Zeumann and Hampel, 2017, Impact of Cocos Ridge (Central America) subduction on the forearc drainage system: Geology, doi: /g
|
|
|
- Vernon McCarthy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GSA Data Repository Zeumann and Hampel, 2017, Impact of Cocos Ridge (Central America) subduction on the forearc drainage system: Geology, doi: /g DESCRIPTION OF CASQUS To implement erosion and sediment deposition, the ridge subduction model is coupled via the ABAQUS user sub-routine CASQUS (Kurfeß and Heidbach, 2009; Maniatis et al., 2009; Hampel and Hetzel, 2016) to the landscape evolution model CASCADE (Braun and Sambridge, 1997). The input for the landscape evolution model is the current surface elevation in the ABAQUS model, which changes in the course of ridge subduction. After the amount of erosion or sedimentation at each point has been calculated by CASCADE, the user sub-routine CASQUS transfers the information on the elevation changes due to the surface processes back into the ABAQUS model to shift the surface nodes to their new elevation. Shifting of the surface nodes is performed using an Arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian approach and adaptive meshing for the associated elements in order to prevent arbitrary stress changes. Hence, the shift of the surface nodes causes only changes in the volume and thus in the mass of the associated elements. The length of the time steps in the model correspond to 10 kyr. The landscape evolution model implemented by CASQUS includes diffusive hillslope processes and fluvial erosion and deposition (cf. Braun and Sambridge, 1997). The former is implemented by the linear diffusion equation, in which the temporal change in elevation of a point is proportional to the second spatial derivative of topography (Kooi and Beaumont, 1992; Braun and Sambridge, 1997): h t k D 2 h, where h is elevation, t time and k D the diffusion constant. The equation above describes the cumulative effect of different types of surface processes such as slope wash, rain splash and soil creep. As high diffusion constants are known to create unrealistic landscapes for grid sizes of 1 km or more (van der Beek and Bishop, 2003), we use a low diffusion constant (0.05 m 2 /a), which also stabilizes the model by avoiding steep slopes between individual cells (Sacek et al., 2012). The temporal change in elevation at a point on the model surface caused by fluvial erosion, sediment transport and deposition is calculated by the relationship h t 1 l f q f, eqb q f, where q f is the sediment flux of a river, q f,eqb the sediment transport capacity and l f the erosion/deposition length scale. The latter constant describes how easily the river substrate can be eroded or how fast sediments are deposited in a river and thus affects how fast the river locally 1
2 tends toward equilibrium. To differentiate between bedrock incision and alluvium, CASCADE uses two different erosion length scales, which we assign values of 100 km and 10 km, respectively, following previous studies (Braun and Sambridge, 1997; van der Beek and Braun, 1998; Tomkin and Braun 1999; Kurfeß and Heidbach, 2009). Erosion occurs for q f < q f,eqb and deposition for q f > dh q f,eqb. The sediment transport capacity q f,eqb is calculated by q f, eqb k f q r dl, where k f is a nondimensional empirical transport coefficient, q r is the fluvial discharge, which depends on the catchment area and the precipitation rate p, and dh/dl is the slope in the flow direction of the river. The parameter that ultimately controls fluvial erosion is the fluvial erosion parameter k f p, in which the dimensionless transport coefficient k f (which does not have a direct meaning outside the model context) and the precipitation rate p are lumped together to obtain a parameter with dimension m/a (van der Beek and Braun, 1998). For the initial model surface, an irregular mesh with 5 m vertical noise is used to avoid the directional bias, which arises from the development of the river network along preferred directions (Braun and Sambridge, 1997). Sediments may leave the model via the model boundaries and via the seaward edge of the CASQUS layer (= model coastline) (Fig 2A). REFERENCES CITED Braun, J., and Sambridge, M., 1997, Modelling landscape evolution on geological time scales: a new method based on irregular spatial discretization: Basin Research, v. 9, p Hampel, A., and Hetzel, R., 2016, Role of climate changes for wind gap formation in a young, actively growing mountain range: Terra Nova, v. 28, p Kooi, H., and Beaumont, C., 1994, Escarpment evolution on high-elevation rifted margins: insights derived from a surface processes model that combines diffusion, advection, and reaction: Journal of Geophysical Research, v. 99, p Kurfeß, D., and Heidbach, O., 2009, CASQUS: a new simulation tool for coupled 3D Finite Element modeling of tectonic and surface processes based on ABAQUS and CASCADE: Computers and Geosciences, v. 35, p Maniatis, G., Kurfeß, D., Hampel, A., and Heidbach, O., 2009, Slip acceleration on normal faults due to erosion and sedimentation - results from a new three-dimensional numerical model coupling tectonics and landscape evolution: Earth and Planetary Science Letters, v. 284, p Sacek, V., Braun, J., and van der Beek, P., 2012, The influence of rifting on escarpment migration 2
3 on high elevation passive continental margins: J. Geophys Res., v. 117, B04407, doi: /2011jb Tomkin, J.H., and Braun, J., 1999, Simple models of drainage reorganization on a tectonically active ridge system: New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics, v. 42, 1, p.1-10, doi: / van der Beek, P. and Braun, J., 1998, Numerical modeling of landscape evolution on geological time scales: a parameter analysis and comparison with the south-eastern highlands of Australia: Basin Research, v. 10, p van der Beek, P., and Bishop, P., 2003, Cenozoic river profile development in the Upper Lachlan catchment (SE Australia) as a test of quantitative fluvial incision models: J. Geophys. Res., v. 108, 2309, doi: /2002jb002125,
4 Figure DR1. Supplementary results from the model with a fluvial erosion parameter of 0.01 m/a. (A) Model river network in map view (color of rivers denotes their flow direction, which is indicated by the colored arrows in the legend) and longitudinal profiles of selected rivers (green color of longitudinal profiles corresponds to color of respective river in map and the arrow indicating the flow direction) at 3.8 and 5 Myr, respectively. (B) Evolution of the trench-normal horizontal strain x during the first 2 Myr of model time. Solid white line marks coastline; dashed white line marks drainage divide (cf. Fig. 3). Note the zone of shortening landward of the coastline, which is equivalent to Fila Costeña thrust belt (cf. Zeumann and Hampel, 2015). 4
