Review of IWM study of river bank erosion management in Polder 29, Khulna, Bangladesh
|
|
|
- Sydney Patterson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review of IWM study of river bank erosion management in Polder 29, Khulna, Bangladesh
2
3 Review of IWM study of river bank erosion management in Polder 29, Khulna, Bangladesh Erik Mosselman Deltares, 2016, B
4
5
6
7 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Points of review Formulation of the assignment Data collection and data analysis Numerical modelling Selection of measures Design considerations Editorial comments 10 3 Conclusions and recommendations Review of report by IWM (2015) Advice on possibilities for low-cost interventions for bank protection 13 4 References 15 Review of IWM study of river bank erosion management in Polder 29, Khulna, Bangladesh i
8
9 1 Introduction Blue Gold is a collaboration programme between the Government of the Netherlands and the Government of Bangladesh. Its overall objective is to reduce poverty for 150,000 households living in 160,000 ha of selected coastal polders in Khulna, Satkhira and Patuakhali by creating a healthy living environment and a sustainable socio-economic development. One of these coastal polders, Polder 29, has been experiencing bank erosion problems for a long time. The embankment was retired several times due to severe erosion along the right bank of the Lower Bhadra river near Chandgar and Baroaria. Blue Gold engaged the Institute of Water Modelling for a study to (i) identify the underlying causes of erosion; (ii) find the extent of erosion in order to control the erosion by providing mitigation and protective measures; and (iii) develop a comprehensive, ecologically sustainable and innovative adaptive approach for the planning, design and implementation of the erosion protection work on the proposed site. The outputs of the study were specified to be: Flow conditions in the peripheral rivers of Polder 29; Erosion and deposition pattern based on model results and data analysis; Area vulnerable to erosion; Critical location for erosion; Most appropriate approach for erosion protection; Comprehensive design parameters on the basis of the developed, updated, calibrated, validated and simulated model results; Detailed design of river bank protection work and allied works; Cost estimate of protective work; Recommendation on the monitoring and maintenance needs on the basis of response analysis. The Institute of Water Modelling reported the results of its study in a draft report dated 10 November 2015 (IWM, 2015). Blue Gold engaged Deltares to review the report by IWM (2015), to evaluate the data, to review selected experiences in Bangladesh with alternative measures of bank protection, and to formulate advice on low-cost interventions for bank protection. The findings are reported in the present document. Review of IWM study of river bank erosion management in Polder 29, Khulna, Bangladesh 1 of 4
10
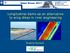
11 2 Points of review 2.1 Formulation of the assignment The current management of river bank erosion along Polder 29 is based on the principles of adaptive delta management and living with water. Wherever bank erosion threatens the embankments, the embankments are retired to a new location. The evolution of river planforms in the 25 years between 1984 and 2010, presented in Figure 2.1 of the present document, demonstrates that the river banks are mostly relatively stable. The planimetric changes due to bank erosion are small compared to the planimetric changes of the major rivers Brahmaputra-Jamuna, Ganges and Padma. The current adaptive approach thus seems feasible. The objective of the study, however, is to develop an approach for erosion protective work, irrespective of the costs involved. This leads to proposing bank protection over a length of in total 3 km. The capital investment for this protection can be estimated roughly to be in the order of a million euro, entailing subsequent maintenance costs in the order of 100,000 euro per year. The report does not present any economic underpinning for this solution. The costs have been compared neither with the annual damage due to erosion nor with the costs of retiring the embankments. Such a comparison is recommended for a good evaluation of different alternative solutions. Figure 2.1. General river planform development around southern part of Polder 29 in period (source: Landsat images at Section 1.4 includes the following products in a list of study outputs: detailed design of river bank protection works; validated model results, cost estimate of protective work; and recommendation of the monitoring and maintenance needs on the basis of response analysis. None of these products are presented in the report. Review of IWM study of river bank erosion management in Polder 29, Khulna, Bangladesh 3 of 4
12 2.2 Data collection and data analysis IWM (2015) analyzed river planform evolution on satellite images from 2000 to In order to extend the period of observation, Figure 2.1 of the present document presents the river planform evolution on satellite images from 1984 to The river banks are mostly found to be relatively stable, with the exception of the bank at Chandgar. Here prominent bank erosion occurs in relation to the straightening of a river bend. Figure 2.2 of the present document shows this development along with an interpretation of the associated main bank erosion. Extrapolation of this development suggests that substantial bank erosion may proceed to Jaliakhali and even the bank East of Baroaria. Figure 5.8 shows, however, that no protection is planned along that vulnerable bank. Figure 2.2. Local river planform development (top) and corresponding interpretation of main bank erosion (bottom) at Chandgar in period (source: Landsat images at Section states on page 34 that available satellite images of 2000, 2009 and 2015 were analyzed. However, Section mentions on page 22 the purchase of satellite images of 2011 and Why was the 2011 image excluded from the analysis? Figure 5.4 shows banklines, but its caption suggests it shows a cross-sectional profile. Page 38 concludes from an image analysis that the river shifted towards East. This must be towards West. 4 of 4 Review of IWM study of river bank erosion management in Polder 29, Khulna, Bangladesh
13 According to page 42, the locations of deep scour holes are among the criteria for selecting areas that are vulnerable to erosion. However, the report does not show any information on these locations. 2.3 Numerical modelling The first equation of Section 4.1 represents conservation of mass. Hence S is not an energy source-dissipation term but a source term for mass supply or withdrawal. Flow velocities have overbars in the equations of Section 4.1, but these overbars are not explained. The overbar is missing in the second term of the second equation. The minus sign at the end of the second equation suggests that the equation is not complete. The pressure, p a, is not explained in the text. On the other hand, sy, by and T ij are explained in the text but do not appear in the equations. The fourth paragraph of Section 4.1 refers to Equations 13 and 14. However, the equations in the report do not have numbers. The fourth paragraph of Section 4.1 refers to processes in the near-shore coastal zone. This is not appropriate for the present study on river bank erosion. Similarly, one would expect a bankline instead of a coastline in the first paragraph of Section 4.2. Section 4.3 has the title Calibration and validation. However, the section presents only a calibration, no verification or validation. According to Section 6.4, the model results lead to the conclusion that groynes making an angle of 40º to the bankline are the most suitable for bank protection. It is not clear, however, how these groynes have been represented on the computational grid of Figure 4.1. Deviations between groyne alignments and grid lines produce numerical artefacts that do not have any physical meaning. It would be useful to reflect on the information that can be derived from the numerical modelling. The modelling provides good insight in the present conditions, but it does not provide precise information on the near-bank flow conditions after implementation of the permeable groynes, because it does not take into account the morphological changes induced by the groynes. A morphological computation might be proposed, but that would not solve this as it would reproduce neither the local scour around the piles nor the resulting attraction of the thalweg towards the bank upstream and downstream of the protection (Mosselman & Sloff, 2002). 2.4 Selection of measures The selection of measures has not considered the full range of possible options. Considerations of costs are missing too. Table 2.1 might be helpful in this respect. Review of IWM study of river bank erosion management in Polder 29, Khulna, Bangladesh 5 of 4
14 Table 2.1. Costs of structures built on Brahmaputra-Jamuna river between 1994 and 2000 (courtesy Dr Knut Oberhagemann, Northwest Hydraulic Consultants, published previously by Mosselman, 2006). Location Structure Total cost (million US$) Protected length (km) Cost per protected length (million US$/km) Banghabandhu two guide bunds with Bridge revetment Sirajganj revetment Sariakandi groynes Bahadurabad revetment Bhuapur revetment Ghutail revetment Kamarjani permeable groynes Kazipur groynes Shovgacha groynes Experiences with bank protection and river training in Bangladesh in the past 20 years have shown that revetment structures with geobags are among the most effective and costeffective solutions. Based on these experiences, groynes, whether permeable or impermeable, are no longer recommended. River bank protection using geobags is one of the most innovative recent developments in Bangladesh, owing much to their promoter Dr Knut Oberhagemann of Northwest Hydraulic Consultants. However, the report does not consider geobags. The report explains the functioning of bottom vanes from helical flow, diversion of slowermoving bottom water towards the bank, sediment pick-up from the suction side of vanes and sediment deposition at the pressure side. In reality, the diversion of slower-moving water hardly plays a role. The other mechanisms do play a role, but do not represent the full picture. A field test of bottom vanes in the Elanjani river (Tangail) by BUET and Delft University of Technology (Hossain & Mosselman, 2006) has shown that overall flow deflection and increased turbulence are important mechanisms too. Figure 2.3 of the present document shows the bottom vanes of the field test under construction. This successful application in Bangladesh is worth mentioning in addition to the failed application in the Meghna Estuary on page 44. Nonetheless, the experiences from the Elanjani river confirm the IWM (2015) assessment that bottom vanes are not suitable for the rivers around Polder 29. Their applicability is limited to relatively small rivers or river channels with a well-defined geometry that experiences only slow changes in time. 6 of 4 Review of IWM study of river bank erosion management in Polder 29, Khulna, Bangladesh
15 Figure 2.3. Bottom vanes under construction in the Elanjani river (Tangail). For bandalling, page 45 refers to recent experiences on the Ganges in India. However, welldocumented experiences are available from pilot tests on the Brahmaputra-Jamuna river in Bangladesh too (Jamuna Test Works Consultants, 2001a). Figure 2.4 of the present document shows the high-water bandals that were tested in this framework at Katlamari. Similarly, page 46 refers to experiences with permeable groynes in Europe and North America, whereas one of the most extensive and well-documented field tests has been carried out on the Brahmaputra-Jamuna river in Bangladesh (Jamuna Test Works Consultants, 2001a). Figures 2.5 and 2.6 of the present document show the corresponding permeable groyne test structures at Kamarjani. It is recommended to review and use the lessons learnt in these Bangladeshi field tests when selecting and designing bank protection along the rivers at Polder 29. Page 46 proposes the absence of dead water zones as an advantage of permeable groynes. However, the areas between impermeable groynes do not present dead water zones either. The flow in these areas circulates in eddies and is refreshed by turbulent mixing in the vortex street that arises at the interface with the main flow. Review of IWM study of river bank erosion management in Polder 29, Khulna, Bangladesh 7 of 4
16 Figure 2.4. High-water bandal test structure in the Brahmaputra-Jamuna river at Katlamari. Figure 2.5. Permeable groyne test structure in the Brahmaputra-Jamuna river at Kamarjani in the dry season. 8 of 4 Review of IWM study of river bank erosion management in Polder 29, Khulna, Bangladesh
17 Figure 2.6. Permeable groyne test structure in the Brahmaputra-Jamuna river at Kamarjani in the wet season. 2.5 Design considerations Figure 5.8 shows that no protection is planned along the bank at Jaliakhali. Extrapolation of the interpretation of bankline development in Figure 2.2 of the present document suggests, however, that substantial erosion may be expected there in the near future. This erosion might proceed even further up to the bank East of Baroaria. The upstream and downstream terminations of river bank protections require special care, as they tend to become exposed by continued bank erosion. As a result, they are attacked from behind, upstream because the presence of the bank protection attracts the thalweg towards the bank, and downstream because flow separation may generate an eddy with returning flow. Moreover, in case of a continuous revetment, flow separation may increase turbulence and thereby produce additional local scour at the downstream termination. The report does not present any information on the design of these upstream and downstream terminations. The oblique groynes at the upstream and downstream ends of the bank protection structures in Figures 6.1 and 6.2 can be expected to increase the vulnerability of the terminations. They promote outflanking, which would enhance the bank erosion around the groynes at the terminations (Die Moran et al, 2013). Page 46 states that the permeable groynes can be constructed with wooden piles, without providing any considerations on the required length of the piles. The river near the bank at Chandgar is about 12 m deep. This depth will increase around the piles due to local scour. Additionally, the piles will have to penetrate sufficiently deep into the river bed for structural stability. Another point on page 46 is that the diameter of these long wooden piles is 1 m. This may pose serious challenges to pile driving. Review of IWM study of river bank erosion management in Polder 29, Khulna, Bangladesh 9 of 4
18 More generally, the report does not provide information on the considerations behind the 50 m groyne length, 50 m groyne spacing and 1 m diameter. No relation is given between the hydraulic loads and the details of the design. It is recommended to use the guidelines and design manual for standardized bank protection structures by Jamuna Test Works Consultants (2001b), albeit with caution because much of its contents has been derived from a single project without thorough testing for other cases. Apparently the guidelines and design manual have been updated later. Dr Knut Oberhagemann of Northwest Hydraulic Consultants might be the best informed person on this. Page 55 states that groynes making an angle of 40º to the bankline are the most suitable for bank protection. This does not comply with common practices in river training. Apparently this statement is based on the results of hydrodynamic modelling that excludes 3D flow effects, morphological response and local scour. Moreover, Section 2.3 of the present document argues that the representation of these groynes on the computational grid of Figure 4.1 may have produced numerical artefacts without physical meaning. Page 55 recommends the use of top-blocked permeable groynes as they will provide a deeper navigation channel. This will require special attention to the floating debris that will pile up against these blocked tops during floods, exerting additional loads on the structure. 2.6 Editorial comments The present review did not include close reading to identify all errors in spelling and grammar. Just a few cases are noted because they would not be found by a spelling checker (e.g. ecosounder must be echo-sounder on page 13). Furthermore, some general guidance is given. Romanization of Bengali names has not been applied consistently. Although there is no official standard for transcription, it is recommended to be consistent at least within the bounds of a single report. The present report by IWM (2015) uses the names Baro-Aria (p. 4), Baraharia (p. 6) and Baroaria (p. 13) for the same village. Similarly it uses Chandgar (pp. 4, 6) next to Chadgar (pp. 15, 30, 32) and Cgadgar (p. 30), Salta (p. 6) next to Shalta (pp. 7, 11), and Gengrail (p. 6) next to Gangrail (p. 7) and Gangreil (pp. 18, 19). It is recommended to observe the rules of science and technology for the notations of physical units. This implies: A space is compulsory between number and unit. For instance, 100m and 250m must be 100 m and 250 m on page 13; The symbol for hectare is ha, not Ha, cf. pages 6, 36 and 38; A valid unit of distance is km (kilometre), not Km (Kelvin metre), cf. page 15; Exponents must be written as a superscript. Hence 2228m3/sec must be 2228 m 3 /s on page 29; The symbol for second is s instead of sec. Hence 2228m3/sec must be 2228 m 3 /s on page 29; A double slash is not allowed. Hence ha/km/yr must be ha/(km.yr), ha/(km yr) or ha 1 km -1 yr -1, cf. pages 36 and 38; 10 of 4 Review of IWM study of river bank erosion management in Polder 29, Khulna, Bangladesh
19 Section states that the dry-period tidal prism in the Lower Bhadra is about 50 Mm 3 = 50 cubic megametres = m 3. This might be visualized as the volume of a 50,000 km high tower on a square surface of 1,000 1,000 km 2. This is incorrect. Correct ways of writing the intended volume are 50 million m 3 or 50 hm 3. The report contains various literature references, such as SWAIWRMP (2004), O Brien (1931, 1969), Lily (1989) and Khaleduzzaman (2004), but no list of references. This list needs to be added. Page 13: eco-sounder must be echo-sounder. The term bathymetric survey on page 15 suggests that the measurements focused on water depths. Figure 5.3 shows, however, that river bed elevations have been measured with respect to Public Works Datum (PWD). This is indeed the correct input for the model. It is therefore recommended to use the term bed topography survey instead of bathymetric survey, or to explain how bed topographies have been derived from bathymetries. Page 16: Aqoustic must be Acoustic. Presumably one of the two last columns of Table 3.2 on page 18 must refer to ebb tide instead of flood tide. Page 18, Section 3.2.4, line 4: gradation must be spatial distribution. The report uses the different terms groyne, groin and spur for the same transverse river training structure. For easier readability it is recommended to use one of the three terms only. The spelling groin is correct in the United States of America, but not in Europe and Canada. In Europe and Canada, it is groyne that refers to a transverse river training structure, whereas groin refers to the part of the body where the two legs meet. Important places such as Chandgar and Baroaria are missing in the study area map of Figure 2.1. They are also not found in the maps in Figures 3.1, 4.1, 5.1 and 5.2. The first time their locations are shown is in Figure 5.3. It is recommended to show them in the beginning of the report. The purpose of Section 2.4 is not clear. The formula for the effect of salinity on the settling of sediments does not play any role in the remainder of the report. Review of IWM study of river bank erosion management in Polder 29, Khulna, Bangladesh 11 of 4
