A Brief History of Life on Earth
|
|
|
- Ernest Stevenson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Brief History of Life on Earth Stephen Freeland
2 Are we an accident? You live here Was this likely? Could it equally well have been somewhere else? (why?) Are we alone? Would other life be like us?
3 4 lectures (i) A History of Life on earth (ii) The Evolution of the Genetic Code (iii) The Evolution of the Amino Acid Alphabet (iv) The origin of life here and elsewhere?
4 4 lectures (i) A History of Life on earth (ii) The Evolution of the Genetic Code (iii) The Evolution of the Amino Acid Alphabet (iv) The origin of life here and elsewhere?
5 What you are about to see is not what evolutionary biologists study, it is the work of... A Brief History of Life on Earth Geneticists, Cell and developmental biologists, Anatomists, Physiologists, Botanists, Zoologists, Mycologists, Bioinformaticians, Paleontologists, Physiologists, Ecologists, Biochemists, Geochemists, Geophysicists, Geologists, Cosmochemists, Astronomers, Astrophysicists, Geographers, Cosmochemists, etc.
6 What you are about to see is not what evolutionary biologists study, it is the work of... A Brief History of Life on Earth Geneticists, Cell and developmental biologists, Anatomists, Physiologists, Botanists, Zoologists, Mycologists, Bioinformaticians, Paleontologists, Physiologists, Ecologists, Biochemists, Geochemists, Geophysicists, Geologists, Cosmochemists, Astronomers, Astrophysicists, Geographers, Cosmochemists, etc. Geo- Phys- Chem- Bio- -ist ~ if this is deliberate conspiracy, then it dwarfs JFK s assassination, Roswell aliens or the moon landings into insignificance...
7 From History to Prehistory BC 1000 Iron Age Years ago Hunter-Gatherer Existence ends pottery, agriculture, domestication of livestock and settlement into villages Weaving, sophistication of stone tools and early domestication of livestock 2,500 BC 2,500 BC 3,500 BC (earliest writing) Late Bronze Age Early Bronze Age Neolithic Final Paleolithic
8 and back to the Stone-Age 0 10,000 20,000 Paleolithic 30,000 40,000
9 and back to the Stone-Age 0 10,000 20,000 Paleolithic 30,000 Glaciation (Ice Ages) over the last 450,000 years 40,000
10 H over Sapiens the last spreads ,000 yrs Homo sapiens has spread from the cradle of life in Africa 40, ,000 40, ,000 60,000
11 The emergence of humans as a species needs another 2 orders of magnitude. 0 1,000,000 2,000,000 3,000,000 4,000,000 5,000,000 6,000,000 Ancestor to chimps and humans 7,000,000 8,000,000 Ancestor to apes, chimps and humans
12 At this timescale, the world is a very different place 0 1,000,000 2,000,000 3,000,000 4,000,000 5,000,000 6,000,000 7,000,000 8,000,000 Just over 3 million years ago, the emergence of a land connection between North and South America (the isthmus of Panama) allowed interchange of species in general the birds (e.g. phorusrhacids) and marsupials (e.g. giant sloths) fared worse when they met and competed with placental mammals from the north
13 Plate Tectonics (used to be called Continental Drift ) 0 1,000,000 2,000,000 3,000,000 4,000,000 5,000,000 6,000,000 7,000,000 8,000,000
14 Plate Tectonics (used to be called Continental Drift ) 0 1,000,000 2,000,000 3,000,000 4,000,000 5,000,000 6,000,000 7,000,000 8,000,000
15 Plate Tectonics (used to be called Continental Drift ) 0 1,000,000 2,000,000 3,000,000 4,000,000 5,000,000 6,000,000 7,000,000 8,000,000
16 (not always a gentle and gradual process!)
17 Plate Tectonics (used to be called Continental Drift ) explains things like Australia contains marsupial counterparts to placental mammals Placentals Marsupials
18 Geological Time The boundaries of geological periods, are generally denoted by significant extinctions (changes in the organisms we find, from one rock layer to the next). (According to fossils, approximately 99.9% of species that have lived are extinct) Eon Era Period Mya Epoch Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Quarternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Carboniferous Devonian Silurian Oridivician Cambrian Pleistocene Pliocene Miocene Oligocene Eocene Paleocene
19 Cenozoic: the age of mammals Eon Era Period Mya Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Quarternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Carboniferous Devonian Silurian Oridivician Cambrian
20 On periods, eras and eons Eon Era Period Mya Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Quarternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Carboniferous Devonian Silurian Oridivician Cambrian 65 The boundaries of geological eras, are marked by mass extinctions.
21 65mya mammals underwent an adaptive radiation The most recent of these (the Cenozoic/Mesozoic boundary) is known as the KT mass extinction Eon Era Period Mya Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Quarternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Carboniferous Devonian Silurian 65 Oridivician Cambrian
22 So what brought on the age of the mammals? Barringer Meteor Crater in northern Arizona, is 180m deep and 1.2km in diameter. The crater was formed sometime between 25,000 and 50,000 years ago by an iron meteorite, somewhere between 30 and 100m in diameter, weighing roughly 60,000 tons. The energy released by the impact was roughly equivalent to 3.5 million tons of TNT
23 Mammal species evolve to fill a void A worldwide layer of compressed ash from 65 mya Eon Era Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Tertiary Cretaceous 65 mya
24 Mammal species evolve to fill a void Eon Era a 10 km diameter meteorite hit earth, triggering huge tsunamis and throwing up a wall of rocks and dust that, carried high into the atmosphere, surrounded the earth as a thick cloud and blacked out the sun. This caused freezing, and the darkness killed plants/plankton the primary producers of earth s ecosystem... Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Tertiary Cretaceous 65 mya
25 Mesozoic: The age of reptiles Lasted about 190 million years... Cynodont - 220mya (a mammal like reptile) Eon Phanerozoic Era Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Allosaurus 152 mya (a forerunner of Tyrannosaurus) Period Quarternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Carboniferous Devonian Silurian Oridivician Cambrian Quetzalcoatlus 65 mya (with a 50 ft wingspan, the largest creature ever to fly) (compare 65 my or 7my)
26 Cretaceous: age of flowering plants Oaks, Maples, Walnuts and Magnolia Eon Era Period Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Quarternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Carboniferous Devonian Silurian Oridivician Cambrian
27 Mesozoic: age of reptiles Eon Era Period Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Quarternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Carboniferous Devonian Silurian Oridivician Cambrian
28 The greatest mass extinction of them all... ~ 95% of known life went extinct. Super-volcanic activity, possible asteroid impact and drastic change in climate wrought havoc... Eon Era Period Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Quarternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Carboniferous Devonian Silurian 248 Oridivician Cambrian
29 Permian: Large tetrapod animals dominate land Dimetrodon (a pelycosaur actually a forerunner of mammals!) Eon Era Period Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Quarternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Carboniferous Devonian Silurian Oridivician Cambrian
30 Where did large land animals come from? 325 mya 230 mya 65 mya Eon Era Period Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Quarternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Carboniferous Devonian Silurian Oridivician Cambrian mya During the late Paleozoic, all land masses converged for the first and only time in the history of multicellular life to form a supercontinent known as Pangaea
