Name Unit Three MC Practice March 15, 2017
|
|
|
- Paul Charles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit Three: Bonding & Molecular Geometry Name Unit Three MC Practice March 15, What is the hybridization of the oxygen atom in water? a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) It is not hybridized 2. When a double bond is formed between two atoms, one of the bonds is a sigma bond and the other is a pi bond. The pi bond is created by the overlap of... a) p orbitals b) sp 3 hybrid orbitals c) sp 2 hybrid orbitals d) s orbitals 3. The central atom in BrF 5 has _?_ bonding pairs of electrons and _?_ non-bonding pairs of electrons. a) b) c) d) Which of the following molecules does not have a net dipole moment? a) H 2O b) NH 3 c) BrF 5 d) BF 3 5. What is the electron-pair geometry of the central oxygen atom of ozone (O 3)? a) linear b) trigonal planar c) tetrahedral d) trigonal bipyramidal 6. What is the molecular geometry for ammonia (NH 3)? a) saw horse b) trigonal planar c) tetrahedral d) trigonal pyramidal 7. Which of the following best represents the 3-dimensional view of H 2N -1? 8. What is the hybridization of the sulfur atom is SF 4? a) sp 2 b) sp 3 c) sp 3 d d) sp 3 d 2 9. What is the hybridization of the xenon atom in XeF 4? a) sp 2 b) sp 3 c) sp 3 d d) sp 3 d According to the octet rule, NO + should contain a: a) single bond b) double bond c) triple bond d) James Bond 1
2 11. According to the octet rule, the carbon-oxygen bond in the molecule COBr 2, in which carbon is bonded to O and Br atoms, is a: a) single bond b) double bond c) triple bond d) quadruple bond Questions 12 and 13 are based on the XeF 4 molecule. 12. The electron pair geometry around the central atom is: a) trigonal planar b) trigonal bipyramidal c) octahedral d) square planar 13. The molecular geometry is: a) tetrahedral b) trigonal bipyramidal c) seesaw d) square planar 14. Which of the following molecules would have the greatest polarity? a) HF b) HCl c) HBr d) HI 15. Ionic solids will typically be formed between atoms in: a) groups I A and VIII A. b) groups II A and VII A. c) groups VI A and VII A d) groups I A and VI B. 16. For which of the following molecules is an expanded octet necessary to describe the bonding in the molecule? a) H 2 b) PF 5 c) H 2O d) CH The geometry of the XeO 4 molecule is best described as: a) square planer b) tetrahedral c) octahedral d) bent Questions 18 through 20 are based on the formaldehyde molecule, CH 2O, where carbon is the central atom and the bond angle H-C-O is 120 degrees. 18. The type of orbitals used on the carbon atom in the formaldehyde mole is: a) sp hybrids b) sp 2 hybrids c) sp 3 hybrids d) sp 3 d hybrids 19. The bond between the carbon and oxygen would be best described as: a) one sigma (s) bond b) two sigma (s) bonds c) one pi (p) bond d) one sigma (s) bond and one pi (p) bond 20. The molecule is best described as: a) a polar molecule containing polar bonds b) a non-polar molecule made up of polar bonds c) a non-polar molecule made up of non-polar bonds d) none of the above 21. Which of the following molecules is NOT polar? a) CCl 4 b) H 2O c) CH 3OH d) NH 3 2
3 22. The reaction between H 2 and F 2 to form HF is because. a) exothermic; H-F bonds are stronger than H-H and F-F bonds b) exothermic; H-F bonds are weaker than H-H and F-F bonds c) endothermic; H-F bonds are stronger than H-H and F-F bonds d) endothermic; H-F bonds are stronger than H-H and F-F bonds 23. Use the table of bond energies given below to estimate ΔH for the reaction: 2 H2O(g) + 2 Cl2(g) ==> O2(g) + 4 HCl(g) Bond H-H F-F H-F Cl-Cl O=O H-O H-Cl Bond Energy (kj/mol) a) +189kJ b) -280kJ c) +120kJ d) +398kJ 24. Which of the following species require a resonance hybrid for its Lewis structure? a) NH 3 b) CO 3 c) OCl - d) OH - Questions 25 and 26 are based on the following structure showing only the sigma (s) or single bond structure. All bond angles are approximately The type of orbitals on the carbon atom that would account for this geometry are: a)sp hybrid orbitals b) sp 2 hybrid orbitals c) sp 3 hybrid orbitals d) sp 3 d hybrid orbitals 26. The bond between the carbon and oxygen is best described by which of the following? a) one sigma (s) bond b) two sigma (s) bonds c) one sigma (s) and one pi (p) bond d) two pi (p) bonds 27. Estimate ΔH in kj for the following gas phase reaction: CFCl3 + HF ==> CF2Cl2 + HCl given the following bond energies in kj/mol: C-F 485, H-F 565, C-Cl 331, H-Cl 431 a) +20kJ b) -20kJ c) -180kJ d) +288kJ 28. The electron configuration of the S ion is. a) [Ne]3s 2 3p 6 b) [Ar]3s 2 3p 2 c) [Ar]3s 2 3p 6 d) [Ne]3s 2 3p Bond enthalpy is. a) sometimes positive, sometimes negative b) always negative c) always positive d) unpredictable 3
4 30. The Cl-Si-Cl bond angle in the SiCl 2F 2 molecule is approximately. a) b) 90 c) 120 d) The blending of one s atomic orbital and two p atomic orbitals produces. a) three sp3 hybrid orbitals b) three sp hybrid orbitals c) two sp3 hybrid orbitals d) three sp2 hybrid orbitals 32. The molecular geometry of the left-most carbon atom in the molecule below is. a) T-shaped b) octahedral c) trigonal bipyramidal d) tetrahedral Consider the following species when answering the question #33: (i) PCl3 (ii) CCl4 (iii) TeCl4 (iv) XeF4 (v) SF6 33. In which of the molecules does the central atom utilize d orbitals to form hybrid orbitals? a) (i) and (ii) b) (iii) only c) (iii), (iv), and (v) d) (v) only 34. The molecular geometry of the CHF 3 molecule is, and the molecule is. a) trigonal pyramidal, polar b) seesaw, polar c) tetrahedral, polar d) tetrahedral, nonpolar 35. The electron-domain geometry and the molecular geometry of a molecule of the general formula ABn will always be the same if. a) n is greater than four b) there is more than one central atom c) n is less than four d) there are no lone pairs on the central atom 36. The hybridizations of iodine in IF 3 and IF 5 are and, respectively. a) sp 3 d 2, sp 3 d b) sp 3 d, sp 3 d 2 c) sp 3, sp 3 d d) sp 3 d 2, sp 3 d The F-B-F bond angle in the BF 3 molecule is. a) 90 b) 120 c) 180 d) The electron-domain geometry of the AsF 6-1 ion is octahedral. The hybrid orbitals used by the As atom for bonding are orbitals. a) sp 3 b) sp 3 d c) sp 3 d 2 d) sp 2 d There are σ and π bonds in the HNC== CNH molecule. a) 8 and 3 b) 5 and 3 c) 4 and 3 d) 3 and 4 4
5 40. The F-N-F bond angle in the NF 3 molecule is slightly less than. a) 90 b) 120 c) 180 d) According to valence bond theory, which orbitals on bromine atoms overlap in the formation of the bond in Br 2? a) 4p b) 3p c) 4s d) 3s For the questions that follow, consider the BEST Lewis structures of the following oxyanions: (i) NO 2 - (ii) NO 3 - (iii) SO 3 (iv) SO 4 (v) BrO There can be four equivalent best resonance structures of. a) i b) ii c) iii d) iv 43. Of the molecules below, the bond in is the most polar. a) H 2 b) HI c) HF d) HCl 44. A valid Lewis structure of cannot be drawn without violating the octet rule. a) SbF 3 b) IF 3 c) NF 3 d) PF The chloride of which of the following metals should have the greatest lattice energy? a) K b) Rb c) Cs d) Li 46. Why don't we draw double bonds between the Be atom and the Cl atoms in BeCl 2? a) That would result in the formal charges not adding up to zero. b) There aren't enough electrons. c) That would result in more than eight electrons around each chlorine atom. d) That would give positive formal charges to the chlorine atoms and a negative formal charge to the beryllium atom 47. Using the table of bond dissociation energies, the ΔH for the following reaction is kj. 2HCl (g) + F2 (g)---- 2HF (g) + Cl2 (g) a) +223kJ b) -359kJ c) +208kJ d) -223kJ 48. How many unpaired electrons are there on the central atom in the Lewis structure of a N 3- ion? a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) A nonpolar bond will form between two atoms of electronegativity. a) similar, different b) identical, equal c) different, opposite d) different, different 50. The image below depicts a T-shaped structure (looking down on the axial atom). Which of the following has such a structure? a) SO 3 b) BCl 3 c) ICl 3 d) PCl 3 5
6 51. How many bonds are there in a triple bond? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) What is the proper order of increasing Cl A Cl angle? A) SCl 2 B) PCl 3 C) SiCl 4 a) C < A < B b) A < B < C c) B < C < A d) A < C < B e) C < B < A 53. Are the following molecules polar? (i) (ii) a) Only i is polar. b) Neither is polar. c) Both i and ii are polar. d) Only ii is polar. 54. The fact that the BF 3 molecule is planar means that the B atom is a) sp 2 -hybridized. b) sp-hybridized. c) unhybridized. d) sp 3 -hybridized. 55. The N-N bonding in HNNH consists of a) one bond and two bonds. b) one bond and no bonds. c) two bond and one bonds. d) two bond and two bonds. e) one bond and one bonds. 56. Which molecule has a nitrogen atom with sp 2 hybridization? a) acetonitrile, CH 3C N: b) trimethylamine, :N(CH 3) 3 c) nitromethane, CH 3NO 2 d) ammonium cation, NH Which of the following shapes is not possible for a molecule in which the central atom has sp 3 d hybridization? a) tetrahedral b) seesaw c) T-shaped d) linear 58. SiF 6 exists, but CF 6 does not. Why? Use the concept of hybrid orbitals in your answer. a) Carbon sp 3 cannot accommodate six ligands (attached atoms). b) Carbon is never found in ions. c) Silicon is less electronegative, so its hybrid orbitals are lower in energy. d) Silicon can hybridize using d orbitals not available in carbon. 59. Are bonds generally stronger or weaker than bonds? Why? a) Weaker. There is less electron density between the atoms. b) Stronger. There is less electron density between the atoms. c) Weaker. There is more electron density between the atoms. d) Stronger. There is more electron density between the atoms. 6
7 60. Consider the Lewis structure for glycine, the simplest amino acid: What is the total number of bonds in the entire molecule, and what is the total number of bonds? a) 8 bonds and two bonds b) 7 bonds and one bond c) 9 bonds and one bond d) 14 bonds and one bond 61. The valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory is based on the idea that a) nonbonded electron domains require more space than bonded electron pairs. b) the electron domains about an atom arrange themselves in such a fashion as to maximize the interaction between each domain. c) the electron domains arrange themselves in such a fashion as to minimize the interaction between each domain. d) nonbonded electron domains require less space than bonded electron domains. e) the relative bond lengths in molecules determine the shape of the molecules. 62. Two isomeric forms of a organic molecule a) have the same structure. b) have different compositions of elements. c) have the same molecular formula. d) have a different content of the isotopes of hydrogen. 63. Which of the following is the correct Lewis dash formula for carbon diselenide? 64. How many unshared pairs of electrons are in the outer shell of the central nitrogen atom of NH3? a. 4 b. 3 c. 2 d. 1 e The number of unshared pairs of electrons in the outer shell of oxygen in Cl 2O is. a. one b. two c. three d. four e. zero 66. Which Lewis Dot Formula below is incorrect? 67. The valence shell is a. the highest energy level occupied by electrons. b. the set of orbitals used to make triple bonds. c. the orbitals belonging to the entire molecule. d. the lowest energy level occupied by electrons. e. the hard covering on crustaceans. 7
8 68. The phosphorus pentachloride molecule is nonpolar and contains no lone (unshared) electron pairs on the phosphorus atom. What are all of the possible Cl-P-Cl bond angles? a. 120 b. 180 c d. 90, 120, and 180 e. 90 and Which of the following statements about the valence bond theory is false? a. For an atom to share more than 8 electrons it must hybridize d orbitals. b. To make 4 single bonds, an atom will make 4 sp3 hybrid orbitals. c. The number of hybrid orbitals formed equals the number of high electron density regions. d. Trigonal planar molecules use sp2 hybrid orbitals e. Atoms that do not complete their octet use either sp3d or sp3d2 hybrid orbitals. 70. The hybridization associated with the central atom of a molecule in which all the bond angles are 120 is. a. sp b. sp2 c. sp3 d. sp3d e. sp3d2 71. Which of the following molecules has 120 bond angles? a. BF 4 - b. CF 4 c. H 2O d. BI 3 e. NH Which of the following statements about molecules with octahedral electronic geometry is false? a. They are sp3d2 hybridized. b. The molecular geometry is square planar if there are two lone pairs of electrons on the central atom. c. The bond angles are 90, 120 or 180. d. Octahedral geometry is symmetrical. e. If there are two lone pairs of electrons on the central atom they will be 180 apart. 73. How many sigma (σ) bonds and how many pi (π) bonds does the ethane (C 2H 2) molecule contain? a. 4 σ, 2 π b. 5 σ, 2 π c. 5 σ, 1 π d. 5 σ, 0 π e. 8 σ, 2 π 74. Which molecule is incorrectly matched with the molecular geometry? a. SF 6 = octahedral b. AsH 3 = pyramidal c. BCl 3 = trigonal planar d. AsF 5 = trigonal bipyramidal e. H 2S = linear 75. Which species is incorrectly matched with the hybridization at the central atom? a. SO 2 = sp2 b. CF 4 = sp3 c. PF 5 = sp3d2 d. SeO 4 = sp3 e. HCN = sp 8
9 76. Which species is incorrectly matched with bond angles? a. SiCl 4 = b. BeI 2 = slightly less than 109 c. SF 6 = 90 (and 180 ) d. AsF 5 = 90, 120 (and 180 ) e. BF 3 = Which one of the following is a nonpolar molecule with polar bonds? a. H 2O b. NH 3 c. PF 5 d. CHCl 3 e. none of these 78. Which set of hybridization states of C1, C2, and N of the following molecule is correct? a. C1 = sp 2, C2 = sp 3, N = sp 3 b. C1 = sp 2, C2 = sp 2, N = sp 3 c. C1 = sp 2, C2 = sp 2, N = sp 2 d. C1 = sp 2, C2 = sp 3, N = sp Which set of hybridization states of C1, C2, and N of the following molecule is correct? a. C1 = sp 2, C2 = sp 3, N = sp 3 b. C1 = sp 3, C2 = sp 2, N = sp 3 c. C1 = sp 3, C2 = sp 2, N = sp 2 d. C1 = sp 2, C2 = sp 2, N = sp 3 9
1. There are paired and unpaired electrons in the Lewis symbol for a phosphorus atom. a. 4, 2 b. 2, 4 c. 2, 3 d. 4, 3 e. 0, 3
 Name: Score: 0 / 42 points (0%) [2 open ended questions not graded] C8&9Practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. There are paired and unpaired
Name: Score: 0 / 42 points (0%) [2 open ended questions not graded] C8&9Practice Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. There are paired and unpaired
Test bank for Chemistry The Central Science 10th Edition by Brown, LeMay, Bursten
 Test bank for Chemistry The Central Science 10th Edition by Brown, LeMay, Bursten Chapter 9, Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Multiple-Choice and Bimodal 1) For a molecule with the formula A) linear
Test bank for Chemistry The Central Science 10th Edition by Brown, LeMay, Bursten Chapter 9, Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Multiple-Choice and Bimodal 1) For a molecule with the formula A) linear
Assignment 09 A. 2- The image below depicts a seesaw structure. Which of the following has such a structure?
 Assignment 09 A 1- Give the total number of electron domains, the number of bonding and nonbonding domains, and the molecular geometry, respectively, for the central atom of P 3. a) four electron domains,
Assignment 09 A 1- Give the total number of electron domains, the number of bonding and nonbonding domains, and the molecular geometry, respectively, for the central atom of P 3. a) four electron domains,
Instant download Test bank for Chemistry The Central Science 10th Edition by Brown, LeMay, Bursten CLICK HERE
 Chemistry, 10e (Brown) Chapter 9, Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Instant download Test bank for Chemistry The Central Science 10th Edition by Brown, LeMay, Bursten CLICK HERE http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-chemistry-the-central-science-10th-edition-by-brown-lemay-bursten/
Chemistry, 10e (Brown) Chapter 9, Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Instant download Test bank for Chemistry The Central Science 10th Edition by Brown, LeMay, Bursten CLICK HERE http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-chemistry-the-central-science-10th-edition-by-brown-lemay-bursten/
Subtopic 4.2 MOLECULAR SHAPE AND POLARITY
 Subtopic 4.2 MOLECULAR SHAPE AND POLARITY 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES (covalent bonding) 1. Draw the Lewis structure of covalent molecules (octet rule such as NH 3, CCl 4, H 2 O, CO 2, N 2 O 4, and exception to
Subtopic 4.2 MOLECULAR SHAPE AND POLARITY 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES (covalent bonding) 1. Draw the Lewis structure of covalent molecules (octet rule such as NH 3, CCl 4, H 2 O, CO 2, N 2 O 4, and exception to
CHM2045 F13--Exam # MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 CHM2045 F13--Exam #2 2013.10.18 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A valid Lewis structure of cannot be drawn without violating the
CHM2045 F13--Exam #2 2013.10.18 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A valid Lewis structure of cannot be drawn without violating the
CHM2045 S13: Exam # MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 CHM2045 S13: Exam #2 2013.03.01 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) How would replacing one of benzene's C atoms and the H atom attached
CHM2045 S13: Exam #2 2013.03.01 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) How would replacing one of benzene's C atoms and the H atom attached
Find the difference in electronegativity between the hydrogen and chlorine atoms
 Answers Questions 16.2 Molecular polarity 1. Write a dot diagram for the HCl molecule. Find the difference in electronegativity between the hydrogen and chlorine atoms Difference in electronegativity =
Answers Questions 16.2 Molecular polarity 1. Write a dot diagram for the HCl molecule. Find the difference in electronegativity between the hydrogen and chlorine atoms Difference in electronegativity =
CHEM 110 Exam 2 - Practice Test 1 - Solutions
 CHEM 110 Exam 2 - Practice Test 1 - Solutions 1D 1 has a triple bond. 2 has a double bond. 3 and 4 have single bonds. The stronger the bond, the shorter the length. 2A A 1:1 ratio means there must be the
CHEM 110 Exam 2 - Practice Test 1 - Solutions 1D 1 has a triple bond. 2 has a double bond. 3 and 4 have single bonds. The stronger the bond, the shorter the length. 2A A 1:1 ratio means there must be the
Adapted from CHM 130 Maricopa County, AZ Molecular Geometry and Lewis Dot Formulas Introduction
 Adapted from CHM 130 Maricopa County, AZ Molecular Geometry and Lewis Dot Formulas Introduction A chemical bond is an intramolecular (within the molecule) force holding two or more atoms together. Covalent
Adapted from CHM 130 Maricopa County, AZ Molecular Geometry and Lewis Dot Formulas Introduction A chemical bond is an intramolecular (within the molecule) force holding two or more atoms together. Covalent
Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
 Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Three Types of Chemical Bonding (1) Ionic: formed by electron transfer (2) Covalent: formed by electron sharing (3) Metallic: attraction between metal
Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Three Types of Chemical Bonding (1) Ionic: formed by electron transfer (2) Covalent: formed by electron sharing (3) Metallic: attraction between metal
Form J. Test #4 Last Name First Name Zumdahl, Chapters 8 and 9 November 23, 2004
 Form J Chemistry 1441-023 Name (please print) Test #4 Last Name First Name Zumdahl, Chapters 8 and 9 November 23, 2004 Instructions: 1. This exam consists of 27 questions. 2. No scratch paper is allowed.
Form J Chemistry 1441-023 Name (please print) Test #4 Last Name First Name Zumdahl, Chapters 8 and 9 November 23, 2004 Instructions: 1. This exam consists of 27 questions. 2. No scratch paper is allowed.
Chapter 9 The Shapes of Molecules Cocaine
 Chapter 9 The Shapes of Molecules 1 Cocaine 10.1 Depicting Molecules & Ions with Lewis Structures 2 Number of Covalent Bonds 3 The number of covalent bonds can be determined from the number of electrons
Chapter 9 The Shapes of Molecules 1 Cocaine 10.1 Depicting Molecules & Ions with Lewis Structures 2 Number of Covalent Bonds 3 The number of covalent bonds can be determined from the number of electrons
Chapter 9. Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Topics Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry and Polarity Valence Bond Theory Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Hybridization in Molecules
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Topics Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry and Polarity Valence Bond Theory Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Hybridization in Molecules
Chemical Bonding II. Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Phys./Chem. Properties Quantum Mechanics Sigma & Pi bonds Hybridization MO theory
 Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Phys./Chem. Properties Quantum Mechanics Sigma & Pi bonds ybridization MO theory 1 Molecular Geometry 3-D arrangement of atoms 2 VSEPR Valence-shell
Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Phys./Chem. Properties Quantum Mechanics Sigma & Pi bonds ybridization MO theory 1 Molecular Geometry 3-D arrangement of atoms 2 VSEPR Valence-shell
General and Inorganic Chemistry I.
 General and Inorganic Chemistry I. Lecture 1 István Szalai Eötvös University István Szalai (Eötvös University) Lecture 1 1 / 29 Outline István Szalai (Eötvös University) Lecture 1 2 / 29 Lewis Formulas
General and Inorganic Chemistry I. Lecture 1 István Szalai Eötvös University István Szalai (Eötvös University) Lecture 1 1 / 29 Outline István Szalai (Eötvös University) Lecture 1 2 / 29 Lewis Formulas
Chemical Bonding AP Chemistry Ms. Grobsky
 Chemical Bonding AP Chemistry Ms. Grobsky What Determines the Type of Bonding in Any Substance? Why do Atoms Bond? The key to answering the first question are found in the electronic structure of the atoms
Chemical Bonding AP Chemistry Ms. Grobsky What Determines the Type of Bonding in Any Substance? Why do Atoms Bond? The key to answering the first question are found in the electronic structure of the atoms
10-1. The Shapes of Molecules, chapter 10
 10-1 The Shapes of Molecules, chapter 10 The Shapes of Molecules; Goals 10.1 Depicting Molecules and Ions with Lewis Structures 10.2 Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory 10.3 Molecular
10-1 The Shapes of Molecules, chapter 10 The Shapes of Molecules; Goals 10.1 Depicting Molecules and Ions with Lewis Structures 10.2 Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory 10.3 Molecular
CHAPTER 8. Molecular Structure & Covalent Bonding Theories
 CAPTER 8 Molecular Structure & Covalent Bonding Theories 1 Chapter Goals 1. A Preview of the Chapter 2. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory 3. Polar Molecules:The Influence of Molecular
CAPTER 8 Molecular Structure & Covalent Bonding Theories 1 Chapter Goals 1. A Preview of the Chapter 2. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory 3. Polar Molecules:The Influence of Molecular
CHEMISTRY 112 LECTURE EXAM II Material
 CHEMISTRY 112 LECTURE EXAM II Material Part I Chemical Bonding I Lewis Theory Chapter 9 pages 376-386 A. Drawing electron dot structures HOW TO: 1. Write e- dot structure for the individual atoms. 2. a)
CHEMISTRY 112 LECTURE EXAM II Material Part I Chemical Bonding I Lewis Theory Chapter 9 pages 376-386 A. Drawing electron dot structures HOW TO: 1. Write e- dot structure for the individual atoms. 2. a)
Bonding: Part Two. Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond. transfer valence e - Metallic bond. (NaCl) (Fe) mobile valence e - Covalent bond
 Bonding: Part Two Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond transfer valence e - Metallic bond mobile valence e - Covalent bond (NaCl) (Fe) shared valence e - (H 2 O) 1 Single Covalent Bond H + H H H H-atoms H
Bonding: Part Two Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond transfer valence e - Metallic bond mobile valence e - Covalent bond (NaCl) (Fe) shared valence e - (H 2 O) 1 Single Covalent Bond H + H H H H-atoms H
Chemical Bonding Chapter 8
 Chemical Bonding Chapter 8 Get your Clicker, 2 magnets, goggles and your handouts Nov 15 6:15 PM Recall that: Ionic-Involves the transfer of electrons - forms between a metal and a nonmetal Covalent-Involves
Chemical Bonding Chapter 8 Get your Clicker, 2 magnets, goggles and your handouts Nov 15 6:15 PM Recall that: Ionic-Involves the transfer of electrons - forms between a metal and a nonmetal Covalent-Involves
I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I)
 I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Isostructural species are those which have the same shape and hybridisation. Among the given species identify the isostructural pairs. (i) [NF 3 and BF 3 ] [BF
I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Isostructural species are those which have the same shape and hybridisation. Among the given species identify the isostructural pairs. (i) [NF 3 and BF 3 ] [BF
Valence Bond Theory - Description
 Bonding and Molecular Structure - PART 2 - Valence Bond Theory and Hybridization 1. Understand and be able to describe the Valence Bond Theory description of covalent bond formation. 2. Understand and
Bonding and Molecular Structure - PART 2 - Valence Bond Theory and Hybridization 1. Understand and be able to describe the Valence Bond Theory description of covalent bond formation. 2. Understand and
COVALENT BONDING CHEMICAL BONDING I: LEWIS MODEL. Chapter 7
 Chapter 7 P a g e 1 COVALENT BONDING Covalent Bonds Covalent bonds occur between two or more nonmetals. The two atoms share electrons between them, composing a molecule. Covalently bonded compounds are
Chapter 7 P a g e 1 COVALENT BONDING Covalent Bonds Covalent bonds occur between two or more nonmetals. The two atoms share electrons between them, composing a molecule. Covalently bonded compounds are
Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, Valence Bond Theory, and Molecular Orbital Theory
 10.1 Artificial Sweeteners: Fooled by Molecular Shape 425 10.2 VSEPR Theory: The Five Basic Shapes 426 10.3 VSEPR Theory: The Effect of Lone Pairs 430 10.4 VSEPR Theory: Predicting Molecular Geometries
10.1 Artificial Sweeteners: Fooled by Molecular Shape 425 10.2 VSEPR Theory: The Five Basic Shapes 426 10.3 VSEPR Theory: The Effect of Lone Pairs 430 10.4 VSEPR Theory: Predicting Molecular Geometries
B. (i), (iii), and (v) C. (iv) D. (i), (ii), (iii), and (v) E. (i), (iii), (iv), and (v) Answer: B. SO 3, and NO 3 - both have 24 VE and have Lewis
 SCCH 161 Homework 3 1. Give the number of lone pairs around the central atom and the molecular geometry of CBr 4. Answer: Carbon has 4 valence electrons and bonds to four bromine atoms (each has 7 VE s).
SCCH 161 Homework 3 1. Give the number of lone pairs around the central atom and the molecular geometry of CBr 4. Answer: Carbon has 4 valence electrons and bonds to four bromine atoms (each has 7 VE s).
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 10
 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 10 Linear Trigonal 180 o planar 120 o Tetrahedral 109.5 o Trigonal Bipyramidal 120 and 90 o Octahedral 90 o linear Linear
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 10 Linear Trigonal 180 o planar 120 o Tetrahedral 109.5 o Trigonal Bipyramidal 120 and 90 o Octahedral 90 o linear Linear
Lewis Structure. Lewis Structures & VSEPR. Octet & Duet Rules. Steps for drawing Lewis Structures
 Lewis Structure Lewis Structures & VSEPR Lewis Structures shows how the are arranged among the atoms of a molecule There are rules for Lewis Structures that are based on the formation of a Atoms want to
Lewis Structure Lewis Structures & VSEPR Lewis Structures shows how the are arranged among the atoms of a molecule There are rules for Lewis Structures that are based on the formation of a Atoms want to
Structures, Shapes and Polarity. of Molecules. Level 2 recap: - Polar and non polar bonds - Lewis diagrams - Lone pairs - Shapes - Polarity
 Structures, Shapes and Polarity Level 2 recap: - Polar and non polar bonds - Lewis diagrams - Lone pairs - Shapes - Polarity of Molecules Do now: Brainstorm what you know/remember about these L2 concepts
Structures, Shapes and Polarity Level 2 recap: - Polar and non polar bonds - Lewis diagrams - Lone pairs - Shapes - Polarity of Molecules Do now: Brainstorm what you know/remember about these L2 concepts
Bonding: Part Two. Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond. transfer valence e - Metallic bond. (NaCl) (Fe) mobile valence e - Covalent bond
 Bonding: Part Two Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond transfer valence e - Metallic bond mobile valence e - Covalent bond (NaCl) (Fe) shared valence e - (H 2 O) 1 Single Covalent Bond H + H H H H-atoms H
Bonding: Part Two Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond transfer valence e - Metallic bond mobile valence e - Covalent bond (NaCl) (Fe) shared valence e - (H 2 O) 1 Single Covalent Bond H + H H H H-atoms H
Molecular shape is determined by the number of bonds that form around individual atoms.
 Chapter 9 CH 180 Major Concepts: Molecular shape is determined by the number of bonds that form around individual atoms. Sublevels (s, p, d, & f) of separate atoms may overlap and result in hybrid orbitals
Chapter 9 CH 180 Major Concepts: Molecular shape is determined by the number of bonds that form around individual atoms. Sublevels (s, p, d, & f) of separate atoms may overlap and result in hybrid orbitals
Shapes of Molecules and Hybridization
 Shapes of Molecules and Hybridization A. Molecular Geometry Lewis structures provide us with the number and types of bonds around a central atom, as well as any NB electron pairs. They do not tell us the
Shapes of Molecules and Hybridization A. Molecular Geometry Lewis structures provide us with the number and types of bonds around a central atom, as well as any NB electron pairs. They do not tell us the
Chapter 13: Phenomena
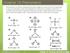 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals
 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals 1 Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry (10.1) Dipole Moments (10.2) Valence Bond Theory (10.3) Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals 1 Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry (10.1) Dipole Moments (10.2) Valence Bond Theory (10.3) Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals
EXAM II Material. Part I Chemical Bonding I Lewis Theory Chapter 9 pages A. Drawing electron dot structures HOW TO:
 CHEMISTRY 112 LECTURE EXAM II Material Part I Chemical Bonding I Lewis Theory Chapter 9 pages 376-386 A. Drawing electron dot structures HOW TO: 1. Write e- dot structure for the individual atoms. 2. a)
CHEMISTRY 112 LECTURE EXAM II Material Part I Chemical Bonding I Lewis Theory Chapter 9 pages 376-386 A. Drawing electron dot structures HOW TO: 1. Write e- dot structure for the individual atoms. 2. a)
Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts
 Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Test Bank for Introductory Chemistry Essentials 5th Edition by Tro
 Test Bank for Introductory Chemistry Essentials 5th Edition by Tro Sample Introductory Chemistry, 5e (Tro) Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding 10.1 True/False Questions 1) Bonding theories are used to predict
Test Bank for Introductory Chemistry Essentials 5th Edition by Tro Sample Introductory Chemistry, 5e (Tro) Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding 10.1 True/False Questions 1) Bonding theories are used to predict
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 10. The Shapes of Molecules 10-1
 Chapter 10 The Shapes of Molecules 10-1 The Shapes of Molecules 10.1 Depicting Molecules and Ions with Lewis Structures 10.2 Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory and Molecular Shape 10.3
Chapter 10 The Shapes of Molecules 10-1 The Shapes of Molecules 10.1 Depicting Molecules and Ions with Lewis Structures 10.2 Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory and Molecular Shape 10.3
Lewis Dot Formulas and Molecular Shapes
 Lewis Dot Formulas and Molecular Shapes Introduction A chemical bond is an intramolecular (within the molecule) force holding two or more atoms together. Covalent chemical bonds are formed by valence electrons
Lewis Dot Formulas and Molecular Shapes Introduction A chemical bond is an intramolecular (within the molecule) force holding two or more atoms together. Covalent chemical bonds are formed by valence electrons
2011, Robert Ayton. All rights reserved.
 Chemical Bonding Outline 1. Lewis Dot Structures 2. Bonds 3. Formal Charges 4. VSEPR (Molecular Geometry and Hybridzation) 5. Common Resonance Structures and Dimerization Review 1. Lewis Dot Structures
Chemical Bonding Outline 1. Lewis Dot Structures 2. Bonds 3. Formal Charges 4. VSEPR (Molecular Geometry and Hybridzation) 5. Common Resonance Structures and Dimerization Review 1. Lewis Dot Structures
CHM1045 Exam 3 Chapters 5, 8, & 9
 1. Which of the following conditions will never result in a decrease in the internal energy of a system? CHM1045 Exam 3 Chapters 5, 8, & 9 a. System loses heat and does work on the surroundings. b. System
1. Which of the following conditions will never result in a decrease in the internal energy of a system? CHM1045 Exam 3 Chapters 5, 8, & 9 a. System loses heat and does work on the surroundings. b. System
CHAPTER-4 CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
 CHAPTER-4 CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE OCTET RULE- During a chemical reaction the atoms tend to adjust their electronic arrangement in such a way that they achieve 8 e - in their outermost
CHAPTER-4 CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE OCTET RULE- During a chemical reaction the atoms tend to adjust their electronic arrangement in such a way that they achieve 8 e - in their outermost
CHEMISTRY. Chapter 10 Theories of Bonding and Structure. The Molecular Nature of Matter. Jespersen Brady Hyslop SIXTH EDITION
 CHEMISTRY The Molecular Nature of Matter SIXTH EDITION Jespersen Brady Hyslop Chapter 10 Theories of Bonding and Structure Copyright 2012 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Molecular Structures Molecules containing
CHEMISTRY The Molecular Nature of Matter SIXTH EDITION Jespersen Brady Hyslop Chapter 10 Theories of Bonding and Structure Copyright 2012 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Molecular Structures Molecules containing
AP Chemistry. Unit #7. Chemical Bonding & Molecular Shape. Zumdahl Chapters 8 & 9 TYPES OF BONDING BONDING. Discrete molecules formed
 AP Chemistry Unit #7 Chemical Bonding & Molecular Shape Zumdahl Chapters 8 & 9 TYPES OF BONDING BONDING INTRA (Within (inside) compounds) STRONG INTER (Interactions between the molecules of a compound)
AP Chemistry Unit #7 Chemical Bonding & Molecular Shape Zumdahl Chapters 8 & 9 TYPES OF BONDING BONDING INTRA (Within (inside) compounds) STRONG INTER (Interactions between the molecules of a compound)
Chapter 4. Molecular Structure and Orbitals
 Chapter 4 Molecular Structure and Orbitals Chapter 4 Table of Contents (4.1) (4.2) (4.3) (4.4) (4.5) (4.6) (4.7) Molecular structure: The VSEPR model Bond polarity and dipole moments Hybridization and
Chapter 4 Molecular Structure and Orbitals Chapter 4 Table of Contents (4.1) (4.2) (4.3) (4.4) (4.5) (4.6) (4.7) Molecular structure: The VSEPR model Bond polarity and dipole moments Hybridization and
Unit 1 Module 1 Forces of Attraction page 1 of 10 Various forces of attraction between molecules
 Unit 1 Module 1 Forces of Attraction page 1 of 10 Various forces of attraction between molecules 1. Ionic bonds 2. Covalent bonds (also co-ordinate covalent bonds) 3. Metallic bonds 4. Van der Waals forces
Unit 1 Module 1 Forces of Attraction page 1 of 10 Various forces of attraction between molecules 1. Ionic bonds 2. Covalent bonds (also co-ordinate covalent bonds) 3. Metallic bonds 4. Van der Waals forces
Honors Chemistry Unit 6 ( )
 Honors Chemistry Unit 6 (2017-2018) Lewis Dot Structures VSEPR Structures 1 We are learning to: 1. Represent compounds with Lewis structures. 2. Apply the VSEPR theory to determine the molecular geometry
Honors Chemistry Unit 6 (2017-2018) Lewis Dot Structures VSEPR Structures 1 We are learning to: 1. Represent compounds with Lewis structures. 2. Apply the VSEPR theory to determine the molecular geometry
Chapter 8. Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 8. Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding 8.1 Chemical Bonds, Lewis Symbols, and the Octet Rule 8.2 Ionic Bonding positive and negative ions form an ionic lattice, in which each cation is surrounded
Chapter 8. Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding 8.1 Chemical Bonds, Lewis Symbols, and the Octet Rule 8.2 Ionic Bonding positive and negative ions form an ionic lattice, in which each cation is surrounded
EXPERIMENT #13 Lewis Structures and Molecular Geometry
 OBJECTIVES: EXPERIMENT #13 s and Draw Lewis structures of atoms, ions, and molecules Build models of linear, trigonal planar tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral arrangements of electron pairs
OBJECTIVES: EXPERIMENT #13 s and Draw Lewis structures of atoms, ions, and molecules Build models of linear, trigonal planar tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral arrangements of electron pairs
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry. Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory
 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Sulfanilamide Lewis Structures and the Real 3D-Shape of Molecules Lewis Theory of Molecular Shape and Polarity
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Sulfanilamide Lewis Structures and the Real 3D-Shape of Molecules Lewis Theory of Molecular Shape and Polarity
Bonding/Lewis Dots Lecture Page 1 of 12 Date. Bonding. What is Coulomb's Law? Energy Profile: Covalent Bonds. Electronegativity and Linus Pauling
 Bonding/Lewis Dots Lecture Page 1 of 12 Date Bonding What is Coulomb's Law? Energy Profile: Covalent Bonds Electronegativity and Linus Pauling 2.1 H 1.0 Li 0.9 Na 0.8 K 0.8 Rb 0.7 Cs 0.7 Fr 1.5 Be 1.2
Bonding/Lewis Dots Lecture Page 1 of 12 Date Bonding What is Coulomb's Law? Energy Profile: Covalent Bonds Electronegativity and Linus Pauling 2.1 H 1.0 Li 0.9 Na 0.8 K 0.8 Rb 0.7 Cs 0.7 Fr 1.5 Be 1.2
Hybridization and Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory
 ybridization and Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory Chapter 10 istorical Models G.N.Lewis and I. Langmuir (~1920) laid out foundations Ionic species were formed by electron transfer Covalent molecules arise
ybridization and Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory Chapter 10 istorical Models G.N.Lewis and I. Langmuir (~1920) laid out foundations Ionic species were formed by electron transfer Covalent molecules arise
Valence Shell Electron Pair repulsion
 Molecular Geometry Valence Shell Electron Pair repulsion The valence shell electron pair repulsion model (VSEPR model) assumes that electron pairs repel one another. (VSEPR) model gives helps determine
Molecular Geometry Valence Shell Electron Pair repulsion The valence shell electron pair repulsion model (VSEPR model) assumes that electron pairs repel one another. (VSEPR) model gives helps determine
Class XI Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Chemistry
 Class XI Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Chemistry Question 4.1: Explain the formation of a chemical bond. A chemical bond is defined as an attractive force that holds the constituents
Class XI Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Chemistry Question 4.1: Explain the formation of a chemical bond. A chemical bond is defined as an attractive force that holds the constituents
Class XI Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Chemistry
 Class XI Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Chemistry Question 4.1: Explain the formation of a chemical bond. A chemical bond is defined as an attractive force that holds the constituents
Class XI Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Chemistry Question 4.1: Explain the formation of a chemical bond. A chemical bond is defined as an attractive force that holds the constituents
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 9.1 Molecular Shapes Read Sec. 9.1 and 9.2, then complete the Sample and Practice Exercises in these sections. Sample Exercise 9.1 (p. 347) Use the VSEPR model to predict the molecular geometries of a)
9.1 Molecular Shapes Read Sec. 9.1 and 9.2, then complete the Sample and Practice Exercises in these sections. Sample Exercise 9.1 (p. 347) Use the VSEPR model to predict the molecular geometries of a)
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories molecular shapes the VSEPR model molecular shape and molecular polarity covalent bonding and orbital overlap hybrid orbitals multiple bonds 9.1 Molecular
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories molecular shapes the VSEPR model molecular shape and molecular polarity covalent bonding and orbital overlap hybrid orbitals multiple bonds 9.1 Molecular
Molecular Geometry. Valence Shell Electron Pair. What Determines the Shape of a Molecule? Repulsion Theory (VSEPR) Localized Electron Model
 Molecular Geometry Learn Shapes you will Because the physical and chemical properties of compounds are tied to their structures, the importance of molecular geometry can not be overstated. Localized Electron
Molecular Geometry Learn Shapes you will Because the physical and chemical properties of compounds are tied to their structures, the importance of molecular geometry can not be overstated. Localized Electron
Chapter 16 Covalent Bonding
 Chemistry/ PEP Name: Date: Chapter 16 Covalent Bonding Chapter 16: 1 26; 28, 30, 31, 35-37, 40, 43-46, Extra Credit: 50-53, 55, 56, 58, 59, 62-67 Section 16.1 The Nature of Covalent Bonding Practice Problems
Chemistry/ PEP Name: Date: Chapter 16 Covalent Bonding Chapter 16: 1 26; 28, 30, 31, 35-37, 40, 43-46, Extra Credit: 50-53, 55, 56, 58, 59, 62-67 Section 16.1 The Nature of Covalent Bonding Practice Problems
LET S FIRST REVIEW IONIC BONDING
 COVALENT BONDING LET S FIRST REVIEW IONIC BONDING In an IONIC bond, electrons are lost or gained, resulting in the formation of IONS in ionic compounds. K F K F K F K F K F K F K + F _ The compound potassium
COVALENT BONDING LET S FIRST REVIEW IONIC BONDING In an IONIC bond, electrons are lost or gained, resulting in the formation of IONS in ionic compounds. K F K F K F K F K F K F K + F _ The compound potassium
 CHAPTER 6 CHEMICAL BONDING TEXT BOOK EXERCISE Q.1. Select the correct statement. i. An ionic compound A + B - is most likely to be formed when ii. iii. a. the ionization energy of A is high and electron
CHAPTER 6 CHEMICAL BONDING TEXT BOOK EXERCISE Q.1. Select the correct statement. i. An ionic compound A + B - is most likely to be formed when ii. iii. a. the ionization energy of A is high and electron
Downloaded from
 CHAPTER-4 CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE OCTET RULE- During a chemical reaction the atoms tend to adjust their electronic arrangement in such a way that they achieve 8 e - in their outermost
CHAPTER-4 CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE OCTET RULE- During a chemical reaction the atoms tend to adjust their electronic arrangement in such a way that they achieve 8 e - in their outermost
Chapter 9. Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory
 Chapter 9 Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Problems with Lewis Theory Lewis theory generally predicts trends in properties, but does not give good numerical predictions.
Chapter 9 Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Problems with Lewis Theory Lewis theory generally predicts trends in properties, but does not give good numerical predictions.
Unit Six --- Ionic and Covalent Bonds
 Unit Six --- Ionic and Covalent Bonds Electron Configuration in Ionic Bonding Ionic Bonds Bonding in Metals Valence Electrons Electrons in the highest occupied energy level of an element s atoms Examples
Unit Six --- Ionic and Covalent Bonds Electron Configuration in Ionic Bonding Ionic Bonds Bonding in Metals Valence Electrons Electrons in the highest occupied energy level of an element s atoms Examples
Ex. 1) F F bond in F = 0 < % covalent, no transfer of electrons
 #60 Notes Unit 8: Bonding Ch. Bonding I. Bond Character Bonds are usually combinations of ionic and covalent character. The electronegativity difference is used to determine a bond s character. Electronegativity
#60 Notes Unit 8: Bonding Ch. Bonding I. Bond Character Bonds are usually combinations of ionic and covalent character. The electronegativity difference is used to determine a bond s character. Electronegativity
Fill in the chart below to determine the valence electrons of elements 3-10
 Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory IV Name: Date: Block: 1. Lewis Diagrams 2. VSEPR Lewis Diagrams Lewis diagrams show the bonding between atoms of a molecule. Only the outermost electrons of an atom (called electrons)
Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory IV Name: Date: Block: 1. Lewis Diagrams 2. VSEPR Lewis Diagrams Lewis diagrams show the bonding between atoms of a molecule. Only the outermost electrons of an atom (called electrons)
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals
 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Valence shell electron
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Valence shell electron
ADVANCED PLACEMENT CHEMISTRY CHAPTERS 7, 8 AND 9 REVIEW QUESTIONS
 1. What is the minimum wavelength (in nm) of a photon of light that can excite an electron in the hydrogen atom from the n = 1 to the n = 8 energy level? 2. A carbonoxygen double bond in a certain organic
1. What is the minimum wavelength (in nm) of a photon of light that can excite an electron in the hydrogen atom from the n = 1 to the n = 8 energy level? 2. A carbonoxygen double bond in a certain organic
MOLECULAR ORBITAL DIAGRAM KEY
 365 MOLECULAR ORBITAL DIAGRAM KEY Draw molecular orbital diagrams for each of the following molecules or ions. Determine the bond order of each and use this to predict the stability of the bond. Determine
365 MOLECULAR ORBITAL DIAGRAM KEY Draw molecular orbital diagrams for each of the following molecules or ions. Determine the bond order of each and use this to predict the stability of the bond. Determine
STD-XI-Science-Chemistry Chemical Bonding & Molecular structure
 STD-XI-Science-Chemistry Chemical Bonding & Molecular structure Chemical Bonding Question 1 What is meant by the term chemical bond? How does Kessel-Lewis approach of bonding differ from the modern views?
STD-XI-Science-Chemistry Chemical Bonding & Molecular structure Chemical Bonding Question 1 What is meant by the term chemical bond? How does Kessel-Lewis approach of bonding differ from the modern views?
Chapter 9 practice questions
 Class: Date: Chapter 9 practice questions Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. All of the following statements concerning valence bond (VB)
Class: Date: Chapter 9 practice questions Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. All of the following statements concerning valence bond (VB)
AP Chapter 8 Study Questions
 Class: Date: AP Chapter 8 Study Questions True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Atoms surrounded by eight valence electrons tend to lose electrons. 2. The greater the lattice energy,
Class: Date: AP Chapter 8 Study Questions True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Atoms surrounded by eight valence electrons tend to lose electrons. 2. The greater the lattice energy,
AP Chemistry- Practice Bonding Questions for Exam
 AP Chemistry- Practice Bonding Questions for Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is a correct Lewis structure for
AP Chemistry- Practice Bonding Questions for Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is a correct Lewis structure for
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 CHE 1401 - Spring 2017 - Chapter 8 Homework 8 (Chapter 8: Basic concepts of chemical bonding) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A
CHE 1401 - Spring 2017 - Chapter 8 Homework 8 (Chapter 8: Basic concepts of chemical bonding) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A
Name Date Class MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS. Distinguish molecular compounds from ionic compounds Identify the information a molecular formula provides
 8.1 MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS Section Review Objectives Distinguish molecular compounds from ionic compounds Identify the information a molecular formula provides Vocabulary covalent bond molecule diatomic molecule
8.1 MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS Section Review Objectives Distinguish molecular compounds from ionic compounds Identify the information a molecular formula provides Vocabulary covalent bond molecule diatomic molecule
Chem 121 Exam 4 Practice Exam
 Chem 121 Exam 4 Practice Exam 1. What is the correct electron configuration for bromine? b. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 9 4s 2 4p 6 c. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 10 4s 2 4p 5 d. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p
Chem 121 Exam 4 Practice Exam 1. What is the correct electron configuration for bromine? b. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 9 4s 2 4p 6 c. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 10 4s 2 4p 5 d. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p
Bonding and IMF practice test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name Bonding and IMF practice test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) There are paired and unpaired electrons in the Lewis symbol
Exam Name Bonding and IMF practice test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) There are paired and unpaired electrons in the Lewis symbol
1. Which molecule or ion does NOT have a pyramidal shape? + 2. Which of these molecules or ions contains a multiple bond? (D) H 2.
 CHEM 1411 Name: Dr. Julie Burrell (Key) Exam 3. Summer I 2017 Questions 1-23, multiple choice questions. 3 points each. 1. Which molecule or ion does NOT have a pyramidal shape? + - (A) SF 3 (B) all are
CHEM 1411 Name: Dr. Julie Burrell (Key) Exam 3. Summer I 2017 Questions 1-23, multiple choice questions. 3 points each. 1. Which molecule or ion does NOT have a pyramidal shape? + - (A) SF 3 (B) all are
Chapter 8. Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 8. Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding 8.1 Chemical Bonds, Lewis Symbols, and the Octet Rule 8.2 Ionic Bonding Consider the reaction between sodium and chlorine: Na(s) + ½ Cl 2 (g) NaCl(s) H o f
Chapter 8. Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding 8.1 Chemical Bonds, Lewis Symbols, and the Octet Rule 8.2 Ionic Bonding Consider the reaction between sodium and chlorine: Na(s) + ½ Cl 2 (g) NaCl(s) H o f
Bonding. Honors Chemistry 412 Chapter 6
 Bonding Honors Chemistry 412 Chapter 6 Chemical Bond Mutual attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds them together. Types of Bonds Ionic Bonds Force of attraction
Bonding Honors Chemistry 412 Chapter 6 Chemical Bond Mutual attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of different atoms that binds them together. Types of Bonds Ionic Bonds Force of attraction
Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure
 CHM 123 Chapter 8 Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure 8.1 Molecular shapes and VSEPR theory VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of
CHM 123 Chapter 8 Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure 8.1 Molecular shapes and VSEPR theory VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of
bond energy- energy required to break a chemical bond -We can measure bond energy to determine strength of interaction
 bond energy- energy required to break a chemical bond -We can measure bond energy to determine strength of interaction ionic compound- a metal reacts with a nonmetal Ionic bonds form when an atom that
bond energy- energy required to break a chemical bond -We can measure bond energy to determine strength of interaction ionic compound- a metal reacts with a nonmetal Ionic bonds form when an atom that
Inorganic Chemistry A. Cl and 37 Cl are and
 S e l f - s t u d y e x e r c i s e s 1 Inorganic Chemistry A Self-study exercises Chapters 1 and 2 1. Calculate the value of A r for naturally occurring chlorine if the distribution of isotopes is 75.77%
S e l f - s t u d y e x e r c i s e s 1 Inorganic Chemistry A Self-study exercises Chapters 1 and 2 1. Calculate the value of A r for naturally occurring chlorine if the distribution of isotopes is 75.77%
1) Based on the octet rule, magnesium most likely forms a ion. A) Mg- B) Mg6+ C) Mg2+ D) Mg6- E) Mg2-
 1) ased on the octet rule, magnesium most likely forms a ion. ) Mg- ) Mg6+ ) Mg2+ ) Mg6- E) Mg2-2) ased on the octet rule, phosphorus most likely forms a ion. ) P5- ) P5+ ) P+ ) P3- E) P3+ 3) Which ion
1) ased on the octet rule, magnesium most likely forms a ion. ) Mg- ) Mg6+ ) Mg2+ ) Mg6- E) Mg2-2) ased on the octet rule, phosphorus most likely forms a ion. ) P5- ) P5+ ) P+ ) P3- E) P3+ 3) Which ion
Lewis Dot Structures and Molecular Geometry
 Experiment 11 Lewis Dot Structures and Molecular Geometry Pre-Lab Assignment Before coming to lab: Read the lab thoroughly. Answer the pre-lab questions that appear at the end of this lab exercise. Purpose
Experiment 11 Lewis Dot Structures and Molecular Geometry Pre-Lab Assignment Before coming to lab: Read the lab thoroughly. Answer the pre-lab questions that appear at the end of this lab exercise. Purpose
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A gas at a pressure of 10.0 Pa exerts a force of N on an area of 5.5 m2. A) 18 B) 0.55
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A gas at a pressure of 10.0 Pa exerts a force of N on an area of 5.5 m2. A) 18 B) 0.55
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 1
 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. How to get the book of
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. How to get the book of
Houston Community College System. Chemistry EXAM # 3A Sample
 Houston Community College System Chemistry 1411 EXAM # A Sample 1 CHEM 1411 EXAM # (Chapters 8, 9,10,and 11) Name: Score: Directions- please answer the following multiple-choice questions next to each
Houston Community College System Chemistry 1411 EXAM # A Sample 1 CHEM 1411 EXAM # (Chapters 8, 9,10,and 11) Name: Score: Directions- please answer the following multiple-choice questions next to each
Chemistry 1210, Section 1 Third Hour Exam November 21, 2011
 Chemistry 1210, Section 1 Third Hour Exam November 21, 2011 Instructions: Do not begin until 8:30 AM. The exam must be turned in by 9:20 AM. Enjoy your thanksgiving break! This exam should have 25 questions.
Chemistry 1210, Section 1 Third Hour Exam November 21, 2011 Instructions: Do not begin until 8:30 AM. The exam must be turned in by 9:20 AM. Enjoy your thanksgiving break! This exam should have 25 questions.
Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory
 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory The Valence -Shell Electron -Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Model predicts the shapes of the molecules and ions by assuming that the valence shell electron pairs
Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory The Valence -Shell Electron -Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Model predicts the shapes of the molecules and ions by assuming that the valence shell electron pairs
5 Polyatomic molecules
 s manual for Burrows et.al. Chemistry 3 Third edition 5 Polyatomic molecules Answers to worked examples WE 5.1 Formal charges in N 2 (on p. 221 in Chemistry 3 ) Use formal charges to decide whether oxygen
s manual for Burrows et.al. Chemistry 3 Third edition 5 Polyatomic molecules Answers to worked examples WE 5.1 Formal charges in N 2 (on p. 221 in Chemistry 3 ) Use formal charges to decide whether oxygen
Shapes of Molecules. Lewis structures are useful but don t allow prediction of the shape of a molecule.
 Shapes of Molecules Lewis structures are useful but don t allow prediction of the shape of a molecule. H O H H O H Can use a simple theory based on electron repulsion to predict structure (for non-transition
Shapes of Molecules Lewis structures are useful but don t allow prediction of the shape of a molecule. H O H H O H Can use a simple theory based on electron repulsion to predict structure (for non-transition
UNIVERSITY OF VICTORIA. CHEMISTRY 101 Mid-Term Test 2, November
 NAME Student No. SECTIN (circle one): A01 (Codding) A02 (Sirk) A03 (Briggs) Version A UNIVERSITY F VICTRIA CEMISTRY 101 Mid-Term Test 2, November 19 2010 Version A This test has two parts and 8 pages,
NAME Student No. SECTIN (circle one): A01 (Codding) A02 (Sirk) A03 (Briggs) Version A UNIVERSITY F VICTRIA CEMISTRY 101 Mid-Term Test 2, November 19 2010 Version A This test has two parts and 8 pages,
Chapter 10. Geometry
 Chapter 10 Molec cular Geometry 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE Molecular Geometry Molecular Polarity VSEPR Model Summary of Molecular Shapes Hybridization Molecular Orbital Theory Bond Angles 2 MOLECULAR GEOMETRY Molecular
Chapter 10 Molec cular Geometry 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE Molecular Geometry Molecular Polarity VSEPR Model Summary of Molecular Shapes Hybridization Molecular Orbital Theory Bond Angles 2 MOLECULAR GEOMETRY Molecular
VSEPR. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory
 VSEPR Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Vocabulary: domain = any electron pair or bond (single, double or triple) is considered one domain. bonding pair = shared pair = any electron pair that
VSEPR Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Vocabulary: domain = any electron pair or bond (single, double or triple) is considered one domain. bonding pair = shared pair = any electron pair that
Ch 10 Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structures for Ionic & Covalent Compounds, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules
 Fructose Water Ch 10 Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structures for Ionic & Covalent Compounds, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules Carbon Dioxide Ammonia Title and Highlight TN Ch 10.1 Topic: EQ: Right Side NOTES
Fructose Water Ch 10 Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structures for Ionic & Covalent Compounds, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules Carbon Dioxide Ammonia Title and Highlight TN Ch 10.1 Topic: EQ: Right Side NOTES
Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 8 Outline Bonding: General Concepts
 Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 8 Outline Bonding: General Concepts Types of Chemical Bonds Information about the strength of a bonding interaction is obtained by measuring the bond energy, which is the energy
Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 8 Outline Bonding: General Concepts Types of Chemical Bonds Information about the strength of a bonding interaction is obtained by measuring the bond energy, which is the energy
CHEMICAL BONDING. Chemical Bonds. Ionic Bonding. Lewis Symbols
 CHEMICAL BONDING Chemical Bonds Lewis Symbols Octet Rule whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen
CHEMICAL BONDING Chemical Bonds Lewis Symbols Octet Rule whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen
Chemical bonding is the combining of elements to form new substances.
 Name Covalent Bonding and Nomenclature: Unit Objective Study Guide Class Period Date Due 1. Define chemical bonding. What is chemical bonding? Chemical bonding is the combining of elements to form new
Name Covalent Bonding and Nomenclature: Unit Objective Study Guide Class Period Date Due 1. Define chemical bonding. What is chemical bonding? Chemical bonding is the combining of elements to form new
