J. Mangas and F.J. Perez-Torrado. Departamento de Física. Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria Las Palmas de Gran Canaria.
|
|
|
- Brent Thomas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Magmatic processes in the oceanic lithosphere: characterization of the ultramafic and mafic materials from the Holocene volcanic centers of Bandama and La Caldera de Pinos de Gáldar (Gran Canaria, Canary Islands) J. Mangas and F.J. Perez-Torrado Departamento de Física. Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria Las Palmas de Gran Canaria. Spain Introduction Mantle and crustal xenoliths carried to the surface by basaltic melts in intraplate oceanic islands represent one very important information source of the deeper parts of the oceanic lithosphere. Thus, our research is based on the study samples of peridotite xenoliths and olivine-pyroxene-amphibol crysts and cumulates from pyroclastic deposits of Bandama and La Caldera de Pinos de Galdar volcanic centers (Gran Canaria, Canary Islands) and samples of lava flows associated to these volcanoes. We have combined data from the volcanological study and the electronic microprobe and microthermomertric analysis of minerals and melt and fluid inclusions, and the bulk-rock analysis of these samples to define some characteristics of magmatism which gave rise to these volcanoes. Gran Canaria island is at the centre of the Canary Archipielago and this is associated to a mantle plume. Geophysical data indicate the occurrence of an oceanictype basement underneath the Gran Canaria island modified by massive intrusions with a Moho depth of 13 kms. Magmatic activity of this island began in the Miocene with an episode of submarine volcanism and their subaerial volcanism have been divided over three main episodes: Old cycle (Miocene, Ma), Roque Nublo cycle (Pliocene, Ma) and Recent cycle (Plio-Quaternary, 3 Ma-Present). Taking into account the hawaiian formation model for intraplate volcanic islands, the Old cycle of Gran Canaria contains magmatic materials associated to the shield building and alkaline declining stages, and the Roque Nublo and Recent cycles represent the rejuvenation stage. Thus, Bandama and La Caldera de Pinos de Galdar Holocene volcanic centers are one of the latest eruptions associated to the rejuvenation stage of Gran Canaria. The Holocene volcanic center of Bandama is made up of a volcanic caldera (La Caldera de Bandama) and a strombolian cone (El Pico de Bandama). Bandama eruption began in the area of La Caldera with a strombolian episode which produced deposits of fall and a basanite lava flow. Later, the magma in the counduit mixed periodically with groundwater, producing both phreatomagmatic eruptions with base surge deposits and strombolian eruptions with fall deposits. Although the volcanism episodes were to continue in the area around La Caldera, most of these manifestations were centred around the NW area of the fisure, producing the strombolian cone known as the Pico Bandama, abundant deposits of fall in the surrounding areas and an intracanyon flow. The genesis of La 1
2 Caldera is posterior to El Pico and was produced as a result of the last effusive-explosive eruptions and the eventual collapse of the volcanic cone located to the SE of the fissure. On the other hand, the Holocene eruption of La Caldera de Pinos de Galdar (2,830 years b.p.) is characterized by an strombolian cone, several lava flows of basanite composition and fall pyroclastic deposits. This volcano and other neighbour volcanic cones (Valleseco, Montañón Negro 2,970 years b.p.--, Hondo de Fagagesto 2,210 years b.p.--, Sao and Los Berrazales) are almost contemporaneous and they form a NW-SE structural lineation of 9 km long. Mineralogical and geochemical characteristics Lava flows of Bandama show basanite composition (SiO % and sum of the alkalis 3.8%) and porphyritic texture with phenocrysts and microcrysts of olivine, pyroxene and oxide (spinel and ilmenite) with sizes under 2 cm. Microprobe analysis of these minerals reveal olivine Fo (Ni/Ca ratio: ) and clinopyroxene Wo 40-52, En (augite-diopside). Spinel appear as subordinate minerals and as inclusions in phenocrysts and have Cr 2 O 3 content between 36.4 and 40.2%. These analysis show variations of composition between the cores and rims of some phenocrysts and reveal different crystal generations. In addition, the lava flows contain some ultramafic and mafic xenolitiths and cumulates On the other hand, the lava flows of La Caldera de Pinos de Galdar have basanitic composition (SiO % and sum of the alkalis 5%), show porphyric texture and these flows contain olivine (Fo ) and augite-diopside (Wo 44-55, En ) phenocrysts, subordinated spinel (#Cr ) and magnetite (#Cr ), and scarce mafic and salic cumulates. Phreatomagmatic eruptions of Caldera de Bandama form base surge and explosive breccia rich in lithics (such as phonolites, tephrites, alkaline basalts, etc.) deposits with spectacular volcanic-sedimentary structures (imbricated channels, sand waves, bomb impacts, etc.). However, the strombolian volcanism is characterized by the presence of fall deposits, containing peridotite xenoliths and olivine-pyroxene-amphibole megacrysts and magmatic cumulates with sizes under 7 cms. Electronic microprobe analysis of these minerals show: 1) phenoscrysts and megacrysts of olivine Fo77-89 (Ni/Ca: and spinel with Cr2O3: %), clinopyroxene Wo34-52, En33-51 (spinel with Cr2O3: %) and kaersutite (destabilized to fassaite --Wo54-57, En , rhönite, olivine and subsaturated melt). 2) ultramafic cumulates (dunite, werhlite, clinopyroxenite with olivine and clinopyroxenite) with olivine Fo (Ni/Ca: and spinels with Cr 2 O 3 : %) and clinopyroxene Wo 39-51, En (spinels with Cr 2 O 3 : %). 2
3 3) ultramafic xenoliths (dunite and lherzolite) with olivine Fo (Ni/Ca: 1-20 and spinels with Cr 2 O 3 : %), orthopyroxene Fo (spinels with Cr 2 O 3 : 31.3%) and clinopyroxene Wo 40-44, En The pyroclastic deposits of La Caldera de Pinos de Galdar display mafic and ultramafic xenoliths and cumulates with sizes below 15 cms and these are characterized by: 1) ultramafic xenoliths: A) dunite (olivine I: Fo 87-91, olivine II: Fo 89-93; spinel I: #Cr 95 and spinel II: #Cr ), B) lherzolite (olivine I: Fo 91 ; olivine II: Fo ; orthopyroxene: Fo 81-96; clinopyroxene: Wo 41-47, En 50-57; spinel I: #Cr and spinel II: #Cr ) and C) harzburgite (olivine I: Fo ; olivine II: Fo ; orthopyroxene: Fo ; clinopyroxene: Wo 40-47, En ; spinel I: #Cr and spinel II: #Cr ). 2) mafic and ultramafic cumulates: A) olivine clinopyroxenite (olivine: Fo ; augite-diopside: Wo 47-56, En ; spinel: #Cr ), B) clinopyroxenite (olivine: Fo ; augite-diopside: Wo 46-55, En 39-51; spinel: #Cr ), C) hornblende clinopyroxenite (olivine: Fo ; augite-diopside: Wo 42-55, En ; spinel: #Cr ), D) clinopyroxenite with apatite and Fe-Ti oxides (augite-diopside: Wo 50-53, En ; magnetite: #Cr <2.1 ; ilmenite: Ilm 55-66, Geik 16-34, Hem ), and E) clinopyroxenite with apatite, titanite and Fe-Ti oxides (augitediopside: Wo 50-56, En ; magnetite: #Cr <1.8 ; ilmenite: Ilm 52-86, Geik 6-34, Hem <19 ; hematite: Hem , Geik <4, Pyroph <3; and Fe sulphides). Clinopyroxene megacrysts (Wo 50-54, En ) containing cristal inclusions of apatite and hematite (Hem , Geik <1, Pyroph <1 ). Melt inclusion study in olivine from fall deposits and lava flows of Bandama volcanic center show SiO 2 content: 35-44%, sum of alkalis: 4.1-7% and high values of S and Cl (<5,500 and <980 ppm, respectively). The melt inclusion compositions are different from the lava whole rock and the intersticial melt. The melting temperatures (Tm) of melt inclusions range between 1,060 and 1,260 C. Microthermometric study of melt and fluid inclusions in olivine and clynopyroxe of Bandama volcanoes shows pure, or almost pure, CO 2 trapped in the gas bubble. These carbonic fluids reveal a wide range of Th of CO 2 (-39 to 31 C) in liquid, indicating minimum depths of mineral formations (at Tm: 1200 C) between Km for olivine-pyroxeneanphibol megacrysts, Km for olivine-pyroxenes cumulates, km for ultramafic xenoliths, and Km for olivine phenocrysts of lava flows. The depth ranges observed indicate magma reservoirs and mineral genesis within the upper mantle and in the lower and upper crust (Fig. 1). 3
4 Figure 1. Interpretative scheme of depth calculated by CO2-rich fluid inclusions trapped in olivine and pyroxene from lava flows, xenoliths, cumulates and megacrysts of the Bandama volcanic center (Gran Canaria, Canary Islands). Discussion The olivine, clinopyroxene and anphibole which make up the crysts (phenocrysts and megacrysts), cumulates and xenoliths of Bandama and La Caldera de Pinos de Galdar volcanoes display different textural, mineralogical, microthermometric and 4
5 chemical composition characteristics. Thus, the lava flows have basanite composition (ultramafic, low-evolved magma), cumulates and megacrists were formed in moreevolved magmas (mafic and ultramafic) and the upper mantle xenoliths have variable peridotitic compositions and textures (ultramafic). In addition, numerous studied minerals reveal generally reaction rims with basanite melts, documenting prolonged magma contact (mineral diffusion zones). Therefore, we can conclude that these studied minerals were originated under variable magmatic conditions and chambers. We propose a model of the multi-stage magma ascent and storage beneath Gran Canaria island (Fig. 1). Therefore, the basanitic magmas which gave rise to Bandama and Pinos de Galdar volcanoes ascended from upper mantle to the surface trapping xenoliths, cumulates and megacrysts of different depths and genesis. The basanite ascending magmas stagnated in several reservoirs en route to the surface between -33 km to 1,5 km, trapping ultramafic xenoliths, mafic and ultramafic cumulates, and olivinepyroxene-amphibole megacrysts from the upper mantle and the upper oceanic crust (- 27 to -4.5 km.). 5
Ore deposits related to mafic igneous rocks Diamonds - GLY 361 Lecture 3
 Ore deposits related to mafic igneous rocks Diamonds - GLY 361 Lecture 3 A short history of diamonds Derived from the ancient Greek αδάμας (adámas): unbreakable Thought to have been first recognized and
Ore deposits related to mafic igneous rocks Diamonds - GLY 361 Lecture 3 A short history of diamonds Derived from the ancient Greek αδάμας (adámas): unbreakable Thought to have been first recognized and
The Nature of Igneous Rocks
 The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann. Grotzinger Jordan. Understanding Earth. Sixth Edition
 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks: Solids from Melts 1 About Igneous Rocks Igneous
Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks: Solids from Melts 1 About Igneous Rocks Igneous
Imagine the first rock and the cycles that it has been through.
 A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Spring 2009 Sc ore / 40
 GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Name Spring 2009 Sc ore / 40 QUIZ 3 1) Name two geologic features that provide physical evidence for the mineralogy of the earth s mantle (2 pts) Ophiolites,
GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Name Spring 2009 Sc ore / 40 QUIZ 3 1) Name two geologic features that provide physical evidence for the mineralogy of the earth s mantle (2 pts) Ophiolites,
Igneous Rocks. Igneous Rocks. Genetic Classification of
 Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals. Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane SGM 210_2013
 Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011
Name Class Date STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY
 Igneous Rocks What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. extrusive igneous rock intrusive
Igneous Rocks What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. extrusive igneous rock intrusive
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals. Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane SGM 210_2013
 Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Intrusive and Effusive Rocks Effusive rocks: rapid cooling small crystalls or glas Lava & ash Magmatic
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Intrusive and Effusive Rocks Effusive rocks: rapid cooling small crystalls or glas Lava & ash Magmatic
Visualizing Earth Science. Chapter Overview. Volcanoes and Eruption Types. By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner. Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other
 Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
Essentials of Geology, 11e
 Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Igneous & Metamorphic Petrology I LECTURE 11
 Igneous & Metamorphic Petrology I LECTURE 11 The Earth s Mantle 1. Structure of the Earth A Reminder The velocities of seismic waves differ with the elastic properties and densities of rocks and allow
Igneous & Metamorphic Petrology I LECTURE 11 The Earth s Mantle 1. Structure of the Earth A Reminder The velocities of seismic waves differ with the elastic properties and densities of rocks and allow
Lecture 3 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Dr. Shwan Omar
 Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
Lecture 24 Hawaii. Hawaii
 Lecture 24 Hawaii Friday, April 22 nd 2005 Hawaii The Hawaiian Islands, in the middle of the Pacific Ocean, are volcanic islands at the end of a long chain of submerged volcanoes. These volcanoes get progressively
Lecture 24 Hawaii Friday, April 22 nd 2005 Hawaii The Hawaiian Islands, in the middle of the Pacific Ocean, are volcanic islands at the end of a long chain of submerged volcanoes. These volcanoes get progressively
High-T heating stage: application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools -
 High-T heating stage: application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools - SZABÓ, Csaba Lithosphere Fluid Research Lab (LRG), Department of Petrology and Geochemistry,
High-T heating stage: application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools - SZABÓ, Csaba Lithosphere Fluid Research Lab (LRG), Department of Petrology and Geochemistry,
GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Spring 2016 Score / 58. Midterm 1 Chapters 1-10
 GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Name KEY Spring 2016 Score / 58 Midterm 1 Chapters 1-10 1) Name two things that petrologists want to know about magmas (1 pt) Formation, source, composition,
GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Name KEY Spring 2016 Score / 58 Midterm 1 Chapters 1-10 1) Name two things that petrologists want to know about magmas (1 pt) Formation, source, composition,
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks
 Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Magma Formation and Behavior
 Magma Formation and Behavior Introduction: The study of body waves as they pass through Earth's interior provides strong evidence that the Earth's mantle is composed almost entirely of solid ultramafic
Magma Formation and Behavior Introduction: The study of body waves as they pass through Earth's interior provides strong evidence that the Earth's mantle is composed almost entirely of solid ultramafic
IGNEOUS ROCKS. SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks?
 Date Period Name IGNEOUS ROCKS SECTION.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
Date Period Name IGNEOUS ROCKS SECTION.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
FACTS FOR DIAMOND OCCURRENCE IN KIMBERLITES
 KIMBERLITES Kimberlite is an ultrabasic olivine-rich igneous rock called peridotite. Peridotites occur at great depths in the earth in a layer called the mantle (100-135 miles below the surface). At this
KIMBERLITES Kimberlite is an ultrabasic olivine-rich igneous rock called peridotite. Peridotites occur at great depths in the earth in a layer called the mantle (100-135 miles below the surface). At this
Name Class Date STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY
 Igneous Rocks What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. extrusive igneous rock intrusive
Igneous Rocks What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. extrusive igneous rock intrusive
Petrogenetic Constraints at Mount Rainier Volcano, Washington
 Petrogenetic Constraints at Mount Rainier Volcano, Washington S. C. Kuehn and P. R. Hooper, Department of Geology, Washington State University, Pullman, WA A. E. Eggers and C. Kerrick, Department of Geology,
Petrogenetic Constraints at Mount Rainier Volcano, Washington S. C. Kuehn and P. R. Hooper, Department of Geology, Washington State University, Pullman, WA A. E. Eggers and C. Kerrick, Department of Geology,
High-T T heating stage: : application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools -
 High-T T heating stage: : application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools - SZABÓ, Csaba Lithosphere Fluid Research Lab (LRG), Department of Petrology and Geochemistry,
High-T T heating stage: : application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools - SZABÓ, Csaba Lithosphere Fluid Research Lab (LRG), Department of Petrology and Geochemistry,
Ultramafic rocks. Types of Ultramafic Rocks. Spinel lherzolite xenolith
 Ultramafic rocks Definition: Color Index > 90, i.e., less than 10% felsic minerals. Not to be confused with Ultrabasic Rocks which are rocks with
Ultramafic rocks Definition: Color Index > 90, i.e., less than 10% felsic minerals. Not to be confused with Ultrabasic Rocks which are rocks with
Magma Formation and Behavior
 Magma Formation and Behavior Questions What causes mantle rock to melt, resulting in magma formation? Why is magma formation restricted to specific plate tectonic settings? Why are mafic (basaltic) magmas
Magma Formation and Behavior Questions What causes mantle rock to melt, resulting in magma formation? Why is magma formation restricted to specific plate tectonic settings? Why are mafic (basaltic) magmas
Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark
 Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Effusive: lavas (e.g., Kilauea) Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Explosive: pyroclastic rocks (e.g., Krakatau) Factors Governing
Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Effusive: lavas (e.g., Kilauea) Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Explosive: pyroclastic rocks (e.g., Krakatau) Factors Governing
Worked Example of Batch Melting: Rb and Sr
 Worked Example of Batch Melting: Rb and Sr Basalt with the mode: Table 9.2. Conversion from mode to weight percent Mineral Mode Density Wt prop Wt% ol 15 3.6 54 0.18 cpx 33 3.4 112.2 0.37 plag 51 2.7 137.7
Worked Example of Batch Melting: Rb and Sr Basalt with the mode: Table 9.2. Conversion from mode to weight percent Mineral Mode Density Wt prop Wt% ol 15 3.6 54 0.18 cpx 33 3.4 112.2 0.37 plag 51 2.7 137.7
LAB 6: COMMON MINERALS IN IGNEOUS ROCKS
 GEOLOGY 17.01: Mineralogy LAB 6: COMMON MINERALS IN IGNEOUS ROCKS Part 2: Minerals in Gabbroic Rocks Learning Objectives: Students will be able to identify the most common silicate minerals in gabbroic
GEOLOGY 17.01: Mineralogy LAB 6: COMMON MINERALS IN IGNEOUS ROCKS Part 2: Minerals in Gabbroic Rocks Learning Objectives: Students will be able to identify the most common silicate minerals in gabbroic
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 2017-2016 Chapter (4) Volcanoes Chapter 4: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity cataclysmic relating to or denoting a violent natural even Eventually the entire
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 2017-2016 Chapter (4) Volcanoes Chapter 4: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity cataclysmic relating to or denoting a violent natural even Eventually the entire
The mantle metasomatism: diversity and impact What the mantle xenoliths tell us?
 The mantle metasomatism: diversity and impact What the mantle xenoliths tell us? Mantle metasomatism Physical and chemical processes that are implemented during the flow of magmas and / or fluids within
The mantle metasomatism: diversity and impact What the mantle xenoliths tell us? Mantle metasomatism Physical and chemical processes that are implemented during the flow of magmas and / or fluids within
A Rock is a solid aggregate of minerals.
 Quartz A Rock is a solid aggregate of minerals. Orthoclase Feldspar Plagioclase Feldspar Biotite Four different minerals are obvious in this piece of Granite. The average automobile contains: Minerals
Quartz A Rock is a solid aggregate of minerals. Orthoclase Feldspar Plagioclase Feldspar Biotite Four different minerals are obvious in this piece of Granite. The average automobile contains: Minerals
Chapter 4 8/27/2013. Igneous Rocks. and Intrusive Igneous Activity. Introduction. The Properties and Behavior of Magma and Lava
 Introduction Chapter 4 Igneous rocks form by the cooling of magma (or lava). Large parts of the continents and all the oceanic crust are composed of. and Intrusive Igneous Activity The Properties and Behavior
Introduction Chapter 4 Igneous rocks form by the cooling of magma (or lava). Large parts of the continents and all the oceanic crust are composed of. and Intrusive Igneous Activity The Properties and Behavior
12 Chemistry (Mg,Fe) 2 SiO 4 Olivine is forms what is called an isomorphous solid solution series that ranges between two end members: Forsterite Mg
 11 Olivine Structure Olivine is a common green or brown rock forming minerals which consists of a solid-solution series between Forsterite (Fo) and Fayalite (Fa). It is an orthorhombic orthosilicate with
11 Olivine Structure Olivine is a common green or brown rock forming minerals which consists of a solid-solution series between Forsterite (Fo) and Fayalite (Fa). It is an orthorhombic orthosilicate with
Unit 4 Lesson 4 Volcanoes. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Magma Magic What is a volcano? A volcano is any place where gas, ash, or melted rock come out of the ground. Many volcanoes are dormant, meaning an eruption has not occurred in a long period of time. What
Magma Magic What is a volcano? A volcano is any place where gas, ash, or melted rock come out of the ground. Many volcanoes are dormant, meaning an eruption has not occurred in a long period of time. What
Introduction. Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth
 Introduction Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth Example: Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii Hot (~1,200 o C) lava pools around the volcanic vent. Hot, syrupy lava runs downhill as a lava flow. The
Introduction Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth Example: Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii Hot (~1,200 o C) lava pools around the volcanic vent. Hot, syrupy lava runs downhill as a lava flow. The
Sphene (Titanite) Plane polarized light. Honey brown/orange Wedge-shaped crystals
 Sphene (Titanite) Plane polarized light Honey brown/orange Wedge-shaped crystals Sphene (Titanite) Crossed nicols High-order, washedout interference colors (light orange) #1 Rule for (Heavy) Radiogenic
Sphene (Titanite) Plane polarized light Honey brown/orange Wedge-shaped crystals Sphene (Titanite) Crossed nicols High-order, washedout interference colors (light orange) #1 Rule for (Heavy) Radiogenic
Vulcanicity. Objectives to identify the basic structure of volcanoes and understand how they form.
 Vulcanicity Objectives to identify the basic structure of volcanoes and understand how they form. Some key terms to start.. Viscosity how well a substance (lava) flows. Acid lavas have a high viscosity,
Vulcanicity Objectives to identify the basic structure of volcanoes and understand how they form. Some key terms to start.. Viscosity how well a substance (lava) flows. Acid lavas have a high viscosity,
THE MONTE MAGGIORE PERIDOTITE (CORSICA)
 MONTE MAGGIORE CAPO CORSO CORSICA Giovanni B. Piccardo THE MONTE MAGGIORE PERIDOTITE (CORSICA) FIELD RELATIONSHIPS MORB Gabbro Spinel (ex-garnet) pyroxenites L ESCURSIONE A MONTE MAGGIORE The Monte Maggiore
MONTE MAGGIORE CAPO CORSO CORSICA Giovanni B. Piccardo THE MONTE MAGGIORE PERIDOTITE (CORSICA) FIELD RELATIONSHIPS MORB Gabbro Spinel (ex-garnet) pyroxenites L ESCURSIONE A MONTE MAGGIORE The Monte Maggiore
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12 Volcanoes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Plate tectonics explains the global pattern of volcanism. Key Figure 12.20 (page
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12 Volcanoes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Plate tectonics explains the global pattern of volcanism. Key Figure 12.20 (page
Plate tectonics, rock cycle
 Dikes, Antarctica Rock Cycle Plate tectonics, rock cycle The Rock Cycle A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one
Dikes, Antarctica Rock Cycle Plate tectonics, rock cycle The Rock Cycle A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one
Volcanoes. Volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than the explosion of an atomic bomb.
 Ch. 13 Volcanoes Volcanoes Volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than the explosion of an atomic bomb. Many of these eruptions are caused by the movement of tectonic plates. Volcanism Volcanism-any activity
Ch. 13 Volcanoes Volcanoes Volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than the explosion of an atomic bomb. Many of these eruptions are caused by the movement of tectonic plates. Volcanism Volcanism-any activity
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes
 Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
Overview of Ch. 4. I. The nature of volcanic eruptions 9/19/2011. Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5
 Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
LAB 9: ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS, CUMULATES AND MELT SOURCES
 Geology 316 (Petrology) (03/26/2012) Name LAB 9: ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS, CUMULATES AND MELT SOURCES INTRODUCTION Ultramafic rocks are igneous rocks containing less than 10% felsic minerals (quartz + feldspars
Geology 316 (Petrology) (03/26/2012) Name LAB 9: ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS, CUMULATES AND MELT SOURCES INTRODUCTION Ultramafic rocks are igneous rocks containing less than 10% felsic minerals (quartz + feldspars
Critical Thinking 1. Contrast How could you tell the difference between a mafic rock and a felsic rock by looking at them?
 CHAPTER 13 2 SECTION Volcanoes Volcanic Eruptions KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: How does the composition of magma affect volcanic eruptions and lava flow? What are the
CHAPTER 13 2 SECTION Volcanoes Volcanic Eruptions KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: How does the composition of magma affect volcanic eruptions and lava flow? What are the
Igneous Rocks. Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members:
 Igneous Rocks Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members: Types of Magma Basaltic, Basic or Mafic very hot (900-1200 C) very fluid
Igneous Rocks Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members: Types of Magma Basaltic, Basic or Mafic very hot (900-1200 C) very fluid
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanic Eruptions. light in color is called a. felsic. b. oceanic. c. mantle. d. mafic. dark in color is called
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanic Eruptions 1. Lava provides an opportunity for scientists to study a. the nature of Earth s inner core. b. the nature of Earth s tectonic plates. c. temperatures
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanic Eruptions 1. Lava provides an opportunity for scientists to study a. the nature of Earth s inner core. b. the nature of Earth s tectonic plates. c. temperatures
Lab 3 - Identification of Igneous Rocks
 Lab 3 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - 1 Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly
Lab 3 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - 1 Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly
Calc-alkaline Volcanic Rocks. Calc-alkali Volcanics. Fabric. Petrography. Compositional Classification. Petrography. Processes.
 Calc-alkaline Volcanic Rocks Calc-alkali Volcanics Winter Chapters 16 & 17 Petrography Processes Field relations Volcanic arcs Petrogenesis Petrography Fabric Classification Alteration Fabric Aphanitic
Calc-alkaline Volcanic Rocks Calc-alkali Volcanics Winter Chapters 16 & 17 Petrography Processes Field relations Volcanic arcs Petrogenesis Petrography Fabric Classification Alteration Fabric Aphanitic
Abstract. 1. Introduction
 Abstract 1. Introduction 2. Geological position and host volcanics 3. Summary of primary mineralogy of Tirich and other peridotites of Dzhilinda River Figure 1. Composition of clinopyroxenes from the Dzhilinda
Abstract 1. Introduction 2. Geological position and host volcanics 3. Summary of primary mineralogy of Tirich and other peridotites of Dzhilinda River Figure 1. Composition of clinopyroxenes from the Dzhilinda
Petrology and Geochronology of Iran Tepe volcano, Eastern Rhodopes, Bulgaria: Age relationship with the Ada Tepe gold deposit. (preliminary data)
 Petrology and Geochronology of Iran Tepe volcano, Eastern Rhodopes, Bulgaria: Age relationship with the Ada Tepe gold deposit. (preliminary data) Peter Kibarov, Peter Marchev, Maria Ovtcharova, Raya Raycheva,
Petrology and Geochronology of Iran Tepe volcano, Eastern Rhodopes, Bulgaria: Age relationship with the Ada Tepe gold deposit. (preliminary data) Peter Kibarov, Peter Marchev, Maria Ovtcharova, Raya Raycheva,
A MICROANALYTICAL APPROACH TO UNDERSTANDING THE ORIGIN OF CUMULATE XENOLITHS FROM MAUNA KEA, HAWAII
 A MICROANALYTICAL APPROACH TO UNDERSTANDING THE ORIGIN OF CUMULATE XENOLITHS FROM MAUNA KEA, HAWAII Megan Pickard, Michael J. Dorais, Eric Christiansen, R. V. Fodor Limited Access to Subsurface Processes
A MICROANALYTICAL APPROACH TO UNDERSTANDING THE ORIGIN OF CUMULATE XENOLITHS FROM MAUNA KEA, HAWAII Megan Pickard, Michael J. Dorais, Eric Christiansen, R. V. Fodor Limited Access to Subsurface Processes
Part A GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET VOLCANOES. Name
 GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET VOLCANOES Name Part A 1. The rough, jumbled blocky or jagged surface of a lava flow is called a. pahoehoe b. lahar c. aa d. phreatic 2. The Cascade volcanoes like Mt. St.
GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET VOLCANOES Name Part A 1. The rough, jumbled blocky or jagged surface of a lava flow is called a. pahoehoe b. lahar c. aa d. phreatic 2. The Cascade volcanoes like Mt. St.
Name Class Date. In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements.
 CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
Study guide chapter 9
 Study guide chapter 9 1. What are the three ways solid mantle material can change phase to a liquid? Associate a boundary/hot spot to each way mantle material changes phase. 1. A decrease in pressure which
Study guide chapter 9 1. What are the three ways solid mantle material can change phase to a liquid? Associate a boundary/hot spot to each way mantle material changes phase. 1. A decrease in pressure which
Igneous Rock. Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere
 Igneous Rock Magma Molten rock under the surface Temperature = 600 o 1400 o C Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere Magma chamber - most all magma consists of silicon and oxygen (silicate)
Igneous Rock Magma Molten rock under the surface Temperature = 600 o 1400 o C Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere Magma chamber - most all magma consists of silicon and oxygen (silicate)
Lab 4 - Identification of Igneous Rocks
 Lab 4 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly recognize
Lab 4 - Identification of Igneous Rocks Page - Introduction A rock is a substance made up of one or more different minerals. Thus an essential part of rock identification is the ability to correctly recognize
Pyroxenes (Mg, Fe 2+ ) 2 Si 2 O 6 (monoclinic) and. MgSiO 3 FeSiO 3 (orthorhombic) Structure (Figure 2 of handout)
 Pyroxenes (Mg, Fe 2+ ) 2 Si 2 O 6 (monoclinic) and 20 MgSiO 3 FeSiO 3 (orthorhombic) Structure (Figure 2 of handout) Chain silicate eg Diopside Mg and Fe ions link SiO 3 chains The chain runs up and down
Pyroxenes (Mg, Fe 2+ ) 2 Si 2 O 6 (monoclinic) and 20 MgSiO 3 FeSiO 3 (orthorhombic) Structure (Figure 2 of handout) Chain silicate eg Diopside Mg and Fe ions link SiO 3 chains The chain runs up and down
Common non-silicate planetary minerals
 Common non-silicate planetary minerals Many of the non-silicate minerals are simple oxides. Corundum Al2O3 Al2+3 O3-2 Rutile Ti2O3 Ti2+3 O3-2 Ilmenite FeTiO3 Fe+3Ti+3O3-2 Hematite Fe2O3 Fe2+3 O3-2 Families
Common non-silicate planetary minerals Many of the non-silicate minerals are simple oxides. Corundum Al2O3 Al2+3 O3-2 Rutile Ti2O3 Ti2+3 O3-2 Ilmenite FeTiO3 Fe+3Ti+3O3-2 Hematite Fe2O3 Fe2+3 O3-2 Families
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 10 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Factors Affecting Eruptions Factors that determine the violence of an eruption
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 10 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Factors Affecting Eruptions Factors that determine the violence of an eruption
INTRODUCTION RESULTS METHODS. ANGELA EKSTRAND Beloit College Sponsor: Jim Rougvie TAMIR ENKHBAATAR Mongolian University of Science and Technology
 PETROGENESIS OF QUATERNARY BASALTS IN SOUTHERN HANGAY MOUNTAINS, CENTRAL MONGOLIA: MANTLE SOURCE AND MAGMATIC EVOLUTION INTRODUCTION Alkaline volcanism of equivocal origin has occurred in a north-south
PETROGENESIS OF QUATERNARY BASALTS IN SOUTHERN HANGAY MOUNTAINS, CENTRAL MONGOLIA: MANTLE SOURCE AND MAGMATIC EVOLUTION INTRODUCTION Alkaline volcanism of equivocal origin has occurred in a north-south
GY303 Igneous & Metamorphic Petrology. Lecture 7: Magma Sources and Tectonic Environments
 GY303 Igneous & Metamorphic Petrology Lecture 7: Magma Sources and Tectonic Environments Factors controlling Magma production Source rock composition Amount of fluids, especially H 2 O Pressure (Depth)
GY303 Igneous & Metamorphic Petrology Lecture 7: Magma Sources and Tectonic Environments Factors controlling Magma production Source rock composition Amount of fluids, especially H 2 O Pressure (Depth)
Overview of the KAHT system. Ian E.M. Smith, School of Environment, University of Auckland
 Overview of the KAHT system Ian E.M. Smith, School of Environment, University of Auckland Tonga-Kermadec-New Zealand Arc Developed on the Pacific - Australian convergent margin Mainly intraoceanic except
Overview of the KAHT system Ian E.M. Smith, School of Environment, University of Auckland Tonga-Kermadec-New Zealand Arc Developed on the Pacific - Australian convergent margin Mainly intraoceanic except
Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity. Aka Volcano Under the City
 Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity Aka Volcano Under the City 18.1 Magma Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Temperature and pressure increase
Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity Aka Volcano Under the City 18.1 Magma Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Temperature and pressure increase
Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100
 Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Major Concepts 1) Igneous rocks form directly from the crystallization of a magma or lava 2)
Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Major Concepts 1) Igneous rocks form directly from the crystallization of a magma or lava 2)
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann
 17.04.2010 Eyjafjallokull Volcano Shield Volcano on Iceland Phreatomagmatic eruption 1 Eyjafjallokull Volcano Shield Volcano on Iceland Phreatomagmatic eruption Eyjafjallokull Volcano Shield Volcano on
17.04.2010 Eyjafjallokull Volcano Shield Volcano on Iceland Phreatomagmatic eruption 1 Eyjafjallokull Volcano Shield Volcano on Iceland Phreatomagmatic eruption Eyjafjallokull Volcano Shield Volcano on
Igneous Rocks of the Convergent Margins
 Page 1 of 10 EENS 2120 Petrology Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Tulane University Igneous Rocks of the This document last updated on 08-Feb-2011 The convergent plate margins are the most intense areas of active
Page 1 of 10 EENS 2120 Petrology Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Tulane University Igneous Rocks of the This document last updated on 08-Feb-2011 The convergent plate margins are the most intense areas of active
Principal Investigator Co-Principal Investigator Co-Principal Investigator Prof. Talat Ahmad Vice-Chancellor Jamia Millia Islamia Delhi
 Subject Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Geology Metamorphic and Igneous Petrology Petrology and Mineralogy of Igneous IV Principal Investigator Co-Principal Investigator Co-Principal
Subject Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Geology Metamorphic and Igneous Petrology Petrology and Mineralogy of Igneous IV Principal Investigator Co-Principal Investigator Co-Principal
Mineral chemistry of submarine lavas from Hilo Ridge, Hawaii: implications for magmatic processes within Hawaiian rift zones
 Contrib Mineral Petrol (1999) 135: 355±372 Ó Springer-Verlag 1999 Huai-Jen Yang á Frederick A. Frey David A. Clague á Michael O. Garcia Mineral chemistry of submarine lavas from Hilo Ridge, Hawaii: implications
Contrib Mineral Petrol (1999) 135: 355±372 Ó Springer-Verlag 1999 Huai-Jen Yang á Frederick A. Frey David A. Clague á Michael O. Garcia Mineral chemistry of submarine lavas from Hilo Ridge, Hawaii: implications
Earth Science 11: Earth Materials: Rock Cycle
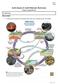 Name: Date: Earth Science 11: Earth Materials: Rock Cycle Chapter 2, pages 44 to 46 2.1: Rock Cycle What is a Rock? A solid mass of mineral or mineral-like matter that occurs naturally as part of our planet
Name: Date: Earth Science 11: Earth Materials: Rock Cycle Chapter 2, pages 44 to 46 2.1: Rock Cycle What is a Rock? A solid mass of mineral or mineral-like matter that occurs naturally as part of our planet
Constitution of Magmas. Magmas. Gas Law. Composition. Atomic Structure of Magma. Structural Model. PV = nrt H 2 O + O -2 = 2(OH) -
 Constitution of Magmas Magmas Best, Ch. 8 Hot molten rock T = 700-1200 degrees C Composed of ions or complexes Phase Homogeneous Separable part of the system With an interface Composition Most components
Constitution of Magmas Magmas Best, Ch. 8 Hot molten rock T = 700-1200 degrees C Composed of ions or complexes Phase Homogeneous Separable part of the system With an interface Composition Most components
lava magma pyroclastic materials lava flow igneous rock volcanic (extrusive igneous) rock plutonic (intrusive igneous) rock felsic magma mafic magma
 magma lava lava flow pyroclastic materials igneous rock volcanic (extrusive igneous) rock plutonic (intrusive igneous) rock felsic magma mafic magma intermediate magma viscosity magma chamber Bowen s reaction
magma lava lava flow pyroclastic materials igneous rock volcanic (extrusive igneous) rock plutonic (intrusive igneous) rock felsic magma mafic magma intermediate magma viscosity magma chamber Bowen s reaction
WHAT IS A MAGMA. Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth.
 UNIT - 8 VOLCANOES WHAT IS A MAGMA Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth. In some instances, it solidifies within the crust to form plutonic
UNIT - 8 VOLCANOES WHAT IS A MAGMA Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth. In some instances, it solidifies within the crust to form plutonic
Earth Science 232 Petrography
 Earth Science 232 Petrography Course notes by Shaun Frape and Alec Blyth Winter 2002 1 Petrology - Introduction Some Definitions Petra Greek for rock Logos Greek for disclosure or explanation Petrology
Earth Science 232 Petrography Course notes by Shaun Frape and Alec Blyth Winter 2002 1 Petrology - Introduction Some Definitions Petra Greek for rock Logos Greek for disclosure or explanation Petrology
Classification of Igneous Rocks
 Classification of Igneous Rocks Textures: Glassy- no crystals formed Aphanitic- crystals too small to see by eye Phaneritic- can see the constituent minerals Fine grained- < 1 mm diameter Medium grained-
Classification of Igneous Rocks Textures: Glassy- no crystals formed Aphanitic- crystals too small to see by eye Phaneritic- can see the constituent minerals Fine grained- < 1 mm diameter Medium grained-
Partial melting of mantle peridotite
 Partial melting of mantle peridotite 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 (TºC) Depth (km) 50 100 150 Plag lherzolite (ol-opx-cpx-pl) Spinel lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-sp) Garnet lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-gar) Graphite Diamond
Partial melting of mantle peridotite 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 (TºC) Depth (km) 50 100 150 Plag lherzolite (ol-opx-cpx-pl) Spinel lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-sp) Garnet lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-gar) Graphite Diamond
Types of Volcanoes. Key Concept: Tectonic plate motions can result in volcanic activity at plate boundaries.
 Types of Volcanoes Key Concept: Tectonic plate motions can result in volcanic activity at plate boundaries. Volcanoes How do volcanoes work? How do volcanoes work? Magma is forced onto Earth s surface.
Types of Volcanoes Key Concept: Tectonic plate motions can result in volcanic activity at plate boundaries. Volcanoes How do volcanoes work? How do volcanoes work? Magma is forced onto Earth s surface.
Rocks. Types of Rocks
 Rocks Rocks are the most common material on Earth. They are naturally occurring aggregates of one or more minerals. 1 Igneous rocks, Types of Rocks Sedimentary rocks and Metamorphic rocks. 2 1 3 4 2 IGNEOUS
Rocks Rocks are the most common material on Earth. They are naturally occurring aggregates of one or more minerals. 1 Igneous rocks, Types of Rocks Sedimentary rocks and Metamorphic rocks. 2 1 3 4 2 IGNEOUS
Geology 1 st Semester Exam YSBAT
 1. What is the role of a geologist? Geology 1 st Semester Exam YSBAT 2016-2017 2. Earth is subdivided into three main layers based on what? 3. What features do you find at divergent boundaries? 4. Rock
1. What is the role of a geologist? Geology 1 st Semester Exam YSBAT 2016-2017 2. Earth is subdivided into three main layers based on what? 3. What features do you find at divergent boundaries? 4. Rock
Rocks. 1) igneous = fiery 2) sedimentary = settled 3) metamorphic = changed form
 Rocks Identified on the basis of composition and texture (arrangement of features). Classification depends on description and interpretation of these features. Three major categories: 1) igneous = fiery
Rocks Identified on the basis of composition and texture (arrangement of features). Classification depends on description and interpretation of these features. Three major categories: 1) igneous = fiery
CHAPTER 3: THE STUDY OF ROCKS
 CHAPTER 3: THE STUDY OF ROCKS INTRODUCTION Rock is defined as a mixtures formed of aggregates of one or more minerals (aggregate of minerals). Rocks can be formed by many different processes such as: (1)
CHAPTER 3: THE STUDY OF ROCKS INTRODUCTION Rock is defined as a mixtures formed of aggregates of one or more minerals (aggregate of minerals). Rocks can be formed by many different processes such as: (1)
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards
 UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 5 Magma and Volcanism Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information: pasakyi@ug.edu.gh College
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 5 Magma and Volcanism Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information: pasakyi@ug.edu.gh College
Advanced Igneous petrology EOSC 530 Laboratory 1: Mantle Xenoliths
 EOSC 530 Labs 1 Instructor: Kopylova Advanced Igneous petrology EOSC 530 Laboratory 1: Mantle Xenoliths Introduction: Upper mantle rocks can be found in ultramafic massifs or as xenoliths in basalts and
EOSC 530 Labs 1 Instructor: Kopylova Advanced Igneous petrology EOSC 530 Laboratory 1: Mantle Xenoliths Introduction: Upper mantle rocks can be found in ultramafic massifs or as xenoliths in basalts and
Florida Atlantic University PETROLOGY -- MIDTERM TWO KEY
 GLY4310 Name 60 points March 26, 2012 12 took exam - Numbers to the left of the question number in red are the number of incorrect responses. Instructor comments are in blue. Florida Atlantic University
GLY4310 Name 60 points March 26, 2012 12 took exam - Numbers to the left of the question number in red are the number of incorrect responses. Instructor comments are in blue. Florida Atlantic University
GEOLOGY. Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02
 GEOLOGY Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02 Topic No. & Title : 37 Magma Bowen Series (Part 01) Academic Script What is Igneous Petrology? Igneous
GEOLOGY Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02 Topic No. & Title : 37 Magma Bowen Series (Part 01) Academic Script What is Igneous Petrology? Igneous
EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4
 Name: EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4 Introduction In the previous lab, we learned about mineral characteristics, properties and identities as well as the three basic rock
Name: EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4 Introduction In the previous lab, we learned about mineral characteristics, properties and identities as well as the three basic rock
Formation of the Hawaiian Islands. Volcanoes, Magma, and Hot Spots
 Formation of the Hawaiian Islands Volcanoes, Magma, and Hot Spots Topics Hawai i Ring of Fire Hot Spots Decompression Melting The Hawai i Hot Spot Topics Hawai i Ring of Fire Hot Spots Decompression Melting
Formation of the Hawaiian Islands Volcanoes, Magma, and Hot Spots Topics Hawai i Ring of Fire Hot Spots Decompression Melting The Hawai i Hot Spot Topics Hawai i Ring of Fire Hot Spots Decompression Melting
Volcano - A Volcano is an opening in the Earth s surface through which molten material or volcanic gases are erupted.
 What is a Volcano? Volcano - A Volcano is an opening in the Earth s surface through which molten material or volcanic gases are erupted. A volcano can either be a classic volcanic cone.. Mt. St. Helens,
What is a Volcano? Volcano - A Volcano is an opening in the Earth s surface through which molten material or volcanic gases are erupted. A volcano can either be a classic volcanic cone.. Mt. St. Helens,
Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms.
 Chapter 10 Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms. Reading Strategy Previewing Before you read the section,
Chapter 10 Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms. Reading Strategy Previewing Before you read the section,
GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca:
 Name: Date: GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca: SiO 2 silicon dioxide. This is quartz when it crystallizes.
Name: Date: GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca: SiO 2 silicon dioxide. This is quartz when it crystallizes.
The Origin of Felsic Lavas in the East African Rift
 The Origin of Felsic Lavas in the East African Rift Gabriel Akec, Pennsylvania State University Dr. Tanya Furman, Professor of Geosciences, Research Mentor Abstract East African Rift is a site of active
The Origin of Felsic Lavas in the East African Rift Gabriel Akec, Pennsylvania State University Dr. Tanya Furman, Professor of Geosciences, Research Mentor Abstract East African Rift is a site of active
SEA-FLOOR SPREADING. In the 1950 s and early 1960 s detailed study of the oceans revealed the following surprising information:-
 SEA-FLOOR SPREADING In the 1950 s and early 1960 s detailed study of the oceans revealed the following surprising information:- Detailed bathymetric (depth) studies showed that there was an extensive submarine
SEA-FLOOR SPREADING In the 1950 s and early 1960 s detailed study of the oceans revealed the following surprising information:- Detailed bathymetric (depth) studies showed that there was an extensive submarine
Topic Page: Peridotite
 Topic Page: Peridotite Definition: peridotite from The Hutchinson Unabridged Encyclopedia with Atlas and Weather Guide Rock consisting largely of the mineral olivine; pyroxene and other minerals may also
Topic Page: Peridotite Definition: peridotite from The Hutchinson Unabridged Encyclopedia with Atlas and Weather Guide Rock consisting largely of the mineral olivine; pyroxene and other minerals may also
ANDESITE CONFERENCE GUIDEBOOK
 STATE OF OREGON DEPARTMENT OF GEOLOGY AND MINERAL 1069 STATE OFFICE BUILDING PORTLAND. OREGON 972Q1 INDUSTRIES ANDESITE CONFERENCE GUIDEBOOK Editor, Hollis M. Dole Cartographer, C. J. Newhouse Bulletin
STATE OF OREGON DEPARTMENT OF GEOLOGY AND MINERAL 1069 STATE OFFICE BUILDING PORTLAND. OREGON 972Q1 INDUSTRIES ANDESITE CONFERENCE GUIDEBOOK Editor, Hollis M. Dole Cartographer, C. J. Newhouse Bulletin
When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere.
 When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere. A volcano is a mountain that forms when magma reaches the
When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere. A volcano is a mountain that forms when magma reaches the
DIAMONDS 101. Table of Contents
 DIAMONDS 101 Diamonds 101 is a generalised summary of information commonly discussed or used in diamond exploration. This information is intended for those with no or little background in diamonds and
DIAMONDS 101 Diamonds 101 is a generalised summary of information commonly discussed or used in diamond exploration. This information is intended for those with no or little background in diamonds and
GY 111: Physical Geology
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 9: Extrusive Igneous Rocks Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) The chemical composition of the crust 2) Crystallization of molten
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 9: Extrusive Igneous Rocks Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) The chemical composition of the crust 2) Crystallization of molten
67. PHASE CHEMISTRY STUDIES ON GABBRO AND PERIDOTITE ROCKS FROM SITE 334, DSDP LEG 37
 67. PHASE CHEMISTRY STUDIES N GABBR AND PERIDTITE RCKS FRM SITE 334, DSDP LEG 37 R.F. Symes, J.C. Bevan, and R. Hutchison, Department of Mineralogy, British Museum (Natural History, London, England INTRDUCTIN
67. PHASE CHEMISTRY STUDIES N GABBR AND PERIDTITE RCKS FRM SITE 334, DSDP LEG 37 R.F. Symes, J.C. Bevan, and R. Hutchison, Department of Mineralogy, British Museum (Natural History, London, England INTRDUCTIN
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore MAGMA For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources, visit:
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore MAGMA For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources, visit:
