River Model (Delft3D)
|
|
|
- Cuthbert Lucas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Short River Model (Delft3D) & DIVERSION ANALYSIS presented by Nina J. Reins, PE, PhD, PMP State of the Coast May 30-June 1, 2018
2 Overview of Presentation Problem Statement & Background Analysis Key Findings & Recommendations UNO Dissertation Research Committee Chair: Dr. Alex McCorquodale, Co-Chair: Dr. Ioannis Georgiou
3 Problem Statement Expedited Analysis of independent and cumulative impacts of diversions. Identify impacts to bathymetric changes due to hydrograph variability Identify independent and cumulative impacts of different diversion schemes Development of shortmodel from calibrated regional model Conduct a comparison between a uniform and variable Mississippi River Discharge Hydrograph. Analyze bathymetric river changes and diversion efficiencies
4 Background: Model Development Regional 3-D Model (MRHDM) Belle Chasse Belle Chasse (RM 75) Mid-Breton Mid Barataria Lower Barataria WPAH Lower Breton HOP HOP
5 Background: Model Development The model was calibrated as part of the Regional Model. No change in grid design between Regional and shortmodel. Diversion locations, orientations, inverts and widths based on Water Institute recommendations. Lateral grid sizes of the order of 50 m with 10 parabolically distributed sigma layers with refinement at the bed. The lateral resolution was adjusted until the observed recirculation eddy in Dr. Mead Allison s Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler (ADCP) data were reproduced in the model. (McCorquodale 2017)
6 Background: Model Inputs Model: Grid and Bathymetry (USACE Decadal Surveys suppl. with ADCIRC data, data from Mississippi River Study & LPBF data) Cut at Belle Chasse (U/S Boundary) Bed Layer Input: Sand thickness distribution of bed (M. Allison, Tulane & USACE) Silt & Clay fraction in the bed (M. Allison, Tulane & USACE) Suspended Sediment Inputs: Sand, Silt and Clay based on Dynamic Rating Curves based on USGS data (Baton Rouge and Belle Chasse). Hydrograph: Water Institute Annual Discharge Hydrograph for Bonnet Carré Section (RM 127). Upstream Boundary Belle Chasse (RM 75.5) Developed 12-Year Variable Hydrograph for comparison to Uniform Hydrograph Sea Level Rise/Subsidence: USACE River Stages + GOM Stage adjusted by 0.5 m ESLR over 50 years. NRC III Sea Level Rise Projection HEC6t (BCG/King) subsidence rates (up to 2.3 cm/yr). Diversion Discharges: Water Institute Discharge Curves for Diversions.
7 Runs with SLR: use NRC III Curve Upstream Boundary: Discharge Hydrograph (Variable & Uniform) Suspended Sediment (5 sediment classes) Belle Chasse & Baton Rouge Gages River Boundaries: Gulf Of Mexico Stage Condition (Source USACE Southwest Pass) Controlled Diversions same as MRHDM (prescribed discharge) Uncontrolled Diversion Runs to validate prescribed flows
8 Simulation Conditions 12 years x 365d per year = 4,380 days (Morphological Time) 12 years x 365 days per year / MORFAC (40) = days (Hydrodynamic Time) Morphological Factor (MORFAC) = 40 same as MRHDM Yields the best compromise between turn-around and accuracy of the morphological predictions. Sediment Transport Calculations = Van Rijn: same as MRHDM The Van Rijn 1984 sand transport model was used for the non-cohesive sediment Silt & Clay were based on Partheniades- Krone formulations
9 Is the equilibrium bathymetry independent of the annual variability of the hydrograph?
10 Observed Increase in Mean Flow One potential explanation could be an increase in participation within the watershed due to climate change.
11 ANALYSIS Both hydrograph cases result in similar erosion/deposition patterns The uniform case has less erosion upstream and less deposition downstream at 48 years.
12 Analysis: Bathymetric Equilibrium Morphological equilibrium is defined as the condition at which the rate of change in deposition approaches zero. Dynamic morphological equilibrium is defined as the condition at which the mean rate of change approaches zero, but the derivative oscillates about the mean. Actual Deposition Difference (Variable Uniform) There is no absolute or dynamic equilibrium in the 48-year simulation.
13 Analysis: Diversion Sand Capture This slight variance can be explained by the slightly higher river flow peaks occurring over time in the variable hydrograph case, providing more energy to transport sand in suspension and diverting it through a diversion structure. Sand captured by the diversion depends on the availability of sand & the hydrograph pattern. The variable case captures approximately 2% more the available sand than the uniform case.
14 Analysis: Diversion Interdependencies Diversion Scenario 1 Scenario 2 Scenario 3 Scenario 4 No Diversions Mid - Breton 0 cfs (Run 3) 35,000 cfs (Run 12) 0 cfs (Run 3) 25,000 cfs (Run 16) 0 cfs (Run 3) 35,000 cfs (Run 12) 0 cfs (Run 3) 40,000 cfs (Run 25) Mid-Barataria 75,000 cfs (Run 6) 25,000 cfs (Run 17) 35,000 cfs (Run 21) 40,000 cfs (Run 26) Lower Barataria 50,000 cfs (Run 13) 25,000 cfs (Run 18) 35,000 cfs (Run 22) 40,000 cfs (Run 27) Lower Breton 50,000 cfs (Run 14) 25,000 cfs (Run 19) 35,000 cfs (Run 23) 40,000 cfs (Run 28) Total 210,000 cfs (Run 15) 100,000 cfs (Run 20) 140,000 cfs (Run 24) 160,000 cfs (Run 29) 12-Year Runs with Variable Hydrographs If the total flow diverted through multiple diversions is less than critical rate, does each diversion function as an independent structure in terms of local deposition and sedimentation captured?
15 Analysis: Evaluation by Reach
16 Analysis: Deposition by Reach Individual Diversion Impacts 210K 160K 100K 140K Four (4) Diversion Scenario Impacts Increase in deposition with increase in total flow is non-linear. 1 larger diversion impacts more reaches than a smaller diversion at the same location.
17 Analysis: Deposition by Reach Dependencies increases with the total diverted flow by a single diversion. For same discharge flows, the deposition increases the closer the diversions are located to HOP. Each diversion does not function independent in terms of local and regional deposition within the Mississippi River.
18 Analysis: Sediment Diverted For total diversion flow < 140,000 cfs, the difference in diverted sand between 1 and 4 diversion cases is < 3%. When excluding the Lower Breton Diversion, a total flow of less than 140,000cfs would only generate a difference of < 1%. Total Diverted Flow should not exceed 140,000 cfs
19 Diverted Sand Load (4 diversions at same time) Regional Model: Sediment Diverted Total Sand Load (Tonnes/day) 35,000 30,000 25,000 20,000 15,000 10,000 Conclusions: 1. Mid-Barataria is 75,000cfs and only derives slightly more sand load than Mid-Breton at 35,000cfs. 2. Lower Breton and Lower Barataria are 50,000cfs and are relatively less efficient due to loss of streampower. Mid-Barataria Mid-Breton Lower Breton Div Lower Barataria Div 5, /1/2015 0:00 1/1/2016 0:00 12/31/2016 0:00 12/31/2017 0:00 12/31/2018 0:00 12/31/2019 0:00
20 Analysis: System Response due to SLR Average loss at year 48 is approx. 18%. (max. 24%) Instantaneous discharge (> 8,000m 3 /s) data were plotted for Venice (RM 11.2). The results show an accelerated loss of stream power with time, which contributes to accelerated deposition.
21 Analysis: Diversion Changes Does the river have sufficient energy to divert the targeted discharges for the 4 main diversion locations? There is sufficient energy in the river to divert the desired flows to the established maximum of 210,000 cfs with an exit channel with 2 m/s velocity. (2m/s is anticipated to prevent sand deposition in the delivery channel) Diversion (2012 Master Plan) Qmax [cfs] RM Invert [ft] Width [ft] Remarks Mid-Barataria 75, Myrtle Grove Mid-Breton 35, White Ditch Lower Barataria 50, Empire Lower Breton 50, Black Bay It is assumed that there are no energy losses due to the control structure, which implies a wide channel opening. Changes in width will warrant revised analysis There is no absolute or dynamic equilibrium in the 48-year simulation.
22 Analysis: Deposition Trends with SLR Uniform Hydrograph Variable Hydrograph Oscillating values 12 Year Periodicity = Hydrograph Period A true equilibrium was neither achieved for the without SLR nor the with SLR scenario evaluated by the 48 year model runs. The depositional trends are accelerated with SLR
23 Analysis: Deposition due to SLR & Diversions Normalized Deposition HOP Belle Chasse Over 48 years the deposition at HOP approaches the 48-year SLR and decreases to approx. 10% of the 48-year SLR at Belle Chasse.
24 Analysis: How does change in sediment load impact morphologic changes? t = 12 years (sand + 50%) t = 0 t = 12 years (Base) A 50% increase in sand load is representative of the uncertainty in the upstream sand concentration. A 50% increase in sand load generates deposition within the river, especially within existing point bars.
25 Analysis: Depocenter Shifts Shift in Depositional Zone due to Increase in Sand at Upstream Boundary Shift in Depositional Zone due to Introduction of 2 Diversions Decreased Stream Power Increased Stream Power
26 Analysis: Sand Diverted due to variability in Sand Supply Maximum Diversion Sand Load Base Case = approx. 300 kg/s Maximum Diversion Sand Load Modified Case = approx. 350 kg/s (when neglecting the transient effect of the first year) 50% sand increase at the upstream boundary results in a proportionally smaller increase of sand load in the diversion.
27 Key Conclusions The absolute bathymetry equilibrium depends on the annual variability of the hydrograph, even if the flow duration curves are the same. A near bathymetric equilibrium is reached upstream of Fort St. Philip, whereas downstream of Fort St. Philip no equilibrium occurred within the 48 year period of the simulation, due to the effect of the distributaries and uncontrolled outflows. Loss of streampower generated by sea level rise and diverted flow results in increased deposition, especially below Fort St. Philip. Morphological changes are dependent on the number and location of multiple diversions. The largest interdependencies occur for the most downstream diversions, and increase with the total diverted flow. Sediment capture showed only minor interdependencies for multiple diversions if the total diverted flow remains below 140,000 cfs. The introduction of larger diversions, like the Mid-Barataria diversion, result in an upstream shift of the depocenter and an increase of cumulative impacts along the river system. A 50% increase in sand concentration had a greater impact on the growth of bars than on the capture efficiency of a diversion. Regional long term trends need to be considered when evaluating local effects due to individual projects. UNO Dissertation Research Committee Chair: Dr. Alex McCorquodale, Co-Chair: Dr. Ioannis Georgiou
28 Recommendations A 48-year variable hydrograph should be developed to represent the actual periodicity of the historical record and include an adjustment for climate change and related discharge trends. Study a combination of proposed diversions and beneficial dredging. Analyze the impacts of removal of upstream point bar material to performance of diversion. Running the Shortmodel for the planned operational procedures as well as the adjusted location and geometry of the Mid-Barataria and Mid-Breton Diversion to identify cumulative impacts and capture rates. UNO Dissertation Research Committee Chair: Dr. Alex McCorquodale, Co-Chair: Dr. Ioannis Georgiou
29 QUESTIONS Nina J. Reins, PhD, PE, PMP 900 Camp Street #3C3 New Orleans, Louisiana UNO Dissertation Research Committee Chair: Dr. Alex McCorquodale, Co-Chair: Dr. Ioannis Georgiou
Mississippi River West Bay Diversion Geomorphic Assessment and 1-D Modeling Plan
 Mississippi River West Bay Diversion Geomorphic Assessment and 1-D Modeling Plan Freddie Pinkard and Charlie Little Research Hydraulic Engineers ERDC-CHL-River Engineering Branch 27 February 2009 Lane
Mississippi River West Bay Diversion Geomorphic Assessment and 1-D Modeling Plan Freddie Pinkard and Charlie Little Research Hydraulic Engineers ERDC-CHL-River Engineering Branch 27 February 2009 Lane
Appendix O. Sediment Transport Modelling Technical Memorandum
 Appendix O Sediment Transport Modelling Technical Memorandum w w w. b a i r d. c o m Baird o c e a n s engineering l a k e s design r i v e r s science w a t e r s h e d s construction Final Report Don
Appendix O Sediment Transport Modelling Technical Memorandum w w w. b a i r d. c o m Baird o c e a n s engineering l a k e s design r i v e r s science w a t e r s h e d s construction Final Report Don
Forecasting Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia under Scenarios of Watershed and River Management
 Forecasting Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia under Scenarios of Watershed and River Management Dubravko Justic and Lixia Wang Department of Oceanography and Coastal Sciences College of the Coast and Environment
Forecasting Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia under Scenarios of Watershed and River Management Dubravko Justic and Lixia Wang Department of Oceanography and Coastal Sciences College of the Coast and Environment
THE IMPORTANCE OF SCIENCE IN COASTAL RESTORATION IN LOUISIANA
 THE IMPORTANCE OF SCIENCE IN COASTAL RESTORATION IN LOUISIANA Barb Kleiss USACE, Mississippi Valley Division August 3, 2011 LCA S&T Office Authorized under WRDA 2007 Designed to address technical issues
THE IMPORTANCE OF SCIENCE IN COASTAL RESTORATION IN LOUISIANA Barb Kleiss USACE, Mississippi Valley Division August 3, 2011 LCA S&T Office Authorized under WRDA 2007 Designed to address technical issues
Development and application of demonstration MIKE 21C morphological model for a bend in Mekong River
 Development and application of demonstration MIKE 21C morphological model for a bend in Mekong River September 2015 0 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Data collection... 3 2.1 Additional data...
Development and application of demonstration MIKE 21C morphological model for a bend in Mekong River September 2015 0 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Data collection... 3 2.1 Additional data...
B-1. Attachment B-1. Evaluation of AdH Model Simplifications in Conowingo Reservoir Sediment Transport Modeling
 Attachment B-1 Evaluation of AdH Model Simplifications in Conowingo Reservoir Sediment Transport Modeling 1 October 2012 Lower Susquehanna River Watershed Assessment Evaluation of AdH Model Simplifications
Attachment B-1 Evaluation of AdH Model Simplifications in Conowingo Reservoir Sediment Transport Modeling 1 October 2012 Lower Susquehanna River Watershed Assessment Evaluation of AdH Model Simplifications
U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Detroit District. Sediment Trap Assessment Saginaw River, Michigan
 U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Detroit District December 2001 December 2001 This report has been prepared for USACE, Detroit District by: W.F. BAIRD & ASSOCIATES LTD. 2981 YARMOUTH GREENWAY MADISON, WISCONSIN
U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Detroit District December 2001 December 2001 This report has been prepared for USACE, Detroit District by: W.F. BAIRD & ASSOCIATES LTD. 2981 YARMOUTH GREENWAY MADISON, WISCONSIN
Journal of Hydrology
 Journal of Hydrology 472 473 (2012) 340 354 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Journal of Hydrology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jhydrol Numerical modeling of hydrodynamics
Journal of Hydrology 472 473 (2012) 340 354 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Journal of Hydrology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jhydrol Numerical modeling of hydrodynamics
KEY CONTROLS ON SEDIMENT BUDGETING IN THE MISSISSIPPI RIVER FROM SOURCE TO SINK
 KEY CONTROLS ON SEDIMENT BUDGETING IN THE MISSISSIPPI RIVER FROM SOURCE TO SINK Mead Allison The Water Institute of the Gulf & Tulane University What Controls the Availability of Sediment in the Restoration
KEY CONTROLS ON SEDIMENT BUDGETING IN THE MISSISSIPPI RIVER FROM SOURCE TO SINK Mead Allison The Water Institute of the Gulf & Tulane University What Controls the Availability of Sediment in the Restoration
MISSISSIPPI RIVER DELTA OVERVIEW
 MISSISSIPPI RIVER DELTA OVERVIEW Science and Engineering Special Team Conference Louisiana State University October 9, 2012 Introduction Basics of the Mississippi Delta Natural and Human-Induced Land Loss
MISSISSIPPI RIVER DELTA OVERVIEW Science and Engineering Special Team Conference Louisiana State University October 9, 2012 Introduction Basics of the Mississippi Delta Natural and Human-Induced Land Loss
Remaining Capacity in Great Lakes Reservoirs
 US Army Corps of Engineers Detroit District Remaining Capacity in Great Lakes Reservoirs Storage Capacity Behind Great Lakes Dams Field Data and Modeling Motivation for project Project overview Data and
US Army Corps of Engineers Detroit District Remaining Capacity in Great Lakes Reservoirs Storage Capacity Behind Great Lakes Dams Field Data and Modeling Motivation for project Project overview Data and
Sediment Transport Analysis for Stream Restoration Design: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly.
 Sediment Transport Analysis for Stream Restoration Design: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. Brett Jordan Phd, PE HydroGeo Designs LLC. Land and Water Services Inc. THE GOOD THE BAD THE UGLY THE GOOD THE
Sediment Transport Analysis for Stream Restoration Design: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. Brett Jordan Phd, PE HydroGeo Designs LLC. Land and Water Services Inc. THE GOOD THE BAD THE UGLY THE GOOD THE
The Mississippi River: Its Role in Restoration Efforts and Potential Effects of Climate Change
 The Mississippi River: Its Role in Restoration Efforts and Potential Effects of Climate Change Clinton S. Willson, P.E., Ph.D. Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering Louisiana State University
The Mississippi River: Its Role in Restoration Efforts and Potential Effects of Climate Change Clinton S. Willson, P.E., Ph.D. Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering Louisiana State University
A 3-D Hydrodynamic Modeling at Head of Passes of the Mississippi River
 University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO University of New Orleans Theses and Dissertations Dissertations and Theses Spring 5-16-2014 A 3-D Hydrodynamic Modeling at Head of Passes of the Mississippi
University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO University of New Orleans Theses and Dissertations Dissertations and Theses Spring 5-16-2014 A 3-D Hydrodynamic Modeling at Head of Passes of the Mississippi
One-Dimensional Modeling of Sedimentation Impacts for the Mississippi River at the West Bay Diversion
 Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 2013, 5, 16-29 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jwarp.2013.59a002 Published Online September 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jwarp) One-Dimensional Modeling of Sedimentation
Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 2013, 5, 16-29 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jwarp.2013.59a002 Published Online September 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jwarp) One-Dimensional Modeling of Sedimentation
Sediment Traps. CAG Meeting May 21, 2012
 Sediment Traps CAG Meeting May 21, 2012 Agenda Background Fundamentals of Sediment Transport Sediment Trap Existing Information Next Steps 2 The Site Saginaw River 22 mile river beginning at confluence
Sediment Traps CAG Meeting May 21, 2012 Agenda Background Fundamentals of Sediment Transport Sediment Trap Existing Information Next Steps 2 The Site Saginaw River 22 mile river beginning at confluence
Hydrodynamic model of St. Clair River with Telemac-2D Phase 2 report
 Hydrodynamic model of St. Clair River with Telemac-2D Phase 2 report Controlled Technical Report CHC-CTR-084 revision 1 March 2009 NRC-CHC has prepared this report for the International Joint Commission
Hydrodynamic model of St. Clair River with Telemac-2D Phase 2 report Controlled Technical Report CHC-CTR-084 revision 1 March 2009 NRC-CHC has prepared this report for the International Joint Commission
Lower Susquehanna River Reservoir System Proposed Modeling Enhancements
 Lower Susquehanna River Reservoir System Proposed Modeling Enhancements Presented at the Chesapeake Bay Program Scientific and Technical Advisory Committee (STAC) Workshop January 13, 2016 Overview Due
Lower Susquehanna River Reservoir System Proposed Modeling Enhancements Presented at the Chesapeake Bay Program Scientific and Technical Advisory Committee (STAC) Workshop January 13, 2016 Overview Due
Modeling of long-term sedimentation in the Osijek port basin
 Water Management and Hydraulic Engineering 2015 Litera Brno, ISBN 978-80-214-5230-5, ISSN 2410-5910 Modeling of long-term sedimentation in the Osijek port basin G. Gilja, N. Kuspilić (Faculty of civil
Water Management and Hydraulic Engineering 2015 Litera Brno, ISBN 978-80-214-5230-5, ISSN 2410-5910 Modeling of long-term sedimentation in the Osijek port basin G. Gilja, N. Kuspilić (Faculty of civil
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Coupled Process Studies and Numerical Simulations of Channel Hydrodynamics and Sand Dynamics in Tide-Dominated River Channels:
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Coupled Process Studies and Numerical Simulations of Channel Hydrodynamics and Sand Dynamics in Tide-Dominated River Channels:
Measurements of lateral flow from the Mississippi River at Mardi Gras Pass in the Bohemia Spillway using synoptic ADCP
 Measurements of lateral flow from the Mississippi River at Mardi Gras Pass in the Bohemia Spillway using synoptic ADCP A Technical Report Submitted to: The Lake Pontchartrain Basin Foundation Submitted
Measurements of lateral flow from the Mississippi River at Mardi Gras Pass in the Bohemia Spillway using synoptic ADCP A Technical Report Submitted to: The Lake Pontchartrain Basin Foundation Submitted
Mississippi River and Tributaries Project Mississippi River Geomorphology and Potamology Program
 Mississippi River and Tributaries Project Mississippi River Geomorphology and Potamology Program Barb Kleiss, Mississippi Valley Division Freddie Pinkard, Vicksburg District June, 2016 Program Objectives
Mississippi River and Tributaries Project Mississippi River Geomorphology and Potamology Program Barb Kleiss, Mississippi Valley Division Freddie Pinkard, Vicksburg District June, 2016 Program Objectives
How to predict the sedimentological impacts of reservoir operations?
 ICSE 212 How to predict the sedimentological impacts of reservoir operations? E. Valette EDF CIH eric.valette@edf.fr M. Jodeau EDF R&D LNHE magali.jodeau@edf.fr Presentation of the numerical code Courlis
ICSE 212 How to predict the sedimentological impacts of reservoir operations? E. Valette EDF CIH eric.valette@edf.fr M. Jodeau EDF R&D LNHE magali.jodeau@edf.fr Presentation of the numerical code Courlis
The Yellow River Initiative: The Birth of a System Approach to Challenges Facing the Everglades of the North
 The Yellow River Initiative: The Birth of a System Approach to Challenges Facing the Everglades of the North Robert Barr and Siavash Beik 2016 INAFSM Annual Conference Belterra Conference Center, Indiana
The Yellow River Initiative: The Birth of a System Approach to Challenges Facing the Everglades of the North Robert Barr and Siavash Beik 2016 INAFSM Annual Conference Belterra Conference Center, Indiana
HEC-RAS Reservoir Transport Simulation of Three Reservoirs in the Lower Susquehanna River Basin. Mike Langland and Ed Koerkle
 HEC-RAS Reservoir Transport Simulation of Three Reservoirs in the Lower Susquehanna River Basin Mike Langland and Ed Koerkle Topics Background / Project Objectives Data Selection - Sediment and Geometric
HEC-RAS Reservoir Transport Simulation of Three Reservoirs in the Lower Susquehanna River Basin Mike Langland and Ed Koerkle Topics Background / Project Objectives Data Selection - Sediment and Geometric
Bishopville Prong Study
 Bathymetric and Sediment Assessment in the Bishopville Prong of St. Martin River Darlene V. Wells, Richard A. Ortt, Jr., and Stephen Van Ryswick Funded by MCBP 2011-2012 Implementation Grant Objectives
Bathymetric and Sediment Assessment in the Bishopville Prong of St. Martin River Darlene V. Wells, Richard A. Ortt, Jr., and Stephen Van Ryswick Funded by MCBP 2011-2012 Implementation Grant Objectives
7.3 Sediment Delivery Analysis
 7.3 Sediment Delivery Analysis In order to evaluate potential changes in sedimentation patterns that could occur due to impacts from the FCP and LPP alignments, sediment assessment models were constructed
7.3 Sediment Delivery Analysis In order to evaluate potential changes in sedimentation patterns that could occur due to impacts from the FCP and LPP alignments, sediment assessment models were constructed
Sediment and Nutrient Mass Balance Model of ConowingoPool
 Sediment and Nutrient Mass Balance Model of ConowingoPool Mark Velleux and Jim Fitzpatrick HDR Engineering Chesapeake Bay Program Modeling Quarterly Review: August 10, 2016 Model Grid and Spatial Resolution
Sediment and Nutrient Mass Balance Model of ConowingoPool Mark Velleux and Jim Fitzpatrick HDR Engineering Chesapeake Bay Program Modeling Quarterly Review: August 10, 2016 Model Grid and Spatial Resolution
St. Clair River Conveyance Change 2007 to 2012
 St. Clair River Conveyance Change 2007 to 2012 Morphologic Change in the St. Clair River 2007 2012 Conveyance Change Report U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Detroit District Great Lakes Hydraulics and Hydrology
St. Clair River Conveyance Change 2007 to 2012 Morphologic Change in the St. Clair River 2007 2012 Conveyance Change Report U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Detroit District Great Lakes Hydraulics and Hydrology
Numerical modeling of sediment flushing from Lewis and Clark Lake
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln US Army Research U.S. Department of Defense 2013 Numerical modeling of sediment flushing from Lewis and Clark Lake Jungkyu
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln US Army Research U.S. Department of Defense 2013 Numerical modeling of sediment flushing from Lewis and Clark Lake Jungkyu
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Coupled Process Studies and Numerical Simulations of Channel Hydrodynamics and Sand Dynamics in Tide-Dominated River Channels:
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Coupled Process Studies and Numerical Simulations of Channel Hydrodynamics and Sand Dynamics in Tide-Dominated River Channels:
Temporal variability of partially-contaminated sediments in a strongly regulated reservoir of the upper Rhine River
 Temporal variability of partially-contaminated sediments in a strongly regulated reservoir of the upper Rhine River Germain Antoine 1,2,, Thomas Pretet 1,3,, Matthieu Secher 3,, and Anne Clutier 3, 1 Laboratoire
Temporal variability of partially-contaminated sediments in a strongly regulated reservoir of the upper Rhine River Germain Antoine 1,2,, Thomas Pretet 1,3,, Matthieu Secher 3,, and Anne Clutier 3, 1 Laboratoire
Morphodynamic evolution of a lower Mississippi River channel bar after sand mining
 EARTH SURFACE PROCESSES AND LANDFORMS Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 41, 526 542 (2016) Copyright 2015 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. Published online 5 November 2015 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com)
EARTH SURFACE PROCESSES AND LANDFORMS Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 41, 526 542 (2016) Copyright 2015 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. Published online 5 November 2015 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com)
The Mississippi River and its Role in Restoration Efforts
 The Mississippi River and its Role in Restoration Efforts Clinton S. Willson, P.E., Ph.D. Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering Louisiana State University Acknowledgements LA Department of Natural
The Mississippi River and its Role in Restoration Efforts Clinton S. Willson, P.E., Ph.D. Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering Louisiana State University Acknowledgements LA Department of Natural
Sediment Dynamics from the Summit to the Sea
 Sediment Dynamics from the Summit to the Sea 435 (Proceedings of a symposium held in New Orleans, Louisiana, USA, 11 14 December 214) (IAHS Publ. 367, 214). Effects of salinity and particle concentration
Sediment Dynamics from the Summit to the Sea 435 (Proceedings of a symposium held in New Orleans, Louisiana, USA, 11 14 December 214) (IAHS Publ. 367, 214). Effects of salinity and particle concentration
Reactivation of Klingnau reservoir sidearm: Numerical simulation of sediment release downstream
 River Flow 2014 Schleiss et al. (Eds) 2014 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-02674-2 Reactivation of Klingnau reservoir sidearm: Numerical simulation of sediment release downstream A. Amini
River Flow 2014 Schleiss et al. (Eds) 2014 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-02674-2 Reactivation of Klingnau reservoir sidearm: Numerical simulation of sediment release downstream A. Amini
Sediment Transport, Numerical Modeling and Reservoir Management some Concepts and Applications
 Sediment Transport, Numerical Modeling and Reservoir Management some Concepts and Applications CEMRACS 2013 August 6 th Magali Jodeau EDF R&D LNHE magali.jodeau@edf.fr Overview of the presentation What
Sediment Transport, Numerical Modeling and Reservoir Management some Concepts and Applications CEMRACS 2013 August 6 th Magali Jodeau EDF R&D LNHE magali.jodeau@edf.fr Overview of the presentation What
Stream Restoration and Environmental River Mechanics. Objectives. Pierre Y. Julien. 1. Peligre Dam in Haiti (deforestation)
 Stream Restoration and Environmental River Mechanics Pierre Y. Julien Malaysia 2004 Objectives Brief overview of environmental river mechanics and stream restoration: 1. Typical problems in environmental
Stream Restoration and Environmental River Mechanics Pierre Y. Julien Malaysia 2004 Objectives Brief overview of environmental river mechanics and stream restoration: 1. Typical problems in environmental
Tarbela Dam in Pakistan. Case study of reservoir sedimentation
 Tarbela Dam in Pakistan. HR Wallingford, Wallingford, UK Published in the proceedings of River Flow 2012, 5-7 September 2012 Abstract Reservoir sedimentation is a main concern in the Tarbela reservoir
Tarbela Dam in Pakistan. HR Wallingford, Wallingford, UK Published in the proceedings of River Flow 2012, 5-7 September 2012 Abstract Reservoir sedimentation is a main concern in the Tarbela reservoir
Hindcasting morphodynamic evolution with sand mud interactions in the Yangtze Estuary
 doi:10.5194/piahs-368-430-2015 430 Remote Sensing and GIS for Hydrology and Water Resources (IAHS Publ. 368, 2015) (Proceedings RSHS14 and ICGRHWE14, Guangzhou, China, August 2014). Hindcasting morphodynamic
doi:10.5194/piahs-368-430-2015 430 Remote Sensing and GIS for Hydrology and Water Resources (IAHS Publ. 368, 2015) (Proceedings RSHS14 and ICGRHWE14, Guangzhou, China, August 2014). Hindcasting morphodynamic
The investigation of sediment processes in rivers by means of the Acoustic Doppler Profiler
 368 Evolving Water Resources Systems: Understanding, Predicting and Managing Water Society Interactions Proceedings of ICWRS014, Bologna, Italy, June 014 (IAHS Publ. 364, 014). The investigation of sediment
368 Evolving Water Resources Systems: Understanding, Predicting and Managing Water Society Interactions Proceedings of ICWRS014, Bologna, Italy, June 014 (IAHS Publ. 364, 014). The investigation of sediment
Rivers and Streams. Streams. Hydrologic Cycle. Drainage Basins and Divides. Colorado River Drainage Basin. Colorado Drainage Basins.
 Chapter 14 Hydrologic Cycle Rivers and Streams Streams A stream is a body of water that is confined in a channel and moves downhill under the influence of gravity. This definition includes all sizes of
Chapter 14 Hydrologic Cycle Rivers and Streams Streams A stream is a body of water that is confined in a channel and moves downhill under the influence of gravity. This definition includes all sizes of
Erosion Rate is a Function of Erodibility and Excess Shear Stress = k ( o - c ) From Relation between Shear Stress and Erosion We Calculate c and
 Equilibrium, Shear Stress, Stream Power and Trends of Vertical Adjustment Andrew Simon USDA-ARS, Oxford, MS asimon@msa-oxford.ars.usda.gov Non-Cohesive versus Cohesive Materials Non-cohesive: sands and
Equilibrium, Shear Stress, Stream Power and Trends of Vertical Adjustment Andrew Simon USDA-ARS, Oxford, MS asimon@msa-oxford.ars.usda.gov Non-Cohesive versus Cohesive Materials Non-cohesive: sands and
COASTAL DATA APPLICATION
 2015 Coastal GeoTools Proactive By Design. Our Company Commitment COASTAL DATA APPLICATION Projecting Future Coastal Flood Risk for Massachusetts Bay Bin Wang, Tianyi Liu, Daniel Stapleton & Michael Mobile
2015 Coastal GeoTools Proactive By Design. Our Company Commitment COASTAL DATA APPLICATION Projecting Future Coastal Flood Risk for Massachusetts Bay Bin Wang, Tianyi Liu, Daniel Stapleton & Michael Mobile
PART 2:! FLUVIAL HYDRAULICS" HYDROEUROPE
 PART 2:! FLUVIAL HYDRAULICS" HYDROEUROPE 2009 1 HYDROEUROPE 2009 2 About shear stress!! Extremely complex concept, can not be measured directly!! Computation is based on very primitive hypotheses that
PART 2:! FLUVIAL HYDRAULICS" HYDROEUROPE 2009 1 HYDROEUROPE 2009 2 About shear stress!! Extremely complex concept, can not be measured directly!! Computation is based on very primitive hypotheses that
HYDRAULIC STRUCTURES, EQUIPMENT AND WATER DATA ACQUISITION SYSTEMS - Vol. I - Hydraulics of Two-Phase Flow: Water and Sediment - G R Basson
 HYDRAULICS OF TWO-PHASE FLOWS: WATER AND SEDIMENT G R Basson Dept. of Civil Engineering, University of Stellenbosch, South Africa. Keywords: sediment, sediment transport, turbulence, river regime, stream
HYDRAULICS OF TWO-PHASE FLOWS: WATER AND SEDIMENT G R Basson Dept. of Civil Engineering, University of Stellenbosch, South Africa. Keywords: sediment, sediment transport, turbulence, river regime, stream
Influence of the Major Drainages to the Mississippi River and Implications for System Level Management
 Influence of the Major Drainages to the Mississippi River and Implications for System Level Management Brian M. Vosburg Geologist Louisiana Coastal Protection and Restoration Authority brian.vosburg@la.gov
Influence of the Major Drainages to the Mississippi River and Implications for System Level Management Brian M. Vosburg Geologist Louisiana Coastal Protection and Restoration Authority brian.vosburg@la.gov
The evolution of sandbars along the Colorado River downstream of the Glen Canyon Dam
 The evolution of sandbars along the Colorado River downstream of the Glen Canyon Dam Liz Kemp April 2010 i Cover photo: Andrew Pernick, Bureau of Reclamation Aerial view of Glen Canyon Dam during high-flow
The evolution of sandbars along the Colorado River downstream of the Glen Canyon Dam Liz Kemp April 2010 i Cover photo: Andrew Pernick, Bureau of Reclamation Aerial view of Glen Canyon Dam during high-flow
Big Wood River. General Information
 General Information The flows out of the southern portion of the Sawtooth National Recreation Area in central Idaho. The study reach is about a,200 ft length of river about.5 miles upstream from the discontinued
General Information The flows out of the southern portion of the Sawtooth National Recreation Area in central Idaho. The study reach is about a,200 ft length of river about.5 miles upstream from the discontinued
ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 100. Figure 7-3 Maximum velocity magnitudes for existing conditions for 100-year flood event
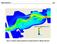 ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 100 Figure 7-3 Maximum velocity magnitudes for existing conditions for 100-year flood event ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 101 Figure 7-4 Model schematization of Option 1 Figure 7-5 Bed displacement
ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 100 Figure 7-3 Maximum velocity magnitudes for existing conditions for 100-year flood event ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 101 Figure 7-4 Model schematization of Option 1 Figure 7-5 Bed displacement
Stop 1: Marmot Dam Stop 1: Marmot Dam
 Stop 1: Marmot Dam Stop 1: Marmot Dam Following the removal of Marmot Dam in 2007, the fate of the reservoir sediments has been monitored through a series of surveys and sediment transport measurements.
Stop 1: Marmot Dam Stop 1: Marmot Dam Following the removal of Marmot Dam in 2007, the fate of the reservoir sediments has been monitored through a series of surveys and sediment transport measurements.
Overview of fluvial and geotechnical processes for TMDL assessment
 Overview of fluvial and geotechnical processes for TMDL assessment Christian F Lenhart, Assistant Prof, MSU Research Assoc., U of M Biosystems Engineering Fluvial processes in a glaciated landscape Martin
Overview of fluvial and geotechnical processes for TMDL assessment Christian F Lenhart, Assistant Prof, MSU Research Assoc., U of M Biosystems Engineering Fluvial processes in a glaciated landscape Martin
Lower Susquehanna River Integrated Sediment & Nutrient Monitoring Program
 Lower Susquehanna River Integrated Sediment & Nutrient Monitoring Program Presented at the Chesapeake Bay Program Scientific and Technical Advisory Committee (STAC) Workshop January 13, 2016 Background
Lower Susquehanna River Integrated Sediment & Nutrient Monitoring Program Presented at the Chesapeake Bay Program Scientific and Technical Advisory Committee (STAC) Workshop January 13, 2016 Background
Reducing Nitrogen Removal Uncertainty for Operation of Mississippi River Sediment Diversions: Nitrate Reduction Rates In Turbulent Flow Conditions
 Reducing Nitrogen Removal Uncertainty for Operation of Mississippi River Sediment Diversions: Nitrate Reduction Rates In Turbulent Flow Conditions Nia R. Hurst, John R. White, Kehui Xu, and MingCheng Ren
Reducing Nitrogen Removal Uncertainty for Operation of Mississippi River Sediment Diversions: Nitrate Reduction Rates In Turbulent Flow Conditions Nia R. Hurst, John R. White, Kehui Xu, and MingCheng Ren
Longitudinal dams as an alternative to wing dikes in river engineering. Fredrik Huthoff
 Longitudinal dams as an alternative to wing dikes in river engineering Fredrik Huthoff Contents Introduction Why consider longitudinal dams? Room for the river in the Netherlands The pilot study The Dutch
Longitudinal dams as an alternative to wing dikes in river engineering Fredrik Huthoff Contents Introduction Why consider longitudinal dams? Room for the river in the Netherlands The pilot study The Dutch
Sediment and Nutrient Mass Balance Model of Conowingo Pool
 Sediment and Nutrient Mass Balance Model of Conowingo Pool Mark Velleux and Jim Fitzpatrick HDR Engineering Status Update: April 27, 2016 Chesapeake Bay Program Modeling Quarterly Review Model Grid and
Sediment and Nutrient Mass Balance Model of Conowingo Pool Mark Velleux and Jim Fitzpatrick HDR Engineering Status Update: April 27, 2016 Chesapeake Bay Program Modeling Quarterly Review Model Grid and
Preparation of a Hydrodynamic model of. Detroit River- St. Clair River waterways. with Telemac-2D
 Preparation of a Hydrodynamic model of Detroit River- St. Clair River waterways with Telemac-2D Controlled Technical Report CHC-CTR-085 March 2009 CTR-CHC-085 NRC-CHC has prepared this report for the International
Preparation of a Hydrodynamic model of Detroit River- St. Clair River waterways with Telemac-2D Controlled Technical Report CHC-CTR-085 March 2009 CTR-CHC-085 NRC-CHC has prepared this report for the International
Appendix D. Summary of Hydrodynamic, Sediment Transport, and Wave Modeling
 Appendix D Summary of Hydrodynamic, Sediment Transport, and Wave Modeling Appendix D Summary of Hydrodynamic, Sediment Transport, and Wave Modeling Spirit Lake Sediment Site Prepared for U. S. Steel Corporation
Appendix D Summary of Hydrodynamic, Sediment Transport, and Wave Modeling Appendix D Summary of Hydrodynamic, Sediment Transport, and Wave Modeling Spirit Lake Sediment Site Prepared for U. S. Steel Corporation
Squaw Creek. General Information
 General Information is a tributary to the Salmon River. It enters the north side of the river about 0 miles downstream of North Fork, Idaho. The study reach is about a 30 ft length of stream about 2 miles
General Information is a tributary to the Salmon River. It enters the north side of the river about 0 miles downstream of North Fork, Idaho. The study reach is about a 30 ft length of stream about 2 miles
Sediment Deposition LET THE RIVER RUN T E A C H E R. Activity Overview. Activity at a Glance. Time Required. Level of Complexity.
 Activity at a Glance Grade: 6 9 Subject: Science Category: Physical Science, Earth Science Topic: Deposition, River Systems Time Required Two 45-minute periods Level of Complexity Medium Materials* TI-73
Activity at a Glance Grade: 6 9 Subject: Science Category: Physical Science, Earth Science Topic: Deposition, River Systems Time Required Two 45-minute periods Level of Complexity Medium Materials* TI-73
Decline of Lake Michigan-Huron Levels Caused by Erosion of the St. Clair River
 Decline of Lake Michigan-Huron Levels Caused by Erosion of the St. Clair River W.F. & Associates Coastal Engineers (in association with Frank Quinn) April 13, 2005 Outline Problem Definition Understanding
Decline of Lake Michigan-Huron Levels Caused by Erosion of the St. Clair River W.F. & Associates Coastal Engineers (in association with Frank Quinn) April 13, 2005 Outline Problem Definition Understanding
Regional Sediment Management Science Workshop: Sediment in San Francisco Bay
 Regional Sediment Management Science Workshop: Sediment in San Francisco Bay Purpose Co-sponsored by BCDC and USGS April 19-20, 2010 at USGS, Menlo Park, CA Discuss recent scientific results related to
Regional Sediment Management Science Workshop: Sediment in San Francisco Bay Purpose Co-sponsored by BCDC and USGS April 19-20, 2010 at USGS, Menlo Park, CA Discuss recent scientific results related to
Probabilistic Evaluation of a Meandering Low-Flow Channel. February 24 th, UMSRS
 Probabilistic Evaluation of a Meandering Low-Flow Channel February 24 th, 2014 2014 UMSRS 1 2 acknowledgments Low- Flow Channel (LFC) overview Proposed Diversion Channel collects runoff from: The Rush
Probabilistic Evaluation of a Meandering Low-Flow Channel February 24 th, 2014 2014 UMSRS 1 2 acknowledgments Low- Flow Channel (LFC) overview Proposed Diversion Channel collects runoff from: The Rush
Final Report. Prepared for. American Rivers, California Trout, Friends of the River and Trout Unlimited
 A of the Potential Downstream Sediment Deposition Following the Removal of Iron Gate, Copco, and J.C. Boyle Dams, Klamath River, CA Final Report Prepared for American Rivers, California Trout, Friends
A of the Potential Downstream Sediment Deposition Following the Removal of Iron Gate, Copco, and J.C. Boyle Dams, Klamath River, CA Final Report Prepared for American Rivers, California Trout, Friends
Examination of Direct Discharge Measurement Data and Historic Daily Data for Selected Gages on the Middle Mississippi River,
 Examination of Direct Discharge Measurement Data and Historic Daily Data for Selected Gages on the Middle Mississippi River, 1861-2008 - Richard J. Huizinga, P.E. U.S. Geological Survey Missouri Water
Examination of Direct Discharge Measurement Data and Historic Daily Data for Selected Gages on the Middle Mississippi River, 1861-2008 - Richard J. Huizinga, P.E. U.S. Geological Survey Missouri Water
Technical Memorandum No Sediment Model
 Pajaro River Watershed Study in association with Technical Memorandum No. 1.2.9 Sediment Model Task: Development of Sediment Model To: PRWFPA Staff Working Group Prepared by: Gregory Morris and Elsie Parrilla
Pajaro River Watershed Study in association with Technical Memorandum No. 1.2.9 Sediment Model Task: Development of Sediment Model To: PRWFPA Staff Working Group Prepared by: Gregory Morris and Elsie Parrilla
Highland Lake Bathymetric Survey
 Highland Lake Bathymetric Survey Final Report, Prepared For: The Town of Highland Lake 612 Lakeshore Drive Oneonta, AL 35121 Prepared By: Tetra Tech 2110 Powers Ferry Road SE Suite 202 Atlanta, GA 30339
Highland Lake Bathymetric Survey Final Report, Prepared For: The Town of Highland Lake 612 Lakeshore Drive Oneonta, AL 35121 Prepared By: Tetra Tech 2110 Powers Ferry Road SE Suite 202 Atlanta, GA 30339
Modelling of flow and sediment transport in rivers and freshwater deltas Peggy Zinke
 1 Modelling of flow and sediment transport in rivers and freshwater deltas Peggy Zinke with contributions from Norwegian and international project partners 2 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Basic ideas of flow
1 Modelling of flow and sediment transport in rivers and freshwater deltas Peggy Zinke with contributions from Norwegian and international project partners 2 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Basic ideas of flow
Appendix K.2: Sediment Management Excerpt from South Orange County Hydromodification Management Plan
 Appendix K.2: Sediment Management Excerpt from South Orange County Hydromodification Management Plan 4 Sediment Supply Management Requirements Permit Order R9-2013-0001 as amended by Order No. R9-2015-0001Section
Appendix K.2: Sediment Management Excerpt from South Orange County Hydromodification Management Plan 4 Sediment Supply Management Requirements Permit Order R9-2013-0001 as amended by Order No. R9-2015-0001Section
SEA LEVEL RISE IN THE 2017 COASTAL MASTER PLAN
 SEA LEVEL RISE IN THE 2017 COASTAL MASTER PLAN James W. Pahl, Ph.D. Coastal Resources Scientist, Senior Presentation to the Barataria-Terrebonne National Estuary Program Management Conference Meeting Nicholls
SEA LEVEL RISE IN THE 2017 COASTAL MASTER PLAN James W. Pahl, Ph.D. Coastal Resources Scientist, Senior Presentation to the Barataria-Terrebonne National Estuary Program Management Conference Meeting Nicholls
MEANDER MIGRATION MODEL ASSESSMENT FOR THE JANUARY 2005 STORM, WHITMAN PROPERTY, SAN ANTONIO CREEK, VENTURA COUNTY, CALIFORNIA
 MEANDER MIGRATION MODEL ASSESSMENT FOR THE JANUARY 2005 STORM, WHITMAN PROPERTY, SAN ANTONIO CREEK, VENTURA COUNTY, CALIFORNIA Prepared by Eric Larsen, Ph.D. Mark Rains, Ph.D. October 2006 INTRODUCTION
MEANDER MIGRATION MODEL ASSESSMENT FOR THE JANUARY 2005 STORM, WHITMAN PROPERTY, SAN ANTONIO CREEK, VENTURA COUNTY, CALIFORNIA Prepared by Eric Larsen, Ph.D. Mark Rains, Ph.D. October 2006 INTRODUCTION
PREDICTION ON MORPHOLOGICAL RESPONSE OF DREDGED SAND-BORROW PITS. Qimiao Lu 1 and Robert B. Nairn 1
 PREDICTION ON MORPHOLOGICAL RESPONSE OF DREDGED SAND-BORROW PITS Qimiao Lu 1 and Robert B. Nairn 1 Dredged pits in coastal zones are generally required for sand borrows for beach nourishment. The morphological
PREDICTION ON MORPHOLOGICAL RESPONSE OF DREDGED SAND-BORROW PITS Qimiao Lu 1 and Robert B. Nairn 1 Dredged pits in coastal zones are generally required for sand borrows for beach nourishment. The morphological
Annual transport rates at two locations on the fore-slope.
 Sediment Transport by Currents Fore-slope Sediment transport rates and sediment concentrations were computed from the hydrodynamic model runs as well as from direct measurements of current velocities at
Sediment Transport by Currents Fore-slope Sediment transport rates and sediment concentrations were computed from the hydrodynamic model runs as well as from direct measurements of current velocities at
Morphological Modeling of Inlets and Adjacent Shorelines on Engineering Timescales
 CB&I Morphological Modeling of Inlets and Adjacent Shorelines on Engineering Timescales Challenges and Model Improvements based on Recent Studies Dobrochinski, J.P.H.; Benedet, L.; Signorin, M.; Pierro,
CB&I Morphological Modeling of Inlets and Adjacent Shorelines on Engineering Timescales Challenges and Model Improvements based on Recent Studies Dobrochinski, J.P.H.; Benedet, L.; Signorin, M.; Pierro,
Final Exam. Running Water Erosion and Deposition. Willamette Discharge. Running Water
 Final Exam Running Water Erosion and Deposition Earth Science Chapter 5 Pages 120-135 Scheduled for 8 AM, March 21, 2006 Bring A scantron form A calculator Your 3 x 5 paper card of formulas Review questions
Final Exam Running Water Erosion and Deposition Earth Science Chapter 5 Pages 120-135 Scheduled for 8 AM, March 21, 2006 Bring A scantron form A calculator Your 3 x 5 paper card of formulas Review questions
Coastal Litigation in the Context of Science Literacy
 Coastal Litigation in the Context of Science Literacy Chris McLindon New Orleans Geological Society February 6, 7 Science Literacy The value of community participation in scientific research is widely
Coastal Litigation in the Context of Science Literacy Chris McLindon New Orleans Geological Society February 6, 7 Science Literacy The value of community participation in scientific research is widely
L OWER N OOKSACK R IVER P ROJECT: A LTERNATIVES A NALYSIS A PPENDIX A: H YDRAULIC M ODELING. PREPARED BY: LandC, etc, LLC
 L OWER N OOKSACK R IVER P ROJECT: A LTERNATIVES A NALYSIS A PPENDIX A: H YDRAULIC M ODELING PREPARED BY: LandC, etc, LLC TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Introduction... 1 2 Methods... 1 2.1 Hydraulic Model... 1 2.2
L OWER N OOKSACK R IVER P ROJECT: A LTERNATIVES A NALYSIS A PPENDIX A: H YDRAULIC M ODELING PREPARED BY: LandC, etc, LLC TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Introduction... 1 2 Methods... 1 2.1 Hydraulic Model... 1 2.2
Final Report for TWDB Contract No
 Final Report for TWDB Contract No. 1004831127 Sediment Transport Modeling of Channel Scale Geomorphic Processes J.K. Haschenburger University of Texas at San Antonio July 31, 2012 1 Introduction This study
Final Report for TWDB Contract No. 1004831127 Sediment Transport Modeling of Channel Scale Geomorphic Processes J.K. Haschenburger University of Texas at San Antonio July 31, 2012 1 Introduction This study
Quantification of Bed-Load Transport on the Upper Mississippi River Using Multibeam Survey Data and Traditional Methods
 Quantification of Bed-Load Transport on the Upper Mississippi River Using Multibeam Survey Data and Traditional Methods by David D. Abraham and Thad Pratt PURPOSE: This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering
Quantification of Bed-Load Transport on the Upper Mississippi River Using Multibeam Survey Data and Traditional Methods by David D. Abraham and Thad Pratt PURPOSE: This Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering
Hydraulic and Sediment Transport Modeling Strategy
 Appendix B Hydraulic and Sediment Transport Modeling Strategy May 2014 Technical Memorandum Channel Capacity Report January 2015 San Joaquin River Restoration Program Hydraulic and Sediment Transport Modeling
Appendix B Hydraulic and Sediment Transport Modeling Strategy May 2014 Technical Memorandum Channel Capacity Report January 2015 San Joaquin River Restoration Program Hydraulic and Sediment Transport Modeling
River Restoration and Rehabilitation. Pierre Y. Julien
 River Restoration and Rehabilitation Pierre Y. Julien Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Colorado State University Fort Collins, Colorado River Mechanics and Sediment Transport Lima Peru
River Restoration and Rehabilitation Pierre Y. Julien Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Colorado State University Fort Collins, Colorado River Mechanics and Sediment Transport Lima Peru
Swift Creek Sediment Management Action Plan (SCSMAP)
 Swift Creek Sediment Management Action Plan (SCSMAP) PHASE 2 PROJECT PLAN PROPOSAL Whatcom County Public Works Department 322 N. Commercial Street, Suite 210 Bellingham, WA 98225 (360) 676-6692 June 2013
Swift Creek Sediment Management Action Plan (SCSMAP) PHASE 2 PROJECT PLAN PROPOSAL Whatcom County Public Works Department 322 N. Commercial Street, Suite 210 Bellingham, WA 98225 (360) 676-6692 June 2013
Technical Review of Pak Beng Hydropower Project (1) Hydrology & Hydraulics and (2) Sediment Transport & River Morphology
 Technical Review of Pak Beng Hydropower Project (1) Hydrology & Hydraulics and (2) Sediment Transport & River Morphology The 2 nd Regional Stakeholder Forum The Pak Beng Hydropower Project 5 th May 2017
Technical Review of Pak Beng Hydropower Project (1) Hydrology & Hydraulics and (2) Sediment Transport & River Morphology The 2 nd Regional Stakeholder Forum The Pak Beng Hydropower Project 5 th May 2017
ΛTKINS. Applications of Regional Sediment Management Concepts in Texas Estuarine Restoration Projects. Riparian Workshop Fort Worth, October 17, 2012
 Juan C Moya, PhD., PG Coastal Planning and Restoration Applications of Regional Sediment Management Concepts in Texas Estuarine Restoration Projects Riparian Workshop Fort Worth, October 17, 2012 West
Juan C Moya, PhD., PG Coastal Planning and Restoration Applications of Regional Sediment Management Concepts in Texas Estuarine Restoration Projects Riparian Workshop Fort Worth, October 17, 2012 West
Technical Memorandum No
 Pajaro River Watershed Study in association with Technical Memorandum No. 1.2.10 Task: Evaluation of Four Watershed Conditions - Sediment To: PRWFPA Staff Working Group Prepared by: Gregory Morris and
Pajaro River Watershed Study in association with Technical Memorandum No. 1.2.10 Task: Evaluation of Four Watershed Conditions - Sediment To: PRWFPA Staff Working Group Prepared by: Gregory Morris and
Chapter 3 Erosion in the Las Vegas Wash
 Chapter 3 Erosion in the Las Vegas Wash Introduction As described in Chapter 1, the Las Vegas Wash (Wash) has experienced considerable change as a result of development of the Las Vegas Valley (Valley).
Chapter 3 Erosion in the Las Vegas Wash Introduction As described in Chapter 1, the Las Vegas Wash (Wash) has experienced considerable change as a result of development of the Las Vegas Valley (Valley).
3 Theoretical Basis for SAM.sed Calculations
 3 Theoretical Basis for SAM.sed Calculations Purpose Sediment transport functions can be used to calculate the bed material portion of the sediment discharge rating curve. This rating curve can then be
3 Theoretical Basis for SAM.sed Calculations Purpose Sediment transport functions can be used to calculate the bed material portion of the sediment discharge rating curve. This rating curve can then be
Dynamics of the Ems Estuary
 Dynamics of the Ems Estuary Physics of coastal systems Jerker Menninga 0439738 Utrecht University Institute for Marine and Atmospheric research Utrecht Lecturer: Prof. dr. H.E. de Swart Abstract During
Dynamics of the Ems Estuary Physics of coastal systems Jerker Menninga 0439738 Utrecht University Institute for Marine and Atmospheric research Utrecht Lecturer: Prof. dr. H.E. de Swart Abstract During
River Meandering and Braiding. Pierre Y. Julien. Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Colorado State University Fort Collins, Colorado
 River Meandering and Braiding Pierre Y. Julien Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Colorado State University Fort Collins, Colorado River Mechanics and Sediment Transport Lima Peru January
River Meandering and Braiding Pierre Y. Julien Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Colorado State University Fort Collins, Colorado River Mechanics and Sediment Transport Lima Peru January
Assessment of the Hood River Delta Hood River, Oregon
 Assessment of the Hood River Delta Hood River, Oregon Pacific Northwest Waterways Association Annual Meeting October 13, 2010 Michael McElwee, Executive Director Port of Hood River Overview U.S. Army Corps
Assessment of the Hood River Delta Hood River, Oregon Pacific Northwest Waterways Association Annual Meeting October 13, 2010 Michael McElwee, Executive Director Port of Hood River Overview U.S. Army Corps
(3) Sediment Movement Classes of sediment transported
 9/17/15 (3) Sediment Movement Classes of sediment transported Dissolved load Suspended load Important for scouring algae Bedload (5-10% total load) Moves along bed during floods Source of crushing for
9/17/15 (3) Sediment Movement Classes of sediment transported Dissolved load Suspended load Important for scouring algae Bedload (5-10% total load) Moves along bed during floods Source of crushing for
Mapping of Future Coastal Hazards. for Southern California. January 7th, David Revell, Ph.D. E.
 Mapping of Future Coastal Hazards for Southern California January 7th, 2014 David Revell, Ph.D. drevell@esassoc.com E. Vandebroek, 2012 Outline Coastal erosion hazard zones Flood hazard zones: Coastal
Mapping of Future Coastal Hazards for Southern California January 7th, 2014 David Revell, Ph.D. drevell@esassoc.com E. Vandebroek, 2012 Outline Coastal erosion hazard zones Flood hazard zones: Coastal
DESIGN OF DIVERSIONS OF THE MISSISSIPPI RIVER TO BUILD NEW LAND IN SOUTHERN LOUISIANA
 DESIGN OF DIVERSIONS OF THE MISSISSIPPI RIVER TO BUILD NEW LAND IN SOUTHERN LOUISIANA Gary Parker, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign along with Matthew Czapiga, Benjamin Hobbs, Melissa Kenney, Wonsuck
DESIGN OF DIVERSIONS OF THE MISSISSIPPI RIVER TO BUILD NEW LAND IN SOUTHERN LOUISIANA Gary Parker, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign along with Matthew Czapiga, Benjamin Hobbs, Melissa Kenney, Wonsuck
RESERVOIR DRAWDOWN RATES/RESERVOIR DRAWDOWN TEST Iron Gate, Copco (I & II), and JC Boyle Dams
 TECHNICAL MEMORANDUM No. 1 TO: Michael Bowen California Coastal Conservancy Geotechnical & Earthquake Engineering Consultants CC: Eric Ginney Philip Williams & Associates PREPARED BY: Paul Grant SUBJECT:
TECHNICAL MEMORANDUM No. 1 TO: Michael Bowen California Coastal Conservancy Geotechnical & Earthquake Engineering Consultants CC: Eric Ginney Philip Williams & Associates PREPARED BY: Paul Grant SUBJECT:
PRESENTATION TITLE. Regional Sediment Management Application of a Coastal Model at the St. Johns River Entrance BUILDING STRONG
 PRESENTATION TITLE Regional Sediment Management Application of a Coastal Model at the St. Johns River Entrance Steven Bratos Senior Coastal Engineer U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Jacksonville District February
PRESENTATION TITLE Regional Sediment Management Application of a Coastal Model at the St. Johns River Entrance Steven Bratos Senior Coastal Engineer U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Jacksonville District February
Sessom Creek Sand Bar Removal HCP Task 5.4.6
 Sessom Creek Sand Bar Removal HCP Task 5.4.6 Prepared by: Dr. Thomas Hardy Texas State University Dr. Nolan Raphelt Texas Water Development Board January 6, 2013 DRAFT 1 Introduction The confluence of
Sessom Creek Sand Bar Removal HCP Task 5.4.6 Prepared by: Dr. Thomas Hardy Texas State University Dr. Nolan Raphelt Texas Water Development Board January 6, 2013 DRAFT 1 Introduction The confluence of
Strategies for managing sediment in dams. Iwona Conlan Consultant to IKMP, MRCS
 Strategies for managing sediment in dams Iwona Conlan Consultant to IKMP, MRCS 1 Sediment trapping by dams Active storage capacity Dead storage coarse material (bed load) Fine materials (suspension) Francis
Strategies for managing sediment in dams Iwona Conlan Consultant to IKMP, MRCS 1 Sediment trapping by dams Active storage capacity Dead storage coarse material (bed load) Fine materials (suspension) Francis
Optimal Design of Sediment Diversions for Delta Restoration: lessons learned from examples
 Optimal Design of Sediment Diversions for Delta Restoration: lessons learned from examples Samuel Bentley 1, Angelina Freeman 2, Clinton S. Willson 1, Liviu Giosan 3, Jaye Cable 4 1 LSU 2 EDF 3 WHOI 4
Optimal Design of Sediment Diversions for Delta Restoration: lessons learned from examples Samuel Bentley 1, Angelina Freeman 2, Clinton S. Willson 1, Liviu Giosan 3, Jaye Cable 4 1 LSU 2 EDF 3 WHOI 4
Suspended Sediment Rating Curve for Tigris River Upstream Al- Betera Regulator
 International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 2320-9364, ISSN (Print): 2320-9356 Volume 3 Issue 8 ǁ August. 2015 ǁ PP.61-65 Suspended Sediment Rating Curve for Tigris
International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 2320-9364, ISSN (Print): 2320-9356 Volume 3 Issue 8 ǁ August. 2015 ǁ PP.61-65 Suspended Sediment Rating Curve for Tigris
Updated Fluvial Geomorphology Modeling Approach
 (FERC No. 14241) Updated Fluvial Geomorphology Modeling Approach Technical Memorandum Prepared for Prepared by Tetra Tech Original Submitted June 30, 2013 Updated May 2014 Page intentionally left blank
(FERC No. 14241) Updated Fluvial Geomorphology Modeling Approach Technical Memorandum Prepared for Prepared by Tetra Tech Original Submitted June 30, 2013 Updated May 2014 Page intentionally left blank
