Hong Kong Landscapes. Bernie Owen, Raynor Shaw. Published by Hong Kong University Press, HKU. For additional information about this book
|
|
|
- Aldous Sharp
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hong Kong Landscapes Bernie Owen, Raynor Shaw Published by Hong Kong University Press, HKU Owen, Bernie & Shaw, Raynor. Hong Kong Landscapes: Shaping the Barren Rock. Hong Kong: Hong Kong University Press, HKU, Project MUSE., For additional information about this book No institutional affiliation (9 Nov :00 GMT)
2 Index Che Kwu Shan Formation chi A Chinese graves adits... 78,99, 114, 167 Chinese white dolphin afforestation... 23,85,97-99, Chi Ma Wan Granite agriculture Chi Ma Wan Peninsula , air-fall eruptions alluvium clans ammonites... 8 Clear Water Bay Formation ,224 amphibians and reptiles cliffs (sea) ancient settlement Closed Frontier Area Anderson Road Quarry coal animal biodiversity coastal environments anticline... 52, 193 coastal processes antiform beach boulders asymmetrical mountains beach deposits beach processes B beach terminology back-arc basin , 105 breakers badlands... 90, coral coasts basalt deltas base level... 56, delta sediments batholiths fluid density Beacon Hill , 186 headland erosion Beaufort Channel joint slots bedding planes... 26, 71 longshore drift beds artificial shores bioturbation... 57, 143 mangroves and muddy flats black-eared kite pebble beach (Tong Fuk) Bluff Head Formation... 29, 69, 122 planar cross beds borrow areas (offshore) ripples boulder fields rip currents breccia... 27, 228 sea arches bricks sea caves Brides Pool sea stacks Burmese python swash and backwash , 163 butterflies tidal flats tombolo... 76, C wavelength calderas... 8, , 154, 222 wave refraction calderas and columnar joints Cape D'Aguilar Marine Reserve Captain Charles Elliot Castle Peak Range.. 38, 84, 90, 92, 94, 96 catchwaters coastlines College of Medicine colluvium... 91, 158 compression conglomerate... 27, 68, 71-72,122,227 Chek Lap KokAirport contaminated mud
3 Intkx coquinas... 27, 143 Tolo Channel Fault Zone corals... 81, ,206,209,225 fault types corestones... 39, Fei Ngo Shan , 173 cormorants Feng Shui country parks Feng Shui woodland crested goshawk fissure eruptions , 135 Crooked Harbour floral diversity... 5 Crooked Island (See Kat 0) folds cuesta ,25 footpaths foraminifera D formations debris flows forts ,224 Deep Bay... 41,49,61 Fung Wong Shan deforestation detrital G diatoms gei wei... 41,55,64 differential erosion , 50, 71, 89 geological dating... 6 dip angle geological history ,29 dip slopes , Gin Drinker's Bay Discovery Bay glacials and interglacials dolphins ,209,215,218 golf courses , 226 dolphin habitat problems Government Hill Double Haven... 81, 229 Governor's Beach dykes.. 22,137,152, , granite... 22,86-87, 107, 154, ,192,218 dykes, feldsparphyric granite weathering granitic rock suites... 87, 107 E granodiorite... 22, earthquake risks graphite schist... 27,216 Earth movements... 25, 35, 52 Grassy Hill East Lamma Channel... 33, 211, 214 gullies... 90, erosion... 89, 148,200 escarpments H eutaxite Hakka , 111, 127, 145, 151 eutrophication half-life... 6 extrusive igneous rocks haze High Island Formation ,222,224 F hill fires Fan Lau historical change Fan Lau Granite City of Victoria faults Hong Kong Island Lantau Kowloon orientation northwest New Territories rock weakening... 19, 194,225 Hoi Ha Wan Marine Park thrust fault (Double Island) Hoklo... 62, 151 thrust fault (Tiu Tang Lung) Hong Kong Island
4 Hong Kong minerals Tung Lung Island Hong Kong and Shanghai Bank Waglan Island human impacts (offshore) ,214 Wang Chau human occupation... 61,82, 109, 113 West Brother Island , ,164,204 Yim Tin Tsai isostacy I Ice Age J ignimbrite James Hutton insects joints intrusive igneous rocks columnar... 37,45,136 islands ,225 Ap Chau erosion Basalt Island rock weakening , 225 Beaufort Island sheeting... 37,221 Bluff Island structure and types Brothers Islands ,216 tectonic Chek Chau Chek Lap Kok ,216 K Cheung Chau , 220 Kadoorie Farm Dangan Islands Kai Sai Chau Volcanic Group Double Island Karn Tin... 34,63 East Brother Island Karn Tin Valley Hei Ling Chau ,220 kaolin... 34, 167 Jin Island Kap Man Hang... 17, 147 Kat Kat 0 Formation... 29, 228 Kau Sai Chau Kowloon and Canton Railway Kau Yi Chau Kiu Tsui Country Park Lung Kwu Chau koel Ninepin Islands KopTong Peng Chau Kowloon Granite , 176 Ping Chau... 74,81, Kowloon Walled City Po Toi , 222 Kwun Yam See Chau Sharp Island , L Sha Chau ,216 lahars... 9, 106, 153 Shek Kwu Chau Shelter Island , 226 Lai Chi Chong Formation Lai Chi Wo Siu A Chau Lamma Soko Islands Sunshine Island , 220 Tai A Chau ,218 Lam Tei Quarry Lam Tsuen Valley... 33, 54, 56 landfills Tai Tau Chau Tap Mun Town Island Tree Island landscapes (coastal) landscapes (granitic) landscapes (joints & faults) landscapes (sedimentary)
5 Imb.x landscapes (volcanic) landscape colours carbon copper iron manganese landscape photographs Aberdeen Reservoirs Anderson Road Quarry Ap Chau... 24, 70, 228 Basalt Island... 45,226 Beaufort Island Bluff Head... 28,69 Bluff Head Ridge... 25, 67 Bluff Island... 19,45,208,225 boundary stones Brides Pool Buffalo Hill... iii, 245 Byewash Reservoir Castle Peak Range... 23, 84, 90 92,96 Castle Peak Range waterfalls catchwater (Hong Kong Island) Chek Chau... 70, 227 Chek Keng Chek Lap Kok reclamation Cheung Chau ,220 Cheung Sha Beach Cheung Uk Chi Ma Wan Peninsula ,160 Closed Frontier Area columnar jointing , ,223 Crescent Island Crooked Harbour dolphins , 172,216 Double Island Dragon Pool Dragon's Back Fanling Fan Lau... 43, 157 Fan Lau Fort Fei Ngo Shan , 183 Governor's Beach Grassy Hill Hei Ling Chau High Island Reservoir HokTau Hong Kong Island Kai Kung Leng... 34, 48, 53 Kam Shan Country Park... III Kam Shan (reservoirs) Kam Tin (floodplain) Kap Man Hang... 16, 229 Kat ,74, 229 KopTong Kowloon ,180,234 Ko Lau Wan Kwun Yam... 34, 106 Lai Chi Wo Lamma , 199,222,238 Lamma (Sham Wan) Lamma (slump) Lam Tsuen Valley Lam Uk
6 Lantau Peak , 156, 167 Sai Kung East Country Park Legislative Council (building) Sai Kung (islands) , 148 Lin Ma Hang (bats) Sai Wan , 148 Lin Ma Hang (mine)... 78, 79 Sharp Island Lion Rock... v,47, 174, 176, 186 Sharp Peak... 14, 131, 148 Long Harbour Sha Chau Long Ke Sha Lo Tung Long Ke Tsai Sha Tau Kok Lower Shing Mun Reservoir Sha Tin , 109, 115 Lui Ta Shek (panorama) Shek N ga Shan Luk Keng ShekO Lung Kwu Chau Shing Mun Gorge Lung Kwu Tan... 20,23 Shing Mun Redoubt (tunnels) Lung Tsai Ng Yuen Gardens shotcrete macaques , 188 Shui Hau tidal flat Mai Po... 32,41,49,55,62 Shui Lo Cho , 162 silver mine (Mui Wo) mangroves , 160 Siu A Chau MaanShan ,14,117 slopes (mist nets) Ma On Shan Country Park slopes (stone pitching) Ma On Shan (landslips) Soko Islands , 217 Ma Shi Chau South Ninepin Island Ma Wan Chung squatter communities Mirror Pool St. John's (cathedral) Murray House Stone Trail... 16, 236 Nei Lak Shan stream erosion Ngau Ngak Shan Sunset Peak Nga Ying Shan Sunshine Island N gong Ping Tai Hang Valley North Lantau Expressway Tai Lam Country Park... 85, 96 North Ninepin Island Tai Lam Reservoir Pat Sin Leng... 17,80 Tai Long Wan... 1, 40, 140 Pearl River Estuary (islands) Tai Mo Shan , 103, 106 Peng Chau Tai , 166 pill boxes ,205 Tai Po Ping Chau... 30, 74, 228 Tai Tam Tuk Reservoir Ping Fung Shan... 18,70 Tai To Yan... 34, 53 Plover Cove Reservoir TapMun Plover Cove Country Park tea terraces Pok Fu Lam Reservoir Tian Tan Buddha Pok Fu Lam Valley Tin Hau temple Po Pin Chau Tiu Tang Lung... 70,74 Po Toi Tolo Channel Queen's Rd Town Island Robin's Nest (panorama) Tung Chung Sai Kung coastal erosion trawling
7 Tsim Chau Tsing Ma Bridge TuenMun Tung Lung Island Turret Hill Two International Finance Centre 198 University of Hong Kong Victoria Harbour , 173, 189 Waglan Island Wang Leng Waterfall Bay weathered profiles white-bellied sea eagles Wong Chuk Shan Wu Kau Tang Yam , 169 Yi landslides ,202 land animals... 5 land area... 4 land sales Lantau... 36,42,87, Lantau (country parks) Lantau (dyke swarm) Lantau Granite , 192 Lantau Peak Lantau (vegetation) Lantau Volcanic Group Lan Tau Pai Lau Fau Shan lead Lead Mine Pass Legislative Council (building) Lei Yue Mun Gap leopard cat levee Lianhuashan Fault Zone limestone... 7, 27 Lin Fa Shan Lin Ma Hang Lion Rock Lok Ma Chau Formation Long Harbour Long Harbour Formation Luk Chau Shan M macaques , 188, 206 magma ,22,86, , 192,220 magma chambers... 8,86, 107, 121,218 Mai Po... 49, 55, mangroves... 41,49,64, 142 Mang Kung Uk Formation maps (geology) central New Territories eastern New Territories Hong Kong... 13,21,25 Hong Kong Island and Lamma islands (off eastern Lantau) islands (Mirs Bay) islands (Po Toi group) islands (Rocky Harbour and Port Shelter) islands (Soko) islands (southeastern) islands (western) Kowloon and Lion Rock Lantau Ma On Shan (iron mine) Needle Hill northeastern New Territories northwestern New Territories southeastern New Territories Shui Hau (tidal flat) Victoria Peak western New Territories maps (miscellaneous) calderas Cape D'Aguilar Marine Reserve Castle Peak Range central New Territories city of Victoria coastal change (Mai Po) coastal change (northwestern New Territories) coastal erosion eastern New Territories faults (Kowloon reservoirs) fault valleys (Hong Kong Island) Hong Kong Island human impacts (sea floor) islands (Hong Kong)
8 Japanese Invasion Kam Tin River Kowloon and Lion Rock (hills) Kowloon (pluton) Kowloon (weathering front) Lantau Lantau (country parks) late Quaternary late Quaternary (shorelines) late Quaternary (vegetation) Ma On Shan (iron mine) northeastern New Territories NgTung River north Lantau (marine problems) northwestern New Territories ocean currents Ping Chau Marine Park Pleistocene (rivers) , 212 reclamations (Victoria Harbour) reclamations (western New Territories) Scheduled Areas sea floor bathymmetry sea Levels (Sai Kung) Sha Tin Valley (development) Shing Mun Redoubt southeastern New Territories tidal pathways Tolo Channel (fault) Tuen Mun (weathering front) weather western New Territories Yan Chau Tong Marine Park marble... 7,27,50, 116, 123 mariculture , 229 marine parks marine salinity gradients mass movements Ma On Shan , 123 Ma On Shan Formation Ma On Shan (iron mine) , 124 metamorphic rocks migrating volcanoes minerals biotite , 100 calcite feldspar... 22, 86, 100, 154 fluorite galena... 78, 100, 114, 166 graphite ,216 haematite hornblende limonite magnetite molybdenite , 114 pyrite quartz... 22, 78, 86, 100, 154 silver sphalerite wolframite , 114, 167 mining kaolin Lin Fa Shan (tungsten, adits) Lin Ma Hang (lead) Ma On Shan (iron) Needle Hill (tungsten) Silver Mine Bay (silver) West Brother Island (graphite) mining (landscape scars) Mirs Bay mist nets monzonite mountain streams Mt. Butler Granite ,176,192 Mt. Butler Quarry Mt. Stenhouse mudstone... 27, 71 mud flats Mui Wo Murray House N Nautilus... 8 NeedleHill ,114 Needle Hill Granite , 114, ,175 Nei Lak Shan , 172 New Towns Ngau Ngak Shan , 123 Ngo Mei Chau Formation NgTung Chai Waterfalls nuee ardente
9 nullahs photographs (marine) anemones o corals (Hoi Ha Wan) ocean currents corals (Ping Chau)... 81, 209 ocean waves corals (Soko Islands) offshore buried landscapes diatoms oldest lighthouse foraminifera oysters mudskippers ray (Soko Islands) p starfish (Soko Islands) Pat Sin Leng... 17,67 Pat Sin Leng Formation ,69-70 paved trackways Peak Tram pearls Pearl River photographs (aerial) Kowloon and Sha Tin... 3 photographs (miscellaneous) abandoned villages bedding planes... 26, 71 Kam Tin (nullah) Kam Tin River (point bar) mangrove leaves potholes photographs (rocks and sediments) Lin Fa Shan basalt photographs (historical) basaltic andesite Kowloon Walled City , 180 beach sands Sheung Shui (floodplains) biotite granite Tide Cove (Sha Tin) coal
10 conglomerate... 18,72 population pressures gneiss Port Island Formation ,227 granite... 22, 87 Port Shelter granite (Po Toi) potholes granodiorite Po Lin (monastery) graphite schist... 27,216 Po Shan Road (landslide) ignimbrite Po Toi Granite limestone public housing marble Punti... 62, 127 monzonite pebbles (Tong Fuk coast) pebbles (and Tai 0 Formation) phyllite porphyry Q quarries , quartz veins pumice tuffs R rhyodacite radioactive elements... 6 rhyolite... 22, 121, 135, 155 reclamations rhyolite (feldsparphyric) Central rhyolitic hyaloclastite Chek Lap Kok sand coastal sandstone (Bluff Head) Kowloon , 182 sandstone (Chek Chau) nonhwest New Territories sandstone (Ping Fung Shan) Sha Tin sandy ripples red tides schist reefs shale... 51, 72 religion and Lantau shale (Sai Kung Country Park) Repulse Bay Volcanic Group siltstone (Ma Shi Chau) reservoirs siltstone (Ping Chau) Aberdeen Reservoir siltstone (Shek Uk Shan) siltstone and quartz tuff... 15, 18, 135 pill boxes Byewash Reservoir High Island Reservoir Hong Kong Kowloon Ping Chau Formation... 29,228 Kowloon Reservoir Ping Fung Shan... 18, 26, 30 Plover Cove Reservoir Ping Shan Pok Fu Lam Reservoir pirates and fons Reception Reservoir plantation trees Shek Lei Pui Reservoir plate boundary... 14, 105 Shek Pik Reservoir , 156 plate tectonics Pleistocene rivers Plover Cove plunge pool... 72, 94 plutons... 22, 176 pollution , 234 population movements Shing Mun Reservoir Tai Lam Chung Reservoir Tai Tam Reservoir Wong Nei Chung Reservoir rhyodacite ,218 rhyolite ,22, 122, ,221 ria
11 Intkx rills rivers alluvium base level... 56, 59 floodplains... 54, 56, levee maturity nullahs oxbow lake point bar ,66 rejuvenation river processes terraces Robin's Nest rock carvings (Nam Tam Wan) rock platforms... 46,76 S Sai Lau Kong Formation salt pans (Lan tau) sandstone... 27,68,71, 122,227,229 sand dunes Scheduled Areas sea caves... 45, 139 sea level change... 10, , sedimentary formations sedimentary rock colours seismic profiles Sha Chau and Lung KwuChau Marine Park ,215 Sham Chun River Sham Wan Sha Lo Wan Sha Tau Kok... 18,33,63,75 Sha Tin , Sha Tin Granite ,121,154,175 Sha Tin Valley... 33, 108 sheeting joints (See joints, sheeting) Shek Kip Mei (squatter village) Shek Kong Shek 0 Quarry Shek Uk Shan Shing MUll Formation , 133, 153 Shing MUll Redoubt , 188 Shing MUll Valley shotcrete Shui Chuen 0 Granite , 121, 175 Shui Hau Shui Ngau Shan silica sills siltstone... 27, 68, 227 Sir Murray MacLehose skarn slopes (stability and maintenance) slumps , soil pipes Sok Kwu Wan Quarry sombrero islands South Lamma Granite spheroidal weathering spring sapping stacks... 45, 138 Starling Inlet stone pitching Strike-slip fault (See faults, types) subduction... 14, 88, 105 subtidal platforms Sunset Peak superposition... 6 supratidal platforms syncline... 52, 193 synform T Tai Chau Tai Lam Country Park Tai Lam Granite Tai LongTsui Tai Long Wan... 47, 140 Tai Mo Shan Tai Mo Shan Formation , 228 Tai Tai 0 Formation Tai Po Granodiorite , 192 Tai Po Kau Tai Po Pass Tanka Tate's Cairn tea terraces tension (crustal) terrace walls
12 thrust fault (See faults, types) volcanic groups Tian Tan Buddha volcanic rocks tidal channels volcanoes tides Tin Hau ,218 W Tolo Channel... 33,74, 108 Wang Leng Tolo Channel Formation waterfalls... 16, 37, 71-73, 94-95, 102 Tolo Harbour Formation ,153, tors weather toxic sea floor pits weathered granite , 92 Trappist Haven Monastery (Lantau) weathering , 176, 179 tropical hardwoods (Yam 0) weathering front tropical rainforests... 60, 129 weepholes Tsing Ma Bridge wetlands... 41,49,55 Tsing Shan Granite white-bellied sea eagle Tsuen Wan wildlife... 77, , 116 Tsuen Wan Volcanic Group , ,160,188, TuenMun wildlife (marine) ,226 tuffs , 19,68,87, 121, 193 wild boar , Wong Leng Tung Chung , 232 World War II Turret Hill Wu Kau Tang turtle nesting Two International Finance Centre Yan Chau Tong U Yim Tin Tsai Formation , 193 unconformity Yuen Long uncontaminated mud dumping Yuen Long Formation uniformitarianism Yuen Long Plain... 54, 55 University of Hong Kong Yuen Tsuen (ancient trail) urbanisation and streams urban canyons urban climates urban development urban geological mapping urban geology urban pollution Urmston Rd V valley deltas and progradation Victoria Peak Vietnamese refugees volcanic arc volcanic ash volcanic bomb y 252
13 253
14
Geology of Hong Kong A Summary. Prof LS Chan The University of Hong Kong
 Geology of Hong Kong A Summary Prof LS Chan The University of Hong Kong Student Expeditions Geology of HK Eurasia Late Cretaceous Orogen Collapse Eurasia Sunda Early Cenozoic Crustal Extension Jointed
Geology of Hong Kong A Summary Prof LS Chan The University of Hong Kong Student Expeditions Geology of HK Eurasia Late Cretaceous Orogen Collapse Eurasia Sunda Early Cenozoic Crustal Extension Jointed
"2014 Hong Kong Definitive Stamps" Issue Date: 24 July 2014
 "2014 Hong Kong Definitive Stamps" Issue Date: 24 July 2014 Hong Kong is an international metropolis of skyscrapers. On the outskirts of this bustling city, however, there lies a great expanse of countryside
"2014 Hong Kong Definitive Stamps" Issue Date: 24 July 2014 Hong Kong is an international metropolis of skyscrapers. On the outskirts of this bustling city, however, there lies a great expanse of countryside
STUDY OF COASTAL SUBSOIL GEOTECHNICAL CONDITIONS
 SPECIAL PROJECT REPORT SPR1/2003 STUDY OF COASTAL SUBSOIL GEOTECHNICAL CONDITIONS W.P. Lee, T.C. Chan, W.C. Siu, C.K. Chu April 2003 Technical Services Division - 2 - - 4 - - 5 - CONTENTS Title Page 1
SPECIAL PROJECT REPORT SPR1/2003 STUDY OF COASTAL SUBSOIL GEOTECHNICAL CONDITIONS W.P. Lee, T.C. Chan, W.C. Siu, C.K. Chu April 2003 Technical Services Division - 2 - - 4 - - 5 - CONTENTS Title Page 1
Term Knowledge Using and applying Grade Criteria Autumn 1 Assessment window October Natural hazards pose major risks to people and property.
 Assessment Schedule Year 9 2015/6 Term Knowledge Using and applying Grade Criteria Autumn 1 Assessment window October 2015 3.1.1.2 Tectonic Natural hazards pose major risks to people and property. Definition
Assessment Schedule Year 9 2015/6 Term Knowledge Using and applying Grade Criteria Autumn 1 Assessment window October 2015 3.1.1.2 Tectonic Natural hazards pose major risks to people and property. Definition
Chapter 10. Chapter Rocks and the Rock Cycle. Rocks. Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle
 Chapter 10 Rocks 1 Chapter 10 Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle 2 10.1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Magma is the parent material for all rocks. Once the magma cools and hardens, many changes can occur. Geology:
Chapter 10 Rocks 1 Chapter 10 Section 1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle 2 10.1 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Magma is the parent material for all rocks. Once the magma cools and hardens, many changes can occur. Geology:
No. of Periods. Syllabus Topics Specific Objectives Teaching Strategies. rational to live in hazard-prone areas?
 (Syllabus for F.4 Geog. September 2016 - July 2017) -1- SING YIN SECONDARY SCHOOL SYLLABUS FOR GEOGRAPHY -- SEPTEMBER 2016 - JULY 2017 FORM FOUR Textbooks : Senior Secondary Exploring Geography 1 (Second
(Syllabus for F.4 Geog. September 2016 - July 2017) -1- SING YIN SECONDARY SCHOOL SYLLABUS FOR GEOGRAPHY -- SEPTEMBER 2016 - JULY 2017 FORM FOUR Textbooks : Senior Secondary Exploring Geography 1 (Second
Hong Kong s Sea-level Record
 Hong Kong s Sea-level Record Wyss W.-S. Yim ISEIS, Chinese University of Hong Kong / Association for Geoconservation, Hong Kong / Commission on Quaternary Shorelines, International Union for Quaternary
Hong Kong s Sea-level Record Wyss W.-S. Yim ISEIS, Chinese University of Hong Kong / Association for Geoconservation, Hong Kong / Commission on Quaternary Shorelines, International Union for Quaternary
Example Quiz on Earthquakes
 Example Quizzes, Tests, and Review Information A Example Quiz on Earthquakes Quizzes such as this one are given at the beginning of each lab. 1. The point beneath the Earth s surface at which an earthquake
Example Quizzes, Tests, and Review Information A Example Quiz on Earthquakes Quizzes such as this one are given at the beginning of each lab. 1. The point beneath the Earth s surface at which an earthquake
Theory Paper (Paper version of on-screen assessment)
 Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number GCSE 4250/01 GEOLOGY Theory Paper (Paper version of on-screen assessment) A.M. FRIDAY, 18 May 2012 1 1 2 hours ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to this
Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number GCSE 4250/01 GEOLOGY Theory Paper (Paper version of on-screen assessment) A.M. FRIDAY, 18 May 2012 1 1 2 hours ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to this
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy)
 Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
The Marine Environment
 The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write or. 1.
The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write or. 1.
NAME HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #3 MATERIAL COVERS CHAPTERS 8, 9, 10, 11
 NAME HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #3 MATERIAL OVERS HAPTERS 8, 9, 10, 11 Assignment is due the beginning of the class period on November 23, 2004. Answers for each chapter will be discussed in class, as Exam #3
NAME HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #3 MATERIAL OVERS HAPTERS 8, 9, 10, 11 Assignment is due the beginning of the class period on November 23, 2004. Answers for each chapter will be discussed in class, as Exam #3
B) color B) Sediment must be compacted and cemented before it can change to sedimentary rock. D) igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks
 1. Which characteristic of nonsedimentary rocks would provide the least evidence about the environment in which the rocks were formed? A) structure B) color C) crystal size D) mineral composition 2. Which
1. Which characteristic of nonsedimentary rocks would provide the least evidence about the environment in which the rocks were formed? A) structure B) color C) crystal size D) mineral composition 2. Which
Practice Test Rocks and Minerals. Name. Page 1
 Name Practice Test Rocks and Minerals 1. Which rock would be the best source of the mineral garnet? A) basalt B) limestone C) schist D) slate 2. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? A) hematite
Name Practice Test Rocks and Minerals 1. Which rock would be the best source of the mineral garnet? A) basalt B) limestone C) schist D) slate 2. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? A) hematite
Objectives: Define Relative Age, Absolute Age
 S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth s surface is formed. c. Classify rocks by their process of formation. g. Describe how fossils show evidence of the changing surface
S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth s surface is formed. c. Classify rocks by their process of formation. g. Describe how fossils show evidence of the changing surface
Chapter 17. Ocean and Coastal Processes
 Chapter 17 Ocean and Coastal Processes Ocean Basins and Plates Ocean Basins Ocean Basins are profoundly different from the continents. Ocean crust is thin and dense and young. New ocean crust is generated
Chapter 17 Ocean and Coastal Processes Ocean Basins and Plates Ocean Basins Ocean Basins are profoundly different from the continents. Ocean crust is thin and dense and young. New ocean crust is generated
Read Across America. Listen as I read for facts about Volcanoes. In the Shadow of the Volcano
 Read Across America Listen as I read for facts about Volcanoes. In the Shadow of the Volcano Constructive & Destructive Processes Earth s surface is always changing. Blowing wind and flowing water causes
Read Across America Listen as I read for facts about Volcanoes. In the Shadow of the Volcano Constructive & Destructive Processes Earth s surface is always changing. Blowing wind and flowing water causes
Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment
 Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment From sediments to sedimentary rocks (transportation, deposition, preservation and lithification) Types of sedimentary rocks (clastic, chemical and organic) Sedimentary
Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment From sediments to sedimentary rocks (transportation, deposition, preservation and lithification) Types of sedimentary rocks (clastic, chemical and organic) Sedimentary
Geology 12 Exam Review Package
 Geology 12 Exam Review Package Exam Date: Supplies: Thursday June 11 th, 1:00pm to 4:00pm Pen, pencil, eraser, calculator (all graphing calculators will have their memories cleared at the start of the
Geology 12 Exam Review Package Exam Date: Supplies: Thursday June 11 th, 1:00pm to 4:00pm Pen, pencil, eraser, calculator (all graphing calculators will have their memories cleared at the start of the
Geology 12 FINAL EXAM PREP. Possible Written Response Exam Questions
 Geology 12 FINAL EXAM PREP Possible Written Response Exam Questions Use this study guide to prepare for the written response portion of the final exam. Name FINAL EXAM - POSSIBLE WRITTEN RESPONSE QUESTIONS
Geology 12 FINAL EXAM PREP Possible Written Response Exam Questions Use this study guide to prepare for the written response portion of the final exam. Name FINAL EXAM - POSSIBLE WRITTEN RESPONSE QUESTIONS
CEE 437 Lecture 10 Rock Classification. Thomas Doe
 CEE 437 Lecture 10 Rock Classification Thomas Doe Igneous Origins Intrusive Batholithic or plutonic: phaneritic Dikes or sills that chill rapidly: aphanitic Extrusive deposition as melt (lava) pyroclastic
CEE 437 Lecture 10 Rock Classification Thomas Doe Igneous Origins Intrusive Batholithic or plutonic: phaneritic Dikes or sills that chill rapidly: aphanitic Extrusive deposition as melt (lava) pyroclastic
Module 10: Resources and Virginia Geology Topic 4 Content: Virginia Geology Notes
 Virginia is composed of a very diverse landscape that extends from the beaches and barrier islands all of the way to the highly elevated Appalachian Plateau. Geologists have discovered ancient shallow
Virginia is composed of a very diverse landscape that extends from the beaches and barrier islands all of the way to the highly elevated Appalachian Plateau. Geologists have discovered ancient shallow
Geology : Embedded Inquiry
 Geology : Embedded Inquiry Conceptual Strand Understandings about scientific inquiry and the ability to conduct inquiry are essential for living in the 21 st century. Guiding Question What tools, skills,
Geology : Embedded Inquiry Conceptual Strand Understandings about scientific inquiry and the ability to conduct inquiry are essential for living in the 21 st century. Guiding Question What tools, skills,
Writing Earth s History
 Earths History Writing Earth s History How is Earths History like writing in your Journal? Everyday, something happens and, with a pen, it is written down in the pages of your journal. As you continue,
Earths History Writing Earth s History How is Earths History like writing in your Journal? Everyday, something happens and, with a pen, it is written down in the pages of your journal. As you continue,
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 5
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 5 Sedimentation Rocks Formed by Surface Processes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Mineralogy of sandstones Key Figure 5.12
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 5 Sedimentation Rocks Formed by Surface Processes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Mineralogy of sandstones Key Figure 5.12
L wave Lahar Lava Magma
 Very large collapsed volcanic crater, often containing a lake eg. Lake Taupo The process which provides the force to move the tectonic plates Innermost part of the Earth, made of a liquid outer core and
Very large collapsed volcanic crater, often containing a lake eg. Lake Taupo The process which provides the force to move the tectonic plates Innermost part of the Earth, made of a liquid outer core and
Ocean and Coastal Processes. Ocean Basins. Chapter 20. Ocean Basins and Plates. Ocean Terms. Sea Arch Bay-mouth Bar Spit Tombolo Coast.
 Chapter 20 Ocean Basins and Plates Ocean and Coastal Processes Tide Wave Height Length Period Base Refraction Tsunami Beach Sea stack Ocean Terms Sea Arch Bay-mouth Bar Spit Tombolo Coast Emergent Submergent
Chapter 20 Ocean Basins and Plates Ocean and Coastal Processes Tide Wave Height Length Period Base Refraction Tsunami Beach Sea stack Ocean Terms Sea Arch Bay-mouth Bar Spit Tombolo Coast Emergent Submergent
The Marine Environment
 The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write true or
The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write true or
New GCSE Geography AQA
 Learning Checklist Half Term 1 26 th September 3 rd October 10 th October 17 th October 1.1.1 Tectonic Hazards Plate tectonics theory. Global distribution of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions and their
Learning Checklist Half Term 1 26 th September 3 rd October 10 th October 17 th October 1.1.1 Tectonic Hazards Plate tectonics theory. Global distribution of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions and their
Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures
 Name: Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary rocks account for a negligibly small fraction of Earth s mass, yet they are commonly encountered because the processes that form them are ubiquitous in the
Name: Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary rocks account for a negligibly small fraction of Earth s mass, yet they are commonly encountered because the processes that form them are ubiquitous in the
 Page 1 of 9 Name: Base your answer to the question on the diagram below. The arrows show the direction in which sediment is being transported along the shoreline. A barrier beach has formed, creating a
Page 1 of 9 Name: Base your answer to the question on the diagram below. The arrows show the direction in which sediment is being transported along the shoreline. A barrier beach has formed, creating a
STEWARDS POOI KEI COLLEGE 2011/12. S4 Class List
 S4 Joy CHAN Hau Ling F Geography Business, Accounting & Finanical Studies CHAN Kin Yu M Geography Business, Accounting & Finanical Studies CHAN Wai Yiu Christy F Geography Biology CHAN Yan Yin F Chinese
S4 Joy CHAN Hau Ling F Geography Business, Accounting & Finanical Studies CHAN Kin Yu M Geography Business, Accounting & Finanical Studies CHAN Wai Yiu Christy F Geography Biology CHAN Yan Yin F Chinese
The Coast: Beaches and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10
 The Coast: es and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10 Oceanography 101 Chapter Objectives Recognize the various landforms characteristic of beaches and coastal regions. Identify seasonal
The Coast: es and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10 Oceanography 101 Chapter Objectives Recognize the various landforms characteristic of beaches and coastal regions. Identify seasonal
The Coast: Beaches and Shoreline Processes
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Coast: es and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10 Oceanography 101 Chapter Objectives Recognize the various landforms characteristic of beaches and coastal regions.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Coast: es and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10 Oceanography 101 Chapter Objectives Recognize the various landforms characteristic of beaches and coastal regions.
General Geology Lab #7: Geologic Time & Relative Dating
 General Geology 89.101 Name: General Geology Lab #7: Geologic Time & Relative Dating Purpose: To use relative dating techniques to interpret geological cross sections. Procedure: Today we will be interpreting
General Geology 89.101 Name: General Geology Lab #7: Geologic Time & Relative Dating Purpose: To use relative dating techniques to interpret geological cross sections. Procedure: Today we will be interpreting
transform boundary Photograph by Robert E. Wallace, USGS.
 transform boundary The San Andreas Fault is undoubtedly the most famous transform boundary in the world. To the west of the fault is the Pacific plate, which is moving northwest. To the east is the North
transform boundary The San Andreas Fault is undoubtedly the most famous transform boundary in the world. To the west of the fault is the Pacific plate, which is moving northwest. To the east is the North
Answers. Rocks. Year 8 Science Chapter 8
 Answers Rocks Year 8 Science Chapter 8 p171 1 Rocks are made up of minerals such as quartz, feldspars, micas, and calcite. Different rocks are made up of different combinations of minerals. 2 Igneous,
Answers Rocks Year 8 Science Chapter 8 p171 1 Rocks are made up of minerals such as quartz, feldspars, micas, and calcite. Different rocks are made up of different combinations of minerals. 2 Igneous,
40-50 Minutes, 3 minutes per station, 13 Stations, samples provided by UWM and Pierre Couture
 Event: Judge: Rocks & Minerals Pierre couture 40-50 Minutes, 3 minutes per station, 13 Stations, samples provided by UWM and Pierre Couture 1-4 Minerals (50 points total) 5-7 Igneous Rocks (50 points total)
Event: Judge: Rocks & Minerals Pierre couture 40-50 Minutes, 3 minutes per station, 13 Stations, samples provided by UWM and Pierre Couture 1-4 Minerals (50 points total) 5-7 Igneous Rocks (50 points total)
FIREPLACE GEOLOGY. Dining Hall
 FIREPLACE GEOLOGY Dining Hall The Dining Hall fireplace represents a slice through a Cascade Mountain volcano. Volcanoes are formed from molten magma rising up from within the Earth s crust. Magma that
FIREPLACE GEOLOGY Dining Hall The Dining Hall fireplace represents a slice through a Cascade Mountain volcano. Volcanoes are formed from molten magma rising up from within the Earth s crust. Magma that
A. IGNEOUS Rocks formed by cooling and hardening of hot molten rock called magma (within crust or at its surface).
 EARTH SCIENCE 11 CHAPTER 5 NOTES KEY How Earth's Rocks Were Formed Early geologists believed that the physical features of the Earth were formed by sudden spectacular events called CATASTROPHES. Modern
EARTH SCIENCE 11 CHAPTER 5 NOTES KEY How Earth's Rocks Were Formed Early geologists believed that the physical features of the Earth were formed by sudden spectacular events called CATASTROPHES. Modern
As compaction and cementation of these sediments eventually occur, which area will become siltstone? A) A B) B C) C D) D
 1. A student obtains a cup of quartz sand from a beach. A saltwater solution is poured into the sand and allowed to evaporate. The mineral residue from the saltwater solution cements the sand grains together,
1. A student obtains a cup of quartz sand from a beach. A saltwater solution is poured into the sand and allowed to evaporate. The mineral residue from the saltwater solution cements the sand grains together,
Earth s Geological Cycle
 Earth s Geological Cycle What Are the Earth s Major Geological Processes? Main Processes: 1. Plate Tectonics 2. Rock Cycle 3. Soil Formation LITHOSPHERE The Earth s Structure Earth s Interior Core (Nickel
Earth s Geological Cycle What Are the Earth s Major Geological Processes? Main Processes: 1. Plate Tectonics 2. Rock Cycle 3. Soil Formation LITHOSPHERE The Earth s Structure Earth s Interior Core (Nickel
R.Suhasini., Assistant Professor Page 1
 UNIT I PHYSICAL GEOLOGY Geology in civil engineering branches of geology structure of earth and its composition weathering of rocks scale of weathering soils - landforms and processes associated with river,
UNIT I PHYSICAL GEOLOGY Geology in civil engineering branches of geology structure of earth and its composition weathering of rocks scale of weathering soils - landforms and processes associated with river,
Geol 117 Lecture 18 Beaches & Coastlines. I. Types of Coastlines A. Definition:
 I. Types of Coastlines A. Definition: 1. Shore = narrow zone where ocean meets land (e.g. beach) 2. Coast is a broad area where both ocean and land processes act a. Includes onshore marshes, dunes, sea
I. Types of Coastlines A. Definition: 1. Shore = narrow zone where ocean meets land (e.g. beach) 2. Coast is a broad area where both ocean and land processes act a. Includes onshore marshes, dunes, sea
Review - Unit 2 - Rocks and Minerals
 Review - Unit 2 - Rocks and Minerals Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows the results of three different physical tests, A, B, and C, that were performed on a mineral.
Review - Unit 2 - Rocks and Minerals Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below, which shows the results of three different physical tests, A, B, and C, that were performed on a mineral.
Section 1: Earth s Interior and Plate Tectonics Section 2: Earthquakes and Volcanoes Section 3: Minerals and Rocks Section 4: Weathering and Erosion
 Section 1: Earth s Interior and Plate Tectonics Section 2: Earthquakes and Volcanoes Section 3: Minerals and Rocks Section 4: Weathering and Erosion Key Terms Crust Mantle Core Lithosphere Plate Tectonics
Section 1: Earth s Interior and Plate Tectonics Section 2: Earthquakes and Volcanoes Section 3: Minerals and Rocks Section 4: Weathering and Erosion Key Terms Crust Mantle Core Lithosphere Plate Tectonics
Sediment and Sedimentary rock
 Sediment and Sedimentary rock Sediment: An accumulation of loose mineral grains, such as boulders, pebbles, sand, silt or mud, which are not cemented together. Mechanical and chemical weathering produces
Sediment and Sedimentary rock Sediment: An accumulation of loose mineral grains, such as boulders, pebbles, sand, silt or mud, which are not cemented together. Mechanical and chemical weathering produces
A TRIP THROUGH VIRGINIA GEOLOGY FROM AN ENGINEER S PERSPECTIVE
 A TRIP THROUGH VIRGINIA GEOLOGY FROM AN ENGINEER S PERSPECTIVE Bob Moss, PE Principal Engineer ECS Mid Atlantic, LLC The Engineer Parent WHY IS AN UNDERSTANDING OF LOCAL GEOLOGY IMPORTANT? It provides
A TRIP THROUGH VIRGINIA GEOLOGY FROM AN ENGINEER S PERSPECTIVE Bob Moss, PE Principal Engineer ECS Mid Atlantic, LLC The Engineer Parent WHY IS AN UNDERSTANDING OF LOCAL GEOLOGY IMPORTANT? It provides
4. The map below shows a meandering stream. Points A, B, C, and D represent locations along the stream bottom.
 1. Sediment is deposited as a river enters a lake because the A) velocity of the river decreases B) force of gravity decreases C) volume of water increases D) slope of the river increases 2. Which diagram
1. Sediment is deposited as a river enters a lake because the A) velocity of the river decreases B) force of gravity decreases C) volume of water increases D) slope of the river increases 2. Which diagram
Fukien Secondary School Monthly Vocabulary/Expression List for EMI Subjects Secondary Two. Subject: Geography
 Focus: General Specific : Section Two : Unit One 1 Landslide 2 Downslope movement 3 Rock 4 Soil 5 Gravity 6 Natural hazard 7 Rainwater 8 Friction 9 Hilly relief 10 Unstable 11 Season 12 Saturated 13 Construction
Focus: General Specific : Section Two : Unit One 1 Landslide 2 Downslope movement 3 Rock 4 Soil 5 Gravity 6 Natural hazard 7 Rainwater 8 Friction 9 Hilly relief 10 Unstable 11 Season 12 Saturated 13 Construction
3. [ES 3] 1. [ST8.2] Some processes that shape Earth s surface are slow. Other processes are rapid. Which statement describes a rapid change?
![3. [ES 3] 1. [ST8.2] Some processes that shape Earth s surface are slow. Other processes are rapid. Which statement describes a rapid change? 3. [ES 3] 1. [ST8.2] Some processes that shape Earth s surface are slow. Other processes are rapid. Which statement describes a rapid change?](/thumbs/89/98260180.jpg) Science 8 SCIENCE QUARTERLY ASSESSMENT 2 3. [ES 3] S 1. [ST8.2] Some processes that shape Earth s surface are slow. Other processes are rapid. Which statement describes a rapid change? A. Glaciers melt
Science 8 SCIENCE QUARTERLY ASSESSMENT 2 3. [ES 3] S 1. [ST8.2] Some processes that shape Earth s surface are slow. Other processes are rapid. Which statement describes a rapid change? A. Glaciers melt
Classify Rock (rock1)
 Name: Date: 1. Cleavage of a mineral is related to a mineral's A. chemical composition. B. streak color. C. luster. D. crystalline structure. 2. Which is not part of the definition of a mineral? A. naturally
Name: Date: 1. Cleavage of a mineral is related to a mineral's A. chemical composition. B. streak color. C. luster. D. crystalline structure. 2. Which is not part of the definition of a mineral? A. naturally
PROMOTING NATURE CONSERVATION AND SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT IN THE RURAL AREAS OF HONG KONG
 1 PROMOTING NATURE CONSERVATION AND SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT IN THE RURAL AREAS OF HONG KONG Director of Agriculture, Fisheries and Conservation Dr. LEUNG Siu-fai A STONE S THROW AWAY FROM
1 PROMOTING NATURE CONSERVATION AND SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT IN THE RURAL AREAS OF HONG KONG Director of Agriculture, Fisheries and Conservation Dr. LEUNG Siu-fai A STONE S THROW AWAY FROM
Constructive and Destructive Forces. Processes That Act Upon Earth s Surface Features
 Constructive and Destructive Forces Processes That Act Upon Earth s Surface Features What are Constructive and Destructive Forces? Constructive Force A constructive force is a process that raises or builds
Constructive and Destructive Forces Processes That Act Upon Earth s Surface Features What are Constructive and Destructive Forces? Constructive Force A constructive force is a process that raises or builds
Chapter 3 Erosion and Deposition. The Big Question:
 Chapter 3 Erosion and Deposition The Big Question: 1 Design a way to represent and describe the 4 types of mass movement. You may use pictures, diagrams, list, web, chart, etc 2 Chapter 3: Erosion and
Chapter 3 Erosion and Deposition The Big Question: 1 Design a way to represent and describe the 4 types of mass movement. You may use pictures, diagrams, list, web, chart, etc 2 Chapter 3: Erosion and
Geology 12. Resource Exam A. Exam Booklet
 Geology 12 Resource Exam A Exam Booklet Contents: 28 pages Examination: 2 hours 64 multiple-choice questions in the Exam Booklet Additional Time Permitted: 60 minutes 9 written-response questions in the
Geology 12 Resource Exam A Exam Booklet Contents: 28 pages Examination: 2 hours 64 multiple-choice questions in the Exam Booklet Additional Time Permitted: 60 minutes 9 written-response questions in the
Section I: Multiple Choice Select the best answer to each question. Mark your final answer on the answer sheet. (1 pt each)
 Sedimentary Rocks & Surface Processes Quest Name: Earth Science 2013 Block: Date: Section I: Multiple Choice Select the best answer to each question. Mark your final answer on the answer sheet. (1 pt each)
Sedimentary Rocks & Surface Processes Quest Name: Earth Science 2013 Block: Date: Section I: Multiple Choice Select the best answer to each question. Mark your final answer on the answer sheet. (1 pt each)
Section 11.1 pp Where Mountains Form
 Section 11.1 pp. 236 237 Where Mountains Form Chapter 11 Set a Purpose: TE, p. 236 Reading Study Guide, p. 36 Discussion: TE, p. 236 Differentiating ion Reading Support: TE, p. 236 Visual Teaching Interpret
Section 11.1 pp. 236 237 Where Mountains Form Chapter 11 Set a Purpose: TE, p. 236 Reading Study Guide, p. 36 Discussion: TE, p. 236 Differentiating ion Reading Support: TE, p. 236 Visual Teaching Interpret
Name: Which rock layers appear to be most resistant to weathering? A) A, C, and E B) B and D
 Name: 1) The formation of soil is primarily the result of A) stream deposition and runoff B) precipitation and wind erosion C) stream erosion and mass movement D) weathering and biological activity 2)
Name: 1) The formation of soil is primarily the result of A) stream deposition and runoff B) precipitation and wind erosion C) stream erosion and mass movement D) weathering and biological activity 2)
CE6301 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY UNIT I 2 MARKS
 YEAR : II SEMESTER : III DEPARTMENT : CIVIL CE6301 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY UNIT I 1. What is Physical weathering? 2. Define Stratigraphy and Palaeontology? 3. What is meant by chemical weathering 4. Describe
YEAR : II SEMESTER : III DEPARTMENT : CIVIL CE6301 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY UNIT I 1. What is Physical weathering? 2. Define Stratigraphy and Palaeontology? 3. What is meant by chemical weathering 4. Describe
Geology 12 Past Provincial Exam Workbook Includes Answer Key and Data Booklets
 1 Geology 12 Past Provincial Exam Workbook Includes Answer Key and Data Booklets June 1999 Exam June 2000 Exam January 2001 Exam June 2001Exam June 2002 Exam June 2003 Exam June 2004 Exam August 2005 Exam
1 Geology 12 Past Provincial Exam Workbook Includes Answer Key and Data Booklets June 1999 Exam June 2000 Exam January 2001 Exam June 2001Exam June 2002 Exam June 2003 Exam June 2004 Exam August 2005 Exam
Rock Carvings in Hong Kong and the New Territories S. G. DAVIS, SHIRLEE EDELSTEIN, LAN TAU ISLAND
 Rock Carvings in Hong Kong and the New Territories Received 26 September 1973 S. G. DAVIS, SHIRLEE EDELSTEIN, AND MADELEINE H. TANG LAN TAU ISLAND WHEN the Shek Pik district on Lantau Island (Fig. 1) was
Rock Carvings in Hong Kong and the New Territories Received 26 September 1973 S. G. DAVIS, SHIRLEE EDELSTEIN, AND MADELEINE H. TANG LAN TAU ISLAND WHEN the Shek Pik district on Lantau Island (Fig. 1) was
Page 1. Name: 1) Which diagram best shows the grain size of some common sedimentary rocks?
 Name: 1) Which diagram best shows the grain size of some common sedimentary rocks? 1663-1 - Page 1 5) The flowchart below illustrates the change from melted rock to basalt. 2) Which processes most likely
Name: 1) Which diagram best shows the grain size of some common sedimentary rocks? 1663-1 - Page 1 5) The flowchart below illustrates the change from melted rock to basalt. 2) Which processes most likely
Geology 12. Rocks and the Rock Cycle Provincial Exam Questions EXTRA PRACTICE TEST #3 KEY
 Geology 12 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Provincial Exam Questions EXTRA PRACTICE TEST #3 KEY 2003 GEOLOGICAL MAP Drill hole pond T U V 80 S X Y W 50 m Unit T Coal Unit U Shale Igneous rock S Unit V Sandstone
Geology 12 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Provincial Exam Questions EXTRA PRACTICE TEST #3 KEY 2003 GEOLOGICAL MAP Drill hole pond T U V 80 S X Y W 50 m Unit T Coal Unit U Shale Igneous rock S Unit V Sandstone
Geologic Trips San Francisco and the Bay Area
 Excerpt from Geologic Trips San Francisco and the Bay Area by Ted Konigsmark ISBN 0-9661316-4-9 GeoPress All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced without written permission in writing,
Excerpt from Geologic Trips San Francisco and the Bay Area by Ted Konigsmark ISBN 0-9661316-4-9 GeoPress All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced without written permission in writing,
TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology
 Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY: An overview. Definitions. Faulting. Folding GEOLOGIC PROCESSES 9/17/2013 TOPOGRAPHIC RELIEF
 TOPOGRAPHIC RELIEF PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY: An overview Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 0913 2 Definitions GEOLOGIC PROCESSES Geography: Study of people living on the surface of the earth. Geology: the study of the
TOPOGRAPHIC RELIEF PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY: An overview Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 0913 2 Definitions GEOLOGIC PROCESSES Geography: Study of people living on the surface of the earth. Geology: the study of the
Why is quartz one of the most weathering-resistant minerals?
 Why is it a poor idea to use limestone for tombstones in a wet hot area like the Amazon rainforest? A) Because limestone weathers at a very fast rate B) Because limestone weathers at a very low rate C)
Why is it a poor idea to use limestone for tombstones in a wet hot area like the Amazon rainforest? A) Because limestone weathers at a very fast rate B) Because limestone weathers at a very low rate C)
Name. 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different soil horizons, A, B, C, and D, are shown.
 Name 1. In the cross section of the hill shown below, which rock units are probably most resistant to weathering? 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different
Name 1. In the cross section of the hill shown below, which rock units are probably most resistant to weathering? 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different
Name a sedimentary rock and explain how was it formed. Y11 Changing landscapes of the UK
 Name a sedimentary rock and explain how was it formed Small particles that have been transported and deposited in layers, such as sandstone; or from the remains of plants and animals e.g. chalk. Pressure
Name a sedimentary rock and explain how was it formed Small particles that have been transported and deposited in layers, such as sandstone; or from the remains of plants and animals e.g. chalk. Pressure
Science 8 - Water Systems Test - Chapters 1-2
 Science 8 - Water Systems Test - Chapters 1-2 Multiple Choice (30 marks) Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What percentage represents the amount of fresh
Science 8 - Water Systems Test - Chapters 1-2 Multiple Choice (30 marks) Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What percentage represents the amount of fresh
How to Build a Mountain and other Geologic Structures. But first a short review
 How to Build a Mountain and other Geologic Structures But first a short review Where do we see deep earthquakes? What is happening there? What can happen at a plate boundary? 1. Plates can move apart
How to Build a Mountain and other Geologic Structures But first a short review Where do we see deep earthquakes? What is happening there? What can happen at a plate boundary? 1. Plates can move apart
The Geology of Sebago Lake State Park
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities September, 2002 43 55 17.46 N, 70 34 13.07 W Text by Robert Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by Robert Johnston Introduction Sebago
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities September, 2002 43 55 17.46 N, 70 34 13.07 W Text by Robert Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by Robert Johnston Introduction Sebago
CAPE Unit 1 Module 2 & 3. Topic Specific Objectives Content Explain the main concepts, flows and processes associated with coastal environments
 # Week(s) Wks 1-3 CAPE Unit 1 Module 2 & 3 Topic Specific Objectives Content Explain the main concepts, flows and processes associated with coastal environments Wave formation, structure, types Textbook
# Week(s) Wks 1-3 CAPE Unit 1 Module 2 & 3 Topic Specific Objectives Content Explain the main concepts, flows and processes associated with coastal environments Wave formation, structure, types Textbook
Characteristics and processes associated with the development of Hilly Landscapes
 GRADE 11 GEOGRAPHY SESSION 1: GEOMORPHOLOGY I (TOPOGRAPHY) Key Concepts In this lesson we will focus on summarising what you need to know about: Topography associated with Horizontally Layered Rocks Topography
GRADE 11 GEOGRAPHY SESSION 1: GEOMORPHOLOGY I (TOPOGRAPHY) Key Concepts In this lesson we will focus on summarising what you need to know about: Topography associated with Horizontally Layered Rocks Topography
Earth Science Chapter 9. Day 6 - Finish Capillary Action Lab - Quiz over Notes - Review Worksheets over Sections 9.2 and 9.3
 Earth Science Chapter 9 Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Read Section 9.1 Surface Water Chapter 9 Term Sheet Notes over Section 9.1 Surface Water Section 9.1 Review Worksheets Quiz over Section 9.1 Notes Virtual Lab
Earth Science Chapter 9 Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Read Section 9.1 Surface Water Chapter 9 Term Sheet Notes over Section 9.1 Surface Water Section 9.1 Review Worksheets Quiz over Section 9.1 Notes Virtual Lab
Pacific Northwest Rock Lab, Part II. Igneous Rocks. Name Per.
 Name Per. Pacific Northwest Rock Lab, Part II After you ve classified all your rocks, place their numbers next to the names and read the information about the rock. Check the classifications here (igneous,
Name Per. Pacific Northwest Rock Lab, Part II After you ve classified all your rocks, place their numbers next to the names and read the information about the rock. Check the classifications here (igneous,
1/6/ th Grade Earth s Surface. Chapter 3: Erosion and Deposition. Lesson 1 (Mass Movement)
 Lesson 1 (Mass Movement) 7 th Grade Earth s Surface Chapter 3: Erosion and Deposition Weathering the chemical and physical processes that break down rock at Earth s surface Mechanical weathering when rock
Lesson 1 (Mass Movement) 7 th Grade Earth s Surface Chapter 3: Erosion and Deposition Weathering the chemical and physical processes that break down rock at Earth s surface Mechanical weathering when rock
GCSE 4250/01 GEOLOGY Theory Paper (Paper version of on-screen assessment)
 Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number GCSE 4250/01 GEOLOGY Theory Paper (Paper version of on-screen assessment) A.M. THURSDAY, 16 May 2013 1 1 2 hours ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to
Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number GCSE 4250/01 GEOLOGY Theory Paper (Paper version of on-screen assessment) A.M. THURSDAY, 16 May 2013 1 1 2 hours ADDITIONAL MATERIALS In addition to
Quiz 1. 3) Which of the following planetary bodies has the least number of impact craters on its surface? A) Mercury B) Mars C) the Moon D) Earth
 Quiz 1 1) Earth's atmosphere is unique among the moons and planets in that A) it has a nitrogen (N2) rich atmosphere. B) it is rich in oxygen (O2) and nitrogen (N2). C) it is rich in carbon dioxide because
Quiz 1 1) Earth's atmosphere is unique among the moons and planets in that A) it has a nitrogen (N2) rich atmosphere. B) it is rich in oxygen (O2) and nitrogen (N2). C) it is rich in carbon dioxide because
How mountains are made. We will talk about valleys (erosion and weathering later)
 How mountains are made We will talk about valleys (erosion and weathering later) http://www.ilike2learn.com/ilike2learn/mountainmaps/mountainranges.html Continent-continent plate convergence Less dense,
How mountains are made We will talk about valleys (erosion and weathering later) http://www.ilike2learn.com/ilike2learn/mountainmaps/mountainranges.html Continent-continent plate convergence Less dense,
Landforms in Canada. Canada is made up of three dis;nct types of landforms: Canadian Shield Highlands Lowlands
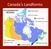 Canada s Landforms What is a Landform? A landform is any physical feature of the Earth s surface having a characteris;c, recognizable shape, produced by natural causes. Landforms include major features
Canada s Landforms What is a Landform? A landform is any physical feature of the Earth s surface having a characteris;c, recognizable shape, produced by natural causes. Landforms include major features
Structural Geology Lab. The Objectives are to gain experience
 Geology 2 Structural Geology Lab The Objectives are to gain experience 1. Drawing cross sections from information given on geologic maps. 2. Recognizing folds and naming their parts on stereoscopic air
Geology 2 Structural Geology Lab The Objectives are to gain experience 1. Drawing cross sections from information given on geologic maps. 2. Recognizing folds and naming their parts on stereoscopic air
What is weathering and how does it change Earth s surface? Answer the question using
 7 th Grade Lesson What is weathering and how does it change Earth s surface? Answer the question using the sentence frame. You have 4 minutes. Weathering is. This changes the Earth s surface because. 1
7 th Grade Lesson What is weathering and how does it change Earth s surface? Answer the question using the sentence frame. You have 4 minutes. Weathering is. This changes the Earth s surface because. 1
Potential short answer questions: What is Pangea? Describe at least 4 pieces of evidence that led Wegener to suggest the theory of Continental Drift.
 6th Grade Earth Science Fall Semester Mid-Term Study Guide The mid-term may include: 4 short answer questions,1-2 sketches to draw and/or label, 4 partially filled charts which you should complete, 30
6th Grade Earth Science Fall Semester Mid-Term Study Guide The mid-term may include: 4 short answer questions,1-2 sketches to draw and/or label, 4 partially filled charts which you should complete, 30
What are the different ways rocks can be weathered?
 Romano - 223 What are the different ways rocks can be weathered? Weathering - the breakdown of rocks and minerals at the Earth s surface 1. 2. PHYSICAL WEATHERING Rock is broken into smaller pieces with
Romano - 223 What are the different ways rocks can be weathered? Weathering - the breakdown of rocks and minerals at the Earth s surface 1. 2. PHYSICAL WEATHERING Rock is broken into smaller pieces with
Name Date Class. Directions: Use the diagram below to answer question Florida Progress Monitoring and Benchmark Assessments
 b e n c h m a r k t e s t : e a r t h a n d s p a c e s c i e n c e Multiple Choice 1. Geologists obtain indirect evidence about Earth s interior by A measuring pressure differences at Earth s surface.
b e n c h m a r k t e s t : e a r t h a n d s p a c e s c i e n c e Multiple Choice 1. Geologists obtain indirect evidence about Earth s interior by A measuring pressure differences at Earth s surface.
Figure 1 The map shows the top view of a meandering stream as it enters a lake. At which points along the stream are erosion and deposition dominant?
 1. In which type of climate does chemical weathering usually occur most rapidly? 1. hot and dry 3. cold and dry 2. hot and wet 4. cold and wet 2. Figure 1 The map shows the top view of a meandering stream
1. In which type of climate does chemical weathering usually occur most rapidly? 1. hot and dry 3. cold and dry 2. hot and wet 4. cold and wet 2. Figure 1 The map shows the top view of a meandering stream
What landforms make up Australia?!
 What landforms make up Australia? The tectonic forces of folding, faulting and volcanic activity have created many of Australia's major landforms. Other forces that work on the surface of Australia, and
What landforms make up Australia? The tectonic forces of folding, faulting and volcanic activity have created many of Australia's major landforms. Other forces that work on the surface of Australia, and
How to Build a Mountain and other Geologic Structures. But first, questions
 How to Build a Mountain and other Geologic Structures But first, questions Questions your students might ask How were Montana s mountains formed? How old are the mountains? What are the different ways
How to Build a Mountain and other Geologic Structures But first, questions Questions your students might ask How were Montana s mountains formed? How old are the mountains? What are the different ways
Science EOG Review: Landforms
 Mathematician Science EOG Review: Landforms Vocabulary Definition Term canyon deep, large, V- shaped valley formed by a river over millions of years of erosion; sometimes called gorges (example: Linville
Mathematician Science EOG Review: Landforms Vocabulary Definition Term canyon deep, large, V- shaped valley formed by a river over millions of years of erosion; sometimes called gorges (example: Linville
Lecture Outline Wednesday - Friday February 14-16, 2018
 Lecture Outline Wednesday - Friday February 14-16, 2018 Quiz 2 scheduled for Friday Feb 23 (Interlude B, Chapters 6,7) Questions? Chapter 6 Pages of the Past: Sedimentary Rocks Key Points for today Be
Lecture Outline Wednesday - Friday February 14-16, 2018 Quiz 2 scheduled for Friday Feb 23 (Interlude B, Chapters 6,7) Questions? Chapter 6 Pages of the Past: Sedimentary Rocks Key Points for today Be
A physical feature of the Earth s surface
 Earth s Landforms A physical feature of the Earth s surface A physical feature of the Earth s surface LANDFORM Highest of Earth s physical features Highest of Earth s physical features MOUNTAIN Low area
Earth s Landforms A physical feature of the Earth s surface A physical feature of the Earth s surface LANDFORM Highest of Earth s physical features Highest of Earth s physical features MOUNTAIN Low area
UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA
 UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA A map that shows Earth s Topographic Map surface topography, which is Earth s shape and features Contour
UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA A map that shows Earth s Topographic Map surface topography, which is Earth s shape and features Contour
Late 20 th Century Tests of the Continental Drift Hypothesis
 Late 20 th Century Tests of the Continental Drift Hypothesis 5 Characteristics of the Ocean Trenches Unless otherwise noted the artwork and photographs in this slide show are original and by Burt Carter.
Late 20 th Century Tests of the Continental Drift Hypothesis 5 Characteristics of the Ocean Trenches Unless otherwise noted the artwork and photographs in this slide show are original and by Burt Carter.
Coasts Key Word Glossary
 Coasts Key Word Glossary Abrasion Also known as corrosion. It is the wearing away of the cliff by sand, fragments of rock and boulders that are being hurled at the cliff by the waves. It causes grinding
Coasts Key Word Glossary Abrasion Also known as corrosion. It is the wearing away of the cliff by sand, fragments of rock and boulders that are being hurled at the cliff by the waves. It causes grinding
Black Point & Bihler Point
 Black Point & Bihler Point Conglomerate Photo: looking north toward end of Black Point (south of post 1) All of the rocks in this photo are conglomerate. Both Black Point and Bihler Point are formed from
Black Point & Bihler Point Conglomerate Photo: looking north toward end of Black Point (south of post 1) All of the rocks in this photo are conglomerate. Both Black Point and Bihler Point are formed from
Pratice Surface Processes Test
 1. The cross section below shows the movement of wind-driven sand particles that strike a partly exposed basalt cobble located at the surface of a windy desert. Which cross section best represents the
1. The cross section below shows the movement of wind-driven sand particles that strike a partly exposed basalt cobble located at the surface of a windy desert. Which cross section best represents the
1 Shoreline Landforms 2. 2 Emergent v. Submergent 2. 3 Wavecutting 3. 4 Planview 4. 5 Marine Terraces 5. 6 California 7. 7 Tombolos, Sea Stacks 8
 Shorelines November 9, 2008 Contents 1 Shoreline Landforms 2 2 Emergent v. Submergent 2 3 Wavecutting 3 4 Planview 4 5 Marine Terraces 5 6 California 7 7 Tombolos, Sea Stacks 8 8 Active Processes 9 9 Emergence
Shorelines November 9, 2008 Contents 1 Shoreline Landforms 2 2 Emergent v. Submergent 2 3 Wavecutting 3 4 Planview 4 5 Marine Terraces 5 6 California 7 7 Tombolos, Sea Stacks 8 8 Active Processes 9 9 Emergence
UNIT 4: Earth Science Chapter 21: Earth s Changing Surface (pages )
 CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be turned in to your teacher
CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be turned in to your teacher