5 Figure DR2. Results from experiments with a fluvial erosion parameter of m/a. Shown is at different time steps the model river network in map view (A-D). For river networks at 1.7 and 1.8 Myr see Fig. DR3. River networks in figure parts A and B are shown together with the elevation of the model surface, which is omitted for clarity in the other figure parts. (E) Maps of the model surface showing erosion and sedimentation rates (averaged over 10 kyr) at 1.5 and 2.0 Myr of model time. 5
6 Figure DR3. Results of a sensitivity analysis with respect to the (A) fluvial erosion parameter and (B) width of the ridge front (cf. Fig. 2B). In both figure parts A and B, the river networks from the different experiment are shown at the timepoints before and after the drainage divide reaches the landward edge of the forearc. Note that all experiments show a symmetric drainage pattern relative to the ridge crest and a similar timing ( Myr) for the arrival of the drainage divide at the landward edge of the forearc. 6
Drainage Basin Geomorphology. Nick Odoni s Slope Profile Model
 Drainage Basin Geomorphology Nick Odoni s Slope Profile Model Odoni s Slope Profile Model This model is based on solving the mass balance (sediment budget) equation for a hillslope profile This is achieved
Drainage Basin Geomorphology Nick Odoni s Slope Profile Model Odoni s Slope Profile Model This model is based on solving the mass balance (sediment budget) equation for a hillslope profile This is achieved
GSA DATA REPOSITORY Sternai et al. 1. Algorithm Flow Chart
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2012311 Sternai et al. 1. Algorithm Flow Chart Figure DR1: Flow chart of the algorithm to further clarify the calculation scheme. 2. Reconstruction of the Pre-Glacial Alpine Topography
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2012311 Sternai et al. 1. Algorithm Flow Chart Figure DR1: Flow chart of the algorithm to further clarify the calculation scheme. 2. Reconstruction of the Pre-Glacial Alpine Topography
Effects of transient topography and drainage basin evolution on detrital thermochronometer data
 UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN Effects of transient topography and drainage basin evolution on detrital thermochronometer data Contents Acknowledgments...3 Abstract...4 1. Introduction...5 2. Model setup...6 2.1
UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN Effects of transient topography and drainage basin evolution on detrital thermochronometer data Contents Acknowledgments...3 Abstract...4 1. Introduction...5 2. Model setup...6 2.1
Surface changes caused by erosion and sedimentation were treated by solving: (2)
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 214279 GUY SIMPSON Model with dynamic faulting and surface processes The model used for the simulations reported in Figures 1-3 of the main text is based on two dimensional (plane strain)
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 214279 GUY SIMPSON Model with dynamic faulting and surface processes The model used for the simulations reported in Figures 1-3 of the main text is based on two dimensional (plane strain)
Stratigraphic modelling using CHILD
 5 Stratigraphic modelling using CHILD 5.1 Triangular irregular network Surface process models are widely used in geomorphology and geology, and the developments in the field follow each other rapidly.
5 Stratigraphic modelling using CHILD 5.1 Triangular irregular network Surface process models are widely used in geomorphology and geology, and the developments in the field follow each other rapidly.
1. What define planetary surfaces geologically? 2. What controls the evolution of planetary surfaces?
 Planetary Surfaces: 1. What define planetary surfaces geologically? 2. What controls the evolution of planetary surfaces? 3. How do surface-shaping processes scale across planetary bodies of different
Planetary Surfaces: 1. What define planetary surfaces geologically? 2. What controls the evolution of planetary surfaces? 3. How do surface-shaping processes scale across planetary bodies of different
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer GEOMORPHOLOGY Rivers split as mountains grow Citation for published version: Attal, M 2009, 'GEOMORPHOLOGY Rivers split as mountains grow' Nature Geoscience, vol. 2, no. 11,
Edinburgh Research Explorer GEOMORPHOLOGY Rivers split as mountains grow Citation for published version: Attal, M 2009, 'GEOMORPHOLOGY Rivers split as mountains grow' Nature Geoscience, vol. 2, no. 11,
Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1)
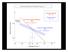 Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1) Detachment Limited S d >> S t Transport Limited Channel Gradient (m/m) 10-1 Stochastic Variation { Detachment Limited Equilibrium Slope S d = k sd A -θ d S
Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1) Detachment Limited S d >> S t Transport Limited Channel Gradient (m/m) 10-1 Stochastic Variation { Detachment Limited Equilibrium Slope S d = k sd A -θ d S
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output
 mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
Constraining the stream power law: a novel approach combining a landscape evolution model and an inversion method
 doi:10.5194/esurf-2-155-2014 Author(s) 2014. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Earth Surface Dynamics Open Access Constraining the stream power law: a novel approach combining a landscape evolution model and
doi:10.5194/esurf-2-155-2014 Author(s) 2014. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Earth Surface Dynamics Open Access Constraining the stream power law: a novel approach combining a landscape evolution model and
Continental Landscapes
 Continental Landscapes Landscape influenced by tectonics, climate & differential weathering Most landforms developed within the last 2 million years System moves toward an equilibrium Continental Landscapes
Continental Landscapes Landscape influenced by tectonics, climate & differential weathering Most landforms developed within the last 2 million years System moves toward an equilibrium Continental Landscapes
