Monitoring Mount Sinabung in Indonesia Using Multi- Temporal InSAR
|
|
|
- Warren Stafford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Korean Journal of Remote Sensing, Vol.33, No.1, 2017, pp.37~46 ISSN ( Print ) ISSN (Online) Article Monitoring Mount Sinabung in Indonesia Using Multi- Temporal InSAR Chang-Wook Lee*, Zhong Lu** and Jin Woo Kim** * Division of Science Education, College of Education, Kangwon National University ** Roy M Huffington Department of Earth Sciences, Southern Methodist University Abstract : Sinabung volcano in Indonesia was formed due to the subduction between the Eurasian and Indo-Australian plates along the Pacific Ring of Fire. After being dormant for about 400 years, Sinabung volcano erupted on the 29th of August, 2010 and most recently on the 1st of November, We measured the deformation of Sinabung volcano using Advanced Land Observing Satellite/Phased Array type L-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (ALOS/PALSAR) interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) images acquired from February 2007 to January Based on multi-temporal InSAR processing, we mapped the ground surface deformation before, during, and after the 2010 eruption with time-series InSAR technique. During the 3 years before the 2010 eruption, the volcano inflated at an average rate of ~1.7 cm/yr with a markedly higher rate of 6.6 cm/yr during the 6 months prior to the 2010 eruption. The inflation was constrained to the top of the volcano. From the 2010 eruption to January 2011, the volcano subsided by approximately 3 cm (~6 cm/yr). We interpreted that the inflation was due to magma accumulation in a shallow reservoir beneath Sinabung. The deflation was attributed to magma withdrawal from the shallow reservoir during the eruption as well as thermo-elastic compaction of erupted material. This result demonstrates once again the utility of InSAR for volcano monitoring. Key Words : Sinabung volcano, surface deformation, InSAR, time-series 1. Introduction The Island of Sumatra is located along a segment of the Ring of Fire, on the northern boundary of the Australian plate and the southern boundary of the Eurasian plate (Global Volcanism Program). From the geologic record it is apparent that during the past 2.5 million years, this region has been experiencing significant seismic and volcanic activity. The Island of Sumatra has been the location for three of the world s twelve largest earthquakes all with magnitudes higher than Mw 8.5. The 2004 Sumatra earthquake, which is the third largest earthquake (Mw 9.1), was particularly devastating because it was accompanied by a tsunami that killed more than 227,000 people from 14 countries in South Asia and East Africa. The largest eruption Received February 9, 2017; Revised February 10, 2017; Accepted February 11, Corresponding Author: Jin Woo Kim (jinwook@smu.edu) This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited 37
2 Korean Journal of Remote Sensing, Vol.33, No.1, 2017 event in this region, with a volcanic explosivity index volcano has been poorly monitored. The latest eruption 50 km southeast of Sinabung. kilometers above the crater and forced the evacuation at Sinabung began on the 29th of August, This (VEI) of 8, occurred between 69,000 and 77,000 years explosive eruption produced ash plumes rising several ago at Toba volcano on the Island of Sumatra, less than of 20,000 to 30,000 people within a 6 km radius of the Mount Sinabung is a stratovolcano in the volcano. Two individual ash plumes from separate vents northwestern part of the Island of Sumatra in Indonesia near the summit were produced during this eruption, one (Fig. 1a). The volcano was formed during the vertical and one horizontal (Figs. 2a and b). Explosions Pleistocene to Holocene and consists of andesitic and and ash plumes accompanied by strong volcanic dacitic lavas. Sinabung s 2,460-m-high conical structure tremors, which were felt by residents as far as 8 km has four overlapping craters (Global Volcanism away, continued until the 22nd of September. Program). It is mostly covered with dense vegetation According to the Center of Volcanology and Geological and only the top of the volcano is free of vegetation (Fig. Hazard Mitigation (CVGHM), the ash plume, over the 1b). The four summit vents are elongated from north- duration of this eruption, reached a maximum height of south and range from 60 m to 300 m in diameter (Figs. 5 km above the crater floor on the 7th of September. 1c and d). Little is known about the volcano s eruption The volcano remained dormant for another three history, but the last historical eruption occurred around years before erupting again on the 15th of September, 400 years ago. Because of this long dormancy, the Fig. 1. (a) Sinabung volcano, located in the northern region of the Island of Sumatra, Indonesia. (b) Landsat-7 image acquired on May 19, 2003 of the Mount Sinabung area. (c) Averaged SAR amplitude image between January 1, 2007 and January 16, (d) Combined Landsat-7 and averaged SAR images. Red arrows indicate the location of multi-craters and the yellow dotted lines delineate the extent of the rocky area. 3 8
3 Monitoring Mount Sinabung in Indonesia Using Multi-Temporal InSAR Fig. 2. Twin ash plumes from Sinabung volcano eruption of 29-30th of August, Picture by the Jakarta Post on the 29th of August (a) and the 30th of August (b). (c) Landsat 7 image (RGB = 3,2,1) acquired on September 11, During this eruption the ash plume rose to an Simons, 2004; Lu et al., 2010; Lu and Dzurisin, 2014; Chaussard and Amelung, 2012; Ebmeier et al., 2010; altitude of 6.1 km, and 3,700 people within a 3-km Philibosian and Simon, 2011; Furuta, 2009). Because radius of the volcano were evacuated. Moreover, Sinabung is heavily vegetated, there is too much loss volcanic ash fell as far away as 50 km from the volcano of coherence in C-band InSAR imagery. However, in the northeast direction. Landsat 7 satellite image Chaussard and Amelung (2010, 2012) processed (Fig. 2c) acquired 4 days before the eruption thirteen L-band ALOS/PALSAR images from (September 11, 2013) shows a white ash cloud over the Sinabung, acquired before 2010 that show a summit of Sinabung and a grey volcanic ash plume on progressive rate of inflation of 2.2 cm/yr. In this study, the east side of the volcano. we used twenty ALOS/PALSAR data (Table 1) with The size of Sinabung volcano and the frequent and calibrated radar backscatter at HH polarization, complex nature of its eruptions make it difficult to study including seven new images acquired in 2010 and the deformation that is occurring here using traditional January 2011, to study deformation of the volcano. methods that require surface based instruments. InSAR We applied a small baseline subset (SBAS) InSAR is an efficient method for measuring surface technique (Berardino et al., 2002; Lee et al., 2011) to deformation over large areas (Massonnet and Feigl, estimate time-series surface deformation using a multi- 1998; Rignot, 2008; Ng et al., 2009; Lu et al., 2009; interferogram processing approach (Rignot, 2008; Pan Jung et al., 2013a), and has been applied worldwide in the study of volcanic deformation (Pritchard and 3 9 and Tang, 2010). Atmospheric artifacts are reduced
4 Korean Journal of Remote Sensing, Vol.33, No.1, 2017 Table 1. Characteristics of ALOS/PALSAR data used in this study Number Mission (Polarization) Orbit number Date Perpendicular (YYYYMMDD) baseline (m) 1 ALOS/PALSAR(HH) (M) 2 ALOS/PALSAR(HH) (S) 3 ALOS/PALSAR(HH) (S) 4 ALOS/PALSAR(HH) (S) 5 ALOS/PALSAR(HH) (S) 6 ALOS/PALSAR(HH) (S) 7 ALOS/PALSAR(HH) (S) 8 ALOS/PALSAR(HH) (S) 9 ALOS/PALSAR(HH) (S) 10 ALOS/PALSAR(HH) (S) 11 ALOS/PALSAR(HH) (S) 12 ALOS/PALSAR(HH) (S) 13 ALOS/PALSAR(HH) (S) 14 ALOS/PALSAR(HH) (S) 15 ALOS/PALSAR(HH) (S) 16 ALOS/PALSAR(HH) (S) 17 ALOS/PALSAR(HH) (S) 18 ALOS/PALSAR(HH) (S) 19 ALOS/PALSAR(HH) (S) 20 ALOS/PALSAR(HH) (S) Perpendicular baseline (m): calculation perpendicular baseline information of Master (M) image corresponding to Slave (S) images respectively. through spatio-temporal filtering after the mean deformation is obtained (Jung et al., 2013b) and iterative processing can further improve the time-series deformation estimates (Lee et al., 2011). When using this algorithm, the deformation for a specific time period can be calculated more precisely by minimizing all error components (Lee et al., 2012). This technique of a refined SBAS time-series analysis can successfully measure deformation with an error of 0.2 to 0.9 mm in the temporal domain and a root mean square error (RMSE) of 0.66 mm/yr in the spatial domain (Lee et al., 2012). 2. Data processing We initially applied InSAR processing to our SAR dataset, and then carried out the SBAS processing and stacking to characterize the surface deformation of the Sinabung volcano in spatio-temporal domain. Using twenty ALOS/PALSAR images from the 20th of February, 2007 to the 16th of January, 2011 (Table 1), we generated 39 interferograms (Fig. 3). Most of the interferograms had a perpendicular baseline of less than 400 m, but one interferogram had a baseline of 550 m. The best coherence was constrained on the volcano summit. Outside the summit, coherence was maintained only at many scattered patches of rocky and less-vegetated areas (i.e. selected interferograms in Fig. 4). Figs. 4(a)-(k) show interferograms acquired from the 20th of February, 2007 to the 31st of August, 2010, spanning 1 to 3 years. These images show 2 to 6 cm of surface uplift in the direction of the satellite s line of site (LOS) over the 40
