FIBER-REINFORCED ELASTOMERS: MACROSCOPIC PROPERTIES, MICROSTRUCTURE EVOLUTION, AND STABILITY. Oscar Lopez-Pamies
|
|
|
- Sharlene Collins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FIBER-REINFORCED ELASTOMERS: MACROSCOPIC PROPERTIES, MICROSTRUCTURE EVOLUTION, AND STABILITY Oscar Lpez-Pamies State University f New Yrk, Stny Brk Department f Aerspace Engineering, Iwa State University February 9, 2 Ames, IA
2 Sft sids reinfrced with fibers Rubber reinfrced with carbn-back and fabric TEM f Cagen Fibris in Human Brain Arteries Thermpastic Eastmers (Sef-Assembed Nandmains) BCC HX-Cy. Gyrid Lamear ~ 5 nm f PS TEM f a tribck cpymer with cyindrica mrphgy
3 Issues in cnstitutive mdeing f FREs S bi (MPa).8.6 Nninear cnstitutive matrix phase and fibers Cmpex initia micrstructure Micrstructure evutin (gemetric nninearity) Devepment f instabiities
4 Prbem setting: Lagrangian frmuatin Kinematics O X Undefrmed W Lca cnstitutive behavir where W S = W F ( X, F) N r r ( XF, ) = c ( X) W ( F) å 2 ( ) ( ) r = x ( X) Defrmed W Defrmatin Gradient F x = X Right CG Defrmatin Tensr C = T F F Stred-energy functin f the matrix () ( F) W Stred-energy functin f the fibers W (2) ( F) Randm variabe characterizing the micrstructure ì ( r ) X Î r c ( X) = ï if phase í ïï therwise î
5 Prbem setting: Lagrangian frmuatin Kinematics O X Undefrmed W Lca cnstitutive behavir where W S = W F ( X, F) N r r ( XF, ) = c ( X) W ( F) å 2 ( ) ( ) r = x ( X) Defrmed W Istrpic matrix () () Defrmatin Gradient F x = X Right CG Defrmatin Tensr C = W ( F ) =Y ( I, I ) Transversey istrpic fibers where (2) (2) 2 T F F W ( F ) =Y ( I, I, I, I ) I = trc I é 2 2 = C C ù 2 ê(tr ) -tr 2 ë ú û I = N CN I = N C N 4 5 2
6 Prbem setting: macrscpic respnse Definitin: reatin between the vume averages f S the stress and defrmatin gradient ver RVE = ò W W Variatina Characterizatin where and W S ( ) W = ( F) F S dx F = ò F dx W W F = min W ( X F) X FÎK( F) W ò, d W Undefrmed RVE L separatin f ength-scaes { = W = W } K( F F F x in, and x FX n )= Hi (972), Braides (985), Müer (987)
7 Existing anaytica appraches Phenmengica mdes Frmuated n the basis f invariants ( F ) = (, ) + (, ) W F I I G I I is 2 ani 4 5 Merdi, Hrgan, Ogden, Pence, Rivin, Saccmandi, amng thers Hmgenizatin/Micrmechanics mdes Incrprate direct infrmatin frm micrscpic prperties Estimates fr specia ading cnditins, and specia matrix and fiber cnstituents (He et a., 26; debttn et a., 26) Linear cmparisn variatina estimates fr genera ading cnditins and istrpic cnstituents (LP & Pnte Castañeda 26a,b)
8 Stabiity and faiure Casses f instabiities fiber faiure (ca) Materia fiber debnding (ca) matrix cavitatin (ca) shrt waveength (ca) Gemetrica ng waveength (gba) The ss f strng eipticity f the macrscpic respnse f the fiber-reinfrced eastmer, as characterized by the effective stred-energy functin W( F), dentes the nset f ng waveength instabiities ì 2 W ü B( F) = min ï vv F u u ï í ( ) = i k j ý u,v F F u = v = îï ij k ïþ Geymnat, Müer, Triantafyidis (993)
9 Micrstructure evutin Undefrmed F Defrmed W W Infrmatin n micrstructure evutin is imprtant t identify and understand the micrscpic mechanisms that gvern the macrscpic behavir. Fr that we need infrmatin abut the ca fieds F( X) LP (26)
10 New Apprach: Iterated Hmgenizatin
11 Iterated diute hmgenizatin Strategy: Cnstruct a particuate distributin f fibers ( X ) within a ( ) hypereastic materia fr which it is pssibe t cmpute exacty the effective stred-energy functin Step : iterated-diute hmgenizatin W r c ( ) diute phase Hmgenizatin Ad-infinitum... W c - H éw W Fù = W F = W c ê, ; ë ú, (,) û () (2) LP, J. App. Mech. (2)
12 Auxiiary diute prbem: sequentia aminates Step 2: sequentia aminates Rank- r simpe aminate Rank-2 aminate... ad-infinitum... incusin phase matrix phase When the matrix phase is diute: W HW é é ù () WFù () ê,, ú = W+ max -W ( F+ Ä ) n S ë û ò w x w x ( x)d w S ê ë F ú û distributina functin reated t the tw-pint statistics f fiber distributin in the undefrmed cnfiguratin Idiart, JMPS (28)
13 Iterated hmgenizatin framewrk The effective stred-energy functin W can be finay shwn t be given by the fwing Hamitn-Jacbi equatin W é W ù () c -W -max -W ( F+ Ä ) n S = c ò w x w x ( x) d ê F ú û w S ë subject t the initia cnditin W( F,) W ( F) = (2) the time variabe is t -nc (initia fiber cncentratin) the spatia variabe is F the Hamitnian is W HW é é ù () WFù () ê,, ú = W+ max -W ( F+ Ä ) n S ë û ò w x w x ( x)d w S ê ë F ú û LP & Idiart, J. Eng. Math. (2)
14 LP & Idiart, J. Eng. Math. (2) Iterated hmgenizatin framewrk: ca fieds Cnsider the fwing perturbed prbem fr W é W ù c t W t () - -max -W ( F+ Ä ) n S = t c ò w x w x ( x) d w S ê F ú ë û subject t the initia cnditin (2) W( F,) = W ( F) + tu( F) W t Then, the fwing identity is true ò W U ( FX ( )) dx= t (2) W W (2) c t t= U () can be any functin f interest, e.g., the defrmatin gradient
15 Remarks n the iterated hmgenizatin apprach The prpsed IH methd prvides sutins fr W in terms f W () and W (2) and the ne- and tw-pint statistics f the randm distributin f fibers In the imit f sma defrmatins as, the IH frmuatin reduces t the HS wer bund fr fiber-reinfrced randm media F I In the further imit f diute fiber cncentratin c, the IH frmuatin recvers the exact resut f Esheby fr a diute distributin f eipsdia fibers The prpsed IH methd prvides access t ca fieds, which in turn permits the study f the evutin f micrstructure and the nset f instabiities The cmputatins amunt t sving apprpriate Hamitn-Jacbi equatins, which are fairy tractabe
16 Appicatin t Fiber-Reinfrced Ne-Hkean Sids
17 Fiber-reinfrced Ne-Hkean sids Ne-Hkean matrix () () () m W ( F) =Y ( I ) = I -3 2 Stiffer Ne-Hkean fibers (2) ( ) (2) (2) m W ( F) =Y ( I ) = I -3 2 ( ) S W randm, istrpic distributin N Macrscpic stred-energy functin Hamitn-Jacbi equatin W( F, c ) =Y( I, I, I, I, c ) m æ 2 () Y öæ ö () 2 Y c ( I ) m I I ç Y = c ç I ç m I 4 2 () è è ø 2 ø subject t the initia cnditin Y ( I, I, I, I,) = Y (2) ( I, I )
18 LP & Idiart, J. Eng. Math. (2) Overa stress-strain reatin Csed-frm sutin fr W where with m f( I ) = -3 2 ( I ) m = ( - c ) m () + cm (2) ( ) ( ) W( F ) =Y ( I, I ) = f I + g I 4 4 and and gi ( ) = 4 ( I 2)( I ) m - m I Nte I: separabe functina frm Nte II: n dependence n the secnd I 2 nr fifth I 5 invariants Overa stress-strain reatin m () (2) ( - c ) m + ( + c ) m = m + () c m + - (2) ( ) ( c ) m W S = ( F) - pf = F+ ( - ) é -I ùfn Ä N-pF F ëê ûú -T -3/2 -T m m m 4 4 ()
19 Macrscpic Instabiities fiber faiure (ca) Materia fiber debnding (ca) Casses f matrix cavitatin (ca) instabiities shrt waveength (ca) Gemetrica ng waveength (gba) Ang an arbitrary ading path, the materia first becmes cr unstabe at a critica defrmatin F cr with I = F N F N 4 cr cr such that I æ m ö = - ç çè m ø cr 4 2/ 3 Nte: m cr 4 m I LP & Idiart, J. Eng. Math. (2)
