WATER IN THE EARTH S MANTLE:
|
|
|
- Bryan Briggs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WATER IN THE EARTH S MANTLE: NATHALIE BOLFAN-CASANOVA LABORATOIRE MAGMAS ET VOLCANS
2 => Heterogeneous distribution of water in the mantle > pmm wt H2O ~ pmm wt H2O ~ 1000 pmm wt H2O
3 On what form do we find water? Fluids Hydrous magmas Hydrous phases?? NAMs
4 Pearson et al. (2005)
5 Water in the transition zone H2O wt% Mg2SiO4 wadsleyite Inoue et al. (1995) H2O wt % Mg2SiO4 wadsleyite Demouchy et al. (2005) H2O wt % (Mg,Fe)2SiO4 wadsleyite Kawamoto et al. (1996) H2O wt % Mg2SiO4 Ringwoodite Ohtani et al. (2000) km 520 km 670 km 3 H 2 O wt % Ringwoodite inclusion in diamond from Pearson et al. (2014) T( C) => In agreement with water-saturated conditions
6 Water recycling through subduction
7 Peridotite + H 2 O phase diagram redrawn from Iwamory (2004) from Syracuse et al. (2010) => Slabs are not that hot after all
8 H defects are ubiquituous in most mantle samples Demouchy et al. (2004) Demouchy and Bolfan-Casanova (2015)
9 Water circulation in cratons => water content in NAMs from enoliths in kimberlite Shirey et al. (2013)
10 Water circulation in cratons => new messages from NAMs inclusions in diamonds Novella et al. (2015) => Maimum 5 ppm wt H 2 O in olivine Shirey et al. (2013)
11 Effect of CO 2 on water incorporation Sokol et al. (2013)
12 Constraints on the water content in the mantle From the water content in MORBs: -> [H2O] MORB ~3000 ppm wt -> water partitioning D solid/liquid ~0.01 -> melting degree F = 10% => [H2O]source = 300 ppm pds
13 Constraints on the water content in the mantle From the water content in MORBs From the water content in NAMs in mantle enoliths Mineral Water contents (ppm wt H 2 O) Olivine < 1 to > 100 Orthopyroene Clinopyroene up to 1200 Garnet < 1 to 200 * kimberlites and alkali basalts 250 ppm by weight in the source, the lithospheric mantle! Volatile loss during ascent Bell and Rossmann (1992)
14 Diffusion profile of H across olivine Demouchy et al. (2004) => Water content in the source under-estimated
15 Why is such water important? What are the effects of water on mantle physical properties?
16 Effect of water on mantle melting Aubaud et al. (2004) The melt fraction is higher Melting starts at higher depth
17 Effect of water on chemical diffusion Hier-Majumder et al. (2005)
18 D Me X V and X V C OH Hier-Majumder et al. (2005)
19 AC r H OHep( RT H ) Gardès et al. (2014)
20 Seismic discontiuities Frost and Doleij (2007)
21 Elastic softening Effect of hydration on density Jacobsen (2006)
22 Jacobsen (2006)
23 WHAT IS THE STORAGE OF WATER IN THE EARTH S MANTLE NATURAL SYNTHETIC Coutrsy of S. Demouchy Irifune and Isshiki (1998)
24 Water storage capacity of the Earth s? Eperimental approach + Absorption coefficient (cm -1 ) FTIR forsterite synthesized hydrothermally at 9 GPa and 1250 C // a ais // b ais // c ais Wavenumber (cm -1 ) From Bali et al. (2008)
25 Incorporation of water in NAMs In olivine: Mg 2+ = 2 H +
26 Incorporation of water in NAMs In olivine: Mg 2+ = 2 H + Notation de Kröger Vink : Mg Me + OO + H2 O = 2 OH O. + VMe + MgO i.e. MgSiO 3 + Mg Me + 2OO + H2 O = 2 OH O. + VMe + Mg 2 SiO 4
27 Incorporation of water in NAMs In olivine: Mg 2+ = 2 H + Notation de Kröger Vink : Mg Me + OO + H2 O = 2 OH O. + VMe + MgO i.e. MgSiO 3 + Mg Me + 2OO + H2 O = 2 OH O. + VMe + Mg 2 SiO 4 (2H) Me
28 Incorporation of water in NAMs In olivine: Mg 2+ = 2 H + Notation de Kröger Vink : i.e. MgSiO 3 + Mg Me + 2OO + H2 O = (2H) Me + Mg 2 SiO 4 [(2H a a Mg2SiO4 Me)] K fh2o MgSiO3 n [OH] 2 ep( RT G O ) fh2
29 Incorporation of water in NAMs In olivine: Mg 2+ = 2 H + Notation de Kröger Vink : soit MgSiO 3 + Mg Me + 2OO + H2 O = (2H) Me + Mg 2 SiO 4 [(2H a a Mg2SiO4 Me)] K fh2o MgSiO3 [OH] A(P) fh2 n ep( O n [OH] 2 ep( RT G O ) fh2 H RT P V ) and n=1
30 Incorporation of water in NAMs In garnet : Si 4+ = 4 H + Notation de Kröger Vink : Si Si + OO + 2 H2 O = 4 OH O. + VSi + SiO 2
31 Incorporation of water in NAMs In garnet : Si 4+ = 4 H + Notation de Kröger Vink : Si Si + OO + 2 H2 O = 4 OH O. + VSi + SiO 2 (4H) Si
32 Incorporation of water in NAMs In garnet : Si 4+ = 4 H + Notation de Kröger Vink : Si Si + OO + 2 H2 O = 4 OH O. + VSi + SiO 2 [(4H Si )] a K SiO2 f 2 H2O n [OH] 4fH2O ep( RT G )
33 Incorporation of water in NAMs Dans le grenat : Si 4+ = 4 H + Notation de Kröger Vink : Si Si + OO + 2 H2 O = 4 OH O. + VSi + SiO 2 [(4H Si )] a K SiO2 f 2 H2O [OH] A(P) fh2 n ep( O n [OH] 4fH2O ep( RT G ) H RT P V ) and n=2
34 Incorporation of water in NAMs In enstatite: incorporation of aluminum Anhydrous case: Mg 2+ + Si 4+ = 2Al 3+ (Mg Al)(Al Si) O 6 (Tschermak) Hydrous case 1: 2 Mg 2+ = Al 3+ + H + (H Al)(Si Si) O 6 Hydrous case 2: Si 4+ = Al 3+ + H + (Mg Mg) (Al H) Si O 6 Keppler and Bolfan-Casanova (2006)
35 Recycling of H at low temperature in the wedge mantle Thermodynamics of H incorporation [OH] 2 ep( RT G O ) fh2 Pression kj/mole) S J/mole/K) V cc/mole) GPa 37.1 ± ± Kohlstedt et al. (1996) Mosenfelder et al. (2006) Zhao et al. (2006) Bali et al. (2008) Férot and Bolfan-Casanova (2012)
36 Recycling of H at low temperature in the wedge mantle 10 4 Thermodynamics of H incorporation [OH] 2 ep( RT G O ) fh2 Pression kj/mole) S J/mole/K) V cc/mole) GPa 37.1 ± ± log [H2O] ppm wt GPa 2.5 GPa 5 GPa 7.5 GPa Kohlstedt et al. (1996) Mosenfelder et al. (2006) Zhao et al. (2006) Bali et al. (2008) Férot and Bolfan-Casanova (2012) T( C)
37 Recycling of H at low temperature in the wedge mantle 10 4 Thermodynamics of H incorporation [OH] 2 ep( RT G O ) fh2 Pression kj/mole) S J/mole/K) V cc/mole) GPa 37.1 ± ± log [H2O] ppm wt GPa 2.5 GPa 5 GPa 7.5 GPa 3 GPa Kohlstedt et al. (1996) Mosenfelder et al. (2006) Zhao et al. (2006) Bali et al. (2008) Férot and Bolfan-Casanova (2012) T( C)
38 410-km Water storage in olivine in simple MFASH system 1600 Férot and Bolfan-Casanova (2012) Ardia et al. (2012) 1450 C Tenner et al. (2012) 1400 C Water content (ppm wt H 2 O) P (GPa)
39 Partitioning of water into orthopyroene Férot and Bolfan-Casanova (2012)
40 Partitioning of water into orthopyroene 3 y = ² 2.5 Dp/ol P(GPa) Férot and Bolfan-Casanova (2012)
41 Water storage in the convecting upper mantle For garnet : D water gt/ol of 0.9 Novella et al. (2014) at 6 GPa and 1400 C water storage (ppm wt H O) Ol contribution OPX contribution CPX contribution GT contribution Mantle storage curve +/- 100 ppm depth (km)
42 Water storage in the convecting upper mantle ~ 800 ppm wt H 2 O at the base of the upper mantle => In agreement with estimates for the source of Reunion Island OIB water storage (ppm wt H O) Ol contribution OPX contribution CPX contribution GT contribution Mantle storage curve +/- 100 ppm depth (km) From Férot and Bolfan-Casanova (2012)
43 Rewind Water content in the deep upper mantle is anchored at a minimum of 800 ppm wt H 2 O. Olivine can transport ~1000 ppm wt H 2 O in the subducting slab. Different type of fluids travel through cratons through their history.
44 Eperimentally determined water storage in olivine Low Velocity Zone P (GPa) Water storage average Water content (ppm wt H 2 O) /- 100 ppm wt H 2 O in simple MFASH system km From Férot and Bolfan-Casanova (2012) depth (km) => Water storage in olivine reaches ~ 1000 ppm wt H 2 0 at the 410 km discontinuity
45 Implications for the water content determination in the upper mantle Low velocity layer above the 410 km discontinuity Tauzin et al. (2010) LVL interpreted as being due to the occurence of melt The presence of water is necessary to invoke melting
46 L eau dans le manteau inférieur Bolfan-Casanova et al. (2000)
47
Hydration of Olivine and. Earth s Deep Water Cycle
 Hydration of Olivine and Earth s Deep Water Cycle IASPEI October 5, 2005 Olivine Hydration and Earth s Deep Water Cycle J. R. Smyth, (University of Colorado) Dan Frost and Fabrizio Nestola (Bayerisches
Hydration of Olivine and Earth s Deep Water Cycle IASPEI October 5, 2005 Olivine Hydration and Earth s Deep Water Cycle J. R. Smyth, (University of Colorado) Dan Frost and Fabrizio Nestola (Bayerisches
Effect of water on the spinel-postspinel transformation in Mg 2 SiO 4
 Effect of water on the spinel-postspinel transformation in Mg 2 SiO 4 * Pressures for spinel postspinel phase boundary has been subject of debate - XRD measurements indicates that the transition pressure
Effect of water on the spinel-postspinel transformation in Mg 2 SiO 4 * Pressures for spinel postspinel phase boundary has been subject of debate - XRD measurements indicates that the transition pressure
Why cold slabs stagnate in the transition zone
 GSA Data Repository 2015085 Model 1 Model 2 Model 3 Model 4 Model 5 Model 6 Why cold slabs stagnate in the transition zone Scott D. King 1,2, Daniel J. Frost 2, and David C. Rubie 2 1 Department of Geosciences,
GSA Data Repository 2015085 Model 1 Model 2 Model 3 Model 4 Model 5 Model 6 Why cold slabs stagnate in the transition zone Scott D. King 1,2, Daniel J. Frost 2, and David C. Rubie 2 1 Department of Geosciences,
Whole Mantle Convection
 Whole Mantle Convection Overview 1. Evidence for whole mantle convection 2. Model of whole mantle convection reconciling geophysical and geochemical data Transition Zone Water Filter Model 3. Evidence
Whole Mantle Convection Overview 1. Evidence for whole mantle convection 2. Model of whole mantle convection reconciling geophysical and geochemical data Transition Zone Water Filter Model 3. Evidence
The Effect of H 2 O on the 410-km Seismic Discontinuity
 The Effect of H 2 O on the 410-km Seismic Discontinuity B.J. Wood Science Paper (1995) Presented by HuajianYao Background Seismic discontinuities at 410 km and 660 km ------ important jumps in mantle density
The Effect of H 2 O on the 410-km Seismic Discontinuity B.J. Wood Science Paper (1995) Presented by HuajianYao Background Seismic discontinuities at 410 km and 660 km ------ important jumps in mantle density
Deep and persistent melt layer in the Archaean mantle
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-017-0053-9 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Deep and persistent melt layer in the Archaean mantle Denis Andrault 1 *,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-017-0053-9 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Deep and persistent melt layer in the Archaean mantle Denis Andrault 1 *,
Water, Melting, and the Deep Earth H 2 O Cycle
 Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2006. 34:629 53 First published online as a Review in Advance on January 31, 2006 The Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Science is online at earth.annualreviews.org doi:
Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2006. 34:629 53 First published online as a Review in Advance on January 31, 2006 The Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Science is online at earth.annualreviews.org doi:
Fluids, melts, and supercriticality in the MSH system and element transport in subduction zones
 cosmic rays Fluids, s, and supercriticality in the MSH system and element transport in subduction zones 10 Be volcanic front N, O 10 Be ocean water + CO 2 tracing petrologic and geotectonic processes (trace)
cosmic rays Fluids, s, and supercriticality in the MSH system and element transport in subduction zones 10 Be volcanic front N, O 10 Be ocean water + CO 2 tracing petrologic and geotectonic processes (trace)
Effect of tectonic setting on chemistry of mantle-derived melts
 Effect of tectonic setting on chemistry of mantle-derived melts Lherzolite Basalt Factors controlling magma composition Composition of the source Partial melting process Fractional crystallization Crustal
Effect of tectonic setting on chemistry of mantle-derived melts Lherzolite Basalt Factors controlling magma composition Composition of the source Partial melting process Fractional crystallization Crustal
GSA DATA REPOSITORY
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2013019 Supplemental information for The Solidus of Alkaline Carbonatite in the Deep Mantle Konstantin D. Litasov, Anton Shatskiy, Eiji Ohtani, and Gregory M. Yaxley EXPERIMENTAL METHODS
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2013019 Supplemental information for The Solidus of Alkaline Carbonatite in the Deep Mantle Konstantin D. Litasov, Anton Shatskiy, Eiji Ohtani, and Gregory M. Yaxley EXPERIMENTAL METHODS
Geochemical and mineralogical technics to investigate the lithosphere and the asthenosphere. 07/11/2017 GEO-DEEP 9300 Claire Aupart
 Geochemical and mineralogical technics to investigate the lithosphere and the asthenosphere 07/11/2017 GEO-DEEP 9300 Claire Aupart Introduction Introduction Getting samples Cores: Maximum depth reach in
Geochemical and mineralogical technics to investigate the lithosphere and the asthenosphere 07/11/2017 GEO-DEEP 9300 Claire Aupart Introduction Introduction Getting samples Cores: Maximum depth reach in
N = N 0 e -λt D* = N 0 -N D* = N 0 (1-e -λt ) or N(e λt -1) where N is number of parent atoms at time t, N 0
 N = N 0 e -λt D* = N 0 -N D* = N 0 (1-e -λt ) or N(e λt -1) where N is number of parent atoms at time t, N 0 is initial number of parents, D* is number of radiogenic daughter atoms, and λ is the decay
N = N 0 e -λt D* = N 0 -N D* = N 0 (1-e -λt ) or N(e λt -1) where N is number of parent atoms at time t, N 0 is initial number of parents, D* is number of radiogenic daughter atoms, and λ is the decay
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Sample selection A high proportion of xenoliths from the highest P beneath the Kaapvaal craton have higher temperatures compared to the calculated cratonic geotherm 1. They may thus record a thermal disturbance
Sample selection A high proportion of xenoliths from the highest P beneath the Kaapvaal craton have higher temperatures compared to the calculated cratonic geotherm 1. They may thus record a thermal disturbance
Solubility of water in pyrope-rich garnet at high pressures and temperature
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37, L03310, doi:10.1029/2009gl041289, 2010 Solubility of water in pyrope-rich garnet at high pressures and temperature Mainak Mookherjee 1
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37, L03310, doi:10.1029/2009gl041289, 2010 Solubility of water in pyrope-rich garnet at high pressures and temperature Mainak Mookherjee 1
Interpreting Geophysical Data for Mantle Dynamics. Wendy Panero University of Michigan
 Interpreting Geophysical Data for Mantle Dynamics Wendy Panero University of Michigan Chemical Constraints on Density Distribution Atomic Fraction 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 opx cpx C2/c garnet il olivine wadsleyite
Interpreting Geophysical Data for Mantle Dynamics Wendy Panero University of Michigan Chemical Constraints on Density Distribution Atomic Fraction 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 opx cpx C2/c garnet il olivine wadsleyite
α phase In the lower mantle, dominant mineralogy is perovskite [(Mg,Fe)SiO 3 ] The pyrolite mantle consists of: 60% olivine and 40% pyroxene.
![α phase In the lower mantle, dominant mineralogy is perovskite [(Mg,Fe)SiO 3 ] The pyrolite mantle consists of: 60% olivine and 40% pyroxene. α phase In the lower mantle, dominant mineralogy is perovskite [(Mg,Fe)SiO 3 ] The pyrolite mantle consists of: 60% olivine and 40% pyroxene.](/thumbs/78/77484223.jpg) Summary of Dan Shim s lecture on 3/1/05 Phase transitions in the Earth s mantle In this lecture, we focused on phase transitions associated with the transition zone 1. 410 km alpha olivine beta wadsleyite
Summary of Dan Shim s lecture on 3/1/05 Phase transitions in the Earth s mantle In this lecture, we focused on phase transitions associated with the transition zone 1. 410 km alpha olivine beta wadsleyite
high and ultrahigh pressures.
 Stability of hydrous phases in serpentinites to high and ultrahigh pressures. Study of fluid and multiphase solid inclusions in high, very high pressure rocks and metamorphic veins The crust to mantle
Stability of hydrous phases in serpentinites to high and ultrahigh pressures. Study of fluid and multiphase solid inclusions in high, very high pressure rocks and metamorphic veins The crust to mantle
The mantle metasomatism: diversity and impact What the mantle xenoliths tell us?
 The mantle metasomatism: diversity and impact What the mantle xenoliths tell us? Mantle metasomatism Physical and chemical processes that are implemented during the flow of magmas and / or fluids within
The mantle metasomatism: diversity and impact What the mantle xenoliths tell us? Mantle metasomatism Physical and chemical processes that are implemented during the flow of magmas and / or fluids within
Origin of Basaltic Magma. Geology 346- Petrology
 Origin of Basaltic Magma Geology 346- Petrology 2 principal types of basalt in the ocean basins Tholeiitic Basalt and Alkaline Basalt Table 10-1 Common petrographic differences between tholeiitic and alkaline
Origin of Basaltic Magma Geology 346- Petrology 2 principal types of basalt in the ocean basins Tholeiitic Basalt and Alkaline Basalt Table 10-1 Common petrographic differences between tholeiitic and alkaline
Where are these melts generated in the mantle wedge?
 Melt generation processes in subduction zones T.L. Grove, C.B. Till, N. Chatterjee, E. Medard, S.W. Parman New experiments on H2O-saturated melting of mantle peridotite - The role of H2O in mantle wedge
Melt generation processes in subduction zones T.L. Grove, C.B. Till, N. Chatterjee, E. Medard, S.W. Parman New experiments on H2O-saturated melting of mantle peridotite - The role of H2O in mantle wedge
Diamonds and the Geology of Mantle Carbon
 Diamonds and the Geology of Mantle Carbon Steven B. Shirey 1 Pierre Cartigny 2 Daniel J. Frost 3 Shantanu Keshav 4 Fabrizio Nestola 5 Paolo Nimis 5 D. Graham Pearson 6 Nikolai V. Sobolev 7 Michael J. Walter
Diamonds and the Geology of Mantle Carbon Steven B. Shirey 1 Pierre Cartigny 2 Daniel J. Frost 3 Shantanu Keshav 4 Fabrizio Nestola 5 Paolo Nimis 5 D. Graham Pearson 6 Nikolai V. Sobolev 7 Michael J. Walter
Mantle Dynamics and Geochemical Cycle: What can Ocean Drilling contribute?
 Mantle Dynamics and Geochemical Cycle: What can Ocean Drilling contribute? Geochemical Cycle: input and output Subduction Factory Carbon Transfer at Deep Mantle Diamond in Oceanic Mantle? Carbon/Water
Mantle Dynamics and Geochemical Cycle: What can Ocean Drilling contribute? Geochemical Cycle: input and output Subduction Factory Carbon Transfer at Deep Mantle Diamond in Oceanic Mantle? Carbon/Water
What can noble gases really say about mantle. 2) Extent of mantle degassing
 What can noble gases really say about mantle convection and the deep Earth volatile cycles? 1) Constraints on mass flow 1) Constraints on mass flow 2) Extent of mantle degassing Outline: -Noble gas geochemistry
What can noble gases really say about mantle convection and the deep Earth volatile cycles? 1) Constraints on mass flow 1) Constraints on mass flow 2) Extent of mantle degassing Outline: -Noble gas geochemistry
doi: /nature09369
 doi:10.1038/nature09369 Supplementary Figure S1 Scanning electron microscope images of experimental charges with vapour and vapour phase quench. Experimental runs are in the order of added water concentration
doi:10.1038/nature09369 Supplementary Figure S1 Scanning electron microscope images of experimental charges with vapour and vapour phase quench. Experimental runs are in the order of added water concentration
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11294 Review of previous works on deep-liquid properties The major parameters controlling the buoyancy of deep-mantle melts are (i) the changes in atomic packing
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11294 Review of previous works on deep-liquid properties The major parameters controlling the buoyancy of deep-mantle melts are (i) the changes in atomic packing
The upper mantle is the source of almost all magmas. It contains major
 The Upper Mantle and Transition Zone Daniel J. Frost * DOI: 10.2113/GSELEMENTS.4.3.171 The upper mantle is the source of almost all magmas. It contains major transitions in rheological and thermal behaviour
The Upper Mantle and Transition Zone Daniel J. Frost * DOI: 10.2113/GSELEMENTS.4.3.171 The upper mantle is the source of almost all magmas. It contains major transitions in rheological and thermal behaviour
Nominally Anhydrous Minerals and Earth s Deep Water Cycle
 Nominally Anhydrous Minerals and Earth s Deep Water Cycle Joseph R. Smyth Department of Geological Sciences, University of Colorado, Boulder, CO 80309 USA Steven D. Jacobsen Department of Geological Sciences,
Nominally Anhydrous Minerals and Earth s Deep Water Cycle Joseph R. Smyth Department of Geological Sciences, University of Colorado, Boulder, CO 80309 USA Steven D. Jacobsen Department of Geological Sciences,
Anderson RN, Uyeda S, Miyashiro A. (1976) Geophysical and geochemical constraints
 REFERENCES RELEVANT TO PERIDOTITE PARTIAL MELTING IN THE MANTLE WEDGE Anderson RN, Uyeda S, Miyashiro A. (1976) Geophysical and geochemical constraints at converging plate boundaries - I: Dehydration in
REFERENCES RELEVANT TO PERIDOTITE PARTIAL MELTING IN THE MANTLE WEDGE Anderson RN, Uyeda S, Miyashiro A. (1976) Geophysical and geochemical constraints at converging plate boundaries - I: Dehydration in
Zhu Mao. Department of Geological Sciences The University of Texas at Austin Austin, TX
 Zhu Mao Department of Geological Sciences The University of Texas at Austin Austin, TX 78712 310-341-9655 zhumao@mail.utexas.edu Education: Princeton University Ph.D. Gepphysics 2009 M.S. Geophysics 2006
Zhu Mao Department of Geological Sciences The University of Texas at Austin Austin, TX 78712 310-341-9655 zhumao@mail.utexas.edu Education: Princeton University Ph.D. Gepphysics 2009 M.S. Geophysics 2006
The Composition of Hydrous Partial Melts of Garnet Peridotite at 6 GPa: Implications for the Origin of Group II Kimberlites
 JOURNAL OF PETROLOGY VOLUME 55 NUMBER11 PAGES 2097^2124 2014 doi:10.1093/petrology/egu051 The Composition of Hydrous Partial Melts of Garnet Peridotite at 6 GPa: Implications for the Origin of Group II
JOURNAL OF PETROLOGY VOLUME 55 NUMBER11 PAGES 2097^2124 2014 doi:10.1093/petrology/egu051 The Composition of Hydrous Partial Melts of Garnet Peridotite at 6 GPa: Implications for the Origin of Group II
Thermo-chemical structure, dynamics and evolution of the deep mantle: spherical convection calculations
 Thermo-chemical structure, dynamics and evolution of the deep mantle: spherical convection calculations Paul J. Tackley ETH Zürich, Switzerland With help from Takashi Nakagawa, Frédéric Deschamps, James
Thermo-chemical structure, dynamics and evolution of the deep mantle: spherical convection calculations Paul J. Tackley ETH Zürich, Switzerland With help from Takashi Nakagawa, Frédéric Deschamps, James
Constitution of Magmas. Magmas. Gas Law. Composition. Atomic Structure of Magma. Structural Model. PV = nrt H 2 O + O -2 = 2(OH) -
 Constitution of Magmas Magmas Best, Ch. 8 Hot molten rock T = 700-1200 degrees C Composed of ions or complexes Phase Homogeneous Separable part of the system With an interface Composition Most components
Constitution of Magmas Magmas Best, Ch. 8 Hot molten rock T = 700-1200 degrees C Composed of ions or complexes Phase Homogeneous Separable part of the system With an interface Composition Most components
EMMR25 Mineralogy: Ol + opx + chlorite + cpx + amphibole + serpentine + opaque
 GSA Data Repository 2017365 Marshall et al., 2017, The role of serpentinite derived fluids in metasomatism of the Colorado Plateau (USA) lithospheric mantle: Geology, https://doi.org/10.1130/g39444.1 Appendix
GSA Data Repository 2017365 Marshall et al., 2017, The role of serpentinite derived fluids in metasomatism of the Colorado Plateau (USA) lithospheric mantle: Geology, https://doi.org/10.1130/g39444.1 Appendix
High-T heating stage: application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools -
 High-T heating stage: application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools - SZABÓ, Csaba Lithosphere Fluid Research Lab (LRG), Department of Petrology and Geochemistry,
High-T heating stage: application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools - SZABÓ, Csaba Lithosphere Fluid Research Lab (LRG), Department of Petrology and Geochemistry,
On the hydration of majoritic garnet
 University of Colorado, Boulder CU Scholar Geological Sciences Graduate Theses & Dissertations Geological Sciences Spring 1-1-2011 On the hydration of majoritic garnet David Andrew Brown University of
University of Colorado, Boulder CU Scholar Geological Sciences Graduate Theses & Dissertations Geological Sciences Spring 1-1-2011 On the hydration of majoritic garnet David Andrew Brown University of
Structural study of the coherent dehydration of wadsleyite
 American Mineralogist, Volume 96, pages 1760 1767, 2011 Structural study of the coherent dehydration of wadsleyite YU YE, 1, * JOSEPH R. SMYTH, 2 AND DANIEL J. FROST 3 1 Department of Physics, University
American Mineralogist, Volume 96, pages 1760 1767, 2011 Structural study of the coherent dehydration of wadsleyite YU YE, 1, * JOSEPH R. SMYTH, 2 AND DANIEL J. FROST 3 1 Department of Physics, University
Structure of the Earth and the Origin of Magmas
 Page 1 of 12 EENS 2120 Petrology Tulane University Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Structure of the Earth and the Origin of Magmas This document last updated on 23-Jan-2015 Magmas do not form everywhere beneath
Page 1 of 12 EENS 2120 Petrology Tulane University Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Structure of the Earth and the Origin of Magmas This document last updated on 23-Jan-2015 Magmas do not form everywhere beneath
Earth and Planetary Science Letters
 Earth and Planetary Science Letters 293 (2010) 250 258 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Earth and Planetary Science Letters journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl Velocity crossover between
Earth and Planetary Science Letters 293 (2010) 250 258 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Earth and Planetary Science Letters journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl Velocity crossover between
Effect of Water on the Sound Velocities of Ringwoodite in the Transition Zone
 Effect of Water on the Sound Velocities of Ringwoodite in the Transition Zone Steven D. Jacobsen Department of Geological Sciences, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL 60208 Joseph R. Smyth Department
Effect of Water on the Sound Velocities of Ringwoodite in the Transition Zone Steven D. Jacobsen Department of Geological Sciences, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL 60208 Joseph R. Smyth Department
Infrared signatures of OH-defects in wadsleyite: a first-principles study. and Hélène Bureau 1
 1 Revision 1 2 May 2013 2 3 Infrared signatures of OH-defects in wadsleyite: a first-principles study 4 5 6 Marc Blanchard 1,*, Mathilde Roberge 1, Etienne Balan 1, Guillaume Fiquet 1 and Hélène Bureau
1 Revision 1 2 May 2013 2 3 Infrared signatures of OH-defects in wadsleyite: a first-principles study 4 5 6 Marc Blanchard 1,*, Mathilde Roberge 1, Etienne Balan 1, Guillaume Fiquet 1 and Hélène Bureau
Stability of hydrous silicate at high pressures and water transport to the deep lower mantle
 Stability of hydrous silicate at high pressures and water transport to the deep lower mantle Supplementary Figure 1: Compositions of dense hydrous magnesium silicates on the H2O-MgO-SiO2 diagram. PhH,
Stability of hydrous silicate at high pressures and water transport to the deep lower mantle Supplementary Figure 1: Compositions of dense hydrous magnesium silicates on the H2O-MgO-SiO2 diagram. PhH,
Petrogenetic grid in the system MgO-SiO 2 -H 2 O up to 30 GPa, 1600 C: Applications to hydrous peridotite subducting into the Earth s deep interior
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2003jb002651, 2004 Petrogenetic grid in the system MgO-SiO 2 -H 2 O up to 30 GPa, 1600 C: Applications to hydrous peridotite subducting into the
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2003jb002651, 2004 Petrogenetic grid in the system MgO-SiO 2 -H 2 O up to 30 GPa, 1600 C: Applications to hydrous peridotite subducting into the
The two main sites of mantle upwelling in the Earth are
 Whole-mantle convection and the transition-zone water filter hypothesis David Bercovici & Shun-ichiro Karato Department of Geology and Geophysics, Yale University, PO Box 208109, New Haven, Connecticut
Whole-mantle convection and the transition-zone water filter hypothesis David Bercovici & Shun-ichiro Karato Department of Geology and Geophysics, Yale University, PO Box 208109, New Haven, Connecticut
Composition of the Earth and its reservoirs: Geochemical observables
 Composition of the Earth and its reservoirs: Geochemical observables Cin-Ty A. Lee Rice University MYRES-I 2004 The Earth is dynamic and heterogeneous Atmosphere Midocean Ridge Plume Ocean Crust Oceanic
Composition of the Earth and its reservoirs: Geochemical observables Cin-Ty A. Lee Rice University MYRES-I 2004 The Earth is dynamic and heterogeneous Atmosphere Midocean Ridge Plume Ocean Crust Oceanic
Magmatic Processes at Subduction Zones
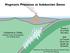 Magmatic Processes at Subduction Zones Katherine A. Kelley Graduate School of Oceanography Univ. of Rhode Island Thanks to Terry Plank Erik Hauri GVP: Liz Cottrell Simon Carn Jennifer Jay Ed Venzke Subduction
Magmatic Processes at Subduction Zones Katherine A. Kelley Graduate School of Oceanography Univ. of Rhode Island Thanks to Terry Plank Erik Hauri GVP: Liz Cottrell Simon Carn Jennifer Jay Ed Venzke Subduction
LAB 9: ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS, CUMULATES AND MELT SOURCES
 Geology 316 (Petrology) (03/26/2012) Name LAB 9: ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS, CUMULATES AND MELT SOURCES INTRODUCTION Ultramafic rocks are igneous rocks containing less than 10% felsic minerals (quartz + feldspars
Geology 316 (Petrology) (03/26/2012) Name LAB 9: ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS, CUMULATES AND MELT SOURCES INTRODUCTION Ultramafic rocks are igneous rocks containing less than 10% felsic minerals (quartz + feldspars
Weidner and Wang (1999) Phase transformations - implications for mantle structure
 Weidner and Wang (1999) Phase transformations - implications for mantle structure The Transition Zone Complex Interactions among Minerals in the Transition Zone Mg-Si-O Mg-Fe-Si-O Mg-Fe-Ca-Al-Si-O (this
Weidner and Wang (1999) Phase transformations - implications for mantle structure The Transition Zone Complex Interactions among Minerals in the Transition Zone Mg-Si-O Mg-Fe-Si-O Mg-Fe-Ca-Al-Si-O (this
Rare Earth Elements in some representative arc lavas
 Rare Earth Elements in some representative arc lavas Low-K (tholeiitic), Medium-K (calc-alkaline), and High-K basaltic andesites and andesites. A typical N-MORB pattern is included for reference Notes:
Rare Earth Elements in some representative arc lavas Low-K (tholeiitic), Medium-K (calc-alkaline), and High-K basaltic andesites and andesites. A typical N-MORB pattern is included for reference Notes:
Raman spectroscopy at high pressure and temperature for the study of Earth's mantle and planetary minerals
 Raman spectroscopy at high pressure and temperature for the study of Earth's mantle and planetary minerals Bruno Reynard, Gilles Montagnac, and Hervé Cardon Laboratoire de Géologie de Lyon Coupling HP
Raman spectroscopy at high pressure and temperature for the study of Earth's mantle and planetary minerals Bruno Reynard, Gilles Montagnac, and Hervé Cardon Laboratoire de Géologie de Lyon Coupling HP
Geos 306, Mineralogy Final Exam, Dec 12, pts
 Name: Geos 306, Mineralogy Final Exam, Dec 12, 2014 200 pts 1. (9 pts) What are the 4 most abundant elements found in the Earth and what are their atomic abundances? Create a reasonable hypothetical charge-balanced
Name: Geos 306, Mineralogy Final Exam, Dec 12, 2014 200 pts 1. (9 pts) What are the 4 most abundant elements found in the Earth and what are their atomic abundances? Create a reasonable hypothetical charge-balanced
Continental Alkaline Magmatism. The East African Rift
 Announcements No lecture on Friday Lab final begins at 1 PM Today s agenda: Lecture/Demo Go through field trip pics Call for pizza Lab review Lecture Review Make poster Continental Alkaline Magmatism.
Announcements No lecture on Friday Lab final begins at 1 PM Today s agenda: Lecture/Demo Go through field trip pics Call for pizza Lab review Lecture Review Make poster Continental Alkaline Magmatism.
GEOL 3313 Petrology of Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks Study Guide for Final Examination Glen Mattioli
 GEOL 3313 Petrology of Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks Study Guide for Final Examination Glen Mattioli Chapter 5: Crystal-Melt phase diagrams Effect of water pressure on feldspar stability Hypersolvus vs.
GEOL 3313 Petrology of Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks Study Guide for Final Examination Glen Mattioli Chapter 5: Crystal-Melt phase diagrams Effect of water pressure on feldspar stability Hypersolvus vs.
- low FeO*/MgO is controlled by the reaction relation oliv + liq! opx.
 Mantle melting trend to high-sio 2 - low FeO*/MgO is controlled by the reaction relation oliv + liq! opx. 4 3 2 1 Ol+Opx +Cpx+Sp +liq 79-35g 82-66 87S35 85-44 85-41c -ol +opx Mantle melting/reaction 0
Mantle melting trend to high-sio 2 - low FeO*/MgO is controlled by the reaction relation oliv + liq! opx. 4 3 2 1 Ol+Opx +Cpx+Sp +liq 79-35g 82-66 87S35 85-44 85-41c -ol +opx Mantle melting/reaction 0
High-T T heating stage: : application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools -
 High-T T heating stage: : application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools - SZABÓ, Csaba Lithosphere Fluid Research Lab (LRG), Department of Petrology and Geochemistry,
High-T T heating stage: : application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools - SZABÓ, Csaba Lithosphere Fluid Research Lab (LRG), Department of Petrology and Geochemistry,
Ultramafic rocks. Types of Ultramafic Rocks. Spinel lherzolite xenolith
 Ultramafic rocks Definition: Color Index > 90, i.e., less than 10% felsic minerals. Not to be confused with Ultrabasic Rocks which are rocks with
Ultramafic rocks Definition: Color Index > 90, i.e., less than 10% felsic minerals. Not to be confused with Ultrabasic Rocks which are rocks with
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L04610, doi: /2004gl019430, 2004
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31,, doi:10.1029/2004gl019430, 2004 Solubility of hydrogen and ferric iron in rutile and TiO 2 (II): Implications for phase assemblages during ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31,, doi:10.1029/2004gl019430, 2004 Solubility of hydrogen and ferric iron in rutile and TiO 2 (II): Implications for phase assemblages during ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism
Harzburgite melting with and without H 2 O: Experimental data and predictive modeling
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2003jb002566, 2004 Harzburgite ing with and without H 2 O: Experimental data and predictive modeling Stephen W. Parman and Timothy L. Grove Department
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2003jb002566, 2004 Harzburgite ing with and without H 2 O: Experimental data and predictive modeling Stephen W. Parman and Timothy L. Grove Department
An Experimental Study of Water in Nominally AnhydrousMineralsintheUpperMantlenear the Water-saturated Solidus
 JOURNAL OF PETROLOGY VOLUME 53 NUMBER10 PAGES 2067^2093 2012 doi:10.1093/petrology/egs044 An Experimental Study of Water in Nominally AnhydrousMineralsintheUpperMantlenear the Water-saturated Solidus ISTVA
JOURNAL OF PETROLOGY VOLUME 53 NUMBER10 PAGES 2067^2093 2012 doi:10.1093/petrology/egs044 An Experimental Study of Water in Nominally AnhydrousMineralsintheUpperMantlenear the Water-saturated Solidus ISTVA
What can isotopes tell us about mantle dynamics? Sujoy Mukhopadhyay. Harvard University
 What can isotopes tell us about mantle dynamics? Sujoy Mukhopadhyay Harvard University The mantle zoo Hofmann, 1997 187 Os/ 188 Os 0.168 0.156 0.144 0.132 EM1 Hawaii Pitcairn DMM peridotites Shield Basalts
What can isotopes tell us about mantle dynamics? Sujoy Mukhopadhyay Harvard University The mantle zoo Hofmann, 1997 187 Os/ 188 Os 0.168 0.156 0.144 0.132 EM1 Hawaii Pitcairn DMM peridotites Shield Basalts
G 3. AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society. A new parameterization of hydrous mantle melting
 Geosystems G 3 AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society Article Volume 4, Number 9 9 September 2003 1073, doi:10.1029/2002gc000433 ISSN: 1525-2027 A new
Geosystems G 3 AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society Article Volume 4, Number 9 9 September 2003 1073, doi:10.1029/2002gc000433 ISSN: 1525-2027 A new
Metal saturation in the upper mantle
 Vol 449 27 September 2007 Metal saturation in the upper mantle A. Rohrbach, C. Ballhaus, U. Golla Schindler, P. Ulmer,V.S. Kamenetsky, D.V. Kuzmin NS seminar 2007.10.25 The uppermost mantle is oxidized.
Vol 449 27 September 2007 Metal saturation in the upper mantle A. Rohrbach, C. Ballhaus, U. Golla Schindler, P. Ulmer,V.S. Kamenetsky, D.V. Kuzmin NS seminar 2007.10.25 The uppermost mantle is oxidized.
Partial melting of mantle peridotite
 Partial melting of mantle peridotite 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 (TºC) Depth (km) 50 100 150 Plag lherzolite (ol-opx-cpx-pl) Spinel lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-sp) Garnet lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-gar) Graphite Diamond
Partial melting of mantle peridotite 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 (TºC) Depth (km) 50 100 150 Plag lherzolite (ol-opx-cpx-pl) Spinel lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-sp) Garnet lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-gar) Graphite Diamond
*Revision 2 for Manuscript 5783* A Review and Update of Mantle Thermobarometry for Primitive Arc Magmas
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 *Revision 2 for Manuscript 5783* A Review and Update of Mantle Thermobarometry for Primitive Arc Magmas Christy B. Till School of Earth &
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 *Revision 2 for Manuscript 5783* A Review and Update of Mantle Thermobarometry for Primitive Arc Magmas Christy B. Till School of Earth &
Lecture 25 Subduction Related Magmatism
 Lecture 25 Subduction Related Magmatism Monday, May 2 nd 2005 Subduction Related Magmatism Activity along arcuate volcanic chains along subduction zones Distinctly different from the mainly basaltic provinces
Lecture 25 Subduction Related Magmatism Monday, May 2 nd 2005 Subduction Related Magmatism Activity along arcuate volcanic chains along subduction zones Distinctly different from the mainly basaltic provinces
Phase Transitions in the Lowermost Mantle
 Phase Transitions in the Lowermost Mantle S.-H. Dan Shim 1, B. Grocholski 2, K. Catalli 3, and V. Prakapenka 4 1 Arizona State University, 2 Smithsonian Institution, 3 Livermore National Lab 4 University
Phase Transitions in the Lowermost Mantle S.-H. Dan Shim 1, B. Grocholski 2, K. Catalli 3, and V. Prakapenka 4 1 Arizona State University, 2 Smithsonian Institution, 3 Livermore National Lab 4 University
Subduction zones 3 arc magmatism
 5. 3 Subduction zones 3 arc magmatism Where can we observe magmatic/volcanic activities along subduction zones? Characteristics of arc magmatism (vs. mid-ocean ridge/intraplate magmatism) Structure of
5. 3 Subduction zones 3 arc magmatism Where can we observe magmatic/volcanic activities along subduction zones? Characteristics of arc magmatism (vs. mid-ocean ridge/intraplate magmatism) Structure of
HP and UHP garnet peridotites and pyroxenites
 HP and UHP garnet peridotites and pyroxenites Mantle wedge The least known piece of the subduction factory Mantle-wedge peridotites emplace within subducting continental crust (Brueckner, 998; van Roermund
HP and UHP garnet peridotites and pyroxenites Mantle wedge The least known piece of the subduction factory Mantle-wedge peridotites emplace within subducting continental crust (Brueckner, 998; van Roermund
Pyroxenes (Mg, Fe 2+ ) 2 Si 2 O 6 (monoclinic) and. MgSiO 3 FeSiO 3 (orthorhombic) Structure (Figure 2 of handout)
 Pyroxenes (Mg, Fe 2+ ) 2 Si 2 O 6 (monoclinic) and 20 MgSiO 3 FeSiO 3 (orthorhombic) Structure (Figure 2 of handout) Chain silicate eg Diopside Mg and Fe ions link SiO 3 chains The chain runs up and down
Pyroxenes (Mg, Fe 2+ ) 2 Si 2 O 6 (monoclinic) and 20 MgSiO 3 FeSiO 3 (orthorhombic) Structure (Figure 2 of handout) Chain silicate eg Diopside Mg and Fe ions link SiO 3 chains The chain runs up and down
12 Chemistry (Mg,Fe) 2 SiO 4 Olivine is forms what is called an isomorphous solid solution series that ranges between two end members: Forsterite Mg
 11 Olivine Structure Olivine is a common green or brown rock forming minerals which consists of a solid-solution series between Forsterite (Fo) and Fayalite (Fa). It is an orthorhombic orthosilicate with
11 Olivine Structure Olivine is a common green or brown rock forming minerals which consists of a solid-solution series between Forsterite (Fo) and Fayalite (Fa). It is an orthorhombic orthosilicate with
Q. WANG, Q-K. XIA, S. Y. O REILLY, W. L. GRIFFIN, E. E. BEYER AND H. K. BRUECKNER
 Pressure- and stress-induced fabric transition in olivine from peridotites in the Western Gneiss Region (Norway): implications for mantle seismic anisotropy Q. WANG, Q-K. XIA, S. Y. O REILLY, W. L. GRIFFIN,
Pressure- and stress-induced fabric transition in olivine from peridotites in the Western Gneiss Region (Norway): implications for mantle seismic anisotropy Q. WANG, Q-K. XIA, S. Y. O REILLY, W. L. GRIFFIN,
Sorosilicates, Colors in Minerals (cont), and Deep Earth Minerals. ESS212 January 20, 2006
 Sorosilicates, Colors in Minerals (cont), and Deep Earth Minerals ESS212 January 20, 2006 Double tetrahedron Sorosilicate is defined by the Si 2 O 7 group. Three groups of minerals, commonly, Epidote Zoisite
Sorosilicates, Colors in Minerals (cont), and Deep Earth Minerals ESS212 January 20, 2006 Double tetrahedron Sorosilicate is defined by the Si 2 O 7 group. Three groups of minerals, commonly, Epidote Zoisite
Textures in experimentally deformed olivine aggregates: the effects of added water and melt.
 Textures in experimentally deformed olivine aggregates: the effects of added water and melt. F. Heidelbach 1, a, B. Holtzman 2, b, S. Hier-Majumder 2, c and D. Kohlstedt 2, d 1 Bayerisches Geoinstitut,
Textures in experimentally deformed olivine aggregates: the effects of added water and melt. F. Heidelbach 1, a, B. Holtzman 2, b, S. Hier-Majumder 2, c and D. Kohlstedt 2, d 1 Bayerisches Geoinstitut,
Experimental petrology of peridotites, including effects of water and carbon on melting in the Earth s upper mantle
 DOI 10.1007/s00269-014-0729-2 ORIGINAL PAPER Experimental petrology of peridotites, including effects of water and carbon on melting in the Earth s upper mantle David H. Green Received: 8 October 2014
DOI 10.1007/s00269-014-0729-2 ORIGINAL PAPER Experimental petrology of peridotites, including effects of water and carbon on melting in the Earth s upper mantle David H. Green Received: 8 October 2014
Transition metals in the transition zone: partitioning of Ni, Co, and Zn between olivine, wadsleyite, ringwoodite, and clinoenstatite
 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-018-1478-x ORIGINAL PAPER Transition metals in the transition zone: partitioning of Ni, Co, and Zn between olivine, wadsleyite, ringwoodite, and clinoenstatite Li Zhang 1,2
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-018-1478-x ORIGINAL PAPER Transition metals in the transition zone: partitioning of Ni, Co, and Zn between olivine, wadsleyite, ringwoodite, and clinoenstatite Li Zhang 1,2
Magma Formation and Behavior
 Magma Formation and Behavior Introduction: The study of body waves as they pass through Earth's interior provides strong evidence that the Earth's mantle is composed almost entirely of solid ultramafic
Magma Formation and Behavior Introduction: The study of body waves as they pass through Earth's interior provides strong evidence that the Earth's mantle is composed almost entirely of solid ultramafic
Seismology and Deep Mantle Temperature Structure. Thorne Lay
 Seismology and Deep Mantle Temperature Structure Thorne Lay Travel time of seismic phases vs. angular distance PREM Preliminary Reference Earth Model Dziewonski and Anderson [1981, PEPI] Basic fact:
Seismology and Deep Mantle Temperature Structure Thorne Lay Travel time of seismic phases vs. angular distance PREM Preliminary Reference Earth Model Dziewonski and Anderson [1981, PEPI] Basic fact:
Subsolidus and melting experiments of a K-rich basaltic composition to 27 GPa: Implication for the behavior of potassium in the mantle
 American Mineralogist, Volume 84, pages 357 361, 1999 Subsolidus and melting experiments of a K-rich basaltic composition to 27 GPa: Implication for the behavior of potassium in the mantle WUYI WANG* AND
American Mineralogist, Volume 84, pages 357 361, 1999 Subsolidus and melting experiments of a K-rich basaltic composition to 27 GPa: Implication for the behavior of potassium in the mantle WUYI WANG* AND
Laboratory Electrical Conductivity Measurement of Mantle Minerals
 Laboratory Electrical Conductivity Measurement of Mantle Minerals Takashi Yoshino Institute for Study of the Earth s Interior, Okayama University Outline 1. Brief introduction 2. Conduction mechanisms
Laboratory Electrical Conductivity Measurement of Mantle Minerals Takashi Yoshino Institute for Study of the Earth s Interior, Okayama University Outline 1. Brief introduction 2. Conduction mechanisms
THE INTERIOR OF THE EARTH
 THE INTERIOR OF THE EARTH Introduction: Nebular hypothesis and the origin of solar system, which indicates that there is a differentiation (layering) in the earth. * Sources of our knowledge about the
THE INTERIOR OF THE EARTH Introduction: Nebular hypothesis and the origin of solar system, which indicates that there is a differentiation (layering) in the earth. * Sources of our knowledge about the
THE MONTE MAGGIORE PERIDOTITE (CORSICA)
 MONTE MAGGIORE CAPO CORSO CORSICA Giovanni B. Piccardo THE MONTE MAGGIORE PERIDOTITE (CORSICA) FIELD RELATIONSHIPS MORB Gabbro Spinel (ex-garnet) pyroxenites L ESCURSIONE A MONTE MAGGIORE The Monte Maggiore
MONTE MAGGIORE CAPO CORSO CORSICA Giovanni B. Piccardo THE MONTE MAGGIORE PERIDOTITE (CORSICA) FIELD RELATIONSHIPS MORB Gabbro Spinel (ex-garnet) pyroxenites L ESCURSIONE A MONTE MAGGIORE The Monte Maggiore
CO 2 quantification in magmatic systems
 CO 2 quantification in magmatic systems Innovative coupling of X-ray micro-tomography, in-situ microanalysis and thermodynamic modelling By Laura Créon Créon et al. (2018) Problematics 7 years work to
CO 2 quantification in magmatic systems Innovative coupling of X-ray micro-tomography, in-situ microanalysis and thermodynamic modelling By Laura Créon Créon et al. (2018) Problematics 7 years work to
Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors
 Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors 177 (2009) 103 115 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/pepi Structure
Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors 177 (2009) 103 115 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/pepi Structure
Post-perovskite 1. Galley Proofs
 16 September 2005 21:39 YB061180.tex McGraw Hill YB of Science & Technology Keystroked: 29/08/2005 Initial MS Page Sequence Stamp: 02350 Article Title: Post-perovskite Article ID: YB061180 1st Classification
16 September 2005 21:39 YB061180.tex McGraw Hill YB of Science & Technology Keystroked: 29/08/2005 Initial MS Page Sequence Stamp: 02350 Article Title: Post-perovskite Article ID: YB061180 1st Classification
Theoretical mineralogy, density, seismic wavespeeds and H 2
 The Cascadia Subduction Zone and Related Subduction Systems 133 Theoretical mineralogy, density, seismic wavespeeds and H 2 O content of the Cascadia subduction zone, with implications for intermediate-depth
The Cascadia Subduction Zone and Related Subduction Systems 133 Theoretical mineralogy, density, seismic wavespeeds and H 2 O content of the Cascadia subduction zone, with implications for intermediate-depth
Crystal chemistry of hydrous forsterite and its vibrational properties up to 41 GPa
 American Mineralogist, Volume 94, pages 751 760, 2009 Crystal chemistry of hydrous forsterite and its vibrational properties up to 41 GPa AnwAr HusHur, 1 Murli H. MAngHnAni, 1, * JosepH r. smyth, 2 FAbrizio
American Mineralogist, Volume 94, pages 751 760, 2009 Crystal chemistry of hydrous forsterite and its vibrational properties up to 41 GPa AnwAr HusHur, 1 Murli H. MAngHnAni, 1, * JosepH r. smyth, 2 FAbrizio
First principles investigation of the structural and elastic properties of hydrous wadsleyite under pressure
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jb005841, 2009 First principles investigation of the structural and elastic properties of hydrous wadsleyite under pressure Jun Tsuchiya 1,2
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008jb005841, 2009 First principles investigation of the structural and elastic properties of hydrous wadsleyite under pressure Jun Tsuchiya 1,2
Water in Natural Mantle Minerals II: Olivine, Garnet and Accessory Minerals
 Reviews in Mineralogy & Geochemistry Vol. 62, pp. 169-191, 2006 Copyright Mineralogical Society of America 8 Water in Natural Mantle Minerals II: Olivine, Garnet and Accessory Minerals Anton Beran and
Reviews in Mineralogy & Geochemistry Vol. 62, pp. 169-191, 2006 Copyright Mineralogical Society of America 8 Water in Natural Mantle Minerals II: Olivine, Garnet and Accessory Minerals Anton Beran and
amphibole PART 3 Pyroxene: augite CHAIN SILICATES
 amphibole PART 3 Pyroxene: augite CHAIN SILICATES CHAIN SILICATES = INOSILICATES inos = chains Basic structural group: Si 2 O 6 (each tetrahedra shared two corners) Simple or double chains linked by cations
amphibole PART 3 Pyroxene: augite CHAIN SILICATES CHAIN SILICATES = INOSILICATES inos = chains Basic structural group: Si 2 O 6 (each tetrahedra shared two corners) Simple or double chains linked by cations
II-1 HYDROUS, LOW-CARBON MELTING OF GARNET PERIDOTITE. J. Brian Balta. Paul D. Asimow. Jed L. Mosenfelder
 II-1 HYDROUS, LOW-CARBON MELTING OF GARNET PERIDOTITE By J. Brian Balta Paul D. Asimow Jed L. Mosenfelder II-2 ABSTRACT The presence of volatile species in Earth s upper mantle drives the formation of
II-1 HYDROUS, LOW-CARBON MELTING OF GARNET PERIDOTITE By J. Brian Balta Paul D. Asimow Jed L. Mosenfelder II-2 ABSTRACT The presence of volatile species in Earth s upper mantle drives the formation of
NMR in Mineralogy. Sharon Ashbrook School of Chemistry, University of St Andrews
 NMR in Mineralogy Sharon Ashbrook School of Chemistry, University of St Andrews Structure of the Earth Study of minerals is important for determining the physical and chemical properties of the Earth O
NMR in Mineralogy Sharon Ashbrook School of Chemistry, University of St Andrews Structure of the Earth Study of minerals is important for determining the physical and chemical properties of the Earth O
Composition of bulk silicate Earth and global geodynamics
 Composition of bulk silicate Earth and global geodynamics Jun Korenaga Department of Geology and Geophysics Yale University March 23, 2007 @ Hawaii Geoneutrino Workshop Overview Motivation: Thermal evolution
Composition of bulk silicate Earth and global geodynamics Jun Korenaga Department of Geology and Geophysics Yale University March 23, 2007 @ Hawaii Geoneutrino Workshop Overview Motivation: Thermal evolution
Deep upper-mantle melting beneath the Tasman and Coral Seas detected with multiple ScS reverberations
 Earth and Planetary Science Letters 259 (2007) 66 76 www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl Deep upper-mantle melting beneath the Tasman and Coral Seas detected with multiple ScS reverberations Anna M. Courtier,
Earth and Planetary Science Letters 259 (2007) 66 76 www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl Deep upper-mantle melting beneath the Tasman and Coral Seas detected with multiple ScS reverberations Anna M. Courtier,
Mg/Si ratios of aqueous fluids coexisting with forsterite and enstatite based on the phase relations in the Mg 2 SiO 4 -SiO 2 -H 2 O system
 American Mineralogist, Volume 89, pages 1433 1437, 2004 Mg/Si ratios of aqueous fluids coexisting with forsterite and enstatite based on the phase relations in the Mg 2 SiO 4 -SiO 2 -H 2 O system TATSUHIKO
American Mineralogist, Volume 89, pages 1433 1437, 2004 Mg/Si ratios of aqueous fluids coexisting with forsterite and enstatite based on the phase relations in the Mg 2 SiO 4 -SiO 2 -H 2 O system TATSUHIKO
Supplementary Figure 1 Map of the study area Sample locations and main physiographic features of the study area. Contour interval is 200m (a) and 40m
 Supplementary Figure 1 Map of the study area Sample locations and main physiographic features of the study area. Contour interval is 200m (a) and 40m (b). Dashed lines represent the two successive ridge
Supplementary Figure 1 Map of the study area Sample locations and main physiographic features of the study area. Contour interval is 200m (a) and 40m (b). Dashed lines represent the two successive ridge
What is going on here?
 Major Digression! Atoms? Elements? Compounds? Minerals? Rocks? What is going on here? Source:SERC @ Carleton College http://www.brocku.ca/earthsciences/people/gfinn/petrology/periodic.gif http://www.meta-synthesis.com/webbook/35_pt/pt_database.php?pt_id=335
Major Digression! Atoms? Elements? Compounds? Minerals? Rocks? What is going on here? Source:SERC @ Carleton College http://www.brocku.ca/earthsciences/people/gfinn/petrology/periodic.gif http://www.meta-synthesis.com/webbook/35_pt/pt_database.php?pt_id=335
A Water-Rich Transition Zone Beneath the Eastern United States and Gulf of Mexico from Multiple ScS Reverberations
 A Water-Rich Transition Zone Beneath the Eastern United States and Gulf of Mexico from Multiple ScS Reverberations Anna M. Courtier* and Justin Revenaugh Department of Geology and Geophysics, University
A Water-Rich Transition Zone Beneath the Eastern United States and Gulf of Mexico from Multiple ScS Reverberations Anna M. Courtier* and Justin Revenaugh Department of Geology and Geophysics, University
A mechanism for low extent melts at the lithosphere asthenosphere boundary
 Article Volume 11, Number 10 27 October 2010 Q10015, doi:10.1029/2010gc003234 ISSN: 1525 2027 A mechanism for low extent melts at the lithosphere asthenosphere boundary Christy B. Till and Linda T. Elkins
Article Volume 11, Number 10 27 October 2010 Q10015, doi:10.1029/2010gc003234 ISSN: 1525 2027 A mechanism for low extent melts at the lithosphere asthenosphere boundary Christy B. Till and Linda T. Elkins
High pressure crystal chemistry of hydrous ringwoodite and water in the Earth s interior
 High pressure crystal chemistry of hydrous ringwoodite and water in the Earth s interior Joseph R. Smyth a, Christopher M. Holl a, Daniel J. Frost b, Steven D. Jacobsen b a Department of Geological Sciences,
High pressure crystal chemistry of hydrous ringwoodite and water in the Earth s interior Joseph R. Smyth a, Christopher M. Holl a, Daniel J. Frost b, Steven D. Jacobsen b a Department of Geological Sciences,
The Redox State of Earth s Mantle
 ANNUAL REVIEWS Further Click here for quick links to Annual Reviews content online, including: Other articles in this volume Top cited articles Top downloaded articles Our comprehensive search Annu. Rev.
ANNUAL REVIEWS Further Click here for quick links to Annual Reviews content online, including: Other articles in this volume Top cited articles Top downloaded articles Our comprehensive search Annu. Rev.
Layer Composition Thickness State of Matter
 Unit 4.2 Test Review Earth and Its Layers 1. Label the layers of the earth. oceanic crust continental crust lithosphere asthenosphere mantle outer core inner core 2. Complete the Following Table about
Unit 4.2 Test Review Earth and Its Layers 1. Label the layers of the earth. oceanic crust continental crust lithosphere asthenosphere mantle outer core inner core 2. Complete the Following Table about
