n to trnsmit power over long istnes (inste of using shfts n gers. The use of flexible elements simplifies
CH 17: lexible Mehnil Elements lexible mehnil elements (belts, hins, ropes re use in onveying systems n to trnsmit power over long istnes (inste of using shfts n gers. The use of flexible elements simplifies
Chapter 16: Magnetic Materials and a Few Devices
 ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY HANDBOOK 1 Chpter 16: Mgneti Mterils n Few Devies 16.1 For the mgneti iruit given in Figure 1 ontining liner mterils (free spe surrouns the ore), etermine the flu, mgneti
ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY HANDBOOK 1 Chpter 16: Mgneti Mterils n Few Devies 16.1 For the mgneti iruit given in Figure 1 ontining liner mterils (free spe surrouns the ore), etermine the flu, mgneti
State space systems analysis (continued) Stability. A. Definitions A system is said to be Asymptotically Stable (AS) when it satisfies
 Stte spce systems nlysis (continued) Stbility A. Definitions A system is sid to be Asymptoticlly Stble (AS) when it stisfies ut () = 0, t > 0 lim xt () 0. t A system is AS if nd only if the impulse response
Stte spce systems nlysis (continued) Stbility A. Definitions A system is sid to be Asymptoticlly Stble (AS) when it stisfies ut () = 0, t > 0 lim xt () 0. t A system is AS if nd only if the impulse response
Lecture 10: PN Junction & MOS Capacitors
 Lecture 10: P Junction & MOS Cpcitors Prof. iknej eprtment of EECS Lecture Outline Review: P Junctions Therml Equilibrium P Junctions with Reverse Bis (3.3-3.6 MOS Cpcitors (3.7-3.9: Accumultion, epletion,
Lecture 10: P Junction & MOS Cpcitors Prof. iknej eprtment of EECS Lecture Outline Review: P Junctions Therml Equilibrium P Junctions with Reverse Bis (3.3-3.6 MOS Cpcitors (3.7-3.9: Accumultion, epletion,
Factorising FACTORISING.
 Ftorising FACTORISING www.mthletis.om.u Ftorising FACTORISING Ftorising is the opposite of expning. It is the proess of putting expressions into rkets rther thn expning them out. In this setion you will
Ftorising FACTORISING www.mthletis.om.u Ftorising FACTORISING Ftorising is the opposite of expning. It is the proess of putting expressions into rkets rther thn expning them out. In this setion you will
CARLETON UNIVERSITY. 1.0 Problems and Most Solutions, Sect B, 2005
 RLETON UNIVERSIT eprtment of Eletronis ELE 2607 Swithing iruits erury 28, 05; 0 pm.0 Prolems n Most Solutions, Set, 2005 Jn. 2, #8 n #0; Simplify, Prove Prolem. #8 Simplify + + + Reue to four letters (literls).
RLETON UNIVERSIT eprtment of Eletronis ELE 2607 Swithing iruits erury 28, 05; 0 pm.0 Prolems n Most Solutions, Set, 2005 Jn. 2, #8 n #0; Simplify, Prove Prolem. #8 Simplify + + + Reue to four letters (literls).
y = c 2 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQ's) (Each question carries one mark) is...
 . Liner Equtions in Two Vriles C h p t e r t G l n e. Generl form of liner eqution in two vriles is x + y + 0, where 0. When we onsier system of two liner equtions in two vriles, then suh equtions re lle
. Liner Equtions in Two Vriles C h p t e r t G l n e. Generl form of liner eqution in two vriles is x + y + 0, where 0. When we onsier system of two liner equtions in two vriles, then suh equtions re lle
Particle Physics. Michaelmas Term 2011 Prof Mark Thomson. Handout 3 : Interaction by Particle Exchange and QED. Recap
 Prtile Physis Mihelms Term 2011 Prof Mrk Thomson g X g X g g Hnout 3 : Intertion y Prtile Exhnge n QED Prof. M.A. Thomson Mihelms 2011 101 Rep Working towrs proper lultion of ey n sttering proesses lnitilly
Prtile Physis Mihelms Term 2011 Prof Mrk Thomson g X g X g g Hnout 3 : Intertion y Prtile Exhnge n QED Prof. M.A. Thomson Mihelms 2011 101 Rep Working towrs proper lultion of ey n sttering proesses lnitilly
Thermal energy 2 U Q W. 23 April The First Law of Thermodynamics. Or, if we want to obtain external work: The trick of using steam
 April 08 Therml energy Soures of het Trnsport of het How to use het The First Lw of Thermoynmis U W Or, if we wnt to otin externl work: U W 009 vrije Universiteit msterm Close yle stem power plnt The trik
April 08 Therml energy Soures of het Trnsport of het How to use het The First Lw of Thermoynmis U W Or, if we wnt to otin externl work: U W 009 vrije Universiteit msterm Close yle stem power plnt The trik
NEW CIRCUITS OF HIGH-VOLTAGE PULSE GENERATORS WITH INDUCTIVE-CAPACITIVE ENERGY STORAGE
 NEW CIRCUITS OF HIGH-VOLTAGE PULSE GENERATORS WITH INDUCTIVE-CAPACITIVE ENERGY STORAGE V.S. Gordeev, G.A. Myskov Russin Federl Nuler Center All-Russi Sientifi Reserh Institute of Experimentl Physis (RFNC-VNIIEF)
NEW CIRCUITS OF HIGH-VOLTAGE PULSE GENERATORS WITH INDUCTIVE-CAPACITIVE ENERGY STORAGE V.S. Gordeev, G.A. Myskov Russin Federl Nuler Center All-Russi Sientifi Reserh Institute of Experimentl Physis (RFNC-VNIIEF)
The Stirling Engine: The Heat Engine
 Memoril University of Newfounln Deprtment of Physis n Physil Oenogrphy Physis 2053 Lortory he Stirling Engine: he Het Engine Do not ttempt to operte the engine without supervision. Introution Het engines
Memoril University of Newfounln Deprtment of Physis n Physil Oenogrphy Physis 2053 Lortory he Stirling Engine: he Het Engine Do not ttempt to operte the engine without supervision. Introution Het engines
Physics Lecture 14: MON 29 SEP
 Physics 2113 Physics 2113 Lecture 14: MON 29 SEP CH25: Cpcitnce Von Kleist ws le to store electricity in the jr. Unknowingly, he h ctully invente novel evice to store potentil ifference. The wter in the
