Degradation Concerns related to Bridge Structures in Alberta
|
|
|
- Rodney Howard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Degradation Concerns related to Bridge Structures in Alberta Introduction There has been recent discussion regarding the identification and assessment of stream degradation in terms of how it relates to the design of bridge structures for Alberta Transportation (TRANS). Degradation is defined as the long term lowering of a channel elevation over a significant distance. Degradation can occur naturally or as a result of manmade influences. Further background information related to degradation processes, common concerns, and TRANS case studies are provided in the Appendix. Assessment To assess whether degradation is occurring at a particular site, or along a particular stream reach, a river engineering review should be conducted. For a small culvert site, this may include a file history review and site inspection (if insufficient site photos are available). For more major sites (bridges or major culverts), or those where an initial screening warranted further investigation, analysis could include: desktop site history review: o comparison of historical streambed surveys, o history of hydraulic structures, o history of channel modifications, o maintenance concerns, etc. temporal aerial photography review to assess: o stream planform changes, o channel realignments, o bank failures over a considerable distance, o valley instabilities, etc. site visit, where degradation indicators could include: o streambed lowering over an extended reach, o vegetation levels high in comparison to streambed elevations, o bank toe erosion resulting in vertical banks, o steep ravines approaching a confluence, o geotechnical instabilities, etc. This analysis should help assess i) if degradation is occurring ii) the extent iii) the cause (natural or manmade), and iv) the timeframe (single event or continual), from which recommendations can be made.
2 Recommendations For sites where stream degradation is not obvious from an engineering assessment, it is recommended to follow existing guidelines. For sites where degradation is a concern, remedial measures are typically recommended until structure condition warrants replacement, with possible solutions as outlined below. Remediation options for bridges may include: doing nothing (allow degradation to progress upstream), installing a grade control structure (culvert, weir, cutoff wall, etc.), channel work (regrading, installation of riprap, etc.), adding a span, headslope trimming and protection Remediation options for culverts may include: using the existing structure as a control structure, installing a grade control structure, channel work, extending the existing structure Replacement options for culverts: 1. Prevent degradation from progressing upstream set downstream invert elevation to match existing streambed plus standard burial make up existing elevation drop with a multi slope (drop) structure or by installing the structure on a steeper slope Potential Issues: may impede fish passage, creation of hydraulic jumps is likely, may require more extensive outlet protection works (prevent structure undermining, energy dissipation), may require downstream remediation in the future, may make drift passage more difficult, may make future structures more difficult (greater elevation difference) 2. Allow degradation to progress upstream set downstream invert elevation lower than existing streambed (to a maximum of 1m) match culvert slope to downstream channel slope Potential Issues: may require substantial excavation (particularly on the upstream end), larger footprint will be required (RoW, culvert length, transition to natural channel), may cause issues to progress upstream (landowner impacts, geotechnical instabilities) may require maintenance, may require outlet protection works to prevent structure undermining in the future.
3 APPENDIX Background Natural degradation can occur as a result of stream progression to a state of equilibrium. The majority of watercourse s in Alberta are geologically young and are prone to natural bed lowering over time. This can be particularly evident in small tributaries downcutting to meet large waterbodies. In general, a stream will have a profile as shown, consisting of an erosion, transport, and deposition reach, as furtherr defined below. Figure 1: Typical Stream Profile (BIM, 2007) ) Figure 2: Stream Profile for McLeod River Erosion Reach - Initially, the stream will be quite steep. It will be actively eroding as the stream picks up sediment to complement its sediment transport capacity. Most of the sediment transport will be in the form of bed load with larger particles tumbling along the
4 Stream bed. These reaches may be actively degrading. Unstable braided stream patterns are common, such as those seen along the upper McLeod River (Figure 3). Figure 3: Upper McLeod River Reach Planform (Google Earth, 2012) Transport Reach - This reach is characterized by a balance between erosion and deposition. The channel may still be actively eroding laterally, but will not be degrading. The typical channel pattern in this reach is the meandering river. Channel slopes will be flatter. Sediment transport will include both bed load and suspended sediment (Figure 4). Figure 4: Middle McLeod River Reach Planform (Google Earth, 2012)
5 Deposition Reach - As the slope gets even flatter, the stream will lose its sediment transport capacity and there will be a net deposition of material. These reaches may be actively aggrading, and lateral channel stability decreases. These reaches may be characterized by alluvial fans and deltas. Downcutting - An alternative to the deposition reach near the mouth of the river is a downcutting reach, where the channel may be actively degrading in order to match the elevation of the receiving stream. Figure 5: Lower Reach McLeod River Planform; Downcutting to meet the Athabasca River (Google Earth, 2012) Manmade degradation can be a result of channel realignment, where the new channel is shorter or steeper than the original channel. The relationship QS ~ Q s D (where Q is discharge, S is energy gradeline slope, Q s is the sediment discharge, and D is mean bed material size) describes channel response in terms of transport capacity. This relationship can be observed in the case of a dam installation (Figure 6). Upstream of the dam, the energy gradeline slope is decreased by the creation of a backwater curve behind the dam. This decrease corresponds to a decrease in sediment discharge (assuming the stream discharge and bed material remains unchanged), leading to sediment deposition (aggradation). Similarly, downstream of the dam, the water discharged will have a very low sediment discharge. This reduction is balanced by a decrease in energy gradeline slope (lowering of the stream bed over a considerable distance), resulting in degradation. Figure 7 below shows how this concept applies to a channelized stream. Over time, aggradation and degradation will occur to achieve a new equilibrium. Examples of manmade stream degradation in Alberta include Bear River, West Prairie River, and Cucumber Creek.
6 Figure 6: River Response due to Transport Capacity (BIM, 2007) Figure 7: Reestablishment of Natural Equilibrium after Channelizationn (adapted from FHWA, 1991) The current AT process of embedding bridge size culverts by D/4 (to a maximum 1m) accounts for the temporal geological stream lowering process over the life of a structure. This practice also provides environmental connectivity and allows for natural substrate to be transported into the structure to establish a naturall streambed equilibrium over time. Common Concerns Degradation is sometimes misinterpreted as general (constriction) scour, the lowering of the streambed through a bridge crossing. Higherr stream velocities, due to channel constriction, cause a general lowering of the stream bed acrosss its width. The depth of scour will dependd on the degree of constriction of the flow, the geotechnical conditions, and the runoff hydrograph properties. General scour (Figure 8) is confined to the vicinity of the structure while degradation will occur along the watercourse as well.
