Chapter 3 Erosion in the Las Vegas Wash
|
|
|
- Alice Clarke
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
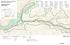
1 Chapter 3 Erosion in the Las Vegas Wash Introduction As described in Chapter 1, the Las Vegas Wash (Wash) has experienced considerable change as a result of development of the Las Vegas Valley (Valley). Erosion has created dramatic and far-reaching effects in the Wash. Excessive erosion along the Wash has resulted in loss of wetlands and wildlife habitat, loss of property, damage to infrastructure, excessive sediment transport to Lake Mead and water quality concerns in the Wash and Lake Mead. The Wash is a natural channel that drains the entire 1,600-square-mile Valley. The Valley is about 50 miles long and is five to 25 miles wide. Figure 3.1 shows a satellite image of the Las Vegas Valley Hydrographic Basin and indicates the location of Las Vegas Wash and tributaries. The Wash discharges into Las Vegas Bay at Lake Mead. In August 1999, the Stormwater and Erosion Study Team, in cooperation with the Las Vegas Wash Coordination Committee, sponsored an Engineering Workshop that discussed and developed recommendations regarding erosion in the Wash. Details of the workshop, which includes prototype design and siting of erosion control structures, are discussed in greater detail by the Erosion and Stormwater Study Team in Chapter 7. History The Wash was formed during the Miocene and Pleistocene Epochs, within the last 25 million years. The flood plain of the Wash was formed as a result of filling of the Valley by sediments derived from erosion of the surrounding ranges and higher elevations. The majority of these sediments consist of easily eroded silts and clays with minor amounts of sand and 65
2 gravel. Geologic evidence indicates that the Wash has undergone at least three natural cycles of down-cutting and subsequent backfilling prior to modern development. The ancient stream course of the Wash can be traced from Indian Springs south to Corn Creek Springs, Tule Springs, Big Springs and into the Colorado River. During the period 6,000 to 14,000 years ago, Indian Springs, Corn Creek Springs, Tule Springs, Big Springs and numerous springs in the vicinity of present day Las Vegas apparently were active and drained into the Wash. Later, with increased temperature, decreased precipitation and lowered water table, spring activity decreased. The Wash has apparently been dry for the last 1,000 to 4,000 years. The latest phase of back-filling of the Wash began about 2,500 years ago. Figure Satellite image of Las Vegas Valley Hydrographic Basin depicting the Las Vegas Wash and associated tributaries. The flow from the springs originally supported grassy meadows, mesquites and other phreatophytes along the small tributary washes. The plant growth entirely consumed the flow from the springs. Except for occasional flood flows there was no flow down the Wash (USBR, 1982). Prior to urbanization of the Valley, the Wash was defined by an evenly graded, stable flood plain typical of arid environments. Figure 3.2 shows an aerial photo of the Las Vegas Wash in 1950, prior to perennial flow and substantial wetland development. 66
3 1950s 1960s During the late 1950s, increased wastewater volumes resulted in a perennial flow in Las Vegas Wash that meandered through the southeast part of the Valley to Las Vegas Bay of Lake Mead. This was the first time in more than 2,500 years that flow in the Wash reached this far downstream. As a result of these flows (approximately 15 cubic feet per second in 1960), wetland vegetation and wildlife habitat expanded. The wetlands served to control erosion until increasing wastewater Chapter 3: Erosion in the Las Vegas Wash Figure 3.2 Aerial photo of Las Vegas Wash, flows in the late 1960s began to erode the channel in the lower reach of the Wash. Figure 3.3 shows an aerial photo of the Las Vegas Wash indicating a vast amount of wetland vegetation along the Wash channel. 1960s 1970s As discussed in Chapter 1, History of Las Vegas Wash, in the late 1960s and early 1970s wastewater flow ranged between 25 and 39 cubic feet per second (cfs) and erosion became evident at two sites, the tributary from Three Kids Mine and the culverts at the Northshore Road crossing. At these sites, lateral flow was confined, thereby increasing flow velocities and erosion potential. From these sites, headcut erosion was initiated, increasing vertically and laterally upstream. Removal of the culverts and construction of Northshore Bridge allowed a series of headcuts to move upstream resulting in erosion and disruption of Figure 3.3 Aerial photo of Las Vegas Wash,
4 Telephone Line and Pabco Roads and the need to tunnel the Las Vegas Lateral water supply pipeline deep beneath the channel. Figure 3.4 Historic view of Las Vegas Wash from Northshore Road, 1975 (Pat A. Glancy, USGS). 1970s 1980s During the early to mid 1970s, erosion became more evident in the lower reaches of the Wash (downstream from Three Kids Wash). The reaches above Three Kids continued to be dominated by wetlands habitat. The flood plain was still relatively flat and broad during this period and flourished with vegetation and wildlife fed by the gradually increasing flows from upstream. Figure are a series of photos taken at Northshore Road in the lower reach of the Wash. These photos show conditions in 1975, 1985, and Figure 3.5 Historic view of Las Vegas Wash from Northshore Road, 1985 (Pat A. Glancy, USGS). Figure 3.6 View of Las Vegas Wash from Northshore Road, 1999 (Pat. A. Glancy, USGS). 1980s 1990s By the early 1980s average daily flow in the Wash had increased to about 100 cfs. These flows were sufficient to down-cut the channel creating an unstable, relatively narrow flow path. Numerous erosional headcuts were active along the reach from Pabco Road to Lake Mead by the early 1980s. The summer of 1984 included extended monsoonal periods and multiple flash flood events that greatly widened the flow path and effectively destroyed the majority of wetlands downstream of Pabco Road. Estimated total sediment removal from the late 1960s through 1984 amounts to over 4 million cubic feet (Glancy, 1999). Figure 3.7 shows a historical elevation profile along the Wash from the Clark County Advanced Wastewater Treatment Facility to the intake at Lake Las Vegas. Current average daily flows in the Wash are approximately 240 cfs. Recent flood events in July and September 1998 and July 1999 have taken advantage of increasingly unstable conditions and caused catastrophic erosion in some reaches of the Wash. Continued erosion has resulted in the loss of about 68
5
