Fluids, melts, and supercriticality in the MSH system and element transport in subduction zones
|
|
|
- Egbert Cameron
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 cosmic rays Fluids, s, and supercriticality in the MSH system and element transport in subduction zones 10 Be volcanic front N, O 10 Be ocean water + CO 2 tracing petrologic and geotectonic processes (trace) element signature? o C mass transfer agent P-T conditions, phases, liquid present? geodynamics 1
2 Fluids, s, and supercritical liquids Fluids = rich in volatile component, low in solute Melts = rich in silicate component, moderate in volatiles Supercritical liquids = a continuum from volatile to silicate component - predicted by Ricci (1951), - experimentally proven for geological systems (quartz+h2o) by Kennedy et al. (1962) - brought back to our attention by Shen and Keppler (1997) Silicate H 2 O system without hydrous phase U>Th, high Li,B; low Be wt% H 2 O A + + cpx + = ±gar critical point wt% H 2 O Th>U, high Be A + x Shen and Keppler (1997) -saturated solidus Silicate H 2 O system without hydrous phase Silicate H 2 O system with hydrous phase supercritical liquid All of this was laid out by Ricci (1951) -absent solidus A + supercritical liquid Silicate H 2 O system without hydrous phase cpx + phengite = + gar cpx + phengite + = ±gar + A + A + + A + scep A + scep = second critical endpoint A + supercritical A + cp + P + A + -saturated solidus cp = critical point A + 2
3 Silicate H 2 O system without hydrous phase Silicate H 2 O system with hydrous phase -absent solidus } + A + + P A + -saturated solidus -absent solidus Silicate H 2 O system with hydrous phase Terminology - P-T-diagrams with critical endpoint supercritical liquid hydrous critical curve (crest of misc.gap) Fluids are supercritical above the first critical endpoint near 25 MPa, 375 o C saturated solidus isochores 3
4 Terminology (not just pure semantics) - P-T-diagrams with critical endpoint Metagreywacke Ricci (1951) Technique for the extraction of silicate (or ) supercritical liquid 2.CEP CEV - -5,0 1,5 GPa 1000 C 800 C CEV - 1,5 GPa 800 C supercritical 1.CEP critical curve of miscibility gap µm 10 µm - Inert trap - liquid-matrix connexion chemical equilibrium - works even for low fractions - allows the precise P-T location of the solidus - Defocused electron beam reduces losses of Na - A single contamination source : quartz easy correction 1.5 GPa, 800 C 4
5 Metapelite, 4GPa, 850C At > At > 100 km, clastic sediments and basaltic rocks have the same eclogitic mineralogy: garnet+cpx+phengite +rutile+quartz 180 km 150 km Schmidt, Vielzeuf and Auzanneau, EPSL 2004) 5
6 back to our little A-H2-H1-H 2 O - diagram... For meta-granite/greywacke/pelite: H1 = phengite H2 = biotite supercritical liquid scl supercritical secondcritical critical point (cp) 6
7 5. Frontiers - Metamorphic s at high P Supercritical s and their implications 5. Frontiers - Metamorphic s at high P Supercritical s and their implications Isopleths = log m(si) Kennedy et al. (1962), Peacock (1993), Manning (1994) After Shen & Keppler (1997), Stalder et al. (2000) 7
8 Up to 3 sets of H 2 O-isopleths possible Up to 3 sets of H 2 O-isopleths possible Hydrous + vs. supercritical liquids Temperatures above the critical point (at a given P) of the hydrous - immiscibility gap imply a continuum in physical and chemical properties of the supercritical liquid (e.g. solubilities, density, viscosity etc ) How to determine critical phenomena: direct observation (DAC, synchrotron) Shen and Keppler (1997) Pressures above the intersection of the critical P- T-curve of the immiscibility gap with the saturated solidus imply - the continuum spans the entire temperature range - nevertheless, isopleths of constant H 2 O and composition of an scl in equilibrium with silicates are still defined Fluid -absent ing continues beyond pressures of the solidus critical endpoint + very sensitive on 2 phase / 1 phase transition - limited in temperature and thus chemical system (external heated DAC) - Pressure somewhat uncertain not explored for partially crystallized systems 8
9 How to determine critical phenomena: direct observation (DAC, synchrotron) one one How to determine critical phenomena: direct observation (DAC, synchrotron) Sr-plagioclase H 2 O Sr-plagioclase H 2 O + potentially large P-T range - Few experiments possible (synchrotron) - Run durations limited - Limit of detection ( Z)? - Depends on formation of bubbles Mibe et al. (2004) + potentially large P-T range - Few experiments possible (synchrotron) - Run durations limited - Limit of detection ( Z)? - Depends on formation of bubbles Mibe et al. (2004) phengite + cpx + coesite + = ± garnet At > 100 km, clastic sediments and basaltic rocks have the same eclogitic mineralogy: garnet+cpx+phengite +rutile+quartz pelite greywacke MORB Schmidt, Vielzeuf, Auzanneau (2004) 9
10 K-enriched (0.5 wt%) MORB at 7 GPa, 1050 o C How to determine critical phenomena: textural observation Pelite at 4 GPa 7.3 GPa until mid 90's no MORB+H 2 O solidus published for > 4 GPa + equilibrium A high pressure experiments pelite should in complex have 25 % systems mica - only reliable if the ing/dissolution reaction exhausts a phase, and garnet if s clinopyroxene are quenchable (jd) coesite kyanite rutile (i.e. siliceous) - no composition + supercritical of the involved liquid s/s/liquids How to determine critical phenomena: chemical measurement of trapped liquids Now: liquid N 2 replaced by 2 Peltier elements (Aerts+Hack and coworkers) Melting experiments on K-free MORB To ICP Dry Argon: - visibility - laser beam transmission cpx diamond-trap Cu-metal block as chamber base garnet homogeneous eclogite Liquid N 2 to pump 10
11 Rocking multi-anvil diamond-trap Éxperiment strategy: - rigid diamonds keep open space which is then filled by supercritical during the experiment - after quench and depressurization, capsule is frozen before opening and kept frozen during analyses - we measure the composition of solidified mud/ ice, that retains all elements (in contrast to letting escape the ) 6 GPa supercritical liquid How to determine critical phenomena: chemical measurement of trapped liquids H is not measured but Cs which is to >99% in the H:Cs ratio in starting material is known H 2 O content calculated from Cs-concentration 5 GPa 4 GPa cpx diamond-trap garnet homogeneous eclogite -absent solidus -saturated solidus Silicate H 2 O system with hydrous phase in situ methods The MgO-SiO 2 -H 2 O system and Dense Hydrous Magnesium silicates +P 11 and 13.5 GPa o C 8 GPa 3 GPa quench methods phase A (Mg 7 Si 2 O 8 (OH) 6 ) clinohumite (Mg 9 Si 4 O 16 (OH) 2 ) chondrodite (Mg 5 Si 2 O 8 (OH) 2 ) phase B (Mg 12 Si 4 O 19 (OH) 2 ) superhydrous B (Mg 10 Si 3 O 14 (OH) 4 ) hydrous wadsleyite (Mg 1.89 Si 0.98 O 0.37 (OH) 0.3 ) 11
12 Laser ablation ICP MS 1.0 Phase A Fluid = 0.6 chondrodite Melt 11 GPa BSE image 13.5 GPa Melenkhova et al. (2007) GCA 12
13 (final) supercriticity in MgO-SiO 2 -H 2 O Secondcritical endpoints in MgO-SiO 2 -H 2 O pressure Phase A + Fl Forsterite + Fl Enstatite + Fl Qz + En + Fl Quartz + Fluid Liquid volume in MgO-SiO 2 -H 2 O pressure Phase A + Fl Forsterite + Fl Enstatite + Fl Qz + En + Fl Quartz + Fluid 13
