Research Article Risk Assessment of Drought in the Yangtze River Delta Based on Natural Disaster Risk Theory
|
|
|
- Logan Norton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hindawi Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society Volume 2017, Article ID , 7 pages Research Article Risk Assessment of Drought in the Yangtze River Delta Based on Natural Disaster Risk Theory Gaofeng Fan, 1 Yong Zhang, 2 Yue He, 1 and Kuo Wang 1 1 Zhejiang Climate Center, Hangzhou , China 2 Meteorological Observation Centre, China Meteorological Administration, Beijing , China Correspondence should be addressed to Yong Zhang; yzhang@cma.gov.cn Received 13 January 2017; Revised 16 April 2017; Accepted 9 May 2017; Published 31 May 2017 Academic Editor: Yong Zhou Copyright 2017 Gaofeng Fan et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. The risk of drought in the Yangtze River Delta Region (YRDR) was assessed using the method of natural disaster risk assessment. Based on the index of disaster risk, the assessment results of risk elements such as drought hazard and vulnerability were calculated in the YRDR. The division of relative drought risk levels in the YRDR was produced at the scale of county (city, district) and township. The results indicated that the areas of highest hazard of drought are located in the northern area of the YRDR. Areas with the greatest vulnerability of drought included Shanghai, Jiaxing, Wuxi, and Hangzhou. The highest risks of drought were mainly distributed in the north of the YRDR; the proportion of slightly high and extremely high risk areas in Shanghai, Nantong, Zhenjiang, Yangzhou, and Taizhou (Jiangsu province) is over 95%. The lowest-risk areas included the southeast coastal area of the YRDR, especially in Hangzhou, and Taizhou (Zhejiang province), where the proportion of slightly high and extremely high risk areas is below 5%. Based on this drought risk assessment, it is critical to establish a drought assessment system including both guarding against and addressing drought. 1. Introduction In its series of assessment reports, the IPCC noted that drought is the most common natural disaster in the world. According to estimates, global economic losses of $6 8 billion per year are caused by drought. Not only are drought costs much higher than the costs of other meteorological disasters, but drought risk has also shown an increasing trend [1]. To confirm the impact of drought in the future, the governments of various countries have implemented large numbers of engineering-based and non-engineering-based disaster mitigation actions. However, mitigation actions generally involve adjusting huge capital investments or affect a wide range of social systems. Uninformed mitigation actions will inevitably lead to misuse of human, material, and financial resources, which is contrary to the original goal of mitigation. To avoid the blindness that can lead to misuse of resources, it is important to perform scientific and systematic analyses of disaster preparation, occurrence, and development [2, 3]. A conceptual framework, which emphasizes the combined role of hazard and vulnerability in defining risk, is used for the study [4]. Based on the framework, the relative drought level or the absolute risk is calculated for the purpose of disaster risk zoning and risk management [5, 6]. Regarding techniques, some studies use information diffusion theory, GIS, and remote sensing techniques to identify the degrees and levels of drought risk, drought evaluation, or drought monitoring [7 9]. These studies of drought risk assessment have built a solid foundation. There are two stages of research on drought risk assessment. The first stage ( ) focused on responses to crisis and risk management awareness. Several global droughts triggered a new understanding of the harm of drought, as people began to realize that drought was associated with notonlyanaturalprocessbutalsothemeasurestakento address such disasters. Investigating the factors that affect drought based on a summary of past disasters, scientists became aware of the existence of drought risk, recognized the role of some nonnatural factors in drought, and began
2 2 Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society taking the initiative to ascertain the effects of drought. Consciousness of risk management became stronger [10, 11]. The second stage (since 2001) has focused on the occurrence of drought and highlighted the role of nonnatural factors in its mitigation. With the deepening study of global climate change, people s awareness of risk became more and more intense and addressing future disaster risk became a subject of study [12]. A series of studies examined climate change and the development of drought, the vulnerability of drought, and the risk assessment methods of drought. Most of these studies werefromaquantitativeorsemiquantitativeperspective;they explored the laws of drought development and emphasized the roles of human society, the economy, and environment in the face of drought pressure and the response to drought. These studies also actively tested measures to address future drought risk [13 15]. The Yangtze River Delta Region (YRDR) is the alluvial delta by the Yangtze River and the Qiantang River, which covers 210 thousand square kilometers and includes the southeastofjiangsuprovince(8cities:nanjing,suzhou,wuxi, Changzhou, Zhenjiang, Nantong, Yangzhou, and Taizhou), Shanghai, and the northeast of Zhejiang province (7 cities: Hangzhou, Ningbo, Huzhou, Jiaxing, Shaoxing, Zhoushan, and Taizhou). YRDR is one of the most developed areas in China, but drought has a huge impact on society in this region. Disaster risk assessment is an important way for scientifically and systematically analyzing disaster risk and is a key process in the formation of disaster prevention and mitigation policies. Therefore, it is critical to study the process of drought risk assessment. 2. Data The data sources used for risk assessment and zoning of drought in the YRDR include basic geographic information data, social economic statistics, and basic meteorological observation data. Basic geographic information data consists of 1 : basic geographic information pieces of data in the YRDR, including topography, water distribution, land use types, and administrative boundaries. These data are provided by the surveying and mapping department. Meteorological observation data consists of meteorological data from 105 National Weather Stations in the YRDR from 1961 to 2014, including daily rainfall and temperature. Social economic data consists of statistical yearbook data from counties in the YRDR from 2000 to 2014, including administrative region land area, arable land area, total population, rural population, GDP, agricultural output value, local fiscal expenditure, total power of agricultural machinery, and social welfare statistical indicators. 3. Method 3.1. Risk Assessment Model. From the view of the mechanism of natural disasters, the following conditions are necessary for disaster formation: first, factors inducing disasters, such as drought caused by long-term lack of rain, and second, vulnerability of disaster, composed of the disaster-forming Table 1: Drought rank of MDCI. Rank Drought grade MDCI 1 Normalorwet 0.6 < MDCI 2 Light drought 1.2< MDCI Mediumdrought 1.8 < MDCI Drought 2.4 < MDCI Severedrought MDCI 2.4 environment and the disaster-bearing bodies. The disasterforming environment includes topography, water distribution,vegetationcover,andotherfactors.thedisaster-forming environment enlarges or reduces the hazard factors. From the perspective of the disaster-bearing body, the disasterforming environment is an important factor in determining the vulnerability of the disaster-bearing body. The disasterbearing body, including population, economic, and other factors, and the quantity and space distribution of the disaster-prone environment determine the vulnerability of hazard-affected bodies in a drought [16 18]. Referring to the natural disaster risk index, the drought risk assessment model is established as follows [19]: RI = HI VI, (1) where RI is the disaster risk, HI is the drought hazard, and VI is the drought vulnerability Drought Hazard Assessment. The drought hazard is the possibility of a certain intensity of drought, which is usuallydeterminedbythefrequencyandintensityofdrought. The first step is to determine the index system, which can reasonably evaluate the severity of drought. As the cause of drought is very complex and many factors are involved, many drought indicators are used for specific research purposes, so the drought index has different spatial and temporal scales [19]. Some indicators reflect drought that is related to various physical processes (such as soil moisture evaporation, surface runoff, and ground water replenishment) through the mechanism of drought research, which aims to improve the accuracy of predicting drought intensity and duration [20, 21]. Other drought indexes reflect the intensity and duration of drought using statistical methods of precipitation distribution [22, 23]. For real-time drought monitoring and early warnings, a drought index should be established which can not only accurately monitor drought occurrence, development, and termination but also match different seasons and regions. The Meteorological Drought Composite Index (MDCI) is used to diagnose drought hazard assessment. MDCI is the national drought monitoring standard of china [24]. MDCI is a comprehensive index based on Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) and Relative Moisture Index (RMI): MDCI = 0.4Z M Z 9, (2) where Z 3 and Z 9 represent the SPI for last 30 and 90 days, respectively, and M 3 is the RMI for last 30 days; computing method follows Shahid and Behrawan (2008) [19]. Using observationaldailydata,mdciiscalculateddaybydayand thedroughtrankisdefinedintable1.
3 Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society 3 Define the regional drought hazard index (HI) as follows: NH = 0.095D l D m D d D s HI = NH M, (3) where the NH is for the annual regional drought index; D l, D m, D d,andd s represent the days of occurrence at a single station for light drought, medium drought, drought, and severe drought, respectively. HI is the regional drought intensity index, NH is the sum of the annual drought index, and M is the total number of years Drought Vulnerability Assessment. Drought vulnerability is composed of the disaster-forming environment and disaster-bearing bodies [19]. The vulnerability of the disasterforming environment in the YRDR is analyzed mainly using its topographic features, water system distribution, and land use characteristics [11]. Generally speaking, areas at low altitude are less vulnerable to drought, and higher areas are relatively more vulnerable. In addition, there is a close relationship between drought and topography. If there is fluctuation in the terrain, surface runoff will be collected in the gully and will discharge, and thus drought occurs more easily. The river and reservoir have very important effects on water storage and irrigation areas. Thus, the distribution density of the river network is also an important factor that cannot be ignored when considering drought. The degree of drought in various types of land is different, and the impact of drought is greatest on arable land. In the field of disaster risk, the administrative unit is usually regarded as the disaster-bearing body, and its vulnerability usually reflects its population structure, social economic structure, and other social statistical indicators [14].Thevulnerabilityofadisaster-bearingbodyismainly determined by the number of disaster-bearing bodies; the vulnerable evaluation factors of a disaster-bearing body involve the ratio of the agricultural GDP accounted for in the total GDP, the proportion of the agricultural population, the average regional GDP, and the ratio of farm crop-sown areas accountedforinlandarea.thesumtotalofeachfactoris calculated after normalization. Based on former analysis, drought vulnerability includes 7 factors: the topographic factors, the water system factors, different types of land, the ratio of the agricultural GDP accounted for in the total GDP, the proportion of the agricultural population, the average regional GDP, and the ratio of farm crop-sown areas accounted for in land area. (1) The Topographic Factors. The topographic factors are calculated as standard deviations of terrain in the YRDR [25, 26], with the selected range of 100 m 100 m (5 5pitch), by the Digital Elevation Model (DEM) with resolution of 25 m 25 m. The terrain vulnerability is shown in Table 2. (2) The Water System Factors. Two factors are considered as influencing factors in the vulnerability index of water system: the density of river network and the buffer of rivers and lakes [25, 26]. Because of the high density of river network, the area Terrain elevation (m) Table 2: Assignment table of terrain vulnerability. Topographic standard deviation < Table 3: Classification criteria for buffer widths and their susceptible index in different waters. Type of water Buffer width (km)/impact index First level buffer Second level buffer km 2 reservoir/lake 0.5/0.3 1/ km 2 reservoir/lake 2/0.35 4/ km 2 reservoir/lake 3/0.4 6/0.2 >100 km 2 reservoir/lake 5/0.45 9/0.25 First level river 4/0.45 8/0.25 Second level river 3/0.35 6/0.15 irrigation conditions are fine and the effects of the drought degree are light. By normalizing the river network density, the high density area is converted to low drought vulnerability. The river network density index is calculated, and the formula is as follows: Den = (X max X) (X max X min ), (4) where Den is the river network density index, X max is the maximum density of the river network, X min is the minimal density of the river network, and X represents the river network density. For calculation of rivers and lakes buffer, rivers are divided into primary rivers (such as the Yangtze River and Huaihe River) and secondary rivers, such as tributaries and other rivers. Lakes are divided into primary buffers and secondary buffers, with appropriate weights of vulnerability factors according to the water area; the principle is to use the maximum for the primary river and large bodies of water andtheminimumforthesecondaryriversandsmallbodies of water. Table 3 shows the width of different buffer zones and the corresponding impact index; when the index value is greater, the effect of drought risk is smaller. The vulnerability of water system is calculated by a comprehensive evaluation method, such as the following formula: WF = Den (1 Bu), (5) where WF represents the water system vulnerability index, Den is the river network density index, and Bu is the buffer vulnerability index. (3) Different Types of Land. Different types of land use can reflect the distribution of social and economic value and
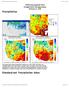
4 4 Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society Table 4: Weight of different land types for drought. Cultivated land Grassland Woodland Land for urban and rural residents Wetlands and water bodies Other Influence degree natural ecological value. According to different types of social and natural values, a certain weight is applied based on vulnerability to drought (Table 4). N (4) Others. The ratio of the agricultural GDP accounted for in the total GDP, the proportion of the agricultural population, theaverageregionalgdp,andtheratiooffarmcrop-sown areas accounted for in land area are four normalization factors calculated based on social and economic statistical data from each of the counties or districts. The composite drought vulnerability index (VI) of the integrated layers is calculated by using the following formula: VI = TF + WF + DF + AF + PF + GF + CF, (6) 7 whereviratingsareassignedtodroughtvulnerability;tf ratings are assigned to the topographic factors; WF ratings are assigned to the water system factors; DF ratings are assigned to different types of land; AF ratings are assigned to the ratio of the agricultural GDP accounted for in the total GDP; PF ratings are assigned to the proportion of the agricultural population; GF ratings are assigned to the average regional GDP; CF ratings are assigned to the ratio of farm crop-sown areas accounted for in land area Drought Risk Index Analysis. Based on formula (1) of the drought risk index, the drought hazard and vulnerability are calculated by the layer operation function of ArcGIS software; the drought risk index layer is obtained. In the YRDR, the drought risk index is divided into five risk levels using natural break point classification in ArcGIS, extremely high, slightly high, medium, slightly low, and extremely low, to obtain the relative risk grade division of drought. 4. Results The assessment of drought hazard over the Yangtze River Delta shows that the hazard distribution increased gradually from south to north in the YRDR (Figure 1), with the higher hazard region at the north of the Yangtze River and the lowest hazard region along the coast of Zhejiang province. Due to the complex topography and precipitation distribution, the hazard faced by islands is higher than other areas in Zhejiang province. The vulnerability is generally higher in the southern partoftheyrdr(figure2).becausethenorthernpart of the YRDR is the Yangtze River estuary plain, the flat terrain, dense river network, and numerous lakes make this area s disaster-forming vulnerability low overall. In contrast, the southern part of the YRDR is a mountainous region, where higher terrain and a sparse river network enhance Extremely high Slightly high Medium (km) Slightly low Extremely low Figure 1: Distribution of drought hazard grades in the YRDR. the drought hazard factor and increase vulnerability. Moreover, there are developed strong economies, high population densities, crop acreages, and a large number of industrial enterprises in the southern part of Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Shanghai. The results of calculating the grade division and relative risk index of drought in the YRDR are shown in Figure 3. The extremely high risk areas are mainly concentrated in the northern part of the YRDR, including Taizhou (Jiangsu province), Yangzhou, and most parts of Nantong. The slightly high risk areas are concentrated in Changzhou, Suzhou, Nanjing, Zhenjiang, and Zhoushan; Shanghai and Jiaxing are also included. The extremely low and slightly low risk areas areconcentratedinthesouthoftheyrdr,especiallyinthe southeast coastal area, Taizhou (Zhejiang province), Ningbo, Shaoxing, and Hangzhou, while the rest of the YRDR are medium risk areas. Table 5 shows the statistics of the risk levels for drought in the YRDR cities. The relative risk level in most areas of Shanghai is slightly high (68.59%) or extremely high (26.47%). In the northern YRDR, the proportion of slightly high and extremely high risk areas in Nantong, Zhenjiang, Yangzhou, and Taizhou (Jiangsu province) is more than 95%. The overall level of risk in Zhejiang province is lower than that in Jiangsu province especially in Hangzhou and Taizhou, where the proportion of slightly high and extremely highriskareasisbelow5%.thelevelofdroughtriskin Jiaxing and Zhoushan, where the proportions of slightly high
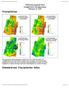
5 Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society 5 Table 5: Statistics of risk levels of drought disasters in the YRDR. Administrative region Comprehensive risk level (area/percentage, km 2 /%) Provinces Prefecture level city Extremely low Slightlylow Medium Slightlyhigh Extremely high Shanghai 0.00/ / / / /26.47 Nanjing 7.17/ / / / /15.72 Wuxi 12.30/ / / / /44.49 Changzhou 0.00/ / / / /15.93 Jiangsu Suzhou 0.00/ / / / /20.26 Nantong 0.00/ / / / /67.93 Yangzhou 0.00/ / / / /74.85 Zhenjiang 0.00/ / / / /42.62 Taizhou 0.00/ / / / /89.86 Hangzhou / / / / /0.00 Ningbo / / / / /0.75 Huzhou / / / / /0.66 Zhejiang Jiaxing 0.00/ / / / /22.23 Shaoxing / / / / /0.03 Zhoushan 0.00/ / / / /25.00 Taizhou / / / / /1.22 N N (km) (km) Extremely high Slightly high Medium Slightly low Extremely low Extremely high Slightly high Medium Slightly low Extremely low Figure 2: Distribution of drought vulnerability grades in the YRDR. Figure 3: The risk distribution of drought in the YRDR. and extremely high risk areas are over 80%, respectively, is relatively high compared with other cities in Zhejiang province. 5. Conclusions Natural disaster risk assessment is applied to drought in the YRDR. Using this method, natural disaster risk is caused by hazardandvulnerability.therelativelevelofdroughtrisk zoning in the YRDR is achieved based on calculating the drought risk index. There is high drought hazard in the north of the YRDR, while the coastal areas of Zhejiang face the lowest hazard. The higher drought vulnerability in the YRDR is mainly distributed in economically developed areas such as the southern part of Jiangsu, the northern part of Zhejiang, and Shanghai. Additionally, the northern part of the YRDR consists of the Yangtze River estuary plain, flat terrain, dense
6 6 Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society river network, and numerous lakes; the drought vulnerability is a little low overall. In contrast, the southern part of the YRDR is a mountainous region, where higher terrain and a sparse river network enhance the drought factor and increase the drought vulnerability. The areas at extremely high risk for drought are mainly concentrated in the northern part of the YRDR, including Yangzhou and most parts of Taizhou (Jiangsu province). The slightly high risk areas are concentrated in Nanjing, Changzhou, Nantong, Zhoushan, Jiaxing, and Shanghai. The extremely low and slightly low risk areas are concentrated in the south of the YRDR, especially in the southeast coastal area, Taizhou (Zhejiang province), Shaoxing, and Hangzhou, whiletherestoftheyrdraremediumriskareas. Building on the foundation of drought risk assessment, research and development regarding drought risk management systems are important issues for the future. At present, because of the lack of awareness of drought risk management, most departments focus on responses to disaster while ignoring disaster prevention. An important aspect of establishing a drought risk management system is to reduce drought losses; this approach integrates drought risk assessment, risk assessment, risk response strategy, and public risk awareness. Conflicts of Interest The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper. Acknowledgments The research has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no ) and the National Science and Technology Support Program: research on the risk assessment technology of natural disasters in the YRDR (Grant no. 2008BAK50B07). References [1] IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change), Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability, Cambridge University Press, New York, NY, USA, [2] J. Strutt, Risk Management Centre of Industrial Safety and Reliability, American Risk and Insurance Association, Grandfield University, 1999, [3] K. Wang, G.-L. Feng, Y.-X. Zeng, and X.-J. Wang, Analysis of stable components in the extended-range forecast for the coming days in winter 2010 and 2011, Chinese Physics B, vol.22,no.12,articleid129202,2013. [4] K. Hewitt, Regions of Risk, Longman Singapore Publisher Ltd, [5]A.Amendola,Y.Ermoliev,T.Y.Ermolieva,V.Gitis,G.Koff, and J. Linnerooth-Bayer, A systems approach to modeling catastrophic risk and insurability, Natural Hazards,vol.21,no. 2-3, pp , [6] R. Djalante, C. Holley, and F. Thomalla, Adaptive governance and managing resilience to natural hazards, International Disaster Risk Science, vol. 2, no. 4, [7] P. K. Das, S. Murthy C, and S. Mvr, Monitoring of seasonal dryness/wetness conditions using shortwave angle slope index for early season agricultural drought assessment, Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk,vol.5,no.3,pp ,2014. [8] X.J.Liu,J.Q.Zhang,D.L.Ma,Y.L.Bao,Z.J.Tong,andX.P.Liu, Dynamic risk assessment of drought disaster for maize based on integrating multi-sources data in the region of the northwest of Liaoning Province, China, Natural Hazards, vol. 65, no. 3, pp , [9] N.R.Dalezios,A.Blanta,N.V.Spyropoulos,andA.M.Tarquis, Risk identification of agricultural drought for sustainable Agroecosystems, Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, vol.14,no.9,pp ,2014. [10] D. A. Wilhite, Drought as a natural hazard: concepts and definitions, in Drought: A Global Assessment, A. Wilhite, Ed., Natural hazards and disasters series, pp. 3 18, Routledge, New York, NY, USA, Chapter Wilhite A edition, [11] P. Blaikie, T. Cannon, I. Davis, and B. Wisner, At Risk: Natural Hazards, People s Vulnerability and Disasters, Routledge,London, UK, [12] K.Wang,G.Feng,T.Ye,X.Wang,andP.Liu, Thevariation characteristics of Asian surface temperature and precipitation in the early 21st century, Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society, vol. 2016, Article ID , [13] S. S. Mishra and R. Nagarajan, Spatio-temporal drought assessment in Tel river basin using Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) and GIS, Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk,vol. 2, no. 1, pp , [14] L. C. Botterill and M. J. Hayes, Drought triggers and declarations: Science and policy considerations for drought risk management, Natural Hazards,vol.64,no.1,pp ,2012. [15] IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change), Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental PanelonClimateChange, Cambridge University Press, New York, NY, USA, [16] V. Blauhut, L. Gudmundsson, and K. Stahl, Towards pan- European drought risk maps: Quantifying the link between drought indices and reported drought impacts, Environmental Research Letters,vol.10,no.1,ArticleID014008,2015. [17] S. Jülich, Development of a composite index with quantitative indicators for drought disaster risk analysis at the micro level, Human and Ecological Risk Assessment,vol.21,no.1,pp.37 66, [18] K. Strzepek, G. Yohe, J. Neumann, and B. Boehlert, Characterizing changes in drought risk for the United States from climate change, Environmental Research Letters,vol.5,no.4,ArticleID , [19] S. Shahid and H. Behrawan, Drought risk assessment in the western part of Bangladesh, Natural Hazards, vol. 46,no. 3, pp , [20] W. C. Palmer, Meteorological Drought, U.S. department of Commerce Weather Bureau Research Paper, [21] W. C. Palmer, Keeping track of crop moisture condition, nationwise: the new crop moisture index, Weatherwise,vol.21, no. 4, pp , [22] M. J. Hayes, M. D. Svoboda, D. A. Wilhite, and O. V. Vanyarkho, Monitoring the 1996 drought using the standardized precipitation index, Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society,vol. 80,no.3,pp ,1999. [23] X.-C. Yuan, Y.-L. Zhou, J.-L. Jin, and Y.-M. Wei, Risk analysis for drought hazard in China: A case study in Huaibei Plain, Natural Hazards,vol.67,no.2,pp ,2013.
7 Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society 7 [24] GB/T , Classification of Meteorological Drought, China Standards Press, [25] X.N.Lu,J.Hong,andL.L.Wang, Droughtriskassessmentin complex landform area, Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,vol.31,no.1,pp ,2015. [26] W. H. Cao, H. P. Tao, and B. Kong, Automatic identification of geomorphology partition of Southwest China based on DEM data, in Soil and Water Conservation in China,vol.3,pp.38 41, 2011.
8 Advances in Operations Research Advances in Decision Sciences Applied Mathematics Algebra Probability and Statistics The Scientific World Journal International Differential Equations Submit your manuscripts at International Advances in Combinatorics Mathematical Physics Complex Analysis International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Mathematical Problems in Engineering Mathematics Volume 201 Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society Function Spaces Abstract and Applied Analysis International Stochastic Analysis Optimization
Analysis on Competitiveness of Regional Central Cities:
 Int. Statistical Inst.: Proc. 58th World Statistical Congress, 2011, Dublin (Session IPS031) p.476 Analysis on Competitiveness of Regional Central Cities: the case of Yangtze River Delta Xiaolin Pang,
Int. Statistical Inst.: Proc. 58th World Statistical Congress, 2011, Dublin (Session IPS031) p.476 Analysis on Competitiveness of Regional Central Cities: the case of Yangtze River Delta Xiaolin Pang,
Analysis of Impact of Urban Agglomeration Planning of Middle and Lower Yangtze River on International Trade Development in Central China.
 International Conference on Education, Management and Computing Technology (ICEMCT 2015) Analysis of Impact of Urban Agglomeration Planning of Middle and Lower Yangtze River on International Trade Development
International Conference on Education, Management and Computing Technology (ICEMCT 2015) Analysis of Impact of Urban Agglomeration Planning of Middle and Lower Yangtze River on International Trade Development
Emerging Needs, Challenges and Response Strategy
 Emerging Needs, Challenges and Response Strategy Development of Integrated Observing Systems in China JIAO Meiyan Deputy Administrator China Meteorological Administration September 2011 Geneva Outline
Emerging Needs, Challenges and Response Strategy Development of Integrated Observing Systems in China JIAO Meiyan Deputy Administrator China Meteorological Administration September 2011 Geneva Outline
FLOOD HAZARD MAPPING OF DHAKA-NARAYANGANJ-DEMRA (DND) PROJECT USING GEO-INFORMATICS TOOLS
 FLOOD HAZARD MAPPING OF DHAKA-NARAYANGANJ-DEMRA (DND) PROJECT USING GEO-INFORMATICS TOOLS Md. Aminul Islam MEE07178 Supervisor: Prof. Kuniyoshi TAKEUCHI ABSTRACT Dhaka-Narayanganj-Demra (DND) Project is
FLOOD HAZARD MAPPING OF DHAKA-NARAYANGANJ-DEMRA (DND) PROJECT USING GEO-INFORMATICS TOOLS Md. Aminul Islam MEE07178 Supervisor: Prof. Kuniyoshi TAKEUCHI ABSTRACT Dhaka-Narayanganj-Demra (DND) Project is
DROUGHT RISK EVALUATION USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS : A CASE STUDY IN LOP BURI PROVINCE
 DROUGHT RISK EVALUATION USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS : A CASE STUDY IN LOP BURI PROVINCE K. Prathumchai, Kiyoshi Honda, Kaew Nualchawee Asian Centre for Research on Remote Sensing STAR Program, Asian Institute
DROUGHT RISK EVALUATION USING REMOTE SENSING AND GIS : A CASE STUDY IN LOP BURI PROVINCE K. Prathumchai, Kiyoshi Honda, Kaew Nualchawee Asian Centre for Research on Remote Sensing STAR Program, Asian Institute
Surface Connects Author Index
 Surface Connects Author Index Shixin WANG, Yi ZHOU, Gewei LI, Weiqi ZHOU, Yalan LIU & Shirong CHEN NETWORK PLATFORM OF REMOTE SENSING FOR NATURAL DISASTER MONITORING & INFORMATION SERVING AND ITS APPLICATIONS
Surface Connects Author Index Shixin WANG, Yi ZHOU, Gewei LI, Weiqi ZHOU, Yalan LIU & Shirong CHEN NETWORK PLATFORM OF REMOTE SENSING FOR NATURAL DISASTER MONITORING & INFORMATION SERVING AND ITS APPLICATIONS
DROUGHT ASSESSMENT USING SATELLITE DERIVED METEOROLOGICAL PARAMETERS AND NDVI IN POTOHAR REGION
 DROUGHT ASSESSMENT USING SATELLITE DERIVED METEOROLOGICAL PARAMETERS AND NDVI IN POTOHAR REGION Researcher: Saad-ul-Haque Supervisor: Dr. Badar Ghauri Department of RS & GISc Institute of Space Technology
DROUGHT ASSESSMENT USING SATELLITE DERIVED METEOROLOGICAL PARAMETERS AND NDVI IN POTOHAR REGION Researcher: Saad-ul-Haque Supervisor: Dr. Badar Ghauri Department of RS & GISc Institute of Space Technology
Flood hazard mapping in Urban Council limit, Vavuniya District, Sri Lanka- A GIS approach
 International Research Journal of Environment Sciences E-ISSN 2319 1414 Flood hazard mapping in Urban Council limit, Vavuniya District, Sri Lanka- A GIS approach Abstract M.S.R. Akther* and G. Tharani
International Research Journal of Environment Sciences E-ISSN 2319 1414 Flood hazard mapping in Urban Council limit, Vavuniya District, Sri Lanka- A GIS approach Abstract M.S.R. Akther* and G. Tharani
A Research on the Level of the Coordinated Development in the Yangtze River Delta
 Modern Economy, 2014, 5, 414-423 Published Online April 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/me http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/me.2014.54040 A Research on the Level of the Coordinated Development in
Modern Economy, 2014, 5, 414-423 Published Online April 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/me http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/me.2014.54040 A Research on the Level of the Coordinated Development in
Government GIS and its Application for Decision Support
 Government GIS and its Application for Decision Support Zhang Qingpu (Chinese Academy of Surveying and Mapping, Email: zhangqp@casm.ac.cn) Abstract: Application of GIS in government agencies is called
Government GIS and its Application for Decision Support Zhang Qingpu (Chinese Academy of Surveying and Mapping, Email: zhangqp@casm.ac.cn) Abstract: Application of GIS in government agencies is called
USING STANDARDIZED PRECIPITATION EVAPOTRANSPIRATION INDEX TO ASSESS LOW FLOWS IN SOUTHERN BUH RIVER
 Sept. 14. Vol.. No. ISSN 11-4 1-14 IJREES & K.A.J. All rights reserved USING STANDARDIZED PRECIPITATION EVAPOTRANSPIRATION INDEX TO ASSESS LOW FLOWS IN SOUTHERN BUH RIVER NATALIIA YERMOLENKO, VALERIY KHOKHLOV
Sept. 14. Vol.. No. ISSN 11-4 1-14 IJREES & K.A.J. All rights reserved USING STANDARDIZED PRECIPITATION EVAPOTRANSPIRATION INDEX TO ASSESS LOW FLOWS IN SOUTHERN BUH RIVER NATALIIA YERMOLENKO, VALERIY KHOKHLOV
Empirical Study on the Relationship between Chemical Industry Agglomeration and Regional Economic Growth in Anhui Province
 1477 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 62, 2017 Guest Editors: Fei Song, Haibo Wang, Fang He Copyright 2017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-60-0; ISSN 2283-9216 The Italian
1477 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 62, 2017 Guest Editors: Fei Song, Haibo Wang, Fang He Copyright 2017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-60-0; ISSN 2283-9216 The Italian
Technological Progress, Industrial Transformation and Regional Development
 23/11/2012,RSA. London, UK Technological Progress, Industrial Transformation and Regional Development A Case Study of Yangtze River Delta Zhen Feng School of Architecture and Urban Planning, Nanjing University
23/11/2012,RSA. London, UK Technological Progress, Industrial Transformation and Regional Development A Case Study of Yangtze River Delta Zhen Feng School of Architecture and Urban Planning, Nanjing University
8 Current Issues and Research on Sediment Movement in the River Catchments of Japan
 8 Current Issues and Research on Sediment Movement in the River Catchments of Japan YUTAKA ICHIKAWA INTRODUCTION Prediction of sediment movement is one of the challenging tasks in water-related research.
8 Current Issues and Research on Sediment Movement in the River Catchments of Japan YUTAKA ICHIKAWA INTRODUCTION Prediction of sediment movement is one of the challenging tasks in water-related research.
Chapter 2 Urbanization in Jiangsu Province and Zhejiang Province in China Since ca. 1930
 Chapter 2 Urbanization in Jiangsu Province and Zhejiang Province in China Since ca. 1930 Yukio Himiyama, Miho Ikeshita and Tetsuya Shinde Abstract This chapter reports on the compilation and preliminary
Chapter 2 Urbanization in Jiangsu Province and Zhejiang Province in China Since ca. 1930 Yukio Himiyama, Miho Ikeshita and Tetsuya Shinde Abstract This chapter reports on the compilation and preliminary
Use of Geospatial data for disaster managements
 Use of Geospatial data for disaster managements Source: http://alertsystemsgroup.com Instructor : Professor Dr. Yuji Murayama Teaching Assistant : Manjula Ranagalage What is GIS? A powerful set of tools
Use of Geospatial data for disaster managements Source: http://alertsystemsgroup.com Instructor : Professor Dr. Yuji Murayama Teaching Assistant : Manjula Ranagalage What is GIS? A powerful set of tools
DROUGHT IN MAINLAND PORTUGAL
 DROUGHT IN MAINLAND Ministério da Ciência, Tecnologia e Ensino Superior Instituto de Meteorologia, I. P. Rua C Aeroporto de Lisboa Tel.: (351) 21 844 7000 e-mail:informacoes@meteo.pt 1749-077 Lisboa Portugal
DROUGHT IN MAINLAND Ministério da Ciência, Tecnologia e Ensino Superior Instituto de Meteorologia, I. P. Rua C Aeroporto de Lisboa Tel.: (351) 21 844 7000 e-mail:informacoes@meteo.pt 1749-077 Lisboa Portugal
FLOOD HAZARD AND RISK ASSESSMENT IN MID- EASTERN PART OF DHAKA, BANGLADESH
 FLOOD HAZARD AND RISK ASSESSMENT IN MID- EASTERN PART OF DHAKA, BANGLADESH Muhammad MASOOD MEE07180 Supervisor: Prof. Kuniyoshi TAKEUCHI ABSTRACT An inundation simulation has been done for the mid-eastern
FLOOD HAZARD AND RISK ASSESSMENT IN MID- EASTERN PART OF DHAKA, BANGLADESH Muhammad MASOOD MEE07180 Supervisor: Prof. Kuniyoshi TAKEUCHI ABSTRACT An inundation simulation has been done for the mid-eastern
A Spatial Decision Support System for Agriculture and Natural Resources Management in China
 9 th APGEOSS Symposium Xiangzheng Deng A Spatial Decision Support System for Agriculture and Natural Resources Management in China Need to take decisions and make critical day-to-day and long-term planning
9 th APGEOSS Symposium Xiangzheng Deng A Spatial Decision Support System for Agriculture and Natural Resources Management in China Need to take decisions and make critical day-to-day and long-term planning
VILLAGE INFORMATION SYSTEM (V.I.S) FOR WATERSHED MANAGEMENT IN THE NORTH AHMADNAGAR DISTRICT, MAHARASHTRA
 VILLAGE INFORMATION SYSTEM (V.I.S) FOR WATERSHED MANAGEMENT IN THE NORTH AHMADNAGAR DISTRICT, MAHARASHTRA Abstract: The drought prone zone in the Western Maharashtra is not in position to achieve the agricultural
VILLAGE INFORMATION SYSTEM (V.I.S) FOR WATERSHED MANAGEMENT IN THE NORTH AHMADNAGAR DISTRICT, MAHARASHTRA Abstract: The drought prone zone in the Western Maharashtra is not in position to achieve the agricultural
EVALUATION OF REGIONAL INNOVATION CAPABILITY IN JIANGSU PROVINCE BASED ON MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS
 EVALUATION OF REGIONAL INNOVATION CAPABILITY IN JIANGSU PROVINCE BASED ON MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS He Yangyang Institute for Management Science and Engineering Henan University, Kaifeng CHINA Yao Yuan Institute
EVALUATION OF REGIONAL INNOVATION CAPABILITY IN JIANGSU PROVINCE BASED ON MULTIVARIATE STATISTICS He Yangyang Institute for Management Science and Engineering Henan University, Kaifeng CHINA Yao Yuan Institute
An analysis on the relationship between land subsidence and floods at the Kujukuri Plain in Chiba Prefecture, Japan
 doi:10.5194/piahs-372-163-2015 Author(s) 2015. CC Attribution 3.0 License. An analysis on the relationship between land subsidence and floods at the Kujukuri Plain in Chiba Prefecture, Japan Y. Ito 1,
doi:10.5194/piahs-372-163-2015 Author(s) 2015. CC Attribution 3.0 License. An analysis on the relationship between land subsidence and floods at the Kujukuri Plain in Chiba Prefecture, Japan Y. Ito 1,
Spatio-temporal pattern of drought in Northeast of Iran
 Spatio-temporal pattern of drought in Northeast of Iran Akhtari R., Bandarabadi S.R., Saghafian B. in López-Francos A. (ed.). Drought management: scientific and technological innovations Zaragoza : CIHEAM
Spatio-temporal pattern of drought in Northeast of Iran Akhtari R., Bandarabadi S.R., Saghafian B. in López-Francos A. (ed.). Drought management: scientific and technological innovations Zaragoza : CIHEAM
DISTRIBUTION AND DIURNAL VARIATION OF WARM-SEASON SHORT-DURATION HEAVY RAINFALL IN RELATION TO THE MCSS IN CHINA
 3 DISTRIBUTION AND DIURNAL VARIATION OF WARM-SEASON SHORT-DURATION HEAVY RAINFALL IN RELATION TO THE MCSS IN CHINA Jiong Chen 1, Yongguang Zheng 1*, Xiaoling Zhang 1, Peijun Zhu 2 1 National Meteorological
3 DISTRIBUTION AND DIURNAL VARIATION OF WARM-SEASON SHORT-DURATION HEAVY RAINFALL IN RELATION TO THE MCSS IN CHINA Jiong Chen 1, Yongguang Zheng 1*, Xiaoling Zhang 1, Peijun Zhu 2 1 National Meteorological
Drought risk assessment using GIS and remote sensing: A case study of District Khushab, Pakistan
 15 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 31 August to 2 September 2017 Drought risk assessment using GIS and remote sensing: A case study of District Khushab,
15 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 31 August to 2 September 2017 Drought risk assessment using GIS and remote sensing: A case study of District Khushab,
Description DESCRIPTION
 DESCRIPTION The location of the Upper James Watershed is located in northeastern South Dakota as well as southeastern North Dakota. It includes the following counties located in North Dakota Barnes, Dickey,
DESCRIPTION The location of the Upper James Watershed is located in northeastern South Dakota as well as southeastern North Dakota. It includes the following counties located in North Dakota Barnes, Dickey,
This table connects the content provided by Education Perfect to the NSW Syllabus.
 Education Perfect Geography provides teachers with a wide range of quality, engaging and innovative content to drive positive student learning outcomes. Designed by teachers and written by our in-house
Education Perfect Geography provides teachers with a wide range of quality, engaging and innovative content to drive positive student learning outcomes. Designed by teachers and written by our in-house
Generation of Three-Dimensional Meteorological Field based on Sounding Data
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 186 The Open Cybernetics & Systemics Journal, 2015, 9, 186-198 Open Access Generation of Three-Dimensional Meteorological Field based on Sounding
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 186 The Open Cybernetics & Systemics Journal, 2015, 9, 186-198 Open Access Generation of Three-Dimensional Meteorological Field based on Sounding
GROUNDWATER CONFIGURATION IN THE UPPER CATCHMENT OF MEGHADRIGEDDA RESERVOIR, VISAKHAPATNAM DISTRICT, ANDHRA PRADESH
 GROUNDWATER CONFIGURATION IN THE UPPER CATCHMENT OF MEGHADRIGEDDA RESERVOIR, VISAKHAPATNAM DISTRICT, ANDHRA PRADESH Prof.P.Jagadeesara Rao Department of Geo-Engineering and Centre for Remote Sensing, College
GROUNDWATER CONFIGURATION IN THE UPPER CATCHMENT OF MEGHADRIGEDDA RESERVOIR, VISAKHAPATNAM DISTRICT, ANDHRA PRADESH Prof.P.Jagadeesara Rao Department of Geo-Engineering and Centre for Remote Sensing, College
Rong Jiang. Map of River. Table of Basic Data. China 14. Serial No. : China-14
 Rong Jiang Map of River Table of Basic Data Name(s): Rong Jiang Location: Guangdong Province, Coastways China Area: 4,408 km 2 Serial No. : China-14 N 23 11' ~ 23 55' E 115 37' ~ 116 38' Length of the
Rong Jiang Map of River Table of Basic Data Name(s): Rong Jiang Location: Guangdong Province, Coastways China Area: 4,408 km 2 Serial No. : China-14 N 23 11' ~ 23 55' E 115 37' ~ 116 38' Length of the
Report. Developing a course component on disaster management
 Report Developing a course component on disaster management By Chira Prangkio Tawee Chaipimonplin Department of Geography, Faculty of Social Sciences, Chiang Mai University Thailand Presented at Indian
Report Developing a course component on disaster management By Chira Prangkio Tawee Chaipimonplin Department of Geography, Faculty of Social Sciences, Chiang Mai University Thailand Presented at Indian
Progress Report. Flood Hazard Mapping in Thailand
 Progress Report Flood Hazard Mapping in Thailand Prepared By: Mr. PAITOON NAKTAE Chief of Safety Standard sub-beuro Disaster Prevention beuro Department of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation THAILAND E-mail:
Progress Report Flood Hazard Mapping in Thailand Prepared By: Mr. PAITOON NAKTAE Chief of Safety Standard sub-beuro Disaster Prevention beuro Department of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation THAILAND E-mail:
Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry 2017; 6(4): Sujitha E and Shanmugasundaram K
 2017; 6(4): 452-457 E-ISSN: 2278-4136 P-ISSN: 2349-8234 JPP 2017; 6(4): 452-457 Received: 01-05-2017 Accepted: 02-06-2017 Sujitha E Research Scholar, Department of Soil and Water Conservation Engineering,
2017; 6(4): 452-457 E-ISSN: 2278-4136 P-ISSN: 2349-8234 JPP 2017; 6(4): 452-457 Received: 01-05-2017 Accepted: 02-06-2017 Sujitha E Research Scholar, Department of Soil and Water Conservation Engineering,
Multiple-Year Droughts In Nebraska
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Drought Mitigation Center Faculty Publications Drought -- National Drought Mitigation Center 2005 Multiple-Year Droughts
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Drought Mitigation Center Faculty Publications Drought -- National Drought Mitigation Center 2005 Multiple-Year Droughts
Analysis of the Ecological Sensitivity of Pengyang County Based on Key Factors
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Biotechnology Journal, 2015, 9, 21-26 21 Open Access Analysis of the Ecological Sensitivity of Pengyang County Based on Key Factors Shi Yun
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae The Open Biotechnology Journal, 2015, 9, 21-26 21 Open Access Analysis of the Ecological Sensitivity of Pengyang County Based on Key Factors Shi Yun
A new approach for fast calculation of sloped terrace earthwork based on GIS in the hilly regions
 A new approach for fast calculation of sloped terrace earthwork based on GIS in the hilly regions Qingchun Zhang 1 1 Land Consolidation and Rehabilitation Center, the Ministry of Land and Resources; 1
A new approach for fast calculation of sloped terrace earthwork based on GIS in the hilly regions Qingchun Zhang 1 1 Land Consolidation and Rehabilitation Center, the Ministry of Land and Resources; 1
Flood Risk Map Based on GIS, and Multi Criteria Techniques (Case Study Terengganu Malaysia)
 Journal of Geographic Information System, 2015, 7, 348-357 Published Online August 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jgis http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jgis.2015.74027 Flood Risk Map Based on GIS,
Journal of Geographic Information System, 2015, 7, 348-357 Published Online August 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jgis http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jgis.2015.74027 Flood Risk Map Based on GIS,
Effect of land use/land cover changes on runoff in a river basin: a case study
 Water Resources Management VI 139 Effect of land use/land cover changes on runoff in a river basin: a case study J. Letha, B. Thulasidharan Nair & B. Amruth Chand College of Engineering, Trivandrum, Kerala,
Water Resources Management VI 139 Effect of land use/land cover changes on runoff in a river basin: a case study J. Letha, B. Thulasidharan Nair & B. Amruth Chand College of Engineering, Trivandrum, Kerala,
Analysis of Historical Pattern of Rainfall in the Western Region of Bangladesh
 24 25 April 214, Asian University for Women, Bangladesh Analysis of Historical Pattern of Rainfall in the Western Region of Bangladesh Md. Tanvir Alam 1*, Tanni Sarker 2 1,2 Department of Civil Engineering,
24 25 April 214, Asian University for Women, Bangladesh Analysis of Historical Pattern of Rainfall in the Western Region of Bangladesh Md. Tanvir Alam 1*, Tanni Sarker 2 1,2 Department of Civil Engineering,
GRASS COVER CHANGE MODEL BASED ON CELLULAR AUTOMATA
 GRASS COVER CHANGE MODEL BASED ON CELLULAR AUTOMATA Shuai Zhang *, Jingyin Zhao, Linyi Li Digital Agricultural Engineering Technological Research Center, Shanghai Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Shanghai,
GRASS COVER CHANGE MODEL BASED ON CELLULAR AUTOMATA Shuai Zhang *, Jingyin Zhao, Linyi Li Digital Agricultural Engineering Technological Research Center, Shanghai Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Shanghai,
Precipitation. Standardized Precipitation Index. NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System September 5, 2017
 9/6/2017 NIDIS Drought and Water Assessment NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System September 5, 2017 Precipitation The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP, CoCoRaHS,
9/6/2017 NIDIS Drought and Water Assessment NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System September 5, 2017 Precipitation The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP, CoCoRaHS,
MONITORING OF SURFACE WATER RESOURCES IN THE MINAB PLAIN BY USING THE STANDARDIZED PRECIPITATION INDEX (SPI) AND THE MARKOF CHAIN MODEL
 MONITORING OF SURFACE WATER RESOURCES IN THE MINAB PLAIN BY USING THE STANDARDIZED PRECIPITATION INDEX (SPI) AND THE MARKOF CHAIN MODEL Bahari Meymandi.A Department of Hydraulic Structures, college of
MONITORING OF SURFACE WATER RESOURCES IN THE MINAB PLAIN BY USING THE STANDARDIZED PRECIPITATION INDEX (SPI) AND THE MARKOF CHAIN MODEL Bahari Meymandi.A Department of Hydraulic Structures, college of
GIS-BASED DISASTER WARNING SYSTEM OF LOW TEMPERATURE AND SPARE SUNLIGHT IN GREENHOUSE
 GIS-BASED DISASTER WARNING SYSTEM OF LOW TEMPERATURE AND SPARE SUNLIGHT IN GREENHOUSE 1,2,* 1,2 Ruijiang Wei, Chunqiang Li, Xin Wang 1, 2 1 Hebei Provincial Institute of Meteorology, Shijiazhuang, Hebei
GIS-BASED DISASTER WARNING SYSTEM OF LOW TEMPERATURE AND SPARE SUNLIGHT IN GREENHOUSE 1,2,* 1,2 Ruijiang Wei, Chunqiang Li, Xin Wang 1, 2 1 Hebei Provincial Institute of Meteorology, Shijiazhuang, Hebei
NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System December 18, 2018
 NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System December 18, 2018 Precipitation The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP, CoCoRaHS, and CoAgMet stations. From top to bottom,
NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System December 18, 2018 Precipitation The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP, CoCoRaHS, and CoAgMet stations. From top to bottom,
Forecasting Drought in Tel River Basin using Feed-forward Recursive Neural Network
 2012 International Conference on Environmental, Biomedical and Biotechnology IPCBEE vol.41 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Forecasting Drought in Tel River Basin using Feed-forward Recursive Neural
2012 International Conference on Environmental, Biomedical and Biotechnology IPCBEE vol.41 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Forecasting Drought in Tel River Basin using Feed-forward Recursive Neural
3/3/2013. The hydro cycle water returns from the sea. All "toilet to tap." Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e
 Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Running Water: summary in haiku form Edward A. Keller Chapter 9 Rivers and Flooding Lecture Presentation prepared by X. Mara Chen, Salisbury University The hydro
Introduction to Environmental Geology, 5e Running Water: summary in haiku form Edward A. Keller Chapter 9 Rivers and Flooding Lecture Presentation prepared by X. Mara Chen, Salisbury University The hydro
Workshop on Drought and Extreme Temperatures: Preparedness and Management for Sustainable Agriculture, Forestry and Fishery
 Workshop on Drought and Extreme Temperatures: Preparedness and Management for Sustainable Agriculture, Forestry and Fishery 16-17 Feb.2009, Beijing, China Modeling Apple Tree Bud burst time and frost risk
Workshop on Drought and Extreme Temperatures: Preparedness and Management for Sustainable Agriculture, Forestry and Fishery 16-17 Feb.2009, Beijing, China Modeling Apple Tree Bud burst time and frost risk
GEOGRAPHY. In relation to the above aims, candidates should, after completing this syllabus, be able to
 GEOGRAPHY AIMS The aims of this syllabus are to enable candidates 1. to recognize and understand the arrangement of phenomena and features on Earth as well as the inter-relationship and interaction among
GEOGRAPHY AIMS The aims of this syllabus are to enable candidates 1. to recognize and understand the arrangement of phenomena and features on Earth as well as the inter-relationship and interaction among
UNCERTAINTY IN THE POPULATION GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM
 UNCERTAINTY IN THE POPULATION GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM 1. 2. LIU De-qin 1, LIU Yu 1,2, MA Wei-jun 1 Chinese Academy of Surveying and Mapping, Beijing 100039, China Shandong University of Science and
UNCERTAINTY IN THE POPULATION GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEM 1. 2. LIU De-qin 1, LIU Yu 1,2, MA Wei-jun 1 Chinese Academy of Surveying and Mapping, Beijing 100039, China Shandong University of Science and
Analysis of Meteorological drought condition for Bijapur region in the lower Bhima basin, India
 Analysis of Meteorological drought condition for Bijapur region in the lower Bhima basin, India Mamatha.K PG Student Department of WLM branch VTU, Belagavi Dr. Nagaraj Patil Professor and Head of the Department
Analysis of Meteorological drought condition for Bijapur region in the lower Bhima basin, India Mamatha.K PG Student Department of WLM branch VTU, Belagavi Dr. Nagaraj Patil Professor and Head of the Department
NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System September 4, 2018
 NIDIS Drought and Water Assessment NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System September 4, 2018 Precipitation The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP, CoCoRaHS, and
NIDIS Drought and Water Assessment NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System September 4, 2018 Precipitation The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP, CoCoRaHS, and
Activities and Outlook related to Disaster Reduction in CMA
 Activities and Outlook related to Disaster Reduction in CMA WANG Bangzhong China Meteorological Administration March 15-17 2006 ADENDA Situation about MD and related disasters in CHINA Guidance for MD/RD
Activities and Outlook related to Disaster Reduction in CMA WANG Bangzhong China Meteorological Administration March 15-17 2006 ADENDA Situation about MD and related disasters in CHINA Guidance for MD/RD
Analysis on Climate Change of Guangzhou in Nearly 65 Years
 , pp.111-117 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016.138.24 Analysis on Climate Change of Guangzhou in Nearly 65 Years Wenzheng Yu, Haitao Liu, Chunyong Yin, Jin Wang College of Environmental Science and
, pp.111-117 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016.138.24 Analysis on Climate Change of Guangzhou in Nearly 65 Years Wenzheng Yu, Haitao Liu, Chunyong Yin, Jin Wang College of Environmental Science and
ColomboArts. Volume II Issue I Dynamic Trends of Intensity of Rainfall Extremes in Sri Lanka
 ColomboArts Volume II Issue I 2017 Dynamic Trends of Intensity of Rainfall Extremes in Sri Lanka R.M.S.S.Sanjeewani, 1 Lasantha Manawadu 2 1 Department of Transport and Logistics Management, University
ColomboArts Volume II Issue I 2017 Dynamic Trends of Intensity of Rainfall Extremes in Sri Lanka R.M.S.S.Sanjeewani, 1 Lasantha Manawadu 2 1 Department of Transport and Logistics Management, University
Chapter 12 Monitoring Drought Using the Standardized Precipitation Index
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Drought Mitigation Center Faculty Publications Drought -- National Drought Mitigation Center 2000 Chapter 12 Monitoring
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Drought Mitigation Center Faculty Publications Drought -- National Drought Mitigation Center 2000 Chapter 12 Monitoring
Changes in Climate Factors and Extreme Climate Events in South China during
 ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH 4(1): 1 11, 2013 www.climatechange.cn DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1248.2013.001 SPECIAL TOPIC ON REGIONAL CLIMATE CHANGE Editor s notes: The Working Group (WG) Reports and Synthesis
ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH 4(1): 1 11, 2013 www.climatechange.cn DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1248.2013.001 SPECIAL TOPIC ON REGIONAL CLIMATE CHANGE Editor s notes: The Working Group (WG) Reports and Synthesis
Spati-temporal Changes of NDVI and Their Relations with Precipitation and Temperature in Yangtze River Catchment from 1992 to 2001
 Spati-temporal Changes of NDVI and Their Relations with Precipitation and Temperature in Yangtze River Catchment from 1992 to 2001 ZHANG Li 1, CHEN Xiao-Ling 1, 2 1State Key Laboratory of Information Engineering
Spati-temporal Changes of NDVI and Their Relations with Precipitation and Temperature in Yangtze River Catchment from 1992 to 2001 ZHANG Li 1, CHEN Xiao-Ling 1, 2 1State Key Laboratory of Information Engineering
NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System November 14, 2017
 NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System November 14, 2017 Precipitation The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP, CoCoRaHS, and CoAgMet stations. From top to bottom,
NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System November 14, 2017 Precipitation The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP, CoCoRaHS, and CoAgMet stations. From top to bottom,
1990 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Impacts Assessment
 1990 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Impacts Assessment Although the variability of weather and associated shifts in the frequency and magnitude of climate events were not available from the
1990 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Impacts Assessment Although the variability of weather and associated shifts in the frequency and magnitude of climate events were not available from the
NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System February 6, 2018
 NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System February 6, 2018 Precipitation The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP, CoCoRaHS, and CoAgMet stations. From top to bottom,
NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System February 6, 2018 Precipitation The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP, CoCoRaHS, and CoAgMet stations. From top to bottom,
Assessment of Snow Cover Vulnerability over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau
 ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH 2(2): 93 100, 2011 www.climatechange.cn DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1248.2011.00093 ARTICLE Assessment of Snow Cover Vulnerability over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau Lijuan Ma 1,
ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH 2(2): 93 100, 2011 www.climatechange.cn DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1248.2011.00093 ARTICLE Assessment of Snow Cover Vulnerability over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau Lijuan Ma 1,
Study of risk and early warning index of rainstorm waterlogging in Wuhan City
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Study of risk and early warning index of rainstorm waterlogging in Wuhan City To cite this article: Z Y Huang et al 2017 IOP Conf.
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Study of risk and early warning index of rainstorm waterlogging in Wuhan City To cite this article: Z Y Huang et al 2017 IOP Conf.
MARS AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM GRADE: Grade 4
 MARS AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM GRADE: Grade 4 Course Title: Social Studies Brief Description Overview: Students will explore the history, geography, government, and economy of the United States with
MARS AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM GRADE: Grade 4 Course Title: Social Studies Brief Description Overview: Students will explore the history, geography, government, and economy of the United States with
Study on Precipitation Forecast and Testing Methods of Numerical Forecast in Fuxin Area
 Journal of Geoscience and Environment Protection, 2017, 5, 32-38 http://www.scirp.org/journal/gep ISSN Online: 2327-4344 ISSN Print: 2327-4336 Study on Precipitation Forecast and Testing Methods of Numerical
Journal of Geoscience and Environment Protection, 2017, 5, 32-38 http://www.scirp.org/journal/gep ISSN Online: 2327-4344 ISSN Print: 2327-4336 Study on Precipitation Forecast and Testing Methods of Numerical
Illinois Drought Update, December 1, 2005 DROUGHT RESPONSE TASK FORCE Illinois State Water Survey, Department of Natural Resources
 Illinois Drought Update, December 1, 2005 DROUGHT RESPONSE TASK FORCE Illinois State Water Survey, Department of Natural Resources For more drought information please go to http://www.sws.uiuc.edu/. SUMMARY.
Illinois Drought Update, December 1, 2005 DROUGHT RESPONSE TASK FORCE Illinois State Water Survey, Department of Natural Resources For more drought information please go to http://www.sws.uiuc.edu/. SUMMARY.
Modeling Great Britain s Flood Defenses. Flood Defense in Great Britain. By Dr. Yizhong Qu
 Modeling Great Britain s Flood Defenses AIRCurrents Editor s note: AIR launched its Inland Flood Model for Great Britain in December 2008. The hazard module captures the physical processes of rainfall-runoff
Modeling Great Britain s Flood Defenses AIRCurrents Editor s note: AIR launched its Inland Flood Model for Great Britain in December 2008. The hazard module captures the physical processes of rainfall-runoff
West meets East: Monitoring and modeling urbanization in China Land Cover-Land Use Change Program Science Team Meeting April 3, 2012
 West meets East: Monitoring and modeling urbanization in China Land Cover-Land Use Change Program Science Team Meeting April 3, 2012 Annemarie Schneider Center for Sustainability and the Global Environment,
West meets East: Monitoring and modeling urbanization in China Land Cover-Land Use Change Program Science Team Meeting April 3, 2012 Annemarie Schneider Center for Sustainability and the Global Environment,
Analysis on Characteristics of Precipitation Change from 1957 to 2015 in Weishan County
 Journal of Geoscience and Environment Protection, 2017, 5, 125-133 http://www.scirp.org/journal/gep ISSN Online: 2327-4344 ISSN Print: 2327-4336 Analysis on Characteristics of Precipitation Change from
Journal of Geoscience and Environment Protection, 2017, 5, 125-133 http://www.scirp.org/journal/gep ISSN Online: 2327-4344 ISSN Print: 2327-4336 Analysis on Characteristics of Precipitation Change from
World Meteorological Organization
 World Meteorological Organization Opportunities and Challenges for Development of Weather-based Insurance and Derivatives Markets in Developing Countries By Maryam Golnaraghi, Ph.D. Head of WMO Disaster
World Meteorological Organization Opportunities and Challenges for Development of Weather-based Insurance and Derivatives Markets in Developing Countries By Maryam Golnaraghi, Ph.D. Head of WMO Disaster
Application of Atmosphere Precipitation Resources Distribution Remote Sensed by Ground-based GPS in the West of Taiwan Strait.
 4th International Conference on Mechatronics, Materials, Chemistry and Computer Engineering (ICMMCCE 2015) Application of Atmosphere Precipitation Resources Distribution Remote Sensed by Ground-based GPS
4th International Conference on Mechatronics, Materials, Chemistry and Computer Engineering (ICMMCCE 2015) Application of Atmosphere Precipitation Resources Distribution Remote Sensed by Ground-based GPS
I. PRACTICAL GEOGRAPHY A. Maps. B. Scale and measurement. C. Map reading and interpretation; D. Interpretation of statistical data;
 TOPICS/CONTENTS/NOTES OBJECTIVES I. PRACTICAL GEOGRAPHY A. Maps Ai define and identify different types and uses of maps B. Scale and measurement distances, areas reduction and enlargement, directions,
TOPICS/CONTENTS/NOTES OBJECTIVES I. PRACTICAL GEOGRAPHY A. Maps Ai define and identify different types and uses of maps B. Scale and measurement distances, areas reduction and enlargement, directions,
NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System April 18, 2017
 1 of 11 4/18/2017 3:42 PM Precipitation NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System April 18, 2017 The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP, CoCoRaHS, and CoAgMet stations.
1 of 11 4/18/2017 3:42 PM Precipitation NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System April 18, 2017 The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP, CoCoRaHS, and CoAgMet stations.
By Geri Flanary To accompany AP Human Geography: A Study Guide 3 rd edition By Ethel Wood
 Session 1 By Geri Flanary To accompany AP Human Geography: A Study Guide 3 rd edition By Ethel Wood WHAT IS DEMOGRAPHY? It is the scientific or statistical study of population. It comes from the Greek
Session 1 By Geri Flanary To accompany AP Human Geography: A Study Guide 3 rd edition By Ethel Wood WHAT IS DEMOGRAPHY? It is the scientific or statistical study of population. It comes from the Greek
A GIS-based Study on Grassland Degradation and. Increase of Dust Storms in China
 1 A GIS-based Study on Grassland Degradation and Increase of Dust Storms in China Qinxue WANG* and Kuninori OTSUBO* * National Institute for Environmental Studies, 16-2 Onogawa, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8506,
1 A GIS-based Study on Grassland Degradation and Increase of Dust Storms in China Qinxue WANG* and Kuninori OTSUBO* * National Institute for Environmental Studies, 16-2 Onogawa, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8506,
GIS BASED ANALYSIS ON ENVIRONMENTAL SENSITIVE AREAS AND IDENTIFICATION OF THE POTENTIAL DISASTER HAZARDOUS LOCATIONS IN SOUTHERN SRI LANKA
 International Journal of Civil & Environmental Engineering IJCEE Vol: 9 No: 9-311 - GIS BASED ANALYSIS ON ENVIRONMENTAL SENSITIVE AREAS AND IDENTIFICATION OF THE POTENTIAL DISASTER HAZARDOUS LOCATIONS
International Journal of Civil & Environmental Engineering IJCEE Vol: 9 No: 9-311 - GIS BASED ANALYSIS ON ENVIRONMENTAL SENSITIVE AREAS AND IDENTIFICATION OF THE POTENTIAL DISASTER HAZARDOUS LOCATIONS
Temporal and Spatial Analysis of Drought over a Tropical Wet Station of India in the Recent Decades Using the SPI Method
 Temporal and Spatial Analysis of Drought over a Tropical Wet Station of India in the Recent Decades Using the SPI Method Keerthi Sasikumar 1 and Dr. Venu G.Nair 2 1 Department of Atmospheric Sciences,
Temporal and Spatial Analysis of Drought over a Tropical Wet Station of India in the Recent Decades Using the SPI Method Keerthi Sasikumar 1 and Dr. Venu G.Nair 2 1 Department of Atmospheric Sciences,
Hydrologic Modelling of the Upper Malaprabha Catchment using ArcView SWAT
 Hydrologic Modelling of the Upper Malaprabha Catchment using ArcView SWAT Technical briefs are short summaries of the models used in the project aimed at nontechnical readers. The aim of the PES India
Hydrologic Modelling of the Upper Malaprabha Catchment using ArcView SWAT Technical briefs are short summaries of the models used in the project aimed at nontechnical readers. The aim of the PES India
THE STUDY OF NUMBERS AND INTENSITY OF TROPICAL CYCLONE MOVING TOWARD THE UPPER PART OF THAILAND
 THE STUDY OF NUMBERS AND INTENSITY OF TROPICAL CYCLONE MOVING TOWARD THE UPPER PART OF THAILAND Aphantree Yuttaphan 1, Sombat Chuenchooklin 2 and Somchai Baimoung 3 ABSTRACT The upper part of Thailand
THE STUDY OF NUMBERS AND INTENSITY OF TROPICAL CYCLONE MOVING TOWARD THE UPPER PART OF THAILAND Aphantree Yuttaphan 1, Sombat Chuenchooklin 2 and Somchai Baimoung 3 ABSTRACT The upper part of Thailand
Dataset of Classification and Land Use of the Ecological Core Areas of China
 Journal of Global Change Data & Discovery. 2017, 1(4):426-430 DOI:10.3974/geodp.2017.04.07 www.geodoi.ac.cn 2017 GCdataPR Global Change Research Data Publishing & Repository Dataset of Classification and
Journal of Global Change Data & Discovery. 2017, 1(4):426-430 DOI:10.3974/geodp.2017.04.07 www.geodoi.ac.cn 2017 GCdataPR Global Change Research Data Publishing & Repository Dataset of Classification and
Application of remote sensing for agricultural disasters
 Application of remote sensing for agricultural disasters Bingfang Wu, Sheng Chang Institute of Remote Sensing and Digital Earth (RADI) Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) wubf@radi.ac.cn, changsheng@radi.ac.cn
Application of remote sensing for agricultural disasters Bingfang Wu, Sheng Chang Institute of Remote Sensing and Digital Earth (RADI) Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) wubf@radi.ac.cn, changsheng@radi.ac.cn
DEM-based Ecological Rainfall-Runoff Modelling in. Mountainous Area of Hong Kong
 DEM-based Ecological Rainfall-Runoff Modelling in Mountainous Area of Hong Kong Qiming Zhou 1,2, Junyi Huang 1* 1 Department of Geography and Centre for Geo-computation Studies, Hong Kong Baptist University,
DEM-based Ecological Rainfall-Runoff Modelling in Mountainous Area of Hong Kong Qiming Zhou 1,2, Junyi Huang 1* 1 Department of Geography and Centre for Geo-computation Studies, Hong Kong Baptist University,
Historical Perspectives of Land-use and Land-cover Changes in Beijing
 1 Historical Perspectives of Land-use and Land-cover Changes in Beijing Qi LU Institute of Geography, Chinese Academy of Sciences Abstract Beijing is one of ancient cities in China.In history, the land
1 Historical Perspectives of Land-use and Land-cover Changes in Beijing Qi LU Institute of Geography, Chinese Academy of Sciences Abstract Beijing is one of ancient cities in China.In history, the land
Space Application in Support of Land Management for SDG Implementation
 Space Application in Support of Land Management for SDG Implementation Regional Expert Workshop on Land Accounting for SDG Monitoring and Reporting 26 September 2017 Space Application Section Information
Space Application in Support of Land Management for SDG Implementation Regional Expert Workshop on Land Accounting for SDG Monitoring and Reporting 26 September 2017 Space Application Section Information
C Y P A D A P T. M. Petrakis C. Giannakopoulos G. Lemesios.
 Development of a national strategy for adaptation to climate change adverse impacts in Cyprus C Y P A D A P T National Observatory of Athens, Institute for Environmental Research and Sustainable Development
Development of a national strategy for adaptation to climate change adverse impacts in Cyprus C Y P A D A P T National Observatory of Athens, Institute for Environmental Research and Sustainable Development
Coastal Vulnerability Assessment in Semarang City, Indonesia Based on Sea Level Rise and Land Subsidence Scenarios
 Coastal Vulnerability Assessment in Semarang City, Indonesia Based on Sea Level Rise and Land Subsidence Scenarios I. M. Radjawane, D. Hartadi and W. R. Lusano Oceanography Research Division Fac. of Earth
Coastal Vulnerability Assessment in Semarang City, Indonesia Based on Sea Level Rise and Land Subsidence Scenarios I. M. Radjawane, D. Hartadi and W. R. Lusano Oceanography Research Division Fac. of Earth
Analysis of China s Haze Days in the Winter Half-Year and the Climatic Background during
 ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH 5(1): 1-6, 2014 www.climatechange.cn DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1248.2014.001 CHANGES IN CLIMATE SYSTEM Analysis of China s Haze Days in the Winter Half-Year and the Climatic
ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH 5(1): 1-6, 2014 www.climatechange.cn DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1248.2014.001 CHANGES IN CLIMATE SYSTEM Analysis of China s Haze Days in the Winter Half-Year and the Climatic
By Lillian Ntshwarisang Department of Meteorological Services Phone:
 By Lillian Ntshwarisang Department of Meteorological Services Phone: +267 3612200 Email: lntshwarisang@gov.bw/ lntshwarisang@gmail.com Introduction Mandate of DMS Function of the Department Services to
By Lillian Ntshwarisang Department of Meteorological Services Phone: +267 3612200 Email: lntshwarisang@gov.bw/ lntshwarisang@gmail.com Introduction Mandate of DMS Function of the Department Services to
NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System February 12, 2019
 NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System February 12, 2019 Precipitation The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP, CoCoRaHS, and CoAgMet stations. From top to bottom,
NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System February 12, 2019 Precipitation The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP, CoCoRaHS, and CoAgMet stations. From top to bottom,
Impacts of the climate change on the precipitation regime on the island of Cyprus
 Impacts of the climate change on the precipitation regime on the island of Cyprus Michael Petrakis, Christos Giannakopoulos, Giannis Lemesios Institute for Environmental Research and Sustainable Development,
Impacts of the climate change on the precipitation regime on the island of Cyprus Michael Petrakis, Christos Giannakopoulos, Giannis Lemesios Institute for Environmental Research and Sustainable Development,
Precipitation. Standardized Precipitation Index. NIDIS Intermountain West Regional Drought Early Warning System January 3, 2017
 1/3/2017 NIDIS Drought and Water Assessment NIDIS Intermountain West Regional Drought Early Warning System January 3, 2017 Precipitation The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP,
1/3/2017 NIDIS Drought and Water Assessment NIDIS Intermountain West Regional Drought Early Warning System January 3, 2017 Precipitation The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP,
AN INTEGRATED MULTI-GOAL REGIONAL PLANNING PLATFORM BASED ON REMOTE SENSING AND GIS
 AN INTEGRATED MULTI-GOAL REGIONAL PLANNING PLATFORM BASED ON REMOTE SENSING AND GIS Xinhui Ma, Bingfang Wu *, Zhiming Luo, Lan Zeng Institute of Remote Sensing Applicat ions, Chinese Academy of Sciences,
AN INTEGRATED MULTI-GOAL REGIONAL PLANNING PLATFORM BASED ON REMOTE SENSING AND GIS Xinhui Ma, Bingfang Wu *, Zhiming Luo, Lan Zeng Institute of Remote Sensing Applicat ions, Chinese Academy of Sciences,
Drought Impacts in the Southern Great Plains. Mark Shafer University of Oklahoma Norman, OK
 Drought Impacts in the Southern Great Plains Mark Shafer University of Oklahoma Norman, OK Causes of Drought: Large-Scale, Stationary High Pressure Air rotates clockwise around high pressure steers storms
Drought Impacts in the Southern Great Plains Mark Shafer University of Oklahoma Norman, OK Causes of Drought: Large-Scale, Stationary High Pressure Air rotates clockwise around high pressure steers storms
TOOLS FOR RISK MANAGEMENT Related to climate change
 TOOLS FOR RISK MANAGEMENT Related to climate change copyright CONTENT 1 CLIMATE CHANGE AND ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES 2 METHODS AND TOOLS DEVELOPED BY EGIS For infrastructures For urban areas For crisis management
TOOLS FOR RISK MANAGEMENT Related to climate change copyright CONTENT 1 CLIMATE CHANGE AND ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES 2 METHODS AND TOOLS DEVELOPED BY EGIS For infrastructures For urban areas For crisis management
Determination of flood risks in the yeniçiftlik stream basin by using remote sensing and GIS techniques
 Determination of flood risks in the yeniçiftlik stream basin by using remote sensing and GIS techniques İrfan Akar University of Atatürk, Institute of Social Sciences, Erzurum, Turkey D. Maktav & C. Uysal
Determination of flood risks in the yeniçiftlik stream basin by using remote sensing and GIS techniques İrfan Akar University of Atatürk, Institute of Social Sciences, Erzurum, Turkey D. Maktav & C. Uysal
Flash flood disaster in Bayangol district, Ulaanbaatar
 Flash flood disaster in Bayangol district, Ulaanbaatar Advanced Training Workshop on Reservoir Sedimentation Management 10-16 October 2007. IRTCES, Beijing China Janchivdorj.L, Institute of Geoecology,MAS
Flash flood disaster in Bayangol district, Ulaanbaatar Advanced Training Workshop on Reservoir Sedimentation Management 10-16 October 2007. IRTCES, Beijing China Janchivdorj.L, Institute of Geoecology,MAS
Quick Response Report #126 Hurricane Floyd Flood Mapping Integrating Landsat 7 TM Satellite Imagery and DEM Data
 Quick Response Report #126 Hurricane Floyd Flood Mapping Integrating Landsat 7 TM Satellite Imagery and DEM Data Jeffrey D. Colby Yong Wang Karen Mulcahy Department of Geography East Carolina University
Quick Response Report #126 Hurricane Floyd Flood Mapping Integrating Landsat 7 TM Satellite Imagery and DEM Data Jeffrey D. Colby Yong Wang Karen Mulcahy Department of Geography East Carolina University
Preliminary Research on Grassland Fineclassification
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science OPEN ACCESS Preliminary Research on Grassland Fineclassification Based on MODIS To cite this article: Z W Hu et al 2014 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ.
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science OPEN ACCESS Preliminary Research on Grassland Fineclassification Based on MODIS To cite this article: Z W Hu et al 2014 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ.
SWIM and Horizon 2020 Support Mechanism
 SWIM and Horizon 2020 Support Mechanism Working for a Sustainable Mediterranean, Caring for our Future REG-7: Training Session #1: Drought Hazard Monitoring Example from real data from the Republic of
SWIM and Horizon 2020 Support Mechanism Working for a Sustainable Mediterranean, Caring for our Future REG-7: Training Session #1: Drought Hazard Monitoring Example from real data from the Republic of
Indices and Indicators for Drought Early Warning
 Indices and Indicators for Drought Early Warning ADRIAN TROTMAN CHIEF, APPLIED METEOROLOGY AND CLIMATOLOGY CARIBBEAN INSTITUTE FOR METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY IN COLLABORATION WITH THE NATIONAL DROUGHT MITIGATION
Indices and Indicators for Drought Early Warning ADRIAN TROTMAN CHIEF, APPLIED METEOROLOGY AND CLIMATOLOGY CARIBBEAN INSTITUTE FOR METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY IN COLLABORATION WITH THE NATIONAL DROUGHT MITIGATION
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: APRIL 18, 2017 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP,
 Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: APRIL 18, 2017 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sroot@weatherbank.com MARCH 2017 Climate Highlights The Month in Review The average contiguous
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: APRIL 18, 2017 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sroot@weatherbank.com MARCH 2017 Climate Highlights The Month in Review The average contiguous