7 Figure 8: General Scour at a Bridge Opening (BIM, 2007) Degradation may also be misinterprete ed as local scour, such as the lowering of a streambed downstream of a culvert. In the past, TRANS installed culverts at streambed elevation, with minimal protection works, and, oftentimes, at a slope greater than that of the natural channel. Historical culverts also hadd a tendency to be hydraulically undersized. These past practices resulted in high exit velocities and resulted in scour holes forming at many outlets. These scour holes, at times, have been misinterpreted as degradation. It is important to note thatt degradation is a global channel process while scour is a local process. The examination of the stream away from a structure during a site assessment can help differentiate between local or general scour and channel degradation. Case Studies BF74852 Local Road over Bear River Site History: 1958 Bridge built. Deck height = 11 (~ ~3.3m) 1969 LaCrete drainage project: meander cutoffs to steepen channel (S~0.006 vs. S~0.0034) and alleviate upstream flooding. Drop structures and bridge protection were recommended but not installed Bridge built. Deck height = 18 (~ ~5.4m) Drop structures installed. Aggradation expected Deck height = 7.9m 1992 Deck height = 7.6m 1993 Deck height = 7.3m
8 1987 Photo: note paint elevation and vertical banks Assessment: steepening and shortening of the channel in 1969 resulted in degradation (about 2.1m in almost 20 years) until drop structures were constructed. The channel was attempting to achieve a new equilibrium (Figure 6). Since streambed surveys were not obtained over the years, we do not know the timing and progression of the degradation. The majority of degradation could have occurred initially with minimal progression in the later years, it could have occurred at an average rate per year, or as a scenario in between. installation of the drop structures resulted in aggradation at the bridge site (about 0.6m over 5 years). Remediation: Do nothing. The existing drop structures are minimizing streambed elevation changes and threat is no threat of foundation undermining at the current bridge structure
9 BF73235 Local Road over Cucumber Creek Site History: x x 15 culverts. Highwater over grade x 57 arch pipe installed Deck height = 7 (2.1m); 24 culvert installed, u/s end raised 2, grade raised by 1.5. Highwater over grade Culvert washout. 16 bridge built, deck height = 8, u/s channel straightened m culvert installed High flow event, streambed surveyed 2007 Photo note vegetation elevation, near vertical banks
10 BF73235 Cucumber Ck 2007 Photo note hanging outlet, vertical banks BIM Stream Profile from DTM
11 DTM Survey Elevation (m) Station (m) Local Stream Profile in Comparison to DTM Assessment: there is a lack in historical information from 1966 to 2006 to assess if the straightening undertaken in 1966 had an impact on the channel (aggradation/degradation). The lack of information may suggest that major issues were not observed. from the local streambed survey and DTM extracted survey, it is evident that the channel downstream of the culvert has degraded (by 2.5m +/-) and that the culvert is acting as a control structure preventing the progression of this degradation upstream. the break in slope seen in the DTM slope, with a steeper portion closer to the receiving stream, is evidence of the stream downcutting to meet a receiving channel. Cucumber Creek is degrading to match the elevation of the receiving North Saskatchewan River Remediation: if the structure integrity is not comprised, remediation may include preventing future structure issues, namely undermining. This may involve the design of a cut off wall to hold up the outlet and/or installation of protection works (rip rap) to prevent loss of backfill material and to dissipate high outlet velocities. for a new structure design, considerations could involve allowing the degradation to progress upstream (cost, potential liabilities), installing a structure to act as a control (maintain status quo), or somewhere in between (allow for a certain amount of degradation). For each option, there should be consideration given to cost (both capital and future maintenance) and potential risks or liabilities (known vs. potential concerns, legal consequences).
12 BF75700 Highway 733 over Bad Heart River Site History: mm culverts installed on stream diversion (Figure below) 1990 Highwater event. Hanging outlets (~1.5m above streambed) 2001 Cut off wall installed beneath hanging outlets Structure condition warrants replacement Stream Diversion Profile (extracted from DD385, 1963)
13 Looking at Downstream (note banks slumping/vertical banks) Looking at Upstream Channel from Upstream of the Drift Catcher
14 Looking at outlets from Downstream (note ~2m drop, scour hole) 2007 Airphoto (note number of slides d/s compared to u/s)
15 2012 Streambed Survey, ~500m u/s and d/s from structure (note local scour hole downstream, elevation difference between u/s and d/s) Assessment: from sites photos, a large scour hole downstream of the outlet can be seen. This local scour hole is also seen on the survey. Site photos also show slumping, vertical banks in the downstream channel which could be indicative of degradation (if occurring along an entire section) and/or lateral stream instability (if occurring locally; outside of meander bends). from the 2012 survey, it is evident that degradation has occurred in the past and that the existing culvert structures are acting as controls to prevent degradation progression upstream. The stream has approximately the same slope upstream and downstream, with an elevation difference of about 2m. the air photo shows a much greater number of landslides downstream of the structure than upstream. This could be from degradation (toe slope undermining). A review of historical air photos may help to determine if this was a continual process over time or occurred as a result of a specific event(s). Remediation: since the structure condition warrants replacement, remediation was not considered. In the past, a cutoff wall was installed to support the culvert structures and riprap was placed in the scour hole to dissipate outlet velocities and prevent structure undermining. Replacement: two options were considered during replacement 1) setting the invert downstream and matching the downstream channel slope (upstream invert below streambed); allowing degradation to progress upstream and 2) setting the invert downstream and upstream to the existing streambed elevations (slope steeper than natural stream), preventing degradation progression
16 Schematic for Option 1 Schematic for Option 2 Option 1 Pros: better connectivity for fish passage, better for watercraft navigability, lower velocities within the structure (no hydraulic jump created). Cons: greater depth of fill (potential settlement concerns), greater depth of excavation (potential constructability, geotechnical concerns), greater culvert length, greater length of channel impacted, more RoW required, greater risk (uncertainty associated with progression of degradation upstream).
17 Option 2 Pros: less fill depth, shallow excavation, shorter structure, shorter length of channel impacted, less RoW required, less risk. Cons: worse for fish passage, worse for watercraft navigability, high velocities within the structure requiring energy dissipation design. Discussion Since fish sampling revealed only forage fish, fish passage was not considered a governing factor for design. Transport Canada advised that this stream was considered non-navigable due to high levels of drift and shallow water level. Navigability was therefore not considered a governing factor for design. Geotechnical review revealed unstable banks within the Bad Heart River valley Large volumes of drift were viewed to be a major concern for both options with either option requiring a flared inlet with additional freeboard allowance. Replacement Option 2 was recommended as the replacement structure.
18 References Hydrotechnical Considerations, BIM Course Presentation, Alberta Transportation, Design Guidelines for Bridge Size Culverts, Alberta Transportation, Federal Highway Administration, HEC-20, Stream Stability at Highway Structures, 1991.
Why Geomorphology for Fish Passage
 Channel Morphology - Stream Crossing Interactions An Overview Michael Love Michael Love & Associates mlove@h2odesigns.com (707) 476-8938 Why Geomorphology for Fish Passage 1. Understand the Scale of the
Channel Morphology - Stream Crossing Interactions An Overview Michael Love Michael Love & Associates mlove@h2odesigns.com (707) 476-8938 Why Geomorphology for Fish Passage 1. Understand the Scale of the