14 phase A, E, B, superhydrous B, clinohumite, chondrodite, hydrous wadsleyite, forsterite, enstatite,,, scl E E E fo en scl? 15 GPa 11 GPa phase E 1000 o C 1300 o C Second Critical Endpoints MSH peridotite peridotite Mibe et al The H 2 O-saturated solidus for K-free MORB lies between 850 and 900 o C at 4 GPa and between 1000 and 1050 o C at 5 GPa. No solidus at 6 GPa. The dichotomy of dissolution vs. ing at 4-5 GPa is expressed through contrasting behaviour of many trace elements (U/Th, Sr, Ba, Be, LREE). 14
15 Problem: What transport capacities does the mobile phase have (e.g. how much Be is transferred under what conditions)? volcanic front ocean water + CO 2 Trace element signature of supercritical liquids Why -saturated ing? In subducting lithosphere serpentine dehydration is a huge source just at the right temperature for wet ing What do the observed trace Element (Be) concentrations in arcs allow to deduce about transfer conditions? Investigate experimentally element distribution minerals/mobile phase 80 km 250 km To what depth does classical -present ing exist? To some pressure, the - dichotomy with clearly distinguished chemical charcteristics of the mobile phase exists, what happens at higher pressure? The above question does not concern -absent ing, i.e. ing without external source Plank and coworkers: >50% Be are transfered to arc magmas, thus, slabs must, thus temperatures of the subducted crust below the arcmust be >750 o C U>Th, high Li,B; low Be wt% H 2 O cpx + = ±gar A GPa supercritical liquid Chemical continuum with a supercritical liquid in SZ at > 160 km depth dichotomy of vs. production in SZ wt% H 2 O Th>U, high Be A + 5 GPa 4 GPa x sediment ing signature - high recycling rates of > 60% of the subducted Be, La, and Th in many arcs, including e.g. Tonga - these elements are mostly insoluble in crustal s, thus sediment ing was proposed to generally occur (Plank et al.) 15
16 phase compositions for a K-free meta-morb eclogite phase compositions for a K-free meta-morb eclogite peralkaline: Na+K >> Al metaaluminous: Na+K ~ Al = feldspar peraluminous: Na+K << Al excess Al-phases such as garnet, muscovite D(Be)=5-7 D(Be)=7-25 U/Th= Conclusions Supercritical liquids in subducted crust at 160 km depth La/Lu= 1100 U/Th=0.5 MSH becomes entirely supercritical at P > 11 GPa Fluid-absent ing in crust and mantle take place to higher P phengite in crust, phase E possibly in mantle D(Be)=1 La/Lu= 67 U/Th=1.4 La/Lu= The sediment ing signature (Ba-La-Th mobility) is identical to the supercritical liquid signature no direct temperature implication - dichotomy -like supercritical liquids A lot of work is still needed to understand the systematics and geochemical consequences of supercriticality 16
Chapter 18: Granitoid Rocks. Chapter 18: Granitoid Rocks. Melting of crustal materials at high pressure
 Melting of crustal materials at high pressure Melting in the crust: the traditional low pressure view to be applied to HP CaO P 2 O 5 Zircon from a HP granite HP-HT garnets from Massif Central (Vielzeuf
Melting of crustal materials at high pressure Melting in the crust: the traditional low pressure view to be applied to HP CaO P 2 O 5 Zircon from a HP granite HP-HT garnets from Massif Central (Vielzeuf
N = N 0 e -λt D* = N 0 -N D* = N 0 (1-e -λt ) or N(e λt -1) where N is number of parent atoms at time t, N 0
 N = N 0 e -λt D* = N 0 -N D* = N 0 (1-e -λt ) or N(e λt -1) where N is number of parent atoms at time t, N 0 is initial number of parents, D* is number of radiogenic daughter atoms, and λ is the decay
N = N 0 e -λt D* = N 0 -N D* = N 0 (1-e -λt ) or N(e λt -1) where N is number of parent atoms at time t, N 0 is initial number of parents, D* is number of radiogenic daughter atoms, and λ is the decay
Effect of tectonic setting on chemistry of mantle-derived melts
 Effect of tectonic setting on chemistry of mantle-derived melts Lherzolite Basalt Factors controlling magma composition Composition of the source Partial melting process Fractional crystallization Crustal
Effect of tectonic setting on chemistry of mantle-derived melts Lherzolite Basalt Factors controlling magma composition Composition of the source Partial melting process Fractional crystallization Crustal
GSA DATA REPOSITORY
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2013019 Supplemental information for The Solidus of Alkaline Carbonatite in the Deep Mantle Konstantin D. Litasov, Anton Shatskiy, Eiji Ohtani, and Gregory M. Yaxley EXPERIMENTAL METHODS
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2013019 Supplemental information for The Solidus of Alkaline Carbonatite in the Deep Mantle Konstantin D. Litasov, Anton Shatskiy, Eiji Ohtani, and Gregory M. Yaxley EXPERIMENTAL METHODS
High-T T heating stage: : application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools -
 High-T T heating stage: : application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools - SZABÓ, Csaba Lithosphere Fluid Research Lab (LRG), Department of Petrology and Geochemistry,
High-T T heating stage: : application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools - SZABÓ, Csaba Lithosphere Fluid Research Lab (LRG), Department of Petrology and Geochemistry,
Partial melting of mantle peridotite
 Partial melting of mantle peridotite 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 (TºC) Depth (km) 50 100 150 Plag lherzolite (ol-opx-cpx-pl) Spinel lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-sp) Garnet lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-gar) Graphite Diamond
Partial melting of mantle peridotite 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 (TºC) Depth (km) 50 100 150 Plag lherzolite (ol-opx-cpx-pl) Spinel lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-sp) Garnet lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-gar) Graphite Diamond
High-T heating stage: application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools -
 High-T heating stage: application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools - SZABÓ, Csaba Lithosphere Fluid Research Lab (LRG), Department of Petrology and Geochemistry,
High-T heating stage: application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools - SZABÓ, Csaba Lithosphere Fluid Research Lab (LRG), Department of Petrology and Geochemistry,
NADIA MALASPINA. PLINIUS n. 32, 2006
 ULTRAHIGH-PRESSURE METAMORPHISM AND METASOMATISM IN MAFIC-ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS FROM EASTERN CHINA: IMPLICATIONS FOR FLUID RELEASE AND VOLATILE TRANSFER AT SUBDUCTION ZONES NADIA MALASPINA Dipartimento per
ULTRAHIGH-PRESSURE METAMORPHISM AND METASOMATISM IN MAFIC-ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS FROM EASTERN CHINA: IMPLICATIONS FOR FLUID RELEASE AND VOLATILE TRANSFER AT SUBDUCTION ZONES NADIA MALASPINA Dipartimento per
Constitution of Magmas. Magmas. Gas Law. Composition. Atomic Structure of Magma. Structural Model. PV = nrt H 2 O + O -2 = 2(OH) -
 Constitution of Magmas Magmas Best, Ch. 8 Hot molten rock T = 700-1200 degrees C Composed of ions or complexes Phase Homogeneous Separable part of the system With an interface Composition Most components
Constitution of Magmas Magmas Best, Ch. 8 Hot molten rock T = 700-1200 degrees C Composed of ions or complexes Phase Homogeneous Separable part of the system With an interface Composition Most components
Where are these melts generated in the mantle wedge?
 Melt generation processes in subduction zones T.L. Grove, C.B. Till, N. Chatterjee, E. Medard, S.W. Parman New experiments on H2O-saturated melting of mantle peridotite - The role of H2O in mantle wedge
Melt generation processes in subduction zones T.L. Grove, C.B. Till, N. Chatterjee, E. Medard, S.W. Parman New experiments on H2O-saturated melting of mantle peridotite - The role of H2O in mantle wedge
TWO COMPONENT (BINARY) PHASE DIAGRAMS. Experimental Determination of 2-Component Phase Diagrams
 Page 1 of 12 EENS 211 Earth Materials Tulane University Prof. Stephen A. Nelson TWO COMPONENT (BINARY) PHASE DIAGRAMS This document last updated on 08-Oct-2003 Experimental Determination of 2-Component
Page 1 of 12 EENS 211 Earth Materials Tulane University Prof. Stephen A. Nelson TWO COMPONENT (BINARY) PHASE DIAGRAMS This document last updated on 08-Oct-2003 Experimental Determination of 2-Component
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks
 Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
GEOL 3313 Petrology of Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks Study Guide for Final Examination Glen Mattioli
 GEOL 3313 Petrology of Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks Study Guide for Final Examination Glen Mattioli Chapter 5: Crystal-Melt phase diagrams Effect of water pressure on feldspar stability Hypersolvus vs.
GEOL 3313 Petrology of Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks Study Guide for Final Examination Glen Mattioli Chapter 5: Crystal-Melt phase diagrams Effect of water pressure on feldspar stability Hypersolvus vs.
Igneous Rocks of the Convergent Margins
 Page 1 of 10 EENS 2120 Petrology Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Tulane University Igneous Rocks of the This document last updated on 08-Feb-2011 The convergent plate margins are the most intense areas of active
Page 1 of 10 EENS 2120 Petrology Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Tulane University Igneous Rocks of the This document last updated on 08-Feb-2011 The convergent plate margins are the most intense areas of active
GY303 Igneous & Metamorphic Petrology. Lecture 7: Magma Sources and Tectonic Environments
 GY303 Igneous & Metamorphic Petrology Lecture 7: Magma Sources and Tectonic Environments Factors controlling Magma production Source rock composition Amount of fluids, especially H 2 O Pressure (Depth)
GY303 Igneous & Metamorphic Petrology Lecture 7: Magma Sources and Tectonic Environments Factors controlling Magma production Source rock composition Amount of fluids, especially H 2 O Pressure (Depth)
Hydration of Olivine and. Earth s Deep Water Cycle
 Hydration of Olivine and Earth s Deep Water Cycle IASPEI October 5, 2005 Olivine Hydration and Earth s Deep Water Cycle J. R. Smyth, (University of Colorado) Dan Frost and Fabrizio Nestola (Bayerisches
Hydration of Olivine and Earth s Deep Water Cycle IASPEI October 5, 2005 Olivine Hydration and Earth s Deep Water Cycle J. R. Smyth, (University of Colorado) Dan Frost and Fabrizio Nestola (Bayerisches
12 Chemistry (Mg,Fe) 2 SiO 4 Olivine is forms what is called an isomorphous solid solution series that ranges between two end members: Forsterite Mg
 11 Olivine Structure Olivine is a common green or brown rock forming minerals which consists of a solid-solution series between Forsterite (Fo) and Fayalite (Fa). It is an orthorhombic orthosilicate with
11 Olivine Structure Olivine is a common green or brown rock forming minerals which consists of a solid-solution series between Forsterite (Fo) and Fayalite (Fa). It is an orthorhombic orthosilicate with
Metamorphic Petrology GLY 262 Metamorphic fluids
 Metamorphic Petrology GLY 262 Metamorphic fluids The metamorphic fluid is arguably the most geologically important phase Spear (1993) The great volumetric abundance of hydrate-rich and carbonate-rich minerals
Metamorphic Petrology GLY 262 Metamorphic fluids The metamorphic fluid is arguably the most geologically important phase Spear (1993) The great volumetric abundance of hydrate-rich and carbonate-rich minerals
Rare Earth Elements in some representative arc lavas
 Rare Earth Elements in some representative arc lavas Low-K (tholeiitic), Medium-K (calc-alkaline), and High-K basaltic andesites and andesites. A typical N-MORB pattern is included for reference Notes:
Rare Earth Elements in some representative arc lavas Low-K (tholeiitic), Medium-K (calc-alkaline), and High-K basaltic andesites and andesites. A typical N-MORB pattern is included for reference Notes:
Subduction zones 3 arc magmatism
 5. 3 Subduction zones 3 arc magmatism Where can we observe magmatic/volcanic activities along subduction zones? Characteristics of arc magmatism (vs. mid-ocean ridge/intraplate magmatism) Structure of
5. 3 Subduction zones 3 arc magmatism Where can we observe magmatic/volcanic activities along subduction zones? Characteristics of arc magmatism (vs. mid-ocean ridge/intraplate magmatism) Structure of
GSA Data Repository
 GSA Data Repository 218145 Parolari et al., 218, A balancing act of crust creation and destruction along the western Mexican convergent margin: Geology, https://doi.org/1.113/g39972.1. 218145_Tables DR1-DR4.xls
GSA Data Repository 218145 Parolari et al., 218, A balancing act of crust creation and destruction along the western Mexican convergent margin: Geology, https://doi.org/1.113/g39972.1. 218145_Tables DR1-DR4.xls
Lecture 38. Igneous geochemistry. Read White Chapter 7 if you haven t already
 Lecture 38 Igneous geochemistry Read White Chapter 7 if you haven t already Today. Magma mixing/afc 2. Spot light on using the Rare Earth Elements (REE) to constrain mantle sources and conditions of petrogenesis
Lecture 38 Igneous geochemistry Read White Chapter 7 if you haven t already Today. Magma mixing/afc 2. Spot light on using the Rare Earth Elements (REE) to constrain mantle sources and conditions of petrogenesis
Interpreting Phase Diagrams
 Interpreting Phase Diagrams Understanding chemical reactions requires that we know something about how materials behave as the temperature and pressure change. For a single component (like quartz or ice)
Interpreting Phase Diagrams Understanding chemical reactions requires that we know something about how materials behave as the temperature and pressure change. For a single component (like quartz or ice)
WATER IN THE EARTH S MANTLE:
 WATER IN THE EARTH S MANTLE: NATHALIE BOLFAN-CASANOVA LABORATOIRE MAGMAS ET VOLCANS => Heterogeneous distribution of water in the mantle > 10000 pmm wt H2O ~ 10000 pmm wt H2O ~ 1000 pmm wt H2O On what
WATER IN THE EARTH S MANTLE: NATHALIE BOLFAN-CASANOVA LABORATOIRE MAGMAS ET VOLCANS => Heterogeneous distribution of water in the mantle > 10000 pmm wt H2O ~ 10000 pmm wt H2O ~ 1000 pmm wt H2O On what
Differentiation 2: mantle, crust OUTLINE
 Differentiation 2: mantle, crust OUTLINE Reading this week: Should have been White Ch 10 and 11!! 7- Nov Differentiation of the Earth, Core formation W 10.6.6, 11.4 9- Nov Moon, crust, mantle, atmosphere
Differentiation 2: mantle, crust OUTLINE Reading this week: Should have been White Ch 10 and 11!! 7- Nov Differentiation of the Earth, Core formation W 10.6.6, 11.4 9- Nov Moon, crust, mantle, atmosphere
Imagine the first rock and the cycles that it has been through.