6 Headcutting is the erosion of a streambed that occurs at a steep section of the channel and migrates upstream due to the water eroding the bed material. The upstream advance of gully and vertical channel downcutting by erosion, is the primary form of erosion in the lower Wash. 1,800 acres of the established wetlands and viable wildlife habitat. Other undesirable impacts of erosion on the Wash include dramatically increased sediment loading to Las Vegas Bay of Lake Mead, potential impacts to water quality in the Wash and Lake Mead, required infrastructure modifications, loss of property and destruction of road crossings. Sediment erosion was covered in great detail by the Sediment Subcommittee of the Lake Mead Water Quality Forum. In their 1998 report, the Sediment Subcommittee indicated that the sedimentation rate for the time period of March 19 25, 1997 was 1400 to 1600 tons per day as measured by total suspended solids at a sample collection point above Lake Las Vegas. That amount of sediment being carried downstream during that time period by the Wash is 20 times greater than that reported in 1991 by Tipton & Kalmbach Inc. Of the sediment sampled in March 1997, 90 percent of the total suspended solids discharged to Lake Mead are inorganic, indicating that streambed erosion is a major contributor. Erosion Control The physical condition and soils of the Wash were mapped as they existed in Due to ever increasing daily flows, on the order of five times the flow that initiated erosion, the stream system is no longer in equilibrium. A properly functioning equilibrium in a stream system is a balance between sediment erosion and sediment deposition. Imbalance in the Wash has been evident when high peak flows remove more sediment than is deposited during low flows. This imbalance has reduced the area of the floodplain, reduced retention times, minimized spreading of water on the floodplain, and drained existing ground water into adjacent channels. In the early 1980s it was determined that the Las Vegas Lateral (Lateral), the main drinking water supply pipeline for the Valley, was threatened by erosion in the Wash. A study was conducted to determine characteristics of the Wash in relation to proposed pipeline crossing alternatives. Part of the goal was to determine a stable equilibrium slope for the Wash which generally determines at what slope erosion will not occur based on flow and sediment load from upstream. For the reach from the Las Vegas Lateral upstream to Pabco Road the stable equilibrium slope was determined to be approximately vertical feet per horizontal foot. Resulting headcut will total 157 feet if no erosion control is in place, assuming this equilibrium slope from the Lake Las Vegas intake to the Clark County Advanced Wastewater Treatment Plant, based on projected wastewater flow amounts. Furthermore, lateral erosion has been determined to be approximately 22 feet for every foot of vertical streambed erosion. 70
7 During design, a series of flood events further threatened the Lateral, prompting the construction of a temporary Grace Control Structure (GCS) by the Colorado River Commission. The GCS, constructed in 1984, was a rip rap grouted structure approximately 7 feet high by 450 feet in length and was designed to last about two years. Photos taken after completion of the GCS show extensive wetlands development in areas behind the structure (Figure 3.8). The GCS was left in place after the Lateral relocation was completed (1987) and required only minor repairs until flood events in resulted in an extensive breach of the GCS and increased erosion of the Wash above the abandoned Lateral. Figure 3.8 Grade Control Structure at Las Vegas Lateral, 1985 (Pat A. Glancy, USGS). In July 1998, the Southern Nevada Water Authority (SNWA) and Clark County Parks & Recreation entered into a cooperative agreement to permanently repair the GCS site. During this process, a flood event in September 1998 caused extensive erosion in the Wash and resulted in the entire Wash flow passing under the abandoned Figure 3.9 Las Vegas Wash flowing under abandoned Lateral, October 1998 (Southern Nevada Water Authority). Lateral by early October (Figure 3.9). Realizing that continued erosion may result in loss of the abandoned Lateral and the remaining GCS, the 71
8 Figure 3.10 Grade control structure site after emergency repairs completed, November 1998 (Southern Nevada Water Authority). SNWA s general manager declared an emergency action. Within four weeks emergency repairs were completed resulting in stabilization of the GCS. The emergency repair involved placing approximately 2,000 tons of rock rip rap below the abandoned lateral. Rock rip rap was granitic in composition and size ranged from approximately 2 to 4 feet in diameter. Design included a weir section adjacent to the abandoned lateral, a stilling basin and counterweir for energy dissipation. The upstream weir section keyed into the remaining abutments of the original GCS, constructed of rock rip rap with concrete grout. Upon completion, the emergency repair was approximately 100 feet wide and 90 feet long (Figure 3.10). The July 8, 1999, flood event took place during the bidding process for permanent repairs to the GCS. Observation during the flood showed that the emergency repairs withstood greater than design flows prior to failure. Failure originated at the concrete grouted rock rip rap abutments, from the original GCS, then progressively removed materials placed during emergency repairs. Floodwaters extensively altered the site resulting in postponement of the repairs and total redesign of the structure (Figure 3.11). The Las Vegas Lateral GCS is currently being redesigned and is planned for construction late- to mid Figure 3.11 Grade control structure site after July 1999 storm event (Southern Nevada Water Authority). Similarly, the construction process for the Pabco Road GCS planned to be 72
9 built in the early 1990s has required redesign three times due to flood events altering the site. The Pabco Road GCS is currently being designed and is planned for construction in early Recommendations of Clark County Comprehensive Planning s Las Vegas Wash Erosion Mitigation Plan include the construction of 15 grade control structures along the 9.5-mile reach of the Wash extending from the Advanced Wastewater Treatment Plant to Lake Las Vegas. These structures were anticipated to be placed at headcut locations, as they existed at the time, and to stabilize the Wash at the stable equilibrium slope of Further recommendations for erosion control are discussed in Chapter 6, Erosion & Stormwater Study Team. References Glancy, P.A. (1999). U. S. Geological Survey, Press Release. Tipton & Klambach, Inc. (1991). Sediment Bedload Study for Lake Las Vegas. Chapter 3: Erosion in the Las Vegas Wash U.S. Bureau of Reclamation (1982). Colorado River Basin Salinity Control Project, Point Source Division, Las Vegas Wash Unit, Nevada, Status Report. 73
10 74
Erosion Surface Water. moving, transporting, and depositing sediment.
 + Erosion Surface Water moving, transporting, and depositing sediment. + Surface Water 2 Water from rainfall can hit Earth s surface and do a number of things: Slowly soak into the ground: Infiltration
+ Erosion Surface Water moving, transporting, and depositing sediment. + Surface Water 2 Water from rainfall can hit Earth s surface and do a number of things: Slowly soak into the ground: Infiltration
Why Geomorphology for Fish Passage
 Channel Morphology - Stream Crossing Interactions An Overview Michael Love Michael Love & Associates mlove@h2odesigns.com (707) 476-8938 Why Geomorphology for Fish Passage 1. Understand the Scale of the
Channel Morphology - Stream Crossing Interactions An Overview Michael Love Michael Love & Associates mlove@h2odesigns.com (707) 476-8938 Why Geomorphology for Fish Passage 1. Understand the Scale of the
The last three sections of the main body of this report consist of:
 Threatened and Endangered Species Geological Hazards Floodplains Cultural Resources Hazardous Materials A Cost Analysis section that provides comparative conceptual-level costs follows the Environmental
Threatened and Endangered Species Geological Hazards Floodplains Cultural Resources Hazardous Materials A Cost Analysis section that provides comparative conceptual-level costs follows the Environmental
