experiment11 Molecular Structures
|
|
|
- Ella McCarthy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 59 experiment11 OBJECTIVES To determine the number of valence electrons in molecules. To determine the Lewis structure of molecules. To determine the electron pair geometry and geometry (shape) of molecules. To determine the hybridization of molecules. To build molecular models. To draw three-dimensional picture of models. Students will work in pairs. You do not need to write a full lab report for this experiment. Complete the Chem21 worksheet assignment. IN THE LAB
2 60 EXPERIMENT 11: WASTE None SAFETY Students need to wear goggles for this experiment. A team of researchers looking into developing new drugs are using molecular modeling to see how the new drugs fit into the cell s receptors for this drug. Molecular modeling uses mathematical models to describe molecular properties and behaviors of molecules and generally displays that information in the form of a picture. Before the researchers can build their mathematical models, they need you to help provide some information about the basic structures of some simple molecules. For each of the molecules in the lists below, use your model kit to construct a model of the compounds and to provide the researchers with the following information: Total number of electrons: 1. Valence electrons 2. electrons 3. Non-bonding electrons Number of bonds single, double, triple Hybridization Number of electron groups Electron geometry Molecular geometry 3-D drawing of molecule All information needs to be provided to your supervisor through the Chem21 Web site, so that it can easily be converted into the mathematical models. Your TA will tell you which list you should report on. Your supervisor has provided the following instructions in regards to using the molecular model kits available to you. Materials Molecular model set with the following parts: 16 sp 3 (black) 10 sp 2 (gray) 2 half double bond (blue) 4 double bond (purple) 4 octahedral (metallic gold) 2 linear (orange) 2 trigonal (copper) 1 triple bond (yellow) 2 bond extenders (silver) marker balls Model Sets 12 white (hydrogen) 6 green (halogens) 6 red (oxygen and nitrogen) 2 hot pink (undesignated atoms) These model sets are from Darling Models ( Sets similar to this one and many others are available at a very reasonable price if you are interested in having your own set or if you will be taking Organic Chemistry. Most Organic Chemistry courses will require or recommend that you have a model set.
3 EXPERIMENT 11: 61 Assembly and Disassembly of Molecular Visions Atoms Darling Models ; pieces shown in Figure Slide the U openings together at right angles (see Figure 11.3). 2. Pinch the two pieces together until they click (see Figure 11.4). 3. Grasp the two pieces against the central U. Pull sharply with the left hand and push sharply with the right hand until there is a second click as shown in Figure Figure From top to bottom, sp 3 piece, trigonal atoms, octahedral pieces, and linear bond. The Atom Figure The final step to assemble the tetrahedral atom with bonds. Figure The U shaped center of the atom piece. Each atom consists of a U shaped center as shown in Figure 11.2, with two or three bonds. The bonds end in a rod or tube. The small teeth at the opening of the U serve to grip the square at the end of the other piece, locking the two pieces to form an atom with bonds. The procedure for joining two atom pieces is shown in the following paragraphs. The tetrahedron may be taken apart by gently spreading the V shaped bonds on one piece, to unlock the teeth, while pushing it out of its locked position. This may be accomplished in one motion with one hand, by placing two or four fingers across the V of one piece and the ball of the thumb on the opposite side. A gentle squeeze will spread the V slightly and push the two pieces apart. In Figure 11.5, the left hand stabilizes the piece while the right hand spreads both pieces and separates them. The Tetrahedral Atom Figure Assembling the tetrahedral atom with bonds. Figure Disassembling the tetrahedral atom.
4 62 EXPERIMENT 11: The Trigonal-Bipyramid Atom The Octahedral Atom Figure Assembly of a trigonal bipyramid. Figure Assembly of an octahedral atom. The octahedral atom is assembled by pushing the two octahedral pieces together. Figure Disassembly of a trigonal bipyramid. The octahedral atom is disassembled by placing two fingers of each hand around the horizontal bonds of each respective piece and gently pulling the pieces apart as shown in Figure A linear bond is joined at right angles with a trigonal atom using the same push-pull motion as for the tetrahedral atom. The trigonal bipyramid is disassembled by slightly spreading the opening of the trigonal atom with the thumbs while using the two fingers of the right hand to pull the linear bond toward the user. Figure Disassembly of the octahedral atom.
5 EXPERIMENT 11: 63 Creating Bonds between Atoms Bonds are formed between atoms by joining the rod of one atom with the tube of another. The pieces should be gripped firmly as shown to prevent bending of the rod. Electron Groups Electron groups are any electron cloud that acts to repel another group of electrons. This would include single, double, triple bonds as well as lone pairs. The idea of an electron group or cloud is at the heart of the VSEPR model describing the repulsive interactions that result from coulombic forces within atoms. How much of a repulsive force occurs determines the geometry of the molecule (Table 11.1). Figure Creating bonds between atoms. Instructions courtesy of Darling Models TM, P.O. Box 1818, Stow, OH or on the Web at Hybridization When atoms come together to form molecules, the orbitals found within the atom are not the same as they were when they were a single atom. Hybridization is the mathematical way in which the changes in the shapes and energies of orbitals are described and occurs most frequently with atoms in the interior of molecules. The type of hybridization that occurs depends on the number of available orbitals participating in the bonding, such that the number of atomic orbitals that goes in equals the number of degenerate hybrid orbitals that come out. Table VSEPR geometry. # of e Groups e Pair Geometry # of Lone Pairs Molecular Geometry Ideal Bond Angles 2 linear 0 linear trigonal planar 0 trigonal planar trigonal planar 1 bent tetrahedral 0 tetrahedral tetrahedral 1 trigonal pyramid tetrahedral 2 bent trigonal bipyramidal 0 trigonal bipyramidal 90, 120, trigonal bipyramidal 1 seesaw 90, 120, trigonal bipyramidal 2 t-shaped 90, trigonal bipyramidal 3 linear octahedral 0 octahedral 90 6 octahedral 1 square pyramidal 90 6 octahedral 2 square planar 90
6 64 EXPERIMENT 11: Drawing Molecules in 3-D Use the model you build to help you draw a 3-D drawing of the molecule. Rotate the molecule so that as many bonds and/or lone pairs as possible are in the same plane. Draw this portion of the molecule. Without moving the model, look for bonds projecting out of the plane. Any bonds projected toward you should be indicated with a solid wedge and bonds projected away from you should be drawn with a dashed triangle. See example for water molecule shown on page 66. The lone pairs are in the plane, while one O H bond projects toward you and the other O H bond is projecting out of the plane away from you. Multiple Central Atoms For molecules with more than one central atom, give the electron pair geometry and geometry (shape) around each central atom. Mark the information for each atom so that it is apparent which information goes with which atom. See the second example for more information. Table List of molecules. List 1 List 2 List 3 List 4 1 CCl 4 NH 4 + PO 4 3 CF 4 2 PCl 5 NO 2 NO 3 CO 2 3 SO 3 2 PBr 5 SbF 5 CH 3 Cl 4 CO 3 2 PCl 6 IF 3 AsI 5 5 ICl 2 ICl 3 ICl 2 + BrF 5 6 CHCH NH 2 NH 2 C 2 O CH 3 OH CH 3 OCH 3 (O is bonded to two carbons) CH 3 CHO CHOCH 3 (O is bonded to two carbons) 8 CH 3 CN CH Cl CH 3 COO CH 3 NH 2 9 SF 6 XeF 2 SeF 4 SF 2 10 XeF 4 ClO 3 PCl 3 PF 3 11 C 6 H 6 (all carbons in the ring, don t forget resonance structures) O 3 (center O, don t forget resonance structures) C 6 F 6 (all carbons in the ring, don t forget resonance structures) O=CN (don t forget resonance structures) 12 C 7 H 14 (all carbons in the ring) C 4 H 8 (all carbons in the ring) C 5 H 10 (all carbons in the ring) C 6 H 6 (all carbons in the ring)
7 EXPERIMENT 11: 65 For you and your lab partner to work on the same computer, you will need to have two different browsers open. For example, you would need to log onto Chem21 using Internet Explorer while your lab partner logged onto Chem21 using Chrome or Firefox. You and your lab partner MUST enter the same List Number so that you are working on the same list of molecules. Compound 1: CH 3 CH Number of Number of Bonds Valence Non- Points Single Double Triple Points Hybridization/Geometry Electron Groups Hybridization Electron Geometry Molecular Geometry 3D Drawing
8 66 EXPERIMENT 11: Examples Compound 1: H 2 O Number of Number of Bonds Valence Non- Points Single Double Triple Points Hybridization/Geometry Electron Groups Hybridization Electron Geometry Molecular Geometry 4 sp 3 tetrahedral bent 3D Drawing
9 EXPERIMENT 11: 67 Compound 2: CH 3 CH Number of Number of Bonds Valence Non- Points Single Double Triple Points Hybridization/Geometry Electron Groups Hybridization Electron Geometry Molecular Geometry 3 sp 2 trigonal planar trigonal planar 3D Drawing
10 68 EXPERIMENT 11:
Chapter 13: Phenomena
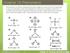 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure
 CHM 123 Chapter 8 Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure 8.1 Molecular shapes and VSEPR theory VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of
CHM 123 Chapter 8 Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure 8.1 Molecular shapes and VSEPR theory VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of
Experiment 12 Molecular Architecture
 Experiment 12 Molecular Architecture PRE-LABORATORY QUESTIONS The following preparatory questions should be answered before coming to laboratory. They are intended to introduce you to several ideas that
Experiment 12 Molecular Architecture PRE-LABORATORY QUESTIONS The following preparatory questions should be answered before coming to laboratory. They are intended to introduce you to several ideas that
VSEPR. Ch10. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory allows you to predict molecular shape. Lewis Dot theory extended to 3 dimensions.
 Ch10 VSEPR Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory allows you to predict molecular shape. Lewis Dot theory extended to 3 dimensions. version 1.5 Nick DeMello, PhD. 2007-2016 Valence Shell Electron
Ch10 VSEPR Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory allows you to predict molecular shape. Lewis Dot theory extended to 3 dimensions. version 1.5 Nick DeMello, PhD. 2007-2016 Valence Shell Electron
EXPERIMENT #13 Lewis Structures and Molecular Geometry
 OBJECTIVES: EXPERIMENT #13 s and Draw Lewis structures of atoms, ions, and molecules Build models of linear, trigonal planar tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral arrangements of electron pairs
OBJECTIVES: EXPERIMENT #13 s and Draw Lewis structures of atoms, ions, and molecules Build models of linear, trigonal planar tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral arrangements of electron pairs
Valence Shell Electron Pair repulsion
 Molecular Geometry Valence Shell Electron Pair repulsion The valence shell electron pair repulsion model (VSEPR model) assumes that electron pairs repel one another. (VSEPR) model gives helps determine
Molecular Geometry Valence Shell Electron Pair repulsion The valence shell electron pair repulsion model (VSEPR model) assumes that electron pairs repel one another. (VSEPR) model gives helps determine
Lewis structures show the number and type of bonds between atoms in a molecule or polyatomic ion.
 VSEPR & Geometry Lewis structures show the number and type of bonds between atoms in a molecule or polyatomic ion. Lewis structures are not intended to show the 3-dimensional structure (i.e. shape or geometry)
VSEPR & Geometry Lewis structures show the number and type of bonds between atoms in a molecule or polyatomic ion. Lewis structures are not intended to show the 3-dimensional structure (i.e. shape or geometry)
At the end of this lesson, students should be able to :
 At the end of this lesson, students should be able to : (a) Explain Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory (VSEPR) (b) Draw the basic molecular shapes: linear, planar, tetrahedral, and octahedral.
At the end of this lesson, students should be able to : (a) Explain Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory (VSEPR) (b) Draw the basic molecular shapes: linear, planar, tetrahedral, and octahedral.
Lewis Dot Structures for Methane, CH 4 The central C atom is bonded by single bonds (-) to 4 individual H atoms
 Chapter 10 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry Bonding Theory and Molecular Structure This chapter deals with two additional approaches chemists use to describe chemical bonding: valence-shell electron pair
Chapter 10 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry Bonding Theory and Molecular Structure This chapter deals with two additional approaches chemists use to describe chemical bonding: valence-shell electron pair
Fill in the chart below to determine the valence electrons of elements 3-10
 Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory IV Name: Date: Block: 1. Lewis Diagrams 2. VSEPR Lewis Diagrams Lewis diagrams show the bonding between atoms of a molecule. Only the outermost electrons of an atom (called electrons)
Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory IV Name: Date: Block: 1. Lewis Diagrams 2. VSEPR Lewis Diagrams Lewis diagrams show the bonding between atoms of a molecule. Only the outermost electrons of an atom (called electrons)
Lewis Structure. Lewis Structures & VSEPR. Octet & Duet Rules. Steps for drawing Lewis Structures
 Lewis Structure Lewis Structures & VSEPR Lewis Structures shows how the are arranged among the atoms of a molecule There are rules for Lewis Structures that are based on the formation of a Atoms want to
Lewis Structure Lewis Structures & VSEPR Lewis Structures shows how the are arranged among the atoms of a molecule There are rules for Lewis Structures that are based on the formation of a Atoms want to
Electron Geometry Hybrid Orbitals
 Molecular Shape and Hybridized Orbitals CH2000: Introduction to General Chemistry, Plymouth State University Introduction: In chemistry, the three dimensional shape of a molecule is as important as the
Molecular Shape and Hybridized Orbitals CH2000: Introduction to General Chemistry, Plymouth State University Introduction: In chemistry, the three dimensional shape of a molecule is as important as the
Electron Geometry Hybrid Orbitals
 Molecular Shape and Hybridized Orbitals CH2000: Introduction to General Chemistry, Plymouth State University, Fall 2014 Introduction: In chemistry, the three dimensional shape of a molecule is as important
Molecular Shape and Hybridized Orbitals CH2000: Introduction to General Chemistry, Plymouth State University, Fall 2014 Introduction: In chemistry, the three dimensional shape of a molecule is as important
VSEPR. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory
 VSEPR Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Vocabulary: domain = any electron pair or bond (single, double or triple) is considered one domain. bonding pair = shared pair = any electron pair that
VSEPR Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Vocabulary: domain = any electron pair or bond (single, double or triple) is considered one domain. bonding pair = shared pair = any electron pair that
CHEMICAL BONDING. Chemical Bonds. Ionic Bonding. Lewis Symbols
 CHEMICAL BONDING Chemical Bonds Lewis Symbols Octet Rule whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen
CHEMICAL BONDING Chemical Bonds Lewis Symbols Octet Rule whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen
LESSON 10. Glossary: Molecular Geometry. a quantitative measure of the degree of charge separation in a molecule. Dipole moment
 LESSON 10 Glossary: Molecular Geometry Dipole moment Electronegativity Molecular geometry Pi bond Polar covalent bond Sigma bond Valence-shell electronpair repulsion (VSEPR) model a quantitative measure
LESSON 10 Glossary: Molecular Geometry Dipole moment Electronegativity Molecular geometry Pi bond Polar covalent bond Sigma bond Valence-shell electronpair repulsion (VSEPR) model a quantitative measure
CHEM 110 Exam 2 - Practice Test 1 - Solutions
 CHEM 110 Exam 2 - Practice Test 1 - Solutions 1D 1 has a triple bond. 2 has a double bond. 3 and 4 have single bonds. The stronger the bond, the shorter the length. 2A A 1:1 ratio means there must be the
CHEM 110 Exam 2 - Practice Test 1 - Solutions 1D 1 has a triple bond. 2 has a double bond. 3 and 4 have single bonds. The stronger the bond, the shorter the length. 2A A 1:1 ratio means there must be the
Check Your Solution A comparison with the figures in Figure 4.31 on page 234 of the student textbook confirms the results.
 Predicting the Shape of a Molecule (Student textbook page 236) 11. What molecular shape is represented by each of the following VSEPR notations? a. AX 3 b. AX 5 E You need to assign a molecular shape that
Predicting the Shape of a Molecule (Student textbook page 236) 11. What molecular shape is represented by each of the following VSEPR notations? a. AX 3 b. AX 5 E You need to assign a molecular shape that
Introduction to VSEPR Theory 1
 1 Class 8: Introduction to VSEPR Theory Sec 10.2 VSEPR Theory: The Five Basic Shapes Two Electron Groups: Linear Geometry Three Electron Groups: Trigonal Planar Geometry Four Electron Groups: Tetrahedral
1 Class 8: Introduction to VSEPR Theory Sec 10.2 VSEPR Theory: The Five Basic Shapes Two Electron Groups: Linear Geometry Three Electron Groups: Trigonal Planar Geometry Four Electron Groups: Tetrahedral
Molecular Geometry. Valence Shell Electron Pair. What Determines the Shape of a Molecule? Repulsion Theory (VSEPR) Localized Electron Model
 Molecular Geometry Learn Shapes you will Because the physical and chemical properties of compounds are tied to their structures, the importance of molecular geometry can not be overstated. Localized Electron
Molecular Geometry Learn Shapes you will Because the physical and chemical properties of compounds are tied to their structures, the importance of molecular geometry can not be overstated. Localized Electron
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 10
 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 10 Linear Trigonal 180 o planar 120 o Tetrahedral 109.5 o Trigonal Bipyramidal 120 and 90 o Octahedral 90 o linear Linear
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 10 Linear Trigonal 180 o planar 120 o Tetrahedral 109.5 o Trigonal Bipyramidal 120 and 90 o Octahedral 90 o linear Linear
Chemical Bonds, Molecular Models, and Molecular Shapes
 Chemical Bonds, Molecular Models, and Molecular Shapes PRELAB ASSINGMENT Read the entire laboratory write up and answer the following questions before coming to lab. Read the entire laboratory write up
Chemical Bonds, Molecular Models, and Molecular Shapes PRELAB ASSINGMENT Read the entire laboratory write up and answer the following questions before coming to lab. Read the entire laboratory write up
Ex. 1) F F bond in F = 0 < % covalent, no transfer of electrons
 #60 Notes Unit 8: Bonding Ch. Bonding I. Bond Character Bonds are usually combinations of ionic and covalent character. The electronegativity difference is used to determine a bond s character. Electronegativity
#60 Notes Unit 8: Bonding Ch. Bonding I. Bond Character Bonds are usually combinations of ionic and covalent character. The electronegativity difference is used to determine a bond s character. Electronegativity
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry. Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory
 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Sulfanilamide Lewis Structures and the Real 3D-Shape of Molecules Lewis Theory of Molecular Shape and Polarity
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Sulfanilamide Lewis Structures and the Real 3D-Shape of Molecules Lewis Theory of Molecular Shape and Polarity
Shapes of Molecules and Hybridization
 Shapes of Molecules and Hybridization A. Molecular Geometry Lewis structures provide us with the number and types of bonds around a central atom, as well as any NB electron pairs. They do not tell us the
Shapes of Molecules and Hybridization A. Molecular Geometry Lewis structures provide us with the number and types of bonds around a central atom, as well as any NB electron pairs. They do not tell us the
MOLECULAR MODELS OBJECTIVES
 MOLECULAR MODELS OBJECTIVES 1. To learn to draw Lewis structures for common compounds 2. To identify electron pairs as bonding pairs or lone pairs 3. To use electron pair repulsion theory to predict electronic
MOLECULAR MODELS OBJECTIVES 1. To learn to draw Lewis structures for common compounds 2. To identify electron pairs as bonding pairs or lone pairs 3. To use electron pair repulsion theory to predict electronic
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometries. and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories Coverage of Chapter 9 9.1 All 9.2 All 9.3 All 9.4 All 9.5 Omit Hybridization Involving d Orbitals 9.6 All 9.7 and 9.8 Omit ALL MOLECULAR SHAPES The shape
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories Coverage of Chapter 9 9.1 All 9.2 All 9.3 All 9.4 All 9.5 Omit Hybridization Involving d Orbitals 9.6 All 9.7 and 9.8 Omit ALL MOLECULAR SHAPES The shape
Chapter 9. Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory
 Chapter 9 Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Problems with Lewis Theory Lewis theory generally predicts trends in properties, but does not give good numerical predictions.
Chapter 9 Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Problems with Lewis Theory Lewis theory generally predicts trends in properties, but does not give good numerical predictions.
CHEMISTRY 112 LECTURE EXAM II Material
 CHEMISTRY 112 LECTURE EXAM II Material Part I Chemical Bonding I Lewis Theory Chapter 9 pages 376-386 A. Drawing electron dot structures HOW TO: 1. Write e- dot structure for the individual atoms. 2. a)
CHEMISTRY 112 LECTURE EXAM II Material Part I Chemical Bonding I Lewis Theory Chapter 9 pages 376-386 A. Drawing electron dot structures HOW TO: 1. Write e- dot structure for the individual atoms. 2. a)
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories PART I Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories PART I Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
MOLECULAR ORBITAL DIAGRAM KEY
 365 MOLECULAR ORBITAL DIAGRAM KEY Draw molecular orbital diagrams for each of the following molecules or ions. Determine the bond order of each and use this to predict the stability of the bond. Determine
365 MOLECULAR ORBITAL DIAGRAM KEY Draw molecular orbital diagrams for each of the following molecules or ions. Determine the bond order of each and use this to predict the stability of the bond. Determine
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals
 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals 1 Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry (10.1) Dipole Moments (10.2) Valence Bond Theory (10.3) Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals 1 Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry (10.1) Dipole Moments (10.2) Valence Bond Theory (10.3) Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals
Experiment 15. The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory of Directed Valency: An exercise
 Experiment 15 The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory of Directed Valency: An exercise Attempts to understand and predict the shapes of molecules using either the valencebond theory or
Experiment 15 The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory of Directed Valency: An exercise Attempts to understand and predict the shapes of molecules using either the valencebond theory or
General and Inorganic Chemistry I.
 General and Inorganic Chemistry I. Lecture 1 István Szalai Eötvös University István Szalai (Eötvös University) Lecture 1 1 / 29 Outline István Szalai (Eötvös University) Lecture 1 2 / 29 Lewis Formulas
General and Inorganic Chemistry I. Lecture 1 István Szalai Eötvös University István Szalai (Eötvös University) Lecture 1 1 / 29 Outline István Szalai (Eötvös University) Lecture 1 2 / 29 Lewis Formulas
2011, Robert Ayton. All rights reserved.
 Chemical Bonding Outline 1. Lewis Dot Structures 2. Bonds 3. Formal Charges 4. VSEPR (Molecular Geometry and Hybridzation) 5. Common Resonance Structures and Dimerization Review 1. Lewis Dot Structures
Chemical Bonding Outline 1. Lewis Dot Structures 2. Bonds 3. Formal Charges 4. VSEPR (Molecular Geometry and Hybridzation) 5. Common Resonance Structures and Dimerization Review 1. Lewis Dot Structures
Activity Formal Charge and VSEPR Theory for Expanded Octets
 Activity 201 7 Formal Charge and VSEPR Theory for Expanded Octets Directions: This Guided Learning Activity (GLA) goes over formal charge and the structures of molecules with expanded octets. Part A introduces
Activity 201 7 Formal Charge and VSEPR Theory for Expanded Octets Directions: This Guided Learning Activity (GLA) goes over formal charge and the structures of molecules with expanded octets. Part A introduces
From 2-D to 3-D. Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry
 From 2-D to 3-D Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry 1 Moving on to Shapes A chemical formula tells us The identity of atoms The number of atoms The Lewis structure tells us The identity of atoms The number of
From 2-D to 3-D Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry 1 Moving on to Shapes A chemical formula tells us The identity of atoms The number of atoms The Lewis structure tells us The identity of atoms The number of
Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 Group 5 Group 6 Group 7 Group 8. Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar
 CHM 111 Chapters 7 and 8 Worksheet and Study Guide Purpose: This is a guide for your as you work through the chapter. The major topics are provided so that you can write notes on each topic and work the
CHM 111 Chapters 7 and 8 Worksheet and Study Guide Purpose: This is a guide for your as you work through the chapter. The major topics are provided so that you can write notes on each topic and work the
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Models
 25 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Models A chemical bond is a force that holds groups of two or more atoms together and makes them function as a unit. Bonding involves only the valence (outer shell) electrons
25 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Models A chemical bond is a force that holds groups of two or more atoms together and makes them function as a unit. Bonding involves only the valence (outer shell) electrons
Chapter 13: Phenomena
 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
EXAM II Material. Part I Chemical Bonding I Lewis Theory Chapter 9 pages A. Drawing electron dot structures HOW TO:
 CHEMISTRY 112 LECTURE EXAM II Material Part I Chemical Bonding I Lewis Theory Chapter 9 pages 376-386 A. Drawing electron dot structures HOW TO: 1. Write e- dot structure for the individual atoms. 2. a)
CHEMISTRY 112 LECTURE EXAM II Material Part I Chemical Bonding I Lewis Theory Chapter 9 pages 376-386 A. Drawing electron dot structures HOW TO: 1. Write e- dot structure for the individual atoms. 2. a)
Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory
 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory The Valence -Shell Electron -Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Model predicts the shapes of the molecules and ions by assuming that the valence shell electron pairs
Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory The Valence -Shell Electron -Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Model predicts the shapes of the molecules and ions by assuming that the valence shell electron pairs
Practice Worksheet for Lewis Structures (Mahaffy Ch )
 Practice Worksheet for Lewis Structures (Mahaffy Ch. 10.1 10.5 ) 1. Main concepts Lewis Structures a. Connectivity b. Bonds & Lone pairs c. Electron Geometry & Molecular Shape d. Resonance Structures Formal
Practice Worksheet for Lewis Structures (Mahaffy Ch. 10.1 10.5 ) 1. Main concepts Lewis Structures a. Connectivity b. Bonds & Lone pairs c. Electron Geometry & Molecular Shape d. Resonance Structures Formal
Shapes of Molecules. Lewis structures are useful but don t allow prediction of the shape of a molecule.
 Shapes of Molecules Lewis structures are useful but don t allow prediction of the shape of a molecule. H O H H O H Can use a simple theory based on electron repulsion to predict structure (for non-transition
Shapes of Molecules Lewis structures are useful but don t allow prediction of the shape of a molecule. H O H H O H Can use a simple theory based on electron repulsion to predict structure (for non-transition
AP Chemistry - Problem Drill 15: Lewis Structures and VSEPR Theory
 AP Chemistry - Problem Drill 15: Lewis Structures and VSEPR Theory No. 1 of 10 1. Which shape would have sp 3 hybridization? (A) Linear (B) Bent (C) Tetrahedron (D) Trigonal planar (E) Octahedron C. Correct.
AP Chemistry - Problem Drill 15: Lewis Structures and VSEPR Theory No. 1 of 10 1. Which shape would have sp 3 hybridization? (A) Linear (B) Bent (C) Tetrahedron (D) Trigonal planar (E) Octahedron C. Correct.
To visualize the three-dimensional structures of some common molecules. To obtain bond angle, bond length, and hybridization data for molecules.
 Molecular Geometry PURPOSE A B C To explore some simple molecular structures. To explore the relationship between bond order and bond length. To explore resonance structures. GOALS To compare Lewis structures
Molecular Geometry PURPOSE A B C To explore some simple molecular structures. To explore the relationship between bond order and bond length. To explore resonance structures. GOALS To compare Lewis structures
Molecular Geometry and intermolecular forces. Unit 4 Chapter 9 and 11.2
 1 Molecular Geometry and intermolecular forces Unit 4 Chapter 9 and 11.2 2 Unit 4.1 Chapter 9.1-9.3 3 Review of bonding Ionic compound (metal/nonmetal) creates a lattice Formula doesn t tell the exact
1 Molecular Geometry and intermolecular forces Unit 4 Chapter 9 and 11.2 2 Unit 4.1 Chapter 9.1-9.3 3 Review of bonding Ionic compound (metal/nonmetal) creates a lattice Formula doesn t tell the exact
Experiment 21 Lewis structures and VSEPR Theory
 Experiment 21 Lewis structures and VSEPR Theory Introduction 1. Lewis Structures and Formal Charge LG.N. Lewis, at the University of California at Berkeley devised a simple way to understand the nature
Experiment 21 Lewis structures and VSEPR Theory Introduction 1. Lewis Structures and Formal Charge LG.N. Lewis, at the University of California at Berkeley devised a simple way to understand the nature
CHEMISTRY. Chapter 10 Theories of Bonding and Structure. The Molecular Nature of Matter. Jespersen Brady Hyslop SIXTH EDITION
 CHEMISTRY The Molecular Nature of Matter SIXTH EDITION Jespersen Brady Hyslop Chapter 10 Theories of Bonding and Structure Copyright 2012 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Molecular Structures Molecules containing
CHEMISTRY The Molecular Nature of Matter SIXTH EDITION Jespersen Brady Hyslop Chapter 10 Theories of Bonding and Structure Copyright 2012 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Molecular Structures Molecules containing
Instant download Test bank for Chemistry The Central Science 10th Edition by Brown, LeMay, Bursten CLICK HERE
 Chemistry, 10e (Brown) Chapter 9, Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Instant download Test bank for Chemistry The Central Science 10th Edition by Brown, LeMay, Bursten CLICK HERE http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-chemistry-the-central-science-10th-edition-by-brown-lemay-bursten/
Chemistry, 10e (Brown) Chapter 9, Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Instant download Test bank for Chemistry The Central Science 10th Edition by Brown, LeMay, Bursten CLICK HERE http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-chemistry-the-central-science-10th-edition-by-brown-lemay-bursten/
Chemical Bonds, Molecular Models, and Molecular Shapes
 Chemical Bonds, Molecular Models, and Molecular Shapes PRELAB ASSINGMENT Write an objective, and answer the following questions in your laboratory notebook before coming to lab. Read the entire laboratory
Chemical Bonds, Molecular Models, and Molecular Shapes PRELAB ASSINGMENT Write an objective, and answer the following questions in your laboratory notebook before coming to lab. Read the entire laboratory
 Hybridisation 1. Hybridisation involves 1. Inter mixing of electron s 2. Inter mixing and redistribution of atomic orbitals of only one atom 3. Inter mixing and redistribution of atomic orbitals of different
Hybridisation 1. Hybridisation involves 1. Inter mixing of electron s 2. Inter mixing and redistribution of atomic orbitals of only one atom 3. Inter mixing and redistribution of atomic orbitals of different
CHM2045 F13--Exam # MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 CHM2045 F13--Exam #2 2013.10.18 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A valid Lewis structure of cannot be drawn without violating the
CHM2045 F13--Exam #2 2013.10.18 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A valid Lewis structure of cannot be drawn without violating the
Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, Valence Bond Theory, and Molecular Orbital Theory
 10.1 Artificial Sweeteners: Fooled by Molecular Shape 425 10.2 VSEPR Theory: The Five Basic Shapes 426 10.3 VSEPR Theory: The Effect of Lone Pairs 430 10.4 VSEPR Theory: Predicting Molecular Geometries
10.1 Artificial Sweeteners: Fooled by Molecular Shape 425 10.2 VSEPR Theory: The Five Basic Shapes 426 10.3 VSEPR Theory: The Effect of Lone Pairs 430 10.4 VSEPR Theory: Predicting Molecular Geometries
Molecular Models: The shape of simple molecules and ions
 Molecular Models: The shape of simple molecules and ions Background The shape of a molecule is very important when investigating its properties and reactivity. For example, compare CO 2 and SO 2. Carbon
Molecular Models: The shape of simple molecules and ions Background The shape of a molecule is very important when investigating its properties and reactivity. For example, compare CO 2 and SO 2. Carbon
CHEM1101 Worksheet 6: Lone Pairs and Molecular Geometry
 CHEM1101 Worksheet 6: Lone Pairs and Molecular Geometry Model 1: Oxidation numbers Oxidation numbers are a useful accountancy tool to help keep track of electrons in compounds and reactions. This is particularly
CHEM1101 Worksheet 6: Lone Pairs and Molecular Geometry Model 1: Oxidation numbers Oxidation numbers are a useful accountancy tool to help keep track of electrons in compounds and reactions. This is particularly
Chemical Bonding. Types of Bonds. Ionic Bonding. Resonance Structures. Molecular Geometries. VSEPR Basic Shapes 3-D Notation Hybridization (Lab)
 Chemical Bonding Types of Bonds Ionic Bonding Lewis Structures Covalent Bonding Resonance Structures Octet Rule Polar Molecules Molecular Geometries VSEPR Basic Shapes 3-D Notation Hybridization (Lab)
Chemical Bonding Types of Bonds Ionic Bonding Lewis Structures Covalent Bonding Resonance Structures Octet Rule Polar Molecules Molecular Geometries VSEPR Basic Shapes 3-D Notation Hybridization (Lab)
Lab #11- Molecular Geometry
 Objectives Chesapeake Campus Chemistry 111 Laboratory Lab #11- Molecular Geometry Determine the shape of a molecule using the VSEPR. Draw the Lewis structures of a molecule including bond angles and formal
Objectives Chesapeake Campus Chemistry 111 Laboratory Lab #11- Molecular Geometry Determine the shape of a molecule using the VSEPR. Draw the Lewis structures of a molecule including bond angles and formal
Molecular Geometry. Objectives N H H. The objectives of this laboratory are to:
 Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are to: Molecular Geometry Write Lewis structure representations of the bonding and valence electrons in molecules. Use the VSEPR model to predict the molecular
Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are to: Molecular Geometry Write Lewis structure representations of the bonding and valence electrons in molecules. Use the VSEPR model to predict the molecular
Chemistry 212 MOLECULAR STRUCTURES AND GEOMETRIES
 Chemistry 212 MOLECULAR STRUCTURES AND GEOMETRIES LEARNING OBJECTIVES To build models of selected molecules using VSEPR theory. To illustrate patterns of molecular shapes. BACKGROUND The shapes exhibited
Chemistry 212 MOLECULAR STRUCTURES AND GEOMETRIES LEARNING OBJECTIVES To build models of selected molecules using VSEPR theory. To illustrate patterns of molecular shapes. BACKGROUND The shapes exhibited
Honors Chemistry Unit 6 ( )
 Honors Chemistry Unit 6 (2017-2018) Lewis Dot Structures VSEPR Structures 1 We are learning to: 1. Represent compounds with Lewis structures. 2. Apply the VSEPR theory to determine the molecular geometry
Honors Chemistry Unit 6 (2017-2018) Lewis Dot Structures VSEPR Structures 1 We are learning to: 1. Represent compounds with Lewis structures. 2. Apply the VSEPR theory to determine the molecular geometry
Molecular Structure. Valence Bond Theory Overlap of atomic orbitals is a covalent bond that joins atoms together to form a molecule
 Molecular Structure Topics 3-D structure shape (location of atoms in space) Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Hybrid Orbitals Multiple Bonds VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) Valence Bond
Molecular Structure Topics 3-D structure shape (location of atoms in space) Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Hybrid Orbitals Multiple Bonds VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) Valence Bond
8.3 Bonding Theories > Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding. 8.3 Bonding Theories. 8.1 Molecular Compounds 8.2 The Nature of Covalent Bonding
 Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding 8.1 Molecular Compounds 8.2 The Nature of Covalent Bonding 8.3 Bonding Theories 8.4 Polar Bonds and Molecules 1 Molecular Shape What information does a structural formula give
Chapter 8 Covalent Bonding 8.1 Molecular Compounds 8.2 The Nature of Covalent Bonding 8.3 Bonding Theories 8.4 Polar Bonds and Molecules 1 Molecular Shape What information does a structural formula give
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories molecular shapes the VSEPR model molecular shape and molecular polarity covalent bonding and orbital overlap hybrid orbitals multiple bonds 9.1 Molecular
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories molecular shapes the VSEPR model molecular shape and molecular polarity covalent bonding and orbital overlap hybrid orbitals multiple bonds 9.1 Molecular
Structures, Shapes and Polarity. of Molecules. Level 2 recap: - Polar and non polar bonds - Lewis diagrams - Lone pairs - Shapes - Polarity
 Structures, Shapes and Polarity Level 2 recap: - Polar and non polar bonds - Lewis diagrams - Lone pairs - Shapes - Polarity of Molecules Do now: Brainstorm what you know/remember about these L2 concepts
Structures, Shapes and Polarity Level 2 recap: - Polar and non polar bonds - Lewis diagrams - Lone pairs - Shapes - Polarity of Molecules Do now: Brainstorm what you know/remember about these L2 concepts
Name Unit Three MC Practice March 15, 2017
 Unit Three: Bonding & Molecular Geometry Name Unit Three MC Practice March 15, 2017 1. What is the hybridization of the oxygen atom in water? a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) It is not hybridized 2. When a double
Unit Three: Bonding & Molecular Geometry Name Unit Three MC Practice March 15, 2017 1. What is the hybridization of the oxygen atom in water? a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) It is not hybridized 2. When a double
Chapter 9. Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Topics Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry and Polarity Valence Bond Theory Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Hybridization in Molecules
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Topics Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry and Polarity Valence Bond Theory Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Hybridization in Molecules
Chemical Bonds. Chapter 6
 Chemical Bonds Chapter 6 1 Ch. 6 Chemical Bonding I. How and Why Atoms Bond A. Vocabulary B. Chemical Bonds - Basics C. Chemical Bonds Types D. Chemical Bonds Covalent E. Drawing Lewis Diagrams F. Bond
Chemical Bonds Chapter 6 1 Ch. 6 Chemical Bonding I. How and Why Atoms Bond A. Vocabulary B. Chemical Bonds - Basics C. Chemical Bonds Types D. Chemical Bonds Covalent E. Drawing Lewis Diagrams F. Bond
AP Chemistry- Practice Bonding Questions for Exam
 AP Chemistry- Practice Bonding Questions for Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is a correct Lewis structure for
AP Chemistry- Practice Bonding Questions for Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is a correct Lewis structure for
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 9.1 Molecular Shapes Read Sec. 9.1 and 9.2, then complete the Sample and Practice Exercises in these sections. Sample Exercise 9.1 (p. 347) Use the VSEPR model to predict the molecular geometries of a)
9.1 Molecular Shapes Read Sec. 9.1 and 9.2, then complete the Sample and Practice Exercises in these sections. Sample Exercise 9.1 (p. 347) Use the VSEPR model to predict the molecular geometries of a)
Announcements. 10pm Room assignments for Exam III and TA Exam Review Sessions are posted on website. Look under Exam Info link
 Announcements 1. Exam #3: Thursday, Dec. 6 th, 7:00-8:15pm (Conflict: 5:15-6:30pm) No calculators allowed 2. Activity 3: Making Models of Molecules lab write-up due tomorrow in discussion 3. Lon-capa HW
Announcements 1. Exam #3: Thursday, Dec. 6 th, 7:00-8:15pm (Conflict: 5:15-6:30pm) No calculators allowed 2. Activity 3: Making Models of Molecules lab write-up due tomorrow in discussion 3. Lon-capa HW
Chemistry and the material world Lecture 3
 Chemistry and the material world 123.102 Lecture 3 Electronic bookkeeping we need a way of finding out in which proportions two or more atoms make up a molecule is it CH 3 or CH 4 or CH 5? counting valence
Chemistry and the material world 123.102 Lecture 3 Electronic bookkeeping we need a way of finding out in which proportions two or more atoms make up a molecule is it CH 3 or CH 4 or CH 5? counting valence
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories MOLECULAR SHAPES 2 Molecular Shapes Lewis Structures show bonding and lone pairs do not denote shape Use Lewis Structures to determine shapes Molecular
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories MOLECULAR SHAPES 2 Molecular Shapes Lewis Structures show bonding and lone pairs do not denote shape Use Lewis Structures to determine shapes Molecular
Test bank for Chemistry The Central Science 10th Edition by Brown, LeMay, Bursten
 Test bank for Chemistry The Central Science 10th Edition by Brown, LeMay, Bursten Chapter 9, Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Multiple-Choice and Bimodal 1) For a molecule with the formula A) linear
Test bank for Chemistry The Central Science 10th Edition by Brown, LeMay, Bursten Chapter 9, Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Multiple-Choice and Bimodal 1) For a molecule with the formula A) linear
COVALENT BONDING CHEMICAL BONDING I: LEWIS MODEL. Chapter 7
 Chapter 7 P a g e 1 COVALENT BONDING Covalent Bonds Covalent bonds occur between two or more nonmetals. The two atoms share electrons between them, composing a molecule. Covalently bonded compounds are
Chapter 7 P a g e 1 COVALENT BONDING Covalent Bonds Covalent bonds occur between two or more nonmetals. The two atoms share electrons between them, composing a molecule. Covalently bonded compounds are
Molecular shape is determined by the number of bonds that form around individual atoms.
 Chapter 9 CH 180 Major Concepts: Molecular shape is determined by the number of bonds that form around individual atoms. Sublevels (s, p, d, & f) of separate atoms may overlap and result in hybrid orbitals
Chapter 9 CH 180 Major Concepts: Molecular shape is determined by the number of bonds that form around individual atoms. Sublevels (s, p, d, & f) of separate atoms may overlap and result in hybrid orbitals
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Ch 13: Covalent Bonding
 Ch 13: Covalent Bonding Section 13: Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion 1. Recall the rules for drawing Lewis dot structures 2. Remember the special situations: - Resonance structures - ormal charges
Ch 13: Covalent Bonding Section 13: Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion 1. Recall the rules for drawing Lewis dot structures 2. Remember the special situations: - Resonance structures - ormal charges
Chapter 10. VSEPR Model: Geometries
 Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry VSEPR Model: Geometries Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Electron pairs repel and get as far apart as possible Example: Water Four electron pairs Farthest apart
Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry VSEPR Model: Geometries Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Electron pairs repel and get as far apart as possible Example: Water Four electron pairs Farthest apart
The Shapes of Molecules. Chemistry II
 The Shapes of Molecules Chemistry II Lewis Structures DEFINITIN: A structure of a molecule showing how the valence electrons are arranged. 1) nly the valence electrons appear in a Lewis structure. 2) The
The Shapes of Molecules Chemistry II Lewis Structures DEFINITIN: A structure of a molecule showing how the valence electrons are arranged. 1) nly the valence electrons appear in a Lewis structure. 2) The
Covalent Bonds: overlap of orbitals σ-bond π-bond Molecular Orbitals
 Covalent Bonding What is covalent bonding? Covalent Bonds: overlap of orbitals σ-bond π-bond Molecular Orbitals Hybrid Orbital Formation Shapes of Hybrid Orbitals Hybrid orbitals and Multiple Bonds resonance
Covalent Bonding What is covalent bonding? Covalent Bonds: overlap of orbitals σ-bond π-bond Molecular Orbitals Hybrid Orbital Formation Shapes of Hybrid Orbitals Hybrid orbitals and Multiple Bonds resonance
Chapters 8 and 9. Octet Rule Breakers Shapes
 Chapters 8 and 9 Octet Rule Breakers Shapes Bond Energies Bond Energy (review): The energy needed to break one mole of covalent bonds in the gas phase Breaking bonds consumes energy; forming bonds releases
Chapters 8 and 9 Octet Rule Breakers Shapes Bond Energies Bond Energy (review): The energy needed to break one mole of covalent bonds in the gas phase Breaking bonds consumes energy; forming bonds releases
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 1
 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. How to get the book of
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. How to get the book of
14.1 Shapes of molecules and ions (HL)
 14.1 Shapes of molecules and ions (HL) The octet is the most common electron arrangement because of its stability. Exceptions: a) Fewer electrons (incomplete octet) if the central atom is a small atoms,
14.1 Shapes of molecules and ions (HL) The octet is the most common electron arrangement because of its stability. Exceptions: a) Fewer electrons (incomplete octet) if the central atom is a small atoms,
Homework 08 VSEPR. The active ingredient in some oral anesthetics used in sore throat sprays. What is the molar mass of phenol?
 HW08 VSEPR This is a preview of the published version of the quiz Started: Oct 21 at 11:14am Quiz Instruc ons Homework 08 VSEPR Question 1 Consider the structural formula of phenol. The active ingredient
HW08 VSEPR This is a preview of the published version of the quiz Started: Oct 21 at 11:14am Quiz Instruc ons Homework 08 VSEPR Question 1 Consider the structural formula of phenol. The active ingredient
Illinois Central College CHEMISTRY 130 Laboratory Section: To predict the shapes of molecules based on their Lewis Structures.
 Exercise 12 Page 1 Illinois Central College CEMISTRY 130 Laboratory Section: Molecular Structure Name: Objectives To predict the shapes of molecules based on their Lewis Structures. Background The Valence
Exercise 12 Page 1 Illinois Central College CEMISTRY 130 Laboratory Section: Molecular Structure Name: Objectives To predict the shapes of molecules based on their Lewis Structures. Background The Valence
Chemical Bonding II. Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Phys./Chem. Properties Quantum Mechanics Sigma & Pi bonds Hybridization MO theory
 Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Phys./Chem. Properties Quantum Mechanics Sigma & Pi bonds ybridization MO theory 1 Molecular Geometry 3-D arrangement of atoms 2 VSEPR Valence-shell
Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Phys./Chem. Properties Quantum Mechanics Sigma & Pi bonds ybridization MO theory 1 Molecular Geometry 3-D arrangement of atoms 2 VSEPR Valence-shell
Form J. Test #4 Last Name First Name Zumdahl, Chapters 8 and 9 November 23, 2004
 Form J Chemistry 1441-023 Name (please print) Test #4 Last Name First Name Zumdahl, Chapters 8 and 9 November 23, 2004 Instructions: 1. This exam consists of 27 questions. 2. No scratch paper is allowed.
Form J Chemistry 1441-023 Name (please print) Test #4 Last Name First Name Zumdahl, Chapters 8 and 9 November 23, 2004 Instructions: 1. This exam consists of 27 questions. 2. No scratch paper is allowed.
Subtopic 4.2 MOLECULAR SHAPE AND POLARITY
 Subtopic 4.2 MOLECULAR SHAPE AND POLARITY 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES (covalent bonding) 1. Draw the Lewis structure of covalent molecules (octet rule such as NH 3, CCl 4, H 2 O, CO 2, N 2 O 4, and exception to
Subtopic 4.2 MOLECULAR SHAPE AND POLARITY 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES (covalent bonding) 1. Draw the Lewis structure of covalent molecules (octet rule such as NH 3, CCl 4, H 2 O, CO 2, N 2 O 4, and exception to
Helpful Hints Lewis Structures Octet Rule For Lewis structures of covalent compounds least electronegative
 Helpful Hints Lewis Structures Octet Rule Lewis structures are a basic representation of how atoms are arranged in compounds based on bond formation by the valence electrons. A Lewis dot symbol of an atom
Helpful Hints Lewis Structures Octet Rule Lewis structures are a basic representation of how atoms are arranged in compounds based on bond formation by the valence electrons. A Lewis dot symbol of an atom
Focus Learning Targets for Periodic Trends and Bonding (1) Discuss the development of the periodic table by Mendeleev. (2) Locate and state important
 Focus Learning Targets for Periodic Trends and Bonding (1) Discuss the development of the periodic table by Mendeleev. (2) Locate and state important properties of main chemical families including the
Focus Learning Targets for Periodic Trends and Bonding (1) Discuss the development of the periodic table by Mendeleev. (2) Locate and state important properties of main chemical families including the
electronegativity difference greater than or equal to Ionic Bonding occurs between a metal and a nonmetal when there is an
 Chemistry Unit 4 Review Packet Sweeeeeeeettt ANSWER KEY For the following compounds identify the bond types as one of the following: Ionic, Metallic, Polar Covalent, Non Polar Covalent, and Moderately
Chemistry Unit 4 Review Packet Sweeeeeeeettt ANSWER KEY For the following compounds identify the bond types as one of the following: Ionic, Metallic, Polar Covalent, Non Polar Covalent, and Moderately
Molecular Modeling 1: Classic Molecular Modeling
 Molecular Modeling 1: Classic Molecular Modeling Author: J. M. McCormick* Last Update: January 31, 2011 Introduction Dalton's Atomic Theory revolutionized chemistry by explaining chemical properties in
Molecular Modeling 1: Classic Molecular Modeling Author: J. M. McCormick* Last Update: January 31, 2011 Introduction Dalton's Atomic Theory revolutionized chemistry by explaining chemical properties in
Lewis Dot Structures and Molecular Geometry
 Experiment 11 Lewis Dot Structures and Molecular Geometry Pre-Lab Assignment Before coming to lab: Read the lab thoroughly. Answer the pre-lab questions that appear at the end of this lab exercise. Purpose
Experiment 11 Lewis Dot Structures and Molecular Geometry Pre-Lab Assignment Before coming to lab: Read the lab thoroughly. Answer the pre-lab questions that appear at the end of this lab exercise. Purpose
(A) 1 bonding pair (B) 1 bonding pair and 1 lone pair (C) 2 bonding pairs (D) 2 bonding pairs and 2 lone pairs
 AP Chemistry - Problem Drill 13: Lewis Structures and VSPER No. 1 of 10 1. Lewis structure is used to model covalent bonds of a molecule or ion. Covalent bonds are a type of chemical bonding formed by
AP Chemistry - Problem Drill 13: Lewis Structures and VSPER No. 1 of 10 1. Lewis structure is used to model covalent bonds of a molecule or ion. Covalent bonds are a type of chemical bonding formed by
5 Polyatomic molecules
 s manual for Burrows et.al. Chemistry 3 Third edition 5 Polyatomic molecules Answers to worked examples WE 5.1 Formal charges in N 2 (on p. 221 in Chemistry 3 ) Use formal charges to decide whether oxygen
s manual for Burrows et.al. Chemistry 3 Third edition 5 Polyatomic molecules Answers to worked examples WE 5.1 Formal charges in N 2 (on p. 221 in Chemistry 3 ) Use formal charges to decide whether oxygen
Chapter Molecules are 3D. Shapes and Bonds. Chapter 9 1. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
 Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure 1 Shape 9.1 Molecules are 3D Angle Linear 180 Planar triangular (trigonal planar) 120 Tetrahedral 109.5 2 Shapes and Bonds Imagine a molecule where the
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure 1 Shape 9.1 Molecules are 3D Angle Linear 180 Planar triangular (trigonal planar) 120 Tetrahedral 109.5 2 Shapes and Bonds Imagine a molecule where the
10-1. The Shapes of Molecules, chapter 10
 10-1 The Shapes of Molecules, chapter 10 The Shapes of Molecules; Goals 10.1 Depicting Molecules and Ions with Lewis Structures 10.2 Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory 10.3 Molecular
10-1 The Shapes of Molecules, chapter 10 The Shapes of Molecules; Goals 10.1 Depicting Molecules and Ions with Lewis Structures 10.2 Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory 10.3 Molecular
Chemical Bonding 4.8. Valence Bond Theory Hybrid Orbital Theory Multiple Bonds High School Chem Solutions. All rights reserved.
 Chemical Bonding 4.8 Valence Bond Theory Hybrid Orbital Theory Multiple Bonds Valence Bond Theory Combines Lewis theory of filling octets by sharing pairs of electrons with the electron configuration of
Chemical Bonding 4.8 Valence Bond Theory Hybrid Orbital Theory Multiple Bonds Valence Bond Theory Combines Lewis theory of filling octets by sharing pairs of electrons with the electron configuration of
Chapter 9 The Shapes of Molecules Cocaine
 Chapter 9 The Shapes of Molecules 1 Cocaine 10.1 Depicting Molecules & Ions with Lewis Structures 2 Number of Covalent Bonds 3 The number of covalent bonds can be determined from the number of electrons
Chapter 9 The Shapes of Molecules 1 Cocaine 10.1 Depicting Molecules & Ions with Lewis Structures 2 Number of Covalent Bonds 3 The number of covalent bonds can be determined from the number of electrons
