3.4. Classify each of the following pure substances as either an element or a compound.
|
|
|
- Mark Ryan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CH 112 Chapter 3 Homework Key (Due 4/17/2018) 3.4. Classify each of the followin pure substances as either an element or a compound. a. Helium as (He) element b. Mercury (H) in a thermometer element c. Suar (C 12H 22O 11) compound d. Sulfur (S) element e. Lye (NaOH) compound 3.6. Classify each of the followin mixtures as homoeneous or heteroeneous. a. Nonfat milk Either. Nonfat milk is sometimes referred to a homoenized milk, but lobules of protein may be present, leadin to a heteroeneous mixture. b. Chocolate-chip ice cream Heteroeneous c. Gasoline Homoeneous d. Peanut butter sandwich Heteroeneous e. Cranberry juice Homoeneous Describe each of the followin as a chemical or physical property. a. Neon is a colorless as at room temperature Physical b. Apple slices turn brown when exposed to air Chemical c. Phosphorus will inite in air Chemical d. Mercury is a liquid at room temperature Physical e. Propane as is compressed to a liquid for storae Physical Describe each property of the element zirconium as physical or chemical. a. Melts at 1852 C Physical b. Is resistant to corrosion Chemical c. Has a rayish-white color Physical d. Inites spontaneously in air Chemical
2 e. Is a shiny metal Physical Calculate the unknown temperature in each of the followin: a. 25 C = 77 F b. 155 C = 311 F c. 25 F = - 32 C d. 224 K = - 49 C e. 145 C = 418 K **Remember, you need to know the formulas to do these conversions for Exam 1** Indicate whether each of the followin describes potential or kinetic enery: a. The enery in your food Potential (from chemical enery) b. A tihtly wound sprin Potential (from position) c. An earthquake Kinetic (associated with motion) d. A car speedin down the road Kinetic (associated with motion) Usin the enery values for foods (table 3.7), determine each of the followin (round off the answers in kcal or k to the tens place). a. The total k in two tablespoons of crunchy peanut butter than contains 6 carbohydrate, 16 fat, and 7 protein: 17 k 38 k 17 k (6 carbohydrate ) + (16 fat ) + (7 protein ) = 829 k = 830 k b. The rams of protein in 1 cup of soup with 110 kcal that contains 9 carbohydrate and 6 fat. (9 carbohydrate 4 kcal ) + (6 fat 9 kcal ) + (X protein 4 kcal ) = 110 kcal Solve for X to find there should be 5 of protein. c. The kcal in one can of cola if it has 40. of carbohydrate and no fat or protein. (40 carbohydrate 4 kcal ) = 160 kcal
3 d. The total kcal for a diet that consists of 68 carbohydrate, 9 of fat, and 150 protein. (68 carbohydrate 4 kcal ) + (9 fat 9 kcal ) + (150 protein 4 kcal ) = 953 kcal = 950 kcal For lunch, a patient consumed 3 oz of skinless chicken, 3 oz of broccoli, 1 medium apple, and 1 cup of nonfat milk (see table 3.8). How many kcal did the patient obtain from lunch? (110 kcal chicken) + (30 kcal broccoli) + (60 kcal apple) + (90 kcal milk) = 290 kcal Use the heat equation to calculate the enery (in and cal) for each of the followin: a. To heat 5.25 of water from 5.5 C to 64.8 C. (5.25 water) (4.184 ) ( ) = 1300 (5.25 water) (1.00 cal ) ( ) = 310 cal b. Lost when 75.0 of water cools from 86.4 C to 2.1 C. (75.0 water) (4.184 ) ( ) = (75.0 water) (1.00 cal ) ( ) = 6300 cal **The minus sin indicates that the heat is leavin the system, i.e., the water** c. To heat 10.0 of silver from 112 C to 275 C. (10.0 silver) (0.235 ) ( ) = 383 (10.0 silver) ( cal ) ( ) = 91.6 cal
4 d. Lost when 18.0 of old cools from 224 C to 118 C. (18.0 old) (0.129 ) ( ) = 246 (18.0 old) ( cal ) ( ) = 58.8 cal Identify each of the followin chanes of state as meltin, freezin, sublimation, or deposition. a. Dry ice in an ice-cream cart disappears. Solid as. Sublimation. b. Snow on the round turns to liquid water. Solid liquid. Meltin. c. Heat is removed from 125 of water at 0 de C Liquid solid. Freezin. d. Frost forms on the walls of a freezer. Gas solid. Deposition (see pae 85) Calculate the heat chane at 100 C for each of the followin and indicate whether heat was absorbed or released. **Use the heat of vaporization conversion!** a. calories to condense 10.0 of steam. Condense means as liquid, use heat of vaporization. Heat is lost from the system steam * 540 cal/ steam = 5400 cal (heat lost) b. joules to condense 7.60 of steam. Heat is lost steam *2260 / steam = (heat lost, 3 si fis) c. kilocalories to vaporize 44 of water Heat absorbed for vaporization. 44 water*540 cal/ water*1 kcal/1000 cal= kcal 24 kcal (2 si fis) d. kilojoules to vaporize 5.00 k of water. Heat is absorbed k * 1000 /k * 2260 / * 1 k/1000 = k (3 si fis) Draw a coolin curve for a sample of steam that cools from 110 de C to -10 de C. Indicate the sement of the raph that corresponds to each of the followin: a. solid b. freezin c. liquid d. condensation e. as
5 3.52. Usin the values for the heat of fusion, specific heat of water, and/or vaporization, calculate the amount of heat enery in each of the followin: a. released when 125 of steam at 100 C condenses and cools to a liquid at 15.0 C. Step 1: Condensation from as to liquid. 125 *2260 / = Step 2: Cool the liquid water. 125 * 4.18 / C * 85 C = Step 3: Sum the two steps, round: round to 1 si fi (100 C) b. kcal needed to melt a 525 ice sculpture at 0 C and warm the water to 15.0 C. Step 1: Meltin the solid to liquid. 525 * 80. cal/ = cal Step 2: Warm the water. 525 * 1.00 cal/ C * 15 C = 7875 cal Step 3: Sum, round, convert unit cal cal 50. kcal c. k released when 85.0 of steam condenses at 100 C, cools, and freezes at 0 C. Step 1: Condense from as to liquid * 2260 / = Step 2: Cool the water: 85.0 * 4.18 / C * 100 C = Step 3: Freeze liquid to solid: 85.0 * 334 / = Step 4: Sum all steps, round, convert units: k
6 3.102*. A 125 piece of metal is heated to 288 C and dropped into 85.0 of water at 12.0 C. The metal and the water come to the same temperature of 24.0 C. What is the specific heat (in / C) of the metal? heat lost by metal = heat ained by water (125 )(Cs)(264 C) = (85.0 )(4.18 / C)(12 C) Cs metal = / C (The metal is old)
Matter and Energy. Chapter 3
 Matter and Energy Chapter 3 Matter Anything that has mass and takes up space Two categories Pure substances Mixtures Pure Substances Matter with a fixed composition Either an element or compound Element
Matter and Energy Chapter 3 Matter Anything that has mass and takes up space Two categories Pure substances Mixtures Pure Substances Matter with a fixed composition Either an element or compound Element
Chapter States and Properties of Matter. The Periodic Table of the Elements Classification of Matter. 3.5 Energy and Nutrition
