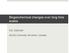
Supplementary Figure 1: Modern burial of organic carbon in deep sea sediment (gc m -2 a -1 ) 1.
|
|
|
- Quentin Morrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Figure 1: Modern burial of organic carbon in deep sea sediment (gc m -2 a -1 ) 1.
2 Supplementary Figure 2: The 7 province maps used in this study. Each color corresponds to a single province: a. Ocean subdivision following 2 ; b. Seas following 2 ; c. Longhurst Bioregion 3 updated by 4 ; d. Simplified Longhurst bioregion 1 (30 provinces); e. Simplified Longhurst bioregion 1 with depth subdivision at 1500 m (60 provinces); f. Simplified Longhurst bioregion 2 (15 provinces; used in Fig. 1); e. Simplified Longhurst bioregion 2 with depth subdivision at 1500 m (30 provinces).
3 Supplementary Figure 3: Relative changes in downcore TOC MAR (LGM/Holocene) in each province for province map.c,.d, and.f in Supplementary figure 2 (panel a., b., and c. respectively). Panel b. corresponds to the results show in Fig. 1a. Box plot shows 0 % (bottom whiskers), 25 %, 50 % (median; red lines), 75 %, and 100 % (top whiskers) quantiles, as well as mean (green cross) and outliers (red cross), for each provinces. Provinces were sorted depending on their contribution to modern TOC MAR (bottom blue curve), and the number of record used is displayed in green.
4 Supplementary Figure 4: Relative changes in deep-sea TOC MAR (a) and biogenic opal MAR(b) for LGM to Holocene transition. Shadings correspond to the mean ratio in each province (province map d). Relative changes in TOC and opal MAR in equatorial Atlantic (c), and Subantarctic zone (d) over the last 150ka (province map f. in Supplementary Fig. 2).
5 Supplementary Figure 5: LR04 benthic foraminifera δ 18 O stack; Reconstructed global TOC MAR in deep sea sediment (each line corresponds to a different province set scenario; the black thick line is the mean of all scenarios, Supplementary Data 1); Iron flux at ODP ; εnd in the northern Atlantic 6 ; and reconstructed oxygenation in the northern Atlantic 7. Grey horizontal bar on the bottom panel corresponds to the upper limit of oxygen content quantification for the method used in this study 7. Yellow vertical bands correspond to interglacial periods (Holocene and Marine Isotopic Stage (MIS) 5e), blue vertical bands correspond to glacial condition (Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), MIS 4, and MIS6).
6 Supplementary Figure 6: Province map a., b., d., and f. from Supplementary Fig. 2 were split into coastal and open ocean provinces, using a distance from the closest shoreline of 500 km, 1000 km and 1500 km. Each color corresponds to a single province. Global TOC MAR variations for split Oceans and Seas maps, are displayed in Supplementary Fig. 7.
7 Supplementary Figure 7: TOC MAR over the last 150 ka, for province map Ocean and Seas (bottom and top line of maps in Supplementary Fig. 6), including split provinces with distance from the coast. Blue lines correspond to the burial calculated with the original province maps. Black lines correspond to the sum of open ocean provinces, red lines to the sum of the coastal provinces. Green lines are the sum of open ocean and coastal region for each new province maps. Dotted lines are the scenarios based on the Ocean province maps, dashed lines are for Sea province maps.
8 Supplementary Figure 8: Log(TOC MARLGM /TOC MARHol) of sedimentary records versus the distance from the closest 150 m isobath. The right and top panels display boxplot of log(lgm MAR/Holocene MAR) and log(distance from the shelf), separated by oceanic bassins. Box plot shows 0 % (bottom whiskers), 25 %, 50 % (median; middle line), 75 %, and 100 % (top whiskers) quantiles, as well as outliers (isolated ticks).
9 Supplementary Figure 9: Global TOC MAR using different modern TOC MAR maps. Map 1 is for the modern map used in this study 1, Map 2 corresponds to an updated TOC content map, and only the Jahnke bulk MAR map 8 ; and Map 3 corresponds to the global map of modeled organic carbon flux to the seafloor from Ref. 9 (see Methods). Each thin line corresponds to one province map scenario, thick lines correspond to the mean of the different scenarios, for each modern burial map. Note that this figure presents results for the province map shown in Supplementary Fig. 2 and 6.
10 Supplementary Figure 10: a. Original reconstructions (lines) and long-term trends (dotted lines) in TOC MAR over the past 150 ka for each province map scenarios. b. Detrended reconstructions (Supplementary data 1).
11 Supplementary references: 1. Dunne JP, Sarmiento JL, Gnanadesikan A. A synthesis of global particle export from the surface ocean and cycling through the ocean interior and on the seafloor. Global Biogeochem Cycles 21, GB4006 (2007). 2. International Hydrographic Organization. Limits of Oceans and Seas. International Hydrographic Organization, Special Publication 23, (1953). 3. Longhurst A. Seasonal cycles of pelagic production and consumption. Prog Oceanogr 36, (1995). 4. Reygondeau G, Longhurst A, Martinez E, Beaugrand G, Antoine D, Maury O. Dynamic biogeochemical provinces in the global ocean. Global Biogeochem Cycles 27, (2013). 5. Martinez-Garcia A, Rosell-Mele A, Jaccard SL, Geibert W, Sigman DM, Haug GH. Southern Ocean dust-climate coupling over the past four million years. Nature 476, (2011). 6. Bohm E, et al. Strong and deep Atlantic meridional overturning circulation during the last glacial cycle. Nature 517, (2015). 7. Hoogakker BAA, Elderfield H, Schmiedl G, McCave IN, Rickaby REM. Glacialinterglacial changes in bottom-water oxygen content on the Portuguese margin. Nature Geosci 8, (2015). 8. Jahnke RA. The global ocean flux of particulate organic carbon: Areal distribution and magnitude. Global Biogeochem Cycles 10, (1996). 9. Dunne JP, Hales B, Toggweiler JR. Global calcite cycling constrained by sediment preservation controls. Global Biogeochem Cycles 26, GB3023 (2012).
