Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids
|
|
|
- Angela Perkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids Marc R. Roussel March 8, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids March 8, / 22
2 Organic acids The acid dissociation constant, K a The strength of an acid A is measured by the acid dissociation constant, K a, the equilibrium constant for the dissociation of the acid into a proton and its conjugate base: A + + A It is sometimes useful to think of K a as the equilibrium constant for the reaction of an acid with water: Larger K a = stronger acid A + 2 O 3 O + + A Marc R. Roussel Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids March 8, / 22
3 Organic acids pk a K a values range over many orders of magnitude, so they are not very convenient for some purposes (e.g. comparisons between acids). Define pk a = log 10 K a Smaller pk a = stronger acid Strong acids may have negative pk a values (dissociate completely in water). Marc R. Roussel Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids March 8, / 22
4 Organic acids Organic acids Functional group pk a Stronger acid Carboxylic acids 3 5 Phenols 1 10 Water 14 (pk w ) Weaker acid Alcohols Marc R. Roussel Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids March 8, / 22
5 Organic acids Acidity of carboxylic acids O C O Carboxylic acids are among the most acidic organic compounds. Acid strength depends on the polarity of the bond to the dissociable hydrogen (in this case the O- bond), and the stability of the conjugate base. Marc R. Roussel Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids March 8, / 22
6 Organic acids Acidity of carboxylic acids Polarity of the O- bond O C O The carbonyl group is electron withdrawing: Because of the large electronegativity of oxygen, electron density is pulled away from the carbon atom. This in turn pulls electron density away from the hydrogen atom, increasing the partial positive charge on this atom. Marc R. Roussel Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids March 8, / 22
7 Organic acids Acidity of carboxylic acids Stability of carboxylate ions Carboxylate anions are resonance stabilized: O O C O The negative charge is therefore spread over a larger region of the molecule, which tends to stabilize the anion. ow would this manifest itself in an MO description? C O Marc R. Roussel Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids March 8, / 22
8 Organic acids Substituents on the adjacent carbon to the carboxylic acid functional group can have a substantial effect on the pk a. Consider the following series: Molecule C 3 COO FC 2 COO F 2 CCOO F 3 CCOO pk a The fluorine atom is very electronegative and pulls electron density to itself. This decreases the negative charge carried by the carboxylate group, which stabilizes the conjugate base. Base C 3 COO FC 2 COO F 2 CCOO F 3 CCOO Charge of O This is called an inductive effect. Marc R. Roussel Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids March 8, / 22
9 Organic acids Alcohols Unlike carboxylic acids, most alcohols are only about as acidic as water itself. Why? No electron-withdrawing group (in an ordinary alcohol) to increase the polarization of the O- bond No resonance stabilization of the negative charge of the conjugate base Inductive effects can increase the acidity of an alcohol. Example: Molecule C 3 C 2 O Cl 3 CC 2 O pk a Marc R. Roussel Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids March 8, / 22
10 Organic acids Phenols Phenols are much more acidic than ordinary alcohols. Phenol itself has a pk a of 9.95, vs 17 for cyclohexanol. Why? Resonance stabilization of the charge on the phenolate anion:.. :O: :O: :O: :O: Marc R. Roussel Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids March 8, / 22
11 Organic acids Some phenols are even more acidic because the substituents can participate in charge delocalization. Example: p-nitrophenol has a pk a of :O: :O: :O: N.... N.... O.. O:.. O.. O:.. O N.. O:.. :O: :O:.... O.. + N.. O:.. + N.... :O.. O:.. Marc R. Roussel Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids March 8, / 22
12 Acid dissociation equilibria Acid dissociation equilibria If we know the K a and concentration of an acid, we can calculate the p. Reminder: p = log 10 a + We usually don t need to take the autoionization of water into account unless the concentration of protons liberated from the acid is similar to the concentration of protons generated by autoionization. We often can treat the acid as if it s mostly undissociated. Note that we ll assume 25 C in all of the following calculations. Marc R. Roussel Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids March 8, / 22
13 Acid dissociation equilibria Example: Calculating the p for a solution of a given concentration of acid Calculate the p of a a 0.32 M phenol solution. The pk a of phenol is Answer: p = 5.22 Marc R. Roussel Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids March 8, / 22
14 Acid dissociation equilibria Example: Calculate the p of a M ethanoic (acetic) acid solution. The pk a of ethanoic acid is Answer: p = 4.71 Marc R. Roussel Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids March 8, / 22
15 Acid dissociation equilibria Balance of acid and conjugate base at given p Sometimes, we put an acid into a solution of fixed p (a buffer) and want to know how much is in the acid and how much in the conjugate base form. This is an easy problem because the p fixes a +, which immediately gives us the ratio of the conjugate base to the acid: K a a + = a A a A This can easily be converted to percentages of the two forms if we add the equation [A] + [A ] = 100% (with a slight abuse of notation). Marc R. Roussel Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids March 8, / 22
16 Acid dissociation equilibria Example: ethanoic acid at p 4 Suppose that we want to calculate the proportions of ethanoic acid (K a = ) and of the ethanoate ion (conjugate base) at p 4. K a a + = = = [C 3COO ] [C 3 COO] [C 3 COO ] = 0.174[C 3 COO] (1) and [C 3 COO] + [C 3 COO ] = 100% (2) Substituting equation (1) into (2), we get [C 3 COO] [C 3 COO] = 1.174[C 3 COO] = 100% [C 3 COO] = 85% [C 3 COO ] = 15% Marc R. Roussel Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids March 8, / 22
17 Acid dissociation equilibria Distribution curves If we repeat the above calculation at a number of different p values and plot the results, we obtain distribution curves for the acid and its conjugate base. Note: If p = pk a, we have a A a A = 10 pka 10 p = 1 In other words, 50% of the acid is undissociated, and 50% in the form of the conjugate base when p = pk a. Marc R. Roussel Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids March 8, / 22
18 Acid dissociation equilibria Distribution curve of ethanoic acid acid base % p Marc R. Roussel Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids March 8, / 22
19 Acid dissociation equilibria Distribution curves for polyprotic acids The calculation is analogous for polyprotic acids except that there are two (or more) equilibria and three (or more) forms of the acid to consider. When the pk a s of a polyprotic acid differ by several units, the distribution curves look like a simple superposition of distribution curves for the monoprotic case. Marc R. Roussel Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids March 8, / 22