Appendix F Channel Grade Control Structures
 Stream Simulation Appendix F Channel Grade Control Structures This appendix briefly describes permanent grade control structures that are sometimes needed in the upstream and/or downstream reaches adjacent
Stream Simulation Appendix F Channel Grade Control Structures This appendix briefly describes permanent grade control structures that are sometimes needed in the upstream and/or downstream reaches adjacent
Stream Geomorphology. Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012
 Stream Geomorphology Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012 What Functions do Healthy Streams Provide? Flood mitigation Water supply Water quality Sediment storage and transport Habitat Recreation Transportation
Stream Geomorphology Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012 What Functions do Healthy Streams Provide? Flood mitigation Water supply Water quality Sediment storage and transport Habitat Recreation Transportation
Fluvial Geomorphic Guidelines
 Fluvial Geomorphic Guidelines FACT SHEET I: GEOMORPHOLOGICAL HAZARDS CONFINED AND UNCONFINED WATERCOURSES Channel migration and erosion can create substantial risk to inappropriately located infrastructure
Fluvial Geomorphic Guidelines FACT SHEET I: GEOMORPHOLOGICAL HAZARDS CONFINED AND UNCONFINED WATERCOURSES Channel migration and erosion can create substantial risk to inappropriately located infrastructure
Step 5: Channel Bed and Planform Changes
 Step 5: Channel Bed and Planform Changes When disturbed, streams go through a series of adjustments to regain equilibrium with the flow and sediment supply of their watersheds. These adjustments often
Step 5: Channel Bed and Planform Changes When disturbed, streams go through a series of adjustments to regain equilibrium with the flow and sediment supply of their watersheds. These adjustments often
Tom Ballestero University of New Hampshire. 1 May 2013
 Tom Ballestero University of New Hampshire 1 May 2013 1 Hydrology 2 Basic Hydrology Low flows most common Flows that fill the stream to the banks and higher are much less common Filling the stream to the
Tom Ballestero University of New Hampshire 1 May 2013 1 Hydrology 2 Basic Hydrology Low flows most common Flows that fill the stream to the banks and higher are much less common Filling the stream to the
Fish Passage at Road Crossings
 Fish Passage at Road Crossings 1 Crossing Design Workshop Outline 1:00 to 2:00 Intro, Design Overview, Channel Width 2:00 to 2:15 Break 2:15 to 3:15 No-Slope, Stream Simulation Design 3:15 to 3:30 Break
Fish Passage at Road Crossings 1 Crossing Design Workshop Outline 1:00 to 2:00 Intro, Design Overview, Channel Width 2:00 to 2:15 Break 2:15 to 3:15 No-Slope, Stream Simulation Design 3:15 to 3:30 Break
GEOMORPHIC CHANGES IN LOWER CACHE CREEK 2012
 GEOMORPHIC CHANGES IN LOWER CACHE CREEK 2012 Eric W. Larsen Technical Memorandum Prepared for Cache Creek Technical Advisory Committee Natural Resources Program Yolo County Board of Supervisors 2012 Prepared
GEOMORPHIC CHANGES IN LOWER CACHE CREEK 2012 Eric W. Larsen Technical Memorandum Prepared for Cache Creek Technical Advisory Committee Natural Resources Program Yolo County Board of Supervisors 2012 Prepared
Forest Service AOP Meeting Objectives of Stream Simulation: Examples and Talking Points
 Forest Service AOP Meeting Objectives of Stream Simulation: Examples and Talking Points Traci Sylte, P.E. Hydrology/Fluvial Geomorphology Lolo National Forest Is It True? Are Road Crossings a Dam with
Forest Service AOP Meeting Objectives of Stream Simulation: Examples and Talking Points Traci Sylte, P.E. Hydrology/Fluvial Geomorphology Lolo National Forest Is It True? Are Road Crossings a Dam with
Summary of Hydraulic and Sediment-transport. Analysis of Residual Sediment: Alternatives for the San Clemente Dam Removal/Retrofit Project,
 Appendix N SUMMARY OF HYDRAULIC AND SEDIMENT-TRANSPORT ANALYSIS OF RESIDUAL SEDIMENT: ALTERNATIVES FOR THE SAN CLEMENTE DAM REMOVAL/RETROFIT PROJECT, CALIFORNIA the San Clemente Dam Removal/Retrofit Project,
Appendix N SUMMARY OF HYDRAULIC AND SEDIMENT-TRANSPORT ANALYSIS OF RESIDUAL SEDIMENT: ALTERNATIVES FOR THE SAN CLEMENTE DAM REMOVAL/RETROFIT PROJECT, CALIFORNIA the San Clemente Dam Removal/Retrofit Project,
Countermeasure Calculations and Design
 Countermeasure Calculations and Design Summarized from Bridge Scour and Stream Instability Countermeasures, Experience, Selection, and Design Guidance, Second Edition, Publication No. FHWA NHI 01-003,
Countermeasure Calculations and Design Summarized from Bridge Scour and Stream Instability Countermeasures, Experience, Selection, and Design Guidance, Second Edition, Publication No. FHWA NHI 01-003,
Streams. Stream Water Flow
 CHAPTER 14 OUTLINE Streams: Transport to the Oceans Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. Streams Streams are the major geological agents
CHAPTER 14 OUTLINE Streams: Transport to the Oceans Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. Streams Streams are the major geological agents
NORTHUMBERLAND COUNTY, PA
 QUAKER RUN Stream and Wetland Restoration As-Built Completion Report and First Year Monitoring Data Coal Township NORTHUMBERLAND COUNTY, PA Upstream Before Upstream After Prepared for: COAL TOWNSHIP 805
QUAKER RUN Stream and Wetland Restoration As-Built Completion Report and First Year Monitoring Data Coal Township NORTHUMBERLAND COUNTY, PA Upstream Before Upstream After Prepared for: COAL TOWNSHIP 805
Case Study 2: Twenty-mile Creek Rock Fords
 Case Study : Twenty-mile Creek Rock Fords Location Crossing Description Washington. Okanagan National Forest. Methow Valley Ranger District. Chewuch river basin, East Chewuch Road. The Twenty-mile Creek
Case Study : Twenty-mile Creek Rock Fords Location Crossing Description Washington. Okanagan National Forest. Methow Valley Ranger District. Chewuch river basin, East Chewuch Road. The Twenty-mile Creek
CASE STUDIES. Introduction
 Introduction The City of Winston-Salem faces the challenge of maintaining public infrastructure (e.g., water and sewer lines, storm drains, roads, culverts and bridges) while minimizing the potential impacts
Introduction The City of Winston-Salem faces the challenge of maintaining public infrastructure (e.g., water and sewer lines, storm drains, roads, culverts and bridges) while minimizing the potential impacts
Probabilistic Evaluation of a Meandering Low-Flow Channel. February 24 th, UMSRS
 Probabilistic Evaluation of a Meandering Low-Flow Channel February 24 th, 2014 2014 UMSRS 1 2 acknowledgments Low- Flow Channel (LFC) overview Proposed Diversion Channel collects runoff from: The Rush
Probabilistic Evaluation of a Meandering Low-Flow Channel February 24 th, 2014 2014 UMSRS 1 2 acknowledgments Low- Flow Channel (LFC) overview Proposed Diversion Channel collects runoff from: The Rush
Four Mile Run Levee Corridor Stream Restoration
 Four Mile Run Levee Corridor Stream Restoration 30% Design Summary U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Baltimore District Presentation Outline Four Mile Run 1.) Historic Perspective 2.) Existing Conditions 3.)
Four Mile Run Levee Corridor Stream Restoration 30% Design Summary U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Baltimore District Presentation Outline Four Mile Run 1.) Historic Perspective 2.) Existing Conditions 3.)
Running Water Earth - Chapter 16 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College
 Running Water Earth - Chapter 16 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Hydrologic Cycle The hydrologic cycle is a summary of the circulation of Earth s water supply. Processes involved in the hydrologic
Running Water Earth - Chapter 16 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Hydrologic Cycle The hydrologic cycle is a summary of the circulation of Earth s water supply. Processes involved in the hydrologic
When Creek Meets Valley Wall: Prioritizing Erosion Mitigation alongside the Oshawa Landfill
 1 When Creek Meets Valley Wall: Prioritizing Erosion Mitigation alongside the Oshawa Landfill Robin McKillop 1, Dan McParland 1 & Cassie Scobie 2 TRIECA conference March 22-23, 2017 1 Palmer Environmental
1 When Creek Meets Valley Wall: Prioritizing Erosion Mitigation alongside the Oshawa Landfill Robin McKillop 1, Dan McParland 1 & Cassie Scobie 2 TRIECA conference March 22-23, 2017 1 Palmer Environmental
Gully Erosion Part 1 GULLY EROSION AND ITS CAUSES. Introduction. The mechanics of gully erosion
 Gully Erosion Part 1 GULLY EROSION AND ITS CAUSES Gully erosion A complex of processes whereby the removal of soil is characterised by incised channels in the landscape. NSW Soil Conservation Service,
Gully Erosion Part 1 GULLY EROSION AND ITS CAUSES Gully erosion A complex of processes whereby the removal of soil is characterised by incised channels in the landscape. NSW Soil Conservation Service,
GEOL 1121 Earth Processes and Environments
 GEOL 1121 Earth Processes and Environments Wondwosen Seyoum Department of Geology University of Georgia e-mail: seyoum@uga.edu G/G Bldg., Rm. No. 122 Seyoum, 2015 Chapter 6 Streams and Flooding Seyoum,
GEOL 1121 Earth Processes and Environments Wondwosen Seyoum Department of Geology University of Georgia e-mail: seyoum@uga.edu G/G Bldg., Rm. No. 122 Seyoum, 2015 Chapter 6 Streams and Flooding Seyoum,
HYDROLOGY AND HYDRAULICS MUSKEG RIVER BRIDGE
 PUBLIC WORKS CANADA HYDROLOGY AND HYDRAULICS MUSKEG RIVER BRIDGE KILOMETRE 207.9, LIARD HIGKWAY December 1978 I I f I I I I # Bolter Parish Trimble Ltd. ONLIULTINO Public Works, Canada, 9925-109 Street,
PUBLIC WORKS CANADA HYDROLOGY AND HYDRAULICS MUSKEG RIVER BRIDGE KILOMETRE 207.9, LIARD HIGKWAY December 1978 I I f I I I I # Bolter Parish Trimble Ltd. ONLIULTINO Public Works, Canada, 9925-109 Street,
Why Stabilizing the Stream As-Is is Not Enough
 Why Stabilizing the Stream As-Is is Not Enough Several examples of alternatives to the County s design approach have been suggested. A common theme of these proposals is a less comprehensive effort focusing
Why Stabilizing the Stream As-Is is Not Enough Several examples of alternatives to the County s design approach have been suggested. A common theme of these proposals is a less comprehensive effort focusing
Technical Memorandum No
 Pajaro River Watershed Study in association with Technical Memorandum No. 1.2.10 Task: Evaluation of Four Watershed Conditions - Sediment To: PRWFPA Staff Working Group Prepared by: Gregory Morris and
Pajaro River Watershed Study in association with Technical Memorandum No. 1.2.10 Task: Evaluation of Four Watershed Conditions - Sediment To: PRWFPA Staff Working Group Prepared by: Gregory Morris and
1. PROJECT BACKGROUND. July 18, Alberta Infrastructure & Transportation Central Region #401, Street Red Deer, Alberta T4N 6K8
 July 18, 2005 Alberta Infrastructure & Transportation Central Region #401, 4902 51 Street Red Deer, Alberta T4N 6K8 Mr. Alain Momedi, P.Eng. Project Engineer Dear Mr. Momedi: H11:04 km 11.1 Erosion along
July 18, 2005 Alberta Infrastructure & Transportation Central Region #401, 4902 51 Street Red Deer, Alberta T4N 6K8 Mr. Alain Momedi, P.Eng. Project Engineer Dear Mr. Momedi: H11:04 km 11.1 Erosion along
Design and Construction
 Design and Construction Stream Simulation With power point slides shamelessly stolen from: Forest Service AOP Training Course Bob Gubernick Paul Anderson John Kattell USDA Forest Service Interim Directive
Design and Construction Stream Simulation With power point slides shamelessly stolen from: Forest Service AOP Training Course Bob Gubernick Paul Anderson John Kattell USDA Forest Service Interim Directive
Black Gore Creek 2013 Sediment Source Monitoring and TMDL Sediment Budget
 Black Gore Creek 2013 Sediment Source Monitoring and TMDL Sediment Budget Prepared for: Prepared By: - I. Introduction The Black Gore Creek Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) was developed in collaboration
Black Gore Creek 2013 Sediment Source Monitoring and TMDL Sediment Budget Prepared for: Prepared By: - I. Introduction The Black Gore Creek Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) was developed in collaboration
Addressing the Impact of Road-Stream Crossing Structures on the Movement of Aquatic Organisms
 Scott Jackson University of Massachusetts Amherst Addressing the Impact of Road-Stream Crossing Structures on the Movement of Aquatic Organisms Dams Sub-standard Culverts Excessive Velocities Inlet Drop
Scott Jackson University of Massachusetts Amherst Addressing the Impact of Road-Stream Crossing Structures on the Movement of Aquatic Organisms Dams Sub-standard Culverts Excessive Velocities Inlet Drop
1 INTRODUCTION AND MAJOR FINDINGS... 1
 Memorandum To: Lindsey Clark, Stillwater Valley Watershed Council Coordinator From: Chad Raisland, Pioneer Technical Services, Inc. and Karin Boyd, Applied Geomorphology, Inc. CC: Tanya Lester, Stillwater
Memorandum To: Lindsey Clark, Stillwater Valley Watershed Council Coordinator From: Chad Raisland, Pioneer Technical Services, Inc. and Karin Boyd, Applied Geomorphology, Inc. CC: Tanya Lester, Stillwater
Erosion Surface Water. moving, transporting, and depositing sediment.
 + Erosion Surface Water moving, transporting, and depositing sediment. + Surface Water 2 Water from rainfall can hit Earth s surface and do a number of things: Slowly soak into the ground: Infiltration
+ Erosion Surface Water moving, transporting, and depositing sediment. + Surface Water 2 Water from rainfall can hit Earth s surface and do a number of things: Slowly soak into the ground: Infiltration
APPENDIX B Hydraulic Considerations for Pipeline Crossings of Stream Channels
 APPENDIX B Hydraulic Considerations for Pipeline Crossings of Stream Channels B-1 B-2 APPENDIX B HYDRAULIC CONSIDERATIONS FOR PIPELINE CROSSINGS OF STREAM CHANNELS Pipeline crossings of perennial, intermittent,
APPENDIX B Hydraulic Considerations for Pipeline Crossings of Stream Channels B-1 B-2 APPENDIX B HYDRAULIC CONSIDERATIONS FOR PIPELINE CROSSINGS OF STREAM CHANNELS Pipeline crossings of perennial, intermittent,
Hydrologic hazards can be considered in three categories; An indication of flooding potential for areas located
 4.0 General Hydrologic Design Critera 4.1 Hydrologic Hazards Hydrologic hazards can be considered in three categories; flooding, channel migration, and tributary stajility. An indication of flooding potential
4.0 General Hydrologic Design Critera 4.1 Hydrologic Hazards Hydrologic hazards can be considered in three categories; flooding, channel migration, and tributary stajility. An indication of flooding potential
December 11, 2006 File:
 December 11, 2006 File: 15-85-38 Alberta Infrastructure and Transportation Room 301, Provincial Building 9621-96 Avenue Peace River, Alberta T8S 1T4 Attention: Mr. Ed Szmata PEACE REGION (SWAN HILLS AREA)
December 11, 2006 File: 15-85-38 Alberta Infrastructure and Transportation Room 301, Provincial Building 9621-96 Avenue Peace River, Alberta T8S 1T4 Attention: Mr. Ed Szmata PEACE REGION (SWAN HILLS AREA)
Chapter 3 Erosion in the Las Vegas Wash
 Chapter 3 Erosion in the Las Vegas Wash Introduction As described in Chapter 1, the Las Vegas Wash (Wash) has experienced considerable change as a result of development of the Las Vegas Valley (Valley).
Chapter 3 Erosion in the Las Vegas Wash Introduction As described in Chapter 1, the Las Vegas Wash (Wash) has experienced considerable change as a result of development of the Las Vegas Valley (Valley).
7.3 Sediment Delivery Analysis
 7.3 Sediment Delivery Analysis In order to evaluate potential changes in sedimentation patterns that could occur due to impacts from the FCP and LPP alignments, sediment assessment models were constructed
7.3 Sediment Delivery Analysis In order to evaluate potential changes in sedimentation patterns that could occur due to impacts from the FCP and LPP alignments, sediment assessment models were constructed
Rock Sizing for Waterway & Gully Chutes
 Rock Sizing for Waterway & Gully Chutes WATERWAY MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Rock-lined waterway chute Photo 2 Rock-lined gully chute 1. Introduction A waterway chute is a stabilised section of channel
Rock Sizing for Waterway & Gully Chutes WATERWAY MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Rock-lined waterway chute Photo 2 Rock-lined gully chute 1. Introduction A waterway chute is a stabilised section of channel
LOCATIONS OF SELECTED MITIGATION SITES IN JAPAN
 LOCATIOS OF SELECTED MITIGATIO SITES I JAPA Hyogo prefecture near Kobe, Japan Hyogo province Gifu province Osaka Kobe Gifu prefecture near Takayama, Japan akao Kamikochi ational Park Mount Yake Tateyama
LOCATIOS OF SELECTED MITIGATIO SITES I JAPA Hyogo prefecture near Kobe, Japan Hyogo province Gifu province Osaka Kobe Gifu prefecture near Takayama, Japan akao Kamikochi ational Park Mount Yake Tateyama
Flood and Stream Restoration
 2 3 4 Pedestrian bridge under construction 3 CSPs perched on DS side Large area of sand deposition Bottom layer of gabions has been scoured out large bar of gabion stone Gabions slumping bank slope failure
2 3 4 Pedestrian bridge under construction 3 CSPs perched on DS side Large area of sand deposition Bottom layer of gabions has been scoured out large bar of gabion stone Gabions slumping bank slope failure
Aquifer an underground zone or layer of sand, gravel, or porous rock that is saturated with water.