 A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes
 Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 GSA Data Repository 080 Schorn et al., 08, Thermal buffering in the orogenic crust: Geology, https://doi.org/0.30/g4046.. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION 3 PHASE DIAGRAM MODELING 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 3 4 Phase diagrams
GSA Data Repository 080 Schorn et al., 08, Thermal buffering in the orogenic crust: Geology, https://doi.org/0.30/g4046.. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION 3 PHASE DIAGRAM MODELING 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 3 4 Phase diagrams
Volatile rich Fe-oxide melts: base and precious metals enrichment trends. Is there an IOCG connection?
 Volatile rich Fe-oxide melts: base and precious metals enrichment trends. Is there an IOCG connection? Gregory W Lester M.A., MSc., PhD Curtin University Background Nelsonites and Low Ti, FeO deposits
Volatile rich Fe-oxide melts: base and precious metals enrichment trends. Is there an IOCG connection? Gregory W Lester M.A., MSc., PhD Curtin University Background Nelsonites and Low Ti, FeO deposits
Magma Formation and Behavior
 Magma Formation and Behavior Questions What causes mantle rock to melt, resulting in magma formation? Why is magma formation restricted to specific plate tectonic settings? Why are mafic (basaltic) magmas
Magma Formation and Behavior Questions What causes mantle rock to melt, resulting in magma formation? Why is magma formation restricted to specific plate tectonic settings? Why are mafic (basaltic) magmas
Chapter 4 8/27/2013. Igneous Rocks. and Intrusive Igneous Activity. Introduction. The Properties and Behavior of Magma and Lava
 Introduction Chapter 4 Igneous rocks form by the cooling of magma (or lava). Large parts of the continents and all the oceanic crust are composed of. and Intrusive Igneous Activity The Properties and Behavior
Introduction Chapter 4 Igneous rocks form by the cooling of magma (or lava). Large parts of the continents and all the oceanic crust are composed of. and Intrusive Igneous Activity The Properties and Behavior
Essentials of Geology, 11e
 Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann. Grotzinger Jordan. Understanding Earth. Sixth Edition
 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks: Solids from Melts 1 About Igneous Rocks Igneous
Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks: Solids from Melts 1 About Igneous Rocks Igneous
What is going on here?
 Major Digression! Atoms? Elements? Compounds? Minerals? Rocks? What is going on here? Source:SERC @ Carleton College http://www.brocku.ca/earthsciences/people/gfinn/petrology/periodic.gif http://www.meta-synthesis.com/webbook/35_pt/pt_database.php?pt_id=335
Major Digression! Atoms? Elements? Compounds? Minerals? Rocks? What is going on here? Source:SERC @ Carleton College http://www.brocku.ca/earthsciences/people/gfinn/petrology/periodic.gif http://www.meta-synthesis.com/webbook/35_pt/pt_database.php?pt_id=335
C = 3: Ternary Systems: Example 1: Ternary Eutectic
 Phase Equilibrium C = 3: Ternary Systems: Example 1: Ternary Eutectic Adding components, becomes increasingly difficult to depict 1-C: P - T diagrams easy 2-C: isobaric T-X, isothermal P-X 3-C:?? Still
Phase Equilibrium C = 3: Ternary Systems: Example 1: Ternary Eutectic Adding components, becomes increasingly difficult to depict 1-C: P - T diagrams easy 2-C: isobaric T-X, isothermal P-X 3-C:?? Still
1 Potassic adakite magmas and where they come from: a mystery solved?
 1 Potassic adakite magmas and where they come from: a mystery solved? 2 3 John Clemens Kingston University (London) Long Xiao China University of Geosciences (Wuhan) 4 Adakites are volcanic and intrusive
1 Potassic adakite magmas and where they come from: a mystery solved? 2 3 John Clemens Kingston University (London) Long Xiao China University of Geosciences (Wuhan) 4 Adakites are volcanic and intrusive
GEOL FORENSIC GEOLOGY ROCK IDENTIFICATION
 GEOL.2150 - FORENSIC GEOLOGY ROCK IDENTIFICATION Name I. Introduction There are three basic types of rocks - igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic: Igneous. Igneous rocks have solidified from molten matter
GEOL.2150 - FORENSIC GEOLOGY ROCK IDENTIFICATION Name I. Introduction There are three basic types of rocks - igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic: Igneous. Igneous rocks have solidified from molten matter
Fluids and trace element transport in subduction zones
 1 Manuscript 5716, 1 st revision 2 3 Fluids and trace element transport in subduction zones 4 5 HANS KEPPLER 6 7 8 Bayerisches Geoinstitut, Universität Bayreuth, 95440 Bayreuth, Germany hans.keppler@uni-bayreuth.de
1 Manuscript 5716, 1 st revision 2 3 Fluids and trace element transport in subduction zones 4 5 HANS KEPPLER 6 7 8 Bayerisches Geoinstitut, Universität Bayreuth, 95440 Bayreuth, Germany hans.keppler@uni-bayreuth.de
Geochemical and mineralogical technics to investigate the lithosphere and the asthenosphere. 07/11/2017 GEO-DEEP 9300 Claire Aupart
 Geochemical and mineralogical technics to investigate the lithosphere and the asthenosphere 07/11/2017 GEO-DEEP 9300 Claire Aupart Introduction Introduction Getting samples Cores: Maximum depth reach in
Geochemical and mineralogical technics to investigate the lithosphere and the asthenosphere 07/11/2017 GEO-DEEP 9300 Claire Aupart Introduction Introduction Getting samples Cores: Maximum depth reach in
high and ultrahigh pressures.