Supplementary Figure 1. New downcore data from this study. Triangles represent the depth of radiocarbon dates. Error bars represent 2 standard error
 Supplementary Figure 1. New downcore data from this study. Triangles represent the depth of radiocarbon dates. Error bars represent 2 standard error of measurement (s.e.m.). 1 Supplementary Figure 2. Particle
Supplementary Figure 1. New downcore data from this study. Triangles represent the depth of radiocarbon dates. Error bars represent 2 standard error of measurement (s.e.m.). 1 Supplementary Figure 2. Particle
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NGEO168 "Strength and geometry of the glacial Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation" S2 Map of core locations Core locations of the Holocene and LGM 231 / 23
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NGEO168 "Strength and geometry of the glacial Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation" S2 Map of core locations Core locations of the Holocene and LGM 231 / 23
Supplementary Figure S1: Separated benthic 18 O data over 5 Myr. (a) Benthic LR04 benthic 18 O stack 16 ( ) in black with seawater 18 O ( w ) in blue
 Supplementary Figure S1: Separated benthic 18 O data over 5 Myr. (a) Benthic LR04 benthic 18 O stack 16 ( ) in black with seawater 18 O ( w ) in blue and temperature contribution ( T ) in green. (b) Surface-air
Supplementary Figure S1: Separated benthic 18 O data over 5 Myr. (a) Benthic LR04 benthic 18 O stack 16 ( ) in black with seawater 18 O ( w ) in blue and temperature contribution ( T ) in green. (b) Surface-air
Geochemical fingerprints of the ice-age (Southern) Ocean
 Geochemical fingerprints of the ice-age (Southern) Ocean THE SOUTHERN OCEAN, ITS DYNAMICS, BIOGEOCHEMISTRY AND ROLE IN THE CLIMATE SYSTEM NCAR, Boulder, CO 10-13 April 2017 Bob Anderson Motivation: Ice
Geochemical fingerprints of the ice-age (Southern) Ocean THE SOUTHERN OCEAN, ITS DYNAMICS, BIOGEOCHEMISTRY AND ROLE IN THE CLIMATE SYSTEM NCAR, Boulder, CO 10-13 April 2017 Bob Anderson Motivation: Ice
What can we learn from the paleo record about past changes in ocean productivity and controls of atmospheric CO 2?
 What can we learn from the paleo record about past changes in ocean productivity and controls of atmospheric CO 2? QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Bob Anderson,
What can we learn from the paleo record about past changes in ocean productivity and controls of atmospheric CO 2? QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Bob Anderson,
Carbon burial in deep-sea sediment and implications for oceanic inventories of carbon and alkalinity over the last glacial cycle Abstract.
 Carbon burial in deep-sea sediment and implications for oceanic inventories of carbon and alkalinity over the last glacial cycle Olivier Cartapanis 1,2, Eric D. Galbraith 2,3,4, Daniele Bianchi, and Samuel
Carbon burial in deep-sea sediment and implications for oceanic inventories of carbon and alkalinity over the last glacial cycle Olivier Cartapanis 1,2, Eric D. Galbraith 2,3,4, Daniele Bianchi, and Samuel
Two modes of change in Southern Ocean productivity over the past million years
 1 Two modes of change in Southern Ocean productivity over the past million years 2 3 4 Jaccard, S.L. 1, Hayes, C.T. 2, Martinez-Garcia, A. 1, Hodell, D.A. 3, Anderson, R.F. 2, Sigman, D.M. 4, Haug, G.H.
1 Two modes of change in Southern Ocean productivity over the past million years 2 3 4 Jaccard, S.L. 1, Hayes, C.T. 2, Martinez-Garcia, A. 1, Hodell, D.A. 3, Anderson, R.F. 2, Sigman, D.M. 4, Haug, G.H.
Biogeochemical changes over long time scales
 Biogeochemical changes over long time scales Eric Galbraith McGill University, Montreal, Canada Overview What is a long time? Long timescale observations from marine sediments Very quick look at biogeochemical
Biogeochemical changes over long time scales Eric Galbraith McGill University, Montreal, Canada Overview What is a long time? Long timescale observations from marine sediments Very quick look at biogeochemical
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Site Information: Table S1: Sites Modern Location Modern SST ( C) PO4(µM)-0m PO4(µM)-75m 130-806 0.5N, 159.5E 29.2 0.24 0.34 *(6) 154-925 4.5N, 43.5W 27.4 0.24 0.35 *(S35) 198-1208
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Site Information: Table S1: Sites Modern Location Modern SST ( C) PO4(µM)-0m PO4(µM)-75m 130-806 0.5N, 159.5E 29.2 0.24 0.34 *(6) 154-925 4.5N, 43.5W 27.4 0.24 0.35 *(S35) 198-1208
A multi-proxy study of planktonic foraminifera to identify past millennialscale. climate variability in the East Asian Monsoon and the Western Pacific
 This pdf file consists of all pages containing figures within: A multi-proxy study of planktonic foraminifera to identify past millennialscale climate variability in the East Asian Monsoon and the Western
This pdf file consists of all pages containing figures within: A multi-proxy study of planktonic foraminifera to identify past millennialscale climate variability in the East Asian Monsoon and the Western
Tracers. 1. Conservative tracers. 2. Non-conservative tracers. Temperature, salinity, SiO 2, Nd, 18 O. dissolved oxygen, phosphate, nitrate
 Tracers 1. Conservative tracers Temperature, salinity, SiO 2, Nd, 18 O 2. Non-conservative tracers dissolved oxygen, phosphate, nitrate Temperature itself is a tracer but other tracers (like oxygen isotopes)
Tracers 1. Conservative tracers Temperature, salinity, SiO 2, Nd, 18 O 2. Non-conservative tracers dissolved oxygen, phosphate, nitrate Temperature itself is a tracer but other tracers (like oxygen isotopes)
Abyssal Atlantic circulation during the Last Glacial Maximum: Constraining the ratio between transport and vertical mixing
 PALEOCEANOGRAPHY, VOL. 26,, doi:10.1029/2010pa001938, 2011 Abyssal Atlantic circulation during the Last Glacial Maximum: Constraining the ratio between transport and vertical mixing D. C. Lund, 1 J. F.
PALEOCEANOGRAPHY, VOL. 26,, doi:10.1029/2010pa001938, 2011 Abyssal Atlantic circulation during the Last Glacial Maximum: Constraining the ratio between transport and vertical mixing D. C. Lund, 1 J. F.
PMIP Ocean Workshop 2013 Program Outline
 PMIP Ocean Workshop 2013 Program Outline We, Dec. 4 8:30-9:15 Introductory Discussion 9:15-10:15 Model-Data Comparison 10:30-12:00 Quantifying Uncertainties 1:00-2:30 LGM and Deglacial Changes in the Tropics
PMIP Ocean Workshop 2013 Program Outline We, Dec. 4 8:30-9:15 Introductory Discussion 9:15-10:15 Model-Data Comparison 10:30-12:00 Quantifying Uncertainties 1:00-2:30 LGM and Deglacial Changes in the Tropics
A Broecker Brief Origin of the Atlantic s glacial age lower deep water
 A Broecker Brief Origin of the Atlantic s glacial age lower deep water Today s deep Atlantic shows no hint of nutrient stratification (see Figure 1). By contrast, during the last glacial maximum (LGM),
A Broecker Brief Origin of the Atlantic s glacial age lower deep water Today s deep Atlantic shows no hint of nutrient stratification (see Figure 1). By contrast, during the last glacial maximum (LGM),
Early diagenesis in marine sediments
 Early diagenesis in marine sediments Why study this part of the ocean? Particle flux to the sea floor ocean surface sediments early diagenesis layer Biogeochemical reactions Why study this part of the
Early diagenesis in marine sediments Why study this part of the ocean? Particle flux to the sea floor ocean surface sediments early diagenesis layer Biogeochemical reactions Why study this part of the
lecture 12 Paleoclimate
 lecture 12 Paleoclimate OVERVIEW OF EARTH S CLIMATIC HISTORY Geologic time scales http://www.snowballearth.org/index.html Features of the climate during the Cretaceous period the land-sea distribution
lecture 12 Paleoclimate OVERVIEW OF EARTH S CLIMATIC HISTORY Geologic time scales http://www.snowballearth.org/index.html Features of the climate during the Cretaceous period the land-sea distribution
FINE-GRAINED INORGANIC SEDIMENT CHARACTERISTICS AND SIZE. Paul Robert Auerbach
 FINE-GRAINED INORGANIC SEDIMENT CHARACTERISTICS AND SIZE Paul Robert Auerbach SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF COMBINED HONOURS BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN EARTH SCIENCES
FINE-GRAINED INORGANIC SEDIMENT CHARACTERISTICS AND SIZE Paul Robert Auerbach SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF COMBINED HONOURS BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN EARTH SCIENCES
Climate of the Past. A. Govin et al.
 Clim. Past Discuss., 9, C3570 C3579, 2014 www.clim-past-discuss.net/9/c3570/2014/ Author(s) 2014. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribute 3.0 License. Climate of the Past Discussions
Clim. Past Discuss., 9, C3570 C3579, 2014 www.clim-past-discuss.net/9/c3570/2014/ Author(s) 2014. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribute 3.0 License. Climate of the Past Discussions
Processes affecting continental shelves
 Marine Sediments Continental Shelves Processes affecting continental shelves 1. Glaciation 2. Sea-level change (±130 m during continental glaciation) 3. Waves and currents 4. Sedimentation 5. Carbonate
Marine Sediments Continental Shelves Processes affecting continental shelves 1. Glaciation 2. Sea-level change (±130 m during continental glaciation) 3. Waves and currents 4. Sedimentation 5. Carbonate
Last Time. Submarine Canyons and Fans. Turbidites. MAS 603: Geological Oceanography. Lecture 16: Greenhouse vs. Icehouse Earths
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA Last Time MAS 603: Geological Oceanography Lecture 16: Greenhouse vs. Icehouse Earths Submarine Fans Definition and morphology Transport mechanisms (density currents) Submarine
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA Last Time MAS 603: Geological Oceanography Lecture 16: Greenhouse vs. Icehouse Earths Submarine Fans Definition and morphology Transport mechanisms (density currents) Submarine
Ice on Earth: An overview and examples on physical properties
 Ice on Earth: An overview and examples on physical properties - Ice on Earth during the Pleistocene - Present-day polar and temperate ice masses - Transformation of snow to ice - Mass balance, ice deformation,
Ice on Earth: An overview and examples on physical properties - Ice on Earth during the Pleistocene - Present-day polar and temperate ice masses - Transformation of snow to ice - Mass balance, ice deformation,
Global phosphorus cycle
 Global phosphorus cycle OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 11 April 2013 2013 Arisa Okazaki and Kathleen Ruttenberg Outline 1. Introduction on global phosphorus (P) cycle 2. Terrestrial environment 3. Atmospheric
Global phosphorus cycle OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 11 April 2013 2013 Arisa Okazaki and Kathleen Ruttenberg Outline 1. Introduction on global phosphorus (P) cycle 2. Terrestrial environment 3. Atmospheric
Supplementary Figure 1. Foraminifer shell weights and coating composition. Correlation of mean foraminiferal shell weights of (a) G.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Foraminifer shell weights and coating composition. Correlation of mean foraminiferal shell weights of (a) G. bulloides and (b) Uvigerina spp. with respective U/Ca cc+c (grey) and
Supplementary Figure 1. Foraminifer shell weights and coating composition. Correlation of mean foraminiferal shell weights of (a) G. bulloides and (b) Uvigerina spp. with respective U/Ca cc+c (grey) and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:./nature97 G. ruber G. sacculifer G. ruber Ren et al. 9 G. sacculifer Ren et al. 9 FB-δ N ( vs. air) 7 Supplementary Figure. FB-δ N of single planktonic species G. ruber (dark green) and G. sacculifer
doi:./nature97 G. ruber G. sacculifer G. ruber Ren et al. 9 G. sacculifer Ren et al. 9 FB-δ N ( vs. air) 7 Supplementary Figure. FB-δ N of single planktonic species G. ruber (dark green) and G. sacculifer
The role of sub-antarctic mode water in global biological production. Jorge Sarmiento
 The role of sub-antarctic mode water in global biological production Jorge Sarmiento Original motivation Sediment traps suggest that ~one-third of the particulate organic matter flux at 200 m continues
The role of sub-antarctic mode water in global biological production Jorge Sarmiento Original motivation Sediment traps suggest that ~one-third of the particulate organic matter flux at 200 m continues
M. Ballarotta 1, L. Brodeau 1, J. Brandefelt 2, P. Lundberg 1, and K. Döös 1. This supplementary part includes the Figures S1 to S16 and Table S1.
 Supplementary Information: Last Glacial Maximum World-Ocean simulations at eddy-permitting and coarse resolutions: Do eddies contribute to a better consistency between models and paleo-proxies? M. Ballarotta
Supplementary Information: Last Glacial Maximum World-Ocean simulations at eddy-permitting and coarse resolutions: Do eddies contribute to a better consistency between models and paleo-proxies? M. Ballarotta
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Extreme deepening of the Atlantic overturning circulation during deglaciation Stephen Barker, Gregor Knorr, Maryline Vautravers, Paula Diz and Luke Skinner Supplementary Information
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Extreme deepening of the Atlantic overturning circulation during deglaciation Stephen Barker, Gregor Knorr, Maryline Vautravers, Paula Diz and Luke Skinner Supplementary Information
Correction notice: Sequestration of carbon in the deep Atlantic during the last glaciation
 Correction notice: Sequestration of carbon in the deep Atlantic during the last glaciation J. Yu, L. Menviel, Z. D. Jin, D. J. R. Thornalley, S. Barker, G. Marino, E. J. Rohling, Y. Cai, F. Zhang, X. Wang,
Correction notice: Sequestration of carbon in the deep Atlantic during the last glaciation J. Yu, L. Menviel, Z. D. Jin, D. J. R. Thornalley, S. Barker, G. Marino, E. J. Rohling, Y. Cai, F. Zhang, X. Wang,
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation
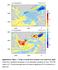 Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Ratio of coccolith CaCO 3 to foraminifera CaCO 3 in late Holocene deep sea sediments
 PALEOCEANOGRAPHY, VOL. 24,, doi:10.1029/2009pa001731, 2009 Ratio of coccolith CaCO 3 to foraminifera CaCO 3 in late Holocene deep sea sediments Wallace Broecker 1 and Elizabeth Clark 1 Received 30 December
PALEOCEANOGRAPHY, VOL. 24,, doi:10.1029/2009pa001731, 2009 Ratio of coccolith CaCO 3 to foraminifera CaCO 3 in late Holocene deep sea sediments Wallace Broecker 1 and Elizabeth Clark 1 Received 30 December
Introduction to Quaternary Geology (MA-Modul 3223) Prof. C. Breitkreuz, SS2012, TU Freiberg
 Introduction to Quaternary Geology (MA-Modul 3223) Prof. C. Breitkreuz, SS2012, TU Freiberg 1. Introduction: - Relevance, and relations to other fields of geoscience - Lower stratigraphic boundary and
Introduction to Quaternary Geology (MA-Modul 3223) Prof. C. Breitkreuz, SS2012, TU Freiberg 1. Introduction: - Relevance, and relations to other fields of geoscience - Lower stratigraphic boundary and
England 1,2. L. Menviel, University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia. System Science, Australia
 PALEOCEANOGRAPHY, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, Supporting Information for Poorly ventilated deep ocean at the Last Glacial Maximum inferred from carbon isotopes: a data-model comparison study L. Menviel
PALEOCEANOGRAPHY, VOL.???, XXXX, DOI:10.1029/, Supporting Information for Poorly ventilated deep ocean at the Last Glacial Maximum inferred from carbon isotopes: a data-model comparison study L. Menviel
The Sea Floor. Chapter 2
 The Sea Floor Chapter 2 Geography of the Ocean Basins World ocean is the predominant feature on the Earth in total area Northern Hemisphere = 61% of the total area is ocean. Southern Hemisphere = about
The Sea Floor Chapter 2 Geography of the Ocean Basins World ocean is the predominant feature on the Earth in total area Northern Hemisphere = 61% of the total area is ocean. Southern Hemisphere = about
Diatom-bound 15 N/ 14 N: New support for enhanced nutrient consumption in the ice age subantarctic
 PALEOCEANOGRAPHY, VOL. 20,, doi:10.1029/2004pa001114, 2005 Diatom-bound 15 N/ 14 N: New support for enhanced nutrient consumption in the ice age subantarctic Rebecca S. Robinson, 1 Daniel M. Sigman, 1
PALEOCEANOGRAPHY, VOL. 20,, doi:10.1029/2004pa001114, 2005 Diatom-bound 15 N/ 14 N: New support for enhanced nutrient consumption in the ice age subantarctic Rebecca S. Robinson, 1 Daniel M. Sigman, 1
Broecker Brief #7. June As shown in Figure 1, although similar, the shape for the atmospheric CO 2 content record
 Broecker Brief #7 Elements of the last glacial cycle CO 2 decline and recovery Introduction: June 2017 In an attempt to distinguish between the two major means by which the atmosphere s CO 2 content was
Broecker Brief #7 Elements of the last glacial cycle CO 2 decline and recovery Introduction: June 2017 In an attempt to distinguish between the two major means by which the atmosphere s CO 2 content was
GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 24, GB4023, doi: /2010gb003790, 2010
 GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 24,, doi:10.1029/2010gb003790, 2010 Carbon dioxide effects of Antarctic stratification, North Atlantic Intermediate Water formation, and subantarctic nutrient drawdown
GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 24,, doi:10.1029/2010gb003790, 2010 Carbon dioxide effects of Antarctic stratification, North Atlantic Intermediate Water formation, and subantarctic nutrient drawdown
Opal burial in the equatorial Atlantic Ocean over the last 30 ka: Implications for glacial-interglacial changes in the ocean silicon cycle
 Click Here for Full Article PALEOCEANOGRAPHY, VOL. 22,, doi:10.1029/2007pa001443, 2007 Opal burial in the equatorial Atlantic Ocean over the last 30 ka: Implications for glacial-interglacial changes in
Click Here for Full Article PALEOCEANOGRAPHY, VOL. 22,, doi:10.1029/2007pa001443, 2007 Opal burial in the equatorial Atlantic Ocean over the last 30 ka: Implications for glacial-interglacial changes in
Air sea temperature decoupling in western Europe during the last interglacial glacial transition
 María Fernanda Sánchez Goñi, Edouard Bard, Amaelle Landais, Linda Rossignol, Francesco d Errico SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1924 Air sea temperature decoupling in western Europe during the
María Fernanda Sánchez Goñi, Edouard Bard, Amaelle Landais, Linda Rossignol, Francesco d Errico SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1924 Air sea temperature decoupling in western Europe during the
In the new age model developed for MD , vegetation-derived climatic phases
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2012185 Sánchez Goñi et al. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION Methods Age model In the new age model developed for MD04-2845, vegetation-derived climatic phases
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2012185 Sánchez Goñi et al. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION Methods Age model In the new age model developed for MD04-2845, vegetation-derived climatic phases
Muted change in Atlantic overturning circulation over some glacial-aged Heinrich events
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2045 Muted change in Atlantic overturning circulation over some glacial-aged Heinrich events Jean Lynch-Stieglitz 1, Matthew W. Schmidt 2, L. Gene Henry 1,7,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2045 Muted change in Atlantic overturning circulation over some glacial-aged Heinrich events Jean Lynch-Stieglitz 1, Matthew W. Schmidt 2, L. Gene Henry 1,7,
Making Sediments: Biogenic Production, Carbonate Saturation and Sediment Distributions
 Making Sediments: Biogenic Production, Carbonate Saturation and Sediment Distributions OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography Reading: Libes, Chapters 15 and 16 Outline I. Deep sea sedimentation Detrital sediments
Making Sediments: Biogenic Production, Carbonate Saturation and Sediment Distributions OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography Reading: Libes, Chapters 15 and 16 Outline I. Deep sea sedimentation Detrital sediments
Supporting Information for Glacial Atlantic overturning increased by wind stress in climate models
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS Supporting Information for Glacial Atlantic overturning increased by wind stress in climate models Juan Muglia 1 and Andreas Schmittner 1 Contents of this file 1. Figures S1
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS Supporting Information for Glacial Atlantic overturning increased by wind stress in climate models Juan Muglia 1 and Andreas Schmittner 1 Contents of this file 1. Figures S1
Radiocarbon constraints on the glacial ocean circulation and its impact on atmospheric CO 2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 Radiocarbon constraints on the glacial ocean circulation and its impact on atmospheric
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 Radiocarbon constraints on the glacial ocean circulation and its impact on atmospheric
EKSAMEN i GEO-3121, Marin geologi. Du kan bruke linjal, kalkulator og ordbok! You are allowed to use a ruler, a calculator, and a dictionary!