Data Repository. Spatiotemporal trends in erosion rates across a pronounced rainfall gradient: examples from the south central Andes
 Data Repository Spatiotemporal trends in erosion rates across a pronounced rainfall gradient: examples from the south central Andes Bodo Bookhagen 1 and Manfred R. Strecker 2 1 Geography Department, Ellison
Data Repository Spatiotemporal trends in erosion rates across a pronounced rainfall gradient: examples from the south central Andes Bodo Bookhagen 1 and Manfred R. Strecker 2 1 Geography Department, Ellison
Lab # - Ocean Bottom Topography. Background Information:
 Name Lab Grade /10 Date Period Lab # - Ocean Bottom Topography Background Information: Ocean depth varies markedly from one location to another. Over large areas water depth is less than 200m (650 ft);
Name Lab Grade /10 Date Period Lab # - Ocean Bottom Topography Background Information: Ocean depth varies markedly from one location to another. Over large areas water depth is less than 200m (650 ft);
Predictions of steady state and transient landscape morphology using sediment-flux-dependent river incision models
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jf000567, 2007 Predictions of steady state and transient landscape morphology using sediment-flux-dependent river
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jf000567, 2007 Predictions of steady state and transient landscape morphology using sediment-flux-dependent river
UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA
 UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA A map that shows Earth s Topographic Map surface topography, which is Earth s shape and features Contour
UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA A map that shows Earth s Topographic Map surface topography, which is Earth s shape and features Contour
FRACTAL RIVER BASINS
 FRACTAL RIVER BASINS CHANCE AND SELF-ORGANIZATION Ignacio Rodriguez-Iturbe Texas A & M University Andrea Rinaldo University of Padua, Italy CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Foreword Preface page xiii
FRACTAL RIVER BASINS CHANCE AND SELF-ORGANIZATION Ignacio Rodriguez-Iturbe Texas A & M University Andrea Rinaldo University of Padua, Italy CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Foreword Preface page xiii
The finite difference code (fully staggered grid) includes a marker-in-cell Lagrangian marker
 GSA Data Repository 2018289 Ruh et al., 2018, Shale-related minibasins atop a massive olistostrome in an active accretionary wedge setting: Two-dimensional numerical modeling applied to the Iranian Makran:
GSA Data Repository 2018289 Ruh et al., 2018, Shale-related minibasins atop a massive olistostrome in an active accretionary wedge setting: Two-dimensional numerical modeling applied to the Iranian Makran:
GLY Coastal Geomorphology Notes
 GLY 4734 - Coastal Geomorphology Notes Dr. Peter N. Adams Spring 2011 2 Coastal Classification In this lecture, we discuss some successful classification schemes of the coastal landscape, and pay particular
GLY 4734 - Coastal Geomorphology Notes Dr. Peter N. Adams Spring 2011 2 Coastal Classification In this lecture, we discuss some successful classification schemes of the coastal landscape, and pay particular
Supplementary Information Methods:
 Supplementary Information Methods: Numerical Model Initial and Boundary Conditions. Initial conditions in most runs consist of a barebedrock plane 400 m wide by 2000 m long (extending from local base level
Supplementary Information Methods: Numerical Model Initial and Boundary Conditions. Initial conditions in most runs consist of a barebedrock plane 400 m wide by 2000 m long (extending from local base level
Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education
 Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education Tibetan Plateau and Himalaya -southern Asia 11.00.a VE 10X
Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education Tibetan Plateau and Himalaya -southern Asia 11.00.a VE 10X
GLG101: What-To-Know List
 Exam 3, Page 1 GLG101: What-To-Know List (Derived from Before You Leave This Page Lists) This list is intended to guide your reading and to help you prepare for the online multiple-choice quizzes. Each
Exam 3, Page 1 GLG101: What-To-Know List (Derived from Before You Leave This Page Lists) This list is intended to guide your reading and to help you prepare for the online multiple-choice quizzes. Each
Chapter 10: Deformation and Mountain Building. Fig. 10.1
 Chapter 10: Deformation and Mountain Building Fig. 10.1 OBJECTIVES Describe the processes of rock deformation and compare and contrast ductile and brittle behavior in rocks. Explain how strike and dip
Chapter 10: Deformation and Mountain Building Fig. 10.1 OBJECTIVES Describe the processes of rock deformation and compare and contrast ductile and brittle behavior in rocks. Explain how strike and dip
Landslides & Debris Flows
 T.#Perron# #12.001# #Landslides#&#Debris#Flows# 1# Landslides & Debris Flows Many geologic processes, including those shaping the land surface, are slowacting, involving feedbacks that operate over many
T.#Perron# #12.001# #Landslides#&#Debris#Flows# 1# Landslides & Debris Flows Many geologic processes, including those shaping the land surface, are slowacting, involving feedbacks that operate over many
24. Ocean Basins p
 24. Ocean Basins p. 350-372 Background The majority of the planet is covered by ocean- about %. So the majority of the Earth s crust is. This crust is hidden from view beneath the water so it is not as
24. Ocean Basins p. 350-372 Background The majority of the planet is covered by ocean- about %. So the majority of the Earth s crust is. This crust is hidden from view beneath the water so it is not as
by west-dipping subduction of the North American Plate
 GSA Data Repository 2019133 Supplementary information for Kimberlite magmatism induced by west-dipping subduction of the North American Plate Wenbo Zhang 1*, Stephen T. Johnston 1, and Claire A. Currie
GSA Data Repository 2019133 Supplementary information for Kimberlite magmatism induced by west-dipping subduction of the North American Plate Wenbo Zhang 1*, Stephen T. Johnston 1, and Claire A. Currie
Geodynamics. Climatic, geomorphic and geodynamic processes Lecture Orogenic wedges. Lecturer: David Whipp
 Geodynamics Climatic, geomorphic and geodynamic processes Lecture 13.3 - Orogenic wedges Lecturer: David Whipp david.whipp@helsinki.fi Geodynamics www.helsinki.fi/yliopisto 1 Goals of this lecture Introduce