5 Monitoring Mount Sinabung in Indonesia Using Multi-Temporal InSAR Fig. 3. Thirty-nine high-coherence interferograms according to perpendicular baseline using 20 SAR images. Fig. 4. (a)-(k) represent surface deformation (inflation) on the summit with a high-coherence area before the eruption. (l) shows surface deformation (deflation) in the opposite direction compared to (a)-(k). 4 1
6 Korean Journal of Remote Sensing, Vol.33, No.1, 2017 volcano summit while the interferogram from the 31st of August, 2010, to the 16th of January, 2011, that spans the 2010 eruption, show 3 cm of subsidence over the summit area. 3. Results An averaged surface deformation rate map (Fig. 5) was generated from 39 interferograms using SBAS processing. The areas of each interferogram with the coherence less than 0.4 were excluded from our analysis. The volcano summit (P1) experienced about 9 cm of inflation from the 20th of February, 2007, to the 31st of August, 2010 (Fig. 5). The inflation was likely due to the intrusion of magma from a deep source to the shallow reservoir. At locations P2, P3, and P4, surface deformation was not significant during the observation period (Fig. 5). This suggests that the inflation at Sinabung was constrained within a radius of about 500 m from the volcano summit. The time-series surface deformation generated by SBAS processing includes two noticeable fluctuations around early and late 2008 at the summit (P(1) in Fig. 6) compared to the stability at other selected points (P(2), P(3), and P(4) in Fig. 6). This phenomenon may have been caused by the depressurization of the magma chamber due to periodic volcanic degassing at the summit of Sinabung. In accordance with this analysis, surface deformation of the summit area steadily increased from the period of Fig. 7(a) until the period of Fig. 7(o) with a ground uplift pattern. However, Figs. 7(p) and (q) show rapid ground uplift after 138 and 184 days, respectively, from Fig. 7(o). It is especially rapid when compared with Fig. 7(o) at the summit, where there is one fringe (4 cm) of increased surface deformation. The deformation in these interferograms is consistent with the ground movement at P(1) in Fig. 5 between the 13th of January, 2010, and the 31st of August, On the contrary, Figs. 7(r)-(t) displays clear deformation of one fringe (4 cm) in the opposite direction, away from the Fig. 5. SBAS-estimated mean surface deformation rate map over high coherence areas (>0.4) exploiting the SAR dataset from 2/20/07 to 1/16/11. P1 represents one of highest deformation areas in the summit. P(2-4) were selected for comparison with a major deformation area (P1). P2 is an additional point separated from the summit area of Sinabung mountain. P(3-4) are far from the summit point P1 within the Sinabung mountain area. 42
7 Monitoring Mount Sinabung in Indonesia Using Multi-Temporal InSAR Fig. 6. Time series surface deformation estimated by SBAS processing from 2007 to Red diamond P(1) shows large surface deformation point on the summit area at Sinabung volcano. Black inverted triangle P(2) represents a reference point in the bare soil zone. Green cross P(3) and purple triangle P(4) display the northern and southern parts of the mountain from Fig. 5. Fig. 7. Cumulative surface deformation maps around summit area (red rectangle in Fig. 5) from the SBAS processing. 4 3
8 Korean Journal of Remote Sensing, Vol.33, No.1, 2017 sensor, after the August-September 2010 eruption events. Such a large deformation could be due to a combined effects of depressurization of the shallow magma reservoir due to cooling, and thermo-elastic contraction and poro-elastic settling of eruptive deposits (e.g., Lu et al., 2005; Wadge et al., 2006; Lee et al., 2008; Poland, 2010). 4. Discussion and Conclusion The SBAS technique was used to precisely estimate surface deformation rates and time-series measurements at Sinabung volcano between 2007 and Sinabung volcano displayed gradual inflation (~1.7 cm/yr) for approximately 3 years and then transitioned to a period of rapid inflation (~6.6 cm/yr) at the summit of the volcano during the 6 months prior to the main eruption event. A similarly rapid period of deflation (~5.8 cm/yr) occurred during the 4 months of the post-eruption period. The greatest surface deformation was measured to be 8-10 cm at the summit of the mountain a few months before the 2010 eruption. The Sinabung volcano has a relatively simple eruption cycle model that includes two primary processes. First, the magma chamber is fed from below, causing surface uplift. The inflation trend is punctuated by episodic deflation caused by depressurization of the shallow magma reservoir due to degassing or other processes. When the resulting pressure in the magma reservoir is sufficient, magma is forced to erupt through the conduit to the surface until the pressure inside the reservoir decreases. Second, the cooling of the magma inside the reservoir as well as the thermo-elastic contraction of the erupted material generated surface deflation as the 2010 eruption. These observations and interpretations are consistent with previous study of volcanic deformation in the area of Sinabung volcano (Chussard and Amelung, 2010, 2012). We can compare InSAR time-series results with GPS observation data from March 24 th 2011 to verify the movement of the surface inflation or deflation with another SAR satellite mission in future work because GPS stations were installed and monitored on Sinabung volcano early of 2011 after 2010 eruption (Kriswati et al., 2014). This study shows how the use of InSAR and timeseries technique can facilitate the monitoring of dynamic processes on especially hazardous volcanoes. The spatially dense measurements of surface deformation help constrain the causes of the observed deformation and the magma plumbing system. Continuous monitoring of ground deformation at Sinabung and other volcanoes worldwide will help reduce volcanic hazards. Acknowledgment This research was funded by the Korean Society of Remote Sensing. This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (NRF- 2015M1A3A3A ) and the Korea Meteorological Administration Research and Development Program under Grant KMIPA ( ). The SAR data used in this study are copyrighted by the Alaska Satellite Facility and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. References Berardino, P, G. Fornaro, R. Lanari, and E. Sansoti, A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms, IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 40(11): Chaussard, E. and F. Amelung, Monitoring the 44
9 Monitoring Mount Sinabung in Indonesia Using Multi-Temporal InSAR ups and downs of Sumatra and Java with D- Insar time-series, American Geophysical Union. Fall Meeting 2010, abstract #G23C Chaussard, E., and F. Amelung, Precursory inflation of shallow magma reservoirs at west Sunda volcanoes detected by InSAR, Geophysical Research Letters, 39(21). Ebmeier, S. K., J. Biggs, T. A. Mather, G. Wadge, and F. Amelung, Steady downslope movement on the western flank of Arenal volcano, Costa Rica, Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosysttem, 11(12): Q Furuta, R., Case study of small scale surface deformation detection using ALOS PALSAR differential interferometry, Proc. Fringe 2009 workshop, Frascati Italy. Global Volcanism Program, Volcanoes of the World, Smithsonian Institution, Jung, H.S., Z. Lu, and L. Zhang, 2013a. Feasibility of along-track displacement measurement from Sentinel-1 interferometric wide-swath mode. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 51: Jung, H.S., D.T. Lee, Z. Lu, and J.S. Won, 2013b. Ionospheric Correction in SAR Interferogram by Multiple-Aperture Interferometry, IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 51(5): Kriswati, E., H. Kuncoro, and I. Meilano, Low Rate of Sinabung Deformation Inferred by GPS Measurement, Proc. of AIP Conference, 4th International Symposium on Earthquake and Disaster Mitigation 2014, 1658(1): Lee, C.W., Z. Lu, O. Kwoun, and J. S. Won, Deformation of Augustine volcano, Alaska, , measured by ERS and ENVISAT SAR interferometry, Earth, planets and space, 60(5): Lee, C.W., Z. Lu, H.S. Jung, J.S. Won, and D. Dzurisin, Surface Deformation of Augustine Volcano (Alaska), , from Multiple- Interferogram Processing Using a Refined SBAS InSAR Approach, USGS Professional Papers, 1769, Lee, C.W., Z. Lu, and H.S. Jung, Simulation of time series surface deformation to validate multi-interferogram InSAR processing technique, International Journal of Remote Sensing, 33(22): Lu, Z., Masterlark, T., and Dzurisin, D., Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) Study of Okmok Volcano, Alaska, : Magma Supply Dynamics and Post-emplacement Lava Flow Deformation, Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 110: B Lu, Z., J.W. Kim, H. Lee, C.K. Shum, J. Duan, M. Ibaraki, O. Akyilmaz, and C.H. Read, Helmand River Hydrologic Studies Using ALOS PALSAR InSAR and ENVISAT Altimetry, Marine Geodesy, 32(3): Lu, Z., Dzurisin, D., Biggs, J., Wicks, C., Jr, and McNutt, S., Ground surface deformation patterns, magma supply, and magma storage at Okmok volcano, Alaska, from InSAR analysis: 1. Intereruption deformation, , Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 115(B5): B00B02. Lu, Z. and D. Dzurisin, InSAR Imaging of Aleutian Volcanoes, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg. Massonnet, D. and K.L. Feigl, Radar interferometry and its application to changes in the Earth s surface, Reviews of Geophysics, 36(4): Ng, A.H.M., H.C. Chang, L. Ge, C. Rizos, and M. 45
10 Korean Journal of Remote Sensing, Vol.33, No.1, 2017 Omura, Assessment of radar interferometry performance for ground subsidence monitoring due to underground mining, Earth Planets Space, (61): Pan, G. and D. Tang, Damage information derived from multi-sensor data of the Wenchuan Earthquake of May 2008, International Journal of Remote Sensing, 31(13): Philibosian, B. and M. Simon, A survey of volcanic deformation on Java using ALOS PALSAR interferometric time series, Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 12(11): Pritchard, M. E. and M. Simons, Surveying volcanic arcs with satellite radar interferometry: The central Andes. Kamchatka, and beyond, GSA Today, 14(8): Poland, M., Localized surface disruptions observed by InSAR during strong earthquakes in Java and Hawaii, Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 100(2): Rignot, E., Changes in West Antarctic ice stream dynamics observed with ALOS PALSAR data, Geophysical Research Letters, 35(12): L1205. Wadge, G., G.S. Mattioli, and R.A. Herd, Ground deformation at Soufriére Hills Volcano, Montserrat during measured by radar interferometry and GPS, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 152(1):
Research Article Mapping Pyroclastic Flow Inundation Using Radar and Optical Satellite Images and Lahar Modeling
 Hindawi Journal of Sensors Volume 218, Article ID 8217565, 12 pages https://doi.org/1.1155/218/8217565 Research Article Mapping Pyroclastic Flow Inundation Using Radar and Optical Satellite Images and
Hindawi Journal of Sensors Volume 218, Article ID 8217565, 12 pages https://doi.org/1.1155/218/8217565 Research Article Mapping Pyroclastic Flow Inundation Using Radar and Optical Satellite Images and
Diverse deformation patterns of Aleutian volcanoes from InSAR
 Diverse deformation patterns of Aleutian volcanoes from InSAR Zhong Lu 1, Dan Dzurisin 1, Chuck Wicks 2, and John Power 3 U.S. Geological Survey 1 Cascades Volcano Observatory, Vancouver, Washington 2
Diverse deformation patterns of Aleutian volcanoes from InSAR Zhong Lu 1, Dan Dzurisin 1, Chuck Wicks 2, and John Power 3 U.S. Geological Survey 1 Cascades Volcano Observatory, Vancouver, Washington 2
In order to obtain a long term monitoring result for the Kilauea Volcano, ALOS PALSAR images taken on Track 287, Frame 38, ascending orbit with 21.5 d
 ALOS PALSAR OBSERVATION OF KILAUEA VOLCANO ACTIVITIES FROM 2006 TO 2009 Zhe Hu, Linlin Ge, Xiaojing Li, Kui Zhang, Alex Hay-Man NG and Chris Rizos Cooperative Research Centre for Spatial Information &
ALOS PALSAR OBSERVATION OF KILAUEA VOLCANO ACTIVITIES FROM 2006 TO 2009 Zhe Hu, Linlin Ge, Xiaojing Li, Kui Zhang, Alex Hay-Man NG and Chris Rizos Cooperative Research Centre for Spatial Information &
Slow Deformation of Mt. Baekdu Stratovolcano Observed by Satellite Radar Interferometry
 Slow Deformation of Mt. Baekdu Stratovolcano Observed by Satellite Radar Interferometry Sang-Wan Kim and Joong-Sun Won Department of Earth System Sciences, Yonsei University 134 Shinchon-dong, Seodaemun-gu,
Slow Deformation of Mt. Baekdu Stratovolcano Observed by Satellite Radar Interferometry Sang-Wan Kim and Joong-Sun Won Department of Earth System Sciences, Yonsei University 134 Shinchon-dong, Seodaemun-gu,
GSNL - Geohazard Supersites and Natural Laboratories. Biennial report for Candidate/Permanent Supersite. Hawaiʻi Supersite. Annex to report
 Introduction Biennial report for Candidate/Permanent Supersite Hawaiʻi Supersite Annex to 2014 2016 report During 2014 2016, the Hawaiʻi Supersite achieved a number of noteworthy results. This annex details
Introduction Biennial report for Candidate/Permanent Supersite Hawaiʻi Supersite Annex to 2014 2016 report During 2014 2016, the Hawaiʻi Supersite achieved a number of noteworthy results. This annex details
Deformation of the Augustine Volcano, Alaska, , measured by ERS and ENVISAT SAR interferometry
 Earth Planets Space, 60, 447 452, 2008 Deformation of the Augustine Volcano, Alaska, 1992 2005, measured by ERS and ENVISAT SAR interferometry Chang-Wook Lee 1,3, Zhong Lu 2, Oh-Ig Kwoun 3, and Joong-Sun
Earth Planets Space, 60, 447 452, 2008 Deformation of the Augustine Volcano, Alaska, 1992 2005, measured by ERS and ENVISAT SAR interferometry Chang-Wook Lee 1,3, Zhong Lu 2, Oh-Ig Kwoun 3, and Joong-Sun
MEASURING VOLCANIC DEFORMATION AT UNIMAK ISLAND FROM 2003 TO 2010 USING
 MEASURING VOLCANIC DEFORMATION AT UNIMAK ISLAND FROM 2003 TO 2010 USING WEATHER MODEL-ASSISTED TIME SERIES INSAR Gong, W. a, Meyer, F. J. a, Lee, C. W. b, Lu, Z. c, Freymueller, J a. a. Geophysical Institute,
MEASURING VOLCANIC DEFORMATION AT UNIMAK ISLAND FROM 2003 TO 2010 USING WEATHER MODEL-ASSISTED TIME SERIES INSAR Gong, W. a, Meyer, F. J. a, Lee, C. W. b, Lu, Z. c, Freymueller, J a. a. Geophysical Institute,
Earth Observatory of Singapore. Nina Lin 22 Jan 2018
 Earth Observatory of Singapore Nina Lin 22 Jan 2018 EOS Our Mission Our Mission Director Prof. Kerry Sieh The Earth Observatory of Singapore conducts fundamental research on earthquakes, volcanic eruptions,
Earth Observatory of Singapore Nina Lin 22 Jan 2018 EOS Our Mission Our Mission Director Prof. Kerry Sieh The Earth Observatory of Singapore conducts fundamental research on earthquakes, volcanic eruptions,
3D temporal evolution of displacements recorded on Mt. Etna from the 2007 to 2010 through the SISTEM method
 3D temporal evolution of displacements recorded on Mt. Etna from the 2007 to 2010 through the SISTEM method Bonforte A., Guglielmino F.,, Puglisi G. INGV Istituto Nazionale di Gofisica e vulcanologia Osservatorio
3D temporal evolution of displacements recorded on Mt. Etna from the 2007 to 2010 through the SISTEM method Bonforte A., Guglielmino F.,, Puglisi G. INGV Istituto Nazionale di Gofisica e vulcanologia Osservatorio
Supporting the response to the 2018 lower East Rift Zone and summit collapse at Kīlauea Volcano, Hawaiʻi
 Hawaiʻi Supersite success story Supporting the response to the 2018 lower East Rift Zone and summit collapse at Kīlauea Volcano, Hawaiʻi Since 1983, Kīlauea Volcano, on the Island of Hawaiʻi, has actively
Hawaiʻi Supersite success story Supporting the response to the 2018 lower East Rift Zone and summit collapse at Kīlauea Volcano, Hawaiʻi Since 1983, Kīlauea Volcano, on the Island of Hawaiʻi, has actively
ERS Track 98 SAR Data and InSAR Pairs Used in the Analysis
 ERS Track 98 SAR Data and InSAR Pairs Used in the Analysis Date 1 Date 2 Date 1 Date 2 Date 1 Date 2 Date 1 Date 2 7/17/1992 6/19/2000 7/17/1992 7/2/1993 9/10/1993 10/28/1996 9/3/1995 10/18/1999 9/25/1992
ERS Track 98 SAR Data and InSAR Pairs Used in the Analysis Date 1 Date 2 Date 1 Date 2 Date 1 Date 2 Date 1 Date 2 7/17/1992 6/19/2000 7/17/1992 7/2/1993 9/10/1993 10/28/1996 9/3/1995 10/18/1999 9/25/1992
What is the Relationship between Pressure & Volume Change in a Magma Chamber and Surface Deformation at Active Volcanoes?
 SSAC-pv2007.QE522.PL1.1 What is the Relationship between Pressure & Volume Change in a Magma Chamber and Surface Deformation at Active Volcanoes? What factors control the magnitude of surface deformation?
SSAC-pv2007.QE522.PL1.1 What is the Relationship between Pressure & Volume Change in a Magma Chamber and Surface Deformation at Active Volcanoes? What factors control the magnitude of surface deformation?
