CHAPTER 13 Temperature and Kinetic Theory. Units
|
|
|
- Ezra Atkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 13 Temperature and Kinetic Thery Units Atmic Thery f Matter Temperature and Thermmeters Thermal Equilibrium and the Zerth Law f Thermdynamics Thermal Expansin Thermal Stress The Gas Laws and Abslute Temperature The Ideal Gas Law Prblem Slving with the Ideal Gas Law Ideal Gas Law in Terms f Mlecules: Avgadr s Number Kinetic Thery and the Mlecular Interpretatin f Temperature Distributin f Mlecular Speeds Real Gases and Changes f Phase Vapr Pressure and Humidity Diffusin Atmic Thery f Matter Atmic and mlecular masses are measured in unified atmic mass units (u). This unit is defined s that the carbn-1 atm has a mass f exactly u. Expressed in kilgrams: Brwnian mtin is the jittery mtin f tiny flecks in water; these are the result f cllisins with individual water mlecules. On a micrscpic scale, the arrangements f mlecules in slids (a), liquids (b), and gases (c) are quite different. 1
2 Temperature and Thermmeters Temperature is a measure f hw ht r cld smething is. Mst materials expand when heated. Thermmeters are instruments designed t measure temperature. In rder t d this, they take advantage f sme prperty f matter that changes with temperature. Cmmn thermmeters used tday include the liquid-in-glass type and the bimetallic strip. Temperature is generally measured using either the Fahrenheit r the Celsius scale. The freezing pint f water is 0 C, r 3 F; the biling pint f water is 100 C, r 1 F. Kelvin Scale When the pressure f a gas ges t zer, its temperature is 73.15º C This temperature is called abslute zer This is the zer pint f the Kelvin scale 73.15º C = 0 K T cnvert: T C = T K The size f the degree in the Kelvin scale is the same as the size f a Celsius degree
3 Cmparing Temperature Scales Cnverting Amng Temperature Scales T C T K TF TC TC TF TF TC 5 Thermal Equilibrium and the Zerth Law f Thermdynamics Tw bjects placed in thermal cntact will eventually cme t the same temperature. When they d, we say they are in thermal equilibrium. The Zerth law f thermdynamics says that if tw bjects are each in equilibrium with a third bject, they are als in thermal equilibrium with each ther. Thermal Expansin The thermal expansin f an bject is a cnsequence f the change in the average separatin between its cnstituent atms r mlecules At rdinary temperatures, mlecules vibrate with a small amplitude As temperature increases, the amplitude increases This causes the verall bject as a whle t expand Linear expansin ccurs when an bject is heated. Here, α is the cefficient f linear expansin. Vlume expansin is similar, except that it is relevant fr liquids and gases as well as slids: Here, β is the cefficient f vlume expansin. Fr unifrm slids, 3
4 Example 1: Bridge Expansin The steel bed f a suspensin bridge is 00 m lng at 0 C. If the extremes f temperature t which it might be expsed are 30 C t 40 C, hw much will it cntract and expand? 6 L (1 x10 / C )(00 m)(40 C 0 C) 4.8x10 m expand 6 L (1 x10 / C)(00 m)( 50 C ) 1.0x10 m cntract Example : A steel railrad track has a length f 30,000 m when the temperature is 0 C. What is its length n a ht day when the temperature is 40 C? If the track can t mve what is the stress in the track due t the temperature change? 6 1 a) [11 10 ( L L T x C) ](40.0 C) 0.013m L L L m b) F L 0.013m A L 30.0m 11 7 Y (.00x10 Pa) 8.67x10 Pa Example 3: Ring n a Rd An irn ring is t fit snugly n a cylindrical irn rd. At 0 C, the diameter f the rd is cm and the inside diameter f the ring is 6.40 cm. T slip ver the rd, the ring must be slightly larger than the rd diameter by abut cm. T what temperature must the ring be brught if its hle is t be large enugh s it will slip ver the rd? L 6.453cm 6.40cm T 430C 6 1 L (1 x10 C )(6.40 cm) S it must be raised at least t: T (0 C 430 C ) 450 C Example 4: Gas tank in the sun The 70-L steel gas tank f a car is filled t the tp with gasline at 0 C. The car is then left t sit in the sun, and the tank reaches a temperature f 40 C. Hw much gasline d yu expect t verflw frm the tank? The gasline expands: 6 01 V V ( )(70 )(0 T x C L C ) 1.3L The tank increases in vlume by: 6 01 V (36x10 C )(70 L(0 C ) L 4
5 Water behaves differently frm mst ther slids its minimum vlume ccurs when its temperature is 4 C. As it cls further, it expands, as anyne wh has left a bttle in the freezer t cl and then frgets abut it can testify. Example 5: Glbal Warming and Castal Flding Estimate the fractinal change in the vlume f Earth s ceans due t an average temperature change f 1 3 C. Use the fact that the average depth f the cean is 4.00x10 m t estimate the 4 1 change in depth. Nte that water.07x10 ( C) a) Find the fractinal change in vlume V V T Divide the vlume expansin equatin by b) Find the apprximate increase in depth V and substitute V T (.07x10 ( C) x10 V L LT LT ( L x C) (4000 m)(1 C) 0.3m Unusual Behavir f Water As the temperature f water increases frm 0ºC t 4 ºC, it cntracts and its density increases Abve 4 ºC, water exhibits the expected expansin with increasing temperature Maximum density f water is 1000 kg/m 3 at 4 ºC Thermal Stresses A material may be fixed at its ends and therefre be unable t expand when the temperature changes. It will then experience large cmpressive r tensile stress thermal stress when its temperature changes. The frce required t keep the material frm expanding is given by: 5
6 where E is the Yung s mdulus f the material. Therefre, the stress is: F TEA Example 6: Stress in cncrete n a ht day A highway is t be made f blcks f cncrete 10 m lng placed end t end with n space in between them t allw fr expansin. If the blcks were placed at a temperature f 10 C, what frce f cmpressin wuld ccur if the temperature reached 40 C? The cntact area between each blck is 0.0 m. Will fracture ccur? F TEA 6 9 (1 10 / x C )(30 C )(0x10 N / m )(0.0 m ) 6 1.4x10 N The stress, F/A is (1.4 x10 N)/(0.0 m ) 7.0x10 N / m 6 6 This is nt far frm the ultimate strength f cncrete. Ideal Gas A gas des nt have a fixed vlume r pressure In a cntainer, the gas expands t fill the cntainer Mst gases at rm temperature and pressure behave apprximately as an ideal gas Characteristics f an Ideal Gas Mles Cllectin f atms r mlecules that mve randmly Exert n lng-range frce n ne anther Each particle is individually pint-like Occupying a negligible vlume It s cnvenient t express the amunt f gas in a given vlume in terms f the number f mles, n mass n mlar mass One mle is the amunt f the substance that cntains as many particles as there are atms in 1 g f carbn-1 Fr example, the number f mles in 13 g f CO is 13g n 3.0 ml. 44 g / ml This prprtin can be written as an equatin: PV nrt 6
7 Ideal Gas Law PV = n R T R is the Universal Gas Cnstant R = 8.31 J / mle. K R = L. atm / mle. K Is the equatin f state fr an ideal gas The Gas Laws and Abslute Temperature The relatinship between the vlume, pressure, temperature, and mass f a gas is called an equatin f state. We will deal here with gases that are nt t dense. Byle s Law: the vlume f a given amunt f gas is inversely prprtinal t the pressure as lng as the temperature is cnstant. The vlume is linearly prprtinal t the temperature, as lng as the temperature is smewhat abve the cndensatin pint and the pressure is cnstant: Extraplating, the vlume becmes zer at C; this temperature is called abslute zer. Prblem Slving with the Ideal Gas Law Useful facts and definitins: Standard temperature and pressure (STP) Vlume f 1 ml f an ideal gas is.4 L If the amunt f gas des nt change: 7
8 Always measure T in kelvins P must be the abslute pressure Example 7: Vlume f ne ml at STP Determine the vlume f 1.00 ml f any gas at STP, assuming it behaves like an ideal gas. nrt (1.00 ml)(8.315 J / ml K)(73 K) V 5 P (1.013 x10 N / m ) Since 1 liter is 1000cm 1x10 m, 1 ml f any gas has a vlume f.4 L at STP Example 8: The mass f gas 3 A flexible cntainer f xygen (O, mlecular mass = 3u) at STP has a vlume f 10.0m. What is the mass f gas enclsed? n 3 (10.0 m ) 3 3 (.4x10 m / ml) 446 ml. Since 1 ml has a mass f kg, the mass f xygen is.4x10 m (446 ml)(0.030 kg / ml) 14.3kg m 3 3 Ideal Gas Law in Terms f Mlecules: Avgadr s Number Since the gas cnstant is universal, the number f mlecules in ne mle is the same fr all gases. That number is called Avgadr s number: 3 NA 6.0x10 The number f mlecules in a gas is the number f mles times Avgadr s number: Kinetic Thery and the Mlecular Interpretatin f Temperature The mlecules interact nly by shrt-range frces during elastic cllisins The mlecules make elastic cllisins with the walls The gas under cnsideratin is a pure substance, all the mlecules are identical Pressure f an Ideal Gas The pressure is prprtinal t the number f mlecules per unit vlume and t the average translatinal kinetic energy f a mlecule 8
9 The pressure is prprtinal t the number f mlecules per unit vlume and t the average translatinal kinetic energy f the mlecule Pressure can be increased by Increasing the number f mlecules per unit vlume in the cntainer Increasing the average translatinal kinetic energy f the mlecules Increasing the temperature f the gas Example 9: The ideal gas law t analyze a system f gas. An ideal gas at 0 5 C and a pressure f 1.50x10 Pa is in a cntainer having a vlume f 1.00L. a) Determine the number f mles f gas in the cntainer: PV nrt PV (1.50 x10 Pa)(1.00 x10 m ) n 6.61x10 ml RT (8.31 J / ml K)(93 K) b) The gas pushes against a pistn, expanding t twice its riginal vlume, while the pressure falls t atmspheric pressure. Find the temperature after the gas expands t.00 L. Divide the ideal gas law fr the final state by the ideal gas law fr the initial state. Pf Vf nrt f Pf Vf Tf PV nrt PV T i i i i i i 5 PV f f (1.01 x10 Pa)(.00 L) Tf Ti 5 (93 K ) 395 K PV (1.50 x10 Pa)(1.00 L) i i Kinetic Thery and the Mlecular Interpretatin f Temperature cnt. Assumptins f kinetic thery: large number f mlecules, mving in randm directins with a variety f speeds mlecules are far apart, n average mlecules bey laws f classical mechanics and interact nly when clliding cllisins are perfectly elastic Temperature is prprtinal t the average kinetic energy f the mlecules 1 3 mv k T B The ttal kinetic energy is prprtinal t the abslute temperature 3 KEttal nrt Example 10: Mlecular KE What is the average translatinal kinetic energy f mlecules in a gas at37 C? 3 KE kt 3 ( / )(310 ) x J K K x J 9
10 Internal Energy In a mnatmic gas, the KE is the nly type f energy the mlecules can have U is the internal energy f the gas In a plyatmic gas, additinal pssibilities fr cntributins t the internal energy are rtatinal and vibratinal energy in the mlecules Speed f the Mlecules 3 U nrt Expressed as the rt-mean-square (rms) speed v rms 3 kb T 3 RT m M At a given temperature, lighter mlecules mve faster, n average, than heavier nes Lighter mlecules can mre easily reach escape speed frm the earth Example 11: Speeds f air mlecules What is the rms speed f air mlecules (O and N) at rm temperature (0 C )? Thus fr xygen 7 6 m( O ) (3)1.67 x10 kg) 5.3x10 kg 7 6 m( N) (8)(1.68 x10 kg) 4.7x10 kg v rms 3 3 kt (3)(1.38x10 J / K)(93 K) 6 m (5.3x10 kg) 480 m / s Fr nitrgen v = 510 m/s (abut 1000 mi/hr) Example 1: Armageddn! 4 A cmet half a km in radius cnsisting f ice at 73K hits Earth at a speed f 4x10 m / s (assume that all KE cnverts t thermal energy n impact and all thermal energy ges int warming the cmet. a) Calculate the vlume and mass f the ice (3.14)(500 ) V r m x m m V (917 kg / m )(5.3x10 m ) 4.80x10 kg b) Use cnservatin f energy t find the final temperature f the cmet material. 10
11 Qmelt Qwater Qvapr K 0 1 ml f mcwater Twater mlv mcsteamt steam mv 1 mc T K mv steam ( 373 ) 0 The first three terms are negligible cmpared t the KE. (0 ) v (4.00 x 10 m / s ) c 010 J / Kg K 4 5 T 373K 373K 3.98x10 K steam c) Assuming the steam retains a spherical shape and has the same initial vlume as the cmet, calculate the pressure f the steam using the ideal gas law. This law actually desn t apply t a system at such high pressure and temperature, but can be used t get an estimate. 11 1ml 15 n (4.80x10 kg).67x10 ml 0.018kg 13 5 nrt (.67x10 ml)(8.31 J / ml K)(3.98x10 K) 11 P 8 3 P 1.69x10 Pa V 5.3x10 m several 100 x greater than shear stress f steel Real Gases and Changes f Phase The curves here represent the behavir f the gas at different temperatures. The cler it gets, the farther the gas is frm ideal. In curve D, the gas becmes liquid; it begins cndensing at (b) and is entirely liquid at (a). The pint (c) is called the critical pint. Belw the critical temperature, the gas can liquefy if the pressure is sufficient; abve it, n amunt f pressure will suffice. 11
12 A PT diagram is called a phase diagram; it shws all three phases f matter. The slid-liquid transitin is melting r freezing; the liquid-vapr ne is biling r cndensing; and the slid-vapr ne is sublimatin. Phase diagram f water The triple pint is the nly pint where all three phases can cexist in equilibrium. Phase diagram f carbn dixide Vapr Pressure and Humidity An pen cntainer f water can evaprate, rather than bil, away. The fastest mlecules are escaping frm the water s surface, s evapratin is a cling prcess as well. The inverse prcess is called cndensatin. When the evapratin and cndensatin prcesses are in equilibrium, the vapr just abve the liquid is said t be saturated, and its pressure is the saturated vapr pressure. The saturated vapr pressure increases with temperature. 1
13 A liquid bils when its saturated vapr pressure equals the external pressure. Partial pressure is the pressure each cmpnent f a mixture f gases wuld exert if it were the nly gas present. The partial pressure f water in the air can be as lw as zer, and as high as the saturated vapr pressure at that temperature. Relative humidity is a measure f the saturatin f the air. When the humidity is high, it feels muggy; it is hard fr any mre water t evaprate. The dew pint is the temperature at which the air wuld be saturated with water. If the temperature ges belw the dew pint, dew, fg, r even rain may ccur. Diffusin Even withut stirring, a few drps f dye in water will gradually spread thrughut. This prcess is called diffusin. 13
14 Diffusin ccurs frm a regin f high cncentratin twards a regin f lwer cncentratin. The rate f diffusin is given by: In this equatin, D is the diffusin cnstant. 14
General Chemistry II, Unit I: Study Guide (part I)
 1 General Chemistry II, Unit I: Study Guide (part I) CDS Chapter 14: Physical Prperties f Gases Observatin 1: Pressure- Vlume Measurements n Gases The spring f air is measured as pressure, defined as the
1 General Chemistry II, Unit I: Study Guide (part I) CDS Chapter 14: Physical Prperties f Gases Observatin 1: Pressure- Vlume Measurements n Gases The spring f air is measured as pressure, defined as the
Physics 262/266. George Mason University. Prof. Paul So
 Physics 262/266 Gerge Masn University Prf. Paul S PHYS 262/266 Annuncements WELCOME TO A NEW SEMESTER! Curse Website - http://cmplex.gmu.edu/www-phys/phys262 - http://cmplex.gmu.edu/www-phys/phys266 Recitatins
Physics 262/266 Gerge Masn University Prf. Paul S PHYS 262/266 Annuncements WELCOME TO A NEW SEMESTER! Curse Website - http://cmplex.gmu.edu/www-phys/phys262 - http://cmplex.gmu.edu/www-phys/phys266 Recitatins
GASES. PV = nrt N 2 CH 4 CO 2 O 2 HCN N 2 O NO 2. Pressure & Boyle s Law Temperature & Charles s Law Avogadro s Law IDEAL GAS LAW
 GASES Pressure & Byle s Law Temperature & Charles s Law Avgadr s Law IDEAL GAS LAW PV = nrt N 2 CH 4 CO 2 O 2 HCN N 2 O NO 2 Earth s atmsphere: 78% N 2 21% O 2 sme Ar, CO 2 Sme Cmmn Gasses Frmula Name
GASES Pressure & Byle s Law Temperature & Charles s Law Avgadr s Law IDEAL GAS LAW PV = nrt N 2 CH 4 CO 2 O 2 HCN N 2 O NO 2 Earth s atmsphere: 78% N 2 21% O 2 sme Ar, CO 2 Sme Cmmn Gasses Frmula Name
State of matter characteristics solid Retains shape and volume
 **See attachment fr graphs States f matter The fundamental difference between states f matter is the distance between particles Gas Ttal disrder Much empty space Particles have cmpletely freedm f mtin
**See attachment fr graphs States f matter The fundamental difference between states f matter is the distance between particles Gas Ttal disrder Much empty space Particles have cmpletely freedm f mtin
Downloaded from Downloaded from
 MATTER IN OUR SURROUNDINGS Date Diagram Observatin Explanatin Cnclusin ACTIVITY 1.1 (10 marks) date n which the experiment was perfrmed. I have drawn a diagram. My diagram is neat. My diagram is well labeled.