 Chapter 3 Atoms are the building blocks from which all other things are built. The Periodic Table of the Elements 3.1 - Classification of Matter 3.2 States and Properties of Matter 3.3 Temperature 3.4
Chapter 3 Atoms are the building blocks from which all other things are built. The Periodic Table of the Elements 3.1 - Classification of Matter 3.2 States and Properties of Matter 3.3 Temperature 3.4
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Chapter 2 Matter and Energy. 2.1 Classification of Matter. Matter. Pure Substances
 Slide 1 Chapter 2 Matter and Energy 1 2.1 Classification of Matter Slide 2 2 Matter Matter is the material that makes up all things is anything that has mass and occupies space Slide 3 Pure Substances
Slide 1 Chapter 2 Matter and Energy 1 2.1 Classification of Matter Slide 2 2 Matter Matter is the material that makes up all things is anything that has mass and occupies space Slide 3 Pure Substances
Chapter 5 Energy and States of Matter. Changes of State. Melting and Freezing. Calculations Using Heat of Fusion
 Chapter 5 Energy and States of Matter Changes of State 5.6 Melting and Freezing 5.7 Boiling and Condensation 1 2 Melting and Freezing A substance is melting while it changes from a solid to a liquid. A
Chapter 5 Energy and States of Matter Changes of State 5.6 Melting and Freezing 5.7 Boiling and Condensation 1 2 Melting and Freezing A substance is melting while it changes from a solid to a liquid. A
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry. Fourth Edition Karen Timberlake. Chapter 2. Energy and Matter Pearson Education, Inc.
 General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Fourth Edition Karen Timberlake Chapter 2 Energy and Matter 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Section 2.1 Energy Energy is the ability to do work or transfer heat.
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Fourth Edition Karen Timberlake Chapter 2 Energy and Matter 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Section 2.1 Energy Energy is the ability to do work or transfer heat.
Chapter 2 Energy and Matter
 Chapter 2 Energy and Matter Energy makes objects move makes things stop is needed to do work Kinetic Energy Work is done when you climb you lift a bag of groceries you ride a bicycle you breathe your heart
Chapter 2 Energy and Matter Energy makes objects move makes things stop is needed to do work Kinetic Energy Work is done when you climb you lift a bag of groceries you ride a bicycle you breathe your heart
Chapter 2 Energy and Matter 2.1 Energy
 Chapter 2 Energy and Matter 2.1 Energy 1 Energy Energy makes objects move. makes things stop. is needed to do work. 2 Work Work is done when you climb. you lift a bag of groceries. you ride a bicycle.
Chapter 2 Energy and Matter 2.1 Energy 1 Energy Energy makes objects move. makes things stop. is needed to do work. 2 Work Work is done when you climb. you lift a bag of groceries. you ride a bicycle.
Chapter 4. Properties of Matter
 Chapter 4 Properties of Matter A burning log undergoes chemical change resulting in the release of energy in the form of heat and light. The physical properties of the log change during the Introduction
Chapter 4 Properties of Matter A burning log undergoes chemical change resulting in the release of energy in the form of heat and light. The physical properties of the log change during the Introduction
Thermochemistry. The study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions and changes in state.
 Energy Thermochemistry The study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions and changes in state. The Nature of Energy Energy - the ability to do work or produce heat Energy is stored in the
Energy Thermochemistry The study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions and changes in state. The Nature of Energy Energy - the ability to do work or produce heat Energy is stored in the
Energy and Energy Calculations Test Provide the correct answer as a word, phrase or sentence. (3 points each) 1) Define Matter.
 Provide the correct answer as a word, phrase or sentence. (3 points each) 1) Define Matter. 2) What is ENERGY? 3) Give an example of an endothermic process. 4) Give an example of an exothermic process.
Provide the correct answer as a word, phrase or sentence. (3 points each) 1) Define Matter. 2) What is ENERGY? 3) Give an example of an endothermic process. 4) Give an example of an exothermic process.
CHAPTER 17 Thermochemistry
 CHAPTER 17 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry The study of the heat changes that occur during chemical reactions and physical changes of state. Chemical Change: new substances created during chemical reaction
CHAPTER 17 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry The study of the heat changes that occur during chemical reactions and physical changes of state. Chemical Change: new substances created during chemical reaction
Chapter 2 Heat, Temperature and the First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 2 Heat, Temperature and the First Law of Thermodynamics 2.1. Temperature and the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics 2.2. Thermal Expansion 2.3. Heat and the Absorption of Heat by Solids and Liquids 2.4.
Chapter 2 Heat, Temperature and the First Law of Thermodynamics 2.1. Temperature and the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics 2.2. Thermal Expansion 2.3. Heat and the Absorption of Heat by Solids and Liquids 2.4.
1. Base your answer to the following question on the information below and on your knowledge of chemistry.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the information below and on your knowledge of chemistry. A beaker contains a liquid sample of a molecular substance. Both the beaker and the liquid are
1. Base your answer to the following question on the information below and on your knowledge of chemistry. A beaker contains a liquid sample of a molecular substance. Both the beaker and the liquid are
3. When the external pressure is kpa torr, water will boil at what temperature? a C b C c. 100 C d. 18 C
 Chemistry EOC Review 5: Physical Behavior of Matter 1. Which gas is monatomic at STP? a. chlorine b. fluorine c. neon d. nitrogen 2. What Kelvin temperature is equal to 25 C? a. 248 K b. 298 K c. 100 K
Chemistry EOC Review 5: Physical Behavior of Matter 1. Which gas is monatomic at STP? a. chlorine b. fluorine c. neon d. nitrogen 2. What Kelvin temperature is equal to 25 C? a. 248 K b. 298 K c. 100 K
SUMMARY OF PROPERTIES OF MATTER State Shape Volume Particles Compressibility Solid Definite Definite Densely packed Very slight
 MATTER & ITS FORMS Matter is defined as anything that has mass and occupies space. Matter can be classified by its states: solid, liquid, and gas. Solid: Densely packed matter with definite shape and volume.