Geodynamics Climatic, geomorphic and geodynamic processes Lecture 13.3 - Orogenic wedges Lecturer: David Whipp david.whipp@helsinki.fi Geodynamics www.helsinki.fi/yliopisto 1 Goals of this lecture Introduce
Steady State Convergent Orogens, Erosion Balances, Lateral and Vertical Mountain Topography
 Steady State Convergent Orogens, Erosion Balances, Lateral and Vertical Mountain Topography Dr. N.L. Dongre. In this picture Oregenic convergent structure appears to be partially controlled by the addition
Steady State Convergent Orogens, Erosion Balances, Lateral and Vertical Mountain Topography Dr. N.L. Dongre. In this picture Oregenic convergent structure appears to be partially controlled by the addition
Earth s Continents and Seafloors. GEOL100 Physical Geology Ray Rector - Instructor
 Earth s Continents and Seafloors GEOL100 Physical Geology Ray Rector - Instructor OCEAN BASINS and CONTINENTAL PLATFORMS Key Concepts I. Earth s rocky surface covered by of two types of crust Dense, thin,
Earth s Continents and Seafloors GEOL100 Physical Geology Ray Rector - Instructor OCEAN BASINS and CONTINENTAL PLATFORMS Key Concepts I. Earth s rocky surface covered by of two types of crust Dense, thin,
KEY CHAPTER 12 TAKE-HOME QUIZ INTERNAL STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES Score Part B = / 55 PART B
 GEOLOGY 12 KEY CHAPTER 12 TAKE-HOME QUIZ INTERNAL STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES Score Part B = / 55 PART B CHAPTER 12 Isostacy and Structural Geology 1. Using the terms below, label the following diagrams and
GEOLOGY 12 KEY CHAPTER 12 TAKE-HOME QUIZ INTERNAL STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES Score Part B = / 55 PART B CHAPTER 12 Isostacy and Structural Geology 1. Using the terms below, label the following diagrams and
Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands
 Page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands Section A Overview of Lands with Dry Climates The definition of a dry climate is tied to an understanding of the hydrologic cycle
Page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands Section A Overview of Lands with Dry Climates The definition of a dry climate is tied to an understanding of the hydrologic cycle
Surface process models and the links between tectonics and topography
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health - Papers Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2006 Surface process models and the links between tectonics and topography
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health - Papers Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2006 Surface process models and the links between tectonics and topography
TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology
 Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Determination of uplift rates of fluvial terraces across the Siwaliks Hills, Himalayas of central Nepal
 Determination of uplift rates of fluvial terraces across the Siwaliks Hills, Himalayas of central Nepal Martina Böhme Institute of Geology, University of Mining and Technology, Freiberg, Germany Abstract.
Determination of uplift rates of fluvial terraces across the Siwaliks Hills, Himalayas of central Nepal Martina Böhme Institute of Geology, University of Mining and Technology, Freiberg, Germany Abstract.
Ge Problem Set 1
 Ge 101 2012 Problem Set 1 This problem set covers basic techniques in structural geology, geomorphology and the construction of cross sections. Questions 2 and 3 are simple exercises; 1 and 4 are reallife
Ge 101 2012 Problem Set 1 This problem set covers basic techniques in structural geology, geomorphology and the construction of cross sections. Questions 2 and 3 are simple exercises; 1 and 4 are reallife
Earth Systems Science Chapter 7. Earth Systems Science Chapter 7 11/11/2010. Seismology: study of earthquakes and related phenomena
 Earth Systems Science Chapter 7 I. Structure of the Earth II. Plate Tectonics The solid part of the earth system includes processes, just like the atmosphere and oceans. However, the time scales for processes
Earth Systems Science Chapter 7 I. Structure of the Earth II. Plate Tectonics The solid part of the earth system includes processes, just like the atmosphere and oceans. However, the time scales for processes
1.72, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #5: Groundwater Flow Patterns. Local Flow System. Intermediate Flow System
 1.72, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #5: Groundwater Flow Patterns c Local Flow System 10,000 feet Intermediate Flow System Regional Flow System 20,000 feet Hydrologic section
1.72, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #5: Groundwater Flow Patterns c Local Flow System 10,000 feet Intermediate Flow System Regional Flow System 20,000 feet Hydrologic section
A) B) C) D) 4. Which diagram below best represents the pattern of magnetic orientation in the seafloor on the west (left) side of the ocean ridge?
 1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
Notice that the Grand Canyon is a knickpoint on the long profile. Cartoon examples of knickpoint migration:
 Earth and Planetary Surface Processes Winter 2017 - Lab 5. River channel long profiles. Hinds 440, 10:30a-11:20a Grades are not assigned for lab, but attendance is required. If you are unable to make a
Earth and Planetary Surface Processes Winter 2017 - Lab 5. River channel long profiles. Hinds 440, 10:30a-11:20a Grades are not assigned for lab, but attendance is required. If you are unable to make a
Whole Earth Structure and Plate Tectonics
 Whole Earth Structure and Plate Tectonics Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 4/5/2017 14:45 We Discuss Whole Earth Structure and Plate
Whole Earth Structure and Plate Tectonics Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 4/5/2017 14:45 We Discuss Whole Earth Structure and Plate
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann. Press & Siever, compressive forces. Compressive forces cause folding and faulting.
 Press & Siever, 1995 compressive forces Compressive forces cause folding and faulting. faults 1 Uplift is followed by erosion, which creates new horizontal surface. lava flows Volcanic eruptions cover
Press & Siever, 1995 compressive forces Compressive forces cause folding and faulting. faults 1 Uplift is followed by erosion, which creates new horizontal surface. lava flows Volcanic eruptions cover
60% water. Big Bang: 14,000 millions years ago The Earth originated about 4,500 millions years ago its orbit allows water to exist in a liquid state!
