- low FeO*/MgO is controlled by the reaction relation oliv + liq! opx.
|
|
|
- Earl Short
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mantle melting trend to high-sio 2 - low FeO*/MgO is controlled by the reaction relation oliv + liq! opx Ol+Opx +Cpx+Sp +liq 79-35g S c -ol +opx Mantle melting/reaction SiO Opx = 0.5 Oliv Liq TH CA fractional crystallization paths Structural and metamorphic studies of exhumed high pressure subduction complexes (Enami et al., 2004; Maekawa et al., 2004; Kombayashi, 2004) show: Serpentinites were formed in the mantle wedge above the subducted plate. These were transported to depth in the subduction zone along with the sediments and basalts associated with the slab.
2 Serpentinite a common product of ocean floor tectonic processes (Ranero et al., 2003) Experimental Details Au capsules Piston cylinder GPa Hart & Zindler Primitive Mantle Oxide starting mix With MgO added as Mg(OH) 2 = 14 wt. % H 2 O Run Duration hours ( a few at 24 hrs) Experimental Products Homogeneous olivine, opx, cpx, spinel and/or garnet Melt or vapor phase (supercritical fluid) Equilibrium QUILF used to check Temp. from Opx-Cpx within 1 sigma of uncertainty and f O2 from oliv-opx-spinel (Ballhaus et al., 1994) =QFM + 0.8
3 PREVIOUS STUDIES Run Times H 2 O added Capsule High T melting Kushiro et al. (1968) 5 30 min 30% Mo & Pt Millhollen et al. (1974) hrs. 5.7 % Pt Green (1973) 1 6 hrs. 10 % AgPd alloy Low T melting Mysen and Boettcher (1975) hrs % AgPd alloy THIS STUDY hrs % Au Silver and Stolper (1985) speciation model for melting in simple two component systems mineral H 2 O Includes molecular H 2 O OH speciation and leads to a planar T P X H2O solid melt boundary Note linearity of liquidus boundary. This melting behavior is adjusted for perid.
4 Symmetry in melt % and H 2 O content in upper part of wedge In this region temperature decreases in overlying mantle wedge. Melt amount decreases, melt crystallizes. Oliv + liquid react and form pyroxene. OR Diapiric flow? H 2 O content increases latent heat is released = increasing T. OR Diapiric flow? The melting model:. We use our phase diagram & measured H 2 O solubility vs. pressure in forsterite H 2 O to predict the peridotite melt boundary in T P XH 2 O space. The expression is: 7290*P - 810*T *H 2 O = 0 where T is in o C, P is in kilobars and H 2 O content is in wt. %. At P2, T2 the amount of melt (F P2,T2 ) is given by: F P2,T2 = ((X init X P2,T2 )/X init ) * F init + F init
5 Note the proximity of the Mt. Shasta Medicine Lake systems to the projection of the Blanco Fracture Zone on the Juan de Fuca plate beneath western edge of North America.
6 Newberry volcano, Oregon, Big Obsidian Flow and West Paulina Lake Jay TLG Christy Mike Etienne Shasta from the N. side looking S.
7 Climbing Shasta from the S. side. At the Red Banks. Mt. Shasta on the S. side looking N. toward the summit.
8 Just below Mt. Shasta summit Steve Parman and boiling sulfur springs. Sisson & Grove (1993) Estimation of pre-eruptive H 2 O content
9 Sampling of Mt. Shasta stratocone and surrounding volcanic vents Minerals in Shasta mixed andesite and dacite lavas
10 MPa, H 2 O-saturated, Ni-NiO buffer Ol Cpx Sp Pl Amp Ol Cpx Sp Opx Pl c = Basaltic Andesite 53 % SiO 2 10 % MgO Fo = Primitive Magnesian Andesite 58 % SiO 2 9 % MgO Fo 93.6 Fe-Mg silicates and spinel appear early, plagioclase is late and Ca, Al rich!"#$%&"'()*+,-./)'01(23"405)'06$7(3%&"8 90:;003)'(1<)%0'"0%)$35):01:(3"1)%0=32 More than One trend And Each Arc Distinctive Miyashiro (1974) established the existence of multiple types of liquid lines of descent in sub-alkaline rock series and that these were found in distinct tectonic settings.
11 Tholeiitic - 6"?@"5%)A'(C)D"%%(3)E)F'(G0)$35)A(')HI)$35)J!I)KLL TH Galapagos CA!J$ g S Mf 1471Mb c SiO 2 Here are crustal level liquid lines of descent defined by experiments. Galapagos trend is the so-called iron-enrichment trend from Juster et al. (1989). H 2 O-bearing experiments are from Sisson and Grove (1993), Medicine Lake and Mt. Shasta experiments discussed on previous days. The oliv+opx melting reaction followed during hydrous mantle melting after cpx + sp are exhausted is shown by The gray arrow and defines the trend of increasing degree of mantle melting. Circle shows compositon of hydrous mantle melts from Gaetani & Grove (1998).
12 Mt. Shasta andesites, dacites and primitive satellite cone lavas along with experimentally determined liquid lines of descent at 200 MPa and NNO buffer. Mt. Shasta lavas compared with Ewart s average orogenic andesite averages M"2&BD"N K )6(;)O0NPQ!2N)6$G$%)$'0)50'"G05)9# Shasta A'$17(3$6)1'#%:$66"4$7(3)(A)'(@%)C$3:60 Adak TH CA Setouchi C06:%)%02'02$:05)$:):(8)(A)C$3:60);0520R Andean MPa 85-41c 200 MPa Fractional Crystallization 1 Mantle Melting SiO Here we compare the distinct suites of lavas at Setouchi and Adak with the Mt. Shasta lavas and hydrous experimental liquids lines of descent.
13 Major element compositional variations in Mt. Shasta region lavas. Also shown are compositions of BA and PMA lavas and experimentally determined liquid lines of descent from 200 MPa, NNO buffered, H 2 O-saturated crystallization experiments on and 85-41c and 0.1 MPa QFM-buffered anhydrous experiments on 85-41c Spidergrams for Mt. Shasta lavas and a comparison of a calculated fractional crystallization model from a primitive magnesian andesite (PMA) parent. Absense of compositional zoning in Mt. Shasta andesite lava flows. Mixing is very efficient.
14 Compositional range of plagioclase produced in 200 MPa, H 2 O-saturated and 0.1 MPa anhydrous crystallization experiments on primitive magnesian andesite (PMA) 85-41c and basaltic andesite (BA) Variation in plagioclase phenocryst core compositions of andesites and dacites from the Shastina and Misery eruptive stages. Pyroxene core compositions in Mt. Shasta andesites and dacites. Horizontal axis: (Mg# = 100*Mg/(Mg+Fe*)). Each eruptive stage contains preserved evidence for mixing of two or more batches of magma that are at different stages in compositional evolution.
15 Compositional range of orthopyroxene and augite produced in 200 MPa, H 2 O-saturated and 0.1 MPa anhydrous crystallization experiments on basaltic andesite (BA) and primitive magnesian andesite (PMA) 85-41c. Variation in phenocryst core composition found in orthopyroxene (opx) and augite (cpx) of andesites and dacites from the Misery eruptive stage. Variation in phenocryst core compositions of amphibole (A) and olivine (B) from all Shasta region andesites and dacites. Horizontal axis is (Mg# = 100*Mg/(Mg+Fe*)). Numbers in parentheses are the number of analyses used in each histogram. Experimental amphiboles are from 200 and 800 MPa, H 2 O- saturated experiments on Experimental olivine compositions are from 200 MPa runs.
16 Amphibole in Shastina lava in overgrowth reaction with rthopyroxene. ~ 0.5 mm FOV Backscattered images of magnesian amphbole overgrowing Mg-rich pyroxene and olivine in Mt. Shasta andesites.
17 Oxide thermobarometry from magnetiteulvospinel ss and hematite-ilmenite ss assemblages. Note the range of oxygen fugacities. Experimental calibration of pressure and H 2 O content of crystallization of amphiboles found in Shasta andesite lavas and quenched magmatic inclusions. Trace element abundance variations in Mt. Shasta stratocone lavas and a fractional crystallization model. Model uses phase proportions from 200 MPa crystallization experiments on the primitive magnesian andesite (PMA).
18 Constraints on magma eruptability beneath the Mt. Shasta edifice.
19 Phase relations at 200 MPA for the primitive lavas at Mt. Shasta. Projection schemes use oxygen units.
20 !"#$"%&'()*++,-#%,-%./*%0(1*' 2'3+. 2)50%(30% 6 7 8&%239,2305&0:+0,(-0)3%&%+2))();&<,9%3 =>0,0&(%&-2;-2&+,4<0%%();&4<<9,,();&()&3>0 F>2%32
21 &C4 &!4 &C4
22
23 A successful inclusion hunt at Mt. Shasta
24 Red Butte host lava 2mm FOV Textural variability in quenched magmatic inclusions in Mt. Shasta lavas
25 DE DF GE
26 E%<I"'%00J F>2%32 P)50%(30% H%<I"'%00J &!4%JKLMN< C4%J7LOM< H%<I"'%00J G,4/0&03&2'E&7HHI :C%JKLMM :/"+."%4-5*+,.*+
27 9K%!&" 2LM HFF%!&" 2LM 2LM N7B N7B NLM N7B NLM 4$L/ :,N H EFF%!&" 2LM DFF%!&" 2LM N7B NLM 4$L/ N7B 4$L/ NLM GE DF DE
28 Distributary reaction relation that leads to the appearance of amphibole. From Sisson and Grove (1993). HFF%µ$ O( DP %N7,B,-* &"'#"+,.*,-)73+,(- &"'#"+,.*!#Q%GR9P
29 !S-.*-*'%*.%"79%HFFK Oxide thermobarometry from magnetiteulvospinel ss and hematite-ilmenite ss assemblages. Note the range of oxygen fugacities. Experimental calibration of pressure and H 2 O content of crystallization of amphiboles found in Shasta andesite lavas and quenched magmatic inclusions.
30 Constraints on magma eruptability beneath the Mt. Shasta edifice.
31
32
Where are these melts generated in the mantle wedge?
 Melt generation processes in subduction zones T.L. Grove, C.B. Till, N. Chatterjee, E. Medard, S.W. Parman New experiments on H2O-saturated melting of mantle peridotite - The role of H2O in mantle wedge
Melt generation processes in subduction zones T.L. Grove, C.B. Till, N. Chatterjee, E. Medard, S.W. Parman New experiments on H2O-saturated melting of mantle peridotite - The role of H2O in mantle wedge
Lecture 25 Subduction Related Magmatism
 Lecture 25 Subduction Related Magmatism Monday, May 2 nd 2005 Subduction Related Magmatism Activity along arcuate volcanic chains along subduction zones Distinctly different from the mainly basaltic provinces
Lecture 25 Subduction Related Magmatism Monday, May 2 nd 2005 Subduction Related Magmatism Activity along arcuate volcanic chains along subduction zones Distinctly different from the mainly basaltic provinces
GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Spring 2009 Sc ore / 40
 GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Name Spring 2009 Sc ore / 40 QUIZ 3 1) Name two geologic features that provide physical evidence for the mineralogy of the earth s mantle (2 pts) Ophiolites,
GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Name Spring 2009 Sc ore / 40 QUIZ 3 1) Name two geologic features that provide physical evidence for the mineralogy of the earth s mantle (2 pts) Ophiolites,
Igneous Rocks of the Convergent Margins
 Page 1 of 10 EENS 2120 Petrology Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Tulane University Igneous Rocks of the This document last updated on 08-Feb-2011 The convergent plate margins are the most intense areas of active
Page 1 of 10 EENS 2120 Petrology Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Tulane University Igneous Rocks of the This document last updated on 08-Feb-2011 The convergent plate margins are the most intense areas of active
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks
 Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
The influence of H 2 O on mantle wedge melting
 Earth and Planetary Science Letters 249 (2006) 74 89 www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl The influence of H 2 O on mantle wedge melting Timothy L. Grove, Nilanjan Chatterjee, Stephen W. Parman, Etienne Médard
Earth and Planetary Science Letters 249 (2006) 74 89 www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl The influence of H 2 O on mantle wedge melting Timothy L. Grove, Nilanjan Chatterjee, Stephen W. Parman, Etienne Médard
*Revision 2 for Manuscript 5783* A Review and Update of Mantle Thermobarometry for Primitive Arc Magmas
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 *Revision 2 for Manuscript 5783* A Review and Update of Mantle Thermobarometry for Primitive Arc Magmas Christy B. Till School of Earth &
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 *Revision 2 for Manuscript 5783* A Review and Update of Mantle Thermobarometry for Primitive Arc Magmas Christy B. Till School of Earth &
Imagine the first rock and the cycles that it has been through.
 A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
Trace Elements. Today s lecture
 Trace Elements 300 Ni 200 ppm 100 0 300 Zr 200 100 0 40 50 60 70 80 SiO 2 wt. % Updates: M&M due date: Tuesday Today s lecture Topics: Trace element compositions Trace element behavior Partitioning Spider(
Trace Elements 300 Ni 200 ppm 100 0 300 Zr 200 100 0 40 50 60 70 80 SiO 2 wt. % Updates: M&M due date: Tuesday Today s lecture Topics: Trace element compositions Trace element behavior Partitioning Spider(
Worked Example of Batch Melting: Rb and Sr
 Worked Example of Batch Melting: Rb and Sr Basalt with the mode: Table 9.2. Conversion from mode to weight percent Mineral Mode Density Wt prop Wt% ol 15 3.6 54 0.18 cpx 33 3.4 112.2 0.37 plag 51 2.7 137.7
Worked Example of Batch Melting: Rb and Sr Basalt with the mode: Table 9.2. Conversion from mode to weight percent Mineral Mode Density Wt prop Wt% ol 15 3.6 54 0.18 cpx 33 3.4 112.2 0.37 plag 51 2.7 137.7
Anderson RN, Uyeda S, Miyashiro A. (1976) Geophysical and geochemical constraints
 REFERENCES RELEVANT TO PERIDOTITE PARTIAL MELTING IN THE MANTLE WEDGE Anderson RN, Uyeda S, Miyashiro A. (1976) Geophysical and geochemical constraints at converging plate boundaries - I: Dehydration in
REFERENCES RELEVANT TO PERIDOTITE PARTIAL MELTING IN THE MANTLE WEDGE Anderson RN, Uyeda S, Miyashiro A. (1976) Geophysical and geochemical constraints at converging plate boundaries - I: Dehydration in
E. Martin I. Bindeman T. L. Grove
 DOI 10.1007/s00410-011-0633-4 ORIGINAL PAPER The origin of high-mg magmas in Mt Shasta and Medicine Lake volcanoes, Cascade Arc (California): higher and lower than mantle oxygen isotope signatures attributed
DOI 10.1007/s00410-011-0633-4 ORIGINAL PAPER The origin of high-mg magmas in Mt Shasta and Medicine Lake volcanoes, Cascade Arc (California): higher and lower than mantle oxygen isotope signatures attributed
Straddling the tholeiitic/calc-alkaline transition: the effects of modest amounts of water on magmatic differentiation at Newberry Volcano, Oregon
 Straddling the tholeiitic/calc-alkaline transition: the effects of modest amounts of water on magmatic differentiation at Newberry Volcano, Oregon The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available.
Straddling the tholeiitic/calc-alkaline transition: the effects of modest amounts of water on magmatic differentiation at Newberry Volcano, Oregon The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available.
The Nature of Igneous Rocks
 The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
12 Chemistry (Mg,Fe) 2 SiO 4 Olivine is forms what is called an isomorphous solid solution series that ranges between two end members: Forsterite Mg
 11 Olivine Structure Olivine is a common green or brown rock forming minerals which consists of a solid-solution series between Forsterite (Fo) and Fayalite (Fa). It is an orthorhombic orthosilicate with
11 Olivine Structure Olivine is a common green or brown rock forming minerals which consists of a solid-solution series between Forsterite (Fo) and Fayalite (Fa). It is an orthorhombic orthosilicate with
Petrogenetic Constraints at Mount Rainier Volcano, Washington
 Petrogenetic Constraints at Mount Rainier Volcano, Washington S. C. Kuehn and P. R. Hooper, Department of Geology, Washington State University, Pullman, WA A. E. Eggers and C. Kerrick, Department of Geology,
Petrogenetic Constraints at Mount Rainier Volcano, Washington S. C. Kuehn and P. R. Hooper, Department of Geology, Washington State University, Pullman, WA A. E. Eggers and C. Kerrick, Department of Geology,
doi: /nature09369
 doi:10.1038/nature09369 Supplementary Figure S1 Scanning electron microscope images of experimental charges with vapour and vapour phase quench. Experimental runs are in the order of added water concentration
doi:10.1038/nature09369 Supplementary Figure S1 Scanning electron microscope images of experimental charges with vapour and vapour phase quench. Experimental runs are in the order of added water concentration
Constitution of Magmas. Magmas. Gas Law. Composition. Atomic Structure of Magma. Structural Model. PV = nrt H 2 O + O -2 = 2(OH) -
 Constitution of Magmas Magmas Best, Ch. 8 Hot molten rock T = 700-1200 degrees C Composed of ions or complexes Phase Homogeneous Separable part of the system With an interface Composition Most components
Constitution of Magmas Magmas Best, Ch. 8 Hot molten rock T = 700-1200 degrees C Composed of ions or complexes Phase Homogeneous Separable part of the system With an interface Composition Most components
Metal saturation in the upper mantle
 Vol 449 27 September 2007 Metal saturation in the upper mantle A. Rohrbach, C. Ballhaus, U. Golla Schindler, P. Ulmer,V.S. Kamenetsky, D.V. Kuzmin NS seminar 2007.10.25 The uppermost mantle is oxidized.
Vol 449 27 September 2007 Metal saturation in the upper mantle A. Rohrbach, C. Ballhaus, U. Golla Schindler, P. Ulmer,V.S. Kamenetsky, D.V. Kuzmin NS seminar 2007.10.25 The uppermost mantle is oxidized.
Partial melting of mantle peridotite
 Partial melting of mantle peridotite 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 (TºC) Depth (km) 50 100 150 Plag lherzolite (ol-opx-cpx-pl) Spinel lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-sp) Garnet lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-gar) Graphite Diamond
Partial melting of mantle peridotite 1100 1200 1300 1400 1500 (TºC) Depth (km) 50 100 150 Plag lherzolite (ol-opx-cpx-pl) Spinel lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-sp) Garnet lherzolite (Ol-opx-cpx-gar) Graphite Diamond
GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Spring 2016 Score / 58. Midterm 1 Chapters 1-10
 GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Name KEY Spring 2016 Score / 58 Midterm 1 Chapters 1-10 1) Name two things that petrologists want to know about magmas (1 pt) Formation, source, composition,
GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Name KEY Spring 2016 Score / 58 Midterm 1 Chapters 1-10 1) Name two things that petrologists want to know about magmas (1 pt) Formation, source, composition,
Magmatic Processes at Subduction Zones
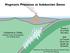 Magmatic Processes at Subduction Zones Katherine A. Kelley Graduate School of Oceanography Univ. of Rhode Island Thanks to Terry Plank Erik Hauri GVP: Liz Cottrell Simon Carn Jennifer Jay Ed Venzke Subduction
Magmatic Processes at Subduction Zones Katherine A. Kelley Graduate School of Oceanography Univ. of Rhode Island Thanks to Terry Plank Erik Hauri GVP: Liz Cottrell Simon Carn Jennifer Jay Ed Venzke Subduction
Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100
 Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Major Concepts 1) Igneous rocks form directly from the crystallization of a magma or lava 2)
Igneous Rock Classification, Processes and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Major Concepts 1) Igneous rocks form directly from the crystallization of a magma or lava 2)
Ultramafic rocks. Types of Ultramafic Rocks. Spinel lherzolite xenolith
 Ultramafic rocks Definition: Color Index > 90, i.e., less than 10% felsic minerals. Not to be confused with Ultrabasic Rocks which are rocks with
Ultramafic rocks Definition: Color Index > 90, i.e., less than 10% felsic minerals. Not to be confused with Ultrabasic Rocks which are rocks with
Effect of tectonic setting on chemistry of mantle-derived melts
 Effect of tectonic setting on chemistry of mantle-derived melts Lherzolite Basalt Factors controlling magma composition Composition of the source Partial melting process Fractional crystallization Crustal
Effect of tectonic setting on chemistry of mantle-derived melts Lherzolite Basalt Factors controlling magma composition Composition of the source Partial melting process Fractional crystallization Crustal
Chapter 9: Trace Elements
 Chapter 9: Trace Elements Note magnitude of major element changes Figure 8.2. Harker variation diagram for 310 analyzed volcanic rocks from Crater Lake (Mt. Mazama), Oregon Cascades. Data compiled by Rick
Chapter 9: Trace Elements Note magnitude of major element changes Figure 8.2. Harker variation diagram for 310 analyzed volcanic rocks from Crater Lake (Mt. Mazama), Oregon Cascades. Data compiled by Rick
Structure of the Earth and the Origin of Magmas
 Page 1 of 12 EENS 2120 Petrology Tulane University Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Structure of the Earth and the Origin of Magmas This document last updated on 23-Jan-2015 Magmas do not form everywhere beneath
Page 1 of 12 EENS 2120 Petrology Tulane University Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Structure of the Earth and the Origin of Magmas This document last updated on 23-Jan-2015 Magmas do not form everywhere beneath
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals. Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane SGM 210_2013
 Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011
Chapter 9: Trace Elements
 Lecture 13 Introduction to Trace Elements Wednesday, March 9, 2005 Chapter 9: Trace Elements Note magnitude of major element changes Figure 8-2. Harker variation diagram for 310 analyzed volcanic rocks
Lecture 13 Introduction to Trace Elements Wednesday, March 9, 2005 Chapter 9: Trace Elements Note magnitude of major element changes Figure 8-2. Harker variation diagram for 310 analyzed volcanic rocks
GSA Data Repository
 GSA Data Repository 218145 Parolari et al., 218, A balancing act of crust creation and destruction along the western Mexican convergent margin: Geology, https://doi.org/1.113/g39972.1. 218145_Tables DR1-DR4.xls
GSA Data Repository 218145 Parolari et al., 218, A balancing act of crust creation and destruction along the western Mexican convergent margin: Geology, https://doi.org/1.113/g39972.1. 218145_Tables DR1-DR4.xls
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann. Grotzinger Jordan. Understanding Earth. Sixth Edition
 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks: Solids from Melts 1 About Igneous Rocks Igneous
Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks: Solids from Melts 1 About Igneous Rocks Igneous
1 Potassic adakite magmas and where they come from: a mystery solved?
 1 Potassic adakite magmas and where they come from: a mystery solved? 2 3 John Clemens Kingston University (London) Long Xiao China University of Geosciences (Wuhan) 4 Adakites are volcanic and intrusive
1 Potassic adakite magmas and where they come from: a mystery solved? 2 3 John Clemens Kingston University (London) Long Xiao China University of Geosciences (Wuhan) 4 Adakites are volcanic and intrusive
Michel Pichavant, Ray Macdonald. To cite this version: HAL Id: insu https://hal-insu.archives-ouvertes.fr/insu
 Crystallization of primitive basaltic magmas at crustal pressures and genesis of the calc-alkaline igneous suite: experimental evidence from St Vincent, Lesser Antilles arc Michel Pichavant, Ray Macdonald
Crystallization of primitive basaltic magmas at crustal pressures and genesis of the calc-alkaline igneous suite: experimental evidence from St Vincent, Lesser Antilles arc Michel Pichavant, Ray Macdonald
Melts of garnet lherzolite: experiments, models and comparison to melts of pyroxenite and carbonated lherzolite
 Melts of garnet lherzolite: experiments, models and comparison to melts of pyroxenite and carbonated lherzolite The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Melts of garnet lherzolite: experiments, models and comparison to melts of pyroxenite and carbonated lherzolite The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
GY303 Igneous & Metamorphic Petrology. Lecture 7: Magma Sources and Tectonic Environments
 GY303 Igneous & Metamorphic Petrology Lecture 7: Magma Sources and Tectonic Environments Factors controlling Magma production Source rock composition Amount of fluids, especially H 2 O Pressure (Depth)
GY303 Igneous & Metamorphic Petrology Lecture 7: Magma Sources and Tectonic Environments Factors controlling Magma production Source rock composition Amount of fluids, especially H 2 O Pressure (Depth)
THE MONTE MAGGIORE PERIDOTITE (CORSICA)
 MONTE MAGGIORE CAPO CORSO CORSICA Giovanni B. Piccardo THE MONTE MAGGIORE PERIDOTITE (CORSICA) FIELD RELATIONSHIPS MORB Gabbro Spinel (ex-garnet) pyroxenites L ESCURSIONE A MONTE MAGGIORE The Monte Maggiore
MONTE MAGGIORE CAPO CORSO CORSICA Giovanni B. Piccardo THE MONTE MAGGIORE PERIDOTITE (CORSICA) FIELD RELATIONSHIPS MORB Gabbro Spinel (ex-garnet) pyroxenites L ESCURSIONE A MONTE MAGGIORE The Monte Maggiore
Harzburgite melting with and without H 2 O: Experimental data and predictive modeling
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2003jb002566, 2004 Harzburgite ing with and without H 2 O: Experimental data and predictive modeling Stephen W. Parman and Timothy L. Grove Department
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 109,, doi:10.1029/2003jb002566, 2004 Harzburgite ing with and without H 2 O: Experimental data and predictive modeling Stephen W. Parman and Timothy L. Grove Department
Pyroxenes (Mg, Fe 2+ ) 2 Si 2 O 6 (monoclinic) and. MgSiO 3 FeSiO 3 (orthorhombic) Structure (Figure 2 of handout)
 Pyroxenes (Mg, Fe 2+ ) 2 Si 2 O 6 (monoclinic) and 20 MgSiO 3 FeSiO 3 (orthorhombic) Structure (Figure 2 of handout) Chain silicate eg Diopside Mg and Fe ions link SiO 3 chains The chain runs up and down
Pyroxenes (Mg, Fe 2+ ) 2 Si 2 O 6 (monoclinic) and 20 MgSiO 3 FeSiO 3 (orthorhombic) Structure (Figure 2 of handout) Chain silicate eg Diopside Mg and Fe ions link SiO 3 chains The chain runs up and down
Volatile solubility models and their application to magma storage and transport in the mantle and he crust. Julie Roberge ESIA-Ticoman, IPN Mexico
 Volatile solubility models and their application to magma storage and transport in the mantle and he crust Julie Roberge ESIA-Ticoman, IPN Mexico Melt Inclusions What are they? How to use them volatiles
Volatile solubility models and their application to magma storage and transport in the mantle and he crust Julie Roberge ESIA-Ticoman, IPN Mexico Melt Inclusions What are they? How to use them volatiles
Essentials of Geology, 11e
 Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Calc-alkaline Volcanic Rocks. Calc-alkali Volcanics. Fabric. Petrography. Compositional Classification. Petrography. Processes.
 Calc-alkaline Volcanic Rocks Calc-alkali Volcanics Winter Chapters 16 & 17 Petrography Processes Field relations Volcanic arcs Petrogenesis Petrography Fabric Classification Alteration Fabric Aphanitic
Calc-alkaline Volcanic Rocks Calc-alkali Volcanics Winter Chapters 16 & 17 Petrography Processes Field relations Volcanic arcs Petrogenesis Petrography Fabric Classification Alteration Fabric Aphanitic
Subduction zones 3 arc magmatism
 5. 3 Subduction zones 3 arc magmatism Where can we observe magmatic/volcanic activities along subduction zones? Characteristics of arc magmatism (vs. mid-ocean ridge/intraplate magmatism) Structure of
5. 3 Subduction zones 3 arc magmatism Where can we observe magmatic/volcanic activities along subduction zones? Characteristics of arc magmatism (vs. mid-ocean ridge/intraplate magmatism) Structure of
Origin of Basaltic Magma. Geology 346- Petrology
 Origin of Basaltic Magma Geology 346- Petrology 2 principal types of basalt in the ocean basins Tholeiitic Basalt and Alkaline Basalt Table 10-1 Common petrographic differences between tholeiitic and alkaline
Origin of Basaltic Magma Geology 346- Petrology 2 principal types of basalt in the ocean basins Tholeiitic Basalt and Alkaline Basalt Table 10-1 Common petrographic differences between tholeiitic and alkaline
Fluids, melts, and supercriticality in the MSH system and element transport in subduction zones
 cosmic rays Fluids, s, and supercriticality in the MSH system and element transport in subduction zones 10 Be volcanic front N, O 10 Be ocean water + CO 2 tracing petrologic and geotectonic processes (trace)
cosmic rays Fluids, s, and supercriticality in the MSH system and element transport in subduction zones 10 Be volcanic front N, O 10 Be ocean water + CO 2 tracing petrologic and geotectonic processes (trace)
DIFFERENTIATION OF MAGMAS BY FRACTIONAL CRYSTALLIZATION THE M&M MAGMA CHAMBER
 Geol 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Spring 2009 Name DIFFERENTIATION OF MAGMAS BY FRACTIONAL CRYSTALLIZATION THE M&M MAGMA CHAMBER Objective: This exercise is intended to improve understanding
Geol 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Spring 2009 Name DIFFERENTIATION OF MAGMAS BY FRACTIONAL CRYSTALLIZATION THE M&M MAGMA CHAMBER Objective: This exercise is intended to improve understanding
How 2 nd half labs will work
 How 2 nd half labs will work Continue to use your mineral identification skills Learn to describe, classify, interpret rock hand samples: Igneous sedimentary metamorphic volcanic plutonic (1 week) (1 wk)
How 2 nd half labs will work Continue to use your mineral identification skills Learn to describe, classify, interpret rock hand samples: Igneous sedimentary metamorphic volcanic plutonic (1 week) (1 wk)
The mantle metasomatism: diversity and impact What the mantle xenoliths tell us?
 The mantle metasomatism: diversity and impact What the mantle xenoliths tell us? Mantle metasomatism Physical and chemical processes that are implemented during the flow of magmas and / or fluids within
The mantle metasomatism: diversity and impact What the mantle xenoliths tell us? Mantle metasomatism Physical and chemical processes that are implemented during the flow of magmas and / or fluids within
Lecture 3 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Dr. Shwan Omar
 Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Overview of the KAHT system. Ian E.M. Smith, School of Environment, University of Auckland
 Overview of the KAHT system Ian E.M. Smith, School of Environment, University of Auckland Tonga-Kermadec-New Zealand Arc Developed on the Pacific - Australian convergent margin Mainly intraoceanic except
Overview of the KAHT system Ian E.M. Smith, School of Environment, University of Auckland Tonga-Kermadec-New Zealand Arc Developed on the Pacific - Australian convergent margin Mainly intraoceanic except
Chapter 7 Metamorphism, Metamorphic Rocks, and Hydrothermal Rocks
 Chapter 7 Metamorphism, Metamorphic Rocks, and Hydrothermal Rocks Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Metamorphism What happens to rocks that are
Chapter 7 Metamorphism, Metamorphic Rocks, and Hydrothermal Rocks Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Metamorphism What happens to rocks that are
Magma Formation and Behavior
 Magma Formation and Behavior Questions What causes mantle rock to melt, resulting in magma formation? Why is magma formation restricted to specific plate tectonic settings? Why are mafic (basaltic) magmas
Magma Formation and Behavior Questions What causes mantle rock to melt, resulting in magma formation? Why is magma formation restricted to specific plate tectonic settings? Why are mafic (basaltic) magmas
Lecture 24 Hawaii. Hawaii
 Lecture 24 Hawaii Friday, April 22 nd 2005 Hawaii The Hawaiian Islands, in the middle of the Pacific Ocean, are volcanic islands at the end of a long chain of submerged volcanoes. These volcanoes get progressively
Lecture 24 Hawaii Friday, April 22 nd 2005 Hawaii The Hawaiian Islands, in the middle of the Pacific Ocean, are volcanic islands at the end of a long chain of submerged volcanoes. These volcanoes get progressively
Notes for Use of the Cpx-Plag-Ol Thermobar Workbook Last Updated:
 Notes for Use of the Cpx-Plag-Ol Thermobar Workbook Last Updated: 7-22-05 Cpx-Plag-Ol Thermobar is an Excel workbook that can be used to calculate crystallization pressures and temperatures for clinopyroxene-
Notes for Use of the Cpx-Plag-Ol Thermobar Workbook Last Updated: 7-22-05 Cpx-Plag-Ol Thermobar is an Excel workbook that can be used to calculate crystallization pressures and temperatures for clinopyroxene-
Larsen, H.C., Duncan, R.A., Allan, J.F., Brooks, K. (Eds.), 1999 Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Vol.
 Larsen, H.C., Duncan, R.A., Allan, J.F., Brooks, K. (Eds.), 1999 Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Vol. 163 9. LOW-PRESSURE MELTING STUDIES OF BASALT AND BASALTIC ANDESITE
Larsen, H.C., Duncan, R.A., Allan, J.F., Brooks, K. (Eds.), 1999 Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Vol. 163 9. LOW-PRESSURE MELTING STUDIES OF BASALT AND BASALTIC ANDESITE
EMMR25 Mineralogy: Ol + opx + chlorite + cpx + amphibole + serpentine + opaque
 GSA Data Repository 2017365 Marshall et al., 2017, The role of serpentinite derived fluids in metasomatism of the Colorado Plateau (USA) lithospheric mantle: Geology, https://doi.org/10.1130/g39444.1 Appendix
GSA Data Repository 2017365 Marshall et al., 2017, The role of serpentinite derived fluids in metasomatism of the Colorado Plateau (USA) lithospheric mantle: Geology, https://doi.org/10.1130/g39444.1 Appendix
PLATE TECTONICS, VOLCANISM AND IGNEOUS ROCKS
 PLATE TECTONICS, VOLCANISM AND IGNEOUS ROCKS PLATE TECTONICS TO IGNEOUS ROCKS Internal Heat Seafloor Spreading/Plate Tectonics Volcanism Plate Boundary Intra-plate (hot spot) Divergent Convergent Igneous
PLATE TECTONICS, VOLCANISM AND IGNEOUS ROCKS PLATE TECTONICS TO IGNEOUS ROCKS Internal Heat Seafloor Spreading/Plate Tectonics Volcanism Plate Boundary Intra-plate (hot spot) Divergent Convergent Igneous
Rare Earth Elements in some representative arc lavas
 Rare Earth Elements in some representative arc lavas Low-K (tholeiitic), Medium-K (calc-alkaline), and High-K basaltic andesites and andesites. A typical N-MORB pattern is included for reference Notes:
Rare Earth Elements in some representative arc lavas Low-K (tholeiitic), Medium-K (calc-alkaline), and High-K basaltic andesites and andesites. A typical N-MORB pattern is included for reference Notes:
Igneous Rocks. Igneous Rocks. Genetic Classification of
 Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
C = 3: Ternary Systems: Example 1: Ternary Eutectic
 Phase Equilibrium C = 3: Ternary Systems: Example 1: Ternary Eutectic Adding components, becomes increasingly difficult to depict 1-C: P - T diagrams easy 2-C: isobaric T-X, isothermal P-X 3-C:?? Still
Phase Equilibrium C = 3: Ternary Systems: Example 1: Ternary Eutectic Adding components, becomes increasingly difficult to depict 1-C: P - T diagrams easy 2-C: isobaric T-X, isothermal P-X 3-C:?? Still
Melts of garnet lherzolite: experiments, models and comparison to melts of pyroxenite and carbonated lherzolite
 Contrib Mineral Petrol (2013) 166:887 910 DOI 10.1007/s00410-013-0899-9 ORIGINAL PAPER Melts of garnet lherzolite: experiments, models and comparison to melts of pyroxenite and carbonated lherzolite Timothy
Contrib Mineral Petrol (2013) 166:887 910 DOI 10.1007/s00410-013-0899-9 ORIGINAL PAPER Melts of garnet lherzolite: experiments, models and comparison to melts of pyroxenite and carbonated lherzolite Timothy
IGNEOUS ROCKS. SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks?
 Date Period Name IGNEOUS ROCKS SECTION.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
Date Period Name IGNEOUS ROCKS SECTION.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
Magma Formation and Behavior
 Magma Formation and Behavior Introduction: The study of body waves as they pass through Earth's interior provides strong evidence that the Earth's mantle is composed almost entirely of solid ultramafic
Magma Formation and Behavior Introduction: The study of body waves as they pass through Earth's interior provides strong evidence that the Earth's mantle is composed almost entirely of solid ultramafic
III-1 MANGANESE PARTITIONING DURING HYDROUS MELTING OF PERIDOTITE. J. Brian Balta. Paul D. Asimow. Jed L. Mosenfelder
 III-1 MANGANESE PARTITIONING DURING HYDROUS MELTING OF PERIDOTITE By J. Brian Balta Paul D. Asimow Jed L. Mosenfelder III-2 ABSTRACT Manganese contents and the iron/manganese ratio of igneous rocks have
III-1 MANGANESE PARTITIONING DURING HYDROUS MELTING OF PERIDOTITE By J. Brian Balta Paul D. Asimow Jed L. Mosenfelder III-2 ABSTRACT Manganese contents and the iron/manganese ratio of igneous rocks have
Silicic volcanism and plutonism in the IBM arc
 NSF-IFREE MARGINS Subduction Factory Workshop Hawaii, 8-12 September 2002 MARGINS Web Site: http://www.ldeo.columbia.edu/margins Silicic volcanism and plutonism in the IBM arc Yoshihiko Tamura IFREE, JAMSTEC,
NSF-IFREE MARGINS Subduction Factory Workshop Hawaii, 8-12 September 2002 MARGINS Web Site: http://www.ldeo.columbia.edu/margins Silicic volcanism and plutonism in the IBM arc Yoshihiko Tamura IFREE, JAMSTEC,
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes
 Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
Partitioning of chlorine between H 2 O-bearing fluid and basaltic melt of Mt. Etna
 Partitioning of chlorine between H 2 O-bearing fluid and basaltic melt of Mt. Etna Oliver Beermann Jan Stelling XXVII. (14.) Arbeitstagung DGK, Arbeitskreis Nichtkristalline und Partiellkristalline Strukturen
Partitioning of chlorine between H 2 O-bearing fluid and basaltic melt of Mt. Etna Oliver Beermann Jan Stelling XXVII. (14.) Arbeitstagung DGK, Arbeitskreis Nichtkristalline und Partiellkristalline Strukturen
LECTURE #11: Volcanic Disasters: Lava Properties & Eruption Types
 GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #11: Volcanic Disasters: Lava Properties & Eruption Types Date: 13 February 2018 I. Exam I grades are posted on the class website (link at the bottom
GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #11: Volcanic Disasters: Lava Properties & Eruption Types Date: 13 February 2018 I. Exam I grades are posted on the class website (link at the bottom
Petrology of Volcanic Rocks from Bequia and St. Vincent*
 Petrology of Volcanic Rocks from Bequia and St. Vincent* Michal Camejo 1, Richard Robertson 1, Elena Melekhova 2, Anna Hicks 3, and Thomas Christopher 1,4 Search and Discovery Article #51171 (15)** Posted
Petrology of Volcanic Rocks from Bequia and St. Vincent* Michal Camejo 1, Richard Robertson 1, Elena Melekhova 2, Anna Hicks 3, and Thomas Christopher 1,4 Search and Discovery Article #51171 (15)** Posted
Along-Arc Variations in the Pre-Eruptive H 2 O Contents of Mariana Arc Magmas Inferred from Fractionation Paths
 JOURNAL OF PETROLOGY VOLUME 52 NUMBER 2 PAGES 257^278 2011 doi:10.1093/petrology/egq079 Along-Arc Variations in the Pre-Eruptive H 2 O Contents of Mariana Arc Magmas Inferred from Fractionation Paths S.
JOURNAL OF PETROLOGY VOLUME 52 NUMBER 2 PAGES 257^278 2011 doi:10.1093/petrology/egq079 Along-Arc Variations in the Pre-Eruptive H 2 O Contents of Mariana Arc Magmas Inferred from Fractionation Paths S.
LAB 9: ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS, CUMULATES AND MELT SOURCES
 Geology 316 (Petrology) (03/26/2012) Name LAB 9: ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS, CUMULATES AND MELT SOURCES INTRODUCTION Ultramafic rocks are igneous rocks containing less than 10% felsic minerals (quartz + feldspars
Geology 316 (Petrology) (03/26/2012) Name LAB 9: ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS, CUMULATES AND MELT SOURCES INTRODUCTION Ultramafic rocks are igneous rocks containing less than 10% felsic minerals (quartz + feldspars
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
High-T heating stage: application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools -
 High-T heating stage: application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools - SZABÓ, Csaba Lithosphere Fluid Research Lab (LRG), Department of Petrology and Geochemistry,
High-T heating stage: application for igneous petrogenesis and mantle processes - melt inclusions as key tools - SZABÓ, Csaba Lithosphere Fluid Research Lab (LRG), Department of Petrology and Geochemistry,
SEA-FLOOR SPREADING. In the 1950 s and early 1960 s detailed study of the oceans revealed the following surprising information:-
 SEA-FLOOR SPREADING In the 1950 s and early 1960 s detailed study of the oceans revealed the following surprising information:- Detailed bathymetric (depth) studies showed that there was an extensive submarine
SEA-FLOOR SPREADING In the 1950 s and early 1960 s detailed study of the oceans revealed the following surprising information:- Detailed bathymetric (depth) studies showed that there was an extensive submarine
Igneous Rock. Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere
 Igneous Rock Magma Molten rock under the surface Temperature = 600 o 1400 o C Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere Magma chamber - most all magma consists of silicon and oxygen (silicate)
Igneous Rock Magma Molten rock under the surface Temperature = 600 o 1400 o C Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere Magma chamber - most all magma consists of silicon and oxygen (silicate)
Petrology and Geochronology of Iran Tepe volcano, Eastern Rhodopes, Bulgaria: Age relationship with the Ada Tepe gold deposit. (preliminary data)
 Petrology and Geochronology of Iran Tepe volcano, Eastern Rhodopes, Bulgaria: Age relationship with the Ada Tepe gold deposit. (preliminary data) Peter Kibarov, Peter Marchev, Maria Ovtcharova, Raya Raycheva,
Petrology and Geochronology of Iran Tepe volcano, Eastern Rhodopes, Bulgaria: Age relationship with the Ada Tepe gold deposit. (preliminary data) Peter Kibarov, Peter Marchev, Maria Ovtcharova, Raya Raycheva,
Structure of the Earth
 And the ROCK CYCLE Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density High in silicon (Si) and oxygen (O) Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High
And the ROCK CYCLE Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density High in silicon (Si) and oxygen (O) Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High
Differentiation of Magmas By Fractional Crystallization
 Wirth Magmatic Differentiation Using M&M s 1 HANDOUT Differentiation of Magmas By Fractional Crystallization Objective The objective of this exercise is to gain first-hand knowledge of the process of magmatic
Wirth Magmatic Differentiation Using M&M s 1 HANDOUT Differentiation of Magmas By Fractional Crystallization Objective The objective of this exercise is to gain first-hand knowledge of the process of magmatic
Igneous activity is related to convergent plate situations that result in the subduction of one plate beneath another Ocean-ocean Island Arc
 Igneous activity related to subduction (Chapters 16, 17) Subduction-related activity Igneous activity is related to convergent plate situations that result in the subduction of one plate beneath another
Igneous activity related to subduction (Chapters 16, 17) Subduction-related activity Igneous activity is related to convergent plate situations that result in the subduction of one plate beneath another
Olivine-hosted melt inclusions in Hawaiian picrites: equilibration, melting, and plume source characteristics
 Chemical Geology 183 (2002) 143 168 www.elsevier.com/locate/chemgeo Olivine-hosted melt inclusions in Hawaiian picrites: equilibration, melting, and plume source characteristics Marc D. Norman a, *, Michael
Chemical Geology 183 (2002) 143 168 www.elsevier.com/locate/chemgeo Olivine-hosted melt inclusions in Hawaiian picrites: equilibration, melting, and plume source characteristics Marc D. Norman a, *, Michael
Name Class Date. In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements.
 CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
Plate tectonics, rock cycle
 Dikes, Antarctica Rock Cycle Plate tectonics, rock cycle The Rock Cycle A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one
Dikes, Antarctica Rock Cycle Plate tectonics, rock cycle The Rock Cycle A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one
Chapter 4 8/27/2013. Igneous Rocks. and Intrusive Igneous Activity. Introduction. The Properties and Behavior of Magma and Lava
 Introduction Chapter 4 Igneous rocks form by the cooling of magma (or lava). Large parts of the continents and all the oceanic crust are composed of. and Intrusive Igneous Activity The Properties and Behavior
Introduction Chapter 4 Igneous rocks form by the cooling of magma (or lava). Large parts of the continents and all the oceanic crust are composed of. and Intrusive Igneous Activity The Properties and Behavior
Structure of the Earth
 Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High in Magnesium (Mg) and Iron (Fe) Core: High in Nickel
Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High in Magnesium (Mg) and Iron (Fe) Core: High in Nickel
Electronic Appendix A: Supplementary material to accompany the manuscript, Fe 3+ / Fe in Mariana Arc basalts and primary fo 2.
 Electronic Appendix A: Supplementary material to accompany the manuscript, Fe 3+ / Fe in Mariana Arc basalts and primary fo 2. Screening for olivine interference in Fe-µ-XANES spectra When collecting Fe-µ-XANES
Electronic Appendix A: Supplementary material to accompany the manuscript, Fe 3+ / Fe in Mariana Arc basalts and primary fo 2. Screening for olivine interference in Fe-µ-XANES spectra When collecting Fe-µ-XANES
Contrib Mineral Petrol (1998) 130: 304±319 Ó Springer-Verlag 1998
 Contrib Mineral Petrol (1998) 130: 304±319 Ó Springer-Verlag 1998 Gordon Moore á I.S.E. Carmichael The hydrous phase equilibria (to 3 kbar) of an andesite and basaltic andesite from western Mexico: constraints
Contrib Mineral Petrol (1998) 130: 304±319 Ó Springer-Verlag 1998 Gordon Moore á I.S.E. Carmichael The hydrous phase equilibria (to 3 kbar) of an andesite and basaltic andesite from western Mexico: constraints
J. Mangas and F.J. Perez-Torrado. Departamento de Física. Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria Las Palmas de Gran Canaria.
 Magmatic processes in the oceanic lithosphere: characterization of the ultramafic and mafic materials from the Holocene volcanic centers of Bandama and La Caldera de Pinos de Gáldar (Gran Canaria, Canary
Magmatic processes in the oceanic lithosphere: characterization of the ultramafic and mafic materials from the Holocene volcanic centers of Bandama and La Caldera de Pinos de Gáldar (Gran Canaria, Canary
Name Class Date STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY
 Igneous Rocks What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. extrusive igneous rock intrusive
Igneous Rocks What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. extrusive igneous rock intrusive
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Crustal thickness control on Sr/Y signatures of recent arc magmas: an Earth scale perspective Massimo Chiaradia Section of Earth and Environmental Sciences, University of Geneva,
Supplementary Information Crustal thickness control on Sr/Y signatures of recent arc magmas: an Earth scale perspective Massimo Chiaradia Section of Earth and Environmental Sciences, University of Geneva,
Mantle Wedge Oxygen Fugacity Katherine A. Kelley Graduate School of Oceanography, Univ. of Rhode Island
 Mantle Wedge Oxygen Fugacity Katherine A. Kelley Graduate School of Oceanography, Univ. of Rhode Island With contributions from: M. Brounce GSO/URI E. Cottrell & O. Lopez Smithsonian Inst. J. Warren &
Mantle Wedge Oxygen Fugacity Katherine A. Kelley Graduate School of Oceanography, Univ. of Rhode Island With contributions from: M. Brounce GSO/URI E. Cottrell & O. Lopez Smithsonian Inst. J. Warren &
WORKING WITH ELECTRON MICROPROBE DATA FROM A HIGH PRESSURE EXPERIMENT CALCULATING MINERAL FORMULAS, UNIT CELL CONTENT, AND GEOTHERMOMETRY
 WORKING WITH ELECTRON MICROPROBE DATA FROM A HIGH PRESSURE EXPERIMENT CALCULATING MINERAL FORMULAS, UNIT CELL CONTENT, AND GEOTHERMOMETRY Brandon E. Schwab Department of Geology Humboldt State University
WORKING WITH ELECTRON MICROPROBE DATA FROM A HIGH PRESSURE EXPERIMENT CALCULATING MINERAL FORMULAS, UNIT CELL CONTENT, AND GEOTHERMOMETRY Brandon E. Schwab Department of Geology Humboldt State University
GEOL 3313 Petrology of Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks Study Guide for Final Examination Glen Mattioli
 GEOL 3313 Petrology of Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks Study Guide for Final Examination Glen Mattioli Chapter 5: Crystal-Melt phase diagrams Effect of water pressure on feldspar stability Hypersolvus vs.
GEOL 3313 Petrology of Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks Study Guide for Final Examination Glen Mattioli Chapter 5: Crystal-Melt phase diagrams Effect of water pressure on feldspar stability Hypersolvus vs.
EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4
 Name: EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4 Introduction In the previous lab, we learned about mineral characteristics, properties and identities as well as the three basic rock
Name: EPS 50 Lab 2: Igneous Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 4 Introduction In the previous lab, we learned about mineral characteristics, properties and identities as well as the three basic rock
Mineral chemistry of submarine lavas from Hilo Ridge, Hawaii: implications for magmatic processes within Hawaiian rift zones
 Contrib Mineral Petrol (1999) 135: 355±372 Ó Springer-Verlag 1999 Huai-Jen Yang á Frederick A. Frey David A. Clague á Michael O. Garcia Mineral chemistry of submarine lavas from Hilo Ridge, Hawaii: implications
Contrib Mineral Petrol (1999) 135: 355±372 Ó Springer-Verlag 1999 Huai-Jen Yang á Frederick A. Frey David A. Clague á Michael O. Garcia Mineral chemistry of submarine lavas from Hilo Ridge, Hawaii: implications
Near-solidus melting of the shallow upper mantle: Partial melting experiments on depleted peridotite
 Near-solidus melting of the shallow upper mantle: Partial melting experiments on depleted peridotite Wasylenki, Laura E. 1, Baker, Michael B., Kent, Adam J.R. 2, and Stolper, Edward M. Division of Geological
Near-solidus melting of the shallow upper mantle: Partial melting experiments on depleted peridotite Wasylenki, Laura E. 1, Baker, Michael B., Kent, Adam J.R. 2, and Stolper, Edward M. Division of Geological
A Hornblende Basalt from Western Mexico: Water-saturated Phase Relations Constrain a Pressure---Temperature Window of Eruptibility
 JOURNAL OF PETROLOGY VOLUME 45 NUMBER 3 PAGES 485±506 2004 DOI: 10.1093/petrology/egg091 A Hornblende Basalt from Western Mexico: Water-saturated Phase Relations Constrain a Pressure---Temperature Window
JOURNAL OF PETROLOGY VOLUME 45 NUMBER 3 PAGES 485±506 2004 DOI: 10.1093/petrology/egg091 A Hornblende Basalt from Western Mexico: Water-saturated Phase Relations Constrain a Pressure---Temperature Window
predictive mineral discovery*cooperative Research Centre A legacy for mineral exploration science Mineral Systems Q3 Fluid reservoirs
 Mineral Systems Q3 Fluid reservoirs 1 Key Parameter Mineral System Exploration is reflected in scale-dependent translation A. Gradient in hydraulic potential B. Permeability C. Solubility sensitivity to
Mineral Systems Q3 Fluid reservoirs 1 Key Parameter Mineral System Exploration is reflected in scale-dependent translation A. Gradient in hydraulic potential B. Permeability C. Solubility sensitivity to
A Rock is a solid aggregate of minerals.
 Quartz A Rock is a solid aggregate of minerals. Orthoclase Feldspar Plagioclase Feldspar Biotite Four different minerals are obvious in this piece of Granite. The average automobile contains: Minerals
Quartz A Rock is a solid aggregate of minerals. Orthoclase Feldspar Plagioclase Feldspar Biotite Four different minerals are obvious in this piece of Granite. The average automobile contains: Minerals
Depths of Partial Crystallization of H 2 O-bearing MORB: Phase Equilibria Simulations of Basalts at the MAR near Ascension Island (7^118S)
 JOURNAL OF PETROLOGY VOLUME 49 NUMBER1 PAGES 25^45 2008 doi:10.1093/petrology/egm068 Depths of Partial Crystallization of H 2 O-bearing MORB: Phase Equilibria Simulations of Basalts at the MAR near Ascension
JOURNAL OF PETROLOGY VOLUME 49 NUMBER1 PAGES 25^45 2008 doi:10.1093/petrology/egm068 Depths of Partial Crystallization of H 2 O-bearing MORB: Phase Equilibria Simulations of Basalts at the MAR near Ascension
II-1 HYDROUS, LOW-CARBON MELTING OF GARNET PERIDOTITE. J. Brian Balta. Paul D. Asimow. Jed L. Mosenfelder
 II-1 HYDROUS, LOW-CARBON MELTING OF GARNET PERIDOTITE By J. Brian Balta Paul D. Asimow Jed L. Mosenfelder II-2 ABSTRACT The presence of volatile species in Earth s upper mantle drives the formation of
II-1 HYDROUS, LOW-CARBON MELTING OF GARNET PERIDOTITE By J. Brian Balta Paul D. Asimow Jed L. Mosenfelder II-2 ABSTRACT The presence of volatile species in Earth s upper mantle drives the formation of
Differentiation of Magmas By Fractional Crystallization Modified from Karl Wirth, rev. July 2011
 M&M s Magma Chamber 1 Differentiation of Magmas By Fractional Crystallization Modified from Karl Wirth, rev. July 2011 Objective The objective of this exercise is to gain first-hand knowledge of the process
M&M s Magma Chamber 1 Differentiation of Magmas By Fractional Crystallization Modified from Karl Wirth, rev. July 2011 Objective The objective of this exercise is to gain first-hand knowledge of the process