MATTER & ITS FORMS Matter is defined as anything that has mass and occupies space. Matter can be classified by its states: solid, liquid, and gas. Solid: Densely packed matter with definite shape and volume.
Thermodynamics Test Clio Invitational January 26, 2013
 Thermodynamics Test Clio Invitational January 26, 2013 School Name: Team Number: Variables specified: s = specific heat C = heat capacity H f = heat of fusion H v = heat of vaporization Given information:
Thermodynamics Test Clio Invitational January 26, 2013 School Name: Team Number: Variables specified: s = specific heat C = heat capacity H f = heat of fusion H v = heat of vaporization Given information:
Name: Class: Date: ID: A
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Chpter 17 review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of these phase changes is an endothermic process? a.
Name: Class: _ Date: _ ID: A Chpter 17 review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of these phase changes is an endothermic process? a.
Ch. 17 Thermochemistry
 Ch. 17 Thermochemistry 17.1 The Flow of Energy Energy Transformations Thermochemistry: study of energy changes in chemical reactions and changes in state Chemical potential energy: energy stored in bonds
Ch. 17 Thermochemistry 17.1 The Flow of Energy Energy Transformations Thermochemistry: study of energy changes in chemical reactions and changes in state Chemical potential energy: energy stored in bonds
Liquids and Solids: The Molecular Kinetic Theory II. Unit 5
 Liquids and Solids: The Molecular Kinetic Theory II Unit 5 Energy Definition Energy is the ability to do work. The ability to make something happen. Different Kinds of Energy: Heat (Thermal) Energy energy
Liquids and Solids: The Molecular Kinetic Theory II Unit 5 Energy Definition Energy is the ability to do work. The ability to make something happen. Different Kinds of Energy: Heat (Thermal) Energy energy
Matter and Energy Homework Problems
 Matter and Energy Homework Problems 1. For each of the following, determine if E is positive, negative, or zero. a. Energy is released b. Energy is consumed c. Water absorbs heat. d. The velocity of an
Matter and Energy Homework Problems 1. For each of the following, determine if E is positive, negative, or zero. a. Energy is released b. Energy is consumed c. Water absorbs heat. d. The velocity of an
solid IMF>liquid IMF>gas IMF Draw a diagram to represent the 3 common states of matter of a given substance: solid liquid gas
 Thermochemistry Part 1 Notes States of Matter and Intermolecular Forces (IMF) Chemistry HP At the end of this unit, students should be able to: Describe the various states of matter in terms of kinetic
Thermochemistry Part 1 Notes States of Matter and Intermolecular Forces (IMF) Chemistry HP At the end of this unit, students should be able to: Describe the various states of matter in terms of kinetic
3.3 Phase Changes Charactaristics of Phase Changes phase change
 A large iceberg contains enough fresh water to supply millions of people with water for a year. As it moves into warmer areas, the ice changes to liquid water and eventually disappears. What happens when
A large iceberg contains enough fresh water to supply millions of people with water for a year. As it moves into warmer areas, the ice changes to liquid water and eventually disappears. What happens when
2. If the volume of a container holding a gas is reduced, what will happen to the presure within the container?
 1. Which gas law states that the volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its Kelvin temperature if the pressure is kept constant? A. Boyle s law B. Charles law C. Dalton s law D. Gay-Lussac
1. Which gas law states that the volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its Kelvin temperature if the pressure is kept constant? A. Boyle s law B. Charles law C. Dalton s law D. Gay-Lussac
The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability to do work or produce Heat, q or Q, is ; flows due to temperature differences (always to )
 CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry 2014-2015 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the study of energy that occur during chemical and physical changes (changes of state) The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability
CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry 2014-2015 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the study of energy that occur during chemical and physical changes (changes of state) The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability
Matter and Energy Review Packet
 Name Date Matter and Energy Review Packet 1. A compound differs from a mixture in that a compound always has a (1) homogeneous composition (2) maximum of two components (3) minimum of three components
Name Date Matter and Energy Review Packet 1. A compound differs from a mixture in that a compound always has a (1) homogeneous composition (2) maximum of two components (3) minimum of three components
CHAPTER 17: THERMOCHEMISTRY. Mrs. Brayfield
 CHAPTER 17: THERMOCHEMISTRY Mrs. Brayfield REVIEW What is the law of conservation of energy? It states that energy cannot be created or destroyed So the energy of any process is the same THERMOCHEMISTRY
CHAPTER 17: THERMOCHEMISTRY Mrs. Brayfield REVIEW What is the law of conservation of energy? It states that energy cannot be created or destroyed So the energy of any process is the same THERMOCHEMISTRY
What are the states of Matter?
 What are the states of Matter? Solid Lowest energy/heat Molecules barely moving Definite, uniform shape Example: ice States of Matter Liquid Medium energy/heat Molecules slowly moving Shape of container
What are the states of Matter? Solid Lowest energy/heat Molecules barely moving Definite, uniform shape Example: ice States of Matter Liquid Medium energy/heat Molecules slowly moving Shape of container
Test Review # 7. Combined Gas Law PV T PV T. Ideal Gas Law PV = nrt. Chemistry H-3: Form TR7.6A
 Chemistry H-3: Form TR7.6A TEST 9 REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 7 ENERGY Calculatin Joules. When you heat a solid, it s temperature enerally oes up. There is a relationship between heat and temperature,
Chemistry H-3: Form TR7.6A TEST 9 REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 7 ENERGY Calculatin Joules. When you heat a solid, it s temperature enerally oes up. There is a relationship between heat and temperature,
What kinds of energy do you see?