Stream Geomorphology. Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012
 Stream Geomorphology Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012 What Functions do Healthy Streams Provide? Flood mitigation Water supply Water quality Sediment storage and transport Habitat Recreation Transportation
Stream Geomorphology Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012 What Functions do Healthy Streams Provide? Flood mitigation Water supply Water quality Sediment storage and transport Habitat Recreation Transportation
Earth Science Chapter 6 Section 2 Review
 Name: Class: Date: Earth Science Chapter 6 Section Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Most streams carry the largest part of their
Name: Class: Date: Earth Science Chapter 6 Section Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Most streams carry the largest part of their
3.12 Geology and Topography Affected Environment
 3 Affected Environment and Environmental Consequences 3.12 Geology and Topography 3.12.1 Affected Environment 3.12.1.1 Earthquakes Sterling Highway MP 45 60 Project Draft SEIS The Kenai Peninsula is predisposed
3 Affected Environment and Environmental Consequences 3.12 Geology and Topography 3.12.1 Affected Environment 3.12.1.1 Earthquakes Sterling Highway MP 45 60 Project Draft SEIS The Kenai Peninsula is predisposed
L _*" I_
 -- @ o*.d 8 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA-RENO ---^^_ lo-k L - - -- --- - _*" I lll-l-lllll Nevada Bureau of Fdlines and Goology LJriivrts~ly o: Nevada tierlo Ficnn, Novnda 8055 7 OORO (102) it34 6691 NEMG OPEN
-- @ o*.d 8 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA-RENO ---^^_ lo-k L - - -- --- - _*" I lll-l-lllll Nevada Bureau of Fdlines and Goology LJriivrts~ly o: Nevada tierlo Ficnn, Novnda 8055 7 OORO (102) it34 6691 NEMG OPEN
Step 5: Channel Bed and Planform Changes
 Step 5: Channel Bed and Planform Changes When disturbed, streams go through a series of adjustments to regain equilibrium with the flow and sediment supply of their watersheds. These adjustments often
Step 5: Channel Bed and Planform Changes When disturbed, streams go through a series of adjustments to regain equilibrium with the flow and sediment supply of their watersheds. These adjustments often
GEOL 1121 Earth Processes and Environments
 GEOL 1121 Earth Processes and Environments Wondwosen Seyoum Department of Geology University of Georgia e-mail: seyoum@uga.edu G/G Bldg., Rm. No. 122 Seyoum, 2015 Chapter 6 Streams and Flooding Seyoum,
GEOL 1121 Earth Processes and Environments Wondwosen Seyoum Department of Geology University of Georgia e-mail: seyoum@uga.edu G/G Bldg., Rm. No. 122 Seyoum, 2015 Chapter 6 Streams and Flooding Seyoum,
APPENDIX E. GEOMORPHOLOGICAL MONTORING REPORT Prepared by Steve Vrooman, Keystone Restoration Ecology September 2013
 APPENDIX E GEOMORPHOLOGICAL MONTORING REPORT Prepared by Steve Vrooman, Keystone Restoration Ecology September 2 Introduction Keystone Restoration Ecology (KRE) conducted geomorphological monitoring in
APPENDIX E GEOMORPHOLOGICAL MONTORING REPORT Prepared by Steve Vrooman, Keystone Restoration Ecology September 2 Introduction Keystone Restoration Ecology (KRE) conducted geomorphological monitoring in
Bank Erosion and Morphology of the Kaskaskia River
 Bank Erosion and Morphology of the Kaskaskia River US Army Corps Of Engineers St. Louis District Fayette County Soil and Water Conservation District Team Partners : Carlyle Lake Ecosystem Partnership Vicinity
Bank Erosion and Morphology of the Kaskaskia River US Army Corps Of Engineers St. Louis District Fayette County Soil and Water Conservation District Team Partners : Carlyle Lake Ecosystem Partnership Vicinity
NORTHUMBERLAND COUNTY, PA
 QUAKER RUN Stream and Wetland Restoration As-Built Completion Report and First Year Monitoring Data Coal Township NORTHUMBERLAND COUNTY, PA Upstream Before Upstream After Prepared for: COAL TOWNSHIP 805
QUAKER RUN Stream and Wetland Restoration As-Built Completion Report and First Year Monitoring Data Coal Township NORTHUMBERLAND COUNTY, PA Upstream Before Upstream After Prepared for: COAL TOWNSHIP 805
Why Stabilizing the Stream As-Is is Not Enough
 Why Stabilizing the Stream As-Is is Not Enough Several examples of alternatives to the County s design approach have been suggested. A common theme of these proposals is a less comprehensive effort focusing
Why Stabilizing the Stream As-Is is Not Enough Several examples of alternatives to the County s design approach have been suggested. A common theme of these proposals is a less comprehensive effort focusing
REDWOOD VALLEY SUBAREA
 Independent Science Review Panel Conceptual Model of Watershed Hydrology, Surface Water and Groundwater Interactions and Stream Ecology for the Russian River Watershed Appendices A-1 APPENDIX A A-2 REDWOOD
Independent Science Review Panel Conceptual Model of Watershed Hydrology, Surface Water and Groundwater Interactions and Stream Ecology for the Russian River Watershed Appendices A-1 APPENDIX A A-2 REDWOOD
CR AAO Bridge. Dead River Flood & Natural Channel Design. Mitch Koetje Water Resources Division UP District
 CR AAO Bridge Dead River Flood & Natural Channel Design Mitch Koetje Water Resources Division UP District Old County Road AAO Bridge Map courtesy of Marquette County Silver Lake Basin McClure Basin
CR AAO Bridge Dead River Flood & Natural Channel Design Mitch Koetje Water Resources Division UP District Old County Road AAO Bridge Map courtesy of Marquette County Silver Lake Basin McClure Basin
Fish Passage at Road Crossings
 Fish Passage at Road Crossings 1 Crossing Design Workshop Outline 1:00 to 2:00 Intro, Design Overview, Channel Width 2:00 to 2:15 Break 2:15 to 3:15 No-Slope, Stream Simulation Design 3:15 to 3:30 Break
Fish Passage at Road Crossings 1 Crossing Design Workshop Outline 1:00 to 2:00 Intro, Design Overview, Channel Width 2:00 to 2:15 Break 2:15 to 3:15 No-Slope, Stream Simulation Design 3:15 to 3:30 Break
Project (Project No. US-CA-62-2) Maintenance Inspection and Reports (Subtask 14.1) Inspection Report No.2
 MEMORANDUM TO: FROM: Jim Well, Ducks Unlimited Mike Harvey, PhD, PG SUBJECT: M&T/ Llano Seco Fish Screen Project (Project No. US-CA-62-2) Maintenance Inspection and Reports (Subtask 14.1) Inspection Report
MEMORANDUM TO: FROM: Jim Well, Ducks Unlimited Mike Harvey, PhD, PG SUBJECT: M&T/ Llano Seco Fish Screen Project (Project No. US-CA-62-2) Maintenance Inspection and Reports (Subtask 14.1) Inspection Report
Avoiding Geohazards in the Mid-Atlantic Highlands by Using Natural Stream Principles
 Avoiding Geohazards in the Mid-Atlantic Highlands by Using Natural Stream Principles J. Steven Kite, WVU Neal Carte, WVDOT Will Harman, Michael Baker Corp. Donald D. Gray, WVU Photo: W. Gillespie North
Avoiding Geohazards in the Mid-Atlantic Highlands by Using Natural Stream Principles J. Steven Kite, WVU Neal Carte, WVDOT Will Harman, Michael Baker Corp. Donald D. Gray, WVU Photo: W. Gillespie North
TSEGI WASH 50% DESIGN REPORT
 TSEGI WASH 50% DESIGN REPORT 2/28/2014 Daniel Larson, Leticia Delgado, Jessica Carnes I Table of Contents Acknowledgements... IV 1.0 Project Description... 1 1.1 Purpose... 1 Figure 1. Erosion of a Headcut...
TSEGI WASH 50% DESIGN REPORT 2/28/2014 Daniel Larson, Leticia Delgado, Jessica Carnes I Table of Contents Acknowledgements... IV 1.0 Project Description... 1 1.1 Purpose... 1 Figure 1. Erosion of a Headcut...
B-1. Attachment B-1. Evaluation of AdH Model Simplifications in Conowingo Reservoir Sediment Transport Modeling
 Attachment B-1 Evaluation of AdH Model Simplifications in Conowingo Reservoir Sediment Transport Modeling 1 October 2012 Lower Susquehanna River Watershed Assessment Evaluation of AdH Model Simplifications
Attachment B-1 Evaluation of AdH Model Simplifications in Conowingo Reservoir Sediment Transport Modeling 1 October 2012 Lower Susquehanna River Watershed Assessment Evaluation of AdH Model Simplifications
Technical Memorandum No Sediment Model
 Pajaro River Watershed Study in association with Technical Memorandum No. 1.2.9 Sediment Model Task: Development of Sediment Model To: PRWFPA Staff Working Group Prepared by: Gregory Morris and Elsie Parrilla
Pajaro River Watershed Study in association with Technical Memorandum No. 1.2.9 Sediment Model Task: Development of Sediment Model To: PRWFPA Staff Working Group Prepared by: Gregory Morris and Elsie Parrilla
1 INTRODUCTION AND MAJOR FINDINGS... 1
 Memorandum To: Lindsey Clark, Stillwater Valley Watershed Council Coordinator From: Chad Raisland, Pioneer Technical Services, Inc. and Karin Boyd, Applied Geomorphology, Inc. CC: Tanya Lester, Stillwater
Memorandum To: Lindsey Clark, Stillwater Valley Watershed Council Coordinator From: Chad Raisland, Pioneer Technical Services, Inc. and Karin Boyd, Applied Geomorphology, Inc. CC: Tanya Lester, Stillwater
Case Study 2: Twenty-mile Creek Rock Fords
 Case Study : Twenty-mile Creek Rock Fords Location Crossing Description Washington. Okanagan National Forest. Methow Valley Ranger District. Chewuch river basin, East Chewuch Road. The Twenty-mile Creek
Case Study : Twenty-mile Creek Rock Fords Location Crossing Description Washington. Okanagan National Forest. Methow Valley Ranger District. Chewuch river basin, East Chewuch Road. The Twenty-mile Creek
Assessment. Assessment
 2001 SPRINGBROOK CREEK RESTORATION - THREE YEAR POST-CONSTRUCTION REVIEW - Presented by Bruce Henderson and Andy Harris 2005 River Restoration Northwest Symposium Skamania Lodge, Washington www.hendersonlandservices.com
2001 SPRINGBROOK CREEK RESTORATION - THREE YEAR POST-CONSTRUCTION REVIEW - Presented by Bruce Henderson and Andy Harris 2005 River Restoration Northwest Symposium Skamania Lodge, Washington www.hendersonlandservices.com
Working with Natural Stream Systems
 Working with Natural Stream Systems Graydon Dutcher Delaware County Soil & Water Conservation District Stream Corridor Management Program Tropical Storm Sandy October 29,2012 What is a Watershed?
Working with Natural Stream Systems Graydon Dutcher Delaware County Soil & Water Conservation District Stream Corridor Management Program Tropical Storm Sandy October 29,2012 What is a Watershed?
Dolores River Watershed Study
 CHAPTER 4: RIVER AND FLOODPLAIN ISSUES The Dolores River falls into a category of streams in Colorado that share some unique characteristics. Like some other mountain streams in the state, it has a steep
CHAPTER 4: RIVER AND FLOODPLAIN ISSUES The Dolores River falls into a category of streams in Colorado that share some unique characteristics. Like some other mountain streams in the state, it has a steep
Rivers. Regents Earth Science Weathering & Erosion
 Regents Earth Science Weathering & Erosion Name: Rivers Use your notes, the handout Weathering and Erosion and your review book to answer the following questions on Rivers. Be sure to read the information
Regents Earth Science Weathering & Erosion Name: Rivers Use your notes, the handout Weathering and Erosion and your review book to answer the following questions on Rivers. Be sure to read the information
CASE STUDIES. Introduction
 Introduction The City of Winston-Salem faces the challenge of maintaining public infrastructure (e.g., water and sewer lines, storm drains, roads, culverts and bridges) while minimizing the potential impacts
Introduction The City of Winston-Salem faces the challenge of maintaining public infrastructure (e.g., water and sewer lines, storm drains, roads, culverts and bridges) while minimizing the potential impacts
Rivers and Streams. Streams. Hydrologic Cycle. Drainage Basins and Divides. Colorado River Drainage Basin. Colorado Drainage Basins.
 Chapter 14 Hydrologic Cycle Rivers and Streams Streams A stream is a body of water that is confined in a channel and moves downhill under the influence of gravity. This definition includes all sizes of
Chapter 14 Hydrologic Cycle Rivers and Streams Streams A stream is a body of water that is confined in a channel and moves downhill under the influence of gravity. This definition includes all sizes of
Gully Erosion Part 1 GULLY EROSION AND ITS CAUSES. Introduction. The mechanics of gully erosion
 Gully Erosion Part 1 GULLY EROSION AND ITS CAUSES Gully erosion A complex of processes whereby the removal of soil is characterised by incised channels in the landscape. NSW Soil Conservation Service,
Gully Erosion Part 1 GULLY EROSION AND ITS CAUSES Gully erosion A complex of processes whereby the removal of soil is characterised by incised channels in the landscape. NSW Soil Conservation Service,
Historical channel change on the Upper Gila River, Arizona and New Mexico in response to anthropogenic modifications and extreme floods
 Historical channel change on the Upper Gila River, Arizona and New Mexico in response to anthropogenic modifications and extreme floods www.archives.gov www.paztcn.wr.usgs.gov wrh.noaa.gov Upper Gila River
Historical channel change on the Upper Gila River, Arizona and New Mexico in response to anthropogenic modifications and extreme floods www.archives.gov www.paztcn.wr.usgs.gov wrh.noaa.gov Upper Gila River
3/3/2013. The hydro cycle water returns from the sea. All "toilet to tap." Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e
 Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Running Water: summary in haiku form Edward A. Keller Chapter 9 Rivers and Flooding Lecture Presentation prepared by X. Mara Chen, Salisbury University The hydro
Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Running Water: summary in haiku form Edward A. Keller Chapter 9 Rivers and Flooding Lecture Presentation prepared by X. Mara Chen, Salisbury University The hydro
How Do Human Impacts and Geomorphological Responses Vary with Spatial Scale in the Streams and Rivers of the Illinois Basin?
 How Do Human Impacts and Geomorphological Responses Vary with Spatial Scale in the Streams and Rivers of the Illinois Basin? Bruce Rhoads Department of Geography University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
How Do Human Impacts and Geomorphological Responses Vary with Spatial Scale in the Streams and Rivers of the Illinois Basin? Bruce Rhoads Department of Geography University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Rosgen Classification Unnamed Creek South of Dunka Road
 Rosgen Classification Unnamed Creek South of Dunka Road Prepared for Poly Met Mining Inc. September 2013 Rosgen Classification Unnamed Creek South of Dunka Road Prepared for Poly Met Mining Inc. September
Rosgen Classification Unnamed Creek South of Dunka Road Prepared for Poly Met Mining Inc. September 2013 Rosgen Classification Unnamed Creek South of Dunka Road Prepared for Poly Met Mining Inc. September
Highland Lake Bathymetric Survey
 Highland Lake Bathymetric Survey Final Report, Prepared For: The Town of Highland Lake 612 Lakeshore Drive Oneonta, AL 35121 Prepared By: Tetra Tech 2110 Powers Ferry Road SE Suite 202 Atlanta, GA 30339
Highland Lake Bathymetric Survey Final Report, Prepared For: The Town of Highland Lake 612 Lakeshore Drive Oneonta, AL 35121 Prepared By: Tetra Tech 2110 Powers Ferry Road SE Suite 202 Atlanta, GA 30339
Summary. Streams and Drainage Systems
 Streams and Drainage Systems Summary Streams are part of the hydrologic cycle and the chief means by which water returns from the land to the sea. They help shape the Earth s surface and transport sediment
Streams and Drainage Systems Summary Streams are part of the hydrologic cycle and the chief means by which water returns from the land to the sea. They help shape the Earth s surface and transport sediment
Upper Truckee River Restoration Lake Tahoe, California Presented by Brendan Belby Sacramento, California
 Upper Truckee River Restoration Lake Tahoe, California Presented by Brendan Belby Sacramento, California Mike Rudd (Project Manager), Charley Miller & Chad Krofta Declines in Tahoe s Water Clarity The
Upper Truckee River Restoration Lake Tahoe, California Presented by Brendan Belby Sacramento, California Mike Rudd (Project Manager), Charley Miller & Chad Krofta Declines in Tahoe s Water Clarity The
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output
 mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
Griswold Creek August 22, 2013
 Creek August 22, 2013 1 Lake Erie Protection Fund Creek Study ver Evaluate the overall condition of Creek Determine stable channel dimensions & appropriate restoration techniques Starting Stat gpoint for
Creek August 22, 2013 1 Lake Erie Protection Fund Creek Study ver Evaluate the overall condition of Creek Determine stable channel dimensions & appropriate restoration techniques Starting Stat gpoint for
STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY. Surface Water Movement
 Surface Water SECTION 9.1 Surface Water Movement In your textbook, read about surface water and the way in which it moves sediment. Complete each statement. 1. An excessive amount of water flowing downslope
Surface Water SECTION 9.1 Surface Water Movement In your textbook, read about surface water and the way in which it moves sediment. Complete each statement. 1. An excessive amount of water flowing downslope
Laboratory Exercise #3 The Hydrologic Cycle and Running Water Processes
 Laboratory Exercise #3 The Hydrologic Cycle and Running Water Processes page - 1 Section A - The Hydrologic Cycle Figure 1 illustrates the hydrologic cycle which quantifies how water is cycled throughout
Laboratory Exercise #3 The Hydrologic Cycle and Running Water Processes page - 1 Section A - The Hydrologic Cycle Figure 1 illustrates the hydrologic cycle which quantifies how water is cycled throughout
ES 105 Surface Processes I. Hydrologic cycle A. Distribution % in oceans 2. >3% surface water a. +99% surface water in glaciers b.
 ES 105 Surface Processes I. Hydrologic cycle A. Distribution 1. +97% in oceans 2. >3% surface water a. +99% surface water in glaciers b. >1/3% liquid, fresh water in streams and lakes~1/10,000 of water
ES 105 Surface Processes I. Hydrologic cycle A. Distribution 1. +97% in oceans 2. >3% surface water a. +99% surface water in glaciers b. >1/3% liquid, fresh water in streams and lakes~1/10,000 of water
Surface Water and Stream Development
 Surface Water and Stream Development Surface Water The moment a raindrop falls to earth it begins its return to the sea. Once water reaches Earth s surface it may evaporate back into the atmosphere, soak
Surface Water and Stream Development Surface Water The moment a raindrop falls to earth it begins its return to the sea. Once water reaches Earth s surface it may evaporate back into the atmosphere, soak
Degradation Concerns related to Bridge Structures in Alberta
 Degradation Concerns related to Bridge Structures in Alberta Introduction There has been recent discussion regarding the identification and assessment of stream degradation in terms of how it relates to
Degradation Concerns related to Bridge Structures in Alberta Introduction There has been recent discussion regarding the identification and assessment of stream degradation in terms of how it relates to
low turbidity high turbidity
 What is Turbidity? Turbidity refers to how clear the water is. The greater the amount of total suspended solids (TSS) in the water, the murkier it appears and the higher the measured turbidity. Excessive
What is Turbidity? Turbidity refers to how clear the water is. The greater the amount of total suspended solids (TSS) in the water, the murkier it appears and the higher the measured turbidity. Excessive
Stop 1: Marmot Dam Stop 1: Marmot Dam
 Stop 1: Marmot Dam Stop 1: Marmot Dam Following the removal of Marmot Dam in 2007, the fate of the reservoir sediments has been monitored through a series of surveys and sediment transport measurements.
Stop 1: Marmot Dam Stop 1: Marmot Dam Following the removal of Marmot Dam in 2007, the fate of the reservoir sediments has been monitored through a series of surveys and sediment transport measurements.
Streams. Stream Water Flow
 CHAPTER 14 OUTLINE Streams: Transport to the Oceans Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. Streams Streams are the major geological agents
CHAPTER 14 OUTLINE Streams: Transport to the Oceans Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. Streams Streams are the major geological agents
STREAM SYSTEMS and FLOODS
 STREAM SYSTEMS and FLOODS The Hydrologic Cycle Precipitation Evaporation Infiltration Runoff Transpiration Earth s Water and the Hydrologic Cycle The Hydrologic Cycle The Hydrologic Cycle Oceans not filling
STREAM SYSTEMS and FLOODS The Hydrologic Cycle Precipitation Evaporation Infiltration Runoff Transpiration Earth s Water and the Hydrologic Cycle The Hydrologic Cycle The Hydrologic Cycle Oceans not filling
Precipitation Evaporation Infiltration Earth s Water and the Hydrologic Cycle. Runoff Transpiration
 STREAM SYSTEMS and FLOODS The Hydrologic Cycle Precipitation Evaporation Infiltration Earth s Water and the Hydrologic Cycle Runoff Transpiration The Hydrologic Cycle The Hydrologic Cycle Oceans not filling
STREAM SYSTEMS and FLOODS The Hydrologic Cycle Precipitation Evaporation Infiltration Earth s Water and the Hydrologic Cycle Runoff Transpiration The Hydrologic Cycle The Hydrologic Cycle Oceans not filling
Surface Water Short Study Guide
 Name: Class: Date: Surface Water Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The three ways in which a stream carries
Name: Class: Date: Surface Water Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The three ways in which a stream carries
11/12/2014. Running Water. Introduction. Water on Earth. The Hydrologic Cycle. Fluid Flow
 Introduction Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars share a similar history, but Earth is the only terrestrial planet with abundant water! Mercury is too small and hot Venus has a runaway green house effect so
Introduction Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars share a similar history, but Earth is the only terrestrial planet with abundant water! Mercury is too small and hot Venus has a runaway green house effect so
Riparian Assessment. Steps in the right direction... Drainage Basin/Watershed: Start by Thinking Big. Riparian Assessment vs.
 Riparian Assessment vs. Monitoring Riparian Assessment What is a healthy stream? Determine stream/riparian health Determine change or trend, especially in response to mgmt Classification = designation
Riparian Assessment vs. Monitoring Riparian Assessment What is a healthy stream? Determine stream/riparian health Determine change or trend, especially in response to mgmt Classification = designation
 Red River Flooding June 2015 Caddo and Bossier Parishes Presented by: Flood Technical Committee Where the Rain Falls Matters I-30 versus I-20 I-20 Backwater and Tributary Floods (Localized) 2016 Flood
Red River Flooding June 2015 Caddo and Bossier Parishes Presented by: Flood Technical Committee Where the Rain Falls Matters I-30 versus I-20 I-20 Backwater and Tributary Floods (Localized) 2016 Flood
Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands
 Page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands Section A Overview of Lands with Dry Climates The definition of a dry climate is tied to an understanding of the hydrologic cycle
Page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands Section A Overview of Lands with Dry Climates The definition of a dry climate is tied to an understanding of the hydrologic cycle
The Geology of Sebago Lake State Park
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities September, 2002 43 55 17.46 N, 70 34 13.07 W Text by Robert Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by Robert Johnston Introduction Sebago
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities September, 2002 43 55 17.46 N, 70 34 13.07 W Text by Robert Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by Robert Johnston Introduction Sebago
Black Gore Creek 2013 Sediment Source Monitoring and TMDL Sediment Budget
 Black Gore Creek 2013 Sediment Source Monitoring and TMDL Sediment Budget Prepared for: Prepared By: - I. Introduction The Black Gore Creek Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) was developed in collaboration
Black Gore Creek 2013 Sediment Source Monitoring and TMDL Sediment Budget Prepared for: Prepared By: - I. Introduction The Black Gore Creek Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) was developed in collaboration
Strategies for managing sediment in dams. Iwona Conlan Consultant to IKMP, MRCS
 Strategies for managing sediment in dams Iwona Conlan Consultant to IKMP, MRCS 1 Sediment trapping by dams Active storage capacity Dead storage coarse material (bed load) Fine materials (suspension) Francis
Strategies for managing sediment in dams Iwona Conlan Consultant to IKMP, MRCS 1 Sediment trapping by dams Active storage capacity Dead storage coarse material (bed load) Fine materials (suspension) Francis
Solutions to Flooding on Pescadero Creek Road
 Hydrology Hydraulics Geomorphology Design Field Services Photo courtesy Half Moon Bay Review Solutions to Flooding on Pescadero Creek Road Prepared for: San Mateo County Resource Conservation District
Hydrology Hydraulics Geomorphology Design Field Services Photo courtesy Half Moon Bay Review Solutions to Flooding on Pescadero Creek Road Prepared for: San Mateo County Resource Conservation District
Field Trip Number One. By: Pat Dryer. Geography 360
 Field Trip Number One By: Pat Dryer Geography 360 Table of Contents Introduction. Page 1 Stop One... Page 2 Stop Two... Page 4 Stop Three... Page 5 Stop Four... Page 7 Bibliography Page 8 Campus Map Source:
Field Trip Number One By: Pat Dryer Geography 360 Table of Contents Introduction. Page 1 Stop One... Page 2 Stop Two... Page 4 Stop Three... Page 5 Stop Four... Page 7 Bibliography Page 8 Campus Map Source:
Which map shows the stream drainage pattern that most likely formed on the surface of this volcano? A) B)
 1. When snow cover on the land melts, the water will most likely become surface runoff if the land surface is A) frozen B) porous C) grass covered D) unconsolidated gravel Base your answers to questions
1. When snow cover on the land melts, the water will most likely become surface runoff if the land surface is A) frozen B) porous C) grass covered D) unconsolidated gravel Base your answers to questions
High-Gradient Streams
 Chapter 4 Surface Processes Section 4 High-Gradient Streams What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Use models and real-time streamflow data to understand the characteristics of highgradient
Chapter 4 Surface Processes Section 4 High-Gradient Streams What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Use models and real-time streamflow data to understand the characteristics of highgradient
Running Water Earth - Chapter 16 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College
 Running Water Earth - Chapter 16 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Hydrologic Cycle The hydrologic cycle is a summary of the circulation of Earth s water supply. Processes involved in the hydrologic
Running Water Earth - Chapter 16 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Hydrologic Cycle The hydrologic cycle is a summary of the circulation of Earth s water supply. Processes involved in the hydrologic
NATURE OF RIVERS B-1. Channel Function... ALLUVIAL FEATURES. ... to successfully carry sediment and water from the watershed. ...dissipate energy.
 1 2 Function... Sevier River... to successfully carry sediment and water from the watershed....dissipate energy. 3 ALLUVIAL FEATURES 4 CHANNEL DIMENSION The purpose of a stream is to carry water and sediment
1 2 Function... Sevier River... to successfully carry sediment and water from the watershed....dissipate energy. 3 ALLUVIAL FEATURES 4 CHANNEL DIMENSION The purpose of a stream is to carry water and sediment
Illinois State Water Survey Division
 Illinois State Water Survey Division SURFACE WATER SECTION SWS Contract Report 413 AT THE UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS SEDIMENTATION SURVEY OF DAWSON LAKE, MORAINE VIEW STATE PARK, MC LEAN COUNTY, ILLINOIS by
Illinois State Water Survey Division SURFACE WATER SECTION SWS Contract Report 413 AT THE UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS SEDIMENTATION SURVEY OF DAWSON LAKE, MORAINE VIEW STATE PARK, MC LEAN COUNTY, ILLINOIS by
Landscape Development
 Landscape Development Slopes Dominate Natural Landscapes Created by the interplay of tectonic and igneous activity and gradation Deformation and uplift Volcanic activity Agents of gradation Mass wasting
Landscape Development Slopes Dominate Natural Landscapes Created by the interplay of tectonic and igneous activity and gradation Deformation and uplift Volcanic activity Agents of gradation Mass wasting
PolyMet NorthMet Project
 RS 26 Draft-01 December 8, 2005 RS26 Partridge River Level 1 Rosgen Geomorphic Survey Rosgen Classification Partridge River from Headwaters to Colby Lake Prepared for PolyMet NorthMet Project December
RS 26 Draft-01 December 8, 2005 RS26 Partridge River Level 1 Rosgen Geomorphic Survey Rosgen Classification Partridge River from Headwaters to Colby Lake Prepared for PolyMet NorthMet Project December
Fluvial Erosion Impacts on Infrastructure Along Indiana Rivers and Streams
 Fluvial Erosion Impacts on Infrastructure Along Indiana Rivers and Streams Siavash Beik, Robert Barr, Brian Meunier 2017 Purdue Road School March 6-9, 2017 In June 2008, flooding damaged or destroyed
Fluvial Erosion Impacts on Infrastructure Along Indiana Rivers and Streams Siavash Beik, Robert Barr, Brian Meunier 2017 Purdue Road School March 6-9, 2017 In June 2008, flooding damaged or destroyed
Aquifer an underground zone or layer of sand, gravel, or porous rock that is saturated with water.
 Aggradation raising of the streambed by deposition that occurs when the energy of the water flowing through a stream reach is insufficient to transport sediment conveyed from upstream. Alluvium a general
Aggradation raising of the streambed by deposition that occurs when the energy of the water flowing through a stream reach is insufficient to transport sediment conveyed from upstream. Alluvium a general
PR206 NARRATIVE Updated 16 June 2015
 PR206 NARRATIVE Updated 16 June 2015 Cross section PR206 was established in 1977 in a fairly straight reach of Powder River about a kilometer downriver of the Highway 212 bridge at Broadus. The section
PR206 NARRATIVE Updated 16 June 2015 Cross section PR206 was established in 1977 in a fairly straight reach of Powder River about a kilometer downriver of the Highway 212 bridge at Broadus. The section
Illinois State Water Survey Division
 Illinois State Water Survey Division SURFACE WATER SECTION SWS Miscellaneous Publication 108 SEDIMENT YIELD AND ACCUMULATION IN THE LOWER CACHE RIVER by Misganaw Demissie Champaign, Illinois June 1989
Illinois State Water Survey Division SURFACE WATER SECTION SWS Miscellaneous Publication 108 SEDIMENT YIELD AND ACCUMULATION IN THE LOWER CACHE RIVER by Misganaw Demissie Champaign, Illinois June 1989
Environmental Geology Chapter 9 Rivers and Flooding
 Environmental Geology Chapter 9 Rivers and Flooding Flooding in Pakistan 2010-1600 killed/20000 affected The hydrologic cycle is powered by the Sun The cycle includes evaporation, precipitation, infiltration,
Environmental Geology Chapter 9 Rivers and Flooding Flooding in Pakistan 2010-1600 killed/20000 affected The hydrologic cycle is powered by the Sun The cycle includes evaporation, precipitation, infiltration,
Rock Sizing for Waterway & Gully Chutes
 Rock Sizing for Waterway & Gully Chutes WATERWAY MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Rock-lined waterway chute Photo 2 Rock-lined gully chute 1. Introduction A waterway chute is a stabilised section of channel
Rock Sizing for Waterway & Gully Chutes WATERWAY MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Rock-lined waterway chute Photo 2 Rock-lined gully chute 1. Introduction A waterway chute is a stabilised section of channel
SILT FENCE EFFECTIVENESS
 SILT FENCE EFFECTIVENESS Michelle G. Holloway, Department of Earth Sciences, University of South Alabama, Mobile, AL 36688. E-mail: MLG@jaguar1.usouthal.edu. Sediment is the number one pollutant in Dog
SILT FENCE EFFECTIVENESS Michelle G. Holloway, Department of Earth Sciences, University of South Alabama, Mobile, AL 36688. E-mail: MLG@jaguar1.usouthal.edu. Sediment is the number one pollutant in Dog
Continuing Education Associated with Maintaining CPESC and CESSWI Certification
 Continuing Education Associated with Maintaining CPESC and CESSWI Certification Module 2: Stormwater Management Principles for Earth Disturbing Activities Sponsors: ODOTs Local Technical Assistance Program
Continuing Education Associated with Maintaining CPESC and CESSWI Certification Module 2: Stormwater Management Principles for Earth Disturbing Activities Sponsors: ODOTs Local Technical Assistance Program
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY. By Brett Lucas
 PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas FLUVIAL PROCESSES Fluvial Processes The Impact of Fluvial Processes on the Landscape Streams and Stream Systems Stream Channels Structural Relationships The Shaping and
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas FLUVIAL PROCESSES Fluvial Processes The Impact of Fluvial Processes on the Landscape Streams and Stream Systems Stream Channels Structural Relationships The Shaping and
HAW CREEK, PIKE COUNTY, MISSOURI-TRIB TO SALT RIVER ERODING STREAM THREATHENING COUNTY ROAD #107, FOURTEEN FT TALL ERODING BANK WITHIN 4 FT OF THE
 HAW CREEK, PIKE COUNTY, MISSOURI-TRIB TO SALT RIVER ERODING STREAM THREATHENING COUNTY ROAD #107, FOURTEEN FT TALL ERODING BANK WITHIN 4 FT OF THE ROAD, PROJECT CONSTRUCTED IN 1 DAY, MARCH 10, 2009 BY
HAW CREEK, PIKE COUNTY, MISSOURI-TRIB TO SALT RIVER ERODING STREAM THREATHENING COUNTY ROAD #107, FOURTEEN FT TALL ERODING BANK WITHIN 4 FT OF THE ROAD, PROJECT CONSTRUCTED IN 1 DAY, MARCH 10, 2009 BY
Field Observations and One-Dimensional Flow Modeling of Summit Creek in Mack Park, Smithfield, Utah
 Intermountain Center for River Rehabilitation and Restoration, Utah State University 31 July 2018 Field Observations and One-Dimensional Flow Modeling of Summit Creek in Mack Park, Smithfield, Utah I.
Intermountain Center for River Rehabilitation and Restoration, Utah State University 31 July 2018 Field Observations and One-Dimensional Flow Modeling of Summit Creek in Mack Park, Smithfield, Utah I.
Learning Objectives: I can identify and interpret river flows and directions.
 Learning Objectives: I can identify and interpret river flows and directions. Bellringer Review: Check for Understanding Questions: 1 2 What Are The Key Parts Of A River s Anatomy? In your data notebooks
Learning Objectives: I can identify and interpret river flows and directions. Bellringer Review: Check for Understanding Questions: 1 2 What Are The Key Parts Of A River s Anatomy? In your data notebooks
Overview of fluvial and geotechnical processes for TMDL assessment
 Overview of fluvial and geotechnical processes for TMDL assessment Christian F Lenhart, Assistant Prof, MSU Research Assoc., U of M Biosystems Engineering Fluvial processes in a glaciated landscape Martin
Overview of fluvial and geotechnical processes for TMDL assessment Christian F Lenhart, Assistant Prof, MSU Research Assoc., U of M Biosystems Engineering Fluvial processes in a glaciated landscape Martin
GEOMORPHIC CHANGES IN LOWER CACHE CREEK 2012
 GEOMORPHIC CHANGES IN LOWER CACHE CREEK 2012 Eric W. Larsen Technical Memorandum Prepared for Cache Creek Technical Advisory Committee Natural Resources Program Yolo County Board of Supervisors 2012 Prepared
GEOMORPHIC CHANGES IN LOWER CACHE CREEK 2012 Eric W. Larsen Technical Memorandum Prepared for Cache Creek Technical Advisory Committee Natural Resources Program Yolo County Board of Supervisors 2012 Prepared
Materials. Use materials meeting the following.
 208.01 Section 208. SOIL EROSION AND SEDIMENTATION CONTROL 208.01 Description. Install and maintain erosion and sedimentation controls to minimize soil erosion and to control sedimentation from affecting
208.01 Section 208. SOIL EROSION AND SEDIMENTATION CONTROL 208.01 Description. Install and maintain erosion and sedimentation controls to minimize soil erosion and to control sedimentation from affecting
Hydrologic hazards can be considered in three categories; An indication of flooding potential for areas located
 4.0 General Hydrologic Design Critera 4.1 Hydrologic Hazards Hydrologic hazards can be considered in three categories; flooding, channel migration, and tributary stajility. An indication of flooding potential
4.0 General Hydrologic Design Critera 4.1 Hydrologic Hazards Hydrologic hazards can be considered in three categories; flooding, channel migration, and tributary stajility. An indication of flooding potential
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards
 UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Flood and Flood Hazards Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG, Legon College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Flood and Flood Hazards Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG, Legon College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education
Four Mile Run Levee Corridor Stream Restoration
 Four Mile Run Levee Corridor Stream Restoration 30% Design Summary U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Baltimore District Presentation Outline Four Mile Run 1.) Historic Perspective 2.) Existing Conditions 3.)
Four Mile Run Levee Corridor Stream Restoration 30% Design Summary U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Baltimore District Presentation Outline Four Mile Run 1.) Historic Perspective 2.) Existing Conditions 3.)