 Stability of hydrous phases in serpentinites to high and ultrahigh pressures. Study of fluid and multiphase solid inclusions in high, very high pressure rocks and metamorphic veins The crust to mantle
Stability of hydrous phases in serpentinites to high and ultrahigh pressures. Study of fluid and multiphase solid inclusions in high, very high pressure rocks and metamorphic veins The crust to mantle
GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Spring 2016 Score / 58. Midterm 1 Chapters 1-10
 GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Name KEY Spring 2016 Score / 58 Midterm 1 Chapters 1-10 1) Name two things that petrologists want to know about magmas (1 pt) Formation, source, composition,
GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Name KEY Spring 2016 Score / 58 Midterm 1 Chapters 1-10 1) Name two things that petrologists want to know about magmas (1 pt) Formation, source, composition,
Continental Alkaline Magmatism. The East African Rift
 Announcements No lecture on Friday Lab final begins at 1 PM Today s agenda: Lecture/Demo Go through field trip pics Call for pizza Lab review Lecture Review Make poster Continental Alkaline Magmatism.
Announcements No lecture on Friday Lab final begins at 1 PM Today s agenda: Lecture/Demo Go through field trip pics Call for pizza Lab review Lecture Review Make poster Continental Alkaline Magmatism.
Classification and Origin of Granites. A Multi-faceted Question
 Classification and Origin of Granites A Multi-faceted Question What is a granite? IUGS classification Based on Modal Mineralogy Plutonic rock with less than 90% mafic minerals Alkali Granite Granite Quartz
Classification and Origin of Granites A Multi-faceted Question What is a granite? IUGS classification Based on Modal Mineralogy Plutonic rock with less than 90% mafic minerals Alkali Granite Granite Quartz
The Nature of Igneous Rocks
 The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
A Rock is a solid aggregate of minerals.
 Quartz A Rock is a solid aggregate of minerals. Orthoclase Feldspar Plagioclase Feldspar Biotite Four different minerals are obvious in this piece of Granite. The average automobile contains: Minerals
Quartz A Rock is a solid aggregate of minerals. Orthoclase Feldspar Plagioclase Feldspar Biotite Four different minerals are obvious in this piece of Granite. The average automobile contains: Minerals
Earth Science 232 Petrography
 Earth Science 232 Petrography Course notes by Shaun Frape and Alec Blyth Winter 2002 1 Petrology - Introduction Some Definitions Petra Greek for rock Logos Greek for disclosure or explanation Petrology
Earth Science 232 Petrography Course notes by Shaun Frape and Alec Blyth Winter 2002 1 Petrology - Introduction Some Definitions Petra Greek for rock Logos Greek for disclosure or explanation Petrology
Igneous Rocks. Sedimentary Rocks. Metamorphic Rocks
 Name: Date: Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from the solidification of magma either below (intrusive igneous rocks) or above (extrusive igneous rocks) the Earth s surface. For example, the igneous rock
Name: Date: Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from the solidification of magma either below (intrusive igneous rocks) or above (extrusive igneous rocks) the Earth s surface. For example, the igneous rock
Zircon/fluid trace element partition coefficients measured by recrystallization of Mud Tank zircon at 1.5 GPa and C
 Zircon/fluid trace element partition coefficients measured by recrystallization of Mud Tank zircon at 1.5 GPa and 800-1000 C Tim Peters and John C. Ayers Vanderbilt University Funding by National Science
Zircon/fluid trace element partition coefficients measured by recrystallization of Mud Tank zircon at 1.5 GPa and 800-1000 C Tim Peters and John C. Ayers Vanderbilt University Funding by National Science
GEOLOGY. Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02
 GEOLOGY Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02 Topic No. & Title : 37 Magma Bowen Series (Part 01) Academic Script What is Igneous Petrology? Igneous
GEOLOGY Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02 Topic No. & Title : 37 Magma Bowen Series (Part 01) Academic Script What is Igneous Petrology? Igneous
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals. Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane SGM 210_2013
 Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011
METAMORPHIC ROCKS CHAPTER 8
 Lecture 6 October 18, 20, 23 October 19, 24 METAMORPHIC ROCKS CHAPTER 8 This is only an outline of the lecture. You will need to go to class to fill in the outline, although much of the relevant information
Lecture 6 October 18, 20, 23 October 19, 24 METAMORPHIC ROCKS CHAPTER 8 This is only an outline of the lecture. You will need to go to class to fill in the outline, although much of the relevant information
Igneous Rocks. Igneous Rocks. Genetic Classification of
 Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
doi: /nature09369
 doi:10.1038/nature09369 Supplementary Figure S1 Scanning electron microscope images of experimental charges with vapour and vapour phase quench. Experimental runs are in the order of added water concentration
doi:10.1038/nature09369 Supplementary Figure S1 Scanning electron microscope images of experimental charges with vapour and vapour phase quench. Experimental runs are in the order of added water concentration
Structure of the Earth and the Origin of Magmas
 Page 1 of 12 EENS 2120 Petrology Tulane University Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Structure of the Earth and the Origin of Magmas This document last updated on 23-Jan-2015 Magmas do not form everywhere beneath
Page 1 of 12 EENS 2120 Petrology Tulane University Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Structure of the Earth and the Origin of Magmas This document last updated on 23-Jan-2015 Magmas do not form everywhere beneath
HP and UHP garnet peridotites and pyroxenites
 HP and UHP garnet peridotites and pyroxenites Mantle wedge The least known piece of the subduction factory Mantle-wedge peridotites emplace within subducting continental crust (Brueckner, 998; van Roermund
HP and UHP garnet peridotites and pyroxenites Mantle wedge The least known piece of the subduction factory Mantle-wedge peridotites emplace within subducting continental crust (Brueckner, 998; van Roermund
Happy Tuesday. Pull out a ½ sheet of paper
 Happy Tuesday Pull out a ½ sheet of paper 1. Physical properties of a mineral are predominantly related to 1. the external conditions of temperature, pressure, and amount of space available for growth.
Happy Tuesday Pull out a ½ sheet of paper 1. Physical properties of a mineral are predominantly related to 1. the external conditions of temperature, pressure, and amount of space available for growth.
Silicates. The most common group of minerals forming the silicate Earth
 Silicates The most common group of minerals forming the silicate Earth 25% of all minerals (~1000) 40% of rock forming minerals 90% of earth s crust i.e those minerals you are likely to find ~100 of earth
Silicates The most common group of minerals forming the silicate Earth 25% of all minerals (~1000) 40% of rock forming minerals 90% of earth s crust i.e those minerals you are likely to find ~100 of earth
Breeding et al., Data Repository Material Figure DR1. Athens. Study Area
 Breeding, Ague, and Brocker 1 Figure DR1 21 o 24 Greece o A 38 o Athens Tinos 37 o Syros Attic-Cycladic Blueschist Belt Syros Kampos B Study Area Ermoupoli N Vari Unit Cycladic HP-LT Unit Marble horizons
Breeding, Ague, and Brocker 1 Figure DR1 21 o 24 Greece o A 38 o Athens Tinos 37 o Syros Attic-Cycladic Blueschist Belt Syros Kampos B Study Area Ermoupoli N Vari Unit Cycladic HP-LT Unit Marble horizons
Mechanisms of metamorphism and metasomatism on the local mineral scale : The role of dissolution-reprecipitation during mineral re-equilibration
 Chapter 5 Mechanisms of metamorphism and metasomatism on the local mineral scale : The role of dissolution-reprecipitation during mineral re-equilibration Andrew Putnis & Håkon Austrheim Equilibration
Chapter 5 Mechanisms of metamorphism and metasomatism on the local mineral scale : The role of dissolution-reprecipitation during mineral re-equilibration Andrew Putnis & Håkon Austrheim Equilibration
Lecture 25 Subduction Related Magmatism
 Lecture 25 Subduction Related Magmatism Monday, May 2 nd 2005 Subduction Related Magmatism Activity along arcuate volcanic chains along subduction zones Distinctly different from the mainly basaltic provinces
Lecture 25 Subduction Related Magmatism Monday, May 2 nd 2005 Subduction Related Magmatism Activity along arcuate volcanic chains along subduction zones Distinctly different from the mainly basaltic provinces
Description of Supplementary Files
 Description of Supplementary Files File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Tables and Supplementary References File Name: Peer Review File Supplementary figure
Description of Supplementary Files File Name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Tables and Supplementary References File Name: Peer Review File Supplementary figure
Lecture 36. Igneous geochemistry
 Lecture 36 Igneous geochemistry Reading - White Chapter 7 Today 1. Overview 2. solid-melt distribution coefficients Igneous geochemistry The chemistry of igneous systems provides clues to a number of important
Lecture 36 Igneous geochemistry Reading - White Chapter 7 Today 1. Overview 2. solid-melt distribution coefficients Igneous geochemistry The chemistry of igneous systems provides clues to a number of important
Magmatic Processes at Subduction Zones
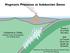 Magmatic Processes at Subduction Zones Katherine A. Kelley Graduate School of Oceanography Univ. of Rhode Island Thanks to Terry Plank Erik Hauri GVP: Liz Cottrell Simon Carn Jennifer Jay Ed Venzke Subduction
Magmatic Processes at Subduction Zones Katherine A. Kelley Graduate School of Oceanography Univ. of Rhode Island Thanks to Terry Plank Erik Hauri GVP: Liz Cottrell Simon Carn Jennifer Jay Ed Venzke Subduction
Metamorphism and Metamorphic Rocks
 Page 1 of 13 EENS 1110 Tulane University Physical Geology Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Metamorphism and Metamorphic Rocks This page last updated on 25-Sep-2017 Definition of Metamorphism The word "Metamorphism"
Page 1 of 13 EENS 1110 Tulane University Physical Geology Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Metamorphism and Metamorphic Rocks This page last updated on 25-Sep-2017 Definition of Metamorphism The word "Metamorphism"
Worked Example of Batch Melting: Rb and Sr
 Worked Example of Batch Melting: Rb and Sr Basalt with the mode: Table 9.2. Conversion from mode to weight percent Mineral Mode Density Wt prop Wt% ol 15 3.6 54 0.18 cpx 33 3.4 112.2 0.37 plag 51 2.7 137.7
Worked Example of Batch Melting: Rb and Sr Basalt with the mode: Table 9.2. Conversion from mode to weight percent Mineral Mode Density Wt prop Wt% ol 15 3.6 54 0.18 cpx 33 3.4 112.2 0.37 plag 51 2.7 137.7
Chapter 7 Metamorphism, Metamorphic Rocks, and Hydrothermal Rocks
 Chapter 7 Metamorphism, Metamorphic Rocks, and Hydrothermal Rocks Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Metamorphism What happens to rocks that are
Chapter 7 Metamorphism, Metamorphic Rocks, and Hydrothermal Rocks Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Metamorphism What happens to rocks that are
Regional geology of study areas 3
 1 Introduction Central part Indonesia geographically is including Kalimantan, Sulawesi and Java islands. Accretionary and metamorphic complexes expose in the Central Java, South Kalimantan and South Central
1 Introduction Central part Indonesia geographically is including Kalimantan, Sulawesi and Java islands. Accretionary and metamorphic complexes expose in the Central Java, South Kalimantan and South Central
Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100
 Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Major Concepts 1) Igneous rocks form directly from the crystallization of a magma or lava 2)
Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Major Concepts 1) Igneous rocks form directly from the crystallization of a magma or lava 2)
Composition of the Earth and its reservoirs: Geochemical observables
 Composition of the Earth and its reservoirs: Geochemical observables Cin-Ty A. Lee Rice University MYRES-I 2004 The Earth is dynamic and heterogeneous Atmosphere Midocean Ridge Plume Ocean Crust Oceanic
Composition of the Earth and its reservoirs: Geochemical observables Cin-Ty A. Lee Rice University MYRES-I 2004 The Earth is dynamic and heterogeneous Atmosphere Midocean Ridge Plume Ocean Crust Oceanic
Ultramafic rocks. Types of Ultramafic Rocks. Spinel lherzolite xenolith
 Ultramafic rocks Definition: Color Index > 90, i.e., less than 10% felsic minerals. Not to be confused with Ultrabasic Rocks which are rocks with
Ultramafic rocks Definition: Color Index > 90, i.e., less than 10% felsic minerals. Not to be confused with Ultrabasic Rocks which are rocks with
Theoretical mineralogy, density, seismic wavespeeds and H 2
 The Cascadia Subduction Zone and Related Subduction Systems 133 Theoretical mineralogy, density, seismic wavespeeds and H 2 O content of the Cascadia subduction zone, with implications for intermediate-depth
The Cascadia Subduction Zone and Related Subduction Systems 133 Theoretical mineralogy, density, seismic wavespeeds and H 2 O content of the Cascadia subduction zone, with implications for intermediate-depth
Evidences for geochemically distinct mantle components
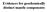 Evidences for geochemically distinct mantle components 1 Mantle Array Oceanic basalts, including seamounts, oceanic islands and middle ocean ridge basalts, were used. 2 Binary All analyses fall between
Evidences for geochemically distinct mantle components 1 Mantle Array Oceanic basalts, including seamounts, oceanic islands and middle ocean ridge basalts, were used. 2 Binary All analyses fall between
GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Spring 2009 Sc ore / 40
 GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Name Spring 2009 Sc ore / 40 QUIZ 3 1) Name two geologic features that provide physical evidence for the mineralogy of the earth s mantle (2 pts) Ophiolites,
GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Name Spring 2009 Sc ore / 40 QUIZ 3 1) Name two geologic features that provide physical evidence for the mineralogy of the earth s mantle (2 pts) Ophiolites,
Feldspars. Structure. The feldspars are by far the most abundant group of minerals and are found in igneous, metamorphic and many sedimentary rocks.
 Feldspars The feldspars are by far the most abundant group of minerals and are found in igneous, metamorphic and many sedimentary rocks. Structure Felsdpars are framework silicates where each silica tetrahedra
Feldspars The feldspars are by far the most abundant group of minerals and are found in igneous, metamorphic and many sedimentary rocks. Structure Felsdpars are framework silicates where each silica tetrahedra
Ch 6: Internal Constitution of the Earth
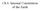 Ch 6: Internal Constitution of the Earth Mantle composition Geological background 88 elements found in the Earth's crust -- of these, only 8 make up 98%: oxygen, silicon, aluminum, iron, calcium, magnesium,
Ch 6: Internal Constitution of the Earth Mantle composition Geological background 88 elements found in the Earth's crust -- of these, only 8 make up 98%: oxygen, silicon, aluminum, iron, calcium, magnesium,
muscovite PART 4 SHEET SILICATES
 muscovite PART 4 SHEET SILICATES SHEET SILICATES = PHYLLOSILICATES Phyllon = leaf Large group of mineral including many common minerals: muscovite, biotite, serpentine, chlorite, talc, clay minerals Structure:
muscovite PART 4 SHEET SILICATES SHEET SILICATES = PHYLLOSILICATES Phyllon = leaf Large group of mineral including many common minerals: muscovite, biotite, serpentine, chlorite, talc, clay minerals Structure:
doi: /nature09940
 LETTER doi:10.1038/nature09940 Spin crossover and iron-rich silicate melt in the Earth s deep mantle Ryuichi Nomura 1,2, Haruka Ozawa 1,3, Shigehiko Tateno 1, Kei Hirose 1,3, John Hernlund 4, Shunsuke
LETTER doi:10.1038/nature09940 Spin crossover and iron-rich silicate melt in the Earth s deep mantle Ryuichi Nomura 1,2, Haruka Ozawa 1,3, Shigehiko Tateno 1, Kei Hirose 1,3, John Hernlund 4, Shunsuke
12. Data from Ito et al. (1987) Chemical Geology, 62, ; Figure ; and LeRoex et al. (1983) J. Petrol., 24,
 Announcements Reading for Wed: p.363-399!!! p.362-366; p.373-378; p.383-386; p.392-394; p.395-399 Last lecture on Wednesday Bring food for pizza party Bring class notes, labs, book N-MORBs: 87 Sr/ 86 Sr
Announcements Reading for Wed: p.363-399!!! p.362-366; p.373-378; p.383-386; p.392-394; p.395-399 Last lecture on Wednesday Bring food for pizza party Bring class notes, labs, book N-MORBs: 87 Sr/ 86 Sr
What processes control the chemical compositions of arc front stratovolcanoes?
 What processes control the chemical compositions of arc front stratovolcanoes? The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters
What processes control the chemical compositions of arc front stratovolcanoes? The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters
Geoffrey Abers. Water and volcanism. Imaging. Lessons from Central America. Oceanic. Terrestrial
 Imaging Circum-Pacific Subduction Zones with Earthquakes: Fluid Pathways and the Origins of Volcanic Arcs Geoffrey Abers Oceanic Terrestrial Water and volcanism Imaging Lessons from Central America Wet
Imaging Circum-Pacific Subduction Zones with Earthquakes: Fluid Pathways and the Origins of Volcanic Arcs Geoffrey Abers Oceanic Terrestrial Water and volcanism Imaging Lessons from Central America Wet
Magma Formation and Behavior
 Magma Formation and Behavior Introduction: The study of body waves as they pass through Earth's interior provides strong evidence that the Earth's mantle is composed almost entirely of solid ultramafic
Magma Formation and Behavior Introduction: The study of body waves as they pass through Earth's interior provides strong evidence that the Earth's mantle is composed almost entirely of solid ultramafic
Aqueous fluids and hydrous melts in high-pressure and ultra-high pressure rocks: Implications for element transfer in subduction zones
 Lithos 92 (2006) 399 417 www.elsevier.com/locate/lithos Aqueous fluids and hydrous melts in high-pressure and ultra-high pressure rocks: Implications for element transfer in subduction zones Jörg Hermann
Lithos 92 (2006) 399 417 www.elsevier.com/locate/lithos Aqueous fluids and hydrous melts in high-pressure and ultra-high pressure rocks: Implications for element transfer in subduction zones Jörg Hermann
Hornblende (Ca,Na)2-3(Fe,Mg,Al)5Si6(Si,Al)2O22(OH)2. Kaolinite (clay) Al2Si2O5(OH)4. Foliation ANIMATION
 1 Hornblende (Ca,Na)2-3(Fe,Mg,Al)5Si6(Si,Al)2O22(OH)2 Kaolinite (clay) Al2Si2O5(OH)4 Foliation ANIMATION 2 Grade Foliation type How does change as grade increases? Density increases (volume shrinks) Foliation
1 Hornblende (Ca,Na)2-3(Fe,Mg,Al)5Si6(Si,Al)2O22(OH)2 Kaolinite (clay) Al2Si2O5(OH)4 Foliation ANIMATION 2 Grade Foliation type How does change as grade increases? Density increases (volume shrinks) Foliation
Table 7.1 Mineralogy of metamorphic rocks related to protolith and grade
 Geology 101 Name(s): Lab 7: Metamorphic rocks Metamorphic rocks have been subjected to sufficient heat and/or pressure to melt some of their constituent minerals, but not all of them. As a result of this
Geology 101 Name(s): Lab 7: Metamorphic rocks Metamorphic rocks have been subjected to sufficient heat and/or pressure to melt some of their constituent minerals, but not all of them. As a result of this
Pyroxenes (Mg, Fe 2+ ) 2 Si 2 O 6 (monoclinic) and. MgSiO 3 FeSiO 3 (orthorhombic) Structure (Figure 2 of handout)
 Pyroxenes (Mg, Fe 2+ ) 2 Si 2 O 6 (monoclinic) and 20 MgSiO 3 FeSiO 3 (orthorhombic) Structure (Figure 2 of handout) Chain silicate eg Diopside Mg and Fe ions link SiO 3 chains The chain runs up and down
Pyroxenes (Mg, Fe 2+ ) 2 Si 2 O 6 (monoclinic) and 20 MgSiO 3 FeSiO 3 (orthorhombic) Structure (Figure 2 of handout) Chain silicate eg Diopside Mg and Fe ions link SiO 3 chains The chain runs up and down
The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks
 The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks Igneous rocks form as molten magma or lava cools and solidifies. Magma is completely or partly molten
The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks Igneous rocks form as molten magma or lava cools and solidifies. Magma is completely or partly molten
amphibole PART 3 Pyroxene: augite CHAIN SILICATES
 amphibole PART 3 Pyroxene: augite CHAIN SILICATES CHAIN SILICATES = INOSILICATES inos = chains Basic structural group: Si 2 O 6 (each tetrahedra shared two corners) Simple or double chains linked by cations