20
21 3 Conclusions and recommendations 3.1 Review of report by IWM (2015) The report provides good insight in the conditions on the rivers at Polder 29, based on field measurements and 2D depth-averaged hydrodynamic modelling. The numerical modelling does not provide precise information on the near-bank flow conditions after implementation of the permeable groynes, because the morphological changes induced by the groynes are not taken into account. The report does not present any economic underpinning of the proposed bank protection works. It also does not present any in-depth comparison of alternative solutions, or any indepth structural design. It is therefore recommended to set up the project from a wider perspective that includes economic underpinning and structural design issues in a more thorough manner. 3.2 Advice on possibilities for low-cost interventions for bank protection Flat slopes and accreting environments offer possibilities for Building-with-Nature-type of solutions. Figure 2.2 of the present document suggests that the wide river area at Chandgar might be suitable for this. It might be possible to dredge the dying bend of this area and to dump the dredged material in the channel along the actively eroding bank. A feasibility study for this solution is recommended. Review of IWM study of river bank erosion management in Polder 29, Khulna, Bangladesh 13 of 4
22
23 4 References Die Moran, A, K. El Kadi Abderrazzak, E. Mosselman, H. Habersack, F. Lebert, D. Aelbrecht & E. Laperrousaz (2013), Physical model experiments for sediment supply to the old Rhine through induced bank erosion. International Journal of Sediment Research, Vol.28, No.4, pp , DOI: /S (14) Hossain, M.M. & E. Mosselman (2006), Research Project No 3: Experimental research on the effect of bottom vane on river flow and morphology. Final Technical Report, BUET-DUT Linkage Project phase III, Capacity building in the field of water resources engineering and management in Bangladesh, BUET & TU Delft, May IWM (2015), The study of river bank erosion management in Polder 29, Khulna. Draft final report, Institute of Water Modelling, Dhaka, 10 November Jamuna Test Works Consultants (2001a), Bank Protection and river training (AFPM) pilot project FAP 21/22; Final project evaluation report. Report to Government of Bangladesh, Ministry of Water Resources, Water Resources Planning Organization. Volume I: Main report, Part A: Bank protection pilot project, Part B: River training (AFPM) pilot project. Volume II: Annex 1: Morphological investigations, Annex 2: Socio-economic aspects, Annex 3: Ecological assessment. Volume III: Annex 4: The groyne test structure; design report, Annex 5: The groyne test structure; procurement and construction report. Volume IV: Annex 6: The groyne test structure; monitoring report, Annex 7: The groyne test structure; evaluation of hydraulic loads and river response. Volume V: Annex 8: The revetment test structure; design report, Annex 9: The revetment test structure; procurement and construction report. Volume VI: Annex 10: The revetment test structure; monitoring report, Annex 11: The revetment test structure; evaluation of hydraulic loads and river response. Jamuna Test Works Consultants (2001b), Guidelines and design manual for standardized bank protection structures. Government of Bangladesh, Ministry of Water Resources, Water Resources Planning Organization, December Mosselman, E. & C.J. Sloff (2002), Effect of local scour holes on macroscale river morphology. In: River Flow 2002, Eds. D. Bousmar & Y. Zech, Proc. Int. Conf. Fluvial Hydraulics, Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, 4-6 September 2002, pp Mosselman, E. (2006), Bank protection and river training along the braided Brahmaputra- Jamuna River, Bangladesh. In: Braided rivers; Process, deposits, ecology and management, Eds. G.H. Sambrook Smith, J. Best, C.S. Bristow & G.E. Petts, Spec. Publ. No.36 of the Int. Assoc. of Sedimentologists, Blackwell Publ., ISBN-10: , pp Review of IWM study of river bank erosion management in Polder 29, Khulna, Bangladesh 15 of 4
SCOUR AND EROSION ALONGSIDE BANK PROTECTION WORK: CASE STUDIES FROM BANGLADESH
 SCOUR AND EROSION ALONGSIDE BANK PROTECTION WORK: CASE STUDIES FROM BANGLADESH KNUT OBERHAGEMANN Northwest Hydraulic Consultants Lt. 4823 99 th Street Edmonton, Alberta T6E 4Y1, Canada ABDUN NOOR Bangladesh
SCOUR AND EROSION ALONGSIDE BANK PROTECTION WORK: CASE STUDIES FROM BANGLADESH KNUT OBERHAGEMANN Northwest Hydraulic Consultants Lt. 4823 99 th Street Edmonton, Alberta T6E 4Y1, Canada ABDUN NOOR Bangladesh
Optimization of Alignment of Proposed Canal and Revetment in the old Madhumati River Using Physical Modelling: A Case Study
 International Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 2014, 3(2): 68-75 DOI: 10.5923/j.ijhe.20140302.03 Optimization of Alignment of Proposed Canal and Revetment in the old Madhumati River Using Physical Modelling:
International Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 2014, 3(2): 68-75 DOI: 10.5923/j.ijhe.20140302.03 Optimization of Alignment of Proposed Canal and Revetment in the old Madhumati River Using Physical Modelling:
Domino Effect of River Training in Large Sand-Bed Braiding Rivers
 6 th International Conference on Structural Engineering and Construction Management 2015, Kandy, Sri Lanka, 11 th -13 th December 2015 SECM/15/176 Domino Effect of River Training in Large Sand-Bed Braiding
6 th International Conference on Structural Engineering and Construction Management 2015, Kandy, Sri Lanka, 11 th -13 th December 2015 SECM/15/176 Domino Effect of River Training in Large Sand-Bed Braiding
Countermeasure Calculations and Design
 Countermeasure Calculations and Design Summarized from Bridge Scour and Stream Instability Countermeasures, Experience, Selection, and Design Guidance, Second Edition, Publication No. FHWA NHI 01-003,
Countermeasure Calculations and Design Summarized from Bridge Scour and Stream Instability Countermeasures, Experience, Selection, and Design Guidance, Second Edition, Publication No. FHWA NHI 01-003,
MORPHOLOGICAL PROCESSES AND EFFECTIVE RIVER EROSION MANAGEMENT: A CASE STUDY OF THE ARIAL KHAN RIVER IN BANGLADESH
 MORPHOLOGICAL PROCESSES AND EFFECTIVE RIVER EROSION MANAGEMENT: A CASE STUDY OF THE ARIAL KHAN RIVER IN BANGLADESH Jakia Akter* 1, Maminul Haque Sarker, Preetha Haque 1 Center for environmental and Geographic
MORPHOLOGICAL PROCESSES AND EFFECTIVE RIVER EROSION MANAGEMENT: A CASE STUDY OF THE ARIAL KHAN RIVER IN BANGLADESH Jakia Akter* 1, Maminul Haque Sarker, Preetha Haque 1 Center for environmental and Geographic
An environmentally sensitive erosion control technique in the Mekong River Delta: 10 years on
 7 th Australian Stream Management Conference - Full Paper An environmentally sensitive erosion control technique in the Mekong River Delta: 10 years on John Tilleard 1, Tony Ladson 2 1 Moroka Pty Ltd,
7 th Australian Stream Management Conference - Full Paper An environmentally sensitive erosion control technique in the Mekong River Delta: 10 years on John Tilleard 1, Tony Ladson 2 1 Moroka Pty Ltd,
A STUDY OF LOCAL SCOUR AT BRIDGE PIERS OF EL-MINIA
 A STUDY OF LOCAL SCOUR AT BRIDGE PIERS OF EL-MINIA Dr. Gamal A. Sallam 1 and Dr. Medhat Aziz 2 ABSTRACT Bridges are critical structures that require a substantial investment to construct and serve an important
A STUDY OF LOCAL SCOUR AT BRIDGE PIERS OF EL-MINIA Dr. Gamal A. Sallam 1 and Dr. Medhat Aziz 2 ABSTRACT Bridges are critical structures that require a substantial investment to construct and serve an important
Development and application of demonstration MIKE 21C morphological model for a bend in Mekong River
 Development and application of demonstration MIKE 21C morphological model for a bend in Mekong River September 2015 0 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Data collection... 3 2.1 Additional data...
Development and application of demonstration MIKE 21C morphological model for a bend in Mekong River September 2015 0 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Data collection... 3 2.1 Additional data...
A STUDY ON HYDRODYNAMIC AND MORPHOLOGICAL BEHAVIOR OF PADMA RIVER USING DELFT3D MODEL
 Proceedings of the 3 rd International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2016), 12~14 February 2016, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh (ISBN: 978-984-34-0265-3) A STUDY ON HYDRODYNAMIC
Proceedings of the 3 rd International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2016), 12~14 February 2016, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh (ISBN: 978-984-34-0265-3) A STUDY ON HYDRODYNAMIC
Annual transport rates at two locations on the fore-slope.
 Sediment Transport by Currents Fore-slope Sediment transport rates and sediment concentrations were computed from the hydrodynamic model runs as well as from direct measurements of current velocities at
Sediment Transport by Currents Fore-slope Sediment transport rates and sediment concentrations were computed from the hydrodynamic model runs as well as from direct measurements of current velocities at
RIVER BANK EROSION AND SUSTAINABLE PROTECTION STRATEGIES
 B-11 Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion 2008 RIVER BANK EROSION AND SUSTAINABLE PROTECTION STRATEGIES Md.. Shofiul Islam 1 1 Scientific Officer, River Research Institute (RRI) (Faridpur
B-11 Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion 2008 RIVER BANK EROSION AND SUSTAINABLE PROTECTION STRATEGIES Md.. Shofiul Islam 1 1 Scientific Officer, River Research Institute (RRI) (Faridpur
Use of morphological simulation for delineating navigation route in Ganges-Jamuna confluence
 Use of morphological simulation for delineating navigation route in Ganges-Jamuna confluence Muhammed A. Bhuiyan, Professor, Dept. of Water Resources Engg., Bangladesh Univ. of Engg. & Technology (BUET),
Use of morphological simulation for delineating navigation route in Ganges-Jamuna confluence Muhammed A. Bhuiyan, Professor, Dept. of Water Resources Engg., Bangladesh Univ. of Engg. & Technology (BUET),
Texas A & M University and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation Hydrologic Modeling Inventory Model Description Form
 Texas A & M University and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation Hydrologic Modeling Inventory Model Description Form JUNE, 1999 Name of Model: Two-Dimensional Alluvial River and Floodplain Model (MIKE21 CHD & CST)
Texas A & M University and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation Hydrologic Modeling Inventory Model Description Form JUNE, 1999 Name of Model: Two-Dimensional Alluvial River and Floodplain Model (MIKE21 CHD & CST)
Longitudinal dams as an alternative to wing dikes in river engineering. Fredrik Huthoff
 Longitudinal dams as an alternative to wing dikes in river engineering Fredrik Huthoff Contents Introduction Why consider longitudinal dams? Room for the river in the Netherlands The pilot study The Dutch
Longitudinal dams as an alternative to wing dikes in river engineering Fredrik Huthoff Contents Introduction Why consider longitudinal dams? Room for the river in the Netherlands The pilot study The Dutch
Appendix G.19 Hatch Report Pacific NorthWest LNG Lelu Island LNG Maintenance Dredging at the Materials Offloading Facility
 Appendix G.19 Hatch Report Pacific NorthWest LNG Lelu Island LNG Maintenance Dredging at the Materials Offloading Facility Project Memo H345670 To: Capt. David Kyle From: O. Sayao/L. Absalonsen December
Appendix G.19 Hatch Report Pacific NorthWest LNG Lelu Island LNG Maintenance Dredging at the Materials Offloading Facility Project Memo H345670 To: Capt. David Kyle From: O. Sayao/L. Absalonsen December
Design of Levee Breaches in Sheltered Water for Flood Risk Reduction & Marsh Restoration ASFMP; June 5, 2014 Presented By:
 Design of Levee Breaches in Sheltered Water for Flood Risk Reduction & Marsh Restoration ASFMP; June 5, 2014 Presented By: Rohin Saleh Alameda County Flood Control District Matt Powers, P.E. GEI Consultants
Design of Levee Breaches in Sheltered Water for Flood Risk Reduction & Marsh Restoration ASFMP; June 5, 2014 Presented By: Rohin Saleh Alameda County Flood Control District Matt Powers, P.E. GEI Consultants
Appendix O. Sediment Transport Modelling Technical Memorandum
 Appendix O Sediment Transport Modelling Technical Memorandum w w w. b a i r d. c o m Baird o c e a n s engineering l a k e s design r i v e r s science w a t e r s h e d s construction Final Report Don
Appendix O Sediment Transport Modelling Technical Memorandum w w w. b a i r d. c o m Baird o c e a n s engineering l a k e s design r i v e r s science w a t e r s h e d s construction Final Report Don
Indigenous technical knowledge for bank erosion and flood management
 2017 APEC Typhoon Symposium, May 2 4, 2017, GIS NTU Convention Center, Taipei Indigenous technical knowledge for bank erosion and flood management Hao Zhang 1) and Hajime Nakagawa 2) 1) Associate Professor,
2017 APEC Typhoon Symposium, May 2 4, 2017, GIS NTU Convention Center, Taipei Indigenous technical knowledge for bank erosion and flood management Hao Zhang 1) and Hajime Nakagawa 2) 1) Associate Professor,
River training works for Padma multipurpose bridge, Bangladesh
 IABSE-JSCE Joint Conference on Advances in Bridge Engineering-II, August 8-10, 2010, Dhaka, Bangladesh. ISBN: 978-984-33-1893-0 Amin, Okui, Bhuiyan (eds.) www.iabse-bd.org River training works for Padma
IABSE-JSCE Joint Conference on Advances in Bridge Engineering-II, August 8-10, 2010, Dhaka, Bangladesh. ISBN: 978-984-33-1893-0 Amin, Okui, Bhuiyan (eds.) www.iabse-bd.org River training works for Padma
UNDERSTANDING FALLING APRONS EXPERIENCE FROM THE LOWER BRAHMAPUTRA / JAMUNA RIVER
 B-9 Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion 2008 UNDERSTANDING FALLING APRONS EXPERIENCE FROM THE LOWER BRAHMAPUTRA / JAMUNA RIVER Knut OBERHAGEMANN 1, Philemon DIGGELMANN 2 and MUKHLES-UZ-ZAMAN
B-9 Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion 2008 UNDERSTANDING FALLING APRONS EXPERIENCE FROM THE LOWER BRAHMAPUTRA / JAMUNA RIVER Knut OBERHAGEMANN 1, Philemon DIGGELMANN 2 and MUKHLES-UZ-ZAMAN
CONSIDERATION OF SOIL PROPERTIES FOR STABILITY ANALYSES OFPADMA AND JAMUNA RIVERBANK
 CONSIDERATION OF SOIL PROPERTIES FOR STABILITY ANALYSES OFPADMA AND JAMUNA RIVERBANK M.S. Islam 1*, L. Sarker 1, M.A. Islam 1, M.A. Islam 1 & R. Karim 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering, Bangladesh University
CONSIDERATION OF SOIL PROPERTIES FOR STABILITY ANALYSES OFPADMA AND JAMUNA RIVERBANK M.S. Islam 1*, L. Sarker 1, M.A. Islam 1, M.A. Islam 1 & R. Karim 2 1 Department of Civil Engineering, Bangladesh University
Prediction of changes in tidal system and deltas at Nakdong estuary due to construction of Busan new port
 Prediction of changes in tidal system and deltas at Nakdong estuary due to construction of Busan new port H. Gm1 & G.-Y. park2 l Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering, Kookmin University, Korea
Prediction of changes in tidal system and deltas at Nakdong estuary due to construction of Busan new port H. Gm1 & G.-Y. park2 l Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering, Kookmin University, Korea
THE HYDRAULIC PERFORMANCE OF ORIENTED SPUR DIKE IMPLEMENTATION IN OPEN CHANNEL
 Tenth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC10 2006, Alexandria, Egypt 281 THE HYDRAULIC PERFORMANCE OF ORIENTED SPUR DIKE IMPLEMENTATION IN OPEN CHANNEL Karima Attia 1 and Gamal El Saied 2 1
Tenth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC10 2006, Alexandria, Egypt 281 THE HYDRAULIC PERFORMANCE OF ORIENTED SPUR DIKE IMPLEMENTATION IN OPEN CHANNEL Karima Attia 1 and Gamal El Saied 2 1
Appendix G.18 Hatch Report Pacific NorthWest LNG Lelu Island LNG Potential Impacts of the Marine Structures on the Hydrodynamics and Sedimentation
 Appendix G.18 Hatch Report Pacific NorthWest LNG Lelu Island LNG Potential Impacts of the Marine Structures on the Hydrodynamics and Sedimentation Patterns Project Memo H345670 To: Capt. David Kyle From:
Appendix G.18 Hatch Report Pacific NorthWest LNG Lelu Island LNG Potential Impacts of the Marine Structures on the Hydrodynamics and Sedimentation Patterns Project Memo H345670 To: Capt. David Kyle From:
LOCAL SCOUR INDUCED BY 3D FLOW AROUND ATTRACTING AND DEFLECTING GROINS
 LOCAL SCOUR INDUCED BY 3D FLOW AROUND ATTRACTING AND DEFLECTING GROINS TAISUKE ISHIGAKI Disaster Prevention Research Institute, Kyoto University Fushimi, Kyoto 612-8235, Japan YASUYUKI BABA Disaster Prevention
LOCAL SCOUR INDUCED BY 3D FLOW AROUND ATTRACTING AND DEFLECTING GROINS TAISUKE ISHIGAKI Disaster Prevention Research Institute, Kyoto University Fushimi, Kyoto 612-8235, Japan YASUYUKI BABA Disaster Prevention
Stream Geomorphology. Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012
 Stream Geomorphology Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012 What Functions do Healthy Streams Provide? Flood mitigation Water supply Water quality Sediment storage and transport Habitat Recreation Transportation
Stream Geomorphology Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012 What Functions do Healthy Streams Provide? Flood mitigation Water supply Water quality Sediment storage and transport Habitat Recreation Transportation
COASTAL VULNERABILITY DUE TO SEA-LEVEL RISE HAZARDS IN THE BANGLADESH DELTA: BAND-AID
 Band-Aid Project NASA NASA ESA ESA JAXA NASA/DLR COASTAL VULNERABILITY DUE TO SEA-LEVEL RISE HAZARDS IN THE BANGLADESH DELTA: BAND-AID R. Rietbroek, B. Uebbing, C.K. Shum, V. Ballu, S. Calmant, J. Duan,
Band-Aid Project NASA NASA ESA ESA JAXA NASA/DLR COASTAL VULNERABILITY DUE TO SEA-LEVEL RISE HAZARDS IN THE BANGLADESH DELTA: BAND-AID R. Rietbroek, B. Uebbing, C.K. Shum, V. Ballu, S. Calmant, J. Duan,
WORKSHOP #2 [Modeling and Sediment Transfers Review of alternative solutions] Bucharest 07 October 2015
![WORKSHOP #2 [Modeling and Sediment Transfers Review of alternative solutions] Bucharest 07 October 2015 WORKSHOP #2 [Modeling and Sediment Transfers Review of alternative solutions] Bucharest 07 October 2015](/thumbs/82/85703998.jpg) STUDIU DE FEZABILITATE PENTRU SOLUŢII TEHNICE ALTERNATIVE/COMPLEMENTARE PRIVIND LUCRĂRILE CE SE VOR EXECUTA ÎN PUNCTUL CRITIC 01 BALA DIN CADRUL PROIECTULUI ÎMBUNĂTĂŢIREA CONDIŢIILOR DE NAVIGAŢIE PE DUNĂRE
STUDIU DE FEZABILITATE PENTRU SOLUŢII TEHNICE ALTERNATIVE/COMPLEMENTARE PRIVIND LUCRĂRILE CE SE VOR EXECUTA ÎN PUNCTUL CRITIC 01 BALA DIN CADRUL PROIECTULUI ÎMBUNĂTĂŢIREA CONDIŢIILOR DE NAVIGAŢIE PE DUNĂRE
Pirai river (Bolivia)
 Pirai river (Bolivia) Confluent of the Amazon river which average discharge is only 6 m3/s, but with peak discharge over 5000 m3/s, a challenge for river basin management and for flood control HYDROEUROPE
Pirai river (Bolivia) Confluent of the Amazon river which average discharge is only 6 m3/s, but with peak discharge over 5000 m3/s, a challenge for river basin management and for flood control HYDROEUROPE
Impact of Climate Change on Riverbank Erosion
 International Journal of Sciences: Basic and Applied Research (IJSBAR) ISSN 2307-4531 http://gssrr.org/index.php?journal=journalofbasicandapplied Impact of Climate Change on Riverbank Erosion Most. Nazneen
International Journal of Sciences: Basic and Applied Research (IJSBAR) ISSN 2307-4531 http://gssrr.org/index.php?journal=journalofbasicandapplied Impact of Climate Change on Riverbank Erosion Most. Nazneen
Factors affecting confluence scour
 & Wang (eds) River Sedimentation 1999., Balkema, Rotterdam. ISBN 9 9 3. 17 19 Factors affecting confluence scour R. B. Rezaur & A. W. Jayawardena. Department of Civil Engineering, The University of Hong
& Wang (eds) River Sedimentation 1999., Balkema, Rotterdam. ISBN 9 9 3. 17 19 Factors affecting confluence scour R. B. Rezaur & A. W. Jayawardena. Department of Civil Engineering, The University of Hong
Quasi-three dimensional computations for flows and bed variations in curved channel with gently sloped outer bank
 River Sedimentation Wieprecht et al. (Eds) 2017 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-02945-3 Quasi-three dimensional computations for flows and bed variations in curved channel with gently sloped
River Sedimentation Wieprecht et al. (Eds) 2017 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-02945-3 Quasi-three dimensional computations for flows and bed variations in curved channel with gently sloped
Upper Mississippi River Basin Environmental Management Program Workshop
 Presentation to the Upper Mississippi River Basin Environmental Management Program Workshop by Michael Rodgers River Engineer US Army Corps of Engineers, St. Louis District August 17, 2007 Engineering
Presentation to the Upper Mississippi River Basin Environmental Management Program Workshop by Michael Rodgers River Engineer US Army Corps of Engineers, St. Louis District August 17, 2007 Engineering
ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 100. Figure 7-3 Maximum velocity magnitudes for existing conditions for 100-year flood event
 ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 100 Figure 7-3 Maximum velocity magnitudes for existing conditions for 100-year flood event ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 101 Figure 7-4 Model schematization of Option 1 Figure 7-5 Bed displacement
ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 100 Figure 7-3 Maximum velocity magnitudes for existing conditions for 100-year flood event ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 101 Figure 7-4 Model schematization of Option 1 Figure 7-5 Bed displacement
Project (Project No. US-CA-62-2) Maintenance Inspection and Reports (Subtask 14.1) Inspection Report No.2
 MEMORANDUM TO: FROM: Jim Well, Ducks Unlimited Mike Harvey, PhD, PG SUBJECT: M&T/ Llano Seco Fish Screen Project (Project No. US-CA-62-2) Maintenance Inspection and Reports (Subtask 14.1) Inspection Report
MEMORANDUM TO: FROM: Jim Well, Ducks Unlimited Mike Harvey, PhD, PG SUBJECT: M&T/ Llano Seco Fish Screen Project (Project No. US-CA-62-2) Maintenance Inspection and Reports (Subtask 14.1) Inspection Report
FUTURE MEANDER BEND MIGRATION AND FLOODPLAIN DEVELOPMENT PATTERNS NEAR RIVER MILES 200 TO 191 OF THE SACRAMENTO RIVER PHASE III REPORT
 FUTURE MEANDER BEND MIGRATION AND FLOODPLAIN DEVELOPMENT PATTERNS NEAR RIVER MILES 200 TO 191 OF THE SACRAMENTO RIVER PHASE III REPORT Eric W. Larsen REPORT FOR DUCKS UNLIMITED March 31, 2006-1 - Contents
FUTURE MEANDER BEND MIGRATION AND FLOODPLAIN DEVELOPMENT PATTERNS NEAR RIVER MILES 200 TO 191 OF THE SACRAMENTO RIVER PHASE III REPORT Eric W. Larsen REPORT FOR DUCKS UNLIMITED March 31, 2006-1 - Contents
Laboratory Investigation of Submerged Vane Shapes Effect on River Banks Protection
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(12): 1402-1407, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 Laboratory Investigation of Submerged Vane Shapes Effect on River Banks Protection Touraj Samimi Behbahan Department
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(12): 1402-1407, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 Laboratory Investigation of Submerged Vane Shapes Effect on River Banks Protection Touraj Samimi Behbahan Department
ENGINEERING APPROACHES TO SHORELINE PLACEMENT FROM COAST TO COAST
 ENGINEERING APPROACHES TO SHORELINE PLACEMENT FROM COAST TO COAST 237 237 237 217 217 217 200 200 200 0 0 0 163 163 163 131 132 122 80 119 27 252 174.59 83 36 118 110 135 120 112 92 56 62 102 130 Comparing
ENGINEERING APPROACHES TO SHORELINE PLACEMENT FROM COAST TO COAST 237 237 237 217 217 217 200 200 200 0 0 0 163 163 163 131 132 122 80 119 27 252 174.59 83 36 118 110 135 120 112 92 56 62 102 130 Comparing
J-river engineering for Vietnam
 J-river engineering for Vietnam Workshop on erosion control in the Mekong Delta Soc Trang, June 2015 Onga river, Japan Dr. MATSUKI Trung: JICA Expert 1 Project for Building Disaster Resilient Society in
J-river engineering for Vietnam Workshop on erosion control in the Mekong Delta Soc Trang, June 2015 Onga river, Japan Dr. MATSUKI Trung: JICA Expert 1 Project for Building Disaster Resilient Society in
Two-Dimensional Simulation of Truckee River Hydrodynamics
 Two-Dimensional Simulation of Truckee River Hydrodynamics by Stephen H. Scott PURPOSE: The purpose of this Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note (CHETN) is to demonstrate the use of multidimensional
Two-Dimensional Simulation of Truckee River Hydrodynamics by Stephen H. Scott PURPOSE: The purpose of this Coastal and Hydraulics Engineering Technical Note (CHETN) is to demonstrate the use of multidimensional
Securing Manoeuverability of a Deep Draft Ship in a Sediment loaded Tidal River Berth
 Securing Manoeuverability of a Deep Draft Ship in a Sediment loaded Tidal River Berth O. Stoschek 1, A. Matheja 1 & C. Zimmermann 1 1 Franzius-Institute for Hydraulic, Waterways and Coastal Engineering,
Securing Manoeuverability of a Deep Draft Ship in a Sediment loaded Tidal River Berth O. Stoschek 1, A. Matheja 1 & C. Zimmermann 1 1 Franzius-Institute for Hydraulic, Waterways and Coastal Engineering,
SEDIMENTATION AND ITS COUNTERMEASURE AT THE OFF-TAKE AREA OF NEW DHALESWARI RIVER
 SEDIMENTATION AND ITS COUNTERMEASURE AT THE OFF-TAKE AREA OF NEW DHALESWARI RIVER Tanjir Saif AHMED* MEE15634 Supervisors: Prof. EGASHIRA Shinji** Assoc. Prof. YOROZUYA Atsuhiro*** ABSTRACT Present study
SEDIMENTATION AND ITS COUNTERMEASURE AT THE OFF-TAKE AREA OF NEW DHALESWARI RIVER Tanjir Saif AHMED* MEE15634 Supervisors: Prof. EGASHIRA Shinji** Assoc. Prof. YOROZUYA Atsuhiro*** ABSTRACT Present study
Experimental Study of Discharge Characteristics in a Compound Meandering River
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-07, pp-136-140 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Experimental Study of Discharge Characteristics
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-07, pp-136-140 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Experimental Study of Discharge Characteristics
Assessment of Hydro-Morphological Change of Surma-Kushiyara River System
 Journal of Modern Science and Technology Vol. 6. No. 1. March 2018 Issue. Pp.113-123 Assessment of Hydro-Morphological Change of Surma-Kushiyara River System Md. Sabbir Mostafa Khan 1* and Purnima Das
Journal of Modern Science and Technology Vol. 6. No. 1. March 2018 Issue. Pp.113-123 Assessment of Hydro-Morphological Change of Surma-Kushiyara River System Md. Sabbir Mostafa Khan 1* and Purnima Das
Strategies for managing sediment in dams. Iwona Conlan Consultant to IKMP, MRCS
 Strategies for managing sediment in dams Iwona Conlan Consultant to IKMP, MRCS 1 Sediment trapping by dams Active storage capacity Dead storage coarse material (bed load) Fine materials (suspension) Francis
Strategies for managing sediment in dams Iwona Conlan Consultant to IKMP, MRCS 1 Sediment trapping by dams Active storage capacity Dead storage coarse material (bed load) Fine materials (suspension) Francis
DESIGN ENGINEERING ANALYSIS FOR TERMINAL GROIN LENGTH
 APPENDIX F DESIGN ENGINEERING ANALYSIS FOR TERMINAL GROIN LENGTH (Prepared by Olsen Associates, Inc.) DRAFT Environmental Impact Statement Village of Bald Head Island Shoreline Protection Project Brunswick
APPENDIX F DESIGN ENGINEERING ANALYSIS FOR TERMINAL GROIN LENGTH (Prepared by Olsen Associates, Inc.) DRAFT Environmental Impact Statement Village of Bald Head Island Shoreline Protection Project Brunswick
Numerical Simulation Of Sediment Transport And Bedmorphology Around A Hydraulic Structure On A River
 City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works International Conference on Hydroinformatics 8-1-2014 Numerical Simulation Of Sediment Transport And Bedmorphology Around A Hydraulic Structure On
City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works International Conference on Hydroinformatics 8-1-2014 Numerical Simulation Of Sediment Transport And Bedmorphology Around A Hydraulic Structure On
Decline of Lake Michigan-Huron Levels Caused by Erosion of the St. Clair River
 Decline of Lake Michigan-Huron Levels Caused by Erosion of the St. Clair River W.F. & Associates Coastal Engineers (in association with Frank Quinn) April 13, 2005 Outline Problem Definition Understanding
Decline of Lake Michigan-Huron Levels Caused by Erosion of the St. Clair River W.F. & Associates Coastal Engineers (in association with Frank Quinn) April 13, 2005 Outline Problem Definition Understanding
Island 32 Erosion. prepared for Ministry of Environment, Lands and Parks A Street Surrey, British Columbia, V3R 7P8. and
 Island 32 Erosion prepared for Ministry of Environment, Lands and Parks 10334 152A Street Surrey, British Columbia, V3R 7P8 and District of Chilliwack 8550 Young Road Chilliwack, British Columbia, V2P
Island 32 Erosion prepared for Ministry of Environment, Lands and Parks 10334 152A Street Surrey, British Columbia, V3R 7P8 and District of Chilliwack 8550 Young Road Chilliwack, British Columbia, V2P
Dam Removal Analysis Guidelines for Sediment
 A review of: Dam Removal Analysis Guidelines for Sediment Joe Rathbun (Retired) rathbunj@sbcglobal.net Some Potential Sediment Issues Reservoir restoration Downstream water quality Downstream deposition
A review of: Dam Removal Analysis Guidelines for Sediment Joe Rathbun (Retired) rathbunj@sbcglobal.net Some Potential Sediment Issues Reservoir restoration Downstream water quality Downstream deposition
River bed classification using multi-beam echo-sounder backscatter data. Niels KINNEGING Rijkswaterstaat Centre for Water Management
 River bed classification using multi-beam echo-sounder backscatter data Niels KINNEGING Rijkswaterstaat Centre for Water Management Mirjam SNELLEN Delft University of Techonology Dimitrios ELEFTHERAKIS
River bed classification using multi-beam echo-sounder backscatter data Niels KINNEGING Rijkswaterstaat Centre for Water Management Mirjam SNELLEN Delft University of Techonology Dimitrios ELEFTHERAKIS
Morphological Changes of Reach Two of the Nile River
 ICHE 2014, Hamburg - Lehfeldt & Kopmann (eds) - 2014 Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-3-939230-32-8 Morphological Changes of Reach Two of the Nile River E. Said Egyptian Environmental Affairs Agency,
ICHE 2014, Hamburg - Lehfeldt & Kopmann (eds) - 2014 Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau ISBN 978-3-939230-32-8 Morphological Changes of Reach Two of the Nile River E. Said Egyptian Environmental Affairs Agency,
3.0 ROBERTS BANK TIDAL FLAT MORPHOLOGY
 Vancouver Port Authority Northwest Hydraulic Consultants Ltd. /Triton Consultants Ltd. Roberts Bank Container Expansion File: 33863 Coastal Geomorphology Study - 19 - November 2004 3.0 ROBERTS BANK TIDAL
Vancouver Port Authority Northwest Hydraulic Consultants Ltd. /Triton Consultants Ltd. Roberts Bank Container Expansion File: 33863 Coastal Geomorphology Study - 19 - November 2004 3.0 ROBERTS BANK TIDAL
EAGLES NEST AND PIASA ISLANDS
 EAGLES NEST AND PIASA ISLANDS HABITAT REHABILITATION AND ENHANCEMENT PROJECT MADISON AND JERSEY COUNTIES, ILLINOIS ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT PROGRAM ST. LOUIS DISTRICT FACT SHEET I. LOCATION The proposed
EAGLES NEST AND PIASA ISLANDS HABITAT REHABILITATION AND ENHANCEMENT PROJECT MADISON AND JERSEY COUNTIES, ILLINOIS ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT PROGRAM ST. LOUIS DISTRICT FACT SHEET I. LOCATION The proposed
A STUDY ON HYDRODYNAMIC AND MORPHOLOGICAL BEHAVIOR OF GORAI RIVER USING DELFT 3D
 Proceedings of the 3 rd International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2016), 12~14 February 2016, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh (ISBN: 978-984-34-0265-3) A STUDY ON HYDRODYNAMIC
Proceedings of the 3 rd International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2016), 12~14 February 2016, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh (ISBN: 978-984-34-0265-3) A STUDY ON HYDRODYNAMIC
PART 2:! FLUVIAL HYDRAULICS" HYDROEUROPE
 PART 2:! FLUVIAL HYDRAULICS" HYDROEUROPE 2009 1 HYDROEUROPE 2009 2 About shear stress!! Extremely complex concept, can not be measured directly!! Computation is based on very primitive hypotheses that
PART 2:! FLUVIAL HYDRAULICS" HYDROEUROPE 2009 1 HYDROEUROPE 2009 2 About shear stress!! Extremely complex concept, can not be measured directly!! Computation is based on very primitive hypotheses that
River Meandering and Braiding. Pierre Y. Julien. Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Colorado State University Fort Collins, Colorado
 River Meandering and Braiding Pierre Y. Julien Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Colorado State University Fort Collins, Colorado River Mechanics and Sediment Transport Lima Peru January
River Meandering and Braiding Pierre Y. Julien Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Colorado State University Fort Collins, Colorado River Mechanics and Sediment Transport Lima Peru January
Solutions to Flooding on Pescadero Creek Road
 Hydrology Hydraulics Geomorphology Design Field Services Photo courtesy Half Moon Bay Review Solutions to Flooding on Pescadero Creek Road Prepared for: San Mateo County Resource Conservation District
Hydrology Hydraulics Geomorphology Design Field Services Photo courtesy Half Moon Bay Review Solutions to Flooding on Pescadero Creek Road Prepared for: San Mateo County Resource Conservation District
CFD Modeling for Structure Designs in Environmental Impacts Mitigation
 CFD Modeling for Structure Designs in Environmental Impacts Mitigation June 05 Navid Nekouee, Hugo Rodriguez and Steven Davie Environmental Impact Mitigation Design Savannah Harbor Expansion Project (SHEP)
CFD Modeling for Structure Designs in Environmental Impacts Mitigation June 05 Navid Nekouee, Hugo Rodriguez and Steven Davie Environmental Impact Mitigation Design Savannah Harbor Expansion Project (SHEP)
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 2, 2011
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 2, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Changing trends of channel pattern
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 2, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 0976 4380 Changing trends of channel pattern
Two Dimensional Hydrodynamic Modelling of Northern Bay of Bengal Coastal Waters
 Computational Water, Energy, and Environmental Engineering, 2014, 3, 140-151 Published Online October 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/cweee http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/cweee.2014.34015 Two Dimensional
Computational Water, Energy, and Environmental Engineering, 2014, 3, 140-151 Published Online October 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/cweee http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/cweee.2014.34015 Two Dimensional
CHAPTER 126 ^^^C^SR, SEDIMENTATION STUDIES ON THE NIGER RIVER DELTA
 CHAPTER 126 SEDIMENTATION STUDIES ON THE NIGER RIVER DELTA Ramiro Mayor-Mora, D. Eng. (1) Preben Mortensen, M.Sc. (2) Jorgen Fredsoe, M.Sc. (2) 1. Introduction An area of the Niger River Delta was studied
CHAPTER 126 SEDIMENTATION STUDIES ON THE NIGER RIVER DELTA Ramiro Mayor-Mora, D. Eng. (1) Preben Mortensen, M.Sc. (2) Jorgen Fredsoe, M.Sc. (2) 1. Introduction An area of the Niger River Delta was studied
MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF FLUVIAL SEDIMENT DELIVERY, NEKA RIVER, IRAN. S.E. Kermani H. Golmaee M.Z. Ahmadi
 JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL HYDROLOGY The Electronic Journal of the International Association for Environmental Hydrology On the World Wide Web at http://www.hydroweb.com VOLUME 16 2008 MATHEMATICAL MODELING
JOURNAL OF ENVIRONMENTAL HYDROLOGY The Electronic Journal of the International Association for Environmental Hydrology On the World Wide Web at http://www.hydroweb.com VOLUME 16 2008 MATHEMATICAL MODELING
The effect of different gate opening patterns on reservoir flushing and morphological changes downstream a dam
 The effect of different gate opening patterns on reservoir flushing and morphological changes downstream a dam Amgad Y. A. Omer Ymkje Huismans Kees Sloff Yuichi Kitamura Deltares Deltares Deltares & TU