Physics 2113 Physics 2113 Lecture 14: MON 29 SEP CH25: Cpcitnce Von Kleist ws le to store electricity in the jr. Unknowingly, he h ctully invente novel evice to store potentil ifference. The wter in the
SOLUTIONS TO ASSIGNMENT NO The given nonrecursive signal processing structure is shown as
 SOLUTIONS TO ASSIGNMENT NO.1 3. The given nonreursive signl proessing struture is shown s X 1 1 2 3 4 5 Y 1 2 3 4 5 X 2 There re two ritil pths, one from X 1 to Y nd the other from X 2 to Y. The itertion
SOLUTIONS TO ASSIGNMENT NO.1 3. The given nonreursive signl proessing struture is shown s X 1 1 2 3 4 5 Y 1 2 3 4 5 X 2 There re two ritil pths, one from X 1 to Y nd the other from X 2 to Y. The itertion
I 3 2 = I I 4 = 2A
 ECE 210 Eletril Ciruit Anlysis University of llinois t Chigo 2.13 We re ske to use KCL to fin urrents 1 4. The key point in pplying KCL in this prolem is to strt with noe where only one of the urrents
ECE 210 Eletril Ciruit Anlysis University of llinois t Chigo 2.13 We re ske to use KCL to fin urrents 1 4. The key point in pplying KCL in this prolem is to strt with noe where only one of the urrents
Lecture 6: Coding theory
 Leture 6: Coing theory Biology 429 Crl Bergstrom Ferury 4, 2008 Soures: This leture loosely follows Cover n Thoms Chpter 5 n Yeung Chpter 3. As usul, some of the text n equtions re tken iretly from those
Leture 6: Coing theory Biology 429 Crl Bergstrom Ferury 4, 2008 Soures: This leture loosely follows Cover n Thoms Chpter 5 n Yeung Chpter 3. As usul, some of the text n equtions re tken iretly from those
1 This diagram represents the energy change that occurs when a d electron in a transition metal ion is excited by visible light.
 1 This igrm represents the energy hnge tht ours when eletron in trnsition metl ion is exite y visile light. Give the eqution tht reltes the energy hnge ΔE to the Plnk onstnt, h, n the frequeny, v, of the
1 This igrm represents the energy hnge tht ours when eletron in trnsition metl ion is exite y visile light. Give the eqution tht reltes the energy hnge ΔE to the Plnk onstnt, h, n the frequeny, v, of the
New Expansion and Infinite Series
 Interntionl Mthemticl Forum, Vol. 9, 204, no. 22, 06-073 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikri.com http://dx.doi.org/0.2988/imf.204.4502 New Expnsion nd Infinite Series Diyun Zhng College of Computer Nnjing University
Interntionl Mthemticl Forum, Vol. 9, 204, no. 22, 06-073 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikri.com http://dx.doi.org/0.2988/imf.204.4502 New Expnsion nd Infinite Series Diyun Zhng College of Computer Nnjing University
Counting Paths Between Vertices. Isomorphism of Graphs. Isomorphism of Graphs. Isomorphism of Graphs. Isomorphism of Graphs. Isomorphism of Graphs
 Isomorphism of Grphs Definition The simple grphs G 1 = (V 1, E 1 ) n G = (V, E ) re isomorphi if there is ijetion (n oneto-one n onto funtion) f from V 1 to V with the property tht n re jent in G 1 if
Isomorphism of Grphs Definition The simple grphs G 1 = (V 1, E 1 ) n G = (V, E ) re isomorphi if there is ijetion (n oneto-one n onto funtion) f from V 1 to V with the property tht n re jent in G 1 if
Appendix A: HVAC Equipment Efficiency Tables
 Appenix A: HVAC Equipment Effiieny Tles Figure A.1 Resientil Centrl Air Conitioner FEMP Effiieny Reommention Prout Type Reommene Level Best Aville 11.0 or more EER 14.6 EER Split Systems 13.0 or more SEER
Appenix A: HVAC Equipment Effiieny Tles Figure A.1 Resientil Centrl Air Conitioner FEMP Effiieny Reommention Prout Type Reommene Level Best Aville 11.0 or more EER 14.6 EER Split Systems 13.0 or more SEER
CS 2204 DIGITAL LOGIC & STATE MACHINE DESIGN SPRING 2014
 S 224 DIGITAL LOGI & STATE MAHINE DESIGN SPRING 214 DUE : Mrh 27, 214 HOMEWORK III READ : Relte portions of hpters VII n VIII ASSIGNMENT : There re three questions. Solve ll homework n exm prolems s shown
S 224 DIGITAL LOGI & STATE MAHINE DESIGN SPRING 214 DUE : Mrh 27, 214 HOMEWORK III READ : Relte portions of hpters VII n VIII ASSIGNMENT : There re three questions. Solve ll homework n exm prolems s shown
U Q W The First Law of Thermodynamics. Efficiency. Closed cycle steam power plant. First page of S. Carnot s paper. Sadi Carnot ( )
 0-9-0 he First Lw of hermoynmis Effiieny When severl lterntive proesses involving het n work re ville to hnge system from n initil stte hrterize y given vlues of the mrosopi prmeters (pressure p i, temperture
0-9-0 he First Lw of hermoynmis Effiieny When severl lterntive proesses involving het n work re ville to hnge system from n initil stte hrterize y given vlues of the mrosopi prmeters (pressure p i, temperture
22: Union Find. CS 473u - Algorithms - Spring April 14, We want to maintain a collection of sets, under the operations of:
 22: Union Fin CS 473u - Algorithms - Spring 2005 April 14, 2005 1 Union-Fin We wnt to mintin olletion of sets, uner the opertions of: 1. MkeSet(x) - rete set tht ontins the single element x. 2. Fin(x)
22: Union Fin CS 473u - Algorithms - Spring 2005 April 14, 2005 1 Union-Fin We wnt to mintin olletion of sets, uner the opertions of: 1. MkeSet(x) - rete set tht ontins the single element x. 2. Fin(x)
Sections 5.3: Antiderivatives and the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Theory:
 Setions 5.3: Antierivtives n the Funmentl Theorem of Clulus Theory: Definition. Assume tht y = f(x) is ontinuous funtion on n intervl I. We ll funtion F (x), x I, to be n ntierivtive of f(x) if F (x) =
Setions 5.3: Antierivtives n the Funmentl Theorem of Clulus Theory: Definition. Assume tht y = f(x) is ontinuous funtion on n intervl I. We ll funtion F (x), x I, to be n ntierivtive of f(x) if F (x) =