 Aggradation raising of the streambed by deposition that occurs when the energy of the water flowing through a stream reach is insufficient to transport sediment conveyed from upstream. Alluvium a general
Aggradation raising of the streambed by deposition that occurs when the energy of the water flowing through a stream reach is insufficient to transport sediment conveyed from upstream. Alluvium a general
Vermont Stream Geomorphic Assessment. Appendix E. River Corridor Delineation Process. VT Agency of Natural Resources. April, E0 - April, 2004
 Vermont Stream Geomorphic Assessment Appendix E River Corridor Delineation Process Vermont Agency of Natural Resources - E0 - River Corridor Delineation Process Purpose A stream and river corridor delineation
Vermont Stream Geomorphic Assessment Appendix E River Corridor Delineation Process Vermont Agency of Natural Resources - E0 - River Corridor Delineation Process Purpose A stream and river corridor delineation
Dolores River Watershed Study
 CHAPTER 4: RIVER AND FLOODPLAIN ISSUES The Dolores River falls into a category of streams in Colorado that share some unique characteristics. Like some other mountain streams in the state, it has a steep
CHAPTER 4: RIVER AND FLOODPLAIN ISSUES The Dolores River falls into a category of streams in Colorado that share some unique characteristics. Like some other mountain streams in the state, it has a steep
HAW CREEK, PIKE COUNTY, MISSOURI-TRIB TO SALT RIVER ERODING STREAM THREATHENING COUNTY ROAD #107, FOURTEEN FT TALL ERODING BANK WITHIN 4 FT OF THE
 HAW CREEK, PIKE COUNTY, MISSOURI-TRIB TO SALT RIVER ERODING STREAM THREATHENING COUNTY ROAD #107, FOURTEEN FT TALL ERODING BANK WITHIN 4 FT OF THE ROAD, PROJECT CONSTRUCTED IN 1 DAY, MARCH 10, 2009 BY
HAW CREEK, PIKE COUNTY, MISSOURI-TRIB TO SALT RIVER ERODING STREAM THREATHENING COUNTY ROAD #107, FOURTEEN FT TALL ERODING BANK WITHIN 4 FT OF THE ROAD, PROJECT CONSTRUCTED IN 1 DAY, MARCH 10, 2009 BY
LEVEE DESIGN FOR FLOOD PROTECTION ON ALLUVIAL FANS
 LEVEE DESIGN FOR FLOOD PROTECTION ON ALLUVIAL FANS BRUCE M. PHILLIPS 1 ABSTRACT The dynamic nature of alluvial fans in arid environments offers numerous floodplain management challenges primarily due to
LEVEE DESIGN FOR FLOOD PROTECTION ON ALLUVIAL FANS BRUCE M. PHILLIPS 1 ABSTRACT The dynamic nature of alluvial fans in arid environments offers numerous floodplain management challenges primarily due to
Historical channel change on the Upper Gila River, Arizona and New Mexico in response to anthropogenic modifications and extreme floods
 Historical channel change on the Upper Gila River, Arizona and New Mexico in response to anthropogenic modifications and extreme floods www.archives.gov www.paztcn.wr.usgs.gov wrh.noaa.gov Upper Gila River
Historical channel change on the Upper Gila River, Arizona and New Mexico in response to anthropogenic modifications and extreme floods www.archives.gov www.paztcn.wr.usgs.gov wrh.noaa.gov Upper Gila River
CE415L Applied Fluid Mechanics Laboratory
 Applied Fluid Mechanics Laboratory Learning Objective Following completion of this experiment and the analysis of the data, you should be able to 1. generalize results of introducing changes to a natural
Applied Fluid Mechanics Laboratory Learning Objective Following completion of this experiment and the analysis of the data, you should be able to 1. generalize results of introducing changes to a natural
Instream Erosion Control General
 Instream Erosion Control General EROSION CONTROL TECHNIQUES Revegetation Temperate Climates Short-Term Non Vegetation Wet Tropics Long-Term Weed Control [1] Semi-Arid Zones Permanent [1] Weed control attributes
Instream Erosion Control General EROSION CONTROL TECHNIQUES Revegetation Temperate Climates Short-Term Non Vegetation Wet Tropics Long-Term Weed Control [1] Semi-Arid Zones Permanent [1] Weed control attributes
January 12, 2006 File:
 January 12, 2006 File: 15-85-13 Alberta Infrastructure and Transportation Room 301, Provincial Building 9621-96 Avenue Peace River, Alberta T8S 1T4 Attention: Mr. Ed Szmata PEACE REGION (PEACE HIGH LEVEL
January 12, 2006 File: 15-85-13 Alberta Infrastructure and Transportation Room 301, Provincial Building 9621-96 Avenue Peace River, Alberta T8S 1T4 Attention: Mr. Ed Szmata PEACE REGION (PEACE HIGH LEVEL
Final Exam. Running Water Erosion and Deposition. Willamette Discharge. Running Water
 Final Exam Running Water Erosion and Deposition Earth Science Chapter 5 Pages 120-135 Scheduled for 8 AM, March 21, 2006 Bring A scantron form A calculator Your 3 x 5 paper card of formulas Review questions
Final Exam Running Water Erosion and Deposition Earth Science Chapter 5 Pages 120-135 Scheduled for 8 AM, March 21, 2006 Bring A scantron form A calculator Your 3 x 5 paper card of formulas Review questions
Subcommittee on Sedimentation Draft Sediment Analysis Guidelines for Dam Removal
 Subcommittee on Sedimentation Draft Sediment Analysis Guidelines for Dam Removal August 4, 2011 Jennifer Bountry, M.S., P.E. Tim Randle, M.S., P.E., D.WRE. Blair Greimann, Ph.D., P.E. Sedimentation and
Subcommittee on Sedimentation Draft Sediment Analysis Guidelines for Dam Removal August 4, 2011 Jennifer Bountry, M.S., P.E. Tim Randle, M.S., P.E., D.WRE. Blair Greimann, Ph.D., P.E. Sedimentation and
The last three sections of the main body of this report consist of:
 Threatened and Endangered Species Geological Hazards Floodplains Cultural Resources Hazardous Materials A Cost Analysis section that provides comparative conceptual-level costs follows the Environmental
Threatened and Endangered Species Geological Hazards Floodplains Cultural Resources Hazardous Materials A Cost Analysis section that provides comparative conceptual-level costs follows the Environmental
Technical Memorandum. To: From: Copies: Date: 10/19/2017. Subject: Project No.: Greg Laird, Courtney Moore. Kevin Pilgrim and Travis Stroth
 Technical Memorandum To: From: Greg Laird, Courtney Moore Kevin Pilgrim and Travis Stroth 5777 Central Avenue Suite 228 Boulder, CO 80301 www.otak.com Copies: [Electronic submittal] Date: 10/19/2017 Subject:
Technical Memorandum To: From: Greg Laird, Courtney Moore Kevin Pilgrim and Travis Stroth 5777 Central Avenue Suite 228 Boulder, CO 80301 www.otak.com Copies: [Electronic submittal] Date: 10/19/2017 Subject:
R.M.HARW & ASSOCIATES LTD. GEOTECHNICAL INVESTIGATION PROPOSED BRIDGE SITE. HELAVA CREEKl MILE MACKENZIE HIGHWAY E-2510 OCTOBER 16, 1973
 El R.M.HARW & ASSOCIATES LTD. GEOTECHNICAL INVESTIGATION PROPOSED BRIDGE SITE HELAVA CREEKl MILE 616.4 MACKENZIE HIGHWAY E-2510 OCTOBER 16, 1973 R,M,HARDV & ASSOCIATES LTD. CONSULTING ENGINEERING & TESTING
El R.M.HARW & ASSOCIATES LTD. GEOTECHNICAL INVESTIGATION PROPOSED BRIDGE SITE HELAVA CREEKl MILE 616.4 MACKENZIE HIGHWAY E-2510 OCTOBER 16, 1973 R,M,HARDV & ASSOCIATES LTD. CONSULTING ENGINEERING & TESTING
SELBY CREEK STREAM HABITAT RESTORATION AND RIPARIAN REVEGETATION PROJECT: GEOMORPHIC ANALYSIS AND REVIEW
 SELBY CREEK STREAM HABITAT RESTORATION AND RIPARIAN REVEGETATION PROJECT: GEOMORPHIC ANALYSIS AND REVIEW Submitted to Bioengineering Institute P.O. Box 1554 Laytonville, CA 95454 By Matthew O Connor, PhD,
SELBY CREEK STREAM HABITAT RESTORATION AND RIPARIAN REVEGETATION PROJECT: GEOMORPHIC ANALYSIS AND REVIEW Submitted to Bioengineering Institute P.O. Box 1554 Laytonville, CA 95454 By Matthew O Connor, PhD,
Environmental Geology Chapter 9 Rivers and Flooding
 Environmental Geology Chapter 9 Rivers and Flooding Flooding in Pakistan 2010-1600 killed/20000 affected The hydrologic cycle is powered by the Sun The cycle includes evaporation, precipitation, infiltration,
Environmental Geology Chapter 9 Rivers and Flooding Flooding in Pakistan 2010-1600 killed/20000 affected The hydrologic cycle is powered by the Sun The cycle includes evaporation, precipitation, infiltration,
Stone Outlet Sediment Trap