amphibole PART 3 Pyroxene: augite CHAIN SILICATES CHAIN SILICATES = INOSILICATES inos = chains Basic structural group: Si 2 O 6 (each tetrahedra shared two corners) Simple or double chains linked by cations
Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
 1 Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Presentation modified from: Instructor Resource Center on CD-ROM, Foundations of Earth Science,, 4 th Edition, Lutgens/Tarbuck, Rock Cycle Igneous Rocks Today 2 Rock
1 Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Presentation modified from: Instructor Resource Center on CD-ROM, Foundations of Earth Science,, 4 th Edition, Lutgens/Tarbuck, Rock Cycle Igneous Rocks Today 2 Rock
WORKING WITH ELECTRON MICROPROBE DATA FROM A HIGH PRESSURE EXPERIMENT CALCULATING MINERAL FORMULAS, UNIT CELL CONTENT, AND GEOTHERMOMETRY
 WORKING WITH ELECTRON MICROPROBE DATA FROM A HIGH PRESSURE EXPERIMENT CALCULATING MINERAL FORMULAS, UNIT CELL CONTENT, AND GEOTHERMOMETRY Brandon E. Schwab Department of Geology Humboldt State University
WORKING WITH ELECTRON MICROPROBE DATA FROM A HIGH PRESSURE EXPERIMENT CALCULATING MINERAL FORMULAS, UNIT CELL CONTENT, AND GEOTHERMOMETRY Brandon E. Schwab Department of Geology Humboldt State University
Evolution of the Earth
 Evolution of the Earth http://static.newworldencyclopedia.org/f/fe/geologic_clock.jpg Evolution of the Earth Solar system, 4.6 byr Collapse of a nebula Star forms as gravity concentrates material at center
Evolution of the Earth http://static.newworldencyclopedia.org/f/fe/geologic_clock.jpg Evolution of the Earth Solar system, 4.6 byr Collapse of a nebula Star forms as gravity concentrates material at center
Questions on the characteristics and generation of subduction-related andesitic magmas at convergent margins (not covered on Midterm exam)
 Study Guide for GEOL 285 - Petrology Final Exam Fall 2005 The exam will be held at 8-10 am, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2005 in Room 310, White Hall will be available to answer questions on Monday, Dec. 12, and
Study Guide for GEOL 285 - Petrology Final Exam Fall 2005 The exam will be held at 8-10 am, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2005 in Room 310, White Hall will be available to answer questions on Monday, Dec. 12, and
Rocks and the Rock Cycle. Banded Iron Formation
 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Banded Iron Formation Rocks Big rocks into pebbles, Pebbles into sand. I really hold a million, million Rocks here in my hand. Florence Parry Heide How do rocks change? How are
Rocks and the Rock Cycle Banded Iron Formation Rocks Big rocks into pebbles, Pebbles into sand. I really hold a million, million Rocks here in my hand. Florence Parry Heide How do rocks change? How are
Plate tectonics, rock cycle
 Dikes, Antarctica Rock Cycle Plate tectonics, rock cycle The Rock Cycle A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one
Dikes, Antarctica Rock Cycle Plate tectonics, rock cycle The Rock Cycle A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one
predictive mineral discovery*cooperative Research Centre A legacy for mineral exploration science Mineral Systems Q3 Fluid reservoirs
 Mineral Systems Q3 Fluid reservoirs 1 Key Parameter Mineral System Exploration is reflected in scale-dependent translation A. Gradient in hydraulic potential B. Permeability C. Solubility sensitivity to
Mineral Systems Q3 Fluid reservoirs 1 Key Parameter Mineral System Exploration is reflected in scale-dependent translation A. Gradient in hydraulic potential B. Permeability C. Solubility sensitivity to
Archean Terranes. Archean Rocks. Southeastern Africa. West Greenland. Kaapvaal Craton. Ancient Gneiss Complex
 Archean Terranes Archean Rocks Chapter 15A >2.5 Gy old Younger supracrustal sequences Greenstone belts Calc-alkaline metavolcanic rocks Older gneiss complexes Quartzo-feldspathic rocks Tonalites and migmatites
Archean Terranes Archean Rocks Chapter 15A >2.5 Gy old Younger supracrustal sequences Greenstone belts Calc-alkaline metavolcanic rocks Older gneiss complexes Quartzo-feldspathic rocks Tonalites and migmatites
What we know about subduction zones from the metamorphic rock record. Sarah Penniston-Dorland University of Maryland
 What we know about subduction zones from the metamorphic rock record Sarah Penniston-Dorland University of Maryland Subduction zones are complex We can learn a lot about processes occurring within active
What we know about subduction zones from the metamorphic rock record Sarah Penniston-Dorland University of Maryland Subduction zones are complex We can learn a lot about processes occurring within active
UNIVERSITY OF EDINBURGH. College of Science and Engineering School of GeoSciences. Earth Materials UO4824 DEGREE EXAMINATION (MOCK) xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
 UNIVERSITY OF EDINBURGH College of Science and Engineering School of GeoSciences Earth Materials UO4824 DEGREE EXAMINATION (MOCK) xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Chairman: External Examiners:
UNIVERSITY OF EDINBURGH College of Science and Engineering School of GeoSciences Earth Materials UO4824 DEGREE EXAMINATION (MOCK) xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx Chairman: External Examiners:
Trace Elements. Today s lecture
 Trace Elements 300 Ni 200 ppm 100 0 300 Zr 200 100 0 40 50 60 70 80 SiO 2 wt. % Updates: M&M due date: Tuesday Today s lecture Topics: Trace element compositions Trace element behavior Partitioning Spider(
Trace Elements 300 Ni 200 ppm 100 0 300 Zr 200 100 0 40 50 60 70 80 SiO 2 wt. % Updates: M&M due date: Tuesday Today s lecture Topics: Trace element compositions Trace element behavior Partitioning Spider(
Stability of hydrous silicate at high pressures and water transport to the deep lower mantle
 Stability of hydrous silicate at high pressures and water transport to the deep lower mantle Supplementary Figure 1: Compositions of dense hydrous magnesium silicates on the H2O-MgO-SiO2 diagram. PhH,
Stability of hydrous silicate at high pressures and water transport to the deep lower mantle Supplementary Figure 1: Compositions of dense hydrous magnesium silicates on the H2O-MgO-SiO2 diagram. PhH,