 Energy Transfer ICP FTF Day 2 April 16, 2012 HW: none Topic: Light (last day) Questions: 1. When light passes through a prism, which colors of light are bent the most? 2. Which two colors of paint could
Energy Transfer ICP FTF Day 2 April 16, 2012 HW: none Topic: Light (last day) Questions: 1. When light passes through a prism, which colors of light are bent the most? 2. Which two colors of paint could
SPECIFIC HEAT OF WATER LAB 11-2
 CONCEPT Heat of Fusion Changes of state (phase changes) involve the conversion or transition of matter from one of the common states (solid, liquid or gas) to another. Examples include fusion or melting
CONCEPT Heat of Fusion Changes of state (phase changes) involve the conversion or transition of matter from one of the common states (solid, liquid or gas) to another. Examples include fusion or melting
Chapter 2: Properties of Matter Student Outline 2.1 Classifying Matter A. Pure Substances
 Name: Date: Physical Science Period: Chapter 2: Properties of Matter Student Outline GA Performance Standards SPS1. Students will investigate our current understanding of the atom. SPS2. Students will
Name: Date: Physical Science Period: Chapter 2: Properties of Matter Student Outline GA Performance Standards SPS1. Students will investigate our current understanding of the atom. SPS2. Students will
Lesson 9: States of Matter
 Lesson 9: States of Matter Do Now 6O, 6S 11.8.18 Take out HW 6.14 to be checked. Copy info into CJ keep CJ out and open on desk throughout class. On Do Now Page #5, copy and answer: 1. If you use a magnet
Lesson 9: States of Matter Do Now 6O, 6S 11.8.18 Take out HW 6.14 to be checked. Copy info into CJ keep CJ out and open on desk throughout class. On Do Now Page #5, copy and answer: 1. If you use a magnet
Chapter 11. Thermochemistry: Heat & Chemical Change
 Chapter 11 Thermochemistry: Heat & Chemical Change The Flow of Energy Thermochemistry: Study of heat changes that occur during physical processes and chemical reactions Energy Energy is the capacity to
Chapter 11 Thermochemistry: Heat & Chemical Change The Flow of Energy Thermochemistry: Study of heat changes that occur during physical processes and chemical reactions Energy Energy is the capacity to
Preview. Heat Section 1. Section 1 Temperature and Thermal Equilibrium. Section 2 Defining Heat. Section 3 Changes in Temperature and Phase
 Heat Section 1 Preview Section 1 Temperature and Thermal Equilibrium Section 2 Defining Heat Section 3 Changes in Temperature and Phase Heat Section 1 TEKS The student is expected to: 6E describe how the
Heat Section 1 Preview Section 1 Temperature and Thermal Equilibrium Section 2 Defining Heat Section 3 Changes in Temperature and Phase Heat Section 1 TEKS The student is expected to: 6E describe how the
Chapter 5: Thermochemistry. Problems: , , 5.100, 5.106, 5.108, , 5.121, 5.126
 Chapter 5: Thermochemistry Problems: 5.1-5.95, 5.97-98, 5.100, 5.106, 5.108, 5.118-5.119, 5.121, 5.126 Energy: Basic Concepts and Definitions energy: capacity to do work or to produce heat thermodynamics:
Chapter 5: Thermochemistry Problems: 5.1-5.95, 5.97-98, 5.100, 5.106, 5.108, 5.118-5.119, 5.121, 5.126 Energy: Basic Concepts and Definitions energy: capacity to do work or to produce heat thermodynamics:
CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry
 CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the study of energy that occur during chemical reactions and phase changes (changes of state) The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability
CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the study of energy that occur during chemical reactions and phase changes (changes of state) The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability
Practice Packet: Energy. Regents Chemistry: Dr. Shanzer. Practice Packet. Chapter 4: Energy.
 Regents Chemistry: Dr. Shanzer Practice Packet Chapter 4: Energy http:/drshanzerchemistry.weebly.com Energy Objectives Define energy. Demonstrate the difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions
Regents Chemistry: Dr. Shanzer Practice Packet Chapter 4: Energy http:/drshanzerchemistry.weebly.com Energy Objectives Define energy. Demonstrate the difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions
Notes: Matter & Change (text Ch. 1 &10)
 Name Per. Notes: Matter & Change (text Ch. 1 &10) NOTE: This set of class notes is not complete. We will be filling in information in class. If you are absent, it is your responsibility to get missing
Name Per. Notes: Matter & Change (text Ch. 1 &10) NOTE: This set of class notes is not complete. We will be filling in information in class. If you are absent, it is your responsibility to get missing
#2 Matter & Energy Quantitative Chemistry
 Name #2 Matter & Energy Quantitative Chemistry Student Learning Map Unit EQ: What are matter and energy, and how are they important to Chemistry? Key Learning: The universe is composed of multiple types
Name #2 Matter & Energy Quantitative Chemistry Student Learning Map Unit EQ: What are matter and energy, and how are they important to Chemistry? Key Learning: The universe is composed of multiple types
Exam Accelerated Chemistry Study Sheet Chap12 Solids/Liquids/Intermolecular Forces
 Exam Accelerated Chemistry Study Sheet Chap12 Solids/Liquids/Intermolecular Forces Name /66 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Intermolecular
Exam Accelerated Chemistry Study Sheet Chap12 Solids/Liquids/Intermolecular Forces Name /66 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Intermolecular
Name Chemistry / / Understanding Phase Changes
 Name Chemistry / / Understanding Phase Changes As a piece of ice is exposed to a warmer environment, it begins to absorb heat. The heat causes the solid molecules to vibrate faster. Eventually, the ice
Name Chemistry / / Understanding Phase Changes As a piece of ice is exposed to a warmer environment, it begins to absorb heat. The heat causes the solid molecules to vibrate faster. Eventually, the ice
Matter & Changes in Matter
 Matter & Changes in Matter Changing States- MELTING Melting- solid liquid Melting point of H20 is 32 F or 0 C Thermal energy is ABSORBED! Example: Ice cubes absorb thermal energy and melt. Changing States-
Matter & Changes in Matter Changing States- MELTING Melting- solid liquid Melting point of H20 is 32 F or 0 C Thermal energy is ABSORBED! Example: Ice cubes absorb thermal energy and melt. Changing States-
Topic 5: Energetics. Heat & Calorimetry. Thursday, March 22, 2012
 Topic 5: Energetics Heat & Calorimetry 1 Heat is energy that is transferred from one object to another due to a difference in temperature Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of a body
Topic 5: Energetics Heat & Calorimetry 1 Heat is energy that is transferred from one object to another due to a difference in temperature Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of a body
Physics Mechanics
 1 Physics 170 - Mechanics Lecture 35 Heat 2 Definition and Units of Heat Heat is a form of energy, and therefore is measured in joules. There are other units of heat, the most common one is the kilocalorie:
1 Physics 170 - Mechanics Lecture 35 Heat 2 Definition and Units of Heat Heat is a form of energy, and therefore is measured in joules. There are other units of heat, the most common one is the kilocalorie:
CHEM1301. F2014 Chapter 1 and 3
 CHEM1301 F2014 Chapter 1 and 3 Chemistry:Why am I here? Chemistry The science that seeks to understand the behavior of matter by studying the BEHAVIOR of atoms and molecules. Not just a cause and effect
CHEM1301 F2014 Chapter 1 and 3 Chemistry:Why am I here? Chemistry The science that seeks to understand the behavior of matter by studying the BEHAVIOR of atoms and molecules. Not just a cause and effect
Chapter 15 Energy and Chemical Change
 Chapter 15 Energy and Chemical Change Chemical reactions usually absorb or release energy. Section 1: Energy Section 2: Heat Section 3: Thermochemical Equations Section 4: Calculating Enthalpy Change Section
Chapter 15 Energy and Chemical Change Chemical reactions usually absorb or release energy. Section 1: Energy Section 2: Heat Section 3: Thermochemical Equations Section 4: Calculating Enthalpy Change Section
2.1 Properties of Matter > Chapter 2 Matter and Change. 2.1 Properties of Matter. 2.2 Mixtures 2.3 Elements and Compounds 2.4 Chemical Reactions
 21 Properties of Matter > 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc, or its affiliates All Rights Reserved Chapter 2 Matter and Change 21 Properties of Matter 22 Mixtures 23 Elements and Compounds 24 Chemical
21 Properties of Matter > 1 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc, or its affiliates All Rights Reserved Chapter 2 Matter and Change 21 Properties of Matter 22 Mixtures 23 Elements and Compounds 24 Chemical
Temperature and Its Measurement
 Temperature and Its Measurement When the physical properties are no longer changing, the objects are said to be in thermal equilibrium. Two or more objects in thermal equilibrium have the same temperature.
Temperature and Its Measurement When the physical properties are no longer changing, the objects are said to be in thermal equilibrium. Two or more objects in thermal equilibrium have the same temperature.
I. The Nature of Energy A. Energy
 I. The Nature of Energy A. Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat. It exists in 2 forms: 1. Potential energy is energy due to the composition or position of an object. 2. Kinetic energy is energy
I. The Nature of Energy A. Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat. It exists in 2 forms: 1. Potential energy is energy due to the composition or position of an object. 2. Kinetic energy is energy
Chapter 5. Thermochemistry
 Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Energy Thermodynamics Study of the relationship between heat, work, and other forms of energy Thermochemistry A branch of thermodynamics Focuses on the study of heat given off
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Energy Thermodynamics Study of the relationship between heat, work, and other forms of energy Thermochemistry A branch of thermodynamics Focuses on the study of heat given off
Name Date Class THERMOCHEMISTRY
 Name Date Class 17 THERMOCHEMISTRY SECTION 17.1 THE FLOW OF ENERGY HEAT AND WORK (pages 505 510) This section explains the relationship between energy and heat, and distinguishes between heat capacity
Name Date Class 17 THERMOCHEMISTRY SECTION 17.1 THE FLOW OF ENERGY HEAT AND WORK (pages 505 510) This section explains the relationship between energy and heat, and distinguishes between heat capacity
Temperature Energy and Heat
 CHAPTER 3 Temperature Energy and Heat 3.1 Temperature What is temperature? Why is temperature important in chemistry? How is energy related to temperature? 2 3.1 Temperature Milk fat particles are being
CHAPTER 3 Temperature Energy and Heat 3.1 Temperature What is temperature? Why is temperature important in chemistry? How is energy related to temperature? 2 3.1 Temperature Milk fat particles are being
This reaction is ENDOTHERMIC. Energy is being transferred from the room/flask/etc. (the SURROUNDINGS) to the reaction itself (the SYSTEM).
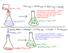 151 This reaction is EXOTHERMIC. Energy is transferred from the reactants and products (the SYSTEM) to the water in the flask, the flask, etc. (the SURROUNDINGS) This reaction is ENDOTHERMIC. Energy is
151 This reaction is EXOTHERMIC. Energy is transferred from the reactants and products (the SYSTEM) to the water in the flask, the flask, etc. (the SURROUNDINGS) This reaction is ENDOTHERMIC. Energy is
Name /100. 1) Matter is defined as anything that is visible to the human eye. 1) 2) An amorphous solid has long range, repeating order.
 Ch 3 Matter and Energy Study Sheet Accelerated Chemistry Name /100 TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) Matter is defined as anything that is visible to
Ch 3 Matter and Energy Study Sheet Accelerated Chemistry Name /100 TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) Matter is defined as anything that is visible to
1/04/2018. Bilingual material 4 th level of Primary Education. By MACS
 By MACS By MACS By MACS ACTIVITIES 1. Answer these questions. What is matter?. What is the difference between an element and a compound?.. Is sea water a mixture or a pure substance?.. Why?.. What are
By MACS By MACS By MACS ACTIVITIES 1. Answer these questions. What is matter?. What is the difference between an element and a compound?.. Is sea water a mixture or a pure substance?.. Why?.. What are
AlCl3(aq) + 3 NaOH(aq) Al(OH)3(s) + 3 NaCl(aq)
 1. Under which conditions does a real gas behave most like an ideal gas? A) at low temperatures and high pressures B) at low temperatures and low pressures C) at high temperatures and high pressures D)
1. Under which conditions does a real gas behave most like an ideal gas? A) at low temperatures and high pressures B) at low temperatures and low pressures C) at high temperatures and high pressures D)
What Do You Think? Investigate GOALS. Part A: Freezing Water
 Activity 5 Freezing Water GOALS In this activity you will: Determine the freezing point of water. Show graphically what happens to the temperature as water is cooled to freezing and while it is freezing.
Activity 5 Freezing Water GOALS In this activity you will: Determine the freezing point of water. Show graphically what happens to the temperature as water is cooled to freezing and while it is freezing.
Gilbert Kirss Foster. Chapter 9. Thermochemistry. Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions
 Gilbert Kirss Foster Chapter 9 Thermochemistry Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions Chapter Outline 9.1 Energy as a Reactant or Product 9.2 Transferring Heat and Doing Work 9.3 Enthalpy and Enthalpy Changes
Gilbert Kirss Foster Chapter 9 Thermochemistry Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions Chapter Outline 9.1 Energy as a Reactant or Product 9.2 Transferring Heat and Doing Work 9.3 Enthalpy and Enthalpy Changes
Thermochemistry: Heat and Chemical Change
 Thermochemistry: Heat and Chemical Change 1 Heat or Thermal Energy (q) Heat is a form of energy Is heat the same as temperature? Heat flows between two objects at different temperatures. Hot Cold 2 Chemical
Thermochemistry: Heat and Chemical Change 1 Heat or Thermal Energy (q) Heat is a form of energy Is heat the same as temperature? Heat flows between two objects at different temperatures. Hot Cold 2 Chemical
Chapter 12. Temperature and Heat
 Chapter 12 Temperature and Heat 12.1 Common Temperature Scales Temperatures are reported in degrees Celsius or degrees Fahrenheit. Kelvin Scale 100 o C or 212 o F T K = T + 273.15 Temperature changes,
Chapter 12 Temperature and Heat 12.1 Common Temperature Scales Temperatures are reported in degrees Celsius or degrees Fahrenheit. Kelvin Scale 100 o C or 212 o F T K = T + 273.15 Temperature changes,
Topic 19b. Thermal Properties of Matter
 Topic 19b The infra-red image of a head shows the distribution of heat. Different colours indicate different temperatures. Which do you think are the warmest regions? Thermal Properties of Matter contents
Topic 19b The infra-red image of a head shows the distribution of heat. Different colours indicate different temperatures. Which do you think are the warmest regions? Thermal Properties of Matter contents
Ch. 11 States of matter
 Ch. 11 States of matter States of Matter Solid Definite volume Definite shape Liquid Definite volume Indefinite shape (conforms to container) Gas Indefinite volume (fills any container) Indefinite shape
Ch. 11 States of matter States of Matter Solid Definite volume Definite shape Liquid Definite volume Indefinite shape (conforms to container) Gas Indefinite volume (fills any container) Indefinite shape
Chapter 11. Energy in Thermal Processes
 Chapter 11 Energy in Thermal Processes Energy Transfer When two objects of different temperatures are placed in thermal contact, the temperature of the warmer decreases and the temperature of the cooler
Chapter 11 Energy in Thermal Processes Energy Transfer When two objects of different temperatures are placed in thermal contact, the temperature of the warmer decreases and the temperature of the cooler
PHASE CHANGE. Freezing Sublimation
 Melting Graphic Organizer Deposition PHASE CHANGE Freezing Sublimation Boiling Evaporation Condensation PHASE CHANGE Phase change happens as the temperature changes. All matter can move from one state
Melting Graphic Organizer Deposition PHASE CHANGE Freezing Sublimation Boiling Evaporation Condensation PHASE CHANGE Phase change happens as the temperature changes. All matter can move from one state
Qualitative observation descriptive observation has no numerical measurement
 1 Chem 047: Physical and chemical properties Chemistry 047 Properties of substances, and Physical and Chemical Changes A. Some definitions B. Properties of substances C. The Classification of Matter D.
1 Chem 047: Physical and chemical properties Chemistry 047 Properties of substances, and Physical and Chemical Changes A. Some definitions B. Properties of substances C. The Classification of Matter D.
1 Three States of Matter
 CHAPTER 3 1 Three States of Matter SECTION States of Matter BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is matter made of? What are the three most common
CHAPTER 3 1 Three States of Matter SECTION States of Matter BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is matter made of? What are the three most common
Chapter 10 Temperature and Heat
 Chapter 10 Temperature and Heat Thermodynamics deals with 1. Temperature. 2. The transfer and transformation of energy. 3. The relationship between macroscopic properties and microscopic dynamics. Temperature
Chapter 10 Temperature and Heat Thermodynamics deals with 1. Temperature. 2. The transfer and transformation of energy. 3. The relationship between macroscopic properties and microscopic dynamics. Temperature
Chapter 3. Matter, Changes and Energy
 Chapter 3 Matter, Changes and Energy Formulating some questions What are the most basic forms of matter? What are the criteria that allow us to distinguish one substance from another? How do we describe
Chapter 3 Matter, Changes and Energy Formulating some questions What are the most basic forms of matter? What are the criteria that allow us to distinguish one substance from another? How do we describe
Name: Date: Class: CHAPTER 2. Investigation & Enrichment. INVESTIGATION Your material: Mass: Volume: Extensive properties of your material:
 Name: Date: Class: CHAPTER 2 2.1 Properties of Matter Investigation & Enrichment INVESTIGATION Your material: Mass: Volume: Extensive properties of your material: Intensive properties of your material:
Name: Date: Class: CHAPTER 2 2.1 Properties of Matter Investigation & Enrichment INVESTIGATION Your material: Mass: Volume: Extensive properties of your material: Intensive properties of your material:
WARM-UP. 1. What are the four states of matter? 2. What is melting point? 3. How does water change from a liquid to a gas? 4. Define viscosity.
 WARM-UP 1. What are the four states of matter? 2. What is melting point? 3. How does water change from a liquid to a gas? 4. Define viscosity. STATES OF MATTER: WEB QUEST With your lab partner, you will
WARM-UP 1. What are the four states of matter? 2. What is melting point? 3. How does water change from a liquid to a gas? 4. Define viscosity. STATES OF MATTER: WEB QUEST With your lab partner, you will
Name: Regents Review Quiz #1 2016
 Name: Regents Review Quiz #1 2016 1. Which two particle diagrams represent mixtures of diatomic elements? A) A and B B) A and C C) B and C D) B and D 2. At STP, which physical property of aluminum always
Name: Regents Review Quiz #1 2016 1. Which two particle diagrams represent mixtures of diatomic elements? A) A and B B) A and C C) B and C D) B and D 2. At STP, which physical property of aluminum always
A). Yes. B). No. Q15 Is it possible for a solid metal ball to float in mercury?
 Q15 Is it possible for a solid metal ball to float in mercury? A). Yes. B). No. The upward force is the weight of liquid displaced and the downward force is the weight of the ball. If the density of the
Q15 Is it possible for a solid metal ball to float in mercury? A). Yes. B). No. The upward force is the weight of liquid displaced and the downward force is the weight of the ball. If the density of the
Name Class Date. As you read Lesson 17.1, use the cause and effect chart below. Complete the chart with the terms system and surroundings.
 Name Class Date Thermochemistry 17.1 The Flow of Energy As you read Lesson 17.1, use the cause and effect chart below. Complete the chart with the terms system and surroundings. Process Cause Effect endothermic
Name Class Date Thermochemistry 17.1 The Flow of Energy As you read Lesson 17.1, use the cause and effect chart below. Complete the chart with the terms system and surroundings. Process Cause Effect endothermic
- Joule (J): SI unit for energy. It's defined based on the equation for kinetic energy. from. mass. velocity
 153 ENERGY UNITS - calorie (cal): the amount of energy required to change the temperature of one gram of water by one degree Celsius (or Kelvin) 1g 1g add one calorie of energy - Calories in food? The
153 ENERGY UNITS - calorie (cal): the amount of energy required to change the temperature of one gram of water by one degree Celsius (or Kelvin) 1g 1g add one calorie of energy - Calories in food? The
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY. Serkan SAYINER, DVM PhD, Assist. Prof.
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Serkan SAYINER, DVM PhD, Assist. Prof. serkan.sayiner@neu.edu.tr ENERGY AND MATTER The Units of Energy, Energy and Nutrition, The Three States of Matter, Classification of Matter, Intermolecular
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Serkan SAYINER, DVM PhD, Assist. Prof. serkan.sayiner@neu.edu.tr ENERGY AND MATTER The Units of Energy, Energy and Nutrition, The Three States of Matter, Classification of Matter, Intermolecular
The ability of a substance to be rolled. into wire The physical form of matter (solid, liquid, or gas)
 CHAPTER 2 2 Physical Properties SECTION The Properties of Matter BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are physical properties of matter? What
CHAPTER 2 2 Physical Properties SECTION The Properties of Matter BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are physical properties of matter? What
Phase Change Diagram. Rank Solids, liquids and gases from weakest attractive forces to strongest:
 Unit 11 Kinetic molecular theory packet Page 1 of 13 Chemistry Unit 11 Kinetic Theory Unit Quiz: Test Objectives Be able to define pressure and memorize the basic pressure units. Be able to convert to/from:
Unit 11 Kinetic molecular theory packet Page 1 of 13 Chemistry Unit 11 Kinetic Theory Unit Quiz: Test Objectives Be able to define pressure and memorize the basic pressure units. Be able to convert to/from:
Chemistry Heat Review. Heat: Temperature: Enthalpy: Calorimetry: Activation energy:
 Chemistry Heat Review Name Date Vocabulary Heat: Temperature: Enthalpy: Calorimetry: Activation energy: Formulas Heat of phase change Heat for temperature increase Heat of reaction Endothermic/Exothermic
Chemistry Heat Review Name Date Vocabulary Heat: Temperature: Enthalpy: Calorimetry: Activation energy: Formulas Heat of phase change Heat for temperature increase Heat of reaction Endothermic/Exothermic
The graph represents the uniform cooling of water at 1 atmosphere, starting with water as a gas above its boiling point.
 Teacher: Mr. gerraputa Print Close Name: 1. Which graph best represents a change of phase from a gas to a solid? 1. 3. 2. 4. 2. The graph represents the uniform cooling of water at 1 atmosphere, starting
Teacher: Mr. gerraputa Print Close Name: 1. Which graph best represents a change of phase from a gas to a solid? 1. 3. 2. 4. 2. The graph represents the uniform cooling of water at 1 atmosphere, starting
Energy in Thermal Processes. Heat and Internal Energy
 Energy in Thermal Processes Heat and Internal Energy Internal energy U: associated with the microscopic components of a system: kinetic and potential energies. The larger the number of internal degrees
Energy in Thermal Processes Heat and Internal Energy Internal energy U: associated with the microscopic components of a system: kinetic and potential energies. The larger the number of internal degrees
Unit 15 Energy and Thermochemistry Notes
 Name KEY Period CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 15 Energy and Thermochemistry Notes Quiz Date Exam Date Lab Dates Notes, Homework, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS located on CRHS Academic Chemistry Website: https://cincochem.pbworks.com
Name KEY Period CRHS Academic Chemistry Unit 15 Energy and Thermochemistry Notes Quiz Date Exam Date Lab Dates Notes, Homework, Exam Reviews and Their KEYS located on CRHS Academic Chemistry Website: https://cincochem.pbworks.com
Chapter 23 Changes of Phase. Conceptual Physics Chapter 23 1
 Chapter 23 Changes of Phase Conceptual Physics Chapter 23 1 Kinetic Theory Matter exists in three common states or phases solid, liquid and gas. A fourth state plasma makes up over 90% of our universe.
Chapter 23 Changes of Phase Conceptual Physics Chapter 23 1 Kinetic Theory Matter exists in three common states or phases solid, liquid and gas. A fourth state plasma makes up over 90% of our universe.
Name Energy Test period Date
 Name Energy Test period Date 1. The temperature 30. K expressed in degrees Celsius is 1) 243ºC 2) 243ºC 3) 303ºC 4) 303ºC 2. The potential energy diagram for a chemical reaction is shown below. 4. A sample
Name Energy Test period Date 1. The temperature 30. K expressed in degrees Celsius is 1) 243ºC 2) 243ºC 3) 303ºC 4) 303ºC 2. The potential energy diagram for a chemical reaction is shown below. 4. A sample
Chemical Thermodynamics
 Chemical Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics is a Greek term which means, heat power. Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. 2 Thermodynamics Thermochemistry how we observe,
Chemical Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics is a Greek term which means, heat power. Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. 2 Thermodynamics Thermochemistry how we observe,
Matter and Energy Chapter 3
 Copyright 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Matter and Energy Chapter 3 All rights reserved. 1 3.1 Matter Matter is the material the universe is composed of Matter has mass Matter occupies space Matter
Copyright 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Matter and Energy Chapter 3 All rights reserved. 1 3.1 Matter Matter is the material the universe is composed of Matter has mass Matter occupies space Matter
1) Calculate the kinetic energy in J of an electron moving at m / s. The mass of an electron is g.
 Multiple-Choice and Bimodal Questions 6 1) Calculate the kinetic energy in J of an electron moving at 6.00 m / s. The mass of 28 an electron is 9.11 g. A) 4.98 48 B) 3.28 14 C) 1.64 17 D) 2.49 48 E) 6.56
Multiple-Choice and Bimodal Questions 6 1) Calculate the kinetic energy in J of an electron moving at 6.00 m / s. The mass of 28 an electron is 9.11 g. A) 4.98 48 B) 3.28 14 C) 1.64 17 D) 2.49 48 E) 6.56
0 o K is called absolute zero. Water Freezes: 273 o K Water Boils: 373 o K
 Part I Notes Temperature and Heat The terms at the right all mean the same thing. The heat energy of a substance is the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of all of the atoms and molecules in the
Part I Notes Temperature and Heat The terms at the right all mean the same thing. The heat energy of a substance is the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of all of the atoms and molecules in the
Energy and Chemical Change
 Energy and Chemical Change Section 15.1 Energy In your textbook, read about the nature of energy. In the space at the left, write true if the statement is true; if the statement is false, change the italicized
Energy and Chemical Change Section 15.1 Energy In your textbook, read about the nature of energy. In the space at the left, write true if the statement is true; if the statement is false, change the italicized
Matter and Change. Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday. Textbook Activity. Meet in B122. Hw: pg 7 Hw: pg 4. Matter Review
 Matter and Change Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SEPTEMBER 1 2 3 4 5 NO SCHOOL Matter & Change Classifying Matter Textbook Activity Meet in B122 Physical and Chemical Properties and Changes Indiana
Matter and Change Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SEPTEMBER 1 2 3 4 5 NO SCHOOL Matter & Change Classifying Matter Textbook Activity Meet in B122 Physical and Chemical Properties and Changes Indiana
Chapter 9. Preview. Objectives Defining Temperature. Thermal Equilibrium. Thermal Expansion Measuring Temperature. Section 1 Temperature and
 Section 1 Temperature and Thermal Equilibrium Preview Objectives Defining Temperature Thermal Equilibrium Thermal Expansion Measuring Temperature Section 1 Temperature and Thermal Equilibrium Objectives
Section 1 Temperature and Thermal Equilibrium Preview Objectives Defining Temperature Thermal Equilibrium Thermal Expansion Measuring Temperature Section 1 Temperature and Thermal Equilibrium Objectives
Chapter 5 THERMO. THERMO chemistry. 5.4 Enthalpy of Reactions 5.5 Calorimetry 5.6 Hess s Law 5.7 Enthalpies of Formation
 Chapter 5 THERMO THERMO chemistry 5.4 Enthalpy of Reactions 5.5 Calorimetry 5.6 Hess s Law 5.7 Enthalpies of Formation Chemical Equations 1 st WRITE the Chemical Equation 2 nd BALANCE the Chemical Equation
Chapter 5 THERMO THERMO chemistry 5.4 Enthalpy of Reactions 5.5 Calorimetry 5.6 Hess s Law 5.7 Enthalpies of Formation Chemical Equations 1 st WRITE the Chemical Equation 2 nd BALANCE the Chemical Equation
Physical Property. Critical Thinking
 CHAPTER 1 2 Physical Properties SECTION The Properties of Matter BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are physical properties of matter? What
CHAPTER 1 2 Physical Properties SECTION The Properties of Matter BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are physical properties of matter? What
Energy and Chemical Change
 Energy and Chemical Change Section 16.1 Energy In your textbook, read about the nature of energy. In the space at the left, write true if the statement is true; if the statement is false, change the italicized
Energy and Chemical Change Section 16.1 Energy In your textbook, read about the nature of energy. In the space at the left, write true if the statement is true; if the statement is false, change the italicized
Chapter 11. Energy in Thermal Processes
 Chapter 11 Energy in Thermal Processes Energy Transfer When two objects of different temperatures are placed in thermal contact, the temperature of the warmer decreases and the temperature of the cooler
Chapter 11 Energy in Thermal Processes Energy Transfer When two objects of different temperatures are placed in thermal contact, the temperature of the warmer decreases and the temperature of the cooler
SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY AND HEAT OF FUSION
 SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY AND HEAT OF FUSION Apparatus on each table: Thermometer, metal cube, complete calorimeter, outer calorimeter can (aluminum only), balance, 4 styrofoam cups, graduated container,
SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY AND HEAT OF FUSION Apparatus on each table: Thermometer, metal cube, complete calorimeter, outer calorimeter can (aluminum only), balance, 4 styrofoam cups, graduated container,
Chapters 17 &19 Temperature, Thermal Expansion and The Ideal Gas Law
 Chapters 17 &19 Temperature, Thermal Expansion and The Ideal Gas Law Units of Chapter 17 & 19 Temperature and the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Temperature Scales Thermal Expansion Heat and Mechanical Work
Chapters 17 &19 Temperature, Thermal Expansion and The Ideal Gas Law Units of Chapter 17 & 19 Temperature and the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Temperature Scales Thermal Expansion Heat and Mechanical Work
Chapter 5 Principles of Chemical Reactivity: Energy and Chemical Reactions
 Chapter 5 Principles of Chemical Reactivity: Energy and Chemical Reactions Jeffrey Mack California State University, Sacramento Energy & Chemistry Questions that need to be addressed: How do we measure
Chapter 5 Principles of Chemical Reactivity: Energy and Chemical Reactions Jeffrey Mack California State University, Sacramento Energy & Chemistry Questions that need to be addressed: How do we measure
4. Every CHANGE in matter includes a change in, which is conserved in a chemical reaction and. TRANSFORMED from one form to another.
 Part C: Lesson 1.4 - Read pages 20-29 to answer these questions. Add to notes - 1. A physical change alters the form or appearance of matter, such as Change in size, a change in SIZE or. SHAPE shape, or
Part C: Lesson 1.4 - Read pages 20-29 to answer these questions. Add to notes - 1. A physical change alters the form or appearance of matter, such as Change in size, a change in SIZE or. SHAPE shape, or
Page 1 SPH3U. Heat. What is Heat? Thermal Physics. Waterloo Collegiate Institute. Some Definitions. Still More Heat
 SPH3U Thermal Physics electrons and holes in semiconductors An Introductory ourse in Thermodynamics converting energy into work magnetism thin films and surface chemistry thermal radiation (global warming)
SPH3U Thermal Physics electrons and holes in semiconductors An Introductory ourse in Thermodynamics converting energy into work magnetism thin films and surface chemistry thermal radiation (global warming)
Chemical Reactions and Energy. Classwork and Homework. Slide 1 / 75. Slide 2 / 75. Slide 3 / 75. Unit Preview Classwork
 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Slide 1 / 75 Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students and
New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Slide 1 / 75 Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students and
