Disclaimer: The definitions & photos used herein belong to: Organic Chemistry by David Klein 2 nd edition, Wiley publishers
|
|
|
- Brianna Stokes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fall 2017 Organic Chemistry I Review by Elizabeth Ruelke fr SARC 12/2/17 8:00-8:02am Intr/disclaimer 8:02-8:04am Ch1 structure and bnding Mass number weight f the atm Atmic weight S rbital lcated within sigma bnds P rbital lcated within pi bnds Valence electrns lcated n the uter shell Bnding electrns shared between atms Nnbnding electrns lcated lcally n ne atm Lewis structures structure shwing the electrn lcatin n atms Frmal charge charge n the verall mlecule cumulated frm the individual charges n each atm. Ismers same mlecular frmula, different arrangement f atms. Octet rule there must be 8 electrn in the uter shell Resnance electrns mvement thrughut mlecule Delcalized lne pairs participate in resnance Lcalized lne pairs dn t participate in resnance VESPR thery electrn repulsin yields different mlecule gemetry hybridizatins. Sp3 n lne pairs is tetrahedral; ne lne pair is pyramidal; tw lne pairs is bent Sp2trignal planar Splinear Cndensed frmula written ut mlecular frmuala withut written bnds CH 3 CH 2 CH 3 Electrnegativity increases up and t the right f the peridic table 8:04-8:06am Ch2 acids and bases Lewis acid electrn acceptr Brnsted acid prtn dnr (aka LA) Lewis base electrn dnr Brnsted base prtn acceptr (aka LB) Keq= [prducts]/[reactants] pka= -lg Ka Increasing acidity ges dwn and t the right n peridic table Cmparing acidity f certain mlecules: MARIO Mlecule make sure yu re cmparing similar mlecules Atm make sure yu evaluate the electrnegativity f the atms Resnance the mre resnance available the better the acid Inductin the mre inductive effects the mre acidic Orbital the mre s character in rbital the mre acidic Disclaimer: The definitins & phts used herein belng t: Organic Chemistry by David Klein 2 nd editin, Wiley publishers
2 8:07am-8:09am Ch3 rganic mlecules and functinal grups Intermlecular frces van der waals diple-diple hydrgen bnding inic Biling pint increases with mre hydrgen bnding Larger the surface area higher the BP Melting pint mre glbular/symmetrical higher MP SlubilityLike disslves like 8:09am-8:16am Ch4 alkanes Straight chain vs branched chain Cyclalkanes Nmenclature w/substituents Always priritize lwest number t substituents, giving preference t alchls Newman prjectins (staggered, eclipsed) (anti/gauche) Angle strain any angle belw/abve C Cyclprpane Trsinal strain energy frm verlapping grups (eclipsed) Cyclbutane Steric strain energy frm verlapping electrn cluds t-butyl grup base Chair/Bat cnfrmatin (ax/eq) & ring flipping Disclaimer: The definitins & phts used herein belng t: Organic Chemistry by David Klein 2 nd editin, Wiley publishers
3 Cnstitutinal ismers same mlecular frmula, different cnnectins Stereismers (cis/trans) same mlecular frmula, same cnnectins, different special arrangement OIL RIG (xidatin/reductin) Oxidatin is lss f electrns, r increased xygen cnnectins Reductin is gain f electrns, r decreased xygen cnnectins Prblems: Nmenclature: m-chlrphenl Newman prjectin: C2-C3 3-chlr-2-butanl Lwest energy cnfrmer Highest energy cnfrmer Chair/Bat: cis 1,3-diethylcyclhexane vs. trans 1,3-diethylcyclhexane Lwest energy? Highest energy? Stereismers r cnstitutinal ismers r same? (CH 3 ) 3 CCH 2 CH(CH 3 ) 2 and (CH 3 ) 2 CHCH 2 C(CH 3 ) 3 8:16-8:22am Ch5 sterechemistry Achiral vs Chiral R clckwise (dextrrtary: plarized light t the right) S cunterclckwise (levrtary: plarized light t the left) Mes ptically inactive Stereismers: Enantimers mirrr images, nn-superimpsable Diasteremers nt superimpsable and nt mirrr images Tw enantimers have identical physical prperties except plarimetry Optically active has chirality, nt mes, part f chemical prperty f a substance Racemic definitin 50/50 mixture f enantimers Specific rtatin [a]= specific rtatin a=bserved rtatin c=cncentratin (g/ml) l= path length (dm) Enantimeric excess Prblems: Draw bth R/S f 2-chlr-2butanl Draw bth R/S f 3-brm-3-chlrhexane Specific rtatin: Yu add 0.3g f sucrse t 10mL water. Run the sample acrss 10cm length. The bserved rtatin is What is the specific rtatin? Enantimeric excess: Scientist was t create synthetic adrenaline, but experiment is cntaminated. Pure adrenaline is The bserved rtatin is -45. What is the ee%? ***Nte: final number is the excess dn t frget t add the difference f racemic*** 8:22-8:32am Ch6 understanding Organic reactins Substitutin rxn replacing X with Y n a mlecule Additin rxn adding mlecules acrss duble r triple bnds Eliminatin rxn remving HX frm mlecule t create duble bnd Bnd making /bnd frming Cncerted mech single step Stepwise mech tw step, with intermediate state Bnd cleavage: Heterlytic ne f the pair f atms receives bth electrns Carbcatins: C+ Carbanins: C: -- Hmlytic electrns are evenly split between atms Radicals: C Disclaimer: The definitins & phts used herein belng t: Organic Chemistry by David Klein 2 nd editin, Wiley publishers
4 Electrphile atm lacking electrn density, vulnerable t attack Nuclephile atm/bnd with lne pair electrns, will attack substrate H= bnds brken bnds frmed Endthermic + H absrbs heat frm system Exthermic - H releases heat int system Thermdynamics G= H T S Exergnic releases energy int system Endergnic absrbs energy frm system K eq >1 crrelates with G (-) favrs prducts K eq <1 crrelates G (+) favrs reactants Energy diagrams Peaks=transitin state Valley=intermediate Energy f activatin (E a ) difference in energy between reactants and transitin state Catalysts speeds up reactin rate, usually acids r metals; lwer activatin energy Kinetics= study f reactin rate Rate= k [reactants] Sn1 rate= k[reactant] Sn2 rate= k[reactant][nuclephile] Prblems Substitutin, Eliminatin, r Additin? Chlrbutane + HBr Brmbutane + HCl 2,4-dibrmbutane + 2NaH 2-butyne + 2HBr Butane + Br2 1,2-dibrmbutane Acetylene + 2HBr 1,2-dibrmethane 2-brmprpane + NaOH 2-prpanl + HBr 2,2-dichlrpentane + NaNH 2 2-chlr-2-pentene + NH 3 Identify electrphilic and/r nuclephilic sites n the fllwing: Phenl Pentanl 3-brm-2-hexanl Carbxylic acid Draw the fllwing energy diagrams: Exergnic 2 step rxn Endergnic 2 step rxn Exergnic 1 step rxn Endergnic 1 step rxn 8:32am-8:41am Ch7 alkyl halides and nuclephilic substitutin Vinyl halide & Aryl halides unfavred and unreactive in substitutins Allylic halide & Benzylic halide favred and reactive in substitutins Nmenclature Cmmn names: t-butyl-, isbutyl-, sec-butyl-, isprpyl- Bnd plarity based ff relative electrnegativity s f the atms n bnd Gd leaving grups easily leave the mlecule, usually halides Nuclephilicity increases t the right and dwn peridic table Steric hindrance can determine site f attack See NaOH versus t-butxide Disclaimer: The definitins & phts used herein belng t: Organic Chemistry by David Klein 2 nd editin, Wiley publishers
5 Substitutin Reactins Sn1 Sn2 Rate =k[reactant] =k[reactant][nuclephile] Mechanism Stepwise (carbcatin intermediate) Cncerted Substrate Res > 3 > 2 > 1 1 > 2 > 3 Nuclephile Weak Strng Slvent Prtic: water, acetic acid, ammnia Aprtic: DMSO, DMF, acetnitrile Prduct Type Racemic mixture Inverted chirality due t back-side attack Hammnd pstulate (Sn1) shws 3 has lwer activatin energy ver 2 fr carbcatin frmatin Prblems Shw prduct, arrw pushing and indicate Sn1 r Sn2: 2-brm-3-methylpentane + H 2 O 2-brm-3-methylpentane + NaOH 2-pentanl + TsOH/py 2-methyl-3-OTs-pentane + EtOH 2-chlrbutane + NaCN 3-brm-3-methylpentane + H 2 O 1-chlr-3-methylpentane + NaOH 2-methylcyclhexanl + H 2 O 2-idcyclpentane + MeSH 8:41-8:50am Ch8 alkyl halides and eliminatin reactins Eliminatin Reactins E1 E2 Rate =k[reactant] =k[reactant][nuclephile] Mechanism Stepwise (carbcatin intermediate) Cncerted Substrate 3 > 2 > 1 3 > 2 > 1 (antiperiplanar) Base n/a Strng Hammnd pstulate (E2) shws trans substitutin is preferred ver cis Trans Alkene mre stable than cis alkene due t steric strain E/Z nmenclature: E largest grups n ppsite sides f duble bnd Z largest grups n same side f duble bnd Zaitsev rule: indicates the mst stable alkene is the mre substituted duble bnd Zaitsev mre substituted prduct Hffman lesser substituted prduct *** Triethylamine & t-buok give preferential Hffman prduct Nuclephile vs Base Prblems List E1, E2, Sn1, r Sn2 fr belw and majr/minr prducts Chlrpentane + NaBr 3-brm-3methyl-pentane + NaSH 2-brmpentane + NaH Brmpentane + NaOH 2-brmpentane + NaOH 2-brm-3-methylpentane + H2O 8:50-9:00am BREAK TIME Disclaimer: The definitins & phts used herein belng t: Organic Chemistry by David Klein 2 nd editin, Wiley publishers
6 9:00-9:06am Ch9 Alchls, Ethers, and related cmpunds Nmenclature Naming alchls Naming epxides Naming Ethers Synthesis Williamsn ether synthesis Epxide have angle strain Breaking in acid additin at mre substituted side Breaking in base additin at less substituted side Alchl Additin f primary alchl (1. BH3, THF 2. H2O2, OH) Additin f secndary alchl (H2SO4) Eliminatin f alchl via E1 f 2 /3 degree alchl Eliminatin f alchl via E2 f 1 degree alchl LeChatelier s principle Reagents NaH strng base, preparatin f ethers TsCl, py replace OH t be gd leaving grup H2SO4dehydratin if cncentrated, hydratin if dilute HCl acid breaking f epxide KOH base breaking f epxide NaNH2 base NaOCH3 frmatin f ether with base POCl3 in py replace alchl with chlride (backside attack) SOCl2 replace alchl with chlride (backside attack) PBr3 replace alchl with brmine (backside attack) NaCN base, and elngatin f carbn chain Br2/I2 adds trans vicinal halides KSH replace alchl r break epxide ring; adds thil grup (backside attack) Disulfide Zn/Hcl thil grups Prblems: Give prduct(s) Acetylene 1. NaH, 2. MeBr 3. H2, Lindlars 4. Dilute H2SO4 2-butanl 1. H2SO4, heat, 2. HBr 3. t-buok 1,2-epxycyclhexane 1. NaBr 2. NaH 3. Br2 1-pentene 1.BH3, THF 2. H2O2, OH 3. TsOH, py 4. NaSH 1,2-epxy-2-methylcyclhexane 1. NaOH 2. POCl2, py 9:06-9:12am Ch10 alkenes Calculating the degrees f unsaturatin ½(2C +2 + N H X) Each degree represents 2 less H, r an additinal duble bnd Nmenclature (vs alchl, functinal grups, etc) -diene, -triene, E/Z (cis/trans) Disclaimer: The definitins & phts used herein belng t: Organic Chemistry by David Klein 2 nd editin, Wiley publishers
7 Making alkenes -OCH3 vs OC(CH 3 ) 3 different prducts acid (H2SO4 n alchl) vs base (-OCH3) Reagents Hydrhalgenatin (HX) Hydratin (H2O, H2SO4) Halgenatin (X2) Halhydrin frmatin (X2, H2O) Hydrbratin-xidatin (1. BH3, THF, 2. H2O2, -OH) Markvnikv additin hydrgen ges with mre hydrgens Prblems: Shw arrw pushing 2-butanl + H2SO4, heat 2-butanl + -OCH3 Pentene + HBr 2-butene + H2O, H2SO4 2-butene + Br2 2-pentene + Br2/H2O Pentene 1. BH3, THF 2. H2O2, OH 9:12-9:18am Ch11 alkynes Nmenclature (-diynes, -triynes) If alkene and alkyne, g with the lwer numbering Preparatin f alkynes frm alkenes NaNH2, NaH, etc Reactins t alkynes H2, lindlar s (cis additin) H2, pt (reduce t alkane) NaNH3 (trans additin t alkyne) X2 Water additin Acid tautmerizatin (enl t ket) H2O, H2SO4, HgSO4 (mre substituted alchl) BH3, THF 2. H2O2, -OH (lesser substituted alchl) Elngating carbn chains Add epxides (then H2O) t give terminal OH Retrynthesis (final beginning prduct): g back ne step/precursr at a time Synthesis (acetylene) given final Prblems Acetylene 1. NaH 2. EtBr 3. NaH 4. MeBr 5. H2, lindlar s Acetylene 1. NaH 2. PrpylBr 3. Br2 (excess) Acetylene 1. NaH 2. Oxirane 3. H2O Acetylene 1. NaH 2. EtBr 3. BH3, THF 4. H2O2, OH Acetylene 1.NaH 2. MeBr 3.NaH 4. MeBr 5. H2SO4, HgSO4, H2O 9:18-9:25am Ch12 Oxidatin reductin Reducing agents Na NH3 (trans) NaBH4 LiAlH4 (LAH) Oxidatin agents KMnO4/OsO4 syn additin) MCPBA (expy) RCO3H 2. H2O (anti dil additin) O3 2. Zn, H2O (cleavage f alkene) Carbxylic acids n alkynes) K2Cr2O7 (r CrO3 with H2SO4, H2O) (yield ketne) PCC (ketne) Prblems Butanal 1. LAH excess 2. H2O 3.TsOH, py 4. NaBr 5. NaH 2-pentanl 1. CrO3, H2O, H2SO4 2. NaBr 3. H2O Acetylene 1.NaH 2. MeBr 3. Br2 4. KMnO4, cld Disclaimer: The definitins & phts used herein belng t: Organic Chemistry by David Klein 2 nd editin, Wiley publishers
8 Prpanl 1. H2SO4, heat 2. Br2 3. NaH (2eq) 4. NaNH3 5. MCPBA Cyclpentene 1. O3 2. Zn, H2O 3. LAH (excess) 4. H2O 2-methylcyclpentanl 1. TsOH, py 2. NaBr 3. NaH 4. RCO3H 5. H2O 9:25-9:32am Ch13 Mass Spec & IR spectrscpy Mass Spec Yields mlecular frmula, presence f Br/Cl, via fragmentatin and detectin f carbcatins Base peak (100%), mass-t-charge (m/z), (M) + mst cmmn fragment, (M+1) + secnd mst abundant fragment (M+2)+ chlrine (1:3 rati peaks), brmine (1:1 rati peaks) Fragmentatin/Lss: M-15 (methyl), M-29 (ethyl), M-43 (prpyl), M-57 (butyl), M-18 (H2O) Prblems Mlecular frmula? Brmine, Chlrine, r neither? IR spec Yields functinal grups present n mlecule, via bending and stretching Diagnstic regin: (cm -1 ) mst imprtant frequencies Fingerprint regin: (cm -1 ) dn t pay attentin t this Shifting is affect by % s character, bnd length, difference in weight between atms Signals can be brad, strng, r weak Disclaimer: The definitins & phts used herein belng t: Organic Chemistry by David Klein 2 nd editin, Wiley publishers
9 Prblems Carbxylic acid, alchl, neither? Disclaimer: The definitins & phts used herein belng t: Organic Chemistry by David Klein 2 nd editin, Wiley publishers
10 Carbxylic acid, alchl, amine, neither? Match Disclaimer: The definitins & phts used herein belng t: Organic Chemistry by David Klein 2 nd editin, Wiley publishers
11 9:32-9:40am Ch14 NMR H NMR Cmparing signals: hmtrpic, enantitrpic, diasteretrpic Characteristics: Lcatin (aka shift δ) determined by inductive neighbrs Dwnfield (high number) vs upfield (lw number) Disclaimer: The definitins & phts used herein belng t: Organic Chemistry by David Klein 2 nd editin, Wiley publishers
12 Area (integratin I) hw many prtns are represented in the signal Height represents integratin relative t each ther (rati) 2:3:2:3 Shape (splitting m) hw many neighbrs (n+1) Singlet= n neighbrs; dublet= 1 neighbr; triplet= 2 neighbrs, etc. Prblems Determine number f signals Determine number f signals and shift C NMR Identify number f signals f C 13 Range: Disclaimer: The definitins & phts used herein belng t: Organic Chemistry by David Klein 2 nd editin, Wiley publishers
13 Types f C NMR: Prblems Determine number f signals, shift, integratin Determine structure 9:40-9:45am Ch15 Radical Reactins Radical stability: res > 3 > 2 > 1 > Me Disclaimer: The definitins & phts used herein belng t: Organic Chemistry by David Klein 2 nd editin, Wiley publishers
14 Definitins Stages: Initiatr (heat, light, NBS, Acyl perxides) Prpgatin Terminatin Types chlrinatin (mre energy favrable, incmplete prduct frmatin) vs brminatin (cmplete prduct frmatin, higher energy state) Prduct racemic Reagent HBr, ROOR (gives anti-markvnikv prduct) Prblems Acetylene 1.NaH 2.MeBr 3.NaH 4.MeBr 5.HBr, ROOR 2-butene 1.Br2 2. NaH (2eq) 3. NaNH3 4. NBS, hv 9:45-10:00am Final survey, Questins, and Clsing Statements Please leave rm clean Disclaimer: The definitins & phts used herein belng t: Organic Chemistry by David Klein 2 nd editin, Wiley publishers
Types of Reactions 1. Acid-base: Transfer of protons, H+ 2. Substitution 3. Addition 4. Elimination 5. Oxidation and reduction: Loss and gain of O/H
 Types f Reactins 1. Acid-base: Transfer f prtns, H+ 2. Substitutin 3. Additin 4. Eliminatin 5. Oxidatin and reductin: Lss and gain f O/H Acid-Base Reactins - Acids: Prtn dnrs, e- pair acceptr HA + H2O
Types f Reactins 1. Acid-base: Transfer f prtns, H+ 2. Substitutin 3. Additin 4. Eliminatin 5. Oxidatin and reductin: Lss and gain f O/H Acid-Base Reactins - Acids: Prtn dnrs, e- pair acceptr HA + H2O
Organic Chemistry 220 Final Exam Preparation
 Organic Chemistry 220 Final Exam Preparatin D all hmewrk, WebAssign prblems, and wrksheets until yu n lnger have t lk at ntes, bks, r ther prblems t answer them crrectly. Wrk extra prblems t further cncretize
Organic Chemistry 220 Final Exam Preparatin D all hmewrk, WebAssign prblems, and wrksheets until yu n lnger have t lk at ntes, bks, r ther prblems t answer them crrectly. Wrk extra prblems t further cncretize
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 8 Chemical Reactions II Chem 2310
 Nuggets f Knwledge fr Chapter 8 Chemical Reactins II Chem 2310 I. Substitutin, Additin, and Eliminatin Reactins The terms dissciatin, assciatin, and displacement are useful fr describing what happens t
Nuggets f Knwledge fr Chapter 8 Chemical Reactins II Chem 2310 I. Substitutin, Additin, and Eliminatin Reactins The terms dissciatin, assciatin, and displacement are useful fr describing what happens t
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 10 Alkenes (I) Chem alkenes hydrocarbons containing a C=C (not in a benzene ring)
 I. Intrductin t Alkenes Classifying Alkenes Nuggets f Knwledge fr Chapter 10 Alkenes (I) Chem 2310 There are several categries that can be used t describe cmpunds cntaining carbn-carbn duble bnds. alkenes
I. Intrductin t Alkenes Classifying Alkenes Nuggets f Knwledge fr Chapter 10 Alkenes (I) Chem 2310 There are several categries that can be used t describe cmpunds cntaining carbn-carbn duble bnds. alkenes
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 16 Ethers and Epoxides Chem 2320
 Nuggets f Knwledge fr Chapter 16 Ethers and Epxides Chem 2320 I. Intrductin t Ethers, Epxides, and Thiethers Definitin and Examples f Ethers and Thiethers Ethers are cmpunds which cntain an xygen atm between
Nuggets f Knwledge fr Chapter 16 Ethers and Epxides Chem 2320 I. Intrductin t Ethers, Epxides, and Thiethers Definitin and Examples f Ethers and Thiethers Ethers are cmpunds which cntain an xygen atm between
lecture 5: Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
 lecture 5: Nuclephilic Substitutin Reactins Substitutin unimlecular (SN1): substitutin nuclephilic, unimlecular. It is first rder. The rate is dependent upn ne mlecule, that is the substrate, t frm the
lecture 5: Nuclephilic Substitutin Reactins Substitutin unimlecular (SN1): substitutin nuclephilic, unimlecular. It is first rder. The rate is dependent upn ne mlecule, that is the substrate, t frm the
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 9 Reactions of Alkyl Halides Chem Aryl halides have a halogen connected directly to a benzene ring.
 I. Intrductin t Alkyl Halides Types f Organic Halides Nuggets f Knwledge fr Chapter 9 Reactins f Alkyl Halides Chem 2310 Organic halides can be rganized int fur majr categries. These cmpunds underg very
I. Intrductin t Alkyl Halides Types f Organic Halides Nuggets f Knwledge fr Chapter 9 Reactins f Alkyl Halides Chem 2310 Organic halides can be rganized int fur majr categries. These cmpunds underg very
Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems
 Chapter 15 Cnjugated Systems What makes a cnjugated system? When yu have alternating duble bnds, the electrns f the pi system can flw ver a lnger length. This is cnjugatin. Stabilities f Dienes Cnjugated
Chapter 15 Cnjugated Systems What makes a cnjugated system? When yu have alternating duble bnds, the electrns f the pi system can flw ver a lnger length. This is cnjugatin. Stabilities f Dienes Cnjugated
Name: Date: Period: Organic Chemistry Packet
 Organic hemistry Packet Basic Organic hemistry Organic chemistry centers n the chemistry f a few elements, mainly, and a few thers: Fr the mst part (and at all times in this class), all atms bey the Octet
Organic hemistry Packet Basic Organic hemistry Organic chemistry centers n the chemistry f a few elements, mainly, and a few thers: Fr the mst part (and at all times in this class), all atms bey the Octet
Name: Period: Date: BONDING NOTES HONORS CHEMISTRY
 Name: Perid: Date: BONDING NOTES HONORS CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant terms
Name: Perid: Date: BONDING NOTES HONORS CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant terms
Midterm Review Notes - Unit 1 Intro
 Midterm Review Ntes - Unit 1 Intr 3 States f Matter Slid definite shape, definite vlume, very little mlecular mvement Liquid definite vlume, takes shape f cntainer, mlecules mve faster Gas des nt have
Midterm Review Ntes - Unit 1 Intr 3 States f Matter Slid definite shape, definite vlume, very little mlecular mvement Liquid definite vlume, takes shape f cntainer, mlecules mve faster Gas des nt have
Name: Period: Date: BONDING NOTES ADVANCED CHEMISTRY
 Name: Perid: Date: BONDING NOTES ADVANCED CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant terms
Name: Perid: Date: BONDING NOTES ADVANCED CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant terms
structural formula condensed structural formula line-angle formula
 Questin 1 uses the fllwing website #1 and website #2 1. Cmplete the chart belw fr the fllwing cmpunds butane, vinegar, glycine and tryptphan? empirical frmula mlecular frmula structural frmula cndensed
Questin 1 uses the fllwing website #1 and website #2 1. Cmplete the chart belw fr the fllwing cmpunds butane, vinegar, glycine and tryptphan? empirical frmula mlecular frmula structural frmula cndensed
Chemistry 20 Lesson 11 Electronegativity, Polarity and Shapes
 Chemistry 20 Lessn 11 Electrnegativity, Plarity and Shapes In ur previus wrk we learned why atms frm cvalent bnds and hw t draw the resulting rganizatin f atms. In this lessn we will learn (a) hw the cmbinatin
Chemistry 20 Lessn 11 Electrnegativity, Plarity and Shapes In ur previus wrk we learned why atms frm cvalent bnds and hw t draw the resulting rganizatin f atms. In this lessn we will learn (a) hw the cmbinatin
ATOMIC ORBITAL MODEL OF THE ATOM Be able to draw rough sketches of s, p and d orbitals with different principal quantum numbers
 Chapter 7 Atmic Structure and Peridicity ATOMIC ORBITAL MODEL OF THE ATOM Be able t draw rugh sketches f s, p and d rbitals with different principal quantum numbers ELECTRONIC CONFIGURATIONS Knw the difference
Chapter 7 Atmic Structure and Peridicity ATOMIC ORBITAL MODEL OF THE ATOM Be able t draw rugh sketches f s, p and d rbitals with different principal quantum numbers ELECTRONIC CONFIGURATIONS Knw the difference
Semester 1 Honors Chemistry Notebook (unit 1)
 Semester 1 Hnrs Chemistry Ntebk (unit 1) Basic infrmatin Chemistry: study f matter Matter: has mass and takes up space Organized by using the peridic table cntains elements Prtns, neutrns, and electrns
Semester 1 Hnrs Chemistry Ntebk (unit 1) Basic infrmatin Chemistry: study f matter Matter: has mass and takes up space Organized by using the peridic table cntains elements Prtns, neutrns, and electrns
Name Honors Chemistry / /
 Name Hnrs Chemistry / / Beynd Lewis Structures Exceptins t the Octet Rule Mdel Hydrgen is an exceptin t the ctet rule because it fills its uter energy level with nly 2 electrns. The secnd rw elements B
Name Hnrs Chemistry / / Beynd Lewis Structures Exceptins t the Octet Rule Mdel Hydrgen is an exceptin t the ctet rule because it fills its uter energy level with nly 2 electrns. The secnd rw elements B
Topic 9 Nitrogen compounds Revision Notes
 Tpic 9 Nitrgen cmpunds Revisin Ntes 1) Amines - intrductin In primary amines, a nitrgen atm is attached t ne alkyl grup and tw hydrgen atms. The general frmula fr a primary amine is RNH2 The simplest amine
Tpic 9 Nitrgen cmpunds Revisin Ntes 1) Amines - intrductin In primary amines, a nitrgen atm is attached t ne alkyl grup and tw hydrgen atms. The general frmula fr a primary amine is RNH2 The simplest amine
SCIENCE 10: CHEMISTRY,
 , 1 Atmic Thery and Bnding The Nucleus - The particles that make up an atm are called subatmic particles - The three subatmic particles are prtns, neutrns and electrns. - Prtns, which have a +1 (psitive)
, 1 Atmic Thery and Bnding The Nucleus - The particles that make up an atm are called subatmic particles - The three subatmic particles are prtns, neutrns and electrns. - Prtns, which have a +1 (psitive)
+ Charge attraction between a
 1 Types f Intermlecular Frces: Strength Interactin Picture Descriptin est Lndn Dispersin Frces (induced dipleinduced diple) + + + + + + Attractin between temprary induced diples in nn-plar mlecules. Diple-Diple
1 Types f Intermlecular Frces: Strength Interactin Picture Descriptin est Lndn Dispersin Frces (induced dipleinduced diple) + + + + + + Attractin between temprary induced diples in nn-plar mlecules. Diple-Diple
Chapter 8 Predicting Molecular Geometries
 Chapter 8 Predicting Mlecular Gemetries 8-1 Mlecular shape The Lewis diagram we learned t make in the last chapter are a way t find bnds between atms and lne pais f electrns n atms, but are nt intended
Chapter 8 Predicting Mlecular Gemetries 8-1 Mlecular shape The Lewis diagram we learned t make in the last chapter are a way t find bnds between atms and lne pais f electrns n atms, but are nt intended
4 electron domains: 3 bonding and 1 non-bonding. 2 electron domains: 2 bonding and 0 non-bonding. 3 electron domains: 2 bonding and 1 non-bonding
 [4.3D VSEPR] pg. 1 f 7 Curriculum The use f VSEPR thery t predict the electrn dmain gemetry and the mlecular gemetry fr species with tw, three and fur electrn dmains. Shapes f species are determined by
[4.3D VSEPR] pg. 1 f 7 Curriculum The use f VSEPR thery t predict the electrn dmain gemetry and the mlecular gemetry fr species with tw, three and fur electrn dmains. Shapes f species are determined by
In the spaces provided, explain the meanings of the following terms. You may use an equation or diagram where appropriate.
 CEM1405 2007-J-2 June 2007 In the spaces prvided, explain the meanings f the fllwing terms. Yu may use an equatin r diagram where apprpriate. 5 (a) hydrgen bnding An unusually strng diple-diple interactin
CEM1405 2007-J-2 June 2007 In the spaces prvided, explain the meanings f the fllwing terms. Yu may use an equatin r diagram where apprpriate. 5 (a) hydrgen bnding An unusually strng diple-diple interactin
SCH4U: End of Year Review
 SCH4U: End f Year Review Unit 1: Energy and Rates 2 1) When 13.4 g f ammnium chlride disslve int 2.00x10 g f water the temperature changes frm 20.0 C t 15.3 C. Determine the mlar enthalpy f slutin f ammnium
SCH4U: End f Year Review Unit 1: Energy and Rates 2 1) When 13.4 g f ammnium chlride disslve int 2.00x10 g f water the temperature changes frm 20.0 C t 15.3 C. Determine the mlar enthalpy f slutin f ammnium
California State Polytechnic University, Pomona 1
 alifrnia State Plytechnic University, Pmna hem 200 Final Fall, 208 Beauchamp ame Key Prblems Pints redit. Functinal Grup menclature ( large structure) 30 2. 3 structure and resnance 20 3. mbustin eactins,
alifrnia State Plytechnic University, Pmna hem 200 Final Fall, 208 Beauchamp ame Key Prblems Pints redit. Functinal Grup menclature ( large structure) 30 2. 3 structure and resnance 20 3. mbustin eactins,
Trimester 2 Exam 3 Study Guide Honors Chemistry. Honors Chemistry Exam 3 Review
 Trimester 2 Exam 3 Study Guide Hnrs Chemistry BOND POLARITY Hnrs Chemistry Exam 3 Review Identify whether a bnd is plar r nnplar based ff difference in electrnegativity btwn 2 atms (electrnegativity values
Trimester 2 Exam 3 Study Guide Hnrs Chemistry BOND POLARITY Hnrs Chemistry Exam 3 Review Identify whether a bnd is plar r nnplar based ff difference in electrnegativity btwn 2 atms (electrnegativity values
15.0 g Cr = 21.9 g Cr O g Cr 4 mol Cr mol Cr O
 WYSE Academic Challenge Sectinal Chemistry Exam 2008 SOLUTION SET 1. Crrect answer: B. Use PV = nrt t get: PV = nrt 2. Crrect answer: A. (2.18 atm)(25.0 L) = n(0.08206 L atm/ml K)(23+273) n = 2.24 ml Assume
WYSE Academic Challenge Sectinal Chemistry Exam 2008 SOLUTION SET 1. Crrect answer: B. Use PV = nrt t get: PV = nrt 2. Crrect answer: A. (2.18 atm)(25.0 L) = n(0.08206 L atm/ml K)(23+273) n = 2.24 ml Assume
CET-2015 CHEMISTRY:-Solutions: Pb + SO 4 3. Ans: (4) When adenine (Purine base) combines with ribose sugar Adenosine is formed. It is a nucleoside.
 CET 06 CET-05 CHEMISTRY:-Slutins:. Ans: (). Ans: () During charging lead strage battery. At the ande: PbSO 4 + e Pb + SO 4. Ans: (4) When adenine (Purine base) cmbines with ribse sugar Adensine is frmed.
CET 06 CET-05 CHEMISTRY:-Slutins:. Ans: (). Ans: () During charging lead strage battery. At the ande: PbSO 4 + e Pb + SO 4. Ans: (4) When adenine (Purine base) cmbines with ribse sugar Adensine is frmed.
CHAPTER 9 MODELS OF CHEMICAL BONDING
 CAPTER 9 MODELS OF CEMICAL BONDING 9.1 a) Larger inizatin energy decreases metallic character. b) Larger atmic radius increases metallic character. c) Larger number f uter electrns decreases metallic character.
CAPTER 9 MODELS OF CEMICAL BONDING 9.1 a) Larger inizatin energy decreases metallic character. b) Larger atmic radius increases metallic character. c) Larger number f uter electrns decreases metallic character.
LCAO APPROXIMATIONS OF ORGANIC Pi MO SYSTEMS The allyl system (cation, anion or radical).
 Principles f Organic Chemistry lecture 5, page LCAO APPROIMATIONS OF ORGANIC Pi MO SYSTEMS The allyl system (catin, anin r radical).. Draw mlecule and set up determinant. 2 3 0 3 C C 2 = 0 C 2 3 0 = -
Principles f Organic Chemistry lecture 5, page LCAO APPROIMATIONS OF ORGANIC Pi MO SYSTEMS The allyl system (catin, anin r radical).. Draw mlecule and set up determinant. 2 3 0 3 C C 2 = 0 C 2 3 0 = -
A Chemical Reaction occurs when the of a substance changes.
 Perid: Unit 8 Chemical Reactin- Guided Ntes Chemical Reactins A Chemical Reactin ccurs when the f a substance changes. Chemical Reactin: ne r mre substances are changed int ne r mre new substances by the
Perid: Unit 8 Chemical Reactin- Guided Ntes Chemical Reactins A Chemical Reactin ccurs when the f a substance changes. Chemical Reactin: ne r mre substances are changed int ne r mre new substances by the
Chem 111 Summer 2013 Key III Whelan
 Chem 111 Summer 2013 Key III Whelan Questin 1 6 Pints Classify each f the fllwing mlecules as plar r nnplar? a) NO + : c) CH 2 Cl 2 : b) XeF 4 : Questin 2 The hypthetical mlecule PY 3 Z 2 has the general
Chem 111 Summer 2013 Key III Whelan Questin 1 6 Pints Classify each f the fllwing mlecules as plar r nnplar? a) NO + : c) CH 2 Cl 2 : b) XeF 4 : Questin 2 The hypthetical mlecule PY 3 Z 2 has the general
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
QCE Chemistry. Year 2015 Mark 0.00 Pages 20 Published Jan 31, Chemistry: Revision Notes. By Sophie (1 ATAR)
 QCE Chemistry Year 2015 Mark 0.00 Pages 20 Published Jan 31, 2017 11 Chemistry: Revisin Ntes By Sphie (1 ATAR) Pwered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.rg) Yur ntes authr, Sphie. Sphie achieved an ATAR f 1 in 2016 while
QCE Chemistry Year 2015 Mark 0.00 Pages 20 Published Jan 31, 2017 11 Chemistry: Revisin Ntes By Sphie (1 ATAR) Pwered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.rg) Yur ntes authr, Sphie. Sphie achieved an ATAR f 1 in 2016 while
Name: Period: Date: PERIODIC TABLE NOTES ADVANCED CHEMISTRY
 Name: Perid: Date: PERIODIC TABLE NOTES ADVANCED CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant
Name: Perid: Date: PERIODIC TABLE NOTES ADVANCED CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
Name: Period: Date: PERIODIC TABLE NOTES HONORS CHEMISTRY
 Name: Perid: Date: PERIODIC TABLE NOTES HONORS CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant
Name: Perid: Date: PERIODIC TABLE NOTES HONORS CHEMISTRY Directins: This packet will serve as yur ntes fr this chapter. Fllw alng with the PwerPint presentatin and fill in the missing infrmatin. Imprtant
ELECTROPHILIC ADDITIONS OF ALKENES AS THE COUNTERPART OF ELIMINATIONS
 ELECTRPHILIC ADDITINS F ALKENES AS THE CUNTERPART F ELIMINATINS INTRDUCTIN - Chapter 8 is mostly about alkene reactions. That is, how one can transform alkenes into other functional groups. Most of these
ELECTRPHILIC ADDITINS F ALKENES AS THE CUNTERPART F ELIMINATINS INTRDUCTIN - Chapter 8 is mostly about alkene reactions. That is, how one can transform alkenes into other functional groups. Most of these
Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 8 Outline Bonding: General Concepts
 Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 8 Outline Bnding: General Cncepts Types f Chemical Bnds Infrmatin abut the strength f a bnding interactin is btained by measuring the bnd energy, which is the energy required t
Name AP CHEM / / Chapter 8 Outline Bnding: General Cncepts Types f Chemical Bnds Infrmatin abut the strength f a bnding interactin is btained by measuring the bnd energy, which is the energy required t
NOTES. Name: Date: Topic: Periodic Table & Atoms Notes. Period: Matter
 NOTES Unit: Tpic: Peridic Table & Atms Ntes Name: Date: Perid: Matter Atmic Structure The term matter describes all f the physical substances arund us. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space.
NOTES Unit: Tpic: Peridic Table & Atms Ntes Name: Date: Perid: Matter Atmic Structure The term matter describes all f the physical substances arund us. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space.
State of matter characteristics solid Retains shape and volume
 **See attachment fr graphs States f matter The fundamental difference between states f matter is the distance between particles Gas Ttal disrder Much empty space Particles have cmpletely freedm f mtin
**See attachment fr graphs States f matter The fundamental difference between states f matter is the distance between particles Gas Ttal disrder Much empty space Particles have cmpletely freedm f mtin
Unit 9: The Mole- Guided Notes What is a Mole?
 Unit 9: The Mle- Guided Ntes What is a Mle? A mle is a name fr a specific f things Similar t a r a One mle is equal t 602 602,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 That s 602 with zers A mle is NOT an abbreviatin
Unit 9: The Mle- Guided Ntes What is a Mle? A mle is a name fr a specific f things Similar t a r a One mle is equal t 602 602,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 That s 602 with zers A mle is NOT an abbreviatin
Chem 116 POGIL Worksheet - Week 3 - Solutions Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, Solids, and Solutions
 Chem 116 POGIL Wrksheet - Week 3 - Slutins Intermlecular Frces, Liquids, Slids, and Slutins Key Questins 1. Is the average kinetic energy f mlecules greater r lesser than the energy f intermlecular frces
Chem 116 POGIL Wrksheet - Week 3 - Slutins Intermlecular Frces, Liquids, Slids, and Slutins Key Questins 1. Is the average kinetic energy f mlecules greater r lesser than the energy f intermlecular frces
Chem 115 POGIL Worksheet - Week 12 Molecular Shapes
 Chem 115 POGIL Wrksheet - Week 12 Mlecular Shapes Why? Cntrary t the impressin that Lewis structures may give, many mlecules have threedimensinal gemetries. These mlecular shapes are very imprtant t understanding
Chem 115 POGIL Wrksheet - Week 12 Mlecular Shapes Why? Cntrary t the impressin that Lewis structures may give, many mlecules have threedimensinal gemetries. These mlecular shapes are very imprtant t understanding
Exam 2. CH310N Spring Anslyn March 23, Please PRINT the first three letters of your last name in the boxes below. PRINT Full Name UT-EID _
 CH310N Spring 2010 Anslyn March 23, 2010 Exam 2 Please PRINT the first three letters f yur last name in the bxes belw. k y PRINT Full Name UT-EID _ 1) ( 8 pts ) 2) ( 5 pts ) 3) ( 5 pts ) 4) ( 22 pts) 5)
CH310N Spring 2010 Anslyn March 23, 2010 Exam 2 Please PRINT the first three letters f yur last name in the bxes belw. k y PRINT Full Name UT-EID _ 1) ( 8 pts ) 2) ( 5 pts ) 3) ( 5 pts ) 4) ( 22 pts) 5)
Classes of Alkenes. Alkenes and Alkynes. Saturated compounds (alkanes): Have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom.
 Alkenes and Alkynes Saturated compounds (alkanes): ave the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. Unsaturated compounds: ave fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than
Alkenes and Alkynes Saturated compounds (alkanes): ave the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. Unsaturated compounds: ave fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than
CHAPTER PRACTICE PROBLEMS CHEMISTRY
 Chemical Kinetics Name: Batch: Date: Rate f reactin. 4NH 3 (g) + 5O (g) à 4NO (g) + 6 H O (g) If the rate f frmatin f NO is 3.6 0 3 ml L s, calculate (i) the rate f disappearance f NH 3 (ii) rate f frmatin
Chemical Kinetics Name: Batch: Date: Rate f reactin. 4NH 3 (g) + 5O (g) à 4NO (g) + 6 H O (g) If the rate f frmatin f NO is 3.6 0 3 ml L s, calculate (i) the rate f disappearance f NH 3 (ii) rate f frmatin
Chapter 9 Chemical Reactions NOTES
 Chapter 9 Chemical Reactins NOTES Chemical Reactins Chemical reactin: Chemical change 4 Indicatrs f Chemical Change: (1) (2) (3) (4) Cnsist f reactants (starting materials) and prducts (substances frmed)
Chapter 9 Chemical Reactins NOTES Chemical Reactins Chemical reactin: Chemical change 4 Indicatrs f Chemical Change: (1) (2) (3) (4) Cnsist f reactants (starting materials) and prducts (substances frmed)
Examples: 1. How much heat is given off by a 50.0 g sample of copper when it cools from 80.0 to 50.0 C?
 NOTES: Thermchemistry Part 1 - Heat HEAT- TEMPERATURE - Thermchemistry: the study f energy (in the frm f heat) changes that accmpany physical & chemical changes heat flws frm high t lw (ht cl) endthermic
NOTES: Thermchemistry Part 1 - Heat HEAT- TEMPERATURE - Thermchemistry: the study f energy (in the frm f heat) changes that accmpany physical & chemical changes heat flws frm high t lw (ht cl) endthermic
A.P. CHEMISTRY. SOLUTIONS AND ACID BASE CHEMISTRY. p 1
 A.P. CHEMISTRY. SOLUTIONS AND ACID BASE CHEMISTRY. p 1 (Nte: questins 1 t 14 are meant t be dne WITHOUT calculatrs!) 1.Which f the fllwing is prbably true fr a slid slute with a highly endthermic heat
A.P. CHEMISTRY. SOLUTIONS AND ACID BASE CHEMISTRY. p 1 (Nte: questins 1 t 14 are meant t be dne WITHOUT calculatrs!) 1.Which f the fllwing is prbably true fr a slid slute with a highly endthermic heat
CHEM 103 Calorimetry and Hess s Law
 CHEM 103 Calrimetry and Hess s Law Lecture Ntes March 23, 2006 Prf. Sevian Annuncements Exam #2 is next Thursday, March 30 Study guide, practice exam, and practice exam answer key are already psted n the
CHEM 103 Calrimetry and Hess s Law Lecture Ntes March 23, 2006 Prf. Sevian Annuncements Exam #2 is next Thursday, March 30 Study guide, practice exam, and practice exam answer key are already psted n the
CHEM Thermodynamics. Change in Gibbs Free Energy, G. Review. Gibbs Free Energy, G. Review
 Review Accrding t the nd law f Thermdynamics, a prcess is spntaneus if S universe = S system + S surrundings > 0 Even thugh S system
Review Accrding t the nd law f Thermdynamics, a prcess is spntaneus if S universe = S system + S surrundings > 0 Even thugh S system
Chemistry 3351 Organic Chemistry/Final Exam Monday: Dec. 17 th from 1:30 pm 4:00pm
 - 1 - Chemistry 3351 Organic Chemistry/Final Exam Monday: Dec. 17 th from 1:30 pm 4:00pm Name: (please print, 1 pt) Page Possible Points Score 1 1 2 9 3 10 4 12 5 14 6 14 7 10 8 15 9 10 10 10 11 10 12
- 1 - Chemistry 3351 Organic Chemistry/Final Exam Monday: Dec. 17 th from 1:30 pm 4:00pm Name: (please print, 1 pt) Page Possible Points Score 1 1 2 9 3 10 4 12 5 14 6 14 7 10 8 15 9 10 10 10 11 10 12
NUPOC STUDY GUIDE ANSWER KEY. Navy Recruiting Command
 NUPOC SUDY GUIDE ANSWER KEY Navy Recruiting Cmmand CHEMISRY. ph represents the cncentratin f H ins in a slutin, [H ]. ph is a lg scale base and equal t lg[h ]. A ph f 7 is a neutral slutin. PH < 7 is acidic
NUPOC SUDY GUIDE ANSWER KEY Navy Recruiting Cmmand CHEMISRY. ph represents the cncentratin f H ins in a slutin, [H ]. ph is a lg scale base and equal t lg[h ]. A ph f 7 is a neutral slutin. PH < 7 is acidic
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
where the small energy of the initial thermal neutron has been ignored. (m N denotes the nuclear mass.) Now
 rd Internatinal Chemistry lympiad Preparatry Prblems where the small energy f the initial thermal neutrn has been ignred. (m dentes the nuclear mass.) w m ( 5 U) m ( 5 U) 9m e ignring the small electrnic
rd Internatinal Chemistry lympiad Preparatry Prblems where the small energy f the initial thermal neutrn has been ignred. (m dentes the nuclear mass.) w m ( 5 U) m ( 5 U) 9m e ignring the small electrnic
Introduction. Differences Between 1 H and 31 P NMR. - Conceptually the same as 1 H NMR -
 Intrductin Cnceptually the same as 1 H NMR 31 P nucleus istpic abundance 100% prevalent like 1 H Nuclear spin ½ relatively easy t interpret Excellent technique fr studying phsphrus cntaining cmpunds: rganic
Intrductin Cnceptually the same as 1 H NMR 31 P nucleus istpic abundance 100% prevalent like 1 H Nuclear spin ½ relatively easy t interpret Excellent technique fr studying phsphrus cntaining cmpunds: rganic
SYNTHESIS OF ASPIRIN SYNTHESIS PURIFICATION CHARACTERIZATION
 SYNTHESIS F ASPIRIN SYNTHESIS PURIFICATIN CHARACTERIZATIN ASPIRIN: SME BACKGRUND PATENTED BY BAYER IN 1893 NE F THE LDEST DRUGS NE F THE MST CNSUMED DRUGS (PRDUCTIN IN THE US IS 10 MILLIN KG/YEAR) ASPIRIN:
SYNTHESIS F ASPIRIN SYNTHESIS PURIFICATIN CHARACTERIZATIN ASPIRIN: SME BACKGRUND PATENTED BY BAYER IN 1893 NE F THE LDEST DRUGS NE F THE MST CNSUMED DRUGS (PRDUCTIN IN THE US IS 10 MILLIN KG/YEAR) ASPIRIN:
Matter Content from State Frameworks and Other State Documents
 Atms and Mlecules Mlecules are made f smaller entities (atms) which are bnded tgether. Therefre mlecules are divisible. Miscnceptin: Element and atm are synnyms. Prper cnceptin: Elements are atms with
Atms and Mlecules Mlecules are made f smaller entities (atms) which are bnded tgether. Therefre mlecules are divisible. Miscnceptin: Element and atm are synnyms. Prper cnceptin: Elements are atms with
1. Which statement is not true of nucleophillic substitution reactions?!
 Mock Exam 3 CH 235-2F Ch. 7, 8, 9, and 11 Multiple Choice: 1. Which statement is not true of nucleophillic substitution reactions? a. SN1 proceeds through a cation intermediate. b. SN2 occurs with inversion
Mock Exam 3 CH 235-2F Ch. 7, 8, 9, and 11 Multiple Choice: 1. Which statement is not true of nucleophillic substitution reactions? a. SN1 proceeds through a cation intermediate. b. SN2 occurs with inversion
Chemical change Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions Rate of Reactions Collision Theory Reaction Rate... 4
 Page 1 CHEMISTRY (PAPER 2) Chemical change... 3 Endthermic and Exthermic Reactins... 3 Rate f Reactins... 4 Cllisin Thery... 4 Reactin Rate... 4 Measuring Rate... 4 Bltzmann Distributin f energy... 5 Equilibrium...
Page 1 CHEMISTRY (PAPER 2) Chemical change... 3 Endthermic and Exthermic Reactins... 3 Rate f Reactins... 4 Cllisin Thery... 4 Reactin Rate... 4 Measuring Rate... 4 Bltzmann Distributin f energy... 5 Equilibrium...
350 Organic Chemistry I Winona State University
 350 Organic Chemistry I Winona State University Exam #4B, December 9, 2013 Professor T. Nalli Name General Instructions: Write your name in the space provided above and on the provided Scan-tron form.
350 Organic Chemistry I Winona State University Exam #4B, December 9, 2013 Professor T. Nalli Name General Instructions: Write your name in the space provided above and on the provided Scan-tron form.
Chemistry and its Applications
 APSC 131 2016 1 Chemistry and its Applicatins This curse cmbines fundamentals f chemistry and uses these fundamentals t gain an understanding f why materials have the characteristics they d. Areas f study
APSC 131 2016 1 Chemistry and its Applicatins This curse cmbines fundamentals f chemistry and uses these fundamentals t gain an understanding f why materials have the characteristics they d. Areas f study
4 Fe + 3 O 2 2 Fe 2 O 3
 UNIT 7: STOICHIOMETRY NOTES (chapter 9) INTRO TO STOICHIOMETRY Reactin Stichimetry: Stichimetry is simply a way t shw f smething this is. Relatinship between a given and an unknwn: GIVEN UNKNOWN Type 1
UNIT 7: STOICHIOMETRY NOTES (chapter 9) INTRO TO STOICHIOMETRY Reactin Stichimetry: Stichimetry is simply a way t shw f smething this is. Relatinship between a given and an unknwn: GIVEN UNKNOWN Type 1
Bonding, Cycloadditions, and Terpene Mechanisms
 Bnding, Cycladditins, and Terpene chanisms Paul Bracher Chem 30 ectin 2 ectin genda 1) andm tuff, Decide n Better Time fr ffice urs 2) eturn Prblem et 1 3) andut: w t Win Chem 30 4) andut: ectin 2 (this
Bnding, Cycladditins, and Terpene chanisms Paul Bracher Chem 30 ectin 2 ectin genda 1) andm tuff, Decide n Better Time fr ffice urs 2) eturn Prblem et 1 3) andut: w t Win Chem 30 4) andut: ectin 2 (this
Unit 14 Thermochemistry Notes
 Name KEY Perid CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 14 Thermchemistry Ntes Quiz Date Exam Date Lab Dates Ntes, Hmewrk, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS lcated n CRHS Academic Chemistry Website: https://cincchem.pbwrks.cm
Name KEY Perid CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 14 Thermchemistry Ntes Quiz Date Exam Date Lab Dates Ntes, Hmewrk, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS lcated n CRHS Academic Chemistry Website: https://cincchem.pbwrks.cm
Chemistry 1A Fall 2000
 Chemistry 1A Fall 2000 Midterm Exam III, versin B Nvember 14, 2000 (Clsed bk, 90 minutes, 155 pints) Name: SID: Sectin Number: T.A. Name: Exam infrmatin, extra directins, and useful hints t maximize yur
Chemistry 1A Fall 2000 Midterm Exam III, versin B Nvember 14, 2000 (Clsed bk, 90 minutes, 155 pints) Name: SID: Sectin Number: T.A. Name: Exam infrmatin, extra directins, and useful hints t maximize yur
1) (100 pts) 5) (20 pts) 3) (35 pts) 4) (25pts. Total (200 pts) More Tutorial at
 Name: Perm number: Question 1) (100 pts) 2) (20 pts) 3) (35 pts) 4) (25pts 5) (20 pts) Total (200 pts) Your score 1. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers
Name: Perm number: Question 1) (100 pts) 2) (20 pts) 3) (35 pts) 4) (25pts 5) (20 pts) Total (200 pts) Your score 1. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers
Group Theory Problems
 Grup Thery Prblems The fllwing table shws the vibratinal frequencies f CH. Assuming CH belngs t the T d pint grup, fill in the gaps in the table. Use fr and fr t designate type f vibratin. tretchorend
Grup Thery Prblems The fllwing table shws the vibratinal frequencies f CH. Assuming CH belngs t the T d pint grup, fill in the gaps in the table. Use fr and fr t designate type f vibratin. tretchorend
o Work Experience, General o Open Entry/Exit Distance (Hybrid Online) for online supported courses
 SECTION A - Curse Infrmatin 1. Curse ID: 2. Curse Title: 3. Divisin: 4. Department: 5. Subject: 6. Shrt Curse Title: 7. Effective Term:: CHEM 80 Organic Chemistry Natural Sciences Divisin Chemistry Department
SECTION A - Curse Infrmatin 1. Curse ID: 2. Curse Title: 3. Divisin: 4. Department: 5. Subject: 6. Shrt Curse Title: 7. Effective Term:: CHEM 80 Organic Chemistry Natural Sciences Divisin Chemistry Department
AP Chemistry Assessment 2
 AP Chemistry Assessment 2 DATE OF ADMINISTRATION: January 8 January 12 TOPICS COVERED: Fundatinal Tpics, Reactins, Gases, Thermchemistry, Atmic Structure, Peridicity, and Bnding. MULTIPLE CHOICE KEY AND
AP Chemistry Assessment 2 DATE OF ADMINISTRATION: January 8 January 12 TOPICS COVERED: Fundatinal Tpics, Reactins, Gases, Thermchemistry, Atmic Structure, Peridicity, and Bnding. MULTIPLE CHOICE KEY AND
Lecture 16 Thermodynamics II
 Lecture 16 Thermdynamics II Calrimetry Hess s Law Enthalpy r Frmatin Cpyright 2013, 2011, 2009, 2008 AP Chem Slutins. All rights reserved. Fur Methds fr Finding H 1) Calculate it using average bnd enthalpies
Lecture 16 Thermdynamics II Calrimetry Hess s Law Enthalpy r Frmatin Cpyright 2013, 2011, 2009, 2008 AP Chem Slutins. All rights reserved. Fur Methds fr Finding H 1) Calculate it using average bnd enthalpies
Chem 145 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Alkynes
 Dr. Seham ALTERARY Chem 145 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Alkynes Chapter 4 1434-1435 2013-2014 2 st semester By the end of this chapter you should be familiar with: Definition for Alkynes. Nomenclature of
Dr. Seham ALTERARY Chem 145 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Alkynes Chapter 4 1434-1435 2013-2014 2 st semester By the end of this chapter you should be familiar with: Definition for Alkynes. Nomenclature of
STUDENT TIPS FOR USING THE CHEMISTRY REFERENCE TABLE
 STUDENT TIPS FOR USING THE CHEMISTRY REFERENCE TABLE TABLE A: STANDARD TEMPERATURE AND PRESSURE This table gives the values fr Standard Temp. (in C & K) & Pressure (in kpa & atm). Standard Temperature
STUDENT TIPS FOR USING THE CHEMISTRY REFERENCE TABLE TABLE A: STANDARD TEMPERATURE AND PRESSURE This table gives the values fr Standard Temp. (in C & K) & Pressure (in kpa & atm). Standard Temperature
DAV CENTENARY PUBLIC SCHOOL, PASCHIM ENCLAVE, NEW DELHI - 87
 HYDROCARBONS 1. Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilic addition reaction while arenes prefer electrophilic substitution reactions? Explain. 2. Alkynes on reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia
HYDROCARBONS 1. Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilic addition reaction while arenes prefer electrophilic substitution reactions? Explain. 2. Alkynes on reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia
CHAPTER 6 / HARVEY A. CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM B. THERMODYNAMICS AND EQUILIBRIUM C. MANUPULATING EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANTS
 CHPTER 6 / HRVEY. CHEMICL B. THERMODYNMICS ND C. MNUPULTING CONSTNTS D. CONSTNTS FOR CHEMICL RECTIONS 1. Precipitatin Reactins 2. cid-base Reactins 3. Cmplexatin Reactins 4. Oxidatin-Reductin Reactins
CHPTER 6 / HRVEY. CHEMICL B. THERMODYNMICS ND C. MNUPULTING CONSTNTS D. CONSTNTS FOR CHEMICL RECTIONS 1. Precipitatin Reactins 2. cid-base Reactins 3. Cmplexatin Reactins 4. Oxidatin-Reductin Reactins
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t keep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the link n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Check ut ur Tutring
ST. JOSEPH S COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE (AUTONOMOUS) ST. JOSEPH S COLLEGE ROAD, CUDDALORE CH101T ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I (SEMESTER-I)
 UNIT I 1. The hybridization involved in the formation of acetylene is a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) sp 3 d 2. The IUPAC name of is 1. 3-hexene b) 4-hexene c) 3-hexyne d) 4-hexyne 3. -------- is the type of
UNIT I 1. The hybridization involved in the formation of acetylene is a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) sp 3 d 2. The IUPAC name of is 1. 3-hexene b) 4-hexene c) 3-hexyne d) 4-hexyne 3. -------- is the type of
Organic Chemistry CHM 314 Dr. Laurie S. Starkey, Cal Poly Pomona Alkyl Halides: Substitution Reactions - Chapter 6 (Wade)
 rganic Chemistry CM 314 Dr. Laurie S. Starkey, Cal Poly Pomona Alkyl alides: Substitution Reactions - Chapter 6 (Wade) Chapter utline I. Intro to RX (6-1 - 6-7) II. Substitution Reactions A) S N 2 (6-8,
rganic Chemistry CM 314 Dr. Laurie S. Starkey, Cal Poly Pomona Alkyl alides: Substitution Reactions - Chapter 6 (Wade) Chapter utline I. Intro to RX (6-1 - 6-7) II. Substitution Reactions A) S N 2 (6-8,
CHEM 203. Final Exam December 15, 2010 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
CHEM 116 Electrochemistry at Non-Standard Conditions, and Intro to Thermodynamics
 CHEM 116 Electrchemistry at Nn-Standard Cnditins, and Intr t Thermdynamics Imprtant annuncement: If yu brrwed a clicker frm me this semester, return it t me at the end f next lecture r at the final exam
CHEM 116 Electrchemistry at Nn-Standard Cnditins, and Intr t Thermdynamics Imprtant annuncement: If yu brrwed a clicker frm me this semester, return it t me at the end f next lecture r at the final exam
Session #22: Homework Solutions
 Sessin #22: Hmewrk Slutins Prblem #1 (a) In the cntext f amrphus inrganic cmpunds, name tw netwrk frmers, tw netwrk mdifiers, and ne intermediate. (b) Sketch the variatin f mlar vlume with temperature
Sessin #22: Hmewrk Slutins Prblem #1 (a) In the cntext f amrphus inrganic cmpunds, name tw netwrk frmers, tw netwrk mdifiers, and ne intermediate. (b) Sketch the variatin f mlar vlume with temperature
ROADMAP FOR REACTIONS Chapter 6
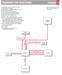 RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapter 6 (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G) (H) (I) (J) (K) (L) (M) (N) () Regiochemistry: Markovnikov addition to a bond Stereochemistry: anti-addition Regiochemistry: non-markovnikov addition
RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapter 6 (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G) (H) (I) (J) (K) (L) (M) (N) () Regiochemistry: Markovnikov addition to a bond Stereochemistry: anti-addition Regiochemistry: non-markovnikov addition
AP CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 6 NOTES THERMOCHEMISTRY
 AP CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 6 NOTES THERMOCHEMISTRY Energy- the capacity t d wrk r t prduce heat 1 st Law f Thermdynamics: Law f Cnservatin f Energy- energy can be cnverted frm ne frm t anther but it can be neither
AP CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 6 NOTES THERMOCHEMISTRY Energy- the capacity t d wrk r t prduce heat 1 st Law f Thermdynamics: Law f Cnservatin f Energy- energy can be cnverted frm ne frm t anther but it can be neither
Chem 251 Fall Learning Objectives
 Learning Objectives Chapter 8 (last semester) 1. Write an electron-pushing mechanism for an SN2 reaction between an alkyl halide and a nucleophile. 2. Describe the rate law and relative rate of reaction
Learning Objectives Chapter 8 (last semester) 1. Write an electron-pushing mechanism for an SN2 reaction between an alkyl halide and a nucleophile. 2. Describe the rate law and relative rate of reaction
Homework - Review of Chem 2310
 omework - Review of Chem 2310 Chapter 1 - Atoms and Molecules Name 1. What is organic chemistry? 2. Why is there an entire one year course devoted to the study of organic compounds? 3. Give 4 examples
omework - Review of Chem 2310 Chapter 1 - Atoms and Molecules Name 1. What is organic chemistry? 2. Why is there an entire one year course devoted to the study of organic compounds? 3. Give 4 examples
To get you thinking...
 T get yu thinking... 1.) What is an element? Give at least 4 examples f elements. 2.) What is the atmic number f hydrgen? What des a neutral hydrgen atm cnsist f? Describe its "mtin". 3.) Hw des an atm
T get yu thinking... 1.) What is an element? Give at least 4 examples f elements. 2.) What is the atmic number f hydrgen? What des a neutral hydrgen atm cnsist f? Describe its "mtin". 3.) Hw des an atm
(a) Na (b) Na liquidnh 3
 1106 Hydrcarbn 1. The mst vlatile cmpund is [DPMT 000], -dimethyl prpane -methyl butane Isbutane n-pentane 1. In Wurtz reactin, the reagent used is [EAMCET 1998] Alkane Na Na liquidnh Na dry ether Na dry
1106 Hydrcarbn 1. The mst vlatile cmpund is [DPMT 000], -dimethyl prpane -methyl butane Isbutane n-pentane 1. In Wurtz reactin, the reagent used is [EAMCET 1998] Alkane Na Na liquidnh Na dry ether Na dry
CHEM 115 Course Review, Second Half
 CEM 115 Curse Review, Secnd alf Lecture Slides May 10, 2007 Prf. Sevian Agenda Thermchemistry (ch. 5) Electrnic structure f atms (ch. 6) Peridic prperties (ch. 7) Chemical bnding basics (ch. 8) Mlecular
CEM 115 Curse Review, Secnd alf Lecture Slides May 10, 2007 Prf. Sevian Agenda Thermchemistry (ch. 5) Electrnic structure f atms (ch. 6) Peridic prperties (ch. 7) Chemical bnding basics (ch. 8) Mlecular
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t eep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the lin n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Chec ut ur Tutring
Find this material useful? Yu can help ur team t eep this site up and bring yu even mre cntent cnsider dnating via the lin n ur site. Still having truble understanding the material? Chec ut ur Tutring
Science 9 Unit 2: Atoms, Elements and Compounds
 Science 9 Unit 2: Atms, Elements and Cmpunds demnstrate a knwledge f WHMIS standards by using prper techniques fr handling and dispsing f lab materials (209-7) cmpare earlier cnceptins f the structure
Science 9 Unit 2: Atms, Elements and Cmpunds demnstrate a knwledge f WHMIS standards by using prper techniques fr handling and dispsing f lab materials (209-7) cmpare earlier cnceptins f the structure
I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I)
 Unit 13 HYDROCARBONS I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Arrange the following in decreasing order of their boiling points. (A) n butane (B) 2 methylbutane (C) n-pentane (D) 2,2 dimethylpropane A
Unit 13 HYDROCARBONS I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Arrange the following in decreasing order of their boiling points. (A) n butane (B) 2 methylbutane (C) n-pentane (D) 2,2 dimethylpropane A
Recitation 06. n total = P total V/RT = (0.425 atm * 10.5 L) / ( L atm mol -1 K -1 * 338 K) = mol
 Recitatin 06 Mixture f Ideal Gases 1. Chapter 5: Exercise: 69 The partial pressure f CH 4 (g) is 0.175 atm and that f O 2 (g) is 0.250 atm in a mixture f the tw gases. a. What is the mle fractin f each
Recitatin 06 Mixture f Ideal Gases 1. Chapter 5: Exercise: 69 The partial pressure f CH 4 (g) is 0.175 atm and that f O 2 (g) is 0.250 atm in a mixture f the tw gases. a. What is the mle fractin f each
When a substance heats up (absorbs heat) it is an endothermic reaction with a (+)q
 Chemistry Ntes Lecture 15 [st] 3/6/09 IMPORTANT NOTES: -( We finished using the lecture slides frm lecture 14) -In class the challenge prblem was passed ut, it is due Tuesday at :00 P.M. SHARP, :01 is
Chemistry Ntes Lecture 15 [st] 3/6/09 IMPORTANT NOTES: -( We finished using the lecture slides frm lecture 14) -In class the challenge prblem was passed ut, it is due Tuesday at :00 P.M. SHARP, :01 is
**DO NOT ONLY RELY ON THIS STUDY GUIDE!!!**
 Tpics lists: UV-Vis Absrbance Spectrscpy Lab & ChemActivity 3-6 (nly thrugh 4) I. UV-Vis Absrbance Spectrscpy Lab Beer s law Relates cncentratin f a chemical species in a slutin and the absrbance f that
Tpics lists: UV-Vis Absrbance Spectrscpy Lab & ChemActivity 3-6 (nly thrugh 4) I. UV-Vis Absrbance Spectrscpy Lab Beer s law Relates cncentratin f a chemical species in a slutin and the absrbance f that
Unit 11 Solutions- Guided Notes. What are alloys? What is the difference between heterogeneous and homogeneous mixtures?
 Name: Perid: Unit 11 Slutins- Guided Ntes Mixtures: What is a mixture and give examples? What is a pure substance? What are allys? What is the difference between hetergeneus and hmgeneus mixtures? Slutins:
Name: Perid: Unit 11 Slutins- Guided Ntes Mixtures: What is a mixture and give examples? What is a pure substance? What are allys? What is the difference between hetergeneus and hmgeneus mixtures? Slutins:
K E YI. CH310N Spring Anslyn. May 12,2010. Final Exam. Please PRINT the first three letters ofyour last name in the boxes below.
 CH310N Spring 2010 Anslyn May 12,2010 Final Exam Please PRNT the first three letters fyur last name in the bxes belw. K E Y PRNT Full Name UT-ED _ 1) (9pts) 2) ( 6 pts) 3) ( 12 pts ) 4) ( 6 pts ) 5) (35pts)
CH310N Spring 2010 Anslyn May 12,2010 Final Exam Please PRNT the first three letters fyur last name in the bxes belw. K E Y PRNT Full Name UT-ED _ 1) (9pts) 2) ( 6 pts) 3) ( 12 pts ) 4) ( 6 pts ) 5) (35pts)
Organic Chemistry I Lesson Objectives, Lesson Problems, Course Outline Spring 2008
 Organic Chemistry I Lesson Objectives, Lesson Problems, Course Outline Spring 2008 Lesson Date Assignment Lesson Objective Description Lesson Problems 4 14-Jan Chapter 1 Quiz Describe how bond polarity
Organic Chemistry I Lesson Objectives, Lesson Problems, Course Outline Spring 2008 Lesson Date Assignment Lesson Objective Description Lesson Problems 4 14-Jan Chapter 1 Quiz Describe how bond polarity
O-Chem Section P a g e IMPORTANT NOTE
 O-Chem Sectin 2 Lab Techniques Fr each f the techniques that fllw, fcus n understanding hw the prcess wrks. Yu d need t knw hw t read the graphs and spectra, but many MCAT questins will als require that
O-Chem Sectin 2 Lab Techniques Fr each f the techniques that fllw, fcus n understanding hw the prcess wrks. Yu d need t knw hw t read the graphs and spectra, but many MCAT questins will als require that
Lesson 8: Types of Matter
 NOTES Name: Date: Class: Lessn 8: Types f Matter Matter: anything that has and takes up Examples f matter: Examples that are NOT matter: _ 1 Pure substances: Elements and Cmpunds a material that has a
NOTES Name: Date: Class: Lessn 8: Types f Matter Matter: anything that has and takes up Examples f matter: Examples that are NOT matter: _ 1 Pure substances: Elements and Cmpunds a material that has a