 Ch2. The Sea Floor #1 Why geology of the oceans? Marine habitats are directly shaped by geological processes The form of the coastlines The depth of the water Type of bottom (muddy, sandy, rocky) #2 Geological
Ch2. The Sea Floor #1 Why geology of the oceans? Marine habitats are directly shaped by geological processes The form of the coastlines The depth of the water Type of bottom (muddy, sandy, rocky) #2 Geological
Stream Geomorphology. Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012
 Stream Geomorphology Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012 What Functions do Healthy Streams Provide? Flood mitigation Water supply Water quality Sediment storage and transport Habitat Recreation Transportation
Stream Geomorphology Leslie A. Morrissey UVM July 25, 2012 What Functions do Healthy Streams Provide? Flood mitigation Water supply Water quality Sediment storage and transport Habitat Recreation Transportation
Lecture Marine Provinces
 Lecture Marine Provinces Measuring bathymetry Ocean depths and topography of ocean floor Sounding Rope/wire with heavy weight Known as lead lining Echo sounding Reflection of sound signals 1925 German
Lecture Marine Provinces Measuring bathymetry Ocean depths and topography of ocean floor Sounding Rope/wire with heavy weight Known as lead lining Echo sounding Reflection of sound signals 1925 German
Crags, Cracks, and Crumples: Crustal Deformation and Mountain Building
 Crags, Cracks, and Crumples: Crustal Deformation and Mountain Building Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts Based on slides prepared
Crags, Cracks, and Crumples: Crustal Deformation and Mountain Building Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts Based on slides prepared
Topographic metrics and bedrock channels Outline of this lecture
 Topographic metrics and bedrock channels Outline of this lecture Topographic metrics Fluvial scaling and slope-area relationships Channel steepness sensitivity to rock uplift Advancing understanding of
Topographic metrics and bedrock channels Outline of this lecture Topographic metrics Fluvial scaling and slope-area relationships Channel steepness sensitivity to rock uplift Advancing understanding of
Pleistocene alteration of drainage network and diverse surface morphology forced by basement structure in the foreland of the Eastern Alps
 This study was carried out in the framework of a project sponsored by the Hungarian National Science Foundation (OTKA NK83400) and TÁMOP-4.2.2/B-10/1-2010-0030 Pleistocene alteration of drainage network
This study was carried out in the framework of a project sponsored by the Hungarian National Science Foundation (OTKA NK83400) and TÁMOP-4.2.2/B-10/1-2010-0030 Pleistocene alteration of drainage network
Name HW - Landscapes
 Name HW - Landscapes 1. New York s Tug Hill landscape region is classified as a plateau because this region has a A) high elevation with distorted bedrock B) high elevation with nearly horizontal layers
Name HW - Landscapes 1. New York s Tug Hill landscape region is classified as a plateau because this region has a A) high elevation with distorted bedrock B) high elevation with nearly horizontal layers
Active Tectonics. Earthquakes, Uplift, and Landscape. Edward A. Keller University of California, Santa Barbara
 Prentice Hall Earth Science Series SUB Gottingen 214 80416X, im ^, 2002 A 7883 lllllllilwii Active Tectonics Earthquakes, Uplift, and Landscape Second Edition V Edward A. Keller University of California,
Prentice Hall Earth Science Series SUB Gottingen 214 80416X, im ^, 2002 A 7883 lllllllilwii Active Tectonics Earthquakes, Uplift, and Landscape Second Edition V Edward A. Keller University of California,
Passive Margin Salt Tectonics: Effects of Margin Tilt, Sediment Progradation, and Regional Extension
 Passive Margin Salt Tectonics: Effects of Margin Tilt, Sediment Progradation, and Regional Etension Steven J. Ings* Department of Earth Sciences, Dalhousie University, Halifa, NS, BH J sings@dal.ca and
Passive Margin Salt Tectonics: Effects of Margin Tilt, Sediment Progradation, and Regional Etension Steven J. Ings* Department of Earth Sciences, Dalhousie University, Halifa, NS, BH J sings@dal.ca and
Long-term landscape evolution: Linking tectonics and surface processes. Paul Bishop Department of Geographical and Earth Sciences
 Long-term landscape evolution: Linking tectonics and surface processes Paul Bishop Department of Geographical and Earth Sciences Collaboration PhDs: Daniel Campanile, Miguel Castillo, Tibi Codilean, Kate
Long-term landscape evolution: Linking tectonics and surface processes Paul Bishop Department of Geographical and Earth Sciences Collaboration PhDs: Daniel Campanile, Miguel Castillo, Tibi Codilean, Kate
Plate Tectonics. entirely rock both and rock
 Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Earth Science, (Tarbuck/Lutgens) Chapter 10: Mountain Building
 Earth Science, (Tarbuck/Lutgens) Chapter 10: Mountain Building 1) A(n) fault has little or no vertical movements of the two blocks. A) stick slip B) oblique slip C) strike slip D) dip slip 2) In a(n) fault,
Earth Science, (Tarbuck/Lutgens) Chapter 10: Mountain Building 1) A(n) fault has little or no vertical movements of the two blocks. A) stick slip B) oblique slip C) strike slip D) dip slip 2) In a(n) fault,
Drainage rearrangement: a modelling approach
 Drainage rearrangement: a modelling approach Maricke van Leeuwen June, 2013 i ii Drainage rearrangement: a modelling approach MSc thesis (SGL-80436) Maricke van Leeuwen 901027509070 MSc Earth and Environment,
Drainage rearrangement: a modelling approach Maricke van Leeuwen June, 2013 i ii Drainage rearrangement: a modelling approach MSc thesis (SGL-80436) Maricke van Leeuwen 901027509070 MSc Earth and Environment,
Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift
 Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift Predecessor to modern plate tectonics Shape and fit of the continents was the initial evidence Snider-Pelligrini (1858) Taylor (1908) Wegner (1915) Fig.
Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift Predecessor to modern plate tectonics Shape and fit of the continents was the initial evidence Snider-Pelligrini (1858) Taylor (1908) Wegner (1915) Fig.
Marine Science and Oceanography
 Marine Science and Oceanography Marine geology- study of the ocean floor Physical oceanography- study of waves, currents, and tides Marine biology study of nature and distribution of marine organisms Chemical
Marine Science and Oceanography Marine geology- study of the ocean floor Physical oceanography- study of waves, currents, and tides Marine biology study of nature and distribution of marine organisms Chemical
Section 11.1 pp Where Mountains Form
 Section 11.1 pp. 236 237 Where Mountains Form Chapter 11 Set a Purpose: TE, p. 236 Reading Study Guide, p. 36 Discussion: TE, p. 236 Differentiating ion Reading Support: TE, p. 236 Visual Teaching Interpret
Section 11.1 pp. 236 237 Where Mountains Form Chapter 11 Set a Purpose: TE, p. 236 Reading Study Guide, p. 36 Discussion: TE, p. 236 Differentiating ion Reading Support: TE, p. 236 Visual Teaching Interpret
An integral approach to bedrock river profile analysis
 1 An integral approach to bedrock river profile analysis 2 3 J. Taylor Perron and Leigh Royden 4 5 6 Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge
1 An integral approach to bedrock river profile analysis 2 3 J. Taylor Perron and Leigh Royden 4 5 6 Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge
The Marine Environment
 The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write true or
The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write true or
Sensitivity analysis and parameter space exploration
 GSA Data Repository 2018013 Gray et al., 2018, Off-fault deformation rate along the southern San Andreas fault at Mecca Hills, southern California, inferred from landscape modeling of curved drainages:
GSA Data Repository 2018013 Gray et al., 2018, Off-fault deformation rate along the southern San Andreas fault at Mecca Hills, southern California, inferred from landscape modeling of curved drainages:
Landforms. Why does the land look like it does? 1. Controlled by water 2. Controlled by the rocks
 Landforms Why does the land look like it does? 1. Controlled by water 2. Controlled by the rocks Landforms Made by Running Water Stream erosion The evolution of a river system Entrenched meanders Fluvial
Landforms Why does the land look like it does? 1. Controlled by water 2. Controlled by the rocks Landforms Made by Running Water Stream erosion The evolution of a river system Entrenched meanders Fluvial
Supplementary Material for. Mantle induced subsidence and compression in SE Asia
 Supplementary Material for Mantle induced subsidence and compression in SE Asia Ting Yang 1 *, Michael Gurnis 1, Sabin Zahirovic 2 1 Seismological Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena,
Supplementary Material for Mantle induced subsidence and compression in SE Asia Ting Yang 1 *, Michael Gurnis 1, Sabin Zahirovic 2 1 Seismological Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena,
Lecture 26: Marine Geology Read: Chapter 21 Homework due December 3
 Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 26: Marine Geology Read: Chapter 21 Homework due December 3 What we ll learn today:! 1. Describe the world s five oceans! 2. Understand patterns of ocean circulation! 3.
Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 26: Marine Geology Read: Chapter 21 Homework due December 3 What we ll learn today:! 1. Describe the world s five oceans! 2. Understand patterns of ocean circulation! 3.
MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY
 MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY Bathymetry BATHYMETRY BATHYMETRY THE UNDERWATER EQUIVALENT TO TOPOGRAPHY THE STUDY OF WATER DEPTH A BATHYMETRIC MAP SHOWS FLOOR RELIEF OR TERRAIN AS CONTOUR LINES Bathymetry
MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY Bathymetry BATHYMETRY BATHYMETRY THE UNDERWATER EQUIVALENT TO TOPOGRAPHY THE STUDY OF WATER DEPTH A BATHYMETRIC MAP SHOWS FLOOR RELIEF OR TERRAIN AS CONTOUR LINES Bathymetry
Captain s Tryouts 2017
 Captain s Tryouts 2017 Dynamic Planet Test Written by: Araneesh Pratap (Chattahoochee High School) Name: Date: Answer all questions on the answer sheet. Point values are given next to each question or
Captain s Tryouts 2017 Dynamic Planet Test Written by: Araneesh Pratap (Chattahoochee High School) Name: Date: Answer all questions on the answer sheet. Point values are given next to each question or
Actual bathymetry (with vertical exaggeration) Geometry of the ocean 1/17/2018. Patterns and observations? Patterns and observations?
 Patterns and observations? Patterns and observations? Observations? Patterns? Observations? Patterns? Geometry of the ocean Actual bathymetry (with vertical exaggeration) Continental Continental Basin
Patterns and observations? Patterns and observations? Observations? Patterns? Observations? Patterns? Geometry of the ocean Actual bathymetry (with vertical exaggeration) Continental Continental Basin
Importance of Understanding Coastal Landforms
 Importance of Understanding Coastal Landforms Costa Concordia Shipwreck, Isola del Giglio, Italy Depositional Coastal Landforms Can interpret landforms in light of geomorphic processes, both terrestrial
Importance of Understanding Coastal Landforms Costa Concordia Shipwreck, Isola del Giglio, Italy Depositional Coastal Landforms Can interpret landforms in light of geomorphic processes, both terrestrial
Running Water Earth - Chapter 16 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College
 Running Water Earth - Chapter 16 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Hydrologic Cycle The hydrologic cycle is a summary of the circulation of Earth s water supply. Processes involved in the hydrologic
Running Water Earth - Chapter 16 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Hydrologic Cycle The hydrologic cycle is a summary of the circulation of Earth s water supply. Processes involved in the hydrologic
Ch 10 Deposition Practice Questions
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the data table below. Six identical cylinders, A through F, were filled with equal volumes of sorted spherical particles. The data table shows the particle
1. Base your answer to the following question on the data table below. Six identical cylinders, A through F, were filled with equal volumes of sorted spherical particles. The data table shows the particle
Surface Water and Stream Development
 Surface Water and Stream Development Surface Water The moment a raindrop falls to earth it begins its return to the sea. Once water reaches Earth s surface it may evaporate back into the atmosphere, soak
Surface Water and Stream Development Surface Water The moment a raindrop falls to earth it begins its return to the sea. Once water reaches Earth s surface it may evaporate back into the atmosphere, soak
HW #2 Landscape Travel from A to B 12,
 HW #2 Landscape 2016 Section: Name: ate: 1. ase your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the map below, which represents two bridges that cross the Green River. Letters,, and represent locations
HW #2 Landscape 2016 Section: Name: ate: 1. ase your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the map below, which represents two bridges that cross the Green River. Letters,, and represent locations
Cenozoic river profile development in the Upper Lachlan catchment (SE Australia) as a test of quantitative fluvial incision models
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B6, 2309, doi:10.1029/2002jb002125, 2003 Cenozoic river profile development in the Upper Lachlan catchment (SE Australia) as a test of quantitative fluvial
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 108, NO. B6, 2309, doi:10.1029/2002jb002125, 2003 Cenozoic river profile development in the Upper Lachlan catchment (SE Australia) as a test of quantitative fluvial
Terrain Units PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION. Present Geology of NYS. Detailed Geologic Map of NYS
 NYS TOPOGRAPHY Why so? PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 014 Present Geology of NYS Detailed Geologic Map of NYS Generalized Geology Detailed Geology Hot links to the fold out
NYS TOPOGRAPHY Why so? PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 014 Present Geology of NYS Detailed Geologic Map of NYS Generalized Geology Detailed Geology Hot links to the fold out
COSMOGENIC 10 BE EROSION HISTORY OF THE BLUE RIDGE ESCARPMENT A LONG-LIVED FEATURE OF THE SOUTHERN APPALACHAINS
 COSMOGENIC 10 BE EROSION HISTORY OF THE BLUE RIDGE ESCARPMENT A LONG-LIVED FEATURE OF THE SOUTHERN APPALACHAINS A Thesis Progress Report Presented by Colleen L. Sullivan to The Faculty of the Geology Department
COSMOGENIC 10 BE EROSION HISTORY OF THE BLUE RIDGE ESCARPMENT A LONG-LIVED FEATURE OF THE SOUTHERN APPALACHAINS A Thesis Progress Report Presented by Colleen L. Sullivan to The Faculty of the Geology Department
Supplementary information on the West African margin
 Huismans and Beaumont 1 Data repository Supplementary information on the West African margin Interpreted seismic cross-sections of the north Angolan to south Gabon west African passive margins 1-3, including
Huismans and Beaumont 1 Data repository Supplementary information on the West African margin Interpreted seismic cross-sections of the north Angolan to south Gabon west African passive margins 1-3, including
Mountains are then built by deforming crust: Deformation & Mountain Building. Mountains form where stresses are high!
 Deformation & Mountain Building Where are mountains located? Deformation and Folding Mountain building Mountains form where stresses are high! Mountains form at all three types of plate boundaries where
Deformation & Mountain Building Where are mountains located? Deformation and Folding Mountain building Mountains form where stresses are high! Mountains form at all three types of plate boundaries where
8 th Grade Science Plate Tectonics and Topography Review
 8 th Grade Science Plate Tectonics and Topography Review #1 Scientists believe that the land masses of Earth were once joined together as one supercontinent called. A: Australia B: Wegner C: Pangaea D:
8 th Grade Science Plate Tectonics and Topography Review #1 Scientists believe that the land masses of Earth were once joined together as one supercontinent called. A: Australia B: Wegner C: Pangaea D:
What type of land feature is located at Point A? A Cliff B Delta C Mountain D Valley
 1 What type of land feature is located at Point A? A Cliff B Delta C Mountain D Valley Alfred Wegener s theory of continental drift was 2 not accepted by scientists when the theory was first proposed.
1 What type of land feature is located at Point A? A Cliff B Delta C Mountain D Valley Alfred Wegener s theory of continental drift was 2 not accepted by scientists when the theory was first proposed.
GENERAL GEOLOGY Fall Chapter 18: The Sea Floor. Partial Examination IV Study Guide Dr. Glen S. Mattioli
 GENERAL GEOLOGY 1113-005 Fall 2008 Partial Examination IV Study Guide Dr. Glen S. Mattioli Note that these are NOT questions, but rather are a list of topics that we have covered either in class or are
GENERAL GEOLOGY 1113-005 Fall 2008 Partial Examination IV Study Guide Dr. Glen S. Mattioli Note that these are NOT questions, but rather are a list of topics that we have covered either in class or are
Surface Processes Focus on Mass Wasting (Chapter 10)
 Surface Processes Focus on Mass Wasting (Chapter 10) 1. What is the distinction between weathering, mass wasting, and erosion? 2. What is the controlling force in mass wasting? What force provides resistance?
Surface Processes Focus on Mass Wasting (Chapter 10) 1. What is the distinction between weathering, mass wasting, and erosion? 2. What is the controlling force in mass wasting? What force provides resistance?
Landscape Development
 Landscape Development Slopes Dominate Natural Landscapes Created by the interplay of tectonic and igneous activity and gradation Deformation and uplift Volcanic activity Agents of gradation Mass wasting
Landscape Development Slopes Dominate Natural Landscapes Created by the interplay of tectonic and igneous activity and gradation Deformation and uplift Volcanic activity Agents of gradation Mass wasting
Rivers T. Perron
 1 Rivers T. Perron 12.001 After our discussions of large-scale topography, how we represent topography in maps, and how topography interacts with geologic structures, you should be frothing at the mouth
1 Rivers T. Perron 12.001 After our discussions of large-scale topography, how we represent topography in maps, and how topography interacts with geologic structures, you should be frothing at the mouth
3/5/05 Dr. Stewart 1
 I. Physiography of Appalachian Mountains A. Introduction 1. These mountains extend from NE Canada to Georgia 2. They are the remains of a deeply eroded, ancient mountain chain once larger than the Himalayans
I. Physiography of Appalachian Mountains A. Introduction 1. These mountains extend from NE Canada to Georgia 2. They are the remains of a deeply eroded, ancient mountain chain once larger than the Himalayans
4. The map below shows a meandering stream. Points A, B, C, and D represent locations along the stream bottom.
 1. Sediment is deposited as a river enters a lake because the A) velocity of the river decreases B) force of gravity decreases C) volume of water increases D) slope of the river increases 2. Which diagram
1. Sediment is deposited as a river enters a lake because the A) velocity of the river decreases B) force of gravity decreases C) volume of water increases D) slope of the river increases 2. Which diagram
PHYSICAL GEOLOGY AND THE ENVIRONMENT (2 ND CANADIAN EDITION)
 Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics Chapter Summary: Plate tectonics is a theory that suggests Earth's surface is divided into several large plates that change position and size. Intense geologic activity occurs
Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics Chapter Summary: Plate tectonics is a theory that suggests Earth's surface is divided into several large plates that change position and size. Intense geologic activity occurs
UNRAVELING THE HISTORY OF A LANDSCAPE: Using geomorphology, tephrochronology, and stratigraphy. Photo by: Josh Roering
 UNRAVELING THE HISTORY OF A LANDSCAPE: Using geomorphology, tephrochronology, and stratigraphy Photo by: Josh Roering Photo: Eric Bilderback Photo by: Josh Roering Goal 1. Reconstruct the paleo-landscape
UNRAVELING THE HISTORY OF A LANDSCAPE: Using geomorphology, tephrochronology, and stratigraphy Photo by: Josh Roering Photo: Eric Bilderback Photo by: Josh Roering Goal 1. Reconstruct the paleo-landscape