The Santorini Inflation Episode, Monitored by InSAR and GPS
 The Santorini Inflation Episode, Monitored by InSAR and GPS Ioannis Papoutsis 1,2, Xanthos Papanikolaou 2, Michael Floyd 3, Kang Hyeun Ji 4, Charalampos Kontoes 1, Demitris Paradissis 2, Demitris Anastasiou
The Santorini Inflation Episode, Monitored by InSAR and GPS Ioannis Papoutsis 1,2, Xanthos Papanikolaou 2, Michael Floyd 3, Kang Hyeun Ji 4, Charalampos Kontoes 1, Demitris Paradissis 2, Demitris Anastasiou
ASAR IMAGES A DIVERSE SET OF DEFORMATION PATTERNS AT KĪLAUEA VOLCANO, HAWAI`I
 ASAR IMAGES A DIVERSE SET OF DEFORMATION PATTERNS AT KĪLAUEA VOLCANO, HAWAI`I Michael P. Poland (1) (1) U.S. Geological Survey, Hawaiian Volcano Observatory, 51 Crater Rim Road, Hawai`i National Park,
ASAR IMAGES A DIVERSE SET OF DEFORMATION PATTERNS AT KĪLAUEA VOLCANO, HAWAI`I Michael P. Poland (1) (1) U.S. Geological Survey, Hawaiian Volcano Observatory, 51 Crater Rim Road, Hawai`i National Park,
Interferometric SAR analysis for Characterizing Surface Changes of an Active Volcano using Open Source Software
 Interferometric SAR analysis for Characterizing Surface Changes of an Active Volcano using Open Source Software Asep SAEPULOH1, Katsuaki KOIKE1, Makoto OMURA2 1 Department of Life and Environmental Sciences,
Interferometric SAR analysis for Characterizing Surface Changes of an Active Volcano using Open Source Software Asep SAEPULOH1, Katsuaki KOIKE1, Makoto OMURA2 1 Department of Life and Environmental Sciences,
GEO-VIII November Geohazard Supersites and Natural Laboratories Progress Report. Document 9
 GEO-VIII 16-17 November 2011 Geohazard Supersites and Natural Laboratories Progress Report Document 9 This document is submitted to GEO-VIII for information. Geohazard Supersites and Natural Laboratories
GEO-VIII 16-17 November 2011 Geohazard Supersites and Natural Laboratories Progress Report Document 9 This document is submitted to GEO-VIII for information. Geohazard Supersites and Natural Laboratories
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (February, 2011)
 Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (February, 2011) Japan Meteorological Agency Izu-Oshima[ Alert Level : 1] Earthquakes at the western offshore areas of Izu-Oshima increased on 9 th temporarily in this
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (February, 2011) Japan Meteorological Agency Izu-Oshima[ Alert Level : 1] Earthquakes at the western offshore areas of Izu-Oshima increased on 9 th temporarily in this
68. Izu-Torishima. Summary. Latitude: 30 29'02" N, Longitude: '11" E, Elevation: 394 m (Ioyama) (Elevation Point) (68.
 68. Izu-Torishima Latitude: 30 29'02" N, Longitude: 140 18'11" E, Elevation: 394 m (Ioyama) (Elevation Point) Izu-Torishima taken from southeast side on August 12, 2002. Courtesy of the Maritime Safety
68. Izu-Torishima Latitude: 30 29'02" N, Longitude: 140 18'11" E, Elevation: 394 m (Ioyama) (Elevation Point) Izu-Torishima taken from southeast side on August 12, 2002. Courtesy of the Maritime Safety
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (March 2013)
 Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (March 2013) Hakoneyama (Alert Level: 1) Shallow earthquake activity from the area near Mt. Komagatake to Sengokuhara has largely remained at low levels since the middle
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (March 2013) Hakoneyama (Alert Level: 1) Shallow earthquake activity from the area near Mt. Komagatake to Sengokuhara has largely remained at low levels since the middle
Chapter 18. Abstract. Introduction. By Chang-Wook Lee 1, Zhong Lu 2, Hyung-Sup Jung 3, Joong-Sun Won 4, and Daniel Dzurisin 5
 The 2006 Eruption of Augustine Volcano, Alaska Power, J.A., Coombs, M.L., and Freymueller, J.T., editors U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1769 Chapter 18 Surface Deformation of Augustine Volcano,
The 2006 Eruption of Augustine Volcano, Alaska Power, J.A., Coombs, M.L., and Freymueller, J.T., editors U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1769 Chapter 18 Surface Deformation of Augustine Volcano,
Radar Remote Sensing: Monitoring Ground Deformations and Geohazards from Space
 Radar Remote Sensing: Monitoring Ground Deformations and Geohazards from Space Xiaoli Ding Department of Land Surveying and Geo-Informatics The Hong Kong Polytechnic University A Question 100 km 100 km
Radar Remote Sensing: Monitoring Ground Deformations and Geohazards from Space Xiaoli Ding Department of Land Surveying and Geo-Informatics The Hong Kong Polytechnic University A Question 100 km 100 km
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (July, 2012)
 Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (July, 2012) Tokachidake [Alert Level: 1] Volcanic glows have been observed in the Taisho crater with a high-sensitivity camera at night from the night of June 30th to
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (July, 2012) Tokachidake [Alert Level: 1] Volcanic glows have been observed in the Taisho crater with a high-sensitivity camera at night from the night of June 30th to
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (March, 2011)
 Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (March, 2011) Japan Meteorological Agency Yakedake[ Alert Level : 1] Just after "The 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake" on 11th March, seismicity became higher
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (March, 2011) Japan Meteorological Agency Yakedake[ Alert Level : 1] Just after "The 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake" on 11th March, seismicity became higher
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (February 2016)
 Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (February 2016) Japan Meteorological Agency Azumayama (Alert Level: 2) Fumarolic activity at the Oana crater has remained at relatively high levels. Aerial observation
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (February 2016) Japan Meteorological Agency Azumayama (Alert Level: 2) Fumarolic activity at the Oana crater has remained at relatively high levels. Aerial observation
EAS 116 Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 EAS 116 Earthquakes and Volcanoes J. Haase Forecasting Volcanic Eruptions Assessment of Volcanic Hazard Is that volcano active? Mount Lassen: 12000 BP and 1915 Santorini, IT: 180,000 BP, 70,000 BP, 21000
EAS 116 Earthquakes and Volcanoes J. Haase Forecasting Volcanic Eruptions Assessment of Volcanic Hazard Is that volcano active? Mount Lassen: 12000 BP and 1915 Santorini, IT: 180,000 BP, 70,000 BP, 21000
Surface deformation monitoring of Sinabung volcano using multi temporal InSAR method and GIS analysis for affected area assessment
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Surface deformation monitoring of Sinabung volcano using multi temporal InSAR method and GIS analysis for affected area assessment
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Surface deformation monitoring of Sinabung volcano using multi temporal InSAR method and GIS analysis for affected area assessment
Committee on Earth Observation Satellites. The CEOS Volcano Demonstrator Rationale and Implementation
 Committee on Earth Observation Satellites The CEOS Volcano Demonstrator Rationale and Implementation Why focus on volcanoes? Over 300,000 people have been killed by volcanoes since the 1600s Globally,
Committee on Earth Observation Satellites The CEOS Volcano Demonstrator Rationale and Implementation Why focus on volcanoes? Over 300,000 people have been killed by volcanoes since the 1600s Globally,
to: Interseismic strain accumulation and the earthquake potential on the southern San
 Supplementary material to: Interseismic strain accumulation and the earthquake potential on the southern San Andreas fault system by Yuri Fialko Methods The San Bernardino-Coachella Valley segment of the
Supplementary material to: Interseismic strain accumulation and the earthquake potential on the southern San Andreas fault system by Yuri Fialko Methods The San Bernardino-Coachella Valley segment of the
Geohazard Supersites and Natural Laboratories
 Geohazard Supersites and Natural Laboratories FRINGE 2011, Frascati, Italy, September 19, 2011 Wolfgang Lengert, ESA Falk Amelung, University of Miami, GEO task lead Craig Dobson, NASA, CEOS task lead
Geohazard Supersites and Natural Laboratories FRINGE 2011, Frascati, Italy, September 19, 2011 Wolfgang Lengert, ESA Falk Amelung, University of Miami, GEO task lead Craig Dobson, NASA, CEOS task lead
MAGMATIC, ERUPTIVE AND TECTONIC PROCESSES IN THE ALEUTIAN ARC, ALASKA
 MAGMATIC, ERUPTIVE AND TECTONIC PROCESSES IN THE ALEUTIAN ARC, ALASKA Introduction The Aleutian Arc contains roughly ten percent of the world s active volcanoes. Hardly a year goes by without a major eruption
MAGMATIC, ERUPTIVE AND TECTONIC PROCESSES IN THE ALEUTIAN ARC, ALASKA Introduction The Aleutian Arc contains roughly ten percent of the world s active volcanoes. Hardly a year goes by without a major eruption
Time-series deformation monitoring over mining regions with SAR intensity-based offset measurements
 Remote Sensing Letters Vol. 4, No. 5, May 2013, 436 445 Time-series deformation monitoring over mining regions with SAR intensity-based offset measurements CHAOYING ZHAO, ZHONG LU* and QIN ZHANG College
Remote Sensing Letters Vol. 4, No. 5, May 2013, 436 445 Time-series deformation monitoring over mining regions with SAR intensity-based offset measurements CHAOYING ZHAO, ZHONG LU* and QIN ZHANG College
Aira/Sakura-jima. Kyushu, Japan N, E; summit elev m. All times are local (= UTC + 9 hours)
 Aira/Sakura-jima Kyushu, Japan 31.593 N, 130.657 E; summit elev. 1117 m All times are local (= UTC + 9 hours) 2012-2013 Ongoing frequent explosions; ashfall on Kagoshima City This report summarizes activity
Aira/Sakura-jima Kyushu, Japan 31.593 N, 130.657 E; summit elev. 1117 m All times are local (= UTC + 9 hours) 2012-2013 Ongoing frequent explosions; ashfall on Kagoshima City This report summarizes activity
Volcanoes. Table of Contents Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Landforms
 Volcanoes Table of Contents Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Landforms What is a volcano? cone Conduit Or Pipe vent Side vent Central vent Crater A volcano is a vent or 'chimney'
Volcanoes Table of Contents Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Landforms What is a volcano? cone Conduit Or Pipe vent Side vent Central vent Crater A volcano is a vent or 'chimney'
Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR): Its Past, Present and Future
 Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR): Its Past, Present and Future by Zhong Lu, Ohig Kwoun, and Russell Rykhus Introduction Very simply, interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) involves
Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR): Its Past, Present and Future by Zhong Lu, Ohig Kwoun, and Russell Rykhus Introduction Very simply, interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) involves
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (April 2013)
 Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (April 2013) Zaozan (Calm) Small-amplitude volcanic tremors were recorded on April 7 (duration: 3 min 20 sec), 9 (4 min 20 sec) and 21 (5 min 40 sec). These were the first
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (April 2013) Zaozan (Calm) Small-amplitude volcanic tremors were recorded on April 7 (duration: 3 min 20 sec), 9 (4 min 20 sec) and 21 (5 min 40 sec). These were the first
Application of differential SAR interferometry for studying eruptive event of 22 July 1998 at Mt. Etna. Abstract
 Application of differential SAR interferometry for studying eruptive event of 22 July 1998 at Mt. Etna Coltelli M. 1, Puglisi G. 1, Guglielmino F. 1, Palano M. 2 1 Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia,
Application of differential SAR interferometry for studying eruptive event of 22 July 1998 at Mt. Etna Coltelli M. 1, Puglisi G. 1, Guglielmino F. 1, Palano M. 2 1 Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia,
Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems. Supporting Information for
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems Supporting Information for Volcano Deformation Survey over the Northern and Central Andes with ALOS InSAR Time Series Anieri M. Morales Rivera 1, Falk
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems Supporting Information for Volcano Deformation Survey over the Northern and Central Andes with ALOS InSAR Time Series Anieri M. Morales Rivera 1, Falk
THREE DIMENSIONAL DETECTION OF VOLCANIC DEPOSIT ON MOUNT MAYON USING SAR INTERFEROMETRY
 ABSTRACT THREE DIMENSIONAL DETECTION OF VOLCANIC DEPOSIT ON MOUNT MAYON USING SAR INTERFEROMETRY Francis X.J. Canisius, Kiyoshi Honda, Mitsuharu Tokunaga and Shunji Murai Space Technology Application and
ABSTRACT THREE DIMENSIONAL DETECTION OF VOLCANIC DEPOSIT ON MOUNT MAYON USING SAR INTERFEROMETRY Francis X.J. Canisius, Kiyoshi Honda, Mitsuharu Tokunaga and Shunji Murai Space Technology Application and
REFERENCE: The Blue Planet An Introduction to Earth System Science. Brian J. Skinner and Barbara W. Murck (2011) Third Edition. John Wiley and Sons
 REFERENCE: The Blue Planet An Introduction to Earth System Science. Brian J. Skinner and Barbara W. Murck (2011) Third Edition. John Wiley and Sons Inc. PLATE BOUNDARIES OCEAN FLOOR SEISMIC ACTIVITY WORLD'S
REFERENCE: The Blue Planet An Introduction to Earth System Science. Brian J. Skinner and Barbara W. Murck (2011) Third Edition. John Wiley and Sons Inc. PLATE BOUNDARIES OCEAN FLOOR SEISMIC ACTIVITY WORLD'S
Earth Structures and Processes Teacher Notes
 Aleutian Islands String of islands resulting from volcanic activity Part of the Pacific Ring of Fire Coast is very jagged and rocky with steep cliffs and mountains Underwater eruptions form new landforms
Aleutian Islands String of islands resulting from volcanic activity Part of the Pacific Ring of Fire Coast is very jagged and rocky with steep cliffs and mountains Underwater eruptions form new landforms
The March 11, 2011, Tohoku-oki earthquake (Japan): surface displacement and source modelling
 The March 11, 2011, Tohoku-oki earthquake (Japan): surface displacement and source modelling Salvatore Stramondo Bignami C., Borgstrom S., Chini M., Guglielmino F., Melini D., Puglisi G., Siniscalchi V.,
The March 11, 2011, Tohoku-oki earthquake (Japan): surface displacement and source modelling Salvatore Stramondo Bignami C., Borgstrom S., Chini M., Guglielmino F., Melini D., Puglisi G., Siniscalchi V.,
Urban land and infrastructure deformation monitoring by satellite radar interferometry
 Urban land and infrastructure deformation monitoring by satellite radar interferometry Lei Zhang and Xiaoli Ding Department of Land Surveying and Geo-Informatics (LSGI) The Hong Kong Polytechnic University
Urban land and infrastructure deformation monitoring by satellite radar interferometry Lei Zhang and Xiaoli Ding Department of Land Surveying and Geo-Informatics (LSGI) The Hong Kong Polytechnic University
3-Dimension Deformation Mapping from InSAR & Multiaperture. Hyung-Sup Jung The Univ. of Seoul, Korea Zhong Lu U.S. Geological Survey, U.S.A.
 3-Dimension Deformation Mapping from InSAR & Multiaperture InSAR Hyung-Sup Jung The Univ. of Seoul, Korea Zhong Lu U.S. Geological Survey, U.S.A. Outline Introduction to multiple-aperture InSAR (MAI) 3-D
3-Dimension Deformation Mapping from InSAR & Multiaperture InSAR Hyung-Sup Jung The Univ. of Seoul, Korea Zhong Lu U.S. Geological Survey, U.S.A. Outline Introduction to multiple-aperture InSAR (MAI) 3-D
Geohazard Supersites and Natural Laboratories
 Geohazard Supersites and Natural Laboratories FRINGE 2011, Frascati, Italy, September 19, 2011 Wolfgang Lengert, ESA Falk Amelung, University of Miami, GEO task lead Craig Dobson, NASA, CEOS task lead
Geohazard Supersites and Natural Laboratories FRINGE 2011, Frascati, Italy, September 19, 2011 Wolfgang Lengert, ESA Falk Amelung, University of Miami, GEO task lead Craig Dobson, NASA, CEOS task lead
Deformation measurement using SAR interferometry: quantitative aspects
 Deformation measurement using SAR interferometry: quantitative aspects Michele Crosetto (1), Erlinda Biescas (1), Ismael Fernández (1), Ivan Torrobella (1), Bruno Crippa (2) (1) (2) Institute of Geomatics,
Deformation measurement using SAR interferometry: quantitative aspects Michele Crosetto (1), Erlinda Biescas (1), Ismael Fernández (1), Ivan Torrobella (1), Bruno Crippa (2) (1) (2) Institute of Geomatics,
DETECTING ICE MOTION IN GROVE MOUNTAINS, EAST ANTARCTICA WITH ALOS/PALSAR AND ENVISAT/ASAR DATA
 DETECTING ICE MOTION IN GROVE MOUNTAINS, EAST ANTARCTICA WITH ALOS/PALSAR AND ENVISAT/ASAR DATA TIAN Xin (1), LIAO Mingsheng (1), ZHOU Chunxia (2), ZHOU Yu (3) (1) State Key Laboratory of Information Engineering
DETECTING ICE MOTION IN GROVE MOUNTAINS, EAST ANTARCTICA WITH ALOS/PALSAR AND ENVISAT/ASAR DATA TIAN Xin (1), LIAO Mingsheng (1), ZHOU Chunxia (2), ZHOU Yu (3) (1) State Key Laboratory of Information Engineering
The Removal of Lava Flow Subsidence Signals from deformation interferograms at Nyamuragira Volcano, D.R. Congo
 The Removal of Lava Flow Subsidence Signals from deformation interferograms at Nyamuragira Volcano, D.R. Congo Andy Toombs & Geoff Wadge Environmental Systems Science Centre National Centre for Earth Observation
The Removal of Lava Flow Subsidence Signals from deformation interferograms at Nyamuragira Volcano, D.R. Congo Andy Toombs & Geoff Wadge Environmental Systems Science Centre National Centre for Earth Observation
The Potential of High Resolution Satellite Interferometry for Monitoring Enhanced Oil Recovery
 The Potential of High Resolution Satellite Interferometry for Monitoring Enhanced Oil Recovery Urs Wegmüller a Lutz Petrat b Karsten Zimmermann c Issa al Quseimi d 1 Introduction Over the last years land
The Potential of High Resolution Satellite Interferometry for Monitoring Enhanced Oil Recovery Urs Wegmüller a Lutz Petrat b Karsten Zimmermann c Issa al Quseimi d 1 Introduction Over the last years land
Evolution of the 2007 earthquake swarm, Tanzania: Envisat and ALOS interferometry, ground observations and elastic modeling
 Evolution of the 2007 earthquake swarm, Tanzania: Envisat and ALOS interferometry, ground observations and elastic modeling Gidon Baer, Yariv Hamiel, Gadi Shamir, Ran Nof Geological Survey of Israel East
Evolution of the 2007 earthquake swarm, Tanzania: Envisat and ALOS interferometry, ground observations and elastic modeling Gidon Baer, Yariv Hamiel, Gadi Shamir, Ran Nof Geological Survey of Israel East
High-resolution temporal imaging of. Howard Zebker
 High-resolution temporal imaging of crustal deformation using InSAR Howard Zebker Stanford University InSAR Prehistory SEASAT Topographic Fringes SEASAT Deformation ERS Earthquake Image Accurate imaging
High-resolution temporal imaging of crustal deformation using InSAR Howard Zebker Stanford University InSAR Prehistory SEASAT Topographic Fringes SEASAT Deformation ERS Earthquake Image Accurate imaging
A - Piton de la Fournaise activity
 OVPF-IPGP August 2018 Page 1/7 Monthly bulletin of the Piton de la Fournaise Volcanological Observatory ISSN ISSN 2610-5101 A - Piton de la Fournaise activity PITON DE LA FOURNAISE (VNUM #233020) Latitude:
OVPF-IPGP August 2018 Page 1/7 Monthly bulletin of the Piton de la Fournaise Volcanological Observatory ISSN ISSN 2610-5101 A - Piton de la Fournaise activity PITON DE LA FOURNAISE (VNUM #233020) Latitude:
IEEE GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING LETTERS, VOL. 11, NO. 8, AUGUST
 IEEE GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING LETTERS, VOL. 11, NO. 8, AUGUST 2014 1355 Multitemporal Multitrack Monitoring of Wetland Water Levels in the Florida Everglades Using ALOS PALSAR Data With Interferometric
IEEE GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING LETTERS, VOL. 11, NO. 8, AUGUST 2014 1355 Multitemporal Multitrack Monitoring of Wetland Water Levels in the Florida Everglades Using ALOS PALSAR Data With Interferometric
Geodesy (InSAR, GPS, Gravity) and Big Earthquakes
 Geodesy (InSAR, GPS, Gravity) and Big Earthquakes Mathew Pritchard Teh-Ru A. Song Yuri Fialko Luis Rivera Mark Simons UJNR Earthquake Research Panel, Morioka, Japan - Nov 6, 2002 Goals Accurate and high
Geodesy (InSAR, GPS, Gravity) and Big Earthquakes Mathew Pritchard Teh-Ru A. Song Yuri Fialko Luis Rivera Mark Simons UJNR Earthquake Research Panel, Morioka, Japan - Nov 6, 2002 Goals Accurate and high
P079 First Results from Spaceborne Radar Interferometry for the Study of Ground Displacements in Urban Areas SUMMARY
 P079 First Results from Spaceborne Radar Interferometry for the Study of Ground Displacements in Urban Areas C.M. Crosetto (Instituto de Geomatica), C.A. Casas (University of Barcelona), R.G. Ranieri (University
P079 First Results from Spaceborne Radar Interferometry for the Study of Ground Displacements in Urban Areas C.M. Crosetto (Instituto de Geomatica), C.A. Casas (University of Barcelona), R.G. Ranieri (University
A - Piton de la Fournaise activity
 OVPF-IPGP September 2018 Page 1/10 Monthly bulletin of the Piton de la Fournaise Volcanological Observatory ISSN ISSN 2610-5101 A - Piton de la Fournaise activity PITON DE LA FOURNAISE (VNUM #233020) Latitude:
OVPF-IPGP September 2018 Page 1/10 Monthly bulletin of the Piton de la Fournaise Volcanological Observatory ISSN ISSN 2610-5101 A - Piton de la Fournaise activity PITON DE LA FOURNAISE (VNUM #233020) Latitude:
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (August 2015)
 Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (August 2015) Japan Meteorological Agency Meakandake (Alert Level: 2) Volcanic seismicity in shallow parts under the area around the Ponmachineshiri crater began to fluctuate
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (August 2015) Japan Meteorological Agency Meakandake (Alert Level: 2) Volcanic seismicity in shallow parts under the area around the Ponmachineshiri crater began to fluctuate
Implementation of Multi-Temporal InSAR to monitor pumping induced land subsidence in Pingtung Plain, Taiwan
 Implementation of Multi-Temporal InSAR to monitor pumping induced land subsidence in Pingtung Plain, Taiwan Presenter: Oswald Advisor: Chuen-Fa Ni Date: March 09, 2017 Literature Review Pingtung Plain
Implementation of Multi-Temporal InSAR to monitor pumping induced land subsidence in Pingtung Plain, Taiwan Presenter: Oswald Advisor: Chuen-Fa Ni Date: March 09, 2017 Literature Review Pingtung Plain
LECTURE #11: Volcanoes: Monitoring & Mitigation
 GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #11: Volcanoes: Monitoring & Mitigation Date: 15 February 2018 I. What is volcanic monitoring? the continuous collection of one or more data sources
GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #11: Volcanoes: Monitoring & Mitigation Date: 15 February 2018 I. What is volcanic monitoring? the continuous collection of one or more data sources
Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model
 Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model The Cascadia tectonic margin is caught between several tectonic forces, during the relentless motions of the giant Pacific Plate, the smaller subducting
Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model The Cascadia tectonic margin is caught between several tectonic forces, during the relentless motions of the giant Pacific Plate, the smaller subducting
TABLE OF CONTENTS. Student Letter Exploring the Strategies Unit One: Play Unit Two: Fantasy Unit Three: Mystery...
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Student Letter........................................... 2 Exploring the Strategies................................... 3 Unit One: Play........................................... 4 Unit
TABLE OF CONTENTS Student Letter........................................... 2 Exploring the Strategies................................... 3 Unit One: Play........................................... 4 Unit
Chapter 4. The Earth s Surface: Shaping the crust
 Chapter 4 The Earth s Surface: Shaping the crust Learning outcomes In this chapter you will learn: That the earth is made up of layers Why the earth is shaped as it is What plates are and how they move
Chapter 4 The Earth s Surface: Shaping the crust Learning outcomes In this chapter you will learn: That the earth is made up of layers Why the earth is shaped as it is What plates are and how they move
Pavlof. Alaska Peninsula N, W; summit elev. 2,519 m. All times are local (= UTC - 9 hours)
 Pavlof Alaska Peninsula 55.42 N, 161.887 W; summit elev. 2,519 m All times are local (= UTC - 9 hours) Eruption in May-June 2013 with lava flows and ash emissions to ~8.5 km a.s.l. Pavlof, the most active
Pavlof Alaska Peninsula 55.42 N, 161.887 W; summit elev. 2,519 m All times are local (= UTC - 9 hours) Eruption in May-June 2013 with lava flows and ash emissions to ~8.5 km a.s.l. Pavlof, the most active
Volcanoes Session. Chairs: Y. Fukushima & G. Puglisi
 Volcanoes Session Chairs: Y. Fukushima & G. Puglisi Presentation Summary We had presentations on volcanoes all over the world, more than the last FRINGE workshops: Etna, Campi Flegrei, Ethiopian rift,
Volcanoes Session Chairs: Y. Fukushima & G. Puglisi Presentation Summary We had presentations on volcanoes all over the world, more than the last FRINGE workshops: Etna, Campi Flegrei, Ethiopian rift,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115, B00B02, doi: /2009jb006969, 2010
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jb006969, 2010 Ground surface deformation patterns, magma supply, and magma storage at Okmok volcano, Alaska, from
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jb006969, 2010 Ground surface deformation patterns, magma supply, and magma storage at Okmok volcano, Alaska, from
GPS and GIS Assisted Radar Interferometry
 GPS and GIS Assisted Radar Interferometry Linlin Ge, Xiaojing Li, Chris Rizos, and Makoto Omura Abstract Error in radar satellite orbit determination is a common problem in radar interferometry (INSAR).
GPS and GIS Assisted Radar Interferometry Linlin Ge, Xiaojing Li, Chris Rizos, and Makoto Omura Abstract Error in radar satellite orbit determination is a common problem in radar interferometry (INSAR).
ERS-ENVISAT CROSS-INTERFEROMETRY SIGNATURES OVER DESERTS. Urs Wegmüller, Maurizio Santoro and Christian Mätzler
 ERS-ENVISAT CROSS-INTERFEROMETRY SIGNATURES OVER DESERTS Urs Wegmüller, Maurizio Santoro and Christian Mätzler Gamma Remote Sensing AG, Worbstrasse 225, CH-3073 Gümligen, Switzerland, http://www.gamma-rs.ch,
ERS-ENVISAT CROSS-INTERFEROMETRY SIGNATURES OVER DESERTS Urs Wegmüller, Maurizio Santoro and Christian Mätzler Gamma Remote Sensing AG, Worbstrasse 225, CH-3073 Gümligen, Switzerland, http://www.gamma-rs.ch,
Volcanoes. What is a volcano
 What is a volcano The crust of the Earth floats on the 'liquid' mantle. At some points where the crust might be weaker there are concentrations of magma. The magma is liquid rock. These concentrations
What is a volcano The crust of the Earth floats on the 'liquid' mantle. At some points where the crust might be weaker there are concentrations of magma. The magma is liquid rock. These concentrations
Plates & Boundaries The earth's continents are constantly moving due to the motions of the tectonic plates.
 Plates & Boundaries The earth's continents are constantly moving due to the motions of the tectonic plates. As you can see, some of the plates contain continents and others are mostly under the ocean.
Plates & Boundaries The earth's continents are constantly moving due to the motions of the tectonic plates. As you can see, some of the plates contain continents and others are mostly under the ocean.
A - Piton de la Fournaise activity
 OVPF-IPGP November 2018 Page 1/7 Monthly bulletin of the Piton de la Fournaise Volcanological Observatory ISSN ISSN 2610-5101 A - Piton de la Fournaise activity PITON DE LA FOURNAISE (VNUM #233020) Latitude:
OVPF-IPGP November 2018 Page 1/7 Monthly bulletin of the Piton de la Fournaise Volcanological Observatory ISSN ISSN 2610-5101 A - Piton de la Fournaise activity PITON DE LA FOURNAISE (VNUM #233020) Latitude:
From Punchbowl to Panum: Long Valley Volcanism and the Mono-Inyo Crater Chain
 From Punchbowl to Panum: Leslie Schaffer E105 2002 Final Paper Long Valley Volcanism and the Mono-Inyo Crater Chain Figure 1. After a sequence of earthquakes during the late 1970 s to the early 1980 s
From Punchbowl to Panum: Leslie Schaffer E105 2002 Final Paper Long Valley Volcanism and the Mono-Inyo Crater Chain Figure 1. After a sequence of earthquakes during the late 1970 s to the early 1980 s
MONITORING OF GLACIAL CHANGE IN THE HEAD OF THE YANGTZE RIVER FROM 1997 TO 2007 USING INSAR TECHNIQUE
 MONITORING OF GLACIAL CHANGE IN THE HEAD OF THE YANGTZE RIVER FROM 1997 TO 2007 USING INSAR TECHNIQUE Hong an Wu a, *, Yonghong Zhang a, Jixian Zhang a, Zhong Lu b, Weifan Zhong a a Chinese Academy of
MONITORING OF GLACIAL CHANGE IN THE HEAD OF THE YANGTZE RIVER FROM 1997 TO 2007 USING INSAR TECHNIQUE Hong an Wu a, *, Yonghong Zhang a, Jixian Zhang a, Zhong Lu b, Weifan Zhong a a Chinese Academy of
Module 1, Investigation 3: Predicting Eruptions
 Module 1, Investigation 3: Predicting Eruptions Introduction Welcome! Volcanoes are either "active" or "extinct". Active means that the volcano has erupted during the past 10,000 years. It can also mean
Module 1, Investigation 3: Predicting Eruptions Introduction Welcome! Volcanoes are either "active" or "extinct". Active means that the volcano has erupted during the past 10,000 years. It can also mean
About Volcanoes Volcanology IMPORTANT TERMS
 About Volcanoes IMPORTANT TERMS magma Rock that is molten (in liquid form due to heating). When magma reaches the surface, it is called lava. lava magma reservoir An underground pool that is filled with
About Volcanoes IMPORTANT TERMS magma Rock that is molten (in liquid form due to heating). When magma reaches the surface, it is called lava. lava magma reservoir An underground pool that is filled with
DETECTION OF CRUSTAL DEFORMATION OF THE NORTHERN PAKISTAN EARTHQUAKE BY SATELLITE DATA. Submitted by Japan **
 UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.97/5/CRP. 5 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL Seventeenth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for Asia and the Pacific Bangkok, 18-22 September 2006 Item 6 (b) of the provisional
UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.97/5/CRP. 5 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL Seventeenth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for Asia and the Pacific Bangkok, 18-22 September 2006 Item 6 (b) of the provisional
Volcanic Monitoring in Long Valley, California. creating a ten-mile by twenty-mile caldera in the Eastern Sierra Nevada region of
 Jensen Grimmer G188 6/6/2013 Volcanic Monitoring in Long Valley, California Abstract: Around 760,000 years ago an explosive eruption shook the western United States creating a ten-mile by twenty-mile caldera
Jensen Grimmer G188 6/6/2013 Volcanic Monitoring in Long Valley, California Abstract: Around 760,000 years ago an explosive eruption shook the western United States creating a ten-mile by twenty-mile caldera
Crustal Activity. Plate Tectonics - Plates - Lithosphere - Asthenosphere - Earth s surface consists of a major plates and some minor ones
 Name: Date: Period: Tectonics The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES Tectonics - s - Lithosphere - Asthenosphere - Earth s surface consists of a major plates and some minor ones The plates are
Name: Date: Period: Tectonics The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES Tectonics - s - Lithosphere - Asthenosphere - Earth s surface consists of a major plates and some minor ones The plates are
InSAR results from the WInSAR Consortium
 InSAR results from the WInSAR Consortium Matt Pritchard (1); Eric Fielding (2); Shimon Wdowinski (3); Scott Baker (4); Zhong Lu (5); and 160 WInSAR Institution members (6) 1: Cornell University; 2: Jet
InSAR results from the WInSAR Consortium Matt Pritchard (1); Eric Fielding (2); Shimon Wdowinski (3); Scott Baker (4); Zhong Lu (5); and 160 WInSAR Institution members (6) 1: Cornell University; 2: Jet
TEMPORAL VARIABILITY OF ICE FLOW ON HOFSJÖKULL, ICELAND, OBSERVED BY ERS SAR INTERFEROMETRY
 TEMPORAL VARIABILITY OF ICE FLOW ON HOFSJÖKULL, ICELAND, OBSERVED BY ERS SAR INTERFEROMETRY Florian Müller (1), Helmut Rott (2) (1) ENVEO IT, Environmental Earth Observation GmbH, Technikerstrasse 21a,
TEMPORAL VARIABILITY OF ICE FLOW ON HOFSJÖKULL, ICELAND, OBSERVED BY ERS SAR INTERFEROMETRY Florian Müller (1), Helmut Rott (2) (1) ENVEO IT, Environmental Earth Observation GmbH, Technikerstrasse 21a,
Erupted and killed approximately 15,000 people 200 years ago
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Chapter 8 Volcanic Activity Volcanoes: summary in haiku form A volcano forms. Magma comes to the surface - explodes, if felsic. Case History: Mt.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Chapter 8 Volcanic Activity Volcanoes: summary in haiku form A volcano forms. Magma comes to the surface - explodes, if felsic. Case History: Mt.
The financial and communal impact of a catastrophe instantiated by. volcanoes endlessly impact on lives and damage expensive infrastructure every
 Chapter 1 Introduction The financial and communal impact of a catastrophe instantiated by geophysical activity is significant. Landslides, subsidence, earthquakes and volcanoes endlessly impact on lives
Chapter 1 Introduction The financial and communal impact of a catastrophe instantiated by geophysical activity is significant. Landslides, subsidence, earthquakes and volcanoes endlessly impact on lives
Dynamic Earth A B1. Which type of plate boundary is located at the Jordan Fault? (1) divergent (3) convergent (2) subduction (4) transform
 Dynamic Earth A B1 1. The edges of most lithospheric plates are characterized by (1) reversed magnetic orientation (2) unusually rapid radioactive decay (3) frequent volcanic activity (4) low P-wave and
Dynamic Earth A B1 1. The edges of most lithospheric plates are characterized by (1) reversed magnetic orientation (2) unusually rapid radioactive decay (3) frequent volcanic activity (4) low P-wave and
DIFFERENTIAL INSAR STUDIES IN THE BOREAL FOREST ZONE IN FINLAND
 DIFFERENTIAL INSAR STUDIES IN THE BOREAL FOREST ZONE IN FINLAND Kirsi Karila (1,2), Mika Karjalainen (1), Juha Hyyppä (1) (1) Finnish Geodetic Institute, P.O. Box 15, FIN-02431 Masala, Finland, Email:
DIFFERENTIAL INSAR STUDIES IN THE BOREAL FOREST ZONE IN FINLAND Kirsi Karila (1,2), Mika Karjalainen (1), Juha Hyyppä (1) (1) Finnish Geodetic Institute, P.O. Box 15, FIN-02431 Masala, Finland, Email:
V. Pinel, A. Hooper, S. de la Cruz-Reyna, G. Reyes-Davila, M.P. Doin
 !"#$%&'(&")*&$*('+,-".'/&(.*0$&'(&"1'&-2".3*&4*5.2-/& 6"+-"'3'02-/'*6 78'9'2-"*9*"0 -/$&&:'0.,- ;'02-/'
!"#$%&'(&")*&$*('+,-".'/&(.*0$&'(&"1'&-2".3*&4*5.2-/& 6"+-"'3'02-/'*6 78'9'2-"*9*"0 -/$&&:'0.,- ;'02-/'
Get in Touch with Tapasvi IAS
 Barren Island Volcano Erupted Again, Facts About Barren Island Get in Touch with Tapasvi IAS Join us on Facebook for daily updates and important material for UPSC Join Now Join our Telegram Channel and
Barren Island Volcano Erupted Again, Facts About Barren Island Get in Touch with Tapasvi IAS Join us on Facebook for daily updates and important material for UPSC Join Now Join our Telegram Channel and
Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire
 Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire On July 16, 1990, a large earthquake struck Luzon, an island in the Philippines. The earthquake devastated cities for hundreds of
Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire On July 16, 1990, a large earthquake struck Luzon, an island in the Philippines. The earthquake devastated cities for hundreds of
Subsidence-induced fault
 Surveying Monitoring underground coal mining-induced subsidence by Yaobin Sheng, Linlin Ge, Chris Rizos, University of New South Wales, and Yunjia Wang, China University of Mining and Technology This paper
Surveying Monitoring underground coal mining-induced subsidence by Yaobin Sheng, Linlin Ge, Chris Rizos, University of New South Wales, and Yunjia Wang, China University of Mining and Technology This paper
DLR s TerraSAR-X contributes to international fleet of radar satellites to map the Arctic and Antarctica
 DLR s TerraSAR-X contributes to international fleet of radar satellites to map the Arctic and Antarctica The polar regions play an important role in the Earth system. The snow and ice covered ocean and
DLR s TerraSAR-X contributes to international fleet of radar satellites to map the Arctic and Antarctica The polar regions play an important role in the Earth system. The snow and ice covered ocean and
Università di Roma La Sapienza, Facoltà d Ingegneria, Dipartimento di Idraulica,Trasporti e Strade (D.I.T.S.) 00185, Roma, Italy
 DORIS FP7-EU PROJECT: EXPLOITATION OF 20 YEARS DINSAR DATA ARCHIVE FOR LANDSLIDE MONITORING Manunta M. (1), Calò F. (1), Paglia L., (1), Bonano M. (1,2), Lanari R. (1) (1) IREA-CNR, Via Diocleziano 328,
DORIS FP7-EU PROJECT: EXPLOITATION OF 20 YEARS DINSAR DATA ARCHIVE FOR LANDSLIDE MONITORING Manunta M. (1), Calò F. (1), Paglia L., (1), Bonano M. (1,2), Lanari R. (1) (1) IREA-CNR, Via Diocleziano 328,
Real Time Subsidence Monitoring Techniques in Undercity Mining and a Case Study: Zonguldak Undercity Applications-Turkey
 Real Time Subsidence Monitoring Techniques in Undercity Mining and a Case Study: Zonguldak Undercity Hakan AKCIN, Hakan S. KUTOGLU, Turkey Keywords: Undercity mining, subsidence, PALSAR, RADARSAT, GNSS.
Real Time Subsidence Monitoring Techniques in Undercity Mining and a Case Study: Zonguldak Undercity Hakan AKCIN, Hakan S. KUTOGLU, Turkey Keywords: Undercity mining, subsidence, PALSAR, RADARSAT, GNSS.
Indian Ocean Tsunami Warning System: Example from the 12 th September 2007 Tsunami
 Indian Ocean Tsunami Warning System: Example from the 12 th September 2007 Tsunami Charitha Pattiaratchi 1 Professor of Coastal Oceanography, The University of Western Australia Email: chari.pattiaratchi@uwa.edu.au
Indian Ocean Tsunami Warning System: Example from the 12 th September 2007 Tsunami Charitha Pattiaratchi 1 Professor of Coastal Oceanography, The University of Western Australia Email: chari.pattiaratchi@uwa.edu.au
Magnitude 8.3 SEA OF OKHOTSK
 A powerful earthquake in Russia's Far East was felt as far away as Moscow, about 7,000 kilometers (4,400 miles) west of the epicenter, but no casualties or damage were reported. The epicenter was in the
A powerful earthquake in Russia's Far East was felt as far away as Moscow, about 7,000 kilometers (4,400 miles) west of the epicenter, but no casualties or damage were reported. The epicenter was in the
Application of satellite InSAR data for hydrocarbon reservoir monitoring
 Application of satellite InSAR data for hydrocarbon reservoir monitoring A. Tamburini, A. Belson, A. Ferretti, F. Novali TRE Milano, Italy Copyright - Tele-Rilevamento Europa - 2004 Outline SqueeSAR TM
Application of satellite InSAR data for hydrocarbon reservoir monitoring A. Tamburini, A. Belson, A. Ferretti, F. Novali TRE Milano, Italy Copyright - Tele-Rilevamento Europa - 2004 Outline SqueeSAR TM
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (November 2015)
 Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (November 2015) Japan Meteorological Agency Meakandake (Alert Level: 1) Alert level downgrade from 2 to 1 on 13 November A field survey conducted from 2 to 5 November showed
Monthly Volcanic Activity Report (November 2015) Japan Meteorological Agency Meakandake (Alert Level: 1) Alert level downgrade from 2 to 1 on 13 November A field survey conducted from 2 to 5 November showed
Available online at GHGT-9. Detection of surface deformation related with CO 2 injection by DInSAR at In Salah, Algeria
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 100 (2009) (2008) 2177 2184 000 000 Energy Procedia www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia www.elsevier.com/locate/xxx GHGT-9 Detection of surface deformation
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Energy Procedia 100 (2009) (2008) 2177 2184 000 000 Energy Procedia www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia www.elsevier.com/locate/xxx GHGT-9 Detection of surface deformation
MAPPING DEFORMATION OF MAN-MADE LINEAR FEATURES USING DINSAR TECHNIQUE
 MAPPING DEFORMATION OF MAN-MADE LINEAR FEATURES USING DINSAR TECHNIQUE H. Wu a, *, Y. Zhang a, J. Zhang a, X. Chen b a Key Laboratory of Mapping from Space of State Bureau of Surveying and Mapping, Chinese
MAPPING DEFORMATION OF MAN-MADE LINEAR FEATURES USING DINSAR TECHNIQUE H. Wu a, *, Y. Zhang a, J. Zhang a, X. Chen b a Key Laboratory of Mapping from Space of State Bureau of Surveying and Mapping, Chinese
Basics of the modelling of the ground deformations produced by an earthquake. EO Summer School 2014 Frascati August 13 Pierre Briole
 Basics of the modelling of the ground deformations produced by an earthquake EO Summer School 2014 Frascati August 13 Pierre Briole Content Earthquakes and faults Examples of SAR interferograms of earthquakes
Basics of the modelling of the ground deformations produced by an earthquake EO Summer School 2014 Frascati August 13 Pierre Briole Content Earthquakes and faults Examples of SAR interferograms of earthquakes
Plate Tectonics Tutoiral. Questions. Teacher: Mrs. Zimmerman. Plate Tectonics and Mountains Practice Test
 Teacher: Mrs. Zimmerman Print Close Plate Tectonics and Mountains Practice Test Plate Tectonics Tutoiral URL: http://www.hartrao.ac.za/geodesy/tectonics.html Questions 1. Fossils of organisms that lived
Teacher: Mrs. Zimmerman Print Close Plate Tectonics and Mountains Practice Test Plate Tectonics Tutoiral URL: http://www.hartrao.ac.za/geodesy/tectonics.html Questions 1. Fossils of organisms that lived
A) B) C) D) 4. Which diagram below best represents the pattern of magnetic orientation in the seafloor on the west (left) side of the ocean ridge?
 1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
The Evidence of Earth s Violent Geologic Past
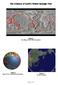 The Evidence of Earth s Violent Geologic Past Figure 1 The Ring of Fire (Flat Projection) Figure 2 Ring of Fire, (Spherical Projection) Figure 3 Ocean Trenches Page 1 of 10 Figure 4 Kamchatka Peninsula
The Evidence of Earth s Violent Geologic Past Figure 1 The Ring of Fire (Flat Projection) Figure 2 Ring of Fire, (Spherical Projection) Figure 3 Ocean Trenches Page 1 of 10 Figure 4 Kamchatka Peninsula
Inflation of the Aira Caldera (Japan) detected over Kokubu urban area using SAR interferometry ERS data
 Inflation of the Aira Caldera (Japan) detected over Kokubu urban area using SAR interferometry ERS data D. Remy, S. Bonvalot, M. Murakami, P. Briole, S. Okuyama To cite this version: D. Remy, S. Bonvalot,
Inflation of the Aira Caldera (Japan) detected over Kokubu urban area using SAR interferometry ERS data D. Remy, S. Bonvalot, M. Murakami, P. Briole, S. Okuyama To cite this version: D. Remy, S. Bonvalot,