20 Acid dissociation equilibria Example: Ethanedioic (oxalic) acid at p 3 We want to calculate the fraction (or percentage) of ethanedioic acid in each of the three possible ionization states (COO) 2, OOCCOO and (COO) 2 2 at p 3. The pk a s of the two protons are 1.27 and Answer: [OOCCOO ] = 93%, [(COO) 2 2 ] = 5.0% and [(COO) 2 ] = 1.7% Marc R. Roussel Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids March 8, / 22
21 Acid dissociation equilibria Distribution curves of ethanedioic acid (COO) 2 OOCCOO - (COO) % p Marc R. Roussel Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids March 8, / 22
22 Acid dissociation equilibria Take a log, have an equation named after you... We are now familiar with the equation K a = (a A )(a +) a A If we take the negative log of this equation, we get ( ) aa log 10 K a = log 10 a + log 10 ( ) aa pk a = p log 10 a A ( ) aa or p = pk a + log 10 a A a A This last equation is called the enderson-asselbalch equation. Marc R. Roussel Chemistry 2000 Lecture 19: Organic acids March 8, / 22
Acid-Base Chemistry & Organic Compounds. Chapter 2
 Acid-Base Chemistry & Organic Compounds Chapter 2 Brønsted Lowry Acids & Bases! Brønsted-Lowry Acid: Proton (H + ) Donor! Brønsted-Lowry Base: Proton (H + ) Acceptor! General reaction: HA + B: A - + BH
Acid-Base Chemistry & Organic Compounds Chapter 2 Brønsted Lowry Acids & Bases! Brønsted-Lowry Acid: Proton (H + ) Donor! Brønsted-Lowry Base: Proton (H + ) Acceptor! General reaction: HA + B: A - + BH
CHEM 109A Organic Chemistry
 CHEM 109A Organic Chemistry https://labs.chem.ucsb.edu/zakarian/armen/courses.html Chapter 2 Acids and Bases Central to Understanding Organic Chemistry Draw the conjugate acid of each of the following:
CHEM 109A Organic Chemistry https://labs.chem.ucsb.edu/zakarian/armen/courses.html Chapter 2 Acids and Bases Central to Understanding Organic Chemistry Draw the conjugate acid of each of the following:
Lecture Presentation. Chapter 16. Acid Base Equilibria. John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 16 Acid Base Equilibria John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Some Definitions Arrhenius An acid is a substance that, when dissolved in water, increases
Lecture Presentation Chapter 16 Acid Base Equilibria John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Some Definitions Arrhenius An acid is a substance that, when dissolved in water, increases
Acid Dissociation Constant
 CE 131 Lecture 37 Lewis Acids and Bases Chapter 16: pp. 800-802. Acid Dissociation Constant C 2 3 2 + 2 3 + + C 2 3-2 [ 3 + ][C 2 3-2 ] K = [ 2 ][C 2 3 2 ] [ 3 + ][C 2 3-2 ] K a = K [ 2 ] = [C 2 3 2 ]
CE 131 Lecture 37 Lewis Acids and Bases Chapter 16: pp. 800-802. Acid Dissociation Constant C 2 3 2 + 2 3 + + C 2 3-2 [ 3 + ][C 2 3-2 ] K = [ 2 ][C 2 3 2 ] [ 3 + ][C 2 3-2 ] K a = K [ 2 ] = [C 2 3 2 ]
Midterm Exam III. CHEM 181: Introduction to Chemical Principles November 25, 2014 Answer Key
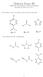 Midterm Exam III EM 181: Introduction to hemical Principles ovember 25, 2014 Answer Key 1. For reference, here are the pk a values for three weak acids: 3 pk a = 7.2 pk a = 4.8 pk a = 15 ow consider this
Midterm Exam III EM 181: Introduction to hemical Principles ovember 25, 2014 Answer Key 1. For reference, here are the pk a values for three weak acids: 3 pk a = 7.2 pk a = 4.8 pk a = 15 ow consider this
Acid-Base Chemistry. Chapter Brønsted Acid-Base Chemistry R P
 Chapter 5 Acid-Base Chemistry 5.1 Brønsted Acid-Base Chemistry R P The equilibrium constant (K eq ) gives quick insight into whether the reactant or product is more stable, and the extent to which the
Chapter 5 Acid-Base Chemistry 5.1 Brønsted Acid-Base Chemistry R P The equilibrium constant (K eq ) gives quick insight into whether the reactant or product is more stable, and the extent to which the
Chapter 16. Chemistry, The Central Science, 11th edition Theodore L. Brown, H. Eugene LeMay, Jr., and Bruce E. Bursten
 Chemistry, The Central Science, 11th edition Theodore L. Brown, H. Eugene LeMay, Jr., Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 16 John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Some Definitions Arrhenius
Chemistry, The Central Science, 11th edition Theodore L. Brown, H. Eugene LeMay, Jr., Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 16 John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Some Definitions Arrhenius
Acids and Bases. Acids and Bases
 BrØnsted-Lowry A BrØnsted-Lowry acid is a proton donor. A BrØnsted-Lowry base is a proton acceptor. H + = proton BrØnsted-Lowry Some molecules contain both hydrogen atoms and lone pairs and thus, can act
BrØnsted-Lowry A BrØnsted-Lowry acid is a proton donor. A BrØnsted-Lowry base is a proton acceptor. H + = proton BrØnsted-Lowry Some molecules contain both hydrogen atoms and lone pairs and thus, can act
6.2 Electron Movements in Brønsted Acid Base Reactions. Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1
 6.2 Electron Movements in Brønsted Acid Base Reactions Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1 Recall: Brønsted Acid Base Reactions often simply termed acid base reactions Recall: H + does not actually
6.2 Electron Movements in Brønsted Acid Base Reactions Copyright 2018 by Nelson Education Limited 1 Recall: Brønsted Acid Base Reactions often simply termed acid base reactions Recall: H + does not actually
C H C H 3. aspirin CHEMISTRY Topic #4: Organic Chemistry Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises in Topic 12
 = = 3 EMISTY 2000 aspirin Topic #4: rganic hemistry Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises in Topic 12 rganic Acids (arboxylic Acids) When you hear the term organic acid, it s generally referring to
= = 3 EMISTY 2000 aspirin Topic #4: rganic hemistry Fall 2018 Dr. Susan Findlay See Exercises in Topic 12 rganic Acids (arboxylic Acids) When you hear the term organic acid, it s generally referring to
ACIDS AND BASES. Note: For most of the acid-base reactions, we will be using the Bronsted-Lowry definitions.
 DEFINITIONS: ACIDS AND BASES Arrhenius Definition An acid in aqueous solution produces H + ions. A base in aqueous solution produces OH - ions. Bronsted Lowry Theory An acid is a proton donor A base is
DEFINITIONS: ACIDS AND BASES Arrhenius Definition An acid in aqueous solution produces H + ions. A base in aqueous solution produces OH - ions. Bronsted Lowry Theory An acid is a proton donor A base is
Aqueous Equilibria: Acids and Bases
 /3/014 Aqueous Equilibria: Acids and Bases Ch. 16 What is an? What is a? There are actually multiple definitions Arrhenius: Dealt with species in aqueous solutions. Most basic definition of acis. Acid:
/3/014 Aqueous Equilibria: Acids and Bases Ch. 16 What is an? What is a? There are actually multiple definitions Arrhenius: Dealt with species in aqueous solutions. Most basic definition of acis. Acid:
Name. Chapter 4 covers acid-base chemistry. That should help you get going.
 Name Chapter 4 covers acid-base chemistry. That should help you get going. 1 Use curved arrows to illustrate the transfer of a proton (i.e. an + ) from benzoic acid to phenoxide, and draw the products.
Name Chapter 4 covers acid-base chemistry. That should help you get going. 1 Use curved arrows to illustrate the transfer of a proton (i.e. an + ) from benzoic acid to phenoxide, and draw the products.
Module 2 Acids and Bases. Lecture 3 Acids and Bases
 Module 2 Acids and Bases Lecture 3 Acids and Bases 2.1 Concepts A compound is classified as an acid or a base based on certain properties. At present there are several theories which define the concepts
Module 2 Acids and Bases Lecture 3 Acids and Bases 2.1 Concepts A compound is classified as an acid or a base based on certain properties. At present there are several theories which define the concepts
Acid-Base Chemistry. Introduction to Reaction Mechanism
 Acid-Base Chemistry Introduction to Reaction Mechanism What is an acid and what is a base? Bronsted-Lowry definition Acids are proton donors (A-H) e.g. HCl, H 2 SO 4, HBr, HNO 3, HI etc. Bronsted-Lowry
Acid-Base Chemistry Introduction to Reaction Mechanism What is an acid and what is a base? Bronsted-Lowry definition Acids are proton donors (A-H) e.g. HCl, H 2 SO 4, HBr, HNO 3, HI etc. Bronsted-Lowry
Chapter 8. Acidity, Basicity and pk a
 Chapter 8 Acidity, Basicity and pk a p182 In this reaction water is acting as a base, according to our definition above, by accepting a proton from HCl which in turn is acting as an acid by donating a
Chapter 8 Acidity, Basicity and pk a p182 In this reaction water is acting as a base, according to our definition above, by accepting a proton from HCl which in turn is acting as an acid by donating a
Note that side chains serve as a) stabilizers of protein structure, b) reactive centers, and c) micro-environments. * + H 3 N-C-COOH H 2 N-C-COO -
 BIOCEMISTRY I AMINO ACIDS I. Amino Acid Structure One of the most important macromolecules (chains of distinct molecular units) in the biosphere is protein. Proteins are needed for catalysis, reaction,
BIOCEMISTRY I AMINO ACIDS I. Amino Acid Structure One of the most important macromolecules (chains of distinct molecular units) in the biosphere is protein. Proteins are needed for catalysis, reaction,
Chapter 3 An Introduction to Organic Reactions: Acids and Bases
 There are 4 types of Organic Reactions Chapter 3 An Introduction to Organic Reactions: SUBSTITUTION: ADDITION: X Y + A X A + Y Example Example A B + X Y A B X Y ELIMINATION There are 4 Types of Organic
There are 4 types of Organic Reactions Chapter 3 An Introduction to Organic Reactions: SUBSTITUTION: ADDITION: X Y + A X A + Y Example Example A B + X Y A B X Y ELIMINATION There are 4 Types of Organic
Chemistry 304B, Spring 99 Lecture 2 1
 Chemistry 04B, Spring 99 Lecture 2 1 Consider Acidity and Basicity Recall carboxylic acids and amines (base). Jones: p 27-8; 149, 291, 822-826, 1086-1090, 958-96, 878-882 General terms: Lewis acid: capable
Chemistry 04B, Spring 99 Lecture 2 1 Consider Acidity and Basicity Recall carboxylic acids and amines (base). Jones: p 27-8; 149, 291, 822-826, 1086-1090, 958-96, 878-882 General terms: Lewis acid: capable
Chapter 3 Acids and Bases"
 Chapter 3 Acids and Bases BrØnsted-Lowry Acids and Bases A BrØnsted-Lowry acid is a proton donor. A BrØnsted-Lowry base is a proton acceptor. H + = proton Acids and Bases Reactions of BrØnsted-Lowry Acids
Chapter 3 Acids and Bases BrØnsted-Lowry Acids and Bases A BrØnsted-Lowry acid is a proton donor. A BrØnsted-Lowry base is a proton acceptor. H + = proton Acids and Bases Reactions of BrØnsted-Lowry Acids
Chapter 2 Lecture Outline
 Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 2 Lecture Outline Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 2 Lecture Outline Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chem 261 Dec 6, 2017
 209 Chem 261 Dec 6, 2017 REVIEW: Example: K!! + 3 C + 3 C K tert-butoxide (an alkoxide) methanol tert-butanol pka = 16 pka = 19 methoxide stronger base stronger acid (lower pka, more acidic) weaker acid
209 Chem 261 Dec 6, 2017 REVIEW: Example: K!! + 3 C + 3 C K tert-butoxide (an alkoxide) methanol tert-butanol pka = 16 pka = 19 methoxide stronger base stronger acid (lower pka, more acidic) weaker acid
Chapter 2: Acids and Bases
 hapter 2: Acids and Bases 32 hapter 2: Acids and Bases Problems 2.1 Write each acid- reaction as a proton-transfer reaction. Label which reactant is the acid and which the, as well as which product is
hapter 2: Acids and Bases 32 hapter 2: Acids and Bases Problems 2.1 Write each acid- reaction as a proton-transfer reaction. Label which reactant is the acid and which the, as well as which product is
Chapter 3 Acids and Bases
 hapter 3 Acids and Bases Basic Definitions Associated with Acids and Bases Molecular Definitions of Acids and Bases Molecular Models of Selected Acids Brønsted-Lowry Theory 1. In a Brønsted-Lowry reaction,
hapter 3 Acids and Bases Basic Definitions Associated with Acids and Bases Molecular Definitions of Acids and Bases Molecular Models of Selected Acids Brønsted-Lowry Theory 1. In a Brønsted-Lowry reaction,
If somehow it is possible to increase the stability of a given base, then it
 Text Related to Segment.04 00 laude E. Wintner If somehow it is possible to increase the stability of a given base, then it should be true that the corresponding acid will be stronger than would be so
Text Related to Segment.04 00 laude E. Wintner If somehow it is possible to increase the stability of a given base, then it should be true that the corresponding acid will be stronger than would be so
Acids and Bases: Molecular Structure and Acidity
 Tutorial Contents A. Introduction B. Resonance C. Atomic Radius D. Electronegativity E. Inductive Effect F. Exercises G. Exercise Solutions Acids and Bases: Molecular Structure and Acidity Review the Acids
Tutorial Contents A. Introduction B. Resonance C. Atomic Radius D. Electronegativity E. Inductive Effect F. Exercises G. Exercise Solutions Acids and Bases: Molecular Structure and Acidity Review the Acids
Chapter 01 Structure Determines Properties part 2
 Chapter 01 Structure Determines Properties part 2 CEM 341: Spring 2012 Prof. Greg Cook Resonance Section 1.8 Resonance Some molecules may have more than one correct Lewis structure These are NT isomers.
Chapter 01 Structure Determines Properties part 2 CEM 341: Spring 2012 Prof. Greg Cook Resonance Section 1.8 Resonance Some molecules may have more than one correct Lewis structure These are NT isomers.