31 The Carboniferous: age of coal forests (and diversifying insects) Vast forest-swamps of tree-ferns, horsetails & club mosses, producing atmospheric oxygen levels of 35% (twice what we have today) Eon Era Period Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Quarternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Carboniferous Devonian Silurian Oridivician Meganeura a dragonfly with a 3 ft wingspan there were also enormous flies, cockroaches and so on! Cambrian
32 Devonian: the First Large Land Animals - amphibians... Eon Era Period Icthyostega Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Quarternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Carboniferous Devonian Silurian Oridivician Cambrian
33 Devonian: the First Large Land Animals - Evolved from lobe-finned fish... Eusthenopterons Eon Era Period Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Quarternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Carboniferous Devonian Silurian Oridivician Cambrian
34 Devonian: the First Large Land Animals emerged to eat... Eon Era Period Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Quarternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Carboniferous Devonian Silurian Oridivician Cambrian Insects, myriapods and arachnids evolve from crustaceans and horseshoe-crabs
35 Devonian: an age of fish ft long Eon Era Period Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Quarternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Carboniferous Devonian Silurian Oridivician Cambrian
36 Devonian: an age of fish... Eon Era Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Period Quarternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Carboniferous Devonian Silurian Oridivician Cambrian
37 Silurian: complex marine reef ecosystems 7ft Eon Era Period a eurypterid ~ fierce, top carnivore of the age Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Quarternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Carboniferous Devonian Silurian Oridivician Cambrian
38 Silurian: first land plants Eon Era Period Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Quarternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Carboniferous Devonian Silurian Oridivician Cambrian
39 Ordivician: the first coral reefs Eon Era Period Rugose Corals long extinct Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Quarternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Carboniferous Devonian Silurian Oridivician Cambrian
40 Cambrian: early experiments in animal architecture Eon Era Period Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Quarternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Carboniferous Devonian Silurian Oridivician Cambrian
41 Cambrian: early experiments in animal architecture Eon Era Period Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Quarternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Carboniferous Devonian Silurian Oridivician Cambrian
42 Cambrian: early experiments in animal architecture Eon Era Period Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Quarternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Carboniferous Devonian Silurian Oridivician Cambrian
43 Cambrian: early experiments in animal architecture Eon Era Period Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Quarternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Carboniferous Devonian Silurian Oridivician Cambrian
44 Cambrian: early experiments in animal architecture Notochord: a fore runner of the spinal cord Eon Era Period Phanerozoic Cenozoic Mesozoic Quarternary Tertiary Cretaceous Jurassic Triassic Permian Carboniferous Devonian ~ representative Paleozoic of the group that gave rise to all vertebrates Silurian (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds mammals, humans) Oridivician Cambrian Myotomes: muscle blocks
45 Life on earth to scale... Today 1,000 Mya 2,000 Mya Up until the 1960 s, the lack of a pre- Cambrian fossil record was still being widely cited as evidence for a divine creation: 3,000 Mya 4,000 Mya
46 Ediacaran fauna: earliest multicellular fossils... Today Pteridium a modern cnidarian (jellyfish) Cambrian explosion Earliest Multicellular Fossils 730 mya 1,000 Mya 2,000 Mya 3,000 Mya Oldest known fossils 4,000 Mya
47 The big picture... Life in a day... Recorded history starts at 11:59pm, 59s Homo sapiens arrives at 11:59pm Dinosaurs go extinct at 11:00pm Cambrian explosion at 9:00pm Earliest multicellular organisms 8:45pm Cambrian explosion Earliest Multicellular Fossils Today 730 mya 1,000 Mya 2,000 Mya 6am 6am 3,000 Mya Noo n Oldest known fossils 4,000 Mya
48 Genetic glimpses into the PreCambrian... These dots are actually bacteria, labeled with radioactive molecular probes
49 Genetic glimpses into the PreCambrian... A collection of marine microbes. The darkest ones are a very common filamentous form that at present have not been formerly identified in scientific literature. The large pink ovoid is a cell of Chromatium a purple sulphur bacterium, the green is a cyanobacterium. The curving structure at about 2 o'clock is a diatom (Nitzschia), which is a photosynthetic eukaryote. Photo credit: D. J. Patterson, L. Amaral-Zettler and V. Edgcomb One litre of seawater can contain more than 20,000 different types of bacteria, scientists have found. The extraordinary number has been established by an international project attempting to catalogue all ocean life. It suggests microbial biodiversity is much greater than previously thought, say Mitchell Sogin and colleagues. It was undertaken using a new technique that allows for the rapid identification of distinct organisms by probing just small snippets of DNA. BBC News, July 21 st 2006 These dots are actually bacteria, labeled with radioactive molecular probes
50 The Pre-Cambrian (Paleozoic) Today 1953: American geologist Stanley Tyler sets out to investigate the geology of the Gunflint Formation, a mid-precambrian (2,100-Ma-old) iron-rich rock unit that straddles the U.S.-Canada border between northern Minnesota and southern Ontario Cambrian explosion Earliest Multicellular Fossils Oldest known fossils 1,000 Mya 2,000 Mya 2,100 mya 3,000 Mya 4,000 Mya
51 The Pre-Cambrian (Paleozoic) Today He finds a curious black chert, unlike known rocks of this type. Placing it under the microscope, he sees the following Cambrian explosion 1,000 Mya Earliest Multicellular Fossils 2,000 Mya 2,100 mya 3,000 Mya (from the right rocks) we now recognize that the Pre-Cambrian was teaming with life ~ microscopic life. These are now found as microfossils Oldest known fossils 4,000 Mya
52 A genetic tree of life s diversity...
53 The Pre-Cambrian (Paleozoic) Today Cambrian explosion earliest metazoa 1,000 Mya Eukaryotes originate about 2 bya 2,000 2,000 mya Mya 3,000 Mya (distinguished by size and morphology within the microfossil fauna/flora) Oldest known fossils 4,000 Mya
54 Oxygen: the most toxic gas on earth All aerobic eukaryotes use mitochondria to process oxygen (controlling its corrosive powers by using it to burn sugar, producing energy)
55 Stromatolites ~ the oldest living fossils Today Cambrian explosion Earliest Multicellular Fossils 1,000 Mya 2,000 Mya 2,300 mya 3,000 Mya 2.3 bya stromatolites, Transvaal Oldest known fossils 4,000 Mya
56 Stromatolites ~ the oldest living fossils Today Cambrian explosion Earliest Multicellular Fossils 1,000 Mya Today s stromatolites, Shark Bay 2,000 Mya 2,300 mya 3,000 Mya 2.3 bya stromatolites, Transvaal Oldest known fossils 4,000 Mya
57 Stromatolites ~ the oldest living fossils these ecosystems are microbial coral reefs in terms of rich, complex species interactions Bacteria (red) are intimately associated with carbonate precipitates (blue).
