Tidal River Management (TRM) for Selected Coastal Area of Bangladesh to Mitigate Drainage Congestion
|
|
|
- Adrian Reed
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
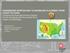
1 Tidal River Management (TRM) for Selected Coastal Area of Bangladesh to Mitigate Drainage Congestion Shampa, Md. Ibne Mayaz Pramanik Abstract The drainage congestion and sedimentation has been major issues over the years in Kobadak river basin, Bangladesh. Kobadak River has been experiencing huge siltation over a long reach that reduces the drainage capacity of river and causing prolonged drainage congestion. It affects every sphere of life including cultivable lands, employments, culture fish production, grazing land, bio-diversity and live-stocks. Human interventions such as construction of polders, bridges and encroachment into the river for cultivation deteriorated the condition of Kobadak River. The decrease of flushing flow from upstream and substantial reduction of tidal flooding area along the river by constructing polders caused s evere siltation over a long stretch of the river. Sedimentation mainly occurs during dry season since tidal flow is restricted over the flood plain by constructing polders and there is no fresh water flow into Kobadak River from the Ganges River to flush the sediment during low tide. This study focuses on prevailing problems and solutions of long standing drainage congestion by applying TRM in Kobadak River basin area under Satkhira district in Jalalpur beel area. In this study to solve the drainage congestion problem for a long period of time by TRM process two options are suggested eac h with two different scenarios. Each option is assessed with cross dam without cross dam scenarios using MIKE-11 hydrodynamic modeling system. Index Terms Beel, Drainage congestion, Kobadak river, MIKE-11, Sedimentation, Tidal basin, TRM. 1 INTRODUCTION Bangladesh is the biggest delta of the world formed by sediments carried by Ganges, Brahmaputra and Meghna river system. The rivers of southwestern region in Bangladesh are characterized by active deposition of sediment causing significant reduction in their drainage capacity [1]. Besides, construction of coastal polders that de-linked the flood plains from the rivers, and diminished upstream flow during the dry season deteriorated the sedimentation problem in the region[2]. Consequently, the area has been experiencing severe drainage congestion and water logging since the early eighties. The sedimentation effect of similar river and flood plain interventions were described by Sarker (2004)[3]. To solve these long standing problems, the Khulna-Jessore drainage rehabilitation project known as KJDRP was implemented during [4]. Later on, a popular concept based on generations of indigenous water management practices, formally known as a Tidal River Management (TRM), was adopted. TRM would allow natural movement of sediment-borne tidal water into a beel which is called tidal basin and allow deposition of sediment in the beel. During low tide the outgoing water would erode the river bed and increase the drainage capacity. After implementation of the project the prevailing drainage congestion was partially solved and agricultural, social and economic benefits were achieved[5]. Sediment management is the most challenging yet important aspect of TRM in the study area [6]. People allow their land to be used for tidal basin operation without any compensation, hoping that the land will rise after three or four years. However, monitoring results and community consultation reveal that almost in all cases sedimentation inside the tidal basin does not occur as expected. This result in people s a functional sediment management plan would be very helpful for successful TRM practice in future [7]. 1.1 Objectives Understand the drainage congestion problem in the coastal areas of Khulna region. Review of different approaches undertaken to mitigate the drainage congestion in that coastal region. Assess Tidal River Management (TRM) approach for alleviation of drainage congestion in selected area. 1.2 STUDY AREA Geographic Location The study area is located in the southwest region of Bangladesh within the Khulna division, Bangladesh and falls under the administrative jurisdiction of Tala upazila in Satkhira district. The study area lies in between 22044`40.3``N 23010`27.1``North Latitude and 88013`36.44``N 89050`00.00`` East Longitude (WGS 84). A location map for study area is shown in Figure 1 Shampa, currently working as professional at Centre for Environmental and Geographic Services, Bangladesh shampa_buet_05@yahoo.com or shampa@cegis.bd.com Md. Ibne Mayaz Pramanik, Bangladesh mayazpolok@yahoo.com Figure 1: Base map of the study area 1
2 1.2.4 Physical Setting The Kobadak River is situated in the southwest region of Bangladesh. The Kobadak River flows through Jessore, Satkhira and Khulna districts. Total length of the Kobadak River is 240 km (upper & lower) from Taherpur and Niamotkati. Due to the siltation of Kobadak River at Katakhali major flow of the river flows to Sibsa River through the Haria River and Minhaj-nadi. The study area is the basin area of Kobadak River under Jessore, Satkhira and Khulna districts. The study area covers mainly Chaugacha, Jhikargacha, Manirampur and Keshobpur of Jessore district and Koloroa, Tala, Asasuni and Syamnagar of Satkhira district including Paikgacha and Koira of Khulna district, which is shown in Figure 1. Total catchment area of Kobadak River is 1,02,000 ha (upper & lower Kobadak).The study area covers the upper part of Kobadak river from Taherpur to Katakhali which is about 75,000 ha. Figure 2: Beels in the Kobadak river basin area 2 TIDAL BASINS AND BEELS 2.1 Tidal Basins and Beels and Concepts of TRM A beel is a natural depression. Bangladesh being a deltaic country, land in the plains has been formed by sediments carried down by Ganges, Brahmaputra and Meghna river systems. Depressions are formed by numerous causes like subsidence of top soil caused by creation of a vacuum below by decomposition of organic substances mixed with silt, subsidence by tectonic movement, or degradable floods deposit sediment close to the river bank. But the land between two rivers remains low lying. Such a low lying land is also known as a beel. A tidal basin is a depressed low lying or beel adjacent to the sediment-laden tidal rivers. In the southwestern part of Bangladesh there are several tidal basins which are very useful for sediment management of sediment laden tidal rivers. Figure 2 shows the beels in Kobadak river basin. The concept of sediment management in tidal basin originated in the 1880s to serve both as visual centerpiece and as means for flushing the Washington channel, a harbor separated from the Potmic River by fill lands where East Potomic Park is situated[ 8]. Tidal basin of Potomac River. Shown in figure ORIGIN OF RIVER SEDIMENT IN THE SOUTHWESTERN AREA OF BANGLADESH Sedimentation in the tidal rivers of the southwestern area of Bangladesh is the main reason of the problem of water logging. These troublesome sediments have blocked the rivers and caused upstream drainage congestion and flooding. In most catchments where excessive sedimentation is taking place in the downstream river system, the origin of the problem is in the upstream catchment where land use changes have taken place in relatively steeply sloping areas. However, this is clearly not the case in the Satkhira area where upstream areas are very flat and excessive erosion is not occurring on these mainly agricultural upstream lands. It is clear from casual observation of the rivers in the study area during the dry season, when upstream flows are non-existent; the sediments are transported into these rivers by tidal flows. This movement of sediment is also confirmed by the field measurements of sediments concentrations and tidal flows by SWMC (June 1996 and October 1996) and other measurement programs. In the Satkhira area, the sediment derived from the downstream tidal rivers by natural erosion processes and transported upstream by tidal movements seems to be the most plausible explanation of their origin [6]. 2.3 Adverse Impacts of Coastal Polders In the early 1980s polders became a bane rather than a boon for the people, as rivers failed to maintain their natural courses. Tides deposited silt on the riverbeds rather than the floodplains for more than two decades halting the natural flow of the rivers. The consequent dearth of land formation left floodplains inside the polders lower than riverbanks outsides the polders. Rainwater, therefore, could not drain from the area s leading to chronic water logging. Adding to the tragedy, by construction of Farakka Barrage on the Ganges river and unilateral diversion of its water from 1975 started deteriorating the balanced (fresh water-tidal flow) ecosystem of the river region [7]. This was further aggravated by construction of reservoirs on the upper catchment of all trans-boundary rivers of the southwestern region. During the dry period of the year (January to April), the area receives almost no unplanned fresh water flow. Under the changed hydrological situation, many tidal channels outside the polders started experiencing abnormal sedimentation blocking the drainage paths of the polders. Prolonged water logging inside the polders were so severe in some cases the people of the area had the only option of migration. Bangladesh Water Development Board (BWDB) was fully aware and concerned about the drainage congestion of the polders of the Southwestern region. But the spatial extent of the problem and prevailing hydro-geomorphological conditions of the area are so complex that a holistic and well planned approach was needed. BWDB conducted six studies by engaging international and local consultants between 1986 to1998. Besides this planning exercise, BWDB dredged some badly silted up channels for immediate relief of the drainage congestion problems. From 1996 to 1998, about million cubic meters were reexcavated (manual and mechanical) to keep the main river system active. Dredging and re-excavation was done several times but it faced siltation every time. Figure 4 shows the Kobadak river with polders. Figure 3:Tidal basin of Potomac River 2
3 River Cross Sectional Area(A) - m 2 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC & TECHNOLOGY RESEARCH VOLUME 1, ISSUE 5, JUNE 2012 ISSN A B Figure 4: (A).Kobadak River with 2010 Landsat Image (B) Kobadak river with coastal polders 2.4 THEORETICAL BASIS OF TIDAL BASIN SEDIMENTATION A number of scientists opine that there is a relationship between the general dimension of the entrance to tidal estuary or tidal river in a sandy coast and the tidal prism. But it appears that there was no previous attempt to determine a definite correlation until Le Conte (1905)[9] proposed an equilibrium area concept for tidal inlets. O Brien (1931, 1969)[10,11] examined field data inlets through sandy barriers in West Coast of the United States and determined a relationship between the minimum cross-sectional flow area of the entrance channel and the observed tidal prism, and established a relationship as: Ac=C.Pn (2.1) Where, Ac=the minimum inlet cross-sectional area in the equilibrium condition, C= an empirically determined coefficient, P=the tidal prism (typically during the spring tide/mean tide), and n=an exponent usually slightly less than unity. Similar analysis was carried out for the Hari River. With a view to establishing a consistent relation, data of the Pussur River were incorporated in developing the relationship, as it is also a highly tide dominated river in the South West Region. In doing this, a district relationship was found between cross-sectional area and tidal prism: Ac =43.42 P.9985 (2.2) Where, P= mean tidal prism (million m3), Ac =cross-sectional area (m2). The cross-sectional area and the corresponding tidal volume of Hari River generated by the East Beel Khuksia tidal basin at Ranai is fitted to established relationship of cross sectional area and tidal prism of the Hari River as shown in Figure Equation to line A = 43.42V Farleigh(1981, 1984), data of March-April 1980 ADC and ACE(1986), data of July 1981 KJDRP(1996), SWMC data of April 1996 Feasibility Study for Improvement of Navigability of Mongla Port, IWM data of March 2004 KJDRP (2004), IWM data of March 2004 KJDRP (2004), IWM data of May 2004 East Beel Khuksia TRM Basin (2007), IWM data of May Tidal Volume (V) -Million-m 3 Figure 5: O Brien equilibrium relationship for coastal river of Bangladesh Simple empirical equilibrium relationship shows that the crosssectional area of a tidal channel reduces in size if the tidal prism is reduced. Hence closing of a tidal river branch from the tidal system causes a reduction in the tidal prism in the whole tidal system downstream of the closure. The related reduction in the channel size, which will ultimately occur, can be estimated with the above mentioned relationship. The validity of the relationship also means that increasing a cross section by dredging without increasing the local tidal prism will result in an unsustainable solution. Natural forces will tend to restore the equilibrium condition by sedimentation in the dredged area. The reduced flow velocities in the enlarged river cross section will cause a gradient in the river velocity and consequently deposit sediment in the dredged river reach. This process stops when the equilibrium profile has been restored and the gradient in flow velocities has disappeared. 3
4 water Level(m) INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC & TECHNOLOGY RESEARCH VOLUME 1, ISSUE 5, JUNE 2012 ISSN Physical Method of Tidal River Management Tidal river management (TRM) involves taking full advantage of the natural tide movement in rivers. During flood tide, tide is allowed to enter into an embanked low-lying area (tidal basin) where the sediment carried in by flood tide is deposited. During ebb tide, water flows out of the tidal basin with greatly reduced sediment load and eventually erodes the downstream riverbed. The natural movement of flood and ebb tide along the tidal basin and along the downstream river maintains a proper drainage capacity in that river. Figure 6 shows the conceptual model of TRM Before TRM operation the critically silted stretches of the river needs to be de-silted by capital dredging and manual excavations to increase the drainage capacity otherwise TRM will not be effective. Tidal prism of the river is calculated. Then comparison is made between the existing tidal prism and the required tidal prism to maintain the design cross-section. A beel with adequate volume to accommodate the tidal prism is selected. Design and construction of link canal. Finally connecting the beel to the river through the link canal. 3.1 Data Collection and Processing Data (cross-section and bathymetric data, water level, discharge) are mainly collected from Institute of Water Modelling (IWM) Bangladesh Water Development Board (BWDB) 3.2 Model Setup The Tidal River Management model is done using MIKE-11 software. MIKE 11 is such a program that simulates flow and water level, water quality and sediment transport in rivers, flood plains, irrigation canals, reservoirs and other inland water bodies. MIKE 11 is a 1 dimensional river model developed by Danish Hydraulic Institute. Half hourly basis 24 hour s water level measurement data of river Haria and Minhaj in January has been used as downstream boundary of the model. The model has been used to simulate the dry flow such as February to May and hence the run-off from the catchment was not considered in the model setup. The upstream boundary is located near Mellekbari. The downstream boundary is located near Gadapur. Observed water level has been used as downstream boundary in the model. This TRM model consists of one upstream discharge boundary and two downstream water level boundaries. Constant zero flow has been used as dead end of the river and existing water levels in the beels. 3.3 Calibration of the Model The model has been calibrated to examine the degree of agreement between the model results and observed data. In the study the model was calibrated against water level. A sample plot of water level comparison at Niamotkati is shown in Figure Figure 6: Conceptual model of TRM 0 3 METHODOLOGY The methodologies followed in the study can be categorized in three groups: Input,Analysis, Output.The detailed methodology of the study are given in the chart Time(hr) Nimotkati_simulated Nimotkati_measured Input Literature review Secondary Data Collection Water level Discharge Cross-section Consultation with stake holders Analysis Understanding the main causes of drainage congestion Selection of beels for the study Data compilation and organization for Model input Model Development and simulation Chart 1: Methodology of the study Output To understand the drainage congestion problem in the coastal areas of Khulna region Assessment of Tidal River Management (TRM) for alleviation of drainage congestion in selected area. Figure 7: Calibration of the model 4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Before TRM operation the critical silted stretches of Kobadak River need to be de-silted by capital dredging and manual excavations to increase the drainage capacity otherwise TRM will not be effective. From hydrological data analysis the smallest design cross-section is taken Bed width, b= 25m Side slope, z= 1:3 Height h= 5m Bed slope= 1.25 cm/km Bed level= -1.0mPWD to -2mPWD So the cross-sectional area, Ac Ac = (b+z*h)*h 4
5 = (25+3*5)*5 =200m2 From equation Ac=43.42P Tidal prism, P=4.62 Million-m3 (for Ac =200 m2) This tidal prism is needed to maintain the required drainage capacity at chainage km but in the existing condition the tidal prism is 3.48Mm3.(from model result) It implies that if tidal prism is not increased then drainage capacity of the river will gradually shrink. Tidal prism can be increased in Kobadak River by allowing natural tidal movements into beels through link canal. The effectiveness of beel Jalalpur is assessed through model analysis. Based on number of link canal two different scenarios are assessed for beel Jalalpur. The results show that options with cross dam are more effective. But construction of seasonal cross dam is very costly and it needs to be removed before monsoon to drain excess water from upstream. It implies that without cross dam Jalalpur TRM is more effective. However cross dam is needed in the first year of operation to make the TRM more effective. Table 1 to5 show the detail results of the models. Table.1: Potential options for TRM in Kobadak River Option Description 1 One link canal: The only link canal is connected at 148 km chainage of Kobadak river 2 Two link canal: The first link canal is connected at 148 km chainage and the second link canal is connected at 150km chainage of Kobadak river Based on cross dam another two different scenarios are also assessed for beel Jalalpur Table 2: Potential scenarios for different options Scenario Description 1 Option 1 with cross dam 2 Option 2 with cross dam Based on these scenarios the tidal prism bellow of Kobadak River at chainage km is given in Table.3. Table.3: Tidal prisms for different options in Kobadak River Option1 Option2 Option Option with with Scenario 1 2 cross cross dam dam Tidal prism (Mm It implies Option 2 without cross dam is more effective. Here one link canal is connected to beel Jalalpur and another is connected to beel Jetua. Table.4: The tidal prism at link Jalalpur at 0.11 km chainage Option1 Scenario Option 1 Option 2 with cross Option2 with cross dam dam Tidal prism Mm Table.5: The tidal prism at link Jetua at km chainage Scenario Option 2 Option2 with cross dam Tidal prism 3 Mm Key Findings Two link canals need to be connected with the river. The first link canal is connected at 148 km chainage and the second link canal is connected at 150 km chainage of Kobadak River which gives the river total tidal prism 6.41 Mm3 in one tidal cycle throughout the entire TRM operation period. For more effective TRM operation a cross dam needs to be constructed during dry period in first year of TRM operation. Beel Jalalpur acts very effective as a tidal basin for Kobadak River. 