Constitution of Magmas. Magmas. Gas Law. Composition. Atomic Structure of Magma. Structural Model. PV = nrt H 2 O + O -2 = 2(OH) -
|
|
|
- Dominick Booker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Constitution of Magmas Magmas Best, Ch. 8 Hot molten rock T = degrees C Composed of ions or complexes Phase Homogeneous Separable part of the system With an interface Composition Most components Low vapor pressure Designated by mole fraction (X i ) Volatile components Mainly exist as a gas Designated by vapor pressure (p i ) Fluid pressure = sum of partial pressures Gas Law PV = nrt Atomic Structure of Magma Quenched to form a glass Si & Al are polymerized with O Forming networks of Si-O chains Short-range structural order Structural Model Network formers Si, Al Network modifiers Ca, Mg, etc Dissolved water has a strong effect H 2 O + O -2 = 2(OH) -
2 Magma Generation Source Regions Magmas form at perturbations in P,T,X Convergent plates Divergent plates Must originate in the mantle or crust At Hawaii 60 km deep Only 1 to 3% melt in peridotite Peridotite mantle source Melting Heat of fusion About 300 times the rock s specific heat Melting of rock consumes much heat Mechanisms for melting Temperature increase by mass transfer Decompression Changes in composition reducing melting point Temperature Increase Mechanical deformation Friction generates heat Mass transfer of rock Descending oceanic lithosphere Basaltic underplating of continental crust Decompression Upwelling mantle Beneath oceanic or continental rift Adiabatic system Pressure causes all temperature change Changes in Composition Increase in water pressure Lowers the solidus Subduction zones Peridotite wedge Over subducting oceanic crust
3 Magma From Solid Rock Basalt & peridotite systems Granite systems Basalt & Peridotite Equilibrium fusion Solid and liquid remain in equilibrium Continuous but limited composition range Fractional fusion Liquid is immediately removed from host rock Melts are both oversaturated & undersaturated with respect to Si Influence of Pressure Pressure strongly influences the cotectic Partial melts of mantle peridotite are basalts At higher pressures partial melts are more silica deficient Role of CO 2 Role of H 2 O Polymerizes melt Contracts olivine field Favors silica-poor alkali melts Repeated melting episodes favors incompatible element enrichment Depolymerizes melt & stabilizes olivine Partial melts more silica rich Favors tholeiitic basalts
4 Mantle-derived Primary Melts Wide range of melt compositions possible Fractional crystallization vs. Partial melting Primary melt Segregated from peridotite source rock First crystallized minerals similar to mantle source zone Derivative melt Modified after leaving the source region Volcanic Rocks of Island Arcs Complex tectonic situation and broad spectrum High proportion of basaltic andesite and andesite Most andesites occur in subduction zone settings Major Elements and Magma Series Tholeiitic (MORB, OIT) Alkaline (OIA) Calc-Alkaline (~ restricted to SZ) Granitic (Rhyolitic) Systems Impossible to generate granites by partial melting of mantle peridotite or subducted oceanic floor basalt Their origin is related to older sialic crust Granites concentrated along old subduction zones
5 Water Saturation Water Undersaturation Common granite mineral assemblage Saturated granite melts have 10 to 15% H 2 O Natural granite melts have about 4% H 2 O Biotite, K-spar, Fe-Ti oxide ½ O 2 + biotite = K-spar + Fe 3 O 4 + H 2 O Excess water drives this reaction to the left Hence, most granites are not water saturated Origin of Granites Partial Melting of lower crust Source in mica-amphibolites Contain 1-2% H 2 O Lowest T melts are K-rich granite Higher T, deeper melts are Ca-rich granodiorite Subduction Zone Magma Subducted slab Mafic primary melts Peridotite mantle wedge Mafic primary melts Dehydration Beneath Orogen Large amount of water in oceanic slab Water in pore space Water in alteration minerals Heating dehydrates the slab Liberated water promotes partial melting of peridotite Composition is Si-saturated tholeiite
6 Structure of an Island Arc Schematic cross section through a typical island arc after Gill (1981) Instabilities Diapirs A layer of less dense material overlain by a denser material is unstable The upper layer develops undulations and bulges (Rayleigh-Taylor instabilities) The spacing of the bulges depends on the thickness of the light layer and its density contrast with the heavy layer Diapir Ascent Velocity of ascent depends on diapir size and shape A sphere is the most efficient shape Surface area ~ frictional resistance Volume ~ buoyant driving force Rise velocity proportional to area squared Neutral Buoyancy Positively buoyant Melt less dense than surrounding rocks Primary basalt magma surrounded by mantle peridotite Negatively buoyant Melt more dense than surrounding rocks Olivine basalt intruded into continental crust
7 Density Filter Crustal rocks block the ascent of denser magmas Heat from these magmas melt the lower crust Residual melts may rise Exsolved volatiles also facilitate rise Emplacement Process Stoping Brecciation Doming Ballooning Void zones Magma Diversification Magmatic differentiation Gravitational settling Liquid immiscibility Crystal-liquid liquid Fractionation Regular pattern of compositional variation Variation of MgO is a good measure of olivine fractionation Computer mixing programs can be used
8 Magma Mixing Two different magmas may blend to produce a hybrid Common with calc-alkali magma Blended magmas should have linear composition with the parents Volcanic Rocks of Island Arcs Complex tectonic situation and broad spectrum High proportion of basaltic andesite and andesite Most andesites occur in subduction zone settings Major Elements and Magma Series Tholeiitic (MORB, OIT) Alkaline (OIA) Calc-Alkaline (~ restricted to SZ) Magma Ascent and Emplacement Best Chapter 9 Topics How does magma ascend? How do dikes form? How is magma emplaced? Magma Generation Partial melting Upper mantle Deep crust Magma density Less than surroundings
9 Buoyancy Magma Rise Driving force is density difference Resisting force is the magma viscosity Silicic magma High viscosity requires large volume Mafic magma Low viscosity allows small volumes to rise Energy Sources Thermal energy Melting caused by decompression or volatile flux Gravitational energy Driven by density differential Instabilities Diapirs A layer of less dense material overlain by a denser material is unstable The upper layer develops undulations and bulges (Rayleigh-Taylor instabilities) The spacing of the bulges depends on the thickness of the light layer and its density contrast with the heavy layer Diapir Ascent Velocity of ascent depends on diapir size and shape A sphere is the most efficient shape Surface area ~ frictional resistance Volume ~ buoyant driving force Rise velocity proportional to area squared Neutral Buoyancy Positively buoyant Melt that is less dense than surrounding rocks Primary basalt magma surrounded by mantle peridotite Negatively buoyant Melt that is more dens than surrounding rocks Olivine basalt intruded into continental crust
10 Density Filter Crustal rocks block the ascent of denser magmas Heat from these magmas melt the lower crust Residual melts may rise Exsolved volatiles also facilitate rise How Can Dense Magma Rise? Volumetric expansion on melting? Exsolution of bubbles? There must be another cause. Magma Overpressure For a magma lens, pressure is equal to the lithostatic load P m = ρ r g z The pressure can be greater in a conduit connecting a deeper pocket to the surface This overpressure can be great enough to bring denser magma to the surface Dikes Magma Ascent Sub-vertical cracks in brittle rock Diapirs Bodies of buoyant magma They squeeze through ductile material Dikes Intrusions with very small aspect ratio Aspect: width/length = 10-2 to 10-4 Near vertical orientation Generally 1-2 meters thick
11 Dike Swarms Hundreds of contemporaneous dikes May be radial Large radial swarms associated with mantle plumes Intrusion into Dikes Stress perpendicular to the fracture is less than magma pressure Pressure must overcome resistance to viscous flow Magma can hydrofracture to rock and propagate itself Stress for Dikes Dikes are hydraulic tensile fractures σ 1 vertical σ 3 vertical They lie in the plane of σ 1 and σ 2 They open in the direction of σ 3 They are good paleostress indicators Orientation Near-vertical dikes imply horizontal σ 3 Typical in areas of tectonic extension Can be used to interpret past stress fields Dikes commonly form fingers upwards En Echelon Dikes Sub-parallel overlapping alignments Suggest a rotation of σ 3 in the horizontal
12 Radial Dikes Spanish Peaks, Colorado Spanish Peaks, Colorado Stress orientation around a central intrusion σ 1 is perpendicular to the contact (radial) σ 3 is horizontal and tangential to contact Radial dikes are radial from intrusion Far dikes assume the regional trend
Topics. Magma Ascent and Emplacement. Magma Generation. Magma Rise. Energy Sources. Instabilities. How does magma ascend? How do dikes form?
 Magma Ascent and Emplacement Reading: Encyclopedia of Volcanoes: Physical Properties of Magmas (pp. 171-190) Magma Chambers (pp. 191-206) Plumbing Systems (pp. 219-236) Magma ascent at shallow levels (pp.237-249)
Magma Ascent and Emplacement Reading: Encyclopedia of Volcanoes: Physical Properties of Magmas (pp. 171-190) Magma Chambers (pp. 191-206) Plumbing Systems (pp. 219-236) Magma ascent at shallow levels (pp.237-249)
Magma Formation and Behavior
 Magma Formation and Behavior Questions What causes mantle rock to melt, resulting in magma formation? Why is magma formation restricted to specific plate tectonic settings? Why are mafic (basaltic) magmas
Magma Formation and Behavior Questions What causes mantle rock to melt, resulting in magma formation? Why is magma formation restricted to specific plate tectonic settings? Why are mafic (basaltic) magmas
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks
 Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Magma Formation and Behavior
 Magma Formation and Behavior Introduction: The study of body waves as they pass through Earth's interior provides strong evidence that the Earth's mantle is composed almost entirely of solid ultramafic
Magma Formation and Behavior Introduction: The study of body waves as they pass through Earth's interior provides strong evidence that the Earth's mantle is composed almost entirely of solid ultramafic
Essentials of Geology, 11e
 Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Igneous Rocks. Definition of Igneous Rocks. Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma
 Igneous Rocks Definition of Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma Magma molten rock within the Earth Lava molten rock on the Earth s s surface Igneous
Igneous Rocks Definition of Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma Magma molten rock within the Earth Lava molten rock on the Earth s s surface Igneous
Structure of the Earth and the Origin of Magmas
 Page 1 of 12 EENS 2120 Petrology Tulane University Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Structure of the Earth and the Origin of Magmas This document last updated on 23-Jan-2015 Magmas do not form everywhere beneath
Page 1 of 12 EENS 2120 Petrology Tulane University Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Structure of the Earth and the Origin of Magmas This document last updated on 23-Jan-2015 Magmas do not form everywhere beneath
Chapter 4 8/27/2013. Igneous Rocks. and Intrusive Igneous Activity. Introduction. The Properties and Behavior of Magma and Lava
 Introduction Chapter 4 Igneous rocks form by the cooling of magma (or lava). Large parts of the continents and all the oceanic crust are composed of. and Intrusive Igneous Activity The Properties and Behavior
Introduction Chapter 4 Igneous rocks form by the cooling of magma (or lava). Large parts of the continents and all the oceanic crust are composed of. and Intrusive Igneous Activity The Properties and Behavior
The Nature of Igneous Rocks
 The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
Igneous Rocks. Igneous Rocks. Genetic Classification of
 Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
Chapter 4 Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks
 Chapter 4 Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts
Chapter 4 Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Up from the Inferno: Magma and Igneous Rocks Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts
Imagine the first rock and the cycles that it has been through.
 A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann. Grotzinger Jordan. Understanding Earth. Sixth Edition
 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks: Solids from Melts 1 About Igneous Rocks Igneous
Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks: Solids from Melts 1 About Igneous Rocks Igneous
Plate tectonics, rock cycle
 Dikes, Antarctica Rock Cycle Plate tectonics, rock cycle The Rock Cycle A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one
Dikes, Antarctica Rock Cycle Plate tectonics, rock cycle The Rock Cycle A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one
Most mafic magmas come from the upper mantle and lower crust. This handout will address five questions:
 Geology 101 Origin of Magma From our discussions of the structure of the interior of the Earth, it is clear that the upper parts of the Earth (crust and mantle) are mostly solid because s-waves penetrate
Geology 101 Origin of Magma From our discussions of the structure of the interior of the Earth, it is clear that the upper parts of the Earth (crust and mantle) are mostly solid because s-waves penetrate
GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Spring 2009 Sc ore / 40
 GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Name Spring 2009 Sc ore / 40 QUIZ 3 1) Name two geologic features that provide physical evidence for the mineralogy of the earth s mantle (2 pts) Ophiolites,
GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Name Spring 2009 Sc ore / 40 QUIZ 3 1) Name two geologic features that provide physical evidence for the mineralogy of the earth s mantle (2 pts) Ophiolites,
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 2017-2016 Chapter (4) Volcanoes Chapter 4: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity cataclysmic relating to or denoting a violent natural even Eventually the entire
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 2017-2016 Chapter (4) Volcanoes Chapter 4: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity cataclysmic relating to or denoting a violent natural even Eventually the entire
Volcanic Eruptions and Hydrovolcanism
 Find the Face Volcanic Eruptions and Hydrovolcanism Ocean Ridges Continental Rifts Subduction Zones: Continental Oceanic Back Arc Basins Hot Spots Plumes Cinder Cones Composite Volcanoes Shield VolcanoesCinder
Find the Face Volcanic Eruptions and Hydrovolcanism Ocean Ridges Continental Rifts Subduction Zones: Continental Oceanic Back Arc Basins Hot Spots Plumes Cinder Cones Composite Volcanoes Shield VolcanoesCinder
GY303 Igneous & Metamorphic Petrology. Lecture 7: Magma Sources and Tectonic Environments
 GY303 Igneous & Metamorphic Petrology Lecture 7: Magma Sources and Tectonic Environments Factors controlling Magma production Source rock composition Amount of fluids, especially H 2 O Pressure (Depth)
GY303 Igneous & Metamorphic Petrology Lecture 7: Magma Sources and Tectonic Environments Factors controlling Magma production Source rock composition Amount of fluids, especially H 2 O Pressure (Depth)
Introduction. Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth
 Introduction Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth Example: Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii Hot (~1,200 o C) lava pools around the volcanic vent. Hot, syrupy lava runs downhill as a lava flow. The
Introduction Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth Example: Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii Hot (~1,200 o C) lava pools around the volcanic vent. Hot, syrupy lava runs downhill as a lava flow. The
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
Full file at
 Chapter 2 PLATE TECTONICS AND PHYSICAL HAZARDS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. What direction is the Pacific Plate currently moving, based on the chain of Hawaiian Islands with only the easternmost island
Chapter 2 PLATE TECTONICS AND PHYSICAL HAZARDS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. What direction is the Pacific Plate currently moving, based on the chain of Hawaiian Islands with only the easternmost island
GEOLOGY. Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02
 GEOLOGY Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02 Topic No. & Title : 37 Magma Bowen Series (Part 01) Academic Script What is Igneous Petrology? Igneous
GEOLOGY Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02 Topic No. & Title : 37 Magma Bowen Series (Part 01) Academic Script What is Igneous Petrology? Igneous
When magma is ejected by a volcano or other vent, the material is called lava. Magma that has cooled into a solid is called igneous rock.
 This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 4) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry magma For the
This website would like to remind you: Your browser (Apple Safari 4) is out of date. Update your browser for more security, comfort and the best experience on this site. Encyclopedic Entry magma For the
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals. Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane SGM 210_2013
 Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore MAGMA For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources, visit:
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore MAGMA For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources, visit:
Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity. Aka Volcano Under the City
 Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity Aka Volcano Under the City 18.1 Magma Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Temperature and pressure increase
Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity Aka Volcano Under the City 18.1 Magma Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Temperature and pressure increase
Most mafic magmas come from the upper mantle and lower crust. This handout will address five questions:
 IDS 102 Origin of Magma From our discussions of the structure of the interior of the Earth, it is clear that the upper parts of the Earth (crust and mantle) are mostly solid because s-waves penetrate those
IDS 102 Origin of Magma From our discussions of the structure of the interior of the Earth, it is clear that the upper parts of the Earth (crust and mantle) are mostly solid because s-waves penetrate those
Lecture 3 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Dr. Shwan Omar
 Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Archean Terranes. Archean Rocks. Southeastern Africa. West Greenland. Kaapvaal Craton. Ancient Gneiss Complex
 Archean Terranes Archean Rocks Chapter 15A >2.5 Gy old Younger supracrustal sequences Greenstone belts Calc-alkaline metavolcanic rocks Older gneiss complexes Quartzo-feldspathic rocks Tonalites and migmatites
Archean Terranes Archean Rocks Chapter 15A >2.5 Gy old Younger supracrustal sequences Greenstone belts Calc-alkaline metavolcanic rocks Older gneiss complexes Quartzo-feldspathic rocks Tonalites and migmatites
Igneous Rock. Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere
 Igneous Rock Magma Molten rock under the surface Temperature = 600 o 1400 o C Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere Magma chamber - most all magma consists of silicon and oxygen (silicate)
Igneous Rock Magma Molten rock under the surface Temperature = 600 o 1400 o C Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere Magma chamber - most all magma consists of silicon and oxygen (silicate)
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 10 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Factors Affecting Eruptions Factors that determine the violence of an eruption
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 10 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Factors Affecting Eruptions Factors that determine the violence of an eruption
Theory of Plate Tectonics
 Plate Tectonics Theory of Plate Tectonics Lithosphere is made of sections called plates that move around called continental drift Plates move because they float on the asthenosphere Most plates consist
Plate Tectonics Theory of Plate Tectonics Lithosphere is made of sections called plates that move around called continental drift Plates move because they float on the asthenosphere Most plates consist
Overview of Ch. 4. I. The nature of volcanic eruptions 9/19/2011. Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5
 Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Formation of the Hawaiian Islands. Volcanoes, Magma, and Hot Spots
 Formation of the Hawaiian Islands Volcanoes, Magma, and Hot Spots Topics Hawai i Ring of Fire Hot Spots Decompression Melting The Hawai i Hot Spot Topics Hawai i Ring of Fire Hot Spots Decompression Melting
Formation of the Hawaiian Islands Volcanoes, Magma, and Hot Spots Topics Hawai i Ring of Fire Hot Spots Decompression Melting The Hawai i Hot Spot Topics Hawai i Ring of Fire Hot Spots Decompression Melting
ERTH 456 / GEOL 556 Volcanology. Lecture 06: Conduits
 1 / 28 ERTH 456 / GEOL 556 Volcanology Lecture 06: Conduits Ronni Grapenthin rg@nmt.edu MSEC 356, x5924 hours: TR 3-4PM or appt. September 12, 2016 2 / 28 How does magma get from source to surface? What
1 / 28 ERTH 456 / GEOL 556 Volcanology Lecture 06: Conduits Ronni Grapenthin rg@nmt.edu MSEC 356, x5924 hours: TR 3-4PM or appt. September 12, 2016 2 / 28 How does magma get from source to surface? What
Layer Composition Thickness State of Matter
 Unit 4.2 Test Review Earth and Its Layers 1. Label the layers of the earth. oceanic crust continental crust lithosphere asthenosphere mantle outer core inner core 2. Complete the Following Table about
Unit 4.2 Test Review Earth and Its Layers 1. Label the layers of the earth. oceanic crust continental crust lithosphere asthenosphere mantle outer core inner core 2. Complete the Following Table about
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes
 Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
L.O: THE CRUST USE REFERENCE TABLE PAGE 10
 USE REFERENCE TABLE PAGE 10 1. The oceanic crust is thought to be composed mainly of A) granite B) sandstone C) basalt D) rhyolite 2. To get sample material from the mantle, drilling will be done through
USE REFERENCE TABLE PAGE 10 1. The oceanic crust is thought to be composed mainly of A) granite B) sandstone C) basalt D) rhyolite 2. To get sample material from the mantle, drilling will be done through
Plate Tectonics. Why Continents and Ocean Basins Exist
 Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics Why Continents and Ocean Basins Exist Topics Density Structure of Earth Isostasy Sea-Floor Spreading Mechanical Structure of Earth Driving Mechanism of Plate Tectonics Lithospheric
Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics Why Continents and Ocean Basins Exist Topics Density Structure of Earth Isostasy Sea-Floor Spreading Mechanical Structure of Earth Driving Mechanism of Plate Tectonics Lithospheric
Structure of the Earth
 Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High in Magnesium (Mg) and Iron (Fe) Core: High in Nickel
Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High in Magnesium (Mg) and Iron (Fe) Core: High in Nickel
Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms.
 Chapter 10 Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms. Reading Strategy Previewing Before you read the section,
Chapter 10 Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms. Reading Strategy Previewing Before you read the section,
Partial melting of mantle peridotite
 Partial melting of mantle peridotite 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 (TºC) Depth (km) 50 100 150 Plag lherzolite (ol-opx-cpx-pl) Spinel lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-sp) Garnet lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-gar) Graphite Diamond
Partial melting of mantle peridotite 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 (TºC) Depth (km) 50 100 150 Plag lherzolite (ol-opx-cpx-pl) Spinel lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-sp) Garnet lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-gar) Graphite Diamond
Plate Tectonics. Continental Drift Sea Floor Spreading Plate Boundaries
 Plate Tectonics Continental Drift Sea Floor Spreading Plate Boundaries Continental Drift 1915, Alfred Wegener - Pangea hypothesis: suggested Earth s continents were part of a large super-continent 200
Plate Tectonics Continental Drift Sea Floor Spreading Plate Boundaries Continental Drift 1915, Alfred Wegener - Pangea hypothesis: suggested Earth s continents were part of a large super-continent 200
10. Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering Curves.
 Map of ocean floor Evidence in Support of the Theory of Plate Tectonics 10. Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering Curves. The Earth's magnetic field behaves as if there were a bar magnet in the center of
Map of ocean floor Evidence in Support of the Theory of Plate Tectonics 10. Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering Curves. The Earth's magnetic field behaves as if there were a bar magnet in the center of
Lecture 24: Convergent boundaries November 22, 2006
 Lecture 24: Convergent boundaries November 22, 2006 Convergent boundaries are characterized by consumption of oceaninc crust in subduction zones, with attendant arc volcanism, metamorphism and uplift.
Lecture 24: Convergent boundaries November 22, 2006 Convergent boundaries are characterized by consumption of oceaninc crust in subduction zones, with attendant arc volcanism, metamorphism and uplift.
Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100
 Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Major Concepts 1) Igneous rocks form directly from the crystallization of a magma or lava 2)
Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Major Concepts 1) Igneous rocks form directly from the crystallization of a magma or lava 2)
Calc-alkaline Volcanic Rocks. Calc-alkali Volcanics. Fabric. Petrography. Compositional Classification. Petrography. Processes.
 Calc-alkaline Volcanic Rocks Calc-alkali Volcanics Winter Chapters 16 & 17 Petrography Processes Field relations Volcanic arcs Petrogenesis Petrography Fabric Classification Alteration Fabric Aphanitic
Calc-alkaline Volcanic Rocks Calc-alkali Volcanics Winter Chapters 16 & 17 Petrography Processes Field relations Volcanic arcs Petrogenesis Petrography Fabric Classification Alteration Fabric Aphanitic
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards
 UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 5 Magma and Volcanism Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information: pasakyi@ug.edu.gh College
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 5 Magma and Volcanism Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information: pasakyi@ug.edu.gh College
Plate Tectonics. Structure of the Earth
 Plate Tectonics Structure of the Earth The Earth can be considered as being made up of a series of concentric spheres, each made up of materials that differ in terms of composition and mechanical properties.
Plate Tectonics Structure of the Earth The Earth can be considered as being made up of a series of concentric spheres, each made up of materials that differ in terms of composition and mechanical properties.
Important information from Chapter 1
 Important information from Chapter 1 Distinguish between: Natural hazard // Disaster // Catastrophe What role does human population play in these categories? Know how to read a Hazard Map, such as Figure
Important information from Chapter 1 Distinguish between: Natural hazard // Disaster // Catastrophe What role does human population play in these categories? Know how to read a Hazard Map, such as Figure
Plate Tectonics Lab II: Background Information
 Plate Tectonics Lab II: Background Information This lab is based on a UW ESS101 Lab. Note: Hand in only the Answer Sheet at the back of this guide to your Instructor Introduction One of the more fundamental
Plate Tectonics Lab II: Background Information This lab is based on a UW ESS101 Lab. Note: Hand in only the Answer Sheet at the back of this guide to your Instructor Introduction One of the more fundamental
Plate Tectonics. Why Continents and Ocean Basins Exist
 Plate Tectonics Why Continents and Ocean Basins Exist Topics Density Structure of Earth Isostasy Sea-Floor Spreading Mechanical Structure of Earth Driving Mechanism of Plate Tectonics Lithospheric Plate
Plate Tectonics Why Continents and Ocean Basins Exist Topics Density Structure of Earth Isostasy Sea-Floor Spreading Mechanical Structure of Earth Driving Mechanism of Plate Tectonics Lithospheric Plate
Chapter 7 Metamorphism, Metamorphic Rocks, and Hydrothermal Rocks
 Chapter 7 Metamorphism, Metamorphic Rocks, and Hydrothermal Rocks Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Metamorphism What happens to rocks that are
Chapter 7 Metamorphism, Metamorphic Rocks, and Hydrothermal Rocks Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Metamorphism What happens to rocks that are
Plate Tectonics. A. Continental Drift Theory 1. Early development 2. Alfred Wegener s mechanism
 Plate Tectonics A. Continental Drift Theory 1. Early development 2. Alfred Wegener s mechanism B. Seafloor Spreading 1. Earthquakes and volcanoes 2. Seafloor maps and dates 3. Continental drift revisited
Plate Tectonics A. Continental Drift Theory 1. Early development 2. Alfred Wegener s mechanism B. Seafloor Spreading 1. Earthquakes and volcanoes 2. Seafloor maps and dates 3. Continental drift revisited
Chapter 10: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Section 1: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions I. Factors Affecting Eruptions Group # Main Idea:
 Chapter 10: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Section 1: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions I. Factors Affecting Eruptions Group # A. Viscosity Group # B. Dissolved Gases Group # II. Volcanic Material
Chapter 10: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Section 1: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions I. Factors Affecting Eruptions Group # A. Viscosity Group # B. Dissolved Gases Group # II. Volcanic Material
Chapter 8 10/19/2012. Introduction. Metamorphism. and Metamorphic Rocks. Introduction. Introduction. The Agents of Metamorphism
 Chapter 8 Metamorphism Introduction Metamorphism - The transformation of rocks, usually beneath Earth's surface, as the result of heat, pressure, and/or fluid activity, produces metamorphic rocks During
Chapter 8 Metamorphism Introduction Metamorphism - The transformation of rocks, usually beneath Earth's surface, as the result of heat, pressure, and/or fluid activity, produces metamorphic rocks During
Chapter 7: Volcanoes 8/18/2014. Section 1 (Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics) 8 th Grade. Ring of Fire
 Section 1 (Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics) Chapter 7: Volcanoes 8 th Grade Ring of Fire a major belt of es that rims the Pacific Ocean Volcanic belts form along the boundaries of Earth s plates as they
Section 1 (Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics) Chapter 7: Volcanoes 8 th Grade Ring of Fire a major belt of es that rims the Pacific Ocean Volcanic belts form along the boundaries of Earth s plates as they
Welcome to GEO 101 Introduction to Geology
 Welcome to GEO 101 Introduction to Geology so what is Geology? not just rocks! Geology is... study of Earth and planetary bodies processes responsible for formation processes that modify all areas of geology
Welcome to GEO 101 Introduction to Geology so what is Geology? not just rocks! Geology is... study of Earth and planetary bodies processes responsible for formation processes that modify all areas of geology
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. Some volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than a(n) a. hand grenade. b. earthquake. c. geyser. d. atomic bomb. 2. The cause
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. Some volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than a(n) a. hand grenade. b. earthquake. c. geyser. d. atomic bomb. 2. The cause
Plate Tectonics. entirely rock both and rock
 Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
The influence of short wavelength variations in viscosity on subduction dynamics
 1 Introduction Deformation within the earth, driven by mantle convection due primarily to cooling and subduction of oceanic lithosphere, is expressed at every length scale in various geophysical observations.
1 Introduction Deformation within the earth, driven by mantle convection due primarily to cooling and subduction of oceanic lithosphere, is expressed at every length scale in various geophysical observations.
Plate Tectonics: The New Paradigm
 Earth s major plates Plate Tectonics: The New Paradigm Associated with Earth's strong, rigid outer layer: Known as the lithosphere Consists of uppermost mantle and overlying crust Overlies a weaker region
Earth s major plates Plate Tectonics: The New Paradigm Associated with Earth's strong, rigid outer layer: Known as the lithosphere Consists of uppermost mantle and overlying crust Overlies a weaker region
Visualizing Earth Science. Chapter Overview. Volcanoes and Eruption Types. By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner. Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other
 Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
Part A GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET VOLCANOES. Name
 GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET VOLCANOES Name Part A 1. The rough, jumbled blocky or jagged surface of a lava flow is called a. pahoehoe b. lahar c. aa d. phreatic 2. The Cascade volcanoes like Mt. St.
GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET VOLCANOES Name Part A 1. The rough, jumbled blocky or jagged surface of a lava flow is called a. pahoehoe b. lahar c. aa d. phreatic 2. The Cascade volcanoes like Mt. St.
Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
 1 Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Presentation modified from: Instructor Resource Center on CD-ROM, Foundations of Earth Science,, 4 th Edition, Lutgens/Tarbuck, Rock Cycle Igneous Rocks Today 2 Rock
1 Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Presentation modified from: Instructor Resource Center on CD-ROM, Foundations of Earth Science,, 4 th Edition, Lutgens/Tarbuck, Rock Cycle Igneous Rocks Today 2 Rock
Thursday, October 4 th
 Thursday, October 4 th Objective: We will use and define the different ways to classify igneous rocks. Warm-up: 1. Which type of lava is most viscous? 2. Which type of lava has the least amount of silicate?
Thursday, October 4 th Objective: We will use and define the different ways to classify igneous rocks. Warm-up: 1. Which type of lava is most viscous? 2. Which type of lava has the least amount of silicate?
NC Earth Science Essential Standards
 NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
PLATE TECTONICS, VOLCANISM AND IGNEOUS ROCKS
 PLATE TECTONICS, VOLCANISM AND IGNEOUS ROCKS PLATE TECTONICS TO IGNEOUS ROCKS Internal Heat Seafloor Spreading/Plate Tectonics Volcanism Plate Boundary Intra-plate (hot spot) Divergent Convergent Igneous
PLATE TECTONICS, VOLCANISM AND IGNEOUS ROCKS PLATE TECTONICS TO IGNEOUS ROCKS Internal Heat Seafloor Spreading/Plate Tectonics Volcanism Plate Boundary Intra-plate (hot spot) Divergent Convergent Igneous
Petrology. Petrology: the study of rocks, especially aspects such as physical, chemical, spatial and chronoligic. Associated fields include:
 Petrology Petrology: the study of rocks, especially aspects such as physical, chemical, spatial and chronoligic. Associated fields include: Petrography: study of description and classification of rocks
Petrology Petrology: the study of rocks, especially aspects such as physical, chemical, spatial and chronoligic. Associated fields include: Petrography: study of description and classification of rocks
Summary and Conclusions
 Chapter 9 Summary and Conclusions 9.1 Summary The contents of this thesis revolve around the question of what type of geodynamics was active in the Early Earth and other terrestrial planets. The geology
Chapter 9 Summary and Conclusions 9.1 Summary The contents of this thesis revolve around the question of what type of geodynamics was active in the Early Earth and other terrestrial planets. The geology
Chapter 21: Metamorphism. Fresh basalt and weathered basalt
 Chapter 21: Metamorphism Fresh basalt and weathered basalt Chapter 21: Metamorphism The IUGS-SCMR proposed this definition: Metamorphism is a subsolidus process leading to changes in mineralogy and/or
Chapter 21: Metamorphism Fresh basalt and weathered basalt Chapter 21: Metamorphism The IUGS-SCMR proposed this definition: Metamorphism is a subsolidus process leading to changes in mineralogy and/or
GEOL 3313 Petrology of Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks Study Guide for Final Examination Glen Mattioli
 GEOL 3313 Petrology of Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks Study Guide for Final Examination Glen Mattioli Chapter 5: Crystal-Melt phase diagrams Effect of water pressure on feldspar stability Hypersolvus vs.
GEOL 3313 Petrology of Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks Study Guide for Final Examination Glen Mattioli Chapter 5: Crystal-Melt phase diagrams Effect of water pressure on feldspar stability Hypersolvus vs.
Questions and Topics
 Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift Questions and Topics 1. What are the theories of Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift? 2. What is the evidence that Continents move? 3. What are the forces that
Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift Questions and Topics 1. What are the theories of Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift? 2. What is the evidence that Continents move? 3. What are the forces that
Differentiation 2: mantle, crust OUTLINE
 Differentiation 2: mantle, crust OUTLINE Reading this week: Should have been White Ch 10 and 11!! 7- Nov Differentiation of the Earth, Core formation W 10.6.6, 11.4 9- Nov Moon, crust, mantle, atmosphere
Differentiation 2: mantle, crust OUTLINE Reading this week: Should have been White Ch 10 and 11!! 7- Nov Differentiation of the Earth, Core formation W 10.6.6, 11.4 9- Nov Moon, crust, mantle, atmosphere
Volcanoes. Volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than the explosion of an atomic bomb.
 Ch. 13 Volcanoes Volcanoes Volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than the explosion of an atomic bomb. Many of these eruptions are caused by the movement of tectonic plates. Volcanism Volcanism-any activity
Ch. 13 Volcanoes Volcanoes Volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than the explosion of an atomic bomb. Many of these eruptions are caused by the movement of tectonic plates. Volcanism Volcanism-any activity
Volcanology. The study of volcanoes
 Volcanology The study of volcanoes Magma forms wherever temperature and pressure are high enough to melt rock. Some magma forms at the aesthenosphere Magma also forms at plate boundaries, where intense
Volcanology The study of volcanoes Magma forms wherever temperature and pressure are high enough to melt rock. Some magma forms at the aesthenosphere Magma also forms at plate boundaries, where intense
The mantle under the crust (about 2,890 km deep) is composed mostly of silicate rocks rich in magnesium and iron. The elements of the crust have
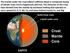 The mantle under the crust (about 2,890 km deep) is composed mostly of silicate rocks rich in magnesium and iron. The elements of the crust have derived from the mantle by fractional melting that operates
The mantle under the crust (about 2,890 km deep) is composed mostly of silicate rocks rich in magnesium and iron. The elements of the crust have derived from the mantle by fractional melting that operates
Chapter 8: The Dynamic Planet
 Chapter 8: The Dynamic Planet I. The Pace of Change A. The Geologic Time Scale II. Earth s Structure and Internal Energy A. The Earth s Core B. The Earth s Mantle C. The Earth s Crust III. The Geologic
Chapter 8: The Dynamic Planet I. The Pace of Change A. The Geologic Time Scale II. Earth s Structure and Internal Energy A. The Earth s Core B. The Earth s Mantle C. The Earth s Crust III. The Geologic
The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks
 The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks Igneous rocks form as molten magma or lava cools and solidifies. Magma is completely or partly molten
The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks Igneous rocks form as molten magma or lava cools and solidifies. Magma is completely or partly molten
Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark
 Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Effusive: lavas (e.g., Kilauea) Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Explosive: pyroclastic rocks (e.g., Krakatau) Factors Governing
Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Effusive: lavas (e.g., Kilauea) Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Explosive: pyroclastic rocks (e.g., Krakatau) Factors Governing
UNIT 4: Earth Science Chapter 12: Earth s Internal Processes (pages )
 CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be turned in to your teacher
CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be turned in to your teacher
Introduction. Introduction. Introduction 10/15/2014. The Agents of Metamorphism. Metamorphism. and Metamorphic Rocks
 Introduction Metamorphism The transformation of rocks, usually beneath Earth's surface, as the result of heat, pressure, and/or fluid activity, produces metamorphic rocks Metamorphism and Metamorphic Rocks
Introduction Metamorphism The transformation of rocks, usually beneath Earth's surface, as the result of heat, pressure, and/or fluid activity, produces metamorphic rocks Metamorphism and Metamorphic Rocks
Igneous activity is related to convergent plate situations that result in the subduction of one plate beneath another Ocean-ocean Island Arc
 Igneous activity related to subduction (Chapters 16, 17) Subduction-related activity Igneous activity is related to convergent plate situations that result in the subduction of one plate beneath another
Igneous activity related to subduction (Chapters 16, 17) Subduction-related activity Igneous activity is related to convergent plate situations that result in the subduction of one plate beneath another
Basaltic and Gabbroic Rocks
 Page 1 of 18 EENS 212 Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Basaltic and Gabbroic Rocks Petrology Tulane University This document last updated on 04-Mar-2004 Although basaltic and gabbroic rocks are found in nearly
Page 1 of 18 EENS 212 Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Basaltic and Gabbroic Rocks Petrology Tulane University This document last updated on 04-Mar-2004 Although basaltic and gabbroic rocks are found in nearly
Lecture Outline Friday January 12 Friday January 19, 2018
 Lecture Outline Friday January 12 Friday January 19, 2018 Questions?? Key Points for today The structure of the Earth Introduction to Plate Tectonic Theory and Convection Chapter 2 Development of the Plate
Lecture Outline Friday January 12 Friday January 19, 2018 Questions?? Key Points for today The structure of the Earth Introduction to Plate Tectonic Theory and Convection Chapter 2 Development of the Plate
EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4
 Name: EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4 Introduction In the previous lab, we learned about mineral characteristics, properties and identities as well as the three basic rock
Name: EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4 Introduction In the previous lab, we learned about mineral characteristics, properties and identities as well as the three basic rock
Lecture 12 COMPLEX MELTING MODELS. (see books by Shaw, Trace Elements in Magmas (2006) and Zou, Quantitative Geochemistry (2007))
 Lecture 12 COMPLEX MELTING MODELS (see books by Shaw, Trace Elements in Magmas (2006) and Zou, Quantitative Geochemistry (2007)) Thus far we have considered two end-member melting models, batch melting
Lecture 12 COMPLEX MELTING MODELS (see books by Shaw, Trace Elements in Magmas (2006) and Zou, Quantitative Geochemistry (2007)) Thus far we have considered two end-member melting models, batch melting
Structure of the Earth
 And the ROCK CYCLE Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density High in silicon (Si) and oxygen (O) Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High
And the ROCK CYCLE Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density High in silicon (Si) and oxygen (O) Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High
EASC100: EXAM1 (07) Lithosphere and Hydrosphere
 EASC100: EXAM1 (07) Lithosphere and Hydrosphere Name: 1. Why do Mercury and the Moon lack an atmosphere? A) They formed after all the gas had been used up. B) They are so cold that all their gases have
EASC100: EXAM1 (07) Lithosphere and Hydrosphere Name: 1. Why do Mercury and the Moon lack an atmosphere? A) They formed after all the gas had been used up. B) They are so cold that all their gases have
Rare Earth Elements in some representative arc lavas
 Rare Earth Elements in some representative arc lavas Low-K (tholeiitic), Medium-K (calc-alkaline), and High-K basaltic andesites and andesites. A typical N-MORB pattern is included for reference Notes:
Rare Earth Elements in some representative arc lavas Low-K (tholeiitic), Medium-K (calc-alkaline), and High-K basaltic andesites and andesites. A typical N-MORB pattern is included for reference Notes:
Dissolution and precipitation during flow in porous media
 1/25 Class project for GEOS 692: Transport processes and physical properties of rocks Dissolution and precipitation during flow in porous media Gry Andrup-Henriksen Fall 2006 1 2/25 Outline Introduction
1/25 Class project for GEOS 692: Transport processes and physical properties of rocks Dissolution and precipitation during flow in porous media Gry Andrup-Henriksen Fall 2006 1 2/25 Outline Introduction
5. Convergent boundaries produce a relatively low number of earthquakes compared to other boundaries. a. True
 1. Earth s crust is thinner than its mantle. ANSWER: True 2. The concept of isostacy states that high-density rock will stand higher than low-density rock, which explains the formation of subduction zones.
1. Earth s crust is thinner than its mantle. ANSWER: True 2. The concept of isostacy states that high-density rock will stand higher than low-density rock, which explains the formation of subduction zones.
Chapter. Graphics by Tasa Graphic Arts. Inc.
 Earth Chapter Plate Science 9 Tectonics Graphics by Tasa Graphic Arts. Inc. 1 I. Earth s surface is made up of lithospheric plates. A. Lithospheric plates are composed of the crust and part of the upper
Earth Chapter Plate Science 9 Tectonics Graphics by Tasa Graphic Arts. Inc. 1 I. Earth s surface is made up of lithospheric plates. A. Lithospheric plates are composed of the crust and part of the upper
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12 Volcanoes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Plate tectonics explains the global pattern of volcanism. Key Figure 12.20 (page
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12 Volcanoes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Plate tectonics explains the global pattern of volcanism. Key Figure 12.20 (page
Block: Igneous Rocks. From this list, select the terms which answer the following questions.
 Geology 12 Name: Mix and Match: Igneous Rocks Refer to the following list. Block: porphyritic volatiles mafic glassy magma mixing concordant discontinuous reaction series igneous vesicular partial melting
Geology 12 Name: Mix and Match: Igneous Rocks Refer to the following list. Block: porphyritic volatiles mafic glassy magma mixing concordant discontinuous reaction series igneous vesicular partial melting
Chapter 8 Lecture. Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology. Twelfth Edition. Metamorphism. Rocks. Tarbuck and Lutgens Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 8 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Twelfth Edition Metamorphism and dmetamorphic Rocks Tarbuck and Lutgens Chapter 8 Metamorphic Rocks What Is Metamorphism? Metamorphism means
Chapter 8 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Twelfth Edition Metamorphism and dmetamorphic Rocks Tarbuck and Lutgens Chapter 8 Metamorphic Rocks What Is Metamorphism? Metamorphism means
Petrology. Petrology: the study of rocks, especially aspects such as physical, chemical, spatial and chronoligic. Classification:
 Petrology Petrology: the study of rocks, especially aspects such as physical, chemical, spatial and chronoligic. Associated fields include: Petrography: study of description and classification of rocks
Petrology Petrology: the study of rocks, especially aspects such as physical, chemical, spatial and chronoligic. Associated fields include: Petrography: study of description and classification of rocks
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. What can cause some of the most dramatic changes to Earth s surface? a. solar activity b. tides c. geysers d. volcanic eruptions
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. What can cause some of the most dramatic changes to Earth s surface? a. solar activity b. tides c. geysers d. volcanic eruptions
Why Does Oceanic Crust Sink Beneath Continental Crust At Convergent Boundaries
 Why Does Oceanic Crust Sink Beneath Continental Crust At Convergent Boundaries What is the process by which oceanic crust sinks beneath a deep-ocean Why does oceanic crust sink beneath continental crust
Why Does Oceanic Crust Sink Beneath Continental Crust At Convergent Boundaries What is the process by which oceanic crust sinks beneath a deep-ocean Why does oceanic crust sink beneath continental crust