4.9 GEOLOGY AND SOILS
 4.9 GEOLOGY AND SOILS 4.9.1 EXISTING CONDITIONS TOPOGRAPHY AND RELIEF Zone 40 is located in the central portion of Sacramento County. The topography of the county is represented by three physiographic
4.9 GEOLOGY AND SOILS 4.9.1 EXISTING CONDITIONS TOPOGRAPHY AND RELIEF Zone 40 is located in the central portion of Sacramento County. The topography of the county is represented by three physiographic
EAGLES NEST AND PIASA ISLANDS
 EAGLES NEST AND PIASA ISLANDS HABITAT REHABILITATION AND ENHANCEMENT PROJECT MADISON AND JERSEY COUNTIES, ILLINOIS ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT PROGRAM ST. LOUIS DISTRICT FACT SHEET I. LOCATION The proposed
EAGLES NEST AND PIASA ISLANDS HABITAT REHABILITATION AND ENHANCEMENT PROJECT MADISON AND JERSEY COUNTIES, ILLINOIS ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT PROGRAM ST. LOUIS DISTRICT FACT SHEET I. LOCATION The proposed
PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING DISTRICT 3-0
 PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING DISTRICT 3-0 LYCOMING COUNTY S.R.15, SECTION C41 FINAL HYDROLOGIC AND HYDRAULIC REPORT STEAM VALLEY RUN STREAM RELOCATION DATE: June, 2006 REVISED:
PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING DISTRICT 3-0 LYCOMING COUNTY S.R.15, SECTION C41 FINAL HYDROLOGIC AND HYDRAULIC REPORT STEAM VALLEY RUN STREAM RELOCATION DATE: June, 2006 REVISED:
R.M.HARW & ASSOCIATES LTD. GEOTECHNICAL INVESTIGATION PROPOSED BRIDGE SITE. HELAVA CREEKl MILE MACKENZIE HIGHWAY E-2510 OCTOBER 16, 1973
 El R.M.HARW & ASSOCIATES LTD. GEOTECHNICAL INVESTIGATION PROPOSED BRIDGE SITE HELAVA CREEKl MILE 616.4 MACKENZIE HIGHWAY E-2510 OCTOBER 16, 1973 R,M,HARDV & ASSOCIATES LTD. CONSULTING ENGINEERING & TESTING
El R.M.HARW & ASSOCIATES LTD. GEOTECHNICAL INVESTIGATION PROPOSED BRIDGE SITE HELAVA CREEKl MILE 616.4 MACKENZIE HIGHWAY E-2510 OCTOBER 16, 1973 R,M,HARDV & ASSOCIATES LTD. CONSULTING ENGINEERING & TESTING
Final Exam. Running Water Erosion and Deposition. Willamette Discharge. Running Water
 Final Exam Running Water Erosion and Deposition Earth Science Chapter 5 Pages 120-135 Scheduled for 8 AM, March 21, 2006 Bring A scantron form A calculator Your 3 x 5 paper card of formulas Review questions
Final Exam Running Water Erosion and Deposition Earth Science Chapter 5 Pages 120-135 Scheduled for 8 AM, March 21, 2006 Bring A scantron form A calculator Your 3 x 5 paper card of formulas Review questions
QUANTITY, MARCH 1962
 BASE-FLOW STUDIES, GUADALUPE RIVER COMAL COUNTY, TEXAS QUANTITY, MARCH 1962 TEXAS WATER COMMISSION BULLETIN 6503 MARCH 1965 TEXAS WATER COMMISSION Joe William D E 0. F. Dent Carter, Chairman Berger, Commissioner
BASE-FLOW STUDIES, GUADALUPE RIVER COMAL COUNTY, TEXAS QUANTITY, MARCH 1962 TEXAS WATER COMMISSION BULLETIN 6503 MARCH 1965 TEXAS WATER COMMISSION Joe William D E 0. F. Dent Carter, Chairman Berger, Commissioner
PR122A NARRATIVE Updated 25 July 2014
 PR122A NARRATIVE Updated 25 July 2014 Cross section PR122A was established in 1979 across a new cutoff channel that had formed during the 1978 flood across the neck of a meander bend in Powder River at
PR122A NARRATIVE Updated 25 July 2014 Cross section PR122A was established in 1979 across a new cutoff channel that had formed during the 1978 flood across the neck of a meander bend in Powder River at
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 5 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 5 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 5 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Flood and Stream Restoration
 2 3 4 Pedestrian bridge under construction 3 CSPs perched on DS side Large area of sand deposition Bottom layer of gabions has been scoured out large bar of gabion stone Gabions slumping bank slope failure
2 3 4 Pedestrian bridge under construction 3 CSPs perched on DS side Large area of sand deposition Bottom layer of gabions has been scoured out large bar of gabion stone Gabions slumping bank slope failure
Fish Passage and Abundance around Grade Control Structures on Incised Streams in Western Iowa
 Fish Passage and Abundance around Grade Control Structures on Incised Streams in Western Iowa John Thomas Hungry Canyons Alliance Mary Culler Iowa State University / Missouri DNR Dimitri Dermisis IIHR
Fish Passage and Abundance around Grade Control Structures on Incised Streams in Western Iowa John Thomas Hungry Canyons Alliance Mary Culler Iowa State University / Missouri DNR Dimitri Dermisis IIHR
Geomorphic Importance of Winter Peak Flows and Annual Snowmelt Hydrographs in a Sierra Nevada Boulder-Bedrock River
 Geomorphic Importance of Winter Peak Flows and Annual Snowmelt Hydrographs in a Sierra Nevada Boulder-Bedrock River Scott McBain and Bill Trush McBain & Trush, Inc. Clavey River and Cherry Creek vicinity
Geomorphic Importance of Winter Peak Flows and Annual Snowmelt Hydrographs in a Sierra Nevada Boulder-Bedrock River Scott McBain and Bill Trush McBain & Trush, Inc. Clavey River and Cherry Creek vicinity
Assessment of Lake Forest Lake Sediment Trapping Efficiency and Capacity. Marlon R. Cook Groundwater Assessment Program Geological Survey of Alabama
 Assessment of Lake Forest Lake Sediment Trapping Efficiency and Capacity Marlon R. Cook Groundwater Assessment Program Geological Survey of Alabama Impacts of the Lake at Lake Forest on the connectivity
Assessment of Lake Forest Lake Sediment Trapping Efficiency and Capacity Marlon R. Cook Groundwater Assessment Program Geological Survey of Alabama Impacts of the Lake at Lake Forest on the connectivity
Carmel River Bank Stabilization at Rancho San Carlos Road Project Description and Work Plan March 2018
 Carmel River Bank Stabilization at Rancho San Carlos Road Project Description and Work Plan March 2018 EXISTING CONDITION The proposed Carmel River Bank Stabilization at Rancho San Carlos Road Project
Carmel River Bank Stabilization at Rancho San Carlos Road Project Description and Work Plan March 2018 EXISTING CONDITION The proposed Carmel River Bank Stabilization at Rancho San Carlos Road Project
STABILIZATION OF THE H&CT RAILWAY STONE DAM WALTER E. SKIPWITH, PE, JOYCE CRUM, AIA AND JOHN BAUMGARTNER, PE. Introduction.
 STABILIZATION OF THE H&CT RAILWAY STONE DAM WALTER E. SKIPWITH, PE, JOYCE CRUM, AIA AND JOHN BAUMGARTNER, PE I. A. Introduction General The Old Stone Dam is located in the upper reach of Cottonwood Creek
STABILIZATION OF THE H&CT RAILWAY STONE DAM WALTER E. SKIPWITH, PE, JOYCE CRUM, AIA AND JOHN BAUMGARTNER, PE I. A. Introduction General The Old Stone Dam is located in the upper reach of Cottonwood Creek
Unit 7.2 W.E.D. & Topography Test
 Name: Score: Unit 7.2 W.E.D. & Topography Test 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 1. The formation of mountains is due mainly to while the destruction
Name: Score: Unit 7.2 W.E.D. & Topography Test 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 1. The formation of mountains is due mainly to while the destruction
Rock Sizing for Small Dam Spillways
 Rock Sizing for Small Dam Spillways STORMWATER MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Rock-lined spillway on a construction site sediment basin Photo 2 Rock-lined spillway on a small farm dam 1. Introduction A chute
Rock Sizing for Small Dam Spillways STORMWATER MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Rock-lined spillway on a construction site sediment basin Photo 2 Rock-lined spillway on a small farm dam 1. Introduction A chute