 EKSAMEN i GEO-3121, Marin geologi Tirsdag 13. desember, 2005, klokka 09.00-13.00 Asg5rdveien 9 Du kan bruke linjal, kalkulator og ordbok! You are allowed to use a ruler, a calculator, and a dictionary!
EKSAMEN i GEO-3121, Marin geologi Tirsdag 13. desember, 2005, klokka 09.00-13.00 Asg5rdveien 9 Du kan bruke linjal, kalkulator og ordbok! You are allowed to use a ruler, a calculator, and a dictionary!
Oil. Oil. Early common mistakes in the oil business.
 Oil www.priweb.org/ed/pgws/history/pennsylvania/pennsylvania.html Early common mistakes in the oil business Oil www.priweb.org/ed/pgws/history/pennsylvania/pennsylvania.html 1 Climate More recent common
Oil www.priweb.org/ed/pgws/history/pennsylvania/pennsylvania.html Early common mistakes in the oil business Oil www.priweb.org/ed/pgws/history/pennsylvania/pennsylvania.html 1 Climate More recent common
17. DATA REPORT: CARBONATE, ORGANIC CARBON, AND OPAL CONCENTRATIONS SOUTHWEST AFRICA MARGIN 1
 Wefer, G., Berger, W.H., and Richter, C. (Eds.) Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results Volume 175 17. DATA REPORT: CARBONATE, ORGANIC CARBON, AND OPAL CONCENTRATIONS AND ORGANIC
Wefer, G., Berger, W.H., and Richter, C. (Eds.) Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results Volume 175 17. DATA REPORT: CARBONATE, ORGANIC CARBON, AND OPAL CONCENTRATIONS AND ORGANIC
A bit of background on carbonates. CaCO 3 (solid)
 A bit of background on carbonates CaCO 3 (solid) Organisms need both carbon dioxide and carbonate Kleypas et al 2005 The two pumps put CO 2 into the deep ocean The long term record of climate change Or:
A bit of background on carbonates CaCO 3 (solid) Organisms need both carbon dioxide and carbonate Kleypas et al 2005 The two pumps put CO 2 into the deep ocean The long term record of climate change Or:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO3053 1 2 Contribution of topographically-generated submesoscale turbulence to Southern Ocean overturning 3
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO3053 1 2 Contribution of topographically-generated submesoscale turbulence to Southern Ocean overturning 3
Development of the Global Environment
 Development of the Global Environment G302: Spring 2004 A course focused on exploration of changes in the Earth system through geological history Simon C. Brassell Geological Sciences simon@indiana.edu
Development of the Global Environment G302: Spring 2004 A course focused on exploration of changes in the Earth system through geological history Simon C. Brassell Geological Sciences simon@indiana.edu
Father of Glacial theory. First investigations of glaciers and mountain geology,
 First investigations of glaciers and mountain geology, 1750-1800 Glaciation happens! -- Historical perspective It happens in cycles -- How do we know this? What are Milankovitch cycles? Sub-Milankovitch
First investigations of glaciers and mountain geology, 1750-1800 Glaciation happens! -- Historical perspective It happens in cycles -- How do we know this? What are Milankovitch cycles? Sub-Milankovitch
GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 21, GB1024, doi: /2006gb002803, 2007
 Click Here for Full Article GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 21,, doi:10.1029/2006gb002803, 2007 Relating estimates of CaCO 3 production, export, and dissolution in the water column to measurements of
Click Here for Full Article GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 21,, doi:10.1029/2006gb002803, 2007 Relating estimates of CaCO 3 production, export, and dissolution in the water column to measurements of
Quaternary Science Reviews
 Quaternary Science Reviews 29 (2010) 170 181 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Quaternary Science Reviews journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/quascirev Changes in deep Pacific temperature
Quaternary Science Reviews 29 (2010) 170 181 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Quaternary Science Reviews journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/quascirev Changes in deep Pacific temperature
Chapter Two. Figure 02_02. Geography of the Ocean Basins. The Sea Floor
 Chapter Two The Sea Floor Geography of the Ocean Basins Figure 02_02 The world ocean is the predominant feature on the Earth in total area. In the Northern Hemisphere, 61% of the total area is ocean. In
Chapter Two The Sea Floor Geography of the Ocean Basins Figure 02_02 The world ocean is the predominant feature on the Earth in total area. In the Northern Hemisphere, 61% of the total area is ocean. In
Liverpool NEMO Shelf Arctic Ocean modelling
 St. Andrews 22 July 2013 ROAM @ Liverpool NEMO Shelf Arctic Ocean modelling Maria Luneva, Jason Holt, Sarah Wakelin NEMO shelf Arctic Ocean model About 50% of the Arctic is shelf sea (
St. Andrews 22 July 2013 ROAM @ Liverpool NEMO Shelf Arctic Ocean modelling Maria Luneva, Jason Holt, Sarah Wakelin NEMO shelf Arctic Ocean model About 50% of the Arctic is shelf sea (
Impact of Glacial/Interglacial Sea Level Change on the Ocean Nitrogen Cycle
 Old Dominion University ODU Digital Commons OEAS Faculty Publications Ocean, Earth & Atmospheric Sciences 217 Impact of Glacial/Interglacial Sea Level Change on the Ocean Nitrogen Cycle Haojia Ren Daniel
Old Dominion University ODU Digital Commons OEAS Faculty Publications Ocean, Earth & Atmospheric Sciences 217 Impact of Glacial/Interglacial Sea Level Change on the Ocean Nitrogen Cycle Haojia Ren Daniel
An Investigation of Antarctic Circumpolar Current Strength in Response to Changes in Climate. Presented by Matt Laffin
 An Investigation of Antarctic Circumpolar Current Strength in Response to Changes in Climate Presented by Matt Laffin Presentation Outline Introduction to Marine Sediment as a Proxy Introduction to McCave
An Investigation of Antarctic Circumpolar Current Strength in Response to Changes in Climate Presented by Matt Laffin Presentation Outline Introduction to Marine Sediment as a Proxy Introduction to McCave
A modeling case for high atmospheric oxygen concentrations during the Mesozoic and Cenozoic Mills et al.
 GSA Data Repository 2016343 A modeling case for high atmospheric oxygen concentrations during the Mesozoic and Cenozoic Mills et al. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 APPENDIX APPENDIX
GSA Data Repository 2016343 A modeling case for high atmospheric oxygen concentrations during the Mesozoic and Cenozoic Mills et al. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 APPENDIX APPENDIX
Nitrogen isotopic evidence for a poleward decrease in surface nitrate within the ice age Antarctic
 Quaternary Science Reviews 27 (2008) 1076 1090 Nitrogen isotopic evidence for a poleward decrease in surface nitrate within the ice age Antarctic Rebecca S. Robinson a,, Daniel M. Sigman b a Graduate School
Quaternary Science Reviews 27 (2008) 1076 1090 Nitrogen isotopic evidence for a poleward decrease in surface nitrate within the ice age Antarctic Rebecca S. Robinson a,, Daniel M. Sigman b a Graduate School
Introduction After reviewing the classification of continental margins (not plate margins) in your textbook, answer the following questions:
 Investigating the continental margins of North America using GeoMapApp. This exercise is designed to familiarize you with the features of continental margins. Through the analysis of color-coded bathymetric
Investigating the continental margins of North America using GeoMapApp. This exercise is designed to familiarize you with the features of continental margins. Through the analysis of color-coded bathymetric
M. Wary et al. Correspondence to: M. Wary
 Supplement of Clim. Past, 11, 1507 1525, 2015 http://www.clim-past.net/11/1507/2015/ doi:10.5194/cp-11-1507-2015-supplement Author(s) 2015. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Supplement of Stratification of surface
Supplement of Clim. Past, 11, 1507 1525, 2015 http://www.clim-past.net/11/1507/2015/ doi:10.5194/cp-11-1507-2015-supplement Author(s) 2015. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Supplement of Stratification of surface
Carbon pathways in the South Atlantic
 Carbon pathways in the South Atlantic Olga T. Sato, Ph.D. Paulo Polito, Ph.D. olga.sato@usp.br - polito@usp.br Oceanographic Institute University of São Paulo Olga Sato and Paulo Polito (IOUSP) Carbon
Carbon pathways in the South Atlantic Olga T. Sato, Ph.D. Paulo Polito, Ph.D. olga.sato@usp.br - polito@usp.br Oceanographic Institute University of São Paulo Olga Sato and Paulo Polito (IOUSP) Carbon
The Transport Matrix Method (TMM) (for fast, offline simulation of passive tracers in the ocean) Samar Khatiwala
 The Transport Matrix Method (TMM) (for fast, offline simulation of passive tracers in the ocean) Samar Khatiwala Department of Earth Sciences University of Oxford Why do we need alternatives to GCMs? Ocean
The Transport Matrix Method (TMM) (for fast, offline simulation of passive tracers in the ocean) Samar Khatiwala Department of Earth Sciences University of Oxford Why do we need alternatives to GCMs? Ocean
Marine Sediments. Introductory Oceanography. Ray Rector: Instructor
 Marine Sediments Introductory Oceanography Ray Rector: Instructor Ocean Basins are Vast Sinks for Huge Amounts of Sediment from Numerous Different Sources Four Major Types of Seafloor Sediments 1. Lithogenous
Marine Sediments Introductory Oceanography Ray Rector: Instructor Ocean Basins are Vast Sinks for Huge Amounts of Sediment from Numerous Different Sources Four Major Types of Seafloor Sediments 1. Lithogenous
We re living in the Ice Age!
 Chapter 18. Coping with the Weather: Causes and Consequences of Naturally Induce Climate Change 지구시스템의이해 We re living in the Ice Age! 1 Phanerozoic Climate 서늘해지고 더웠고 따뜻했고 3 Climate Rollercoaster 4 2 Time
Chapter 18. Coping with the Weather: Causes and Consequences of Naturally Induce Climate Change 지구시스템의이해 We re living in the Ice Age! 1 Phanerozoic Climate 서늘해지고 더웠고 따뜻했고 3 Climate Rollercoaster 4 2 Time
Tropical Ocean Temperatures Over the Past 3.5 Million Years
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/328/5985/1530/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Tropical Ocean Temperatures Over the Past 3.5 Million Years Timothy D. Herbert, Laura Cleaveland Peterson, Kira T. Lawrence,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/328/5985/1530/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Tropical Ocean Temperatures Over the Past 3.5 Million Years Timothy D. Herbert, Laura Cleaveland Peterson, Kira T. Lawrence,
Sediments, Sedimentation, and Paleoceanography. -Types of sediments -Distribution of ocean sediments and Processes of sedimentation -Paleoceanography
 Sediments, Sedimentation, and Paleoceanography -Types of sediments -Distribution of ocean sediments and Processes of sedimentation -Paleoceanography Sediments Sources of sediment: 1. living organisms (biogenic:
Sediments, Sedimentation, and Paleoceanography -Types of sediments -Distribution of ocean sediments and Processes of sedimentation -Paleoceanography Sediments Sources of sediment: 1. living organisms (biogenic:
Simulating low frequency changes in atmospheric CO 2 during the last years
 Author(s) 2006. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Climate of the Past Simulating low frequency changes in atmospheric CO 2 during the last 740 000 years P. Köhler and H. Fischer Alfred
Author(s) 2006. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Climate of the Past Simulating low frequency changes in atmospheric CO 2 during the last 740 000 years P. Köhler and H. Fischer Alfred
the 2 past three decades
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2840 Atlantic-induced 1 pan-tropical climate change over the 2 past three decades 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 POP simulation forced by the Atlantic-induced atmospheric
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2840 Atlantic-induced 1 pan-tropical climate change over the 2 past three decades 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 POP simulation forced by the Atlantic-induced atmospheric
Deep Atlantic carbon sequestration and atmospheric CO2 decline during the last glaciation
 1 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 2 24 25 26 27 28 Deep Atlantic carbon sequestration and atmospheric CO2 decline during the last glaciation J. Yu 1 *, L. Menviel 2,, Z. Jin 4, D.J.R.
1 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 2 24 25 26 27 28 Deep Atlantic carbon sequestration and atmospheric CO2 decline during the last glaciation J. Yu 1 *, L. Menviel 2,, Z. Jin 4, D.J.R.
Covariant Glacial-Interglacial Dust Fluxes in the Equatorial Pacific and Antarctica
 Covariant Glacial-Interglacial Dust Fluxes in the Equatorial Pacific and Antarctica Gisela Winckler, 1 * Robert F. Anderson, 1,2 Martin Q. Fleisher, 1 David McGee, 1,2 Natalie Mahowald 3 1 Lamont-Doherty
Covariant Glacial-Interglacial Dust Fluxes in the Equatorial Pacific and Antarctica Gisela Winckler, 1 * Robert F. Anderson, 1,2 Martin Q. Fleisher, 1 David McGee, 1,2 Natalie Mahowald 3 1 Lamont-Doherty
Acceleration of oxygen decline in the tropical Pacific over the past decades by aerosol pollutants
 Acceleration of oxygen decline in the tropical Pacific over the past decades by aerosol pollutants T. Ito 1 *, A. Nenes 1,2,3,4, M. S. Johnson 5, N. Meskhidze 6 and C. Deutsch 7 Dissolved oxygen in the
Acceleration of oxygen decline in the tropical Pacific over the past decades by aerosol pollutants T. Ito 1 *, A. Nenes 1,2,3,4, M. S. Johnson 5, N. Meskhidze 6 and C. Deutsch 7 Dissolved oxygen in the
G 3. AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society
 Geosystems G 3 AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society Forum Volume 5, Number 4 6 April 2004 Q04002, doi:10.1029/2003gc000670 ISSN: 1525-2027 Switching
Geosystems G 3 AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society Forum Volume 5, Number 4 6 April 2004 Q04002, doi:10.1029/2003gc000670 ISSN: 1525-2027 Switching
Chapter 9 Lecture Outline. Oceans: The Last Frontier
 Chapter 9 Lecture Outline Oceans: The Last Frontier The Vast World Ocean Earth is referred to as the blue planet 71% of Earth s surface is oceans and marginal seas Continents and islands comprise the remaining
Chapter 9 Lecture Outline Oceans: The Last Frontier The Vast World Ocean Earth is referred to as the blue planet 71% of Earth s surface is oceans and marginal seas Continents and islands comprise the remaining
Testing the Silica Leakage Hypothesis
 Testing the Silica Leakage Hypothesis Lauren McLean Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Combined Honours Bachelor of Science in Earth Sciences and Oceanography at Dalhousie
Testing the Silica Leakage Hypothesis Lauren McLean Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Combined Honours Bachelor of Science in Earth Sciences and Oceanography at Dalhousie
Glacial-interglacial variations in marine phosphorus cycling: Implications for ocean productivity
 Click Here for Full Article GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 22,, doi:10.1029/2007gb003054, 2008 Glacial-interglacial variations in marine phosphorus cycling: Implications for ocean productivity I. Tsandev,
Click Here for Full Article GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 22,, doi:10.1029/2007gb003054, 2008 Glacial-interglacial variations in marine phosphorus cycling: Implications for ocean productivity I. Tsandev,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 1. Simulation of Glacial Background Climate Globally averaged surface air is 3 K cooler than in the pre-industrial simulation. This is less than the 4-7 K cooling estimated for the Last Glacial Maximum
1. Simulation of Glacial Background Climate Globally averaged surface air is 3 K cooler than in the pre-industrial simulation. This is less than the 4-7 K cooling estimated for the Last Glacial Maximum
Announcements. First problem set due next Tuesday. Review for first exam next Thursday. Quiz on Booth (1994) after break today.
 Announcements First problem set due next Tuesday. Review for first exam next Thursday. Quiz on Booth (1994) after break today. Intertidal, Lowes Cove, ME Marine Sediments: Clues to the ocean s past There
Announcements First problem set due next Tuesday. Review for first exam next Thursday. Quiz on Booth (1994) after break today. Intertidal, Lowes Cove, ME Marine Sediments: Clues to the ocean s past There
Simulating low frequency changes in atmospheric CO2 during the last years
 Simulating low frequency changes in atmospheric CO2 during the last 740 000 years P. Köhler, H. Fischer To cite this version: P. Köhler, H. Fischer. Simulating low frequency changes in atmospheric CO2
Simulating low frequency changes in atmospheric CO2 during the last 740 000 years P. Köhler, H. Fischer To cite this version: P. Köhler, H. Fischer. Simulating low frequency changes in atmospheric CO2
Reading Material. See class website. Sediments, from Oceanography M.G. Gross, Prentice-Hall
 Reading Material See class website Sediments, from Oceanography M.G. Gross, Prentice-Hall Materials filling ocean basins Dissolved chemicals especially from rivers and mid-ocean ridges (volcanic eruptions)
Reading Material See class website Sediments, from Oceanography M.G. Gross, Prentice-Hall Materials filling ocean basins Dissolved chemicals especially from rivers and mid-ocean ridges (volcanic eruptions)
Carbon and Nutrient Cycles on Continental Shelves - Current Advances and Thoughts for Future Research
 Carbon and Nutrient Cycles on Continental Shelves - Current Advances and Thoughts for Future Research 1. Brief summary of N-based productivity measures. 2. Thoughts for future studies of the ocean margin
Carbon and Nutrient Cycles on Continental Shelves - Current Advances and Thoughts for Future Research 1. Brief summary of N-based productivity measures. 2. Thoughts for future studies of the ocean margin
Carbon Exchanges between the Continental Margins and the Open Ocean
 Carbon Exchanges between the Continental Margins and the Open Ocean Outline: 1. Introduction to problem 2. Example of how circulation can export carbon to open ocean 3. Example of how particle transport
Carbon Exchanges between the Continental Margins and the Open Ocean Outline: 1. Introduction to problem 2. Example of how circulation can export carbon to open ocean 3. Example of how particle transport
Natural and anthropogenic climate change Lessons from ice cores
 Natural and anthropogenic climate change Lessons from ice cores Eric Wolff British Antarctic Survey, Cambridge ewwo@bas.ac.uk ASE Annual Conference 2011; ESTA/ESEU lecture Outline What is British Antarctic
Natural and anthropogenic climate change Lessons from ice cores Eric Wolff British Antarctic Survey, Cambridge ewwo@bas.ac.uk ASE Annual Conference 2011; ESTA/ESEU lecture Outline What is British Antarctic
G 3. AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society
 Geosystems G 3 AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society Article Volume 7, Number 11 3 November 2006 Q11N06, doi:10.1029/2005gc001228 ISSN: 1525-2027 A model-based
Geosystems G 3 AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society Article Volume 7, Number 11 3 November 2006 Q11N06, doi:10.1029/2005gc001228 ISSN: 1525-2027 A model-based
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Preparation line for purifying and separating diatom and radiolarian opal for isotope measurements. Supplementary Figure 2. Examples of different size
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Preparation line for purifying and separating diatom and radiolarian opal for isotope measurements. Supplementary Figure 2. Examples of different size
Ecosystem History of Florida Bay and the Southern Estuaries Five Year Update. G. Lynn Wingard (USGS)
 Ecosystem History of Florida Bay and the Southern Estuaries Five Year Update G. Lynn Wingard (USGS) Progress since 2003 Florida Bay Science Conference Expansion of Ecosystem History Research into surrounding
Ecosystem History of Florida Bay and the Southern Estuaries Five Year Update G. Lynn Wingard (USGS) Progress since 2003 Florida Bay Science Conference Expansion of Ecosystem History Research into surrounding
Lecture 16 - Stable isotopes
 Lecture 16 - Stable isotopes 1. The fractionation of different isotopes of oxygen and their measurement in sediment cores has shown scientists that: (a) ice ages are common and lasted for hundreds of millions
Lecture 16 - Stable isotopes 1. The fractionation of different isotopes of oxygen and their measurement in sediment cores has shown scientists that: (a) ice ages are common and lasted for hundreds of millions
Substantial energy input to the mesopelagic ecosystem from the seasonal mixed-layer pump
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2818 Substantial energy input to the mesopelagic ecosystem from the seasonal mixed-layer pump Giorgio Dall Olmo, James Dingle, Luca Polimene, Robert J. W. Brewin
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2818 Substantial energy input to the mesopelagic ecosystem from the seasonal mixed-layer pump Giorgio Dall Olmo, James Dingle, Luca Polimene, Robert J. W. Brewin
Quarternary Climate Variations
 Quarternary Climate Variations EAS 303 Lecture 34 Background and History Louis Agassiz (1840): recognition of Ice Ages Harold Urey (1947): The Thermodynamic Properties of Isotopic Substances calculated
Quarternary Climate Variations EAS 303 Lecture 34 Background and History Louis Agassiz (1840): recognition of Ice Ages Harold Urey (1947): The Thermodynamic Properties of Isotopic Substances calculated
Lecture #13 notes, Geology 3950 Spring 2006: CR Stern Magnetic reversals (text pages th edition and in the 5 th edition)
 Lecture #13 notes, Geology 3950 Spring 2006: CR Stern Magnetic reversals (text pages 35-37 4 th edition and 53-55 in the 5 th edition) The earth has a magnetic field generated by circulation of charged
Lecture #13 notes, Geology 3950 Spring 2006: CR Stern Magnetic reversals (text pages 35-37 4 th edition and 53-55 in the 5 th edition) The earth has a magnetic field generated by circulation of charged
Ice Sheets and Late Quaternary Environmental Change
 Ice Sheets and Late Quaternary Environmental Change Martin J. Siegert Bristol Glaciology Centre, School of Geographical Sciences University of Bristol JOHN WILEY & SONS, LTD Chichester New York Weinheim
Ice Sheets and Late Quaternary Environmental Change Martin J. Siegert Bristol Glaciology Centre, School of Geographical Sciences University of Bristol JOHN WILEY & SONS, LTD Chichester New York Weinheim
North Atlantic ocean circulation and abrupt climate change during the last glaciation
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 North Atlantic ocean circulation and abrupt climate change during the last glaciation Authors: L. G. Henry 1*, J. F. McManus 1, W. B. Curry 2,3, N. L. Roberts 4, A. M. Piotrowski 4, L.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 North Atlantic ocean circulation and abrupt climate change during the last glaciation Authors: L. G. Henry 1*, J. F. McManus 1, W. B. Curry 2,3, N. L. Roberts 4, A. M. Piotrowski 4, L.
Persistent effects of the Yellow River on the Chinese marginal seas began at least. ~880 ka ago
 Persistent effects of the Yellow River on the Chinese marginal seas began at least ~880 ka ago Zhengquan Yao, Xuefa Shi, Shuqing Qiao, Qingsong Liu, Selvaraj Kandasamy, Jianxing Liu, Yanguang Liu, Jihua
Persistent effects of the Yellow River on the Chinese marginal seas began at least ~880 ka ago Zhengquan Yao, Xuefa Shi, Shuqing Qiao, Qingsong Liu, Selvaraj Kandasamy, Jianxing Liu, Yanguang Liu, Jihua
common time scale developed for Greenland and Antarctic ice core records. Central to this
 1 Supplemental Material Age scale: For the dating of the EDML and EDC ice cores (Figure S1) we used for the first time a new common time scale developed for Greenland and Antarctic ice core records. Central
1 Supplemental Material Age scale: For the dating of the EDML and EDC ice cores (Figure S1) we used for the first time a new common time scale developed for Greenland and Antarctic ice core records. Central
A Broecker Brief. Origin of the Glacial Ramp. Although there is no doubt that cycles in the Earth s orbital parameters pace glaciation,
 A Broecker Brief Origin of the Glacial Ramp Although there is no doubt that cycles in the Earth s orbital parameters pace glaciation, their physical link to the 100-kyr climate cycle remains unresolved.
A Broecker Brief Origin of the Glacial Ramp Although there is no doubt that cycles in the Earth s orbital parameters pace glaciation, their physical link to the 100-kyr climate cycle remains unresolved.
SCOPE 35 Scales and Global Change (1988)
 1. Types and origins of marine sediments 2. Distribution of sediments: controls and patterns 3. Sedimentary diagenesis: (a) Sedimentary and organic matter burial (b) Aerobic and anaerobic decomposition
1. Types and origins of marine sediments 2. Distribution of sediments: controls and patterns 3. Sedimentary diagenesis: (a) Sedimentary and organic matter burial (b) Aerobic and anaerobic decomposition
High-latitude forcing of interior ocean D 13 C
 PALEOCEANOGRAPHY, VOL. 21,, doi:10.1029/2005pa001226, 2006 High-latitude forcing of interior ocean D 13 C Randye L. Rutberg 1 and Synte L. Peacock 2 Received 16 September 2005; accepted 17 January 2006;
PALEOCEANOGRAPHY, VOL. 21,, doi:10.1029/2005pa001226, 2006 High-latitude forcing of interior ocean D 13 C Randye L. Rutberg 1 and Synte L. Peacock 2 Received 16 September 2005; accepted 17 January 2006;
Water, that currently bathes Site 593, forms between the two fronts. Map adapted from
 Supplementary Figure 1. Location bathymetry map of DSDP Site 593 (this study) in the Tasman Sea. Position of important frontal regions is also shown. Antarctic Intermediate Water, that currently bathes
Supplementary Figure 1. Location bathymetry map of DSDP Site 593 (this study) in the Tasman Sea. Position of important frontal regions is also shown. Antarctic Intermediate Water, that currently bathes
Past, present and future
 Southern New Jersey and Delaware sea levels: Past, present and future Benjamin P. Horton Sea Level Research Department of Marine and Coastal Science Rutgers University bphorton@marine.rutgers.edu DRIVERS
Southern New Jersey and Delaware sea levels: Past, present and future Benjamin P. Horton Sea Level Research Department of Marine and Coastal Science Rutgers University bphorton@marine.rutgers.edu DRIVERS
POLAR EXPLORER EXPLORING SEA LEVEL RISE
 POLAR EXPLORER EXPLORING SEA i LEVEL RISE Developed by: Margie Turrin, mkt@ldeo.columbia.edu As a polar explorer you and your team will be collec@ng evidence of changes occurring throughout the world that
POLAR EXPLORER EXPLORING SEA i LEVEL RISE Developed by: Margie Turrin, mkt@ldeo.columbia.edu As a polar explorer you and your team will be collec@ng evidence of changes occurring throughout the world that