2.4 Theoretical Foundations
 2 Progrmming Lnguge Syntx 2.4 Theoretil Fountions As note in the min text, snners n prsers re se on the finite utomt n pushown utomt tht form the ottom two levels of the Chomsky lnguge hierrhy. At eh level
2 Progrmming Lnguge Syntx 2.4 Theoretil Fountions As note in the min text, snners n prsers re se on the finite utomt n pushown utomt tht form the ottom two levels of the Chomsky lnguge hierrhy. At eh level
Appendix C Partial discharges. 1. Relationship Between Measured and Actual Discharge Quantities
 Appendi Prtil dishrges. Reltionship Between Mesured nd Atul Dishrge Quntities A dishrging smple my e simply represented y the euilent iruit in Figure. The pplied lternting oltge V is inresed until the
Appendi Prtil dishrges. Reltionship Between Mesured nd Atul Dishrge Quntities A dishrging smple my e simply represented y the euilent iruit in Figure. The pplied lternting oltge V is inresed until the
PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES
 PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES. Two liner equtions in the sme two vriles re lled pir of liner equtions in two vriles. The most generl form of pir of liner equtions is x + y + 0 x + y + 0 where,,,,,,
PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES. Two liner equtions in the sme two vriles re lled pir of liner equtions in two vriles. The most generl form of pir of liner equtions is x + y + 0 x + y + 0 where,,,,,,
Polynomial Approximations for the Natural Logarithm and Arctangent Functions. Math 230
 Polynomil Approimtions for the Nturl Logrithm nd Arctngent Functions Mth 23 You recll from first semester clculus how one cn use the derivtive to find n eqution for the tngent line to function t given
Polynomil Approimtions for the Nturl Logrithm nd Arctngent Functions Mth 23 You recll from first semester clculus how one cn use the derivtive to find n eqution for the tngent line to function t given
Chapter E - Problems
 Chpter E - Prolems Blinn College - Physics 2426 - Terry Honn Prolem E.1 A wire with dimeter d feeds current to cpcitor. The chrge on the cpcitor vries with time s QHtL = Q 0 sin w t. Wht re the current
Chpter E - Prolems Blinn College - Physics 2426 - Terry Honn Prolem E.1 A wire with dimeter d feeds current to cpcitor. The chrge on the cpcitor vries with time s QHtL = Q 0 sin w t. Wht re the current
for all x in [a,b], then the area of the region bounded by the graphs of f and g and the vertical lines x = a and x = b is b [ ( ) ( )] A= f x g x dx
![for all x in [a,b], then the area of the region bounded by the graphs of f and g and the vertical lines x = a and x = b is b [ ( ) ( )] A= f x g x dx for all x in [a,b], then the area of the region bounded by the graphs of f and g and the vertical lines x = a and x = b is b [ ( ) ( )] A= f x g x dx](/thumbs/74/70408252.jpg) Applitions of Integrtion Are of Region Between Two Curves Ojetive: Fin the re of region etween two urves using integrtion. Fin the re of region etween interseting urves using integrtion. Desrie integrtion
Applitions of Integrtion Are of Region Between Two Curves Ojetive: Fin the re of region etween two urves using integrtion. Fin the re of region etween interseting urves using integrtion. Desrie integrtion
I1 = I2 I1 = I2 + I3 I1 + I2 = I3 + I4 I 3
 2 The Prllel Circuit Electric Circuits: Figure 2- elow show ttery nd multiple resistors rrnged in prllel. Ech resistor receives portion of the current from the ttery sed on its resistnce. The split is
2 The Prllel Circuit Electric Circuits: Figure 2- elow show ttery nd multiple resistors rrnged in prllel. Ech resistor receives portion of the current from the ttery sed on its resistnce. The split is
Now we must transform the original model so we can use the new parameters. = S max. Recruits
 MODEL FOR VARIABLE RECRUITMENT (ontinue) Alterntive Prmeteriztions of the pwner-reruit Moels We n write ny moel in numerous ifferent ut equivlent forms. Uner ertin irumstnes it is onvenient to work with
MODEL FOR VARIABLE RECRUITMENT (ontinue) Alterntive Prmeteriztions of the pwner-reruit Moels We n write ny moel in numerous ifferent ut equivlent forms. Uner ertin irumstnes it is onvenient to work with
A Study on the Properties of Rational Triangles
 Interntionl Journl of Mthemtis Reserh. ISSN 0976-5840 Volume 6, Numer (04), pp. 8-9 Interntionl Reserh Pulition House http://www.irphouse.om Study on the Properties of Rtionl Tringles M. Q. lm, M.R. Hssn
Interntionl Journl of Mthemtis Reserh. ISSN 0976-5840 Volume 6, Numer (04), pp. 8-9 Interntionl Reserh Pulition House http://www.irphouse.om Study on the Properties of Rtionl Tringles M. Q. lm, M.R. Hssn
TIME-VARYING AND NON-LINEAR DYNAMICAL SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION USING THE HILBERT TRANSFORM
 Proeeings of ASME VIB 5: th Biennil Conferene on Mehnil Virtion n Noise Septemer 4-8, 5 Long Beh, CA, USA DETC5-84644 TIME-VARYING AND NON-LINEAR DYNAMICAL SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION USING THE HILBERT TRANSFORM
Proeeings of ASME VIB 5: th Biennil Conferene on Mehnil Virtion n Noise Septemer 4-8, 5 Long Beh, CA, USA DETC5-84644 TIME-VARYING AND NON-LINEAR DYNAMICAL SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION USING THE HILBERT TRANSFORM
Applications of Bernoulli s theorem. Lecture - 7
 Applictions of Bernoulli s theorem Lecture - 7 Prcticl Applictions of Bernoulli s Theorem The Bernoulli eqution cn be pplied to gret mny situtions not just the pipe flow we hve been considering up to now.
Applictions of Bernoulli s theorem Lecture - 7 Prcticl Applictions of Bernoulli s Theorem The Bernoulli eqution cn be pplied to gret mny situtions not just the pipe flow we hve been considering up to now.
is the cut off frequency in rads.
 0 ELETRIAL IRUITS 9. HIGH RDER ATIVE FILTERS (With Tle) Introdution Thi development explin how to deign Butterworth (Mximlly Flt) or heyhev (Equl Ripple) Low P, High P or Bnd P tive filter. Thi tretment
0 ELETRIAL IRUITS 9. HIGH RDER ATIVE FILTERS (With Tle) Introdution Thi development explin how to deign Butterworth (Mximlly Flt) or heyhev (Equl Ripple) Low P, High P or Bnd P tive filter. Thi tretment
Core 2 Logarithms and exponentials. Section 1: Introduction to logarithms
 Core Logrithms nd eponentils Setion : Introdution to logrithms Notes nd Emples These notes ontin subsetions on Indies nd logrithms The lws of logrithms Eponentil funtions This is n emple resoure from MEI
Core Logrithms nd eponentils Setion : Introdution to logrithms Notes nd Emples These notes ontin subsetions on Indies nd logrithms The lws of logrithms Eponentil funtions This is n emple resoure from MEI
Eigenvectors and Eigenvalues
 MTB 050 1 ORIGIN 1 Eigenvets n Eigenvlues This wksheet esries the lger use to lulte "prinipl" "hrteristi" iretions lle Eigenvets n the "prinipl" "hrteristi" vlues lle Eigenvlues ssoite with these iretions.
MTB 050 1 ORIGIN 1 Eigenvets n Eigenvlues This wksheet esries the lger use to lulte "prinipl" "hrteristi" iretions lle Eigenvets n the "prinipl" "hrteristi" vlues lle Eigenvlues ssoite with these iretions.
The Regulated and Riemann Integrals
 Chpter 1 The Regulted nd Riemnn Integrls 1.1 Introduction We will consider severl different pproches to defining the definite integrl f(x) dx of function f(x). These definitions will ll ssign the sme vlue
Chpter 1 The Regulted nd Riemnn Integrls 1.1 Introduction We will consider severl different pproches to defining the definite integrl f(x) dx of function f(x). These definitions will ll ssign the sme vlue
Table of Content. c 1 / 5
 Tehnil Informtion - t nd t Temperture for Controlger 03-2018 en Tble of Content Introdution....................................................................... 2 Definitions for t nd t..............................................................
Tehnil Informtion - t nd t Temperture for Controlger 03-2018 en Tble of Content Introdution....................................................................... 2 Definitions for t nd t..............................................................
Chapter 14. Matrix Representations of Linear Transformations
 Chpter 4 Mtrix Representtions of Liner Trnsformtions When considering the Het Stte Evolution, we found tht we could describe this process using multipliction by mtrix. This ws nice becuse computers cn
Chpter 4 Mtrix Representtions of Liner Trnsformtions When considering the Het Stte Evolution, we found tht we could describe this process using multipliction by mtrix. This ws nice becuse computers cn
Comparing the Pre-image and Image of a Dilation
 hpter Summry Key Terms Postultes nd Theorems similr tringles (.1) inluded ngle (.2) inluded side (.2) geometri men (.) indiret mesurement (.6) ngle-ngle Similrity Theorem (.2) Side-Side-Side Similrity
hpter Summry Key Terms Postultes nd Theorems similr tringles (.1) inluded ngle (.2) inluded side (.2) geometri men (.) indiret mesurement (.6) ngle-ngle Similrity Theorem (.2) Side-Side-Side Similrity
1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1. Given a right angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
 1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 1 Pythgors Theorem In this setion we will present geometri proof of the fmous theorem of Pythgors. Given right ngled tringle, the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the
1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 1 Pythgors Theorem In this setion we will present geometri proof of the fmous theorem of Pythgors. Given right ngled tringle, the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the
Lecture 14: Quadrature
 Lecture 14: Qudrture This lecture is concerned with the evlution of integrls fx)dx 1) over finite intervl [, b] The integrnd fx) is ssumed to be rel-vlues nd smooth The pproximtion of n integrl by numericl
Lecture 14: Qudrture This lecture is concerned with the evlution of integrls fx)dx 1) over finite intervl [, b] The integrnd fx) is ssumed to be rel-vlues nd smooth The pproximtion of n integrl by numericl
For the percentage of full time students at RCC the symbols would be:
 Mth 17/171 Chpter 7- ypothesis Testing with One Smple This chpter is s simple s the previous one, except it is more interesting In this chpter we will test clims concerning the sme prmeters tht we worked
Mth 17/171 Chpter 7- ypothesis Testing with One Smple This chpter is s simple s the previous one, except it is more interesting In this chpter we will test clims concerning the sme prmeters tht we worked
Project 6: Minigoals Towards Simplifying and Rewriting Expressions
 MAT 51 Wldis Projet 6: Minigols Towrds Simplifying nd Rewriting Expressions The distriutive property nd like terms You hve proly lerned in previous lsses out dding like terms ut one prolem with the wy
MAT 51 Wldis Projet 6: Minigols Towrds Simplifying nd Rewriting Expressions The distriutive property nd like terms You hve proly lerned in previous lsses out dding like terms ut one prolem with the wy
System Validation (IN4387) November 2, 2012, 14:00-17:00
 System Vlidtion (IN4387) Novemer 2, 2012, 14:00-17:00 Importnt Notes. The exmintion omprises 5 question in 4 pges. Give omplete explntion nd do not onfine yourself to giving the finl nswer. Good luk! Exerise
System Vlidtion (IN4387) Novemer 2, 2012, 14:00-17:00 Importnt Notes. The exmintion omprises 5 question in 4 pges. Give omplete explntion nd do not onfine yourself to giving the finl nswer. Good luk! Exerise
Surds and Indices. Surds and Indices. Curriculum Ready ACMNA: 233,
 Surs n Inies Surs n Inies Curriulum Rey ACMNA:, 6 www.mthletis.om Surs SURDS & & Inies INDICES Inies n surs re very losely relte. A numer uner (squre root sign) is lle sur if the squre root n t e simplifie.
Surs n Inies Surs n Inies Curriulum Rey ACMNA:, 6 www.mthletis.om Surs SURDS & & Inies INDICES Inies n surs re very losely relte. A numer uner (squre root sign) is lle sur if the squre root n t e simplifie.
Scientific notation is a way of expressing really big numbers or really small numbers.
 Scientific Nottion (Stndrd form) Scientific nottion is wy of expressing relly big numbers or relly smll numbers. It is most often used in scientific clcultions where the nlysis must be very precise. Scientific
Scientific Nottion (Stndrd form) Scientific nottion is wy of expressing relly big numbers or relly smll numbers. It is most often used in scientific clcultions where the nlysis must be very precise. Scientific
Fig. 1. Open-Loop and Closed-Loop Systems with Plant Variations
 ME 3600 Control ystems Chrcteristics of Open-Loop nd Closed-Loop ystems Importnt Control ystem Chrcteristics o ensitivity of system response to prmetric vritions cn be reduced o rnsient nd stedy-stte responses
ME 3600 Control ystems Chrcteristics of Open-Loop nd Closed-Loop ystems Importnt Control ystem Chrcteristics o ensitivity of system response to prmetric vritions cn be reduced o rnsient nd stedy-stte responses
The Periodically Forced Harmonic Oscillator
 The Periodiclly Forced Hrmonic Oscilltor S. F. Ellermeyer Kennesw Stte University July 15, 003 Abstrct We study the differentil eqution dt + pdy + qy = A cos (t θ) dt which models periodiclly forced hrmonic
The Periodiclly Forced Hrmonic Oscilltor S. F. Ellermeyer Kennesw Stte University July 15, 003 Abstrct We study the differentil eqution dt + pdy + qy = A cos (t θ) dt which models periodiclly forced hrmonic
9.1 Day 1 Warm Up. Solve the equation = x x 2 = March 1, 2017 Geometry 9.1 The Pythagorean Theorem 1
 9.1 Dy 1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 1, 2017 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 9.1 Dy 2 Wrm Up Use the Pythgoren
9.1 Dy 1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 1, 2017 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 9.1 Dy 2 Wrm Up Use the Pythgoren
CIT 596 Theory of Computation 1. Graphs and Digraphs
 CIT 596 Theory of Computtion 1 A grph G = (V (G), E(G)) onsists of two finite sets: V (G), the vertex set of the grph, often enote y just V, whih is nonempty set of elements lle verties, n E(G), the ege
CIT 596 Theory of Computtion 1 A grph G = (V (G), E(G)) onsists of two finite sets: V (G), the vertex set of the grph, often enote y just V, whih is nonempty set of elements lle verties, n E(G), the ege
z TRANSFORMS z Transform Basics z Transform Basics Transfer Functions Back to the Time Domain Transfer Function and Stability
 TRASFORS Trnsform Bsics Trnsfer Functions Bck to the Time Domin Trnsfer Function nd Stility DSP-G 6. Trnsform Bsics The definition of the trnsform for digitl signl is: -n X x[ n is complex vrile The trnsform
TRASFORS Trnsform Bsics Trnsfer Functions Bck to the Time Domin Trnsfer Function nd Stility DSP-G 6. Trnsform Bsics The definition of the trnsform for digitl signl is: -n X x[ n is complex vrile The trnsform
Intro to Nuclear and Particle Physics (5110)
 Intro to Nucler nd Prticle Physics (5110) Feb, 009 The Nucler Mss Spectrum The Liquid Drop Model //009 1 E(MeV) n n(n-1)/ E/[ n(n-1)/] (MeV/pir) 1 C 16 O 0 Ne 4 Mg 7.7 14.44 19.17 8.48 4 5 6 6 10 15.4.41
Intro to Nucler nd Prticle Physics (5110) Feb, 009 The Nucler Mss Spectrum The Liquid Drop Model //009 1 E(MeV) n n(n-1)/ E/[ n(n-1)/] (MeV/pir) 1 C 16 O 0 Ne 4 Mg 7.7 14.44 19.17 8.48 4 5 6 6 10 15.4.41
6.5 Improper integrals
 Eerpt from "Clulus" 3 AoPS In. www.rtofprolemsolving.om 6.5. IMPROPER INTEGRALS 6.5 Improper integrls As we ve seen, we use the definite integrl R f to ompute the re of the region under the grph of y =
Eerpt from "Clulus" 3 AoPS In. www.rtofprolemsolving.om 6.5. IMPROPER INTEGRALS 6.5 Improper integrls As we ve seen, we use the definite integrl R f to ompute the re of the region under the grph of y =
Section 3.6. Definite Integrals
 The Clulus of Funtions of Severl Vribles Setion.6 efinite Integrls We will first define the definite integrl for funtion f : R R nd lter indite how the definition my be extended to funtions of three or
The Clulus of Funtions of Severl Vribles Setion.6 efinite Integrls We will first define the definite integrl for funtion f : R R nd lter indite how the definition my be extended to funtions of three or
= x x 2 = 25 2
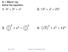 9.1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 7, 2016 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 9.1
9.1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 7, 2016 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 9.1
The steps of the hypothesis test
 ttisticl Methods I (EXT 7005) Pge 78 Mosquito species Time of dy A B C Mid morning 0.0088 5.4900 5.5000 Mid Afternoon.3400 0.0300 0.8700 Dusk 0.600 5.400 3.000 The Chi squre test sttistic is the sum of
ttisticl Methods I (EXT 7005) Pge 78 Mosquito species Time of dy A B C Mid morning 0.0088 5.4900 5.5000 Mid Afternoon.3400 0.0300 0.8700 Dusk 0.600 5.400 3.000 The Chi squre test sttistic is the sum of
THE EXISTENCE-UNIQUENESS THEOREM FOR FIRST-ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS.
 THE EXISTENCE-UNIQUENESS THEOREM FOR FIRST-ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS RADON ROSBOROUGH https://intuitiveexplntionscom/picrd-lindelof-theorem/ This document is proof of the existence-uniqueness theorem
THE EXISTENCE-UNIQUENESS THEOREM FOR FIRST-ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS RADON ROSBOROUGH https://intuitiveexplntionscom/picrd-lindelof-theorem/ This document is proof of the existence-uniqueness theorem
MATH 122, Final Exam
 MATH, Finl Exm Winter Nme: Setion: You must show ll of your work on the exm pper, legily n in etil, to reeive reit. A formul sheet is tthe.. (7 pts eh) Evlute the following integrls. () 3x + x x Solution.
MATH, Finl Exm Winter Nme: Setion: You must show ll of your work on the exm pper, legily n in etil, to reeive reit. A formul sheet is tthe.. (7 pts eh) Evlute the following integrls. () 3x + x x Solution.
63. Representation of functions as power series Consider a power series. ( 1) n x 2n for all 1 < x < 1
 3 9. SEQUENCES AND SERIES 63. Representtion of functions s power series Consider power series x 2 + x 4 x 6 + x 8 + = ( ) n x 2n It is geometric series with q = x 2 nd therefore it converges for ll q =
3 9. SEQUENCES AND SERIES 63. Representtion of functions s power series Consider power series x 2 + x 4 x 6 + x 8 + = ( ) n x 2n It is geometric series with q = x 2 nd therefore it converges for ll q =
15. Quantisation Noise and Nonuniform Quantisation
 5. Quntistion Noise nd Nonuniform Quntistion In PCM, n nlogue signl is smpled, quntised, nd coded into sequence of digits. Once we hve quntised the smpled signls, the exct vlues of the smpled signls cn
5. Quntistion Noise nd Nonuniform Quntistion In PCM, n nlogue signl is smpled, quntised, nd coded into sequence of digits. Once we hve quntised the smpled signls, the exct vlues of the smpled signls cn
ECE Microwave Engineering. Fall Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE. Notes 7. Waveguides Part 4: Rectangular and Circular Waveguide
 ECE 5317-6351 Mirowve Engineering Fll 01 Prof. Dvid R. Jkson Dept. of ECE Notes 7 Wveguides Prt 4: Retngulr nd Cirulr Wveguide 1 Retngulr Wveguide One of the erliest wveguides. Still ommon for high power
ECE 5317-6351 Mirowve Engineering Fll 01 Prof. Dvid R. Jkson Dept. of ECE Notes 7 Wveguides Prt 4: Retngulr nd Cirulr Wveguide 1 Retngulr Wveguide One of the erliest wveguides. Still ommon for high power
Lecture 6. CMOS Static & Dynamic Logic Gates. Static CMOS Circuit. PMOS Transistors in Series/Parallel Connection
 NMOS Trnsistors in Series/Prllel onnetion Leture 6 MOS Stti & ynmi Logi Gtes Trnsistors n e thought s swith ontrolled y its gte signl NMOS swith loses when swith ontrol input is high Peter heung eprtment
NMOS Trnsistors in Series/Prllel onnetion Leture 6 MOS Stti & ynmi Logi Gtes Trnsistors n e thought s swith ontrolled y its gte signl NMOS swith loses when swith ontrol input is high Peter heung eprtment
ECE Microwave Engineering
 ECE 5317-6351 Mirowve Engineering Apte from notes Prof. Jeffer T. Willims Fll 18 Prof. Dvi R. Jkson Dept. of ECE Notes 1 Wveguiing Strutures Prt 5: Coil Cle 1 TEM Solution Proess A) Solve Lple s eqution
ECE 5317-6351 Mirowve Engineering Apte from notes Prof. Jeffer T. Willims Fll 18 Prof. Dvi R. Jkson Dept. of ECE Notes 1 Wveguiing Strutures Prt 5: Coil Cle 1 TEM Solution Proess A) Solve Lple s eqution
Solutions for HW9. Bipartite: put the red vertices in V 1 and the black in V 2. Not bipartite!
 Solutions for HW9 Exerise 28. () Drw C 6, W 6 K 6, n K 5,3. C 6 : W 6 : K 6 : K 5,3 : () Whih of the following re iprtite? Justify your nswer. Biprtite: put the re verties in V 1 n the lk in V 2. Biprtite:
Solutions for HW9 Exerise 28. () Drw C 6, W 6 K 6, n K 5,3. C 6 : W 6 : K 6 : K 5,3 : () Whih of the following re iprtite? Justify your nswer. Biprtite: put the re verties in V 1 n the lk in V 2. Biprtite:
f a L Most reasonable functions are continuous, as seen in the following theorem:
 Limits Suppose f : R R. To sy lim f(x) = L x mens tht s x gets closer n closer to, then f(x) gets closer n closer to L. This suggests tht the grph of f looks like one of the following three pictures: f
Limits Suppose f : R R. To sy lim f(x) = L x mens tht s x gets closer n closer to, then f(x) gets closer n closer to L. This suggests tht the grph of f looks like one of the following three pictures: f
Technology Mapping Method for Low Power Consumption and High Performance in General-Synchronous Framework
 R-17 SASIMI 015 Proeeings Tehnology Mpping Metho for Low Power Consumption n High Performne in Generl-Synhronous Frmework Junki Kwguhi Yukihie Kohir Shool of Computer Siene, the University of Aizu Aizu-Wkmtsu
R-17 SASIMI 015 Proeeings Tehnology Mpping Metho for Low Power Consumption n High Performne in Generl-Synhronous Frmework Junki Kwguhi Yukihie Kohir Shool of Computer Siene, the University of Aizu Aizu-Wkmtsu
SUMMER KNOWHOW STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE
 SUMMER KNOWHOW STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Indices & Logrithms 2 Contents Indices.2 Frctionl Indices.4 Logrithms 6 Exponentil equtions. Simplifying Surds 13 Opertions on Surds..16 Scientific Nottion..18
SUMMER KNOWHOW STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Indices & Logrithms 2 Contents Indices.2 Frctionl Indices.4 Logrithms 6 Exponentil equtions. Simplifying Surds 13 Opertions on Surds..16 Scientific Nottion..18
Generalization of 2-Corner Frequency Source Models Used in SMSIM
 Generliztion o 2-Corner Frequeny Soure Models Used in SMSIM Dvid M. Boore 26 Mrh 213, orreted Figure 1 nd 2 legends on 5 April 213, dditionl smll orretions on 29 My 213 Mny o the soure spetr models ville
Generliztion o 2-Corner Frequeny Soure Models Used in SMSIM Dvid M. Boore 26 Mrh 213, orreted Figure 1 nd 2 legends on 5 April 213, dditionl smll orretions on 29 My 213 Mny o the soure spetr models ville
The DOACROSS statement
 The DOACROSS sttement Is prllel loop similr to DOALL, ut it llows prouer-onsumer type of synhroniztion. Synhroniztion is llowe from lower to higher itertions sine it is ssume tht lower itertions re selete
The DOACROSS sttement Is prllel loop similr to DOALL, ut it llows prouer-onsumer type of synhroniztion. Synhroniztion is llowe from lower to higher itertions sine it is ssume tht lower itertions re selete
Applications of Definite Integral
 Chpter 5 Applitions of Definite Integrl 5.1 Are Between Two Curves In this setion we use integrls to find res of regions tht lie between the grphs of two funtions. Consider the region tht lies between
Chpter 5 Applitions of Definite Integrl 5.1 Are Between Two Curves In this setion we use integrls to find res of regions tht lie between the grphs of two funtions. Consider the region tht lies between
Bisimulation, Games & Hennessy Milner logic
 Bisimultion, Gmes & Hennessy Milner logi Leture 1 of Modelli Mtemtii dei Proessi Conorrenti Pweł Soboiński Univeristy of Southmpton, UK Bisimultion, Gmes & Hennessy Milner logi p.1/32 Clssil lnguge theory
Bisimultion, Gmes & Hennessy Milner logi Leture 1 of Modelli Mtemtii dei Proessi Conorrenti Pweł Soboiński Univeristy of Southmpton, UK Bisimultion, Gmes & Hennessy Milner logi p.1/32 Clssil lnguge theory
Conservation Law. Chapter Goal. 6.2 Theory
 Chpter 6 Conservtion Lw 6.1 Gol Our long term gol is to unerstn how mthemticl moels re erive. Here, we will stuy how certin quntity chnges with time in given region (sptil omin). We then first erive the
Chpter 6 Conservtion Lw 6.1 Gol Our long term gol is to unerstn how mthemticl moels re erive. Here, we will stuy how certin quntity chnges with time in given region (sptil omin). We then first erive the
1.3 SCALARS AND VECTORS
 Bridge Course Phy I PUC 24 1.3 SCLRS ND VECTORS Introdution: Physis is the study of nturl phenomen. The study of ny nturl phenomenon involves mesurements. For exmple, the distne etween the plnet erth nd
Bridge Course Phy I PUC 24 1.3 SCLRS ND VECTORS Introdution: Physis is the study of nturl phenomen. The study of ny nturl phenomenon involves mesurements. For exmple, the distne etween the plnet erth nd
PHYS102 - Electric Energy - Capacitors
 PHYS102 - lectric nerg - Cpcitors Dr. Suess Februr 14, 2007 Plcing Chrges on Conuctors................................................. 2 Plcing Chrges on Conuctors II................................................
PHYS102 - lectric nerg - Cpcitors Dr. Suess Februr 14, 2007 Plcing Chrges on Conuctors................................................. 2 Plcing Chrges on Conuctors II................................................
Lesson 2.1 Inductive Reasoning
 Lesson 2.1 Inutive Resoning Nme Perio Dte For Eerises 1 7, use inutive resoning to fin the net two terms in eh sequene. 1. 4, 8, 12, 16,, 2. 400, 200, 100, 50, 25,, 3. 1 8, 2 7, 1 2, 4, 5, 4. 5, 3, 2,
Lesson 2.1 Inutive Resoning Nme Perio Dte For Eerises 1 7, use inutive resoning to fin the net two terms in eh sequene. 1. 4, 8, 12, 16,, 2. 400, 200, 100, 50, 25,, 3. 1 8, 2 7, 1 2, 4, 5, 4. 5, 3, 2,
Exam 1 September 21, 2012 Instructor: Timothy Martin
 PHY 232 Exm 1 Sept 21, 212 Exm 1 September 21, 212 Instructor: Timothy Mrtin Stuent Informtion Nme n section: UK Stuent ID: Set #: Instructions Answer the questions in the spce provie. On the long form
PHY 232 Exm 1 Sept 21, 212 Exm 1 September 21, 212 Instructor: Timothy Mrtin Stuent Informtion Nme n section: UK Stuent ID: Set #: Instructions Answer the questions in the spce provie. On the long form
Applications of Definite Integral
 Chpter 5 Applitions of Definite Integrl 5.1 Are Between Two Curves In this setion we use integrls to find res of regions tht lie between the grphs of two funtions. Consider the region tht lies between
Chpter 5 Applitions of Definite Integrl 5.1 Are Between Two Curves In this setion we use integrls to find res of regions tht lie between the grphs of two funtions. Consider the region tht lies between
Momentum and Energy Review
 Momentum n Energy Review Nme: Dte: 1. A 0.0600-kilogrm ll trveling t 60.0 meters per seon hits onrete wll. Wht spee must 0.0100-kilogrm ullet hve in orer to hit the wll with the sme mgnitue of momentum
Momentum n Energy Review Nme: Dte: 1. A 0.0600-kilogrm ll trveling t 60.0 meters per seon hits onrete wll. Wht spee must 0.0100-kilogrm ullet hve in orer to hit the wll with the sme mgnitue of momentum
Tests for the Ratio of Two Poisson Rates
 Chpter 437 Tests for the Rtio of Two Poisson Rtes Introduction The Poisson probbility lw gives the probbility distribution of the number of events occurring in specified intervl of time or spce. The Poisson
Chpter 437 Tests for the Rtio of Two Poisson Rtes Introduction The Poisson probbility lw gives the probbility distribution of the number of events occurring in specified intervl of time or spce. The Poisson
Chapter 6 Notes, Larson/Hostetler 3e
 Contents 6. Antiderivtives nd the Rules of Integrtion.......................... 6. Are nd the Definite Integrl.................................. 6.. Are............................................ 6. Reimnn
Contents 6. Antiderivtives nd the Rules of Integrtion.......................... 6. Are nd the Definite Integrl.................................. 6.. Are............................................ 6. Reimnn
Lesson 55 - Inverse of Matrices & Determinants
 // () Review Lesson - nverse of Mtries & Determinnts Mth Honors - Sntowski - t this stge of stuying mtries, we know how to, subtrt n multiply mtries i.e. if Then evlute: () + B (b) - () B () B (e) B n
// () Review Lesson - nverse of Mtries & Determinnts Mth Honors - Sntowski - t this stge of stuying mtries, we know how to, subtrt n multiply mtries i.e. if Then evlute: () + B (b) - () B () B (e) B n
AP CALCULUS Test #6: Unit #6 Basic Integration and Applications
 AP CALCULUS Test #6: Unit #6 Bsi Integrtion nd Applitions A GRAPHING CALCULATOR IS REQUIRED FOR SOME PROBLEMS OR PARTS OF PROBLEMS IN THIS PART OF THE EXAMINATION. () The ext numeril vlue of the orret
AP CALCULUS Test #6: Unit #6 Bsi Integrtion nd Applitions A GRAPHING CALCULATOR IS REQUIRED FOR SOME PROBLEMS OR PARTS OF PROBLEMS IN THIS PART OF THE EXAMINATION. () The ext numeril vlue of the orret
13: Diffusion in 2 Energy Groups
 3: Diffusion in Energy Groups B. Rouben McMster University Course EP 4D3/6D3 Nucler Rector Anlysis (Rector Physics) 5 Sept.-Dec. 5 September Contents We study the diffusion eqution in two energy groups
3: Diffusion in Energy Groups B. Rouben McMster University Course EP 4D3/6D3 Nucler Rector Anlysis (Rector Physics) 5 Sept.-Dec. 5 September Contents We study the diffusion eqution in two energy groups
a) Read over steps (1)- (4) below and sketch the path of the cycle on a P V plot on the graph below. Label all appropriate points.
 Prole 3: Crnot Cyle of n Idel Gs In this prole, the strting pressure P nd volue of n idel gs in stte, re given he rtio R = / > of the volues of the sttes nd is given Finlly onstnt γ = 5/3 is given You
Prole 3: Crnot Cyle of n Idel Gs In this prole, the strting pressure P nd volue of n idel gs in stte, re given he rtio R = / > of the volues of the sttes nd is given Finlly onstnt γ = 5/3 is given You
UNIFORM CONVERGENCE. Contents 1. Uniform Convergence 1 2. Properties of uniform convergence 3
 UNIFORM CONVERGENCE Contents 1. Uniform Convergence 1 2. Properties of uniform convergence 3 Suppose f n : Ω R or f n : Ω C is sequence of rel or complex functions, nd f n f s n in some sense. Furthermore,
UNIFORM CONVERGENCE Contents 1. Uniform Convergence 1 2. Properties of uniform convergence 3 Suppose f n : Ω R or f n : Ω C is sequence of rel or complex functions, nd f n f s n in some sense. Furthermore,
AQA Further Pure 1. Complex Numbers. Section 1: Introduction to Complex Numbers. The number system
 Complex Numbers Section 1: Introduction to Complex Numbers Notes nd Exmples These notes contin subsections on The number system Adding nd subtrcting complex numbers Multiplying complex numbers Complex
Complex Numbers Section 1: Introduction to Complex Numbers Notes nd Exmples These notes contin subsections on The number system Adding nd subtrcting complex numbers Multiplying complex numbers Complex
c n φ n (x), 0 < x < L, (1) n=1
 SECTION : Fourier Series. MATH4. In section 4, we will study method clled Seprtion of Vribles for finding exct solutions to certin clss of prtil differentil equtions (PDEs. To do this, it will be necessry
SECTION : Fourier Series. MATH4. In section 4, we will study method clled Seprtion of Vribles for finding exct solutions to certin clss of prtil differentil equtions (PDEs. To do this, it will be necessry
Section 6: Area, Volume, and Average Value
 Chpter The Integrl Applied Clculus Section 6: Are, Volume, nd Averge Vlue Are We hve lredy used integrls to find the re etween the grph of function nd the horizontl xis. Integrls cn lso e used to find
Chpter The Integrl Applied Clculus Section 6: Are, Volume, nd Averge Vlue Are We hve lredy used integrls to find the re etween the grph of function nd the horizontl xis. Integrls cn lso e used to find
Übungen zur Theoretischen Physik Fa WS 17/18
 Krlsruher Institut für ehnologie Institut für heorie der Kondensierten Mterie Übungen zur heoretishen Physik F WS 17/18 Prof Dr A Shnirmn Bltt 4 PD Dr B Nrozhny Lösungsvorshlg 1 Nihtwehselwirkende Spins:
Krlsruher Institut für ehnologie Institut für heorie der Kondensierten Mterie Übungen zur heoretishen Physik F WS 17/18 Prof Dr A Shnirmn Bltt 4 PD Dr B Nrozhny Lösungsvorshlg 1 Nihtwehselwirkende Spins:
