The Bishop Tuff. Leah French COAS E105: Volcanoes of the Sierra Nevada
|
|
|
- Angelica Oliver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Bishop Tuff Leah French COAS E105: Volcanoes of the Sierra Nevada Photo by Leah French (Michael Hamburger and Adam Schau walk through the Bishop Tuff in the Owens River Gorge) Location: 37.6N, 118.8W California s Sierra Nevada is filled with many fascinating geological mysteries, more than one lifetime can reveal. Though each geological phenomena is within a very close proximity of each other, they are actually strikingly different from one another. Sierra Nevada is filled with rivers, sand dunes, basins, ranges, earthquakes, volcanoes, and the list goes on. However, one paper cannot begin to investigate all the geologic happenings and this paper will mainly focus only on the formation of the Long Valley Caldera and the subsequent tefra, named Bishop Tuff. The word caldera refers to a large basin, usually a circular or cirque shaped volcanic depression, with a diameter many times greater than that of the included volcanic vents (Dictionary of Geologic terms). The Long Valley Caldera is an elliptical
2 depression two to three km deep. It extends east to west about 32 km, and 17 km north to south with an area of 450 km squared. The western half of the caldera is forested with high relief, and on average reaches 2440 m. The eastern half differs much from the western half, with lower elevations averaging 2070 m, low relief, and covered primarily with grass and sage (Bailey). Bishop Tuff acquired its name from the small town Bishop, which is 50 km south east of the Long Valley Caldera. Tuff refers to rocks that are formed from compacted volcanic fragments, generally smaller than 4 millimeters in diameter (Dictionary of Geological terms). orth_america/california/long_valley.html Volcanic history within the Long Valley region initially began roughly 3.2 million years ago. One method that scientists use to obtain this information about the age and history of Bishop Tuff and other rock formations is through K-Ar dating. The K-Ar dating method requires a compositional measurement of both elemental potassium and the argon isotope in the same sample (Bailey). Most samples were from outcrops in the Long Valley region and had to be tested for purity before use.
3 While the obsidian was crushed between 2 and 4 mm before testing, the basalt and andesite samples were examined in small sections to make sure that the rock samples were homogeneous. Large amounts of basalt and andesite inclusions found in postsubsidence intracaldera rocks support the common idea that trachybasalt and trachyandesite lavas dominated the early igneous formations in this area. Basalt from an Old Mammoth mine and andesite from San Joaquin ridge both dated back to 3.1 million years ago (Bailey). However, these igneous formations are not directly related to the Long Valley magma chamber, but conceivably signify an early part of the volcanic cycle. The first volcanic rocks that can be traced back to the Long Valley magma chamber were the ryholites of Glass Mountain. The vents of Glass Mountain are arranged parallel to the Long Valley magma chamber which suggest that the rhyolites were construed from the Long Valley magma chamber through caldera ring fractures. The ring fractures related to the Glass Mountain are the earliest detected in the Long Valley Caldera. Approximately 730,000 years ago the catastrophic rhyolitic eruption of Bishop Tuff produced an unimaginable amount of ash and tefra, which made up 80% of the total erupted rhyolitic magma throughout the last 2.1 million years (Wilson and Hildreth). The Long Valley Caldera eruption had a force 2,000 times greater then Mt. Saint Helen s eruption. Initially the extremely powerful Pilinian eruption was coming from a single vent. However, after only 20% of the total magma had erupted, the roof of the volcano could no longer support itself and it collapsed to produce a caldera. While the caldera collapsed and subsided, it produced several ring fractures, which allowed Bishop Tuff to surface in enormous volumes. It forced 150 cubic miles of rhyolitic magma to the surface in the form of Plinian ash columns as well as air falls and ash flows.
4 Photo by Leah French: An Example of an actual Bishop Tuff ash fall deposit. The arrangement of Bishop Tuff occurred in a very short amount of time, most likely within a couple of hours or days (Hildtreth and Mahood). Many of the ring-fault vents that were active during the eruption were thought to be fissures with openings hundreds of meters wide. Such large openings caused a colossal discharge rate of Bishop Tuff. Many of the ring-fault fissures collapsed from no structural support immediately after the initial Bishop Tuff erupted, trapping the remaining Bishop Tuff underground. This explains why two-thirds of the magma never erupted and stayed within the caldera. Inside the caldera Bishop Tuff was discovered to be over 1000 meters thick with an estimated volume of 350 km cubed. The vents were then buried within the caldera s perimeter under layers of caldera fill and Bishop Tuff making it difficult to trace any fault lines. However, one fault along the east wall of the caldera can still be traced as far as 12 km and has a maximum displacement of 250 m (Bailey).
5 Spewing from these enormous vents, the Bishop Tuff spread out radially and the volume of magma projected from the Long Valley Caldera is estimated to be some where around 600 km cubed. The ash covered an area between km squared. Some Bishop Tuff traveled down wind in Plinian ash clouds, thousands of km as far as Kansas and Nebraska. Temperatures of the erupted initial ash falls were estimated at 745 degrees Celsius and under less than 2 kbar of pressure. The initial ash flow eruption temperature is estimated at 800 degrees Celsius under 3 kbar of pressure. The roof of the magma chamber was 6 km below the surface and after the initial eruption the last ash falls were coming from a depth of 10 km. This means that the caldera roof collapsed approximately 3 km (Bailey). K-Ar dating has shown Bishop Tuff samples that range from million years.
6 This information correlates with the interpretation that it took no longer than a few centuries for the Bishop Tuff ash flow to be placed in its current position (Bailey). Water filled the Long Valley depression and formed a Pleistocene Long Valley Lake. The lake filled quickly when the normal runoff from the Sierras was greatly increased due to the hot blanket of Bishop Tuff covering and melting the glaciers more rapidly. By studying the terraces on the east wall of the caldera, one can conclude that the level of the lake rose to at least 2,320 m (Bailey). This lake occupied the Long Valley Caldera for most of its history, and it started draining when the resurgent dome began to uplift the west central part of the caldera floor. Upward pressure caused this uplift due to the intrusion of molten rock into the magma chamber underneath the caldera floor. The resurgent dome pushed upward within 100,000 years or less of the caldera-forming eruption 730,000 years ago. Layers of lava flows, tephra, and pyroclastic flows make up the composition of the resurgent dome. The volcanic tephra was erupted onto the caldera floor soon after the caldera formed. The dome, 10 km in diameter, consisted of 500 m of fault-bounded blocks.
7 The resurgent dome was an island in the caldera lake for most of its history. As the resurgent dome grew, the lake s waters climbed too high for the caldera walls to contain, and the water overflowed at the southeast rim. The water cut into the nonwelded Bishop Tuff until it reached welded Bishop Tuff where the water was temporarily stabilized. The lake eventually drained fully about 0.1 million years ago (Bailey). Volcanic activity persisted almost immediately after the eruption and subsidence of the Long Valley Caldera. Crystal-poor rhyolite tuffs and domes accumulated on the caldera s floor rose to at least 500 m (Bailey). These rhyolite tuffs contained great amounts of Bishop Tuff inclusions and a few fragments of granite and metamorphic rock, Indicating that all of these rock types must be within the cauldron block. These rocks did not show ripple marks, however, they are believed to have at least partly formed in the caldera lake. A minimum of 12 vents near the center of the caldera erupted in a span of
8 no more than 100,000 years, and could have occurred within 40,000 years after the Bishop Tuff eruption. These vents produced what is known as the early rhyolites. Additional vents were most likely buried in the caldera itself. The youngest volcanic formations of the Long Valley Caldera are within the Inyo Crater chain. Photo by R. Forrest Hopson The Inyo Crater chain consists of a line of domes and craters 10 km long. The Inyo domes consist of five rhyolitic to rhyodacitic lava domes (Bailey). The three youngest domes, Obsidian dome, Glass Creek dome, and Deadman Creek dome, are less than 720 years old and erupted within a few years or even months of each other. These young domes are of significance because the lava is heterogeneous, meaning that the domes consist of two distinctly different rocks. One type is a light, coarsely porphyrtic rock that tends to be pumiceous, and the second is dark rhyolitic obsidian. The composition of the Inyo dome rocks resemble that of the magma bodies of the Long Valley Caldera and the Mono craters. This represents a possibility that a mixing of magmas occurred before eruption through a connecting fissure (Bailey).
9 The Inyo craters at the south end of the chain were possibly caused by the rise of rhyodacitic magma, similar to Bishop Tuff, and caused the waters to turn to steam (Bailey). The craters could be as young as 550 year old, which leads to the conclusion that the Long Valley magma chamber possibly had remaining magma close to the surface as recent as 550 years ago. Photo by Leah French: South Inyo Crater Outside the caldera, the Owens River has cut a deep gorge in the Bishop tuff and revealed some interesting formations. The Bishop Tuff formed columnar-joints as well as rosettes or radial columnar jointing which could have formed in many different ways.
10 Photo By Leah French: Owens River George with rosettes in upper right corner Some of the joints are effects of cooling. Joints increase the surface area of the hot tuff, which allows heat to escape more rapidly and the in return the tuff cools at a faster rate. Some joints, called late joins, are effects of stress. Once one crack forms in the tuff it produces more stress on the rest of the tuff, causing another crack. Soon these cracks become deep and form joints. Steam vents or fumarolic activity was yet another reason for these particular joints to develop in the Owen River Gorge. Fumarolic fractures show strong preferred orientation, which differs from late joint, and they are also deeper and longer than cooling joints. The history of fumarolic joints is very complex and hard to understand. It is believed that the Bishop Tuff went through two different phases. One phase included the welding and cooling of the tuff, in between the phases was a dormant period, and the other phase integrated the fumarolic activity. These phases partly
11 contributed to the fact that Bishop Tuff in the Owen Gorge is composed of two separate parts. The lower part consists of strongly welded tuff, which has less jointing, and the upper part consists of nonwelded tuff. The lower, welded region of the Bishop Tuff contains less jointing partly because it erupted with lower energy and did not mix well with the atmosphere, and was able to cool at a slower rate. The upper section of the Bishop Tuff contains columns that range from three to five feet, and the oriented vertically as well as horizontally. It is thought that these columns are arranged along the isothermic (areas with the same temperature) heat line. Bishop Tuff is an excellent clock which helps to determine other geologic happenings. Geologists can identify the very distinct layer of Bishop Tuff in the crust with the knowledge that it occurred around 730,000 years ago. In one instance, a core of the dry Owen Lake riverbed was taken and the Bishop Tuff was identified. It was a great discovery, which allowed geologists to determine that all the samples taken from the core above the Bishop Tuff occurred before 730,000 years ago. Subsequently the samples taken beneath the Bishop Tuff were older than 730,000 years old. This discovery allowed scientists to understand the region of the Owens River to a much higher degree. The Long Valley Caldera was created by a massively powerful eruption, which saturated the entire Long Valley region with a huge layer of tefra. The intricate formations that we can see today show the amazing history that this region has endured. Geologists who study the details of Bishop Tuff and the formation of the Long Valley Caldera can use their knowledge and relate it to other geologic happenings around the globe.
12 Works Cited Bailey, Roy A. Geologic Map OF Long Valley Caldera, Mono-Inyo Creaters Volcanic Chain, and Vicinity, Easter California. Crossdating- The Basic Principal of Dendrochronology May 2002 Dictionary of Geological Terms. Anchor Press/Doubleday Garden City, New York Hildresth, Wes and Mahood, Gail A. Ring-Fracture eruption of the Bishop Tuff. Geological Society of American Bulletin, v. 97, p , 5 fig, April Long Valley Caldera and Mono-Inyo Craters Volcanic Field, California html. 17 Dec 2002 Sheridan, Michael F. Fumarolic Mounds and Ridges of the Bishop Tuff, California. Arizona State University, Tempe, Arizona. United States Geological Survey, Long Valley Observatory. Photos of the Resurgent Dome, Long Valley Caldera Dec 2002 Wilson, Colin J.N. and Hildreth, Wes. The Bishop Tuff. The Journal of Geology, 1997, v.105 p
From Punchbowl to Panum: Long Valley Volcanism and the Mono-Inyo Crater Chain
 From Punchbowl to Panum: Leslie Schaffer E105 2002 Final Paper Long Valley Volcanism and the Mono-Inyo Crater Chain Figure 1. After a sequence of earthquakes during the late 1970 s to the early 1980 s
From Punchbowl to Panum: Leslie Schaffer E105 2002 Final Paper Long Valley Volcanism and the Mono-Inyo Crater Chain Figure 1. After a sequence of earthquakes during the late 1970 s to the early 1980 s
History of the Long Valley Caldera Abstract The history of the Long Valley Caldera is an active one that began 280 ma years before
 Alicia Pardoski 1 History of the Long Valley Caldera Abstract The history of the Long Valley Caldera is an active one that began 280 ma years before present with the building and eruption of Glass Mountain.
Alicia Pardoski 1 History of the Long Valley Caldera Abstract The history of the Long Valley Caldera is an active one that began 280 ma years before present with the building and eruption of Glass Mountain.
The Bishop Tuff : An Overview of the World s Roughest and Toughest Volcanic Landform
 The Bishop Tuff : An Overview of the World s Roughest and Toughest Volcanic Landform Charity J. Southworth Indiana University, 2012 Abstract The Bishop Tuff is a welded tuff that was created 760,000 years
The Bishop Tuff : An Overview of the World s Roughest and Toughest Volcanic Landform Charity J. Southworth Indiana University, 2012 Abstract The Bishop Tuff is a welded tuff that was created 760,000 years
The Bishop Tuff Eruption. This paper provides a general overview of the Bishop Tuff eruption, one of
 Max Price G190 Final The Bishop Tuff Eruption Abstract This paper provides a general overview of the Bishop Tuff eruption, one of the most prominent volcanic eruptions in recent history. Introduced with
Max Price G190 Final The Bishop Tuff Eruption Abstract This paper provides a general overview of the Bishop Tuff eruption, one of the most prominent volcanic eruptions in recent history. Introduced with
The Mono-Inyo Crater/Dome Chain of Long Valley Caldera/ Mono Basin Region of the Eastern Sierra Nevada. By Cassie Geraghty
 The Mono-Inyo Crater/Dome Chain of Long Valley Caldera/ Mono Basin Region of the Eastern Sierra Nevada By Cassie Geraghty Abstract The Mono-Inyo Crater/Dome Chain contains some of the youngest, of many,
The Mono-Inyo Crater/Dome Chain of Long Valley Caldera/ Mono Basin Region of the Eastern Sierra Nevada By Cassie Geraghty Abstract The Mono-Inyo Crater/Dome Chain contains some of the youngest, of many,
L wave Lahar Lava Magma
 Very large collapsed volcanic crater, often containing a lake eg. Lake Taupo The process which provides the force to move the tectonic plates Innermost part of the Earth, made of a liquid outer core and
Very large collapsed volcanic crater, often containing a lake eg. Lake Taupo The process which provides the force to move the tectonic plates Innermost part of the Earth, made of a liquid outer core and
The Quaternary and Pliocene Yellowstone Plateau Volcanic Field of Wyoming, Idaho and Montana Robert L. Christenson, USGS PP 729-G
 The Quaternary and Pliocene Yellowstone Plateau Volcanic Field of Wyoming, Idaho and Montana Robert L. Christenson, USGS PP 729-G Three Volcanic Cycles of Yellowstone Three extraordinarily large explosive
The Quaternary and Pliocene Yellowstone Plateau Volcanic Field of Wyoming, Idaho and Montana Robert L. Christenson, USGS PP 729-G Three Volcanic Cycles of Yellowstone Three extraordinarily large explosive
Igneous Rock Notes. Page #:
 Page #: Igneous Rock Notes Magma and lava form very different types of igneous rocks. Igneous rocks form from molten rock, but where does molten rock come from? The temperature inside Earth with depth.
Page #: Igneous Rock Notes Magma and lava form very different types of igneous rocks. Igneous rocks form from molten rock, but where does molten rock come from? The temperature inside Earth with depth.
The Devils Postpile and its Unusual Surroundings. Shannon B. Carpenter A May 3, 2001
 The Devils Postpile and its Unusual Surroundings Shannon B. Carpenter A25584605 May 3, 2001 Abstract: The Devils Postpile is located in the eastern Sierra Nevada region just a few miles southwest of the
The Devils Postpile and its Unusual Surroundings Shannon B. Carpenter A25584605 May 3, 2001 Abstract: The Devils Postpile is located in the eastern Sierra Nevada region just a few miles southwest of the
Volcano: a weak spot in the crust where molten material or magma comes to the surface
 Chapter 7 Volcano: a weak spot in the crust where molten material or magma comes to the surface Magma: a molten mixture of rock forming substances, gases and H 2 O from the mantle Volcanic Belts: Form
Chapter 7 Volcano: a weak spot in the crust where molten material or magma comes to the surface Magma: a molten mixture of rock forming substances, gases and H 2 O from the mantle Volcanic Belts: Form
Bishop Tuff and the Long Valley Caldera. Abstract: The formation of the Bishop Tuff ash deposit, and the eruption that was its
 Rachael Fleck Bishop Tuff and the Long Valley Caldera Abstract: The formation of the Bishop Tuff ash deposit, and the eruption that was its predecessor occurred nearly 760,000 thousand years ago. This
Rachael Fleck Bishop Tuff and the Long Valley Caldera Abstract: The formation of the Bishop Tuff ash deposit, and the eruption that was its predecessor occurred nearly 760,000 thousand years ago. This
Effects of Eruptions. Most active in the world Kilauea, Hawaii.
 Inside of Old Smokey, All covered with snow, Lurk tons of hot magma, Getting ready to blow, Objectives: From deep in the chamber, Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Up a vent to the top, Describe
Inside of Old Smokey, All covered with snow, Lurk tons of hot magma, Getting ready to blow, Objectives: From deep in the chamber, Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Up a vent to the top, Describe
Visualizing Earth Science. Chapter Overview. Volcanoes and Eruption Types. By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner. Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other
 Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
Part A GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET VOLCANOES. Name
 GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET VOLCANOES Name Part A 1. The rough, jumbled blocky or jagged surface of a lava flow is called a. pahoehoe b. lahar c. aa d. phreatic 2. The Cascade volcanoes like Mt. St.
GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET VOLCANOES Name Part A 1. The rough, jumbled blocky or jagged surface of a lava flow is called a. pahoehoe b. lahar c. aa d. phreatic 2. The Cascade volcanoes like Mt. St.
Objectives: Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Describe conditions that cause volcanoes. Describe the relationship between volcanoes and Earth
 Objectives: Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Describe conditions that cause volcanoes. Describe the relationship between volcanoes and Earth s moving plates. Inside of Old Smokey, All covered
Objectives: Describe how volcanoes can affect people. Describe conditions that cause volcanoes. Describe the relationship between volcanoes and Earth s moving plates. Inside of Old Smokey, All covered
Igneous Rocks. Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members:
 Igneous Rocks Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members: Types of Magma Basaltic, Basic or Mafic very hot (900-1200 C) very fluid
Igneous Rocks Magma molten rock material consisting of liquid rock and crystals. A variety exists, but here are the end members: Types of Magma Basaltic, Basic or Mafic very hot (900-1200 C) very fluid
Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire
 Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire On July 16, 1990, a large earthquake struck Luzon, an island in the Philippines. The earthquake devastated cities for hundreds of
Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire Mount Pinatubo and the Ring of Fire On July 16, 1990, a large earthquake struck Luzon, an island in the Philippines. The earthquake devastated cities for hundreds of
Magma. Objectives. Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary.
 Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Calderas. Myojin Knoll Submarine Caldera m. 500 m. 5 km. (after Kennedy and Stix, 2003)
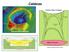 Calderas Myojin Knoll Submarine Caldera 1400 m 500 m 5 km (after Kennedy and Stix, 2003) Definition Outline Relationships to Eruption Volume and VEI Structural Components Types Caldera Genetic Models and
Calderas Myojin Knoll Submarine Caldera 1400 m 500 m 5 km (after Kennedy and Stix, 2003) Definition Outline Relationships to Eruption Volume and VEI Structural Components Types Caldera Genetic Models and
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 2017-2016 Chapter (4) Volcanoes Chapter 4: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity cataclysmic relating to or denoting a violent natural even Eventually the entire
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 2017-2016 Chapter (4) Volcanoes Chapter 4: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity cataclysmic relating to or denoting a violent natural even Eventually the entire
GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca:
 Name: Date: GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca: SiO 2 silicon dioxide. This is quartz when it crystallizes.
Name: Date: GEOL1 Physical Geology Laboratory Manual College of the Redwoods Lesson Five: Volcanoes Background Reading: Volcanoes Volcanic Terms: Silca: SiO 2 silicon dioxide. This is quartz when it crystallizes.
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanic Eruptions. light in color is called a. felsic. b. oceanic. c. mantle. d. mafic. dark in color is called
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanic Eruptions 1. Lava provides an opportunity for scientists to study a. the nature of Earth s inner core. b. the nature of Earth s tectonic plates. c. temperatures
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanic Eruptions 1. Lava provides an opportunity for scientists to study a. the nature of Earth s inner core. b. the nature of Earth s tectonic plates. c. temperatures
3.2 Notes: Volcanoes Form as Molten Rock Erupts
 3.2 Notes: Volcanoes Form as Molten Rock Erupts Think about What happens when a volcano erupts? Volcanoes erupt many types of material Earth s thin outer layer is, but most of Earth is extremely hot rock
3.2 Notes: Volcanoes Form as Molten Rock Erupts Think about What happens when a volcano erupts? Volcanoes erupt many types of material Earth s thin outer layer is, but most of Earth is extremely hot rock
Section 5. Rock Units and Your Community. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 5 Rock Units and Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Recognize that rocks are arranged in Earth s crust as well-defined
Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 5 Rock Units and Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Recognize that rocks are arranged in Earth s crust as well-defined
Overview of Ch. 4. I. The nature of volcanic eruptions 9/19/2011. Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5
 Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
A Volcano is An opening in Earth s crust through
 Volcanoes A Volcano is An opening in Earth s crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt. Also, the landform that develops around this opening. Kinds of Eruptions Geologists classify volcanic
Volcanoes A Volcano is An opening in Earth s crust through which molten rock, gases, and ash erupt. Also, the landform that develops around this opening. Kinds of Eruptions Geologists classify volcanic
TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology
 Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 volcano sample test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Volcanic belts form along a. islands in the Pacific Ocean. b. North American
volcano sample test Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Volcanic belts form along a. islands in the Pacific Ocean. b. North American
A physical feature of the Earth s surface
 Earth s Landforms A physical feature of the Earth s surface A physical feature of the Earth s surface LANDFORM Highest of Earth s physical features Highest of Earth s physical features MOUNTAIN Low area
Earth s Landforms A physical feature of the Earth s surface A physical feature of the Earth s surface LANDFORM Highest of Earth s physical features Highest of Earth s physical features MOUNTAIN Low area
Magma. Objectives. Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary.
 Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Unit 4 Lesson 4 Volcanoes. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Magma Magic What is a volcano? A volcano is any place where gas, ash, or melted rock come out of the ground. Many volcanoes are dormant, meaning an eruption has not occurred in a long period of time. What
Magma Magic What is a volcano? A volcano is any place where gas, ash, or melted rock come out of the ground. Many volcanoes are dormant, meaning an eruption has not occurred in a long period of time. What
Plate Tectonics. By Destiny, Jarrek, Kaidence, and Autumn
 Plate Tectonics By Destiny, Jarrek, Kaidence, and Autumn .The Denali Fault and San Andreas Fault - The San Andreas Fault is a continental transform fault that extends roughly 1300 km (810 miles) through
Plate Tectonics By Destiny, Jarrek, Kaidence, and Autumn .The Denali Fault and San Andreas Fault - The San Andreas Fault is a continental transform fault that extends roughly 1300 km (810 miles) through
The domes and craters of the Mono-Inyo volcanic chain are a result of eruptions
 Madeline Lewis G190 Summer 2013 FORMATION OF THE MONO-INYO VOLCANIC CHAIN ABSTRACT The domes and craters of the Mono-Inyo volcanic chain are a result of eruptions stemming from different magma intrusions.
Madeline Lewis G190 Summer 2013 FORMATION OF THE MONO-INYO VOLCANIC CHAIN ABSTRACT The domes and craters of the Mono-Inyo volcanic chain are a result of eruptions stemming from different magma intrusions.
Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway
 Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway The Earth is more than a giant ball made up of dirt, rocks, and minerals. The Earth may look like a giant ball from when looking at it from
Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway The Earth is more than a giant ball made up of dirt, rocks, and minerals. The Earth may look like a giant ball from when looking at it from
Magma vs. Lava. Molten rock below Earth s surface is called magma. The magma that reaches the surface and erupts out of a volcano is called lava.
 CH. 10.1 Be able to Explain the factors that determine the type of volcanic eruption. List the 3 types of volcanoes Describe the features of a volcano. What is a Volcano? Volcanoes are sites where molten
CH. 10.1 Be able to Explain the factors that determine the type of volcanic eruption. List the 3 types of volcanoes Describe the features of a volcano. What is a Volcano? Volcanoes are sites where molten
Plates & Boundaries The earth's continents are constantly moving due to the motions of the tectonic plates.
 Plates & Boundaries The earth's continents are constantly moving due to the motions of the tectonic plates. As you can see, some of the plates contain continents and others are mostly under the ocean.
Plates & Boundaries The earth's continents are constantly moving due to the motions of the tectonic plates. As you can see, some of the plates contain continents and others are mostly under the ocean.
A bowl shaped depression formed by the collapse of a volcano is called a. Magma that has left the vent of a volcano is known as. Lava.
 Magma that has left the vent of a volcano is known as Lava A bowl shaped depression formed by the collapse of a volcano is called a Caldera This can form in a caldera when magma starts to come back up
Magma that has left the vent of a volcano is known as Lava A bowl shaped depression formed by the collapse of a volcano is called a Caldera This can form in a caldera when magma starts to come back up
Section 1: Earth s Interior and Plate Tectonics Section 2: Earthquakes and Volcanoes Section 3: Minerals and Rocks Section 4: Weathering and Erosion
 Section 1: Earth s Interior and Plate Tectonics Section 2: Earthquakes and Volcanoes Section 3: Minerals and Rocks Section 4: Weathering and Erosion Key Terms Crust Mantle Core Lithosphere Plate Tectonics
Section 1: Earth s Interior and Plate Tectonics Section 2: Earthquakes and Volcanoes Section 3: Minerals and Rocks Section 4: Weathering and Erosion Key Terms Crust Mantle Core Lithosphere Plate Tectonics
Volcanoes. Table of Contents Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Landforms
 Volcanoes Table of Contents Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Landforms What is a volcano? cone Conduit Or Pipe vent Side vent Central vent Crater A volcano is a vent or 'chimney'
Volcanoes Table of Contents Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics Volcanic Eruptions Volcanic Landforms What is a volcano? cone Conduit Or Pipe vent Side vent Central vent Crater A volcano is a vent or 'chimney'
Rocks. Types of Rocks
 Rocks Rocks are the most common material on Earth. They are naturally occurring aggregates of one or more minerals. 1 Igneous rocks, Types of Rocks Sedimentary rocks and Metamorphic rocks. 2 1 3 4 2 IGNEOUS
Rocks Rocks are the most common material on Earth. They are naturally occurring aggregates of one or more minerals. 1 Igneous rocks, Types of Rocks Sedimentary rocks and Metamorphic rocks. 2 1 3 4 2 IGNEOUS
Earth has more than 600 active volcanoes. An active volcano is one that has erupted within recorded history.
 Volcanoes A volcano is an opening in Earth s surface that erupts gases, ash, and lava. These materials pile up in layers around the opening, forming volcanic mountains. Earth has more than 600 active volcanoes.
Volcanoes A volcano is an opening in Earth s surface that erupts gases, ash, and lava. These materials pile up in layers around the opening, forming volcanic mountains. Earth has more than 600 active volcanoes.
Calc-alkaline Volcanic Rocks. Calc-alkali Volcanics. Fabric. Petrography. Compositional Classification. Petrography. Processes.
 Calc-alkaline Volcanic Rocks Calc-alkali Volcanics Winter Chapters 16 & 17 Petrography Processes Field relations Volcanic arcs Petrogenesis Petrography Fabric Classification Alteration Fabric Aphanitic
Calc-alkaline Volcanic Rocks Calc-alkali Volcanics Winter Chapters 16 & 17 Petrography Processes Field relations Volcanic arcs Petrogenesis Petrography Fabric Classification Alteration Fabric Aphanitic
SCIENCE IN THE NEWS Plate Tectonics
 SCIENCE IN THE NEWS Plate Tectonics From VOA Learning English, this is Science in the News. I m Anna Matteo. And I m Christopher Cruise. Scientists who study the Earth tell us the continents and ocean
SCIENCE IN THE NEWS Plate Tectonics From VOA Learning English, this is Science in the News. I m Anna Matteo. And I m Christopher Cruise. Scientists who study the Earth tell us the continents and ocean
Name: Geology Study Guide Date:
 Name: Geology Study Guide Date: Vocabulary You must know the following terms and definitions: 1. bedrock- a solid rock mass that is undisturbed by environmental conditions on the Earth s crust 2. Continental
Name: Geology Study Guide Date: Vocabulary You must know the following terms and definitions: 1. bedrock- a solid rock mass that is undisturbed by environmental conditions on the Earth s crust 2. Continental
WHAT IS A MAGMA. Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth.
 UNIT - 8 VOLCANOES WHAT IS A MAGMA Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth. In some instances, it solidifies within the crust to form plutonic
UNIT - 8 VOLCANOES WHAT IS A MAGMA Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth. In some instances, it solidifies within the crust to form plutonic
Chapter 7: Volcanoes 8/18/2014. Section 1 (Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics) 8 th Grade. Ring of Fire
 Section 1 (Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics) Chapter 7: Volcanoes 8 th Grade Ring of Fire a major belt of es that rims the Pacific Ocean Volcanic belts form along the boundaries of Earth s plates as they
Section 1 (Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics) Chapter 7: Volcanoes 8 th Grade Ring of Fire a major belt of es that rims the Pacific Ocean Volcanic belts form along the boundaries of Earth s plates as they
Introduction to volcanoes. Volcano: an opening in the earth s surface through which lava, hot gases, and rock fragments erupt
 Introduction to volcanoes Volcano: an opening in the earth s surface through which lava, hot gases, and rock fragments erupt Origin of Volcanoes 1. Magma 50-100 miles below the earth s surface slowly begins
Introduction to volcanoes Volcano: an opening in the earth s surface through which lava, hot gases, and rock fragments erupt Origin of Volcanoes 1. Magma 50-100 miles below the earth s surface slowly begins
Mt St Helens was know to have entered into active periods that lasted from years once every years over the last 500 years, (Figure 5).
 Lecture #8 notes; Geology 3950, Spring 2006; CR Stern May 1980 eruption of Mt St Helens volcano (text pages 183-192 in the 4 th edition and 206-222 in the 5 th edition) Mt St Helens in southwest Washington
Lecture #8 notes; Geology 3950, Spring 2006; CR Stern May 1980 eruption of Mt St Helens volcano (text pages 183-192 in the 4 th edition and 206-222 in the 5 th edition) Mt St Helens in southwest Washington
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa
 Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Fires Within: Igneous Activity Foundations, 6e - Chapter 7 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The nature of volcanic eruptions Characteristics
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Fires Within: Igneous Activity Foundations, 6e - Chapter 7 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The nature of volcanic eruptions Characteristics
When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere.
 When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere. A volcano is a mountain that forms when magma reaches the
When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere. A volcano is a mountain that forms when magma reaches the
Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere. Volcanic Activity
 Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere Volcanic Activity Lesson 3 Volcanoes, Part 1 Think About It What happens when you shake a can of soda and then open it? Focus Question How does the composition of magma
Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere Volcanic Activity Lesson 3 Volcanoes, Part 1 Think About It What happens when you shake a can of soda and then open it? Focus Question How does the composition of magma
4.1 Act 2 Rock Cycle: Interactive Website Worksheet
 Name Date Core 4.1 Act 2 Rock Cycle: Interactive Website Worksheet Directions: Go to the website Interactives Rock Cycle. http://www.learner.org/interactives/rockcycle/index.html Follow the directions
Name Date Core 4.1 Act 2 Rock Cycle: Interactive Website Worksheet Directions: Go to the website Interactives Rock Cycle. http://www.learner.org/interactives/rockcycle/index.html Follow the directions
Volcano Vocabulary ROCK CYCLE. Igneous REMELTED REMELTED BURIED BURIED HEAT ERODED DEPOSITED. Metamorphic Sedimentary ERODED, TRANSPORTED DEPOSITED
 Volcano Vocabulary VOLCANISM VENT CRATER CALDERA QUIET ERUPTION EXPLOSIVE ERUPTION PYROCLASTIC DEBRIS CINDER CONE SHIELD VOLCANO COMPOSITE VOLCANO STRATO VOLCANO ACTIVE DORMANT EXTINCT INTRUSION DIKE SILL
Volcano Vocabulary VOLCANISM VENT CRATER CALDERA QUIET ERUPTION EXPLOSIVE ERUPTION PYROCLASTIC DEBRIS CINDER CONE SHIELD VOLCANO COMPOSITE VOLCANO STRATO VOLCANO ACTIVE DORMANT EXTINCT INTRUSION DIKE SILL
Pyroclastic Flows. Lesson 6
 Pyroclastic Flows Lesson 6 P yroclastic flows are one of the most dangerous natural events that occur on our planet. They can at hurricane speeds down the slopes of a mountain, destroying everything in
Pyroclastic Flows Lesson 6 P yroclastic flows are one of the most dangerous natural events that occur on our planet. They can at hurricane speeds down the slopes of a mountain, destroying everything in
The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks
 The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks Igneous rocks form as molten magma or lava cools and solidifies. Magma is completely or partly molten
The Rock Cycle The Rock Cycle illustrates the origin of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks Igneous rocks form as molten magma or lava cools and solidifies. Magma is completely or partly molten
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12 Volcanoes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Plate tectonics explains the global pattern of volcanism. Key Figure 12.20 (page
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12 Volcanoes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Plate tectonics explains the global pattern of volcanism. Key Figure 12.20 (page
Domes of the Mono-Inyo Craters Range. The Mono-Inyo Craters are a chain of volcanic domes, lava flows, and craters in the
 Steven Barajas G 188/190 Michael Hamburger June 12 Domes of the Mono-Inyo Craters Range Abstract The Mono-Inyo Craters are a chain of volcanic domes, lava flows, and craters in the western United States.
Steven Barajas G 188/190 Michael Hamburger June 12 Domes of the Mono-Inyo Craters Range Abstract The Mono-Inyo Craters are a chain of volcanic domes, lava flows, and craters in the western United States.
Part I. Mt. St. Helens
 Name: Date: This contains material adapted from Richard Abbot (Appalachian State University, Department of Geology) and from the USGS Volcanoes! 1997 Teacher packet. Part I. Mt. St. Helens In the illustration
Name: Date: This contains material adapted from Richard Abbot (Appalachian State University, Department of Geology) and from the USGS Volcanoes! 1997 Teacher packet. Part I. Mt. St. Helens In the illustration
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 10 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Factors Affecting Eruptions Factors that determine the violence of an eruption
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 10 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Factors Affecting Eruptions Factors that determine the violence of an eruption
Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity. Aka Volcano Under the City
 Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity Aka Volcano Under the City 18.1 Magma Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Temperature and pressure increase
Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity Aka Volcano Under the City 18.1 Magma Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Temperature and pressure increase
The Little Colorado River
 The Little Colorado River The Little Colorado River Junction of the Little Colorado River and the Colorado Grand Falls of the Little Colorado River The relief/topo map at the right shows the junction of
The Little Colorado River The Little Colorado River Junction of the Little Colorado River and the Colorado Grand Falls of the Little Colorado River The relief/topo map at the right shows the junction of
Tessellations in the Eastern Sierra. In the Eastern Sierra Nevada, landforms formed by fracture tessellations occur in both
 Elizabeth Davis Michael Hamburger, John Rupp, Katie Nold Geol-G188 12 Jun 2012 Tessellations in the Eastern Sierra Abstract In the Eastern Sierra Nevada, landforms formed by fracture tessellations occur
Elizabeth Davis Michael Hamburger, John Rupp, Katie Nold Geol-G188 12 Jun 2012 Tessellations in the Eastern Sierra Abstract In the Eastern Sierra Nevada, landforms formed by fracture tessellations occur
Volcanic Hazards and Activity in the Sierra Nevada s
 Volcanic Hazards and Activity in the Sierra Nevada s Chris Bottorff Long Valley may be the ideal setting of the Wild West, outfitting many with horse back riding, fishing, skiing, rock climbing, and hot
Volcanic Hazards and Activity in the Sierra Nevada s Chris Bottorff Long Valley may be the ideal setting of the Wild West, outfitting many with horse back riding, fishing, skiing, rock climbing, and hot
Orting Community College Proposal
 Orting Community College Proposal Cedric, Celina, Francine, Sarah, Samuel GEO CORP Located in Washington, 42 miles south of Seattle. Situated between two rivers on fertile plains. Built on lahar deposits.
Orting Community College Proposal Cedric, Celina, Francine, Sarah, Samuel GEO CORP Located in Washington, 42 miles south of Seattle. Situated between two rivers on fertile plains. Built on lahar deposits.
1. In the block diagram shown here, which is the oldest rock unit?
 Pre/Post GCI Name (print) 1. In the block diagram shown here, which is the oldest rock unit? 2. Referring to the same diagram as the previous question, which of the labeled rock units is the youngest?
Pre/Post GCI Name (print) 1. In the block diagram shown here, which is the oldest rock unit? 2. Referring to the same diagram as the previous question, which of the labeled rock units is the youngest?
V o l c a n o es. Part I Composition. Types of deposits. Types of volcanoes Distribution
 V o l c a n o es Part I Composition Types of deposits Types of volcanoes Distribution Volcano: A mound of material that is extruded to the Earth s surface from a vent that is connected to a magma chamber
V o l c a n o es Part I Composition Types of deposits Types of volcanoes Distribution Volcano: A mound of material that is extruded to the Earth s surface from a vent that is connected to a magma chamber
General Geology Lab #7: Geologic Time & Relative Dating
 General Geology 89.101 Name: General Geology Lab #7: Geologic Time & Relative Dating Purpose: To use relative dating techniques to interpret geological cross sections. Procedure: Today we will be interpreting
General Geology 89.101 Name: General Geology Lab #7: Geologic Time & Relative Dating Purpose: To use relative dating techniques to interpret geological cross sections. Procedure: Today we will be interpreting
Rock Cycle Reader s Theater
 Rock Cycle Reader s Theater Characters Teacher1 Teacher 2 Student 1 Student 2 Student 3 Sedimentary Rock Crust Wind Water Ice Sediment 1 Sediment 2 Sediment 3 Metamorphic Rock The Rock Cycle Mantel Magma
Rock Cycle Reader s Theater Characters Teacher1 Teacher 2 Student 1 Student 2 Student 3 Sedimentary Rock Crust Wind Water Ice Sediment 1 Sediment 2 Sediment 3 Metamorphic Rock The Rock Cycle Mantel Magma
Chapter 18. Volcanism
 Chapter 18 Volcanism Ring of fire contains 66% of world s active volcanoes Convergent : Divergent: Icelandic Eruption Mount Etna Different Kinds of eruptions: Volcanic activity is controlled by plate tectonics,
Chapter 18 Volcanism Ring of fire contains 66% of world s active volcanoes Convergent : Divergent: Icelandic Eruption Mount Etna Different Kinds of eruptions: Volcanic activity is controlled by plate tectonics,
The Geology of the Mono Basin: A Natural Time Capsule by Stephanie Estes
 1 The Geology of the Mono Basin: A Natural Time Capsule by Stephanie Estes The finest workers in stone are not copper or steel tools, but the gentle touches of air and water working at their leisure with
1 The Geology of the Mono Basin: A Natural Time Capsule by Stephanie Estes The finest workers in stone are not copper or steel tools, but the gentle touches of air and water working at their leisure with
TEACHER BACKGROUND KNOWEDGE. Minerals, Rocks and the Rock Cycle
 TEACHER BACKGROUND KNOWEDGE Minerals, Rocks and the Rock Cycle Core Concepts Rocks in the Earth s crust vary in their form and structure based on process that made them. The constant changing of the form
TEACHER BACKGROUND KNOWEDGE Minerals, Rocks and the Rock Cycle Core Concepts Rocks in the Earth s crust vary in their form and structure based on process that made them. The constant changing of the form
! Profile of Mauna Loa in Hawaii. Mauna Loa is one of five huge shield volcanoes that make up the island of Hawaii.
 - Shield Volcanoes - Low, rounded profiles; slope angles 2-10 ; composed of numerous flows of mafic composition and little explosive activity - Largest of all volcanoes! Shield volcanoes consist of numerous
- Shield Volcanoes - Low, rounded profiles; slope angles 2-10 ; composed of numerous flows of mafic composition and little explosive activity - Largest of all volcanoes! Shield volcanoes consist of numerous
Chapter Twelve: Earthquakes
 The Changing Earth Chapter Twelve: Earthquakes 12.1 Earthquakes 12.2 Volcanoes Investigation 12B Volcanoes How are volcanoes and plate boundaries related? 12.2 Looking inside a volcano A volcano is where
The Changing Earth Chapter Twelve: Earthquakes 12.1 Earthquakes 12.2 Volcanoes Investigation 12B Volcanoes How are volcanoes and plate boundaries related? 12.2 Looking inside a volcano A volcano is where
D) outer core B) 1300 C A) rigid mantle A) 2000 C B) density, temperature, and pressure increase D) stiffer mantle C) outer core
 1. In which area of Earth's interior is the pressure most likely to be 2.5 million atmospheres? A) asthenosphere B) stiffer mantle C) inner core D) outer core Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on
1. In which area of Earth's interior is the pressure most likely to be 2.5 million atmospheres? A) asthenosphere B) stiffer mantle C) inner core D) outer core Base your answers to questions 2 and 3 on
Volcanoes. Volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than the explosion of an atomic bomb.
 Ch. 13 Volcanoes Volcanoes Volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than the explosion of an atomic bomb. Many of these eruptions are caused by the movement of tectonic plates. Volcanism Volcanism-any activity
Ch. 13 Volcanoes Volcanoes Volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than the explosion of an atomic bomb. Many of these eruptions are caused by the movement of tectonic plates. Volcanism Volcanism-any activity
Plate Tectonics. Chapter 8
 Plate Tectonics Chapter 8 Vocabulary Crust Mantle Core Lithosphere Continental Drift Plate Tectonics Plate Boundary Fault What Are The Earth s Layers Made Of? Atmosphere: Contains nitrogen, oxygen, carbon
Plate Tectonics Chapter 8 Vocabulary Crust Mantle Core Lithosphere Continental Drift Plate Tectonics Plate Boundary Fault What Are The Earth s Layers Made Of? Atmosphere: Contains nitrogen, oxygen, carbon
Name: Answer Key Date: Period:
 Name: Answer Key Date: Period: Earth Science Final Exam Study Guide Ch 1: Mapping 1. On the global grid, the equator is at 0 degrees. Is the equator a line of longitude or latitude? Latitude 2. What type
Name: Answer Key Date: Period: Earth Science Final Exam Study Guide Ch 1: Mapping 1. On the global grid, the equator is at 0 degrees. Is the equator a line of longitude or latitude? Latitude 2. What type
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes
 Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
THE EARTH S SURFACE AND BELOW
 THE EARTH S SURFACE AND BELOW Name: Class: Directions: Match the words with the big ideas by writing the letter beside the idea. Use the same words in the short article below. Use key words and phrases
THE EARTH S SURFACE AND BELOW Name: Class: Directions: Match the words with the big ideas by writing the letter beside the idea. Use the same words in the short article below. Use key words and phrases
What is Inside a Volcano?
 Volcanoes What is Inside a Volcano? A magma chamber filled with molten rock deep underground that feeds the volcano Magma is released through vents during an eruption Types of Volcanic Eruptions Non-Explosive
Volcanoes What is Inside a Volcano? A magma chamber filled with molten rock deep underground that feeds the volcano Magma is released through vents during an eruption Types of Volcanic Eruptions Non-Explosive
Name Date Period. Rock Cycle Webquest
 Rock Cycle Webquest Activity # 1 Rock and the Rock Cycle a) Open Rock and the Rock Cycle. Read and fill in the blanks. All rock (except for meteorites) that is on Earth today is made of the stuff as the
Rock Cycle Webquest Activity # 1 Rock and the Rock Cycle a) Open Rock and the Rock Cycle. Read and fill in the blanks. All rock (except for meteorites) that is on Earth today is made of the stuff as the
What Do You See? Learning Outcomes Goals Learning Outcomes Think About It Identify classify In what kinds of environments do igneous rocks form?
 Section 2 Igneous Rocks and the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Identify and classify
Section 2 Igneous Rocks and the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Identify and classify
Volcanoes. 11/25/2013. Geology 15 Lecture 27 VOLCANO!
 Hazard Update Surprise POP Review Tsunami Activity 10 B Today s Material Volcanoes Volcanic Hazards Geology 15 Lecture 27 VOLCANO! http://motherboard.vice.com/blog/watch an erupting volcano create a newisland
Hazard Update Surprise POP Review Tsunami Activity 10 B Today s Material Volcanoes Volcanic Hazards Geology 15 Lecture 27 VOLCANO! http://motherboard.vice.com/blog/watch an erupting volcano create a newisland
GEOL 10: Environmental Geology Activity 9: Topographic Maps and Mt. St. Helens. Name: Date:
 GEOL 10: Environmental Geology Activity 9: Topographic Maps and Mt. St. Helens Name: Date: A topographic map is a two dimensional (flat) representation (model) of a three dimensional land surface (landscape).
GEOL 10: Environmental Geology Activity 9: Topographic Maps and Mt. St. Helens Name: Date: A topographic map is a two dimensional (flat) representation (model) of a three dimensional land surface (landscape).
Plate Tectonics. entirely rock both and rock
 Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
EAS 116 Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 EAS 116 Earthquakes and Volcanoes J. Haase Forecasting Volcanic Eruptions Assessment of Volcanic Hazard Is that volcano active? Mount Lassen: 12000 BP and 1915 Santorini, IT: 180,000 BP, 70,000 BP, 21000
EAS 116 Earthquakes and Volcanoes J. Haase Forecasting Volcanic Eruptions Assessment of Volcanic Hazard Is that volcano active? Mount Lassen: 12000 BP and 1915 Santorini, IT: 180,000 BP, 70,000 BP, 21000
Inside Planet Earth: Surface to Center
 Inside Planet Earth: Surface to Center Section 1: Introduction 1. What percentage of the Earth cannot be accessed by humans? 99% 2. True or False: It would be easier to invent something to travel to the
Inside Planet Earth: Surface to Center Section 1: Introduction 1. What percentage of the Earth cannot be accessed by humans? 99% 2. True or False: It would be easier to invent something to travel to the
Full file at
 Chapter 2 PLATE TECTONICS AND PHYSICAL HAZARDS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. What direction is the Pacific Plate currently moving, based on the chain of Hawaiian Islands with only the easternmost island
Chapter 2 PLATE TECTONICS AND PHYSICAL HAZARDS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. What direction is the Pacific Plate currently moving, based on the chain of Hawaiian Islands with only the easternmost island
Vulcanicity. Objectives to identify the basic structure of volcanoes and understand how they form.
 Vulcanicity Objectives to identify the basic structure of volcanoes and understand how they form. Some key terms to start.. Viscosity how well a substance (lava) flows. Acid lavas have a high viscosity,
Vulcanicity Objectives to identify the basic structure of volcanoes and understand how they form. Some key terms to start.. Viscosity how well a substance (lava) flows. Acid lavas have a high viscosity,
Earth s Dynamic Surface
 Earth s Dynamic Surface Shaping Earth s Surface What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the
Earth s Dynamic Surface Shaping Earth s Surface What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the
Imagine the first rock and the cycles that it has been through.
 A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
Structure of the Earth
 Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High in Magnesium (Mg) and Iron (Fe) Core: High in Nickel
Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High in Magnesium (Mg) and Iron (Fe) Core: High in Nickel
Internet Interactive Rock Cycle
 Internet Interactive Rock Cycle Directions: Go to the website http://www.uky.edu/as/geology/howell/goodies/elearning/module05swf.swf and answer the questions below. Part I: Igneous Rocks (click on Igneous
Internet Interactive Rock Cycle Directions: Go to the website http://www.uky.edu/as/geology/howell/goodies/elearning/module05swf.swf and answer the questions below. Part I: Igneous Rocks (click on Igneous
Unit 6: Interpreting Earth s History
 Unit 6: Interpreting Earth s History How do we know that the Earth has changed over time? Regent s Earth Science Name: Topics Relative Dating Uniformitarianism Superposition Original Horizontality Igneous
Unit 6: Interpreting Earth s History How do we know that the Earth has changed over time? Regent s Earth Science Name: Topics Relative Dating Uniformitarianism Superposition Original Horizontality Igneous
Geography. Key facts. Volcanoes and volcanic eruptions
 Geography Volcanoes and volcanic eruptions Volcanoes form when magma reaches the Earth's surface, causing eruptions of lava and ash. They occur at destructive (compressional) and constructive (tensional)
Geography Volcanoes and volcanic eruptions Volcanoes form when magma reaches the Earth's surface, causing eruptions of lava and ash. They occur at destructive (compressional) and constructive (tensional)
How to Build a Mountain and other Geologic Structures. But first a short review
 How to Build a Mountain and other Geologic Structures But first a short review Where do we see deep earthquakes? What is happening there? What can happen at a plate boundary? 1. Plates can move apart
How to Build a Mountain and other Geologic Structures But first a short review Where do we see deep earthquakes? What is happening there? What can happen at a plate boundary? 1. Plates can move apart
FIREPLACE GEOLOGY. Dining Hall
 FIREPLACE GEOLOGY Dining Hall The Dining Hall fireplace represents a slice through a Cascade Mountain volcano. Volcanoes are formed from molten magma rising up from within the Earth s crust. Magma that
FIREPLACE GEOLOGY Dining Hall The Dining Hall fireplace represents a slice through a Cascade Mountain volcano. Volcanoes are formed from molten magma rising up from within the Earth s crust. Magma that
The Long Valley Caldera/Bishop Tuff Paroxysm: The Geology of a Supervolcanic Eruption
 Ian Carrico June 19, 2014 The Long Valley Caldera/Bishop Tuff Paroxysm: The Geology of a Supervolcanic Eruption Introduction The Bishop Tuff/Long Valley eruption that occurred approximately 760,000 years
Ian Carrico June 19, 2014 The Long Valley Caldera/Bishop Tuff Paroxysm: The Geology of a Supervolcanic Eruption Introduction The Bishop Tuff/Long Valley eruption that occurred approximately 760,000 years
What are two kinds of volcanic eruptions? How does the composition of magma affect eruptions? What are two ways that magma can erupt from a volcano?
 CHAPTER 9 1 Volcanic Eruptions SECTION Volcanoes BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are two kinds of volcanic eruptions? How does the composition
CHAPTER 9 1 Volcanic Eruptions SECTION Volcanoes BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are two kinds of volcanic eruptions? How does the composition
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. Some volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than a(n) a. hand grenade. b. earthquake. c. geyser. d. atomic bomb. 2. The cause
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. Some volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than a(n) a. hand grenade. b. earthquake. c. geyser. d. atomic bomb. 2. The cause