Acid Base Equilibria
 Acid Base Equilibria Acid Ionization, also known as acid dissociation, is the process in where an acid reacts with water to produce a hydrogen ion and the conjugate base ion. HC 2 H 3 O 2(aq) H + (aq)
Acid Base Equilibria Acid Ionization, also known as acid dissociation, is the process in where an acid reacts with water to produce a hydrogen ion and the conjugate base ion. HC 2 H 3 O 2(aq) H + (aq)
CHM 233 : Fall 2018 Quiz #10 - Answer Key
 M 233 : Fall 2018 Quiz #10 - nswer Key Question 1 M20a Which of the following is The strongest Bronsted cid? R- 2 is a carboxylic acid and R-S 3 is a solfonic acid, you will want to draw these two as Lewis
M 233 : Fall 2018 Quiz #10 - nswer Key Question 1 M20a Which of the following is The strongest Bronsted cid? R- 2 is a carboxylic acid and R-S 3 is a solfonic acid, you will want to draw these two as Lewis
OH OH OH CH 2 CH 2 C(CH 3 ) 2 (a) CH 3 CHCH 2 CHCH(CH 3 ) 2. (b)
 hem 226 Problem Set #8 Fundamentals of rganic hemistry, 4 th edition, John McMurry. hapter 8 1. Give IUPA names for the following alcohols. 2 2 ( 3 ) 2 3 2 ( 3 ) 2 Longest chain = 6 carbons:...hexanediol.
hem 226 Problem Set #8 Fundamentals of rganic hemistry, 4 th edition, John McMurry. hapter 8 1. Give IUPA names for the following alcohols. 2 2 ( 3 ) 2 3 2 ( 3 ) 2 Longest chain = 6 carbons:...hexanediol.
1.10 Structural formulas
 1.10 Structural formulas It shows which atoms are bonded to which. There are two types of structural formulas, complete Lewis structures and condensed structural formulas. In addition, there are several
1.10 Structural formulas It shows which atoms are bonded to which. There are two types of structural formulas, complete Lewis structures and condensed structural formulas. In addition, there are several
Chapter 3: Acid-Base Chemistry
 Chapter 3: Acid-Base Chemistry Reaction Classification: Substitution: 3 C Cl + Na 3 C + NaCl Addition: Br 2 Br Br Elimination: Br -Br Rearrangement: We ll deal with these later Bond Cleavage eterolytic
Chapter 3: Acid-Base Chemistry Reaction Classification: Substitution: 3 C Cl + Na 3 C + NaCl Addition: Br 2 Br Br Elimination: Br -Br Rearrangement: We ll deal with these later Bond Cleavage eterolytic
Chemistry: The Central Science. Chapter 16: Acid-Base Equilibria. 16.1: Acids and Bases: A Brief Review
 Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 16: Acid-Base Equilibria 16.1: Acids and Bases: A Brief Review Acids have a sour taste and cause certain dyes to change color Base have a bitter taste and feel slippery
Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 16: Acid-Base Equilibria 16.1: Acids and Bases: A Brief Review Acids have a sour taste and cause certain dyes to change color Base have a bitter taste and feel slippery
Chapter 16. Acid-Base Equilibria
 Chapter 16. Acid-Base Equilibria 16.1 Acids and Bases: A Brief Review Acids taste sour and cause certain dyes to change color. Bases taste bitter and feel soapy. Arrhenius concept of acids and bases: An
Chapter 16. Acid-Base Equilibria 16.1 Acids and Bases: A Brief Review Acids taste sour and cause certain dyes to change color. Bases taste bitter and feel soapy. Arrhenius concept of acids and bases: An
Chapter 16. Dr Ayman Nafady
 Chemistry, The Central Science, 11th edition Theodore L. Brown, H. Eugene LeMay, Jr., Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 16 Dr Ayman Nafady John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Some Definitions
Chemistry, The Central Science, 11th edition Theodore L. Brown, H. Eugene LeMay, Jr., Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 16 Dr Ayman Nafady John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Some Definitions
Chapter 1 Introduction and Review
 Chapter 1 Introduction and Review Concept to review: It is your responsibility to review the following concepts before the first class to ensure success in understanding new concepts: Atomic structure
Chapter 1 Introduction and Review Concept to review: It is your responsibility to review the following concepts before the first class to ensure success in understanding new concepts: Atomic structure
NATURE OF ACIDS & BASES
 General Properties: NATURE OF ACIDS & BASES ACIDS BASES Taste sour Bitter Change color of indicators Blue Litmus turns red no change Red Litmus no change turns blue Phenolphtalein Colorless turns pink
General Properties: NATURE OF ACIDS & BASES ACIDS BASES Taste sour Bitter Change color of indicators Blue Litmus turns red no change Red Litmus no change turns blue Phenolphtalein Colorless turns pink
Chapter 3 Acids and Bases. The Curved-Arrow Notation
 Organic Chemistry, 5th ed. Marc Loudon Chapter 3 Acids and Bases. The Curved-Arrow Notation Eric J. Kantorows ki California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo, CA Chapter 3 Overview 3.1 Lewis
Organic Chemistry, 5th ed. Marc Loudon Chapter 3 Acids and Bases. The Curved-Arrow Notation Eric J. Kantorows ki California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo, CA Chapter 3 Overview 3.1 Lewis
2. Acids and Bases (text )
 2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western ntario 2.1 2. Acids and Bases (text 2.1 2.6) Acid-base reactions are one of the most important reaction types in organic chemistry and biology, e.g.:
2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western ntario 2.1 2. Acids and Bases (text 2.1 2.6) Acid-base reactions are one of the most important reaction types in organic chemistry and biology, e.g.:
Chapter Bonding. Atoms trying to attain the stable configuration of a noble (inert) gas - often referred to as the octet rule
 Chapter 1 1.2-1.3 Bonding Atoms trying to attain the stable configuration of a noble (inert) gas - often referred to as the octet rule 1.2 Ionic Bonding - Electrons Transferred 1.3 Covalent Bonding - Electrons
Chapter 1 1.2-1.3 Bonding Atoms trying to attain the stable configuration of a noble (inert) gas - often referred to as the octet rule 1.2 Ionic Bonding - Electrons Transferred 1.3 Covalent Bonding - Electrons
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles شیمی آلی 2
 Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition The
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition The
The Acidity Constant, K a
 The Acidity Constant, K a The strength of an acid is represented by its ionization constant (acidity constant), K a K a = product of concentrations of ionized species concentration of intact acid K a =
The Acidity Constant, K a The strength of an acid is represented by its ionization constant (acidity constant), K a K a = product of concentrations of ionized species concentration of intact acid K a =
Answers to Practice Test Questions 12 Organic Acids and Bases
 Answers to Practice Test Questions 12 rganic Acids and Bases 1. (a) (b) pppp aa = llllll(kk aa ) KK aa = 10 pppp aa KK aa = 10 4.20 KK aa = 6.3 10 5 (c) Benzoic acid is a weak acid. We know this because
Answers to Practice Test Questions 12 rganic Acids and Bases 1. (a) (b) pppp aa = llllll(kk aa ) KK aa = 10 pppp aa KK aa = 10 4.20 KK aa = 6.3 10 5 (c) Benzoic acid is a weak acid. We know this because
Talk n Acids & Bases... Lady Dog! Definitions
 Talk n Acids & Bases... Lady Dog! Definitions So far in this course, we have looked at processes in chemistry that deal with, or are best explained by, ionic salts or molecules. Now we will turn our attention
Talk n Acids & Bases... Lady Dog! Definitions So far in this course, we have looked at processes in chemistry that deal with, or are best explained by, ionic salts or molecules. Now we will turn our attention
Ch 2 Polar Covalent Bonds
 h 2 Polar ovalent Bonds Two primary bond types: ovalent (shared e -1 s) and Ionic (transferred e -1 s) Ionic bonds can have covalent character, such as with Na:l. An e -1 pair on l -1 can fill the 3s orbital
h 2 Polar ovalent Bonds Two primary bond types: ovalent (shared e -1 s) and Ionic (transferred e -1 s) Ionic bonds can have covalent character, such as with Na:l. An e -1 pair on l -1 can fill the 3s orbital
CHE2060 Lecture 5: Acid-base chemistry. CHE2060 Lecture 5: Acid-base chemistry
 CHE2060 Lecture 5: Acid-base chemistry 5.1 Acids & bases: overview & basics 5.2 Acid & base strength 5.3 Equilibrium acid-base reactions 5.4 The leveling effect of solvents 5.5 Estimation of acidity by
CHE2060 Lecture 5: Acid-base chemistry 5.1 Acids & bases: overview & basics 5.2 Acid & base strength 5.3 Equilibrium acid-base reactions 5.4 The leveling effect of solvents 5.5 Estimation of acidity by
Chapter 2: Acids and Bases
 1. Which of the following statements is a correct definition for a Brønsted-Lowry acid? A) Proton acceptor C) Electron pair acceptor B) Electron pair donor D) Proton donor 2. Which of the following statements
1. Which of the following statements is a correct definition for a Brønsted-Lowry acid? A) Proton acceptor C) Electron pair acceptor B) Electron pair donor D) Proton donor 2. Which of the following statements
Water. Water participates in H-bonding with biomolecules.
 Water Most biochemical reactions occur in an aqueous environment. Water is highly polar because of its bent geometry. Water is highly cohesive because of intermolecular hydrogen bonding. Water participates
Water Most biochemical reactions occur in an aqueous environment. Water is highly polar because of its bent geometry. Water is highly cohesive because of intermolecular hydrogen bonding. Water participates
Chpt 16: Acids and Bases
 Chpt 16 Acids and Bases Defining Acids Arrhenius: Acid: Substances when dissolved in water increase the concentration of H+. Base: Substances when dissolved in water increase the concentration of OH- Brønsted-Lowry:
Chpt 16 Acids and Bases Defining Acids Arrhenius: Acid: Substances when dissolved in water increase the concentration of H+. Base: Substances when dissolved in water increase the concentration of OH- Brønsted-Lowry:
Thermodynamics. Gibbs Free Energy 9/15/2009. Entropy Laws. 1 st law finite amount of energy in the universe
 Thermodynamics 1 st law finite amount of energy in the universe Many forms of energy are possible. 2 nd law Entropy always increases for spontaneous reactions. Couple your reactions an entropy lowering
Thermodynamics 1 st law finite amount of energy in the universe Many forms of energy are possible. 2 nd law Entropy always increases for spontaneous reactions. Couple your reactions an entropy lowering
Chapter In each case the conjugate base is obtained by removing a proton from the acid: (a) OH (b) I (c)
 Practice Exercises 16.1 Conjugate acid base pairs (a), (c), and (f) (b) The conjugate base of I is I (d) The conjugate base of N 2 is N 2 and the conjugate base of N 4 is N 3 (e) The conjugate acid of
Practice Exercises 16.1 Conjugate acid base pairs (a), (c), and (f) (b) The conjugate base of I is I (d) The conjugate base of N 2 is N 2 and the conjugate base of N 4 is N 3 (e) The conjugate acid of
HA(aq) H + (aq) + A (aq) We can write an equilibrium constant expression for this dissociation: [ ][ ]
![HA(aq) H + (aq) + A (aq) We can write an equilibrium constant expression for this dissociation: [ ][ ] HA(aq) H + (aq) + A (aq) We can write an equilibrium constant expression for this dissociation: [ ][ ]](/thumbs/87/96059823.jpg) 16.6 Weak Acids Weak acids are only partially ionized in aqueous solution. There is a mixture of ions and un-ionized acid in solution. Therefore, weak acids are in equilibrium: Or: HA(aq) + H 2 O(l) H
16.6 Weak Acids Weak acids are only partially ionized in aqueous solution. There is a mixture of ions and un-ionized acid in solution. Therefore, weak acids are in equilibrium: Or: HA(aq) + H 2 O(l) H
Aqueous Equilibria, Part 1 AP Chemistry Lecture Outline
 Aqueous Equilibria, Part 1 AP Chemistry Lecture Outline Name: Acids and Bases Arrhenius...acids increase the when dissolved in H 2 O....bases increase the when dissolved in H 2 O. e.g., HCl and NaOH Bronsted-Lowry
Aqueous Equilibria, Part 1 AP Chemistry Lecture Outline Name: Acids and Bases Arrhenius...acids increase the when dissolved in H 2 O....bases increase the when dissolved in H 2 O. e.g., HCl and NaOH Bronsted-Lowry
19.3 Strengths of Acids and Bases > Chapter 19 Acids, Bases, and Salts Strengths of Acids and Bases
 Chapter 19 Acids, Bases, and Salts 19.1 Acid-Base Theories 19.2 Hydrogen Ions and Acidity 19.3 Strengths of Acids and Bases 19.4 Neutralization Reactions 19.5 Salts in Solution 1 Copyright Pearson Education,
Chapter 19 Acids, Bases, and Salts 19.1 Acid-Base Theories 19.2 Hydrogen Ions and Acidity 19.3 Strengths of Acids and Bases 19.4 Neutralization Reactions 19.5 Salts in Solution 1 Copyright Pearson Education,
Lecture 7. Acids. non-metals form anions. metals form cations H+ - Professor Hicks Inorganic Chemistry (CHE152) + anion. molecular compounds
 Lecture 7 Professor icks Inorganic Chemistry (CE152) Acids + + anion + - anion substances that release + ions when dissolved Strong acids Cl NO 3 2 SO 4 + Cl - + NO - 3 2 + SO 2-4 hydrochloric acid nitric
Lecture 7 Professor icks Inorganic Chemistry (CE152) Acids + + anion + - anion substances that release + ions when dissolved Strong acids Cl NO 3 2 SO 4 + Cl - + NO - 3 2 + SO 2-4 hydrochloric acid nitric
Lecture 12 (2/17/17) Phenols. Chapter 18 in Loudon, M.; Parise, J. Organic Chemistry, 6th Ed. W. H. Freeman: New York, NY, 2016
 J. G. Rudick CHE 322: rganic Chemistry IIA Lecture 12 (2/17/17) Phenols Chapter 18 in Loudon, M.; Parise, J. rganic Chemistry, 6th Ed. W. H. Freeman: New York, NY, 2016 Prof. Jon Rudick ffice Hours: CHEM
J. G. Rudick CHE 322: rganic Chemistry IIA Lecture 12 (2/17/17) Phenols Chapter 18 in Loudon, M.; Parise, J. rganic Chemistry, 6th Ed. W. H. Freeman: New York, NY, 2016 Prof. Jon Rudick ffice Hours: CHEM
ADVANCED PLACEMENT CHEMISTRY ACIDS, BASES, AND AQUEOUS EQUILIBRIA
 ADVANCED PLACEMENT CHEMISTRY ACIDS, BASES, AND AQUEOUS EQUILIBRIA Acids- taste sour Bases(alkali)- taste bitter and feel slippery Arrhenius concept- acids produce hydrogen ions in aqueous solution while
ADVANCED PLACEMENT CHEMISTRY ACIDS, BASES, AND AQUEOUS EQUILIBRIA Acids- taste sour Bases(alkali)- taste bitter and feel slippery Arrhenius concept- acids produce hydrogen ions in aqueous solution while
Practice Hour Examination # 1-1
 CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I Fall 2013 Practice Hour Examination # 1-1 Solutions Key Page 1 of 12 CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I (for Majors) Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Practice Hour Examination # 1-1 Monday,
CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I Fall 2013 Practice Hour Examination # 1-1 Solutions Key Page 1 of 12 CHEM 346 Organic Chemistry I (for Majors) Instructor: Paul J. Bracher Practice Hour Examination # 1-1 Monday,
Chapter 16: Acid Base Equilibria Chapter 16 Acid-Base Equilibria Learning Standards & Objectives;
 Chapter 16: Acid Base Equilibria Chapter 16 Acid-Base Equilibria Learning Standards & Objectives; Chapter 16 AP16-1,2-01 AP16-1,2-02 AP16-1,2-03 AP16-3,4-01 AP16-3,4-02 AP16-5-01 AP16-6,7-01 AP16-6,7-02
Chapter 16: Acid Base Equilibria Chapter 16 Acid-Base Equilibria Learning Standards & Objectives; Chapter 16 AP16-1,2-01 AP16-1,2-02 AP16-1,2-03 AP16-3,4-01 AP16-3,4-02 AP16-5-01 AP16-6,7-01 AP16-6,7-02
Acids and Bases. A strong base is a substance that completely ionizes in aqueous solutions to give a cation and a hydroxide ion.
 Acid-Base Theories Arrhenius Acids and Bases (1884) Acids and Bases An acid is a substance that, when dissolved in water, increases the concentration of hydrogen ions. A base is a substance that, when
Acid-Base Theories Arrhenius Acids and Bases (1884) Acids and Bases An acid is a substance that, when dissolved in water, increases the concentration of hydrogen ions. A base is a substance that, when
CHEM1902/ N-8 November Consider the following reaction sequences beginning with the carboxylic acid, E.
 CEM1902/4 2014--8 ovember 2014 Consider the following reaction sequences beginning with the carboxylic acid, E. 6 ame compounds E and G. E: propionic acid G: methyl propionate Propose structures for compounds
CEM1902/4 2014--8 ovember 2014 Consider the following reaction sequences beginning with the carboxylic acid, E. 6 ame compounds E and G. E: propionic acid G: methyl propionate Propose structures for compounds
ACIDS, BASES & ACID/BASE EQUILIBRIA
 Chapter 5 ACIDS, BASES & ACID/BASE EQUILIBRIA ill, Petrucci, McCreary & Perry 4 th Ed. ACIDS & BASES The Arrhenius Definition: In Water: Acid Substance which increases the concentration of ydrogen Ion,
Chapter 5 ACIDS, BASES & ACID/BASE EQUILIBRIA ill, Petrucci, McCreary & Perry 4 th Ed. ACIDS & BASES The Arrhenius Definition: In Water: Acid Substance which increases the concentration of ydrogen Ion,
Full file at
 Essential Organic Chemistry, 2e (Bruice) Chapter 2 Acids and Bases 1) Which of the following is not a conjugate acid-base pair? A) B) C) HSO- 4, H2SO4 D) -OH, O2- E) NO3 -, NO2-2) Which is defined as a
Essential Organic Chemistry, 2e (Bruice) Chapter 2 Acids and Bases 1) Which of the following is not a conjugate acid-base pair? A) B) C) HSO- 4, H2SO4 D) -OH, O2- E) NO3 -, NO2-2) Which is defined as a
Chem 263 March 28, 2006
 Chem 263 March 28, 2006 Properties of Carboxylic Acids Since carboxylic acids are structurally related to both ketones and aldehydes, we would expect to see some similar structural properties. The carbonyl
Chem 263 March 28, 2006 Properties of Carboxylic Acids Since carboxylic acids are structurally related to both ketones and aldehydes, we would expect to see some similar structural properties. The carbonyl
Organic Chem Chapter 3: Acids and Bases
 Organic Chem Chapter 3: Acids and Bases Title and Highlight Right side: NOTES! Topic: EQ: Date NOTES: Write out the notes from my website. Use different types of note-taking methods to help you recall
Organic Chem Chapter 3: Acids and Bases Title and Highlight Right side: NOTES! Topic: EQ: Date NOTES: Write out the notes from my website. Use different types of note-taking methods to help you recall
Learning Guide for Chapter 7 - Organic Reactions I
 Learning Guide for Chapter 7 - rganic Reactions I I. Introduction to Reactions II. Principles of Kinetics III. Principles of Thermodynamics IV. Nucleophiles and Electrophiles V. Acids and Bases What a
Learning Guide for Chapter 7 - rganic Reactions I I. Introduction to Reactions II. Principles of Kinetics III. Principles of Thermodynamics IV. Nucleophiles and Electrophiles V. Acids and Bases What a
The Chemistry of Acids and Bases
 The Chemistry of 1 Acids and Bases 2 Acid and Bases 3 Acid and Bases 4 Acid and Bases 5 Strong and Weak Acids/Bases Generally divide acids and bases into STRONG or WEAK ones. STRONG ACID: HNO 3 (aq) +
The Chemistry of 1 Acids and Bases 2 Acid and Bases 3 Acid and Bases 4 Acid and Bases 5 Strong and Weak Acids/Bases Generally divide acids and bases into STRONG or WEAK ones. STRONG ACID: HNO 3 (aq) +
Lecture 10. More Aromatics. February 18, Chemistry 328N
 Lecture 10 More Aromatics February 18, 2016 eterocyclic Aromatic Compounds N N O S Pyridine Pyrrole Furan Thiophene ückel and Pyridine ückel and Pyrrole uckel and Furan Recognizing Aromatic Compounds Be
Lecture 10 More Aromatics February 18, 2016 eterocyclic Aromatic Compounds N N O S Pyridine Pyrrole Furan Thiophene ückel and Pyridine ückel and Pyrrole uckel and Furan Recognizing Aromatic Compounds Be
Chapter 2 Acids and Bases. Arrhenius Acid and Base Theory. Brønsted-Lowry Acid and Base Theory
 hapter 2 Acids and Bases A significant amount of chemistry can be described using different theories of acids and bases. We ll consider three different acid-base theories (listed in order of increasing
hapter 2 Acids and Bases A significant amount of chemistry can be described using different theories of acids and bases. We ll consider three different acid-base theories (listed in order of increasing
Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases SAMPLE. Chapter Outline
 Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases Chapter utline I. Polar covalent bonds (Sections 2.1 2.3). A. Electronegativity (Section 2.1). 1. Although some bonds are totally ionic and some are totally
Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases Chapter utline I. Polar covalent bonds (Sections 2.1 2.3). A. Electronegativity (Section 2.1). 1. Although some bonds are totally ionic and some are totally
State the strongest type of interaction that occurs between molecules of hydrogen peroxide and water.
 Q1.A hydrogen peroxide molecule can be represented by the structure shown. (a) Suggest a value for the H O O bond angle. (b) Hydrogen peroxide dissolves in water. (i) State the strongest type of interaction
Q1.A hydrogen peroxide molecule can be represented by the structure shown. (a) Suggest a value for the H O O bond angle. (b) Hydrogen peroxide dissolves in water. (i) State the strongest type of interaction
Periodic Table. 8/3/2006 MEDC 501 Fall
 Periodic Table 8/3/2006 MEDC 501 Fall 2006 1 rbitals Shapes of rbitals s - orbital p -orbital 8/3/2006 MEDC 501 Fall 2006 2 Ionic Bond - acl Electronic Structure 11 a :: 1s 2 2s 2 2p x2 2p y2 2p z2 3s
Periodic Table 8/3/2006 MEDC 501 Fall 2006 1 rbitals Shapes of rbitals s - orbital p -orbital 8/3/2006 MEDC 501 Fall 2006 2 Ionic Bond - acl Electronic Structure 11 a :: 1s 2 2s 2 2p x2 2p y2 2p z2 3s
F B - N + H. B-L A B-L B CB CA pka ~15 wkr A ~9. Lewis A Lewis B Lewis A-B complex. N O B-L A B-L B CB CA pka ~5 ~9 wkr A
 CEM 109A 1. Predict the products of the following reactions. Label the acids, bases (Lewis or Bronsted-Lowry) and conjugates (if applicable). Determine the side that is favored at equilibrium for the reactions
CEM 109A 1. Predict the products of the following reactions. Label the acids, bases (Lewis or Bronsted-Lowry) and conjugates (if applicable). Determine the side that is favored at equilibrium for the reactions
Chem 1046 Lecture Notes Chapter 17
 Chem 1046 Lecture Notes Chapter 17 Updated 01-Oct-2012 The Chemistry of Acids and Bases These Notes are to SUPPLIMENT the Text, They do NOT Replace reading the Text Book Material. Additional material that
Chem 1046 Lecture Notes Chapter 17 Updated 01-Oct-2012 The Chemistry of Acids and Bases These Notes are to SUPPLIMENT the Text, They do NOT Replace reading the Text Book Material. Additional material that
Chemistry 1A, Fall 2007 KEY Midterm Exam #2 October 16, 2007 (90 min, closed book)
 Chemistry 1A, Fall 2007 KEY Midterm Exam #2 ctober 16, 2007 (90 min, closed book) ame: SID: GSI ame: ame The test consists of 6 short answer questions and a page of multiple choice questions. Put your
Chemistry 1A, Fall 2007 KEY Midterm Exam #2 ctober 16, 2007 (90 min, closed book) ame: SID: GSI ame: ame The test consists of 6 short answer questions and a page of multiple choice questions. Put your
Properties of Acids and Bases
 Chapter 15 Aqueous Equilibria: Acids and Bases Properties of Acids and Bases Generally, an acid is a compound that releases hydrogen ions, H +, into water. Blue litmus is used to test for acids. Blue litmus
Chapter 15 Aqueous Equilibria: Acids and Bases Properties of Acids and Bases Generally, an acid is a compound that releases hydrogen ions, H +, into water. Blue litmus is used to test for acids. Blue litmus
Chemistry 201: General Chemistry II - Lecture
 Chemistry 201: General Chemistry II - Lecture Dr. Namphol Sinkaset Chapter 17 Study Guide Concepts 1. There are multiple definitions for acids and bases. 2. An Arrhenius acid is a substance that produces
Chemistry 201: General Chemistry II - Lecture Dr. Namphol Sinkaset Chapter 17 Study Guide Concepts 1. There are multiple definitions for acids and bases. 2. An Arrhenius acid is a substance that produces
Structure Determination. How to determine what compound that you have? One way to determine compound is to get an elemental analysis
 Structure Determination How to determine what compound that you have? ne way to determine compound is to get an elemental analysis -basically burn the compound to determine %C, %H, %, etc. from these percentages
Structure Determination How to determine what compound that you have? ne way to determine compound is to get an elemental analysis -basically burn the compound to determine %C, %H, %, etc. from these percentages
CHAPTER 14 ACIDS AND BASES
 CHAPTER 14 ACIDS AND BASES Topics Definition of acids and bases Bronsted-Lowry Concept Dissociation constant of weak acids Acid strength Calculating ph for strong and weak acids and bases Polyprotic acids
CHAPTER 14 ACIDS AND BASES Topics Definition of acids and bases Bronsted-Lowry Concept Dissociation constant of weak acids Acid strength Calculating ph for strong and weak acids and bases Polyprotic acids
Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases. Chapter Outline
 rganic Chemistry 9th Edition McMurry SLUTINS MANUAL Full clear download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/organic-chemistry-9th-edition-mcmurrysolutions-manual/ rganic Chemistry 9th Edition McMurry
rganic Chemistry 9th Edition McMurry SLUTINS MANUAL Full clear download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/organic-chemistry-9th-edition-mcmurrysolutions-manual/ rganic Chemistry 9th Edition McMurry
Weak acids are only partially ionized in aqueous solution: mixture of ions and un-ionized acid in solution.
 16.6 Weak Acids Weak acids are only partially ionized in aqueous solution: mixture of ions and un-ionized acid in solution. Therefore, weak acids are in equilibrium: HA(aq) + H 2 O(l) H 3 O + (aq) + A
16.6 Weak Acids Weak acids are only partially ionized in aqueous solution: mixture of ions and un-ionized acid in solution. Therefore, weak acids are in equilibrium: HA(aq) + H 2 O(l) H 3 O + (aq) + A
Amino acids have the general structure: All amino acids have at least two acidic protons. One is the proton
 Worksheet rganic Acids and Bases II Amino Acids Acids are proton donors in aqueous solutions: A + 2 3 + + A - acid base conjugate conjugate base acid The strength of an acid is measured by the [ 3 + ]
Worksheet rganic Acids and Bases II Amino Acids Acids are proton donors in aqueous solutions: A + 2 3 + + A - acid base conjugate conjugate base acid The strength of an acid is measured by the [ 3 + ]
Introduction to Acids & Bases II. Packet #26
 Introduction to Acids & Bases II Packet #26 1 Review I Svante Arrhenius was the first person to recognize the essential nature of acids and bases. 2 Review II Arrhenius postulated that: Acids produce hydrogen
Introduction to Acids & Bases II Packet #26 1 Review I Svante Arrhenius was the first person to recognize the essential nature of acids and bases. 2 Review II Arrhenius postulated that: Acids produce hydrogen
11/14/10. Properties of Acids! CHAPTER 15 Acids and Bases. Table 18.1
 11/14/10 CHAPTER 15 Acids and Bases 15-1 Properties of Acids! Sour taste React with active metals i.e., Al, Zn, Fe, but not Cu, Ag, or Au 2 Al + 6 HCl 2 AlCl3 + 3 H2 corrosive React with carbonates, producing
11/14/10 CHAPTER 15 Acids and Bases 15-1 Properties of Acids! Sour taste React with active metals i.e., Al, Zn, Fe, but not Cu, Ag, or Au 2 Al + 6 HCl 2 AlCl3 + 3 H2 corrosive React with carbonates, producing
Organic Chemistry 6 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice. Chapter 1. Electronic Structure and Bonding. Acids and Bases Pearson Education, Inc.
 Organic Chemistry 6 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 1 Electronic Structure and Bonding Acids and Bases 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Organic Chemistry Carbon-containing compounds were once considered
Organic Chemistry 6 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 1 Electronic Structure and Bonding Acids and Bases 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Organic Chemistry Carbon-containing compounds were once considered
Chapter 16 Acid-Base Equilibria
 Chapter 16 Acid-Base Equilibria Learning goals and key skills: Understand the nature of the hydrated proton, represented as either H + (aq) or H 3 O + (aq) Define and identify Arrhenuis acids and bases.
Chapter 16 Acid-Base Equilibria Learning goals and key skills: Understand the nature of the hydrated proton, represented as either H + (aq) or H 3 O + (aq) Define and identify Arrhenuis acids and bases.
CHAPTER 2: RESONANCE THEORY
 CAPTER 2: RESACE TERY The Basics. Use the Rules for writing acceptable contributing structures for this exercise (some hydrogens have been added for clarity) 1. For each example, add curved arrows to the
CAPTER 2: RESACE TERY The Basics. Use the Rules for writing acceptable contributing structures for this exercise (some hydrogens have been added for clarity) 1. For each example, add curved arrows to the
Wednesday, February 25, Acid and Base Reactions
 Acid and Base Reactions Dilute aqueous solution of acetic acid, C3COO Aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide, NaO The role of the ydrogen Ion Cl (aq) Æ + (aq) + Cl - (aq) What does the neutral atom consist
Acid and Base Reactions Dilute aqueous solution of acetic acid, C3COO Aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide, NaO The role of the ydrogen Ion Cl (aq) Æ + (aq) + Cl - (aq) What does the neutral atom consist
Nucleophilic Addition Reactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
 Lecture 5: bjectives: Nucleophilic Addition eactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives By the end of this lecture you will be able to: draw the mechanism of a nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction with
Lecture 5: bjectives: Nucleophilic Addition eactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives By the end of this lecture you will be able to: draw the mechanism of a nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction with
Lecture 20 Chapter 17, Sections 4-5 More weak acids and bases. Identifying acids and bases Conjugate acids and bases Salts of weak acids and bases
 Lecture 20 Chapter 17, Sections 4-5 More weak acids and bases Identifying acids and bases Conjugate acids and bases Salts of weak acids and bases Acids and Bases Strong vs. Weak K a vs. K b ph = -log([h])
Lecture 20 Chapter 17, Sections 4-5 More weak acids and bases Identifying acids and bases Conjugate acids and bases Salts of weak acids and bases Acids and Bases Strong vs. Weak K a vs. K b ph = -log([h])
Chapter 1 The Atomic Nature of Matter
 Chapter 1 The Atomic Nature of Matter 1-1 Chemistry: Science of Change 1-2 The Composition of Matter 1-3 The Atomic Theory of Matter 1-4 Chemical Formulas and Relative Atomic Masses 1-5 The Building Blocks
Chapter 1 The Atomic Nature of Matter 1-1 Chemistry: Science of Change 1-2 The Composition of Matter 1-3 The Atomic Theory of Matter 1-4 Chemical Formulas and Relative Atomic Masses 1-5 The Building Blocks
Objective 3. Draw resonance structures, use curved arrows, determine extent of delocalization. Identify major/minor contributor.
 Objective 3 Draw resonance structures, use curved arrows, determine extent of delocalization. Identify major/minor contributor. Structure Should Fit Experimental Data The chemical formula of benzene is
Objective 3 Draw resonance structures, use curved arrows, determine extent of delocalization. Identify major/minor contributor. Structure Should Fit Experimental Data The chemical formula of benzene is
Chapter 14. Objectives
 Section 1 Properties of Acids and Bases Objectives List five general properties of aqueous acids and bases. Name common binary acids and oxyacids, given their chemical formulas. List five acids commonly
Section 1 Properties of Acids and Bases Objectives List five general properties of aqueous acids and bases. Name common binary acids and oxyacids, given their chemical formulas. List five acids commonly
Aqueous Equilibria: Acids and Bases
 6//4 What is an? What is a? There are actually multiple definitions Aqueous quilibria: Acids and Bases Ch. 6 Arrhenius: Dealt with species in aqueous solutions. Most basic definition of acis. Acid: increases
6//4 What is an? What is a? There are actually multiple definitions Aqueous quilibria: Acids and Bases Ch. 6 Arrhenius: Dealt with species in aqueous solutions. Most basic definition of acis. Acid: increases
Covalent bonds can have ionic character These are polar covalent bonds
 Polar Covalent Bonds: Electronegativity Covalent bonds can have ionic character These are polar covalent bonds Bonding electrons attracted more strongly by one atom than by the other Electron distribution
Polar Covalent Bonds: Electronegativity Covalent bonds can have ionic character These are polar covalent bonds Bonding electrons attracted more strongly by one atom than by the other Electron distribution
Chapter 16. Acid-Base Equilibria
 Chapter 16 Acid-Base Equilibria Arrhenius Definition Acids produce hydrogen ions in aqueous solution. Bases produce hydroxide ions when dissolved in water. Limits to aqueous solutions. Only one kind of
Chapter 16 Acid-Base Equilibria Arrhenius Definition Acids produce hydrogen ions in aqueous solution. Bases produce hydroxide ions when dissolved in water. Limits to aqueous solutions. Only one kind of
CHEM 261 Dec 4, 2017
 200 CEM 261 Dec 4, 2017 REVIEW: 1. N 3 2 S 4 1. 2 Al 3 N 2 2. 2 Al 3 2. N 3 2 S 4 N 2 I II For the left hand reaction, I - to create a meta positioned, the first molecule to be subsituted should be N 2,
200 CEM 261 Dec 4, 2017 REVIEW: 1. N 3 2 S 4 1. 2 Al 3 N 2 2. 2 Al 3 2. N 3 2 S 4 N 2 I II For the left hand reaction, I - to create a meta positioned, the first molecule to be subsituted should be N 2,
1. Resonance (section 1.4). Arguably the most important technique to rationalize outcomes in the science majors organic chemistry series
 Chemistry 261 Fall 2017 Lecture 2 Emphasis 1. Resonance (section 1.4). Arguably the most important technique to rationalize outcomes in the science majors organic chemistry series a. Requires an introduction
Chemistry 261 Fall 2017 Lecture 2 Emphasis 1. Resonance (section 1.4). Arguably the most important technique to rationalize outcomes in the science majors organic chemistry series a. Requires an introduction
Resonance and M.O. View of Butadiene. Super-Conjugated or Aromatic p e - Systems
 Resonance and M.. View of Butadiene The different resonance forms of butadiene suggest p bonding character between the two central carbon atoms. 2 2 2 2 carbanion 2 2 carbocation The M.. view of butadiene
Resonance and M.. View of Butadiene The different resonance forms of butadiene suggest p bonding character between the two central carbon atoms. 2 2 2 2 carbanion 2 2 carbocation The M.. view of butadiene
CH 15 Summary. Equilibrium is a balance between products and reactants
 CH 15 Summary Equilibrium is a balance between products and reactants Use stoichiometry to determine reactant or product ratios, but NOT reactant to product ratios. Capital K is used to represent the equilibrium
CH 15 Summary Equilibrium is a balance between products and reactants Use stoichiometry to determine reactant or product ratios, but NOT reactant to product ratios. Capital K is used to represent the equilibrium