The effect of different gate opening patterns on reservoir flushing and morphological changes downstream a dam Amgad Y. A. Omer Ymkje Huismans Kees Sloff Yuichi Kitamura Deltares Deltares Deltares & TU
Technical Review of Pak Beng Hydropower Project (1) Hydrology & Hydraulics and (2) Sediment Transport & River Morphology
 Technical Review of Pak Beng Hydropower Project (1) Hydrology & Hydraulics and (2) Sediment Transport & River Morphology The 2 nd Regional Stakeholder Forum The Pak Beng Hydropower Project 5 th May 2017
Technical Review of Pak Beng Hydropower Project (1) Hydrology & Hydraulics and (2) Sediment Transport & River Morphology The 2 nd Regional Stakeholder Forum The Pak Beng Hydropower Project 5 th May 2017
Tool 2.1.4: Inundation modelling of present day and future floods
 Impacts of Climate Change on Urban Infrastructure & the Built Environment A Toolbox Tool 2.1.4: Inundation modelling of present day and future floods Authors M. Duncan 1 and G. Smart 1 Affiliation 1 NIWA,
Impacts of Climate Change on Urban Infrastructure & the Built Environment A Toolbox Tool 2.1.4: Inundation modelling of present day and future floods Authors M. Duncan 1 and G. Smart 1 Affiliation 1 NIWA,
MODEL TESTS ON GEOBAGS FOR EROSION PROTECTION
 C-4 Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion 2008 MODEL TESTS ON GEOBAGS FOR EROSION PROTECTION Charles NEILL 1, Monica MANNERSTRÖM 2 and Abu Kalam AZAD 3 1 Principal, Northwest Hydraulic Consultants
C-4 Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion 2008 MODEL TESTS ON GEOBAGS FOR EROSION PROTECTION Charles NEILL 1, Monica MANNERSTRÖM 2 and Abu Kalam AZAD 3 1 Principal, Northwest Hydraulic Consultants
Tidal River Management (TRM) for Selected Coastal Area of Bangladesh to Mitigate Drainage Congestion
 Tidal River Management (TRM) for Selected Coastal Area of Bangladesh to Mitigate Drainage Congestion Shampa, Md. Ibne Mayaz Pramanik Abstract The drainage congestion and sedimentation has been major issues
Tidal River Management (TRM) for Selected Coastal Area of Bangladesh to Mitigate Drainage Congestion Shampa, Md. Ibne Mayaz Pramanik Abstract The drainage congestion and sedimentation has been major issues
Karamea floodplain investigation
 Karamea floodplain investigation NIWA Client Report: CHC2010-107 October 2010 NIWA Project: ELF 10234/1 Karamea floodplain investigation Graeme Smart Jo Bind NIWA contact/corresponding author Graeme Smart
Karamea floodplain investigation NIWA Client Report: CHC2010-107 October 2010 NIWA Project: ELF 10234/1 Karamea floodplain investigation Graeme Smart Jo Bind NIWA contact/corresponding author Graeme Smart
SHORELINE AND BEACH PROCESSES: PART 2. Implications for Coastal Engineering
 SHORELINE AND BEACH PROCESSES: PART 2 Implications for Coastal Engineering Objectives of the lecture: Part 2 Show examples of coastal engineering Discuss the practical difficulties of ocean engineering
SHORELINE AND BEACH PROCESSES: PART 2 Implications for Coastal Engineering Objectives of the lecture: Part 2 Show examples of coastal engineering Discuss the practical difficulties of ocean engineering
Model experiments: Influence of floods on sediment deposits in rivers equipped with groynes
 Model experiments: Influence of floods on sediment deposits in rivers equipped with groynes H. Friedrich, B.W. Melville The University of Auckland, New Zealand R. Gasset Ecole Nationale des Travaux Publics
Model experiments: Influence of floods on sediment deposits in rivers equipped with groynes H. Friedrich, B.W. Melville The University of Auckland, New Zealand R. Gasset Ecole Nationale des Travaux Publics
Some hydrotechnical features of Padma River, Bangladesh
 21st Canadian Hydrotechnical Conference 21e congrès spécialisé hydrotechnique canadienne Erosion, Scour, and Sediment transport Banff, Alberta, May 14-17, 2013 / 14 17 Mai 2013 Some hydrotechnical features
21st Canadian Hydrotechnical Conference 21e congrès spécialisé hydrotechnique canadienne Erosion, Scour, and Sediment transport Banff, Alberta, May 14-17, 2013 / 14 17 Mai 2013 Some hydrotechnical features
VICTORIA BEND HYDRAULIC SEDIMENT RESPONSE MODEL INVESTIGATION LOWER MISSISSIPPI RIVER MILES
 Technical Report M48 VICTORIA BEND HYDRAULIC SEDIMENT RESPONSE MODEL INVESTIGATION LOWER MISSISSIPPI RIVER MILES 600-590 By Peter M. Russell, P.E. Jasen L. Brown, P.E Edward J. Brauer, P.E. Robert D. Davinroy,
Technical Report M48 VICTORIA BEND HYDRAULIC SEDIMENT RESPONSE MODEL INVESTIGATION LOWER MISSISSIPPI RIVER MILES 600-590 By Peter M. Russell, P.E. Jasen L. Brown, P.E Edward J. Brauer, P.E. Robert D. Davinroy,
Matsqui Bend Erosion
 Matsqui Bend Erosion prepared for Ministry of Environment, Lands and Parks 10334 152A Street Surrey, British Columbia, V3R 7P8 by Hamish Weatherly, Michael Church, and Darren Ham Department of Geography
Matsqui Bend Erosion prepared for Ministry of Environment, Lands and Parks 10334 152A Street Surrey, British Columbia, V3R 7P8 by Hamish Weatherly, Michael Church, and Darren Ham Department of Geography
Experimental study of scour depth in attracting Groins series
 Experimental study of scour depth in attracting Groins series S. Amini 1, M.R. Kavianpour 2, M.R.M. tabatabai 3, S. Amini 4, K. Amini 5 1-MSc, Water Engineering, Shahid Beheshty University 2-Associate
Experimental study of scour depth in attracting Groins series S. Amini 1, M.R. Kavianpour 2, M.R.M. tabatabai 3, S. Amini 4, K. Amini 5 1-MSc, Water Engineering, Shahid Beheshty University 2-Associate
Monitoring Lower Meghna River of Bangladesh using Remote Sensing and GIS Technology
 Monitoring Lower Meghna River of Bangladesh using Remote Sensing and GIS Technology M Rahman Akhand, S M Mizanur Rahman & M H Sarker Bangladesh Space Research and Remote Sensing Organization (SPARRSO)
Monitoring Lower Meghna River of Bangladesh using Remote Sensing and GIS Technology M Rahman Akhand, S M Mizanur Rahman & M H Sarker Bangladesh Space Research and Remote Sensing Organization (SPARRSO)
Process-based Long Term Morphological Modelling the present state-of-the-art and the way ahead. Dirk-Jan Walstra
 Process-based Long Term Morphological Modelling the present state-of-the-art and the way ahead Dirk-Jan Walstra Deltares Delft Hydraulics Delft University of Technology Les littoraux à l heure du changement
Process-based Long Term Morphological Modelling the present state-of-the-art and the way ahead Dirk-Jan Walstra Deltares Delft Hydraulics Delft University of Technology Les littoraux à l heure du changement
DUNE EROSION NEAR SEA WALLS: MODEL-DATA COMPARISON
 DUNE EROSION NEAR SEA WALLS: MODEL-DATA COMPARISON Pieter van Geer 1, Bram de Vries 2, Ap van Dongeren 1 and Jaap van Thiel de Vries 1,2 This paper describes the validation of the dune erosion model XBeach
DUNE EROSION NEAR SEA WALLS: MODEL-DATA COMPARISON Pieter van Geer 1, Bram de Vries 2, Ap van Dongeren 1 and Jaap van Thiel de Vries 1,2 This paper describes the validation of the dune erosion model XBeach
Adequacy Check of Existing Crest Level of Sea Facing Coastal Polders by the Extreme Value Analysis Method
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 8, Issue 1 (Jul. - Aug. 2013), PP 89-96 Adequacy Check of Existing Crest Level of Sea Facing Coastal
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 8, Issue 1 (Jul. - Aug. 2013), PP 89-96 Adequacy Check of Existing Crest Level of Sea Facing Coastal
12.0 COASTAL PROCESSES
 12.0 COASTAL PROCESSES 12.1 Introduction This Chapter of the EIS considers the potential and likely significant effects of the proposed alterations to the permitted development. The purpose of this chapter
12.0 COASTAL PROCESSES 12.1 Introduction This Chapter of the EIS considers the potential and likely significant effects of the proposed alterations to the permitted development. The purpose of this chapter
Scheepvaart en ecologische doelstellingen
 Scheepvaart en ecologische doelstellingen Margriet Schoor 25 April 2008 The Rhine Delta Rotterdam 2/3 1/3 Scheepvaart en ecologische doelstellingen 2 Germany Navigation on the Rhine Busiest river in Europe
Scheepvaart en ecologische doelstellingen Margriet Schoor 25 April 2008 The Rhine Delta Rotterdam 2/3 1/3 Scheepvaart en ecologische doelstellingen 2 Germany Navigation on the Rhine Busiest river in Europe
Mangrove Erosion in the Mekong delta
 Mangrove Erosion in the Mekong delta 1. Introduction a. Mangrove coast - a balance between different forcing factors Mangroves are coastal environments frequently observed in the tropical muddy coasts.
Mangrove Erosion in the Mekong delta 1. Introduction a. Mangrove coast - a balance between different forcing factors Mangroves are coastal environments frequently observed in the tropical muddy coasts.
Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory
 SAM Hydraulic Design Package for Channels Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory William A. Thomas, Ronald R. Copeland, and Dinah N. McComas September 2002 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.
SAM Hydraulic Design Package for Channels Coastal and Hydraulics Laboratory William A. Thomas, Ronald R. Copeland, and Dinah N. McComas September 2002 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.