12. The diagram below shows the collision of an oceanic plate and a continental plate.
 Review 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below, which shows the boundary between two lithospheric plates. Point X is a location in the continental lithosphere. The depth
Review 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below, which shows the boundary between two lithospheric plates. Point X is a location in the continental lithosphere. The depth
Description of faults
 GLG310 Structural Geology Description of faults Horizontal stretch Crustal thickness Regional elevation Regional character Issues Normal Thrust/reverse Strike-slip >1 1 in one direction and < 1 in
GLG310 Structural Geology Description of faults Horizontal stretch Crustal thickness Regional elevation Regional character Issues Normal Thrust/reverse Strike-slip >1 1 in one direction and < 1 in
Geography of the world s oceans and major current systems. Lecture 2
 Geography of the world s oceans and major current systems Lecture 2 WHY is the GEOMORPHOLOGY OF THE OCEAN FLOOR important? (in the context of Oceanography) WHY is the GEOMORPHOLOGY OF THE OCEAN FLOOR important?
Geography of the world s oceans and major current systems Lecture 2 WHY is the GEOMORPHOLOGY OF THE OCEAN FLOOR important? (in the context of Oceanography) WHY is the GEOMORPHOLOGY OF THE OCEAN FLOOR important?
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) Which property would best distinguish sediment deposited by a river from sediment deposited by a glacier? thickness of sediment layers age of fossils found in the sediment mineral composition
Name: 1) Which property would best distinguish sediment deposited by a river from sediment deposited by a glacier? thickness of sediment layers age of fossils found in the sediment mineral composition
Landscape. Review Note Cards
 Landscape Review Note Cards Last Ice Age Pleistocene Epoch that occurred about 22,000 Years ago Glacier A large, long lasting mass of ice which forms on land and moves downhill because of gravity. Continental
Landscape Review Note Cards Last Ice Age Pleistocene Epoch that occurred about 22,000 Years ago Glacier A large, long lasting mass of ice which forms on land and moves downhill because of gravity. Continental
Erosion and Deposition
 Erosion and Deposition Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Water erosion begins when runoff from rainfall flows in a thin layer over the land
Erosion and Deposition Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Water erosion begins when runoff from rainfall flows in a thin layer over the land
Amplification of bedrock canyon incision by wind
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2381 Amplification of bedrock canyon incision by wind Jonathan P. Perkins, Noah J. Finnegan, Shanaka L. de Silva NATURE GEOSCIENCE www.nature.com/naturegeoscience
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2381 Amplification of bedrock canyon incision by wind Jonathan P. Perkins, Noah J. Finnegan, Shanaka L. de Silva NATURE GEOSCIENCE www.nature.com/naturegeoscience
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Miocene drainage reversal of the Amazon River driven by plate-mantle interaction. Shephard, G.E., Müller, R.D., Liu, L., Gurnis, M. Supplementary Figures SOM Figure 1. Non-dimensional
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Miocene drainage reversal of the Amazon River driven by plate-mantle interaction. Shephard, G.E., Müller, R.D., Liu, L., Gurnis, M. Supplementary Figures SOM Figure 1. Non-dimensional
Crustal Activity. Plate Tectonics - Plates - Lithosphere - Asthenosphere - Earth s surface consists of a major plates and some minor ones
 Name: Date: Period: Tectonics The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES Tectonics - s - Lithosphere - Asthenosphere - Earth s surface consists of a major plates and some minor ones The plates are
Name: Date: Period: Tectonics The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES Tectonics - s - Lithosphere - Asthenosphere - Earth s surface consists of a major plates and some minor ones The plates are
The continental lithosphere
 Simplicity to complexity: The continental lithosphere Reading: Fowler p350-377 Sampling techniques Seismic refraction Bulk crustal properties, thickness velocity profiles Seismic reflection To image specific
Simplicity to complexity: The continental lithosphere Reading: Fowler p350-377 Sampling techniques Seismic refraction Bulk crustal properties, thickness velocity profiles Seismic reflection To image specific
Week 3 (Feb 12): Erosion and Sediment Transport Discussion Leader: Ariel Deutsch
 Week 3 (Feb 12): Erosion and Sediment Transport Discussion Leader: Ariel Deutsch The papers this week explore the topics of erosion and sediment transport, with a major theme revolving around climate-tectonic
Week 3 (Feb 12): Erosion and Sediment Transport Discussion Leader: Ariel Deutsch The papers this week explore the topics of erosion and sediment transport, with a major theme revolving around climate-tectonic
Influence of surface processes and initial topography on lateral fold growth and fold linkage mode
 PUBLICATIONS Tectonics RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: Effects of erosion, sedimentation, and topography on fold linkage Effects of topography on the saddle point location and the reservoir closure Interaction
PUBLICATIONS Tectonics RESEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: Effects of erosion, sedimentation, and topography on fold linkage Effects of topography on the saddle point location and the reservoir closure Interaction
Landscape Development
 CHAPTER 22 Landscape Development Chapter Summary Landscapes are described in terms of their topography: elevation, the altitude of the surface of the Earth above sea level; relief, the difference between
CHAPTER 22 Landscape Development Chapter Summary Landscapes are described in terms of their topography: elevation, the altitude of the surface of the Earth above sea level; relief, the difference between
The Building of the NYC Region
 The Building of the NYC Region Definitions Fall Line marks the area where an upland region (continental bedrock) and a coastal plain meet Piedmont the plateau region of the eastern United States which
The Building of the NYC Region Definitions Fall Line marks the area where an upland region (continental bedrock) and a coastal plain meet Piedmont the plateau region of the eastern United States which
The Sea Floor. Chapter 2
 The Sea Floor Chapter 2 Geography of the Ocean Basins World ocean is the predominant feature on the Earth in total area Northern Hemisphere = 61% of the total area is ocean. Southern Hemisphere = about
The Sea Floor Chapter 2 Geography of the Ocean Basins World ocean is the predominant feature on the Earth in total area Northern Hemisphere = 61% of the total area is ocean. Southern Hemisphere = about