MATTER IN OUR SURROUNDINGS Date Diagram Observatin Explanatin Cnclusin ACTIVITY 1.1 (10 marks) date n which the experiment was perfrmed. I have drawn a diagram. My diagram is neat. My diagram is well labeled.
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 13 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 13 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 13 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
( ) kt. Solution. From kinetic theory (visualized in Figure 1Q9-1), 1 2 rms = 2. = 1368 m/s
 .9 Kinetic Mlecular Thery Calculate the effective (rms) speeds f the He and Ne atms in the He-Ne gas laser tube at rm temperature (300 K). Slutin T find the rt mean square velcity (v rms ) f He atms at
.9 Kinetic Mlecular Thery Calculate the effective (rms) speeds f the He and Ne atms in the He-Ne gas laser tube at rm temperature (300 K). Slutin T find the rt mean square velcity (v rms ) f He atms at
Chapter 11: Atmosphere
 Chapter 11: Atmsphere Sectin 1: Atmspheric Basics Objectives 1. Describe the cmpsitin f the atmsphere. 2. Cmpare and cntrast the varius layers f the atmsphere. 3. Identify three methds f transferring energy
Chapter 11: Atmsphere Sectin 1: Atmspheric Basics Objectives 1. Describe the cmpsitin f the atmsphere. 2. Cmpare and cntrast the varius layers f the atmsphere. 3. Identify three methds f transferring energy
AP CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 6 NOTES THERMOCHEMISTRY
 AP CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 6 NOTES THERMOCHEMISTRY Energy- the capacity t d wrk r t prduce heat 1 st Law f Thermdynamics: Law f Cnservatin f Energy- energy can be cnverted frm ne frm t anther but it can be neither
AP CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 6 NOTES THERMOCHEMISTRY Energy- the capacity t d wrk r t prduce heat 1 st Law f Thermdynamics: Law f Cnservatin f Energy- energy can be cnverted frm ne frm t anther but it can be neither
Thermodynamics and Equilibrium
 Thermdynamics and Equilibrium Thermdynamics Thermdynamics is the study f the relatinship between heat and ther frms f energy in a chemical r physical prcess. We intrduced the thermdynamic prperty f enthalpy,
Thermdynamics and Equilibrium Thermdynamics Thermdynamics is the study f the relatinship between heat and ther frms f energy in a chemical r physical prcess. We intrduced the thermdynamic prperty f enthalpy,
General Chemistry II, Unit II: Study Guide (part 1)
 General Chemistry II, Unit II: Study Guide (part 1) CDS Chapter 21: Reactin Equilibrium in the Gas Phase General Chemistry II Unit II Part 1 1 Intrductin Sme chemical reactins have a significant amunt
General Chemistry II, Unit II: Study Guide (part 1) CDS Chapter 21: Reactin Equilibrium in the Gas Phase General Chemistry II Unit II Part 1 1 Intrductin Sme chemical reactins have a significant amunt
Physics 231 Lecture 31
 Physics 31 Lecture 31 Mi Main pints f tday s lecture: Heat and heat capacity: Q = cmδt Phase transitins and latent heat: Q = LΔm Mechanisms f heat flw. Cnductive heat flw ΔQ kat ( T1 ) H = = Δt L Examples
Physics 31 Lecture 31 Mi Main pints f tday s lecture: Heat and heat capacity: Q = cmδt Phase transitins and latent heat: Q = LΔm Mechanisms f heat flw. Cnductive heat flw ΔQ kat ( T1 ) H = = Δt L Examples
A) 0.77 N B) 0.24 N C) 0.63 N D) 0.31 N E) 0.86 N. v = ω k = 80 = 32 m/s. Ans: (32) 2 = 0.77 N
 Q1. A transverse sinusidal wave travelling n a string is given by: y (x,t) = 0.20 sin (2.5 x 80 t) (SI units). The length f the string is 2.0 m and its mass is 1.5 g. What is the magnitude f the tensin
Q1. A transverse sinusidal wave travelling n a string is given by: y (x,t) = 0.20 sin (2.5 x 80 t) (SI units). The length f the string is 2.0 m and its mass is 1.5 g. What is the magnitude f the tensin
Chapter Outline 4/28/2014. P-V Work. P-V Work. Isolated, Closed and Open Systems. Exothermic and Endothermic Processes. E = q + w
 Islated, Clsed and Open Systems 9.1 Energy as a Reactant r a Prduct 9.2 Transferring Heat and Ding Wrk 9.5 Heats f Reactin and Calrimetry 9.6 Hess s Law and Standard Heats f Reactin 9.7 Heats f Reactin
Islated, Clsed and Open Systems 9.1 Energy as a Reactant r a Prduct 9.2 Transferring Heat and Ding Wrk 9.5 Heats f Reactin and Calrimetry 9.6 Hess s Law and Standard Heats f Reactin 9.7 Heats f Reactin
Trimester 2 Exam 3 Study Guide Honors Chemistry. Honors Chemistry Exam 3 Review
 Trimester 2 Exam 3 Study Guide Hnrs Chemistry BOND POLARITY Hnrs Chemistry Exam 3 Review Identify whether a bnd is plar r nnplar based ff difference in electrnegativity btwn 2 atms (electrnegativity values
Trimester 2 Exam 3 Study Guide Hnrs Chemistry BOND POLARITY Hnrs Chemistry Exam 3 Review Identify whether a bnd is plar r nnplar based ff difference in electrnegativity btwn 2 atms (electrnegativity values
Recitation 06. n total = P total V/RT = (0.425 atm * 10.5 L) / ( L atm mol -1 K -1 * 338 K) = mol
 Recitatin 06 Mixture f Ideal Gases 1. Chapter 5: Exercise: 69 The partial pressure f CH 4 (g) is 0.175 atm and that f O 2 (g) is 0.250 atm in a mixture f the tw gases. a. What is the mle fractin f each
Recitatin 06 Mixture f Ideal Gases 1. Chapter 5: Exercise: 69 The partial pressure f CH 4 (g) is 0.175 atm and that f O 2 (g) is 0.250 atm in a mixture f the tw gases. a. What is the mle fractin f each
Thermochemistry. Thermochemistry
 Thermchemistry Petrucci, Harwd and Herring: Chapter 7 CHEM 1000A 3.0 Thermchemistry 1 Thermchemistry The study energy in chemical reactins A sub-discipline thermdynamics Thermdynamics studies the bulk
Thermchemistry Petrucci, Harwd and Herring: Chapter 7 CHEM 1000A 3.0 Thermchemistry 1 Thermchemistry The study energy in chemical reactins A sub-discipline thermdynamics Thermdynamics studies the bulk
Unit 11 Solutions- Guided Notes. What are alloys? What is the difference between heterogeneous and homogeneous mixtures?
 Name: Perid: Unit 11 Slutins- Guided Ntes Mixtures: What is a mixture and give examples? What is a pure substance? What are allys? What is the difference between hetergeneus and hmgeneus mixtures? Slutins:
Name: Perid: Unit 11 Slutins- Guided Ntes Mixtures: What is a mixture and give examples? What is a pure substance? What are allys? What is the difference between hetergeneus and hmgeneus mixtures? Slutins:
" 1 = # $H vap. Chapter 3 Problems
 Chapter 3 rblems rblem At 1 atmsphere pure Ge melts at 1232 K and bils at 298 K. he triple pint ccurs at =8.4x1-8 atm. Estimate the heat f vaprizatin f Ge. he heat f vaprizatin is estimated frm the Clausius
Chapter 3 rblems rblem At 1 atmsphere pure Ge melts at 1232 K and bils at 298 K. he triple pint ccurs at =8.4x1-8 atm. Estimate the heat f vaprizatin f Ge. he heat f vaprizatin is estimated frm the Clausius
Part One: Heat Changes and Thermochemistry. This aspect of Thermodynamics was dealt with in Chapter 6. (Review)
 CHAPTER 18: THERMODYNAMICS AND EQUILIBRIUM Part One: Heat Changes and Thermchemistry This aspect f Thermdynamics was dealt with in Chapter 6. (Review) A. Statement f First Law. (Sectin 18.1) 1. U ttal
CHAPTER 18: THERMODYNAMICS AND EQUILIBRIUM Part One: Heat Changes and Thermchemistry This aspect f Thermdynamics was dealt with in Chapter 6. (Review) A. Statement f First Law. (Sectin 18.1) 1. U ttal
Matter Content from State Frameworks and Other State Documents
 Atms and Mlecules Mlecules are made f smaller entities (atms) which are bnded tgether. Therefre mlecules are divisible. Miscnceptin: Element and atm are synnyms. Prper cnceptin: Elements are atms with
Atms and Mlecules Mlecules are made f smaller entities (atms) which are bnded tgether. Therefre mlecules are divisible. Miscnceptin: Element and atm are synnyms. Prper cnceptin: Elements are atms with
A.P. CHEMISTRY. SOLUTIONS AND ACID BASE CHEMISTRY. p 1
 A.P. CHEMISTRY. SOLUTIONS AND ACID BASE CHEMISTRY. p 1 (Nte: questins 1 t 14 are meant t be dne WITHOUT calculatrs!) 1.Which f the fllwing is prbably true fr a slid slute with a highly endthermic heat
A.P. CHEMISTRY. SOLUTIONS AND ACID BASE CHEMISTRY. p 1 (Nte: questins 1 t 14 are meant t be dne WITHOUT calculatrs!) 1.Which f the fllwing is prbably true fr a slid slute with a highly endthermic heat
CHEM 103 Calorimetry and Hess s Law
 CHEM 103 Calrimetry and Hess s Law Lecture Ntes March 23, 2006 Prf. Sevian Annuncements Exam #2 is next Thursday, March 30 Study guide, practice exam, and practice exam answer key are already psted n the
CHEM 103 Calrimetry and Hess s Law Lecture Ntes March 23, 2006 Prf. Sevian Annuncements Exam #2 is next Thursday, March 30 Study guide, practice exam, and practice exam answer key are already psted n the
Chemistry 114 First Hour Exam
 Chemistry 114 First Hur Exam Please shw all wrk fr partial credit Name: (4 pints) 1. (12 pints) Espress is made by frcing very ht water under high pressure thrugh finely grund, cmpacted cffee. (Wikipedia)
Chemistry 114 First Hur Exam Please shw all wrk fr partial credit Name: (4 pints) 1. (12 pints) Espress is made by frcing very ht water under high pressure thrugh finely grund, cmpacted cffee. (Wikipedia)
Chapter 17: Thermodynamics: Spontaneous and Nonspontaneous Reactions and Processes
 Chapter 17: hermdynamics: Spntaneus and Nnspntaneus Reactins and Prcesses Learning Objectives 17.1: Spntaneus Prcesses Cmparing and Cntrasting the hree Laws f hermdynamics (1 st Law: Chap. 5; 2 nd & 3
Chapter 17: hermdynamics: Spntaneus and Nnspntaneus Reactins and Prcesses Learning Objectives 17.1: Spntaneus Prcesses Cmparing and Cntrasting the hree Laws f hermdynamics (1 st Law: Chap. 5; 2 nd & 3
Phy 212: General Physics II 1 Chapter 18 Worksheet 3/20/2008
 Phy 1: General Physics II 1 hapter 18 rksheet 3/0/008 Thermal Expansin: 1. A wedding ring cmpsed f pure gld (inner diameter = 1.5 x 10 - m) is placed n a persn s finger (diameter = 1.5 x 10 - m). Bth the
Phy 1: General Physics II 1 hapter 18 rksheet 3/0/008 Thermal Expansin: 1. A wedding ring cmpsed f pure gld (inner diameter = 1.5 x 10 - m) is placed n a persn s finger (diameter = 1.5 x 10 - m). Bth the
Electric Current and Resistance
 Electric Current and Resistance Electric Current Electric current is the rate f flw f charge thrugh sme regin f space The SI unit f current is the ampere (A) 1 A = 1 C / s The symbl fr electric current
Electric Current and Resistance Electric Current Electric current is the rate f flw f charge thrugh sme regin f space The SI unit f current is the ampere (A) 1 A = 1 C / s The symbl fr electric current
Spontaneous Processes, Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Chemical Thermdynamics Spntaneus Prcesses, Entrpy and the Secnd Law f Thermdynamics Review Reactin Rates, Energies, and Equilibrium Althugh a reactin may be energetically favrable (i.e. prducts have lwer
Chemical Thermdynamics Spntaneus Prcesses, Entrpy and the Secnd Law f Thermdynamics Review Reactin Rates, Energies, and Equilibrium Althugh a reactin may be energetically favrable (i.e. prducts have lwer
Lecture 17: Free Energy of Multi-phase Solutions at Equilibrium
 Lecture 17: 11.07.05 Free Energy f Multi-phase Slutins at Equilibrium Tday: LAST TIME...2 FREE ENERGY DIAGRAMS OF MULTI-PHASE SOLUTIONS 1...3 The cmmn tangent cnstructin and the lever rule...3 Practical
Lecture 17: 11.07.05 Free Energy f Multi-phase Slutins at Equilibrium Tday: LAST TIME...2 FREE ENERGY DIAGRAMS OF MULTI-PHASE SOLUTIONS 1...3 The cmmn tangent cnstructin and the lever rule...3 Practical
Unit 9: The Mole- Guided Notes What is a Mole?
 Unit 9: The Mle- Guided Ntes What is a Mle? A mle is a name fr a specific f things Similar t a r a One mle is equal t 602 602,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 That s 602 with zers A mle is NOT an abbreviatin
Unit 9: The Mle- Guided Ntes What is a Mle? A mle is a name fr a specific f things Similar t a r a One mle is equal t 602 602,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 That s 602 with zers A mle is NOT an abbreviatin
Chapter 10. Thermal Physics
 Chapter 10 Thermal Physics Thermal Physics Thermal physics is the study of Temperature Heat How these affect matter Thermal Physics, cont Descriptions require definitions of temperature, heat and internal
Chapter 10 Thermal Physics Thermal Physics Thermal physics is the study of Temperature Heat How these affect matter Thermal Physics, cont Descriptions require definitions of temperature, heat and internal
Natural Sciences I. lecture 7: Heat & Temperature. The Kinetic Molecular Theory
 Natural Sciences I The Kinetic Mlecular Thery lecture 7: Heat & Temperature 1 having t d with grups f atms having t d with mtin The idea that substances are cmpsed f tiny particles (atms) can be traced
Natural Sciences I The Kinetic Mlecular Thery lecture 7: Heat & Temperature 1 having t d with grups f atms having t d with mtin The idea that substances are cmpsed f tiny particles (atms) can be traced
15.0 g Cr = 21.9 g Cr O g Cr 4 mol Cr mol Cr O
 WYSE Academic Challenge Sectinal Chemistry Exam 2008 SOLUTION SET 1. Crrect answer: B. Use PV = nrt t get: PV = nrt 2. Crrect answer: A. (2.18 atm)(25.0 L) = n(0.08206 L atm/ml K)(23+273) n = 2.24 ml Assume
WYSE Academic Challenge Sectinal Chemistry Exam 2008 SOLUTION SET 1. Crrect answer: B. Use PV = nrt t get: PV = nrt 2. Crrect answer: A. (2.18 atm)(25.0 L) = n(0.08206 L atm/ml K)(23+273) n = 2.24 ml Assume
Chapters 29 and 35 Thermochemistry and Chemical Thermodynamics
 Chapters 9 and 35 Thermchemistry and Chemical Thermdynamics 1 Cpyright (c) 011 by Michael A. Janusa, PhD. All rights reserved. Thermchemistry Thermchemistry is the study f the energy effects that accmpany
Chapters 9 and 35 Thermchemistry and Chemical Thermdynamics 1 Cpyright (c) 011 by Michael A. Janusa, PhD. All rights reserved. Thermchemistry Thermchemistry is the study f the energy effects that accmpany
CHAPTER 8b Static Equilibrium Units
 CHAPTER 8b Static Equilibrium Units The Cnditins fr Equilibrium Slving Statics Prblems Stability and Balance Elasticity; Stress and Strain The Cnditins fr Equilibrium An bject with frces acting n it, but
CHAPTER 8b Static Equilibrium Units The Cnditins fr Equilibrium Slving Statics Prblems Stability and Balance Elasticity; Stress and Strain The Cnditins fr Equilibrium An bject with frces acting n it, but
Materials Engineering 272-C Fall 2001, Lecture 7 & 8 Fundamentals of Diffusion
 Materials Engineering 272-C Fall 2001, Lecture 7 & 8 Fundamentals f Diffusin Diffusin: Transprt in a slid, liquid, r gas driven by a cncentratin gradient (r, in the case f mass transprt, a chemical ptential
Materials Engineering 272-C Fall 2001, Lecture 7 & 8 Fundamentals f Diffusin Diffusin: Transprt in a slid, liquid, r gas driven by a cncentratin gradient (r, in the case f mass transprt, a chemical ptential
Phys101 Final Code: 1 Term: 132 Wednesday, May 21, 2014 Page: 1
 Phys101 Final Cde: 1 Term: 1 Wednesday, May 1, 014 Page: 1 Q1. A car accelerates at.0 m/s alng a straight rad. It passes tw marks that are 0 m apart at times t = 4.0 s and t = 5.0 s. Find the car s velcity
Phys101 Final Cde: 1 Term: 1 Wednesday, May 1, 014 Page: 1 Q1. A car accelerates at.0 m/s alng a straight rad. It passes tw marks that are 0 m apart at times t = 4.0 s and t = 5.0 s. Find the car s velcity
Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry. Topic 1: Principles of chemistry. Chemical formulae, equations and calculations. Notes.
 Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry Tpic 1: Principles f chemistry Chemical frmulae, equatins and calculatins Ntes 1.25 write wrd equatins and balanced chemical equatins (including state symbls): fr reactins studied
Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry Tpic 1: Principles f chemistry Chemical frmulae, equatins and calculatins Ntes 1.25 write wrd equatins and balanced chemical equatins (including state symbls): fr reactins studied
Lecture 4. The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Lecture 4. The First Law f Thermdynamics THERMODYNAMICS: Basic Cncepts Thermdynamics: (frm the Greek therme, meaning "heat" and, dynamis, meaning "pwer") is the study f energy cnversin between heat and
Lecture 4. The First Law f Thermdynamics THERMODYNAMICS: Basic Cncepts Thermdynamics: (frm the Greek therme, meaning "heat" and, dynamis, meaning "pwer") is the study f energy cnversin between heat and
Phys102 First Major-122 Zero Version Coordinator: Sunaidi Wednesday, March 06, 2013 Page: 1
 Crdinatr: Sunaidi Wednesday, March 06, 2013 Page: 1 Q1. An 8.00 m lng wire with a mass f 10.0 g is under a tensin f 25.0 N. A transverse wave fr which the wavelength is 0.100 m, and the amplitude is 3.70
Crdinatr: Sunaidi Wednesday, March 06, 2013 Page: 1 Q1. An 8.00 m lng wire with a mass f 10.0 g is under a tensin f 25.0 N. A transverse wave fr which the wavelength is 0.100 m, and the amplitude is 3.70
CHEM 116 Concentrations and Colligative Properties
 UMass stn, Chem 116 CHEM 116 Cncentratins and Clligative Prperties FSG is Mndays 11:00 am Lecture 10 Prf. Sevian and Tuesdays 3:30 pm bth in S-1-89 Tday s agenda Ways f expressing cncentratin Clligative
UMass stn, Chem 116 CHEM 116 Cncentratins and Clligative Prperties FSG is Mndays 11:00 am Lecture 10 Prf. Sevian and Tuesdays 3:30 pm bth in S-1-89 Tday s agenda Ways f expressing cncentratin Clligative
Lecture 23: Lattice Models of Materials; Modeling Polymer Solutions
 Lecture 23: 12.05.05 Lattice Mdels f Materials; Mdeling Plymer Slutins Tday: LAST TIME...2 The Bltzmann Factr and Partitin Functin: systems at cnstant temperature...2 A better mdel: The Debye slid...3
Lecture 23: 12.05.05 Lattice Mdels f Materials; Mdeling Plymer Slutins Tday: LAST TIME...2 The Bltzmann Factr and Partitin Functin: systems at cnstant temperature...2 A better mdel: The Debye slid...3
Compressibility Effects
 Definitin f Cmpressibility All real substances are cmpressible t sme greater r lesser extent; that is, when yu squeeze r press n them, their density will change The amunt by which a substance can be cmpressed
Definitin f Cmpressibility All real substances are cmpressible t sme greater r lesser extent; that is, when yu squeeze r press n them, their density will change The amunt by which a substance can be cmpressed
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
Thermodynamics Partial Outline of Topics
 Thermdynamics Partial Outline f Tpics I. The secnd law f thermdynamics addresses the issue f spntaneity and invlves a functin called entrpy (S): If a prcess is spntaneus, then Suniverse > 0 (2 nd Law!)
Thermdynamics Partial Outline f Tpics I. The secnd law f thermdynamics addresses the issue f spntaneity and invlves a functin called entrpy (S): If a prcess is spntaneus, then Suniverse > 0 (2 nd Law!)
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
Chem 116 POGIL Worksheet - Week 3 - Solutions Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, Solids, and Solutions
 Chem 116 POGIL Wrksheet - Week 3 - Slutins Intermlecular Frces, Liquids, Slids, and Slutins Key Questins 1. Is the average kinetic energy f mlecules greater r lesser than the energy f intermlecular frces
Chem 116 POGIL Wrksheet - Week 3 - Slutins Intermlecular Frces, Liquids, Slids, and Slutins Key Questins 1. Is the average kinetic energy f mlecules greater r lesser than the energy f intermlecular frces
Chem 75 February 16, 2017 Exam 2 Solutions
 1. (6 + 6 pints) Tw quick questins: (a) The Handbk f Chemistry and Physics tells us, crrectly, that CCl 4 bils nrmally at 76.7 C, but its mlar enthalpy f vaprizatin is listed in ne place as 34.6 kj ml
1. (6 + 6 pints) Tw quick questins: (a) The Handbk f Chemistry and Physics tells us, crrectly, that CCl 4 bils nrmally at 76.7 C, but its mlar enthalpy f vaprizatin is listed in ne place as 34.6 kj ml
Lecture 12: Chemical reaction equilibria
 3.012 Fundamentals f Materials Science Fall 2005 Lecture 12: 10.19.05 Chemical reactin equilibria Tday: LAST TIME...2 EQUATING CHEMICAL POTENTIALS DURING REACTIONS...3 The extent f reactin...3 The simplest
3.012 Fundamentals f Materials Science Fall 2005 Lecture 12: 10.19.05 Chemical reactin equilibria Tday: LAST TIME...2 EQUATING CHEMICAL POTENTIALS DURING REACTIONS...3 The extent f reactin...3 The simplest
Session #22: Homework Solutions
 Sessin #22: Hmewrk Slutins Prblem #1 (a) In the cntext f amrphus inrganic cmpunds, name tw netwrk frmers, tw netwrk mdifiers, and ne intermediate. (b) Sketch the variatin f mlar vlume with temperature
Sessin #22: Hmewrk Slutins Prblem #1 (a) In the cntext f amrphus inrganic cmpunds, name tw netwrk frmers, tw netwrk mdifiers, and ne intermediate. (b) Sketch the variatin f mlar vlume with temperature
Chapter One. Matter and Energy - Chemistry the study of matter and its changes the "central science" Natural Laws
 Chapter One Matter and Measurement http://www.chemistry.armstrng.edu/ nivens/curse_list.htm OWL HOMEWORK REQUIRED!!! Matter and Energy - Chemistry the study f matter and its changes the "central science"
Chapter One Matter and Measurement http://www.chemistry.armstrng.edu/ nivens/curse_list.htm OWL HOMEWORK REQUIRED!!! Matter and Energy - Chemistry the study f matter and its changes the "central science"
More Tutorial at
 Answer each questin in the space prvided; use back f page if extra space is needed. Answer questins s the grader can READILY understand yur wrk; nly wrk n the exam sheet will be cnsidered. Write answers,
Answer each questin in the space prvided; use back f page if extra space is needed. Answer questins s the grader can READILY understand yur wrk; nly wrk n the exam sheet will be cnsidered. Write answers,
GOAL... ability to predict
 THERMODYNAMICS Chapter 18, 11.5 Study f changes in energy and transfers f energy (system < = > surrundings) that accmpany chemical and physical prcesses. GOAL............................. ability t predict
THERMODYNAMICS Chapter 18, 11.5 Study f changes in energy and transfers f energy (system < = > surrundings) that accmpany chemical and physical prcesses. GOAL............................. ability t predict
Chapter 17 Free Energy and Thermodynamics
 Chemistry: A Mlecular Apprach, 1 st Ed. Nivald Tr Chapter 17 Free Energy and Thermdynamics Ry Kennedy Massachusetts Bay Cmmunity Cllege Wellesley Hills, MA 2008, Prentice Hall First Law f Thermdynamics
Chemistry: A Mlecular Apprach, 1 st Ed. Nivald Tr Chapter 17 Free Energy and Thermdynamics Ry Kennedy Massachusetts Bay Cmmunity Cllege Wellesley Hills, MA 2008, Prentice Hall First Law f Thermdynamics
MIDTERM EXAM SOLUTIONS
 MIDTERM EXAM SOLUTIONS Science A30 The Atmsphere March 0, 008 INSTRUCTIONS WRITE YOUR NAME ON EVERY PAGE. Exam will last 80 minutes. Cmplete the prblems directly n the exam. Extra paper available if needed.
MIDTERM EXAM SOLUTIONS Science A30 The Atmsphere March 0, 008 INSTRUCTIONS WRITE YOUR NAME ON EVERY PAGE. Exam will last 80 minutes. Cmplete the prblems directly n the exam. Extra paper available if needed.
Heat is energy and is measured in joules (J) or kilojoules (kj). The symbol for heat is H.
 Causes f Change Calrimetry Hw Des Energy Affect Change? Heat vs. Temerature HEAT TEMPERATURE Definitin: Deends n: Examles: Heat is energy and is measured in jules (J) r kiljules (kj). The symbl fr heat
Causes f Change Calrimetry Hw Des Energy Affect Change? Heat vs. Temerature HEAT TEMPERATURE Definitin: Deends n: Examles: Heat is energy and is measured in jules (J) r kiljules (kj). The symbl fr heat
Study Group Report: Plate-fin Heat Exchangers: AEA Technology
 Study Grup Reprt: Plate-fin Heat Exchangers: AEA Technlgy The prblem under study cncerned the apparent discrepancy between a series f experiments using a plate fin heat exchanger and the classical thery
Study Grup Reprt: Plate-fin Heat Exchangers: AEA Technlgy The prblem under study cncerned the apparent discrepancy between a series f experiments using a plate fin heat exchanger and the classical thery
Thermodynamics: Gas Laws
 hermdynamics: Gas Laws Resurces: Serway emperature & hermal Expansin: 10.1, 10.2, & 10.3 Ideal Gas Law: 10.4 & 10.5 AP Physics B Vides Physics B Lessn 25: Mechanical Equivalent f Heat Physics B Lessn 26:
hermdynamics: Gas Laws Resurces: Serway emperature & hermal Expansin: 10.1, 10.2, & 10.3 Ideal Gas Law: 10.4 & 10.5 AP Physics B Vides Physics B Lessn 25: Mechanical Equivalent f Heat Physics B Lessn 26:
Downloaded from
 SUARY * Gas Laws:. yle's law: Fr a given mass f an ideal gas at cnstant temperature, the vlume f a gas is inversely prprtinal t its pressure, i.e. α r cnstant m ( i) cnstant cnstant r m Where density,,
SUARY * Gas Laws:. yle's law: Fr a given mass f an ideal gas at cnstant temperature, the vlume f a gas is inversely prprtinal t its pressure, i.e. α r cnstant m ( i) cnstant cnstant r m Where density,,
EXAM #1 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 103 Spring, 2016
 OBJECTIVES 1. Ft Pressure EXAM #1 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 103 Spring, 2016 Determine the surface area f an bject. Given the weight and surface area, calculate the pressure. 2. Measuring Vlume & Mass Prvided a
OBJECTIVES 1. Ft Pressure EXAM #1 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 103 Spring, 2016 Determine the surface area f an bject. Given the weight and surface area, calculate the pressure. 2. Measuring Vlume & Mass Prvided a
1/2 and e0 e s ' 1+ imm w 4 M s 3 πρ0 r 3 m. n 0 ktr. .Also,since n 0 ktr 1,wehave. 4 3 M sπρ 0 r 3. ktr. 3 M sπρ 0
 Chapter 6 6.1 Shw that fr a very weak slutin drplet (m 4 3 πr3 ρ 0 M s ), (6.8) can be written as e 0 ' 1+ a r b r 3 where a σ 0 /n 0 kt and b imm w / 4 3 M sπρ 0. What is yur interpretatin f thecnd and
Chapter 6 6.1 Shw that fr a very weak slutin drplet (m 4 3 πr3 ρ 0 M s ), (6.8) can be written as e 0 ' 1+ a r b r 3 where a σ 0 /n 0 kt and b imm w / 4 3 M sπρ 0. What is yur interpretatin f thecnd and
Unit 14 Thermochemistry Notes
 Name KEY Perid CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 14 Thermchemistry Ntes Quiz Date Exam Date Lab Dates Ntes, Hmewrk, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS lcated n CRHS Academic Chemistry Website: https://cincchem.pbwrks.cm
Name KEY Perid CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 14 Thermchemistry Ntes Quiz Date Exam Date Lab Dates Ntes, Hmewrk, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS lcated n CRHS Academic Chemistry Website: https://cincchem.pbwrks.cm
QCE Chemistry. Year 2015 Mark 0.00 Pages 20 Published Jan 31, Chemistry: Revision Notes. By Sophie (1 ATAR)
 QCE Chemistry Year 2015 Mark 0.00 Pages 20 Published Jan 31, 2017 11 Chemistry: Revisin Ntes By Sphie (1 ATAR) Pwered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.rg) Yur ntes authr, Sphie. Sphie achieved an ATAR f 1 in 2016 while
QCE Chemistry Year 2015 Mark 0.00 Pages 20 Published Jan 31, 2017 11 Chemistry: Revisin Ntes By Sphie (1 ATAR) Pwered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.rg) Yur ntes authr, Sphie. Sphie achieved an ATAR f 1 in 2016 while
CHAPTER PRACTICE PROBLEMS CHEMISTRY
 Chemical Kinetics Name: Batch: Date: Rate f reactin. 4NH 3 (g) + 5O (g) à 4NO (g) + 6 H O (g) If the rate f frmatin f NO is 3.6 0 3 ml L s, calculate (i) the rate f disappearance f NH 3 (ii) rate f frmatin
Chemical Kinetics Name: Batch: Date: Rate f reactin. 4NH 3 (g) + 5O (g) à 4NO (g) + 6 H O (g) If the rate f frmatin f NO is 3.6 0 3 ml L s, calculate (i) the rate f disappearance f NH 3 (ii) rate f frmatin
Phys102 Final-061 Zero Version Coordinator: Nasser Wednesday, January 24, 2007 Page: 1
 Crdinatr: Nasser Wednesday, January 4, 007 Page: 1 Q1. Tw transmitters, S 1 and S shwn in the figure, emit identical sund waves f wavelength λ. The transmitters are separated by a distance λ /. Cnsider
Crdinatr: Nasser Wednesday, January 4, 007 Page: 1 Q1. Tw transmitters, S 1 and S shwn in the figure, emit identical sund waves f wavelength λ. The transmitters are separated by a distance λ /. Cnsider
Course/ Subject: Chemistry I Grade: Teacher: Hill Oberto Month: September/October (6-8 weeks)
 Curse/ Subject: Chemistry I Grade: 11-12 Teacher: Hill Obert Mnth: September/Octber (6-8 weeks) Natinal Benchmark being addressed State Standards Skills/Cmpetencies Assessment Matter Unit I.All matter
Curse/ Subject: Chemistry I Grade: 11-12 Teacher: Hill Obert Mnth: September/Octber (6-8 weeks) Natinal Benchmark being addressed State Standards Skills/Cmpetencies Assessment Matter Unit I.All matter
Chemistry/ Biotechnology Reference Sheets
 Cmmn Metric Prefixes: Giga (G) = 1,000,000,000 = Kil (k) = 1,000 = Deci (d) =.1 = Milli (m) =.001 = Nan (n) =.000000001 = 9 6 1 10 Mega (M) = 1,000,000 = 1 10 0 1 10 Basic unit = meter, gram, liter, secnd
Cmmn Metric Prefixes: Giga (G) = 1,000,000,000 = Kil (k) = 1,000 = Deci (d) =.1 = Milli (m) =.001 = Nan (n) =.000000001 = 9 6 1 10 Mega (M) = 1,000,000 = 1 10 0 1 10 Basic unit = meter, gram, liter, secnd
Solution to HW14 Fall-2002
 Slutin t HW14 Fall-2002 CJ5 10.CQ.003. REASONING AND SOLUTION Figures 10.11 and 10.14 shw the velcity and the acceleratin, respectively, the shadw a ball that underges unirm circular mtin. The shadw underges
Slutin t HW14 Fall-2002 CJ5 10.CQ.003. REASONING AND SOLUTION Figures 10.11 and 10.14 shw the velcity and the acceleratin, respectively, the shadw a ball that underges unirm circular mtin. The shadw underges
CHEM 116 Electrochemistry at Non-Standard Conditions, and Intro to Thermodynamics
 CHEM 116 Electrchemistry at Nn-Standard Cnditins, and Intr t Thermdynamics Imprtant annuncement: If yu brrwed a clicker frm me this semester, return it t me at the end f next lecture r at the final exam
CHEM 116 Electrchemistry at Nn-Standard Cnditins, and Intr t Thermdynamics Imprtant annuncement: If yu brrwed a clicker frm me this semester, return it t me at the end f next lecture r at the final exam
Edexcel GCSE Physics
 Edexcel GCSE Physics Tpic 10: Electricity and circuits Ntes (Cntent in bld is fr Higher Tier nly) www.pmt.educatin The Structure f the Atm Psitively charged nucleus surrunded by negatively charged electrns
Edexcel GCSE Physics Tpic 10: Electricity and circuits Ntes (Cntent in bld is fr Higher Tier nly) www.pmt.educatin The Structure f the Atm Psitively charged nucleus surrunded by negatively charged electrns
Autumn 2012 CHEM452B Bruce H. Robinson 322 Gould Hall HW 10(A) Homework 10A KEY (there will not be a 10B) 2
 Autumn 0 CHEM45B Bruce H. Rbinsn Guld Hall HW 0(A) Hmewrk 0A KEY (there will nt be a 0B) QA) Let c be the speed f sund in air. he square f the speed f sund, () f the gas with respect t the change in the
Autumn 0 CHEM45B Bruce H. Rbinsn Guld Hall HW 0(A) Hmewrk 0A KEY (there will nt be a 0B) QA) Let c be the speed f sund in air. he square f the speed f sund, () f the gas with respect t the change in the
Study Guide Physics Pre-Comp 2013
 I. Scientific Measurement Metric Units S.I. English Length Meter (m) Feet (ft.) Mass Kilgram (kg) Pund (lb.) Weight Newtn (N) Ounce (z.) r pund (lb.) Time Secnds (s) Secnds (s) Vlume Liter (L) Galln (gal)
I. Scientific Measurement Metric Units S.I. English Length Meter (m) Feet (ft.) Mass Kilgram (kg) Pund (lb.) Weight Newtn (N) Ounce (z.) r pund (lb.) Time Secnds (s) Secnds (s) Vlume Liter (L) Galln (gal)
Types of Energy COMMON MISCONCEPTIONS CHEMICAL REACTIONS INVOLVE ENERGY
 CHEMICAL REACTIONS INVOLVE ENERGY The study energy and its transrmatins is knwn as thermdynamics. The discussin thermdynamics invlve the cncepts energy, wrk, and heat. Types Energy Ptential energy is stred
CHEMICAL REACTIONS INVOLVE ENERGY The study energy and its transrmatins is knwn as thermdynamics. The discussin thermdynamics invlve the cncepts energy, wrk, and heat. Types Energy Ptential energy is stred
CHEM Thermodynamics. Change in Gibbs Free Energy, G. Review. Gibbs Free Energy, G. Review
 Review Accrding t the nd law f Thermdynamics, a prcess is spntaneus if S universe = S system + S surrundings > 0 Even thugh S system
Review Accrding t the nd law f Thermdynamics, a prcess is spntaneus if S universe = S system + S surrundings > 0 Even thugh S system
Midterm Review Notes - Unit 1 Intro
 Midterm Review Ntes - Unit 1 Intr 3 States f Matter Slid definite shape, definite vlume, very little mlecular mvement Liquid definite vlume, takes shape f cntainer, mlecules mve faster Gas des nt have
Midterm Review Ntes - Unit 1 Intr 3 States f Matter Slid definite shape, definite vlume, very little mlecular mvement Liquid definite vlume, takes shape f cntainer, mlecules mve faster Gas des nt have
Surface and Contact Stress
 Surface and Cntact Stress The cncept f the frce is fundamental t mechanics and many imprtant prblems can be cast in terms f frces nly, fr example the prblems cnsidered in Chapter. Hwever, mre sphisticated
Surface and Cntact Stress The cncept f the frce is fundamental t mechanics and many imprtant prblems can be cast in terms f frces nly, fr example the prblems cnsidered in Chapter. Hwever, mre sphisticated
14. Which shows the direction of the centripetal force acting on a mass spun in a vertical circle?
 Physics 0 Public Exam Questins Unit 1: Circular Mtin NAME: August 009---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1. Which describes
Physics 0 Public Exam Questins Unit 1: Circular Mtin NAME: August 009---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1. Which describes
14. Which shows the direction of the centripetal force acting on a mass spun in a vertical circle?
 Physics 3204 Public Exam Questins Unit 1: Circular Mtin NAME: August 2009---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 12. Which
Physics 3204 Public Exam Questins Unit 1: Circular Mtin NAME: August 2009---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 12. Which
Thermochemistry. The study of energy changes that occur during chemical : at constant volume ΔU = q V. no at constant pressure ΔH = q P
 Thermchemistry The study energy changes that ccur during chemical : at cnstant vlume ΔU = q V n at cnstant pressure = q P nly wrk Fr practical reasns mst measurements are made at cnstant, s thermchemistry
Thermchemistry The study energy changes that ccur during chemical : at cnstant vlume ΔU = q V n at cnstant pressure = q P nly wrk Fr practical reasns mst measurements are made at cnstant, s thermchemistry
ALE 21. Gibbs Free Energy. At what temperature does the spontaneity of a reaction change?
 Name Chem 163 Sectin: Team Number: ALE 21. Gibbs Free Energy (Reference: 20.3 Silberberg 5 th editin) At what temperature des the spntaneity f a reactin change? The Mdel: The Definitin f Free Energy S
Name Chem 163 Sectin: Team Number: ALE 21. Gibbs Free Energy (Reference: 20.3 Silberberg 5 th editin) At what temperature des the spntaneity f a reactin change? The Mdel: The Definitin f Free Energy S
CHAPTER Read Chapter 17, sections 1,2,3. End of Chapter problems: 25
 CHAPTER 17 1. Read Chapter 17, sectins 1,2,3. End f Chapter prblems: 25 2. Suppse yu are playing a game that uses tw dice. If yu cunt the dts n the dice, yu culd have anywhere frm 2 t 12. The ways f prducing
CHAPTER 17 1. Read Chapter 17, sectins 1,2,3. End f Chapter prblems: 25 2. Suppse yu are playing a game that uses tw dice. If yu cunt the dts n the dice, yu culd have anywhere frm 2 t 12. The ways f prducing
February 28, 2013 COMMENTS ON DIFFUSION, DIFFUSIVITY AND DERIVATION OF HYPERBOLIC EQUATIONS DESCRIBING THE DIFFUSION PHENOMENA
 February 28, 2013 COMMENTS ON DIFFUSION, DIFFUSIVITY AND DERIVATION OF HYPERBOLIC EQUATIONS DESCRIBING THE DIFFUSION PHENOMENA Mental Experiment regarding 1D randm walk Cnsider a cntainer f gas in thermal
February 28, 2013 COMMENTS ON DIFFUSION, DIFFUSIVITY AND DERIVATION OF HYPERBOLIC EQUATIONS DESCRIBING THE DIFFUSION PHENOMENA Mental Experiment regarding 1D randm walk Cnsider a cntainer f gas in thermal
ES201 - Examination 2 Winter Adams and Richards NAME BOX NUMBER
 ES201 - Examinatin 2 Winter 2003-2004 Adams and Richards NAME BOX NUMBER Please Circle One : Richards (Perid 4) ES201-01 Adams (Perid 4) ES201-02 Adams (Perid 6) ES201-03 Prblem 1 ( 12 ) Prblem 2 ( 24
ES201 - Examinatin 2 Winter 2003-2004 Adams and Richards NAME BOX NUMBER Please Circle One : Richards (Perid 4) ES201-01 Adams (Perid 4) ES201-02 Adams (Perid 6) ES201-03 Prblem 1 ( 12 ) Prblem 2 ( 24
EXAM #1 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 103 FALLF, 2017
 OBJECTIVES 1. Ft Pressure EXAM #1 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 103 FALLF, 2017 Determine the surface area f an bject. Given the weight and surface area, calculate the pressure. 2. Measuring Vlume & Mass Prvided a
OBJECTIVES 1. Ft Pressure EXAM #1 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 103 FALLF, 2017 Determine the surface area f an bject. Given the weight and surface area, calculate the pressure. 2. Measuring Vlume & Mass Prvided a
Lesson 8: Types of Matter
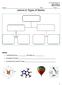 NOTES Name: Date: Class: Lessn 8: Types f Matter Matter: anything that has and takes up Examples f matter: Examples that are NOT matter: _ 1 Pure substances: Elements and Cmpunds a material that has a
NOTES Name: Date: Class: Lessn 8: Types f Matter Matter: anything that has and takes up Examples f matter: Examples that are NOT matter: _ 1 Pure substances: Elements and Cmpunds a material that has a
Calculating the optimum pressure and temperature for vacancy minimization from theory; Niobium is an example. Jozsef Garai
 Calculating the ptimum pressure and temperature fr vacancy minimizatin frm thery; Nibium is an example Jzsef Garai Department f Mechanical and Materials Engineering, Flrida Internatinal University, Miami,
Calculating the ptimum pressure and temperature fr vacancy minimizatin frm thery; Nibium is an example Jzsef Garai Department f Mechanical and Materials Engineering, Flrida Internatinal University, Miami,
Semester 2 AP Chemistry Unit 12
 Cmmn In Effect and Buffers PwerPint The cmmn in effect The shift in equilibrium caused by the additin f a cmpund having an in in cmmn with the disslved substance The presence f the excess ins frm the disslved
Cmmn In Effect and Buffers PwerPint The cmmn in effect The shift in equilibrium caused by the additin f a cmpund having an in in cmmn with the disslved substance The presence f the excess ins frm the disslved
Interference is when two (or more) sets of waves meet and combine to produce a new pattern.
 Interference Interference is when tw (r mre) sets f waves meet and cmbine t prduce a new pattern. This pattern can vary depending n the riginal wave directin, wavelength, amplitude, etc. The tw mst extreme
Interference Interference is when tw (r mre) sets f waves meet and cmbine t prduce a new pattern. This pattern can vary depending n the riginal wave directin, wavelength, amplitude, etc. The tw mst extreme
Supporting information
 Electrnic Supplementary Material (ESI) fr Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics This jurnal is The wner Scieties 01 ydrgen perxide electrchemistry n platinum: twards understanding the xygen reductin reactin
Electrnic Supplementary Material (ESI) fr Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics This jurnal is The wner Scieties 01 ydrgen perxide electrchemistry n platinum: twards understanding the xygen reductin reactin
Physics 212. Lecture 12. Today's Concept: Magnetic Force on moving charges. Physics 212 Lecture 12, Slide 1
 Physics 1 Lecture 1 Tday's Cncept: Magnetic Frce n mving charges F qv Physics 1 Lecture 1, Slide 1 Music Wh is the Artist? A) The Meters ) The Neville rthers C) Trmbne Shrty D) Michael Franti E) Radiatrs
Physics 1 Lecture 1 Tday's Cncept: Magnetic Frce n mving charges F qv Physics 1 Lecture 1, Slide 1 Music Wh is the Artist? A) The Meters ) The Neville rthers C) Trmbne Shrty D) Michael Franti E) Radiatrs
Prof. Dr. I. Nasser Phys530, T142 3-Oct-17 Fermi_gases. 0 f e. and fall off exponentially like Maxwell-Boltzmaan distribution.
 Pr. Dr. I. Nasser Phys, -Oct-7 FERMI_DIRAC GASSES Fermins: Are particles hal-integer spin that bey Fermi-Dirac statistics. Fermins bey the Pauli exclusin principle, which prhibits the ccupancy an available
Pr. Dr. I. Nasser Phys, -Oct-7 FERMI_DIRAC GASSES Fermins: Are particles hal-integer spin that bey Fermi-Dirac statistics. Fermins bey the Pauli exclusin principle, which prhibits the ccupancy an available
C Nitrogen and others. D Oxygen and carbon
 6.5A Knw that an element is a pure substance represented by chemical symbls. Knw AN ELEMENT IS A PURE SUBSTANCE REPRESENTED BY CHEMICAL SYMBOLS Element a pure substance that cannt be brken dwn chemically
6.5A Knw that an element is a pure substance represented by chemical symbls. Knw AN ELEMENT IS A PURE SUBSTANCE REPRESENTED BY CHEMICAL SYMBOLS Element a pure substance that cannt be brken dwn chemically
/ / Chemistry. Chapter 1 Chemical Foundations
 Name Chapter 1 Chemical Fundatins Advanced Chemistry / / Metric Cnversins All measurements in chemistry are made using the metric system. In using the metric system yu must be able t cnvert between ne
Name Chapter 1 Chemical Fundatins Advanced Chemistry / / Metric Cnversins All measurements in chemistry are made using the metric system. In using the metric system yu must be able t cnvert between ne
Flipping Physics Lecture Notes: Simple Harmonic Motion Introduction via a Horizontal Mass-Spring System
 Flipping Physics Lecture Ntes: Simple Harmnic Mtin Intrductin via a Hrizntal Mass-Spring System A Hrizntal Mass-Spring System is where a mass is attached t a spring, riented hrizntally, and then placed
Flipping Physics Lecture Ntes: Simple Harmnic Mtin Intrductin via a Hrizntal Mass-Spring System A Hrizntal Mass-Spring System is where a mass is attached t a spring, riented hrizntally, and then placed
Chapter 4 Thermodynamics and Equilibrium
 Chapter Thermdynamics and Equilibrium Refer t the fllwing figures fr Exercises 1-6. Each represents the energies f fur mlecules at a given instant, and the dtted lines represent the allwed energies. Assume
Chapter Thermdynamics and Equilibrium Refer t the fllwing figures fr Exercises 1-6. Each represents the energies f fur mlecules at a given instant, and the dtted lines represent the allwed energies. Assume
CLASS XI SET A PHYSICS
 PHYSIS. If the acceleratin f wedge in the shwn arrangement is a twards left then at this instant acceleratin f the blck wuld be, (assume all surfaces t be frictinless) a () ( cs )a () a () cs a If the
PHYSIS. If the acceleratin f wedge in the shwn arrangement is a twards left then at this instant acceleratin f the blck wuld be, (assume all surfaces t be frictinless) a () ( cs )a () a () cs a If the
NAME TEMPERATURE AND HUMIDITY. I. Introduction
 NAME TEMPERATURE AND HUMIDITY I. Intrductin Temperature is the single mst imprtant factr in determining atmspheric cnditins because it greatly influences: 1. The amunt f water vapr in the air 2. The pssibility
NAME TEMPERATURE AND HUMIDITY I. Intrductin Temperature is the single mst imprtant factr in determining atmspheric cnditins because it greatly influences: 1. The amunt f water vapr in the air 2. The pssibility
Name: Date: Class: a. How many barium ions are there per formula unit (compound)? b. How many nitride ions are there per formula unit (compound)?
 NOTES Name: Date: Class: Lessn 15 Part 2: Binary II Inic Bnding, Plyatmic Ins Bx 1: 1. Ba 3N 2 is the frmula fr. (name) a. Hw many barium ins are there per frmula unit (cmpund)? b. Hw many nitride ins
NOTES Name: Date: Class: Lessn 15 Part 2: Binary II Inic Bnding, Plyatmic Ins Bx 1: 1. Ba 3N 2 is the frmula fr. (name) a. Hw many barium ins are there per frmula unit (cmpund)? b. Hw many nitride ins
O C S polar - greater force. H polar greater force. H polar. polar H-bond
 hapter 10 : 29, 30, 31, 33, 36, 40, 46, 48, 50, 72, 87, 91, 93, 110 29. a. Lndn e. Lndn b. diple-diple f. diple-diple c. -bnding g. in-in d. in-in 30. a. in-in e. -bnding b. Lndn f. diple-diple c. Lndn
hapter 10 : 29, 30, 31, 33, 36, 40, 46, 48, 50, 72, 87, 91, 93, 110 29. a. Lndn e. Lndn b. diple-diple f. diple-diple c. -bnding g. in-in d. in-in 30. a. in-in e. -bnding b. Lndn f. diple-diple c. Lndn
AP Physics Kinematic Wrap Up
 AP Physics Kinematic Wrap Up S what d yu need t knw abut this mtin in tw-dimensin stuff t get a gd scre n the ld AP Physics Test? First ff, here are the equatins that yu ll have t wrk with: v v at x x
AP Physics Kinematic Wrap Up S what d yu need t knw abut this mtin in tw-dimensin stuff t get a gd scre n the ld AP Physics Test? First ff, here are the equatins that yu ll have t wrk with: v v at x x
