The Shapes of Molecules. Chemistry II
|
|
|
- Garry Moore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 The Shapes of Molecules Chemistry II
3 Lewis Structures DEFINITIN: A structure of a molecule showing how the valence electrons are arranged. 1) nly the valence electrons appear in a Lewis structure.
4 2) The line joining two atoms represents a pair of electrons shared between two atoms. single bond - two shared electrons, one line double triple bond - six shared electrons, three lines bond - four shared electrons, two lines
5 3) Dots placed next to an atom represent nonbonding electrons. Procedure Step 1: Place the atoms relative to each other. If the formula is in the form AB n, place the atom with the lower group number in the center since it needs more e - to form an octet.
6 If atoms have the same group number, place the one with the higher period number (Lowest EN) in the center. can form only 1 bond so it is never in the center. Step 2: Determine the total number of valence electrons available.
7 Step 3: Draw a single bond from each surrounding atom to the central atom. then subtract 2 from the total number of valence electrons for each bond drawn. Step 4: Distribute the remaining electrons in pairs so that each atom obtains eight electrons. (2 for )
8 Start by placing pair of electrons around the more EN atoms to give them the stable octet. If any electrons remain, place them around the central atom. Lewis structures do not indicate shape.
9 Writing Lewis Structures for Molecules with ne Central Atom Write a Lewis structure for the molecule CCl 3, chloroform. Step 1: Cl C Cl Cl
10 Step 2: Count valence electrons. [1xC(4e - )] [1x(1e - )] [3xCl(7e - )] = 26 electrons Step 3: Draw single bonds between the atoms, and subtract 2 electrons per bond. Cl C Cl Cl
11 26 e e- = 18 e-. Step 4: Distribute the remaining electron in pairs beginning with the surrounding atoms. Cl C Cl Cl
12 Writing Lewis Structures for Molecules with More than ne Central Atom! Write the Lewis structure for hydrogen peroxide (molecular formula, 2 2 ) an important household bleach.
13 Step 1. Place the atoms in the best geometry, with the hydrogen atoms having only one bond, they are on the ends or outside, and oxygen can have up to two bonds so put them in the middle.
14 Step 2. Find the sum of electrons: [2 x (1e - )] + [2 x (6e - )] = 14e - Step 3. Add single bonds and subtract 2e - for each bond: e - -6e - = 8e -
15 Step 4. Add the remaining electron in pairs around the oxygen atoms as hydrogen can only have two! - - -
16 Writing Lewis Structure for Molecules with More than ne Central Atom Write the Lewis structure for methanol (molecular formula C 4 ), an important industrial alcohol that is being used as a gasoline alternative in car engines. C and must be next to each other with filling in the bonds. 4(1) = 14 valence e -. : C :
17 Writing Lewis Structures for Molecules with Multiple Bonds Write the Lewis structure for acetylene(c 2 2 ): Use the first 4 steps: placing atoms, counting electrons, placing single bonds, and completing octets.
18 -C -C - Neither of the carbon atoms has an octet, or if they are placed around one atom, the other has only 4! So no octet! Place both pairs into forming multiple bonds, a triple bond! - C C -
19 Lewis Structures of Simple Molecules C C 4 Methane Cl Cl Cl 2 Chlorine C C C Acetic Acid C Cl Cl C Cl C C 2 Carbon Dioxide C Carbon Monoxide Cl CCl 4 Carbon Tetrachloride 2 Water ydrogen xide
20 .. N N.. C N.. ydrocyanic acid ydrogen Cyanide : CN Nitrogen N 2 Molecular xygen : 2 Ethylene : C C C
21 C C K + Ethyl Alcohol (Ethanol) Cl KCl 3 Potassium Chlorate Note brackets and charge CF 4 F F C F F Carbon Tetrafluoride
22 . N. Ammonia.. N C N N Ammonium Ion Urea
23 Resonance: Symmetrical Molecules zone : 3 I II Which is the correct Lewis Structure?
24 Resonance ybrid Structure ne pair of electron s resonances between the two locations! The bonding pairs create what appears to be 1.5 bonds.
25 In single, double, and triple bonds, the e - pairs are attracted by nuclei of two bonded atoms. The e- pairs are localized. Multiple Lewis Structures are caused by e- pair delocalization.
26 Write resonance structures for the nitrate ion, N 3-. Nitrate has 1(5) + 3(6) + 1 = 24 valence e - N N N N does not have an octet; a pair of e - will move in to form a double bond. N N N
27 Benzene C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C
28 The octet rule can be used as a guide. Some central atoms have fewer than 8 e - around them and some have more.
29 Electron Deficient Molecules Gaseous molecules containing Be or B often have fewer than 8 e - around them. Cl Cl Be Cl B Cl Cl
30 Lewis Structures for ctet Rule Exceptions F F Cl F Each fluorine atom has 8 electrons associated. Chlorine has 10 electrons! Unpaired e- is called a free radical N 2 is an odd electron atom. The nitrogen has 7 electrons.. N
31 Free radicals are paramagnetic and extremely reactive. Thought to be dangerous to body tissue.
32 Expanded Valence Shells Sometimes an atom may expand its valence shell in a process that releases energy. This is done using empty outer level d orbitals as well as the occupied p orbitals.
33 Expanded valence shells only occur in central atoms that are Period 3 elements or higher in which d orbitals are available.
34 Resonance Structures - Expanded Valence F F F S F F F Shells S = 12e - p = 10e - F F P F F Sulfur hexafluoride Phosphorous pentafluoride F S Resonance Structures Sulfuric acid S S = 12e -
35 Writing Lewis Structures for Exceptions to the ctet Rule. Write Lewis structures for (a) 3 P 4 and (b) BFCl 2. In (a) decide on the most likely structure. Draw the Lewis structures for the molecule and determine if there is an element which can be an exception to the octet rule. Note that (a) contains P which is a Period-3 element and can have an expanded valence shell P 0 (a) 3 P 4 has two resonance forms and formal charges indicate the more important form P more stable lower formal charges (b) BFCl 2 will have only 1 Lewis structure. Cl F B Cl
36 Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Model Lewis-Dot structures that give a reasonable picture of how the valence electrons are distributed in a molecule. Lewis-Dot structures do not indicate the shape of the molecule.
37 XeF 4 and CF 4 have different shapes even though the central atom is coordinated by four F atoms. Shape can be resolved by using the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Model. (VSEPR model.)
38 VSEPR Definition: Groups of valence electrons around a central atom stay as far away from each other as possible to minimize repulsion.
39 What do groups mean? X X : X= X X Triple Bond Double Bond Lone Pair Single Bond Unpaired e -
40 Each is a group and will repel other groups. Each will try to occupy as much space as possible around the central atom. Minimizing e - pair repulsions. The bonding and non-bonding pairs around a given atom will be positioned as far apart as possible.
41 There are 5 electron arrangements possible about a central atom and these e - groups will repel each other giving rise to 5 different geometries created by the groups.
42 Electron Groups Around Central Atom 2 Groups Linear
43 3 Groups Trigonal planar 4 Groups Tetrahedral
44 5 Groups Trigonal bipyramidal 6 Groups ctahedral
45 Electron-group repulsions and the five basic molecular shapes. Ideal Bond Angles
46 These electron group geometries give rise to identical molecular geometries if each electron pair group is a bond pair to the same atom. If some of the bonding pairs are nonbonding pairs, different molecular geometries exist for all shapes except for the linear geometry.
47 All molecules considered will be of three atoms or more. Simple two atomed molecules are easily understood with Lewis structures. They must be linear.
48 Classification Notation A = central atom X m = bonded atom E n = lone (unbonded) pair m and n are whole numbers
49 VSEPR Rules for Determining Molecular Shapes Draw the Lewis Structure Determine the number of lone and bonding e - pairs around the central atom. Determine the type structure.axe etc and hence the molecular geometry. Determine the bond angles.
50 Example (1) AX 3 E - geometry = Examples: S 3, BF 3, N 3-, C 3 2- trigonal planar X Molecular geometry = A trigonal planar X X All Bond Angles = 120 o
51 Example Examples: (2) AX 2 E S 2, 3, E - geometry = trigonal planar PbCl 2, SnBr 2 E Molecular geometry A = bent X X Why? Bond Angle < 120 o
52 Bond Angle < 120 o The lone pair is only attracted by the central nucleus and not by another nuclei.
53 Therefore the lone pair can expand (taking up more room) and exert a greater repulsion, squeezing the bond angle between the other 2 bonding atoms down from 120 o. This lp-bp repulsion is greater than bp-bp repulsion.
54 Deviations from ideal occur with the following because their electron clouds take different amounts of space around the central atom. Lone pairs Multiple bonds Different surrounding atom Unpaired electron (requires less space rare)
55 Effect of Double Bonds Ideal C
56 Real C Larger EN Greater Electron Density
57 If there is a double bond, it should affect the bond angle, however N 3 - has three equivalent resonance structures, hence bond angle remains at 120 o. The double bond N could be in any of three positions.
58 Example (3) AX 4 E - geometry = Examples: C 4, SiCl 4, S 4 2-, Cl 4 - tetrahedral Molecular geometry = tetrahedral All Bond Angles = 109 o
59 Example Examples: (4) AX 3 E N 3, PF 3 E - geometry = Cl 3, 3 + tetrahedral Molecular geometry = trigonal pyramidal Bond Angles = o
60 Example (5) AX 2 E 2 E - geometry = Examples: 2, F 2 SCl 2 tetrahedral Molecular geometry = Bent V shaped Bond Angles = 104.5
61 Example (6) AX 5 E - geometry = trigonal Examples: PF 5, AsF 5 SF 4 bipyramidal Molecular geometry =trigonal bipyramidal Bond Angles = Axial = 180 o Equatorial = 120 o
62 Example Examples: (7) AX 4 E SF 4,Xe 2 F 2 E - geometry = trigonal IF 4+, I 2 F 2 - bipyramidal Molecular geometry = see saw Bond Angles reduce to 86.8 o and o respectively
63 Example (8) AX 3 E 2 Examples: ClF 3, BrF 3 E - geometry = trigonal bipyramidal Molecular geometry = T - Shaped Bond Angles: Two 90 0 and one 180 o become 86.2 o and o
64 Example (9) AX 3 E 2 Examples: XeF 2, I 3-, IF 2 - E - geometry = trigonal bipyramidal Molecular geometry = Linear Bond Angles: 180 o
65 Example (10) AX 6 Examples: SF 6, IF 5 E - geometry = ctahedral Molecular geometry = ctahedral Bond Angles: six 90 o and three 180 o
66 Example Examples: (11) AX 5 E BrF 5, TeF 5-, XeF 4 E - geometry = ctahedral Molecular geometry = Square Pyramidal Bond Angles: Many 90 o and 180 o are reduced to less than ideal.
67 Example (12) AX 4 E 2 Examples: XeF 4. ICl 4 - E - geometry = ctahedral Molecular geometry = Square Planar Bond Angles: o and 4 90 o
68 Predicting Molecular Shapes with Two, Three, or Four E - Groups Draw the molecular shape and predict the bond angles (relative to the ideal bond angles) of PF 3 and CCl 2. For PF 3 - there are 26 F P F valence electrons, 1 F nonbonding pair.
69 The shape is based upon the tetrahedral arrangement. The F-P-F bond angles should be < due to F P F F the repulsion of the < nonbonding electron pair. The type of shape is AX 3 E. The final shape is trigonal pyramidal.
70 For CCl 2, C has the lowest EN and will be the center atom. There are 24 valence e -, 3 atoms attached to the center atom. Cl C Cl
71 C does not have an octet; a pair of nonbonding electrons will move in C from the to make a double bond. Cl Cl The shape for an atom with three atom attachments and no nonbonding pairs on the central atom is trigonal planar.
72 Type AX 3 The Cl-C-Cl bond angle will be less than due to the electron density of the C= Cl C Cl
73 Predicting Molecular Shapes with Five or Six Electron Groups Determine the molecular shape and predict the bond angles (relative to the ideal bond angles) of SbF 5 and BrF 5. SbF 5-40 valence e - ; all electrons around central atom will be in bonding pairs.
74 F F F Sb F F Shape is AX 5 - trigonal bipyramidal.
75 BrF 5-42 valence e - ; 5 bonding pairs and 1 nonbonding pair on central atom. Shape is AX 5 E, square pyramidal. F F F Br F F
76 Molecular Geometry CCl 4 S 2 gbr 2 C 2 S 3-2 BF 3 Xe 4 AX 4 AX 2 E AX 2 AX 2 AX 3 E AX 3 AX 4 Tetrahedral Bent Linear Linear Trig. Pyramidal Trig. Planar Tetrahedral
77 Molecular Geometry ICl 3 SeF 6 IF 4 + AsCl 5 I 3-1 I 2 F 2-1 XeF 4 AX 3 E 2 AX 6 AX 4 E AX 5 AX 2 E 3 AX 4 E AX 4 E 2 T-shaped ctahedral See-saw Trig. Pyramidal T-shaped See-saw Square Planar
78 The End
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 10. The Shapes of Molecules 10-1
 Chapter 10 The Shapes of Molecules 10-1 The Shapes of Molecules 10.1 Depicting Molecules and Ions with Lewis Structures 10.2 Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory and Molecular Shape 10.3
Chapter 10 The Shapes of Molecules 10-1 The Shapes of Molecules 10.1 Depicting Molecules and Ions with Lewis Structures 10.2 Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory and Molecular Shape 10.3
10-1. The Shapes of Molecules, chapter 10
 10-1 The Shapes of Molecules, chapter 10 The Shapes of Molecules; Goals 10.1 Depicting Molecules and Ions with Lewis Structures 10.2 Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory 10.3 Molecular
10-1 The Shapes of Molecules, chapter 10 The Shapes of Molecules; Goals 10.1 Depicting Molecules and Ions with Lewis Structures 10.2 Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory 10.3 Molecular
Chapter 9 The Shapes of Molecules Cocaine
 Chapter 9 The Shapes of Molecules 1 Cocaine 10.1 Depicting Molecules & Ions with Lewis Structures 2 Number of Covalent Bonds 3 The number of covalent bonds can be determined from the number of electrons
Chapter 9 The Shapes of Molecules 1 Cocaine 10.1 Depicting Molecules & Ions with Lewis Structures 2 Number of Covalent Bonds 3 The number of covalent bonds can be determined from the number of electrons
Chapter 10. The Shapes of Molecules
 Chapter 10 The Shapes of Molecules Molecules are visualized using Lewis Structures Molecular formula Step 1 Atom placement Step 2 Add A-group numbers ctet Rule Sum of valence e - Step 3 Remaining valence
Chapter 10 The Shapes of Molecules Molecules are visualized using Lewis Structures Molecular formula Step 1 Atom placement Step 2 Add A-group numbers ctet Rule Sum of valence e - Step 3 Remaining valence
Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts
 Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chemical bond: is an attractive force that holds 2 atoms together and forms as a result of interactions between electrons found in combining atoms We rarely
Honors Chemistry Unit 6 ( )
 Honors Chemistry Unit 6 (2017-2018) Lewis Dot Structures VSEPR Structures 1 We are learning to: 1. Represent compounds with Lewis structures. 2. Apply the VSEPR theory to determine the molecular geometry
Honors Chemistry Unit 6 (2017-2018) Lewis Dot Structures VSEPR Structures 1 We are learning to: 1. Represent compounds with Lewis structures. 2. Apply the VSEPR theory to determine the molecular geometry
CHEMICAL BONDING. Chemical Bonds. Ionic Bonding. Lewis Symbols
 CHEMICAL BONDING Chemical Bonds Lewis Symbols Octet Rule whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen
CHEMICAL BONDING Chemical Bonds Lewis Symbols Octet Rule whenever possible, valence electrons in covalent compounds distribute so that each main-group element is surrounded by 8 electrons (except hydrogen
Fill in the chart below to determine the valence electrons of elements 3-10
 Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory IV Name: Date: Block: 1. Lewis Diagrams 2. VSEPR Lewis Diagrams Lewis diagrams show the bonding between atoms of a molecule. Only the outermost electrons of an atom (called electrons)
Chemistry 11 Atomic Theory IV Name: Date: Block: 1. Lewis Diagrams 2. VSEPR Lewis Diagrams Lewis diagrams show the bonding between atoms of a molecule. Only the outermost electrons of an atom (called electrons)
COVALENT BONDING CHEMICAL BONDING I: LEWIS MODEL. Chapter 7
 Chapter 7 P a g e 1 COVALENT BONDING Covalent Bonds Covalent bonds occur between two or more nonmetals. The two atoms share electrons between them, composing a molecule. Covalently bonded compounds are
Chapter 7 P a g e 1 COVALENT BONDING Covalent Bonds Covalent bonds occur between two or more nonmetals. The two atoms share electrons between them, composing a molecule. Covalently bonded compounds are
Lewis structures show the number and type of bonds between atoms in a molecule or polyatomic ion.
 VSEPR & Geometry Lewis structures show the number and type of bonds between atoms in a molecule or polyatomic ion. Lewis structures are not intended to show the 3-dimensional structure (i.e. shape or geometry)
VSEPR & Geometry Lewis structures show the number and type of bonds between atoms in a molecule or polyatomic ion. Lewis structures are not intended to show the 3-dimensional structure (i.e. shape or geometry)
VSEPR Theory. Shapes of Molecules. Molecular Structure or Molecular Geometry
 VSEPR Theory VSEPR Theory Shapes of Molecules Molecular Structure or Molecular Geometry The 3-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that make-up a molecule. Determines several properties of a substance,
VSEPR Theory VSEPR Theory Shapes of Molecules Molecular Structure or Molecular Geometry The 3-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that make-up a molecule. Determines several properties of a substance,
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometries. and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories Coverage of Chapter 9 9.1 All 9.2 All 9.3 All 9.4 All 9.5 Omit Hybridization Involving d Orbitals 9.6 All 9.7 and 9.8 Omit ALL MOLECULAR SHAPES The shape
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories Coverage of Chapter 9 9.1 All 9.2 All 9.3 All 9.4 All 9.5 Omit Hybridization Involving d Orbitals 9.6 All 9.7 and 9.8 Omit ALL MOLECULAR SHAPES The shape
Bonding: Part Two. Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond. transfer valence e - Metallic bond. (NaCl) (Fe) mobile valence e - Covalent bond
 Bonding: Part Two Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond transfer valence e - Metallic bond mobile valence e - Covalent bond (NaCl) (Fe) shared valence e - (H 2 O) 1 Single Covalent Bond H + H H H H-atoms H
Bonding: Part Two Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond transfer valence e - Metallic bond mobile valence e - Covalent bond (NaCl) (Fe) shared valence e - (H 2 O) 1 Single Covalent Bond H + H H H H-atoms H
Bonding: Part Two. Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond. transfer valence e - Metallic bond. (NaCl) (Fe) mobile valence e - Covalent bond
 Bonding: Part Two Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond transfer valence e - Metallic bond mobile valence e - Covalent bond (NaCl) (Fe) shared valence e - (H 2 O) 1 Single Covalent Bond H + H H H H-atoms H
Bonding: Part Two Three types of bonds: Ionic Bond transfer valence e - Metallic bond mobile valence e - Covalent bond (NaCl) (Fe) shared valence e - (H 2 O) 1 Single Covalent Bond H + H H H H-atoms H
Chapter 13: Phenomena
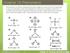 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
CHM2045 F13--Exam # MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 CHM2045 F13--Exam #2 2013.10.18 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A valid Lewis structure of cannot be drawn without violating the
CHM2045 F13--Exam #2 2013.10.18 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A valid Lewis structure of cannot be drawn without violating the
Name Unit Three MC Practice March 15, 2017
 Unit Three: Bonding & Molecular Geometry Name Unit Three MC Practice March 15, 2017 1. What is the hybridization of the oxygen atom in water? a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) It is not hybridized 2. When a double
Unit Three: Bonding & Molecular Geometry Name Unit Three MC Practice March 15, 2017 1. What is the hybridization of the oxygen atom in water? a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) It is not hybridized 2. When a double
Chapter 9. Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Topics Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry and Polarity Valence Bond Theory Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Hybridization in Molecules
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Topics Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry and Polarity Valence Bond Theory Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Hybridization in Molecules
Instant download Test bank for Chemistry The Central Science 10th Edition by Brown, LeMay, Bursten CLICK HERE
 Chemistry, 10e (Brown) Chapter 9, Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Instant download Test bank for Chemistry The Central Science 10th Edition by Brown, LeMay, Bursten CLICK HERE http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-chemistry-the-central-science-10th-edition-by-brown-lemay-bursten/
Chemistry, 10e (Brown) Chapter 9, Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Instant download Test bank for Chemistry The Central Science 10th Edition by Brown, LeMay, Bursten CLICK HERE http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-chemistry-the-central-science-10th-edition-by-brown-lemay-bursten/
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry. Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory
 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Sulfanilamide Lewis Structures and the Real 3D-Shape of Molecules Lewis Theory of Molecular Shape and Polarity
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Sulfanilamide Lewis Structures and the Real 3D-Shape of Molecules Lewis Theory of Molecular Shape and Polarity
Chemical Bonding II. Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Phys./Chem. Properties Quantum Mechanics Sigma & Pi bonds Hybridization MO theory
 Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Phys./Chem. Properties Quantum Mechanics Sigma & Pi bonds ybridization MO theory 1 Molecular Geometry 3-D arrangement of atoms 2 VSEPR Valence-shell
Chemical Bonding II Molecular Geometry Valence Bond Theory Phys./Chem. Properties Quantum Mechanics Sigma & Pi bonds ybridization MO theory 1 Molecular Geometry 3-D arrangement of atoms 2 VSEPR Valence-shell
Lewis Structure and Electron Dot Models
 Lewis Structure and Electron Dot Models The Lewis Structure is a method of displaying the electrons present in any given atom or compound. Steps: 1. Make a skeleton structure 2. Count all e- available
Lewis Structure and Electron Dot Models The Lewis Structure is a method of displaying the electrons present in any given atom or compound. Steps: 1. Make a skeleton structure 2. Count all e- available
Chapters 8 and 9. Octet Rule Breakers Shapes
 Chapters 8 and 9 Octet Rule Breakers Shapes Bond Energies Bond Energy (review): The energy needed to break one mole of covalent bonds in the gas phase Breaking bonds consumes energy; forming bonds releases
Chapters 8 and 9 Octet Rule Breakers Shapes Bond Energies Bond Energy (review): The energy needed to break one mole of covalent bonds in the gas phase Breaking bonds consumes energy; forming bonds releases
2011, Robert Ayton. All rights reserved.
 Chemical Bonding Outline 1. Lewis Dot Structures 2. Bonds 3. Formal Charges 4. VSEPR (Molecular Geometry and Hybridzation) 5. Common Resonance Structures and Dimerization Review 1. Lewis Dot Structures
Chemical Bonding Outline 1. Lewis Dot Structures 2. Bonds 3. Formal Charges 4. VSEPR (Molecular Geometry and Hybridzation) 5. Common Resonance Structures and Dimerization Review 1. Lewis Dot Structures
Helpful Hints Lewis Structures Octet Rule For Lewis structures of covalent compounds least electronegative
 Helpful Hints Lewis Structures Octet Rule Lewis structures are a basic representation of how atoms are arranged in compounds based on bond formation by the valence electrons. A Lewis dot symbol of an atom
Helpful Hints Lewis Structures Octet Rule Lewis structures are a basic representation of how atoms are arranged in compounds based on bond formation by the valence electrons. A Lewis dot symbol of an atom
4.2.7 & Shapes, and bond angles for molecules with two, three and four negative charge centers
 4.2.7 & 4.2.8 Shapes, and bond angles for molecules with two, three and four negative charge centers The shape of a molecule has an important part to play in determining its chemical (e.g. reactivity and
4.2.7 & 4.2.8 Shapes, and bond angles for molecules with two, three and four negative charge centers The shape of a molecule has an important part to play in determining its chemical (e.g. reactivity and
CHEMISTRY. Chapter 10 Theories of Bonding and Structure. The Molecular Nature of Matter. Jespersen Brady Hyslop SIXTH EDITION
 CHEMISTRY The Molecular Nature of Matter SIXTH EDITION Jespersen Brady Hyslop Chapter 10 Theories of Bonding and Structure Copyright 2012 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Molecular Structures Molecules containing
CHEMISTRY The Molecular Nature of Matter SIXTH EDITION Jespersen Brady Hyslop Chapter 10 Theories of Bonding and Structure Copyright 2012 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Molecular Structures Molecules containing
Ch 10 Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structures for Ionic & Covalent Compounds, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules
 Fructose Water Ch 10 Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structures for Ionic & Covalent Compounds, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules Carbon Dioxide Ammonia Title and Highlight TN Ch 10.1 Topic: EQ: Right Side NOTES
Fructose Water Ch 10 Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structures for Ionic & Covalent Compounds, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules Carbon Dioxide Ammonia Title and Highlight TN Ch 10.1 Topic: EQ: Right Side NOTES
Chemical Bonding AP Chemistry Ms. Grobsky
 Chemical Bonding AP Chemistry Ms. Grobsky What Determines the Type of Bonding in Any Substance? Why do Atoms Bond? The key to answering the first question are found in the electronic structure of the atoms
Chemical Bonding AP Chemistry Ms. Grobsky What Determines the Type of Bonding in Any Substance? Why do Atoms Bond? The key to answering the first question are found in the electronic structure of the atoms
Check Your Solution A comparison with the figures in Figure 4.31 on page 234 of the student textbook confirms the results.
 Predicting the Shape of a Molecule (Student textbook page 236) 11. What molecular shape is represented by each of the following VSEPR notations? a. AX 3 b. AX 5 E You need to assign a molecular shape that
Predicting the Shape of a Molecule (Student textbook page 236) 11. What molecular shape is represented by each of the following VSEPR notations? a. AX 3 b. AX 5 E You need to assign a molecular shape that
Shapes of Molecules. Lewis structures are useful but don t allow prediction of the shape of a molecule.
 Shapes of Molecules Lewis structures are useful but don t allow prediction of the shape of a molecule. H O H H O H Can use a simple theory based on electron repulsion to predict structure (for non-transition
Shapes of Molecules Lewis structures are useful but don t allow prediction of the shape of a molecule. H O H H O H Can use a simple theory based on electron repulsion to predict structure (for non-transition
Test bank for Chemistry The Central Science 10th Edition by Brown, LeMay, Bursten
 Test bank for Chemistry The Central Science 10th Edition by Brown, LeMay, Bursten Chapter 9, Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Multiple-Choice and Bimodal 1) For a molecule with the formula A) linear
Test bank for Chemistry The Central Science 10th Edition by Brown, LeMay, Bursten Chapter 9, Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Multiple-Choice and Bimodal 1) For a molecule with the formula A) linear
Molecular shape is determined by the number of bonds that form around individual atoms.
 Chapter 9 CH 180 Major Concepts: Molecular shape is determined by the number of bonds that form around individual atoms. Sublevels (s, p, d, & f) of separate atoms may overlap and result in hybrid orbitals
Chapter 9 CH 180 Major Concepts: Molecular shape is determined by the number of bonds that form around individual atoms. Sublevels (s, p, d, & f) of separate atoms may overlap and result in hybrid orbitals
Test Bank for Introductory Chemistry Essentials 5th Edition by Tro
 Test Bank for Introductory Chemistry Essentials 5th Edition by Tro Sample Introductory Chemistry, 5e (Tro) Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding 10.1 True/False Questions 1) Bonding theories are used to predict
Test Bank for Introductory Chemistry Essentials 5th Edition by Tro Sample Introductory Chemistry, 5e (Tro) Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding 10.1 True/False Questions 1) Bonding theories are used to predict
bond energy- energy required to break a chemical bond -We can measure bond energy to determine strength of interaction
 bond energy- energy required to break a chemical bond -We can measure bond energy to determine strength of interaction ionic compound- a metal reacts with a nonmetal Ionic bonds form when an atom that
bond energy- energy required to break a chemical bond -We can measure bond energy to determine strength of interaction ionic compound- a metal reacts with a nonmetal Ionic bonds form when an atom that
Molecular Geometry. Objectives N H H. The objectives of this laboratory are to:
 Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are to: Molecular Geometry Write Lewis structure representations of the bonding and valence electrons in molecules. Use the VSEPR model to predict the molecular
Objectives The objectives of this laboratory are to: Molecular Geometry Write Lewis structure representations of the bonding and valence electrons in molecules. Use the VSEPR model to predict the molecular
CHAPTER 5: Bonding Theories - Explaining Molecular Geometry. Chapter Outline
 CHAPTER 5: Bonding Theories - Explaining Molecular Geometry Chapter Outline 5.1 Molecular Shape 5.2 Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR) 5.3 Polar Bonds and Polar Molecules» What Makes
CHAPTER 5: Bonding Theories - Explaining Molecular Geometry Chapter Outline 5.1 Molecular Shape 5.2 Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR) 5.3 Polar Bonds and Polar Molecules» What Makes
Chapter 9: Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory. Lewis Theory: An Overview
 Chapter 9: Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory Dr. Chris Kozak Memorial University of ewfoundland, Canada Lewis Theory: An verview Valence e - play a fundamental role in chemical bonding. e - transfer leads
Chapter 9: Chemical Bonding I: Lewis Theory Dr. Chris Kozak Memorial University of ewfoundland, Canada Lewis Theory: An verview Valence e - play a fundamental role in chemical bonding. e - transfer leads
CHM 151LL: Geometry of Covalent Compounds
 CM 151LL: Geometry of Covalent Compounds Introduction Octet Rule A Lewis structure (or electrondot formula) is a twodimensional structural formula showing the arrangement of electrons around atoms in covalently
CM 151LL: Geometry of Covalent Compounds Introduction Octet Rule A Lewis structure (or electrondot formula) is a twodimensional structural formula showing the arrangement of electrons around atoms in covalently
Practice Worksheet for Lewis Structures (Mahaffy Ch )
 Practice Worksheet for Lewis Structures (Mahaffy Ch. 10.1 10.5 ) 1. Main concepts Lewis Structures a. Connectivity b. Bonds & Lone pairs c. Electron Geometry & Molecular Shape d. Resonance Structures Formal
Practice Worksheet for Lewis Structures (Mahaffy Ch. 10.1 10.5 ) 1. Main concepts Lewis Structures a. Connectivity b. Bonds & Lone pairs c. Electron Geometry & Molecular Shape d. Resonance Structures Formal
Molecular Geometry. Valence Shell Electron Pair. What Determines the Shape of a Molecule? Repulsion Theory (VSEPR) Localized Electron Model
 Molecular Geometry Learn Shapes you will Because the physical and chemical properties of compounds are tied to their structures, the importance of molecular geometry can not be overstated. Localized Electron
Molecular Geometry Learn Shapes you will Because the physical and chemical properties of compounds are tied to their structures, the importance of molecular geometry can not be overstated. Localized Electron
General and Inorganic Chemistry I.
 General and Inorganic Chemistry I. Lecture 1 István Szalai Eötvös University István Szalai (Eötvös University) Lecture 1 1 / 29 Outline István Szalai (Eötvös University) Lecture 1 2 / 29 Lewis Formulas
General and Inorganic Chemistry I. Lecture 1 István Szalai Eötvös University István Szalai (Eötvös University) Lecture 1 1 / 29 Outline István Szalai (Eötvös University) Lecture 1 2 / 29 Lewis Formulas
Chemistry and the material world Lecture 3
 Chemistry and the material world 123.102 Lecture 3 Electronic bookkeeping we need a way of finding out in which proportions two or more atoms make up a molecule is it CH 3 or CH 4 or CH 5? counting valence
Chemistry and the material world 123.102 Lecture 3 Electronic bookkeeping we need a way of finding out in which proportions two or more atoms make up a molecule is it CH 3 or CH 4 or CH 5? counting valence
Experiment 15. The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory of Directed Valency: An exercise
 Experiment 15 The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory of Directed Valency: An exercise Attempts to understand and predict the shapes of molecules using either the valencebond theory or
Experiment 15 The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory of Directed Valency: An exercise Attempts to understand and predict the shapes of molecules using either the valencebond theory or
Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, Valence Bond Theory, and Molecular Orbital Theory
 10.1 Artificial Sweeteners: Fooled by Molecular Shape 425 10.2 VSEPR Theory: The Five Basic Shapes 426 10.3 VSEPR Theory: The Effect of Lone Pairs 430 10.4 VSEPR Theory: Predicting Molecular Geometries
10.1 Artificial Sweeteners: Fooled by Molecular Shape 425 10.2 VSEPR Theory: The Five Basic Shapes 426 10.3 VSEPR Theory: The Effect of Lone Pairs 430 10.4 VSEPR Theory: Predicting Molecular Geometries
Valence Shell Electron Pair repulsion
 Molecular Geometry Valence Shell Electron Pair repulsion The valence shell electron pair repulsion model (VSEPR model) assumes that electron pairs repel one another. (VSEPR) model gives helps determine
Molecular Geometry Valence Shell Electron Pair repulsion The valence shell electron pair repulsion model (VSEPR model) assumes that electron pairs repel one another. (VSEPR) model gives helps determine
Chemistry 212 MOLECULAR STRUCTURES AND GEOMETRIES
 Chemistry 212 MOLECULAR STRUCTURES AND GEOMETRIES LEARNING OBJECTIVES To build models of selected molecules using VSEPR theory. To illustrate patterns of molecular shapes. BACKGROUND The shapes exhibited
Chemistry 212 MOLECULAR STRUCTURES AND GEOMETRIES LEARNING OBJECTIVES To build models of selected molecules using VSEPR theory. To illustrate patterns of molecular shapes. BACKGROUND The shapes exhibited
CHEMISTRY 112 LECTURE EXAM II Material
 CHEMISTRY 112 LECTURE EXAM II Material Part I Chemical Bonding I Lewis Theory Chapter 9 pages 376-386 A. Drawing electron dot structures HOW TO: 1. Write e- dot structure for the individual atoms. 2. a)
CHEMISTRY 112 LECTURE EXAM II Material Part I Chemical Bonding I Lewis Theory Chapter 9 pages 376-386 A. Drawing electron dot structures HOW TO: 1. Write e- dot structure for the individual atoms. 2. a)
(A) 1 bonding pair (B) 1 bonding pair and 1 lone pair (C) 2 bonding pairs (D) 2 bonding pairs and 2 lone pairs
 AP Chemistry - Problem Drill 13: Lewis Structures and VSPER No. 1 of 10 1. Lewis structure is used to model covalent bonds of a molecule or ion. Covalent bonds are a type of chemical bonding formed by
AP Chemistry - Problem Drill 13: Lewis Structures and VSPER No. 1 of 10 1. Lewis structure is used to model covalent bonds of a molecule or ion. Covalent bonds are a type of chemical bonding formed by
REVIEW: VALENCE ELECTRONS CHEMICAL BONDS: LEWIS SYMBOLS: CHEMICAL BONDING. What are valence electrons?
 REVIEW: VALENCE ELECTRONS 13 CHEMICAL BONDING What are valence electrons? Which groups on the periodic table readily give up electrons? What group readily accepts electrons? CHEMICAL BONDS: What are chemical
REVIEW: VALENCE ELECTRONS 13 CHEMICAL BONDING What are valence electrons? Which groups on the periodic table readily give up electrons? What group readily accepts electrons? CHEMICAL BONDS: What are chemical
What Do Molecules Look Like?
 What Do Molecules Look Like? The Lewis Dot Structure approach provides some insight into molecular structure in terms of bonding, but what about 3D geometry? Recall that we have two types of electron pairs:
What Do Molecules Look Like? The Lewis Dot Structure approach provides some insight into molecular structure in terms of bonding, but what about 3D geometry? Recall that we have two types of electron pairs:
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 10
 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 10 Linear Trigonal 180 o planar 120 o Tetrahedral 109.5 o Trigonal Bipyramidal 120 and 90 o Octahedral 90 o linear Linear
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Chapter 10 Linear Trigonal 180 o planar 120 o Tetrahedral 109.5 o Trigonal Bipyramidal 120 and 90 o Octahedral 90 o linear Linear
Lewis Structure. Lewis Structures & VSEPR. Octet & Duet Rules. Steps for drawing Lewis Structures
 Lewis Structure Lewis Structures & VSEPR Lewis Structures shows how the are arranged among the atoms of a molecule There are rules for Lewis Structures that are based on the formation of a Atoms want to
Lewis Structure Lewis Structures & VSEPR Lewis Structures shows how the are arranged among the atoms of a molecule There are rules for Lewis Structures that are based on the formation of a Atoms want to
A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE ETHANOL! Count valence electrons
 212 A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE Count valence electrons Pick central atom and draw skeletal structure - central atom is usually the one that needs to gain the most electrons! - skeletal structure
212 A DOT STRUCTURE FOR A LARGER MOLECULE Count valence electrons Pick central atom and draw skeletal structure - central atom is usually the one that needs to gain the most electrons! - skeletal structure
Lecture outline: Section 9. theory 2. Valence bond theory 3. Molecular orbital theory. S. Ensign, Chem. 1210
 Lecture outline: Section 9 Molecular l geometry and bonding theories 1. Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory 2. Valence bond theory 3. Molecular orbital theory 1 Ionic bonding Covalent bonding
Lecture outline: Section 9 Molecular l geometry and bonding theories 1. Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory 2. Valence bond theory 3. Molecular orbital theory 1 Ionic bonding Covalent bonding
SHAPES OF MOLECULES (VSEPR MODEL)
 1 SAPES MLEULES (VSEPR MDEL) Valence Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion model - Electron pairs surrounding atom spread out as to minimize repulsion. - Electron pairs can be bonding pairs (including multiple
1 SAPES MLEULES (VSEPR MDEL) Valence Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion model - Electron pairs surrounding atom spread out as to minimize repulsion. - Electron pairs can be bonding pairs (including multiple
Covalent Bonding and Molecular Structure (key)
 ovalent Bonding and Molecular Structure (key) AX 2 : 2 1. What is the bond angle? 180 2. Which element is more electronegative, carbon, or oxygen? xygen 3. Would you expect 2 to be a polar or a nonpolar
ovalent Bonding and Molecular Structure (key) AX 2 : 2 1. What is the bond angle? 180 2. Which element is more electronegative, carbon, or oxygen? xygen 3. Would you expect 2 to be a polar or a nonpolar
Structures, Shapes and Polarity. of Molecules. Level 2 recap: - Polar and non polar bonds - Lewis diagrams - Lone pairs - Shapes - Polarity
 Structures, Shapes and Polarity Level 2 recap: - Polar and non polar bonds - Lewis diagrams - Lone pairs - Shapes - Polarity of Molecules Do now: Brainstorm what you know/remember about these L2 concepts
Structures, Shapes and Polarity Level 2 recap: - Polar and non polar bonds - Lewis diagrams - Lone pairs - Shapes - Polarity of Molecules Do now: Brainstorm what you know/remember about these L2 concepts
Chapter 4. Molecular Structure and Orbitals
 Chapter 4 Molecular Structure and Orbitals Chapter 4 Table of Contents (4.1) (4.2) (4.3) (4.4) (4.5) (4.6) (4.7) Molecular structure: The VSEPR model Bond polarity and dipole moments Hybridization and
Chapter 4 Molecular Structure and Orbitals Chapter 4 Table of Contents (4.1) (4.2) (4.3) (4.4) (4.5) (4.6) (4.7) Molecular structure: The VSEPR model Bond polarity and dipole moments Hybridization and
Subtopic 4.2 MOLECULAR SHAPE AND POLARITY
 Subtopic 4.2 MOLECULAR SHAPE AND POLARITY 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES (covalent bonding) 1. Draw the Lewis structure of covalent molecules (octet rule such as NH 3, CCl 4, H 2 O, CO 2, N 2 O 4, and exception to
Subtopic 4.2 MOLECULAR SHAPE AND POLARITY 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES (covalent bonding) 1. Draw the Lewis structure of covalent molecules (octet rule such as NH 3, CCl 4, H 2 O, CO 2, N 2 O 4, and exception to
AP Chemistry. Unit #7. Chemical Bonding & Molecular Shape. Zumdahl Chapters 8 & 9 TYPES OF BONDING BONDING. Discrete molecules formed
 AP Chemistry Unit #7 Chemical Bonding & Molecular Shape Zumdahl Chapters 8 & 9 TYPES OF BONDING BONDING INTRA (Within (inside) compounds) STRONG INTER (Interactions between the molecules of a compound)
AP Chemistry Unit #7 Chemical Bonding & Molecular Shape Zumdahl Chapters 8 & 9 TYPES OF BONDING BONDING INTRA (Within (inside) compounds) STRONG INTER (Interactions between the molecules of a compound)
EXAM II Material. Part I Chemical Bonding I Lewis Theory Chapter 9 pages A. Drawing electron dot structures HOW TO:
 CHEMISTRY 112 LECTURE EXAM II Material Part I Chemical Bonding I Lewis Theory Chapter 9 pages 376-386 A. Drawing electron dot structures HOW TO: 1. Write e- dot structure for the individual atoms. 2. a)
CHEMISTRY 112 LECTURE EXAM II Material Part I Chemical Bonding I Lewis Theory Chapter 9 pages 376-386 A. Drawing electron dot structures HOW TO: 1. Write e- dot structure for the individual atoms. 2. a)
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Activity Formal Charge and VSEPR Theory for Expanded Octets
 Activity 201 7 Formal Charge and VSEPR Theory for Expanded Octets Directions: This Guided Learning Activity (GLA) goes over formal charge and the structures of molecules with expanded octets. Part A introduces
Activity 201 7 Formal Charge and VSEPR Theory for Expanded Octets Directions: This Guided Learning Activity (GLA) goes over formal charge and the structures of molecules with expanded octets. Part A introduces
Chapter 8 H H H H. Molecular Compounds & Covalent Bonding. Why do covalent bonds form? 8.1 Molecular Compounds. Properties of Molecular Compounds
 Chapter 8 Molecular Compounds & Covalent Bonding Why do covalent bonds form? If only group 5A, 6A, 7A atoms existed, ionic bonds can t form. NNMETALS Each atom needs electrons so they are not willing to
Chapter 8 Molecular Compounds & Covalent Bonding Why do covalent bonds form? If only group 5A, 6A, 7A atoms existed, ionic bonds can t form. NNMETALS Each atom needs electrons so they are not willing to
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 9.1 Molecular Shapes Read Sec. 9.1 and 9.2, then complete the Sample and Practice Exercises in these sections. Sample Exercise 9.1 (p. 347) Use the VSEPR model to predict the molecular geometries of a)
9.1 Molecular Shapes Read Sec. 9.1 and 9.2, then complete the Sample and Practice Exercises in these sections. Sample Exercise 9.1 (p. 347) Use the VSEPR model to predict the molecular geometries of a)
Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts
 Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chapter 9 Chang & Goldsby Modified by Dr. Hahn Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent
Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts Chapter 9 Chang & Goldsby Modified by Dr. Hahn Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent
Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure
 CHM 123 Chapter 8 Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure 8.1 Molecular shapes and VSEPR theory VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of
CHM 123 Chapter 8 Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure 8.1 Molecular shapes and VSEPR theory VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of
Theories of Covalent Bonding Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals
 Chapter 10 Theories of Covalent Bonding and ybridization of Atomic Orbitals Drawing Lewis Structures 1) Place least electronegative element as the central atom. Recognize that C,S,P and N are often central
Chapter 10 Theories of Covalent Bonding and ybridization of Atomic Orbitals Drawing Lewis Structures 1) Place least electronegative element as the central atom. Recognize that C,S,P and N are often central
EXPERIMENT #13 Lewis Structures and Molecular Geometry
 OBJECTIVES: EXPERIMENT #13 s and Draw Lewis structures of atoms, ions, and molecules Build models of linear, trigonal planar tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral arrangements of electron pairs
OBJECTIVES: EXPERIMENT #13 s and Draw Lewis structures of atoms, ions, and molecules Build models of linear, trigonal planar tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, and octahedral arrangements of electron pairs
Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 8 Outline Bonding: General Concepts
 Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 8 Outline Bonding: General Concepts Types of Chemical Bonds Information about the strength of a bonding interaction is obtained by measuring the bond energy, which is the energy
Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 8 Outline Bonding: General Concepts Types of Chemical Bonds Information about the strength of a bonding interaction is obtained by measuring the bond energy, which is the energy
Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals
 Chemical Bonding II: and ybridization of Atomic rbitals Chapter 10 Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) model: Predict the geometry of the molecule from the electrostatic repulsions between the
Chemical Bonding II: and ybridization of Atomic rbitals Chapter 10 Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) model: Predict the geometry of the molecule from the electrostatic repulsions between the
Announcements. 10pm Room assignments for Exam III and TA Exam Review Sessions are posted on website. Look under Exam Info link
 Announcements 1. Exam #3: Thursday, Dec. 6 th, 7:00-8:15pm (Conflict: 5:15-6:30pm) No calculators allowed 2. Activity 3: Making Models of Molecules lab write-up due tomorrow in discussion 3. Lon-capa HW
Announcements 1. Exam #3: Thursday, Dec. 6 th, 7:00-8:15pm (Conflict: 5:15-6:30pm) No calculators allowed 2. Activity 3: Making Models of Molecules lab write-up due tomorrow in discussion 3. Lon-capa HW
Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
 Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Three Types of Chemical Bonding (1) Ionic: formed by electron transfer (2) Covalent: formed by electron sharing (3) Metallic: attraction between metal
Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Three Types of Chemical Bonding (1) Ionic: formed by electron transfer (2) Covalent: formed by electron sharing (3) Metallic: attraction between metal
11/14/2014. Chemical Bonding. Richard Philips Feynman, Nobel Laureate in Physics ( )
 Chemical Bonding Lewis Theory Valence Bond VSEPR Molecular rbital Theory 1 "...he [his father] knew the difference between knowing the name of something and knowing something" Richard Philips eynman, Nobel
Chemical Bonding Lewis Theory Valence Bond VSEPR Molecular rbital Theory 1 "...he [his father] knew the difference between knowing the name of something and knowing something" Richard Philips eynman, Nobel
Lewis Dot Formulas and Molecular Shapes
 Lewis Dot Formulas and Molecular Shapes Introduction A chemical bond is an intramolecular (within the molecule) force holding two or more atoms together. Covalent chemical bonds are formed by valence electrons
Lewis Dot Formulas and Molecular Shapes Introduction A chemical bond is an intramolecular (within the molecule) force holding two or more atoms together. Covalent chemical bonds are formed by valence electrons
Section 12: Lewis Structures
 Section 12: Lewis Structures The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 12.01 Electronegativity Chemistry (5)(C) 12.02 Electron
Section 12: Lewis Structures The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Science TAC 112.35(c). 12.01 Electronegativity Chemistry (5)(C) 12.02 Electron
EXPERIMENT 12: MOLECULAR ARCHITECTURE
 Name Section EXPERIMENT 12: MLECULAR ARCITECTURE PRE-LABRATRY QUESTINS The following preparatory questions should be answered before coming to lab. They are intended to introduce you to several ideas important
Name Section EXPERIMENT 12: MLECULAR ARCITECTURE PRE-LABRATRY QUESTINS The following preparatory questions should be answered before coming to lab. They are intended to introduce you to several ideas important
8.2 Hybrid Atomic Orbitals
 420 Chapter 8 Advanced Theories of Covalent Bonding Answer: (a) is a π bond with a node along the axis connecting the nuclei while (b) and (c) are σ bonds that overlap along the axis. 8.2 Hybrid Atomic
420 Chapter 8 Advanced Theories of Covalent Bonding Answer: (a) is a π bond with a node along the axis connecting the nuclei while (b) and (c) are σ bonds that overlap along the axis. 8.2 Hybrid Atomic
LET S FIRST REVIEW IONIC BONDING
 COVALENT BONDING LET S FIRST REVIEW IONIC BONDING In an IONIC bond, electrons are lost or gained, resulting in the formation of IONS in ionic compounds. K F K F K F K F K F K F K + F _ The compound potassium
COVALENT BONDING LET S FIRST REVIEW IONIC BONDING In an IONIC bond, electrons are lost or gained, resulting in the formation of IONS in ionic compounds. K F K F K F K F K F K F K + F _ The compound potassium
Chem 105 Friday, 5 Nov 2010
 Chem 105 riday, 5 Nov 2010 Lewis formula practice Sub-octet and expanded-octet molecules Molecular geometry Electron pair geometry vs. molecular geometry 11/5/2010 1 The preferred Lewis formula for CN
Chem 105 riday, 5 Nov 2010 Lewis formula practice Sub-octet and expanded-octet molecules Molecular geometry Electron pair geometry vs. molecular geometry 11/5/2010 1 The preferred Lewis formula for CN
Shapes of Molecules and Hybridization
 Shapes of Molecules and Hybridization A. Molecular Geometry Lewis structures provide us with the number and types of bonds around a central atom, as well as any NB electron pairs. They do not tell us the
Shapes of Molecules and Hybridization A. Molecular Geometry Lewis structures provide us with the number and types of bonds around a central atom, as well as any NB electron pairs. They do not tell us the
Chapter 10. VSEPR Model: Geometries
 Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry VSEPR Model: Geometries Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Electron pairs repel and get as far apart as possible Example: Water Four electron pairs Farthest apart
Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry VSEPR Model: Geometries Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Electron pairs repel and get as far apart as possible Example: Water Four electron pairs Farthest apart
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Geometry James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Shapes Lewis Structures show bonding and lone pairs, but do not denote shape. However, we use Lewis Structures to
Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Geometry James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Shapes Lewis Structures show bonding and lone pairs, but do not denote shape. However, we use Lewis Structures to
At the end of this lesson, students should be able to :
 At the end of this lesson, students should be able to : (a) Explain Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory (VSEPR) (b) Draw the basic molecular shapes: linear, planar, tetrahedral, and octahedral.
At the end of this lesson, students should be able to : (a) Explain Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory (VSEPR) (b) Draw the basic molecular shapes: linear, planar, tetrahedral, and octahedral.
Covalent Bonding and Molecular Structures
 CHAPTERS 9 AND 10 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Structures Objectives You will be able to: 1. Write a description of the formation of the covalent bond between two hydrogen atoms to form a hydrogen molecule.
CHAPTERS 9 AND 10 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Structures Objectives You will be able to: 1. Write a description of the formation of the covalent bond between two hydrogen atoms to form a hydrogen molecule.
Chapter 10. Geometry
 Chapter 10 Molec cular Geometry 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE Molecular Geometry Molecular Polarity VSEPR Model Summary of Molecular Shapes Hybridization Molecular Orbital Theory Bond Angles 2 MOLECULAR GEOMETRY Molecular
Chapter 10 Molec cular Geometry 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE Molecular Geometry Molecular Polarity VSEPR Model Summary of Molecular Shapes Hybridization Molecular Orbital Theory Bond Angles 2 MOLECULAR GEOMETRY Molecular
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories PART I Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories PART I Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Introduction to VSEPR Theory 1
 1 Class 8: Introduction to VSEPR Theory Sec 10.2 VSEPR Theory: The Five Basic Shapes Two Electron Groups: Linear Geometry Three Electron Groups: Trigonal Planar Geometry Four Electron Groups: Tetrahedral
1 Class 8: Introduction to VSEPR Theory Sec 10.2 VSEPR Theory: The Five Basic Shapes Two Electron Groups: Linear Geometry Three Electron Groups: Trigonal Planar Geometry Four Electron Groups: Tetrahedral
Chapter 12. Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Chapter 12 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonding Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer shell (highest energy level) of an atom. A chemical bond is a mutual
Chapter 12 Chemical Bonding Chapter 12 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Chemical Bonding Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer shell (highest energy level) of an atom. A chemical bond is a mutual
Chemical Bonding. Types of Bonds. Ionic Bonding. Resonance Structures. Molecular Geometries. VSEPR Basic Shapes 3-D Notation Hybridization (Lab)
 Chemical Bonding Types of Bonds Ionic Bonding Lewis Structures Covalent Bonding Resonance Structures Octet Rule Polar Molecules Molecular Geometries VSEPR Basic Shapes 3-D Notation Hybridization (Lab)
Chemical Bonding Types of Bonds Ionic Bonding Lewis Structures Covalent Bonding Resonance Structures Octet Rule Polar Molecules Molecular Geometries VSEPR Basic Shapes 3-D Notation Hybridization (Lab)
Chapter 4 Lecture Outline. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 4 Lecture Outline 1 Copyright McGraw-ill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 4.1 Introduction to Covalent Bonding Covalent bonds result from the sharing of electrons between
Chapter 4 Lecture Outline 1 Copyright McGraw-ill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display. 4.1 Introduction to Covalent Bonding Covalent bonds result from the sharing of electrons between
This is Molecular Geometry and Covalent Bonding Models, chapter 9 from the book Principles of General Chemistry (index.html) (v. 1.0M).
 This is Molecular Geometry and Covalent Bonding Models, chapter 9 from the book Principles of General Chemistry (index.html) (v. 1.0M). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
This is Molecular Geometry and Covalent Bonding Models, chapter 9 from the book Principles of General Chemistry (index.html) (v. 1.0M). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
Chapter 9: Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories Learning Outcomes: Predict the three-dimensional shapes of molecules using the VSEPR model.
 Chapter 9: Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories Learning Outcomes: Predict the three-dimensional shapes of molecules using the VSEPR model. Determine whether a molecule is polar or nonpolar based
Chapter 9: Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories Learning Outcomes: Predict the three-dimensional shapes of molecules using the VSEPR model. Determine whether a molecule is polar or nonpolar based
PART 3 Chemical Bonds, Valence Bond Method, and Molecular Shapes. Reference: Chapter 9 10 in textbook
 PART 3 Chemical Bonds, Valence Bond Method, and Molecular Shapes Reference: Chapter 9 10 in textbook 1 Valence Electrons Valence ae Electron Define: the outer shell electrons Important for determination
PART 3 Chemical Bonds, Valence Bond Method, and Molecular Shapes Reference: Chapter 9 10 in textbook 1 Valence Electrons Valence ae Electron Define: the outer shell electrons Important for determination
Chapters 9&10 Structure and Bonding Theories
 Chapters 9&10 Structure and Bonding Theories Ionic Radii Ions, just like atoms, follow a periodic trend in their radii. The metal ions in a given period are smaller than the non-metal ions in the same
Chapters 9&10 Structure and Bonding Theories Ionic Radii Ions, just like atoms, follow a periodic trend in their radii. The metal ions in a given period are smaller than the non-metal ions in the same
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories MOLECULAR SHAPES 2 Molecular Shapes Lewis Structures show bonding and lone pairs do not denote shape Use Lewis Structures to determine shapes Molecular
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories MOLECULAR SHAPES 2 Molecular Shapes Lewis Structures show bonding and lone pairs do not denote shape Use Lewis Structures to determine shapes Molecular
Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 10 1
 Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 10 1 Molecular geometry is the general shape of a molecule, as determined by the relative positions
Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 10 1 Molecular geometry is the general shape of a molecule, as determined by the relative positions
Molecular Geometry and intermolecular forces. Unit 4 Chapter 9 and 11.2
 1 Molecular Geometry and intermolecular forces Unit 4 Chapter 9 and 11.2 2 Unit 4.1 Chapter 9.1-9.3 3 Review of bonding Ionic compound (metal/nonmetal) creates a lattice Formula doesn t tell the exact
1 Molecular Geometry and intermolecular forces Unit 4 Chapter 9 and 11.2 2 Unit 4.1 Chapter 9.1-9.3 3 Review of bonding Ionic compound (metal/nonmetal) creates a lattice Formula doesn t tell the exact
CHAPTER 8. Molecular Structure & Covalent Bonding Theories
 CAPTER 8 Molecular Structure & Covalent Bonding Theories 1 Chapter Goals 1. A Preview of the Chapter 2. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory 3. Polar Molecules:The Influence of Molecular
CAPTER 8 Molecular Structure & Covalent Bonding Theories 1 Chapter Goals 1. A Preview of the Chapter 2. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory 3. Polar Molecules:The Influence of Molecular