ROYAL NETHERLANDS EMBASSY DHAKA BANGLADESH WATER DEVELOPMENT BOARD
 ROYAL NETHERLANDS EMBASSY DHAKA BANGLADESH WATER DEVELOPMENT BOARD Technical Mission EVALUATION AND RECOMMENDATIONS FOR RIVER BANK PROTECTION AT FARIDPUR DISTRICT TOWN PADMA RIVER Technical Assistance
ROYAL NETHERLANDS EMBASSY DHAKA BANGLADESH WATER DEVELOPMENT BOARD Technical Mission EVALUATION AND RECOMMENDATIONS FOR RIVER BANK PROTECTION AT FARIDPUR DISTRICT TOWN PADMA RIVER Technical Assistance
Year 6. Geography. Revision
 Year 6 Geography Revision November 2017 Rivers and World knowledge How the water cycle works and the meaning of the terms evaporation, condensation, precipitation, transpiration, surface run-off, groundwater
Year 6 Geography Revision November 2017 Rivers and World knowledge How the water cycle works and the meaning of the terms evaporation, condensation, precipitation, transpiration, surface run-off, groundwater
COUNTRY PRESENTATION ON MR JAYNAL ABEDIN JOINT SECRETARY ( WORKS & DEVELOPMENT ) MINISTRY OF DEFENCE
 COUNTRY PRESENTATION ON By MR JAYNAL ABEDIN JOINT SECRETARY ( WORKS & DEVELOPMENT ) MINISTRY OF DEFENCE Bangladesh Geographical Location of Bangladesh Bangladesh Country at a Glance Physical Features 1,230
COUNTRY PRESENTATION ON By MR JAYNAL ABEDIN JOINT SECRETARY ( WORKS & DEVELOPMENT ) MINISTRY OF DEFENCE Bangladesh Geographical Location of Bangladesh Bangladesh Country at a Glance Physical Features 1,230
HYDROLOGY AND HYDRAULICS MUSKEG RIVER BRIDGE
 PUBLIC WORKS CANADA HYDROLOGY AND HYDRAULICS MUSKEG RIVER BRIDGE KILOMETRE 207.9, LIARD HIGKWAY December 1978 I I f I I I I # Bolter Parish Trimble Ltd. ONLIULTINO Public Works, Canada, 9925-109 Street,
PUBLIC WORKS CANADA HYDROLOGY AND HYDRAULICS MUSKEG RIVER BRIDGE KILOMETRE 207.9, LIARD HIGKWAY December 1978 I I f I I I I # Bolter Parish Trimble Ltd. ONLIULTINO Public Works, Canada, 9925-109 Street,
Four Mile Run Levee Corridor Stream Restoration
 Four Mile Run Levee Corridor Stream Restoration 30% Design Summary U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Baltimore District Presentation Outline Four Mile Run 1.) Historic Perspective 2.) Existing Conditions 3.)
Four Mile Run Levee Corridor Stream Restoration 30% Design Summary U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Baltimore District Presentation Outline Four Mile Run 1.) Historic Perspective 2.) Existing Conditions 3.)
Project Proposal. Lyme Brook. Newcastle-under-Lyme. 3 rd July 2015
 Project Proposal Lyme Brook Newcastle-under-Lyme 3 rd July 2015 Contents Page 1.0 Introduction... 1.0 2.0 Background and rationale... 2.0 3.0 Proposed measures... 5 4.0 Summary of Recommendations... 10
Project Proposal Lyme Brook Newcastle-under-Lyme 3 rd July 2015 Contents Page 1.0 Introduction... 1.0 2.0 Background and rationale... 2.0 3.0 Proposed measures... 5 4.0 Summary of Recommendations... 10
STABILITY OF OLD STONE GROINS IN THE KATSURA RIVER DURING FLOODS
 B-10 Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion 008 STABILITY OF OLD STONE GROINS IN THE KATSURA RIVER DURING FLOODS Taisuke ISHIGAKI 1, Takahiro ASANO and Ryuji KAWANAKA 3 1 Member of JSCE,
B-10 Fourth International Conference on Scour and Erosion 008 STABILITY OF OLD STONE GROINS IN THE KATSURA RIVER DURING FLOODS Taisuke ISHIGAKI 1, Takahiro ASANO and Ryuji KAWANAKA 3 1 Member of JSCE,
Analysis on River Bank Erosion-Accretion and Bar Dynamics Using Multi-Temporal Satellite Images
 American Journal of Water Resources, 2017, Vol. 5, No. 4, 132-141 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajwr/5/4/6 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajwr-5-4-6 Analysis on River Bank
American Journal of Water Resources, 2017, Vol. 5, No. 4, 132-141 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajwr/5/4/6 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajwr-5-4-6 Analysis on River Bank
Erosion Information Paper - Barrow, Alaska Current as of September 14, 2007
 U.S. Army Corps of Engineers ALASKA BASELINE EROSION ASSESSMENT Erosion Information Paper - Barrow, Alaska Current as of September 14, 2007 Community Information Barrow (BARE-row, a.k.a. Ukpeagvik), population
U.S. Army Corps of Engineers ALASKA BASELINE EROSION ASSESSMENT Erosion Information Paper - Barrow, Alaska Current as of September 14, 2007 Community Information Barrow (BARE-row, a.k.a. Ukpeagvik), population
MORPHODYNAMIC PROCESSES IN ESTUARIES COMPARISON OF MARINE AND LIMNIC TIDAL FLATS
 MORPHODYNAMIC PROCESSES IN ESTUARIES COMPARISON OF MARINE AND LIMNIC TIDAL FLATS Thorsten Albers 1, Dagmar Much 2, Nino Ohle 2, Nicole von Lieberman 1, Eva Falke 1 Tidal flat areas in estuaries are affected
MORPHODYNAMIC PROCESSES IN ESTUARIES COMPARISON OF MARINE AND LIMNIC TIDAL FLATS Thorsten Albers 1, Dagmar Much 2, Nino Ohle 2, Nicole von Lieberman 1, Eva Falke 1 Tidal flat areas in estuaries are affected
Research Topic Updated on Oct. 9, 2014
 Research Topic Updated on Oct. 9, 204 Mixed Cohesive/Non-cohesive Sediments Sedimentation in Estuary: Flocculation Deposition Erosion Transport Consolidation *: It has been recognized that when the fraction
Research Topic Updated on Oct. 9, 204 Mixed Cohesive/Non-cohesive Sediments Sedimentation in Estuary: Flocculation Deposition Erosion Transport Consolidation *: It has been recognized that when the fraction
CE415L Applied Fluid Mechanics Laboratory
 Applied Fluid Mechanics Laboratory Learning Objective Following completion of this experiment and the analysis of the data, you should be able to 1. generalize results of introducing changes to a natural
Applied Fluid Mechanics Laboratory Learning Objective Following completion of this experiment and the analysis of the data, you should be able to 1. generalize results of introducing changes to a natural
Paper 114 Validation of Actual Depth Measurements by Inland Vessels
 Paper 114 Validation of Actual Depth Measurements by Inland Vessels VAN DER MARK C.F. 1 ; VIJVERBERG T. 2 ; OTTEVANGER W. 1 1 Deltares, Delft, the Netherlands 2 Royal HaskoningDHV, Amersfoort, the Netherlands
Paper 114 Validation of Actual Depth Measurements by Inland Vessels VAN DER MARK C.F. 1 ; VIJVERBERG T. 2 ; OTTEVANGER W. 1 1 Deltares, Delft, the Netherlands 2 Royal HaskoningDHV, Amersfoort, the Netherlands
Sediment Traps. CAG Meeting May 21, 2012
 Sediment Traps CAG Meeting May 21, 2012 Agenda Background Fundamentals of Sediment Transport Sediment Trap Existing Information Next Steps 2 The Site Saginaw River 22 mile river beginning at confluence
Sediment Traps CAG Meeting May 21, 2012 Agenda Background Fundamentals of Sediment Transport Sediment Trap Existing Information Next Steps 2 The Site Saginaw River 22 mile river beginning at confluence
2. Governing Equations
 1. Introduction Submarine pipeline, unlike any other hydraulic structures that are vertically erected, are laid horizontally on the bed of oceans and rivers. Hence, the design of submarine pipelines associated
1. Introduction Submarine pipeline, unlike any other hydraulic structures that are vertically erected, are laid horizontally on the bed of oceans and rivers. Hence, the design of submarine pipelines associated
Flood Forecasting in Bangladesh
 Flood Forecasting in Bangladesh Types of Flood ing Flood ing can be divided into two categories: Flood ing in the rivers caused by upstream rise of river stage as well as rainfall in the basin. Overland
Flood Forecasting in Bangladesh Types of Flood ing Flood ing can be divided into two categories: Flood ing in the rivers caused by upstream rise of river stage as well as rainfall in the basin. Overland
MORPHOLOGICAL STUDY OF OLD BRAHMAPUTRA OFFTAKE USING TWO-DIMENSIONAL MATHEMATICAL MODEL FAHMIDA NOOR. Student No: P
 MORPHOLOGICAL STUDY OF OLD BRAHMAPUTRA OFFTAKE USING TWO-DIMENSIONAL MATHEMATICAL MODEL FAHMIDA NOOR Student No: 0409162022P DEPARTMENT OF WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING BANGLADESH UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING
MORPHOLOGICAL STUDY OF OLD BRAHMAPUTRA OFFTAKE USING TWO-DIMENSIONAL MATHEMATICAL MODEL FAHMIDA NOOR Student No: 0409162022P DEPARTMENT OF WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING BANGLADESH UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING
