Chemical Bonding and Molecular Models
|
|
|
- Christopher Simon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 25 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Models A chemical bond is a force that holds groups of two or more atoms together and makes them function as a unit. Bonding involves only the valence (outer shell) electrons of atoms. In an ionic bond, valence electrons are transferred from a metal to a nonmetal. In a covalent bond, valence electrons are shared between atoms forming molecules. In this lab we will only consider covalent bonds. The Lewis structure is a representation of how valence electrons are arranged among atoms in a molecule. It shows us how chemical bonds are used to hold together the atoms in a molecule. In drawing Lewis structures, we include only valence electrons, which are represented as dots. When a covalent bond forms, two electrons are shared, represented as a line. The rules for drawing Lewis structures are based on the Octet Rule, which states that the most important requirement for the formation of a stable compound is that the atoms achieve a noble gas electron configuration, or eight valence electrons. Rules for drawing Lewis structures: 1. Determine the total number of valence electrons (outer shell electrons) for the compound. This corresponds to the "A" group the atom belongs on the periodic table, not the atomic number. For example, CO 2 : carbon is in group IVA and has 4 valence electrons, oxygen is in group VIA and each has 6 valence electrons, giving a total of 16 valence electrons for the molecule. 2. Determine the central atom (often the atom that is least electronegative). a. carbon or silicon are always in the middle. b. hydrogen is never in the middle. c. oxygen is usually not in the middle d. the halogens (F, Cl, Br, I) are usually not in the middle. 3. Draw the basic structure, the central atom surrounded by the remaining atoms. 4. Between the central atom and each surrounding atom, place two electrons or a line to designate a single covalent bond (i.e. C-H) composed of a shared electron pair. 5. The octet rule: Surround each atom with eight electron dots (four pairs of electrons). *Remember, the covalent bond counts as two electrons for each atom to which it is attached. *Remember, hydrogen can only have two valence electrons. 6. Count the number of electrons; each line (covalent bond) counts as two, each dot as one. a. If the number of electrons equals the valence electrons in step 1, this is the Lewis structure. b. If you have more electrons than in step one, you must replace one or more single bonds with multiple bonds. When you draw a double bond, you must erase two electrons from each atom attached to the double bond (erase four electrons total) to satisfy the octet rule. *Hydrogen cannot make a double bond. Halogens do not make double bonds.
2 Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Geometry and Bond Angle Several models are used to describe the three-dimensional geometry of molecules. The number of electron pairs surrounding the central atom determines its electron geometry and molecular shape. All electrons, both shared and unshared, have a negative charge. Since like charges repel, electron pairs try to keep as far from each other as possible. We will refer to electron pairs, both shared and unshared, as electron clouds. Each unshared pair of electrons surrounding the central atom occupy an electron cloud. In addition, each atom attached to the central atom (either by a single, double or triple bond) occupies an electron cloud. In this lab, we will consider molecules in which the central atom is surrounded by two, three, or four electron clouds. In the VSEPR model, all electron clouds are positioned as far apart as possible to minimize electrostatic repulsion between negative charges. When there are two electron clouds surrounding the central atom, the furthest distance apart they can get is 180 o from each other which leads to a linear arrangement in space. When there are three electron clouds, the furthest distance apart is 120 o from each other, in a triangular arrangement in space. When there are four electron clouds, the furthest distance apart is about 109 o. This leads to a tetrahedral (a four sided three dimensional shape) arrangement of electron clouds. [Note that the tetrahedron is more spacious than a square with angles of only 90 o.] Molecular Shape The molecular shape describes the three dimensional arrangement of atoms around the central atom. We have just seen that based on the number of electron clouds surrounding the central atom we can determine the VSEPR geometry and bond angle. By further dividing the electron clouds (into the number of clouds that are unshared pairs and those that surround atoms) we can determine the molecular shape of the compound. In determining VSEPR geometry, all electron clouds are considered. To determine the molecular shape based on the VSEPR geometry, we consider only electron clouds that surround atoms. Below is a chart summarizing electron geometry and molecular shape. Notice that if there are zero nonbonding (unshared) electron pairs, the VSEPR geometry and molecular shape are the same. e-clouds (total) Atom clouds LonePair Clouds VSEPR Geometry Bond Angle Molecular Shape Linear 180 o Linear Planar Triangle 120 o Planar Triangle Planar Triangle 120 o Bent (angular) Tetrahedral 109 o Tetrahedral Tetrahedral 109 o Pyramidal Tetrahedral 109 o Bent (angular) Polarity: Molecules may have a negative end and a positive end. If this is the case they are polar molecules. This imbalance of electrical charge is due to a combination of bond polarities (differences in electronegativities of the bonded atoms) and the shape of the molecule. If all bonds in the molecule are non-polar, the molecule is always non-polar. If there are polar bonds present in the molecule, usually the molecule is polar. There are important exceptions to this generalization, however. For example CCl 4 has polar C-Cl bonds, but is a non-polar molecule because its shape results in all the negative areas canceling each other. Thus the molecule doesn t have a negative and positive end so it is a non-polar molecule. 26
3 27 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Models Name: Construct three-dimensional models of various molecular compounds using a model kit. The balls represent atoms and the sticks represent covalent bonds or pairs of electrons. Two springs = a double bond. The different colored balls represent different types of atoms. (See front of box for details.) PART A: Molecule Val e-` Lewis Structure VSEPRGeo/MolecShape Angle Polar? CO 2 SO 3 SO 2 CH 4 NH 3 H 2 O
4 28 Part B: More Lewis Structures with one central atom Molecule Val e-` Lewis Structure VSEPRGeo/MolecShape Angle Polar? CF 2 Cl 2 HCN PBr 3 CH 2 O N 2 O (N is the central atom.) PART C: Negative charged molecules: add one valence electron for every negative charge. (Indicate geometry, shape, and angle.) NO 3 - CO 3 2- SO 3 2-
5 PART D: More than one central atom. (Indicate geometry, shape, angle and polarity of the entire molecule.) 29 C 2 H 6 C 2 H 4 C 2 H 2 CH 3 OH (Indicate geometry and shape around carbon and also around oxygen) C 2 H 4 Cl 2 (There are two possible structures, called ISOMERS. Draw and describe both structures) Postlab Question: In some chemistry courses, the instructor requires students to purchase a model kit. Suppose you were in such a course and decided to economize by making your kit out of different colored gumdrops and toothpicks. What problems might you have in using your kit?
6 30
Lewis Dot Structures and Molecular Geometry
 Experiment 11 Lewis Dot Structures and Molecular Geometry Pre-Lab Assignment Before coming to lab: Read the lab thoroughly. Answer the pre-lab questions that appear at the end of this lab exercise. Purpose
Experiment 11 Lewis Dot Structures and Molecular Geometry Pre-Lab Assignment Before coming to lab: Read the lab thoroughly. Answer the pre-lab questions that appear at the end of this lab exercise. Purpose
Adapted from CHM 130 Maricopa County, AZ Molecular Geometry and Lewis Dot Formulas Introduction
 Adapted from CHM 130 Maricopa County, AZ Molecular Geometry and Lewis Dot Formulas Introduction A chemical bond is an intramolecular (within the molecule) force holding two or more atoms together. Covalent
Adapted from CHM 130 Maricopa County, AZ Molecular Geometry and Lewis Dot Formulas Introduction A chemical bond is an intramolecular (within the molecule) force holding two or more atoms together. Covalent
Chapter 10. Valence Electrons. Lewis dot symbols. Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding Valence Electrons Recall: the outer electrons in an atom are valence electrons. Valence electrons are related to stability Valence electrons can be represented with dots in
Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding Valence Electrons Recall: the outer electrons in an atom are valence electrons. Valence electrons are related to stability Valence electrons can be represented with dots in
Lewis structures show the number and type of bonds between atoms in a molecule or polyatomic ion.
 VSEPR & Geometry Lewis structures show the number and type of bonds between atoms in a molecule or polyatomic ion. Lewis structures are not intended to show the 3-dimensional structure (i.e. shape or geometry)
VSEPR & Geometry Lewis structures show the number and type of bonds between atoms in a molecule or polyatomic ion. Lewis structures are not intended to show the 3-dimensional structure (i.e. shape or geometry)
MOLECULAR MODELS OBJECTIVES
 MOLECULAR MODELS OBJECTIVES 1. To learn to draw Lewis structures for common compounds 2. To identify electron pairs as bonding pairs or lone pairs 3. To use electron pair repulsion theory to predict electronic
MOLECULAR MODELS OBJECTIVES 1. To learn to draw Lewis structures for common compounds 2. To identify electron pairs as bonding pairs or lone pairs 3. To use electron pair repulsion theory to predict electronic
Lewis Dot Formulas and Molecular Shapes
 Lewis Dot Formulas and Molecular Shapes Introduction A chemical bond is an intramolecular (within the molecule) force holding two or more atoms together. Covalent chemical bonds are formed by valence electrons
Lewis Dot Formulas and Molecular Shapes Introduction A chemical bond is an intramolecular (within the molecule) force holding two or more atoms together. Covalent chemical bonds are formed by valence electrons
Chemical Bonds, Molecular Models, and Molecular Shapes
 Chemical Bonds, Molecular Models, and Molecular Shapes PRELAB ASSINGMENT Read the entire laboratory write up and answer the following questions before coming to lab. Read the entire laboratory write up
Chemical Bonds, Molecular Models, and Molecular Shapes PRELAB ASSINGMENT Read the entire laboratory write up and answer the following questions before coming to lab. Read the entire laboratory write up
Name: Period: Date: What Is VSEPR? Now explore the Compare Two Structures link. Try changing the display to explore different combinations.
 Name: Period: Date: What Is VSEPR? Exploring The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) model. Go to the Purdue University website to explore VSEPR theory. http://www.chem.purdue.edu/gchelp/vsepr/structur2.html
Name: Period: Date: What Is VSEPR? Exploring The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) model. Go to the Purdue University website to explore VSEPR theory. http://www.chem.purdue.edu/gchelp/vsepr/structur2.html
Molecular Geometry & Polarity
 Molecular Geometry & Polarity Learn Shapes you will Because the physical and chemical properties of compounds are tied to their structures, the importance of molecular geometry can not be overstated. Localized
Molecular Geometry & Polarity Learn Shapes you will Because the physical and chemical properties of compounds are tied to their structures, the importance of molecular geometry can not be overstated. Localized
Chapter 6. The Chemical Bond
 Chapter 6 The Chemical Bond Some questions Why do noble gases rarely bond to other elements? How does this relate to why the atoms of other elements do form bonds? Why do certain elements combine to form
Chapter 6 The Chemical Bond Some questions Why do noble gases rarely bond to other elements? How does this relate to why the atoms of other elements do form bonds? Why do certain elements combine to form
CHAPTER 12: CHEMICAL BONDING
 CHAPTER 12: CHEMICAL BONDING Problems: 1-26, 27c, 28, 33-34, 35b, 36(a-c), 37(a,b,d), 38a, 39-40, 41-42(a,c), 43-58, 67-74 12.1 THE CHEMICAL BOND CONCEPT chemical bond: what holds atoms or ions together
CHAPTER 12: CHEMICAL BONDING Problems: 1-26, 27c, 28, 33-34, 35b, 36(a-c), 37(a,b,d), 38a, 39-40, 41-42(a,c), 43-58, 67-74 12.1 THE CHEMICAL BOND CONCEPT chemical bond: what holds atoms or ions together
4/25/2017. VSEPR Theory. Two Electron Groups. Shapes of Molecules. Two Electron Groups with Double Bonds. Three Electron Groups.
 Chapter 10 Lecture Chapter 10 Bonding and Properties of Solids and Liquids 10.3 Shapes of Molecules and Ions (VSEPR Theory) Learning Goal Predict the three-dimensional structure of a molecule or a polyatomic
Chapter 10 Lecture Chapter 10 Bonding and Properties of Solids and Liquids 10.3 Shapes of Molecules and Ions (VSEPR Theory) Learning Goal Predict the three-dimensional structure of a molecule or a polyatomic
Check Your Solution A comparison with the figures in Figure 4.31 on page 234 of the student textbook confirms the results.
 Predicting the Shape of a Molecule (Student textbook page 236) 11. What molecular shape is represented by each of the following VSEPR notations? a. AX 3 b. AX 5 E You need to assign a molecular shape that
Predicting the Shape of a Molecule (Student textbook page 236) 11. What molecular shape is represented by each of the following VSEPR notations? a. AX 3 b. AX 5 E You need to assign a molecular shape that
Chapter 8. Bonding: General Concepts
 Chapter 8 Bonding: General Concepts Chapter 8 Table of Contents 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds 8.3 Bond Polarity and Dipole Moments 8.5 Energy Effects in Binary Ionic Compounds 8.6 Partial Ionic Character
Chapter 8 Bonding: General Concepts Chapter 8 Table of Contents 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds 8.3 Bond Polarity and Dipole Moments 8.5 Energy Effects in Binary Ionic Compounds 8.6 Partial Ionic Character
Bonding Test pg 1 of 4 Name: Pd. Date:
 Bonding Test pg 1 of 4 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) How many electrons are shared in a single covalent bond? 1. A) 2 B) 3 C)
Bonding Test pg 1 of 4 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) How many electrons are shared in a single covalent bond? 1. A) 2 B) 3 C)
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry. Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory
 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Sulfanilamide Lewis Structures and the Real 3D-Shape of Molecules Lewis Theory of Molecular Shape and Polarity
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Sulfanilamide Lewis Structures and the Real 3D-Shape of Molecules Lewis Theory of Molecular Shape and Polarity
Fill in the chart below to determine the valence electrons of elements 3-10
 Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory IV Name: Date: Block: 1. Lewis Diagrams 2. VSEPR Lewis Diagrams Lewis diagrams show the bonding between atoms of a molecule. Only the outermost electrons of an atom (called electrons)
Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory IV Name: Date: Block: 1. Lewis Diagrams 2. VSEPR Lewis Diagrams Lewis diagrams show the bonding between atoms of a molecule. Only the outermost electrons of an atom (called electrons)
Hey, Baby. You and I Have a Bond...Ch. 8
 I. IONIC BONDING FUNDAMENTALS A. They form between... 1. A and a a. A to become b. A to become B. How it happens (Let s first focus on two atoms): 1. When a metal and a nonmetal meet, electrons get transferred
I. IONIC BONDING FUNDAMENTALS A. They form between... 1. A and a a. A to become b. A to become B. How it happens (Let s first focus on two atoms): 1. When a metal and a nonmetal meet, electrons get transferred
CHEM 101: CHAPTER 11: CHEMICAL BONDS: THE FORMATION OF COMPOUNDS FROM ATOMS
 1 CHEM 101: CHAPTER 11: CHEMICAL BONDS: THE FORMATION OF COMPOUNDS FROM ATOMS PERIODIC TRENDS: See pages 214-216, 221 Table 11.3, and 227 + 228 of text. Lewis Structures of Atoms: The Lewis Dot Diagram
1 CHEM 101: CHAPTER 11: CHEMICAL BONDS: THE FORMATION OF COMPOUNDS FROM ATOMS PERIODIC TRENDS: See pages 214-216, 221 Table 11.3, and 227 + 228 of text. Lewis Structures of Atoms: The Lewis Dot Diagram
CHAPTER 12 CHEMICAL BONDING
 CHAPTER 12 CHEMICAL BONDING Core electrons are found close to the nucleus, whereas valence electrons are found in the most distant s and p energy subshells. The valence electrons are responsible for holding
CHAPTER 12 CHEMICAL BONDING Core electrons are found close to the nucleus, whereas valence electrons are found in the most distant s and p energy subshells. The valence electrons are responsible for holding
Honors Chemistry Unit 6 ( )
 Honors Chemistry Unit 6 (2017-2018) Lewis Dot Structures VSEPR Structures 1 We are learning to: 1. Represent compounds with Lewis structures. 2. Apply the VSEPR theory to determine the molecular geometry
Honors Chemistry Unit 6 (2017-2018) Lewis Dot Structures VSEPR Structures 1 We are learning to: 1. Represent compounds with Lewis structures. 2. Apply the VSEPR theory to determine the molecular geometry
SECTION II: BUILDING MODELS
 SECTION II: BUILDING MODELS Lesson 9 New Smells, New Ideas Lesson 10 Two s Company Lesson 11 Let s Build It Lesson 12 What Shape Is That Smell? Lesson 13 Sorting It Out Lesson 14 How Does the Nose Know?
SECTION II: BUILDING MODELS Lesson 9 New Smells, New Ideas Lesson 10 Two s Company Lesson 11 Let s Build It Lesson 12 What Shape Is That Smell? Lesson 13 Sorting It Out Lesson 14 How Does the Nose Know?
Chapter 11 Chemical Bonds: The Formation of Compounds from Atoms Advanced Chemistry Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties Learning Objective
 Chapter 11 Chemical Bonds: The Formation of Compounds from Atoms Advanced Chemistry 11.1 Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties Discuss the atomic trends Metals are located on the left side of the periodic
Chapter 11 Chemical Bonds: The Formation of Compounds from Atoms Advanced Chemistry 11.1 Periodic Trends in Atomic Properties Discuss the atomic trends Metals are located on the left side of the periodic
Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding 7.1 Ionic Bonding Octet rule: In forming compounds atoms lose, gain or share electrons to attain a noble gas configuration with 8 electrons in their outer shell (s 2 p 6 ), except
Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding 7.1 Ionic Bonding Octet rule: In forming compounds atoms lose, gain or share electrons to attain a noble gas configuration with 8 electrons in their outer shell (s 2 p 6 ), except
Bonding: Part Two. Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond. transfer valence e - Metallic bond. (NaCl) (Fe) mobile valence e - Covalent bond
 Bonding: Part Two Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond transfer valence e - Metallic bond mobile valence e - Covalent bond (NaCl) (Fe) shared valence e - (H 2 O) 1 Single Covalent Bond H + H H H H-atoms H
Bonding: Part Two Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond transfer valence e - Metallic bond mobile valence e - Covalent bond (NaCl) (Fe) shared valence e - (H 2 O) 1 Single Covalent Bond H + H H H H-atoms H
CHEMICAL BONDING. Valence Electrons. Chapter Ten
 CHEMICAL BONDING Chapter Ten Valence Electrons! The electrons occupying the outermost energy level of an atom are called the valence electrons; all other electrons are called the core electrons.! The valence
CHEMICAL BONDING Chapter Ten Valence Electrons! The electrons occupying the outermost energy level of an atom are called the valence electrons; all other electrons are called the core electrons.! The valence
Bonding: Part Two. Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond. transfer valence e - Metallic bond. (NaCl) (Fe) mobile valence e - Covalent bond
 Bonding: Part Two Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond transfer valence e - Metallic bond mobile valence e - Covalent bond (NaCl) (Fe) shared valence e - (H 2 O) 1 Single Covalent Bond H + H H H H-atoms H
Bonding: Part Two Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond transfer valence e - Metallic bond mobile valence e - Covalent bond (NaCl) (Fe) shared valence e - (H 2 O) 1 Single Covalent Bond H + H H H H-atoms H
Chapter 12. Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Chemical Bond Concept Recall that an atom has core and valence electrons. Core electrons are found close to the nucleus. Valence electrons are found in the most distant s and
Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Chemical Bond Concept Recall that an atom has core and valence electrons. Core electrons are found close to the nucleus. Valence electrons are found in the most distant s and
Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical Bond
 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical Bond Mutual attraction between the and electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together. Ionic Bond o that results from the attraction between large
Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical Bond Mutual attraction between the and electrons of different atoms that binds the atoms together. Ionic Bond o that results from the attraction between large
Chem 1075 Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Lecture Outline. Chemical Bond Concept
 Chem 1075 Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Lecture Outline Slide 2 Chemical Bond Concept Recall that an atom has and electrons. Core electrons are found to the nucleus. Valence electrons are found in the s
Chem 1075 Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Lecture Outline Slide 2 Chemical Bond Concept Recall that an atom has and electrons. Core electrons are found to the nucleus. Valence electrons are found in the s
Chapter 6 Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 6 Chemical Bonding Section 6-1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonds Valence electrons are attracted to other atoms, and that determines the kind of chemical bonding that occurs between
Chapter 6 Chemical Bonding Section 6-1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonds Valence electrons are attracted to other atoms, and that determines the kind of chemical bonding that occurs between
Chapter 12. Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Chapter 12 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonding Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer shell (highest energy level) of an atom. A chemical bond is a mutual
Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Chapter 12 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonding Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer shell (highest energy level) of an atom. A chemical bond is a mutual
A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE ETHANOL! Count valence electrons
 212 A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE Count valence electrons Pick central atom and draw skeletal structure - central atom is usually the one that needs to gain the most electrons! - skeletal structure
212 A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE Count valence electrons Pick central atom and draw skeletal structure - central atom is usually the one that needs to gain the most electrons! - skeletal structure
Section 12: Lewis Structures
 Section 12: Lewis Structures The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 12.01 Electronegativity Chemistry (5)(C) 12.02 Electron
Section 12: Lewis Structures The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 12.01 Electronegativity Chemistry (5)(C) 12.02 Electron
AIM: HOW TO FORM COVALENT BONDS
 AIM: HOW TO FORM COVALENT BONDS DO NOW: EXPLAIN THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN IONIC BONDING AND COVALENT BONDS. INCLUDE HOW THE PROPERTIES DIFFER IN SALTS AND MOLECULES, AND WHICH ELEMENTS ARE INVOLVED IN EACH
AIM: HOW TO FORM COVALENT BONDS DO NOW: EXPLAIN THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN IONIC BONDING AND COVALENT BONDS. INCLUDE HOW THE PROPERTIES DIFFER IN SALTS AND MOLECULES, AND WHICH ELEMENTS ARE INVOLVED IN EACH
Covalent Bonding 10/29/2013
 Bond Energies or Bond Dissociation Energies Tables 8.4 and 8.5 on page 72 gives a list of the energy required to dissociate or break bonds. This value is used to determine whether covalent bonds will form
Bond Energies or Bond Dissociation Energies Tables 8.4 and 8.5 on page 72 gives a list of the energy required to dissociate or break bonds. This value is used to determine whether covalent bonds will form
Molecular Geometry. Objectives N H H. The objectives of this laboratory are to:
 Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are to: Molecular Geometry Write Lewis structure representations of the bonding and valence electrons in molecules. Use the VSEPR model to predict the molecular
Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are to: Molecular Geometry Write Lewis structure representations of the bonding and valence electrons in molecules. Use the VSEPR model to predict the molecular
Experiment #2. Lewis Structures
 Experiment #2. Lewis Structures A Lewis structure shows how the valence electrons are arranged and indicates the bonding between atoms in a molecule. We represent the elements by their symbols. The shared
Experiment #2. Lewis Structures A Lewis structure shows how the valence electrons are arranged and indicates the bonding between atoms in a molecule. We represent the elements by their symbols. The shared
Lewis Theory of Shapes and Polarities of Molecules
 Lewis Theory of Shapes and Polarities of Molecules Sulfanilamide Lewis Structures and the Real 3D-Shape of Molecules Molecular Shape or Geometry The way in which atoms of a molecule are arranged in space
Lewis Theory of Shapes and Polarities of Molecules Sulfanilamide Lewis Structures and the Real 3D-Shape of Molecules Molecular Shape or Geometry The way in which atoms of a molecule are arranged in space
IB Chemistry. Chapter 4.1
 IB Chemistry Chapter 4.1 Chemical Bonds Atoms or ions that are strongly attached to one another Chemical bonds will form if potential energy decreases (becomes more stable) 2 Valence Electrons Valence
IB Chemistry Chapter 4.1 Chemical Bonds Atoms or ions that are strongly attached to one another Chemical bonds will form if potential energy decreases (becomes more stable) 2 Valence Electrons Valence
Covalent bonding occurs in nonmetal compounds. Use the highlighter to select the compounds that are covalently bonded. HCl
 Covalent bonding occurs in nonmetal compounds. Use the highlighter to select the compounds that are covalently bonded. 2 C 2 Cl Li NaF Mg C 4 N NaCl 3 Drag this to the target to reveal the answers. Properties
Covalent bonding occurs in nonmetal compounds. Use the highlighter to select the compounds that are covalently bonded. 2 C 2 Cl Li NaF Mg C 4 N NaCl 3 Drag this to the target to reveal the answers. Properties
Carbon-based molecules are held together by covalent bonds between atoms
 hapter 1: hemical bonding and structure in organic compounds arbon-based molecules are held together by covalent bonds between atoms omposition: Mainly nonmetals; especially,, O, N, S, P and the halogens
hapter 1: hemical bonding and structure in organic compounds arbon-based molecules are held together by covalent bonds between atoms omposition: Mainly nonmetals; especially,, O, N, S, P and the halogens
Covalent Molecules and Lewis Structures Time required: two 50-minute periods
 Mega Molecules, LLC!!!!! Name: Hands-On Science with Molecular Models!! Date:!!!!!!!! Hour: Introduction Covalent Molecules and Lewis Structures Time required: two 50-minute periods To study covalent molecules,
Mega Molecules, LLC!!!!! Name: Hands-On Science with Molecular Models!! Date:!!!!!!!! Hour: Introduction Covalent Molecules and Lewis Structures Time required: two 50-minute periods To study covalent molecules,
Chapter 9 The Shapes of Molecules Cocaine
 Chapter 9 The Shapes of Molecules 1 Cocaine 10.1 Depicting Molecules & Ions with Lewis Structures 2 Number of Covalent Bonds 3 The number of covalent bonds can be determined from the number of electrons
Chapter 9 The Shapes of Molecules 1 Cocaine 10.1 Depicting Molecules & Ions with Lewis Structures 2 Number of Covalent Bonds 3 The number of covalent bonds can be determined from the number of electrons
INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts and Critical Thinking
 INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts and Critical Thinking Sixth Edition by Charles H. Corwin Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding by Christopher Hamaker 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 12 1 Chemical Bond Concept
INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts and Critical Thinking Sixth Edition by Charles H. Corwin Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding by Christopher Hamaker 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 12 1 Chemical Bond Concept
VSEPR. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory
 VSEPR Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Vocabulary: domain = any electron pair or bond (single, double or triple) is considered one domain. bonding pair = shared pair = any electron pair that
VSEPR Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Vocabulary: domain = any electron pair or bond (single, double or triple) is considered one domain. bonding pair = shared pair = any electron pair that
EXPERIMENT 15: MOLECULAR MODELS
 EXPERIMENT 15: MLEULAR MDELS Introduction: Given formulas of some molecules and ions, you will use the periodic table, valence electron count, and electronegativities to deduce their geometry and polarities.
EXPERIMENT 15: MLEULAR MDELS Introduction: Given formulas of some molecules and ions, you will use the periodic table, valence electron count, and electronegativities to deduce their geometry and polarities.
!"##$%&'()$*+,%'-./'
 !"##$%&()$*+,%-./ 0,1,%$234%5$1673896:2:567$2(),#6;+%& 6!#6+)! CHAPTER 3-4: Concepts to Know! The difference between ionic and covalent bonds! Define cations and anions! Predict cation/anion
!"##$%&()$*+,%-./ 0,1,%$234%5$1673896:2:567$2(),#6;+%& 6!#6+)! CHAPTER 3-4: Concepts to Know! The difference between ionic and covalent bonds! Define cations and anions! Predict cation/anion
CHM 130LL: Molecular Models
 CM 130LL: Molecular Models In this lab, you will study covalently bonded molecules i.e., molecules where nonmetal atoms are held together because they share one or more pairs of electrons. In this experiment,
CM 130LL: Molecular Models In this lab, you will study covalently bonded molecules i.e., molecules where nonmetal atoms are held together because they share one or more pairs of electrons. In this experiment,
Chapter 13: Phenomena
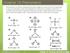 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
CHAPTER 12 CHEMICAL BONDING
 Chemistry Name Hour Chemistry Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 12 CHEMICAL BONDING Day Plans for the day Assignment(s) for the day 1 Begin Chapter
Chemistry Name Hour Chemistry Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 12 CHEMICAL BONDING Day Plans for the day Assignment(s) for the day 1 Begin Chapter
11/14/2014. Chemical Bonding. Richard Philips Feynman, Nobel Laureate in Physics ( )
 Chemical Bonding Lewis Theory Valence Bond VSEPR Molecular rbital Theory 1 "...he [his father] knew the difference between knowing the name of something and knowing something" Richard Philips eynman, Nobel
Chemical Bonding Lewis Theory Valence Bond VSEPR Molecular rbital Theory 1 "...he [his father] knew the difference between knowing the name of something and knowing something" Richard Philips eynman, Nobel
Date: Monday, February 6, Obj: Write electron dot structures. Complete: How many valence electrons in the following? H Be B C.
 Do Now Date: Monday, February 6, 2017 Obj: Write electron dot structures. Complete: How many valence electrons in the following? H Be B C N O F Ne Valence Electrons Remember: in chemical bonds we re talking
Do Now Date: Monday, February 6, 2017 Obj: Write electron dot structures. Complete: How many valence electrons in the following? H Be B C N O F Ne Valence Electrons Remember: in chemical bonds we re talking
Covalent Bonds Ch. Why do atoms bond? Atoms want noble gas configuration ( ) For bonds there is a transfer of electrons to get an octet of electrons
 Covalent Bonds Ch. Why do atoms bond? Atoms want noble gas configuration ( ) For bonds there is a transfer of electrons to get an octet of electrons For covalent bonds there is a of electrons to get an
Covalent Bonds Ch. Why do atoms bond? Atoms want noble gas configuration ( ) For bonds there is a transfer of electrons to get an octet of electrons For covalent bonds there is a of electrons to get an
Chemical Bonding. Burlingame High School
 Chemical Bonding Electronegativity Is a measure of the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. Concept proposed by Linus Pauling 1901-1994 Electronegativity Trends Forms of Chemical
Chemical Bonding Electronegativity Is a measure of the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. Concept proposed by Linus Pauling 1901-1994 Electronegativity Trends Forms of Chemical
bond energy- energy required to break a chemical bond -We can measure bond energy to determine strength of interaction
 bond energy- energy required to break a chemical bond -We can measure bond energy to determine strength of interaction ionic compound- a metal reacts with a nonmetal Ionic bonds form when an atom that
bond energy- energy required to break a chemical bond -We can measure bond energy to determine strength of interaction ionic compound- a metal reacts with a nonmetal Ionic bonds form when an atom that
Chapter #3 Chemical Bonding
 Chapter #3 Chemical Bonding Valence Electrons electrons in the last energy level of an atom. Lewis dot symbols Consists of the symbol of an element and one dot for each valence electron in the atom of
Chapter #3 Chemical Bonding Valence Electrons electrons in the last energy level of an atom. Lewis dot symbols Consists of the symbol of an element and one dot for each valence electron in the atom of
Experiment 21 Lewis structures and VSEPR Theory
 Experiment 21 Lewis structures and VSEPR Theory Introduction 1. Lewis Structures and Formal Charge LG.N. Lewis, at the University of California at Berkeley devised a simple way to understand the nature
Experiment 21 Lewis structures and VSEPR Theory Introduction 1. Lewis Structures and Formal Charge LG.N. Lewis, at the University of California at Berkeley devised a simple way to understand the nature
Name. Molecular Models
 Name Molecular Models Lab Day Introduction: The atom and molecule are truly small; 6 10 23 carbon atoms occupy about 4 cm 3, or each atom has a volume of about 6 10 24 cm 3. Molecules, though larger than
Name Molecular Models Lab Day Introduction: The atom and molecule are truly small; 6 10 23 carbon atoms occupy about 4 cm 3, or each atom has a volume of about 6 10 24 cm 3. Molecules, though larger than
Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display : A force that holds atoms together in a molecule or compound
 : Chemical Bonding 8-1 8.1 Types of Bonds : A force that holds atoms together in a molecule or compound Two types of chemical bonds Ionic Bonds Covalent Bonds 8-2 1 8.1 Types of Bonds 8-3 8.1 Types of
: Chemical Bonding 8-1 8.1 Types of Bonds : A force that holds atoms together in a molecule or compound Two types of chemical bonds Ionic Bonds Covalent Bonds 8-2 1 8.1 Types of Bonds 8-3 8.1 Types of
PREDICTING THE SHAPE OF A MOLECULE FROM ITS STRUCTURAL FROMULAE
 CH 11 TOPIC 24 PREDICTING MOLECULAR SHAPES 1 You have mastered this topic when you can: 1) determine the shape of a molecule based on its Lewis Structure.. PREDICTING THE SHAPE OF A MOLECULE FROM ITS STRUCTURAL
CH 11 TOPIC 24 PREDICTING MOLECULAR SHAPES 1 You have mastered this topic when you can: 1) determine the shape of a molecule based on its Lewis Structure.. PREDICTING THE SHAPE OF A MOLECULE FROM ITS STRUCTURAL
CHM 151LL: Geometry of Covalent Compounds
 CM 151LL: Geometry of Covalent Compounds Introduction Octet Rule A Lewis structure (or electrondot formula) is a twodimensional structural formula showing the arrangement of electrons around atoms in covalently
CM 151LL: Geometry of Covalent Compounds Introduction Octet Rule A Lewis structure (or electrondot formula) is a twodimensional structural formula showing the arrangement of electrons around atoms in covalently
AS91164 Bonding, structure, properties and energychanges Level 2 Credits 5
 AS91164 Bonding, structure, properties and energychanges Level 2 Credits 5 LEWIS DIAGRAMS, SHAPES OF MOLECULES, POLAR AND NON POLAR MOLECULES Lewis diagrams: use dots (or x) to represent electrons, show
AS91164 Bonding, structure, properties and energychanges Level 2 Credits 5 LEWIS DIAGRAMS, SHAPES OF MOLECULES, POLAR AND NON POLAR MOLECULES Lewis diagrams: use dots (or x) to represent electrons, show
SKILL-BUILDING EXERCISE
 4. O and H Solution 1. Carbon has an electronegativity of 2.5, while the value for hydrogen is 2.1. The difference is 0.3, which is rather small. The C H bond is therefore considered nonpolar. 2. Both
4. O and H Solution 1. Carbon has an electronegativity of 2.5, while the value for hydrogen is 2.1. The difference is 0.3, which is rather small. The C H bond is therefore considered nonpolar. 2. Both
At the end of this lesson, students should be able to :
 At the end of this lesson, students should be able to : (a) Explain Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory (VSEPR) (b) Draw the basic molecular shapes: linear, planar, tetrahedral, and octahedral.
At the end of this lesson, students should be able to : (a) Explain Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory (VSEPR) (b) Draw the basic molecular shapes: linear, planar, tetrahedral, and octahedral.
(A) 1 bonding pair (B) 1 bonding pair and 1 lone pair (C) 2 bonding pairs (D) 2 bonding pairs and 2 lone pairs
 AP Chemistry - Problem Drill 13: Lewis Structures and VSPER No. 1 of 10 1. Lewis structure is used to model covalent bonds of a molecule or ion. Covalent bonds are a type of chemical bonding formed by
AP Chemistry - Problem Drill 13: Lewis Structures and VSPER No. 1 of 10 1. Lewis structure is used to model covalent bonds of a molecule or ion. Covalent bonds are a type of chemical bonding formed by
Covalent Bonding. In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons
 In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. They are monatomic - consist of single atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons To form ionic compounds Some elements share
In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. They are monatomic - consist of single atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons To form ionic compounds Some elements share
CHEMICAL BONDING IONIC BONDS COVALENT BONDS HYDROGEN BONDS METALLIC BONDS
 CHEMICAL BONDING IONIC BONDS COVALENT BONDS HYDROGEN BONDS METALLIC BONDS IONIC BONDING When an atom of a nonmetal takes one or more electrons from an atom of a metal so both atoms end up with eight valence
CHEMICAL BONDING IONIC BONDS COVALENT BONDS HYDROGEN BONDS METALLIC BONDS IONIC BONDING When an atom of a nonmetal takes one or more electrons from an atom of a metal so both atoms end up with eight valence
Chemistry 212 MOLECULAR STRUCTURES AND GEOMETRIES
 Chemistry 212 MOLECULAR STRUCTURES AND GEOMETRIES LEARNING OBJECTIVES To build models of selected molecules using VSEPR theory. To illustrate patterns of molecular shapes. BACKGROUND The shapes exhibited
Chemistry 212 MOLECULAR STRUCTURES AND GEOMETRIES LEARNING OBJECTIVES To build models of selected molecules using VSEPR theory. To illustrate patterns of molecular shapes. BACKGROUND The shapes exhibited
of its physical and chemical properties.
 8.4 Molecular Shapes VSEPR Model The shape of a molecule determines many of its physical and chemical properties. Molecular l geometry (shape) can be determined with the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
8.4 Molecular Shapes VSEPR Model The shape of a molecule determines many of its physical and chemical properties. Molecular l geometry (shape) can be determined with the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
Molecular Geometry and Polarity 1
 Experiment Molecular Geometry and Polarity 1 Objectives At the end of this activity you should be able to: o Write Lewis structures for molecules. o Classify bonds as nonpolar covalent, polar covalent,
Experiment Molecular Geometry and Polarity 1 Objectives At the end of this activity you should be able to: o Write Lewis structures for molecules. o Classify bonds as nonpolar covalent, polar covalent,
Ionic and Covalent Bonding
 1. Define the following terms: a) valence electrons Ionic and Covalent Bonding the electrons in the highest occupied energy level always electrons in the s and p orbitals maximum of 8 valence electrons
1. Define the following terms: a) valence electrons Ionic and Covalent Bonding the electrons in the highest occupied energy level always electrons in the s and p orbitals maximum of 8 valence electrons
4.2.7 & Shapes, and bond angles for molecules with two, three and four negative charge centers
 4.2.7 & 4.2.8 Shapes, and bond angles for molecules with two, three and four negative charge centers The shape of a molecule has an important part to play in determining its chemical (e.g. reactivity and
4.2.7 & 4.2.8 Shapes, and bond angles for molecules with two, three and four negative charge centers The shape of a molecule has an important part to play in determining its chemical (e.g. reactivity and
Chemical Bonding. Section 1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding. Section 2 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Compounds
 Chemical Bonding Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Section 2 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Compounds Section 3 Ionic Bonding and Ionic Compounds Section 4 Metallic Bonding Section
Chemical Bonding Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Section 2 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Compounds Section 3 Ionic Bonding and Ionic Compounds Section 4 Metallic Bonding Section
Ex. 1) F F bond in F = 0 < % covalent, no transfer of electrons
 #60 Notes Unit 8: Bonding Ch. Bonding I. Bond Character Bonds are usually combinations of ionic and covalent character. The electronegativity difference is used to determine a bond s character. Electronegativity
#60 Notes Unit 8: Bonding Ch. Bonding I. Bond Character Bonds are usually combinations of ionic and covalent character. The electronegativity difference is used to determine a bond s character. Electronegativity
A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE ETHANOL! Count valence electrons
 212 A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE Count valence electrons Pick central atom and draw skeletal structure - central atom is usually the one that needs to gain the most electrons! - skeletal structure
212 A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE Count valence electrons Pick central atom and draw skeletal structure - central atom is usually the one that needs to gain the most electrons! - skeletal structure
Molecular shapes. Balls and sticks
 Molecular shapes Balls and sticks Learning objectives Apply VSEPR to predict electronic geometry and shapes of simple molecules Determine molecule shape from electronic geometry Distinguish between polar
Molecular shapes Balls and sticks Learning objectives Apply VSEPR to predict electronic geometry and shapes of simple molecules Determine molecule shape from electronic geometry Distinguish between polar
Chapter 4 Lecture Outline. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 4 Lecture Outline 1 Copyright McGraw-ill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 4.1 Introduction to Covalent Bonding Covalent bonds result from the sharing of electrons between
Chapter 4 Lecture Outline 1 Copyright McGraw-ill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 4.1 Introduction to Covalent Bonding Covalent bonds result from the sharing of electrons between
RESONANCE STRUCTURE When a molecule has more than one possible structure. Draw all possible structures and place a double end arrow ( ) in between.
 CHEMISTRY NOTES 6.1 COVALENT BONDS Objectives Explain the role and location of electrons in a covalent bond. Describe the change in energy and stability that takes place as a covalent bond forms. Distinguish
CHEMISTRY NOTES 6.1 COVALENT BONDS Objectives Explain the role and location of electrons in a covalent bond. Describe the change in energy and stability that takes place as a covalent bond forms. Distinguish
Chapter 12 Structure and Shape
 Free Study Guide for Cracolice Peters Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach Second Edition www.brookscole.com/chemistry Chapter 12 Structure and Shape Chapter 12Assignment A: Lewis Diagrams
Free Study Guide for Cracolice Peters Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach Second Edition www.brookscole.com/chemistry Chapter 12 Structure and Shape Chapter 12Assignment A: Lewis Diagrams
Experiment Seven - Molecular Geometry
 Experiment Seven - Geometry Introduction Although it has recently become possible to image molecules and even atoms using a highresolution microscope, our understanding of the molecular world allows us
Experiment Seven - Geometry Introduction Although it has recently become possible to image molecules and even atoms using a highresolution microscope, our understanding of the molecular world allows us
EXPERIMENT #13 Lewis Structures and Molecular Geometry
 OBJECTIVES: EXPERIMENT #13 s and Draw Lewis structures of atoms, ions, and molecules Build models of linear, trigonal planar tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral arrangements of electron pairs
OBJECTIVES: EXPERIMENT #13 s and Draw Lewis structures of atoms, ions, and molecules Build models of linear, trigonal planar tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral arrangements of electron pairs
Chapter 6. Preview. Objectives. Molecular Compounds
 Section 2 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Compounds Preview Objectives Molecular Compounds Formation of a Covalent Bond Characteristics of the Covalent Bond The Octet Rule Electron-Dot Notation Lewis Structures
Section 2 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Compounds Preview Objectives Molecular Compounds Formation of a Covalent Bond Characteristics of the Covalent Bond The Octet Rule Electron-Dot Notation Lewis Structures
INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts and Critical Thinking Seventh Edition by Charles H. Corwin
 Lecture INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts and Critical Thinking Seventh Edition by Charles H. Corwin Chemical Bonding by Christopher G. Hamaker Illinois State University Chemical Bond Concept Recall that
Lecture INTRODUCTORY CHEMISTRY Concepts and Critical Thinking Seventh Edition by Charles H. Corwin Chemical Bonding by Christopher G. Hamaker Illinois State University Chemical Bond Concept Recall that
6.1 Intro to Chemical Bonding Name:
 6.1 Intro to Chemical Bonding Name: A. Chemical bond Favored by nature because: 3 main types of bonds 1. 2. 3. B. Ionic Bonds C. Covalent Bonds D. Metallic Bond E. Bond Determination RECALL: Electronegativity
6.1 Intro to Chemical Bonding Name: A. Chemical bond Favored by nature because: 3 main types of bonds 1. 2. 3. B. Ionic Bonds C. Covalent Bonds D. Metallic Bond E. Bond Determination RECALL: Electronegativity
Chemical Bonding I: Covalent Bonding. How are atoms held together in compounds?
 I: Covalent Bonding How are atoms held together in compounds? IONIC or COVALENT bonds or forces For most atoms, a filled outer shell contains 8 electrons ----- an octet Atoms want to form octets when they
I: Covalent Bonding How are atoms held together in compounds? IONIC or COVALENT bonds or forces For most atoms, a filled outer shell contains 8 electrons ----- an octet Atoms want to form octets when they
Lewis Structures and Molecular Shapes
 Lewis Structures and Molecular Shapes Drawing Lewis Structures Determine from formula if ionic or covalent Count the electrons If ionic : add valence # to charge if (-), subtract if (+) - = 7+1 electrons;
Lewis Structures and Molecular Shapes Drawing Lewis Structures Determine from formula if ionic or covalent Count the electrons If ionic : add valence # to charge if (-), subtract if (+) - = 7+1 electrons;
Name Honors Chemistry / /
 Name Honors Chemistry / / Lewis Structures & Resonance Structures Last chapter we studied ionic compounds. In ionic compounds electrons are gained or lost. In this chapter we are going to study covalent
Name Honors Chemistry / / Lewis Structures & Resonance Structures Last chapter we studied ionic compounds. In ionic compounds electrons are gained or lost. In this chapter we are going to study covalent
BONDING REVIEW. You need a Periodic Table, Electronegativity table & Polarity chart!
 BONDING REVIEW You need a Periodic Table, Electronegativity table & Polarity chart! What is the correct bond angle for Bent with 2 lone pairs on the central atom? 105 What is the predicted bond angle for
BONDING REVIEW You need a Periodic Table, Electronegativity table & Polarity chart! What is the correct bond angle for Bent with 2 lone pairs on the central atom? 105 What is the predicted bond angle for
EXPERIMENT 12: MOLECULAR ARCHITECTURE
 Name Section EXPERIMENT 12: MLECULAR ARCITECTURE PRE-LABRATRY QUESTINS The following preparatory questions should be answered before coming to lab. They are intended to introduce you to several ideas important
Name Section EXPERIMENT 12: MLECULAR ARCITECTURE PRE-LABRATRY QUESTINS The following preparatory questions should be answered before coming to lab. They are intended to introduce you to several ideas important
Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts
 Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
H O H C H H N H H. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion: Predicting Shape & Polarity
 Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion: Predicting Shape & Polarity BJECTIVES Students will develop the ability to: 1. Predict the arrangement that valence e pairs assume around an atom (e pair geometry)
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion: Predicting Shape & Polarity BJECTIVES Students will develop the ability to: 1. Predict the arrangement that valence e pairs assume around an atom (e pair geometry)
Molecular Geometry. Valence Shell Electron Pair. What Determines the Shape of a Molecule? Repulsion Theory (VSEPR) Localized Electron Model
 Molecular Geometry Learn Shapes you will Because the physical and chemical properties of compounds are tied to their structures, the importance of molecular geometry can not be overstated. Localized Electron
Molecular Geometry Learn Shapes you will Because the physical and chemical properties of compounds are tied to their structures, the importance of molecular geometry can not be overstated. Localized Electron
8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds List and define three types of bonding. chapter 8 Bonding General Concepts.notebook. September 10, 2015
 chapter 8 Bonding General Concepts.notebook Chapter 8: Bonding: General Concepts Mar 13 11:15 AM 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds List and define three types of bonding. Bonds are forces that hold groups of
chapter 8 Bonding General Concepts.notebook Chapter 8: Bonding: General Concepts Mar 13 11:15 AM 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds List and define three types of bonding. Bonds are forces that hold groups of
Lewis Structures. Lewis Structures. Lewis Structures. Lewis Structures. What pattern do you see? What pattern do you see?
 Look at the following chart: IA IIA IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA VIIIA 2s1 2s2 2s22p1 2s22p2 2s22p3 2s22p4 2s22p5 2s22p6 The Roman Numerals are the Group numbers from the Periodic Table, Beneath them is the outer
Look at the following chart: IA IIA IIIA IVA VA VIA VIIA VIIIA 2s1 2s2 2s22p1 2s22p2 2s22p3 2s22p4 2s22p5 2s22p6 The Roman Numerals are the Group numbers from the Periodic Table, Beneath them is the outer
REVIEW: VALENCE ELECTRONS CHEMICAL BONDS: LEWIS SYMBOLS: CHEMICAL BONDING. What are valence electrons?
 REVIEW: VALENCE ELECTRONS 13 CHEMICAL BONDING What are valence electrons? Which groups on the periodic table readily give up electrons? What group readily accepts electrons? CHEMICAL BONDS: What are chemical
REVIEW: VALENCE ELECTRONS 13 CHEMICAL BONDING What are valence electrons? Which groups on the periodic table readily give up electrons? What group readily accepts electrons? CHEMICAL BONDS: What are chemical
Study flashcards. Elements Polyatomic ions: be sure to learn the chemical. Slide 1of 29
 Study flashcards Elements Polyatomic ions: be sure to learn the chemical formula AND the charge 1of 29 Write the formula for: 1. Phosphate PO 4 3 2. Nitrate NO 3 3. Carbonate CO 3 2 4. Sulfate SO 4 2 5.
Study flashcards Elements Polyatomic ions: be sure to learn the chemical formula AND the charge 1of 29 Write the formula for: 1. Phosphate PO 4 3 2. Nitrate NO 3 3. Carbonate CO 3 2 4. Sulfate SO 4 2 5.
Bonding - Ch. 7. Types of Bonding
 Types of Bonding I. holds everything together! II. All bonding occurs because of III. Electronegativity difference and bond character A. A between two atoms results in a when those two atoms form a bond.
Types of Bonding I. holds everything together! II. All bonding occurs because of III. Electronegativity difference and bond character A. A between two atoms results in a when those two atoms form a bond.
Chapter 8 Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 8 Chemical Bonding Types of Bonds Ionic Bonding Covalent Bonding Shapes of Molecules 8-1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Table 8.1 Two
Chapter 8 Chemical Bonding Types of Bonds Ionic Bonding Covalent Bonding Shapes of Molecules 8-1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Table 8.1 Two
Chapter 6. Preview. Lesson Starter Objectives Chemical Bond
 Preview Lesson Starter Objectives Chemical Bond Section 1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Lesson Starter Imagine getting onto a crowded elevator. As people squeeze into the confined space, they come in
Preview Lesson Starter Objectives Chemical Bond Section 1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Lesson Starter Imagine getting onto a crowded elevator. As people squeeze into the confined space, they come in