 3.12 Sediment Control Description: A stone outlet sediment trap is a small detention area formed by placing a stone embankment with an integral stone filter outlet across a drainage swale for the purpose
3.12 Sediment Control Description: A stone outlet sediment trap is a small detention area formed by placing a stone embankment with an integral stone filter outlet across a drainage swale for the purpose
Technical Memorandum No Sediment Model
 Pajaro River Watershed Study in association with Technical Memorandum No. 1.2.9 Sediment Model Task: Development of Sediment Model To: PRWFPA Staff Working Group Prepared by: Gregory Morris and Elsie Parrilla
Pajaro River Watershed Study in association with Technical Memorandum No. 1.2.9 Sediment Model Task: Development of Sediment Model To: PRWFPA Staff Working Group Prepared by: Gregory Morris and Elsie Parrilla
PEACE REGION GRANDE PRAIRIE GEOHAZARD RISK ASSESSMENT SITE INSPECTION FORM NAD 83 COORDINATES N 6,178,811 E 403,309
 PEACE REGION GRANDE PRAIRIE GEOHAZARD RISK ASSESSMENT SITE INSPECTION FORM SITE NUMBER GP-4a LEGAL DESCRIPTION LSD 12-10-78-4-W6M SITE NAME Burnt River Bridge - West Approach Slide HIGHWAY & KM Hwy 49:06
PEACE REGION GRANDE PRAIRIE GEOHAZARD RISK ASSESSMENT SITE INSPECTION FORM SITE NUMBER GP-4a LEGAL DESCRIPTION LSD 12-10-78-4-W6M SITE NAME Burnt River Bridge - West Approach Slide HIGHWAY & KM Hwy 49:06
PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING DISTRICT 3-0
 PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING DISTRICT 3-0 LYCOMING COUNTY S.R.15, SECTION C41 FINAL HYDROLOGIC AND HYDRAULIC REPORT STEAM VALLEY RUN STREAM RELOCATION DATE: June, 2006 REVISED:
PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING DISTRICT 3-0 LYCOMING COUNTY S.R.15, SECTION C41 FINAL HYDROLOGIC AND HYDRAULIC REPORT STEAM VALLEY RUN STREAM RELOCATION DATE: June, 2006 REVISED:
MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF FLUVIAL SEDIMENT DELIVERY, NEKA RIVER, IRAN. S.E. Kermani H. Golmaee M.Z. Ahmadi
 JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL HYDROLOGY The Electronic Journal of the International Association for Environmental Hydrology On the World Wide Web at http://www.hydroweb.com VOLUME 16 2008 MATHEMATICAL MODELING
JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL HYDROLOGY The Electronic Journal of the International Association for Environmental Hydrology On the World Wide Web at http://www.hydroweb.com VOLUME 16 2008 MATHEMATICAL MODELING
SCOPE OF PRESENTATION STREAM DYNAMICS, CHANNEL RESTORATION PLANS, & SEDIMENT TRANSPORT ANALYSES IN RELATION TO RESTORATION PLANS
 DESIGN METHODS B: SEDIMENT TRANSPORT PROCESSES FOR STREAM RESTORATION DESIGN PETER KLINGEMAN OREGON STATE UNIVERSITY CIVIL ENGINEERING DEPT., CORVALLIS 2 ND ANNUAL NORTHWEST STREAM RESTORATION DESIGN SYMPOSIUM
DESIGN METHODS B: SEDIMENT TRANSPORT PROCESSES FOR STREAM RESTORATION DESIGN PETER KLINGEMAN OREGON STATE UNIVERSITY CIVIL ENGINEERING DEPT., CORVALLIS 2 ND ANNUAL NORTHWEST STREAM RESTORATION DESIGN SYMPOSIUM
Important Copyright Information
 Important Copyright Information The following content is provided for educational purposes by the workshop presenter. This content may or may not have been peer reviewed. Information, opinions and recommendations
Important Copyright Information The following content is provided for educational purposes by the workshop presenter. This content may or may not have been peer reviewed. Information, opinions and recommendations
Rock Sizing for Batter Chutes
 Rock Sizing for Batter Chutes STORMWATER MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Rock-lined batter chute Photo 2 Rock-lined batter chute 1. Introduction In the stormwater industry a chute is a steep drainage channel,
Rock Sizing for Batter Chutes STORMWATER MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Rock-lined batter chute Photo 2 Rock-lined batter chute 1. Introduction In the stormwater industry a chute is a steep drainage channel,
The Effects of Flooding on Structures. Or What to Expect when the Drought Ends Violently
 The Effects of Flooding on Structures Or What to Expect when the Drought Ends Violently Let s Define Flood Increase in discharge compared to normal level Direct runoff of rainfall (we re talking about
The Effects of Flooding on Structures Or What to Expect when the Drought Ends Violently Let s Define Flood Increase in discharge compared to normal level Direct runoff of rainfall (we re talking about
!"#$%&&'()*+#$%(,-./0*)%(!
 8:30 Sign in Hoosic River Revival Coalition!"#$%&&'()*+#$%(,-./0*)%(! 12-#30+4/#"5-(60 9:00 Welcome and Introductions 9:15 Goals for Today s Program: A Description of the Planning Process 9:30 First Session:
8:30 Sign in Hoosic River Revival Coalition!"#$%&&'()*+#$%(,-./0*)%(! 12-#30+4/#"5-(60 9:00 Welcome and Introductions 9:15 Goals for Today s Program: A Description of the Planning Process 9:30 First Session:
Rock Sizing for Multi-Pipe & Culvert Outlets
 Rock Sizing for Multi-Pipe & Culvert Outlets STORMWATER AND WATERWAY MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Rock pad outlet structure at end of a duel stormwater pipe outlet Photo 2 Rock pad outlet structure at
Rock Sizing for Multi-Pipe & Culvert Outlets STORMWATER AND WATERWAY MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Rock pad outlet structure at end of a duel stormwater pipe outlet Photo 2 Rock pad outlet structure at
Assessment. Assessment
 2001 SPRINGBROOK CREEK RESTORATION - THREE YEAR POST-CONSTRUCTION REVIEW - Presented by Bruce Henderson and Andy Harris 2005 River Restoration Northwest Symposium Skamania Lodge, Washington www.hendersonlandservices.com
2001 SPRINGBROOK CREEK RESTORATION - THREE YEAR POST-CONSTRUCTION REVIEW - Presented by Bruce Henderson and Andy Harris 2005 River Restoration Northwest Symposium Skamania Lodge, Washington www.hendersonlandservices.com
1 PROJECT BACKGROUND. August 14, Alberta Transportation Central Region #401, Street Red Deer, Alberta T4N 6K8
 August 14, 2013 Alberta Transportation Central Region #401, 4902 51 Street Red Deer, Alberta T4N 6K8 Mr. Dennis Grace, P.Eng. Construction Engineer Dear Mr. Grace: Central Region Geohazard Assessment 2013
August 14, 2013 Alberta Transportation Central Region #401, 4902 51 Street Red Deer, Alberta T4N 6K8 Mr. Dennis Grace, P.Eng. Construction Engineer Dear Mr. Grace: Central Region Geohazard Assessment 2013
EAST PLUM CREEK WATERSHED MASTER PLAN PRELIMINARY DESIGN REPORT. Section IV Stream Stability Assessment
 Section IV Stream Stability Assessment 19 IV. Stream Stability Assessment Stream Stability Methodology General Concepts Natural channels, such as East Plum Creek, consist of a natural movable channel
Section IV Stream Stability Assessment 19 IV. Stream Stability Assessment Stream Stability Methodology General Concepts Natural channels, such as East Plum Creek, consist of a natural movable channel
January 17, 2008 File:
 January 17, 2008 File: 15-85-73 Alberta Infrastructure and Transportation Room 301, Provincial Building 9621-96 Avenue Peace River, Alberta T8S 1T4 Attention: Mr. Ed Szmata PEACE REGION (SWAN HILLS AREA)
January 17, 2008 File: 15-85-73 Alberta Infrastructure and Transportation Room 301, Provincial Building 9621-96 Avenue Peace River, Alberta T8S 1T4 Attention: Mr. Ed Szmata PEACE REGION (SWAN HILLS AREA)
Technical note about the monitoring of hydromorphological restoration/management of the Drava River in Slovenia
 Technical note about the monitoring of hydromorphological restoration/management of the Drava River in Slovenia 1 Project: HyMoCARES Work package: WPC. Communication Activity: Web Site Deliverable: Case
Technical note about the monitoring of hydromorphological restoration/management of the Drava River in Slovenia 1 Project: HyMoCARES Work package: WPC. Communication Activity: Web Site Deliverable: Case
[1] Performance of the sediment trap depends on the type of outlet structure and the settling pond surface area.
![[1] Performance of the sediment trap depends on the type of outlet structure and the settling pond surface area. [1] Performance of the sediment trap depends on the type of outlet structure and the settling pond surface area.](/thumbs/76/74245181.jpg) Sediment Trench SEDIMENT CONTROL TECHNIQUE Type 1 System Sheet Flow Sandy Soils Type 2 System [1] Concentrated Flow Clayey Soils Type 3 System [1] Supplementary Trap Dispersive Soils [1] Performance of
Sediment Trench SEDIMENT CONTROL TECHNIQUE Type 1 System Sheet Flow Sandy Soils Type 2 System [1] Concentrated Flow Clayey Soils Type 3 System [1] Supplementary Trap Dispersive Soils [1] Performance of
Fish Passage and Abundance around Grade Control Structures on Incised Streams in Western Iowa
 Fish Passage and Abundance around Grade Control Structures on Incised Streams in Western Iowa John Thomas Hungry Canyons Alliance Mary Culler Iowa State University / Missouri DNR Dimitri Dermisis IIHR
Fish Passage and Abundance around Grade Control Structures on Incised Streams in Western Iowa John Thomas Hungry Canyons Alliance Mary Culler Iowa State University / Missouri DNR Dimitri Dermisis IIHR
Rivers T. Perron
 1 Rivers T. Perron 12.001 After our discussions of large-scale topography, how we represent topography in maps, and how topography interacts with geologic structures, you should be frothing at the mouth
1 Rivers T. Perron 12.001 After our discussions of large-scale topography, how we represent topography in maps, and how topography interacts with geologic structures, you should be frothing at the mouth
Field Observations and One-Dimensional Flow Modeling of Summit Creek in Mack Park, Smithfield, Utah
 Intermountain Center for River Rehabilitation and Restoration, Utah State University 31 July 2018 Field Observations and One-Dimensional Flow Modeling of Summit Creek in Mack Park, Smithfield, Utah I.
Intermountain Center for River Rehabilitation and Restoration, Utah State University 31 July 2018 Field Observations and One-Dimensional Flow Modeling of Summit Creek in Mack Park, Smithfield, Utah I.
Working with Natural Stream Systems
 Working with Natural Stream Systems Graydon Dutcher Delaware County Soil & Water Conservation District Stream Corridor Management Program Tropical Storm Sandy October 29,2012 What is a Watershed?
Working with Natural Stream Systems Graydon Dutcher Delaware County Soil & Water Conservation District Stream Corridor Management Program Tropical Storm Sandy October 29,2012 What is a Watershed?
Surface Water and Stream Development
 Surface Water and Stream Development Surface Water The moment a raindrop falls to earth it begins its return to the sea. Once water reaches Earth s surface it may evaporate back into the atmosphere, soak
Surface Water and Stream Development Surface Water The moment a raindrop falls to earth it begins its return to the sea. Once water reaches Earth s surface it may evaporate back into the atmosphere, soak
SECTION G SEDIMENT BUDGET
 SECTION G SEDIMENT BUDGET INTRODUCTION A sediment budget has been constructed for the for the time period 1952-2000. The purpose of the sediment budget is to determine the relative importance of different
SECTION G SEDIMENT BUDGET INTRODUCTION A sediment budget has been constructed for the for the time period 1952-2000. The purpose of the sediment budget is to determine the relative importance of different
Matsqui Bend Erosion
 Matsqui Bend Erosion prepared for Ministry of Environment, Lands and Parks 10334 152A Street Surrey, British Columbia, V3R 7P8 by Hamish Weatherly, Michael Church, and Darren Ham Department of Geography
Matsqui Bend Erosion prepared for Ministry of Environment, Lands and Parks 10334 152A Street Surrey, British Columbia, V3R 7P8 by Hamish Weatherly, Michael Church, and Darren Ham Department of Geography
Griswold Creek August 22, 2013
 Creek August 22, 2013 1 Lake Erie Protection Fund Creek Study ver Evaluate the overall condition of Creek Determine stable channel dimensions & appropriate restoration techniques Starting Stat gpoint for
Creek August 22, 2013 1 Lake Erie Protection Fund Creek Study ver Evaluate the overall condition of Creek Determine stable channel dimensions & appropriate restoration techniques Starting Stat gpoint for
Rock & Aggregate Drop Inlet Protection
 Rock & Aggregate Drop Inlet Protection SEDIMENT CONTROL TECHNIQUE Type 1 System Sheet Flow Sandy Soils Type 2 System [1] Concentrated Flow Clayey Soils Type 3 System Supplementary Trap Dispersive Soils
Rock & Aggregate Drop Inlet Protection SEDIMENT CONTROL TECHNIQUE Type 1 System Sheet Flow Sandy Soils Type 2 System [1] Concentrated Flow Clayey Soils Type 3 System Supplementary Trap Dispersive Soils
Project Proposal. Lyme Brook. Newcastle-under-Lyme. 3 rd July 2015
 Project Proposal Lyme Brook Newcastle-under-Lyme 3 rd July 2015 Contents Page 1.0 Introduction... 1.0 2.0 Background and rationale... 2.0 3.0 Proposed measures... 5 4.0 Summary of Recommendations... 10
Project Proposal Lyme Brook Newcastle-under-Lyme 3 rd July 2015 Contents Page 1.0 Introduction... 1.0 2.0 Background and rationale... 2.0 3.0 Proposed measures... 5 4.0 Summary of Recommendations... 10
Appendix K.2: Sediment Management Excerpt from South Orange County Hydromodification Management Plan
 Appendix K.2: Sediment Management Excerpt from South Orange County Hydromodification Management Plan 4 Sediment Supply Management Requirements Permit Order R9-2013-0001 as amended by Order No. R9-2015-0001Section
Appendix K.2: Sediment Management Excerpt from South Orange County Hydromodification Management Plan 4 Sediment Supply Management Requirements Permit Order R9-2013-0001 as amended by Order No. R9-2015-0001Section
Fresh Water: Streams, Lakes Groundwater & Wetlands
 Fresh Water:, Lakes Groundwater & Wetlands Oct 27 Glaciers and Ice Ages Chp 13 Nov 3 Deserts and Wind and EXAM #3 Slope hydrologic cycle P = precip I = precip intercepted by veg ET = evapotranspiration
Fresh Water:, Lakes Groundwater & Wetlands Oct 27 Glaciers and Ice Ages Chp 13 Nov 3 Deserts and Wind and EXAM #3 Slope hydrologic cycle P = precip I = precip intercepted by veg ET = evapotranspiration
ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 100. Figure 7-3 Maximum velocity magnitudes for existing conditions for 100-year flood event
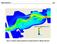 ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 100 Figure 7-3 Maximum velocity magnitudes for existing conditions for 100-year flood event ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 101 Figure 7-4 Model schematization of Option 1 Figure 7-5 Bed displacement
ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 100 Figure 7-3 Maximum velocity magnitudes for existing conditions for 100-year flood event ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 101 Figure 7-4 Model schematization of Option 1 Figure 7-5 Bed displacement
Evaluation of Scour Depth around Bridge Piers with Various Geometrical Shapes
 Evaluation of Scour Depth around Bridge Piers with Various Geometrical Shapes Dr. P. D. Dahe * Department of Civil Engineering, SGGSIE&T, Vishnupuri, Nanded (Maharashtra) S. B. Kharode Department of Civil
Evaluation of Scour Depth around Bridge Piers with Various Geometrical Shapes Dr. P. D. Dahe * Department of Civil Engineering, SGGSIE&T, Vishnupuri, Nanded (Maharashtra) S. B. Kharode Department of Civil
