Outline PGeneral Many body 2Pconsistent Conclusions Basics
|
|
|
- Clarence Lang
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2
3
4 Ĥ = kσ ϵ(k)c kσ c kσ + iσ V i n iσ + U i n i n i { Ĥ ext = d1d2 η σ(1, 2)c σ(1)c σ (2)... σ ] + [η (1, 2)c (1)c (2) + η (1, 2)c (2)c (1)... + ] [ ξ σ(1, 2)c σ (1)c σ (2) + ξ σ(1, 2)c σ(1)c σ(2)... σ ] } + [ ξ (1, 2)c (1)c (2) + ξ (1, 2)c (2)c (1)...
5 [ { )}] Ω[G (0) 1, H] = β 1 log exp β (Ĥ + Ĥ ext µ N G (0) 1 = [iω n ϵ(k) µ] G σσ (k, k ; τ, τ ) = 1 ħ { ρ H T { } { } ρ H = exp βĥ / exp βĥ [ ]} c kσ (τ)c k σ (τ ) = G 2 (12, 34) = 1 [ { ρ ħ 2 H T ψ(1) ψ(3) ψ(4) ψ(2) ]} δω[g (0) 1, H] δg (0) 1 (k, τ; k, τ ) 1 = (R 1, τ 1 )
6 ( ) Φ[G, H] = Ω[G (0) 1, H] d 1 G (0) 1 (1, 1) G 1 (1, 1) G( 1, 1 ) G α δφ[g, H] (12) =, Σ α δφ[g, 0] (12) = δhᾱ(2, 1) δgᾱ(2, 1) H=0 G (2)α δ 2 Φ[G, H] (13, 24) =, Λ α δ 2 Φ[G, 0] (13, 24) = δh α (4, 3)δHᾱ(2, 1) δg α (4, 3)δGᾱ(2, 1) H=0
7 G (0) 1 (1, 2) G 1 (1, 2) = Σ α δφ[g, H] (12) = δg α (2, 1) H=0 [ ] Σ σ (k) = U G σ (k ) 1 1 Γ σ σ (k, k ; q)g σ (k + q)g σ (k + q) βn βn k q Γ(k, k ; q) = Λ α (k, k ; q) [Λ α GG Γ] (k, k ; q) Λ α (13, 24) = δσα (1, 2) δg α (4, 3)
8
9 σk σk σk Γσσ = Λσσ Λσσ Γσσ σ k +q σ k +q σ k +q k k Γ σσ (k, k ; q) = Λ eh σσ (k, k ; q) 1 βn q Λ eh σσ (k, k ; q ) G σ (k + q )G σ (k + q )Γ σσ (k + q, k + q ; q q ) Γ σσ = Λ eh σσ + Keh σσ
10 σk σk σk Γσσ = κσσ κσσ Γσσ σ k +q σ k +q σ k +k +q k k + k + q Γ σσ (k, k ; q) = Λ ee σσ (k, k ; q) 1 βn q Λ ee σσ (k, k + q ; q q ) G σ (k + q q )G σ (k + q )Γ σσ (k + q q, k ; q ) Γ σσ = Λ ee σσ + Kee σσ
11 Γ σσ = Λ ee σσ + Kee σσ = Λeh σσ + Keh σσ I = Λ eh Λ ee K ee K eh = Γ = I K ee K eh = Λ eh Λ ee \ I = I + K eh + K ee = Λ ee + Λ eh I Γ I G σ Λ eh Λ ee Σ Λ α Γ
12
13 σk Σ σ = σk σk σk σk σk σk +q σk +q σk Γ σ σ σk σk k +q σk Σ σ = Λ eh σσ G σ k +q σk σk Σ σ (k, k ) = Σ σ (k) Σ σ (k ) G σ (k, k ) = G σ (k) G σ (k )
14 Γ (k, k ; q) = Λ U 1 Λ U χ (k k )Λ U χ (k k ) χ σσ (q) = (βn) 1 k G σ(k)g σ (k + q) Λ U χ (0) = 1
15 Λ eh Λ U eh Σ (η ) = Λ U η eh η Σ ( η ) = Λ eh
16 Λ ee ee Σ ( ξ ) = Λ ee ξ ee ξ Σ ( ξ ) = Λ ee
17 Σ = Λ U G Σ = Σ (k) = 1 βn Σ (k) = 1 βn Λ eh G Λ U (k, k; q)g (k + q) q k Λ eh (k, k ; 0)G (k )
18 M k,k = δ k,k + Λ (k, k ; 0)G (k )G (k ) Σ Γ σσ G σ [ Σ (k) = U G (k ) 1 1 G (k )G (k + k k ) βn βn k k ] Γ (k, k ; k k )
19 M k,k = δ k,k + Λ (k, k ; 0)G (k )G (k ) Σ Γ σσ G σ [ Σ (k) = U G (k ) 1 1 G (k )G (k + k k ) βn βn k k ] Γ (k, k ; k k )
20 ee
21 Ĥ AD = <ij> t ij c i c j + i V i c i c i X(V i) av = dvρ(v)x(v) ρ(v) = cδ(v ) + (1 c)δ(v + ) { } F av = k B T ln exp βĥad(t ij, V i ) av
22 G(E ±, k) = 1 N Nδ k,k 1 E ± i0 + ϵ(k ) Σ(E ± i0 +, k) k G(E +, k)g(e, q + k) G(E +, k)g(e, q k)
23 eh Γ kk (E +, E ; q) = Λ eh kk (E +, E ; q) + 1 N k Λ eh kk (E +, E ; q) G(E +, k )G(E, k + q)γ k k (E +, E ; q) ee Γ kk (E +, E ; q) = Λ ee kk (E +, E ; q)+ 1 N k Λ ee kk (E +, E ; q+k k ) G(E +, k )G(E, Q k )Γ k k (E +, E ; q + k k ) Q = q + k + k Γ kk (E +, E ; q) = Λ eh kk (E +, E ; q)+λ ee kk (E +, E ; q) I kk (E +, E ; q) I
24 G(k, z) = G( k, z) Γ kk (z +, z ; q) = Γ kk (z +, z ; Q) = Γ k k(z +, z ; Q) Q = q + k + k k+q Γ k k +q k = = Γ k k k k = k+q Γ k k +q k Λ ee kk (z +, z ; q) = Λ eh kk (z +, z ; Q) = Λ eh k k(z +, z ; Q)
25 k ± = k ± q/2 Σ(z +, k + ) Σ(z, k ) = 1 [ Λ kk (z +, z ; q) G(z+, k N +) G(z, k ) ] k G (2) = GG + ΛGG G (2) ω = 0 q = 0 Λ kk (z +, z ; q) Λ kk (z +, z ; q)
26 E ± = E ± i0 + IΣ(E +, k) = 1 Λ kk (E +, 0)IG(E +, k ) N k RΣ(E +, k) = Σ + P dω π IΣ(ω +, k) ω E Λ eh ee Λ Λ kk (q) = Λ kk (q) + 1 Λ kk (q) [G + (k ) G + G + G (k ) N k G + G ] Λ k k (q) G ± = N 1 k G(E ±, k)
27 G k (ω, q) = G(E +, k + ) G(E, k ) Σ k (ω, q) = Σ k+ (E +, k + ) Σ(E, k ) R k (ω, q) = 1 Λ kk (ω, q) G k (ω, q) Σ k (ω, q) N k G(ω, q) 2 = 1 G k (ω, q) 2 N k E ± = E ± ω/2 ± i0 + k ± = k ± q/2 Γ 1 N { [ δ k,k k Λ kk G kr k G 2 R k G k G 2 + R G G k G k G 2 2 G k + G k } Γ k k = Λ kk G kr k G 2 R k G k G 2 + R G G k G k G 2 2 ]
28
29
Diagrammatic extensions of (E)DMFT: Dual boson
 Diagrammatic extensions of (E)DMFT: Dual boson IPhT, CEA Saclay, France ISSP, June 25, 2014 Collaborators Mikhail Katsnelson (University of Nijmegen, The Netherlands) Alexander Lichtenstein (University
Diagrammatic extensions of (E)DMFT: Dual boson IPhT, CEA Saclay, France ISSP, June 25, 2014 Collaborators Mikhail Katsnelson (University of Nijmegen, The Netherlands) Alexander Lichtenstein (University
Klour Q» m i o r L l V I* , tr a d itim i rvpf tr.j UiC lin» tv'ilit* m in 's *** O.hi nf Iiir i * ii, B.lly Q t " '
 / # g < ) / h h #
/ # g < ) / h h #
Supplementary Figure 3: Interaction effects in the proposed state preparation with Bloch oscillations. The numerical results are obtained by
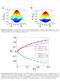 Supplementary Figure : Bandstructure of the spin-dependent hexagonal lattice. The lattice depth used here is V 0 = E rec, E rec the single photon recoil energy. In a and b, we choose the spin dependence
Supplementary Figure : Bandstructure of the spin-dependent hexagonal lattice. The lattice depth used here is V 0 = E rec, E rec the single photon recoil energy. In a and b, we choose the spin dependence
M e t ir c S p a c es
 A G M A A q D q O I q 4 78 q q G q 3 q v- q A G q M A G M 3 5 4 A D O I A 4 78 / 3 v D OI A G M 3 4 78 / 3 54 D D v M q D M 3 v A G M 3 v M 3 5 A 4 M W q x - - - v Z M * A D q q q v W q q q q D q q W q
A G M A A q D q O I q 4 78 q q G q 3 q v- q A G q M A G M 3 5 4 A D O I A 4 78 / 3 v D OI A G M 3 4 78 / 3 54 D D v M q D M 3 v A G M 3 v M 3 5 A 4 M W q x - - - v Z M * A D q q q v W q q q q D q q W q
FREE ELECTRON LASER THEORY USING TWO TIMES GREEN FUNCTION FORMALISM HIROSHI TAKAHASHI. Brookhaven Natioanal Laboratory Upton New York, 11973
 FREE ELECTRON LASER THEORY USING TWO TIMES GREEN FUNCTION FORMALISM HIROSHI TAKAHASHI Brookhaven Natioanal Laboratory Upton New York, 11973 In this paper, we present a quatum theory for free electron laser
FREE ELECTRON LASER THEORY USING TWO TIMES GREEN FUNCTION FORMALISM HIROSHI TAKAHASHI Brookhaven Natioanal Laboratory Upton New York, 11973 In this paper, we present a quatum theory for free electron laser
GW quasiparticle energies
 Chapter 4 GW quasiparticle energies Density functional theory provides a good description of ground state properties by mapping the problem of interacting electrons onto a KS system of independent particles
Chapter 4 GW quasiparticle energies Density functional theory provides a good description of ground state properties by mapping the problem of interacting electrons onto a KS system of independent particles
LINEAR DISPERSIVE WAVES
 LINEAR DISPERSIVE WAVES Nathaniel Egwu December 16, 2009 Outline 1 INTRODUCTION Dispersion Relations Definition of Dispersive Waves 2 SOLUTION AND ASYMPTOTIC ANALYSIS The Beam Equation General Solution
LINEAR DISPERSIVE WAVES Nathaniel Egwu December 16, 2009 Outline 1 INTRODUCTION Dispersion Relations Definition of Dispersive Waves 2 SOLUTION AND ASYMPTOTIC ANALYSIS The Beam Equation General Solution
strong coupling Antonio Vairo INFN and University of Milano
 potential Non-Relativistic QCD strong coupling Antonio Vairo INFN and University of Milano For most of the quarkonium states: 1/r mv Λ QCD (0) V (r) (GeV) 2 1 Υ Υ Υ Υ η ψ c χ ψ ψ 2 0 1 2 r(fm) -1 weak
potential Non-Relativistic QCD strong coupling Antonio Vairo INFN and University of Milano For most of the quarkonium states: 1/r mv Λ QCD (0) V (r) (GeV) 2 1 Υ Υ Υ Υ η ψ c χ ψ ψ 2 0 1 2 r(fm) -1 weak
TKM II: Equation of motion technique - Anderson model and screening (RPA)
 TKM II: Equation of motion technique - Anderson model and screening RPA Dr. Jens Michelsen Contents 1 Preliminaries: Bands etc 2 2 Anderson s model for magnetic impurities 4 2.1 Single level coupled to
TKM II: Equation of motion technique - Anderson model and screening RPA Dr. Jens Michelsen Contents 1 Preliminaries: Bands etc 2 2 Anderson s model for magnetic impurities 4 2.1 Single level coupled to
... surface Green function. Figure 1:
 1 1 Introduction The program calculates the transmission in the L-C or C-R interface. The system the program can calculate is written in the top part of Fig.1. The effects of semi-infinite electrodes,
1 1 Introduction The program calculates the transmission in the L-C or C-R interface. The system the program can calculate is written in the top part of Fig.1. The effects of semi-infinite electrodes,
 g(x) ḧ(ˆx) G(x) Ḧ(ˆx) ḡ(x) g(x) max E [φ(ϱ(x θ))], θ {1,2} x x G(x) θ {1, 2} ϱ(x θ) φ(ϱ) 1 2 g(x), h(x^) x, x^ g( ) h( ) g( ) x h( ) ˆx x supp(g) E(g(x)) := g(x i ) log g(x i ), i=1 supp(g) g(
g(x) ḧ(ˆx) G(x) Ḧ(ˆx) ḡ(x) g(x) max E [φ(ϱ(x θ))], θ {1,2} x x G(x) θ {1, 2} ϱ(x θ) φ(ϱ) 1 2 g(x), h(x^) x, x^ g( ) h( ) g( ) x h( ) ˆx x supp(g) E(g(x)) := g(x i ) log g(x i ), i=1 supp(g) g(
Microscopic Properties of BCS Superconductors (cont.)
 PHYS598 A.J.Leggett Lecture 8 Microscopic Properties of BCS Superconductors (cont.) 1 Microscopic Properties of BCS Superconductors (cont.) References: Tinkham, ch. 3, sections 7 9 In last lecture, examined
PHYS598 A.J.Leggett Lecture 8 Microscopic Properties of BCS Superconductors (cont.) 1 Microscopic Properties of BCS Superconductors (cont.) References: Tinkham, ch. 3, sections 7 9 In last lecture, examined
An imbalanced Fermi gas in 1 + ɛ dimensions. Andrew J. A. James A. Lamacraft
 An imbalanced Fermi gas in 1 + ɛ dimensions Andrew J. A. James A. Lamacraft 2009 Quantum Liquids Interactions and statistics (indistinguishability) Some examples: 4 He 3 He Electrons in a metal Ultracold
An imbalanced Fermi gas in 1 + ɛ dimensions Andrew J. A. James A. Lamacraft 2009 Quantum Liquids Interactions and statistics (indistinguishability) Some examples: 4 He 3 He Electrons in a metal Ultracold
Guiding-center transformation 1. δf = q ( c v f 0, (1) mc (v B 0) v f 0. (3)
 Guidig-ceter trasformatio 1 This is my otes whe readig Liu Che s book[1]. 1 Vlasov equatio The liearized Vlasov equatio is [ t + v x + q m E + v B c ] δf = q v m δe + v δb c v f, 1 where f ad δf are the
Guidig-ceter trasformatio 1 This is my otes whe readig Liu Che s book[1]. 1 Vlasov equatio The liearized Vlasov equatio is [ t + v x + q m E + v B c ] δf = q v m δe + v δb c v f, 1 where f ad δf are the
1. Statement of the problem.
 218 Нелинейные граничные задачи 18, 218-229 (2008 c 2008. M. A. Borodin THE STEFAN PROBLEM The Stefan problem in its classical statement is a mathematical model of the process of propagation of heat in
218 Нелинейные граничные задачи 18, 218-229 (2008 c 2008. M. A. Borodin THE STEFAN PROBLEM The Stefan problem in its classical statement is a mathematical model of the process of propagation of heat in
Quantum Cluster Methods: An introduction
 Quantum Cluster Methods: An introduction David Sénéchal Département de physique, Université de Sherbrooke International summer school on New trends in computational approaches for many-body systems May
Quantum Cluster Methods: An introduction David Sénéchal Département de physique, Université de Sherbrooke International summer school on New trends in computational approaches for many-body systems May
. α β γ δ ε ζ η θ ι κ λ μ Aμ ν(x) ξ ο π ρ ς σ τ υ φ χ ψ ω. Α Β Γ Δ Ε Ζ Η Θ Ι Κ Λ Μ Ν Ξ Ο Π Ρ Σ Τ Υ Φ Χ Ψ Ω. Friday April 1 ± ǁ
 . α β γ δ ε ζ η θ ι κ λ μ Aμ ν(x) ξ ο π ρ ς σ τ υ φ χ ψ ω. Α Β Γ Δ Ε Ζ Η Θ Ι Κ Λ Μ Ν Ξ Ο Π Ρ Σ Τ Υ Φ Χ Ψ Ω Friday April 1 ± ǁ 1 Chapter 5. Photons: Covariant Theory 5.1. The classical fields 5.2. Covariant
. α β γ δ ε ζ η θ ι κ λ μ Aμ ν(x) ξ ο π ρ ς σ τ υ φ χ ψ ω. Α Β Γ Δ Ε Ζ Η Θ Ι Κ Λ Μ Ν Ξ Ο Π Ρ Σ Τ Υ Φ Χ Ψ Ω Friday April 1 ± ǁ 1 Chapter 5. Photons: Covariant Theory 5.1. The classical fields 5.2. Covariant
Pithy P o i n t s Picked I ' p and Patljr Put By Our P e r i p a tetic Pencil Pusher VOLUME X X X X. Lee Hi^h School Here Friday Ni^ht
 G G QQ K K Z z U K z q Z 22 x z - z 97 Z x z j K K 33 G - 72 92 33 3% 98 K 924 4 G G K 2 G x G K 2 z K j x x 2 G Z 22 j K K x q j - K 72 G 43-2 2 G G z G - -G G U q - z q - G x) z q 3 26 7 x Zz - G U-
G G QQ K K Z z U K z q Z 22 x z - z 97 Z x z j K K 33 G - 72 92 33 3% 98 K 924 4 G G K 2 G x G K 2 z K j x x 2 G Z 22 j K K x q j - K 72 G 43-2 2 G G z G - -G G U q - z q - G x) z q 3 26 7 x Zz - G U-
Hopping transport in disordered solids
 Hopping transport in disordered solids Dominique Spehner Institut Fourier, Grenoble, France Workshop on Quantum Transport, Lexington, March 17, 2006 p. 1 Outline of the talk Hopping transport Models for
Hopping transport in disordered solids Dominique Spehner Institut Fourier, Grenoble, France Workshop on Quantum Transport, Lexington, March 17, 2006 p. 1 Outline of the talk Hopping transport Models for
Eikonal method for halo nuclei
 Eikonal method for halo nuclei E. C. Pinilla, P. Descouvemont and D. Baye Université Libre de Bruxelles, Brussels, Belgium 1. Motivation 2. Introduction 3. Four-body eikonal method Elastic scattering 9
Eikonal method for halo nuclei E. C. Pinilla, P. Descouvemont and D. Baye Université Libre de Bruxelles, Brussels, Belgium 1. Motivation 2. Introduction 3. Four-body eikonal method Elastic scattering 9
 5 n N := {1, 2,...} N 0 := {0} N R ++ := (0, ) R + := [0, ) a, b R a b := max{a, b} f g (f g)(x) := f(x) g(x) (Z, Z ) bz Z Z R f := sup z Z f(z) κ: Z R ++ κ f : Z R f(z) f κ := sup z Z κ(z). f κ < f κ
5 n N := {1, 2,...} N 0 := {0} N R ++ := (0, ) R + := [0, ) a, b R a b := max{a, b} f g (f g)(x) := f(x) g(x) (Z, Z ) bz Z Z R f := sup z Z f(z) κ: Z R ++ κ f : Z R f(z) f κ := sup z Z κ(z). f κ < f κ
Non-Perturbative Many-Body Approach to the Hubbard Model and Single-Particle Pseudogap
 J. Phys. I France 7 (1997) 1309 1368 NOVEMBER 1997, PAGE 1309 Non-Perturbative Many-Body Approach to the Hubbard Model and Single-Particle Pseudogap Y.M. Vilk ( 1,2 ) and A.-M.S. Tremblay ( 2, ) ( 1 )
J. Phys. I France 7 (1997) 1309 1368 NOVEMBER 1997, PAGE 1309 Non-Perturbative Many-Body Approach to the Hubbard Model and Single-Particle Pseudogap Y.M. Vilk ( 1,2 ) and A.-M.S. Tremblay ( 2, ) ( 1 )
9 The conservation theorems: Lecture 23
 9 The conservation theorems: Lecture 23 9.1 Energy Conservation (a) For energy to be conserved we expect that the total energy density (energy per volume ) u tot to obey a conservation law t u tot + i
9 The conservation theorems: Lecture 23 9.1 Energy Conservation (a) For energy to be conserved we expect that the total energy density (energy per volume ) u tot to obey a conservation law t u tot + i
Green s functions in N-body quantum mechanics A mathematical perspective
 Green s functions in N-body quantum mechanics A mathematical perspective Eric CANCES Ecole des Ponts and INRIA, Paris, France Aussois, June 19th, 2015 Outline of the course 2 1 Linear operators 2 Electronic
Green s functions in N-body quantum mechanics A mathematical perspective Eric CANCES Ecole des Ponts and INRIA, Paris, France Aussois, June 19th, 2015 Outline of the course 2 1 Linear operators 2 Electronic
The Variational Cluster Approximation. R. Eder. Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Institut für Festkörperphysik
 The Variational Cluster Approximation R. Eder Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Institut für Festkörperphysik Introduction LDA calculations often do not reproduce the single-particle spectra of correlated
The Variational Cluster Approximation R. Eder Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Institut für Festkörperphysik Introduction LDA calculations often do not reproduce the single-particle spectra of correlated
Review of Fundamental Equations Supplementary notes on Section 1.2 and 1.3
 Review of Fundamental Equations Supplementary notes on Section. and.3 Introduction of the velocity potential: irrotational motion: ω = u = identity in the vector analysis: ϕ u = ϕ Basic conservation principles:
Review of Fundamental Equations Supplementary notes on Section. and.3 Introduction of the velocity potential: irrotational motion: ω = u = identity in the vector analysis: ϕ u = ϕ Basic conservation principles:
Lowell Dam Gone Out. Streets Turned I n t o Rivers. No Cause For Alarm Now However As This Happened 35 Years A&o
 V ()\\ ))? K K Y 6 96 Y - Y Y V 5 Z ( z x z \ - \ - - z - q q x x - x 5 9 Q \ V - - Y x 59 7 x x - Y - x - - x z - z x - ( 7 x V 9 z q &? - 9 - V ( x - - - V- [ Z x z - -x > -) - - > X Z z ( V V V
V ()\\ ))? K K Y 6 96 Y - Y Y V 5 Z ( z x z \ - \ - - z - q q x x - x 5 9 Q \ V - - Y x 59 7 x x - Y - x - - x z - z x - ( 7 x V 9 z q &? - 9 - V ( x - - - V- [ Z x z - -x > -) - - > X Z z ( V V V
Summary of Mattuck Chapters 16 and 17
 Summary of Mattuck Chapters 16 and 17 Tomas Petersson Växjö university 2008-02-05 1 Phonons form a Many-Body Viewpoint Hamiltonian for coupled Einstein phonons Definition of Einstein phonon propagator
Summary of Mattuck Chapters 16 and 17 Tomas Petersson Växjö university 2008-02-05 1 Phonons form a Many-Body Viewpoint Hamiltonian for coupled Einstein phonons Definition of Einstein phonon propagator
Recent developments in DMRG. Eric Jeckelmann Institute for Theoretical Physics University of Hanover Germany
 Recent developments in DMRG Eric Jeckelmann Institute for Theoretical Physics University of Hanover Germany Outline 1. Introduction 2. Dynamical DMRG 3. DMRG and quantum information theory 4. Time-evolution
Recent developments in DMRG Eric Jeckelmann Institute for Theoretical Physics University of Hanover Germany Outline 1. Introduction 2. Dynamical DMRG 3. DMRG and quantum information theory 4. Time-evolution
Alexandru Oancea (Strasbourg) joint with Gwénaël Massuyeau (Strasbourg) and Dietmar Salamon (Zurich) Conference Braids in Paris, September 2008
 A Outline Part I: A of the braid group Part II: Morse theory Alexru Oancea (Strasbourg) Gwénaël Massuyeau (Strasbourg) Dietmar Salamon (Zurich) Conference Braids in Paris, September 2008 Outline of Part
A Outline Part I: A of the braid group Part II: Morse theory Alexru Oancea (Strasbourg) Gwénaël Massuyeau (Strasbourg) Dietmar Salamon (Zurich) Conference Braids in Paris, September 2008 Outline of Part
The Effects of Inhomogeneities on the Universe Today. Antonio Riotto INFN, Padova
 The Effects of Inhomogeneities on the Universe Today Antonio Riotto INFN, Padova Frascati, November the 19th 2004 Plan of the talk Short introduction to Inflation Short introduction to cosmological perturbations
The Effects of Inhomogeneities on the Universe Today Antonio Riotto INFN, Padova Frascati, November the 19th 2004 Plan of the talk Short introduction to Inflation Short introduction to cosmological perturbations
Heavy quarkonium physics from Euclidean correlators
 Heavy quarkonium physics from Euclidean correlators Yannis Burnier Albert Einstein Center for Fundamental Physics, Bern University Talk at ECT*, based on [YB, M. Laine, JHEP 1211 (2012) 086] [YB, A.Rothkopf,
Heavy quarkonium physics from Euclidean correlators Yannis Burnier Albert Einstein Center for Fundamental Physics, Bern University Talk at ECT*, based on [YB, M. Laine, JHEP 1211 (2012) 086] [YB, A.Rothkopf,
Liberty unci Union One and Insep,arable. r ' LOWELL. MICHIGAN, WEDNESDAY, AUGUST 10. 1*7
 LLL KL G L L LLL GN N G 7 L LLL K L K) :K : NN : N K N K K L< N L N $ K 2 NG N q 6 [ ):L NN NK L $ L KKX K N X KK NX K: $ $ $ 2 2 2 2 2: 2 < 2 2 7 L ««$ q L N K» KL L K «» K ««LK K «N «L < K 2 N NG ««G
LLL KL G L L LLL GN N G 7 L LLL K L K) :K : NN : N K N K K L< N L N $ K 2 NG N q 6 [ ):L NN NK L $ L KKX K N X KK NX K: $ $ $ 2 2 2 2 2: 2 < 2 2 7 L ««$ q L N K» KL L K «» K ««LK K «N «L < K 2 N NG ««G
Errata for Quantum Mechanics by Ernest Abers August 1, 2004
 Errata for Quantum Mechanics by Ernest Abers August, 004 Preface Page xv: Add a sentence at the end of the next-to-last paragraph: Rudaz (University of Minnesota, and several anonymous reviewers. My special
Errata for Quantum Mechanics by Ernest Abers August, 004 Preface Page xv: Add a sentence at the end of the next-to-last paragraph: Rudaz (University of Minnesota, and several anonymous reviewers. My special
The Theory of the Photon Planck, Einstein the origins of quantum theory Dirac the first quantum field theory The equations of electromagnetism in
 The Theory of the Photon Planck, Einstein the origins of quantum theory Dirac the first quantum field theory The equations of electromagnetism in empty space (i.e., no charged particles are present) using
The Theory of the Photon Planck, Einstein the origins of quantum theory Dirac the first quantum field theory The equations of electromagnetism in empty space (i.e., no charged particles are present) using
Una aad Ark«m*. I cuim tie la.-seit HTni«.ent 9. Twenty.? S 3 S 3 CLOTHS, MEMPHIS, TENN., SATURDAY. JANUARY 18, 1873.
 8! (!> > > ( v 7 q! v Y vq! >5! #! g k gg y y k Q G [x y k xv < zg > 9 _ 7 v ) 6 4 { k & x > 5! k & \ ) >% G > k k x k< G < q k>{> y k k kk k 2 k y y k ( y k y y Y g
8! (!> > > ( v 7 q! v Y vq! >5! #! g k gg y y k Q G [x y k xv < zg > 9 _ 7 v ) 6 4 { k & x > 5! k & \ ) >% G > k k x k< G < q k>{> y k k kk k 2 k y y k ( y k y y Y g
Generalizing the DGLAP Evolution of Fragmentation Functions to the Smallest x Values
 Generalizing the DGLAP Evolution of Fragmentation Functions to the Smallest x Values Bernd Kniehl 1 2nd Institute for Theoretical Physics, University of Hamburg Describe inclusive hadron production,...
Generalizing the DGLAP Evolution of Fragmentation Functions to the Smallest x Values Bernd Kniehl 1 2nd Institute for Theoretical Physics, University of Hamburg Describe inclusive hadron production,...
Dear Professor Weil, . L contains
 Dear Professor Weil, While trying to formulate clearly the question I was asking you before Chern s talk I was led to two more general questions. Your opinion of these questions would be appreciated. I
Dear Professor Weil, While trying to formulate clearly the question I was asking you before Chern s talk I was led to two more general questions. Your opinion of these questions would be appreciated. I
Random Vectors, Random Matrices, and Diagrammatic Fun
 Random Vectors, Random Matrices, and Diagrammatic Fun Cristopher Moore University of New Mexico & Santa Fe Institute joint work with Alexander Russell University of Connecticut A product of inner products
Random Vectors, Random Matrices, and Diagrammatic Fun Cristopher Moore University of New Mexico & Santa Fe Institute joint work with Alexander Russell University of Connecticut A product of inner products
Problem set for the course Skálázás és renormálás a statisztikus fizikában, 2014
 1 Problem set for the course Skálázás és renormálás a statisztikus fizikában, 014 Rules: You can choose at wish from problems having the same main number (i.e. from a given section), but you can collect
1 Problem set for the course Skálázás és renormálás a statisztikus fizikában, 014 Rules: You can choose at wish from problems having the same main number (i.e. from a given section), but you can collect
Lie groupoids, cyclic homology and index theory
 Lie groupoids, cyclic homology and index theory (Based on joint work with M. Pflaum and X. Tang) H. Posthuma University of Amsterdam Kyoto, December 18, 2013 H. Posthuma (University of Amsterdam) Lie groupoids
Lie groupoids, cyclic homology and index theory (Based on joint work with M. Pflaum and X. Tang) H. Posthuma University of Amsterdam Kyoto, December 18, 2013 H. Posthuma (University of Amsterdam) Lie groupoids
Defn: A linear recurrence relation has constant coefficients if the a i s are constant. Ch 14: 1, 4, 5, 10, 13, 18, 22, 24, 25 and
 7.4: linear homogeneous recurrence relation: Defn: A recurrence relation is linear if h n = a 1 (n)h n 1 + a (n)h n +... + a k (n)h n k + b(n) A recurrence relation has order k if a k 0 Ex: Derangement
7.4: linear homogeneous recurrence relation: Defn: A recurrence relation is linear if h n = a 1 (n)h n 1 + a (n)h n +... + a k (n)h n k + b(n) A recurrence relation has order k if a k 0 Ex: Derangement
Higgs-charm Couplings
 Higgs-charm Couplings Wai Kin Lai TUM December 21, 2017 MLL Colloquium, TUM OUTLINE Higgs physics at the LHC OUTLINE Higgs physics at the LHC H J/ψ + γ as a key channel to measure Hc c coupling CHRISTMAS
Higgs-charm Couplings Wai Kin Lai TUM December 21, 2017 MLL Colloquium, TUM OUTLINE Higgs physics at the LHC OUTLINE Higgs physics at the LHC H J/ψ + γ as a key channel to measure Hc c coupling CHRISTMAS
Ph12b Solution Set 4
 Ph Solution Set 4 Feruary 5, 00 The state ψ S un E is transforme to p ψ S un E + p a 0 S γ E + S η E Since γ E an η E aren t mutually orthogonal, we can t use this equation irectly to compute the new ensity
Ph Solution Set 4 Feruary 5, 00 The state ψ S un E is transforme to p ψ S un E + p a 0 S γ E + S η E Since γ E an η E aren t mutually orthogonal, we can t use this equation irectly to compute the new ensity
Anomalies in Exact Renomalization Group
 Anomalies in Exact Renomalization Group at YITP, Jul. 6, 2009 Y. Igarashi, H. Sonoda a, and K. I. Faculty of Education, Niigata University a Department of Physics, Kobe University Anomalies in Exact Renomalization
Anomalies in Exact Renomalization Group at YITP, Jul. 6, 2009 Y. Igarashi, H. Sonoda a, and K. I. Faculty of Education, Niigata University a Department of Physics, Kobe University Anomalies in Exact Renomalization
Relational time and intrinsic decoherence
 Relational time and intrinsic decoherence G. J. Milburn David Poulin Department of Physics, The University of Queensland, QLD 4072 Australia. 1 Quantum state of the universe. Page & Wooters,Phys. Rev 1983.
Relational time and intrinsic decoherence G. J. Milburn David Poulin Department of Physics, The University of Queensland, QLD 4072 Australia. 1 Quantum state of the universe. Page & Wooters,Phys. Rev 1983.
ERRATA. ± Lines are calculated before ( ) or after (+) the Anchor. If the Anchor is a page, t and b indicate, respectively, top and bottom.
 ERRATA 22/02/2010 Fundamentals of Neutrino Physics and Astrophysics C. Giunti and C.. Kim Oxford University Press publication date: 15 March 2007; 728 pages ± Lines are calculated before or after + the
ERRATA 22/02/2010 Fundamentals of Neutrino Physics and Astrophysics C. Giunti and C.. Kim Oxford University Press publication date: 15 March 2007; 728 pages ± Lines are calculated before or after + the
E S T A B L IS H E D. n AT Tnn G.D.O. r.w.-bal'eu. e d n e s d a y. II GRANVILLE HOUSE. GATJDICK ROAD. MEADS. EASTBOUENk
 K q X k K 5 ) ) 5 / K K x x) )? //? q? k X z K 8 5 5? K K K / / $8 ± K K K 8 K / 8 K K X k k X ) k k /» / K / / / k / ] 5 % k / / k k? Z k K ] 8 K K K )» 5 ) # 8 q»)kk q»» )88{ k k k k / k K X 8 8 8 ]
K q X k K 5 ) ) 5 / K K x x) )? //? q? k X z K 8 5 5? K K K / / $8 ± K K K 8 K / 8 K K X k k X ) k k /» / K / / / k / ] 5 % k / / k k? Z k K ] 8 K K K )» 5 ) # 8 q»)kk q»» )88{ k k k k / k K X 8 8 8 ]
Ruijsenaars type deformation of hyperbolic BC n Sutherland m
 Ruijsenaars type deformation of hyperbolic BC n Sutherland model March 2015 History 1. Olshanetsky and Perelomov discovered the hyperbolic BC n Sutherland model by a reduction/projection procedure, but
Ruijsenaars type deformation of hyperbolic BC n Sutherland model March 2015 History 1. Olshanetsky and Perelomov discovered the hyperbolic BC n Sutherland model by a reduction/projection procedure, but
Chapter 4. Fermi-liquid theory (Last version: 29 September 2011) Contents
 Chapter 4 Fermi-liquid theory (Last version: 29 September 2011) Contents 4.1 The quasi-particle concept.................. 270 4.1.1 Landau energy functional E[n]............... 273 4.1.2 Stability of the
Chapter 4 Fermi-liquid theory (Last version: 29 September 2011) Contents 4.1 The quasi-particle concept.................. 270 4.1.1 Landau energy functional E[n]............... 273 4.1.2 Stability of the
Quantum Cluster Methods
 Quantum Cluster Methods An introduction David Sénéchal Université de Sherbrooke Département de physique CIFAR - PITP International Summer School on Numerical Methods for Correlated Systems in Condensed
Quantum Cluster Methods An introduction David Sénéchal Université de Sherbrooke Département de physique CIFAR - PITP International Summer School on Numerical Methods for Correlated Systems in Condensed
Solution of the Anderson impurity model via the functional renormalization group
 Solution of the Anderson impurity model via the functional renormalization group Simon Streib, Aldo Isidori, and Peter Kopietz Institut für Theoretische Physik, Goethe-Universität Frankfurt Meeting DFG-Forschergruppe
Solution of the Anderson impurity model via the functional renormalization group Simon Streib, Aldo Isidori, and Peter Kopietz Institut für Theoretische Physik, Goethe-Universität Frankfurt Meeting DFG-Forschergruppe
An algebraic approach to stochastic duality. Cristian Giardinà
 An algebraic approach to stochastic duality Cristian Giardinà RAQIS18, Annecy 14 September 2018 Collaboration with Gioia Carinci (Delft) Chiara Franceschini (Modena) Claudio Giberti (Modena) Jorge Kurchan
An algebraic approach to stochastic duality Cristian Giardinà RAQIS18, Annecy 14 September 2018 Collaboration with Gioia Carinci (Delft) Chiara Franceschini (Modena) Claudio Giberti (Modena) Jorge Kurchan
How to make the Born-Oppenheimer approximation exact: A fresh look at potential energy surfaces and Berry phases
 How to make the Born-Oppenheimer approximation exact: A fresh look at potential energy surfaces and Berry phases E.K.U. Gross Max-Planck Institute of Microstructure Physics Halle (Saale) Hamiltonian for
How to make the Born-Oppenheimer approximation exact: A fresh look at potential energy surfaces and Berry phases E.K.U. Gross Max-Planck Institute of Microstructure Physics Halle (Saale) Hamiltonian for
An Introduction to Perturbation Methods in Macroeconomics. Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania
 An Introduction to Perturbation Methods in Macroeconomics Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania 1 Introduction Numerous problems in macroeconomics involve functional equations of the form:
An Introduction to Perturbation Methods in Macroeconomics Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania 1 Introduction Numerous problems in macroeconomics involve functional equations of the form:
Short-Ranged Central and Tensor Correlations. Nuclear Many-Body Systems. Reaction Theory for Nuclei far from INT Seattle
 Short-Ranged Central and Tensor Correlations in Nuclear Many-Body Systems Reaction Theory for Nuclei far from Stability @ INT Seattle September 6-, Hans Feldmeier, Thomas Neff, Robert Roth Contents Motivation
Short-Ranged Central and Tensor Correlations in Nuclear Many-Body Systems Reaction Theory for Nuclei far from Stability @ INT Seattle September 6-, Hans Feldmeier, Thomas Neff, Robert Roth Contents Motivation
The effect of asymmetric large-scale dissipation on energy and potential enstrophy injection in two-layer quasi-geostrophic turbulence
 The effect of asymmetric large-scale dissipation on energy and potential enstrophy injection in two-layer quasi-geostrophic turbulence Eleftherios Gkioulekas (1) and Ka-Kit Tung (2) (1) Department of Mathematics,
The effect of asymmetric large-scale dissipation on energy and potential enstrophy injection in two-layer quasi-geostrophic turbulence Eleftherios Gkioulekas (1) and Ka-Kit Tung (2) (1) Department of Mathematics,
Linear response theory and TDDFT
 Linear response theory and TDDFT Claudio Attaccalite http://abineel.grenoble.cnrs.fr/ CECAM Yambo School 2013 (Lausanne) Motivations: +- hν Absorption Spectroscopy Many Body Effects!!! Motivations(II):Absorption
Linear response theory and TDDFT Claudio Attaccalite http://abineel.grenoble.cnrs.fr/ CECAM Yambo School 2013 (Lausanne) Motivations: +- hν Absorption Spectroscopy Many Body Effects!!! Motivations(II):Absorption
Phase Synchronization
 Phase Synchronization Lecture by: Zhibin Guo Notes by: Xiang Fan May 10, 2016 1 Introduction For any mode or fluctuation, we always have where S(x, t) is phase. If a mode amplitude satisfies ϕ k = ϕ k
Phase Synchronization Lecture by: Zhibin Guo Notes by: Xiang Fan May 10, 2016 1 Introduction For any mode or fluctuation, we always have where S(x, t) is phase. If a mode amplitude satisfies ϕ k = ϕ k
Inflationary Trajectories
 Inflationary Trajectories Pascal M. Vaudrevange 19.09.2007 Scanning Inflaton Goals: Reconstruction of Primordial Power Spectra Reconstruction of Inflaton Potential Inflation driven by a scalar field -
Inflationary Trajectories Pascal M. Vaudrevange 19.09.2007 Scanning Inflaton Goals: Reconstruction of Primordial Power Spectra Reconstruction of Inflaton Potential Inflation driven by a scalar field -
QUANTUM FIELD THEORY IN CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS. Wolfgang Belzig
 QUANTUM FIELD THEORY IN CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS Wolfgang Belzig FORMAL MATTERS Wahlpflichtfach 4h lecture + 2h exercise Lecture: Mon & Thu, 10-12, P603 Tutorial: Mon, 14-16 (P912) or 16-18 (P712) 50%
QUANTUM FIELD THEORY IN CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS Wolfgang Belzig FORMAL MATTERS Wahlpflichtfach 4h lecture + 2h exercise Lecture: Mon & Thu, 10-12, P603 Tutorial: Mon, 14-16 (P912) or 16-18 (P712) 50%
POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE CORRELATIONS FOR CONDITIONAL ISING DISTRIBUTIONS
 POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE CORRELATIONS FOR CONDITIONAL ISING DISTRIBUTIONS CAMILLO CAMMAROTA Abstract. In the Ising model at zero external field with ferromagnetic first neighbors interaction the Gibbs measure
POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE CORRELATIONS FOR CONDITIONAL ISING DISTRIBUTIONS CAMILLO CAMMAROTA Abstract. In the Ising model at zero external field with ferromagnetic first neighbors interaction the Gibbs measure
CS 468. Differential Geometry for Computer Science. Lecture 13 Tensors and Exterior Calculus
 CS 468 Differential Geometry for Computer Science Lecture 13 Tensors and Exterior Calculus Outline Linear and multilinear algebra with an inner product Tensor bundles over a surface Symmetric and alternating
CS 468 Differential Geometry for Computer Science Lecture 13 Tensors and Exterior Calculus Outline Linear and multilinear algebra with an inner product Tensor bundles over a surface Symmetric and alternating
Lyapunov small-gain theorems for not necessarily ISS hybrid systems
 Lyapunov small-gain theorems for not necessarily ISS hybrid systems Andrii Mironchenko, Guosong Yang and Daniel Liberzon Institute of Mathematics University of Würzburg Coordinated Science Laboratory University
Lyapunov small-gain theorems for not necessarily ISS hybrid systems Andrii Mironchenko, Guosong Yang and Daniel Liberzon Institute of Mathematics University of Würzburg Coordinated Science Laboratory University
Inofficial Errata List for Dejong/Dave (2011): Structural Macroeconometrics, 2nd Edition. This Version: March 2, 2016
 Johannes Pfeifer Piotr Pieniążek University of Mannheim Polish Academy of Sciences Inofficial Errata List for Dejong/Dave (2011): Structural Macroeconometrics, 2nd Edition 1 Errata This Version: March
Johannes Pfeifer Piotr Pieniążek University of Mannheim Polish Academy of Sciences Inofficial Errata List for Dejong/Dave (2011): Structural Macroeconometrics, 2nd Edition 1 Errata This Version: March
Quantum Cluster Methods (CPT/CDMFT)
 Quantum Cluster Methods (CPT/CDMFT) David Sénéchal Département de physique Université de Sherbrooke Sherbrooke (Québec) Canada Autumn School on Correlated Electrons Forschungszentrum Jülich, Sept. 24,
Quantum Cluster Methods (CPT/CDMFT) David Sénéchal Département de physique Université de Sherbrooke Sherbrooke (Québec) Canada Autumn School on Correlated Electrons Forschungszentrum Jülich, Sept. 24,
3.8. External Source in Quantum-Statistical Path Integral
 3.8. External Source in Quantu-Statistical Path Integral This section studies the quantu statistical evolution alitude ( x b, x a ) ω x ex - ħ d M x + ω x - () x (3.) which will be evaluated in two different
3.8. External Source in Quantu-Statistical Path Integral This section studies the quantu statistical evolution alitude ( x b, x a ) ω x ex - ħ d M x + ω x - () x (3.) which will be evaluated in two different
Numerical methods for PDEs FEM convergence, error estimates, piecewise polynomials
 Platzhalter für Bild, Bild auf Titelfolie hinter das Logo einsetzen Numerical methods for PDEs FEM convergence, error estimates, piecewise polynomials Dr. Noemi Friedman Contents of the course Fundamentals
Platzhalter für Bild, Bild auf Titelfolie hinter das Logo einsetzen Numerical methods for PDEs FEM convergence, error estimates, piecewise polynomials Dr. Noemi Friedman Contents of the course Fundamentals
AanumntBAasciAs. l e t e s auas trasuarbe, amtima*. pay Bna. aaeh t!iacttign. Xat as eling te Trndi'aBd^glit!
 - [ - --- --- ~ - 5 4 G 4? G 8 0 0 0 7 0 - Q - - - 6 8 7 2 75 00 - [ 7-6 - - Q - ] z - 9 - G - 0 - - z / - ] G / - - 4-6 7 - z - 6 - - z - - - - - - G z / - - - G 0 Zz 4 z4 5? - - Z z 2 - - {- 9 9? Z G
- [ - --- --- ~ - 5 4 G 4? G 8 0 0 0 7 0 - Q - - - 6 8 7 2 75 00 - [ 7-6 - - Q - ] z - 9 - G - 0 - - z / - ] G / - - 4-6 7 - z - 6 - - z - - - - - - G z / - - - G 0 Zz 4 z4 5? - - Z z 2 - - {- 9 9? Z G
7.4. Why we have two different types of materials: conductors and insulators?
 Phys463.nb 55 7.3.5. Folding, Reduced Brillouin zone and extended Brillouin zone for free particles without lattices In the presence of a lattice, we can also unfold the extended Brillouin zone to get
Phys463.nb 55 7.3.5. Folding, Reduced Brillouin zone and extended Brillouin zone for free particles without lattices In the presence of a lattice, we can also unfold the extended Brillouin zone to get
Overview of low energy NN interaction and few nucleon systems
 1 Overview of low energy NN interaction and few nucleon systems Renato Higa Theory Group, Jefferson Lab Cebaf Center, A3 (ext6363) higa@jlaborg Lecture II Basics on chiral EFT π EFT Chiral effective field
1 Overview of low energy NN interaction and few nucleon systems Renato Higa Theory Group, Jefferson Lab Cebaf Center, A3 (ext6363) higa@jlaborg Lecture II Basics on chiral EFT π EFT Chiral effective field
- Timur Galimzyanov - Peter Karpov - Mikhail Iontsev -MISIS ECRYS Jan Zaanen - Leiden University, Netherlands
 Euclidean action of superconductor with hidden order S.I. Mukhin Theoretical Physics & Quantum Technologies Department, Moscow Institute for Steel & Alloys, Moscow, Russia - Timur Galimzyanov - Peter Karpov
Euclidean action of superconductor with hidden order S.I. Mukhin Theoretical Physics & Quantum Technologies Department, Moscow Institute for Steel & Alloys, Moscow, Russia - Timur Galimzyanov - Peter Karpov
arxiv:cond-mat/ v3 [cond-mat.str-el] 11 Dec 1997
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v3 [cond-mat.str-el] 11 Dec 1997 arxiv:cond-mat/ v3 [cond-mat.str-el] 11 Dec 1997](/thumbs/72/66514607.jpg) Non-perturbative many-body approach to the Hubbard model and single-particle pseudogap. arxiv:cond-mat/9702188v3 [cond-mat.str-el] 11 Dec 1997 Y.M. Vilk Materials Science Division, Bldg. 223, 9700 S. Case
Non-perturbative many-body approach to the Hubbard model and single-particle pseudogap. arxiv:cond-mat/9702188v3 [cond-mat.str-el] 11 Dec 1997 Y.M. Vilk Materials Science Division, Bldg. 223, 9700 S. Case
Gravitational Waves and New Perspectives for Quantum Gravity
 Gravitational Waves and New Perspectives for Quantum Gravity Ilya L. Shapiro Universidade Federal de Juiz de Fora, Minas Gerais, Brazil Supported by: CAPES, CNPq, FAPEMIG, ICTP Challenges for New Physics
Gravitational Waves and New Perspectives for Quantum Gravity Ilya L. Shapiro Universidade Federal de Juiz de Fora, Minas Gerais, Brazil Supported by: CAPES, CNPq, FAPEMIG, ICTP Challenges for New Physics
SECOND QUANTIZATION. Lecture notes with course Quantum Theory
 SECOND QUANTIZATION Lecture notes with course Quantum Theory Dr. P.J.H. Denteneer Fall 2008 2 SECOND QUANTIZATION 1. Introduction and history 3 2. The N-boson system 4 3. The many-boson system 5 4. Identical
SECOND QUANTIZATION Lecture notes with course Quantum Theory Dr. P.J.H. Denteneer Fall 2008 2 SECOND QUANTIZATION 1. Introduction and history 3 2. The N-boson system 4 3. The many-boson system 5 4. Identical
LOWELL WEEKLY JOURNAL
 Y G Bk b $ 6 G Y 7 B B B B - BB -BY- B Bk B Qk Q k Q k B g (- -- k Bk G Bk k q B - - - - - $ gb q g bg g g b b q )( 6 B 7 B B k 6 g k 6 B b Y k b - b b k b b b g ( \ bg Y b b k b /% /% b k b b g Y Y k
Y G Bk b $ 6 G Y 7 B B B B - BB -BY- B Bk B Qk Q k Q k B g (- -- k Bk G Bk k q B - - - - - $ gb q g bg g g b b q )( 6 B 7 B B k 6 g k 6 B b Y k b - b b k b b b g ( \ bg Y b b k b /% /% b k b b g Y Y k
Hamilton-Jacobi theory on Lie algebroids: Applications to nonholonomic mechanics. Manuel de León Institute of Mathematical Sciences CSIC, Spain
 Hamilton-Jacobi theory on Lie algebroids: Applications to nonholonomic mechanics Manuel de León Institute of Mathematical Sciences CSIC, Spain joint work with J.C. Marrero (University of La Laguna) D.
Hamilton-Jacobi theory on Lie algebroids: Applications to nonholonomic mechanics Manuel de León Institute of Mathematical Sciences CSIC, Spain joint work with J.C. Marrero (University of La Laguna) D.
9 Making Use of Self-Energy Functionals: The Variational Cluster Approximation
 9 Making Use of Self-Energy Functionals: The Variational Cluster Approximation Contents Michael Potthoff I. Institut für Theoretische Physik Universität Hamburg Motivation 2 2 The cluster approach 4 2.
9 Making Use of Self-Energy Functionals: The Variational Cluster Approximation Contents Michael Potthoff I. Institut für Theoretische Physik Universität Hamburg Motivation 2 2 The cluster approach 4 2.
Examination paper for TFY4210 Quantum theory of many-particle systems
 Department of Physics Examination paper for TFY4210 Quantum theory of many-particle systems Academic contact during examination: Associate Professor John Ove Fjærestad Phone: 97 94 00 36 Examination date:
Department of Physics Examination paper for TFY4210 Quantum theory of many-particle systems Academic contact during examination: Associate Professor John Ove Fjærestad Phone: 97 94 00 36 Examination date:
Milnor s Exotic 7-Spheres Jhan-Cyuan Syu ( June, 2017 Introduction
 許展銓 1 2 3 R 4 R 4 R n n 4 R 4 ξ : E π M 2n J : E E R J J(v) = v v E ξ ξ ξ R ξ : E π M M ξ : Ē π M ξ ξ R = ξ R i : E Ē i(cv) = ci(v) c C v E ξ : E π M n M c(ξ) = c i (ξ) H 2n (M, Z) i 0 c 0 (ξ) = 1 c i
許展銓 1 2 3 R 4 R 4 R n n 4 R 4 ξ : E π M 2n J : E E R J J(v) = v v E ξ ξ ξ R ξ : E π M M ξ : Ē π M ξ ξ R = ξ R i : E Ē i(cv) = ci(v) c C v E ξ : E π M n M c(ξ) = c i (ξ) H 2n (M, Z) i 0 c 0 (ξ) = 1 c i
Ricci Dark Energy Chao-Jun Feng SUCA, SHNU
 Ricci Dark Energy 21 2011.3.18-19 Chao-Jun Feng SUCA, SHNU Outline n Introduction to Ricci Dark Energy (RDE) n Stability and the constraint on the parameter n Age problem alleviated in viscous version
Ricci Dark Energy 21 2011.3.18-19 Chao-Jun Feng SUCA, SHNU Outline n Introduction to Ricci Dark Energy (RDE) n Stability and the constraint on the parameter n Age problem alleviated in viscous version
Pairing Phases of Polaritons
 Pairing Phases of Polaritons Jonathan Keeling University of St Andrews 6 YEARS St Petersburg, March 14 Jonathan Keeling Pairing Phases of Polaritons St Petersburg, March 14 1 / 11 Outline 1 Introduction
Pairing Phases of Polaritons Jonathan Keeling University of St Andrews 6 YEARS St Petersburg, March 14 Jonathan Keeling Pairing Phases of Polaritons St Petersburg, March 14 1 / 11 Outline 1 Introduction
SP2 - Damping properties of soil Estimation of hysteretic soil damping from laboratory measurements including strain accumulation
 SP2 - Damping properties of soil Estimation of hysteretic soil damping from laboratory measurements including strain accumulation 21187-1-R 12 May 214 Project Project: Document No.: Document title: Date:
SP2 - Damping properties of soil Estimation of hysteretic soil damping from laboratory measurements including strain accumulation 21187-1-R 12 May 214 Project Project: Document No.: Document title: Date:
Renormalization of microscopic Hamiltonians. Renormalization Group without Field Theory
 Renormalization of microscopic Hamiltonians Renormalization Group without Field Theory Alberto Parola Università dell Insubria (Como - Italy) Renormalization Group Universality Only dimensionality and
Renormalization of microscopic Hamiltonians Renormalization Group without Field Theory Alberto Parola Università dell Insubria (Como - Italy) Renormalization Group Universality Only dimensionality and
Spin models on random graphs with controlled topologies beyond degree constraints
 Spin models on random graphs with controlled topologies beyond degree constraints ACC Coolen (London) and CJ Pérez-Vicente (Barcelona) (work in progress) Motivation - processes on random graphs Deformed
Spin models on random graphs with controlled topologies beyond degree constraints ACC Coolen (London) and CJ Pérez-Vicente (Barcelona) (work in progress) Motivation - processes on random graphs Deformed
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 8 Feb 2014
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 8 Feb 2014 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 8 Feb 2014](/thumbs/79/79522060.jpg) COMBINATORIAL STUDY OF THE DELLAC CONFIGURATIONS AND THE q-extended NORMALIZED MEDIAN GENOCCHI NUMBERS ANGE BIGENI arxiv:1402.1827v1 [math.co] 8 Feb 2014 Abstract. In two recent papers (Mathematical Research
COMBINATORIAL STUDY OF THE DELLAC CONFIGURATIONS AND THE q-extended NORMALIZED MEDIAN GENOCCHI NUMBERS ANGE BIGENI arxiv:1402.1827v1 [math.co] 8 Feb 2014 Abstract. In two recent papers (Mathematical Research
CE 329, Fall 2015 First Mid-Term Exam
 CE 39, Fall 15 First Mid-erm Exam You may only use pencils, pens and erasers while taking this exam. You may NO use a calculator. You may not leave the room for any reason if you do, you must first turn
CE 39, Fall 15 First Mid-erm Exam You may only use pencils, pens and erasers while taking this exam. You may NO use a calculator. You may not leave the room for any reason if you do, you must first turn
G r a y T a k e s P o s t. A s N e w Y S e c ' y
 Z- V XX,, P 10, 1942 26 k P x z V - P g U z - g P U B g,, k - g, x g P g,, B P,,, QU g P g P gz g g g g g, xg gz : J - U, ; z g, -; B x g W, ; U, g g B g k:, J z, g, zg, J, J, Jk,,, "" Pk, K, B K W P 2
Z- V XX,, P 10, 1942 26 k P x z V - P g U z - g P U B g,, k - g, x g P g,, B P,,, QU g P g P gz g g g g g, xg gz : J - U, ; z g, -; B x g W, ; U, g g B g k:, J z, g, zg, J, J, Jk,,, "" Pk, K, B K W P 2
Errata for An Introduction to Particle Physics and the Standard Model
 Errata for An Introduction to Particle Physics and the Standard Model Robert Mann University of Waterloo, Ontario, Canada To my chagrin, and despite my best eorts at proofreading, a number of omissions,
Errata for An Introduction to Particle Physics and the Standard Model Robert Mann University of Waterloo, Ontario, Canada To my chagrin, and despite my best eorts at proofreading, a number of omissions,
Ferromagnetism and Metal-Insulator Transition in Hubbard Model with Alloy Disorder
 Ferromagnetism and Metal-Insulator Transition in Hubbard Model with Alloy Disorder Krzysztof Byczuk Institute of Physics, Augsburg University Institute of Theoretical Physics, Warsaw University October
Ferromagnetism and Metal-Insulator Transition in Hubbard Model with Alloy Disorder Krzysztof Byczuk Institute of Physics, Augsburg University Institute of Theoretical Physics, Warsaw University October
Very basic tsunami physics...
 Very basic tsunami physics... Energy Bottom uplift & Waterberg formation E R 4.8 + 1.5M E T = 1 2 ρglλ(δh)2 L ~ 1 6 m; λ ~ 1 4 m; δh ~ 5m E R 1 18 J 1 2 E T Center of mass falls... Wavelength λ H ~ 4;
Very basic tsunami physics... Energy Bottom uplift & Waterberg formation E R 4.8 + 1.5M E T = 1 2 ρglλ(δh)2 L ~ 1 6 m; λ ~ 1 4 m; δh ~ 5m E R 1 18 J 1 2 E T Center of mass falls... Wavelength λ H ~ 4;
Macroscopic dielectric theory
 Macroscopic dielectric theory Maxwellʼs equations E = 1 c E =4πρ B t B = 4π c J + 1 c B = E t In a medium it is convenient to explicitly introduce induced charges and currents E = 1 B c t D =4πρ H = 4π
Macroscopic dielectric theory Maxwellʼs equations E = 1 c E =4πρ B t B = 4π c J + 1 c B = E t In a medium it is convenient to explicitly introduce induced charges and currents E = 1 B c t D =4πρ H = 4π
Brownian Motion: Fokker-Planck Equation
 Chapter 7 Brownian Motion: Fokker-Planck Equation The Fokker-Planck equation is the equation governing the time evolution of the probability density of the Brownian particla. It is a second order differential
Chapter 7 Brownian Motion: Fokker-Planck Equation The Fokker-Planck equation is the equation governing the time evolution of the probability density of the Brownian particla. It is a second order differential
Green s functions: calculation methods
 M. A. Gusmão IF-UFRGS 1 FIP161 Text 13 Green s functions: calculation methods Equations of motion One of the usual methods for evaluating Green s functions starts by writing an equation of motion for the
M. A. Gusmão IF-UFRGS 1 FIP161 Text 13 Green s functions: calculation methods Equations of motion One of the usual methods for evaluating Green s functions starts by writing an equation of motion for the
Serge Florens. ITKM - Karlsruhe. with: Lars Fritz and Matthias Vojta
 0.5 setgray0 0.5 setgray1 Universal crossovers and critical dynamics for quantum phase transitions in impurity models Serge Florens ITKM - Karlsruhe with: Lars Fritz and Matthias Vojta p. 1 Summary The
0.5 setgray0 0.5 setgray1 Universal crossovers and critical dynamics for quantum phase transitions in impurity models Serge Florens ITKM - Karlsruhe with: Lars Fritz and Matthias Vojta p. 1 Summary The
Internal and Surface Waves in a Two-Layer Fluid
 Internal and Surface Waves in a Two-Layer Fluid BY DEAN LEONARDI B.S. University of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA 1993. M.S. San Jose State University, San Jose, CA, 2002. M.A. University of Texas, Austin,
Internal and Surface Waves in a Two-Layer Fluid BY DEAN LEONARDI B.S. University of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA 1993. M.S. San Jose State University, San Jose, CA, 2002. M.A. University of Texas, Austin,
. α β γ δ ε ζ η θ ι κ λ μ Aμ ν(x) ξ ο π ρ ς σ τ υ φ χ ψ ω. Α Β Γ Δ Ε Ζ Η Θ Ι Κ Λ Μ Ν Ξ Ο Π Ρ Σ Τ Υ Φ Χ Ψ Ω. Wednesday March 30 ± ǁ
 . α β γ δ ε ζ η θ ι κ λ μ Aμ ν(x) ξ ο π ρ ς σ τ υ φ χ ψ ω. Α Β Γ Δ Ε Ζ Η Θ Ι Κ Λ Μ Ν Ξ Ο Π Ρ Σ Τ Υ Φ Χ Ψ Ω Wednesday March 30 ± ǁ 1 Chapter 5. Photons: Covariant Theory 5.1. The classical fields 5.2. Covariant
. α β γ δ ε ζ η θ ι κ λ μ Aμ ν(x) ξ ο π ρ ς σ τ υ φ χ ψ ω. Α Β Γ Δ Ε Ζ Η Θ Ι Κ Λ Μ Ν Ξ Ο Π Ρ Σ Τ Υ Φ Χ Ψ Ω Wednesday March 30 ± ǁ 1 Chapter 5. Photons: Covariant Theory 5.1. The classical fields 5.2. Covariant
k times l times n times
 1. Tensors on vector spaces Let V be a finite dimensional vector space over R. Definition 1.1. A tensor of type (k, l) on V is a map T : V V R k times l times which is linear in every variable. Example
1. Tensors on vector spaces Let V be a finite dimensional vector space over R. Definition 1.1. A tensor of type (k, l) on V is a map T : V V R k times l times which is linear in every variable. Example
A geometric solution of the Kervaire Invariant One problem
 A geometric solution of the Kervaire Invariant One problem Petr M. Akhmet ev 19 May 2009 Let f : M n 1 R n, n = 4k + 2, n 2 be a smooth generic immersion of a closed manifold of codimension 1. Let g :
A geometric solution of the Kervaire Invariant One problem Petr M. Akhmet ev 19 May 2009 Let f : M n 1 R n, n = 4k + 2, n 2 be a smooth generic immersion of a closed manifold of codimension 1. Let g :

 g k b 7? 3 5 y y Qk
g k b 7? 3 5 y y Qk