58 Stromatolites ~ community structure Cyanobacteria produce oxygen through photosynthesis exterior Various bacteria that are tolerant to, but not reliant on, oxygen Various bacteria that are poisoned by oxygen, and photosynthesize other chemicals, e.g. methane interior
59 Oxygen: the most toxic gas on earth
60 BIF s, oxygen and eukaryotes Banded Iron Formation (BIF) From Michigan, dating to around 2.5 Bya Cambrian explosion Earliest Multicellular Fossils Today 1,000 Mya 2,000 2,000 mya Mya Dissolved iron is slowly oxidized to rust (O 2 producing cyanobacteria evolve and spread) 3,000 Mya 3,200 mya Iron is washed from rocks into the ocean 4,000 Mya
61 (Genetic data adds detail to the endosymbiont theory) Today 1,000 Mya 2,000 Mya 3,000 Mya 4,000 Mya
62 Eukaryotes, mitochondria (and choloroplasts) <10µm All aerobic eukaryotes use mitochondria to process oxygen Photosynthetic plants use chloroplasts to process light, carbon dioxide and water into sugars (that store energy) >60µm ~ mitochondria and chloroplasts are about the same size as bacteria; ~ they display a double membrane ~ they retain small amounts of DNA genomes
63 The last universal common ancestor of life (LUCA) What was it like? Today 1,000 Mya 2,000 2,000 mya Mya 3,000 Mya 3,200 mya 4,000 Mya
64 Evolutionary homology gives us insight into the past Different species have separated from one another at different times. The time since divergence (separation) will determine their overall level of similarity Treated carefully, the similarities can indicate the nature of a common ancestor
65 So what homology does all of life share? Today, in every cell of every organism of every species... DNA (information) RNA ( temporary gene) Protein (phenotype) DNA genes are transcribed into RNA messages that are then translated into proteins. Proteins can be structural (e.g. keratin in hair) or enzymatic ~ catalyzing particular chemical reactions
66 The Chemical Alphabets of Life The 4 Nucleotides of the DNA alphabet + Thiamine ( T ) + Adenine ( A ) + Cytosine ( C ) + + Guanine ( G )
67 The Genetic Code maps genetic words into amino acids UUU UUC UUA UUG CUU CUC CUA CUG AUU AUC AUA AUG GUU GUC GUA GUG Phe Leu Leu Ile Met Val UCU UCC UCA UCG CCU CCC CCA CCG ACU ACC ACA ACG GCU GCC GCA GCG Ser Pro Thr Ala UAU UAC UAA UAG CAU CAC CAA CAG AAU AAC AAA AAG CAU CAC CAA CAG Tyr His Gln Asn Lys Asp Glu UGU UGC UGA UGG CGU CGC CGA CGG AGU AGC AGA AGG GGU GGC GGA GGG Cys Trp Arg Ser Arg Gly A triplet Codon of mrna 3 nucleotides, read as a codon are translated into 1 amino acid trna the adaptor molecule Histidine (His) Protein
68 In fact a lot of fundamental biochemistry is shared
69 Life on Earth gets off to an early start... Today 1,000 Mya Nature (1996) 384:55-9. Evidence for life on Earth before 3,800 million years ago, Eiler JM, Mojzsis SJ, Arrhenius G. It is unknown when life first appeared on Earth Here we provide evidence for the emergence of life on Earth by at least 3,800 Myr before present. 2,000 Mya 3,000 Mya 4,000 Mya
70 Life on Earth gets off to an early start... Today 1,000 Mya Nature (1996) 384:55-9. Evidence for life on Earth before 3,800 million years ago, Eiler JM, Mojzsis SJ, Arrhenius G. It is unknown when life first appeared on Earth Here we provide evidence for the emergence of life on Earth by at least 3,800 Myr before present. Oldest known fossil signs of life 2,000 Mya 3,000 Mya The earth was a molten mass, pummeled by BIG impacts 4,000 Mya
71 Life on Earth gets off to an early start... Today One of which is thought to have created our moon 1,000 Mya 2,000 Mya Oldest known fossil signs of life 3,000 Mya The earth was a molten mass, pummeled by BIG impacts 4,000 Mya
72 Physics suggests the following timeline Life on earth? 15 billion years ago 13 billion years ago 10 billion years ago 5 billion years ago
73 So do we expect a galaxy teaming with life? This... image from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope shows hundreds of thousands of stars crowded into the swirling core of our spiral Milky Way galaxy NASA mission news
74 Or are we likely to be alone?
75 3 more lectures (i) A History of Life on earth (ii) The Evolution of the Genetic Code (iii) The Evolution of the Amino Acid Alphabet (iv) The origin of life here and elsewhere?
Objective: You will be able to justify the claim that organisms share many conserved core processes and features.
 Objective: You will be able to justify the claim that organisms share many conserved core processes and features. Do Now: Read Enduring Understanding B Essential knowledge: Organisms share many conserved
Objective: You will be able to justify the claim that organisms share many conserved core processes and features. Do Now: Read Enduring Understanding B Essential knowledge: Organisms share many conserved
How do we learn about ancient life? Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological processes.
 Unit 1B Lesson 4 History of Life on Earth How do we learn about ancient life? Paleontologists scientists that studies fossils Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological
Unit 1B Lesson 4 History of Life on Earth How do we learn about ancient life? Paleontologists scientists that studies fossils Fossil- a trace or imprint of a living thing that is preserved by geological
Aoife McLysaght Dept. of Genetics Trinity College Dublin
 Aoife McLysaght Dept. of Genetics Trinity College Dublin Evolution of genome arrangement Evolution of genome content. Evolution of genome arrangement Gene order changes Inversions, translocations Evolution
Aoife McLysaght Dept. of Genetics Trinity College Dublin Evolution of genome arrangement Evolution of genome content. Evolution of genome arrangement Gene order changes Inversions, translocations Evolution
Earth History. What is the Earth s time scale? Geological time Scale. Pre-Cambrian. FOUR Eras
 The Earth is 4.6 billion years old! Earth History Mrs. Burkey ESS Cy Creek HS 17-18 If the Earth formed at midnight 6:00 am First life appears 10:00 pm First animals/plants on land 11:59 pm First humans
The Earth is 4.6 billion years old! Earth History Mrs. Burkey ESS Cy Creek HS 17-18 If the Earth formed at midnight 6:00 am First life appears 10:00 pm First animals/plants on land 11:59 pm First humans
Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages )
 Name Class Date Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages 417-422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils?
Name Class Date Chapter Study Guide Section 17-1 The Fossil Record (pages 417-422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils?
Module 9: Earth's History Topic 3 Content: A Tour of Geologic Time Notes
 The geologic time scale holds secrets to the life that has existed on Earth since the beginning of time. It is time for you to take a journey through the history of Earth. 1 Click on each of the segments
The geologic time scale holds secrets to the life that has existed on Earth since the beginning of time. It is time for you to take a journey through the history of Earth. 1 Click on each of the segments
2 Eras of the Geologic Time Scale
 CHAPTER 8 2 Eras of the Geologic Time Scale SECTION The History of Life on Earth BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What kinds of organisms evolved
CHAPTER 8 2 Eras of the Geologic Time Scale SECTION The History of Life on Earth BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What kinds of organisms evolved
The History of Life. Fossils and Ancient Life (page 417) How Fossils Form (page 418) Interpreting Fossil Evidence (pages ) Chapter 17
 Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time scale that is used
Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time scale that is used
Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages )
 Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils? What
Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) Key Concepts What is the fossil record? What information do relative dating and radioactive dating provide about fossils? What
Name Class Date. Crossword Puzzle Use the clues below to complete the puzzle.
 Chapter 17 The History of Life Chapter Vocabulary Review Crossword Puzzle Use the clues below to complete the puzzle. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Across 2. time span shorter than an era, such as Quaternary
Chapter 17 The History of Life Chapter Vocabulary Review Crossword Puzzle Use the clues below to complete the puzzle. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Across 2. time span shorter than an era, such as Quaternary
The Phanerozoic Eon. 542 mya Present. Divided into 3 Eras The Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic Eras
 542 mya Present The Phanerozoic Eon Divided into 3 Eras The Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic Eras The ends of the Paleozoic and Mesozoic Eras were marked by mass extinctions The Cenozoic Era is still
542 mya Present The Phanerozoic Eon Divided into 3 Eras The Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic Eras The ends of the Paleozoic and Mesozoic Eras were marked by mass extinctions The Cenozoic Era is still
Geological Time Scale UG Hons.1 st Year) DR. CHANDAN SURABHI DAS ASST. PROF. IN GEOGRAPHY BARASAT GOVT. COLLEGE
 Geological Time Scale UG Hons.1 st Year) 1 DR. CHANDAN SURABHI DAS ASST. PROF. IN GEOGRAPHY BARASAT GOVT. COLLEGE 2 Imagine putting everything that has happened on Earth into a one hour time frame! 3 12:00am
Geological Time Scale UG Hons.1 st Year) 1 DR. CHANDAN SURABHI DAS ASST. PROF. IN GEOGRAPHY BARASAT GOVT. COLLEGE 2 Imagine putting everything that has happened on Earth into a one hour time frame! 3 12:00am
Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages )
 Name Class Date Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time
Name Class Date Chapter 17 The History of Life Section 17 1 The Fossil Record (pages 417 422) This section explains how fossils form and how they can be interpreted. It also describes the geologic time
Using an Artificial Regulatory Network to Investigate Neural Computation
 Using an Artificial Regulatory Network to Investigate Neural Computation W. Garrett Mitchener College of Charleston January 6, 25 W. Garrett Mitchener (C of C) UM January 6, 25 / 4 Evolution and Computing
Using an Artificial Regulatory Network to Investigate Neural Computation W. Garrett Mitchener College of Charleston January 6, 25 W. Garrett Mitchener (C of C) UM January 6, 25 / 4 Evolution and Computing
Spring th Grade
 Spring 2015 8 th Grade The geologic time scale is a record of the major events and diversity of life forms present in Earth s history. The geologic time scale began when Earth was formed and goes on until
Spring 2015 8 th Grade The geologic time scale is a record of the major events and diversity of life forms present in Earth s history. The geologic time scale began when Earth was formed and goes on until
EARTH S HISTORY. What is Geology? logy: science. Geology is the scientific study of the Earth, including its:
 EARTH S HISTORY 1 What is Geology? Geo: earth logy: science Geology is the scientific study of the Earth, including its: composition, structure, and physical properties. 2 1 Geologists study: the origin
EARTH S HISTORY 1 What is Geology? Geo: earth logy: science Geology is the scientific study of the Earth, including its: composition, structure, and physical properties. 2 1 Geologists study: the origin
Earth s history can be broken up into 4 time periods: Precambrian Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era
 Earth s History Video Clip Earth s History Earth s history can be broken up into 4 time periods: Precambrian Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era Scientists have put together a timeline of Earth s history
Earth s History Video Clip Earth s History Earth s history can be broken up into 4 time periods: Precambrian Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era Scientists have put together a timeline of Earth s history
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer Codon usage patterns in Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Drosophila melanogaster and Homo sapiens; a review of the considerable
Edinburgh Research Explorer Codon usage patterns in Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Drosophila melanogaster and Homo sapiens; a review of the considerable
Chapter 25: The Origin and Evolutionary History of Life on Earth
 Chapter 25: The Origin and Evolutionary History of Life on Earth Chemical conditions of the early Earth A model for the first cells First life Life changes the planet: oxygenating Earth s oceans and atmosphere
Chapter 25: The Origin and Evolutionary History of Life on Earth Chemical conditions of the early Earth A model for the first cells First life Life changes the planet: oxygenating Earth s oceans and atmosphere
A p-adic Model of DNA Sequence and Genetic Code 1
 ISSN 2070-0466, p-adic Numbers, Ultrametric Analysis and Applications, 2009, Vol. 1, No. 1, pp. 34 41. c Pleiades Publishing, Ltd., 2009. RESEARCH ARTICLES A p-adic Model of DNA Sequence and Genetic Code
ISSN 2070-0466, p-adic Numbers, Ultrametric Analysis and Applications, 2009, Vol. 1, No. 1, pp. 34 41. c Pleiades Publishing, Ltd., 2009. RESEARCH ARTICLES A p-adic Model of DNA Sequence and Genetic Code
Origins of Life and Extinction
 Origins of Life and Extinction What is evolution? What is evolution? The change in the genetic makeup of a population over time Evolution accounts for the diversity of life on Earth Natural selection is
Origins of Life and Extinction What is evolution? What is evolution? The change in the genetic makeup of a population over time Evolution accounts for the diversity of life on Earth Natural selection is
Origins of Life. Fundamental Properties of Life. The Tree of Life. Chapter 26
 Origins of Life The Tree of Life Cell is the basic unit of life Today all cells come from pre-existing cells Earth formed ~4.5 billion years ago (BYA) Chapter 26 As it cooled, chemically-rich oceans were
Origins of Life The Tree of Life Cell is the basic unit of life Today all cells come from pre-existing cells Earth formed ~4.5 billion years ago (BYA) Chapter 26 As it cooled, chemically-rich oceans were
Genetic Code, Attributive Mappings and Stochastic Matrices
 Genetic Code, Attributive Mappings and Stochastic Matrices Matthew He Division of Math, Science and Technology Nova Southeastern University Ft. Lauderdale, FL 33314, USA Email: hem@nova.edu Abstract: In
Genetic Code, Attributive Mappings and Stochastic Matrices Matthew He Division of Math, Science and Technology Nova Southeastern University Ft. Lauderdale, FL 33314, USA Email: hem@nova.edu Abstract: In
Links to help understand the immensity of the Geologic Time Scale
 Links to help understand the immensity of the Geologic Time Scale http://www.bonnechere.ca/naturalhistory.htm http://comp.uark.edu/~sboss/geotime.htm http://www.britannica.com/ebchecked/media/1650/the-geologic-time-scale-from-650-million-years-ago-to
Links to help understand the immensity of the Geologic Time Scale http://www.bonnechere.ca/naturalhistory.htm http://comp.uark.edu/~sboss/geotime.htm http://www.britannica.com/ebchecked/media/1650/the-geologic-time-scale-from-650-million-years-ago-to
Chapter 14 The History of Life
 Section 1: Fossil Evidence of Change Section 2: The Origin of Life Click on a lesson name to select. 14.1 Fossil Evidence of Change Land Environments Earth formed about 4.6 billion years ago. Gravity pulled
Section 1: Fossil Evidence of Change Section 2: The Origin of Life Click on a lesson name to select. 14.1 Fossil Evidence of Change Land Environments Earth formed about 4.6 billion years ago. Gravity pulled
Genetic code on the dyadic plane
 Genetic code on the dyadic plane arxiv:q-bio/0701007v3 [q-bio.qm] 2 Nov 2007 A.Yu.Khrennikov, S.V.Kozyrev June 18, 2018 Abstract We introduce the simple parametrization for the space of codons (triples
Genetic code on the dyadic plane arxiv:q-bio/0701007v3 [q-bio.qm] 2 Nov 2007 A.Yu.Khrennikov, S.V.Kozyrev June 18, 2018 Abstract We introduce the simple parametrization for the space of codons (triples
In previous lecture. Shannon s information measure x. Intuitive notion: H = number of required yes/no questions.
 In previous lecture Shannon s information measure H ( X ) p log p log p x x 2 x 2 x Intuitive notion: H = number of required yes/no questions. The basic information unit is bit = 1 yes/no question or coin
In previous lecture Shannon s information measure H ( X ) p log p log p x x 2 x 2 x Intuitive notion: H = number of required yes/no questions. The basic information unit is bit = 1 yes/no question or coin
Biology 155 Practice FINAL EXAM
 Biology 155 Practice FINAL EXAM 1. Which of the following is NOT necessary for adaptive evolution? a. differential fitness among phenotypes b. small population size c. phenotypic variation d. heritability
Biology 155 Practice FINAL EXAM 1. Which of the following is NOT necessary for adaptive evolution? a. differential fitness among phenotypes b. small population size c. phenotypic variation d. heritability
Get started on your Cornell notes right away
 UNIT 10: Evolution DAYSHEET 100: Introduction to Evolution Name Biology I Date: Bellringer: 1. Get out your technology and go to www.biomonsters.com 2. Click the Biomonsters Cinema link. 3. Click the CHS
UNIT 10: Evolution DAYSHEET 100: Introduction to Evolution Name Biology I Date: Bellringer: 1. Get out your technology and go to www.biomonsters.com 2. Click the Biomonsters Cinema link. 3. Click the CHS
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certifi cate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level
 *1166350738* UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certifi cate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level CEMISTRY 9701/43 Paper 4 Structured Questions October/November
*1166350738* UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certifi cate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level CEMISTRY 9701/43 Paper 4 Structured Questions October/November
Geological Time How old is the Earth
 Geological Time How old is the Earth How old is everything? Universe? Universe ~ 14 Billion Years Old Milky Way Galaxy? Milky Way Galaxy - 10 Billion Years Old Solar System? Solar System -4.6 Billion Years
Geological Time How old is the Earth How old is everything? Universe? Universe ~ 14 Billion Years Old Milky Way Galaxy? Milky Way Galaxy - 10 Billion Years Old Solar System? Solar System -4.6 Billion Years
Beaming in your answers
 Bio 112 Handout for Evolution 8 This handout contains: Today s iclicker Questions Handouts for today s lecture iclicker Question #5A - before lecture Consider the hypothetical creatures on the last page
Bio 112 Handout for Evolution 8 This handout contains: Today s iclicker Questions Handouts for today s lecture iclicker Question #5A - before lecture Consider the hypothetical creatures on the last page
5 Time Marches On. TAKE A LOOK 1. Identify What kinds of organisms formed the fossils in the picture?
 CHAPTER 6 5 Time Marches On SECTION The Rock and Fossil Record BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do geologists measure time? How has life changed
CHAPTER 6 5 Time Marches On SECTION The Rock and Fossil Record BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do geologists measure time? How has life changed
Chapter 19. History of Life on Earth
 Chapter 19 History of Life on Earth Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Chapter 19 Section 3: Evolution of Life Key Vocabulary Terms Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Cyanobacteria Photosynthetic prokaryotes Adapted
Chapter 19 History of Life on Earth Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Chapter 19 Section 3: Evolution of Life Key Vocabulary Terms Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Cyanobacteria Photosynthetic prokaryotes Adapted
UNIT 4: History Of Biological Diversity
 UNIT 4: History Of Biological Diversity CHAPTER 14: The History of Life PAST NOW FUTURE? What is this? Earth s Early history Approximately 4.6 billion years ago, the Earth was formed when many pieces of
UNIT 4: History Of Biological Diversity CHAPTER 14: The History of Life PAST NOW FUTURE? What is this? Earth s Early history Approximately 4.6 billion years ago, the Earth was formed when many pieces of
Eras of Earth's History Lesson 6
 Eras of Earth's History Lesson 6 May 24 8:42 PM What happened in the Paleozoic Era? What happened in the Mesozoic Era? What happened in the Cenozoic Era? May 24 8:55 PM 1 I. What happened in the Paleozoic
Eras of Earth's History Lesson 6 May 24 8:42 PM What happened in the Paleozoic Era? What happened in the Mesozoic Era? What happened in the Cenozoic Era? May 24 8:55 PM 1 I. What happened in the Paleozoic
Page 143: Geologic Time
 Page 143: Geologic Time Divide pages 144-147 in 6 One for each box: Hadeon Eon Archeon Eon Cambrian Period Ordovician Period Silurian Period Devonian Period Carboniferous Period Mississipian Period Pennsylvanian
Page 143: Geologic Time Divide pages 144-147 in 6 One for each box: Hadeon Eon Archeon Eon Cambrian Period Ordovician Period Silurian Period Devonian Period Carboniferous Period Mississipian Period Pennsylvanian
Visualizing Earth Science. Chapter Overview. The Ever-Changing Earth. Early Life. Evolution and the Fossil Record. Life in the Phanerozoic Eon
 Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 11 A Brief History of Life on Earth Chapter Overview The Ever-Changing Earth Early Life Evolution and the Fossil Record Life in the Phanerozoic
Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 11 A Brief History of Life on Earth Chapter Overview The Ever-Changing Earth Early Life Evolution and the Fossil Record Life in the Phanerozoic
What is the Earth s time scale?
 Earth History What is the Earth s time scale? The Geological time scale is a record of the life forms and geological events in Earth s history. Scientists developed the time scale by fossils world wide.
Earth History What is the Earth s time scale? The Geological time scale is a record of the life forms and geological events in Earth s history. Scientists developed the time scale by fossils world wide.
Geologic Time. Mr. Skirbst
 Geologic Time Mr. Skirbst Geologic Time Geologic Time Scale Describing and dividing major events of Earth s history Like a timeline of your life! Birth Like a timeline of your life! Like a timeline of
Geologic Time Mr. Skirbst Geologic Time Geologic Time Scale Describing and dividing major events of Earth s history Like a timeline of your life! Birth Like a timeline of your life! Like a timeline of
History of Life on Earth
 Lesson 4 The History of Life on Earth ESSENTIAL QUESTION How has life on Earth changed over time? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to describe the evolution of life on Earth over time, using
Lesson 4 The History of Life on Earth ESSENTIAL QUESTION How has life on Earth changed over time? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to describe the evolution of life on Earth over time, using
Unit 1 A. The early life and the Diversification of Prokaryotes (Ch24) B. Origin and Diversification of Eukaryotes (Ch25) C.
 Unit 1 A. The early life and the Diversification of Prokaryotes (Ch24) B. Origin and Diversification of Eukaryotes (Ch25) C. Broad Patterns of Evolution (Ch23) D. Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles (Ch 10)
Unit 1 A. The early life and the Diversification of Prokaryotes (Ch24) B. Origin and Diversification of Eukaryotes (Ch25) C. Broad Patterns of Evolution (Ch23) D. Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles (Ch 10)
Earth s s Geologic History
 The Earth s s Geologic History and The Earth s s Interior Earth s s Geologic History Geologic timescale Divides Earth s s history into relative time periods Relative dating based on: (apply for entire
The Earth s s Geologic History and The Earth s s Interior Earth s s Geologic History Geologic timescale Divides Earth s s history into relative time periods Relative dating based on: (apply for entire
sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Life s Origin & Early Evolution (Ch. 20)
 sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Life s Origin & Early Evolution (Ch. 20) 2007-2008 ARCHEAN Millions of years ago PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC 0 500 1000 Cenozoic
sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Life s Origin & Early Evolution (Ch. 20) 2007-2008 ARCHEAN Millions of years ago PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC 0 500 1000 Cenozoic
Outline. Origin and History of Life
 Origin and History of Life Chapter 19 Primitive Earth Origin of First Cells Fossils The Precambrian The Paleozoic The Mesozoic The Cenozoic Continental Drift Mass Extinctions Outline 1 2 The Primitive
Origin and History of Life Chapter 19 Primitive Earth Origin of First Cells Fossils The Precambrian The Paleozoic The Mesozoic The Cenozoic Continental Drift Mass Extinctions Outline 1 2 The Primitive
Lecture IV A. Shannon s theory of noisy channels and molecular codes
 Lecture IV A Shannon s theory of noisy channels and molecular codes Noisy molecular codes: Rate-Distortion theory S Mapping M Channel/Code = mapping between two molecular spaces. Two functionals determine
Lecture IV A Shannon s theory of noisy channels and molecular codes Noisy molecular codes: Rate-Distortion theory S Mapping M Channel/Code = mapping between two molecular spaces. Two functionals determine
4) Outline the major developments that allowed life to exist on Earth.
 Objectives 4) Outline the major developments that allowed life to exist on Earth. 5) Describe the types of organisms that arose during the four major divisions of the geologic time scale. Each layer of
Objectives 4) Outline the major developments that allowed life to exist on Earth. 5) Describe the types of organisms that arose during the four major divisions of the geologic time scale. Each layer of
17-1 The Fossil Record Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about past life is called the fossil record. The fossil record includes
1 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about past life is called the fossil record. The fossil record includes
17-1 The Fossil Record Slide 2 of 40
 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about
2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life Fossils and Ancient Life Paleontologists are scientists who collect and study fossils. All information about
CHAPTER 19 THE HISTORY OF LIFE. Dr. Bertolotti
 CHAPTER 19 THE HISTORY OF LIFE Dr. Bertolotti Essential Question: HOW DO FOSSILS HELP BIOLOGISTS UNDERSTAND THE HISTORY OF LIFE ON EARTH? WHAT DO FOSSILS REVEAL ABOUT ANCIENT LIFE? FOSSILS AND ANCIENT
CHAPTER 19 THE HISTORY OF LIFE Dr. Bertolotti Essential Question: HOW DO FOSSILS HELP BIOLOGISTS UNDERSTAND THE HISTORY OF LIFE ON EARTH? WHAT DO FOSSILS REVEAL ABOUT ANCIENT LIFE? FOSSILS AND ANCIENT
Summary The Fossil Record Earth s Early History. Name Class Date
 Name Class Date Chapter 17 Summary The History of Life 17 1 The Fossil Record Fossils are preserved traces and remains of ancient life. Scientists who study fossils are called paleontologists. They use
Name Class Date Chapter 17 Summary The History of Life 17 1 The Fossil Record Fossils are preserved traces and remains of ancient life. Scientists who study fossils are called paleontologists. They use
The degeneracy of the genetic code and Hadamard matrices. Sergey V. Petoukhov
 The degeneracy of the genetic code and Hadamard matrices Sergey V. Petoukhov Department of Biomechanics, Mechanical Engineering Research Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences petoukhov@hotmail.com,
The degeneracy of the genetic code and Hadamard matrices Sergey V. Petoukhov Department of Biomechanics, Mechanical Engineering Research Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences petoukhov@hotmail.com,
Lecture II.4. Answers to the Questions.
 Lecture II.4. Answers to the Questions. 1. Animals colonized the land during the Devonian period. This was during the era and the eon. Paleozoic; Phanerozoic 2. The mother of all mass extinctions occurred
Lecture II.4. Answers to the Questions. 1. Animals colonized the land during the Devonian period. This was during the era and the eon. Paleozoic; Phanerozoic 2. The mother of all mass extinctions occurred
Earth - Home Sweet Home. Sunday, August 18, 13
 Earth - Home Sweet Home 1 From Homogeneous to Heterogeneous: Formation of the Solar Systems and Planets 2 Perspective on our place in the The Milky Way Galaxy video Perspective on our place in the The
Earth - Home Sweet Home 1 From Homogeneous to Heterogeneous: Formation of the Solar Systems and Planets 2 Perspective on our place in the The Milky Way Galaxy video Perspective on our place in the The
UNDERSTANDING GEOLOGIC TIME
 Name: Date: Period: UNDERSTANDING GEOLOGIC TIME The earth is 4.6 billion years old. That s a long time! The scale of geologic time is so different from what human beings experience that it s often quite
Name: Date: Period: UNDERSTANDING GEOLOGIC TIME The earth is 4.6 billion years old. That s a long time! The scale of geologic time is so different from what human beings experience that it s often quite
Origin of Life. What is Life? The evolutionary tree of life can be documented with evidence. The Origin of Life on Earth is another
 sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Origin of Life 500 Paleozoic 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 ARCHEAN Millions of years ago 1000 PROTEROZOIC Cenozoic Mesozoic 4000
sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Origin of Life 500 Paleozoic 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 ARCHEAN Millions of years ago 1000 PROTEROZOIC Cenozoic Mesozoic 4000
Fossils Biology 2 Thursday, January 31, 2013
 Fossils Biology 2 Evolution Change in the genetic composition of a group of organisms over time. Causes: Natural Selection Artificial Selection Genetic Engineering Genetic Drift Hybridization Mutation
Fossils Biology 2 Evolution Change in the genetic composition of a group of organisms over time. Causes: Natural Selection Artificial Selection Genetic Engineering Genetic Drift Hybridization Mutation
Study Guide. Section 1: Fossil Evidence of Change CHAPTER 14
 Name Date Class Study Guide CHAPTER 14 Section 1: Fossil Evidence of Change In your textbook, read about Earth s early history. For each statement below, write true or false. 1. Solid Earth formed about
Name Date Class Study Guide CHAPTER 14 Section 1: Fossil Evidence of Change In your textbook, read about Earth s early history. For each statement below, write true or false. 1. Solid Earth formed about
The History of Life. Before You Read. Read to Learn
 14 The History of Life section 1 Fossil Evidence of Change Before You Read Throughout Earth s history, many species have become extinct. On the lines below, name some organisms that have become extinct.
14 The History of Life section 1 Fossil Evidence of Change Before You Read Throughout Earth s history, many species have become extinct. On the lines below, name some organisms that have become extinct.
(continued) Stephen Eikenberry 11 September 2012 AST 2037
 Development of Life (continued) Stephen Eikenberry 11 September 2012 AST 2037 1 Evolutionary Timeline 530 MYa first footprint fossil found on land 505 Mya first true fish in the sea 475 MYa first land
Development of Life (continued) Stephen Eikenberry 11 September 2012 AST 2037 1 Evolutionary Timeline 530 MYa first footprint fossil found on land 505 Mya first true fish in the sea 475 MYa first land
A Minimum Principle in Codon-Anticodon Interaction
 A Minimum Principle in Codon-Anticodon Interaction A. Sciarrino a,b,, P. Sorba c arxiv:0.480v [q-bio.qm] 9 Oct 0 Abstract a Dipartimento di Scienze Fisiche, Università di Napoli Federico II Complesso Universitario
A Minimum Principle in Codon-Anticodon Interaction A. Sciarrino a,b,, P. Sorba c arxiv:0.480v [q-bio.qm] 9 Oct 0 Abstract a Dipartimento di Scienze Fisiche, Università di Napoli Federico II Complesso Universitario
Mathematics of Bioinformatics ---Theory, Practice, and Applications (Part II)
 Mathematics of Bioinformatics ---Theory, Practice, and Applications (Part II) Matthew He, Ph.D. Professor/Director Division of Math, Science, and Technology Nova Southeastern University, Florida, USA December
Mathematics of Bioinformatics ---Theory, Practice, and Applications (Part II) Matthew He, Ph.D. Professor/Director Division of Math, Science, and Technology Nova Southeastern University, Florida, USA December
Earth s Formation: 4.6 Billion Years ago
 Earth s Formation: 4.6 Billion Years ago Formed from interstellar gas & dust into molten planet Earth s early atmosphere was hostile, made of carbon monoxide, methane, ammonia, nitrogen, nitrogen, sulfur,
Earth s Formation: 4.6 Billion Years ago Formed from interstellar gas & dust into molten planet Earth s early atmosphere was hostile, made of carbon monoxide, methane, ammonia, nitrogen, nitrogen, sulfur,
Revision Based on Chapter 19 Grade 11
 Revision Based on Chapter 19 Grade 11 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Most fossils are found in rusty water. volcanic rock. sedimentary
Revision Based on Chapter 19 Grade 11 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Most fossils are found in rusty water. volcanic rock. sedimentary
12.1. KEY CONCEPT Fossils are a record of life that existed in the past. 68 Reinforcement Unit 4 Resource Book
 12.1 THE FOSSIL RECORD KEY CONCEPT Fossils are a record of life that existed in the past. Fossils can form in several different ways: Permineralization occurs when water surrounds a hard structure such
12.1 THE FOSSIL RECORD KEY CONCEPT Fossils are a record of life that existed in the past. Fossils can form in several different ways: Permineralization occurs when water surrounds a hard structure such
CHEMISTRY 9701/42 Paper 4 Structured Questions May/June hours Candidates answer on the Question Paper. Additional Materials: Data Booklet
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Level CHEMISTRY 9701/42 Paper 4 Structured Questions May/June 2014 2 hours Candidates answer on the Question Paper. Additional Materials:
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Level CHEMISTRY 9701/42 Paper 4 Structured Questions May/June 2014 2 hours Candidates answer on the Question Paper. Additional Materials:
Earth s Evolution Through Time
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Earth s Evolution Through Time Earth 9 th edition Chapter 22 Earth s evolution: summary in haiku form Super-continents have come and gone many times: giant bumper cars.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Earth s Evolution Through Time Earth 9 th edition Chapter 22 Earth s evolution: summary in haiku form Super-continents have come and gone many times: giant bumper cars.
The History of Life, the Universe and Everything or What do you get when you multiply six by nine. Chapters 17 (skim) and 18
 The History of Life, the Universe and Everything or What do you get when you multiply six by nine Chapters 17 (skim) and 18 The Origin of Life The problem: Life begets life. There must be a beginning,
The History of Life, the Universe and Everything or What do you get when you multiply six by nine Chapters 17 (skim) and 18 The Origin of Life The problem: Life begets life. There must be a beginning,
PTYS 214 Spring Announcements Midterm #4: two weeks from today!
 PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm #4: two weeks from today! 1 Previously Radiometric Dating Compare parent / daughter to determine # of half lives 14C, 40K, 238U, 232Th, 87Ru Evidence for Early
PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm #4: two weeks from today! 1 Previously Radiometric Dating Compare parent / daughter to determine # of half lives 14C, 40K, 238U, 232Th, 87Ru Evidence for Early
A modular Fibonacci sequence in proteins
 A modular Fibonacci sequence in proteins P. Dominy 1 and G. Rosen 2 1 Hagerty Library, Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA 2 Department of Physics, Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA 19104,
A modular Fibonacci sequence in proteins P. Dominy 1 and G. Rosen 2 1 Hagerty Library, Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA 2 Department of Physics, Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA 19104,
Biology. Slide 1 of 40. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 40 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life The fossil record provides evidence about the history of life on Earth. It also shows how different
Biology 1 of 40 2 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life What is the fossil record? 3 of 40 Fossils and Ancient Life The fossil record provides evidence about the history of life on Earth. It also shows how different
Directed Reading. Section: Precambrian Time and the Paleozoic Era EVOLUTION. beginning of life is called. to. PRECAMBRIAN TIME.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Precambrian Time and the Paleozoic Era 1. Where is the geologic history of Earth recorded? 2. What kind of information can scientists get from the types of rock
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Precambrian Time and the Paleozoic Era 1. Where is the geologic history of Earth recorded? 2. What kind of information can scientists get from the types of rock
History of Life on Earth The Geological Time- Scale
 History of Life on Earth The Geological Time- Scale Agenda or Summary Layout The Geological Time-Scale 1 2 3 The Geological Time-Scale The Beginning of Life Cambrian Explosion The Geological Time-Scale
History of Life on Earth The Geological Time- Scale Agenda or Summary Layout The Geological Time-Scale 1 2 3 The Geological Time-Scale The Beginning of Life Cambrian Explosion The Geological Time-Scale
Reducing Redundancy of Codons through Total Graph
 American Journal of Bioinformatics Original Research Paper Reducing Redundancy of Codons through Total Graph Nisha Gohain, Tazid Ali and Adil Akhtar Department of Mathematics, Dibrugarh University, Dibrugarh-786004,
American Journal of Bioinformatics Original Research Paper Reducing Redundancy of Codons through Total Graph Nisha Gohain, Tazid Ali and Adil Akhtar Department of Mathematics, Dibrugarh University, Dibrugarh-786004,
Evolution Problem Drill 09: The Tree of Life
 Evolution Problem Drill 09: The Tree of Life Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. The age of the Earth is estimated to be about 4.0 to 4.5 billion years old. All of the following methods may be used to estimate
Evolution Problem Drill 09: The Tree of Life Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. The age of the Earth is estimated to be about 4.0 to 4.5 billion years old. All of the following methods may be used to estimate
Evolution and diversity of organisms
 Evolution and diversity of organisms Competency Levels - 7 3.1.1 Uses the theories of origin of life and natural selection to analyze the process of evolution of life 3.2.1 Constructs hierarchy of taxa
Evolution and diversity of organisms Competency Levels - 7 3.1.1 Uses the theories of origin of life and natural selection to analyze the process of evolution of life 3.2.1 Constructs hierarchy of taxa
The Geological Time Scale. Geological time scaled to a cross-country tour of Canada.
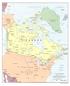 Dryden The Geological Time Scale Geological time scaled to a cross-country tour of anada. The universe came into existence about 14 billion years ago, through an explosion known as the "big bang". ur galaxy
Dryden The Geological Time Scale Geological time scaled to a cross-country tour of anada. The universe came into existence about 14 billion years ago, through an explosion known as the "big bang". ur galaxy
Geological Time Line Time hierarchy. Geological Time Line 1/27/2019
 Chapter 3 What the rocks say: how geology and paleontology reveal the history of life Geological Time Line Time hierarchy Eons Eras Periods Epochs Stages The Geologic Time Line - see handouts Geological
Chapter 3 What the rocks say: how geology and paleontology reveal the history of life Geological Time Line Time hierarchy Eons Eras Periods Epochs Stages The Geologic Time Line - see handouts Geological
Chapters 25 and 26. Searching for Homology. Phylogeny
 Chapters 25 and 26 The Origin of Life as we know it. Phylogeny traces evolutionary history of taxa Systematics- analyzes relationships (modern and past) of organisms Figure 25.1 A gallery of fossils The
Chapters 25 and 26 The Origin of Life as we know it. Phylogeny traces evolutionary history of taxa Systematics- analyzes relationships (modern and past) of organisms Figure 25.1 A gallery of fossils The
Geologic Time. What have scientists learned about Earth s past by studying rocks and fossils?
 Name Geologic Time What have scientists learned about Earth s past by studying rocks and fossils? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about geologic time Record your
Name Geologic Time What have scientists learned about Earth s past by studying rocks and fossils? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about geologic time Record your
~22.5 MYA ~2500 MYA ~3000MYA ~3500 MYA ~1000 MYA ~2100 MYA. Early apes are found. Savannas expand
 Early apes are found. Savannas expand ~22.5 MYA Photosynthesis by blue-green bacteria. Oxygen forms in the atmosphere but immediately reacts with molecules in the ocean and crust of the Earth. The actual
Early apes are found. Savannas expand ~22.5 MYA Photosynthesis by blue-green bacteria. Oxygen forms in the atmosphere but immediately reacts with molecules in the ocean and crust of the Earth. The actual
 The Eras of the Earth In this lesson, we will study the changes that have taken place on the earth since it was formed 4.5 billion years ago. There have been big changes in the temperature of the land,
The Eras of the Earth In this lesson, we will study the changes that have taken place on the earth since it was formed 4.5 billion years ago. There have been big changes in the temperature of the land,
Geologic Time and Life in the Oceans. Oceans and Life. How Old is Earth? The Solar System? Oceans are the birthplace of life.
 Geologic Time and Life in the Oceans Oceans and Life Oceans are the birthplace of life. Life metabolism, growth, reproduction, response to stimuli Metabolism use of energy stored in ambient chemicals Reproduction
Geologic Time and Life in the Oceans Oceans and Life Oceans are the birthplace of life. Life metabolism, growth, reproduction, response to stimuli Metabolism use of energy stored in ambient chemicals Reproduction
2/5/17. #7 Geologic Time #7 Geologic Time
 #7 #7 = all of time since Earth formed (4.6 billion years ago, b.y.a.). Geologists study rocks, fossils, geologic structures (faults, folds) to characterize Earth's history. Natural disasters involve present-day.
#7 #7 = all of time since Earth formed (4.6 billion years ago, b.y.a.). Geologists study rocks, fossils, geologic structures (faults, folds) to characterize Earth's history. Natural disasters involve present-day.
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 12 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 12 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 12 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Chapter 14. The History of the Earth and the Beginning of Life
 Chapter 14 The History of the Earth and the Beginning of Life Hypothesis of early Earth Very hot surface from colliding meteorites Very hot planet core from radioactive materials Volcanoes spewing lava
Chapter 14 The History of the Earth and the Beginning of Life Hypothesis of early Earth Very hot surface from colliding meteorites Very hot planet core from radioactive materials Volcanoes spewing lava
Geologic Time on a Strip of Paper
 Geologic Time on a Strip of Paper Introduction The Earth is 4,600,000,000 years old. That s 4.6 billion years! But what does this mean? This activity is designed to help you get a feel for the age of the
Geologic Time on a Strip of Paper Introduction The Earth is 4,600,000,000 years old. That s 4.6 billion years! But what does this mean? This activity is designed to help you get a feel for the age of the
Bio 1B Lecture Outline (please print and bring along) Fall, 2007
 Bio 1B Lecture Outline (please print and bring along) Fall, 2007 B.D. Mishler, Dept. of Integrative Biology 2-6810, bmishler@berkeley.edu Evolution lecture #7 -- Early earth, continental drift, early life
Bio 1B Lecture Outline (please print and bring along) Fall, 2007 B.D. Mishler, Dept. of Integrative Biology 2-6810, bmishler@berkeley.edu Evolution lecture #7 -- Early earth, continental drift, early life
Lect. 19. Natural Selection I. 4 April 2017 EEB 2245, C. Simon
 Lect. 19. Natural Selection I 4 April 2017 EEB 2245, C. Simon Last Time Gene flow reduces among population variability, reduces structure Interaction of climate, ecology, bottlenecks, drift, and gene flow
Lect. 19. Natural Selection I 4 April 2017 EEB 2245, C. Simon Last Time Gene flow reduces among population variability, reduces structure Interaction of climate, ecology, bottlenecks, drift, and gene flow
Bio 2 Plant and Animal Biology
 Bio 2 Plant and Animal Biology Evolution Evolution as the explanation for life s unity and diversity Darwinian Revolution Two main Points Descent with Modification Natural Selection Biological Species
Bio 2 Plant and Animal Biology Evolution Evolution as the explanation for life s unity and diversity Darwinian Revolution Two main Points Descent with Modification Natural Selection Biological Species
Clues to the Past. Grades 6-8 Educational Program Guide
 Clues to the Past Grades 6-8 Educational Program Guide OAS Science Practices: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8 Program Overview The Clues to the Past program will introduce students to several 300 million years old
Clues to the Past Grades 6-8 Educational Program Guide OAS Science Practices: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8 Program Overview The Clues to the Past program will introduce students to several 300 million years old
*m.y.a. stands for millions of years ago
 1 Earth, and the other planets are the result of stellar material that was ejected from the sun/star as it spun into its spherical shape and condensed hence all the planets are roughly spherical and have
1 Earth, and the other planets are the result of stellar material that was ejected from the sun/star as it spun into its spherical shape and condensed hence all the planets are roughly spherical and have
I. History of Life on Earth
 Evolution I. History of Life on Earth I. History of Life A. Early History of Earth I. Early earth was inhospitable hot, with many volcanoes little free oxygen and lots of carbon dioxide other gases present:
Evolution I. History of Life on Earth I. History of Life A. Early History of Earth I. Early earth was inhospitable hot, with many volcanoes little free oxygen and lots of carbon dioxide other gases present:
History of Life on Earth
 History of Life on Earth Deep Time 4550 mya to present era eon era era Precambrian Eon Hadean Era Geology Birth of solar system - 4.55 bya Escaping gasses create early atmosphere Earth s core forms - 4.4
History of Life on Earth Deep Time 4550 mya to present era eon era era Precambrian Eon Hadean Era Geology Birth of solar system - 4.55 bya Escaping gasses create early atmosphere Earth s core forms - 4.4
Natural Selection. Nothing in Biology makes sense, except in the light of evolution. T. Dobzhansky
 It is interesting to contemplate a tangled bank, clothed with many plants of many kinds, with birds singing on the bushes, with various insects flitting about, and with worms crawling through the damp
It is interesting to contemplate a tangled bank, clothed with many plants of many kinds, with birds singing on the bushes, with various insects flitting about, and with worms crawling through the damp
Fossils & The Geologic Time Scale
 Fossils & The Geologic Time Scale Fossils Preserved remains or traces of an organism that lived in the past. Fossils are formed when organisms die and are buried in sediment. Eventually the sediment builds
Fossils & The Geologic Time Scale Fossils Preserved remains or traces of an organism that lived in the past. Fossils are formed when organisms die and are buried in sediment. Eventually the sediment builds
The Significance of the Fossil Record ( Susan Matthews and Graeme Lindbeck)
 The Significance of the Fossil Record ( Susan Matthews and Graeme Lindbeck) The fossil record indicates the evolutionary history of life. Many events together, including: continental drift, changes in
The Significance of the Fossil Record ( Susan Matthews and Graeme Lindbeck) The fossil record indicates the evolutionary history of life. Many events together, including: continental drift, changes in
Bio94 Discussion Activity week 3: Chapter 27 Phylogenies and the History of Life
 Bio94 Discussion Activity week 3: Chapter 27 Phylogenies and the History of Life 1. Constructing a phylogenetic tree using a cladistic approach Construct a phylogenetic tree using the following table:
Bio94 Discussion Activity week 3: Chapter 27 Phylogenies and the History of Life 1. Constructing a phylogenetic tree using a cladistic approach Construct a phylogenetic tree using the following table:
sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Origin of Life
 sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Origin of Life 2010-2011 ARCHEAN Millions of years ago PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC 0 500 1000 Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Colonization
sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Origin of Life 2010-2011 ARCHEAN Millions of years ago PRECAMBRIAN PROTEROZOIC 0 500 1000 Cenozoic Mesozoic Paleozoic Colonization
Absolute Age - Radioactive Decay. Absolute Age - Isotopes. Absolute Age - Radioactive Decay
 GEOL 100 (Planet Earth) #12 - Earth s Clock Geologic Time - Absolute Age Absolute Age = age of rock (or geologic event) in years. Need constant process as well as record of process; constant process in
GEOL 100 (Planet Earth) #12 - Earth s Clock Geologic Time - Absolute Age Absolute Age = age of rock (or geologic event) in years. Need constant process as well as record of process; constant process in