ADDRESSING GEOMORPHIC AND HYDRAULIC CONTROLS IN OFF-CHANNEL HABITAT DESIGN
 ADDRESSING GEOMORPHIC AND HYDRAULIC CONTROLS IN OFF-CHANNEL HABITAT DESIGN Conor Shea - Hydrologist U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Conservation Partnerships Program Arcata, CA Learning Objectives Examine
ADDRESSING GEOMORPHIC AND HYDRAULIC CONTROLS IN OFF-CHANNEL HABITAT DESIGN Conor Shea - Hydrologist U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Conservation Partnerships Program Arcata, CA Learning Objectives Examine
Rock Sizing for Small Dam Spillways
 Rock Sizing for Small Dam Spillways STORMWATER MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Rock-lined spillway on a construction site sediment basin Photo 2 Rock-lined spillway on a small farm dam 1. Introduction A chute
Rock Sizing for Small Dam Spillways STORMWATER MANAGEMENT PRACTICES Photo 1 Rock-lined spillway on a construction site sediment basin Photo 2 Rock-lined spillway on a small farm dam 1. Introduction A chute
PolyMet NorthMet Project
 RS 26 Draft-01 December 8, 2005 RS26 Partridge River Level 1 Rosgen Geomorphic Survey Rosgen Classification Partridge River from Headwaters to Colby Lake Prepared for PolyMet NorthMet Project December
RS 26 Draft-01 December 8, 2005 RS26 Partridge River Level 1 Rosgen Geomorphic Survey Rosgen Classification Partridge River from Headwaters to Colby Lake Prepared for PolyMet NorthMet Project December
Sixteen Mile Creek Tributaries Meander Belt Width Assessment November 2009
 SIXTEEN MILE CREEK TRIBUTARIES THE CATHOLIC CEMETERIES OF THE DIOCESE OF HAMILTON -MEANDER BELT WIDTH ASSESSMENT - Report to: Attention: From: Director of Cemeteries Catholic Cemeteries of the Diocese
SIXTEEN MILE CREEK TRIBUTARIES THE CATHOLIC CEMETERIES OF THE DIOCESE OF HAMILTON -MEANDER BELT WIDTH ASSESSMENT - Report to: Attention: From: Director of Cemeteries Catholic Cemeteries of the Diocese
ES 105 Surface Processes I. Hydrologic cycle A. Distribution % in oceans 2. >3% surface water a. +99% surface water in glaciers b.
 ES 105 Surface Processes I. Hydrologic cycle A. Distribution 1. +97% in oceans 2. >3% surface water a. +99% surface water in glaciers b. >1/3% liquid, fresh water in streams and lakes~1/10,000 of water
ES 105 Surface Processes I. Hydrologic cycle A. Distribution 1. +97% in oceans 2. >3% surface water a. +99% surface water in glaciers b. >1/3% liquid, fresh water in streams and lakes~1/10,000 of water
Development and application of demonstration MIKE 21C morphological model for a bend in Mekong River
 Development and application of demonstration MIKE 21C morphological model for a bend in Mekong River September 2015 0 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Data collection... 3 2.1 Additional data...
Development and application of demonstration MIKE 21C morphological model for a bend in Mekong River September 2015 0 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Data collection... 3 2.1 Additional data...
3/3/2013. The hydro cycle water returns from the sea. All "toilet to tap." Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e
 Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Running Water: summary in haiku form Edward A. Keller Chapter 9 Rivers and Flooding Lecture Presentation prepared by X. Mara Chen, Salisbury University The hydro
Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Running Water: summary in haiku form Edward A. Keller Chapter 9 Rivers and Flooding Lecture Presentation prepared by X. Mara Chen, Salisbury University The hydro
Chapter 11. Rivers: Shaping our landscape
 Chapter 11 Rivers: Shaping our landscape Learning outcomes In this presentation you will learn: Common terms associated with rivers About the three stages of a river About the processes of river erosion
Chapter 11 Rivers: Shaping our landscape Learning outcomes In this presentation you will learn: Common terms associated with rivers About the three stages of a river About the processes of river erosion
24.0 Mineral Extraction
 Chapter 24 - Mineral Extraction 24.0 Mineral Extraction 24.1 Introduction Apart from gravel, sand, rock, limestone and salt extraction in relatively small quantities mineral extraction is not a strong
Chapter 24 - Mineral Extraction 24.0 Mineral Extraction 24.1 Introduction Apart from gravel, sand, rock, limestone and salt extraction in relatively small quantities mineral extraction is not a strong
DRAFT Design Hydraulic Study. Bridge 04C-0055, Mattole Road Bridge over Mattole River at Honeydew. Humboldt County. Prepared for:
 DRAFT Design Hydraulic Study Bridge 04C-0055, Mattole Road Bridge over Mattole River at Honeydew Humboldt County Prepared for: Morrison Structures Incorporated 1890 Park Marina Drive, Suite 104 Redding,
DRAFT Design Hydraulic Study Bridge 04C-0055, Mattole Road Bridge over Mattole River at Honeydew Humboldt County Prepared for: Morrison Structures Incorporated 1890 Park Marina Drive, Suite 104 Redding,
6.11 Naas River Management Unit
 6.11 Naas River Management Unit 6.11.1 Site 41 Issue: Bed and bank erosion Location: E 0685848 N 6058358 Waterway: Naas River Management Unit: Naas River Facing downstream from Bobeyan Rd bridge Facing
6.11 Naas River Management Unit 6.11.1 Site 41 Issue: Bed and bank erosion Location: E 0685848 N 6058358 Waterway: Naas River Management Unit: Naas River Facing downstream from Bobeyan Rd bridge Facing
Landscape Development
 Landscape Development Slopes Dominate Natural Landscapes Created by the interplay of tectonic and igneous activity and gradation Deformation and uplift Volcanic activity Agents of gradation Mass wasting
Landscape Development Slopes Dominate Natural Landscapes Created by the interplay of tectonic and igneous activity and gradation Deformation and uplift Volcanic activity Agents of gradation Mass wasting
APPENDIX E. GEOMORPHOLOGICAL MONTORING REPORT Prepared by Steve Vrooman, Keystone Restoration Ecology September 2013
 APPENDIX E GEOMORPHOLOGICAL MONTORING REPORT Prepared by Steve Vrooman, Keystone Restoration Ecology September 2 Introduction Keystone Restoration Ecology (KRE) conducted geomorphological monitoring in
APPENDIX E GEOMORPHOLOGICAL MONTORING REPORT Prepared by Steve Vrooman, Keystone Restoration Ecology September 2 Introduction Keystone Restoration Ecology (KRE) conducted geomorphological monitoring in
STREAM SYSTEMS and FLOODS
 STREAM SYSTEMS and FLOODS The Hydrologic Cycle Precipitation Evaporation Infiltration Runoff Transpiration Earth s Water and the Hydrologic Cycle The Hydrologic Cycle The Hydrologic Cycle Oceans not filling
STREAM SYSTEMS and FLOODS The Hydrologic Cycle Precipitation Evaporation Infiltration Runoff Transpiration Earth s Water and the Hydrologic Cycle The Hydrologic Cycle The Hydrologic Cycle Oceans not filling
Precipitation Evaporation Infiltration Earth s Water and the Hydrologic Cycle. Runoff Transpiration
 STREAM SYSTEMS and FLOODS The Hydrologic Cycle Precipitation Evaporation Infiltration Earth s Water and the Hydrologic Cycle Runoff Transpiration The Hydrologic Cycle The Hydrologic Cycle Oceans not filling
STREAM SYSTEMS and FLOODS The Hydrologic Cycle Precipitation Evaporation Infiltration Earth s Water and the Hydrologic Cycle Runoff Transpiration The Hydrologic Cycle The Hydrologic Cycle Oceans not filling