5 CONCLUSIONS TRM is an eco-technical concept design to solve water logging problem in southwestern region of Bangladesh. This study focuses on prevailing problems and solutions of long standing drainage congestion by applying TRM in Kobadak River basin area under Satkhira district. A large area under Satkhira district has been experiencing drainage congestion over the years. Kobadak River lost its fresh water connection more than 100 years ago from Mathabanga River at the north of Taherpur and has become a mere seasonal and tidal river. Human interventions such as construction of polders, bridges and encroachment into the river for cultivation deteriorated the condition of Kobadak River. The decrease of flushing flow from upstream and substantial reduction of tidal flooding area along the river by constructing polders caused severe siltation over a long stretch of the river. Sedimentation mainly occurs during dry season since tidal flow is restricted over the flood plain by constructing polders and there is no fresh water flow into Kobadak River from the Ganges River to flush the sediment during low tide. Monsoon flow does not erode the deposited sediment on river bed because sediment concentration is also high during monsoon; that results huge sedimentation over a considerable reach of the river. Eventually the main Kobadak River, distributaries and tributaries lost drainage capacity causing long standing drainage congestion. Finally the concluding remarks are TRM operation is used to mitigate the drainage congestion in the study area. It is recommended that if the upland flow would increase in a certain amount by Ganges barrage or by any other means then no TRM operation is needed. As there are many beels in Kobadak River basin one at a time only one beel should be used as a tidal basin for TRM. Siltation of the whole beel is not desired though it is quite acceptable to local people who are engaged with agriculture. It destroys the biodiversity of the beel. So siltation should be allowed in a certain amount like 1m or 1.5m which also ensures the required environmental flow in the beel. Sediment inside the beel could be dredged yearly and by this way one beel can be act as tidal basin for many years. It saves the biodiversity of other beels in the study area at the same time keeps the river drainable and navigable for many years. So it is highly recommended from this study. 5
6 Appendix A ABBREVIATION ADB BWDB DEM DHI GOB IWM KJDRP LCS LGED LGI SSC SWMC TB WGS WMA WMO PWD Asian Development Bank Bangladesh Water Development Board Digital Elevation Model Danish Hydraulic Institute (now DHI Water and Environment) Government of Bangladesh Institute of Water Modelling (erstwhile SWMC) Khulna-Jessore Rehabilitation Project Labor Contracting Societies Local Government Engineering Department Local Government Institution Suspended Sediment Concentration Surface Water Modeling Centre (now named as IWM) Tidal Basin World Geodetic System Water Management Association Water Management Organization Public Works Department REFERENCES [1] IWM (2009), Mathematical Modeling Study for Planning and Design of Beel Kapalia Tidal Basin, Final Report, Bangladesh Water Development Board. [2] IWM (2005), Monitoring of Hydrological and Hydraulic Parameters on Tidal River Management under KJDRP Area, Final report, Bangladesh Water Development Board. [3] Sarker, M.H. (2004), Impact of Upstream Human Interventions on the Morphology of the Ganges-Gorai System, [4] IWM (2007), Monitoring the effects of Beel Khuksia TRM Basin and Dredging of Hari River for drainage improvement of Bhabodah area, final report, Bangladesh Water Development Board. [5] SMEC (2002), Khulna Jessore Drainage Rehabilitation Project, Project Completion Report (Final), Bangladesh Water Development Board. [6] SMEC (1997), Khulna-Jessore Drainage Rehabilitation Project, Feasibility Study Report for Overall Drainage Plan, Bangladesh Water Development Board. [7] Amir M S (2010), Socio-Technical Assessment of Sediment Management Options in Tidal Basins in Southwestern Bangladesh, Institute of Water and Flood Management (IWFM), Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology (January 2010). [8] Green, s. (1974), Mills admits Being present during Tidal Basin Scuffle (http;// Post, Retrieved [9] LeConte, L.J., Discussion on the paper, Notes on the improvement of river and harbor outlets in the United States by D. A. Watt, paper no Trans. ASCE 55 (December): [10] O Brien, M.P.(1969) Equilibrium Flow areas of Inlets on sandy coasts, Proc ASCE, Journal, waterways and Harbors Div.,Vol.95, No. WWI, p [11] O Brien, M.P. (1931), Estuary Tidal Prism Relater to Entrance areas, Civil Engineering, Vol.1, No.8, p738 6
Optimization of Alignment of Proposed Canal and Revetment in the old Madhumati River Using Physical Modelling: A Case Study
 International Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 2014, 3(2): 68-75 DOI: 10.5923/j.ijhe.20140302.03 Optimization of Alignment of Proposed Canal and Revetment in the old Madhumati River Using Physical Modelling:
International Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 2014, 3(2): 68-75 DOI: 10.5923/j.ijhe.20140302.03 Optimization of Alignment of Proposed Canal and Revetment in the old Madhumati River Using Physical Modelling:
A STUDY ON HYDRODYNAMIC AND MORPHOLOGICAL BEHAVIOR OF PADMA RIVER USING DELFT3D MODEL
 Proceedings of the 3 rd International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2016), 12~14 February 2016, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh (ISBN: 978-984-34-0265-3) A STUDY ON HYDRODYNAMIC
Proceedings of the 3 rd International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2016), 12~14 February 2016, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh (ISBN: 978-984-34-0265-3) A STUDY ON HYDRODYNAMIC
MORPHOLOGICAL PROCESSES AND EFFECTIVE RIVER EROSION MANAGEMENT: A CASE STUDY OF THE ARIAL KHAN RIVER IN BANGLADESH
 MORPHOLOGICAL PROCESSES AND EFFECTIVE RIVER EROSION MANAGEMENT: A CASE STUDY OF THE ARIAL KHAN RIVER IN BANGLADESH Jakia Akter* 1, Maminul Haque Sarker, Preetha Haque 1 Center for environmental and Geographic
MORPHOLOGICAL PROCESSES AND EFFECTIVE RIVER EROSION MANAGEMENT: A CASE STUDY OF THE ARIAL KHAN RIVER IN BANGLADESH Jakia Akter* 1, Maminul Haque Sarker, Preetha Haque 1 Center for environmental and Geographic
Strategies for managing sediment in dams. Iwona Conlan Consultant to IKMP, MRCS
 Strategies for managing sediment in dams Iwona Conlan Consultant to IKMP, MRCS 1 Sediment trapping by dams Active storage capacity Dead storage coarse material (bed load) Fine materials (suspension) Francis
Strategies for managing sediment in dams Iwona Conlan Consultant to IKMP, MRCS 1 Sediment trapping by dams Active storage capacity Dead storage coarse material (bed load) Fine materials (suspension) Francis
Technical Review of Pak Beng Hydropower Project (1) Hydrology & Hydraulics and (2) Sediment Transport & River Morphology
 Technical Review of Pak Beng Hydropower Project (1) Hydrology & Hydraulics and (2) Sediment Transport & River Morphology The 2 nd Regional Stakeholder Forum The Pak Beng Hydropower Project 5 th May 2017
Technical Review of Pak Beng Hydropower Project (1) Hydrology & Hydraulics and (2) Sediment Transport & River Morphology The 2 nd Regional Stakeholder Forum The Pak Beng Hydropower Project 5 th May 2017
Development and application of demonstration MIKE 21C morphological model for a bend in Mekong River
 Development and application of demonstration MIKE 21C morphological model for a bend in Mekong River September 2015 0 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Data collection... 3 2.1 Additional data...
Development and application of demonstration MIKE 21C morphological model for a bend in Mekong River September 2015 0 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Data collection... 3 2.1 Additional data...
Impact of Climate Change on Riverbank Erosion
 International Journal of Sciences: Basic and Applied Research (IJSBAR) ISSN 2307-4531 http://gssrr.org/index.php?journal=journalofbasicandapplied Impact of Climate Change on Riverbank Erosion Most. Nazneen
International Journal of Sciences: Basic and Applied Research (IJSBAR) ISSN 2307-4531 http://gssrr.org/index.php?journal=journalofbasicandapplied Impact of Climate Change on Riverbank Erosion Most. Nazneen
Tarbela Dam in Pakistan. Case study of reservoir sedimentation
 Tarbela Dam in Pakistan. HR Wallingford, Wallingford, UK Published in the proceedings of River Flow 2012, 5-7 September 2012 Abstract Reservoir sedimentation is a main concern in the Tarbela reservoir
Tarbela Dam in Pakistan. HR Wallingford, Wallingford, UK Published in the proceedings of River Flow 2012, 5-7 September 2012 Abstract Reservoir sedimentation is a main concern in the Tarbela reservoir
National Hydrology committee of Afghanistan (NHCA) Sedimentation in Reservoire
 National Hydrology committee of Afghanistan (NHCA) Sedimentation in Reservoire OCt.2007 Prof. Mohammad Qasem Seddeqy KPU بسم االله الرحمن الرحيم وجعلنامن الماءکل شي ء حی 30 واز ا ب هر چيزی رازنده گردانيدیم
National Hydrology committee of Afghanistan (NHCA) Sedimentation in Reservoire OCt.2007 Prof. Mohammad Qasem Seddeqy KPU بسم االله الرحمن الرحيم وجعلنامن الماءکل شي ء حی 30 واز ا ب هر چيزی رازنده گردانيدیم
24.0 Mineral Extraction
 Chapter 24 - Mineral Extraction 24.0 Mineral Extraction 24.1 Introduction Apart from gravel, sand, rock, limestone and salt extraction in relatively small quantities mineral extraction is not a strong
Chapter 24 - Mineral Extraction 24.0 Mineral Extraction 24.1 Introduction Apart from gravel, sand, rock, limestone and salt extraction in relatively small quantities mineral extraction is not a strong
Solutions to Flooding on Pescadero Creek Road
 Hydrology Hydraulics Geomorphology Design Field Services Photo courtesy Half Moon Bay Review Solutions to Flooding on Pescadero Creek Road Prepared for: San Mateo County Resource Conservation District
Hydrology Hydraulics Geomorphology Design Field Services Photo courtesy Half Moon Bay Review Solutions to Flooding on Pescadero Creek Road Prepared for: San Mateo County Resource Conservation District
USE OF MATHEMATICAL MODEL AS A TOOL FOR MITIGATION OF FLOOD: CASE STUDY SURMA RIVER SYSTEM IN BANGLADESH
 USE OF MATHEMATICAL MODEL AS A TOOL FOR MITIGATION OF FLOOD: CASE STUDY SURMA RIVER SYSTEM IN BANGLADESH Wahiduzzaman PhDEng*, Abu Saleh Khan MScEng**, Faruq Ahmed Mohiuddin MEng***, Kazi Emran Bashar
USE OF MATHEMATICAL MODEL AS A TOOL FOR MITIGATION OF FLOOD: CASE STUDY SURMA RIVER SYSTEM IN BANGLADESH Wahiduzzaman PhDEng*, Abu Saleh Khan MScEng**, Faruq Ahmed Mohiuddin MEng***, Kazi Emran Bashar
Sedimentation in the Nile River
 Advanced Training Workshop on Reservoir Sedimentation Sedimentation in the Nile River Prof. Dr. Abdalla Abdelsalam Ahmed 10-16 Oct. 2007, IRTCES, Beijing, China CWR,Sudan 1 Water is essential for mankind
Advanced Training Workshop on Reservoir Sedimentation Sedimentation in the Nile River Prof. Dr. Abdalla Abdelsalam Ahmed 10-16 Oct. 2007, IRTCES, Beijing, China CWR,Sudan 1 Water is essential for mankind
Earth Science Chapter 6 Section 2 Review
 Name: Class: Date: Earth Science Chapter 6 Section Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Most streams carry the largest part of their
Name: Class: Date: Earth Science Chapter 6 Section Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Most streams carry the largest part of their
Mississippi River West Bay Diversion Geomorphic Assessment and 1-D Modeling Plan
 Mississippi River West Bay Diversion Geomorphic Assessment and 1-D Modeling Plan Freddie Pinkard and Charlie Little Research Hydraulic Engineers ERDC-CHL-River Engineering Branch 27 February 2009 Lane
Mississippi River West Bay Diversion Geomorphic Assessment and 1-D Modeling Plan Freddie Pinkard and Charlie Little Research Hydraulic Engineers ERDC-CHL-River Engineering Branch 27 February 2009 Lane
Chapter 11. Rivers: Shaping our landscape
 Chapter 11 Rivers: Shaping our landscape Learning outcomes In this presentation you will learn: Common terms associated with rivers About the three stages of a river About the processes of river erosion
Chapter 11 Rivers: Shaping our landscape Learning outcomes In this presentation you will learn: Common terms associated with rivers About the three stages of a river About the processes of river erosion
Domino Effect of River Training in Large Sand-Bed Braiding Rivers
 6 th International Conference on Structural Engineering and Construction Management 2015, Kandy, Sri Lanka, 11 th -13 th December 2015 SECM/15/176 Domino Effect of River Training in Large Sand-Bed Braiding
6 th International Conference on Structural Engineering and Construction Management 2015, Kandy, Sri Lanka, 11 th -13 th December 2015 SECM/15/176 Domino Effect of River Training in Large Sand-Bed Braiding
International Journal Of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 7, July ISSN
 International Journal Of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 7, July-2016 709 FLOOD MITIGATION STUDY IN ADAYAR RIVER USING MIKE-FLOOD Vidyapriya.V a and Ramalingam. M b a Research scholar,
International Journal Of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 7, July-2016 709 FLOOD MITIGATION STUDY IN ADAYAR RIVER USING MIKE-FLOOD Vidyapriya.V a and Ramalingam. M b a Research scholar,
Surface Water Short Study Guide
 Name: Class: Date: Surface Water Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The three ways in which a stream carries
Name: Class: Date: Surface Water Short Study Guide Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The three ways in which a stream carries
Monitoring Lower Meghna River of Bangladesh using Remote Sensing and GIS Technology
 Monitoring Lower Meghna River of Bangladesh using Remote Sensing and GIS Technology M Rahman Akhand, S M Mizanur Rahman & M H Sarker Bangladesh Space Research and Remote Sensing Organization (SPARRSO)
Monitoring Lower Meghna River of Bangladesh using Remote Sensing and GIS Technology M Rahman Akhand, S M Mizanur Rahman & M H Sarker Bangladesh Space Research and Remote Sensing Organization (SPARRSO)
Prediction of changes in tidal system and deltas at Nakdong estuary due to construction of Busan new port
 Prediction of changes in tidal system and deltas at Nakdong estuary due to construction of Busan new port H. Gm1 & G.-Y. park2 l Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering, Kookmin University, Korea
Prediction of changes in tidal system and deltas at Nakdong estuary due to construction of Busan new port H. Gm1 & G.-Y. park2 l Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering, Kookmin University, Korea
An investigation on the impacts of density currents on the sedimentation in dam reservoirs using TCM model; case study: Maroon dam
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences - Papers: Part A Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2013 An investigation on the impacts of density
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences - Papers: Part A Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2013 An investigation on the impacts of density
Analysis of Historical Pattern of Rainfall in the Western Region of Bangladesh
 24 25 April 214, Asian University for Women, Bangladesh Analysis of Historical Pattern of Rainfall in the Western Region of Bangladesh Md. Tanvir Alam 1*, Tanni Sarker 2 1,2 Department of Civil Engineering,
24 25 April 214, Asian University for Women, Bangladesh Analysis of Historical Pattern of Rainfall in the Western Region of Bangladesh Md. Tanvir Alam 1*, Tanni Sarker 2 1,2 Department of Civil Engineering,
Appendix O. Sediment Transport Modelling Technical Memorandum
 Appendix O Sediment Transport Modelling Technical Memorandum w w w. b a i r d. c o m Baird o c e a n s engineering l a k e s design r i v e r s science w a t e r s h e d s construction Final Report Don
Appendix O Sediment Transport Modelling Technical Memorandum w w w. b a i r d. c o m Baird o c e a n s engineering l a k e s design r i v e r s science w a t e r s h e d s construction Final Report Don
FOREST RESEARCH INSTITUTE, DEHRADUN
 PROJECT REPORT DRAINAGE AND REPLENISHMENT STUDY OF MINED AREA OF GANGA SHYAMPUR RIVER HARIDWAR Submitted to UTTARAKHAND FOREST DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION (UFDC) 73, Nehru Road, Deharadun Prepared&Submitted
PROJECT REPORT DRAINAGE AND REPLENISHMENT STUDY OF MINED AREA OF GANGA SHYAMPUR RIVER HARIDWAR Submitted to UTTARAKHAND FOREST DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION (UFDC) 73, Nehru Road, Deharadun Prepared&Submitted
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK ASSESSMENT OF RESERVOIR SEDIMENTATION IN PANSHET RESERVOIR BY HYBRID METHOD N.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK ASSESSMENT OF RESERVOIR SEDIMENTATION IN PANSHET RESERVOIR BY HYBRID METHOD N.
Mekong Sediment from the Mekong River Commission Study
 Short Technical Note Mekong Sediment from the Mekong River Commission Study Summary The Mekong River flows through China, Myanmar, Lao PDR, Thailand, Cambodia and Viet Nam. The assessment of various water
Short Technical Note Mekong Sediment from the Mekong River Commission Study Summary The Mekong River flows through China, Myanmar, Lao PDR, Thailand, Cambodia and Viet Nam. The assessment of various water
The Use of Water an Impact to the Eco-system
 Continuous Sediment Transfer ConSedTrans - Method A way to reduce the risk of sedimentation and siltation, flooding, soil and coast erosion, and saltation of groundwater. ACWUA s 5th Best Practices Conference
Continuous Sediment Transfer ConSedTrans - Method A way to reduce the risk of sedimentation and siltation, flooding, soil and coast erosion, and saltation of groundwater. ACWUA s 5th Best Practices Conference
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output
 mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
Fresh Water: Streams, Lakes Groundwater & Wetlands
 Fresh Water:, Lakes Groundwater & Wetlands Oct 27 Glaciers and Ice Ages Chp 13 Nov 3 Deserts and Wind and EXAM #3 Slope hydrologic cycle P = precip I = precip intercepted by veg ET = evapotranspiration
Fresh Water:, Lakes Groundwater & Wetlands Oct 27 Glaciers and Ice Ages Chp 13 Nov 3 Deserts and Wind and EXAM #3 Slope hydrologic cycle P = precip I = precip intercepted by veg ET = evapotranspiration
Mississippi River and Tributaries Project Mississippi River Geomorphology and Potamology Program
 Mississippi River and Tributaries Project Mississippi River Geomorphology and Potamology Program Barb Kleiss, Mississippi Valley Division Freddie Pinkard, Vicksburg District June, 2016 Program Objectives
Mississippi River and Tributaries Project Mississippi River Geomorphology and Potamology Program Barb Kleiss, Mississippi Valley Division Freddie Pinkard, Vicksburg District June, 2016 Program Objectives
3.0 ROBERTS BANK TIDAL FLAT MORPHOLOGY
 Vancouver Port Authority Northwest Hydraulic Consultants Ltd. /Triton Consultants Ltd. Roberts Bank Container Expansion File: 33863 Coastal Geomorphology Study - 19 - November 2004 3.0 ROBERTS BANK TIDAL
Vancouver Port Authority Northwest Hydraulic Consultants Ltd. /Triton Consultants Ltd. Roberts Bank Container Expansion File: 33863 Coastal Geomorphology Study - 19 - November 2004 3.0 ROBERTS BANK TIDAL
RESERVOIR DRAWDOWN RATES/RESERVOIR DRAWDOWN TEST Iron Gate, Copco (I & II), and JC Boyle Dams
 TECHNICAL MEMORANDUM No. 1 TO: Michael Bowen California Coastal Conservancy Geotechnical & Earthquake Engineering Consultants CC: Eric Ginney Philip Williams & Associates PREPARED BY: Paul Grant SUBJECT:
TECHNICAL MEMORANDUM No. 1 TO: Michael Bowen California Coastal Conservancy Geotechnical & Earthquake Engineering Consultants CC: Eric Ginney Philip Williams & Associates PREPARED BY: Paul Grant SUBJECT:
Indexing vulnerability of an embankment reach against breaching: A remote sensing and hydrodynamic based study
 European Water 60: 67-71, 2017. 2017 E.W. Publications Indexing vulnerability of an embankment reach against breaching: A remote sensing and hydrodynamic based study B. Talukdar *, A. Baid and R. Das Civil
European Water 60: 67-71, 2017. 2017 E.W. Publications Indexing vulnerability of an embankment reach against breaching: A remote sensing and hydrodynamic based study B. Talukdar *, A. Baid and R. Das Civil
and the Myanmar economy World Water Day, 2018
 and the Myanmar economy World Water Day, 2018 Hannah.baleta@panda.org Three key messages Myanmar is growing economically and developing socially with a large dependency on natural resources such as the
and the Myanmar economy World Water Day, 2018 Hannah.baleta@panda.org Three key messages Myanmar is growing economically and developing socially with a large dependency on natural resources such as the
Identification of Erosion Potential in an Urban River in North Australia Using GIS and Hydrodynamic Model
 Identification of Erosion Potential in an Urban River in North Australia Using GIS and Hydrodynamic Model L Adair a and A Rahman b a Gold Coast City Council, Gold Coast, Australia b School of Engineering
Identification of Erosion Potential in an Urban River in North Australia Using GIS and Hydrodynamic Model L Adair a and A Rahman b a Gold Coast City Council, Gold Coast, Australia b School of Engineering
ES 105 Surface Processes I. Hydrologic cycle A. Distribution % in oceans 2. >3% surface water a. +99% surface water in glaciers b.
 ES 105 Surface Processes I. Hydrologic cycle A. Distribution 1. +97% in oceans 2. >3% surface water a. +99% surface water in glaciers b. >1/3% liquid, fresh water in streams and lakes~1/10,000 of water
ES 105 Surface Processes I. Hydrologic cycle A. Distribution 1. +97% in oceans 2. >3% surface water a. +99% surface water in glaciers b. >1/3% liquid, fresh water in streams and lakes~1/10,000 of water
SCOPE OF PRESENTATION STREAM DYNAMICS, CHANNEL RESTORATION PLANS, & SEDIMENT TRANSPORT ANALYSES IN RELATION TO RESTORATION PLANS
 DESIGN METHODS B: SEDIMENT TRANSPORT PROCESSES FOR STREAM RESTORATION DESIGN PETER KLINGEMAN OREGON STATE UNIVERSITY CIVIL ENGINEERING DEPT., CORVALLIS 2 ND ANNUAL NORTHWEST STREAM RESTORATION DESIGN SYMPOSIUM
DESIGN METHODS B: SEDIMENT TRANSPORT PROCESSES FOR STREAM RESTORATION DESIGN PETER KLINGEMAN OREGON STATE UNIVERSITY CIVIL ENGINEERING DEPT., CORVALLIS 2 ND ANNUAL NORTHWEST STREAM RESTORATION DESIGN SYMPOSIUM
Assessment of climate change impacts on salinity intrusion in Hong-Thai Binh and Dong Nai river basins
 VNU Journal of Science, Earth Sciences 27 (2011) 54-61 Assessment of climate change impacts on salinity intrusion in Hong-Thai Binh and Dong Nai river basins Tran Hong Thai, Tran Thi Van* Vietnam Institute
VNU Journal of Science, Earth Sciences 27 (2011) 54-61 Assessment of climate change impacts on salinity intrusion in Hong-Thai Binh and Dong Nai river basins Tran Hong Thai, Tran Thi Van* Vietnam Institute
Monitoring of Forest Cover Change in Sundarban mangrove forest using Remote sensing and GIS
 Monitoring of Forest Cover Change in Sundarban mangrove forest using Remote sensing and GIS By Mohammed Monirul Alam April 2008 Content 1: INTRODUCTION 2: OBJECTIVES 3: METHODOLOGY 4: RESULTS & DISCUSSION
Monitoring of Forest Cover Change in Sundarban mangrove forest using Remote sensing and GIS By Mohammed Monirul Alam April 2008 Content 1: INTRODUCTION 2: OBJECTIVES 3: METHODOLOGY 4: RESULTS & DISCUSSION
SEDIMENTATION AND ITS COUNTERMEASURE AT THE OFF-TAKE AREA OF NEW DHALESWARI RIVER
 SEDIMENTATION AND ITS COUNTERMEASURE AT THE OFF-TAKE AREA OF NEW DHALESWARI RIVER Tanjir Saif AHMED* MEE15634 Supervisors: Prof. EGASHIRA Shinji** Assoc. Prof. YOROZUYA Atsuhiro*** ABSTRACT Present study
SEDIMENTATION AND ITS COUNTERMEASURE AT THE OFF-TAKE AREA OF NEW DHALESWARI RIVER Tanjir Saif AHMED* MEE15634 Supervisors: Prof. EGASHIRA Shinji** Assoc. Prof. YOROZUYA Atsuhiro*** ABSTRACT Present study
A STUDY OF LOCAL SCOUR AT BRIDGE PIERS OF EL-MINIA
 A STUDY OF LOCAL SCOUR AT BRIDGE PIERS OF EL-MINIA Dr. Gamal A. Sallam 1 and Dr. Medhat Aziz 2 ABSTRACT Bridges are critical structures that require a substantial investment to construct and serve an important
A STUDY OF LOCAL SCOUR AT BRIDGE PIERS OF EL-MINIA Dr. Gamal A. Sallam 1 and Dr. Medhat Aziz 2 ABSTRACT Bridges are critical structures that require a substantial investment to construct and serve an important
Technical Memorandum No Sediment Model
 Pajaro River Watershed Study in association with Technical Memorandum No. 1.2.9 Sediment Model Task: Development of Sediment Model To: PRWFPA Staff Working Group Prepared by: Gregory Morris and Elsie Parrilla
Pajaro River Watershed Study in association with Technical Memorandum No. 1.2.9 Sediment Model Task: Development of Sediment Model To: PRWFPA Staff Working Group Prepared by: Gregory Morris and Elsie Parrilla
How to predict the sedimentological impacts of reservoir operations?
 ICSE 212 How to predict the sedimentological impacts of reservoir operations? E. Valette EDF CIH eric.valette@edf.fr M. Jodeau EDF R&D LNHE magali.jodeau@edf.fr Presentation of the numerical code Courlis
ICSE 212 How to predict the sedimentological impacts of reservoir operations? E. Valette EDF CIH eric.valette@edf.fr M. Jodeau EDF R&D LNHE magali.jodeau@edf.fr Presentation of the numerical code Courlis
2. PRESENT CONDITION OF THE RESERVOIR 2.1 View of Wonogiri Reservoir (1/3)
 2.1 View of Wonogiri Reservoir (1/3) Wonogiri dam abutment on the left side of dam Spillway forebay on thet left side of dam Bank erosion around Wonogiri reservoir. Wonogiri Dam view from chersonese. An
2.1 View of Wonogiri Reservoir (1/3) Wonogiri dam abutment on the left side of dam Spillway forebay on thet left side of dam Bank erosion around Wonogiri reservoir. Wonogiri Dam view from chersonese. An
Texas A & M University and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation Hydrologic Modeling Inventory Model Description Form
 Texas A & M University and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation Hydrologic Modeling Inventory Model Description Form JUNE, 1999 Name of Model: Two-Dimensional Alluvial River and Floodplain Model (MIKE21 CHD & CST)
Texas A & M University and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation Hydrologic Modeling Inventory Model Description Form JUNE, 1999 Name of Model: Two-Dimensional Alluvial River and Floodplain Model (MIKE21 CHD & CST)
CHAPTER 126 ^^^C^SR, SEDIMENTATION STUDIES ON THE NIGER RIVER DELTA
 CHAPTER 126 SEDIMENTATION STUDIES ON THE NIGER RIVER DELTA Ramiro Mayor-Mora, D. Eng. (1) Preben Mortensen, M.Sc. (2) Jorgen Fredsoe, M.Sc. (2) 1. Introduction An area of the Niger River Delta was studied
CHAPTER 126 SEDIMENTATION STUDIES ON THE NIGER RIVER DELTA Ramiro Mayor-Mora, D. Eng. (1) Preben Mortensen, M.Sc. (2) Jorgen Fredsoe, M.Sc. (2) 1. Introduction An area of the Niger River Delta was studied
SPECIFIC DEGRADATION AND RESERVOIR SEDIMENTATION. By Renee Vandermause & Chun-Yao Yang
 SPECIFIC DEGRADATION AND RESERVOIR SEDIMENTATION By Renee Vandermause & Chun-Yao Yang Outline Sediment Degradation - Erosion vs Sediment Yield - Sediment Yield - Methods for estimation - Defining Sediment
SPECIFIC DEGRADATION AND RESERVOIR SEDIMENTATION By Renee Vandermause & Chun-Yao Yang Outline Sediment Degradation - Erosion vs Sediment Yield - Sediment Yield - Methods for estimation - Defining Sediment
FLOOD HAZARD MAPPING OF DHAKA-NARAYANGANJ-DEMRA (DND) PROJECT USING GEO-INFORMATICS TOOLS
 FLOOD HAZARD MAPPING OF DHAKA-NARAYANGANJ-DEMRA (DND) PROJECT USING GEO-INFORMATICS TOOLS Md. Aminul Islam MEE07178 Supervisor: Prof. Kuniyoshi TAKEUCHI ABSTRACT Dhaka-Narayanganj-Demra (DND) Project is
FLOOD HAZARD MAPPING OF DHAKA-NARAYANGANJ-DEMRA (DND) PROJECT USING GEO-INFORMATICS TOOLS Md. Aminul Islam MEE07178 Supervisor: Prof. Kuniyoshi TAKEUCHI ABSTRACT Dhaka-Narayanganj-Demra (DND) Project is
Morphological Changes of Reach Two of the Nile River
 ICHE 2014, Hamburg - Lehfeldt & Kopmann (eds) - 2014 Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-3-939230-32-8 Morphological Changes of Reach Two of the Nile River E. Said Egyptian Environmental Affairs Agency,
ICHE 2014, Hamburg - Lehfeldt & Kopmann (eds) - 2014 Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-3-939230-32-8 Morphological Changes of Reach Two of the Nile River E. Said Egyptian Environmental Affairs Agency,
Flood Forecasting in Bangladesh
 Flood Forecasting in Bangladesh Types of Flood ing Flood ing can be divided into two categories: Flood ing in the rivers caused by upstream rise of river stage as well as rainfall in the basin. Overland
Flood Forecasting in Bangladesh Types of Flood ing Flood ing can be divided into two categories: Flood ing in the rivers caused by upstream rise of river stage as well as rainfall in the basin. Overland
 Red River Flooding June 2015 Caddo and Bossier Parishes Presented by: Flood Technical Committee Where the Rain Falls Matters I-30 versus I-20 I-20 Backwater and Tributary Floods (Localized) 2016 Flood
Red River Flooding June 2015 Caddo and Bossier Parishes Presented by: Flood Technical Committee Where the Rain Falls Matters I-30 versus I-20 I-20 Backwater and Tributary Floods (Localized) 2016 Flood
Laboratory Exercise #3 The Hydrologic Cycle and Running Water Processes
 Laboratory Exercise #3 The Hydrologic Cycle and Running Water Processes page - 1 Section A - The Hydrologic Cycle Figure 1 illustrates the hydrologic cycle which quantifies how water is cycled throughout
Laboratory Exercise #3 The Hydrologic Cycle and Running Water Processes page - 1 Section A - The Hydrologic Cycle Figure 1 illustrates the hydrologic cycle which quantifies how water is cycled throughout
Subcommittee on Sedimentation Draft Sediment Analysis Guidelines for Dam Removal
 Subcommittee on Sedimentation Draft Sediment Analysis Guidelines for Dam Removal August 4, 2011 Jennifer Bountry, M.S., P.E. Tim Randle, M.S., P.E., D.WRE. Blair Greimann, Ph.D., P.E. Sedimentation and
Subcommittee on Sedimentation Draft Sediment Analysis Guidelines for Dam Removal August 4, 2011 Jennifer Bountry, M.S., P.E. Tim Randle, M.S., P.E., D.WRE. Blair Greimann, Ph.D., P.E. Sedimentation and
Special Public Notice
 Special Public Notice Applicability: General Public Date: June 3, 2014 The purpose of this public notice is to inform you of existing guidance and policy contained in Regulatory Guidance Letter 05-04 concerning
Special Public Notice Applicability: General Public Date: June 3, 2014 The purpose of this public notice is to inform you of existing guidance and policy contained in Regulatory Guidance Letter 05-04 concerning
A STUDY ON BANK EROSION AND BANK LINE MIGRATION PATTERN OF THE SUBANSIRI RIVER IN ASSAM USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS TECHNOLOGY
 The International Journal Of Engineering And Science (IJES) Volume 2 Issue 9 Pages 01-06 2013 ISSN(e): 2319 1813 ISSN(p): 2319 1805 A STUDY ON BANK EROSION AND BANK LINE MIGRATION PATTERN OF THE SUBANSIRI
The International Journal Of Engineering And Science (IJES) Volume 2 Issue 9 Pages 01-06 2013 ISSN(e): 2319 1813 ISSN(p): 2319 1805 A STUDY ON BANK EROSION AND BANK LINE MIGRATION PATTERN OF THE SUBANSIRI
Vulnerability of Flood Hazard in Selected Ayeyarwady Delta Region, Myanmar
 Vulnerability of Flood Hazard in Selected Ayeyarwady Delta Region, Myanmar Khin Thandar Win Department of Civil Engineering Nilar Aye Department of Civil Engineering Kyaw Zaya Htun Department of Remote
Vulnerability of Flood Hazard in Selected Ayeyarwady Delta Region, Myanmar Khin Thandar Win Department of Civil Engineering Nilar Aye Department of Civil Engineering Kyaw Zaya Htun Department of Remote
Appendix G.19 Hatch Report Pacific NorthWest LNG Lelu Island LNG Maintenance Dredging at the Materials Offloading Facility
 Appendix G.19 Hatch Report Pacific NorthWest LNG Lelu Island LNG Maintenance Dredging at the Materials Offloading Facility Project Memo H345670 To: Capt. David Kyle From: O. Sayao/L. Absalonsen December
Appendix G.19 Hatch Report Pacific NorthWest LNG Lelu Island LNG Maintenance Dredging at the Materials Offloading Facility Project Memo H345670 To: Capt. David Kyle From: O. Sayao/L. Absalonsen December
MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF FLUVIAL SEDIMENT DELIVERY, NEKA RIVER, IRAN. S.E. Kermani H. Golmaee M.Z. Ahmadi
 JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL HYDROLOGY The Electronic Journal of the International Association for Environmental Hydrology On the World Wide Web at http://www.hydroweb.com VOLUME 16 2008 MATHEMATICAL MODELING
JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL HYDROLOGY The Electronic Journal of the International Association for Environmental Hydrology On the World Wide Web at http://www.hydroweb.com VOLUME 16 2008 MATHEMATICAL MODELING
Experimental Study of Discharge Characteristics in a Compound Meandering River
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-07, pp-136-140 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Experimental Study of Discharge Characteristics
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-07, pp-136-140 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Experimental Study of Discharge Characteristics
Improvement of navigation conditions on the Danube (Calarasi-Braila and Lower Danube) - Ecological concerns?
 Improvement of navigation conditions on the Danube (Calarasi-Braila and Lower Danube) - Ecological concerns? Georg Rast, Christine Bratrich, Orieta Hulea WWF Germany/DCPO Topics of the presentation Major
Improvement of navigation conditions on the Danube (Calarasi-Braila and Lower Danube) - Ecological concerns? Georg Rast, Christine Bratrich, Orieta Hulea WWF Germany/DCPO Topics of the presentation Major
Annual transport rates at two locations on the fore-slope.
 Sediment Transport by Currents Fore-slope Sediment transport rates and sediment concentrations were computed from the hydrodynamic model runs as well as from direct measurements of current velocities at
Sediment Transport by Currents Fore-slope Sediment transport rates and sediment concentrations were computed from the hydrodynamic model runs as well as from direct measurements of current velocities at
(case study Karaj watershed)
 River sediment monitoring using remote sensing and GIS (case study Karaj watershed) M. Shafaie a,h.ghodosi b, K. H. Mostofi c * a professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University
River sediment monitoring using remote sensing and GIS (case study Karaj watershed) M. Shafaie a,h.ghodosi b, K. H. Mostofi c * a professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University
GTU. Shantilal Shah Engineering College, Bhavnagar
 GTU Shantilal Shah Engineering College, Bhavnagar 2 Around 40,000 large reservoirs worldwide used for water supply, power generation, flood control etc. About 1 % of the total storage volume is lost annually
GTU Shantilal Shah Engineering College, Bhavnagar 2 Around 40,000 large reservoirs worldwide used for water supply, power generation, flood control etc. About 1 % of the total storage volume is lost annually
3/3/2013. The hydro cycle water returns from the sea. All "toilet to tap." Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e
 Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Running Water: summary in haiku form Edward A. Keller Chapter 9 Rivers and Flooding Lecture Presentation prepared by X. Mara Chen, Salisbury University The hydro
Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Running Water: summary in haiku form Edward A. Keller Chapter 9 Rivers and Flooding Lecture Presentation prepared by X. Mara Chen, Salisbury University The hydro
STUDY AREA AND METHODOLOGY
 . CHAPTER 2 STUDY AREA AND METHODOLOGY 26 CHAPTER 2 STUDY AREA AND METHODOLOGY Kundalika is a major river in konkan region of Maharashtra. River originates in Western Ghats at an altitude of 820 m ASL
. CHAPTER 2 STUDY AREA AND METHODOLOGY 26 CHAPTER 2 STUDY AREA AND METHODOLOGY Kundalika is a major river in konkan region of Maharashtra. River originates in Western Ghats at an altitude of 820 m ASL
3. MARINE HABITAT RESTORATION
 Feasibility Study for Restoration of Titlow Lagoon Fish Passage South Puget Sound Salmon Enhancement Group 3. MARINE HABITAT RESTORATION Marine habitat restoration at Titlow Park could include restoration
Feasibility Study for Restoration of Titlow Lagoon Fish Passage South Puget Sound Salmon Enhancement Group 3. MARINE HABITAT RESTORATION Marine habitat restoration at Titlow Park could include restoration
Flow estimations through spillways under submerged tidal conditions
 Computational Methods and Experimental Measurements XIII 137 Flow estimations through spillways under submerged tidal conditions P. D. Scarlatos 1, M. Ansar 2 & Z. Chen 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering
Computational Methods and Experimental Measurements XIII 137 Flow estimations through spillways under submerged tidal conditions P. D. Scarlatos 1, M. Ansar 2 & Z. Chen 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering
Gully Erosion Part 1 GULLY EROSION AND ITS CAUSES. Introduction. The mechanics of gully erosion
 Gully Erosion Part 1 GULLY EROSION AND ITS CAUSES Gully erosion A complex of processes whereby the removal of soil is characterised by incised channels in the landscape. NSW Soil Conservation Service,
Gully Erosion Part 1 GULLY EROSION AND ITS CAUSES Gully erosion A complex of processes whereby the removal of soil is characterised by incised channels in the landscape. NSW Soil Conservation Service,
HYDROLOGIC AND WATER RESOURCES EVALUATIONS FOR SG. LUI WATERSHED
 HYDROLOGIC AND WATER RESOURCES EVALUATIONS FOR SG. LUI WATERSHED 1.0 Introduction The Sg. Lui watershed is the upper part of Langat River Basin, in the state of Selangor which located approximately 20
HYDROLOGIC AND WATER RESOURCES EVALUATIONS FOR SG. LUI WATERSHED 1.0 Introduction The Sg. Lui watershed is the upper part of Langat River Basin, in the state of Selangor which located approximately 20
June 2018 Sediments and Dredging at GBR Ports
 June 2018 Sediments and Dredging at GBR Ports Reef 2050 Long Term Sustainability Plan The Great Barrier Reef is over 2000 km long and covers an area of approximately 350,000 square kilometres. It is a
June 2018 Sediments and Dredging at GBR Ports Reef 2050 Long Term Sustainability Plan The Great Barrier Reef is over 2000 km long and covers an area of approximately 350,000 square kilometres. It is a
Effect of bridge pier on waterways constriction: a case study using 2-D mathematical modeling
 IABSE-JSCE Joint Conference on Advances in Bridge Engineering-II, August 8-10, 2010, Dhaka, Bangladesh. ISBN: 978-984-33-1893-0 Amin, Okui, Bhuiyan (eds.) www.iabse-bd.org Effect of bridge pier on waterways
IABSE-JSCE Joint Conference on Advances in Bridge Engineering-II, August 8-10, 2010, Dhaka, Bangladesh. ISBN: 978-984-33-1893-0 Amin, Okui, Bhuiyan (eds.) www.iabse-bd.org Effect of bridge pier on waterways
Grant 0299-NEP: Water Resources Project Preparatory Facility
 Document Produced under Grant Project Number: 45206 May 2016 Grant 0299-NEP: Water Resources Project Preparatory Facility Final Report Volume 3 East Rapti (1 of 9) Prepared by Pvt. Ltd. For Ministry of
Document Produced under Grant Project Number: 45206 May 2016 Grant 0299-NEP: Water Resources Project Preparatory Facility Final Report Volume 3 East Rapti (1 of 9) Prepared by Pvt. Ltd. For Ministry of
Surface Water and Stream Development
 Surface Water and Stream Development Surface Water The moment a raindrop falls to earth it begins its return to the sea. Once water reaches Earth s surface it may evaporate back into the atmosphere, soak
Surface Water and Stream Development Surface Water The moment a raindrop falls to earth it begins its return to the sea. Once water reaches Earth s surface it may evaporate back into the atmosphere, soak
ENGINEERING HYDROLOGY
 ENGINEERING HYDROLOGY Prof. Rajesh Bhagat Asst. Professor Civil Engineering Department Yeshwantrao Chavan College Of Engineering Nagpur B. E. (Civil Engg.) M. Tech. (Enviro. Engg.) GCOE, Amravati VNIT,
ENGINEERING HYDROLOGY Prof. Rajesh Bhagat Asst. Professor Civil Engineering Department Yeshwantrao Chavan College Of Engineering Nagpur B. E. (Civil Engg.) M. Tech. (Enviro. Engg.) GCOE, Amravati VNIT,
SCOUR AND EROSION ALONGSIDE BANK PROTECTION WORK: CASE STUDIES FROM BANGLADESH
 SCOUR AND EROSION ALONGSIDE BANK PROTECTION WORK: CASE STUDIES FROM BANGLADESH KNUT OBERHAGEMANN Northwest Hydraulic Consultants Lt. 4823 99 th Street Edmonton, Alberta T6E 4Y1, Canada ABDUN NOOR Bangladesh
SCOUR AND EROSION ALONGSIDE BANK PROTECTION WORK: CASE STUDIES FROM BANGLADESH KNUT OBERHAGEMANN Northwest Hydraulic Consultants Lt. 4823 99 th Street Edmonton, Alberta T6E 4Y1, Canada ABDUN NOOR Bangladesh
COASTAL VULNERABILITY DUE TO SEA-LEVEL RISE HAZARDS IN THE BANGLADESH DELTA: BAND-AID
 Band-Aid Project NASA NASA ESA ESA JAXA NASA/DLR COASTAL VULNERABILITY DUE TO SEA-LEVEL RISE HAZARDS IN THE BANGLADESH DELTA: BAND-AID R. Rietbroek, B. Uebbing, C.K. Shum, V. Ballu, S. Calmant, J. Duan,
Band-Aid Project NASA NASA ESA ESA JAXA NASA/DLR COASTAL VULNERABILITY DUE TO SEA-LEVEL RISE HAZARDS IN THE BANGLADESH DELTA: BAND-AID R. Rietbroek, B. Uebbing, C.K. Shum, V. Ballu, S. Calmant, J. Duan,
Year 6. Geography. Revision
 Year 6 Geography Revision November 2017 Rivers and World knowledge How the water cycle works and the meaning of the terms evaporation, condensation, precipitation, transpiration, surface run-off, groundwater
Year 6 Geography Revision November 2017 Rivers and World knowledge How the water cycle works and the meaning of the terms evaporation, condensation, precipitation, transpiration, surface run-off, groundwater
A hydro-sedimentological view of the Samarco disaster, focusing in the Rio Doce estuary and adjacent coastal zone
 A hydro-sedimentological view of the Samarco disaster, focusing in the Rio Doce estuary and adjacent coastal zone Paulo Cesar Colonna Rosman Area of Coastal & Oceanographic Engineering Depart. Water Resources
A hydro-sedimentological view of the Samarco disaster, focusing in the Rio Doce estuary and adjacent coastal zone Paulo Cesar Colonna Rosman Area of Coastal & Oceanographic Engineering Depart. Water Resources
Term Knowledge Using and applying Grade Criteria Autumn 1 Assessment window October Natural hazards pose major risks to people and property.
 Assessment Schedule Year 9 2015/6 Term Knowledge Using and applying Grade Criteria Autumn 1 Assessment window October 2015 3.1.1.2 Tectonic Natural hazards pose major risks to people and property. Definition
Assessment Schedule Year 9 2015/6 Term Knowledge Using and applying Grade Criteria Autumn 1 Assessment window October 2015 3.1.1.2 Tectonic Natural hazards pose major risks to people and property. Definition
State Water Survey Division SURFACE WATER SECTION
 State Water Survey Division SURFACE WATER SECTION AT THE UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS Illinois Department of Energy and Natural Resources SWS Miscellaneous Publication 88 SEDIMENTATION OF POOL 19 ON THE MISSISSIPPI
State Water Survey Division SURFACE WATER SECTION AT THE UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS Illinois Department of Energy and Natural Resources SWS Miscellaneous Publication 88 SEDIMENTATION OF POOL 19 ON THE MISSISSIPPI
Figure 1. Which part of the river is labelled in Figure 1? a) Mouth b) Source c) Lower course d) channel
 Rivers 1. Study Figure 1 showing the long profile of a river Figure 1 A Which part of the river is labelled in Figure 1? a) Mouth b) Source c) Lower course d) channel (1 mark) 2. Complete the sentences
Rivers 1. Study Figure 1 showing the long profile of a river Figure 1 A Which part of the river is labelled in Figure 1? a) Mouth b) Source c) Lower course d) channel (1 mark) 2. Complete the sentences
Programmatic Approaches to Assessing and Mitigating Risk to Pipelines from Natural Forces
 Programmatic Approaches to Assessing and Mitigating Risk to Pipelines from Natural Forces 23 rd International Petroleum Environmental Conference New Orleans, Louisiana November 8-10, 2016 Introduction
Programmatic Approaches to Assessing and Mitigating Risk to Pipelines from Natural Forces 23 rd International Petroleum Environmental Conference New Orleans, Louisiana November 8-10, 2016 Introduction
Assessment of Hydro-Morphological Change of Surma-Kushiyara River System
 Journal of Modern Science and Technology Vol. 6. No. 1. March 2018 Issue. Pp.113-123 Assessment of Hydro-Morphological Change of Surma-Kushiyara River System Md. Sabbir Mostafa Khan 1* and Purnima Das
Journal of Modern Science and Technology Vol. 6. No. 1. March 2018 Issue. Pp.113-123 Assessment of Hydro-Morphological Change of Surma-Kushiyara River System Md. Sabbir Mostafa Khan 1* and Purnima Das
Summary. Streams and Drainage Systems
 Streams and Drainage Systems Summary Streams are part of the hydrologic cycle and the chief means by which water returns from the land to the sea. They help shape the Earth s surface and transport sediment
Streams and Drainage Systems Summary Streams are part of the hydrologic cycle and the chief means by which water returns from the land to the sea. They help shape the Earth s surface and transport sediment
SUB CATCHMENT AREA DELINEATION BY POUR POINT IN BATU PAHAT DISTRICT
 SUB CATCHMENT AREA DELINEATION BY POUR POINT IN BATU PAHAT DISTRICT Saifullizan Mohd Bukari, Tan Lai Wai &Mustaffa Anjang Ahmad Faculty of Civil Engineering & Environmental University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
SUB CATCHMENT AREA DELINEATION BY POUR POINT IN BATU PAHAT DISTRICT Saifullizan Mohd Bukari, Tan Lai Wai &Mustaffa Anjang Ahmad Faculty of Civil Engineering & Environmental University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY. Surface Water Movement
 Surface Water SECTION 9.1 Surface Water Movement In your textbook, read about surface water and the way in which it moves sediment. Complete each statement. 1. An excessive amount of water flowing downslope
Surface Water SECTION 9.1 Surface Water Movement In your textbook, read about surface water and the way in which it moves sediment. Complete each statement. 1. An excessive amount of water flowing downslope
MEANDER MIGRATION MODEL ASSESSMENT FOR THE JANUARY 2005 STORM, WHITMAN PROPERTY, SAN ANTONIO CREEK, VENTURA COUNTY, CALIFORNIA
 MEANDER MIGRATION MODEL ASSESSMENT FOR THE JANUARY 2005 STORM, WHITMAN PROPERTY, SAN ANTONIO CREEK, VENTURA COUNTY, CALIFORNIA Prepared by Eric Larsen, Ph.D. Mark Rains, Ph.D. October 2006 INTRODUCTION
MEANDER MIGRATION MODEL ASSESSMENT FOR THE JANUARY 2005 STORM, WHITMAN PROPERTY, SAN ANTONIO CREEK, VENTURA COUNTY, CALIFORNIA Prepared by Eric Larsen, Ph.D. Mark Rains, Ph.D. October 2006 INTRODUCTION
M14/3/GEOGR/SP2/ENG/TZ0/XX/Q GEOGRAPHY STANDARD LEVEL PAPER 2. Monday 19 May 2014 (morning) 1 hour 20 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
 M14/3/GEOGR/SP2/ENG/TZ0/XX/Q 22145203 GEOGRAPHY STANDARD LEVEL PAPER 2 Monday 19 May 2014 (morning) 1 hour 20 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do
M14/3/GEOGR/SP2/ENG/TZ0/XX/Q 22145203 GEOGRAPHY STANDARD LEVEL PAPER 2 Monday 19 May 2014 (morning) 1 hour 20 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do
CASE STUDY BINGA, PHILIPPINES
 SEDIMENT MANAGEMENT CASE STUDY BINGA, PHILIPPINES Key project features Name: Binga Country: Philippines Category: modify operating rule (focus or redistribute sediment); adaptive strategies Reservoir volume
SEDIMENT MANAGEMENT CASE STUDY BINGA, PHILIPPINES Key project features Name: Binga Country: Philippines Category: modify operating rule (focus or redistribute sediment); adaptive strategies Reservoir volume
CR AAO Bridge. Dead River Flood & Natural Channel Design. Mitch Koetje Water Resources Division UP District
 CR AAO Bridge Dead River Flood & Natural Channel Design Mitch Koetje Water Resources Division UP District Old County Road AAO Bridge Map courtesy of Marquette County Silver Lake Basin McClure Basin
CR AAO Bridge Dead River Flood & Natural Channel Design Mitch Koetje Water Resources Division UP District Old County Road AAO Bridge Map courtesy of Marquette County Silver Lake Basin McClure Basin
Do you think sediment transport is a concern?
 STREAM RESTORATION FRAMEWORK AND SEDIMENT TRANSPORT BASICS Pete Klingeman 1 What is Your Restoration Project Like? k? Do you think sediment transport is a concern? East Fork Lewis River, WA Tidal creek,
STREAM RESTORATION FRAMEWORK AND SEDIMENT TRANSPORT BASICS Pete Klingeman 1 What is Your Restoration Project Like? k? Do you think sediment transport is a concern? East Fork Lewis River, WA Tidal creek,
Appendix G.18 Hatch Report Pacific NorthWest LNG Lelu Island LNG Potential Impacts of the Marine Structures on the Hydrodynamics and Sedimentation
 Appendix G.18 Hatch Report Pacific NorthWest LNG Lelu Island LNG Potential Impacts of the Marine Structures on the Hydrodynamics and Sedimentation Patterns Project Memo H345670 To: Capt. David Kyle From:
Appendix G.18 Hatch Report Pacific NorthWest LNG Lelu Island LNG Potential Impacts of the Marine Structures on the Hydrodynamics and Sedimentation Patterns Project Memo H345670 To: Capt. David Kyle From:
D. MATHEMATICAL MODEL AND SIMULATION
 D. MATHEMATICAL MODEL AND SIMULATION D - i TABLE OF CONTENTS D.1 Objective of Model Development... D - 1 D.2 Selection of Software... D - 1 D.3 General Steps of Simulation by MOUSE... D - 1 D.4 Cases of
D. MATHEMATICAL MODEL AND SIMULATION D - i TABLE OF CONTENTS D.1 Objective of Model Development... D - 1 D.2 Selection of Software... D - 1 D.3 General Steps of Simulation by MOUSE... D - 1 D.4 Cases of
CASE STUDY BINGA, PHILIPPINES
 SEDIMENT MANAGEMENT CASE STUDY BINGA, PHILIPPINES Key project features Name: Binga Country: Philippines Category: modify operating rule (focus or redistribute sediment); adaptive strategies Binga hydropower
SEDIMENT MANAGEMENT CASE STUDY BINGA, PHILIPPINES Key project features Name: Binga Country: Philippines Category: modify operating rule (focus or redistribute sediment); adaptive strategies Binga hydropower
Suspended sediment yields of rivers in Turkey
 Erosion and Sediment Yield: Global and Regional Perspectives (Proceedings of the Exeter Symposium, July 1996). IAHS Publ. no. 236, 1996. 65 Suspended sediment yields of rivers in Turkey FAZLI OZTURK Department
Erosion and Sediment Yield: Global and Regional Perspectives (Proceedings of the Exeter Symposium, July 1996). IAHS Publ. no. 236, 1996. 65 Suspended sediment yields of rivers in Turkey FAZLI OZTURK Department
ENGINEERING APPROACHES TO SHORELINE PLACEMENT FROM COAST TO COAST
 ENGINEERING APPROACHES TO SHORELINE PLACEMENT FROM COAST TO COAST 237 237 237 217 217 217 200 200 200 0 0 0 163 163 163 131 132 122 80 119 27 252 174.59 83 36 118 110 135 120 112 92 56 62 102 130 Comparing
ENGINEERING APPROACHES TO SHORELINE PLACEMENT FROM COAST TO COAST 237 237 237 217 217 217 200 200 200 0 0 0 163 163 163 131 132 122 80 119 27 252 174.59 83 36 118 110 135 120 112 92 56 62 102 130 Comparing
In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. a. any form of water that falls to Earth s
 Skills Worksheet Concept Review In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. 1. condensation 2. floodplain 3. watershed 4. tributary 5. evapotranspiration
Skills Worksheet Concept Review In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. 1. condensation 2. floodplain 3. watershed 4. tributary 5. evapotranspiration
A STUDY ON HYDRODYNAMIC AND MORPHOLOGICAL BEHAVIOR OF GORAI RIVER USING DELFT 3D
 Proceedings of the 3 rd International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2016), 12~14 February 2016, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh (ISBN: 978-984-34-0265-3) A STUDY ON HYDRODYNAMIC
Proceedings of the 3 rd International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2016), 12~14 February 2016, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh (ISBN: 978-984-34-0265-3) A STUDY ON HYDRODYNAMIC
Department of Geography: Vivekananda College for Women. Barisha, Kolkata-8. Syllabus of Post graduate Course in Geography
 India: Regional Problems and Resource management Module 11 (Full Marks 50) Unit I: Region and Regionalisation 1.1 Various bases of regionalisation of India; problems of identification and delineation.
India: Regional Problems and Resource management Module 11 (Full Marks 50) Unit I: Region and Regionalisation 1.1 Various bases of regionalisation of India; problems of identification and delineation.