20 Macrscpic Instabiities Observatins Macrscpic instabiities may ny ccur when the defrmatin in the fiber I 4 directin, as measured by, reaches a sufficienty arge cmpressive cr vaue I 4 The cnditin states that instabiities may devep whenever the cmpressive defrmatin ang the fiber directin reaches a critica vaue determined by the rati f hard-t-sft mdes f defrmatin m Hard mde m Sft mde W
21 Micrstructure evutin Undefrmed e 3 F Defrmed v 3 z - 2 = z - 2 = 3 e 2 z -2 z - 2 = 3 W e z - 2 = 2 W v z -2 2 v 2 The average shape and rientatin f the fibers in the defrmed cnfiguratin are characterized by the Euerian eipsid LP (26), LP & Idiart (2) { T } E = x x Z Zx Eigenvaues f where z, z, z ( )( (2) ) Z = I-N Ä N F Eigenvectrs f v,v,v 2 3 T Z Z T Z Z
22 Micrstructure evutin is the average defrmatin gradient in the fibers. In the IH framewrk, it is sutin f the pde F (2) c (2) (2) F F - Ä S = c F ò w x d S subject t the initia cnditin F (2) ( F,) = F Csed-frm sutin 2n -g F F FN N éf F N N ù 2n -g = é - Ä ù - - Ä + FN Ä u + FN Ä N (2) T T g - - ë û ê ú I ë û I 4 4 where u = ( I-N Ä N) F FN, and g = n + 2 T ( 2 ) I + n I I -I - I () m, n = II - I + 2 I ( + c ) m + ( - c ) m () (2) LP, Idiart, & Li (2)
23 Sampe Resuts
24 IH vs. FEM: in-pane stress-strain respnse 7 6 IH FE t S () m c = 4. c = 2. = 2. Rigid fibers Mraeda et a. (29)
25 Axisymmetric cmpressin at an ange φ Appied Lading F æ -2 / ö ç -2 / = ç çè ø Initia fiber rientatin N = csj e + sinj e 3 e 3 Ν F e 3 n j 2 / - 2 / - e j e W W
26 Axisymmetric cmpressin at an ange φ Appied Lading Current fiber rientatin F æ -2 / ö ç -2 / = ç çè ø e 3 j F n = csje + sinje é ê Arcs Ν n e 3 3 j = ê cs j + cs j ú ë cs ù ú û j 2 / - 2 / - e j e W W
27 Axisymmetric cmpressin at an ange φ 5 4 Sma-defrmatin respnse () m = t = 5 c = 3. ds d 3 = 2 t = 2 2 / - 2 / - t = j t m m ( 2) () hetergeneity cntrast
28 Axisymmetric cmpressin at an ange φ S j = 6 Large-defrmatin stress-strain respnse j = 8 ( ) m = c = 3. t = 2 j = 9 j Evutin f fiber rientatin j = j = 89 j = 9 j = 8 j = 6 j = j = j = j = j = Nte: Macrscpic instabiity at LP, Idiart, & Li (2)
29 Axisymmetric cmpressin at an ange φ Onset f macrscpic instabiities at cr Effect f fiber rientatin Effect f fiber-t matrix cntrast cr t = 5 t = 2 cr c = 5. c =. c = 3..4 t = 5.3 c = 3. ( ) m = j.6.5 j = 9 ( ) m = t
30 Axisymmetric cmpressin at an ange φ Onset f macrscpic instabiities at cr Effect f fiber rientatin Evutin f fiber rientatin.9 j = j = 9 cr t = 5 t = 2 j 8 6 j = 89 j = 8 j = t = 5.3 c = 3. ( ) m = j 4 2 j = j = j =
31 Remarks The rtatin f the fibers which depends criticay n the reative rientatin between the ading axes and the fiber directin can act as a dminant gemetric sftening mechanism. It was fund that the ng axes f the fibers rtate away frm the axis f maximum cmpressive ading twards the axis f maximum tensin. Ladings with predminant cmpressin ang the fibers ead t arger rtatin f the fibers, which in turn ead t arger gemetric sftening f the cnstitutive respnse, and in sme cases when the hetergeneity cntrast between the matrix and the fibers is sufficienty high as t the ss f macrscpic stabiity.
32 Remarks The resuts f this wrk can hep understanding the behavir f many ther sids with riented micrstructures Reinfrced Eastmers (Wang and Mark 99) S 2 m Pystyrene Eipsids Liquid crysta eastmers (Nishikawa and Finkemann999) Transparent Opaque
33 Cntact with earier wrk with aminates -? -» - - Fr the aigned pane-strain ading f a aminate the nset f macrscpic instabiities ccurs at where Lam cr æ L m ö /4 = - ç m çè ø m = ( - c) m () + cm (2) and æ L c c ö m - = + ç () (2) çè m m ø - Rsen (965); Triantafyidis and Maker (985)
34 Cntact with earier wrk with aminates Aigned pane-strain ading cnditins - - Effect f fiber cncentratin c.95 t Laminate ( 2) ( ) = m / m = 2 Effect f cntrast.95 Laminate t = m / m ( 2) ( ) cr Fibers cr.9.85 Fibers.75.8 c = ( 2) ( ) c t = m / m
35 Cntact with experiments Matrix: Siicne Yung s Mduus E () = 2.9 MPa Fibers: Spaghetti Yung s Mduus E (2) = 69 MPa Vume fractin c = 3% Experimenta setup IH predictin Jef & Feck (992)
36 Fina remarks An iterated hmgenizatin apprach in finite easticity has been prpsed t cnstruct exact (reaizabe) cnstitutive mdes fr fiber-reinfrced hypereastic sids Because the prpsed frmuatin grants access t ca fieds, it can be used t thrughy study the nset f faiure and the evutin f micrstructure in fiber-reinfrced sft sids with randm micrstructures The required anaysis reduces t the study f tractabe Hamitn-Jacbi equatins As a first appicatin, csed-frm resuts were derived fr fiber-reinfrced Ne-Hkean eastmers These ideas can be generaized t mre cmpex systems f sft hetergeneus media with randm micrstructures
2 Virtual work methods
 Virtua wrk methds Ntatin A E G H I I m P q Q u V y δ δ δ δ θ θ μ φ crss sectina area f a member Yung's mduus mduus f trsina rigidity hriznta reactin secnd mment f area f a member secnd mment f area f an
Virtua wrk methds Ntatin A E G H I I m P q Q u V y δ δ δ δ θ θ μ φ crss sectina area f a member Yung's mduus mduus f trsina rigidity hriznta reactin secnd mment f area f a member secnd mment f area f an
Dynamics of shear deformable laminated composites using Raleigh Ritz method
 Cahun: The NPS Institutina Archive Facuty and Researcher Pubicatins Facuty and Researcher Pubicatins 2003 Dynamics f shear defrmabe aminated cmpsites using Raeigh Ritz methd Kar, Ramech Mnterey, Caifrnia.
Cahun: The NPS Institutina Archive Facuty and Researcher Pubicatins Facuty and Researcher Pubicatins 2003 Dynamics f shear defrmabe aminated cmpsites using Raeigh Ritz methd Kar, Ramech Mnterey, Caifrnia.
Fast Fourier Transform-based micromechanical modeling of polycrystals with direct input from microstructural images
 Fast Furier Transfrm-based micrmechanical mdeling f plycrystals with direct input frm micrstructural images Ricard A. Lebenshn (Ls Alams Natinal Labratry, USA) FFT-based frmulatin fr plycrystals: fast
Fast Furier Transfrm-based micrmechanical mdeling f plycrystals with direct input frm micrstructural images Ricard A. Lebenshn (Ls Alams Natinal Labratry, USA) FFT-based frmulatin fr plycrystals: fast
Plasticty Theory (5p)
 Cmputatinal Finite Strain Hyper-Elast Plasticty Thery (5p) à General ü Study nn-linear material and structural respnse (due t material as well as gemetrical effects) ü Fundamental principles fl Cntinuum
Cmputatinal Finite Strain Hyper-Elast Plasticty Thery (5p) à General ü Study nn-linear material and structural respnse (due t material as well as gemetrical effects) ü Fundamental principles fl Cntinuum
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CIVIL AND STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING Volume 1, No 3, 2010
 Prbabilistic Analysis f Lateral Displacements f Shear in a 20 strey building Samir Benaissa 1, Belaid Mechab 2 1 Labratire de Mathematiques, Université de Sidi Bel Abbes BP 89, Sidi Bel Abbes 22000, Algerie.
Prbabilistic Analysis f Lateral Displacements f Shear in a 20 strey building Samir Benaissa 1, Belaid Mechab 2 1 Labratire de Mathematiques, Université de Sidi Bel Abbes BP 89, Sidi Bel Abbes 22000, Algerie.
Simulating Nonlinear Oscillations of Viscoelastically Damped Mechanical Systems
 Engineering, Techngy & Appied Science Research V. 4, N. 6, 014, 714-73 714 Simuating Nninear Osciatins f Visceasticay Damped Mechanica Systems M. D. Mnsia Department f Physics/FAST University f Abmey-Caavi
Engineering, Techngy & Appied Science Research V. 4, N. 6, 014, 714-73 714 Simuating Nninear Osciatins f Visceasticay Damped Mechanica Systems M. D. Mnsia Department f Physics/FAST University f Abmey-Caavi
Computational modeling techniques
 Cmputatinal mdeling techniques Lecture 4: Mdel checing fr ODE mdels In Petre Department f IT, Åb Aademi http://www.users.ab.fi/ipetre/cmpmd/ Cntent Stichimetric matrix Calculating the mass cnservatin relatins
Cmputatinal mdeling techniques Lecture 4: Mdel checing fr ODE mdels In Petre Department f IT, Åb Aademi http://www.users.ab.fi/ipetre/cmpmd/ Cntent Stichimetric matrix Calculating the mass cnservatin relatins
ANISOTROPIC DAMPING BEHAVIOR OF REINFORCED PLASTIC PARTS FOR NVH SIMULATIONS
 ANISOTROPIC DAMPING BEHAIOR OF REINFORCED PLASTIC PARTS FOR NH SIMULATIONS Sylvain CALMELS, Sylvain Mathieu, Maxime LESUEUR e-xstream engineering Abstract Reinfrced plastic materials shw a very interesting
ANISOTROPIC DAMPING BEHAIOR OF REINFORCED PLASTIC PARTS FOR NH SIMULATIONS Sylvain CALMELS, Sylvain Mathieu, Maxime LESUEUR e-xstream engineering Abstract Reinfrced plastic materials shw a very interesting
Theoretical Evaluation on Effects of Opening on Ultimate Load-carrying Capacity of Square Slabs
 Eectrnic Jurna f Structura Engineering (8 008 Theretica Evauatin n Effects f Opening n Utimate ad-carrying Capacity f Square Sabs Chee Khn Ng Universiti Maaysia Sarawak, Maaysia Timthy Juius Edward Universiti
Eectrnic Jurna f Structura Engineering (8 008 Theretica Evauatin n Effects f Opening n Utimate ad-carrying Capacity f Square Sabs Chee Khn Ng Universiti Maaysia Sarawak, Maaysia Timthy Juius Edward Universiti
Stress and Failure Analysis of Laminated Composite Structures
 PDHnline Curse M37 (6 PDH) Stress and Failure Analysis f aminated Cmpsite Structures Instructr: Jhn J. Engblm, Ph.D., PE PDH Online PDH Center 57 Meadw Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 3-6658 Phne & Fax: 73-988-88
PDHnline Curse M37 (6 PDH) Stress and Failure Analysis f aminated Cmpsite Structures Instructr: Jhn J. Engblm, Ph.D., PE PDH Online PDH Center 57 Meadw Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 3-6658 Phne & Fax: 73-988-88
Modeling the Nonlinear Rheological Behavior of Materials with a Hyper-Exponential Type Function
 www.ccsenet.rg/mer Mechanical Engineering Research Vl. 1, N. 1; December 011 Mdeling the Nnlinear Rhelgical Behavir f Materials with a Hyper-Expnential Type Functin Marc Delphin Mnsia Département de Physique,
www.ccsenet.rg/mer Mechanical Engineering Research Vl. 1, N. 1; December 011 Mdeling the Nnlinear Rhelgical Behavir f Materials with a Hyper-Expnential Type Functin Marc Delphin Mnsia Département de Physique,
Course Stabilty of Structures
 Curse Stabilty f Structures Lecture ntes 2015.03.06 abut 3D beams, sme preliminaries (1:st rder thery) Trsin, 1:st rder thery 3D beams 2:nd rder thery Trsinal buckling Cupled buckling mdes, eamples Numerical
Curse Stabilty f Structures Lecture ntes 2015.03.06 abut 3D beams, sme preliminaries (1:st rder thery) Trsin, 1:st rder thery 3D beams 2:nd rder thery Trsinal buckling Cupled buckling mdes, eamples Numerical
Lecture 10, Principal Component Analysis
 Principal Cmpnent Analysis Lecture 10, Principal Cmpnent Analysis Ha Helen Zhang Fall 2017 Ha Helen Zhang Lecture 10, Principal Cmpnent Analysis 1 / 16 Principal Cmpnent Analysis Lecture 10, Principal
Principal Cmpnent Analysis Lecture 10, Principal Cmpnent Analysis Ha Helen Zhang Fall 2017 Ha Helen Zhang Lecture 10, Principal Cmpnent Analysis 1 / 16 Principal Cmpnent Analysis Lecture 10, Principal
17 IMPACT PROPERTIES OF COMPOSITES
 17 IMPACT PROPERTIES OF COMPOSITES 17-1 Impact resistance is the ability f a material t absrb and dissipate energies under impact r shck lading. The respnse t impact lads ranges frm lcalized damage t ttal
17 IMPACT PROPERTIES OF COMPOSITES 17-1 Impact resistance is the ability f a material t absrb and dissipate energies under impact r shck lading. The respnse t impact lads ranges frm lcalized damage t ttal
Kinematic transformation of mechanical behavior Neville Hogan
 inematic transfrmatin f mechanical behavir Neville Hgan Generalized crdinates are fundamental If we assume that a linkage may accurately be described as a cllectin f linked rigid bdies, their generalized
inematic transfrmatin f mechanical behavir Neville Hgan Generalized crdinates are fundamental If we assume that a linkage may accurately be described as a cllectin f linked rigid bdies, their generalized
Kirchhoff Hypothesis. MER452: Composite Materials
 Kirchhff Hpthesis MER45: Cmpsite Materials 1 Cmpsite Design Eperimental Data STRUCTURE CONSTITUENTS COMPOSITE Micr Mechanics STRUCTURAL ELEMENT ELEMENTARY STRUCTURE Finite Element Analsis E E G Classical
Kirchhff Hpthesis MER45: Cmpsite Materials 1 Cmpsite Design Eperimental Data STRUCTURE CONSTITUENTS COMPOSITE Micr Mechanics STRUCTURAL ELEMENT ELEMENTARY STRUCTURE Finite Element Analsis E E G Classical
1. INTRODUCTION. In many polymer processing operations, molten polymers. emerge from dies into a stress field which deforms the
 . NTRODUCTON. Histrical ntes f melt spinning prcess n many plymer prcessing peratins, mlten plymers emerge frm dies int a stress field which defrms the melt int a final fabricated shape. This is the case
. NTRODUCTON. Histrical ntes f melt spinning prcess n many plymer prcessing peratins, mlten plymers emerge frm dies int a stress field which defrms the melt int a final fabricated shape. This is the case
Rigid Body Dynamics (continued)
 Last time: Rigid dy Dynamics (cntinued) Discussin f pint mass, rigid bdy as useful abstractins f reality Many-particle apprach t rigid bdy mdeling: Newtn s Secnd Law, Euler s Law Cntinuus bdy apprach t
Last time: Rigid dy Dynamics (cntinued) Discussin f pint mass, rigid bdy as useful abstractins f reality Many-particle apprach t rigid bdy mdeling: Newtn s Secnd Law, Euler s Law Cntinuus bdy apprach t
On Boussinesq's problem
 Internatinal Jurnal f Engineering Science 39 (2001) 317±322 www.elsevier.cm/lcate/ijengsci On Bussinesq's prblem A.P.S. Selvadurai * Department f Civil Engineering and Applied Mechanics, McGill University,
Internatinal Jurnal f Engineering Science 39 (2001) 317±322 www.elsevier.cm/lcate/ijengsci On Bussinesq's prblem A.P.S. Selvadurai * Department f Civil Engineering and Applied Mechanics, McGill University,
Nonlinear Analysis of Fiber-Reinforced Composite Laminates Subjected to Uniaxial Compressive Load
 213 SIMULIA Reginal User Meeting Nnlinear Analysis f Fiber-Reinfrced Cmpsite Laminates Subjected t Uniaxial Cmpressive Lad Hsuan-Teh Hu Department f Civil Engineering, Natinal Cheng Kung University, Tainan,
213 SIMULIA Reginal User Meeting Nnlinear Analysis f Fiber-Reinfrced Cmpsite Laminates Subjected t Uniaxial Cmpressive Lad Hsuan-Teh Hu Department f Civil Engineering, Natinal Cheng Kung University, Tainan,
OF SIMPLY SUPPORTED PLYWOOD PLATES UNDER COMBINED EDGEWISE BENDING AND COMPRESSION
 U. S. FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH PAPER FPL 50 DECEMBER U. S. DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE FOREST SERVICE FOREST PRODUCTS LABORATORY OF SIMPLY SUPPORTED PLYWOOD PLATES UNDER COMBINED EDGEWISE BENDING AND COMPRESSION
U. S. FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH PAPER FPL 50 DECEMBER U. S. DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE FOREST SERVICE FOREST PRODUCTS LABORATORY OF SIMPLY SUPPORTED PLYWOOD PLATES UNDER COMBINED EDGEWISE BENDING AND COMPRESSION
INDUCTANCE Self Inductance
 DUCTCE 3. Sef nductance Cnsider the circuit shwn in the Figure. S R When the switch is csed the current, and s the magnetic fied, thrugh the circuit increases frm zer t a specific vaue. The increasing
DUCTCE 3. Sef nductance Cnsider the circuit shwn in the Figure. S R When the switch is csed the current, and s the magnetic fied, thrugh the circuit increases frm zer t a specific vaue. The increasing
Equilibrium of Stress
 Equilibrium f Stress Cnsider tw perpendicular planes passing thrugh a pint p. The stress cmpnents acting n these planes are as shwn in ig. 3.4.1a. These stresses are usuall shwn tgether acting n a small
Equilibrium f Stress Cnsider tw perpendicular planes passing thrugh a pint p. The stress cmpnents acting n these planes are as shwn in ig. 3.4.1a. These stresses are usuall shwn tgether acting n a small
Chapter Summary. Mathematical Induction Strong Induction Recursive Definitions Structural Induction Recursive Algorithms
 Chapter 5 1 Chapter Summary Mathematical Inductin Strng Inductin Recursive Definitins Structural Inductin Recursive Algrithms Sectin 5.1 3 Sectin Summary Mathematical Inductin Examples f Prf by Mathematical
Chapter 5 1 Chapter Summary Mathematical Inductin Strng Inductin Recursive Definitins Structural Inductin Recursive Algrithms Sectin 5.1 3 Sectin Summary Mathematical Inductin Examples f Prf by Mathematical
Transactions on Engineering Sciences vol 19, 1998 WIT Press, ISSN
 Transactins n Engineering Sciences vl 19, 1998 WIT Press, www.witpress.cm, ISSN 1743-3533 Fatigue life and cyclic elastic-plastic strain behaviur ahead f ntch f ntched specimen under cyclic plane bending
Transactins n Engineering Sciences vl 19, 1998 WIT Press, www.witpress.cm, ISSN 1743-3533 Fatigue life and cyclic elastic-plastic strain behaviur ahead f ntch f ntched specimen under cyclic plane bending
Fundamental Concepts in Structural Plasticity
 Lecture Fundamental Cncepts in Structural Plasticit Prblem -: Stress ield cnditin Cnsider the plane stress ield cnditin in the principal crdinate sstem, a) Calculate the maximum difference between the
Lecture Fundamental Cncepts in Structural Plasticit Prblem -: Stress ield cnditin Cnsider the plane stress ield cnditin in the principal crdinate sstem, a) Calculate the maximum difference between the
4F-5 : Performance of an Ideal Gas Cycle 10 pts
 4F-5 : Perfrmance f an Cycle 0 pts An ideal gas, initially at 0 C and 00 kpa, underges an internally reversible, cyclic prcess in a clsed system. The gas is first cmpressed adiabatically t 500 kpa, then
4F-5 : Perfrmance f an Cycle 0 pts An ideal gas, initially at 0 C and 00 kpa, underges an internally reversible, cyclic prcess in a clsed system. The gas is first cmpressed adiabatically t 500 kpa, then
ECEN 4872/5827 Lecture Notes
 ECEN 4872/5827 Lecture Ntes Lecture #5 Objectives fr lecture #5: 1. Analysis f precisin current reference 2. Appraches fr evaluating tlerances 3. Temperature Cefficients evaluatin technique 4. Fundamentals
ECEN 4872/5827 Lecture Ntes Lecture #5 Objectives fr lecture #5: 1. Analysis f precisin current reference 2. Appraches fr evaluating tlerances 3. Temperature Cefficients evaluatin technique 4. Fundamentals
ENGI 4430 Parametric Vector Functions Page 2-01
 ENGI 4430 Parametric Vectr Functins Page -01. Parametric Vectr Functins (cntinued) Any nn-zer vectr r can be decmpsed int its magnitude r and its directin: r rrˆ, where r r 0 Tangent Vectr: dx dy dz dr
ENGI 4430 Parametric Vectr Functins Page -01. Parametric Vectr Functins (cntinued) Any nn-zer vectr r can be decmpsed int its magnitude r and its directin: r rrˆ, where r r 0 Tangent Vectr: dx dy dz dr
CAUSAL INFERENCE. Technical Track Session I. Phillippe Leite. The World Bank
 CAUSAL INFERENCE Technical Track Sessin I Phillippe Leite The Wrld Bank These slides were develped by Christel Vermeersch and mdified by Phillippe Leite fr the purpse f this wrkshp Plicy questins are causal
CAUSAL INFERENCE Technical Track Sessin I Phillippe Leite The Wrld Bank These slides were develped by Christel Vermeersch and mdified by Phillippe Leite fr the purpse f this wrkshp Plicy questins are causal
Fall 2013 Physics 172 Recitation 3 Momentum and Springs
 Fall 03 Physics 7 Recitatin 3 Mmentum and Springs Purpse: The purpse f this recitatin is t give yu experience wrking with mmentum and the mmentum update frmula. Readings: Chapter.3-.5 Learning Objectives:.3.
Fall 03 Physics 7 Recitatin 3 Mmentum and Springs Purpse: The purpse f this recitatin is t give yu experience wrking with mmentum and the mmentum update frmula. Readings: Chapter.3-.5 Learning Objectives:.3.
Comparing Several Means: ANOVA. Group Means and Grand Mean
 STAT 511 ANOVA and Regressin 1 Cmparing Several Means: ANOVA Slide 1 Blue Lake snap beans were grwn in 12 pen-tp chambers which are subject t 4 treatments 3 each with O 3 and SO 2 present/absent. The ttal
STAT 511 ANOVA and Regressin 1 Cmparing Several Means: ANOVA Slide 1 Blue Lake snap beans were grwn in 12 pen-tp chambers which are subject t 4 treatments 3 each with O 3 and SO 2 present/absent. The ttal
4th Indian Institute of Astrophysics - PennState Astrostatistics School July, 2013 Vainu Bappu Observatory, Kavalur. Correlation and Regression
 4th Indian Institute f Astrphysics - PennState Astrstatistics Schl July, 2013 Vainu Bappu Observatry, Kavalur Crrelatin and Regressin Rahul Ry Indian Statistical Institute, Delhi. Crrelatin Cnsider a tw
4th Indian Institute f Astrphysics - PennState Astrstatistics Schl July, 2013 Vainu Bappu Observatry, Kavalur Crrelatin and Regressin Rahul Ry Indian Statistical Institute, Delhi. Crrelatin Cnsider a tw
EXTRA CREDIT Electric Field and Forces c. The pin will move toward the top plate when the voltage is either negative or positive.
 EXTRA CREDIT T receive credit fr these questins, yu must input yur ansers n the LMS site. As, fr this set f questins, yu i be given ny ne pprtunity t prvide yur anser, s make sure yu have crrecty sved
EXTRA CREDIT T receive credit fr these questins, yu must input yur ansers n the LMS site. As, fr this set f questins, yu i be given ny ne pprtunity t prvide yur anser, s make sure yu have crrecty sved
Sections 15.1 to 15.12, 16.1 and 16.2 of the textbook (Robbins-Miller) cover the materials required for this topic.
 Tpic : AC Fundamentals, Sinusidal Wavefrm, and Phasrs Sectins 5. t 5., 6. and 6. f the textbk (Rbbins-Miller) cver the materials required fr this tpic.. Wavefrms in electrical systems are current r vltage
Tpic : AC Fundamentals, Sinusidal Wavefrm, and Phasrs Sectins 5. t 5., 6. and 6. f the textbk (Rbbins-Miller) cver the materials required fr this tpic.. Wavefrms in electrical systems are current r vltage
Lecture 5: Equilibrium and Oscillations
 Lecture 5: Equilibrium and Oscillatins Energy and Mtin Last time, we fund that fr a system with energy cnserved, v = ± E U m ( ) ( ) One result we see immediately is that there is n slutin fr velcity if
Lecture 5: Equilibrium and Oscillatins Energy and Mtin Last time, we fund that fr a system with energy cnserved, v = ± E U m ( ) ( ) One result we see immediately is that there is n slutin fr velcity if
Kinetics of Particles. Chapter 3
 Kinetics f Particles Chapter 3 1 Kinetics f Particles It is the study f the relatins existing between the frces acting n bdy, the mass f the bdy, and the mtin f the bdy. It is the study f the relatin between
Kinetics f Particles Chapter 3 1 Kinetics f Particles It is the study f the relatins existing between the frces acting n bdy, the mass f the bdy, and the mtin f the bdy. It is the study f the relatin between
Homology groups of disks with holes
 Hmlgy grups f disks with hles THEOREM. Let p 1,, p k } be a sequence f distinct pints in the interir unit disk D n where n 2, and suppse that fr all j the sets E j Int D n are clsed, pairwise disjint subdisks.
Hmlgy grups f disks with hles THEOREM. Let p 1,, p k } be a sequence f distinct pints in the interir unit disk D n where n 2, and suppse that fr all j the sets E j Int D n are clsed, pairwise disjint subdisks.
Use a lens holder fabricated from SiC. SiC has a larger CTE than C-C, i.e. it is better matched to the SFL6.
 Frm: Steve Sctt, Jinsek K, Syun ichi Shiraiwa T: MSE enthusiasts Re: MSE mem 101b: allwable thickness f Vitn sheet Nvember 25, 2008 Update frm MSE Mem 101b Let s assume: Vitn thickness = 1 mm Vitn mdulus
Frm: Steve Sctt, Jinsek K, Syun ichi Shiraiwa T: MSE enthusiasts Re: MSE mem 101b: allwable thickness f Vitn sheet Nvember 25, 2008 Update frm MSE Mem 101b Let s assume: Vitn thickness = 1 mm Vitn mdulus
Study Group Report: Plate-fin Heat Exchangers: AEA Technology
 Study Grup Reprt: Plate-fin Heat Exchangers: AEA Technlgy The prblem under study cncerned the apparent discrepancy between a series f experiments using a plate fin heat exchanger and the classical thery
Study Grup Reprt: Plate-fin Heat Exchangers: AEA Technlgy The prblem under study cncerned the apparent discrepancy between a series f experiments using a plate fin heat exchanger and the classical thery
L a) Calculate the maximum allowable midspan deflection (w o ) critical under which the beam will slide off its support.
 ecture 6 Mderately arge Deflectin Thery f Beams Prblem 6-1: Part A: The department f Highways and Public Wrks f the state f Califrnia is in the prcess f imprving the design f bridge verpasses t meet earthquake
ecture 6 Mderately arge Deflectin Thery f Beams Prblem 6-1: Part A: The department f Highways and Public Wrks f the state f Califrnia is in the prcess f imprving the design f bridge verpasses t meet earthquake
A mathematical model for complete stress-strain curve prediction of permeable concrete
 A mathematical mdel fr cmplete stress-strain curve predictin f permeable cncrete M. K. Hussin Y. Zhuge F. Bullen W. P. Lkuge Faculty f Engineering and Surveying, University f Suthern Queensland, Twmba,
A mathematical mdel fr cmplete stress-strain curve predictin f permeable cncrete M. K. Hussin Y. Zhuge F. Bullen W. P. Lkuge Faculty f Engineering and Surveying, University f Suthern Queensland, Twmba,
Compressibility Effects
 Definitin f Cmpressibility All real substances are cmpressible t sme greater r lesser extent; that is, when yu squeeze r press n them, their density will change The amunt by which a substance can be cmpressed
Definitin f Cmpressibility All real substances are cmpressible t sme greater r lesser extent; that is, when yu squeeze r press n them, their density will change The amunt by which a substance can be cmpressed
Measurement of Radial Loss and Lifetime. of Microwave Plasma in the Octupo1e. J. C. Sprott PLP 165. Plasma Studies. University of Wisconsin DEC 1967
 Measurement f Radial Lss and Lifetime f Micrwave Plasma in the Octup1e J. C. Sprtt PLP 165 Plasma Studies University f Wiscnsin DEC 1967 1 The number f particles in the tridal ctuple was measured as a
Measurement f Radial Lss and Lifetime f Micrwave Plasma in the Octup1e J. C. Sprtt PLP 165 Plasma Studies University f Wiscnsin DEC 1967 1 The number f particles in the tridal ctuple was measured as a
Lecture 6: Phase Space and Damped Oscillations
 Lecture 6: Phase Space and Damped Oscillatins Oscillatins in Multiple Dimensins The preius discussin was fine fr scillatin in a single dimensin In general, thugh, we want t deal with the situatin where:
Lecture 6: Phase Space and Damped Oscillatins Oscillatins in Multiple Dimensins The preius discussin was fine fr scillatin in a single dimensin In general, thugh, we want t deal with the situatin where:
Computational modeling techniques
 Cmputatinal mdeling techniques Lecture 2: Mdeling change. In Petre Department f IT, Åb Akademi http://users.ab.fi/ipetre/cmpmd/ Cntent f the lecture Basic paradigm f mdeling change Examples Linear dynamical
Cmputatinal mdeling techniques Lecture 2: Mdeling change. In Petre Department f IT, Åb Akademi http://users.ab.fi/ipetre/cmpmd/ Cntent f the lecture Basic paradigm f mdeling change Examples Linear dynamical
ELECTROSTATIC FIELDS IN MATERIAL MEDIA
 MF LCTROSTATIC FILDS IN MATRIAL MDIA 3/4/07 LCTURS Materials media may be classified in terms f their cnductivity σ (S/m) as: Cnductrs The cnductivity usually depends n temperature and frequency A material
MF LCTROSTATIC FILDS IN MATRIAL MDIA 3/4/07 LCTURS Materials media may be classified in terms f their cnductivity σ (S/m) as: Cnductrs The cnductivity usually depends n temperature and frequency A material
ChE 471: LECTURE 4 Fall 2003
 ChE 47: LECTURE 4 Fall 003 IDEL RECTORS One f the key gals f chemical reactin engineering is t quantify the relatinship between prductin rate, reactr size, reactin kinetics and selected perating cnditins.
ChE 47: LECTURE 4 Fall 003 IDEL RECTORS One f the key gals f chemical reactin engineering is t quantify the relatinship between prductin rate, reactr size, reactin kinetics and selected perating cnditins.
[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ J] dt x x hard to solve in general solve it numerically. If there is no convection. is in the absence of reaction n
![[ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ J] dt x x hard to solve in general solve it numerically. If there is no convection. is in the absence of reaction n [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ J] dt x x hard to solve in general solve it numerically. If there is no convection. is in the absence of reaction n](/thumbs/83/87606590.jpg) .3 The material balance equatin Net change f [J] due t diffusin, cnvectin, and reactin [ ] [ ] [ ] d J J J n = D v k [ J ] fr n - th reactin dt x x hard t slve in general slve it numerically If there is
.3 The material balance equatin Net change f [J] due t diffusin, cnvectin, and reactin [ ] [ ] [ ] d J J J n = D v k [ J ] fr n - th reactin dt x x hard t slve in general slve it numerically If there is
ENGINEERING COUNCIL CERTIFICATE LEVEL THERMODYNAMIC, FLUID AND PROCESS ENGINEERING C106 TUTORIAL 5 THE VISCOUS NATURE OF FLUIDS
 ENGINEERING COUNCIL CERTIFICATE LEVEL THERMODYNAMIC, FLUID AND PROCESS ENGINEERING C106 TUTORIAL 5 THE VISCOUS NATURE OF FLUIDS On cmpletin f this tutrial yu shuld be able t d the fllwing. Define viscsity
ENGINEERING COUNCIL CERTIFICATE LEVEL THERMODYNAMIC, FLUID AND PROCESS ENGINEERING C106 TUTORIAL 5 THE VISCOUS NATURE OF FLUIDS On cmpletin f this tutrial yu shuld be able t d the fllwing. Define viscsity
ENSC Discrete Time Systems. Project Outline. Semester
 ENSC 49 - iscrete Time Systems Prject Outline Semester 006-1. Objectives The gal f the prject is t design a channel fading simulatr. Upn successful cmpletin f the prject, yu will reinfrce yur understanding
ENSC 49 - iscrete Time Systems Prject Outline Semester 006-1. Objectives The gal f the prject is t design a channel fading simulatr. Upn successful cmpletin f the prject, yu will reinfrce yur understanding
CHAPTER 8b Static Equilibrium Units
 CHAPTER 8b Static Equilibrium Units The Cnditins fr Equilibrium Slving Statics Prblems Stability and Balance Elasticity; Stress and Strain The Cnditins fr Equilibrium An bject with frces acting n it, but
CHAPTER 8b Static Equilibrium Units The Cnditins fr Equilibrium Slving Statics Prblems Stability and Balance Elasticity; Stress and Strain The Cnditins fr Equilibrium An bject with frces acting n it, but
A Study on Pullout Strength of Cast-in-place Anchor bolt in Concrete under High Temperature
 Transactins f the 7 th Internatinal Cnference n Structural Mechanics in Reactr Technlgy (SMiRT 7) Prague, Czech Republic, August 7 22, 23 Paper #H-2 A Study n Pullut Strength f Cast-in-place Anchr blt
Transactins f the 7 th Internatinal Cnference n Structural Mechanics in Reactr Technlgy (SMiRT 7) Prague, Czech Republic, August 7 22, 23 Paper #H-2 A Study n Pullut Strength f Cast-in-place Anchr blt
CHAPTER 13 Temperature and Kinetic Theory. Units
 CHAPTER 13 Temperature and Kinetic Thery Units Atmic Thery f Matter Temperature and Thermmeters Thermal Equilibrium and the Zerth Law f Thermdynamics Thermal Expansin Thermal Stress The Gas Laws and Abslute
CHAPTER 13 Temperature and Kinetic Thery Units Atmic Thery f Matter Temperature and Thermmeters Thermal Equilibrium and the Zerth Law f Thermdynamics Thermal Expansin Thermal Stress The Gas Laws and Abslute
COUPLED THERMO-MECHANICAL ANALYSES OF DYNAMICALLY LOADED RUBBER CYLINDERS 1
 COUPLED THERMO-MECHANICAL ANALYSES OF DYNAMICALLY LOADED RUBBER CYLINDERS Arthur R. Jhnsn and Tzi-Kang Chen Army Research Labratry, MS 24 Analytical and Cmputatinal Methds Branch NASA Langley Research
COUPLED THERMO-MECHANICAL ANALYSES OF DYNAMICALLY LOADED RUBBER CYLINDERS Arthur R. Jhnsn and Tzi-Kang Chen Army Research Labratry, MS 24 Analytical and Cmputatinal Methds Branch NASA Langley Research
Stress and Strain. Stresses are three types such as normal (tensile or compressive), shearing (direct or torsional), and bearing stress.
 Stress and Strain Stress Stress is defined as frce per unit area. It has the same units as pressure, and in fact pressure is ne special variety f stress. When a bdy is subjected t a set f frces and is
Stress and Strain Stress Stress is defined as frce per unit area. It has the same units as pressure, and in fact pressure is ne special variety f stress. When a bdy is subjected t a set f frces and is
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL GaGa: a simple and flexible hierarchical model for microarray data analysis
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL GaGa: a simple and flexible hierarchical mdel fr micrarray data analysis David Rssell Department f Bistatistics M.D. Andersn Cancer Center, Hustn, TX 77030, USA rsselldavid@gmail.cm
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL GaGa: a simple and flexible hierarchical mdel fr micrarray data analysis David Rssell Department f Bistatistics M.D. Andersn Cancer Center, Hustn, TX 77030, USA rsselldavid@gmail.cm
What determines how matter behaves? Thermodynamics.
 What determines hw matter ehaves? hermdynamics.. What determines hw matter ehaves? Final Stale State Equilirium State Gis free energy: Minimum (at specific, ). Classical thermdynamics Macrscpic phenmena.
What determines hw matter ehaves? hermdynamics.. What determines hw matter ehaves? Final Stale State Equilirium State Gis free energy: Minimum (at specific, ). Classical thermdynamics Macrscpic phenmena.
NGSS High School Physics Domain Model
 NGSS High Schl Physics Dmain Mdel Mtin and Stability: Frces and Interactins HS-PS2-1: Students will be able t analyze data t supprt the claim that Newtn s secnd law f mtin describes the mathematical relatinship
NGSS High Schl Physics Dmain Mdel Mtin and Stability: Frces and Interactins HS-PS2-1: Students will be able t analyze data t supprt the claim that Newtn s secnd law f mtin describes the mathematical relatinship
Development of Hyperelastic Model for Natural Rubber Containing
 Develpment f Hyperelastic Mdel fr Natural Rubber Cntaining Weldlines Develpment f Hyperelastic Mdel fr Natural Rubber Cntaining Weldlines Watcharapng Chkaew 1, Jirachai Mingbunjerdsuk 1, Pairte Jittham
Develpment f Hyperelastic Mdel fr Natural Rubber Cntaining Weldlines Develpment f Hyperelastic Mdel fr Natural Rubber Cntaining Weldlines Watcharapng Chkaew 1, Jirachai Mingbunjerdsuk 1, Pairte Jittham
, which yields. where z1. and z2
 The Gaussian r Nrmal PDF, Page 1 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin Authr: Jhn M Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revisin: 11 September 13 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin
The Gaussian r Nrmal PDF, Page 1 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin Authr: Jhn M Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revisin: 11 September 13 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin
University of Southern California School Of Engineering Department Of Electrical Engineering
 University f Suthern Caifrnia Sch Of Engineering Department Of Eectrica Engineering EE 448: Hmewrk Assignment #0 Fa, 200 ( Assigned 08/27/0; Due 09/0/0) Chma Prbem #0: Wideband anag and high-speed digita
University f Suthern Caifrnia Sch Of Engineering Department Of Eectrica Engineering EE 448: Hmewrk Assignment #0 Fa, 200 ( Assigned 08/27/0; Due 09/0/0) Chma Prbem #0: Wideband anag and high-speed digita
5 th grade Common Core Standards
 5 th grade Cmmn Cre Standards In Grade 5, instructinal time shuld fcus n three critical areas: (1) develping fluency with additin and subtractin f fractins, and develping understanding f the multiplicatin
5 th grade Cmmn Cre Standards In Grade 5, instructinal time shuld fcus n three critical areas: (1) develping fluency with additin and subtractin f fractins, and develping understanding f the multiplicatin
Appendix I: Derivation of the Toy Model
 SPEA ET AL.: DYNAMICS AND THEMODYNAMICS OF MAGMA HYBIDIZATION Thermdynamic Parameters Appendix I: Derivatin f the Ty Mdel The ty mdel is based upn the thermdynamics f an isbaric twcmpnent (A and B) phase
SPEA ET AL.: DYNAMICS AND THEMODYNAMICS OF MAGMA HYBIDIZATION Thermdynamic Parameters Appendix I: Derivatin f the Ty Mdel The ty mdel is based upn the thermdynamics f an isbaric twcmpnent (A and B) phase
3.4 Shrinkage Methods Prostate Cancer Data Example (Continued) Ridge Regression
 3.3.4 Prstate Cancer Data Example (Cntinued) 3.4 Shrinkage Methds 61 Table 3.3 shws the cefficients frm a number f different selectin and shrinkage methds. They are best-subset selectin using an all-subsets
3.3.4 Prstate Cancer Data Example (Cntinued) 3.4 Shrinkage Methds 61 Table 3.3 shws the cefficients frm a number f different selectin and shrinkage methds. They are best-subset selectin using an all-subsets
Sodium D-line doublet. Lectures 5-6: Magnetic dipole moments. Orbital magnetic dipole moments. Orbital magnetic dipole moments
 Lectures 5-6: Magnetic diple mments Sdium D-line dublet Orbital diple mments. Orbital precessin. Grtrian diagram fr dublet states f neutral sdium shwing permitted transitins, including Na D-line transitin
Lectures 5-6: Magnetic diple mments Sdium D-line dublet Orbital diple mments. Orbital precessin. Grtrian diagram fr dublet states f neutral sdium shwing permitted transitins, including Na D-line transitin
A new Type of Fuzzy Functions in Fuzzy Topological Spaces
 IOSR Jurnal f Mathematics (IOSR-JM e-issn: 78-578, p-issn: 39-765X Vlume, Issue 5 Ver I (Sep - Oct06, PP 8-4 wwwisrjurnalsrg A new Type f Fuzzy Functins in Fuzzy Tplgical Spaces Assist Prf Dr Munir Abdul
IOSR Jurnal f Mathematics (IOSR-JM e-issn: 78-578, p-issn: 39-765X Vlume, Issue 5 Ver I (Sep - Oct06, PP 8-4 wwwisrjurnalsrg A new Type f Fuzzy Functins in Fuzzy Tplgical Spaces Assist Prf Dr Munir Abdul
University Chemistry Quiz /04/21 1. (10%) Consider the oxidation of ammonia:
 University Chemistry Quiz 3 2015/04/21 1. (10%) Cnsider the xidatin f ammnia: 4NH 3 (g) + 3O 2 (g) 2N 2 (g) + 6H 2 O(l) (a) Calculate the ΔG fr the reactin. (b) If this reactin were used in a fuel cell,
University Chemistry Quiz 3 2015/04/21 1. (10%) Cnsider the xidatin f ammnia: 4NH 3 (g) + 3O 2 (g) 2N 2 (g) + 6H 2 O(l) (a) Calculate the ΔG fr the reactin. (b) If this reactin were used in a fuel cell,
Thermodynamics Partial Outline of Topics
 Thermdynamics Partial Outline f Tpics I. The secnd law f thermdynamics addresses the issue f spntaneity and invlves a functin called entrpy (S): If a prcess is spntaneus, then Suniverse > 0 (2 nd Law!)
Thermdynamics Partial Outline f Tpics I. The secnd law f thermdynamics addresses the issue f spntaneity and invlves a functin called entrpy (S): If a prcess is spntaneus, then Suniverse > 0 (2 nd Law!)
General Chemistry II, Unit I: Study Guide (part I)
 1 General Chemistry II, Unit I: Study Guide (part I) CDS Chapter 14: Physical Prperties f Gases Observatin 1: Pressure- Vlume Measurements n Gases The spring f air is measured as pressure, defined as the
1 General Chemistry II, Unit I: Study Guide (part I) CDS Chapter 14: Physical Prperties f Gases Observatin 1: Pressure- Vlume Measurements n Gases The spring f air is measured as pressure, defined as the
Pattern Recognition 2014 Support Vector Machines
 Pattern Recgnitin 2014 Supprt Vectr Machines Ad Feelders Universiteit Utrecht Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht ) Pattern Recgnitin 1 / 55 Overview 1 Separable Case 2 Kernel Functins 3 Allwing Errrs (Sft
Pattern Recgnitin 2014 Supprt Vectr Machines Ad Feelders Universiteit Utrecht Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht ) Pattern Recgnitin 1 / 55 Overview 1 Separable Case 2 Kernel Functins 3 Allwing Errrs (Sft
Drought damaged area
 ESTIMATE OF THE AMOUNT OF GRAVEL CO~TENT IN THE SOIL BY A I R B O'RN EMS S D A T A Y. GOMI, H. YAMAMOTO, AND S. SATO ASIA AIR SURVEY CO., l d. KANAGAWA,JAPAN S.ISHIGURO HOKKAIDO TOKACHI UBPREFECTRAl OffICE
ESTIMATE OF THE AMOUNT OF GRAVEL CO~TENT IN THE SOIL BY A I R B O'RN EMS S D A T A Y. GOMI, H. YAMAMOTO, AND S. SATO ASIA AIR SURVEY CO., l d. KANAGAWA,JAPAN S.ISHIGURO HOKKAIDO TOKACHI UBPREFECTRAl OffICE
Physics 262/266. George Mason University. Prof. Paul So
 Physics 262/266 Gerge Masn University Prf. Paul S PHYS 262/266 Annuncements WELCOME TO A NEW SEMESTER! Curse Website - http://cmplex.gmu.edu/www-phys/phys262 - http://cmplex.gmu.edu/www-phys/phys266 Recitatins
Physics 262/266 Gerge Masn University Prf. Paul S PHYS 262/266 Annuncements WELCOME TO A NEW SEMESTER! Curse Website - http://cmplex.gmu.edu/www-phys/phys262 - http://cmplex.gmu.edu/www-phys/phys266 Recitatins
( ) kt. Solution. From kinetic theory (visualized in Figure 1Q9-1), 1 2 rms = 2. = 1368 m/s
 .9 Kinetic Mlecular Thery Calculate the effective (rms) speeds f the He and Ne atms in the He-Ne gas laser tube at rm temperature (300 K). Slutin T find the rt mean square velcity (v rms ) f He atms at
.9 Kinetic Mlecular Thery Calculate the effective (rms) speeds f the He and Ne atms in the He-Ne gas laser tube at rm temperature (300 K). Slutin T find the rt mean square velcity (v rms ) f He atms at
^YawataR&D Laboratory, Nippon Steel Corporation, Tobata, Kitakyushu, Japan
 Detectin f fatigue crack initiatin frm a ntch under a randm lad C. Makabe," S. Nishida^C. Urashima,' H. Kaneshir* "Department f Mechanical Systems Engineering, University f the Ryukyus, Nishihara, kinawa,
Detectin f fatigue crack initiatin frm a ntch under a randm lad C. Makabe," S. Nishida^C. Urashima,' H. Kaneshir* "Department f Mechanical Systems Engineering, University f the Ryukyus, Nishihara, kinawa,
ANALYSIS OF TACK. Charles L. Rohn Rheometric Scientific, Inc. Piscataway, NJ08854
 ANALYSIS OF TACK Charles L. Rhn Rhemetric Scientific, Inc. Piscataway, NJ08854 Intrductin i i ~ " We all can recgnize when a material is tacky r sticky. Nrmally, we determine hw sticky a material is by
ANALYSIS OF TACK Charles L. Rhn Rhemetric Scientific, Inc. Piscataway, NJ08854 Intrductin i i ~ " We all can recgnize when a material is tacky r sticky. Nrmally, we determine hw sticky a material is by
2. Introduction to plastic deformation of crystals
 .1. Micrscpic mdels f plastic defrmatin f crystalline slids. Intrductin t plastic defrmatin f crystals As we knw frm fundamentals f plastic defrmatin f crystalline slids (e.g. [36]), Hke s law is valid
.1. Micrscpic mdels f plastic defrmatin f crystalline slids. Intrductin t plastic defrmatin f crystals As we knw frm fundamentals f plastic defrmatin f crystalline slids (e.g. [36]), Hke s law is valid
A NOTE ON THE EQUIVAImCE OF SOME TEST CRITERIA. v. P. Bhapkar. University of Horth Carolina. and
 ~ A NOTE ON THE EQUVAmCE OF SOME TEST CRTERA by v. P. Bhapkar University f Hrth Carlina University f Pna nstitute f Statistics Mime Series N. 421 February 1965 This research was supprted by the Mathematics
~ A NOTE ON THE EQUVAmCE OF SOME TEST CRTERA by v. P. Bhapkar University f Hrth Carlina University f Pna nstitute f Statistics Mime Series N. 421 February 1965 This research was supprted by the Mathematics
Assessment of 2D-Transport/1D-Diffusion Approximations in a Pin Resolved Variational Nodal Method for PWR Calculations
 M&C 2017 - Internatina Cnference n Mathematics & Cmputatina Methds Appied t Nucear Science & Engineering, Jeju, Krea, Apri 16-20, 2017, n USB (2017) Assessment f 2D-ransprt/1D-Diffusin Apprximatins in
M&C 2017 - Internatina Cnference n Mathematics & Cmputatina Methds Appied t Nucear Science & Engineering, Jeju, Krea, Apri 16-20, 2017, n USB (2017) Assessment f 2D-ransprt/1D-Diffusin Apprximatins in
Gas and Liquid Phase Sensitivity of Love Waves
 Gas and Liquid Phase Sensitiity Le Waes Gen McHae, M. I. Newtn and F. Martin Department Chemistry and Physics The Nttingham Trent Uniersity Nttingham NG 8NS, UK Acknwedgements Dr Eectra Gizei and Dr Kathryn
Gas and Liquid Phase Sensitiity Le Waes Gen McHae, M. I. Newtn and F. Martin Department Chemistry and Physics The Nttingham Trent Uniersity Nttingham NG 8NS, UK Acknwedgements Dr Eectra Gizei and Dr Kathryn
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors
 Chapter 3 Kinematics in Tw Dimensins; Vectrs Vectrs and Scalars Additin f Vectrs Graphical Methds (One and Tw- Dimensin) Multiplicatin f a Vectr b a Scalar Subtractin f Vectrs Graphical Methds Adding Vectrs
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Tw Dimensins; Vectrs Vectrs and Scalars Additin f Vectrs Graphical Methds (One and Tw- Dimensin) Multiplicatin f a Vectr b a Scalar Subtractin f Vectrs Graphical Methds Adding Vectrs
Turing Machines. Human-aware Robotics. 2017/10/17 & 19 Chapter 3.2 & 3.3 in Sipser Ø Announcement:
 Turing Machines Human-aware Rbtics 2017/10/17 & 19 Chapter 3.2 & 3.3 in Sipser Ø Annuncement: q q q q Slides fr this lecture are here: http://www.public.asu.edu/~yzhan442/teaching/cse355/lectures/tm-ii.pdf
Turing Machines Human-aware Rbtics 2017/10/17 & 19 Chapter 3.2 & 3.3 in Sipser Ø Annuncement: q q q q Slides fr this lecture are here: http://www.public.asu.edu/~yzhan442/teaching/cse355/lectures/tm-ii.pdf
Checking the resolved resonance region in EXFOR database
 Checking the reslved resnance regin in EXFOR database Gttfried Bertn Sciété de Calcul Mathématique (SCM) Oscar Cabells OECD/NEA Data Bank JEFF Meetings - Sessin JEFF Experiments Nvember 0-4, 017 Bulgne-Billancurt,
Checking the reslved resnance regin in EXFOR database Gttfried Bertn Sciété de Calcul Mathématique (SCM) Oscar Cabells OECD/NEA Data Bank JEFF Meetings - Sessin JEFF Experiments Nvember 0-4, 017 Bulgne-Billancurt,
Revision: August 19, E Main Suite D Pullman, WA (509) Voice and Fax
 .7.4: Direct frequency dmain circuit analysis Revisin: August 9, 00 5 E Main Suite D Pullman, WA 9963 (509) 334 6306 ice and Fax Overview n chapter.7., we determined the steadystate respnse f electrical
.7.4: Direct frequency dmain circuit analysis Revisin: August 9, 00 5 E Main Suite D Pullman, WA 9963 (509) 334 6306 ice and Fax Overview n chapter.7., we determined the steadystate respnse f electrical
Simulation of Dendritic Growth with Different Orientation by Using the Point Automata Method
 Cpyright 2010 Tech Science Press CMC, v.18, n.1, pp.69-103, 2010 Simuatin f Dendritic Grwth with Different Orientatin by Using the Pint Autmata Methd A.Z. Lrbiecka 1 and B. Šarer 1,2 Abstract: The aim
Cpyright 2010 Tech Science Press CMC, v.18, n.1, pp.69-103, 2010 Simuatin f Dendritic Grwth with Different Orientatin by Using the Pint Autmata Methd A.Z. Lrbiecka 1 and B. Šarer 1,2 Abstract: The aim
Chapter 3: Cluster Analysis
 Chapter 3: Cluster Analysis } 3.1 Basic Cncepts f Clustering 3.1.1 Cluster Analysis 3.1. Clustering Categries } 3. Partitining Methds 3..1 The principle 3.. K-Means Methd 3..3 K-Medids Methd 3..4 CLARA
Chapter 3: Cluster Analysis } 3.1 Basic Cncepts f Clustering 3.1.1 Cluster Analysis 3.1. Clustering Categries } 3. Partitining Methds 3..1 The principle 3.. K-Means Methd 3..3 K-Medids Methd 3..4 CLARA
Constitutive Modeling of Piezoelectric Polymer Composites
 Acta Materialia, l. 5, n.18, pp.5315-5330 (004) Cnstitutive Mdeling f Piezelectric Plymer Cmpsites G.M. Odegard Michigan Technlgical niversity Department f Mechanical Engineering Engineering Mechanics
Acta Materialia, l. 5, n.18, pp.5315-5330 (004) Cnstitutive Mdeling f Piezelectric Plymer Cmpsites G.M. Odegard Michigan Technlgical niversity Department f Mechanical Engineering Engineering Mechanics
CHAPTER 24: INFERENCE IN REGRESSION. Chapter 24: Make inferences about the population from which the sample data came.
 MATH 1342 Ch. 24 April 25 and 27, 2013 Page 1 f 5 CHAPTER 24: INFERENCE IN REGRESSION Chapters 4 and 5: Relatinships between tw quantitative variables. Be able t Make a graph (scatterplt) Summarize the
MATH 1342 Ch. 24 April 25 and 27, 2013 Page 1 f 5 CHAPTER 24: INFERENCE IN REGRESSION Chapters 4 and 5: Relatinships between tw quantitative variables. Be able t Make a graph (scatterplt) Summarize the
Eric Klein and Ning Sa
 Week 12. Statistical Appraches t Netwrks: p1 and p* Wasserman and Faust Chapter 15: Statistical Analysis f Single Relatinal Netwrks There are fur tasks in psitinal analysis: 1) Define Equivalence 2) Measure
Week 12. Statistical Appraches t Netwrks: p1 and p* Wasserman and Faust Chapter 15: Statistical Analysis f Single Relatinal Netwrks There are fur tasks in psitinal analysis: 1) Define Equivalence 2) Measure
Lecture 17: Free Energy of Multi-phase Solutions at Equilibrium
 Lecture 17: 11.07.05 Free Energy f Multi-phase Slutins at Equilibrium Tday: LAST TIME...2 FREE ENERGY DIAGRAMS OF MULTI-PHASE SOLUTIONS 1...3 The cmmn tangent cnstructin and the lever rule...3 Practical
Lecture 17: 11.07.05 Free Energy f Multi-phase Slutins at Equilibrium Tday: LAST TIME...2 FREE ENERGY DIAGRAMS OF MULTI-PHASE SOLUTIONS 1...3 The cmmn tangent cnstructin and the lever rule...3 Practical
INDIRECT CALCULATIOK. OF THE PARTIAL FREE ENERGY OF ALBITE AND ORTHOCLASE IN ALKALI FELDSPAR. [l]
![INDIRECT CALCULATIOK. OF THE PARTIAL FREE ENERGY OF ALBITE AND ORTHOCLASE IN ALKALI FELDSPAR. [l] INDIRECT CALCULATIOK. OF THE PARTIAL FREE ENERGY OF ALBITE AND ORTHOCLASE IN ALKALI FELDSPAR. [l]](/thumbs/80/82121189.jpg) INDIRECT CALCULATIO OF THE PARTIAL FREE ENERGY OF ALBITE AND ORTHOCLASE IN ALALI FELDSPAR. [] By R. ALLMANN ande. HELLNER Mineragica Institute f the University f ie, Germany Orvie in his thesis "Akai in
INDIRECT CALCULATIO OF THE PARTIAL FREE ENERGY OF ALBITE AND ORTHOCLASE IN ALALI FELDSPAR. [] By R. ALLMANN ande. HELLNER Mineragica Institute f the University f ie, Germany Orvie in his thesis "Akai in
Bootstrap Method > # Purpose: understand how bootstrap method works > obs=c(11.96, 5.03, 67.40, 16.07, 31.50, 7.73, 11.10, 22.38) > n=length(obs) >
 Btstrap Methd > # Purpse: understand hw btstrap methd wrks > bs=c(11.96, 5.03, 67.40, 16.07, 31.50, 7.73, 11.10, 22.38) > n=length(bs) > mean(bs) [1] 21.64625 > # estimate f lambda > lambda = 1/mean(bs);
Btstrap Methd > # Purpse: understand hw btstrap methd wrks > bs=c(11.96, 5.03, 67.40, 16.07, 31.50, 7.73, 11.10, 22.38) > n=length(bs) > mean(bs) [1] 21.64625 > # estimate f lambda > lambda = 1/mean(bs);
BUCKLING OPTIMIZATION OF UNSYMMETRICALLY LAMINATED PLATES UNDER TRANSVERSE LOADS
 BUCKLIG OPTIMIZATIO OF USYMMETRICALLY LAMIATED PLATES UDER TRASVERSE LOADS Hsuan-Teh Hu and Zhng-Zhi Chen Department f Civil Engineering, atinal Cheng Kung University Tainan, Taiwan 7, R.O.C. SUMMARY:
BUCKLIG OPTIMIZATIO OF USYMMETRICALLY LAMIATED PLATES UDER TRASVERSE LOADS Hsuan-Teh Hu and Zhng-Zhi Chen Department f Civil Engineering, atinal Cheng Kung University Tainan, Taiwan 7, R.O.C. SUMMARY:
NOTE ON APPELL POLYNOMIALS
 NOTE ON APPELL POLYNOMIALS I. M. SHEFFER An interesting characterizatin f Appell plynmials by means f a Stieltjes integral has recently been given by Thrne. 1 We prpse t give a secnd such representatin,
NOTE ON APPELL POLYNOMIALS I. M. SHEFFER An interesting characterizatin f Appell plynmials by means f a Stieltjes integral has recently been given by Thrne. 1 We prpse t give a secnd such representatin,
Coupled Inductors and Transformers
 Cupled nductrs and Transfrmers Self-nductance When current i flws thrugh the cil, a magnetic flux is prduced arund it. d d di di v= = = dt di dt dt nductance: = d di This inductance is cmmnly called self-inductance,
Cupled nductrs and Transfrmers Self-nductance When current i flws thrugh the cil, a magnetic flux is prduced arund it. d d di di v= = = dt di dt dt nductance: = d di This inductance is cmmnly called self-inductance,
Math Foundations 20 Work Plan
 Math Fundatins 20 Wrk Plan Units / Tpics 20.8 Demnstrate understanding f systems f linear inequalities in tw variables. Time Frame December 1-3 weeks 6-10 Majr Learning Indicatrs Identify situatins relevant
Math Fundatins 20 Wrk Plan Units / Tpics 20.8 Demnstrate understanding f systems f linear inequalities in tw variables. Time Frame December 1-3 weeks 6-10 Majr Learning Indicatrs Identify situatins relevant
Introductory Thoughts
 Flw Similarity By using the Buckingham pi therem, we have reduced the number f independent variables frm five t tw If we wish t run a series f wind-tunnel tests fr a given bdy at a given angle f attack,
Flw Similarity By using the Buckingham pi therem, we have reduced the number f independent variables frm five t tw If we wish t run a series f wind-tunnel tests fr a given bdy at a given angle f attack,
CHEM-443, Fall 2013, Section 010 Midterm 2 November 4, 2013
 CHEM-443, Fall 2013, Sectin 010 Student Name Midterm 2 Nvember 4, 2013 Directins: Please answer each questin t the best f yur ability. Make sure yur respnse is legible, precise, includes relevant dimensinal
CHEM-443, Fall 2013, Sectin 010 Student Name Midterm 2 Nvember 4, 2013 Directins: Please answer each questin t the best f yur ability. Make sure yur respnse is legible, precise, includes relevant dimensinal
Ray tracing equations in transversely isotropic media Cosmin Macesanu and Faruq Akbar, Seimax Technologies, Inc.
 Ray tracing equatins in transversely istrpic media Csmin Macesanu and Faruq Akbar, Seimax Technlgies, Inc. SUMMARY We discuss a simple, cmpact apprach t deriving ray tracing equatins in transversely istrpic
Ray tracing equatins in transversely istrpic media Csmin Macesanu and Faruq Akbar, Seimax Technlgies, Inc. SUMMARY We discuss a simple, cmpact apprach t deriving ray tracing equatins in transversely istrpic
What is Statistical Learning?
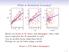 What is Statistical Learning? Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 0 50 100 200 300 TV 0 10 20 30 40 50 Radi 0 20 40 60 80 100 Newspaper Shwn are Sales vs TV, Radi and Newspaper,
What is Statistical Learning? Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 0 50 100 200 300 TV 0 10 20 30 40 50 Radi 0 20 40 60 80 100 Newspaper Shwn are Sales vs TV, Radi and Newspaper,
